instance_id
stringlengths 21
53
| repo
stringclasses 188
values | language
stringclasses 1
value | pull_number
int64 20
148k
| title
stringlengths 6
144
| body
stringlengths 0
83.4k
| created_at
stringdate 2015-09-25 03:17:17
2025-07-10 16:50:35
| problem_statement
stringlengths 188
240k
| hints_text
stringlengths 0
145k
| resolved_issues
listlengths 1
6
| base_commit
stringlengths 40
40
| commit_to_review
dict | reference_review_comments
listlengths 1
62
| merged_commit
stringlengths 40
40
| merged_patch
stringlengths 297
9.87M
| metadata
dict |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
sympy__sympy-22540@d462325
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 22,540
|
Fixed issue with piecewise integration
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #22533
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Currently, `integrate(1/Abs(x))` (where x is real) gives `Piecewise((-log(x), x<= 0), (nan, True))`. The same issue could also occur for piecewise functions whose antiderivatives on some interval are infinite at one of the endpoints. I changed the `_eval_integral` method of sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py to detect such a situation and try to use the antiderivative expression instead of the running sum. With the changes I made, `integrate(1/Abs(x))` now returns `Piecewise((-log(x), x<= 0), (log(x), True))`. The change also gives the correct result for other piecewise functions for which this bug exists.
#### Other comments
None
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* functions
* fixed a bug with integrating certain piecewise functions
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-11-22T12:11:20Z
|
Integral(1/abs(x), x).doit() returns an incomplete answer as output
This was pointed out on the gitter channel a week back or two but I'm not sure if the user remembered to raise the issue on the github page and hence I am raising it before it gets lost in the chat !
On Master
```
>>> x = Symbol('x', real=True)
>>> Integral(1/abs(x), x).doit()
Piecewise((-log(x), x <= 0), (nan, True))
```
The correct answer for this should `sign(x)*log(abs(x))` for all points except 0 where it should be returning `nan` . I'm not sure where this might be going wrong due to my inexperience with the `Integrals` module but the output seems to capture one half of the number line correctly and returns `nan` for all other values of `x`
|
I would love to work on this issue! However, I'm a newbie to sympy contributing so someone might have to guide me through it. I've been playing around with the code and am trying to locate the cause of the issue.
Cool you should go forward with it , though I'm myself inexperienced with the Integrals module so I guess I might not be of much help but surely you'll find people here who could help you with this !
Maybe @oscarbenjamin could get you started with some basic guidance for the same
I think I have found the source of this problem. When you call integrate on `1/Abs(x)` it internally gets converted into a piecewise function. And by default, when a piecewise function is integrated, it calls the `_eval_integral` method, which tries to return an output so that evaluating the output at two different points and subtracting gives the definite integral between those two points. In this case, the definite integral of `1/Abs(x)` on any interval when both endpoints are negative is defined, so you get the correct answer for negative numbers. However, as soon as you cross over to positive numbers, the integral becomes infinite, causing the `nan` for positive numbers. You can get around this problem by rewriting `1/Abs(x)` as a piecewise function and using `piecewise_integrate`, but I still think something should be done about this, since this does not let you use the result of integrate to evaluate definite integrals where both limits are positive.
Perhaps there is some way to automatically detect that an infinity has been produced in `_eval_integral` and fall back on `piecewise_integrate`?
It isn't generally possible to construct an antiderivative that can work for the fundamental theorem of calculus for all possible intervals because the theorem only applies if the function is continuous throughout the region which `1/Abs(x)` is not at `x=0`.
Is a fix even necessary for this issue then?
Perhaps, if the function has an infinite discontinuity on a particular interval, `eval_integral` should not try to make the result wok with the fundamental theorem of calculus. That way, the part of the result for positive numbers would be more helpful than `nan` while keeping the part for negative numbers preserved.
Ideally an indefinite integral would at least give a locally valid antiderivative. In this case the antiderivative is not valid for positive x.
Yeah agreed . I hadn't given much thought about this, though I was initially convinced with what the user had reported in the gitter channel . Closing this as of now . Thank you !
Reopening: `integrate(1/Abs(x), x)` where `x` is a real symbol should give a result that is valid for positive `x`.
I replaced line 519 of functions/elementary/piecewise.py on master, which is
```
args.append((sum, cond))
```
with
```
if sum.has(oo, -oo, S.ComplexInfinity, Undefined) and not anti.has(oo, -oo, S.ComplexInfinity, Undefined):
args.append((anti, cond))
else:
args.append((sum, cond))
```
This seems to fix the issue. Essentially, what this does is that if `anti` evaluated on the current interval results results in a nan or an infinity (which is what causes `sum` to be `nan`), and anti itself does not contain `nan` or some type of infinity, it uses `anti` instead of `sum` for that interval.
I ran the tests in bin/test and bin/doctest and all tests seem to be running OK. Is there something obviously wrong with this change or could it potentially cause any problems? Otherwise, would it be alright if I submitted a pull request for this issue? This is my first sympy contribution so I'm not quite sure what to do at this point.
Edit: With this change `integrate(1/Abs(x), x)` where x is real gives `Piecewise((-log(x), x <= 0), (log(x), True))`
You should maybe discuss your ideas or ask for suggestions here, but if you have a solution already consider creating a pull request and discussing the issue there !
People would also be able to review and acknowledge your changes whereas here people won't possibly be able to check if it is a valid solution or not .
|
[
{
"body": "This was pointed out on the gitter channel a week back or two but I'm not sure if the user remembered to raise the issue on the github page and hence I am raising it before it gets lost in the chat !\r\n\r\nOn Master\r\n```\r\n>>> x = Symbol('x', real=True)\r\n>>> Integral(1/abs(x), x).doit()\r\nPiecewise((-log(x), x <= 0), (nan, True))\r\n```\r\nThe correct answer for this should `sign(x)*log(abs(x))` for all points except 0 where it should be returning `nan` . I'm not sure where this might be going wrong due to my inexperience with the `Integrals` module but the output seems to capture one half of the number line correctly and returns `nan` for all other values of `x`\r\n",
"number": 22533,
"title": "Integral(1/abs(x), x).doit() returns an incomplete answer as output "
}
] |
555c8cbfabffb47fc89e12b936a94dea52fdbae5
|
{
"head_commit": "d462325de4acf2a6a7808ce832fde19fe1c1cfd4",
"head_commit_message": "Piecewise: Fixed piecewise integration error\n\nBefore this change, when attempting to integrate a\npiecewise function (or a function that internally\ngets converted to a piecewise function\n(like 1/Abs(x)), if some part of the\nfunction on some interval evaluates to\nsome type of infinity at an endpoint of\nthe interval it could result in the indefinite\nintegral containing an added infinity or being nan\non that interval. This change fixes this issue.\n\nExample\n\nIn [1]: from sympy import *\n\nIn [2]: x = Symbol('x', real=True)\n\nIn [3]: integrate(1/Abs(x))\n\nOut [3]: Piecewise((-log(x), x <= 0), (log(x), True))\n\nBefore this change, integrate(1/Abs(x)) resulted in\nPiecewise((-log(x), x <= 0), (nan, True))",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\nindex ce288fb916a4..e568b1e7c04e 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\n@@ -512,7 +512,10 @@ def handler(ipw):\n cond = (x < b)\n else:\n cond = (x <= b)\n- args.append((sum, cond))\n+ if sum.has(oo, -oo, S.ComplexInfinity, Undefined):\n+ args.append((anti, cond))\n+ else:\n+ args.append((sum, cond))\n return Piecewise(*args)\n \n def _eval_interval(self, sym, a, b, _first=True):\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py\nindex 40bdeac4009f..f99f57576104 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py\n@@ -1447,3 +1447,9 @@ def test_piecewise_eval():\n ) == (x >= -3) & (x <= oo)\n assert f(Piecewise((x, (Abs(arg(a)) <= 1) | (Abs(arg(a)) < 1)))\n ) == (Abs(arg(a)) <= 1) | (Abs(arg(a)) < 1)\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_22533():\n+ x = Symbol('x', real=True)\n+ f = Piecewise((-1 / x, x <= 0), (1 / x, True))\n+ assert integrate(f, x) == Piecewise((-log(x), x <= 0), (log(x), True))\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -512,7 +512,10 @@ def handler(ipw):\n cond = (x < b)\n else:\n cond = (x <= b)\n- args.append((sum, cond))\n+ if sum.has(oo, -oo, S.ComplexInfinity, Undefined):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 515,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nHow about testing infinities on line 504? \n\n@author:\nTesting infinities on line 504 does not catch infinities produced on line 506. I could change it so that it tests infinities right line 506 if that would help somehow.\n\n@user2:\nI'd suggest using `S.NegativeInfinity` instead of `-oo` to speed up the code (although both are very fast, an expression is created for the current code). An therefore also `S.Infinity` for consistency. What about `S.NaN`?\n\n@user1:\nIf `sum` is infinite or undefined, then it should probably be reset to 0.\n\n@author:\n> If `sum` is infinite or undefined, then it should probably be reset to 0.\r\n\r\nYes, this seems like a good idea. I'll add it in along with oscargus's suggestion.\n\n@author:\n> I'd suggest using `S.NegativeInfinity` instead of `-oo` to speed up the code (although both are very fast, an expression is created for the current code). An therefore also `S.Infinity` for consistency. What about `S.NaN`?\r\n\r\n\r\nI'll replace `oo` and `oo` with `S.NegativeInfinity` and `S.Infinity` respectively. In this file, `Undefined` is set to `S.NaN`, so `S.NaN` is already covered."
}
] |
d6500fddfa3eb5220e5a72b76310ec21fc48a971
|
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py
index ce288fb916a4..b38944ff711b 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py
@@ -8,6 +8,7 @@
from sympy.functions.elementary.miscellaneous import Max, Min
from sympy.logic.boolalg import (And, Boolean, distribute_and_over_or, Not,
true, false, Or, ITE, simplify_logic, to_cnf, distribute_or_over_and)
+from sympy.polys.polyutils import illegal
from sympy.utilities.iterables import uniq, sift, common_prefix
from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent, func_name
@@ -501,9 +502,11 @@ def handler(ipw):
sum = anti
else:
sum = sum.subs(x, a)
- if sum == Undefined:
- sum = 0
- sum += anti._eval_interval(x, a, x)
+ e = anti._eval_interval(x, a, x)
+ if sum.has(*illegal) or e.has(*illegal):
+ sum = anti
+ else:
+ sum += e
# see if we know whether b is contained in original
# condition
if b is S.Infinity:
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py
index 40bdeac4009f..f0f41ed8e36d 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py
@@ -883,7 +883,7 @@ def test_holes():
assert Piecewise((1, x < 2)).integrate(x) == Piecewise(
(x, x < 2), (nan, True))
assert Piecewise((1, And(x > 1, x < 2))).integrate(x) == Piecewise(
- (nan, x < 1), (x - 1, x < 2), (nan, True))
+ (nan, x < 1), (x, x < 2), (nan, True))
assert Piecewise((1, And(x > 1, x < 2))).integrate((x, 0, 3)) is nan
assert Piecewise((1, And(x > 0, x < 4))).integrate((x, 1, 3)) == 2
@@ -1447,3 +1447,9 @@ def test_piecewise_eval():
) == (x >= -3) & (x <= oo)
assert f(Piecewise((x, (Abs(arg(a)) <= 1) | (Abs(arg(a)) < 1)))
) == (Abs(arg(a)) <= 1) | (Abs(arg(a)) < 1)
+
+
+def test_issue_22533():
+ x = Symbol('x', real=True)
+ f = Piecewise((-1 / x, x <= 0), (1 / x, True))
+ assert integrate(f, x) == Piecewise((-log(x), x <= 0), (log(x), True))
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-22433@4a4746d
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 22,433
|
create core.random
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #12628
Fixes #14589
closes #16967 as alternate
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
locate random-related items to the core and provide needed random generators that all run from a single instance of python's `random.Random()`
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-11-06T11:36:24Z
|
as_numer_denom non-deterministically influences the state of Python’s random number generator
When I apply `as_numer_denom` to a power expression, this changes the state of Python’s random number generator. This happens in a non-deterministic fashion, i.e., it isn’t just that random numbers are generated for whatever reason, but the state seems to be reset using some external information (like the system time).
Here is a minimal non-working example:
``` Python
import random
from sympy.abc import x
results = set()
for _ in range(10):
random.seed(42)
(x**2).as_numer_denom()
results.add(random.random())
assert len(results)==1
```
interaction of sympy and random
I noticed the following strange behaviour when generating a random function
`import sympy, random
x = sympy.symbols('x')
random.seed(10)
y = 0
for i in range(4): y += sympy.sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)
random.seed(10)
z = 0
for i in range(4): z += sympy.sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)
`
I get different values for y and z.
|
We should be using a random.Random instance so that it doesn't affect the random seed for other applications.
As a workaround, I suggest doing the same in your own code, so that nothing else can mess with random like this.
> As a workaround, I suggest doing the same in your own code, so that nothing else can mess with random like this.
That’s what I eventually did. I stumbled upon this when checking something quickly and dirtily and since I didn’t expect SymPy to use random numbers for this (let alone in a way that is not even deterministic), I was rather baffled and it took me a while to find out what happened.
For what it's worth I just spent a long time discovering the same thing by process of elimination in my own code.
Same here. Spent about two hours until finding the issue.
I've written another short example because I found something that might be useful: the issue happens only at the first call of `my_test`. Subsequent calls do not affect python's random state.
```python
import sympy as sp
import random
def my_test():
random.seed('HolaAmigo')
# Should print -1735515812038708070 (may vary on your laptop)
print(hash(random.getstate()))
for i in range(100):
x = random.randrange(2) * sp.Symbol('x')
# Should print 3791330111857148225 (may vary on your laptop)
print(hash(random.getstate()))
return
my_test() # fails
my_test() # ok
my_test() # ok
my_test() # ok
```
You may comment out the sp.Symbol to check what the value would be if no intervention from sympy occurred.
I ran into a similar problem, using `sympy.acos`.
The following program shows different results for variable `after` for consecutive runs.
import sympy
import random
random.seed(28)
before = random.uniform(0,1)
print('before: ',before)
m0, m1= sympy.symbols('m_0 m_1', real=True)
result = sympy.acos(-m0/m1)
after = random.uniform(0,1)
print('after: ',after)
What about adding a warning in the documentation about this behavior? I think the section `Gotchas and Pitfalls` would be good for this.
This is a bug. SymPy should be using its own independent random state wherever it is using random numbers. Of course, the simplest workaround is to also do the same in your own code (use `random.Random()` instead of `random`). That's recommended practice regardless, because you never know what other code will be calling the global random number generator.
The values I get do not look different:
```
>>> random.seed(10)
>>> y = 0
>>> for i in range(4): y += sympy.sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)
...
>>> y
-sin(1.42221890649771*x) + sin(1.42805189379827*x) + sin(1.56182602268941*x) - sin(5.87803535720997*x)
>>> random.seed(10)
>>> z = 0
>>> for i in range(4): z += sympy.sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)
...
>>> z
-sin(1.42221890649771*x) + sin(1.42805189379827*x) + sin(1.56182602268941*x) - sin(5.87803535720997*x)
>>>
```
Here is a screenshot :
Le lundi 2 avril 2018 à 13:21:38 UTC+2, Kalevi Suominen <[email protected]> a écrit :
The values I get do not look different:
>>> random.seed(10)
>>> y = 0
>>> for i in range(4): y += sympy.sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)
...
>>> y
-sin(1.42221890649771*x) + sin(1.42805189379827*x) + sin(1.56182602268941*x) - sin(5.87803535720997*x)
>>> random.seed(10)
>>> z = 0
>>> for i in range(4): z += sympy.sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)
...
>>> z
-sin(1.42221890649771*x) + sin(1.42805189379827*x) + sin(1.56182602268941*x) - sin(5.87803535720997*x)
>>>
—
You are receiving this because you authored the thread.
Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub, or mute the thread.
I get
```
>>> y
sin(1.42805189379827*x) + sin(1.55778912915404*x) + sin(5.54243799539346*x) + sin(8.0835978129377*x)
>>> z
-sin(1.42221890649771*x) + sin(1.42805189379827*x) + sin(3.06291637379069*x) - sin(7.68145060132939*x)
```
and I get those same two values each time.
Actually after a second run, I get the same values as @jksuom. So it's probably related to the cache somehow.
@esandier you should be able to get consistent results by using `random.Random` instances, which are seeded independently (this is always a good practice anyway).
Indeed this works. Evaluating the loop within "with evaluate(False)" works as well.
Similar issue: https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/12628
Why did you close this? I don't think it was fixed.
Sorry,
I'm not familiar with how issues are handled, I thought I was supposed to close it after a while
Etienne
Le mardi 1 mai 2018 à 21:33:31 UTC+2, Aaron Meurer <[email protected]> a écrit :
Why did you close this? I don't think it was fixed.
—
You are receiving this because you modified the open/close state.
Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub, or mute the thread.
@esandier : Bonjour, pourriez vous m'écrire ? Je me suis inscrit en follower sur votre projet pywims. Je souhaiterais l'intégrer dans un de mes sites.
Merci.
|
[
{
"body": "When I apply `as_numer_denom` to a power expression, this changes the state of Python’s random number generator. This happens in a non-deterministic fashion, i.e., it isn’t just that random numbers are generated for whatever reason, but the state seems to be reset using some external information (like the system time).\r\n\r\nHere is a minimal non-working example:\r\n\r\n``` Python\r\n\r\nimport random\r\nfrom sympy.abc import x\r\n\r\nresults = set()\r\nfor _ in range(10):\r\n\trandom.seed(42)\r\n\t(x**2).as_numer_denom()\r\n\tresults.add(random.random())\r\nassert len(results)==1\r\n```",
"number": 12628,
"title": "as_numer_denom non-deterministically influences the state of Python’s random number generator"
},
{
"body": "I noticed the following strange behaviour when generating a random function\r\n`import sympy, random\r\n\r\nx = sympy.symbols('x')\r\n\r\nrandom.seed(10)\r\n\r\ny = 0\r\n\r\nfor i in range(4): y += sympy.sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)\r\n\r\nrandom.seed(10)\r\n\r\nz = 0\r\n\r\nfor i in range(4): z += sympy.sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)\r\n`\r\nI get different values for y and z.\r\n",
"number": 14589,
"title": "interaction of sympy and random"
}
] |
3a49fc4d134864a779258d9fca9ea45c4bbe3b3c
|
{
"head_commit": "4a4746db958937816635fc6ed2cd697437dd5b08",
"head_commit_message": "add seed function to core.random",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/benchmarks/bench_symbench.py b/sympy/benchmarks/bench_symbench.py\nindex 2ec37f7bb512..8ea700b44b67 100644\n--- a/sympy/benchmarks/bench_symbench.py\n+++ b/sympy/benchmarks/bench_symbench.py\n@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@\n #!/usr/bin/env python\n-from random import random\n+from sympy.core.random import random\n from sympy.core.numbers import (I, Integer, pi)\n from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol\n from sympy.core.sympify import sympify\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/partitions.py b/sympy/combinatorics/partitions.py\nindex 2742c3cb0683..77266fc3e0e2 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/partitions.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/partitions.py\n@@ -598,7 +598,7 @@ def random_integer_partition(n, seed=None):\n >>> random_integer_partition(1)\n [1]\n \"\"\"\n- from sympy.testing.randtest import _randint\n+ from sympy.core.random import _randint\n \n n = as_int(n)\n if n < 1:\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py\nindex c865b12eadc6..c0b91c85c9b3 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py\n@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@\n-from random import randrange, choice\n+from sympy.core.random import randrange, choice\n from math import log\n from sympy.ntheory import primefactors\n from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol\n@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@\n from sympy.functions.combinatorial.factorials import factorial\n from sympy.ntheory import sieve\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import has_variety, is_sequence, uniq\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange\n+from sympy.core.random import _randrange\n from itertools import islice\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n rmul = Permutation.rmul_with_af\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_schur_number.py b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_schur_number.py\nindex 97f41471147c..a2b9348122cd 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_schur_number.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_schur_number.py\n@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@\n from sympy.core import S, Rational\n from sympy.combinatorics.schur_number import schur_partition, SchurNumber\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import _randint\n+from sympy.core.random import _randint\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n from sympy.core.symbol import symbols\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_testutil.py b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_testutil.py\nindex 393746ce0bd8..e13f4d5b9913 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_testutil.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_testutil.py\n@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@\n _verify_normal_closure\n from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n-from random import shuffle\n+from sympy.core.random import shuffle\n \n \n def test_cmp_perm_lists():\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/assumptions.py b/sympy/core/assumptions.py\nindex cf1f5e04d261..11ac8fd9e451 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/assumptions.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/assumptions.py\n@@ -214,7 +214,7 @@\n from .core import BasicMeta\n from .sympify import sympify\n \n-from random import shuffle\n+from sympy.core.random import shuffle\n \n \n _assume_rules = FactRules([\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py\nindex c9c9e8150c6d..2c71539ee6a9 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/expr.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py\n@@ -491,13 +491,13 @@ def _random(self, n=None, re_min=-1, im_min=-1, re_max=1, im_max=1):\n See Also\n ========\n \n- sympy.testing.randtest.random_complex_number\n+ sympy.core.random.random_complex_number\n \"\"\"\n \n free = self.free_symbols\n prec = 1\n if free:\n- from sympy.testing.randtest import random_complex_number\n+ from sympy.core.random import random_complex_number\n a, c, b, d = re_min, re_max, im_min, im_max\n reps = dict(list(zip(free, [random_complex_number(a, b, c, d, rational=True)\n for zi in free])))\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/random.py b/sympy/core/random.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..a3477b0d52cb\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/sympy/core/random.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,209 @@\n+\"\"\"When you need to use random, import it from here so there is only\n+one generator working for SymPy. Imports from here should behave the\n+same as if they were being imported from Python's random module. But\n+only the routines currently used in SymPy are included here. To use\n+others import `rng` and access the method directly. For example, to\n+capture the current state of the generator use `rng.getstate()`.\n+\n+There is intentionally no Random to import from here. If you want\n+to control the state of the generator, import `seed` and call it\n+with or without an argument to set the state.\n+\n+EXAMPLES\n+========\n+\n+>>> from sympy.core.random import random, seed\n+>>> assert random() < 1\n+>>> seed(1); a = random()\n+>>> b = random()\n+>>> seed(1); c = random()\n+>>> assert a == c\n+>>> assert a != b # remote possibility this will fail\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+import random as _random\n+rng = _random.Random()\n+\n+seed = lambda s=None: rng.seed(s)\n+\n+choice = rng.choice\n+random = rng.random\n+randint = rng.randint\n+randrange = rng.randrange\n+shuffle = rng.shuffle\n+uniform = rng.uniform\n+\n+def random_complex_number(a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1, rational=False, tolerance=None):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Return a random complex number.\n+\n+ To reduce chance of hitting branch cuts or anything, we guarantee\n+ b <= Im z <= d, a <= Re z <= c\n+\n+ When rational is True, a rational approximation to a random number\n+ is obtained within specified tolerance, if any.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ from sympy.core.numbers import I\n+ from sympy.simplify.simplify import nsimplify\n+ A, B = uniform(a, c), uniform(b, d)\n+ if not rational:\n+ return A + I*B\n+ return (nsimplify(A, rational=True, tolerance=tolerance) +\n+ I*nsimplify(B, rational=True, tolerance=tolerance))\n+\n+\n+def verify_numerically(f, g, z=None, tol=1.0e-6, a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Test numerically that f and g agree when evaluated in the argument z.\n+\n+ If z is None, all symbols will be tested. This routine does not test\n+ whether there are Floats present with precision higher than 15 digits\n+ so if there are, your results may not be what you expect due to round-\n+ off errors.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import sin, cos\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n+ >>> from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn\n+ >>> tn(sin(x)**2 + cos(x)**2, 1, x)\n+ True\n+ \"\"\"\n+ from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol\n+ from sympy.core.numbers import comp\n+ from sympy.core.containers import Tuple\n+ f, g, z = Tuple(f, g, z)\n+ z = [z] if isinstance(z, Symbol) else (f.free_symbols | g.free_symbols)\n+ reps = list(zip(z, [random_complex_number(a, b, c, d) for _ in z]))\n+ z1 = f.subs(reps).n()\n+ z2 = g.subs(reps).n()\n+ return comp(z1, z2, tol)\n+\n+\n+def test_derivative_numerically(f, z, tol=1.0e-6, a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Test numerically that the symbolically computed derivative of f\n+ with respect to z is correct.\n+\n+ This routine does not test whether there are Floats present with\n+ precision higher than 15 digits so if there are, your results may\n+ not be what you expect due to round-off errors.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import sin\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n+ >>> from sympy.core.random import test_derivative_numerically as td\n+ >>> td(sin(x), x)\n+ True\n+ \"\"\"\n+ from sympy.core.numbers import comp\n+ from sympy.core.function import Derivative\n+ z0 = random_complex_number(a, b, c, d)\n+ f1 = f.diff(z).subs(z, z0)\n+ f2 = Derivative(f, z).doit_numerically(z0)\n+ return comp(f1.n(), f2.n(), tol)\n+\n+\n+def _randrange(seed=None):\n+ \"\"\"Return a randrange generator. ``seed`` can be\n+ o None - return randomly seeded generator\n+ o int - return a generator seeded with the int\n+ o list - the values to be returned will be taken from the list\n+ in the order given; the provided list is not modified.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy.core.random import _randrange\n+ >>> rr = _randrange()\n+ >>> rr(1000) # doctest: +SKIP\n+ 999\n+ >>> rr = _randrange(3)\n+ >>> rr(1000) # doctest: +SKIP\n+ 238\n+ >>> rr = _randrange([0, 5, 1, 3, 4])\n+ >>> rr(3), rr(3)\n+ (0, 1)\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if seed is None:\n+ return random.randrange\n+ elif isinstance(seed, int):\n+ random.seed(seed)\n+ return random.randrange\n+ elif is_sequence(seed):\n+ seed = list(seed) # make a copy\n+ seed.reverse()\n+\n+ def give(a, b=None, seq=seed):\n+ if b is None:\n+ a, b = 0, a\n+ a, b = as_int(a), as_int(b)\n+ w = b - a\n+ if w < 1:\n+ raise ValueError('_randrange got empty range')\n+ try:\n+ x = seq.pop()\n+ except IndexError:\n+ raise ValueError('_randrange sequence was too short')\n+ if a <= x < b:\n+ return x\n+ else:\n+ return give(a, b, seq)\n+ return give\n+ else:\n+ raise ValueError('_randrange got an unexpected seed')\n+\n+\n+def _randint(seed=None):\n+ \"\"\"Return a randint generator. ``seed`` can be\n+ o None - return randomly seeded generator\n+ o int - return a generator seeded with the int\n+ o list - the values to be returned will be taken from the list\n+ in the order given; the provided list is not modified.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy.core.random import _randint\n+ >>> ri = _randint()\n+ >>> ri(1, 1000) # doctest: +SKIP\n+ 999\n+ >>> ri = _randint(3)\n+ >>> ri(1, 1000) # doctest: +SKIP\n+ 238\n+ >>> ri = _randint([0, 5, 1, 2, 4])\n+ >>> ri(1, 3), ri(1, 3)\n+ (1, 2)\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if seed is None:\n+ return random.randint\n+ elif isinstance(seed, int):\n+ random.seed(seed)\n+ return random.randint\n+ elif is_sequence(seed):\n+ seed = list(seed) # make a copy\n+ seed.reverse()\n+\n+ def give(a, b, seq=seed):\n+ a, b = as_int(a), as_int(b)\n+ w = b - a\n+ if w < 0:\n+ raise ValueError('_randint got empty range')\n+ try:\n+ x = seq.pop()\n+ except IndexError:\n+ raise ValueError('_randint sequence was too short')\n+ if a <= x <= b:\n+ return x\n+ else:\n+ return give(a, b, seq)\n+ return give\n+ else:\n+ raise ValueError('_randint got an unexpected seed')\n+\n+\n+from sympy.utilities.iterables import is_sequence\n+from sympy.utilities.misc import as_int\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/sympify.py b/sympy/core/sympify.py\nindex ae1f95bff9a2..86deba6bf541 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/sympify.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/sympify.py\n@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@\n \n from inspect import getmro\n import string\n-from random import choice\n+from sympy.core.random import choice\n \n from .parameters import global_parameters\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\nindex 1cc63610c734..ac95ead473e3 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\n@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@\n from sympy.core.expr import unchanged\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import cartes\n from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, raises, warns_deprecated_sympy\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically\n from sympy.functions.elementary.trigonometric import asin\n \n \ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_expand.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_expand.py\nindex d041b209048d..25029d4d8e72 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_expand.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_expand.py\n@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@\n from sympy.core.function import expand, expand_multinomial, expand_power_base\n \n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically\n \n from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_function.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_function.py\nindex b83806537e5b..ec89f9d2e127 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_function.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_function.py\n@@ -623,8 +623,7 @@ def ok(a):\n \n \n def test_derivative_numerically():\n- from random import random\n- z0 = random() + I*random()\n+ z0 = x._random()\n assert abs(Derivative(sin(x), x).doit_numerically(z0) - cos(z0)) < 1e-15\n \n \ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_random.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_random.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..16b768e49953\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_random.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@\n+import random\n+from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol, symbols\n+from sympy.functions.elementary.trigonometric import sin, acos\n+from sympy.abc import x\n+\n+def test_random():\n+ random.seed(42)\n+ a = random.random()\n+ random.seed(42)\n+ Symbol('z').is_finite\n+ b = random.random()\n+ assert a == b\n+\n+ got = set()\n+ for i in range(2):\n+ random.seed(28)\n+ m0, m1 = symbols('m_0 m_1', real=True)\n+ _ = acos(-m0/m1)\n+ got.add(random.uniform(0,1))\n+ assert len(got) == 1\n+\n+ random.seed(10)\n+ y = 0\n+ for i in range(4):\n+ y += sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)\n+ random.seed(10)\n+ z = 0\n+ for i in range(4):\n+ z += sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)\n+ assert y == z\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py\nindex eeb5f9afec4d..a28da387c0f3 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py\n@@ -379,7 +379,7 @@ def test_new_relational():\n assert (x < 0) != StrictLessThan(x, 1)\n \n # finally, some fuzz testing\n- from random import randint\n+ from sympy.core.random import randint\n for i in range(100):\n while 1:\n strtype, length = (chr, 65535) if randint(0, 1) else (chr, 255)\ndiff --git a/sympy/crypto/crypto.py b/sympy/crypto/crypto.py\nindex 821398d0aaf9..05d5c1dcefeb 100644\n--- a/sympy/crypto/crypto.py\n+++ b/sympy/crypto/crypto.py\n@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@\n from sympy.polys.polytools import gcd, Poly\n from sympy.utilities.misc import as_int, filldedent, translate\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import uniq, multiset\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange, _randint\n+from sympy.core.random import _randrange, _randint\n \n \n class NonInvertibleCipherWarning(RuntimeWarning):\n@@ -2571,7 +2571,7 @@ def elgamal_private_key(digit=10, seed=None):\n =====\n \n For testing purposes, the ``seed`` parameter may be set to control\n- the output of this routine. See sympy.testing.randtest._randrange.\n+ the output of this routine. See sympy.core.random._randrange.\n \n Examples\n ========\n@@ -2656,7 +2656,7 @@ def encipher_elgamal(i, key, seed=None):\n =====\n \n For testing purposes, the ``seed`` parameter may be set to control\n- the output of this routine. See sympy.testing.randtest._randrange.\n+ the output of this routine. See sympy.core.random._randrange.\n \n Examples\n ========\n@@ -2764,7 +2764,7 @@ def dh_private_key(digit=10, seed=None):\n =====\n \n For testing purposes, the ``seed`` parameter may be set to control\n- the output of this routine. See sympy.testing.randtest._randrange.\n+ the output of this routine. See sympy.core.random._randrange.\n \n Examples\n ========\ndiff --git a/sympy/crypto/tests/test_crypto.py b/sympy/crypto/tests/test_crypto.py\nindex a38af2297dd2..36067bfd0181 100644\n--- a/sympy/crypto/tests/test_crypto.py\n+++ b/sympy/crypto/tests/test_crypto.py\n@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@\n \n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, warns\n \n-from random import randrange\n+from sympy.core.random import randrange\n \n def test_encipher_railfence():\n assert encipher_railfence(\"hello world\",2) == \"hlowrdel ol\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_numbers.py b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_numbers.py\nindex 607bb0362a57..64a30a48c1dc 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_numbers.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_numbers.py\n@@ -492,7 +492,7 @@ def test_nC_nP_nT():\n nP, nC, nT, stirling, _stirling1, _stirling2, _multiset_histogram, _AOP_product)\n \n from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n- from random import choice\n+ from sympy.core.random import choice\n \n c = string.ascii_lowercase\n for i in range(100):\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py\nindex 15a61a455eba..a09dde334499 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py\n@@ -396,7 +396,7 @@ def test_issue_11099():\n assert Max(x, y).evalf(subs=fixed_test_data) == \\\n Max(x, y).subs(fixed_test_data).evalf()\n # randomly generate some test data\n- from random import randint\n+ from sympy.core.random import randint\n for i in range(20):\n random_test_data = {x: randint(-100, 100), y: randint(-100, 100)}\n assert Min(x, y).evalf(subs=random_test_data) == \\\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_bessel.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_bessel.py\nindex 9904823a55cf..a34247545864 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_bessel.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_bessel.py\n@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@\n from sympy.series.series import series\n from sympy.functions.special.bessel import (airyai, airybi,\n airyaiprime, airybiprime, marcumq)\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import (random_complex_number as randcplx,\n+from sympy.core.random import (random_complex_number as randcplx,\n verify_numerically as tn,\n test_derivative_numerically as td,\n _randint)\n@@ -483,7 +483,7 @@ def test_branching():\n assert besseli(n, polar_lift(x)) == besseli(n, x)\n \n def tn(func, s):\n- from random import uniform\n+ from sympy.core.random import uniform\n c = uniform(1, 5)\n expr = func(s, c*exp_polar(I*pi)) - func(s, c*exp_polar(-I*pi))\n eps = 1e-15\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_elliptic_integrals.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_elliptic_integrals.py\nindex 54b783c0d6a7..52f8c09422cb 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_elliptic_integrals.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_elliptic_integrals.py\n@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@\n from sympy.series.order import O\n from sympy.functions.special.elliptic_integrals import (elliptic_k as K,\n elliptic_f as F, elliptic_e as E, elliptic_pi as P)\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import (test_derivative_numerically as td,\n+from sympy.core.random import (test_derivative_numerically as td,\n random_complex_number as randcplx,\n verify_numerically as tn)\n from sympy.abc import z, m, n\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_error_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_error_functions.py\nindex 71e84db48a15..3d8200148ba0 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_error_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_error_functions.py\n@@ -355,7 +355,7 @@ def test_erf2inv():\n \n \n def mytn(expr1, expr2, expr3, x, d=0):\n- from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically, random_complex_number\n+ from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically, random_complex_number\n subs = {}\n for a in expr1.free_symbols:\n if a != x:\n@@ -365,7 +365,7 @@ def mytn(expr1, expr2, expr3, x, d=0):\n \n \n def mytd(expr1, expr2, x):\n- from sympy.testing.randtest import test_derivative_numerically, \\\n+ from sympy.core.random import test_derivative_numerically, \\\n random_complex_number\n subs = {}\n for a in expr1.free_symbols:\n@@ -375,7 +375,7 @@ def mytd(expr1, expr2, x):\n \n \n def tn_branch(func, s=None):\n- from random import uniform\n+ from sympy.core.random import uniform\n \n def fn(x):\n if s is None:\n@@ -508,7 +508,7 @@ def test__eis():\n \n def tn_arg(func):\n def test(arg, e1, e2):\n- from random import uniform\n+ from sympy.core.random import uniform\n v = uniform(1, 5)\n v1 = func(arg*x).subs(x, v).n()\n v2 = func(e1*v + e2*1e-15).n()\n@@ -776,7 +776,7 @@ def test_fresnel():\n meijerg(((), (1,)), ((Rational(1, 4),),\n (Rational(3, 4), 0)), -pi**2*z**4/16)/(2*(-z)**Rational(1, 4)*(z**2)**Rational(1, 4))\n \n- from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically\n+ from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically\n \n verify_numerically(re(fresnels(z)), fresnels(z).as_real_imag()[0], z)\n verify_numerically(im(fresnels(z)), fresnels(z).as_real_imag()[1], z)\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py\nindex 4856db15bbdd..0a200c534be3 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py\n@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@\n from sympy.core.expr import unchanged\n from sympy.core.function import ArgumentIndexError\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import (test_derivative_numerically as td,\n+from sympy.core.random import (test_derivative_numerically as td,\n random_complex_number as randcplx,\n verify_numerically as tn)\n \n@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ def test_gamma_series():\n \n \n def tn_branch(s, func):\n- from random import uniform\n+ from sympy.core.random import uniform\n c = uniform(1, 5)\n expr = func(s, c*exp_polar(I*pi)) - func(s, c*exp_polar(-I*pi))\n eps = 1e-15\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_hyper.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_hyper.py\nindex e8113319f764..716deac580db 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_hyper.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_hyper.py\n@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@\n from sympy.abc import x, z, k\n from sympy.series.limits import limit\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, slow\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import (\n+from sympy.core.random import (\n random_complex_number as randcplx,\n verify_numerically as tn,\n test_derivative_numerically as td)\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_zeta_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_zeta_functions.py\nindex e2d98c073432..90dbeb5855e1 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_zeta_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_zeta_functions.py\n@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@\n from sympy.core.function import ArgumentIndexError\n from sympy.functions.combinatorial.numbers import bernoulli, factorial\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import (test_derivative_numerically as td,\n+from sympy.core.random import (test_derivative_numerically as td,\n random_complex_number as randcplx, verify_numerically)\n \n x = Symbol('x')\ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_entity.py b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_entity.py\nindex e279f86efb43..cecfdb785506 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_entity.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_entity.py\n@@ -6,8 +6,6 @@\n from sympy.geometry.entity import scale, GeometryEntity\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n \n-from random import random\n-\n \n def test_entity():\n x = Symbol('x', real=True)\n@@ -85,8 +83,10 @@ def test_reflect_entity_overrides():\n assert c.area == -cr.area\n \n pent = RegularPolygon((1, 2), 1, 5)\n- l = Line(pent.vertices[1],\n- slope=Rational(random() - .5, random() - .5))\n+ slope = S.ComplexInfinity\n+ while slope is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ slope = Rational(*(x._random()/2).as_real_imag())\n+ l = Line(pent.vertices[1], slope=slope)\n rpent = pent.reflect(l)\n assert rpent.center == pent.center.reflect(l)\n rvert = [i.reflect(l) for i in pent.vertices]\ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_polygon.py b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_polygon.py\nindex ab9216af869a..4f0507ee44d2 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_polygon.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_polygon.py\n@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@\n Polygon, Ray, RegularPolygon, Segment, Triangle,\n are_similar, convex_hull, intersection, Line, Ray2D)\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, slow, warns\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically\n from sympy.geometry.polygon import rad, deg\n from sympy.integrals.integrals import integrate\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_util.py b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_util.py\nindex 45e1a7bcf230..51e119edb452 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_util.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_util.py\n@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ def test_centroid():\n \n \n def test_farthest_points_closest_points():\n- from random import randint\n+ from sympy.core.random import randint\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import subsets\n \n for how in (min, max):\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/rubi/utility_function.py b/sympy/integrals/rubi/utility_function.py\nindex b64bac06f30d..a28d59f850e8 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/rubi/utility_function.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/rubi/utility_function.py\n@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@\n from sympy.simplify.simplify import fraction, simplify, cancel, powsimp, nsimplify\n from sympy.utilities.decorator import doctest_depends_on\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import flatten\n-from random import randint\n+from sympy.core.random import randint\n \n \n class rubi_unevaluated_expr(UnevaluatedExpr):\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_integrals.py b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_integrals.py\nindex b38398aa55d0..5d0634245fec 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_integrals.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_integrals.py\n@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@\n from sympy.physics import units\n from sympy.testing.pytest import (raises, slow, skip, ON_TRAVIS,\n warns_deprecated_sympy)\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically\n \n \n x, y, a, t, x_1, x_2, z, s, b = symbols('x y a t x_1 x_2 z s b')\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_meijerint.py b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_meijerint.py\nindex 7e2961ebb606..1f3f136b8320 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_meijerint.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_meijerint.py\n@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@\n meijerint_indefinite, _inflate_g, _create_lookup_table,\n meijerint_definite, meijerint_inversion)\n from sympy.testing.pytest import slow\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import (verify_numerically,\n+from sympy.core.random import (verify_numerically,\n random_complex_number as randcplx)\n from sympy.abc import x, y, a, b, c, d, s, t, z\n \n@@ -338,7 +338,7 @@ def test_inversion_exp_real_nonreal_shift():\n \n @slow\n def test_lookup_table():\n- from random import uniform, randrange\n+ from sympy.core.random import uniform, randrange\n from sympy.core.add import Add\n from sympy.integrals.meijerint import z as z_dummy\n table = {}\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py b/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py\nindex 101c08a7e23c..4f629b0ebc95 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py\n@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@\n from .primetest import isprime\n from .factor_ import factorint, trailing, totient, multiplicity\n from sympy.utilities.misc import as_int\n-from random import randint, Random\n+from sympy.core.random import _randint, randint\n \n from itertools import cycle, product\n \n@@ -1196,13 +1196,11 @@ def _discrete_log_pollard_rho(n, a, b, order=None, retries=10, rseed=None):\n \n if order is None:\n order = n_order(b, n)\n- prng = Random()\n- if rseed is not None:\n- prng.seed(rseed)\n+ randint = _randint(rseed)\n \n for i in range(retries):\n- aa = prng.randint(1, order - 1)\n- ba = prng.randint(1, order - 1)\n+ aa = randint(1, order - 1)\n+ ba = randint(1, order - 1)\n xa = pow(b, aa, n) * pow(a, ba, n) % n\n \n c = xa % 3\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_bbp_pi.py b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_bbp_pi.py\nindex 806945a6a550..c18188e3c8a3 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_bbp_pi.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_bbp_pi.py\n@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@\n-from random import randint\n+from sympy.core.random import randint\n \n from sympy.ntheory.bbp_pi import pi_hex_digits\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_egyptian_fraction.py b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_egyptian_fraction.py\nindex 10e2ef3e214e..a9a9fac578d9 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_egyptian_fraction.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_egyptian_fraction.py\n@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@\n from sympy.ntheory.egyptian_fraction import egyptian_fraction\n from sympy.core.add import Add\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import random_complex_number\n+from sympy.core.random import random_complex_number\n \n \n def test_egyptian_fraction():\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py\nindex 10a634daf8b6..95fa3ce15e10 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py\n@@ -406,7 +406,7 @@ def random_reduce(circuit, gate_ids, seed=None):\n given by the list\n \n \"\"\"\n- from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange\n+ from sympy.core.random import _randrange\n \n if not gate_ids:\n return circuit\n@@ -460,7 +460,7 @@ def random_insert(circuit, choices, seed=None):\n Indices for insertion should be [0, n] if n is the length of the\n circuit.\n \"\"\"\n- from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange\n+ from sympy.core.random import _randrange\n \n if not choices:\n return circuit\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py\nindex 0dac602c7451..04b00ef208e4 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py\n@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@\n from collections import deque\n-from random import randint\n+from sympy.core.random import randint\n \n from sympy.external import import_module\n from sympy.core.basic import Basic\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_matrixutils.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_matrixutils.py\nindex 8726abfd30fe..af581f7aa236 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_matrixutils.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_matrixutils.py\n@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@\n-from random import randint\n+from sympy.core.random import randint\n \n from sympy.core.numbers import Integer\n from sympy.matrices.dense import (Matrix, ones, zeros)\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/factortools.py b/sympy/polys/factortools.py\nindex 0b7da8e2d26b..c322bef488a2 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/factortools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/factortools.py\n@@ -977,7 +977,7 @@ def dmp_zz_wang(f, u, K, mod=None, seed=None):\n .. [2] [Geddes92]_\n \n \"\"\"\n- from sympy.testing.randtest import _randint\n+ from sympy.core.random import _randint\n \n randint = _randint(seed)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/galoistools.py b/sympy/polys/galoistools.py\nindex ea52353d0581..9ffe6b5dbb45 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/galoistools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/galoistools.py\n@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@\n \"\"\"Dense univariate polynomials with coefficients in Galois fields. \"\"\"\n \n \n-from random import uniform\n+from sympy.core.random import uniform\n from math import ceil as _ceil, sqrt as _sqrt\n \n from sympy.core.mul import prod\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyroots.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyroots.py\nindex fa5900298e01..18a389a41a4e 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyroots.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyroots.py\n@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@\n from sympy.polys.polyutils import _nsort\n \n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, slow\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically\n import mpmath\n from itertools import product\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_cse.py b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_cse.py\nindex 9a0cfa323090..efb39bc2d3ea 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_cse.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_cse.py\n@@ -454,7 +454,7 @@ def test_issue_11230():\n assert not any(i.is_Mul for a in C for i in a.args)\n \n # random tests for the issue\n- from random import choice\n+ from sympy.core.random import choice\n from sympy.core.function import expand_mul\n s = symbols('a:m')\n # 35 Mul tests, none of which should ever fail\ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_fu.py b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_fu.py\nindex 94cd0c8cc368..3bf4f74c522c 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_fu.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_fu.py\n@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@\n TR111, TR2, TR2i, TR3, TR5, TR6, TR7, TR8, TR9, TRmorrie, _TR56 as T,\n TRpower, hyper_as_trig, fu, process_common_addends, trig_split,\n as_f_sign_1)\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically\n from sympy.abc import a, b, c, x, y, z\n \n \ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_hyperexpand.py b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_hyperexpand.py\nindex f770865e84d3..146dadc183eb 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_hyperexpand.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_hyperexpand.py\n@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@\n-from random import randrange\n+from sympy.core.random import randrange\n \n from sympy.simplify.hyperexpand import (ShiftA, ShiftB, UnShiftA, UnShiftB,\n MeijerShiftA, MeijerShiftB, MeijerShiftC, MeijerShiftD,\n@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@\n from sympy.functions.special.hyper import (hyper, meijerg)\n from sympy.abc import z, a, b, c\n from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, raises, slow, ON_TRAVIS, skip\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn\n \n from sympy.core.numbers import (Rational, pi)\n from sympy.functions.elementary.exponential import (exp, exp_polar, log)\ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_trigsimp.py b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_trigsimp.py\nindex a960b3b9bfdd..3fda27955c95 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_trigsimp.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_trigsimp.py\n@@ -379,7 +379,7 @@ def test_issue_15129_trigsimp_methods():\n \n def test_exptrigsimp():\n def valid(a, b):\n- from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn\n+ from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn\n if not (tn(a, b) and a == b):\n return False\n return True\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py\nindex d98971a94435..2f1744e98d56 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py\n@@ -658,7 +658,7 @@ def test_sum_of_three_squares():\n \n \n def test_sum_of_four_squares():\n- from random import randint\n+ from sympy.core.random import randint\n \n # this should never fail\n n = randint(1, 100000000000000)\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py\nindex 24428d0a52d8..1c9487afed93 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py\n@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@\n-from random import randint\n+from sympy.core.random import randint\n from sympy.core.function import Function\n from sympy.core.mul import Mul\n from sympy.core.numbers import (I, Rational, oo)\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\nindex d32e2eb05a53..942810fb63c9 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\n@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@\n from sympy.polys.rootoftools import CRootOf\n \n from sympy.testing.pytest import slow, XFAIL, SKIP, raises\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn\n \n from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, e, k, h, p, x, y, z, t, q, m, R\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\nindex 5b230469083f..236a56dd7c3b 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\n@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import numbered_symbols\n \n from sympy.testing.pytest import (XFAIL, raises, skip, slow, SKIP, _both_exp_pow)\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn\n from sympy.physics.units import cm\n \n from sympy.solvers import solve\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py\nindex a9eb50845ec7..d74525c87629 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py\n@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@\n from sympy.stats.compound_rv import CompoundPSpace\n from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, XFAIL, slow, ignore_warnings\n-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn\n+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn\n \n oo = S.Infinity\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/tensor/tests/test_tensor_operators.py b/sympy/tensor/tests/test_tensor_operators.py\nindex a3aca8dc7898..996d0af06070 100644\n--- a/sympy/tensor/tests/test_tensor_operators.py\n+++ b/sympy/tensor/tests/test_tensor_operators.py\n@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@\n from sympy.matrices.dense import diag\n from sympy.tensor.array import Array\n \n-from random import randint\n+from sympy.core.random import randint\n \n \n L = TensorIndexType(\"L\")\ndiff --git a/sympy/testing/randtest.py b/sympy/testing/randtest.py\nindex 4d5232acd521..588496e9be05 100644\n--- a/sympy/testing/randtest.py\n+++ b/sympy/testing/randtest.py\n@@ -1,174 +1,26 @@\n-\"\"\" Helpers for randomized testing \"\"\"\n-\n-from random import uniform, Random, randrange, randint\n-\n-from sympy.core.containers import Tuple\n-from sympy.core.function import Derivative\n-from sympy.core.numbers import comp, I\n-from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol\n-from sympy.simplify.simplify import nsimplify\n-from sympy.utilities.iterables import is_sequence\n-from sympy.utilities.misc import as_int\n-\n-\n-def random_complex_number(a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1, rational=False, tolerance=None):\n- \"\"\"\n- Return a random complex number.\n-\n- To reduce chance of hitting branch cuts or anything, we guarantee\n- b <= Im z <= d, a <= Re z <= c\n-\n- When rational is True, a rational approximation to a random number\n- is obtained within specified tolerance, if any.\n- \"\"\"\n- A, B = uniform(a, c), uniform(b, d)\n- if not rational:\n- return A + I*B\n- return (nsimplify(A, rational=True, tolerance=tolerance) +\n- I*nsimplify(B, rational=True, tolerance=tolerance))\n-\n-\n-def verify_numerically(f, g, z=None, tol=1.0e-6, a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1):\n- \"\"\"\n- Test numerically that f and g agree when evaluated in the argument z.\n-\n- If z is None, all symbols will be tested. This routine does not test\n- whether there are Floats present with precision higher than 15 digits\n- so if there are, your results may not be what you expect due to round-\n- off errors.\n-\n- Examples\n- ========\n-\n- >>> from sympy import sin, cos\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x\n- >>> from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn\n- >>> tn(sin(x)**2 + cos(x)**2, 1, x)\n- True\n- \"\"\"\n- f, g, z = Tuple(f, g, z)\n- z = [z] if isinstance(z, Symbol) else (f.free_symbols | g.free_symbols)\n- reps = list(zip(z, [random_complex_number(a, b, c, d) for _ in z]))\n- z1 = f.subs(reps).n()\n- z2 = g.subs(reps).n()\n- return comp(z1, z2, tol)\n-\n-\n-def test_derivative_numerically(f, z, tol=1.0e-6, a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1):\n- \"\"\"\n- Test numerically that the symbolically computed derivative of f\n- with respect to z is correct.\n-\n- This routine does not test whether there are Floats present with\n- precision higher than 15 digits so if there are, your results may\n- not be what you expect due to round-off errors.\n-\n- Examples\n- ========\n-\n- >>> from sympy import sin\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x\n- >>> from sympy.testing.randtest import test_derivative_numerically as td\n- >>> td(sin(x), x)\n- True\n- \"\"\"\n- z0 = random_complex_number(a, b, c, d)\n- f1 = f.diff(z).subs(z, z0)\n- f2 = Derivative(f, z).doit_numerically(z0)\n- return comp(f1.n(), f2.n(), tol)\n-\n-\n-def _randrange(seed=None):\n- \"\"\"Return a randrange generator. ``seed`` can be\n- o None - return randomly seeded generator\n- o int - return a generator seeded with the int\n- o list - the values to be returned will be taken from the list\n- in the order given; the provided list is not modified.\n-\n- Examples\n- ========\n-\n- >>> from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange\n- >>> rr = _randrange()\n- >>> rr(1000) # doctest: +SKIP\n- 999\n- >>> rr = _randrange(3)\n- >>> rr(1000) # doctest: +SKIP\n- 238\n- >>> rr = _randrange([0, 5, 1, 3, 4])\n- >>> rr(3), rr(3)\n- (0, 1)\n- \"\"\"\n- if seed is None:\n- return randrange\n- elif isinstance(seed, int):\n- return Random(seed).randrange\n- elif is_sequence(seed):\n- seed = list(seed) # make a copy\n- seed.reverse()\n-\n- def give(a, b=None, seq=seed):\n- if b is None:\n- a, b = 0, a\n- a, b = as_int(a), as_int(b)\n- w = b - a\n- if w < 1:\n- raise ValueError('_randrange got empty range')\n- try:\n- x = seq.pop()\n- except IndexError:\n- raise ValueError('_randrange sequence was too short')\n- if a <= x < b:\n- return x\n- else:\n- return give(a, b, seq)\n- return give\n- else:\n- raise ValueError('_randrange got an unexpected seed')\n-\n-\n-def _randint(seed=None):\n- \"\"\"Return a randint generator. ``seed`` can be\n- o None - return randomly seeded generator\n- o int - return a generator seeded with the int\n- o list - the values to be returned will be taken from the list\n- in the order given; the provided list is not modified.\n-\n- Examples\n- ========\n-\n- >>> from sympy.testing.randtest import _randint\n- >>> ri = _randint()\n- >>> ri(1, 1000) # doctest: +SKIP\n- 999\n- >>> ri = _randint(3)\n- >>> ri(1, 1000) # doctest: +SKIP\n- 238\n- >>> ri = _randint([0, 5, 1, 2, 4])\n- >>> ri(1, 3), ri(1, 3)\n- (1, 2)\n- \"\"\"\n- if seed is None:\n- return randint\n- elif isinstance(seed, int):\n- return Random(seed).randint\n- elif is_sequence(seed):\n- seed = list(seed) # make a copy\n- seed.reverse()\n-\n- def give(a, b, seq=seed):\n- a, b = as_int(a), as_int(b)\n- w = b - a\n- if w < 0:\n- raise ValueError('_randint got empty range')\n- try:\n- x = seq.pop()\n- except IndexError:\n- raise ValueError('_randint sequence was too short')\n- if a <= x <= b:\n- return x\n- else:\n- return give(a, b, seq)\n- return give\n- else:\n- raise ValueError('_randint got an unexpected seed')\n+from sympy.core.random import (\r\n+ random_complex_number as A,\r\n+ verify_numerically as B,\r\n+ test_derivative_numerically as C,\r\n+ _randrange as D,\r\n+ _randint as E)\r\n+from sympy.utilities.decorator import deprecated\r\n+\r\n+random_complex_number = deprecated(useinstead=\"sympy.core.random.random_complex_number\",\r\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.10\", issue=22433)(A)\r\n+\r\n+\r\n+verify_numerically = deprecated(useinstead=\"sympy.core.random.verify_numerically\",\r\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.10\", issue=22433)(B)\r\n+\r\n+\r\n+test_derivative_numerically = deprecated(useinstead=\"sympy.core.random.test_derivative_numerically\",\r\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.10\", issue=22433)(C)\r\n+\r\n+\r\n+_randrange = deprecated(useinstead=\"sympy.core.random._randint\",\r\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.10\", issue=22433)(D)\r\n+\r\n+\r\n+_randint = deprecated(useinstead=\"sympy.core.random._randint\",\r\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.10\", issue=22433)(E)\r\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\nindex 111d3f31bd12..cac0d2e1e081 100644\n--- a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\n@@ -2313,7 +2313,6 @@ def random_derangement(t, choice=None, strict=True):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.utilities.iterables import random_derangement\n- >>> from random import Random\n >>> t = 'SymPy: a CAS in pure Python'\n >>> d = random_derangement(t)\n >>> all(i != j for i, j in zip(d, t))\n@@ -2322,6 +2321,8 @@ def random_derangement(t, choice=None, strict=True):\n A predictable result can be obtained by using a pseudorandom\n generator for the choice:\n \n+ >>> from sympy.core.random import random, Random\n+ >>> random.seed(1)\n >>> c = Random(1).choice\n >>> d = [''.join(random_derangement(t, c)) for i in range(5)]\n >>> assert len(set(d)) != 1 # we got different values\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/randtest.py b/sympy/utilities/randtest.py\nindex d9fb1ec4237f..567fd919b9f2 100644\n--- a/sympy/utilities/randtest.py\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/randtest.py\n@@ -2,8 +2,8 @@\n \n SymPyDeprecationWarning(\n feature=\"Import sympy.utilities.randtest\",\n- useinstead=\"Import from sympy.testing.randtest\",\n+ useinstead=\"Import from sympy.core.random\",\n issue=18095,\n deprecated_since_version=\"1.6\").warn()\n \n-from sympy.testing.randtest import * # noqa:F401\n+from sympy.core.random import * # noqa:F401\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,209 @@\n+\"\"\"When you need to use random, import it from here so there is only\n+one generator working for SymPy. Imports from here should behave the\n+same as if they were being imported from Python's random module. But\n+only the routines currently used in SymPy are included here. To use\n+others import `rng` and access the method directly. For example, to\n+capture the current state of the generator use `rng.getstate()`.\n+\n+There is intentionally no Random to import from here. If you want\n+to control the state of the generator, import `seed` and call it\n+with or without an argument to set the state.\n+\n+EXAMPLES\n+========\n+\n+>>> from sympy.core.random import random, seed\n+>>> assert random() < 1\n+>>> seed(1); a = random()\n+>>> b = random()\n+>>> seed(1); c = random()\n+>>> assert a == c\n+>>> assert a != b # remote possibility this will fail\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+import random as _random\n+rng = _random.Random()\n+\n+seed = lambda s=None: rng.seed(s)\n+\n+choice = rng.choice\n+random = rng.random\n+randint = rng.randint\n+randrange = rng.randrange\n+shuffle = rng.shuffle",
"line": null,
"original_line": 33,
"original_start_line": 27,
"path": "sympy/core/random.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@author:\n```suggestion\r\nchoice = rng.choice\r\nrandom = rng.random\r\nrandint = rng.randint\r\nrandrange = rng.randrange\r\nseed = rng.seed\r\nshuffle = rng.shuffle\r\n```"
}
] |
b573b1c81dcfefaf682825d7fc64e9c08e2e84f8
|
diff --git a/sympy/benchmarks/bench_symbench.py b/sympy/benchmarks/bench_symbench.py
index 2ec37f7bb512..8ea700b44b67 100644
--- a/sympy/benchmarks/bench_symbench.py
+++ b/sympy/benchmarks/bench_symbench.py
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
#!/usr/bin/env python
-from random import random
+from sympy.core.random import random
from sympy.core.numbers import (I, Integer, pi)
from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol
from sympy.core.sympify import sympify
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/partitions.py b/sympy/combinatorics/partitions.py
index 2742c3cb0683..77266fc3e0e2 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/partitions.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/partitions.py
@@ -598,7 +598,7 @@ def random_integer_partition(n, seed=None):
>>> random_integer_partition(1)
[1]
"""
- from sympy.testing.randtest import _randint
+ from sympy.core.random import _randint
n = as_int(n)
if n < 1:
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py
index c865b12eadc6..c0b91c85c9b3 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-from random import randrange, choice
+from sympy.core.random import randrange, choice
from math import log
from sympy.ntheory import primefactors
from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@
from sympy.functions.combinatorial.factorials import factorial
from sympy.ntheory import sieve
from sympy.utilities.iterables import has_variety, is_sequence, uniq
-from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange
+from sympy.core.random import _randrange
from itertools import islice
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
rmul = Permutation.rmul_with_af
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_schur_number.py b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_schur_number.py
index 97f41471147c..a2b9348122cd 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_schur_number.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_schur_number.py
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
from sympy.core import S, Rational
from sympy.combinatorics.schur_number import schur_partition, SchurNumber
-from sympy.testing.randtest import _randint
+from sympy.core.random import _randint
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
from sympy.core.symbol import symbols
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_testutil.py b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_testutil.py
index 393746ce0bd8..e13f4d5b9913 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_testutil.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_testutil.py
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
_verify_normal_closure
from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
-from random import shuffle
+from sympy.core.random import shuffle
def test_cmp_perm_lists():
diff --git a/sympy/core/assumptions.py b/sympy/core/assumptions.py
index cf1f5e04d261..11ac8fd9e451 100644
--- a/sympy/core/assumptions.py
+++ b/sympy/core/assumptions.py
@@ -214,7 +214,7 @@
from .core import BasicMeta
from .sympify import sympify
-from random import shuffle
+from sympy.core.random import shuffle
_assume_rules = FactRules([
diff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py
index c9c9e8150c6d..2c71539ee6a9 100644
--- a/sympy/core/expr.py
+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py
@@ -491,13 +491,13 @@ def _random(self, n=None, re_min=-1, im_min=-1, re_max=1, im_max=1):
See Also
========
- sympy.testing.randtest.random_complex_number
+ sympy.core.random.random_complex_number
"""
free = self.free_symbols
prec = 1
if free:
- from sympy.testing.randtest import random_complex_number
+ from sympy.core.random import random_complex_number
a, c, b, d = re_min, re_max, im_min, im_max
reps = dict(list(zip(free, [random_complex_number(a, b, c, d, rational=True)
for zi in free])))
diff --git a/sympy/core/random.py b/sympy/core/random.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..d0308c67f8f1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sympy/core/random.py
@@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
+"""When you need to use random, import it from here so there is only
+one generator working for SymPy. Imports from here should behave the
+same as if they were being imported from Python's random module. But
+only the routines currently used in SymPy are included here. To use
+others import `rng` and access the method directly. For example, to
+capture the current state of the generator use `rng.getstate()`.
+
+There is intentionally no Random to import from here. If you want
+to control the state of the generator, import `seed` and call it
+with or without an argument to set the state.
+
+EXAMPLES
+========
+
+>>> from sympy.core.random import random, seed
+>>> assert random() < 1
+>>> seed(1); a = random()
+>>> b = random()
+>>> seed(1); c = random()
+>>> assert a == c
+>>> assert a != b # remote possibility this will fail
+"""
+from sympy.utilities.iterables import is_sequence
+from sympy.utilities.misc import as_int
+
+import random as _random
+rng = _random.Random()
+
+choice = rng.choice
+random = rng.random
+randint = rng.randint
+randrange = rng.randrange
+seed = rng.seed
+shuffle = rng.shuffle
+uniform = rng.uniform
+
+def random_complex_number(a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1, rational=False, tolerance=None):
+ """
+ Return a random complex number.
+
+ To reduce chance of hitting branch cuts or anything, we guarantee
+ b <= Im z <= d, a <= Re z <= c
+
+ When rational is True, a rational approximation to a random number
+ is obtained within specified tolerance, if any.
+ """
+ from sympy.core.numbers import I
+ from sympy.simplify.simplify import nsimplify
+ A, B = uniform(a, c), uniform(b, d)
+ if not rational:
+ return A + I*B
+ return (nsimplify(A, rational=True, tolerance=tolerance) +
+ I*nsimplify(B, rational=True, tolerance=tolerance))
+
+
+def verify_numerically(f, g, z=None, tol=1.0e-6, a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1):
+ """
+ Test numerically that f and g agree when evaluated in the argument z.
+
+ If z is None, all symbols will be tested. This routine does not test
+ whether there are Floats present with precision higher than 15 digits
+ so if there are, your results may not be what you expect due to round-
+ off errors.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import sin, cos
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
+ >>> from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn
+ >>> tn(sin(x)**2 + cos(x)**2, 1, x)
+ True
+ """
+ from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol
+ from sympy.core.numbers import comp
+ from sympy.core.containers import Tuple
+ f, g, z = Tuple(f, g, z)
+ z = [z] if isinstance(z, Symbol) else (f.free_symbols | g.free_symbols)
+ reps = list(zip(z, [random_complex_number(a, b, c, d) for _ in z]))
+ z1 = f.subs(reps).n()
+ z2 = g.subs(reps).n()
+ return comp(z1, z2, tol)
+
+
+def test_derivative_numerically(f, z, tol=1.0e-6, a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1):
+ """
+ Test numerically that the symbolically computed derivative of f
+ with respect to z is correct.
+
+ This routine does not test whether there are Floats present with
+ precision higher than 15 digits so if there are, your results may
+ not be what you expect due to round-off errors.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import sin
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
+ >>> from sympy.core.random import test_derivative_numerically as td
+ >>> td(sin(x), x)
+ True
+ """
+ from sympy.core.numbers import comp
+ from sympy.core.function import Derivative
+ z0 = random_complex_number(a, b, c, d)
+ f1 = f.diff(z).subs(z, z0)
+ f2 = Derivative(f, z).doit_numerically(z0)
+ return comp(f1.n(), f2.n(), tol)
+
+
+def _randrange(seed=None):
+ """Return a randrange generator. ``seed`` can be
+ o None - return randomly seeded generator
+ o int - return a generator seeded with the int
+ o list - the values to be returned will be taken from the list
+ in the order given; the provided list is not modified.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.core.random import _randrange
+ >>> rr = _randrange()
+ >>> rr(1000) # doctest: +SKIP
+ 999
+ >>> rr = _randrange(3)
+ >>> rr(1000) # doctest: +SKIP
+ 238
+ >>> rr = _randrange([0, 5, 1, 3, 4])
+ >>> rr(3), rr(3)
+ (0, 1)
+ """
+ if seed is None:
+ return randrange
+ elif isinstance(seed, int):
+ rng.seed(seed)
+ return randrange
+ elif is_sequence(seed):
+ seed = list(seed) # make a copy
+ seed.reverse()
+
+ def give(a, b=None, seq=seed):
+ if b is None:
+ a, b = 0, a
+ a, b = as_int(a), as_int(b)
+ w = b - a
+ if w < 1:
+ raise ValueError('_randrange got empty range')
+ try:
+ x = seq.pop()
+ except IndexError:
+ raise ValueError('_randrange sequence was too short')
+ if a <= x < b:
+ return x
+ else:
+ return give(a, b, seq)
+ return give
+ else:
+ raise ValueError('_randrange got an unexpected seed')
+
+
+def _randint(seed=None):
+ """Return a randint generator. ``seed`` can be
+ o None - return randomly seeded generator
+ o int - return a generator seeded with the int
+ o list - the values to be returned will be taken from the list
+ in the order given; the provided list is not modified.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.core.random import _randint
+ >>> ri = _randint()
+ >>> ri(1, 1000) # doctest: +SKIP
+ 999
+ >>> ri = _randint(3)
+ >>> ri(1, 1000) # doctest: +SKIP
+ 238
+ >>> ri = _randint([0, 5, 1, 2, 4])
+ >>> ri(1, 3), ri(1, 3)
+ (1, 2)
+ """
+ if seed is None:
+ return randint
+ elif isinstance(seed, int):
+ rng.seed(seed)
+ return randint
+ elif is_sequence(seed):
+ seed = list(seed) # make a copy
+ seed.reverse()
+
+ def give(a, b, seq=seed):
+ a, b = as_int(a), as_int(b)
+ w = b - a
+ if w < 0:
+ raise ValueError('_randint got empty range')
+ try:
+ x = seq.pop()
+ except IndexError:
+ raise ValueError('_randint sequence was too short')
+ if a <= x <= b:
+ return x
+ else:
+ return give(a, b, seq)
+ return give
+ else:
+ raise ValueError('_randint got an unexpected seed')
diff --git a/sympy/core/sympify.py b/sympy/core/sympify.py
index ae1f95bff9a2..86deba6bf541 100644
--- a/sympy/core/sympify.py
+++ b/sympy/core/sympify.py
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
from inspect import getmro
import string
-from random import choice
+from sympy.core.random import choice
from .parameters import global_parameters
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
index 1cc63610c734..ac95ead473e3 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@
from sympy.core.expr import unchanged
from sympy.utilities.iterables import cartes
from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, raises, warns_deprecated_sympy
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically
from sympy.functions.elementary.trigonometric import asin
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_expand.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_expand.py
index d041b209048d..25029d4d8e72 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_expand.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_expand.py
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
from sympy.core.function import expand, expand_multinomial, expand_power_base
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically
from sympy.abc import x, y, z
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_function.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_function.py
index b83806537e5b..ec89f9d2e127 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_function.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_function.py
@@ -623,8 +623,7 @@ def ok(a):
def test_derivative_numerically():
- from random import random
- z0 = random() + I*random()
+ z0 = x._random()
assert abs(Derivative(sin(x), x).doit_numerically(z0) - cos(z0)) < 1e-15
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_random.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_random.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..16b768e49953
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_random.py
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+import random
+from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol, symbols
+from sympy.functions.elementary.trigonometric import sin, acos
+from sympy.abc import x
+
+def test_random():
+ random.seed(42)
+ a = random.random()
+ random.seed(42)
+ Symbol('z').is_finite
+ b = random.random()
+ assert a == b
+
+ got = set()
+ for i in range(2):
+ random.seed(28)
+ m0, m1 = symbols('m_0 m_1', real=True)
+ _ = acos(-m0/m1)
+ got.add(random.uniform(0,1))
+ assert len(got) == 1
+
+ random.seed(10)
+ y = 0
+ for i in range(4):
+ y += sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)
+ random.seed(10)
+ z = 0
+ for i in range(4):
+ z += sin(random.uniform(-10,10) * x)
+ assert y == z
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py
index eeb5f9afec4d..a28da387c0f3 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py
@@ -379,7 +379,7 @@ def test_new_relational():
assert (x < 0) != StrictLessThan(x, 1)
# finally, some fuzz testing
- from random import randint
+ from sympy.core.random import randint
for i in range(100):
while 1:
strtype, length = (chr, 65535) if randint(0, 1) else (chr, 255)
diff --git a/sympy/crypto/crypto.py b/sympy/crypto/crypto.py
index 821398d0aaf9..05d5c1dcefeb 100644
--- a/sympy/crypto/crypto.py
+++ b/sympy/crypto/crypto.py
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@
from sympy.polys.polytools import gcd, Poly
from sympy.utilities.misc import as_int, filldedent, translate
from sympy.utilities.iterables import uniq, multiset
-from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange, _randint
+from sympy.core.random import _randrange, _randint
class NonInvertibleCipherWarning(RuntimeWarning):
@@ -2571,7 +2571,7 @@ def elgamal_private_key(digit=10, seed=None):
=====
For testing purposes, the ``seed`` parameter may be set to control
- the output of this routine. See sympy.testing.randtest._randrange.
+ the output of this routine. See sympy.core.random._randrange.
Examples
========
@@ -2656,7 +2656,7 @@ def encipher_elgamal(i, key, seed=None):
=====
For testing purposes, the ``seed`` parameter may be set to control
- the output of this routine. See sympy.testing.randtest._randrange.
+ the output of this routine. See sympy.core.random._randrange.
Examples
========
@@ -2764,7 +2764,7 @@ def dh_private_key(digit=10, seed=None):
=====
For testing purposes, the ``seed`` parameter may be set to control
- the output of this routine. See sympy.testing.randtest._randrange.
+ the output of this routine. See sympy.core.random._randrange.
Examples
========
diff --git a/sympy/crypto/tests/test_crypto.py b/sympy/crypto/tests/test_crypto.py
index a38af2297dd2..36067bfd0181 100644
--- a/sympy/crypto/tests/test_crypto.py
+++ b/sympy/crypto/tests/test_crypto.py
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, warns
-from random import randrange
+from sympy.core.random import randrange
def test_encipher_railfence():
assert encipher_railfence("hello world",2) == "hlowrdel ol"
diff --git a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_numbers.py b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_numbers.py
index 607bb0362a57..64a30a48c1dc 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_numbers.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_numbers.py
@@ -492,7 +492,7 @@ def test_nC_nP_nT():
nP, nC, nT, stirling, _stirling1, _stirling2, _multiset_histogram, _AOP_product)
from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
- from random import choice
+ from sympy.core.random import choice
c = string.ascii_lowercase
for i in range(100):
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py
index 15a61a455eba..a09dde334499 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py
@@ -396,7 +396,7 @@ def test_issue_11099():
assert Max(x, y).evalf(subs=fixed_test_data) == \
Max(x, y).subs(fixed_test_data).evalf()
# randomly generate some test data
- from random import randint
+ from sympy.core.random import randint
for i in range(20):
random_test_data = {x: randint(-100, 100), y: randint(-100, 100)}
assert Min(x, y).evalf(subs=random_test_data) == \
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_bessel.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_bessel.py
index 9904823a55cf..a34247545864 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_bessel.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_bessel.py
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@
from sympy.series.series import series
from sympy.functions.special.bessel import (airyai, airybi,
airyaiprime, airybiprime, marcumq)
-from sympy.testing.randtest import (random_complex_number as randcplx,
+from sympy.core.random import (random_complex_number as randcplx,
verify_numerically as tn,
test_derivative_numerically as td,
_randint)
@@ -483,7 +483,7 @@ def test_branching():
assert besseli(n, polar_lift(x)) == besseli(n, x)
def tn(func, s):
- from random import uniform
+ from sympy.core.random import uniform
c = uniform(1, 5)
expr = func(s, c*exp_polar(I*pi)) - func(s, c*exp_polar(-I*pi))
eps = 1e-15
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_elliptic_integrals.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_elliptic_integrals.py
index 54b783c0d6a7..52f8c09422cb 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_elliptic_integrals.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_elliptic_integrals.py
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
from sympy.series.order import O
from sympy.functions.special.elliptic_integrals import (elliptic_k as K,
elliptic_f as F, elliptic_e as E, elliptic_pi as P)
-from sympy.testing.randtest import (test_derivative_numerically as td,
+from sympy.core.random import (test_derivative_numerically as td,
random_complex_number as randcplx,
verify_numerically as tn)
from sympy.abc import z, m, n
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_error_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_error_functions.py
index 71e84db48a15..3d8200148ba0 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_error_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_error_functions.py
@@ -355,7 +355,7 @@ def test_erf2inv():
def mytn(expr1, expr2, expr3, x, d=0):
- from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically, random_complex_number
+ from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically, random_complex_number
subs = {}
for a in expr1.free_symbols:
if a != x:
@@ -365,7 +365,7 @@ def mytn(expr1, expr2, expr3, x, d=0):
def mytd(expr1, expr2, x):
- from sympy.testing.randtest import test_derivative_numerically, \
+ from sympy.core.random import test_derivative_numerically, \
random_complex_number
subs = {}
for a in expr1.free_symbols:
@@ -375,7 +375,7 @@ def mytd(expr1, expr2, x):
def tn_branch(func, s=None):
- from random import uniform
+ from sympy.core.random import uniform
def fn(x):
if s is None:
@@ -508,7 +508,7 @@ def test__eis():
def tn_arg(func):
def test(arg, e1, e2):
- from random import uniform
+ from sympy.core.random import uniform
v = uniform(1, 5)
v1 = func(arg*x).subs(x, v).n()
v2 = func(e1*v + e2*1e-15).n()
@@ -776,7 +776,7 @@ def test_fresnel():
meijerg(((), (1,)), ((Rational(1, 4),),
(Rational(3, 4), 0)), -pi**2*z**4/16)/(2*(-z)**Rational(1, 4)*(z**2)**Rational(1, 4))
- from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically
+ from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically
verify_numerically(re(fresnels(z)), fresnels(z).as_real_imag()[0], z)
verify_numerically(im(fresnels(z)), fresnels(z).as_real_imag()[1], z)
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py
index 4856db15bbdd..0a200c534be3 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@
from sympy.core.expr import unchanged
from sympy.core.function import ArgumentIndexError
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
-from sympy.testing.randtest import (test_derivative_numerically as td,
+from sympy.core.random import (test_derivative_numerically as td,
random_complex_number as randcplx,
verify_numerically as tn)
@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ def test_gamma_series():
def tn_branch(s, func):
- from random import uniform
+ from sympy.core.random import uniform
c = uniform(1, 5)
expr = func(s, c*exp_polar(I*pi)) - func(s, c*exp_polar(-I*pi))
eps = 1e-15
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_hyper.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_hyper.py
index e8113319f764..716deac580db 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_hyper.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_hyper.py
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
from sympy.abc import x, z, k
from sympy.series.limits import limit
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, slow
-from sympy.testing.randtest import (
+from sympy.core.random import (
random_complex_number as randcplx,
verify_numerically as tn,
test_derivative_numerically as td)
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_zeta_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_zeta_functions.py
index e2d98c073432..90dbeb5855e1 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_zeta_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_zeta_functions.py
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
from sympy.core.function import ArgumentIndexError
from sympy.functions.combinatorial.numbers import bernoulli, factorial
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
-from sympy.testing.randtest import (test_derivative_numerically as td,
+from sympy.core.random import (test_derivative_numerically as td,
random_complex_number as randcplx, verify_numerically)
x = Symbol('x')
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_entity.py b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_entity.py
index e279f86efb43..cecfdb785506 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_entity.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_entity.py
@@ -6,8 +6,6 @@
from sympy.geometry.entity import scale, GeometryEntity
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
-from random import random
-
def test_entity():
x = Symbol('x', real=True)
@@ -85,8 +83,10 @@ def test_reflect_entity_overrides():
assert c.area == -cr.area
pent = RegularPolygon((1, 2), 1, 5)
- l = Line(pent.vertices[1],
- slope=Rational(random() - .5, random() - .5))
+ slope = S.ComplexInfinity
+ while slope is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ slope = Rational(*(x._random()/2).as_real_imag())
+ l = Line(pent.vertices[1], slope=slope)
rpent = pent.reflect(l)
assert rpent.center == pent.center.reflect(l)
rvert = [i.reflect(l) for i in pent.vertices]
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_polygon.py b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_polygon.py
index ab9216af869a..4f0507ee44d2 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_polygon.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_polygon.py
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
Polygon, Ray, RegularPolygon, Segment, Triangle,
are_similar, convex_hull, intersection, Line, Ray2D)
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, slow, warns
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically
from sympy.geometry.polygon import rad, deg
from sympy.integrals.integrals import integrate
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_util.py b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_util.py
index 45e1a7bcf230..51e119edb452 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_util.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_util.py
@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ def test_centroid():
def test_farthest_points_closest_points():
- from random import randint
+ from sympy.core.random import randint
from sympy.utilities.iterables import subsets
for how in (min, max):
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/rubi/utility_function.py b/sympy/integrals/rubi/utility_function.py
index b64bac06f30d..a28d59f850e8 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/rubi/utility_function.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/rubi/utility_function.py
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@
from sympy.simplify.simplify import fraction, simplify, cancel, powsimp, nsimplify
from sympy.utilities.decorator import doctest_depends_on
from sympy.utilities.iterables import flatten
-from random import randint
+from sympy.core.random import randint
class rubi_unevaluated_expr(UnevaluatedExpr):
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_integrals.py b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_integrals.py
index b38398aa55d0..5d0634245fec 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_integrals.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_integrals.py
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@
from sympy.physics import units
from sympy.testing.pytest import (raises, slow, skip, ON_TRAVIS,
warns_deprecated_sympy)
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically
x, y, a, t, x_1, x_2, z, s, b = symbols('x y a t x_1 x_2 z s b')
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_meijerint.py b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_meijerint.py
index 7e2961ebb606..1f3f136b8320 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_meijerint.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_meijerint.py
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
meijerint_indefinite, _inflate_g, _create_lookup_table,
meijerint_definite, meijerint_inversion)
from sympy.testing.pytest import slow
-from sympy.testing.randtest import (verify_numerically,
+from sympy.core.random import (verify_numerically,
random_complex_number as randcplx)
from sympy.abc import x, y, a, b, c, d, s, t, z
@@ -338,7 +338,7 @@ def test_inversion_exp_real_nonreal_shift():
@slow
def test_lookup_table():
- from random import uniform, randrange
+ from sympy.core.random import uniform, randrange
from sympy.core.add import Add
from sympy.integrals.meijerint import z as z_dummy
table = {}
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py b/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py
index 101c08a7e23c..4f629b0ebc95 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
from .primetest import isprime
from .factor_ import factorint, trailing, totient, multiplicity
from sympy.utilities.misc import as_int
-from random import randint, Random
+from sympy.core.random import _randint, randint
from itertools import cycle, product
@@ -1196,13 +1196,11 @@ def _discrete_log_pollard_rho(n, a, b, order=None, retries=10, rseed=None):
if order is None:
order = n_order(b, n)
- prng = Random()
- if rseed is not None:
- prng.seed(rseed)
+ randint = _randint(rseed)
for i in range(retries):
- aa = prng.randint(1, order - 1)
- ba = prng.randint(1, order - 1)
+ aa = randint(1, order - 1)
+ ba = randint(1, order - 1)
xa = pow(b, aa, n) * pow(a, ba, n) % n
c = xa % 3
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_bbp_pi.py b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_bbp_pi.py
index 806945a6a550..c18188e3c8a3 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_bbp_pi.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_bbp_pi.py
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-from random import randint
+from sympy.core.random import randint
from sympy.ntheory.bbp_pi import pi_hex_digits
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_egyptian_fraction.py b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_egyptian_fraction.py
index 10e2ef3e214e..a9a9fac578d9 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_egyptian_fraction.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_egyptian_fraction.py
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
from sympy.ntheory.egyptian_fraction import egyptian_fraction
from sympy.core.add import Add
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
-from sympy.testing.randtest import random_complex_number
+from sympy.core.random import random_complex_number
def test_egyptian_fraction():
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py
index 10a634daf8b6..95fa3ce15e10 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py
@@ -406,7 +406,7 @@ def random_reduce(circuit, gate_ids, seed=None):
given by the list
"""
- from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange
+ from sympy.core.random import _randrange
if not gate_ids:
return circuit
@@ -460,7 +460,7 @@ def random_insert(circuit, choices, seed=None):
Indices for insertion should be [0, n] if n is the length of the
circuit.
"""
- from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange
+ from sympy.core.random import _randrange
if not choices:
return circuit
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py
index 0dac602c7451..04b00ef208e4 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
from collections import deque
-from random import randint
+from sympy.core.random import randint
from sympy.external import import_module
from sympy.core.basic import Basic
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_matrixutils.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_matrixutils.py
index 8726abfd30fe..af581f7aa236 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_matrixutils.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_matrixutils.py
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-from random import randint
+from sympy.core.random import randint
from sympy.core.numbers import Integer
from sympy.matrices.dense import (Matrix, ones, zeros)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/factortools.py b/sympy/polys/factortools.py
index 0b7da8e2d26b..c322bef488a2 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/factortools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/factortools.py
@@ -977,7 +977,7 @@ def dmp_zz_wang(f, u, K, mod=None, seed=None):
.. [2] [Geddes92]_
"""
- from sympy.testing.randtest import _randint
+ from sympy.core.random import _randint
randint = _randint(seed)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/galoistools.py b/sympy/polys/galoistools.py
index ea52353d0581..9ffe6b5dbb45 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/galoistools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/galoistools.py
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
"""Dense univariate polynomials with coefficients in Galois fields. """
-from random import uniform
+from sympy.core.random import uniform
from math import ceil as _ceil, sqrt as _sqrt
from sympy.core.mul import prod
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyroots.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyroots.py
index fa5900298e01..18a389a41a4e 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyroots.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyroots.py
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@
from sympy.polys.polyutils import _nsort
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, slow
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically
import mpmath
from itertools import product
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_cse.py b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_cse.py
index 9a0cfa323090..efb39bc2d3ea 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_cse.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_cse.py
@@ -454,7 +454,7 @@ def test_issue_11230():
assert not any(i.is_Mul for a in C for i in a.args)
# random tests for the issue
- from random import choice
+ from sympy.core.random import choice
from sympy.core.function import expand_mul
s = symbols('a:m')
# 35 Mul tests, none of which should ever fail
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_fu.py b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_fu.py
index 94cd0c8cc368..3bf4f74c522c 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_fu.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_fu.py
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
TR111, TR2, TR2i, TR3, TR5, TR6, TR7, TR8, TR9, TRmorrie, _TR56 as T,
TRpower, hyper_as_trig, fu, process_common_addends, trig_split,
as_f_sign_1)
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically
from sympy.abc import a, b, c, x, y, z
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_hyperexpand.py b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_hyperexpand.py
index f770865e84d3..146dadc183eb 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_hyperexpand.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_hyperexpand.py
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-from random import randrange
+from sympy.core.random import randrange
from sympy.simplify.hyperexpand import (ShiftA, ShiftB, UnShiftA, UnShiftB,
MeijerShiftA, MeijerShiftB, MeijerShiftC, MeijerShiftD,
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@
from sympy.functions.special.hyper import (hyper, meijerg)
from sympy.abc import z, a, b, c
from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, raises, slow, ON_TRAVIS, skip
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn
from sympy.core.numbers import (Rational, pi)
from sympy.functions.elementary.exponential import (exp, exp_polar, log)
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_trigsimp.py b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_trigsimp.py
index a960b3b9bfdd..3fda27955c95 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_trigsimp.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_trigsimp.py
@@ -379,7 +379,7 @@ def test_issue_15129_trigsimp_methods():
def test_exptrigsimp():
def valid(a, b):
- from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn
+ from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn
if not (tn(a, b) and a == b):
return False
return True
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py
index d98971a94435..2f1744e98d56 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py
@@ -658,7 +658,7 @@ def test_sum_of_three_squares():
def test_sum_of_four_squares():
- from random import randint
+ from sympy.core.random import randint
# this should never fail
n = randint(1, 100000000000000)
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py
index 24428d0a52d8..1c9487afed93 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-from random import randint
+from sympy.core.random import randint
from sympy.core.function import Function
from sympy.core.mul import Mul
from sympy.core.numbers import (I, Rational, oo)
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
index d32e2eb05a53..942810fb63c9 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@
from sympy.polys.rootoftools import CRootOf
from sympy.testing.pytest import slow, XFAIL, SKIP, raises
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn
from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, e, k, h, p, x, y, z, t, q, m, R
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
index 5b230469083f..236a56dd7c3b 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@
from sympy.utilities.iterables import numbered_symbols
from sympy.testing.pytest import (XFAIL, raises, skip, slow, SKIP, _both_exp_pow)
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn
from sympy.physics.units import cm
from sympy.solvers import solve
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py
index a9eb50845ec7..d74525c87629 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@
from sympy.stats.compound_rv import CompoundPSpace
from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, XFAIL, slow, ignore_warnings
-from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn
+from sympy.core.random import verify_numerically as tn
oo = S.Infinity
diff --git a/sympy/tensor/tests/test_tensor_operators.py b/sympy/tensor/tests/test_tensor_operators.py
index a3aca8dc7898..996d0af06070 100644
--- a/sympy/tensor/tests/test_tensor_operators.py
+++ b/sympy/tensor/tests/test_tensor_operators.py
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
from sympy.matrices.dense import diag
from sympy.tensor.array import Array
-from random import randint
+from sympy.core.random import randint
L = TensorIndexType("L")
diff --git a/sympy/testing/randtest.py b/sympy/testing/randtest.py
index 4d5232acd521..588496e9be05 100644
--- a/sympy/testing/randtest.py
+++ b/sympy/testing/randtest.py
@@ -1,174 +1,26 @@
-""" Helpers for randomized testing """
-
-from random import uniform, Random, randrange, randint
-
-from sympy.core.containers import Tuple
-from sympy.core.function import Derivative
-from sympy.core.numbers import comp, I
-from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol
-from sympy.simplify.simplify import nsimplify
-from sympy.utilities.iterables import is_sequence
-from sympy.utilities.misc import as_int
-
-
-def random_complex_number(a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1, rational=False, tolerance=None):
- """
- Return a random complex number.
-
- To reduce chance of hitting branch cuts or anything, we guarantee
- b <= Im z <= d, a <= Re z <= c
-
- When rational is True, a rational approximation to a random number
- is obtained within specified tolerance, if any.
- """
- A, B = uniform(a, c), uniform(b, d)
- if not rational:
- return A + I*B
- return (nsimplify(A, rational=True, tolerance=tolerance) +
- I*nsimplify(B, rational=True, tolerance=tolerance))
-
-
-def verify_numerically(f, g, z=None, tol=1.0e-6, a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1):
- """
- Test numerically that f and g agree when evaluated in the argument z.
-
- If z is None, all symbols will be tested. This routine does not test
- whether there are Floats present with precision higher than 15 digits
- so if there are, your results may not be what you expect due to round-
- off errors.
-
- Examples
- ========
-
- >>> from sympy import sin, cos
- >>> from sympy.abc import x
- >>> from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn
- >>> tn(sin(x)**2 + cos(x)**2, 1, x)
- True
- """
- f, g, z = Tuple(f, g, z)
- z = [z] if isinstance(z, Symbol) else (f.free_symbols | g.free_symbols)
- reps = list(zip(z, [random_complex_number(a, b, c, d) for _ in z]))
- z1 = f.subs(reps).n()
- z2 = g.subs(reps).n()
- return comp(z1, z2, tol)
-
-
-def test_derivative_numerically(f, z, tol=1.0e-6, a=2, b=-1, c=3, d=1):
- """
- Test numerically that the symbolically computed derivative of f
- with respect to z is correct.
-
- This routine does not test whether there are Floats present with
- precision higher than 15 digits so if there are, your results may
- not be what you expect due to round-off errors.
-
- Examples
- ========
-
- >>> from sympy import sin
- >>> from sympy.abc import x
- >>> from sympy.testing.randtest import test_derivative_numerically as td
- >>> td(sin(x), x)
- True
- """
- z0 = random_complex_number(a, b, c, d)
- f1 = f.diff(z).subs(z, z0)
- f2 = Derivative(f, z).doit_numerically(z0)
- return comp(f1.n(), f2.n(), tol)
-
-
-def _randrange(seed=None):
- """Return a randrange generator. ``seed`` can be
- o None - return randomly seeded generator
- o int - return a generator seeded with the int
- o list - the values to be returned will be taken from the list
- in the order given; the provided list is not modified.
-
- Examples
- ========
-
- >>> from sympy.testing.randtest import _randrange
- >>> rr = _randrange()
- >>> rr(1000) # doctest: +SKIP
- 999
- >>> rr = _randrange(3)
- >>> rr(1000) # doctest: +SKIP
- 238
- >>> rr = _randrange([0, 5, 1, 3, 4])
- >>> rr(3), rr(3)
- (0, 1)
- """
- if seed is None:
- return randrange
- elif isinstance(seed, int):
- return Random(seed).randrange
- elif is_sequence(seed):
- seed = list(seed) # make a copy
- seed.reverse()
-
- def give(a, b=None, seq=seed):
- if b is None:
- a, b = 0, a
- a, b = as_int(a), as_int(b)
- w = b - a
- if w < 1:
- raise ValueError('_randrange got empty range')
- try:
- x = seq.pop()
- except IndexError:
- raise ValueError('_randrange sequence was too short')
- if a <= x < b:
- return x
- else:
- return give(a, b, seq)
- return give
- else:
- raise ValueError('_randrange got an unexpected seed')
-
-
-def _randint(seed=None):
- """Return a randint generator. ``seed`` can be
- o None - return randomly seeded generator
- o int - return a generator seeded with the int
- o list - the values to be returned will be taken from the list
- in the order given; the provided list is not modified.
-
- Examples
- ========
-
- >>> from sympy.testing.randtest import _randint
- >>> ri = _randint()
- >>> ri(1, 1000) # doctest: +SKIP
- 999
- >>> ri = _randint(3)
- >>> ri(1, 1000) # doctest: +SKIP
- 238
- >>> ri = _randint([0, 5, 1, 2, 4])
- >>> ri(1, 3), ri(1, 3)
- (1, 2)
- """
- if seed is None:
- return randint
- elif isinstance(seed, int):
- return Random(seed).randint
- elif is_sequence(seed):
- seed = list(seed) # make a copy
- seed.reverse()
-
- def give(a, b, seq=seed):
- a, b = as_int(a), as_int(b)
- w = b - a
- if w < 0:
- raise ValueError('_randint got empty range')
- try:
- x = seq.pop()
- except IndexError:
- raise ValueError('_randint sequence was too short')
- if a <= x <= b:
- return x
- else:
- return give(a, b, seq)
- return give
- else:
- raise ValueError('_randint got an unexpected seed')
+from sympy.core.random import (
+ random_complex_number as A,
+ verify_numerically as B,
+ test_derivative_numerically as C,
+ _randrange as D,
+ _randint as E)
+from sympy.utilities.decorator import deprecated
+
+random_complex_number = deprecated(useinstead="sympy.core.random.random_complex_number",
+ deprecated_since_version="1.10", issue=22433)(A)
+
+
+verify_numerically = deprecated(useinstead="sympy.core.random.verify_numerically",
+ deprecated_since_version="1.10", issue=22433)(B)
+
+
+test_derivative_numerically = deprecated(useinstead="sympy.core.random.test_derivative_numerically",
+ deprecated_since_version="1.10", issue=22433)(C)
+
+
+_randrange = deprecated(useinstead="sympy.core.random._randint",
+ deprecated_since_version="1.10", issue=22433)(D)
+
+
+_randint = deprecated(useinstead="sympy.core.random._randint",
+ deprecated_since_version="1.10", issue=22433)(E)
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
index 111d3f31bd12..0d32c26fc658 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
@@ -2307,13 +2307,13 @@ def random_derangement(t, choice=None, strict=True):
then an error will be raised since no derangement is possible. To obtain
a derangement of as many items as possible--with some of the most numerous
remaining in their original positions--pass `strict=False`. To produce a
- pseudorandom derangment, pass a pseudorandom selector like `Random(seed).choice`.
+ pseudorandom derangment, pass a pseudorandom selector like `choice` (see
+ below).
Examples
========
>>> from sympy.utilities.iterables import random_derangement
- >>> from random import Random
>>> t = 'SymPy: a CAS in pure Python'
>>> d = random_derangement(t)
>>> all(i != j for i, j in zip(d, t))
@@ -2322,13 +2322,14 @@ def random_derangement(t, choice=None, strict=True):
A predictable result can be obtained by using a pseudorandom
generator for the choice:
- >>> c = Random(1).choice
+ >>> from sympy.core.random import seed, choice as c
+ >>> seed(1)
>>> d = [''.join(random_derangement(t, c)) for i in range(5)]
>>> assert len(set(d)) != 1 # we got different values
- By resetting c, the same sequence can be obtained:
+ By reseeding, the same sequence can be obtained:
- >>> c = Random(1).choice
+ >>> seed(1)
>>> d2 = [''.join(random_derangement(t, c)) for i in range(5)]
>>> assert d == d2
"""
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/randtest.py b/sympy/utilities/randtest.py
index d9fb1ec4237f..567fd919b9f2 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/randtest.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/randtest.py
@@ -2,8 +2,8 @@
SymPyDeprecationWarning(
feature="Import sympy.utilities.randtest",
- useinstead="Import from sympy.testing.randtest",
+ useinstead="Import from sympy.core.random",
issue=18095,
deprecated_since_version="1.6").warn()
-from sympy.testing.randtest import * # noqa:F401
+from sympy.core.random import * # noqa:F401
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-4218@7d7e60d
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 4,218
|
feat: Ability to call the program by name from callable alias with the same name without the infinite loop error
|
Closes #3159
Now we have transparent way to wrap commands into callable aliases.
Example 1:
```python
def _echo(args):
echo @(args)
aliases['echo'] = _echo
echo ok
# Before: freezed on infinite loop
# After: ok
```
Example 2 - elegant ExecAlias (it will be awesome with #4201):
```python
aliases['echo'] = "echo @('ok')" # ExecAlias
echo
# Before: freezed on infinite loop
# After: ok
```
Example 3 - show error for the user without freezing
```python
aliases['first'] = "second @(1)" # ExecAlias just for demo
aliases['second'] = "first @(1)" # ExecAlias just for demo
first
# Before: freezed on infinite loop
# After: Exception: Infinite loop of calls for "first" alias.
```
## For community
⬇️ **Please click the 👍 reaction instead of leaving a `+1` or 👍 comment**
|
2021-04-03T15:43:05Z
|
Infinite alias call
I'm trying to override 'ls' command to display dotfiles in my $DOTFILES directory.
This code goes into an endless loop because _ls function calls ls command and it calls _ls function.
```python
def _ls():
if $(pwd).rstrip(os.linesep) == $DOTFILES:
ls -Ga
else:
ls -G
aliases['ls'] = _ls
```
## xonfig
<details>
```
+------------------+---------------------+
| xonsh | 0.8.10 |
| Git SHA | 2cb42bdb |
| Commit Date | Feb 6 16:49:16 2019 |
| Python | 3.6.4 |
| PLY | 3.11 |
| have readline | True |
| prompt toolkit | 2.0.7 |
| shell type | prompt_toolkit2 |
| pygments | 2.3.1 |
| on posix | True |
| on linux | False |
| on darwin | True |
| on windows | False |
| on cygwin | False |
| on msys2 | False |
| is superuser | False |
| default encoding | utf-8 |
| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |
| encoding errors | surrogateescape |
+------------------+---------------------+
```
</details>
## Current Behavior
<!--- Tell us what happens instead of the expected behavior -->
<!--- If part of your bug report is a traceback, please first enter debug mode before triggering the error
To enter debug mode, set the environment variableNSH_DEBUG=1` _before_ starting `xonsh`. `XO
On Linux and OSX, an easy way to to do this is to run `env XONSH_DEBUG=1 xonsh` -->
When I input "ls" command, the terminal freezes.
|
Hi @miyashiiii, you can replace the inner `ls` calls with `@$(which -s ls)` which should resolve to your actual `ls` executable.
Hi @lacoch. Thank you for your answer.
I knew the way to avoid this issue, but I think the infinite alias call shouldn't happen.
cf. https://stackoverflow.com/questions/56492258/how-to-override-built-in-command-in-xonsh
I should have written it.
Oh, I see! Thanks for the pointer. I don't really think this is a bug, but if @gforsyth thinks so...
> I should have written it.
Yes, perhaps ;)
I asked @miyashiiii to open the issue. It might not be a bug, but it does seem like a slightly inconsistent behavior to me. It's a common pattern to alias commands + default arguments to the built-in command name and that definitely works when we define it directly, e.g.
```
gil@badcatredux ~ $ aliases['ls'] = ['ls', '--color=auto', '-v']
gil@badcatredux ~ $ ls
aur.archlinux.org github.com
```
|
[
{
"body": "I'm trying to override 'ls' command to display dotfiles in my $DOTFILES directory.\r\nThis code goes into an endless loop because _ls function calls ls command and it calls _ls function.\r\n\r\n```python\r\ndef _ls():\r\n if $(pwd).rstrip(os.linesep) == $DOTFILES:\r\n ls -Ga\r\n else:\r\n ls -G\r\naliases['ls'] = _ls\r\n```\r\n\r\n## xonfig\r\n\r\n<details>\r\n\r\n```\r\n+------------------+---------------------+\r\n| xonsh | 0.8.10 |\r\n| Git SHA | 2cb42bdb |\r\n| Commit Date | Feb 6 16:49:16 2019 |\r\n| Python | 3.6.4 |\r\n| PLY | 3.11 |\r\n| have readline | True |\r\n| prompt toolkit | 2.0.7 |\r\n| shell type | prompt_toolkit2 |\r\n| pygments | 2.3.1 |\r\n| on posix | True |\r\n| on linux | False |\r\n| on darwin | True |\r\n| on windows | False |\r\n| on cygwin | False |\r\n| on msys2 | False |\r\n| is superuser | False |\r\n| default encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| encoding errors | surrogateescape |\r\n+------------------+---------------------+\r\n```\r\n\r\n</details>\r\n\r\n## Current Behavior\r\n<!--- Tell us what happens instead of the expected behavior -->\r\n<!--- If part of your bug report is a traceback, please first enter debug mode before triggering the error\r\nTo enter debug mode, set the environment variableNSH_DEBUG=1` _before_ starting `xonsh`. `XO\r\nOn Linux and OSX, an easy way to to do this is to run `env XONSH_DEBUG=1 xonsh` -->\r\n\r\nWhen I input \"ls\" command, the terminal freezes.\r\n",
"number": 3159,
"title": "Infinite alias call"
}
] |
4dc08232e615a75a524fbf96f17402a7a5b353a5
|
{
"head_commit": "7d7e60de486bfc40f2687af4924be0f14e1d60d0",
"head_commit_message": "Merge branch 'main' of github.com:xonsh/xonsh into fix_aliases_infinite_loop\n\n# Conflicts:\n#\ttests/test_commands_cache.py",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/news/fix_aliases_infinite_loop.rst b/news/fix_aliases_infinite_loop.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..60a5ab3232\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/fix_aliases_infinite_loop.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* Ability to call the tool by the name from callable alias with the same name without the infinite loop error.\n+\n+**Changed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Deprecated:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Removed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Security:**\n+\n+* <news item>\ndiff --git a/tests/test_integrations.py b/tests/test_integrations.py\nindex 9ade1fa802..65dbc1eef1 100644\n--- a/tests/test_integrations.py\n+++ b/tests/test_integrations.py\n@@ -102,6 +102,40 @@ def _f():\n \"hello\\n\",\n 0,\n ),\n+ # testing alias stack: lambda function\n+ (\n+ \"\"\"\n+# skip_if_on_windows\n+def _echo():\n+ echo hello\n+\n+aliases['echo'] = _echo\n+echo\n+\"\"\",\n+ \"hello\\n\",\n+ 0,\n+ ),\n+ # testing alias stack: ExecAlias\n+ (\n+ \"\"\"\n+# skip_if_on_windows \n+aliases['echo'] = \"echo @('hello')\"\n+echo\n+\"\"\",\n+ \"hello\\n\",\n+ 0,\n+ ),\n+ # testing alias stack: callable alias (ExecAlias) + no binary location + infinite loop\n+ (\n+ \"\"\"\n+# skip_if_on_windows \n+aliases['first'] = \"second @(1)\"\n+aliases['second'] = \"first @(1)\"\n+first\n+\"\"\",\n+ lambda out: 'Infinite loop of calls for \"first\" alias.' in out,\n+ 0,\n+ ),\n # test redirecting a function alias to a file\n (\n \"\"\"\n@@ -477,8 +511,13 @@ def _echo(args):\n @pytest.mark.parametrize(\"case\", ALL_PLATFORMS)\n def test_script(case):\n script, exp_out, exp_rtn = case\n+ if ON_WINDOWS and 'skip_if_on_windows' in script:\n+ return\n out, err, rtn = run_xonsh(script)\n- assert exp_out == out\n+ if callable(exp_out):\n+ assert exp_out(out)\n+ else:\n+ assert exp_out == out\n assert exp_rtn == rtn\n \n \ndiff --git a/xonsh/procs/proxies.py b/xonsh/procs/proxies.py\nindex 4e9b100b8c..316ed9270a 100644\n--- a/xonsh/procs/proxies.py\n+++ b/xonsh/procs/proxies.py\n@@ -500,10 +500,16 @@ def run(self):\n sp_stderr = sys.stderr\n # run the function itself\n try:\n+ alias_stack = builtins.__xonsh__.env.get(\"ALIAS_STACK\", \"\")\n+ if self.env[\"ALIAS_NAME\"]:\n+ alias_stack += \":\" + self.env[\"ALIAS_NAME\"]\n+\n with STDOUT_DISPATCHER.register(sp_stdout), STDERR_DISPATCHER.register(\n sp_stderr\n ), xt.redirect_stdout(STDOUT_DISPATCHER), xt.redirect_stderr(\n STDERR_DISPATCHER\n+ ), builtins.__xonsh__.env.swap(\n+ ALIAS_STACK=alias_stack\n ):\n r = self.f(self.args, sp_stdin, sp_stdout, sp_stderr, spec, spec.stack)\n except SystemExit as e:\ndiff --git a/xonsh/procs/specs.py b/xonsh/procs/specs.py\nindex 845c4e5297..5c82663531 100644\n--- a/xonsh/procs/specs.py\n+++ b/xonsh/procs/specs.py\n@@ -355,6 +355,8 @@ def __init__(\n # pure attrs\n self.args = list(cmd)\n self.alias = None\n+ self.alias_name = None\n+ self.alias_stack = builtins.__xonsh__.env.get(\"ALIAS_STACK\", \"\").split(\":\")\n self.binary_loc = None\n self.is_proxy = False\n self.background = False\n@@ -442,6 +444,7 @@ def run(self, *, pipeline_group=None):\n kwargs = {n: getattr(self, n) for n in self.kwnames}\n self.prep_env(kwargs)\n if callable(self.alias):\n+ kwargs[\"env\"][\"ALIAS_NAME\"] = self.alias_name\n p = self.cls(self.alias, self.cmd, **kwargs)\n else:\n self.prep_preexec_fn(kwargs, pipeline_group=pipeline_group)\n@@ -589,17 +592,29 @@ def redirect_trailing(self):\n def resolve_alias(self):\n \"\"\"Sets alias in command, if applicable.\"\"\"\n cmd0 = self.cmd[0]\n+\n+ if cmd0 in self.alias_stack:\n+ # Disabling the alias resolving to prevent infinite loop in call stack\n+ # and futher using binary_loc to resolve the alias name.\n+ self.alias = None\n+ return\n+\n if callable(cmd0):\n alias = cmd0\n else:\n alias = builtins.aliases.get(cmd0, None)\n+ if alias is not None:\n+ self.alias_name = cmd0\n self.alias = alias\n \n def resolve_binary_loc(self):\n \"\"\"Sets the binary location\"\"\"\n alias = self.alias\n if alias is None:\n- binary_loc = xenv.locate_binary(self.cmd[0])\n+ cmd0 = self.cmd[0]\n+ binary_loc = xenv.locate_binary(cmd0)\n+ if binary_loc == cmd0 and cmd0 in self.alias_stack:\n+ raise Exception(f'Infinite loop of calls for \"{cmd0}\" alias.')\n elif callable(alias):\n binary_loc = None\n else:\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -477,8 +511,13 @@ def _echo(args):\n @pytest.mark.parametrize(\"case\", ALL_PLATFORMS)\n def test_script(case):\n script, exp_out, exp_rtn = case\n+ if ON_WINDOWS and 'skip_if_on_windows' in script:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 514,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "tests/test_integrations.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nUse `pytest.param` with `skip_if_on_windows` instead"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -500,10 +500,16 @@ def run(self):\n sp_stderr = sys.stderr\n # run the function itself\n try:\n+ alias_stack = builtins.__xonsh__.env.get(\"ALIAS_STACK\", \"\")\n+ if self.env[\"ALIAS_NAME\"]:\n+ alias_stack += \":\" + self.env[\"ALIAS_NAME\"]\n+\n with STDOUT_DISPATCHER.register(sp_stdout), STDERR_DISPATCHER.register(\n sp_stderr\n ), xt.redirect_stdout(STDOUT_DISPATCHER), xt.redirect_stderr(\n STDERR_DISPATCHER\n+ ), builtins.__xonsh__.env.swap(\n+ ALIAS_STACK=alias_stack",
"line": null,
"original_line": 512,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/procs/proxies.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nDon't we need to add `ALIAS_NAME=\"\"` here as well? \n\n@author:\nNope because we need only stack. If we will have an alias in further calls it will be just checked and added to stack."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -442,6 +444,7 @@ def run(self, *, pipeline_group=None):\n kwargs = {n: getattr(self, n) for n in self.kwnames}\n self.prep_env(kwargs)\n if callable(self.alias):\n+ kwargs[\"env\"][\"ALIAS_NAME\"] = self.alias_name",
"line": null,
"original_line": 447,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/procs/specs.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI'm fine with setting env vars for this, as long as we use names that are obviously internal like `__XONSH_ALIAS_NAME` and `__XONSH_ALIAS_STACK`"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -589,17 +592,29 @@ def redirect_trailing(self):\n def resolve_alias(self):\n \"\"\"Sets alias in command, if applicable.\"\"\"\n cmd0 = self.cmd[0]\n+\n+ if cmd0 in self.alias_stack:\n+ # Disabling the alias resolving to prevent infinite loop in call stack\n+ # and futher using binary_loc to resolve the alias name.\n+ self.alias = None\n+ return\n+\n if callable(cmd0):\n alias = cmd0\n else:\n alias = builtins.aliases.get(cmd0, None)\n+ if alias is not None:\n+ self.alias_name = cmd0\n self.alias = alias\n \n def resolve_binary_loc(self):\n \"\"\"Sets the binary location\"\"\"\n alias = self.alias\n if alias is None:\n- binary_loc = xenv.locate_binary(self.cmd[0])\n+ cmd0 = self.cmd[0]\n+ binary_loc = xenv.locate_binary(cmd0)\n+ if binary_loc == cmd0 and cmd0 in self.alias_stack:\n+ raise Exception(f'Infinite loop of calls for \"{cmd0}\" alias.')",
"line": null,
"original_line": 617,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/procs/specs.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\n raise Exception(f'Recursive calls to \"{cmd0}\" alias.')\n```\n\nWe don't know it's infinite, only that it's recursive :)"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -500,10 +500,16 @@ def run(self):\n sp_stderr = sys.stderr\n # run the function itself\n try:\n+ alias_stack = builtins.__xonsh__.env.get(\"ALIAS_STACK\", \"\")\n+ if self.env[\"ALIAS_NAME\"]:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 504,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/procs/proxies.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\n if self.get(\"ALIAS_NAME\"):\n```"
}
] |
eb8e9464bb5cbe93ee20c5046b4485e0ae145d87
|
diff --git a/news/fix_aliases_infinite_loop.rst b/news/fix_aliases_infinite_loop.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..60a5ab3232
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/fix_aliases_infinite_loop.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+**Added:**
+
+* Ability to call the tool by the name from callable alias with the same name without the infinite loop error.
+
+**Changed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Deprecated:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Removed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Security:**
+
+* <news item>
diff --git a/tests/test_integrations.py b/tests/test_integrations.py
index 9ade1fa802..fb125d28bd 100644
--- a/tests/test_integrations.py
+++ b/tests/test_integrations.py
@@ -472,15 +472,57 @@ def _echo(args):
),
]
+UNIX_TESTS = [
+ # testing alias stack: lambda function
+ (
+ """
+def _echo():
+ echo hello
+
+aliases['echo'] = _echo
+echo
+""",
+ "hello\n",
+ 0,
+ ),
+ # testing alias stack: ExecAlias
+ (
+ """
+aliases['echo'] = "echo @('hello')"
+echo
+""",
+ "hello\n",
+ 0,
+ ),
+ # testing alias stack: callable alias (ExecAlias) + no binary location + infinite loop
+ (
+ """
+aliases['first'] = "second @(1)"
+aliases['second'] = "first @(1)"
+first
+""",
+ lambda out: 'Recursive calls to "first" alias.' in out,
+ 0,
+ ),
+]
@skip_if_no_xonsh
@pytest.mark.parametrize("case", ALL_PLATFORMS)
def test_script(case):
script, exp_out, exp_rtn = case
out, err, rtn = run_xonsh(script)
- assert exp_out == out
+ if callable(exp_out):
+ assert exp_out(out)
+ else:
+ assert exp_out == out
assert exp_rtn == rtn
+@skip_if_no_xonsh
+@skip_if_on_windows
[email protected]("case", UNIX_TESTS)
+def test_unix_tests(case):
+ test_script(case)
+
ALL_PLATFORMS_STDERR = [
# test redirecting a function alias
diff --git a/xonsh/procs/proxies.py b/xonsh/procs/proxies.py
index 4e9b100b8c..d9a5ff749f 100644
--- a/xonsh/procs/proxies.py
+++ b/xonsh/procs/proxies.py
@@ -500,10 +500,16 @@ def run(self):
sp_stderr = sys.stderr
# run the function itself
try:
+ alias_stack = builtins.__xonsh__.env.get("__ALIAS_STACK", "")
+ if self.env.get("__ALIAS_NAME"):
+ alias_stack += ":" + self.env["__ALIAS_NAME"]
+
with STDOUT_DISPATCHER.register(sp_stdout), STDERR_DISPATCHER.register(
sp_stderr
), xt.redirect_stdout(STDOUT_DISPATCHER), xt.redirect_stderr(
STDERR_DISPATCHER
+ ), builtins.__xonsh__.env.swap(
+ __ALIAS_STACK=alias_stack
):
r = self.f(self.args, sp_stdin, sp_stdout, sp_stderr, spec, spec.stack)
except SystemExit as e:
diff --git a/xonsh/procs/specs.py b/xonsh/procs/specs.py
index 845c4e5297..384edf71e4 100644
--- a/xonsh/procs/specs.py
+++ b/xonsh/procs/specs.py
@@ -355,6 +355,8 @@ def __init__(
# pure attrs
self.args = list(cmd)
self.alias = None
+ self.alias_name = None
+ self.alias_stack = builtins.__xonsh__.env.get("__ALIAS_STACK", "").split(":")
self.binary_loc = None
self.is_proxy = False
self.background = False
@@ -442,6 +444,7 @@ def run(self, *, pipeline_group=None):
kwargs = {n: getattr(self, n) for n in self.kwnames}
self.prep_env(kwargs)
if callable(self.alias):
+ kwargs["env"]["__ALIAS_NAME"] = self.alias_name
p = self.cls(self.alias, self.cmd, **kwargs)
else:
self.prep_preexec_fn(kwargs, pipeline_group=pipeline_group)
@@ -589,17 +592,29 @@ def redirect_trailing(self):
def resolve_alias(self):
"""Sets alias in command, if applicable."""
cmd0 = self.cmd[0]
+
+ if cmd0 in self.alias_stack:
+ # Disabling the alias resolving to prevent infinite loop in call stack
+ # and futher using binary_loc to resolve the alias name.
+ self.alias = None
+ return
+
if callable(cmd0):
alias = cmd0
else:
alias = builtins.aliases.get(cmd0, None)
+ if alias is not None:
+ self.alias_name = cmd0
self.alias = alias
def resolve_binary_loc(self):
"""Sets the binary location"""
alias = self.alias
if alias is None:
- binary_loc = xenv.locate_binary(self.cmd[0])
+ cmd0 = self.cmd[0]
+ binary_loc = xenv.locate_binary(cmd0)
+ if binary_loc == cmd0 and cmd0 in self.alias_stack:
+ raise Exception(f'Recursive calls to "{cmd0}" alias.')
elif callable(alias):
binary_loc = None
else:
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-22426@05cec82
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 22,426
|
Coverage doctest fix
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #16716
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Coverage_doctest.py was failing due to name changes between python2 and python3; this pull request updates the names to the python3 versions. It also was not dealing with dynamic docstrings correctly; now it skips them. Variables also have been updated to be more descriptive.
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-11-05T05:36:40Z
|
bin/coverage_doctest.py does not work
```pytb
$./bin/coverage_doctest.py
DOCTEST COVERAGE for /Users/aaronmeurer/Documents/Python/sympy/sympy/sympy
======================================================================
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "./bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 601, in <module>
no_color=args.no_color, sphinx=args.sphinx)
File "./bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 541, in go
verbose=verbose, no_color=no_color, exact=False, sphinx=sphinx)
File "./bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 549, in go
any(name in file for name in skip_paths))):
NameError: name 'skip_paths' is not defined
```
It works if you remove the skip_paths check, but we should look into the history of the file to see what that was, because clearly something broke at some point.
|
> look into the history of the file to see what that was
It was initially a way to skip testing of mpmath in 24eeabe2fe23a1d5103e61c3b8d1ed10c44d9795; it was removed in 9b204c3d1a3e4f6753a7d5186f3074ef13641f36 when mpmath (the only thing being skipped) was removed. The simple fix is to just define `skip_paths` as an empty list again.
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/16729#issuecomment-487160414
I'm not sure that every not frequently used utilities are working.
For example `diagnose_imports` is failing
```
python bin/diagnose_imports
Traceback (most recent call last):
from sympy.core.compatibility import builtins
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'sympy'
```
And also, I see some utilities have optional arguments, but are they correctly tested?
I think that every executable utilites may need to be tested, if there can be a way to do.
Hi, I would like to work on this issue if there isn't any existing pull request for the same. Can someone guide me a little bit regarding this?
I don't think there are any existing pull requests. You should start by running the script and posting whatever output you get here. Then we can figure out what needs to be done to fix whatever errors come up.
@asmeurer this is what I am getting. From what I understand of this, the object returned by ```inspect.getfullargspec(fobj)``` does not have a keywords attribute.
```
(sympy-dev) D:\Documents\sympy>python bin/coverage_doctest.py --no-sphinx
DOCTEST COVERAGE for D:\Documents\sympy\sympy
======================================================================
sympy.abc: ←[0;33mDoctests:←[0m ←[0;32m100% (0 of 0)←[0m
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 623, in <module>
doctests, total_sphinx, num_functions = go(sympy_top, file, verbose=args.verbose,
File "bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 562, in go
_doctests, _total_sphinx, _num_functions = go(sympy_top, '%s/%s' % (file, F),
File "bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 562, in go
_doctests, _total_sphinx, _num_functions = go(sympy_top, '%s/%s' % (file, F),
File "bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 579, in go
return coverage(get_mod_name(file, sympy_top), verbose=verbose,
File "bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 509, in coverage
f_dt, f = process_function(f_name, member, obj,
File "bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 311, in process_function
full_name = _get_arg_list(name, obj)
File "bin/coverage_doctest.py", line 231, in _get_arg_list
if argspec.keywords:
AttributeError: 'FullArgSpec' object has no attribute 'keywords'
```
Hi, I've noticed that no one seems to be working on this issue right now. Is it okay if I try to work on it?
Yes you can.
I think I may have figured out how to fix it already! It looks to me like the issue is that on line 231, `if argspec.keywords:
` is failing because sometimes `keywords` isn't in `argspec`, and changing it to ` if hasattr(argspec, 'keywords') and argspec.keywords:` should fix it.
You should rerun the script to check what the actual issues are. Some of the errors listed here may no longer be accurate. Any problems are likely due to the script being written for an older version of Python. It only needs to support the newest version of Python.
|
[
{
"body": "```pytb\r\n$./bin/coverage_doctest.py\r\nDOCTEST COVERAGE for /Users/aaronmeurer/Documents/Python/sympy/sympy/sympy\r\n======================================================================\r\n\r\nTraceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"./bin/coverage_doctest.py\", line 601, in <module>\r\n no_color=args.no_color, sphinx=args.sphinx)\r\n File \"./bin/coverage_doctest.py\", line 541, in go\r\n verbose=verbose, no_color=no_color, exact=False, sphinx=sphinx)\r\n File \"./bin/coverage_doctest.py\", line 549, in go\r\n any(name in file for name in skip_paths))):\r\nNameError: name 'skip_paths' is not defined\r\n```\r\n\r\nIt works if you remove the skip_paths check, but we should look into the history of the file to see what that was, because clearly something broke at some point. ",
"number": 16716,
"title": "bin/coverage_doctest.py does not work"
}
] |
87cbdd9ac744e8c0c96eae71420f677970aa4e32
|
{
"head_commit": "05cec82bd68167611a803f9f2e7923879ddf46b2",
"head_commit_message": "Removed commented out code",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/bin/coverage_doctest.py b/bin/coverage_doctest.py\nindex 87e4eb74cefb..0e7399414a8b 100755\n--- a/bin/coverage_doctest.py\n+++ b/bin/coverage_doctest.py\n@@ -72,8 +72,8 @@ def print_header(name, underline=None, color=None):\n print(underline*len(name))\n \n \n-def print_coverage(module_path, c, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_sph, f, f_md, f_mdt,\n- f_idt, f_sph, score, total_doctests, total_members,\n+def print_coverage(module_path, c, c_missing_doc, c_missing_doctest, c_indierect_doctest, c_sph, f, f_missing_doc, f_missing_doctest,\n+ f_indierect_doctest, f_sph, score, total_doctests, total_members,\n sphinx_score, total_sphinx, verbose=False, no_color=False,\n sphinx=True):\n \"\"\" Prints details (depending on verbose) of a module \"\"\"\n@@ -137,19 +137,19 @@ def print_coverage(module_path, c, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_sph, f, f_md, f_mdt,\n print_header('No classes found!')\n \n else:\n- if c_md:\n+ if c_missing_doc:\n print_header('Missing docstrings', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)\n- for md in c_md:\n+ for md in c_missing_doc:\n print(' * ' + md)\n- if c_mdt:\n+ if c_missing_doctest:\n print_header('Missing doctests', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)\n- for md in c_mdt:\n+ for md in c_missing_doctest:\n print(' * ' + md)\n- if c_idt:\n+ if c_indierect_doctest:\n # Use \"# indirect doctest\" in the docstring to\n # suppress this warning.\n print_header('Indirect doctests', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)\n- for md in c_idt:\n+ for md in c_indierect_doctest:\n print(' * ' + md)\n print('\\n Use \\\"# indirect doctest\\\" in the docstring to suppress this warning')\n if c_sph:\n@@ -161,17 +161,17 @@ def print_coverage(module_path, c, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_sph, f, f_md, f_mdt,\n if not f:\n print_header('No functions found!')\n else:\n- if f_md:\n+ if f_missing_doc:\n print_header('Missing docstrings', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)\n- for md in f_md:\n+ for md in f_missing_doc:\n print(' * ' + md)\n- if f_mdt:\n+ if f_missing_doctest:\n print_header('Missing doctests', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)\n- for md in f_mdt:\n+ for md in f_missing_doctest:\n print(' * ' + md)\n- if f_idt:\n+ if f_indierect_doctest:\n print_header('Indirect doctests', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)\n- for md in f_idt:\n+ for md in f_indierect_doctest:\n print(' * ' + md)\n print('\\n Use \\\"# indirect doctest\\\" in the docstring to suppress this warning')\n if f_sph:\n@@ -228,8 +228,8 @@ def _get_arg_list(name, fobj):\n # Add var args\n if argspec.varargs:\n arg_list.append(argspec.varargs)\n- if argspec.keywords:\n- arg_list.append(argspec.keywords)\n+ if argspec.varkw:\n+ arg_list.append(argspec.varkw)\n \n # Truncate long arguments\n arg_list = [x[:trunc] for x in arg_list]\n@@ -283,20 +283,20 @@ def find_sphinx(name, mod_path, found={}):\n found[mod_path] = p.is_imported\n return name in p.is_imported\n \n-def process_function(name, c_name, b_obj, mod_path, f_sk, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt,\n- f_has_doctest, sk_list, sph, sphinx=True):\n+def process_function(name, c_name, b_obj, mod_path, f_skip, f_missing_doc, f_missing_doctest, f_indierect_doctest,\n+ f_has_doctest, skip_list, sph, sphinx=True):\n \"\"\"\n Processes a function to get information regarding documentation.\n It is assume that the function calling this subrouting has already\n verified that it is a valid module function.\n \"\"\"\n- if name in sk_list:\n+ if name in skip_list:\n return False, False\n \n # We add in the end, as inspect.getsourcelines is slow\n- add_md = False\n- add_mdt = False\n- add_idt = False\n+ add_missing_doc = False\n+ add_missing_doctest = False\n+ add_indierect_doctest = False\n in_sphinx = True\n f_doctest = False\n function = False\n@@ -311,30 +311,30 @@ def process_function(name, c_name, b_obj, mod_path, f_sk, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt,\n full_name = _get_arg_list(name, obj)\n \n if name.startswith('_'):\n- f_sk.append(full_name)\n+ f_skip.append(full_name)\n else:\n doc = obj.__doc__\n- if type(doc) is str:\n+ if isinstance(doc, str):\n if not doc:\n- add_md = True\n+ add_missing_doc = True\n elif not '>>>' in doc:\n- add_mdt = True\n+ add_missing_doctest = True\n elif _is_indirect(name, doc):\n- add_idt = True\n+ add_indierect_doctest = True\n else:\n f_doctest = True\n elif doc is None:\n # this was a function defined in the docstring\n f_doctest = True\n else:\n- assert None, type(doc)\n+ raise TypeError('Current doc type for ', print(obj), ' is ', type(doc), '. Docstring must be a string, property, or none')\n \n function = True\n \n if sphinx:\n in_sphinx = find_sphinx(obj_name, mod_path)\n \n- if add_md or add_mdt or add_idt or not in_sphinx:\n+ if add_missing_doc or add_missing_doctest or add_indierect_doctest or not in_sphinx:\n try:\n line_no = inspect.getsourcelines(obj)[1]\n except IOError:\n@@ -343,19 +343,19 @@ def process_function(name, c_name, b_obj, mod_path, f_sk, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt,\n return False, False\n \n full_name = \"LINE %d: %s\" % (line_no, full_name)\n- if add_md:\n- f_md.append(full_name)\n- elif add_mdt:\n- f_mdt.append(full_name)\n- elif add_idt:\n- f_idt.append(full_name)\n+ if add_missing_doc:\n+ f_missing_doc.append(full_name)\n+ elif add_missing_doctest:\n+ f_missing_doctest.append(full_name)\n+ elif add_indierect_doctest:\n+ f_indierect_doctest.append(full_name)\n if not in_sphinx:\n sph.append(full_name)\n \n return f_doctest, function\n \n \n-def process_class(c_name, obj, c_sk, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest,\n+def process_class(c_name, obj, c_skip, c_missing_doc, c_missing_doctest, c_indierect_doctest, c_has_doctest,\n mod_path, sph, sphinx=True):\n \"\"\"\n Extracts information about the class regarding documentation.\n@@ -365,7 +365,7 @@ def process_class(c_name, obj, c_sk, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest,\n \n # Skip class case\n if c_name.startswith('_'):\n- c_sk.append(c_name)\n+ c_skip.append(c_name)\n return False, False, None\n \n c = False\n@@ -381,13 +381,13 @@ def process_class(c_name, obj, c_sk, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest,\n c = True\n full_name = \"LINE %d: %s\" % (line_no, c_name)\n doc = obj.__doc__\n- if type(doc) is str:\n+ if isinstance(doc, str):\n if not doc:\n- c_md.append(full_name)\n+ c_missing_doc.append(full_name)\n elif not '>>>' in doc:\n- c_mdt.append(full_name)\n+ c_missing_doctest.append(full_name)\n elif _is_indirect(c_name, doc):\n- c_idt.append(full_name)\n+ c_indierect_doctest.append(full_name)\n else:\n c_dt = True\n c_has_doctest.append(full_name)\n@@ -395,8 +395,12 @@ def process_class(c_name, obj, c_sk, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest,\n # this was a class defined in the docstring\n c_dt = True\n c_has_doctest.append(full_name)\n+ elif isinstance(doc, property):\n+ # skip class with dynamic doc\n+ c_skip.append(c_name)\n+ return False, False, None\n else:\n- assert None, type(doc)\n+ raise TypeError('Current doc type of ', print(obj), ' is ', type(doc), '. Docstring must be a string, property , or none')\n \n in_sphinx = False\n if sphinx:\n@@ -425,19 +429,19 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):\n return 0, 0, 0\n \n c_skipped = []\n- c_md = []\n- c_mdt = []\n+ c_missing_doc = []\n+ c_missing_doctest = []\n c_has_doctest = []\n- c_idt = []\n+ c_indierect_doctest = []\n classes = 0\n c_doctests = 0\n c_sph = []\n \n f_skipped = []\n- f_md = []\n- f_mdt = []\n+ f_missing_doc = []\n+ f_missing_doctest = []\n f_has_doctest = []\n- f_idt = []\n+ f_indierect_doctest = []\n functions = 0\n f_doctests = 0\n f_sph = []\n@@ -465,7 +469,7 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):\n if inspect.isfunction(obj) or inspect.ismethod(obj):\n \n f_dt, f = process_function(member, '', obj, module_path,\n- f_skipped, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt, f_has_doctest, skip_members,\n+ f_skipped, f_missing_doc, f_missing_doctest, f_indierect_doctest, f_has_doctest, skip_members,\n f_sph, sphinx=sphinx)\n if f:\n functions += 1\n@@ -476,8 +480,8 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):\n elif inspect.isclass(obj):\n \n # Process the class first\n- c_dt, c, source = process_class(member, obj, c_skipped, c_md,\n- c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest, module_path, c_sph, sphinx=sphinx)\n+ c_dt, c, source = process_class(member, obj, c_skipped, c_missing_doc,\n+ c_missing_doctest, c_indierect_doctest, c_has_doctest, module_path, c_sph, sphinx=sphinx)\n if not c:\n continue\n else:\n@@ -507,7 +511,7 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):\n if inspect.isfunction(f_obj) or inspect.ismethod(f_obj):\n \n f_dt, f = process_function(f_name, member, obj,\n- module_path, f_skipped, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt, f_has_doctest,\n+ module_path, f_skipped, f_missing_doc, f_missing_doctest, f_indierect_doctest, f_has_doctest,\n skip_members, f_sph, sphinx=sphinx)\n if f:\n functions += 1\n@@ -535,16 +539,16 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):\n sphinx_score = 0\n \n # Sort functions/classes by line number\n- c_md = sorted(c_md, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n- c_mdt = sorted(c_mdt, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n- c_idt = sorted(c_idt, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n+ c_missing_doc = sorted(c_missing_doc, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n+ c_missing_doctest = sorted(c_missing_doctest, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n+ c_indierect_doctest = sorted(c_indierect_doctest, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n \n- f_md = sorted(f_md, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n- f_mdt = sorted(f_mdt, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n- f_idt = sorted(f_idt, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n+ f_missing_doc = sorted(f_missing_doc, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n+ f_missing_doctest = sorted(f_missing_doctest, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n+ f_indierect_doctest = sorted(f_indierect_doctest, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))\n \n- print_coverage(module_path, classes, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_sph, functions, f_md,\n- f_mdt, f_idt, f_sph, score, total_doctests, total_members,\n+ print_coverage(module_path, classes, c_missing_doc, c_missing_doctest, c_indierect_doctest, c_sph, functions, f_missing_doc,\n+ f_missing_doctest, f_indierect_doctest, f_sph, score, total_doctests, total_members,\n sphinx_score, total_sphinx, verbose=verbose,\n no_color=no_color, sphinx=sphinx)\n \n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -425,19 +429,19 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):\n return 0, 0, 0\n \n c_skipped = []\n- c_md = []\n- c_mdt = []\n+ c_missing_doc = []\n+ c_missing_doctest = []\n c_has_doctest = []\n- c_idt = []\n+ c_indierect_doctest = []\n classes = 0\n c_doctests = 0\n c_sph = []\n \n f_skipped = []\n- f_md = []\n- f_mdt = []\n+ f_missing_doc = []\n+ f_missing_doctest = []\n f_has_doctest = []\n- f_idt = []\n+ f_indierect_doctest = []",
"line": null,
"original_line": 444,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "bin/coverage_doctest.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n\"indirect\" is spelled wrong in these variable names."
}
] |
e3e91177fef2661651bb5d53fa6ff1f429921ab4
|
diff --git a/bin/coverage_doctest.py b/bin/coverage_doctest.py
index 87e4eb74cefb..7102dd562b97 100755
--- a/bin/coverage_doctest.py
+++ b/bin/coverage_doctest.py
@@ -72,8 +72,8 @@ def print_header(name, underline=None, color=None):
print(underline*len(name))
-def print_coverage(module_path, c, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_sph, f, f_md, f_mdt,
- f_idt, f_sph, score, total_doctests, total_members,
+def print_coverage(module_path, c, c_missing_doc, c_missing_doctest, c_indirect_doctest, c_sph, f, f_missing_doc, f_missing_doctest,
+ f_indirect_doctest, f_sph, score, total_doctests, total_members,
sphinx_score, total_sphinx, verbose=False, no_color=False,
sphinx=True):
""" Prints details (depending on verbose) of a module """
@@ -137,19 +137,19 @@ def print_coverage(module_path, c, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_sph, f, f_md, f_mdt,
print_header('No classes found!')
else:
- if c_md:
+ if c_missing_doc:
print_header('Missing docstrings', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)
- for md in c_md:
+ for md in c_missing_doc:
print(' * ' + md)
- if c_mdt:
+ if c_missing_doctest:
print_header('Missing doctests', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)
- for md in c_mdt:
+ for md in c_missing_doctest:
print(' * ' + md)
- if c_idt:
+ if c_indirect_doctest:
# Use "# indirect doctest" in the docstring to
# suppress this warning.
print_header('Indirect doctests', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)
- for md in c_idt:
+ for md in c_indirect_doctest:
print(' * ' + md)
print('\n Use \"# indirect doctest\" in the docstring to suppress this warning')
if c_sph:
@@ -161,17 +161,17 @@ def print_coverage(module_path, c, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_sph, f, f_md, f_mdt,
if not f:
print_header('No functions found!')
else:
- if f_md:
+ if f_missing_doc:
print_header('Missing docstrings', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)
- for md in f_md:
+ for md in f_missing_doc:
print(' * ' + md)
- if f_mdt:
+ if f_missing_doctest:
print_header('Missing doctests', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)
- for md in f_mdt:
+ for md in f_missing_doctest:
print(' * ' + md)
- if f_idt:
+ if f_indirect_doctest:
print_header('Indirect doctests', '-', not no_color and small_header_color)
- for md in f_idt:
+ for md in f_indirect_doctest:
print(' * ' + md)
print('\n Use \"# indirect doctest\" in the docstring to suppress this warning')
if f_sph:
@@ -228,8 +228,8 @@ def _get_arg_list(name, fobj):
# Add var args
if argspec.varargs:
arg_list.append(argspec.varargs)
- if argspec.keywords:
- arg_list.append(argspec.keywords)
+ if argspec.varkw:
+ arg_list.append(argspec.varkw)
# Truncate long arguments
arg_list = [x[:trunc] for x in arg_list]
@@ -283,20 +283,20 @@ def find_sphinx(name, mod_path, found={}):
found[mod_path] = p.is_imported
return name in p.is_imported
-def process_function(name, c_name, b_obj, mod_path, f_sk, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt,
- f_has_doctest, sk_list, sph, sphinx=True):
+def process_function(name, c_name, b_obj, mod_path, f_skip, f_missing_doc, f_missing_doctest, f_indirect_doctest,
+ f_has_doctest, skip_list, sph, sphinx=True):
"""
Processes a function to get information regarding documentation.
It is assume that the function calling this subrouting has already
verified that it is a valid module function.
"""
- if name in sk_list:
+ if name in skip_list:
return False, False
# We add in the end, as inspect.getsourcelines is slow
- add_md = False
- add_mdt = False
- add_idt = False
+ add_missing_doc = False
+ add_missing_doctest = False
+ add_indirect_doctest = False
in_sphinx = True
f_doctest = False
function = False
@@ -311,30 +311,30 @@ def process_function(name, c_name, b_obj, mod_path, f_sk, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt,
full_name = _get_arg_list(name, obj)
if name.startswith('_'):
- f_sk.append(full_name)
+ f_skip.append(full_name)
else:
doc = obj.__doc__
- if type(doc) is str:
+ if isinstance(doc, str):
if not doc:
- add_md = True
+ add_missing_doc = True
elif not '>>>' in doc:
- add_mdt = True
+ add_missing_doctest = True
elif _is_indirect(name, doc):
- add_idt = True
+ add_indirect_doctest = True
else:
f_doctest = True
elif doc is None:
# this was a function defined in the docstring
f_doctest = True
else:
- assert None, type(doc)
+ raise TypeError('Current doc type for ', print(obj), ' is ', type(doc), '. Docstring must be a string, property, or none')
function = True
if sphinx:
in_sphinx = find_sphinx(obj_name, mod_path)
- if add_md or add_mdt or add_idt or not in_sphinx:
+ if add_missing_doc or add_missing_doctest or add_indirect_doctest or not in_sphinx:
try:
line_no = inspect.getsourcelines(obj)[1]
except IOError:
@@ -343,19 +343,19 @@ def process_function(name, c_name, b_obj, mod_path, f_sk, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt,
return False, False
full_name = "LINE %d: %s" % (line_no, full_name)
- if add_md:
- f_md.append(full_name)
- elif add_mdt:
- f_mdt.append(full_name)
- elif add_idt:
- f_idt.append(full_name)
+ if add_missing_doc:
+ f_missing_doc.append(full_name)
+ elif add_missing_doctest:
+ f_missing_doctest.append(full_name)
+ elif add_indirect_doctest:
+ f_indirect_doctest.append(full_name)
if not in_sphinx:
sph.append(full_name)
return f_doctest, function
-def process_class(c_name, obj, c_sk, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest,
+def process_class(c_name, obj, c_skip, c_missing_doc, c_missing_doctest, c_indirect_doctest, c_has_doctest,
mod_path, sph, sphinx=True):
"""
Extracts information about the class regarding documentation.
@@ -365,7 +365,7 @@ def process_class(c_name, obj, c_sk, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest,
# Skip class case
if c_name.startswith('_'):
- c_sk.append(c_name)
+ c_skip.append(c_name)
return False, False, None
c = False
@@ -381,13 +381,13 @@ def process_class(c_name, obj, c_sk, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest,
c = True
full_name = "LINE %d: %s" % (line_no, c_name)
doc = obj.__doc__
- if type(doc) is str:
+ if isinstance(doc, str):
if not doc:
- c_md.append(full_name)
+ c_missing_doc.append(full_name)
elif not '>>>' in doc:
- c_mdt.append(full_name)
+ c_missing_doctest.append(full_name)
elif _is_indirect(c_name, doc):
- c_idt.append(full_name)
+ c_indirect_doctest.append(full_name)
else:
c_dt = True
c_has_doctest.append(full_name)
@@ -395,8 +395,12 @@ def process_class(c_name, obj, c_sk, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest,
# this was a class defined in the docstring
c_dt = True
c_has_doctest.append(full_name)
+ elif isinstance(doc, property):
+ # skip class with dynamic doc
+ c_skip.append(c_name)
+ return False, False, None
else:
- assert None, type(doc)
+ raise TypeError('Current doc type of ', print(obj), ' is ', type(doc), '. Docstring must be a string, property , or none')
in_sphinx = False
if sphinx:
@@ -425,19 +429,19 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):
return 0, 0, 0
c_skipped = []
- c_md = []
- c_mdt = []
+ c_missing_doc = []
+ c_missing_doctest = []
c_has_doctest = []
- c_idt = []
+ c_indirect_doctest = []
classes = 0
c_doctests = 0
c_sph = []
f_skipped = []
- f_md = []
- f_mdt = []
+ f_missing_doc = []
+ f_missing_doctest = []
f_has_doctest = []
- f_idt = []
+ f_indirect_doctest = []
functions = 0
f_doctests = 0
f_sph = []
@@ -465,7 +469,7 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):
if inspect.isfunction(obj) or inspect.ismethod(obj):
f_dt, f = process_function(member, '', obj, module_path,
- f_skipped, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt, f_has_doctest, skip_members,
+ f_skipped, f_missing_doc, f_missing_doctest, f_indirect_doctest, f_has_doctest, skip_members,
f_sph, sphinx=sphinx)
if f:
functions += 1
@@ -476,8 +480,8 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):
elif inspect.isclass(obj):
# Process the class first
- c_dt, c, source = process_class(member, obj, c_skipped, c_md,
- c_mdt, c_idt, c_has_doctest, module_path, c_sph, sphinx=sphinx)
+ c_dt, c, source = process_class(member, obj, c_skipped, c_missing_doc,
+ c_missing_doctest, c_indirect_doctest, c_has_doctest, module_path, c_sph, sphinx=sphinx)
if not c:
continue
else:
@@ -507,7 +511,7 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):
if inspect.isfunction(f_obj) or inspect.ismethod(f_obj):
f_dt, f = process_function(f_name, member, obj,
- module_path, f_skipped, f_md, f_mdt, f_idt, f_has_doctest,
+ module_path, f_skipped, f_missing_doc, f_missing_doctest, f_indirect_doctest, f_has_doctest,
skip_members, f_sph, sphinx=sphinx)
if f:
functions += 1
@@ -535,16 +539,16 @@ def coverage(module_path, verbose=False, no_color=False, sphinx=True):
sphinx_score = 0
# Sort functions/classes by line number
- c_md = sorted(c_md, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
- c_mdt = sorted(c_mdt, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
- c_idt = sorted(c_idt, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
+ c_missing_doc = sorted(c_missing_doc, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
+ c_missing_doctest = sorted(c_missing_doctest, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
+ c_indirect_doctest = sorted(c_indirect_doctest, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
- f_md = sorted(f_md, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
- f_mdt = sorted(f_mdt, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
- f_idt = sorted(f_idt, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
+ f_missing_doc = sorted(f_missing_doc, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
+ f_missing_doctest = sorted(f_missing_doctest, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
+ f_indirect_doctest = sorted(f_indirect_doctest, key=lambda x: int(x.split()[1][:-1]))
- print_coverage(module_path, classes, c_md, c_mdt, c_idt, c_sph, functions, f_md,
- f_mdt, f_idt, f_sph, score, total_doctests, total_members,
+ print_coverage(module_path, classes, c_missing_doc, c_missing_doctest, c_indirect_doctest, c_sph, functions, f_missing_doc,
+ f_missing_doctest, f_indirect_doctest, f_sph, score, total_doctests, total_members,
sphinx_score, total_sphinx, verbose=verbose,
no_color=no_color, sphinx=sphinx)
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-22403@44eebbe
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 22,403
|
Added tests for different values of k for limit(x**n - x**(n - k), x, oo)
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Closes #18176
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Added Appropriate tests . The following limit wasn't working properly( all cases except `k=0`) when the issue was reported ( we used to get `NotImplementedError: Result depends on the sign of sign(n - k)` which was wrong ). This has been addressed somewhere else and is working properly. It gives the correct `NotImplementedError` now which is `Result depends on the sign of sign(k)`
```
>>> x = Symbol('x', real=True , positive= True)
>>> n = Symbol('n', integer=True, positive=True)
>>> k = Symbol('k')
>>> limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo)
NotImplementedError: Result depends on the sign of sign(k)
>>> k = 1
>>> limit(x**n-x**(n-k), x, oo)
oo
>>> k = -2
>>> limit(x**n-x**(n-k), x, oo)
-oo
```
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-11-01T09:31:51Z
|
Incorrect value for limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo) when k is a natural number
```
In [64]: x = Symbol('x', real=True , positive= True)
In [65]: n = Symbol('n', integer=True, positive=True);
In [66]: k=0
In [67]: limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo)
Out[67]: 0
In [68]: k=1
In [69]: limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NotImplementedError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-69-e74c61d1f6e7> in <module>
----> 1 limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo)
~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/limits.py in limit(e, z, z0, dir)
69 """
70
---> 71 return Limit(e, z, z0, dir).doit(deep=False)
72
73
~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/limits.py in doit(self, **hints)
259 % (l, r))
260 else:
--> 261 r = gruntz(e, z, z0, dir)
262 if r is S.NaN or l is S.NaN:
263 raise PoleError()
~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in gruntz(e, z, z0, dir)
669
670 try:
--> 671 r = limitinf(e0, z)
672 except ValueError:
673 r = limitinf(e0, z, leadsimp=True)
~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in limitinf(e, x, leadsimp)
448 if leadsimp:
449 c0 = c0.simplify()
--> 450 return limitinf(c0, x, leadsimp) # e0=0: lim f = lim c0
451 else:
452 raise ValueError("{} could not be evaluated".format(sig))
~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in limitinf(e, x, leadsimp)
433 e = e.subs(x, p)
434 x = p
--> 435 c0, e0 = mrv_leadterm(e, x)
436 sig = sign(e0, x)
437 if sig == 1:
~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in mrv_leadterm(e, x)
521 #
522 w = Dummy("w", real=True, positive=True, finite=True)
--> 523 f, logw = rewrite(exps, Omega, x, w)
524 series = calculate_series(f, w, logx=logw)
525 return series.leadterm(w)
~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in rewrite(e, Omega, x, wsym)
593 sig = sign(g.args[0], x)
594 if sig != 1 and sig != -1:
--> 595 raise NotImplementedError('Result depends on the sign of %s' % sig)
596 if sig == 1:
597 wsym = 1/wsym # if g goes to oo, substitute 1/w
NotImplementedError: Result depends on the sign of sign(n - 1)
```
The answer should be `oo` right?
|
This seems to be fixed on master , could close after adding relevant tests !
@sylee957 you could mark this as could close and easy to fix. Thank You
```
>>> k = Symbol('k')
>>> limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo)
NotImplementedError: Result depends on the sign of sign(k)
>>> k = 1
>>> limit(x**n-x**(n-k), x, oo)
oo
>>> k = -2
>>> limit(x**n-x**(n-k), x, oo)
-oo
```
|
[
{
"body": "```\r\nIn [64]: x = Symbol('x', real=True , positive= True) \r\n\r\nIn [65]: n = Symbol('n', integer=True, positive=True); \r\n\r\nIn [66]: k=0 \r\n\r\nIn [67]: limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo) \r\nOut[67]: 0\r\n\r\nIn [68]: k=1 \r\n\r\nIn [69]: limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo) \r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nNotImplementedError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n<ipython-input-69-e74c61d1f6e7> in <module>\r\n----> 1 limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo)\r\n\r\n~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/limits.py in limit(e, z, z0, dir)\r\n 69 \"\"\"\r\n 70 \r\n---> 71 return Limit(e, z, z0, dir).doit(deep=False)\r\n 72 \r\n 73 \r\n\r\n~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/limits.py in doit(self, **hints)\r\n 259 % (l, r))\r\n 260 else:\r\n--> 261 r = gruntz(e, z, z0, dir)\r\n 262 if r is S.NaN or l is S.NaN:\r\n 263 raise PoleError()\r\n\r\n~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in gruntz(e, z, z0, dir)\r\n 669 \r\n 670 try:\r\n--> 671 r = limitinf(e0, z)\r\n 672 except ValueError:\r\n 673 r = limitinf(e0, z, leadsimp=True)\r\n\r\n~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in limitinf(e, x, leadsimp)\r\n 448 if leadsimp:\r\n 449 c0 = c0.simplify()\r\n--> 450 return limitinf(c0, x, leadsimp) # e0=0: lim f = lim c0\r\n 451 else:\r\n 452 raise ValueError(\"{} could not be evaluated\".format(sig))\r\n\r\n~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in limitinf(e, x, leadsimp)\r\n 433 e = e.subs(x, p)\r\n 434 x = p\r\n--> 435 c0, e0 = mrv_leadterm(e, x)\r\n 436 sig = sign(e0, x)\r\n 437 if sig == 1:\r\n\r\n~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in mrv_leadterm(e, x)\r\n 521 #\r\n 522 w = Dummy(\"w\", real=True, positive=True, finite=True)\r\n--> 523 f, logw = rewrite(exps, Omega, x, w)\r\n 524 series = calculate_series(f, w, logx=logw)\r\n 525 return series.leadterm(w)\r\n\r\n~/timepass/reee/gsoc/sympy/sympy/series/gruntz.py in rewrite(e, Omega, x, wsym)\r\n 593 sig = sign(g.args[0], x)\r\n 594 if sig != 1 and sig != -1:\r\n--> 595 raise NotImplementedError('Result depends on the sign of %s' % sig)\r\n 596 if sig == 1:\r\n 597 wsym = 1/wsym # if g goes to oo, substitute 1/w\r\n\r\nNotImplementedError: Result depends on the sign of sign(n - 1)\r\n\r\n```\r\n\r\nThe answer should be `oo` right?",
"number": 18176,
"title": "Incorrect value for limit(x**n-x**(n-k),x,oo) when k is a natural number"
}
] |
9019765edb0d0b4bbd29674a58b93ef4e75b92f8
|
{
"head_commit": "44eebbe8a9b3a2f1337c7061a35e87597fd64c0f",
"head_commit_message": "Added Appropriate tests to close the issue",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\nindex 22201e479d45..28c16cb1cedd 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\n@@ -880,6 +880,14 @@ def test_issue_18118():\n assert limit(sign(sin(x)), x, 0, \"-\") == -1\n assert limit(sign(sin(x)), x, 0, \"+\") == 1\n \n+def test_issue_18176():\n+ x = Symbol('x', real=True , positive= True)\n+ n = Symbol('n', integer=True, positive=True)\n+ k = 1\n+ assert limit(x**n-x**(n-k), x, oo) == oo\n+ k = -2\n+ assert limit(x**n-x**(n-k), x, oo) == -oo\n+\n \n def test_issue_18306():\n assert limit(sin(sqrt(x))/sqrt(sin(x)), x, 0, '+') == 1\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -880,6 +880,14 @@ def test_issue_18118():\n assert limit(sign(sin(x)), x, 0, \"-\") == -1\n assert limit(sign(sin(x)), x, 0, \"+\") == 1\n \n+def test_issue_18176():",
"line": null,
"original_line": 883,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThese seem quite similar to #22230. Perhaps both of these can be mergeg and put into another appropriate test function (like `test_exponential`) rather than making new functions.\n\n@author:\nThanks @user1, I had completely forgotten about the earlier Pr . Do we even need this Pr then both address similar issues ! Or maybe as that has been merged I could put these tests there and change the name of that function ?"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -880,6 +880,14 @@ def test_issue_18118():\n assert limit(sign(sin(x)), x, 0, \"-\") == -1\n assert limit(sign(sin(x)), x, 0, \"+\") == 1\n \n+def test_issue_18176():\n+ x = Symbol('x', real=True , positive= True)\n+ n = Symbol('n', integer=True, positive=True)\n+ k = 1\n+ assert limit(x**n-x**(n-k), x, oo) == oo",
"line": null,
"original_line": 887,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n`k` can directly be substituted here without a separate line for assigning value.\n\n@author:\nYeah sure , I'll do the needful . I just thought that the issue was reported using k so I should go forward with using k explicitly !"
}
] |
62b37f54db5b0a57c77c352780c6dab4356eb07c
|
diff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
index 22201e479d45..996e5d1fbc3d 100644
--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
@@ -607,13 +607,16 @@ def test_issue_8481():
limit(lamda**k * exp(-lamda) / factorial(k), k, oo) == 0
-def test_issue_8635():
+def test_issue_8635_18176():
x = Symbol('x', real=True)
k = Symbol('k', positive=True)
assert limit(x**n - x**(n - 0), x, oo) == 0
assert limit(x**n - x**(n - 5), x, oo) == oo
assert limit(x**n - x**(n - 2.5), x, oo) == oo
assert limit(x**n - x**(n - k - 1), x, oo) == oo
+ x = Symbol('x', positive=True)
+ assert limit(x**n - x**(n - 1), x, oo) == oo
+ assert limit(x**n - x**(n + 2), x, oo) == -oo
def test_issue_8730():
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-11008@8cb1561
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 11,008
|
Create ipv4_conversion.py
|
### Describe your change:
Closes #9718
Closes #11013
* [x] Add an algorithm?
* [ ] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [x] Add or change doctests? -- Note: Please avoid changing both code and tests in a single pull request.
* [ ] Documentation change?
### Checklist:
* [x] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [x] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [x] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [x] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [x] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [x] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [x] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [x] All new algorithms include at least one URL that points to Wikipedia or another similar explanation.
* [ ] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the description above includes the issue number(s) with a [closing keyword](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue): "Fixes #ISSUE-NUMBER".
|
2023-10-26T17:50:04Z
|
Speedup our eight slowest pytests (one at a time please)
### Feature description
At the end of our GitHub Actions `build` jobs, there is a list of the slowest ones.
Are there ways to speed up these tests without reducing our functionality or our code coverage?
Please only fix one algorithm per pull request.
* [ ] 16.64s call neural_network/simple_neural_network.py::neural_network.simple_neural_network.forward_propagation
* [x] 6.15s call backtracking/word_search.py::backtracking.word_search.word_exists
* [x] 4.61s call digital_image_processing/test_digital_image_processing.py::test_local_binary_pattern
* [x] 2.59s call backtracking/power_sum.py::backtracking.power_sum.backtrack
* [x] 2.19s call machine_learning/xgboost_regressor.py::machine_learning.xgboost_regressor.main
* [x] 1.73s call maths/prime_numbers.py::maths.prime_numbers.slow_primes
* [x] 1.43s call backtracking/power_sum.py::backtracking.power_sum.solve
* [x] 1.00s call other/dijkstra_bankers_algorithm.py::other.dijkstra_bankers_algorithm.BankersAlgorithm.main
================= 1506 passed, 25 warnings in 71.23s (0:01:11) =================
Also, those **25 pytest warnings** are worth fixing!!!
|
I pointed out in #8785 that `neural_network/simple_neural_network.py` has multiple issues (I don't think it even implements a neural network) and could do with a rewrite. Ideally whatever new implementation replaces it should run a lot more quickly.
I checked the maths/prime_numbers.py file. In this file, there are three methods for finding prime numbers using different techniques. The simplest method, referred to as slow_prime (which uses a loop to iterate from 2 to n and print prime numbers), is taking a lot of time. Do we need it there? Since the other two methods are faster with just minor modifications for finding prime numbers, do we still need the slow_prime method in there?
Can `slow_prime()` be tested with smaller numbers? We do not want to get rid of it but we want its test to finish faster.
https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/87494f1fa1022368d154477bdc035fd01f9e4382/maths/prime_numbers.py#L20-L21
Let's lower the `10_000` to `1_000`
If 'slow_prime()' is tested on small test cases, then the other two methods will also be tested on small test cases to compare the time taken among them.
If I reduce the test cases, do I need to raise a PR to check whether they finished faster, or is there any other method I can use to verify if the issue is resolved before submitting a PR?
When things are run on CI platforms like GitHub Actions then an environment variable `CI` is defined.
* https://docs.github.com/en/actions/learn-github-actions/variables#default-environment-variables
Can you use https://docs.python.org/3/library/os.html#os.getenv to see if `CI` is defined? If `CI` is defined then set the number to 1_000 for all three tests and it if is not defined then set it to 10_000 for all three.
Okay, thanks. Let me try.
But if it is not defined, setting the test case to 10_000 will take the same amount of time as before, doesn't it?
Yes, but we do not care because it no longer slows down our build process.
I sped it up in #9851.
|
[
{
"body": "### Feature description\n\nAt the end of our GitHub Actions `build` jobs, there is a list of the slowest ones.\r\n\r\nAre there ways to speed up these tests without reducing our functionality or our code coverage?\r\n\r\nPlease only fix one algorithm per pull request.\r\n* [ ] 16.64s call neural_network/simple_neural_network.py::neural_network.simple_neural_network.forward_propagation\r\n* [x] 6.15s call backtracking/word_search.py::backtracking.word_search.word_exists\r\n* [x] 4.61s call digital_image_processing/test_digital_image_processing.py::test_local_binary_pattern\r\n* [x] 2.59s call backtracking/power_sum.py::backtracking.power_sum.backtrack\r\n* [x] 2.19s call machine_learning/xgboost_regressor.py::machine_learning.xgboost_regressor.main\r\n* [x] 1.73s call maths/prime_numbers.py::maths.prime_numbers.slow_primes\r\n* [x] 1.43s call backtracking/power_sum.py::backtracking.power_sum.solve\r\n* [x] 1.00s call other/dijkstra_bankers_algorithm.py::other.dijkstra_bankers_algorithm.BankersAlgorithm.main\r\n================= 1506 passed, 25 warnings in 71.23s (0:01:11) =================\r\n\r\nAlso, those **25 pytest warnings** are worth fixing!!!",
"number": 9718,
"title": "Speedup our eight slowest pytests (one at a time please)"
}
] |
fe4aad0ec94a2d2f28470dd8eaad3ff1bf74c5c8
|
{
"head_commit": "8cb1561f2cda9455073015f4d726388a4a429cfb",
"head_commit_message": "[pre-commit.ci] auto fixes from pre-commit.com hooks\n\nfor more information, see https://pre-commit.ci",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/conversions/ipconversion.py b/conversions/ipconversion.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..f59cbc5f9079\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/conversions/ipconversion.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@\n+# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/convert-ip-address-to-integer-and-vice-versa/\n+\n+\n+def ip_to_decimal(ip_address: str) -> int:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Convert an IPv4 address to its decimal representation.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ ip_address (str): A string representing an IPv4 address (e.g., \"192.168.0.1\").\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ int: The decimal representation of the IP address.\n+\n+ >>> ip_to_decimal(\"192.168.0.1\")\n+ 3232235521\n+ >>> ip_to_decimal(\"10.0.0.255\")\n+ 167772415\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ ip_parts = ip_address.split(\".\")\n+ if len(ip_parts) != 4:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Invalid IPv4 address format\")\n+\n+ decimal_ip = 0\n+ for part in ip_parts:\n+ decimal_ip = (decimal_ip << 8) + int(part)\n+\n+ return decimal_ip\n+\n+\n+def decimal_to_ip(decimal_ip: int) -> str:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Convert a decimal representation of an IP address to its IPv4 format.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ decimal_ip (int): An integer representing the decimal IP address.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ str: The IPv4 representation of the decimal IP address.\n+\n+ >>> decimal_to_ip(3232235521)\n+ '192.168.0.1'\n+ >>> decimal_to_ip(167772415)\n+ '10.0.0.255'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not (0 <= decimal_ip <= 4294967295):\n+ raise ValueError(\"Invalid decimal IP address\")\n+\n+ ip_parts = []\n+ for _ in range(4):\n+ ip_parts.append(str(decimal_ip & 255))\n+ decimal_ip >>= 8\n+\n+ ip_parts.reverse()\n+ return \".\".join(ip_parts)\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ import doctest\n+\n+ doctest.testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@\n+# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/convert-ip-address-to-integer-and-vice-versa/\n+\n+\n+def ip_to_decimal(ip_address: str) -> int:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Convert an IPv4 address to its decimal representation.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ ip_address (str): A string representing an IPv4 address (e.g., \"192.168.0.1\").\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ int: The decimal representation of the IP address.\n+\n+ >>> ip_to_decimal(\"192.168.0.1\")\n+ 3232235521\n+ >>> ip_to_decimal(\"10.0.0.255\")\n+ 167772415\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ ip_parts = ip_address.split(\".\")",
"line": null,
"original_line": 20,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "conversions/ipconversion.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nSee: https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/maths/is_ip_v4_address_valid.py\r\n```suggestion\r\n octets = ip_address.split(\".\")\r\n```\n\n@author:\nUsing more Appropriate variable names indeed make the code easy to understand Thanks!."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@\n+# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/convert-ip-address-to-integer-and-vice-versa/\n+\n+\n+def ip_to_decimal(ip_address: str) -> int:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Convert an IPv4 address to its decimal representation.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ ip_address (str): A string representing an IPv4 address (e.g., \"192.168.0.1\").\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ int: The decimal representation of the IP address.\n+\n+ >>> ip_to_decimal(\"192.168.0.1\")\n+ 3232235521\n+ >>> ip_to_decimal(\"10.0.0.255\")\n+ 167772415\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ ip_parts = ip_address.split(\".\")\n+ if len(ip_parts) != 4:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Invalid IPv4 address format\")\n+\n+ decimal_ip = 0\n+ for part in ip_parts:\n+ decimal_ip = (decimal_ip << 8) + int(part)\n+\n+ return decimal_ip\n+\n+\n+def decimal_to_ip(decimal_ip: int) -> str:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Convert a decimal representation of an IP address to its IPv4 format.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ decimal_ip (int): An integer representing the decimal IP address.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ str: The IPv4 representation of the decimal IP address.\n+\n+ >>> decimal_to_ip(3232235521)\n+ '192.168.0.1'\n+ >>> decimal_to_ip(167772415)\n+ '10.0.0.255'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not (0 <= decimal_ip <= 4294967295):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 47,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "conversions/ipconversion.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis would not catch 10.0.0.256 which is not a valid IP."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@\n+# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/convert-ip-address-to-integer-and-vice-versa/\n+\n+\n+def ip_to_decimal(ip_address: str) -> int:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Convert an IPv4 address to its decimal representation.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ ip_address (str): A string representing an IPv4 address (e.g., \"192.168.0.1\").\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ int: The decimal representation of the IP address.\n+\n+ >>> ip_to_decimal(\"192.168.0.1\")\n+ 3232235521\n+ >>> ip_to_decimal(\"10.0.0.255\")\n+ 167772415\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ ip_parts = ip_address.split(\".\")\n+ if len(ip_parts) != 4:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Invalid IPv4 address format\")\n+\n+ decimal_ip = 0\n+ for part in ip_parts:\n+ decimal_ip = (decimal_ip << 8) + int(part)\n+\n+ return decimal_ip",
"line": null,
"original_line": 28,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "conversions/ipconversion.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```\r\ndef alt_ip_to_decimal(ip_address: str) -> int:\r\n return int(\"0x\" + \"\".join(f\"{int(i):02x}\" for i in ip_address.split(\".\")), 16)\r\n```"
}
] |
586fef389831097f864dd5b9b5673f2242081b5f
|
diff --git a/conversions/ipv4_conversion.py b/conversions/ipv4_conversion.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..862309b7251e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/conversions/ipv4_conversion.py
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/convert-ip-address-to-integer-and-vice-versa/
+
+
+def ipv4_to_decimal(ipv4_address: str) -> int:
+ """
+ Convert an IPv4 address to its decimal representation.
+
+ Args:
+ ip_address: A string representing an IPv4 address (e.g., "192.168.0.1").
+
+ Returns:
+ int: The decimal representation of the IP address.
+
+ >>> ipv4_to_decimal("192.168.0.1")
+ 3232235521
+ >>> ipv4_to_decimal("10.0.0.255")
+ 167772415
+ >>> ipv4_to_decimal("10.0.255")
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Invalid IPv4 address format
+ >>> ipv4_to_decimal("10.0.0.256")
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Invalid IPv4 octet 256
+ """
+
+ octets = [int(octet) for octet in ipv4_address.split(".")]
+ if len(octets) != 4:
+ raise ValueError("Invalid IPv4 address format")
+
+ decimal_ipv4 = 0
+ for octet in octets:
+ if not 0 <= octet <= 255:
+ raise ValueError(f"Invalid IPv4 octet {octet}") # noqa: EM102
+ decimal_ipv4 = (decimal_ipv4 << 8) + int(octet)
+
+ return decimal_ipv4
+
+
+def alt_ipv4_to_decimal(ipv4_address: str) -> int:
+ """
+ >>> alt_ipv4_to_decimal("192.168.0.1")
+ 3232235521
+ >>> alt_ipv4_to_decimal("10.0.0.255")
+ 167772415
+ """
+ return int("0x" + "".join(f"{int(i):02x}" for i in ipv4_address.split(".")), 16)
+
+
+def decimal_to_ipv4(decimal_ipv4: int) -> str:
+ """
+ Convert a decimal representation of an IP address to its IPv4 format.
+
+ Args:
+ decimal_ipv4: An integer representing the decimal IP address.
+
+ Returns:
+ The IPv4 representation of the decimal IP address.
+
+ >>> decimal_to_ipv4(3232235521)
+ '192.168.0.1'
+ >>> decimal_to_ipv4(167772415)
+ '10.0.0.255'
+ >>> decimal_to_ipv4(-1)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Invalid decimal IPv4 address
+ """
+
+ if not (0 <= decimal_ipv4 <= 4294967295):
+ raise ValueError("Invalid decimal IPv4 address")
+
+ ip_parts = []
+ for _ in range(4):
+ ip_parts.append(str(decimal_ipv4 & 255))
+ decimal_ipv4 >>= 8
+
+ return ".".join(reversed(ip_parts))
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import doctest
+
+ doctest.testmod()
diff --git a/neural_network/simple_neural_network.py b/neural_network/simple_neural_network.py
index f2a3234873b5..8751a38908cf 100644
--- a/neural_network/simple_neural_network.py
+++ b/neural_network/simple_neural_network.py
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ def sigmoid_function(value: float, deriv: bool = False) -> float:
def forward_propagation(expected: int, number_propagations: int) -> float:
"""Return the value found after the forward propagation training.
- >>> res = forward_propagation(32, 10000000)
+ >>> res = forward_propagation(32, 450_000) # Was 10_000_000
>>> res > 31 and res < 33
True
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Performance Optimizations"
}
|
sympy__sympy-22369@6eb7e6a
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 22,369
|
line - added fix to define horizontal and vertical lines using Eq instead of Point
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Fixes #22361 and now we can define horizontal and vertical lines using `Eq`. `Line(Eq(x, 1))` now returns `Line2D(Point2D(1, 0), Point2D(1, 1))` instead of `ValueError: could not find y` .
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* geometry
* `Line` class can now define horizontal and vertical lines using `Eq`
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-10-25T17:34:13Z
|
Line with equation doesn't support horizontal or vertical lines
```
from sympy import Point, Eq, symbols
from sympy.geometry import Line, Segment
from sympy.abc import x, y
a, b, c, e, f, g, h = symbols('a, b, c, e, f, g, h')
AC = Line(Eq(y, a*x + c))
DF = Line(Eq(y, f))
```
SymPy throws `ValueError: could not find x` in the last line.
Are there only ways to represent such horizontal or vertical lines with two points, or one point with a slope oo or 0?
|
Sympy throws `ValueError: could not find x` for `Line(Eq(y, f))`.
This error can be avoided by defining `x` as `f` .
```
>>> Line(Eq(y, f), x = f)
Line2D(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(1, 1))
```
Yes. SymPy tries to "do the right thing" but sometimes you have to provide more input. The docstring, too, is helpful in resolving these issues:
```
The line corresponding to an equation in the for `ax + by + c = 0`,
can be entered:
>>> Line(3*x + y + 18)
Line2D(Point2D(0, -18), Point2D(1, -21))
If `x` or `y` has a different name, then they can be specified, too,
as a string (to match the name) or symbol:
>>> Line(Eq(3*a + b, -18), x='a', y=b)
```
Hi @praneethratna and @smichr , both your cases are neither horizontal nor vertical.
I mean, could you provide examples to define such lines just by providing `Eq` instead of `Point`?
For example: `Eq(x, 1)` is a vertical line passing through `Point(1, 0)`, `Eq(y, 1)` is a horizon passing through `Point(0, 1)`. Can you define such lines without inputing `Point(1, 0)` or `Point(0, 1)`?
Sorry for my error paste. The error for the last line is `ValueError: could not find x` but not `ValueError: could not find y`.
|
[
{
"body": "```\r\nfrom sympy import Point, Eq, symbols\r\nfrom sympy.geometry import Line, Segment\r\nfrom sympy.abc import x, y\r\n\r\na, b, c, e, f, g, h = symbols('a, b, c, e, f, g, h')\r\nAC = Line(Eq(y, a*x + c))\r\nDF = Line(Eq(y, f))\r\n```\r\n\r\nSymPy throws `ValueError: could not find x` in the last line.\r\n\r\nAre there only ways to represent such horizontal or vertical lines with two points, or one point with a slope oo or 0?",
"number": 22361,
"title": "Line with equation doesn't support horizontal or vertical lines"
}
] |
0e4bab73562d6f90fcdf5fa079731f26a455347c
|
{
"head_commit": "6eb7e6a42a9dd9dbdf9fe07922e083afa2932456",
"head_commit_message": "fixed error",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_line.py b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_line.py\nindex 89af9cfc844d..7733c056a820 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_line.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_line.py\n@@ -802,3 +802,8 @@ def test_issue_8615():\n a = Line3D(Point3D(6, 5, 0), Point3D(6, -6, 0))\n b = Line3D(Point3D(6, -1, 19/10), Point3D(6, -1, 0))\n assert a.intersection(b) == [Point3D(6, -1, 0)]\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_22361():\n+ assert Line(Eq(x, 1)) == Line2D(Point2D(1, 0), Point2D(1, 1))\n+ assert Line(Eq(y, 1)) == Line2D(Point2D(0, 1), Point2D(1, 1))\ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/util.py b/sympy/geometry/util.py\nindex fb85ecc433e9..4c98f190b0b0 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/util.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/util.py\n@@ -27,7 +27,9 @@ def find(x, equation):\n \n free = equation.free_symbols\n xs = [i for i in free if (i.name if isinstance(x, str) else i) == x]\n- if not xs:\n+ if not xs and (str(equation) != x):\n+ return 1\n+ if str(equation) == x:\n raise ValueError('could not find %s' % x)\n if len(xs) != 1:\n raise ValueError('ambiguous %s' % x)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -27,7 +27,9 @@ def find(x, equation):\n \n free = equation.free_symbols\n xs = [i for i in free if (i.name if isinstance(x, str) else i) == x]\n- if not xs:\n+ if not xs and (str(equation) != x):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 30,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/geometry/util.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI recommend against changing `find` in this way. One might have the equation `2*y + 1` which is another way of saying `y = 1/2`."
}
] |
4fca2b9b9a5b849cf56145506b371bbcf48deabe
|
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/line.py b/sympy/geometry/line.py
index 5bd1c1de553d..035201af0b9b 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/line.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/line.py
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@
from sympy.core.evalf import N
from sympy.core.numbers import Rational, oo
from sympy.core.relational import Eq
-from sympy.core.symbol import _symbol, Dummy
+from sympy.core.symbol import _symbol, Dummy, uniquely_named_symbol
from sympy.functions.elementary.piecewise import Piecewise
from sympy.functions.elementary.trigonometric import (_pi_coeff as pi_coeff, acos, tan, atan2)
from .entity import GeometryEntity, GeometrySet
@@ -1155,14 +1155,27 @@ class Line(LinearEntity):
"""
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if len(args) == 1 and isinstance(args[0], (Expr, Eq)):
- x = kwargs.get('x', 'x')
- y = kwargs.get('y', 'y')
+ missing = uniquely_named_symbol('?', args).name
+ if not kwargs:
+ x = 'x'
+ y = 'y'
+ else:
+ x = kwargs.pop('x', missing)
+ y = kwargs.pop('y', missing)
+ if kwargs:
+ raise ValueError('expecting only x and y as keywords')
+
equation = args[0]
if isinstance(equation, Eq):
equation = equation.lhs - equation.rhs
- xin, yin = x, y
- x = find(x, equation) or Dummy()
- y = find(y, equation) or Dummy()
+
+ def find_or_missing(x):
+ try:
+ return find(x, equation)
+ except ValueError:
+ return missing
+ x = find_or_missing(x)
+ y = find_or_missing(y)
a, b, c = linear_coeffs(equation, x, y)
@@ -1170,7 +1183,8 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
return Line((0, -c/b), slope=-a/b)
if a:
return Line((-c/a, 0), slope=oo)
- raise ValueError('neither %s nor %s were found in the equation' % (xin, yin))
+
+ raise ValueError('not found in equation: %s' % (set('xy') - {x, y}))
else:
if len(args) > 0:
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_line.py b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_line.py
index 89af9cfc844d..646f1fe9007a 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/tests/test_line.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/tests/test_line.py
@@ -24,17 +24,24 @@
def test_object_from_equation():
from sympy.abc import x, y, a, b
assert Line(3*x + y + 18) == Line2D(Point2D(0, -18), Point2D(1, -21))
- assert Line(3*x + 5 * y + 1) == Line2D(Point2D(0, Rational(-1, 5)), Point2D(1, Rational(-4, 5)))
- assert Line(3*a + b + 18, x='a', y='b') == Line2D(Point2D(0, -18), Point2D(1, -21))
+ assert Line(3*x + 5 * y + 1) == Line2D(
+ Point2D(0, Rational(-1, 5)), Point2D(1, Rational(-4, 5)))
+ assert Line(3*a + b + 18, x="a", y="b") == Line2D(
+ Point2D(0, -18), Point2D(1, -21))
assert Line(3*x + y) == Line2D(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(1, -3))
assert Line(x + y) == Line2D(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(1, -1))
- assert Line(Eq(3*a + b, -18), x='a', y=b) == Line2D(Point2D(0, -18), Point2D(1, -21))
- raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(x))
- raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(y))
- raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(x/y))
- raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(a/b, x='a', y='b'))
- raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(y/x))
- raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(b/a, x='a', y='b'))
+ assert Line(Eq(3*a + b, -18), x="a", y=b) == Line2D(
+ Point2D(0, -18), Point2D(1, -21))
+ # issue 22361
+ assert Line(x - 1) == Line2D(Point2D(1, 0), Point2D(1, 1))
+ assert Line(2*x - 2, y=x) == Line2D(Point2D(0, 1), Point2D(1, 1))
+ assert Line(y) == Line2D(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(1, 0))
+ assert Line(2*y, x=y) == Line2D(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(0, 1))
+ assert Line(y, x=y) == Line2D(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(0, 1))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(x / y))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(a / b, x='a', y='b'))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(y / x))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Line(b / a, x='a', y='b'))
raises(ValueError, lambda: Line((x + 1)**2 + y))
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-9861@5442a69
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 9,861
|
Match a pattern and String using backtracking
|
### Describe your change:
created a file with name match_word_pattern.py inside backtracking for Match a pattern and String using backtracking.
* [x] Add an algorithm?
* [ ] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [ ] Documentation change?
### Checklist:
* [x] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [x] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [x] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [x] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [x] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [x] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [x] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [ ] All new algorithms include at least one URL that points to Wikipedia or another similar explanation.
* [x] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the description above includes the issue number(s) with a [closing keyword](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue): "Fixes #9844".
|
2023-10-05T18:32:19Z
|
Match a pattern and String using backtracking
### What would you like to share?
Given a string, find out if string follows a given pattern or not without using any regular expressions. We can solve this problem with the help of Backtracking.
### Additional information
_No response_
|
Please accept the issue with hacktober tag
|
[
{
"body": "### What would you like to share?\n\nGiven a string, find out if string follows a given pattern or not without using any regular expressions. We can solve this problem with the help of Backtracking. \n\n### Additional information\n\n_No response_",
"number": 9844,
"title": "Match a pattern and String using backtracking"
}
] |
cffdf99c55dcda89a5ce0fb2bf3cb685d168d136
|
{
"head_commit": "5442a69bae2dc9865036aa077944f5b3698c6ef4",
"head_commit_message": "fix: issue #9844",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/backtracking/match_word_pattern.py b/backtracking/match_word_pattern.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..f0399ae55118\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/backtracking/match_word_pattern.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@\n+def matchWordPattern(pattern :str, input_string: str) -> bool:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Determine if a given pattern matches a string using backtracking.\n+\n+ pattern: The pattern to match.\n+ input_string: The string to match against the pattern.\n+ return: True if the pattern matches the string, False otherwise.\n+\n+ >>> matchWordPattern(\"aba\", \"GraphTreesGraph\")\n+ True\n+\n+ >>> matchWordPattern(\"xyx\", \"PythonRubyPython\")\n+ True\n+\n+ >>> matchWordPattern(\"GG\", \"PythonJavaPython\")\n+ False\n+ \"\"\"\n+ def backtrack(pattern_index, str_index):\n+ if pattern_index == len(pattern) and str_index == len(input_string):\n+ return True\n+ if pattern_index == len(pattern) or str_index == len(input_string):\n+ return False\n+ \n+ char = pattern[pattern_index]\n+ \n+ if char in pattern_map:\n+ mapped_str = pattern_map[char]\n+ if input_string.startswith(mapped_str, str_index):\n+ return backtrack(pattern_index + 1, str_index + len(mapped_str))\n+ else:\n+ return False\n+ \n+ for end in range(str_index + 1, len(input_string) + 1):\n+ substr = input_string[str_index:end]\n+ if substr in str_map:\n+ continue\n+ \n+ pattern_map[char] = substr\n+ str_map[substr] = char\n+ \n+ if backtrack(pattern_index + 1, end):\n+ return True\n+ \n+ del pattern_map[char]\n+ del str_map[substr]\n+ return False\n+ \n+ pattern_map = {}\n+ str_map = {}\n+ return backtrack(0, 0)\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ import doctest\n+ doctest.testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@\n+def matchWordPattern(pattern :str, input_string: str) -> bool:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "backtracking/match_word_pattern.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nVariable and function names should follow the [`snake_case`](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Snake_case) naming convention. Please update the following name accordingly: `matchWordPattern`"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@\n+def matchWordPattern(pattern :str, input_string: str) -> bool:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Determine if a given pattern matches a string using backtracking.\n+\n+ pattern: The pattern to match.\n+ input_string: The string to match against the pattern.\n+ return: True if the pattern matches the string, False otherwise.\n+\n+ >>> matchWordPattern(\"aba\", \"GraphTreesGraph\")\n+ True\n+\n+ >>> matchWordPattern(\"xyx\", \"PythonRubyPython\")\n+ True\n+\n+ >>> matchWordPattern(\"GG\", \"PythonJavaPython\")\n+ False\n+ \"\"\"\n+ def backtrack(pattern_index, str_index):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 18,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "backtracking/match_word_pattern.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nAs there is no test file in this pull request nor any test function or class in the file `backtracking/match_word_pattern.py`, please provide doctest for the function `backtrack`\n\nPlease provide return type hint for the function: `backtrack`. **If the function does not return a value, please provide the type hint as:** `def function() -> None:`\n\nPlease provide type hint for the parameter: `pattern_index`\n\nPlease provide type hint for the parameter: `str_index`"
}
] |
8df08a3566bf2d0c58fa2f53b36676c4b11ce3ef
|
diff --git a/backtracking/match_word_pattern.py b/backtracking/match_word_pattern.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..bfa9b1354d51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/backtracking/match_word_pattern.py
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+def match_word_pattern(pattern: str, input_string: str) -> bool:
+ """
+ Determine if a given pattern matches a string using backtracking.
+
+ pattern: The pattern to match.
+ input_string: The string to match against the pattern.
+ return: True if the pattern matches the string, False otherwise.
+
+ >>> match_word_pattern("aba", "GraphTreesGraph")
+ True
+
+ >>> match_word_pattern("xyx", "PythonRubyPython")
+ True
+
+ >>> match_word_pattern("GG", "PythonJavaPython")
+ False
+ """
+
+ def backtrack(pattern_index: int, str_index: int) -> bool:
+ """
+ >>> backtrack(0, 0)
+ True
+
+ >>> backtrack(0, 1)
+ True
+
+ >>> backtrack(0, 4)
+ False
+ """
+ if pattern_index == len(pattern) and str_index == len(input_string):
+ return True
+ if pattern_index == len(pattern) or str_index == len(input_string):
+ return False
+ char = pattern[pattern_index]
+ if char in pattern_map:
+ mapped_str = pattern_map[char]
+ if input_string.startswith(mapped_str, str_index):
+ return backtrack(pattern_index + 1, str_index + len(mapped_str))
+ else:
+ return False
+ for end in range(str_index + 1, len(input_string) + 1):
+ substr = input_string[str_index:end]
+ if substr in str_map:
+ continue
+ pattern_map[char] = substr
+ str_map[substr] = char
+ if backtrack(pattern_index + 1, end):
+ return True
+ del pattern_map[char]
+ del str_map[substr]
+ return False
+
+ pattern_map: dict[str, str] = {}
+ str_map: dict[str, str] = {}
+ return backtrack(0, 0)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import doctest
+
+ doctest.testmod()
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-22255@98637f3
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 22,255
|
allow for economical specification of `parse_expr` transformations
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
fixes #21226
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* parsing
* strings 'all' and 'implicit' can be passed to select commonly used transformations; `T` can be sliced to give desired transformations for `parse_expr`
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-10-11T18:36:10Z
|
Make parse_expr with transformations easier to type
Right now to parse an expression with non-standard transformations like implicit multiplication, you have to do
```py
>>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import standard_transformations, implicit_multiplication_application
>>> transformations = (standard_transformations + (implicit_multiplication_application,))
>>> parse_expr("2x + 1", transformations=transformations)
2*x + 1
```
This is too much typing. We should add some kind of shortcut, like `transformations='all'`, to do this common case.
|
I would like to implement this in order to practice the workflow.
Now you can just do this:
x = parse_expr("2x + 1", transformations="all")
print(x)
@ebab, you can still improve the answer.
@NtemKenyor I do not think that it is enough to check if a string was passed or not. Hence I decided to make my own pull request which specifically checks for `all` and has added documentation.
I agree. I thought about it but I thought it would make people free as d
can pass any string and it still works...
Perhaps your idea is better🥺...
On Fri, Apr 2, 2021, 13:21 Erik Babuschkin ***@***.***> wrote:
> @NtemKenyor <https://github.com/NtemKenyor> I do not think that it is
> enough to check if a string was passed or not. Hence I decided to make my
> own pull request which specifically checks for all and has added
> documentation.
>
> —
> You are receiving this because you were mentioned.
> Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub
> <https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/21226#issuecomment-812507077>, or
> unsubscribe
> <https://github.com/notifications/unsubscribe-auth/AOKWIBNK5Q3Y4FVNSKSY45TTGWZFDANCNFSM42H2OU4Q>
> .
>
What about assigning an int to each transformation that corresponds to a power of 2 so `transformation=3` would be the 0th and 1th element in the logical list of transformations?
The `ibin` function could be used to get the elements corresponding to the int:
```python
>>> from sympy.utilities.iterables import ibin
>>> ibin(11)
[1, 0, 1, 1]
transformation = [transformation_list[i] for i,j in enumerate(_[::-1]) if j] # transformation_list is the canonical list of all transformations and would only grow in length, never have any element removed
```
I totally agree👍 and it's a great approach.
I did not think this way before now🤯🤯🤯
On Sat, Apr 3, 2021, 21:51 Christopher Smith ***@***.***>
wrote:
> What about assigning an int to each transformation that corresponds to a
> power of 2 so transformation=3 would be the 0th and 1th element in the
> logical list of transformations?
>
> —
> You are receiving this because you were mentioned.
> Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub
> <https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/21226#issuecomment-812923621>, or
> unsubscribe
> <https://github.com/notifications/unsubscribe-auth/AOKWIBPQPPH2SASK4JRLKPLTG55WVANCNFSM42H2OU4Q>
> .
>
> I did not think this way before now
Perhaps something like the following could be added to iterables and then used:
```python
def int_select(i, L):
"""select items from L based on which bits are 1 in the binary representation of i. e.g.
i = 1 selects item 0 from L, i = -1 selects all items, i = 0 selects none. Any other i must
not be larger than 2**n - 1 where n is the number of elements in L
Examples
========
>>> from sympy.utilities.iterables import ibin
>>> ibin(13)[::-1]
[1, 0, 1, 1]
>>> int_select(13, range(4))
[0, 2, 3]
"""
if i == 0:
return []
if i == -1:
return L[:]
if i < 0 or i >= 2**len(L):
raise ValueError
return [L[j] for j, b in enumerate(ibin(i)[::-1]) if b]
```
Does anyone have preferences for any or all of these:
```python
def parse_expr(..., xforms=None):
"""
...
xforms : int or iterable, options
When provided, selects the transformations to use by either selecting
them according to the position of 1s in the binary representation of
i or by index provided in the iterable, or as the integers given in a
comma/dash separated string.
i transform
-- --------------------
0 lambda_notation,
1 auto_symbol,
2 repeated_decimals,
3 auto_number,
4 rationalize,
5 factorial_notation,
6 implicit_multiplication,
7 implicit_application,
8 implicit_multiplication_application,
9 convert_equals_signs,
10 function_exponentiation,
11 convert_xor,
Examples
========
>>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import parse_expr
>>> parse_expr("1/2")
1/2
>>> type(_)
<class 'sympy.core.numbers.Half'>
>>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import standard_transformations,\\
... implicit_multiplication_application
>>> transformations = (standard_transformations +
... (implicit_multiplication_application,))
>>> parse_expr("2x", transformations=transformations)
2*x
>>> parse_expr("2x", xforms=31+2**8)
2*x
>>> parse_expr("2x", xforms=(1,2,3,4,5,8))
2*x
>>> parse_expr("2x", xforms='1-5, 8')
2*x
```
I would at use strings or named constants or something rather than integer codes.
> I would at use strings or named constants
What strings would be nice to type? First letters from each of the hyphenated words? `ima -> implicit_multiplication_application`, `st -> standard_transformations`, `st, ima -> standard_transformations + (implicit_multiplication_application,)`. If I ever used these I would nearly always have to look up the names to make sure I get the single or plural form right (e.g. `convert_equals_signs` has double plural) and I would prefer to just type their index number as in the `1-5, 8` case.
Indirect addressing by binary digit is not my preference anymore.
|
[
{
"body": "Right now to parse an expression with non-standard transformations like implicit multiplication, you have to do\r\n\r\n```py\r\n>>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import standard_transformations, implicit_multiplication_application\r\n>>> transformations = (standard_transformations + (implicit_multiplication_application,))\r\n>>> parse_expr(\"2x + 1\", transformations=transformations)\r\n2*x + 1\r\n```\r\n\r\nThis is too much typing. We should add some kind of shortcut, like `transformations='all'`, to do this common case. ",
"number": 21226,
"title": "Make parse_expr with transformations easier to type"
}
] |
7d104b61342ac4dbbb4e0cd21a3efc825861a4f3
|
{
"head_commit": "98637f39f1db977d12c995f22b45ed59047862b6",
"head_commit_message": "add implicit and all keywords for parsing",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/matrices/common.py b/sympy/matrices/common.py\nindex e6e6da3fe095..8ebf90bc96f4 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/common.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/common.py\n@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ def __getitem__(self, key):\n \"\"\"Implementations of __getitem__ should accept ints, in which\n case the matrix is indexed as a flat list, tuples (i,j) in which\n case the (i,j) entry is returned, slices, or mixed tuples (a,b)\n- where a and b are any combintion of slices and integers.\"\"\"\n+ where a and b are any combination of slices and integers.\"\"\"\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Subclasses must implement this.\")\n \n def __len__(self):\ndiff --git a/sympy/parsing/sympy_parser.py b/sympy/parsing/sympy_parser.py\nindex 9b4c721167a1..daee583bccf6 100644\n--- a/sympy/parsing/sympy_parser.py\n+++ b/sympy/parsing/sympy_parser.py\n@@ -914,7 +914,7 @@ def eval_expr(code, local_dict, global_dict):\n \n \n def parse_expr(s, local_dict=None, transformations=standard_transformations,\n- global_dict=None, evaluate=True):\n+ global_dict=None, evaluate=True, all=None, implicit=None):\n \"\"\"Converts the string ``s`` to a SymPy expression, in ``local_dict``\n \n Parameters\n@@ -975,6 +975,62 @@ def parse_expr(s, local_dict=None, transformations=standard_transformations,\n >>> b.args\n (x, 1)\n \n+ Note, however, that when these expressions are printed they will\n+ appear the same:\n+\n+ >>> assert str(a) == str(b)\n+\n+ As a convenience, transformations can be seen by printing ``transformations``:\n+\n+ >>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import transformations\n+\n+ >>> print(transformations)\n+ 0: lambda_notation\n+ 1: auto_symbol\n+ 2: repeated_decimals\n+ 3: auto_number\n+ 4: factorial_notation\n+ 5: implicit_multiplication_application\n+ 6: convert_xor\n+ 7: implicit_application\n+ 8: implicit_multiplication\n+ 9: convert_equals_signs\n+ 10: function_exponentiation\n+ 11: rationalize\n+\n+ The ``T`` object provides a way to select these transformations:\n+\n+ >>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import T\n+\n+ If you print it, you will see the same list as shown above.\n+\n+ >>> str(T) == str(transformations)\n+ True\n+\n+ Standard slicing will return a tuple of transformations:\n+\n+ >>> T[:5] == standard_transformations\n+ True\n+\n+ So ``T`` can be used to specify the parsing transformations:\n+\n+ >>> parse_expr(\"2x\", transformations=T[:5])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ SyntaxError: invalid syntax\n+ >>> parse_expr(\"2x\", transformations=T[:6])\n+ 2*x\n+ >>> parse_expr('.3', transformations=T[3, 11])\n+ 3/10\n+ >>> parse_expr('.3x', transformations=T[:])\n+ 3*x/10\n+\n+ As a further convenience, keywords `implicit` and `all`, when set\n+ to True, will select 0-5 and all the transformations, respectively.\n+\n+ >>> parse_expr('.3x', all=True)\n+ 3*x/10\n+\n See Also\n ========\n \n@@ -994,7 +1050,18 @@ def parse_expr(s, local_dict=None, transformations=standard_transformations,\n elif not isinstance(global_dict, dict):\n raise TypeError('expecting global_dict to be a dict')\n \n- transformations = transformations or ()\n+ if all:\n+ if not (implicit is None and\n+ transformations == standard_transformations):\n+ raise ValueError('give transformations or use single selector keyword')\n+ transformations = T[:]\n+ elif implicit:\n+ if not (all is None and\n+ transformations == standard_transformations):\n+ raise ValueError('give transformations or use single selector keyword')\n+ transformations = T[:6]\n+ elif not transformations:\n+ transformations = ()\n if transformations:\n if not iterable(transformations):\n raise TypeError(\n@@ -1130,3 +1197,51 @@ def visit_Call(self, node):\n if isinstance(node.func, ast.Name) and node.func.id in self.functions:\n new_node.keywords.append(ast.keyword(arg='evaluate', value=ast.NameConstant(value=False, ctx=ast.Load())))\n return new_node\n+\n+\n+_transformation = { # items can be added but never re-ordered\n+0: lambda_notation,\n+1: auto_symbol,\n+2: repeated_decimals,\n+3: auto_number,\n+4: factorial_notation,\n+5: implicit_multiplication_application,\n+6: convert_xor,\n+7: implicit_application,\n+8: implicit_multiplication,\n+9: convert_equals_signs,\n+10: function_exponentiation,\n+11: rationalize}\n+\n+transformations = '\\n'.join('%s: %s' % (i, func_name(f)) for i, f in _transformation.items())\n+\n+\n+class _T():\n+ \"\"\"class to retrieve transformations from a given slice\n+\n+ EXAMPLES\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import T, standard_transformations\n+ >>> assert T[:5] == standard_transformations\n+ \"\"\"\n+ def __init__(self):\n+ self.N = len(_transformation)\n+\n+ def __str__(self):\n+ return transformations\n+\n+ def __getitem__(self, t):\n+ if not type(t) is tuple:\n+ t = (t,)\n+ i = []\n+ for ti in t:\n+ if type(ti) is int:\n+ i.append(range(self.N)[ti])\n+ elif type(ti) is slice:\n+ i.extend(list(range(*ti.indices(self.N))))\n+ else:\n+ raise TypeError('unexpected slice arg')\n+ return tuple([_transformation[_] for _ in i])\n+\n+T = _T()\ndiff --git a/sympy/parsing/tests/test_sympy_parser.py b/sympy/parsing/tests/test_sympy_parser.py\nindex 3a0dea6eb394..b60e121818b9 100644\n--- a/sympy/parsing/tests/test_sympy_parser.py\n+++ b/sympy/parsing/tests/test_sympy_parser.py\n@@ -13,8 +13,10 @@\n from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import (\n parse_expr, standard_transformations, rationalize, TokenError,\n split_symbols, implicit_multiplication, convert_equals_signs,\n- convert_xor, function_exponentiation,\n- implicit_multiplication_application,\n+ convert_xor, function_exponentiation, lambda_notation, auto_symbol,\n+ repeated_decimals, implicit_multiplication_application,\n+ auto_number, factorial_notation, implicit_application,\n+ _transformation, T\n )\n \n \n@@ -293,3 +295,26 @@ def test_issue_19501():\n standard_transformations +\n (implicit_multiplication_application,)))\n assert eq.free_symbols == {x}\n+\n+\n+def test_parsing_definitions():\n+ from sympy.abc import x\n+ assert len(_transformation) == 12 # if this changes, extend below\n+ assert _transformation[0] == lambda_notation\n+ assert _transformation[1] == auto_symbol\n+ assert _transformation[2] == repeated_decimals\n+ assert _transformation[3] == auto_number\n+ assert _transformation[4] == factorial_notation\n+ assert _transformation[5] == implicit_multiplication_application\n+ assert _transformation[6] == convert_xor\n+ assert _transformation[7] == implicit_application\n+ assert _transformation[8] == implicit_multiplication\n+ assert _transformation[9] == convert_equals_signs\n+ assert _transformation[10] == function_exponentiation\n+ assert _transformation[11] == rationalize\n+ assert T[:5] == T[0,1,2,3,4] == standard_transformations\n+ t = _transformation\n+ assert T[-1, 0] == (t[len(t) - 1], t[0])\n+ assert T[:5, 8] == standard_transformations + (t[8],)\n+ assert parse_expr('0.3x^2', all=True) == 3*x**2/10\n+ assert parse_expr('sin 3x', implicit=True) == sin(3*x)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -975,6 +975,62 @@ def parse_expr(s, local_dict=None, transformations=standard_transformations,\n >>> b.args\n (x, 1)\n \n+ Note, however, that when these expressions are printed they will\n+ appear the same:\n+\n+ >>> assert str(a) == str(b)\n+\n+ As a convenience, transformations can be seen by printing ``transformations``:\n+\n+ >>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import transformations\n+\n+ >>> print(transformations)\n+ 0: lambda_notation\n+ 1: auto_symbol\n+ 2: repeated_decimals\n+ 3: auto_number\n+ 4: factorial_notation\n+ 5: implicit_multiplication_application\n+ 6: convert_xor\n+ 7: implicit_application\n+ 8: implicit_multiplication\n+ 9: convert_equals_signs\n+ 10: function_exponentiation\n+ 11: rationalize\n+\n+ The ``T`` object provides a way to select these transformations:\n+\n+ >>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import T\n+\n+ If you print it, you will see the same list as shown above.\n+\n+ >>> str(T) == str(transformations)\n+ True\n+\n+ Standard slicing will return a tuple of transformations:\n+\n+ >>> T[:5] == standard_transformations\n+ True\n+\n+ So ``T`` can be used to specify the parsing transformations:\n+\n+ >>> parse_expr(\"2x\", transformations=T[:5])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ SyntaxError: invalid syntax\n+ >>> parse_expr(\"2x\", transformations=T[:6])\n+ 2*x\n+ >>> parse_expr('.3', transformations=T[3, 11])\n+ 3/10\n+ >>> parse_expr('.3x', transformations=T[:])\n+ 3*x/10\n+\n+ As a further convenience, keywords `implicit` and `all`, when set\n+ to True, will select 0-5 and all the transformations, respectively.\n+\n+ >>> parse_expr('.3x', all=True)\n+ 3*x/10",
"line": 1033,
"original_line": 1032,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/parsing/sympy_parser.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhat about `parse_expr(..., transformations='all')`?"
}
] |
1ddc3ba747869c3e52a6511dc901885403fea54a
|
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/common.py b/sympy/matrices/common.py
index e6e6da3fe095..8ebf90bc96f4 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/common.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/common.py
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ def __getitem__(self, key):
"""Implementations of __getitem__ should accept ints, in which
case the matrix is indexed as a flat list, tuples (i,j) in which
case the (i,j) entry is returned, slices, or mixed tuples (a,b)
- where a and b are any combintion of slices and integers."""
+ where a and b are any combination of slices and integers."""
raise NotImplementedError("Subclasses must implement this.")
def __len__(self):
diff --git a/sympy/parsing/sympy_parser.py b/sympy/parsing/sympy_parser.py
index 9b4c721167a1..deceb9cc42b9 100644
--- a/sympy/parsing/sympy_parser.py
+++ b/sympy/parsing/sympy_parser.py
@@ -931,12 +931,13 @@ def parse_expr(s, local_dict=None, transformations=standard_transformations,
with ``from sympy import *``; provide this parameter to override
this behavior (for instance, to parse ``"Q & S"``).
- transformations : tuple, optional
+ transformations : tuple or str, optional
A tuple of transformation functions used to modify the tokens of the
parsed expression before evaluation. The default transformations
convert numeric literals into their SymPy equivalents, convert
undefined variables into SymPy symbols, and allow the use of standard
- mathematical factorial notation (e.g. ``x!``).
+ mathematical factorial notation (e.g. ``x!``). Selection via
+ string is available (see below).
evaluate : bool, optional
When False, the order of the arguments will remain as they were in the
@@ -975,6 +976,62 @@ def parse_expr(s, local_dict=None, transformations=standard_transformations,
>>> b.args
(x, 1)
+ Note, however, that when these expressions are printed they will
+ appear the same:
+
+ >>> assert str(a) == str(b)
+
+ As a convenience, transformations can be seen by printing ``transformations``:
+
+ >>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import transformations
+
+ >>> print(transformations)
+ 0: lambda_notation
+ 1: auto_symbol
+ 2: repeated_decimals
+ 3: auto_number
+ 4: factorial_notation
+ 5: implicit_multiplication_application
+ 6: convert_xor
+ 7: implicit_application
+ 8: implicit_multiplication
+ 9: convert_equals_signs
+ 10: function_exponentiation
+ 11: rationalize
+
+ The ``T`` object provides a way to select these transformations:
+
+ >>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import T
+
+ If you print it, you will see the same list as shown above.
+
+ >>> str(T) == str(transformations)
+ True
+
+ Standard slicing will return a tuple of transformations:
+
+ >>> T[:5] == standard_transformations
+ True
+
+ So ``T`` can be used to specify the parsing transformations:
+
+ >>> parse_expr("2x", transformations=T[:5])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ SyntaxError: invalid syntax
+ >>> parse_expr("2x", transformations=T[:6])
+ 2*x
+ >>> parse_expr('.3', transformations=T[3, 11])
+ 3/10
+ >>> parse_expr('.3x', transformations=T[:])
+ 3*x/10
+
+ As a further convenience, strings 'implicit' and 'all' can be used
+ to select 0-5 and all the transformations, respectively.
+
+ >>> parse_expr('.3x', transformations='all')
+ 3*x/10
+
See Also
========
@@ -995,6 +1052,13 @@ def parse_expr(s, local_dict=None, transformations=standard_transformations,
raise TypeError('expecting global_dict to be a dict')
transformations = transformations or ()
+ if type(transformations) is str:
+ if transformations == 'all':
+ transformations = T[:]
+ elif transformations == 'implicit':
+ transformations = T[:6]
+ else:
+ raise ValueError('unknown transformation group name')
if transformations:
if not iterable(transformations):
raise TypeError(
@@ -1130,3 +1194,51 @@ def visit_Call(self, node):
if isinstance(node.func, ast.Name) and node.func.id in self.functions:
new_node.keywords.append(ast.keyword(arg='evaluate', value=ast.NameConstant(value=False, ctx=ast.Load())))
return new_node
+
+
+_transformation = { # items can be added but never re-ordered
+0: lambda_notation,
+1: auto_symbol,
+2: repeated_decimals,
+3: auto_number,
+4: factorial_notation,
+5: implicit_multiplication_application,
+6: convert_xor,
+7: implicit_application,
+8: implicit_multiplication,
+9: convert_equals_signs,
+10: function_exponentiation,
+11: rationalize}
+
+transformations = '\n'.join('%s: %s' % (i, func_name(f)) for i, f in _transformation.items())
+
+
+class _T():
+ """class to retrieve transformations from a given slice
+
+ EXAMPLES
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import T, standard_transformations
+ >>> assert T[:5] == standard_transformations
+ """
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.N = len(_transformation)
+
+ def __str__(self):
+ return transformations
+
+ def __getitem__(self, t):
+ if not type(t) is tuple:
+ t = (t,)
+ i = []
+ for ti in t:
+ if type(ti) is int:
+ i.append(range(self.N)[ti])
+ elif type(ti) is slice:
+ i.extend(list(range(*ti.indices(self.N))))
+ else:
+ raise TypeError('unexpected slice arg')
+ return tuple([_transformation[_] for _ in i])
+
+T = _T()
diff --git a/sympy/parsing/tests/test_sympy_parser.py b/sympy/parsing/tests/test_sympy_parser.py
index 3a0dea6eb394..dc9910ff3e30 100644
--- a/sympy/parsing/tests/test_sympy_parser.py
+++ b/sympy/parsing/tests/test_sympy_parser.py
@@ -13,8 +13,10 @@
from sympy.parsing.sympy_parser import (
parse_expr, standard_transformations, rationalize, TokenError,
split_symbols, implicit_multiplication, convert_equals_signs,
- convert_xor, function_exponentiation,
- implicit_multiplication_application,
+ convert_xor, function_exponentiation, lambda_notation, auto_symbol,
+ repeated_decimals, implicit_multiplication_application,
+ auto_number, factorial_notation, implicit_application,
+ _transformation, T
)
@@ -293,3 +295,26 @@ def test_issue_19501():
standard_transformations +
(implicit_multiplication_application,)))
assert eq.free_symbols == {x}
+
+
+def test_parsing_definitions():
+ from sympy.abc import x
+ assert len(_transformation) == 12 # if this changes, extend below
+ assert _transformation[0] == lambda_notation
+ assert _transformation[1] == auto_symbol
+ assert _transformation[2] == repeated_decimals
+ assert _transformation[3] == auto_number
+ assert _transformation[4] == factorial_notation
+ assert _transformation[5] == implicit_multiplication_application
+ assert _transformation[6] == convert_xor
+ assert _transformation[7] == implicit_application
+ assert _transformation[8] == implicit_multiplication
+ assert _transformation[9] == convert_equals_signs
+ assert _transformation[10] == function_exponentiation
+ assert _transformation[11] == rationalize
+ assert T[:5] == T[0,1,2,3,4] == standard_transformations
+ t = _transformation
+ assert T[-1, 0] == (t[len(t) - 1], t[0])
+ assert T[:5, 8] == standard_transformations + (t[8],)
+ assert parse_expr('0.3x^2', transformations='all') == 3*x**2/10
+ assert parse_expr('sin 3x', transformations='implicit') == sin(3*x)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-3937@6449364
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 3,937
|
Fallback for `print_color` if shell is not yet initialized
|
Added a fallback for `xonsh.tools.print_color` (and `xonsh.tools.format_color`) if shell is not yet initialized, thus enabling their use in `.xonshrc`.
Fixes #3840 .
|
2020-10-29T12:21:28Z
|
print_color raises exception from RC file
Hi! Xonsh is super incredible! Thanks!
I've found that `print_color` not working when it used in rc-file:
```bash
# bash
cd /tmp
echo 'from xonsh.tools import print_color' > rc
echo 'print_color("{RED}Hello!")' >> rc
XONSH_DEBUG=1 XONSH_SHOW_TRACEBACK=1 xonsh --rc rc
```
Result:
```
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/opt/miniconda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/xonsh/environ.py", line 2245, in xonsh_script_run_control
run_script_with_cache(filename, execer, ctx)
File "/opt/miniconda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/xonsh/codecache.py", line 162, in run_script_with_cache
run_compiled_code(ccode, glb, loc, mode)
File "/opt/miniconda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/xonsh/codecache.py", line 67, in run_compiled_code
func(code, glb, loc)
File "rc", line 3, in <module>
print_color('{RED}123')
File "/opt/miniconda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/xonsh/tools.py", line 1783, in print_color
builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.print_color(string, **kwargs)
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'shell'
```
For example `aliases.py` contain `print_color` and could fail from rc.
It's on current master - `580b675f` (Oct 1 02:48:13 2020).
Please fix. Thanks!
## For community
⬇️ **Please click the 👍 reaction instead of leaving a `+1` or 👍 comment**
|
That would be weird if it is related to THREAD_SUBPROCS. In general, though I would not expect that `print_color()` to work until xonsh is fully started up. There may be some changes that could be made to use the ASCII printing prior to the shell being fully available as sort of a hack to get this working when xonshrc is run.
|
[
{
"body": "Hi! Xonsh is super incredible! Thanks!\r\n\r\nI've found that `print_color` not working when it used in rc-file:\r\n```bash\r\n# bash\r\ncd /tmp\r\necho 'from xonsh.tools import print_color' > rc\r\necho 'print_color(\"{RED}Hello!\")' >> rc\r\nXONSH_DEBUG=1 XONSH_SHOW_TRACEBACK=1 xonsh --rc rc\r\n```\r\nResult:\r\n```\r\nTraceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"/opt/miniconda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/xonsh/environ.py\", line 2245, in xonsh_script_run_control\r\n run_script_with_cache(filename, execer, ctx)\r\n File \"/opt/miniconda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/xonsh/codecache.py\", line 162, in run_script_with_cache\r\n run_compiled_code(ccode, glb, loc, mode)\r\n File \"/opt/miniconda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/xonsh/codecache.py\", line 67, in run_compiled_code\r\n func(code, glb, loc)\r\n File \"rc\", line 3, in <module>\r\n print_color('{RED}123')\r\n File \"/opt/miniconda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/xonsh/tools.py\", line 1783, in print_color\r\n builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.print_color(string, **kwargs)\r\nAttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'shell'\r\n```\r\n\r\nFor example `aliases.py` contain `print_color` and could fail from rc.\r\n\r\nIt's on current master - `580b675f` (Oct 1 02:48:13 2020).\r\n\r\nPlease fix. Thanks!\r\n\r\n## For community\r\n⬇️ **Please click the 👍 reaction instead of leaving a `+1` or 👍 comment**\r\n",
"number": 3840,
"title": "print_color raises exception from RC file"
}
] |
4da940c0365b3686b4620490cbf26d9eea68c6ac
|
{
"head_commit": "6449364fbf5905e7ec70a60a8e4ee4df72aab55c",
"head_commit_message": "no, the news file is not md, it's rst",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/news/print_color_3840.rst b/news/print_color_3840.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..d6465f1b47\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/print_color_3840.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Changed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Deprecated:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Removed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Added ANSI fallback for ``xonsh.tools.print_color`` if shell is not yet initialized. Fixes #3840.\n+\n+**Security:**\n+\n+* <news item>\ndiff --git a/xonsh/tools.py b/xonsh/tools.py\nindex bc18a34507..6efebcedca 100644\n--- a/xonsh/tools.py\n+++ b/xonsh/tools.py\n@@ -1837,7 +1837,14 @@ def format_color(string, **kwargs):\n shell instances method of the same name. The results of this function should\n be directly usable by print_color().\n \"\"\"\n- return builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.format_color(string, **kwargs)\n+ try:\n+ return builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.format_color(string, **kwargs)\n+ except AttributeError:\n+ # fallback for ANSI if shell is not yet initialized\n+ from xonsh.ansi_colors import ansi_partial_color_format\n+\n+ style = builtins.__xonsh__.env.get(\"XONSH_COLOR_STYLE\")\n+ return ansi_partial_color_format(string, style=style)\n \n \n def print_color(string, **kwargs):\n@@ -1845,7 +1852,11 @@ def print_color(string, **kwargs):\n method of the same name. Colors will be formatted if they have not already\n been.\n \"\"\"\n- builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.print_color(string, **kwargs)\n+ try:\n+ builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.print_color(string, **kwargs)\n+ except AttributeError:\n+ # fallback for ANSI if shell is not yet initialized\n+ print(format_color(string, **kwargs))\n \n \n def color_style_names():\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1837,15 +1837,26 @@ def format_color(string, **kwargs):\n shell instances method of the same name. The results of this function should\n be directly usable by print_color().\n \"\"\"\n- return builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.format_color(string, **kwargs)\n+ try:\n+ return builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.format_color(string, **kwargs)\n+ except AttributeError:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1842,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/tools.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nCan you use `if hasattr()' instead please? I believe it is faster than try-except\n\n@author:\nI was curious about this one, so performed a quick test:\r\n```python\r\nclass A():\r\n gotit = 1\r\n\r\na = A()\r\n\r\ndef t_try_happy():\r\n try:\r\n a.gotit\r\n except AttributeError:\r\n pass\r\n\r\ndef t_try_sad():\r\n try:\r\n a.notthere\r\n except AttributeError:\r\n pass\r\n\r\ndef t_hasattr_happy():\r\n if hasattr(a, \"gotit\"):\r\n a.gotit\r\n\r\ndef t_hasattr_sad():\r\n if hasattr(a, \"notthere\"):\r\n a.notthere\r\n```\r\n\r\nResults (cpython 3.8.5):\r\n```\r\n> timeit.timeit(t_try_happy, number=10000)\r\n0.0008203879988286644\r\n> timeit.timeit(t_try_sad, number=10000)\r\n0.0037201289997028653\r\n> timeit.timeit(t_hasattr_happy, number=10000)\r\n0.0011529879993759096\r\n> timeit.timeit(t_hasattr_sad, number=10000)\r\n0.000985652000963455\r\n```\r\n\r\nSo it seems that for the happy path, `try` is a little bit quicker. For the _unhappy_ it's much much slower indeed, but that should really be an edge case (using `print_color` without an initialized shell).\r\n\r\nOf course, I can replace `try` with `hasattr` if you want me to, but I needed to check :)\n\n@user1:\nFirst off, thanks for the timing work! My concern here is that we will be meaning to hit the try-sad case (the slow case) in xonshrc (which is during startup). I am really trying to figure out how to keep startup times as low as possible, with the goal of getting to 100 ms. Does this make sense?\n\n@author:\nSure, now it's more clear, will do the change."
}
] |
2dc5f87bc6912b06f9d1c19a5f38c9e56e4bbf87
|
diff --git a/news/print_color_3840.rst b/news/print_color_3840.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d6465f1b47
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/print_color_3840.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+**Added:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Changed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Deprecated:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Removed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* Added ANSI fallback for ``xonsh.tools.print_color`` if shell is not yet initialized. Fixes #3840.
+
+**Security:**
+
+* <news item>
diff --git a/xonsh/tools.py b/xonsh/tools.py
index bc18a34507..989f94b65a 100644
--- a/xonsh/tools.py
+++ b/xonsh/tools.py
@@ -1837,7 +1837,14 @@ def format_color(string, **kwargs):
shell instances method of the same name. The results of this function should
be directly usable by print_color().
"""
- return builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.format_color(string, **kwargs)
+ if hasattr(builtins.__xonsh__.shell, "shell"):
+ return builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.format_color(string, **kwargs)
+ else:
+ # fallback for ANSI if shell is not yet initialized
+ from xonsh.ansi_colors import ansi_partial_color_format
+
+ style = builtins.__xonsh__.env.get("XONSH_COLOR_STYLE")
+ return ansi_partial_color_format(string, style=style)
def print_color(string, **kwargs):
@@ -1845,7 +1852,11 @@ def print_color(string, **kwargs):
method of the same name. Colors will be formatted if they have not already
been.
"""
- builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.print_color(string, **kwargs)
+ if hasattr(builtins.__xonsh__.shell, "shell"):
+ builtins.__xonsh__.shell.shell.print_color(string, **kwargs)
+ else:
+ # fallback for ANSI if shell is not yet initialized
+ print(format_color(string, **kwargs))
def color_style_names():
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-9625@5923c92
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 9,625
|
serialize deserialize binary tree
|
### Describe your change:
Fixes #9611
* [x] Add an algorithm?
* [ ] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [ ] Documentation change?
### Checklist:
* [x] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [x] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [x] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [x] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [x] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [x] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [x] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [ ] All new algorithms include at least one URL that points to Wikipedia or another similar explanation.
* [ ] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the description above includes the issue number(s) with a [closing keyword](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue): "Fixes #ISSUE-NUMBER".
|
2023-10-03T17:35:07Z
|
Serialize and Deserialize
### Feature description
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
|
@Arunsiva003 I would like to work on this enhancement. Can you assign this to me?
> @Arunsiva003 I would like to work on this enhancement. Can you assign this to me?
You don't have to wait for any approval. make a pull request and proceed!
i started working on this
|
[
{
"body": "### Feature description\n\nDesign an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.",
"number": 9611,
"title": "Serialize and Deserialize"
}
] |
0a84b8f842c4c72f400d96313d992b608d621d07
|
{
"head_commit": "5923c9290dc765458cd698a20ca72e8e3c80645d",
"head_commit_message": "format files",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/data_structures/binary_tree/serialize_deserialize_binary_tree.py b/data_structures/binary_tree/serialize_deserialize_binary_tree.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..e092ecf2c0d0\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/data_structures/binary_tree/serialize_deserialize_binary_tree.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@\n+class TreeNode:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ A binary tree node has a value, left child, and right child.\n+\n+ Props:\n+ val(int): The value of the node.\n+ left: The left child of the node.\n+ right: The right child of the node.\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left=None, right=None) -> None:\n+ if not isinstance(val, int):\n+ raise TypeError(\"Value must be an integer.\")\n+ self.val = val\n+ self.left = left\n+ self.right = right\n+\n+\n+# Helper functions\n+def are_trees_identical(root1: TreeNode, root2: TreeNode) -> bool:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Check if two binary trees are identical.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ root1 (TreeNode): Tree 1\n+ root2 (TreeNode): Tree 2\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ bool: True if the trees are identical, False otherwise.\n+\n+ >>> root1 = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root1.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root1.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> root2 = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root2.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root2.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> are_trees_identical(root1, root2)\n+ True\n+ >>> root1 = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root1.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root1.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> root2 = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root2.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root2.right = TreeNode(4)\n+ >>> are_trees_identical(root1, root2)\n+ False\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not root1 and not root2:\n+ return True\n+ if not root1 or not root2:\n+ return False\n+\n+ return (\n+ root1.val == root2.val\n+ and are_trees_identical(root1.left, root2.left)\n+ and are_trees_identical(root1.right, root2.right)\n+ )\n+\n+\n+# Main functions\n+def serialize(root: TreeNode) -> str:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Serialize a binary tree to a string using preorder traversal.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ root(TreeNode): The root of the binary tree.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ A string representation of the binary tree.\n+\n+ >>> root = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> root.right.left = TreeNode(4)\n+ >>> root.right.right = TreeNode(5)\n+ >>> serialize(root)\n+ '1,2,null,null,3,4,null,null,5,null,null'\n+ >>> root = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> serialize(root)\n+ '1,null,null'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Use \"null\" to represent empty nodes in the serialization\n+ if not root:\n+ return \"null\"\n+\n+ return str(root.val) + \",\" + serialize(root.left) + \",\" + serialize(root.right)\n+\n+\n+def deserialize(data: str) -> TreeNode:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Deserialize a string to a binary tree.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ data(str): The serialized string.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The root of the binary tree.\n+\n+ >>> root = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> root.right.left = TreeNode(4)\n+ >>> root.right.right = TreeNode(5)\n+ >>> serialzed_data = serialize(root)\n+ >>> deserialized = deserialize(serialzed_data)\n+ >>> are_trees_identical(root, deserialized)\n+ True\n+ >>> root = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> serialzed_data = serialize(root)\n+ >>> dummy_data = \"1,2,null,null,3,4,null,null,5,null,null\"\n+ >>> deserialized = deserialize(dummy_data)\n+ >>> are_trees_identical(root, deserialized)\n+ False\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Split the serialized string by comma to get node values\n+ nodes = data.split(\",\")\n+\n+ def build_tree():\n+ # Get the next value from the list\n+ val = nodes.pop(0)\n+\n+ if val == \"null\":\n+ return None\n+\n+ node = TreeNode(int(val))\n+ node.left = build_tree() # Recursively build left subtree\n+ node.right = build_tree() # Recursively build right subtree\n+\n+ return node\n+\n+ return build_tree()\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ import doctest\n+\n+ doctest.testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@\n+class TreeNode:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ A binary tree node has a value, left child, and right child.\n+\n+ Props:\n+ val(int): The value of the node.\n+ left: The left child of the node.\n+ right: The right child of the node.\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left=None, right=None) -> None:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 11,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "data_structures/binary_tree/serialize_deserialize_binary_tree.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nPlease provide type hint for the parameter: `left`\n\nPlease provide type hint for the parameter: `right`"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@\n+class TreeNode:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ A binary tree node has a value, left child, and right child.\n+\n+ Props:\n+ val(int): The value of the node.\n+ left: The left child of the node.\n+ right: The right child of the node.\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left=None, right=None) -> None:\n+ if not isinstance(val, int):\n+ raise TypeError(\"Value must be an integer.\")\n+ self.val = val\n+ self.left = left\n+ self.right = right\n+\n+\n+# Helper functions\n+def are_trees_identical(root1: TreeNode, root2: TreeNode) -> bool:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Check if two binary trees are identical.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ root1 (TreeNode): Tree 1\n+ root2 (TreeNode): Tree 2\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ bool: True if the trees are identical, False otherwise.\n+\n+ >>> root1 = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root1.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root1.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> root2 = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root2.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root2.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> are_trees_identical(root1, root2)\n+ True\n+ >>> root1 = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root1.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root1.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> root2 = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root2.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root2.right = TreeNode(4)\n+ >>> are_trees_identical(root1, root2)\n+ False\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not root1 and not root2:\n+ return True\n+ if not root1 or not root2:\n+ return False\n+\n+ return (\n+ root1.val == root2.val\n+ and are_trees_identical(root1.left, root2.left)\n+ and are_trees_identical(root1.right, root2.right)\n+ )\n+\n+\n+# Main functions\n+def serialize(root: TreeNode) -> str:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Serialize a binary tree to a string using preorder traversal.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ root(TreeNode): The root of the binary tree.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ A string representation of the binary tree.\n+\n+ >>> root = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> root.right.left = TreeNode(4)\n+ >>> root.right.right = TreeNode(5)\n+ >>> serialize(root)\n+ '1,2,null,null,3,4,null,null,5,null,null'\n+ >>> root = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> serialize(root)\n+ '1,null,null'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Use \"null\" to represent empty nodes in the serialization\n+ if not root:\n+ return \"null\"\n+\n+ return str(root.val) + \",\" + serialize(root.left) + \",\" + serialize(root.right)\n+\n+\n+def deserialize(data: str) -> TreeNode:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Deserialize a string to a binary tree.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ data(str): The serialized string.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The root of the binary tree.\n+\n+ >>> root = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> root.left = TreeNode(2)\n+ >>> root.right = TreeNode(3)\n+ >>> root.right.left = TreeNode(4)\n+ >>> root.right.right = TreeNode(5)\n+ >>> serialzed_data = serialize(root)\n+ >>> deserialized = deserialize(serialzed_data)\n+ >>> are_trees_identical(root, deserialized)\n+ True\n+ >>> root = TreeNode(1)\n+ >>> serialzed_data = serialize(root)\n+ >>> dummy_data = \"1,2,null,null,3,4,null,null,5,null,null\"\n+ >>> deserialized = deserialize(dummy_data)\n+ >>> are_trees_identical(root, deserialized)\n+ False\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Split the serialized string by comma to get node values\n+ nodes = data.split(\",\")\n+\n+ def build_tree():",
"line": null,
"original_line": 121,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "data_structures/binary_tree/serialize_deserialize_binary_tree.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nAs there is no test file in this pull request nor any test function or class in the file `data_structures/binary_tree/serialize_deserialize_binary_tree.py`, please provide doctest for the function `build_tree`\n\nPlease provide return type hint for the function: `build_tree`. **If the function does not return a value, please provide the type hint as:** `def function() -> None:`"
}
] |
7cc2602e8bfc0503c92a9bb3106204e95c4a5d3a
|
diff --git a/data_structures/binary_tree/serialize_deserialize_binary_tree.py b/data_structures/binary_tree/serialize_deserialize_binary_tree.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..7d3e0c61f96d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/data_structures/binary_tree/serialize_deserialize_binary_tree.py
@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from collections.abc import Iterator
+from dataclasses import dataclass
+
+
+@dataclass
+class TreeNode:
+ """
+ A binary tree node has a value, left child, and right child.
+
+ Props:
+ value: The value of the node.
+ left: The left child of the node.
+ right: The right child of the node.
+ """
+
+ value: int = 0
+ left: TreeNode | None = None
+ right: TreeNode | None = None
+
+ def __post_init__(self):
+ if not isinstance(self.value, int):
+ raise TypeError("Value must be an integer.")
+
+ def __iter__(self) -> Iterator[TreeNode]:
+ """
+ Iterate through the tree in preorder.
+
+ Returns:
+ An iterator of the tree nodes.
+
+ >>> list(TreeNode(1))
+ [1,null,null]
+ >>> tuple(TreeNode(1, TreeNode(2), TreeNode(3)))
+ (1,2,null,null,3,null,null, 2,null,null, 3,null,null)
+ """
+ yield self
+ yield from self.left or ()
+ yield from self.right or ()
+
+ def __len__(self) -> int:
+ """
+ Count the number of nodes in the tree.
+
+ Returns:
+ The number of nodes in the tree.
+
+ >>> len(TreeNode(1))
+ 1
+ >>> len(TreeNode(1, TreeNode(2), TreeNode(3)))
+ 3
+ """
+ return sum(1 for _ in self)
+
+ def __repr__(self) -> str:
+ """
+ Represent the tree as a string.
+
+ Returns:
+ A string representation of the tree.
+
+ >>> repr(TreeNode(1))
+ '1,null,null'
+ >>> repr(TreeNode(1, TreeNode(2), TreeNode(3)))
+ '1,2,null,null,3,null,null'
+ >>> repr(TreeNode(1, TreeNode(2), TreeNode(3, TreeNode(4), TreeNode(5))))
+ '1,2,null,null,3,4,null,null,5,null,null'
+ """
+ return f"{self.value},{self.left!r},{self.right!r}".replace("None", "null")
+
+ @classmethod
+ def five_tree(cls) -> TreeNode:
+ """
+ >>> repr(TreeNode.five_tree())
+ '1,2,null,null,3,4,null,null,5,null,null'
+ """
+ root = TreeNode(1)
+ root.left = TreeNode(2)
+ root.right = TreeNode(3)
+ root.right.left = TreeNode(4)
+ root.right.right = TreeNode(5)
+ return root
+
+
+def deserialize(data: str) -> TreeNode | None:
+ """
+ Deserialize a string to a binary tree.
+
+ Args:
+ data(str): The serialized string.
+
+ Returns:
+ The root of the binary tree.
+
+ >>> root = TreeNode.five_tree()
+ >>> serialzed_data = repr(root)
+ >>> deserialized = deserialize(serialzed_data)
+ >>> root == deserialized
+ True
+ >>> root is deserialized # two separate trees
+ False
+ >>> root.right.right.value = 6
+ >>> root == deserialized
+ False
+ >>> serialzed_data = repr(root)
+ >>> deserialized = deserialize(serialzed_data)
+ >>> root == deserialized
+ True
+ >>> deserialize("")
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Data cannot be empty.
+ """
+
+ if not data:
+ raise ValueError("Data cannot be empty.")
+
+ # Split the serialized string by a comma to get node values
+ nodes = data.split(",")
+
+ def build_tree() -> TreeNode | None:
+ # Get the next value from the list
+ value = nodes.pop(0)
+
+ if value == "null":
+ return None
+
+ node = TreeNode(int(value))
+ node.left = build_tree() # Recursively build left subtree
+ node.right = build_tree() # Recursively build right subtree
+ return node
+
+ return build_tree()
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import doctest
+
+ doctest.testmod()
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-22217@be7c4a8
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 22,217
|
Problem with solving simple separable ODE fixed
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Fixes #22155
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-10-04T10:18:56Z
|
Problem with solving simple separable ODE
I want to solve by SymPy simple separable equation y'=e^(y-x), but SymPy can't solve it!
```
from sympy import *
x = symbols("x")
y = Function("y")
eq = Eq(Derivative(y(x), x), exp(y(x)-x))
dsolve(eq, y(x))
```
But it solves successfuly similar equation y'=e^(y+x).
Follоwing code
```
eq = Eq(Derivative(y(x), x), exp(y(x)-x))
print(classify_ode(eq,y(x)))
```
returns
`('factorable', 'separable', '1st_power_series', 'lie_group', 'separable_Integral')
`
The method for 'factorable' seems broken. Explicitly using the second method,
`dsolve(eq, y(x), hint='separable')
`
quickly returns the correct solution.
For the second equation y'=e^(y+x), the list of methods is
`('separable', '1st_power_series', 'lie_group', 'separable_Integral')
`
so in this case the problematic method 'factorable' is not used.
Experiments have shown that those equations cannot be solved if their exponents have a minus sign.
|
The problem is that the factorable hint calls `dsolve` recursively but for this example ODE the recursive call will also end up being handled by factorable again leading to infinite recursion. It looks like the last line here is intended to prevent the infinite recursion:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/19b187982f90c868b987a8bbea085874647c98aa/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py#L897-L902
That check fails though because the expressions being compared are unequal:
```
903 -> return fraction(factor(self.eqs[0]))[0]-eq!=0
904 return True
905 for i in factors:
906 if i.has(f(x)):
907 self.eqs.append(i)
908 return len(self.eqs)>0 and len(factors)>1
(Pdb) p self.eqs[0]
-exp(-x + y(x)) + Derivative(y(x), x)
(Pdb) p fraction(factor(self.eqs[0]))[0]
Derivative(y(x), x) - exp(-x)*exp(y(x))
(Pdb) p eq
exp(x)*Derivative(y(x), x) - exp(y(x))
```
The ultimate fix is that factorable should not be a solver hint and should just be part of the preprocessing done by dsolve. Maybe for now that check could be improved. This diff fixes the example shown:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
index 7523b45..a3e5c42 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
@@ -892,14 +892,8 @@ def _matches(self):
if len(self.eqs)>0:
return True
roots = solve(eq, df)
- if len(roots)>0:
+ if len(roots)>1:
self.eqs = [(df - root) for root in roots]
- if len(self.eqs)==1:
- if order>1:
- return False
- if self.eqs[0].has(Float):
- return False
- return fraction(factor(self.eqs[0]))[0]-eq!=0
return True
for i in factors:
if i.has(f(x)):
```
That might potentialy cause problems in other cases though. I'm not sure I understand the logic of this code.
By the way [online version](https://live.sympy.org/) of SymPy (version 1.5.1) solves this kind of equations correctly!
I would like to help
> I would like to help
You could try applying the diff I showed as a PR to see if it breaks any of the tests.
> By the way [online version](https://live.sympy.org/) of SymPy (version 1.5.1) solves this kind of equations correctly!
Using `git bisect` shows that this was working until 1a26cdd3230b543775c77ba2493500166c0ff984 from #18623
CC @Mohitbalwani26
> CC @Mohitbalwani26
Looking into it. Thanks
@oscarbenjamin Sure
@mohajain are you trying this?
Also i think this diff will work :
```diff
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
@@ -875,13 +875,13 @@ class Factorable(SingleODESolver):
has_integral = False
def _matches(self):
- eq = self.ode_problem.eq
+ orig_eq = self.ode_problem.eq
f = self.ode_problem.func.func
x = self.ode_problem.sym
order =self.ode_problem.order
df = f(x).diff(x)
self.eqs = []
- eq = eq.collect(f(x), func = cancel)
+ eq = orig_eq.collect(f(x), func = cancel)
eq = fraction(factor(eq))[0]
factors = Mul.make_args(factor(eq))
roots = [fac.as_base_exp() for fac in factors if len(fac.args)!=0]
@@ -899,7 +899,7 @@ def _matches(self):
return False
if self.eqs[0].has(Float):
return False
- return fraction(factor(self.eqs[0]))[0]-eq!=0
+ return fraction(factor(self.eqs[0]))[0]-eq!=0 and simplify(orig_eq - fraction(factor(self.eqs[0]))[0])!=0
return True
for i in factors:
if i.has(f(x)):
```
Using simplify like that seems flakey. There needs to be a clear robust way of preventing infinite recursion here that does not depend on simplifying anything.
|
[
{
"body": "I want to solve by SymPy simple separable equation y'=e^(y-x), but SymPy can't solve it!\r\n```\r\nfrom sympy import *\r\nx = symbols(\"x\")\r\ny = Function(\"y\")\r\neq = Eq(Derivative(y(x), x), exp(y(x)-x))\r\ndsolve(eq, y(x))\r\n```\r\nBut it solves successfuly similar equation y'=e^(y+x).\r\n\r\nFollоwing code\r\n```\r\neq = Eq(Derivative(y(x), x), exp(y(x)-x))\r\nprint(classify_ode(eq,y(x)))\r\n```\r\nreturns\r\n\r\n`('factorable', 'separable', '1st_power_series', 'lie_group', 'separable_Integral')\r\n`\r\n\r\nThe method for 'factorable' seems broken. Explicitly using the second method,\r\n\r\n`dsolve(eq, y(x), hint='separable')\r\n`\r\n\r\nquickly returns the correct solution.\r\n\r\nFor the second equation y'=e^(y+x), the list of methods is\r\n\r\n`('separable', '1st_power_series', 'lie_group', 'separable_Integral')\r\n`\r\n\r\nso in this case the problematic method 'factorable' is not used. \r\n\r\nExperiments have shown that those equations cannot be solved if their exponents have a minus sign.\r\n",
"number": 22155,
"title": "Problem with solving simple separable ODE"
}
] |
570ad001d7f5a3c733c54635fec90edb8f778443
|
{
"head_commit": "be7c4a8f6c37154928b16bda34d31172ddd1eb31",
"head_commit_message": "test case added",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py\nindex 5bc8b7d65273..d9f55bf4acc0 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py\n@@ -931,7 +931,7 @@ class in it. Note that a hint may do this anyway if\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep_Integral',\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep_Integral')\n >>> classify_ode(f(x).diff(x, 2) + 3*f(x).diff(x) + 2*f(x) - 4)\n- ('nth_linear_constant_coeff_undetermined_coefficients',\n+ ('factorable', 'nth_linear_constant_coeff_undetermined_coefficients',\n 'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters',\n 'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters_Integral')\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py\nindex 7523b4536e86..1076c63ccc9b 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py\n@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@\n from sympy.core.exprtools import factor_terms\n from sympy.core.expr import Expr\n from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef, Derivative, diff, Function, expand, Subs, _mexpand\n-from sympy.core.numbers import Float, zoo\n+from sympy.core.numbers import zoo\n from sympy.core.relational import Equality, Eq\n from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol, Dummy, Wild\n from sympy.core.mul import Mul\n@@ -875,13 +875,12 @@ class Factorable(SingleODESolver):\n has_integral = False\n \n def _matches(self):\n- eq = self.ode_problem.eq\n+ eq_orig = self.ode_problem.eq\n f = self.ode_problem.func.func\n x = self.ode_problem.sym\n- order =self.ode_problem.order\n df = f(x).diff(x)\n self.eqs = []\n- eq = eq.collect(f(x), func = cancel)\n+ eq = eq_orig.collect(f(x), func = cancel)\n eq = fraction(factor(eq))[0]\n factors = Mul.make_args(factor(eq))\n roots = [fac.as_base_exp() for fac in factors if len(fac.args)!=0]\n@@ -894,13 +893,9 @@ def _matches(self):\n roots = solve(eq, df)\n if len(roots)>0:\n self.eqs = [(df - root) for root in roots]\n- if len(self.eqs)==1:\n- if order>1:\n- return False\n- if self.eqs[0].has(Float):\n- return False\n- return fraction(factor(self.eqs[0]))[0]-eq!=0\n- return True\n+ # Avoid infinite recursion\n+ matches = self.eqs != [eq_orig]\n+ return matches\n for i in factors:\n if i.has(f(x)):\n self.eqs.append(i)\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_ode.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_ode.py\nindex 1a92901bf8ca..a90dbf970e3c 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_ode.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_ode.py\n@@ -96,21 +96,21 @@ def test_dsolve_options():\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep_Integral', '1st_linear',\n '1st_linear_Integral', 'Bernoulli', 'Bernoulli_Integral',\n 'almost_linear', 'almost_linear_Integral', 'best', 'best_hint',\n- 'default', 'lie_group',\n+ 'default', 'factorable', 'lie_group',\n 'nth_linear_euler_eq_homogeneous', 'order',\n 'separable', 'separable_Integral']\n Integral_keys = ['1st_exact_Integral',\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep_Integral',\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep_Integral', '1st_linear_Integral',\n 'Bernoulli_Integral', 'almost_linear_Integral', 'best', 'best_hint', 'default',\n- 'nth_linear_euler_eq_homogeneous',\n+ 'factorable', 'nth_linear_euler_eq_homogeneous',\n 'order', 'separable_Integral']\n assert sorted(a.keys()) == keys\n assert a['order'] == ode_order(eq, f(x))\n assert a['best'] == Eq(f(x), C1/x)\n assert dsolve(eq, hint='best') == Eq(f(x), C1/x)\n- assert a['default'] == 'separable'\n- assert a['best_hint'] == 'separable'\n+ assert a['default'] == 'factorable'\n+ assert a['best_hint'] == 'factorable'\n assert not a['1st_exact'].has(Integral)\n assert not a['separable'].has(Integral)\n assert not a['1st_homogeneous_coeff_best'].has(Integral)\n@@ -126,8 +126,8 @@ def test_dsolve_options():\n assert b['order'] == ode_order(eq, f(x))\n assert b['best'] == Eq(f(x), C1/x)\n assert dsolve(eq, hint='best', simplify=False) == Eq(f(x), C1/x)\n- assert b['default'] == 'separable'\n- assert b['best_hint'] == '1st_linear'\n+ assert b['default'] == 'factorable'\n+ assert b['best_hint'] == 'factorable'\n assert a['separable'] != b['separable']\n assert a['1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep'] != \\\n b['1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep']\n@@ -231,7 +231,8 @@ def test_classify_ode():\n '1st_linear_Integral',\n 'Bernoulli_Integral',\n 'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters_Integral')\n- assert c == ('1st_linear',\n+ assert c == ('factorable',\n+ '1st_linear',\n 'Bernoulli',\n '1st_power_series',\n 'lie_group',\n@@ -243,7 +244,7 @@ def test_classify_ode():\n \n assert classify_ode(\n 2*x*f(x)*f(x).diff(x) + (1 + x)*f(x)**2 - exp(x), f(x)\n- ) == ('1st_exact', 'Bernoulli', 'almost_linear', 'lie_group',\n+ ) == ('factorable', '1st_exact', 'Bernoulli', 'almost_linear', 'lie_group',\n '1st_exact_Integral', 'Bernoulli_Integral', 'almost_linear_Integral')\n assert 'Riccati_special_minus2' in \\\n classify_ode(2*f(x).diff(x) + f(x)**2 - f(x)/x + 3*x**(-2), f(x))\n@@ -253,11 +254,11 @@ def test_classify_ode():\n k = Symbol('k')\n assert classify_ode(f(x).diff(x)/(k*f(x) + k*x*f(x)) + 2*f(x)/(k*f(x) +\n k*x*f(x)) + x*f(x).diff(x)/(k*f(x) + k*x*f(x)) + z, f(x)) == \\\n- ('separable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear', 'Bernoulli',\n+ ('factorable', 'separable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear', 'Bernoulli',\n '1st_power_series', 'lie_group', 'separable_Integral', '1st_exact_Integral',\n '1st_linear_Integral', 'Bernoulli_Integral')\n # preprocessing\n- ans = ('nth_algebraic', 'separable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear', 'Bernoulli',\n+ ans = ('factorable', 'nth_algebraic', 'separable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear', 'Bernoulli',\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_best',\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep',\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep',\n@@ -724,7 +725,7 @@ def test_undetermined_coefficients_match():\n def test_issue_4785():\n from sympy.abc import A\n eq = x + A*(x + diff(f(x), x) + f(x)) + diff(f(x), x) + f(x) + 2\n- assert classify_ode(eq, f(x)) == ('1st_exact', '1st_linear',\n+ assert classify_ode(eq, f(x)) == ('factorable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear',\n 'almost_linear', '1st_power_series', 'lie_group',\n 'nth_linear_constant_coeff_undetermined_coefficients',\n 'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters',\n@@ -732,7 +733,7 @@ def test_issue_4785():\n 'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters_Integral')\n # issue 4864\n eq = (x**2 + f(x)**2)*f(x).diff(x) - 2*x*f(x)\n- assert classify_ode(eq, f(x)) == ('1st_exact',\n+ assert classify_ode(eq, f(x)) == ('factorable', '1st_exact',\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_best',\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep',\n '1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep',\n@@ -895,7 +896,7 @@ def test_2nd_power_series_ordinary():\n assert checkodesol(eq, sol) == (True, 0)\n \n eq = (1 + x**2)*(f(x).diff(x, 2)) + 2*x*(f(x).diff(x)) -2*f(x)\n- assert classify_ode(eq) == ('2nd_hypergeometric', '2nd_hypergeometric_Integral',\n+ assert classify_ode(eq) == ('factorable', '2nd_hypergeometric', '2nd_hypergeometric_Integral',\n '2nd_power_series_ordinary')\n \n sol = Eq(f(x), C2*(-x**4/3 + x**2 + 1) + C1*x + O(x**6))\n@@ -903,7 +904,7 @@ def test_2nd_power_series_ordinary():\n assert checkodesol(eq, sol) == (True, 0)\n \n eq = f(x).diff(x, 2) + x*(f(x).diff(x)) + f(x)\n- assert classify_ode(eq) == ('2nd_power_series_ordinary',)\n+ assert classify_ode(eq) == ('factorable', '2nd_power_series_ordinary',)\n sol = Eq(f(x), C2*(x**4/8 - x**2/2 + 1) + C1*x*(-x**2/3 + 1) + O(x**6))\n assert dsolve(eq) == sol\n # FIXME: checkodesol fails for this solution...\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py\nindex 9b029d23d48c..ce422ba68d80 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py\n@@ -389,7 +389,7 @@ def test_lie_group():\n def test_separable_reduced():\n df = f(x).diff(x)\n eq = (x / f(x))*df + tan(x**2*f(x) / (x**2*f(x) - 1))\n- assert classify_ode(eq) == ('separable_reduced', 'lie_group',\n+ assert classify_ode(eq) == ('factorable', 'separable_reduced', 'lie_group',\n 'separable_reduced_Integral')\n _ode_solver_test(_get_examples_ode_sol_separable_reduced)\n \n@@ -1812,6 +1812,12 @@ def _get_examples_ode_sol_separable():\n 'sol': [Eq(v(t), -68.585712797928991/tanh(C1 - 0.14288690166235204*t))],\n 'func': v(t),\n 'checkodesol_XFAIL': True,\n+ },\n+\n+ #https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/22155\n+ 'separable_27': {\n+ 'eq': f(x).diff(x) - exp(f(x) - x),\n+ 'sol': [Eq(f(x), log(-exp(x)/(C1*exp(x) - 1)))],\n }\n }\n }\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_pde.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_pde.py\nindex 1b43eb0b0886..da9e09ba18f6 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_pde.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_pde.py\n@@ -231,4 +231,4 @@ def test_pdsolve_variable_coeff():\n \n eq = exp(2*x)*(u.diff(y)) + y*u - u\n sol = pdsolve(eq, hint='1st_linear_variable_coeff')\n- assert sol == Eq(u, exp((-y**2 + 2*y + 2*F(x))*exp(-2*x)/2))\n+ assert sol == Eq(f(x, y), F(x)*exp(-y*(y - 2)*exp(-2*x)/2))\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -231,4 +231,4 @@ def test_pdsolve_variable_coeff():\n \n eq = exp(2*x)*(u.diff(y)) + y*u - u\n sol = pdsolve(eq, hint='1st_linear_variable_coeff')\n- assert sol == Eq(u, exp((-y**2 + 2*y + 2*F(x))*exp(-2*x)/2))\n+ assert sol == Eq(f(x, y), F(x)*exp(-y*(y - 2)*exp(-2*x)/2))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 234,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/solvers/tests/test_pde.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis should still be `u` rather than `f(x, y)` to keep it consistent with the examples above"
}
] |
ec9e6cee61d6aedcd819bad2b2092929986a12bb
|
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py
index 5bc8b7d65273..d9f55bf4acc0 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py
@@ -931,7 +931,7 @@ class in it. Note that a hint may do this anyway if
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep_Integral',
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep_Integral')
>>> classify_ode(f(x).diff(x, 2) + 3*f(x).diff(x) + 2*f(x) - 4)
- ('nth_linear_constant_coeff_undetermined_coefficients',
+ ('factorable', 'nth_linear_constant_coeff_undetermined_coefficients',
'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters',
'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters_Integral')
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
index 7523b4536e86..1076c63ccc9b 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
from sympy.core.exprtools import factor_terms
from sympy.core.expr import Expr
from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef, Derivative, diff, Function, expand, Subs, _mexpand
-from sympy.core.numbers import Float, zoo
+from sympy.core.numbers import zoo
from sympy.core.relational import Equality, Eq
from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol, Dummy, Wild
from sympy.core.mul import Mul
@@ -875,13 +875,12 @@ class Factorable(SingleODESolver):
has_integral = False
def _matches(self):
- eq = self.ode_problem.eq
+ eq_orig = self.ode_problem.eq
f = self.ode_problem.func.func
x = self.ode_problem.sym
- order =self.ode_problem.order
df = f(x).diff(x)
self.eqs = []
- eq = eq.collect(f(x), func = cancel)
+ eq = eq_orig.collect(f(x), func = cancel)
eq = fraction(factor(eq))[0]
factors = Mul.make_args(factor(eq))
roots = [fac.as_base_exp() for fac in factors if len(fac.args)!=0]
@@ -894,13 +893,9 @@ def _matches(self):
roots = solve(eq, df)
if len(roots)>0:
self.eqs = [(df - root) for root in roots]
- if len(self.eqs)==1:
- if order>1:
- return False
- if self.eqs[0].has(Float):
- return False
- return fraction(factor(self.eqs[0]))[0]-eq!=0
- return True
+ # Avoid infinite recursion
+ matches = self.eqs != [eq_orig]
+ return matches
for i in factors:
if i.has(f(x)):
self.eqs.append(i)
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_ode.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_ode.py
index 1a92901bf8ca..82211858d06f 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_ode.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_ode.py
@@ -96,21 +96,21 @@ def test_dsolve_options():
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep_Integral', '1st_linear',
'1st_linear_Integral', 'Bernoulli', 'Bernoulli_Integral',
'almost_linear', 'almost_linear_Integral', 'best', 'best_hint',
- 'default', 'lie_group',
+ 'default', 'factorable', 'lie_group',
'nth_linear_euler_eq_homogeneous', 'order',
'separable', 'separable_Integral']
Integral_keys = ['1st_exact_Integral',
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep_Integral',
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep_Integral', '1st_linear_Integral',
'Bernoulli_Integral', 'almost_linear_Integral', 'best', 'best_hint', 'default',
- 'nth_linear_euler_eq_homogeneous',
+ 'factorable', 'nth_linear_euler_eq_homogeneous',
'order', 'separable_Integral']
assert sorted(a.keys()) == keys
assert a['order'] == ode_order(eq, f(x))
assert a['best'] == Eq(f(x), C1/x)
assert dsolve(eq, hint='best') == Eq(f(x), C1/x)
- assert a['default'] == 'separable'
- assert a['best_hint'] == 'separable'
+ assert a['default'] == 'factorable'
+ assert a['best_hint'] == 'factorable'
assert not a['1st_exact'].has(Integral)
assert not a['separable'].has(Integral)
assert not a['1st_homogeneous_coeff_best'].has(Integral)
@@ -126,8 +126,8 @@ def test_dsolve_options():
assert b['order'] == ode_order(eq, f(x))
assert b['best'] == Eq(f(x), C1/x)
assert dsolve(eq, hint='best', simplify=False) == Eq(f(x), C1/x)
- assert b['default'] == 'separable'
- assert b['best_hint'] == '1st_linear'
+ assert b['default'] == 'factorable'
+ assert b['best_hint'] == 'factorable'
assert a['separable'] != b['separable']
assert a['1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep'] != \
b['1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep']
@@ -231,7 +231,8 @@ def test_classify_ode():
'1st_linear_Integral',
'Bernoulli_Integral',
'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters_Integral')
- assert c == ('1st_linear',
+ assert c == ('factorable',
+ '1st_linear',
'Bernoulli',
'1st_power_series',
'lie_group',
@@ -243,7 +244,7 @@ def test_classify_ode():
assert classify_ode(
2*x*f(x)*f(x).diff(x) + (1 + x)*f(x)**2 - exp(x), f(x)
- ) == ('1st_exact', 'Bernoulli', 'almost_linear', 'lie_group',
+ ) == ('factorable', '1st_exact', 'Bernoulli', 'almost_linear', 'lie_group',
'1st_exact_Integral', 'Bernoulli_Integral', 'almost_linear_Integral')
assert 'Riccati_special_minus2' in \
classify_ode(2*f(x).diff(x) + f(x)**2 - f(x)/x + 3*x**(-2), f(x))
@@ -253,11 +254,11 @@ def test_classify_ode():
k = Symbol('k')
assert classify_ode(f(x).diff(x)/(k*f(x) + k*x*f(x)) + 2*f(x)/(k*f(x) +
k*x*f(x)) + x*f(x).diff(x)/(k*f(x) + k*x*f(x)) + z, f(x)) == \
- ('separable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear', 'Bernoulli',
+ ('factorable', 'separable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear', 'Bernoulli',
'1st_power_series', 'lie_group', 'separable_Integral', '1st_exact_Integral',
'1st_linear_Integral', 'Bernoulli_Integral')
# preprocessing
- ans = ('nth_algebraic', 'separable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear', 'Bernoulli',
+ ans = ('factorable', 'nth_algebraic', 'separable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear', 'Bernoulli',
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_best',
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep',
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep',
@@ -305,6 +306,13 @@ def test_classify_ode():
a = classify_ode(2*x*f(x)*f(x).diff(x) + (1 + x)*f(x)**2 - exp(x), f(x), dict=True, hint='Bernoulli')
assert sorted(a.keys()) == ['Bernoulli', 'Bernoulli_Integral', 'default', 'order', 'ordered_hints']
+ # test issue 22155
+ a = classify_ode(f(x).diff(x) - exp(f(x) - x), f(x))
+ assert a == ('separable',
+ '1st_exact', '1st_power_series',
+ 'lie_group', 'separable_Integral',
+ '1st_exact_Integral')
+
def test_classify_ode_ics():
# Dummy
@@ -724,7 +732,7 @@ def test_undetermined_coefficients_match():
def test_issue_4785():
from sympy.abc import A
eq = x + A*(x + diff(f(x), x) + f(x)) + diff(f(x), x) + f(x) + 2
- assert classify_ode(eq, f(x)) == ('1st_exact', '1st_linear',
+ assert classify_ode(eq, f(x)) == ('factorable', '1st_exact', '1st_linear',
'almost_linear', '1st_power_series', 'lie_group',
'nth_linear_constant_coeff_undetermined_coefficients',
'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters',
@@ -732,7 +740,7 @@ def test_issue_4785():
'nth_linear_constant_coeff_variation_of_parameters_Integral')
# issue 4864
eq = (x**2 + f(x)**2)*f(x).diff(x) - 2*x*f(x)
- assert classify_ode(eq, f(x)) == ('1st_exact',
+ assert classify_ode(eq, f(x)) == ('factorable', '1st_exact',
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_best',
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep',
'1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_dep_div_indep',
@@ -895,7 +903,7 @@ def test_2nd_power_series_ordinary():
assert checkodesol(eq, sol) == (True, 0)
eq = (1 + x**2)*(f(x).diff(x, 2)) + 2*x*(f(x).diff(x)) -2*f(x)
- assert classify_ode(eq) == ('2nd_hypergeometric', '2nd_hypergeometric_Integral',
+ assert classify_ode(eq) == ('factorable', '2nd_hypergeometric', '2nd_hypergeometric_Integral',
'2nd_power_series_ordinary')
sol = Eq(f(x), C2*(-x**4/3 + x**2 + 1) + C1*x + O(x**6))
@@ -903,7 +911,7 @@ def test_2nd_power_series_ordinary():
assert checkodesol(eq, sol) == (True, 0)
eq = f(x).diff(x, 2) + x*(f(x).diff(x)) + f(x)
- assert classify_ode(eq) == ('2nd_power_series_ordinary',)
+ assert classify_ode(eq) == ('factorable', '2nd_power_series_ordinary',)
sol = Eq(f(x), C2*(x**4/8 - x**2/2 + 1) + C1*x*(-x**2/3 + 1) + O(x**6))
assert dsolve(eq) == sol
# FIXME: checkodesol fails for this solution...
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py
index 9b029d23d48c..ce422ba68d80 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py
@@ -389,7 +389,7 @@ def test_lie_group():
def test_separable_reduced():
df = f(x).diff(x)
eq = (x / f(x))*df + tan(x**2*f(x) / (x**2*f(x) - 1))
- assert classify_ode(eq) == ('separable_reduced', 'lie_group',
+ assert classify_ode(eq) == ('factorable', 'separable_reduced', 'lie_group',
'separable_reduced_Integral')
_ode_solver_test(_get_examples_ode_sol_separable_reduced)
@@ -1812,6 +1812,12 @@ def _get_examples_ode_sol_separable():
'sol': [Eq(v(t), -68.585712797928991/tanh(C1 - 0.14288690166235204*t))],
'func': v(t),
'checkodesol_XFAIL': True,
+ },
+
+ #https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/22155
+ 'separable_27': {
+ 'eq': f(x).diff(x) - exp(f(x) - x),
+ 'sol': [Eq(f(x), log(-exp(x)/(C1*exp(x) - 1)))],
}
}
}
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_pde.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_pde.py
index 1b43eb0b0886..efbb7e42e2ad 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_pde.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_pde.py
@@ -231,4 +231,4 @@ def test_pdsolve_variable_coeff():
eq = exp(2*x)*(u.diff(y)) + y*u - u
sol = pdsolve(eq, hint='1st_linear_variable_coeff')
- assert sol == Eq(u, exp((-y**2 + 2*y + 2*F(x))*exp(-2*x)/2))
+ assert sol == Eq(u, F(x)*exp(-y*(y - 2)*exp(-2*x)/2))
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-3735@98e6d6a
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 3,735
|
Add pip install xonsh [full] and rewrite install doc
|
Resolves #3622
Adds extras tag [full], which installs xonsh with pygments, prompt-toolkit and distro, with the intent that that's what most users will want.
Also update installation section of docs to include this option, but take the opportunity for a thorough rewrite:
collapse separate linux, osx and windows guides into one cross-platform install and config flow; add doc for the 2 startup wizards, modernize the Windows section to prefer Windows Terminal as your getting-started config.
These doc changes are opinionated and potentially controversial, which is not my intent. So I'm prepared to redo based on feedback.
|
2020-08-29T21:47:51Z
|
Please, add 'prompt_toolkit' to general requirements.
I'm having errors in 'abbrevs' and a lot of things printed at the terminal startup.
I use Manjaro Linux and neither the system package, nor the "Arch User Repository" package, nor the package in the "pip" requires the installation of "prompt_toolkit" by DEFAULT.
If possible, as it is undoubtedly an important package, add as required dependency.
In a last look at all the documentation, I found this syntax in the installation instructions for linux: "xonsh[ptk,linux]". I would like to say that, even for those who have a basic knowledge of python, this syntax is a bit obscure. If possible, it would be good to clarify the point.
Thank you very much for this wonderful project.
|
I would protest that the extras syntax is obscure for Pythonistas. It is extremely common and used by many packages with optional dependencies.
The rest of it is up for debate. It is arguable whether various packages should or should not include it. For example, I maintain the containers: `xonsh/xonsh` and `xonsh/action` do not include PTK because the former is meant to be a minimal base package and the latter is meant for automation. `xonsh/interactive` however does include ptk (as well as pygments) because it is meant for humans.
I believe the general logic is to allow xonsh to be used with reduced dependencies (readline only, without ptk+pygments). The way python packaging works is that you can't specify configurations with less dependencies--you can specify extras to extend functionality with new dependencies, but to specify a configuration with less dependencies you'd need a new package.
As with most FOSS, who is responsible for what packages where is a complex question--I think we directly maintain just the PyPI, Conda, and AppImage packages.
On conda-forge a lot of packages are split into xxx-base/xxx to handle the case with optional dependencies. For example [matplotlib ](https://github.com/conda-forge/matplotlib-feedstock/blob/master/recipe/meta.yaml#L20) and seaborn.
I don't think I have seen similar concepts on PyPI but maybe we should think about that. `xonsh` could be a meta package with all dependencies and `xonsh-base` the bare minimum.
> I don't think I have seen similar concepts on PyPI but maybe we should think about that. `xonsh` could be a meta package with all dependencies and `xonsh-base` the bare minimum.
That's an interesting idea. I don't remember seeing such packages at PyPI either.
As for making _prompt_toolkit_ a general "hard" requirement, I also vote "nay". While it certainly is beneficial to interactive users, it is absolutely unnecessary for non-interactive use.
I don't use Manjaro myself, but since it's an Arch-based distro, I'm almost sure, that their Xonsh package lists _python-prompt_toolkit_ as an optional dependency.
Is Xonsh to the point that prompt_toolkit should be a hard requirement for *interactive* use? As in, you get a run-time error if you invoke Xonsh interactively and don't have it? And the configuration wizard offers a warning and / or help if you choose a color scheme or otherwise imply you're interested in interactive use but don't have PTK?
[PTK supports dumb terminal mode](https://github.com/prompt-toolkit/python-prompt-toolkit/pull/1035) if you are running in a really restricted environment, but it works fine on all the mainline environments that you'd use interactively. Maybe readline shell (and the maintenance burden) has outlived its usefulness...
I think we have users that do use the readline shell?
The main use of the readline interface is that it is lighter than the ptk interface. (Although honestly, if weight is a concern, you should probably not use xonsh.)
The basic reasoning here is that xonsh should be able to run on the standard library-only, so that if you have Python, you have your shell
@scopatz What about if we vend PTK similar to what we do with PLY.
We could use the user installed PTK if it is available and recent enough. Otherwise fall back the version we vend.
It would be a annoyin to maintain, but it would improve user experience on systems where PTK is not installed. I just don't know if it would be considered bad practice.
I think that would be OK to do. Annoying to maintain, but it might be worth it.
@scopatz I have been looking at vending PTK.
I place it `xonsh/vended_ptk/prompt_toolkit`, and then I add the `vended_ptk` folde to the python path if "prompt_toolkit" is not installed.
``` python
def vend_prompt_toolkit_if_not_available():
spec = importlib.util.find_spec("prompt_toolkit")
if spec is None:
sys.path.append(str(pathlib.Path(__file__).with_name("vended_ptk").resolve()))
```
Do you know of an other way to import a vended subpackages as it were a toplevel module in `sys.modules`. I don't like the use of `__file__` in this implementation.
Is there a meaningful difference between "vending" and "primary distributables include dependencies"?
|
[
{
"body": "I'm having errors in 'abbrevs' and a lot of things printed at the terminal startup.\r\nI use Manjaro Linux and neither the system package, nor the \"Arch User Repository\" package, nor the package in the \"pip\" requires the installation of \"prompt_toolkit\" by DEFAULT.\r\nIf possible, as it is undoubtedly an important package, add as required dependency.\r\nIn a last look at all the documentation, I found this syntax in the installation instructions for linux: \"xonsh[ptk,linux]\". I would like to say that, even for those who have a basic knowledge of python, this syntax is a bit obscure. If possible, it would be good to clarify the point.\r\nThank you very much for this wonderful project.",
"number": 3622,
"title": "Please, add 'prompt_toolkit' to general requirements."
}
] |
582b5a729abcbf50c2ce23305e5d0505df2221db
|
{
"head_commit": "98e6d6a6d1f1e55e2b20e25e189f2eee3a53a390",
"head_commit_message": "news!",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/.gitignore b/.gitignore\nindex 6382119f29..f16d3f9f76 100644\n--- a/.gitignore\n+++ b/.gitignore\n@@ -37,7 +37,8 @@ bin/\n /lib/\n include/\n venv/\n-.venv/\n+.venv*/\n+\n \n # Mac\n .DS_Store\ndiff --git a/docs/appimage.rst b/docs/appimage.rst\nindex d5bae56fd2..61b5d179b5 100644\n--- a/docs/appimage.rst\n+++ b/docs/appimage.rst\n@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@\n-Portable rootless xonsh build on AppImage\n-=========================================\n+Via AppImage\n+=============\n \n `AppImage <https://appimage.org/>`_ is a format for distributing portable software on Linux without needing superuser permissions to install the application. It tries also to allow Linux distribution-agnostic binary software deployment for application developers, also called Upstream packaging. \n \ndiff --git a/docs/conf.py b/docs/conf.py\nindex cd3f917bae..bbe6224321 100644\n--- a/docs/conf.py\n+++ b/docs/conf.py\n@@ -440,5 +440,5 @@ def make_events():\n def setup(app):\n from xonsh.pyghooks import XonshConsoleLexer\n \n- app.add_lexer(\"xonshcon\", XonshConsoleLexer)\n+ app.add_lexer(\"xonshcon\", XonshConsoleLexer())\n app.add_css_file(\"custom.css\")\ndiff --git a/docs/containers.rst b/docs/containers.rst\nindex 500734f665..fc2c1c2e0c 100644\n--- a/docs/containers.rst\n+++ b/docs/containers.rst\n@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@\n-Containers\n-==========\n+Run from container\n+==================\n \n-xonsh publishes a handful of containers, primarily targeting CI and automation use-cases. All of them are published on `Docker Hub <https://hub.docker.com/u/xonsh>`__.\n+Xonsh publishes a handful of containers, primarily targeting CI and automation use cases. All of them are published on `Docker Hub <https://hub.docker.com/u/xonsh>`__.\n \n * ``xonsh/xonsh``: A base container providing basic xonsh\n * ``xonsh/interactive``: xonsh with additions for people\ndiff --git a/docs/customization.rst b/docs/customization.rst\nindex 89107d2323..47aa2fc322 100644\n--- a/docs/customization.rst\n+++ b/docs/customization.rst\n@@ -234,30 +234,4 @@ variables:\n ...use xonsh inside Emacs?\n ----------------------------------\n \n-**Option A: Comint buffer**\n-\n-You can use xonsh as your `interactive shell in Emacs\n-<https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/manual/html_node/emacs/Interactive-Shell.html>`_\n-in a Comint buffer. This way you keep all the Emacs editing power\n-in the shell, but you loose xonsh's completion feature.\n-\n-Make sure you install xonsh with readline support and in your\n-``.xonshrc`` file define\n-\n-.. code-block:: xonsh\n-\n- $SHELL_TYPE = 'readline'\n-\n-Also, in Emacs set ``explicit-shell-file-name`` to your xonsh executable.\n-\n-**Option B: Ansi-term buffer**\n-\n-The second option is to run xonsh in an Ansi-term buffer inside\n-Emacs. This way you have to switch modes if you want do Emacs-style\n-editing, but you keep xonsh's impressive completion.\n-\n-For this it is preferred to have xonsh installed with the\n-prompt-toolkit. Then you can leave ``$SHELL_TYPE`` at its default.\n-\n-Emacs will prompt you for the path of the xonsh exeutable when you\n-start up ``ansi-term``.\n+see `emacs <editors.html>`_.\ndiff --git a/docs/dependencies.rst b/docs/dependencies.rst\ndeleted file mode 100644\nindex c5db3c31af..0000000000\n--- a/docs/dependencies.rst\n+++ /dev/null\n@@ -1,25 +0,0 @@\n-Dependencies\n-------------\n-Xonsh currently has the following external dependencies,\n-\n-*Run Time:*\n-\n- #. Python v3.5+\n-\n-Pip supports \"extra\" dependencies in the form of ``xonsh[ptk,linux]``, where\n-the list in the brackets identify the optional features\n-\n-Xonsh currently has the following extras\n-\n- #. ``ptk``: prompt-toolkit >= 2.0: *advanced readline library, line-editing*\n- #. ``pygments``: pygments >=2.2: *syntax-highlighting*\n- #. ``proctitle``: setproctitle: *change the title of terminal to reflect the current subprocess*\n- #. ``linux``: distro: *linux specific platform information*\n- #. ``mac``: gnureadline: *GNU's featureful version of readline*\n-\n-In addition, xonsh integrates with Jupyter, an in-browser REPL, enabling the use of xonsh in jupyter notebooks\n-\n-Development Dependencies\n-------------------------\n-\n-If you want to develop xonsh, it is extremely recommended to install the dependencies listed in `requirements/docs.txt <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/blob/master/requirements/docs.txt>`_ (to generate documentation) and `requirements/tests.txt <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/blob/master/requirements/tests.txt>`_ (to run the test suite).\ndiff --git a/docs/editors.rst b/docs/editors.rst\nindex b5a3a03d08..81df39d373 100644\n--- a/docs/editors.rst\n+++ b/docs/editors.rst\n@@ -9,6 +9,9 @@ Editor Support\n Emacs\n =====\n \n+Emacs Xonsh mode\n+----------------\n+\n There is an emacs mode for editing xonsh scripts available from the\n `MELPA repository`_. If you are not familiar see the installation\n instructions there.\n@@ -21,3 +24,34 @@ Then just add this line to your emacs configuration file:\n \n \n .. _MELPA repository: https://melpa.org/#/xonsh-mode\n+\n+\n+Xonsh Comint buffer\n+-------------------\n+\n+You can use xonsh as your `interactive shell in Emacs\n+<https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/manual/html_node/emacs/Interactive-Shell.html>`_\n+in a Comint buffer. This way you keep all the Emacs editing power\n+in the shell, but you loose xonsh's completion feature.\n+\n+Make sure you install xonsh with readline support and in your\n+``.xonshrc`` file define\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $SHELL_TYPE = 'readline'\n+\n+Also, in Emacs set ``explicit-shell-file-name`` to your xonsh executable.\n+\n+Xonsh Ansi-term buffer\n+----------------------\n+\n+The second option is to run xonsh in an Ansi-term buffer inside\n+Emacs. This way you have to switch modes if you want do Emacs-style\n+editing, but you keep xonsh's impressive completion.\n+\n+For this it is preferred to have xonsh installed with the\n+prompt-toolkit. Then you can leave ``$SHELL_TYPE`` at its default.\n+\n+Emacs will prompt you for the path of the xonsh exeutable when you\n+start up ``ansi-term``.\ndiff --git a/docs/installation.rst b/docs/installation.rst\nindex db2af10a4e..b1701ddc6c 100644\n--- a/docs/installation.rst\n+++ b/docs/installation.rst\n@@ -1,20 +1,46 @@\n \n-Getting Started\n-===============\n-\n-.. include:: dependencies.rst\n+Installation\n+============\n \n+Prerequisites\n+-------------\n+* python, V3.6 or later.\n+* for interactive use, an ansi (vt100-compatible) terminal application. On Windows 10, the \n+ separately-installable `Windows Terminal app <https://github.com/microsoft/terminal/releases>`_ \n+ is recommended.\n+ \n Installation\n ------------\n+Xonsh can be installed via package manager, via appimage or just run from a pre-built container:\n \n .. toctree::\n :titlesonly:\n :maxdepth: 2\n \n- linux\n- osx\n- windows\n+ packages\n appimage\n containers\n- customization\n+\n+\n+Installation in specialized environments\n+----------------------------------------\n+\n+.. toctree::\n+ :titlesonly:\n+ :maxdepth: 2\n+\n+ jupyter\n editors\n+\n+Configuration and Customization\n+================================\n+\n+Xonsh uses startup configuration files and provides configuration wizards to help you set them up.\n+\n+.. toctree::\n+ :titlesonly:\n+ :maxdepth: 2\n+\n+ xonshrc\n+ customization\n+ platform-issues\ndiff --git a/docs/jupyter.rst b/docs/jupyter.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..48c255905e\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/docs/jupyter.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@\n+Xonsh kernel for Jupyter\n+========================\n+\n+[placeholder]\ndiff --git a/docs/linux.rst b/docs/linux.rst\ndeleted file mode 100644\nindex 14a8c18ac5..0000000000\n--- a/docs/linux.rst\n+++ /dev/null\n@@ -1,123 +0,0 @@\n-==========================\n-Linux Guide\n-==========================\n-\n-Installation\n-============\n-\n-You can install xonsh using ``conda``, ``pip``, or from source.\n-\n-**conda:**\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ conda config --add channels conda-forge\n- $ conda install xonsh\n-\n-\n-**pip:**\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ pip install xonsh\n-\n-\n-**source:** Download the source `from github <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh>`_\n-(`zip file <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/archive/master.zip>`_), then run\n-the following from the source directory,\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ pip install .\n-\n-\n-Debian/Ubuntu users can install xonsh from the repository with:\n-\n-**apt:**\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ apt install xonsh\n-\n-\n-Xonsh is available on bionic bever (version 0.6.0) and artful aardvark\n-(version 0.5.12).\n-\n-Fedora users can install xonsh from the repository with:\n-\n-**dnf:**\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ dnf install xonsh\n-\n-\n-Arch Linux users can install xonsh from the official community repository with:\n-\n-**pacman:**\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ pacman -S xonsh\n-\n-Note that some of these may require ``sudo``.\n-If you run into any problems, please let us know!\n-\n-.. include:: dependencies.rst\n-\n-Customization\n-=============\n-\n-See the `xonsh customization guide <customization.html>`_ for more details on setting up ``xonsh``!\n-\n-\n-Possible conflicts with Bash\n-============================\n-\n-Depending on how your installation of Bash is configured, Xonsh may have trouble\n-loading certain shell modules. Particularly if you see errors similar to this\n-when launching Xonsh:\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n- bash: error importing function definition for `BASH_FUNC_module'\n- bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n- bash: error importing function definition for `BASH_FUNC_scl'\n- bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n- bash: error importing function definition for `BASH_FUNC_module'\n- bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n- bash: error importing function definition for `BASH_FUNC_scl'\n-\n-...You can correct the problem by unsetting the modules, by adding the following\n-lines to your ``~/.bashrc file``:\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- unset module\n- unset scl\n-\n-\n-Default Ubuntu .bashrc breaks Foreign Shell Functions\n-=====================================================\n-Xonsh supports importing functions from foreign shells using the\n-`ForeignShellFunctionAlias` class, which calls functions as if they were\n-aliases. This is implemented by executing a command that sources the file\n-containing the function definition and then immediately calls the function with\n-any necessary arguments.\n-\n-The default user `~/.bashrc` file in Ubuntu 15.10 has the following snippet at\n-the top, which causes the script to exit immediately if not run interactively.\n-\n-.. code-block:: bash\n-\n- # If not running interactively, don't do anything\n- case $- in\n- *i*) ;;\n- *) return;;\n- esac\n-\n-This means that any function you have added to the file after this point will be\n-registered as a xonsh alias but will fail on execution. Previous versions of\n-Ubuntu have a different test for interactivity at the top of the file that\n-yields the same problem.\ndiff --git a/docs/osx.rst b/docs/osx.rst\ndeleted file mode 100644\nindex f0a98a0d30..0000000000\n--- a/docs/osx.rst\n+++ /dev/null\n@@ -1,114 +0,0 @@\n-==========================\n-OSX Guide\n-==========================\n-\n-Installation\n-============\n-\n-You can install xonsh using a package manager including homebrew, macports, conda, pip, or from source.\n-\n-**homebrew:**\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ brew install xonsh\n-\n-\n-**MacPorts:**\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ sudo port install xonsh\n-\n-**conda:**\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ conda config --add channels conda-forge\n- $ conda install xonsh\n-\n-\n-**pip:**\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ pip3 install xonsh\n-\n-\n-**source:** Download the source `from github <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh>`_\n-(`zip file <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/archive/master.zip>`_), then run\n-the following from the source directory,\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ pip3 install xonsh\n-\n-Extras for macOS\n-==================\n-readline\n---------\n-\n-On macOS, it is *strongly* recommended to install the ``gnureadline`` library if using the readline shell. ``gnureadline`` can be installed via pip:\n-\n-.. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ pip3 install gnureadline\n-\n-Path Helper\n------------\n-\n-macOS provides a `path helper\n-<http://www.softec.lu/site/DevelopersCorner/MasteringThePathHelper>`_,\n-which by default configures paths in bash and other POSIX or C shells. Without\n-including these paths, common tools including those installed by Homebrew\n-may be unavailable. See ``/etc/profile`` for details on how it is done.\n-To ensure the path helper is invoked on xonsh (for all users), add the\n-following to ``/etc/xonshrc``::\n-\n- source-bash $(/usr/libexec/path_helper -s)\n-\n-To incorporate the whole functionality of ``/etc/profile``::\n-\n- source-bash --seterrprevcmd \"\" /etc/profile\n-\n-\n-\n-Tab completion\n---------------\n-Xonsh has support for using bash completion files on the shell, to use it you need to install the bash-completion package. The regular bash-completion package uses v1 which mostly works, but `occasionally has rough edges <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/issues/2111>`_ so we recommend using bash-completion v2.\n-\n-Bash completion comes from <https://github.com/scop/bash-completion> which suggests you use a package manager to install it, this manager will also install a new version of bash without affecting /bin/bash. Xonsh also needs to be told where the bash shell file that builds the completions is, this has to be added to $BASH_COMPLETIONS. The package includes completions for many Unix commands.\n-\n-Common packaging systems for MacOs include\n-\n- - Homebrew where the bash-completion2 package needs to be installed.\n-\n- .. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ brew install bash-completion2\n- \n- This will install the bash_completion file in `/usr/local/share/bash-completion/bash_completion` which is in the current xonsh code and so should just work.\n-\n- - `MacPorts <https://trac.macports.org/wiki/howto/bash-completion>`_ where the bash-completion port needs to be installed.\n-\n- .. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ sudo port install bash-completion\n- \n-\n-\n- This includes a bash_completion file that needs to be added to the environment.\n-\n- .. code-block:: console\n-\n- $ $BASH_COMPLETIONS.insert(0, '/opt/local/share/bash-completion/bash_completion')\n-\n-Note that the `bash completion project page <https://github.com/scop/bash-completion>`_ gives the script to be called as in .../profile.d/bash_completion.sh which will the call the script mentioned above and one in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME . Currently xonsh seems only to be able to read the first script directly.\n-\n-\n-.. include:: dependencies.rst\n-\n-Customization\n-=============\n-\n-See the `xonsh customization guide <customization.html>`_ for more details on setting up ``xonsh``!\ndiff --git a/docs/packages.rst b/docs/packages.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..595a794e33\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/docs/packages.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@\n+Via Package Manager\n+===================\n+\n+You can install xonsh using ``conda``, ``pip`` or the package manager for \n+your operating system distribution.\n+\n+For the fullest interactive user experience, these additional packages should also be installed:\n+\n+ :prompt-toolkit: for command completion, configurable key bindings and especially multi-line line editing.\n+ :pygments: for xonsh and python syntax-specific highlighting\n+ :setproctitle: updates process title (in terminal window and process monitor) to match Xonsh arguments.\n+\n+Installing with these packages is the recommended configuration and is documented first. \n+If you are operating in a specialized or restricted environment, you can install just the xonsh package, as \n+described in `fewer prerequisites`_\n+\n+\n+**conda:**\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ conda config --add channels conda-forge\n+ $ conda install pygments prompt-toolkit setproctitle xonsh\n+\n+\n+**pip:** Typically you will activate a virtual environment and install xonsh there. This will ensure that you invoke the \n+correct python interpreter and ``pip`` module. \n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ pip install pygments prompt-toolkit setproctitle xonsh\n+\n+As a shortcut (for pip only), you can specify all of the above with `extras` syntax:\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ pip install xonsh[full]\n+\n+The above ``pip`` commands may have to be spelled ``pip3`` or ``sudo pip3`` if you are not installing in a virtual environment.\n+\n+**source:** Pip can also install the most recent xonsh source code from the \n+`xonsh project repository <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh>`_.\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ pip install pygments prompt-toolkit setproctitle https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/archive/master.zip\n+\n+Spelling of ``pip`` command may likewise have to be amended as noted above.\n+\n+**platform package managers**\n+Various operating system distributions have platform-specific package managers which may offer a xonsh package. \n+This may not be the most current version of xonsh, but it should have been tested for stability on that platform\n+by the distribution managers.\n+\n+\n+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+---------------------+\n+ | OS or distribution | command | Package(s) |\n+ +===========================+=============================+=====================+\n+ | Debian/Ubuntu | ``$ [sudo] apt install`` | |\n+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+ pygments |\n+ | Fedora | ``$ [sudo] dnf install`` | prompt-toolkit |\n+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+ setproctitle |\n+ | Arch Linux | ``$ [sudo] pacman -S`` | xonsh |\n+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+ |\n+ | OSX | ``$ [sudo] brew install`` | |\n+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+---------------------+\n+\n+\n+If you run into any problems, please let us know!\n+\n+Fewer Prerequisites\n+--------------------\n+\n+A design goal of Xonsh is to run in any environment that supports a (supported) Python interpreter, you \n+can install just the ``xonsh`` package (using any package manager).\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+ \n+ pip install xonsh\n+\n+When it starts up, if xonsh does not find ``pygments`` or ``setproctitle`` packages, it simply does not colorize \n+or highlight syntax or set process title, respectively. \n+\n+If it does not find ``prompt-toolkit`` package, it will \n+use the Python ``readline`` module (which reads configuration file ``.inputrc`` in a manner compatible with ``GNU readline``). \n+To ensure xonsh uses ``readline`` even if ``prompt-toolkit`` is installed, configure this in your\n+``.xonshrc`` file:\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $SHELL_TYPE = 'readline'\n+\ndiff --git a/docs/platform-issues.rst b/docs/platform-issues.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..d527e26332\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/docs/platform-issues.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,227 @@\n+Platform-specific tips and tricks\n+==================================\n+\n+Linux\n+------\n+\n+Possible conflicts with Bash\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+Depending on how your installation of Bash is configured, Xonsh may have trouble\n+loading certain shell modules. If you see errors similar to this\n+when launching Xonsh:\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_module'\n+ bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_scl'\n+ bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_module'\n+ bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_scl'\n+\n+...You can correct the problem by unsetting the modules, by adding the following\n+lines to your ``~/.bashrc file``:\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ unset module\n+ unset scl\n+\n+\n+Default Ubuntu .bashrc breaks Foreign Shell Functions\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+Xonsh supports importing functions from foreign shells using the\n+`ForeignShellFunctionAlias` class, which calls functions as if they were\n+aliases. This is implemented by executing a command that sources the file\n+containing the function definition and then immediately calls the function with\n+any necessary arguments.\n+\n+The default user `~/.bashrc` file in Ubuntu 15.10 has the following snippet at\n+the top, which causes the script to exit immediately if not run interactively.\n+\n+.. code-block:: bash\n+\n+ # If not running interactively, don't do anything\n+ case $- in\n+ *i*) ;;\n+ *) return;;\n+ esac\n+\n+This means that any function you have added to the file after this point will be\n+registered as a xonsh alias but will fail on execution if the \n+shell is not running interactively. Previous versions of\n+Ubuntu have a different test for interactivity at the top of the file that\n+yields the same problem.\n+\n+\n+MacOS, OSX\n+----------\n+\n+readline\n+^^^^^^^^\n+\n+[ed note: This recommendation seems to be `out of date <https://pypi.org/project/gnureadline/>`_. \n+It's retained in the current docs in case you have an older version of Python or MacOS. But if \n+you have Mac platform experience and can clarify, please open an issue or even a PR to correct the documentation.]\n+\n+On macOS, it is *strongly* recommended to install the ``gnureadline`` library if using the readline shell. ``gnureadline`` can be installed via pip:\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ pip3 install gnureadline\n+\n+Path Helper\n+^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+macOS provides a `path helper\n+<http://www.softec.lu/site/DevelopersCorner/MasteringThePathHelper>`_,\n+which by default configures paths in bash and other POSIX or C shells. Without\n+including these paths, common tools including those installed by Homebrew\n+may be unavailable. See ``/etc/profile`` for details on how it is done.\n+To ensure the path helper is invoked on xonsh (for all users), add the\n+following to ``/etc/xonshrc``::\n+\n+ source-bash $(/usr/libexec/path_helper -s)\n+\n+To incorporate the whole functionality of ``/etc/profile``::\n+\n+ source-bash --seterrprevcmd \"\" /etc/profile\n+\n+\n+\n+Tab completion\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+Xonsh has support for using bash completion files on the shell, to use it you need to install \n+the bash-completion package. \n+The regular bash-completion package uses v1 which mostly works, but `occasionally has rough edges <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/issues/2111>`_ so we recommend using bash-completion v2.\n+\n+Bash completion comes from <https://github.com/scop/bash-completion> which suggests you use a package manager to install it, this manager will also install a new version of bash without affecting /bin/bash. Xonsh also needs to be told where the bash shell file that builds the completions is, this has to be added to $BASH_COMPLETIONS. The package includes completions for many Unix commands.\n+\n+Common packaging systems for MacOs include\n+\n+ - Homebrew where the bash-completion2 package needs to be installed.\n+\n+ .. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ brew install bash-completion2\n+ \n+ This will install the bash_completion file in `/usr/local/share/bash-completion/bash_completion` which is in the current xonsh code and so should just work.\n+\n+ - `MacPorts <https://trac.macports.org/wiki/howto/bash-completion>`_ where the bash-completion port needs to be installed.\n+\n+ .. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ sudo port install bash-completion\n+ \n+\n+\n+ This includes a bash_completion file that needs to be added to the environment.\n+\n+ .. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ $BASH_COMPLETIONS.insert(0, '/opt/local/share/bash-completion/bash_completion')\n+\n+Note that the `bash completion project page <https://github.com/scop/bash-completion>`_ gives the script to be called as in .../profile.d/bash_completion.sh which will the call the script mentioned above and one in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME . Currently xonsh seems only to be able to read the first script directly.\n+\n+\n+\n+\n+\n+Windows\n+-------\n+\n+Windows Terminal\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+If you are running a supported version of Windows (which is now Windows 10, version 2004 or later), \n+we recommend the Windows Terminal (``wt.exe``) rather than the time-honored ``cmd.exe``. This provides\n+unicode rendering, better ansi terminal compatibility and all the conveniences you expect \n+from the terminal application in other platforms.\n+\n+You can install it from the `Microsoft Store<https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/p/windows-terminal/9n0dx20hk701>`_ \n+or from `Github<https://github.com/microsoft/terminal>`_.\n+\n+By default Windows Terminal runs Powershell, but comes with a profile tab that runs `cmd.exe` instead, and you can add one for Xonsh as well.\n+\n+Nice colors\n+^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+The dark red and blue colors are completely unreadable in `cmd.exe`.\n+\n+.. image:: _static/intensify-colors-on-win-false.png\n+ :width: 396 px\n+ :alt: intensify-colors-win-false\n+ :align: center\n+\n+Xonsh has some tricks to fix colors. This is controlled by the\n+:ref:`$INTENSIFY_COLORS_ON_WIN <intensify_colors_on_win>`\n+environment variable which is ``True`` by default. \n+\n+\n+:ref:`$INTENSIFY_COLORS_ON_WIN <intensify_colors_on_win>` has the following effect:b \n+\n+On Windows 10:\n+ Windows 10 supports true color in the terminal, so on Windows 10 Xonsh will use\n+ a style with hard coded colors instead of the terminal colors.\n+\n+On older Windows:\n+ Xonsh replaces some of the unreadable dark colors with more readable\n+ alternatives (e.g. blue becomes cyan).\n+\n+\n+Avoid locking the working directory\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+Python (like other processes on Windows) locks the current working directory so\n+it can't be deleted or renamed. ``cmd.exe`` has this behaviour as well, but it\n+is quite annoying for a shell. \n+\n+The :ref:`free_cwd <free_cwd>` xontrib (add-on) for xonsh solves some of this problem. It\n+works by hooking the prompt to reset the current working directory to the root\n+drive folder whenever the shell is idle. It only works with the prompt-toolkit\n+back-end. To enable that behaviour run the following: \n+\n+Add this line to your ``~/.xonshrc`` file to have it always enabled. \n+\n+.. code-block:: xonshcon\n+\n+ >>> xontrib load free_cwd\n+\n+\n+Name space conflicts\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+Due to ambiguity with the Python ``dir`` builtin, to list the current directory\n+you must explicitly request the ``.``, like this:\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonshcon\n+\n+ >>> dir .\n+ Volume in drive C is Windows\n+ Volume Serial Number is 30E8-8B86\n+\n+ Directory of C:\\Users\\snail\\xonsh\n+\n+ 2015-05-12 03:04 <DIR> .\n+ 2015-05-12 03:04 <DIR> ..\n+ 2015-05-01 01:31 <DIR> xonsh\n+ 0 File(s) 0 bytes\n+ 3 Dir(s) 11,008,000,000 bytes free\n+\n+\n+\n+Many people create a ``d`` alias for the ``dir`` command to save\n+typing and avoid the ambiguity altogether:\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonshcon\n+\n+ >>> aliases['d'] = ['cmd', '/c', 'dir']\n+\n+You can add aliases to your ``~/.xonshrc`` to have it always\n+available when xonsh starts.\n+\n+\ndiff --git a/docs/tutorial.rst b/docs/tutorial.rst\nindex b18af1bd01..67a3eb1dfc 100644\n--- a/docs/tutorial.rst\n+++ b/docs/tutorial.rst\n@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@\n *******************\n Tutorial\n *******************\n+\n xonsh is a shell language and command prompt. Unlike other shells, xonsh is\n based on Python, with additional syntax added that makes calling subprocess\n commands, manipulating the environment, and dealing with the file system\ndiff --git a/docs/windows.rst b/docs/windows.rst\ndeleted file mode 100644\nindex 58a6f05b46..0000000000\n--- a/docs/windows.rst\n+++ /dev/null\n@@ -1,183 +0,0 @@\n-==========================\n-Windows Guide\n-==========================\n-\n-Installation\n-================\n-\n-The easy way\n-----------------\n-\n-The easiest way to install xonsh on windows is through the `Anaconda Python\n-Distribution <https://www.anaconda.com/download/>`__ and the conda package manager.\n-\n-.. note::\n-\n- Xonsh is not supported on legacy Python (2.7).\n-\n-Install xonsh with the following command:\n-\n-.. code-block:: bat\n-\n- > conda config --add channels conda-forge\n- > conda install xonsh\n-\n-This will install xonsh and all the recommended dependencies. Next, run xonsh:\n-\n-.. code-block:: bat\n-\n- > xonsh\n- snail@home ~ $\n-\n-\n-Install from source\n--------------------\n-\n-To install xonsh from source on Windows, first install `Python v3.4+`_ from\n-http://python.org. Remember to select \"Add python to PATH\" during installation.\n-\n-Next, install the prompt_toolkit dependency via ``pip``:\n-\n-.. code-block:: bat\n-\n- > pip install prompt-toolkit\n-\n-Download the latest `xonsh-master.zip`_ from github and unzip it\n-to ``xonsh-master``.\n-\n-Now install xonsh:\n-\n-.. code-block:: bat\n-\n- > cd xonsh-master\n- > pip install .\n-\n-Next, run xonsh:\n-\n-.. code-block:: bat\n-\n- > xonsh\n- snail@home ~ $\n-\n-.. _Python v3.4+: https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/\n-.. _xonsh-master.zip: https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/archive/master.zip\n-.. _cmder: http://cmder.net/\n-.. _conemu: https://conemu.github.io/\n-\n-\n-Tips and Tricks\n-================\n-\n-Nice colors\n-----------------------\n-\n-The dark red and blue colors are completely unreadable in Windows' default\n-terminal.\n-\n-.. image:: _static/intensify-colors-on-win-false.png\n- :width: 396 px\n- :alt: intensify-colors-win-false\n- :align: center\n-\n-There are ways to `configure the colors`_ of the old terminal, but to give new users the\n-best experience Xonsh has some tricks to fix colors. This is controlled by the\n-:ref:`$INTENSIFY_COLORS_ON_WIN <intensify_colors_on_win>`\n-environment variable which is ``True`` by default. \n-\n-.. _configure the colors: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/commandline/2017/08/11/introducing-the-windows-console-colortool/\n-\n-:ref:`$INTENSIFY_COLORS_ON_WIN <intensify_colors_on_win>` has the following effect:b \n-\n-On Windows 10:\n- Windows 10 supports true color in the terminal, so on Windows 10 Xonsh will use\n- a style with hard coded colors instead of the terminal colors.\n-\n-On older Windows:\n- Xonsh replaces some of the unreadable dark colors with more readable\n- alternatives (e.g. blue becomes cyan).\n-\n- \n-**The new Windows terminal**\n-\n-The best option on windows is to use the new `Windows Terminal\n-<https://github.com/microsoft/terminal>`__ developed by Microsoft as an open\n-source project. The new terminal supports has many nice features including\n-Unicode rendering. \n-\n-It is highly recommended and can easily be `installed from the Windows Store`_:\n-\n-\n-.. image:: _static/windows_terminal2.png\n- :alt: Unicode support in Windows terminal\n- :align: center\n-\n-\n-.. _installed from the Windows Store: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/commandline/2017/08/11/introducing-the-windows-console-colortool/\n-\n-\n-\n-Avoid locking the working directory\n------------------------------------\n-\n-Python (like other processes on Windows) locks the current working directory so\n-it can't be deleted or renamed. ``cmd.exe`` has this behaviour as well, but it\n-is quite annoying for a shell. \n-\n-The :ref:`free_cwd <free_cwd>` xontrib (add-on) for xonsh solves some of this problem. It\n-works by hooking the prompt to reset the current working directory to the root\n-drive folder whenever the shell is idle. It only works with the prompt-toolkit\n-back-end. To enable that behaviour run the following: \n-\n-Add this line to your ``~/.xonshrc`` file to have it always enabled. \n-\n-.. code-block:: xonshcon\n-\n- >>> xontrib load free_cwd\n-\n-\n-Name space conflicts\n---------------------\n-\n-Due to ambiguity with the Python ``dir`` builtin, to list the current directory\n-via the ``cmd.exe`` builtin you must explicitly request the ``.``, like this:\n-\n-.. code-block:: xonshcon\n-\n- >>> dir .\n- Volume in drive C is Windows\n- Volume Serial Number is 30E8-8B86\n-\n- Directory of C:\\Users\\snail\\xonsh\n-\n- 2015-05-12 03:04 <DIR> .\n- 2015-05-12 03:04 <DIR> ..\n- 2015-05-01 01:31 <DIR> xonsh\n- 0 File(s) 0 bytes\n- 3 Dir(s) 11,008,000,000 bytes free\n-\n-\n-\n-Many people create a ``d`` alias for the ``dir`` command to save\n-typing and avoid the ambiguity altogether:\n-\n-.. code-block:: xonshcon\n-\n- >>> aliases['d'] = ['cmd', '/c', 'dir']\n-\n-You can add aliases to your ``~/.xonshrc`` to have it always\n-available when xonsh starts.\n-\n-\n-\n-Unicode support for Windows\n-----------------------------\n-\n-Python's utf-8 unicode is not compatible with the default console \"conhost\" on Windows.\n-\n-Luckily, Microsoft is developing a new `Windows terminal <https://github.com/microsoft/terminal>`__ as an open source project. The new terminal supports all the nice features of \n-that you find in linux terminals. It is highly recommended and can easily be `installed from the Windows Store`_:\n-\n-.. image:: _static/windows_terminal.png\n- :alt: Unicode support in Windows terminal\n- :align: center\n-\ndiff --git a/docs/xonshrc.rst b/docs/xonshrc.rst\nindex d361db3473..bbf44668b7 100644\n--- a/docs/xonshrc.rst\n+++ b/docs/xonshrc.rst\n@@ -1,13 +1,160 @@\n Run Control File\n =========================\n-Xonsh allows you to have run control files to customize your shell behavior. These are called ``xonshrc`` files.\n+Xonsh allows you to customize your shell behavior with run control files, called \"xonshrc\" files. \n+These files are written in the xonsh language (a superset of Python) and are executed exactly once at startup. \n+The control file usually contains:\n \n-The system-wide ``xonshrc`` file controls options that are applied to all users of Xonsh on a given system. You can create this file in ``/etc/xonshrc`` for Linux and OSX and in ``%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\\xonsh\\xonshrc`` on Windows.\n+* Assignment statements setting `environment variables <envvars.html>`_. This includes standard OS environment variables that affect other programs and many that Xonsh uses for itself.\n+* ``xonfig`` commands to load selected add-ins (\"`xontribs<tutorial_xontrib.html#loading-xontribs>`\")\n+* Xonsh function defintions\n+* `Alias definitions <aliases.html>`_, many of which invoke the above functions with specified arguments.\n \n-Xonsh also allows you to have a run control file in your home directory. It can either be directly in the home directory at ``~/.xonshrc`` or for XDG compliance at ``~/.config/rc.xsh``. The options set in the local ``xonshrc`` only apply to the current user and will override any conflicting settings set in the system-wide control file.\n+The system-wide ``xonshrc`` file controls options that are applied to all users of Xonsh on a given system. \n+You can create this file in ``/etc/xonshrc`` for Linux and OSX and in ``%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\\xonsh\\xonshrc`` on Windows.\n \n-These files are written in the xonsh language, of course. They are executed exactly once\n-at startup. The following is a real-world example of such a file.\n+Xonsh also allows a per-user run control file in your home directory, either\n+directly in the home directory at ``~/.xonshrc`` or, for XDG compliance, at ``~/.config/rc.xsh``. \n+The options set per user override settings in the system-wide control file.\n+\n+Xonsh provides 2 wizards to create your own \"xonshrc\". ``xonfig web`` provides basic settings, and ``xonfig wizard``\n+steps you through all the available options.\n+\n+Xonfig web\n+-----------\n+\n+This helps you choose a color theme, customized prompt and add-in packages (\"xontribs\"). It \n+initializes your personal run control file (usually at ``~/.xonshrc``). To invoke it (from a xonsh prompt):\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonshcon\n+ \n+ >>> xonfig web\n+ Web config started at 'http://localhost:8421'. Hit Crtl+C to stop.\n+ 127.0.0.1 - - [23/Aug/2020 15:04:39] \"GET / HTTP/1.1\" 200 -\n+\n+This will open your default browser on a page served from a local server. You can exit the server by typing ``Ctrl+c`` at any time.\n+\n+The page has:\n+ \n+:Colors: shows the color themes built into Xonsh. \n+ Simply click on a sample to select it. Although color names are standardized across various terminal applications, \n+ their actual appearance is not and do vary widely. Seeing is believing! \n+:Prompts: shows various sample prompts. It is recommended to select one but to then edit \n+ the ``xonshrc`` file to further refine your prompt.\n+:Xontribs: are community-contributed add-ins often used to enhance command completion and line editing, \n+ but can affect any aspect of Xonsh behavior. \n+ Choose one or more to suit your needs but note that they will require installation of additional\n+ packages. You can extend Xonsh by `writing your own xontrib <tutorial_xontrib.html>`_, and are invited/urged to do so!\n+:Save: Click to write the configuration choices to your `~/.xonshrc`. This will add a few tagged lines to your run control file, but will not \n+ overwrite it completely, so you can run `xonfig web` at any time.\n+\n+xonfig wizard\n+--------------\n+\n+This imports settings and tools you have defined in your existing (ordinary) shell such as ``bash``. \n+It also walks you through setting all known environment variables and xontribs \n+in a question-and-answer format:\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonshcon\n+\n+ $ xonfig wizard\n+\n+ Welcome to the xonsh configuration wizard!\n+ ------------------------------------------\n+ This will present a guided tour through setting up the xonsh static\n+ config file. Xonsh will automatically ask you if you want to run this\n+ wizard if the configuration file does not exist. However, you can\n+ always rerun this wizard with the xonfig command:\n+\n+ $ xonfig wizard\n+\n+ This wizard will load an existing configuration, if it is available.\n+ Also never fear when this wizard saves its results! It will create\n+ a backup of any existing configuration automatically.\n+\n+ This wizard has two main phases: foreign shell setup and environment\n+ variable setup. Each phase may be skipped in its entirety.\n+\n+ For the configuration to take effect, you will need to restart xonsh.\n+\n+ '`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'``-.,_,.-*'\n+\n+ To exit the wizard at any time, press Ctrl-C.\n+\n+\n+ '`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'\n+\n+ Foreign Shell Setup\n+ -------------------\n+ The xonsh shell has the ability to interface with foreign shells such\n+ as Bash, or zsh (fish not yet implemented).\n+\n+ For configuration, this means that xonsh can load the environment,\n+ aliases, and functions specified in the config files of these shells.\n+ Naturally, these shells must be available on the system to work.\n+ Being able to share configuration (and source) from foreign shells\n+ makes it easier to transition to and from xonsh.\n+\n+ Add a new foreign shell, yes or no [default: no]? yes\n+ shell name (e.g. bash): bash\n+ interactive shell [bool, default=True]:\n+ login shell [bool, default=False]:\n+ env command [str, default='env']:\n+ alias command [str, default='alias']:\n+ extra command line arguments [list of str, default=[]]:\n+ safely handle exceptions [bool, default=True]:\n+ pre-command [str, default='']:\n+ post-command [str, default='']:\n+ foreign function command [str, default=None]:\n+ source command [str, default=None]: source\n+ Foreign shell added.\n+\n+ Add a new foreign shell, yes or no [default: no]? no\n+\n+ '`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'``-.,_,.-*'\n+\n+ Environment Variable Setup\n+ --------------------------\n+ The xonsh shell also allows you to setup environment variables from\n+ the static configuration file. Any variables set in this way are\n+ superseded by the definitions in the xonshrc or on the command line.\n+ Still, setting environment variables in this way can help define\n+ options that are global to the system or user.\n+\n+ The following lists the environment variable name, its documentation,\n+ the default value, and the current value. The default and current\n+ values are presented as pretty repr strings of their Python types.\n+\n+ Note: Simply hitting enter for any environment variable\n+ will accept the default value for that entry.\n+\n+ Would you like to set env vars now, yes or no [default: no]? yes\n+\n+ $ALLUSERSPROFILE\n+\n+ default value:\n+ current value: 'C:\\\\ProgramData'\n+ >>>\n+\n+ $APPDATA\n+\n+ default value:\n+ current value: 'C:\\\\Users\\\\bobhy\\\\AppData\\\\Roaming'\n+ >>>\n+\n+ $AUTO_CD\n+ Flag to enable changing to a directory by entering the dirname or\n+ full path only (without the cd command).\n+ default value: False\n+ current value: False\n+ >>>\n+\n+ . . .\n+\n+\n+Real world sample xonshrc\n+-------------------------\n+\n+The following is a real-world example of such a file.\n \n :download:`Download xonshrc <xonshrc.xsh>`\n \n@@ -16,12 +163,13 @@ at startup. The following is a real-world example of such a file.\n \n \n Snippets for xonshrc\n-=========================\n-The following are usefull snippets and code that tweaks and adjust xonsh in various ways.\n+--------------------\n+\n+The following are useful snippets and code that tweaks and adjust xonsh in various ways.\n If you have any useful tricks, feel free to share them.\n \n Adjust how git branch label behaves\n--------------------------------------------\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n Xonsh adds a colored branch name to the prompt when working with git or hg repositories.\n This behavior can be controlled with the ``$PROMPT`` environment variable. See how to `customize the prompt`_ .\n The branch name changes color if the work dir is dirty or not. This is controlled by the ``{branch_color}`` formatter string.\n@@ -37,11 +185,11 @@ The following snippet reimplements the formatter also to include untracked files\n else '{BOLD_INTENSE_GREEN}')\n \n \n-.. _customize the prompt: http://xon.sh/tutorial.html#customizing-the-prompt\n+.. _customize the prompt: tutorial.html#customizing-the-prompt\n \n \n Get better colors from the ``ls`` command\n-----------------------------------------------\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n The colors of the ``ls`` command may be hard to read in a dark terminal. If so, this is an excellent addition to the xonshrc file.\n \n .. code-block:: xonshcon\n@@ -49,8 +197,9 @@ The colors of the ``ls`` command may be hard to read in a dark terminal. If so,\n >>> $LS_COLORS='rs=0:di=01;36:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44:ex=01;32:'\n \n Make JSON data directly pastable\n---------------------------------\n-With the following snippet, xonsh will understand JSON data such as ``{ \"name\": \"Tyler\", \"active\": false, \"age\": null }``. Note that, though practical, this is rather hacky and might break other functionality. Use at your own risk.\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+With the following snippet, xonsh will understand JSON data such as ``{ \"name\": \"Tyler\", \"active\": false, \"age\": null }``. \n+Note that, though practical, this is rather hacky and might break other functionality. Use at your own risk.\n \n .. code-block:: xonshcon\n \n@@ -60,7 +209,7 @@ With the following snippet, xonsh will understand JSON data such as ``{ \"name\":\n >>> builtins.null = None\n \n Display different date information every 10th time\n----------------------------------------------------\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n For a compact shell prompts, some people prefer a very condensed time format. But when you have a lengthy shell session you might want the date to show up in your logs every now and then...\n \n .. code-block:: xonshcon\n@@ -77,7 +226,7 @@ For a compact shell prompts, some people prefer a very condensed time format. Bu\n >>> $PROMPT_FIELDS['shelldate'] = get_shelldate\n \n Use the Nix Package manager with Xonsh\n---------------------------------------\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n To users of the `Nix Package Manager <https://www.nixos.org/>`_ these few lines might be life-savers:\n \n .. code-block:: xonshcon\ndiff --git a/news/is_3622.rst b/news/is_3622.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..3c939e8ef7\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/is_3622.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* Setup extras tag '[full]' to install prompt-toolkit and pygments in one fell swoop.\n+ Full feature install can be ``pip install xonsh[full]``.\n+\n+**Changed:**\n+\n+* Rewrote Installation and Configuration sections of Getting Started doc \n+ to clarify install from packages, and generally improve flow.\n+\n+**Deprecated:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Removed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* RST code-block:: xonshcon now works.\n+\n+**Security:**\n+\n+* <news item>\ndiff --git a/setup.cfg b/setup.cfg\nindex 6d97666733..ea607a14aa 100644\n--- a/setup.cfg\n+++ b/setup.cfg\n@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ exclude =\n .vscode/,\n feedstock,\n rever,\n- .venv,\n+ .venv*/,\n # remove later\n pygments_cache.py\n # lint nits that are acceptable in Xonsh project:\ndiff --git a/setup.py b/setup.py\nindex 6861e72172..a2e2dc535a 100755\n--- a/setup.py\n+++ b/setup.py\n@@ -412,6 +412,7 @@ def main():\n \"linux\": [\"distro\"],\n \"proctitle\": [\"setproctitle\"],\n \"zipapp\": ['importlib_resources; python_version < \"3.7\"'],\n+ \"full\" : [\"ptk\", \"pygments\", \"distro\"]\n }\n skw[\"python_requires\"] = \">=3.6\"\n setup(**skw)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,227 @@\n+Platform-specific tips and tricks\n+==================================\n+\n+Linux\n+------\n+\n+Possible conflicts with Bash\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+Depending on how your installation of Bash is configured, Xonsh may have trouble\n+loading certain shell modules. If you see errors similar to this\n+when launching Xonsh:\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_module'\n+ bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_scl'\n+ bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_module'\n+ bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_scl'\n+\n+...You can correct the problem by unsetting the modules, by adding the following\n+lines to your ``~/.bashrc file``:\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ unset module\n+ unset scl\n+\n+\n+Default Ubuntu .bashrc breaks Foreign Shell Functions\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+Xonsh supports importing functions from foreign shells using the\n+`ForeignShellFunctionAlias` class, which calls functions as if they were\n+aliases. This is implemented by executing a command that sources the file\n+containing the function definition and then immediately calls the function with\n+any necessary arguments.\n+\n+The default user `~/.bashrc` file in Ubuntu 15.10 has the following snippet at\n+the top, which causes the script to exit immediately if not run interactively.\n+\n+.. code-block:: bash\n+\n+ # If not running interactively, don't do anything\n+ case $- in\n+ *i*) ;;\n+ *) return;;\n+ esac\n+\n+This means that any function you have added to the file after this point will be\n+registered as a xonsh alias but will fail on execution if the \n+shell is not running interactively. Previous versions of\n+Ubuntu have a different test for interactivity at the top of the file that\n+yields the same problem.\n+\n+\n+MacOS, OSX\n+----------\n+\n+readline\n+^^^^^^^^\n+\n+[ed note: This recommendation seems to be `out of date <https://pypi.org/project/gnureadline/>`_. \n+It's retained in the current docs in case you have an older version of Python or MacOS. But if \n+you have Mac platform experience and can clarify, please open an issue or even a PR to correct the documentation.]\n+\n+On macOS, it is *strongly* recommended to install the ``gnureadline`` library if using the readline shell. ``gnureadline`` can be installed via pip:\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ pip3 install gnureadline\n+\n+Path Helper\n+^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+macOS provides a `path helper\n+<http://www.softec.lu/site/DevelopersCorner/MasteringThePathHelper>`_,\n+which by default configures paths in bash and other POSIX or C shells. Without\n+including these paths, common tools including those installed by Homebrew\n+may be unavailable. See ``/etc/profile`` for details on how it is done.\n+To ensure the path helper is invoked on xonsh (for all users), add the\n+following to ``/etc/xonshrc``::\n+\n+ source-bash $(/usr/libexec/path_helper -s)\n+\n+To incorporate the whole functionality of ``/etc/profile``::\n+\n+ source-bash --seterrprevcmd \"\" /etc/profile\n+\n+\n+\n+Tab completion\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+Xonsh has support for using bash completion files on the shell, to use it you need to install \n+the bash-completion package. \n+The regular bash-completion package uses v1 which mostly works, but `occasionally has rough edges <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/issues/2111>`_ so we recommend using bash-completion v2.\n+\n+Bash completion comes from <https://github.com/scop/bash-completion> which suggests you use a package manager to install it, this manager will also install a new version of bash without affecting /bin/bash. Xonsh also needs to be told where the bash shell file that builds the completions is, this has to be added to $BASH_COMPLETIONS. The package includes completions for many Unix commands.\n+\n+Common packaging systems for MacOs include",
"line": null,
"original_line": 104,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "docs/platform-issues.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nconsistent spelling of macOS"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@\n+Via Package Manager\n+===================\n+\n+You can install xonsh using ``conda``, ``pip`` or the package manager for \n+your operating system distribution.\n+\n+For the fullest interactive user experience, these additional packages should also be installed:\n+\n+ :prompt-toolkit: for command completion, configurable key bindings and especially multi-line line editing.\n+ :pygments: for xonsh and python syntax-specific highlighting\n+ :setproctitle: updates process title (in terminal window and process monitor) to match Xonsh arguments.\n+\n+Installing with these packages is the recommended configuration and is documented first. \n+If you are operating in a specialized or restricted environment, you can install just the xonsh package, as \n+described in `fewer prerequisites`_\n+\n+\n+**conda:**\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ $ conda config --add channels conda-forge\n+ $ conda install pygments prompt-toolkit setproctitle xonsh",
"line": null,
"original_line": 23,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "docs/packages.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think the conda-forge package includes those as deps, so this just needs to be `conda install xonsh`"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,227 @@\n+Platform-specific tips and tricks\n+==================================\n+\n+Linux\n+------\n+\n+Possible conflicts with Bash\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+Depending on how your installation of Bash is configured, Xonsh may have trouble\n+loading certain shell modules. If you see errors similar to this\n+when launching Xonsh:\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_module'\n+ bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_scl'\n+ bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_module'\n+ bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file\n+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_scl'\n+\n+...You can correct the problem by unsetting the modules, by adding the following\n+lines to your ``~/.bashrc file``:\n+\n+.. code-block:: console\n+\n+ unset module\n+ unset scl\n+\n+\n+Default Ubuntu .bashrc breaks Foreign Shell Functions\n+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^\n+\n+Xonsh supports importing functions from foreign shells using the\n+`ForeignShellFunctionAlias` class, which calls functions as if they were\n+aliases. This is implemented by executing a command that sources the file\n+containing the function definition and then immediately calls the function with\n+any necessary arguments.\n+\n+The default user `~/.bashrc` file in Ubuntu 15.10 has the following snippet at",
"line": null,
"original_line": 43,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "docs/platform-issues.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\ndouble backticks"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1,13 +1,160 @@\n Run Control File\n =========================\n-Xonsh allows you to have run control files to customize your shell behavior. These are called ``xonshrc`` files.\n+Xonsh allows you to customize your shell behavior with run control files, called \"xonshrc\" files. \n+These files are written in the xonsh language (a superset of Python) and are executed exactly once at startup. \n+The control file usually contains:\n \n-The system-wide ``xonshrc`` file controls options that are applied to all users of Xonsh on a given system. You can create this file in ``/etc/xonshrc`` for Linux and OSX and in ``%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\\xonsh\\xonshrc`` on Windows.\n+* Assignment statements setting `environment variables <envvars.html>`_. This includes standard OS environment variables that affect other programs and many that Xonsh uses for itself.\n+* ``xonfig`` commands to load selected add-ins (\"`xontribs<tutorial_xontrib.html#loading-xontribs>`\")\n+* Xonsh function defintions\n+* `Alias definitions <aliases.html>`_, many of which invoke the above functions with specified arguments.\n \n-Xonsh also allows you to have a run control file in your home directory. It can either be directly in the home directory at ``~/.xonshrc`` or for XDG compliance at ``~/.config/rc.xsh``. The options set in the local ``xonshrc`` only apply to the current user and will override any conflicting settings set in the system-wide control file.\n+The system-wide ``xonshrc`` file controls options that are applied to all users of Xonsh on a given system. \n+You can create this file in ``/etc/xonshrc`` for Linux and OSX and in ``%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\\xonsh\\xonshrc`` on Windows.\n \n-These files are written in the xonsh language, of course. They are executed exactly once\n-at startup. The following is a real-world example of such a file.\n+Xonsh also allows a per-user run control file in your home directory, either\n+directly in the home directory at ``~/.xonshrc`` or, for XDG compliance, at ``~/.config/rc.xsh``. \n+The options set per user override settings in the system-wide control file.\n+\n+Xonsh provides 2 wizards to create your own \"xonshrc\". ``xonfig web`` provides basic settings, and ``xonfig wizard``\n+steps you through all the available options.\n+\n+Xonfig web",
"line": null,
"original_line": 22,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "docs/xonshrc.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nlowercase `x` to be consistent with heading below"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@\n+Xonsh kernel for Jupyter\n+========================\n+\n+[placeholder]",
"line": null,
"original_line": 4,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "docs/jupyter.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis should be filled out or removed"
}
] |
6f549ca6c3c1a684d6362bfe803688012c2c84a3
|
diff --git a/.gitignore b/.gitignore
index 6382119f29..f16d3f9f76 100644
--- a/.gitignore
+++ b/.gitignore
@@ -37,7 +37,8 @@ bin/
/lib/
include/
venv/
-.venv/
+.venv*/
+
# Mac
.DS_Store
diff --git a/docs/appimage.rst b/docs/appimage.rst
index d5bae56fd2..61b5d179b5 100644
--- a/docs/appimage.rst
+++ b/docs/appimage.rst
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-Portable rootless xonsh build on AppImage
-=========================================
+Via AppImage
+=============
`AppImage <https://appimage.org/>`_ is a format for distributing portable software on Linux without needing superuser permissions to install the application. It tries also to allow Linux distribution-agnostic binary software deployment for application developers, also called Upstream packaging.
diff --git a/docs/conf.py b/docs/conf.py
index cd3f917bae..bbe6224321 100644
--- a/docs/conf.py
+++ b/docs/conf.py
@@ -440,5 +440,5 @@ def make_events():
def setup(app):
from xonsh.pyghooks import XonshConsoleLexer
- app.add_lexer("xonshcon", XonshConsoleLexer)
+ app.add_lexer("xonshcon", XonshConsoleLexer())
app.add_css_file("custom.css")
diff --git a/docs/containers.rst b/docs/containers.rst
index 500734f665..fc2c1c2e0c 100644
--- a/docs/containers.rst
+++ b/docs/containers.rst
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
-Containers
-==========
+Run from container
+==================
-xonsh publishes a handful of containers, primarily targeting CI and automation use-cases. All of them are published on `Docker Hub <https://hub.docker.com/u/xonsh>`__.
+Xonsh publishes a handful of containers, primarily targeting CI and automation use cases. All of them are published on `Docker Hub <https://hub.docker.com/u/xonsh>`__.
* ``xonsh/xonsh``: A base container providing basic xonsh
* ``xonsh/interactive``: xonsh with additions for people
diff --git a/docs/customization.rst b/docs/customization.rst
index 89107d2323..47aa2fc322 100644
--- a/docs/customization.rst
+++ b/docs/customization.rst
@@ -234,30 +234,4 @@ variables:
...use xonsh inside Emacs?
----------------------------------
-**Option A: Comint buffer**
-
-You can use xonsh as your `interactive shell in Emacs
-<https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/manual/html_node/emacs/Interactive-Shell.html>`_
-in a Comint buffer. This way you keep all the Emacs editing power
-in the shell, but you loose xonsh's completion feature.
-
-Make sure you install xonsh with readline support and in your
-``.xonshrc`` file define
-
-.. code-block:: xonsh
-
- $SHELL_TYPE = 'readline'
-
-Also, in Emacs set ``explicit-shell-file-name`` to your xonsh executable.
-
-**Option B: Ansi-term buffer**
-
-The second option is to run xonsh in an Ansi-term buffer inside
-Emacs. This way you have to switch modes if you want do Emacs-style
-editing, but you keep xonsh's impressive completion.
-
-For this it is preferred to have xonsh installed with the
-prompt-toolkit. Then you can leave ``$SHELL_TYPE`` at its default.
-
-Emacs will prompt you for the path of the xonsh exeutable when you
-start up ``ansi-term``.
+see `emacs <editors.html>`_.
diff --git a/docs/dependencies.rst b/docs/dependencies.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index c5db3c31af..0000000000
--- a/docs/dependencies.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
-Dependencies
-------------
-Xonsh currently has the following external dependencies,
-
-*Run Time:*
-
- #. Python v3.5+
-
-Pip supports "extra" dependencies in the form of ``xonsh[ptk,linux]``, where
-the list in the brackets identify the optional features
-
-Xonsh currently has the following extras
-
- #. ``ptk``: prompt-toolkit >= 2.0: *advanced readline library, line-editing*
- #. ``pygments``: pygments >=2.2: *syntax-highlighting*
- #. ``proctitle``: setproctitle: *change the title of terminal to reflect the current subprocess*
- #. ``linux``: distro: *linux specific platform information*
- #. ``mac``: gnureadline: *GNU's featureful version of readline*
-
-In addition, xonsh integrates with Jupyter, an in-browser REPL, enabling the use of xonsh in jupyter notebooks
-
-Development Dependencies
-------------------------
-
-If you want to develop xonsh, it is extremely recommended to install the dependencies listed in `requirements/docs.txt <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/blob/master/requirements/docs.txt>`_ (to generate documentation) and `requirements/tests.txt <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/blob/master/requirements/tests.txt>`_ (to run the test suite).
diff --git a/docs/editors.rst b/docs/editors.rst
index b5a3a03d08..81df39d373 100644
--- a/docs/editors.rst
+++ b/docs/editors.rst
@@ -9,6 +9,9 @@ Editor Support
Emacs
=====
+Emacs Xonsh mode
+----------------
+
There is an emacs mode for editing xonsh scripts available from the
`MELPA repository`_. If you are not familiar see the installation
instructions there.
@@ -21,3 +24,34 @@ Then just add this line to your emacs configuration file:
.. _MELPA repository: https://melpa.org/#/xonsh-mode
+
+
+Xonsh Comint buffer
+-------------------
+
+You can use xonsh as your `interactive shell in Emacs
+<https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/manual/html_node/emacs/Interactive-Shell.html>`_
+in a Comint buffer. This way you keep all the Emacs editing power
+in the shell, but you loose xonsh's completion feature.
+
+Make sure you install xonsh with readline support and in your
+``.xonshrc`` file define
+
+.. code-block:: xonsh
+
+ $SHELL_TYPE = 'readline'
+
+Also, in Emacs set ``explicit-shell-file-name`` to your xonsh executable.
+
+Xonsh Ansi-term buffer
+----------------------
+
+The second option is to run xonsh in an Ansi-term buffer inside
+Emacs. This way you have to switch modes if you want do Emacs-style
+editing, but you keep xonsh's impressive completion.
+
+For this it is preferred to have xonsh installed with the
+prompt-toolkit. Then you can leave ``$SHELL_TYPE`` at its default.
+
+Emacs will prompt you for the path of the xonsh exeutable when you
+start up ``ansi-term``.
diff --git a/docs/installation.rst b/docs/installation.rst
index db2af10a4e..55360c1757 100644
--- a/docs/installation.rst
+++ b/docs/installation.rst
@@ -1,20 +1,36 @@
-Getting Started
-===============
-
-.. include:: dependencies.rst
+Installation
+============
+Prerequisites
+-------------
+* python V3.6 or later.
+* for interactive use, an ansi (vt100-compatible) terminal application. On Windows 10, the
+ separately-installable `Windows Terminal app <https://github.com/microsoft/terminal/releases>`_
+ is recommended.
+
Installation
------------
+Xonsh can be installed via package manager, via appimage or just run from a pre-built container:
.. toctree::
:titlesonly:
:maxdepth: 2
- linux
- osx
- windows
+ packages
appimage
containers
- customization
editors
+
+Configuration and Customization
+================================
+
+Xonsh uses startup configuration files and provides configuration wizards to help you set them up.
+
+.. toctree::
+ :titlesonly:
+ :maxdepth: 2
+
+ xonshrc
+ customization
+ platform-issues
diff --git a/docs/jupyter.rst b/docs/jupyter.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4883e7c3b8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/jupyter.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+Xonsh kernel for Jupyter
+========================
+
+Xonsh provides a kernel for Jupyter Notebook and Lab so you can execute xonsh commands in a notbook cell without any additional magic.
+
+Installation
+-------------
+
+[ed note: this is a stub and the topic is excluded from docs
+till I or someone can get a consistent install procedure to work!]
+
diff --git a/docs/linux.rst b/docs/linux.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 14a8c18ac5..0000000000
--- a/docs/linux.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,123 +0,0 @@
-==========================
-Linux Guide
-==========================
-
-Installation
-============
-
-You can install xonsh using ``conda``, ``pip``, or from source.
-
-**conda:**
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ conda config --add channels conda-forge
- $ conda install xonsh
-
-
-**pip:**
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ pip install xonsh
-
-
-**source:** Download the source `from github <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh>`_
-(`zip file <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/archive/master.zip>`_), then run
-the following from the source directory,
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ pip install .
-
-
-Debian/Ubuntu users can install xonsh from the repository with:
-
-**apt:**
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ apt install xonsh
-
-
-Xonsh is available on bionic bever (version 0.6.0) and artful aardvark
-(version 0.5.12).
-
-Fedora users can install xonsh from the repository with:
-
-**dnf:**
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ dnf install xonsh
-
-
-Arch Linux users can install xonsh from the official community repository with:
-
-**pacman:**
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ pacman -S xonsh
-
-Note that some of these may require ``sudo``.
-If you run into any problems, please let us know!
-
-.. include:: dependencies.rst
-
-Customization
-=============
-
-See the `xonsh customization guide <customization.html>`_ for more details on setting up ``xonsh``!
-
-
-Possible conflicts with Bash
-============================
-
-Depending on how your installation of Bash is configured, Xonsh may have trouble
-loading certain shell modules. Particularly if you see errors similar to this
-when launching Xonsh:
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file
- bash: error importing function definition for `BASH_FUNC_module'
- bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file
- bash: error importing function definition for `BASH_FUNC_scl'
- bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file
- bash: error importing function definition for `BASH_FUNC_module'
- bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file
- bash: error importing function definition for `BASH_FUNC_scl'
-
-...You can correct the problem by unsetting the modules, by adding the following
-lines to your ``~/.bashrc file``:
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- unset module
- unset scl
-
-
-Default Ubuntu .bashrc breaks Foreign Shell Functions
-=====================================================
-Xonsh supports importing functions from foreign shells using the
-`ForeignShellFunctionAlias` class, which calls functions as if they were
-aliases. This is implemented by executing a command that sources the file
-containing the function definition and then immediately calls the function with
-any necessary arguments.
-
-The default user `~/.bashrc` file in Ubuntu 15.10 has the following snippet at
-the top, which causes the script to exit immediately if not run interactively.
-
-.. code-block:: bash
-
- # If not running interactively, don't do anything
- case $- in
- *i*) ;;
- *) return;;
- esac
-
-This means that any function you have added to the file after this point will be
-registered as a xonsh alias but will fail on execution. Previous versions of
-Ubuntu have a different test for interactivity at the top of the file that
-yields the same problem.
diff --git a/docs/osx.rst b/docs/osx.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index f0a98a0d30..0000000000
--- a/docs/osx.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,114 +0,0 @@
-==========================
-OSX Guide
-==========================
-
-Installation
-============
-
-You can install xonsh using a package manager including homebrew, macports, conda, pip, or from source.
-
-**homebrew:**
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ brew install xonsh
-
-
-**MacPorts:**
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ sudo port install xonsh
-
-**conda:**
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ conda config --add channels conda-forge
- $ conda install xonsh
-
-
-**pip:**
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ pip3 install xonsh
-
-
-**source:** Download the source `from github <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh>`_
-(`zip file <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/archive/master.zip>`_), then run
-the following from the source directory,
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ pip3 install xonsh
-
-Extras for macOS
-==================
-readline
---------
-
-On macOS, it is *strongly* recommended to install the ``gnureadline`` library if using the readline shell. ``gnureadline`` can be installed via pip:
-
-.. code-block:: console
-
- $ pip3 install gnureadline
-
-Path Helper
------------
-
-macOS provides a `path helper
-<http://www.softec.lu/site/DevelopersCorner/MasteringThePathHelper>`_,
-which by default configures paths in bash and other POSIX or C shells. Without
-including these paths, common tools including those installed by Homebrew
-may be unavailable. See ``/etc/profile`` for details on how it is done.
-To ensure the path helper is invoked on xonsh (for all users), add the
-following to ``/etc/xonshrc``::
-
- source-bash $(/usr/libexec/path_helper -s)
-
-To incorporate the whole functionality of ``/etc/profile``::
-
- source-bash --seterrprevcmd "" /etc/profile
-
-
-
-Tab completion
---------------
-Xonsh has support for using bash completion files on the shell, to use it you need to install the bash-completion package. The regular bash-completion package uses v1 which mostly works, but `occasionally has rough edges <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/issues/2111>`_ so we recommend using bash-completion v2.
-
-Bash completion comes from <https://github.com/scop/bash-completion> which suggests you use a package manager to install it, this manager will also install a new version of bash without affecting /bin/bash. Xonsh also needs to be told where the bash shell file that builds the completions is, this has to be added to $BASH_COMPLETIONS. The package includes completions for many Unix commands.
-
-Common packaging systems for MacOs include
-
- - Homebrew where the bash-completion2 package needs to be installed.
-
- .. code-block:: console
-
- $ brew install bash-completion2
-
- This will install the bash_completion file in `/usr/local/share/bash-completion/bash_completion` which is in the current xonsh code and so should just work.
-
- - `MacPorts <https://trac.macports.org/wiki/howto/bash-completion>`_ where the bash-completion port needs to be installed.
-
- .. code-block:: console
-
- $ sudo port install bash-completion
-
-
-
- This includes a bash_completion file that needs to be added to the environment.
-
- .. code-block:: console
-
- $ $BASH_COMPLETIONS.insert(0, '/opt/local/share/bash-completion/bash_completion')
-
-Note that the `bash completion project page <https://github.com/scop/bash-completion>`_ gives the script to be called as in .../profile.d/bash_completion.sh which will the call the script mentioned above and one in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME . Currently xonsh seems only to be able to read the first script directly.
-
-
-.. include:: dependencies.rst
-
-Customization
-=============
-
-See the `xonsh customization guide <customization.html>`_ for more details on setting up ``xonsh``!
diff --git a/docs/packages.rst b/docs/packages.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0fa6d00e9f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/packages.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+Via Package Manager
+===================
+
+You can install xonsh using ``conda``, ``pip`` or the package manager for
+your operating system distribution.
+
+For the fullest interactive user experience, these additional packages should also be installed:
+
+ :prompt-toolkit: for command completion, configurable key bindings and especially multi-line line editing.
+ :pygments: for xonsh and Python syntax-specific highlighting
+ :setproctitle: updates process title (in terminal window and process monitor) to match Xonsh arguments.
+
+Installing with these packages is the recommended configuration and is documented first.
+If you are operating in a specialized or restricted environment, you can install just the xonsh package, as
+described in `fewer prerequisites`_
+
+
+**conda:**
+
+.. code-block:: console
+
+ $ conda config --add channels conda-forge
+ $ conda install xonsh
+
+
+**pip:** Typically you will activate a virtual environment and install xonsh there. This will ensure that you invoke the
+correct Python interpreter and ``pip`` module.
+
+.. code-block:: console
+
+ $ pip install xonsh[full]
+
+This uses the pip 'extras' syntax, and is equivalent to:
+
+.. code-block:: console
+
+ $ pip install pygments prompt-toolkit setproctitle xonsh
+
+The above ``pip`` commands may have to be spelled ``pip3`` or ``sudo pip3`` if you are not installing in a virtual environment.
+
+**source:** Pip can also install the most recent xonsh source code from the
+`xonsh project repository <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh>`_.
+
+.. code-block:: console
+
+ $ pip install pygments prompt-toolkit setproctitle https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/archive/master.zip
+
+Spelling of ``pip`` command may likewise have to be amended as noted above.
+
+**platform package managers**
+Various operating system distributions have platform-specific package managers which may offer a xonsh package.
+This may not be the most current version of xonsh, but it should have been tested for stability on that platform
+by the distribution managers.
+
+
+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+---------------------+
+ | OS or distribution | command | Package(s) |
+ +===========================+=============================+=====================+
+ | Debian/Ubuntu | ``$ [sudo] apt install`` | |
+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+ pygments |
+ | Fedora | ``$ [sudo] dnf install`` | prompt-toolkit |
+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+ setproctitle |
+ | Arch Linux | ``$ [sudo] pacman -S`` | xonsh |
+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+ |
+ | OSX | ``$ [sudo] brew install`` | |
+ +---------------------------+-----------------------------+---------------------+
+
+
+If you run into any problems, please let us know!
+
+Fewer Prerequisites
+--------------------
+
+A design goal of Xonsh is to run in any environment that supports a (supported) Python interpreter, you
+can install just the ``xonsh`` package (using any package manager).
+
+.. code-block:: console
+
+ pip install xonsh
+
+When it starts up, if xonsh does not find ``pygments`` or ``setproctitle`` packages, it simply does not colorize
+or highlight syntax or set process title, respectively.
+
+If it does not find ``prompt-toolkit`` package, it will
+use the Python ``readline`` module (which reads configuration file ``.inputrc`` in a manner compatible with ``GNU readline``).
+To ensure xonsh uses ``readline`` even if ``prompt-toolkit`` is installed, configure this in your
+``.xonshrc`` file:
+
+.. code-block:: xonsh
+
+ $SHELL_TYPE = 'readline'
+
diff --git a/docs/platform-issues.rst b/docs/platform-issues.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d3e0bbe342
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/platform-issues.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,266 @@
+Platform-specific tips and tricks
+==================================
+
+Linux
+------
+
+Possible conflicts with Bash
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+
+Depending on how your installation of Bash is configured, Xonsh may have trouble
+loading certain shell modules. If you see errors similar to this
+when launching Xonsh:
+
+.. code-block:: console
+
+ bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file
+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_module'
+ bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file
+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_scl'
+ bash: module: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file
+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_module'
+ bash: scl: line 1: syntax error: unexpected end of file
+ bash: error importing function definition for 'BASH_FUNC_scl'
+
+...You can correct the problem by unsetting the modules, by adding the following
+lines to your ``~/.bashrc file``:
+
+.. code-block:: console
+
+ unset module
+ unset scl
+
+
+Default Ubuntu .bashrc breaks Foreign Shell Functions
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+
+Xonsh supports importing functions from foreign shells using the
+`ForeignShellFunctionAlias` class, which calls functions as if they were
+aliases. This is implemented by executing a command that sources the file
+containing the function definition and then immediately calls the function with
+any necessary arguments.
+
+The default user ``~/.bashrc`` file in Ubuntu 15.10 has the following snippet at
+the top, which causes the script to exit immediately if not run interactively.
+
+.. code-block:: bash
+
+ # If not running interactively, don't do anything
+ case $- in
+ *i*) ;;
+ *) return;;
+ esac
+
+This means that any function you have added to the file after this point will be
+registered as a xonsh alias but will fail on execution if the
+shell is not running interactively. Previous versions of
+Ubuntu have a different test for interactivity at the top of the file that
+yields the same problem.
+
+
+MacOS, OSX
+----------
+
+readline
+^^^^^^^^
+
+[ed note: This recommendation seems to be `out of date <https://pypi.org/project/gnureadline/>`_.
+It's retained in the current docs in case you have an older version of Python or macOS. But if
+you have Mac platform experience and can clarify, please open an issue or even a PR to correct the documentation.]
+
+On macOS, it is *strongly* recommended to install the ``gnureadline`` library if using the readline shell. ``gnureadline`` can be installed via pip:
+
+.. code-block:: console
+
+ $ pip3 install gnureadline
+
+Path Helper
+^^^^^^^^^^^
+
+macOS provides a `path helper
+<http://www.softec.lu/site/DevelopersCorner/MasteringThePathHelper>`_,
+which by default configures paths in bash and other POSIX or C shells. Without
+including these paths, common tools including those installed by Homebrew
+may be unavailable. See ``/etc/profile`` for details on how it is done.
+To ensure the path helper is invoked on xonsh (for all users), add the
+following to ``/etc/xonshrc``:
+
+.. code-block:: xonshcon
+
+ source-bash $(/usr/libexec/path_helper -s)
+
+To incorporate the whole functionality of ``/etc/profile``:
+
+.. code-block:: xonshcon
+
+ source-bash --seterrprevcmd "" /etc/profile
+
+
+
+Tab completion
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+Xonsh has support for using bash completion files on the shell, to use it you need to install
+the bash-completion package.
+The regular bash-completion package uses v1 which mostly works, but `occasionally has rough edges <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/issues/2111>`_ so we recommend using bash-completion v2.
+
+Bash completion comes from <https://github.com/scop/bash-completion> which suggests you use a package manager to install it, this manager will also install a new version of bash without affecting /bin/bash. Xonsh also needs to be told where the bash shell file that builds the completions is, this has to be added to $BASH_COMPLETIONS. The package includes completions for many Unix commands.
+
+Common packaging systems for macOS include
+
+ - Homebrew where the bash-completion2 package needs to be installed.
+
+ .. code-block:: console
+
+ $ brew install bash-completion2
+
+ This will install the bash_completion file in `/usr/local/share/bash-completion/bash_completion` which is in the current xonsh code and so should just work.
+
+ - `MacPorts <https://trac.macports.org/wiki/howto/bash-completion>`_ where the bash-completion port needs to be installed.
+
+ .. code-block:: console
+
+ $ sudo port install bash-completion
+
+
+
+ This includes a bash_completion file that needs to be added to the environment.
+
+ .. code-block:: console
+
+ $ $BASH_COMPLETIONS.insert(0, '/opt/local/share/bash-completion/bash_completion')
+
+Note that the `bash completion project page <https://github.com/scop/bash-completion>`_ gives the script to be called as in .../profile.d/bash_completion.sh which will the call the script mentioned above and one in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME . Currently xonsh seems only to be able to read the first script directly.
+
+
+Windows
+-------
+
+Windows Terminal
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+
+If you are running a supported version of Windows (which is now Windows 10, version 2004 or later),
+we recommend the Windows Terminal (``wt.exe``) rather than the time-honored ``cmd.exe``. This provides
+unicode rendering, better ansi terminal compatibility and all the conveniences you expect
+from the terminal application in other platforms.
+
+You can install it from the `Microsoft Store <https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/p/windows-terminal/9n0dx20hk701>`_
+or from `Github <https://github.com/microsoft/terminal>`_.
+
+By default Windows Terminal runs Powershell, but you can add a profile tab to run Xonsh and even configure it
+to open automatically in xonsh. Here is a sample settings.json:
+
+.. code-block::
+
+ {
+ "$schema": "https://aka.ms/terminal-profiles-schema",
+
+ "defaultProfile": "{61c54bbd-c2c6-5271-96e7-009a87ff44bf}",
+
+ // To learn more about global settings, visit https://aka.ms/terminal-global-settings
+ // To learn more about profiles, visit https://aka.ms/terminal-profile-settings
+ "profiles":
+ {
+ "defaults":
+ {
+ // Put settings here that you want to apply to all profiles.
+ },
+ "list":
+ [
+ {
+ // Guid from https://guidgen.com
+ "guid": "{02639f1c-9437-4b34-a383-2df49b5ed5c5}",
+ "name": "Xonsh",
+ "commandline": "c:\\users\\bobhy\\src\\xonsh\\.venv\\scripts\\xonsh.exe",
+ "hidden": false
+ },
+ {
+ // Make changes here to the powershell.exe profile.
+ "guid": "{61c54bbd-c2c6-5271-96e7-009a87ff44bf}",
+ "name": "Windows PowerShell",
+ "commandline": "powershell.exe",
+ "hidden": false
+ }
+ ]
+ },
+
+ . . .
+
+
+Nice colors
+^^^^^^^^^^^
+
+The dark red and blue colors are completely unreadable in `cmd.exe`.
+
+.. image:: _static/intensify-colors-on-win-false.png
+ :width: 396 px
+ :alt: intensify-colors-win-false
+ :align: center
+
+Xonsh has some tricks to fix colors. This is controlled by the
+:ref:`$INTENSIFY_COLORS_ON_WIN <intensify_colors_on_win>`
+environment variable which is ``True`` by default.
+
+
+:ref:`$INTENSIFY_COLORS_ON_WIN <intensify_colors_on_win>` has the following effect:b
+
+On Windows 10:
+ Windows 10 supports true color in the terminal, so on Windows 10 Xonsh will use
+ a style with hard coded colors instead of the terminal colors.
+
+On older Windows:
+ Xonsh replaces some of the unreadable dark colors with more readable
+ alternatives (e.g. blue becomes cyan).
+
+
+Avoid locking the working directory
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+
+Python (like other processes on Windows) locks the current working directory so
+it can't be deleted or renamed. ``cmd.exe`` has this behaviour as well, but it
+is quite annoying for a shell.
+
+The :ref:`free_cwd <free_cwd>` xontrib (add-on) for xonsh solves some of this problem. It
+works by hooking the prompt to reset the current working directory to the root
+drive folder whenever the shell is idle. It only works with the prompt-toolkit
+back-end. To enable that behaviour run the following:
+
+Add this line to your ``~/.xonshrc`` file to have it always enabled.
+
+.. code-block:: xonshcon
+
+ >>> xontrib load free_cwd
+
+
+Name space conflicts
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+
+Due to ambiguity with the Python ``dir`` builtin, to list the current directory
+you must explicitly request the ``.``, like this:
+
+.. code-block:: xonshcon
+
+ >>> dir .
+ Volume in drive C is Windows
+ Volume Serial Number is 30E8-8B86
+
+ Directory of C:\Users\snail\xonsh
+
+ 2015-05-12 03:04 <DIR> .
+ 2015-05-12 03:04 <DIR> ..
+ 2015-05-01 01:31 <DIR> xonsh
+ 0 File(s) 0 bytes
+ 3 Dir(s) 11,008,000,000 bytes free
+
+
+
+Many people create a ``d`` alias for the ``dir`` command to save
+typing and avoid the ambiguity altogether:
+
+.. code-block:: xonshcon
+
+ >>> aliases['d'] = ['cmd', '/c', 'dir']
+
+You can add aliases to your ``~/.xonshrc`` to have it always
+available when xonsh starts.
+
+
diff --git a/docs/tutorial.rst b/docs/tutorial.rst
index b18af1bd01..67a3eb1dfc 100644
--- a/docs/tutorial.rst
+++ b/docs/tutorial.rst
@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@
*******************
Tutorial
*******************
+
xonsh is a shell language and command prompt. Unlike other shells, xonsh is
based on Python, with additional syntax added that makes calling subprocess
commands, manipulating the environment, and dealing with the file system
diff --git a/docs/windows.rst b/docs/windows.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 58a6f05b46..0000000000
--- a/docs/windows.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,183 +0,0 @@
-==========================
-Windows Guide
-==========================
-
-Installation
-================
-
-The easy way
-----------------
-
-The easiest way to install xonsh on windows is through the `Anaconda Python
-Distribution <https://www.anaconda.com/download/>`__ and the conda package manager.
-
-.. note::
-
- Xonsh is not supported on legacy Python (2.7).
-
-Install xonsh with the following command:
-
-.. code-block:: bat
-
- > conda config --add channels conda-forge
- > conda install xonsh
-
-This will install xonsh and all the recommended dependencies. Next, run xonsh:
-
-.. code-block:: bat
-
- > xonsh
- snail@home ~ $
-
-
-Install from source
--------------------
-
-To install xonsh from source on Windows, first install `Python v3.4+`_ from
-http://python.org. Remember to select "Add python to PATH" during installation.
-
-Next, install the prompt_toolkit dependency via ``pip``:
-
-.. code-block:: bat
-
- > pip install prompt-toolkit
-
-Download the latest `xonsh-master.zip`_ from github and unzip it
-to ``xonsh-master``.
-
-Now install xonsh:
-
-.. code-block:: bat
-
- > cd xonsh-master
- > pip install .
-
-Next, run xonsh:
-
-.. code-block:: bat
-
- > xonsh
- snail@home ~ $
-
-.. _Python v3.4+: https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/
-.. _xonsh-master.zip: https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/archive/master.zip
-.. _cmder: http://cmder.net/
-.. _conemu: https://conemu.github.io/
-
-
-Tips and Tricks
-================
-
-Nice colors
-----------------------
-
-The dark red and blue colors are completely unreadable in Windows' default
-terminal.
-
-.. image:: _static/intensify-colors-on-win-false.png
- :width: 396 px
- :alt: intensify-colors-win-false
- :align: center
-
-There are ways to `configure the colors`_ of the old terminal, but to give new users the
-best experience Xonsh has some tricks to fix colors. This is controlled by the
-:ref:`$INTENSIFY_COLORS_ON_WIN <intensify_colors_on_win>`
-environment variable which is ``True`` by default.
-
-.. _configure the colors: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/commandline/2017/08/11/introducing-the-windows-console-colortool/
-
-:ref:`$INTENSIFY_COLORS_ON_WIN <intensify_colors_on_win>` has the following effect:b
-
-On Windows 10:
- Windows 10 supports true color in the terminal, so on Windows 10 Xonsh will use
- a style with hard coded colors instead of the terminal colors.
-
-On older Windows:
- Xonsh replaces some of the unreadable dark colors with more readable
- alternatives (e.g. blue becomes cyan).
-
-
-**The new Windows terminal**
-
-The best option on windows is to use the new `Windows Terminal
-<https://github.com/microsoft/terminal>`__ developed by Microsoft as an open
-source project. The new terminal supports has many nice features including
-Unicode rendering.
-
-It is highly recommended and can easily be `installed from the Windows Store`_:
-
-
-.. image:: _static/windows_terminal2.png
- :alt: Unicode support in Windows terminal
- :align: center
-
-
-.. _installed from the Windows Store: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/commandline/2017/08/11/introducing-the-windows-console-colortool/
-
-
-
-Avoid locking the working directory
------------------------------------
-
-Python (like other processes on Windows) locks the current working directory so
-it can't be deleted or renamed. ``cmd.exe`` has this behaviour as well, but it
-is quite annoying for a shell.
-
-The :ref:`free_cwd <free_cwd>` xontrib (add-on) for xonsh solves some of this problem. It
-works by hooking the prompt to reset the current working directory to the root
-drive folder whenever the shell is idle. It only works with the prompt-toolkit
-back-end. To enable that behaviour run the following:
-
-Add this line to your ``~/.xonshrc`` file to have it always enabled.
-
-.. code-block:: xonshcon
-
- >>> xontrib load free_cwd
-
-
-Name space conflicts
---------------------
-
-Due to ambiguity with the Python ``dir`` builtin, to list the current directory
-via the ``cmd.exe`` builtin you must explicitly request the ``.``, like this:
-
-.. code-block:: xonshcon
-
- >>> dir .
- Volume in drive C is Windows
- Volume Serial Number is 30E8-8B86
-
- Directory of C:\Users\snail\xonsh
-
- 2015-05-12 03:04 <DIR> .
- 2015-05-12 03:04 <DIR> ..
- 2015-05-01 01:31 <DIR> xonsh
- 0 File(s) 0 bytes
- 3 Dir(s) 11,008,000,000 bytes free
-
-
-
-Many people create a ``d`` alias for the ``dir`` command to save
-typing and avoid the ambiguity altogether:
-
-.. code-block:: xonshcon
-
- >>> aliases['d'] = ['cmd', '/c', 'dir']
-
-You can add aliases to your ``~/.xonshrc`` to have it always
-available when xonsh starts.
-
-
-
-Unicode support for Windows
-----------------------------
-
-Python's utf-8 unicode is not compatible with the default console "conhost" on Windows.
-
-Luckily, Microsoft is developing a new `Windows terminal <https://github.com/microsoft/terminal>`__ as an open source project. The new terminal supports all the nice features of
-that you find in linux terminals. It is highly recommended and can easily be `installed from the Windows Store`_:
-
-.. image:: _static/windows_terminal.png
- :alt: Unicode support in Windows terminal
- :align: center
-
diff --git a/docs/xonshrc.rst b/docs/xonshrc.rst
index d361db3473..19631fb6a1 100644
--- a/docs/xonshrc.rst
+++ b/docs/xonshrc.rst
@@ -1,13 +1,160 @@
Run Control File
=========================
-Xonsh allows you to have run control files to customize your shell behavior. These are called ``xonshrc`` files.
+Xonsh allows you to customize your shell behavior with run control files, called "xonshrc" files.
+These files are written in the xonsh language (a superset of Python) and are executed exactly once at startup.
+The control file usually contains:
-The system-wide ``xonshrc`` file controls options that are applied to all users of Xonsh on a given system. You can create this file in ``/etc/xonshrc`` for Linux and OSX and in ``%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\xonsh\xonshrc`` on Windows.
+* Assignment statements setting `environment variables <envvars.html>`_. This includes standard OS environment variables that affect other programs and many that Xonsh uses for itself.
+* ``xonfig`` commands to load selected add-ins ("`xontribs<tutorial_xontrib.html#loading-xontribs>`")
+* Xonsh function defintions
+* `Alias definitions <aliases.html>`_, many of which invoke the above functions with specified arguments.
-Xonsh also allows you to have a run control file in your home directory. It can either be directly in the home directory at ``~/.xonshrc`` or for XDG compliance at ``~/.config/rc.xsh``. The options set in the local ``xonshrc`` only apply to the current user and will override any conflicting settings set in the system-wide control file.
+The system-wide ``xonshrc`` file controls options that are applied to all users of Xonsh on a given system.
+You can create this file in ``/etc/xonshrc`` for Linux and OSX and in ``%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\xonsh\xonshrc`` on Windows.
-These files are written in the xonsh language, of course. They are executed exactly once
-at startup. The following is a real-world example of such a file.
+Xonsh also allows a per-user run control file in your home directory, either
+directly in the home directory at ``~/.xonshrc`` or, for XDG compliance, at ``~/.config/rc.xsh``.
+The options set per user override settings in the system-wide control file.
+
+Xonsh provides 2 wizards to create your own "xonshrc". ``xonfig web`` provides basic settings, and ``xonfig wizard``
+steps you through all the available options.
+
+xonfig web
+-----------
+
+This helps you choose a color theme, customized prompt and add-in packages ("xontribs"). It
+initializes your personal run control file (usually at ``~/.xonshrc``). To invoke it (from a xonsh prompt):
+
+.. code-block:: xonshcon
+
+ >>> xonfig web
+ Web config started at 'http://localhost:8421'. Hit Crtl+C to stop.
+ 127.0.0.1 - - [23/Aug/2020 15:04:39] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 -
+
+This will open your default browser on a page served from a local server. You can exit the server by typing ``Ctrl+c`` at any time.
+
+The page has:
+
+:Colors: shows the color themes built into Xonsh.
+ Simply click on a sample to select it. Although color names are standardized across various terminal applications,
+ their actual appearance is not and do vary widely. Seeing is believing!
+:Prompts: shows various sample prompts. It is recommended to select one but to then edit
+ the ``xonshrc`` file to further refine your prompt.
+:Xontribs: are community-contributed add-ins often used to enhance command completion and line editing,
+ but can affect any aspect of Xonsh behavior.
+ Choose one or more to suit your needs but note that they will require installation of additional
+ packages. You can extend Xonsh by `writing your own xontrib <tutorial_xontrib.html>`_, and are invited/urged to do so!
+:Save: Click to write the configuration choices to your ``~/.xonshrc``. This will add a few tagged lines to your run control file, but will not
+ overwrite it completely, so you can run `xonfig web` at any time.
+
+xonfig wizard
+--------------
+
+This imports settings and tools you have defined in your existing (ordinary) shell such as ``bash``.
+It also walks you through setting all known environment variables and xontribs
+in a question-and-answer format:
+
+.. code-block:: xonshcon
+
+ $ xonfig wizard
+
+ Welcome to the xonsh configuration wizard!
+ ------------------------------------------
+ This will present a guided tour through setting up the xonsh static
+ config file. Xonsh will automatically ask you if you want to run this
+ wizard if the configuration file does not exist. However, you can
+ always rerun this wizard with the xonfig command:
+
+ $ xonfig wizard
+
+ This wizard will load an existing configuration, if it is available.
+ Also never fear when this wizard saves its results! It will create
+ a backup of any existing configuration automatically.
+
+ This wizard has two main phases: foreign shell setup and environment
+ variable setup. Each phase may be skipped in its entirety.
+
+ For the configuration to take effect, you will need to restart xonsh.
+
+ '`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'``-.,_,.-*'
+
+ To exit the wizard at any time, press Ctrl-C.
+
+
+ '`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'
+
+ Foreign Shell Setup
+ -------------------
+ The xonsh shell has the ability to interface with foreign shells such
+ as Bash, or zsh (fish not yet implemented).
+
+ For configuration, this means that xonsh can load the environment,
+ aliases, and functions specified in the config files of these shells.
+ Naturally, these shells must be available on the system to work.
+ Being able to share configuration (and source) from foreign shells
+ makes it easier to transition to and from xonsh.
+
+ Add a new foreign shell, yes or no [default: no]? yes
+ shell name (e.g. bash): bash
+ interactive shell [bool, default=True]:
+ login shell [bool, default=False]:
+ env command [str, default='env']:
+ alias command [str, default='alias']:
+ extra command line arguments [list of str, default=[]]:
+ safely handle exceptions [bool, default=True]:
+ pre-command [str, default='']:
+ post-command [str, default='']:
+ foreign function command [str, default=None]:
+ source command [str, default=None]: source
+ Foreign shell added.
+
+ Add a new foreign shell, yes or no [default: no]? no
+
+ '`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'`-.,_,.-*'``-.,_,.-*'
+
+ Environment Variable Setup
+ --------------------------
+ The xonsh shell also allows you to setup environment variables from
+ the static configuration file. Any variables set in this way are
+ superseded by the definitions in the xonshrc or on the command line.
+ Still, setting environment variables in this way can help define
+ options that are global to the system or user.
+
+ The following lists the environment variable name, its documentation,
+ the default value, and the current value. The default and current
+ values are presented as pretty repr strings of their Python types.
+
+ Note: Simply hitting enter for any environment variable
+ will accept the default value for that entry.
+
+ Would you like to set env vars now, yes or no [default: no]? yes
+
+ $ALLUSERSPROFILE
+
+ default value:
+ current value: 'C:\\ProgramData'
+ >>>
+
+ $APPDATA
+
+ default value:
+ current value: 'C:\\Users\\bobhy\\AppData\\Roaming'
+ >>>
+
+ $AUTO_CD
+ Flag to enable changing to a directory by entering the dirname or
+ full path only (without the cd command).
+ default value: False
+ current value: False
+ >>>
+
+ . . .
+
+
+Real world sample xonshrc
+-------------------------
+
+The following is a real-world example of such a file.
:download:`Download xonshrc <xonshrc.xsh>`
@@ -16,12 +163,13 @@ at startup. The following is a real-world example of such a file.
Snippets for xonshrc
-=========================
-The following are usefull snippets and code that tweaks and adjust xonsh in various ways.
+--------------------
+
+The following are useful snippets and code that tweaks and adjust xonsh in various ways.
If you have any useful tricks, feel free to share them.
Adjust how git branch label behaves
--------------------------------------------
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
Xonsh adds a colored branch name to the prompt when working with git or hg repositories.
This behavior can be controlled with the ``$PROMPT`` environment variable. See how to `customize the prompt`_ .
The branch name changes color if the work dir is dirty or not. This is controlled by the ``{branch_color}`` formatter string.
@@ -37,11 +185,11 @@ The following snippet reimplements the formatter also to include untracked files
else '{BOLD_INTENSE_GREEN}')
-.. _customize the prompt: http://xon.sh/tutorial.html#customizing-the-prompt
+.. _customize the prompt: tutorial.html#customizing-the-prompt
Get better colors from the ``ls`` command
-----------------------------------------------
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
The colors of the ``ls`` command may be hard to read in a dark terminal. If so, this is an excellent addition to the xonshrc file.
.. code-block:: xonshcon
@@ -49,8 +197,9 @@ The colors of the ``ls`` command may be hard to read in a dark terminal. If so,
>>> $LS_COLORS='rs=0:di=01;36:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44:ex=01;32:'
Make JSON data directly pastable
---------------------------------
-With the following snippet, xonsh will understand JSON data such as ``{ "name": "Tyler", "active": false, "age": null }``. Note that, though practical, this is rather hacky and might break other functionality. Use at your own risk.
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+With the following snippet, xonsh will understand JSON data such as ``{ "name": "Tyler", "active": false, "age": null }``.
+Note that, though practical, this is rather hacky and might break other functionality. Use at your own risk.
.. code-block:: xonshcon
@@ -60,7 +209,7 @@ With the following snippet, xonsh will understand JSON data such as ``{ "name":
>>> builtins.null = None
Display different date information every 10th time
----------------------------------------------------
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
For a compact shell prompts, some people prefer a very condensed time format. But when you have a lengthy shell session you might want the date to show up in your logs every now and then...
.. code-block:: xonshcon
@@ -77,7 +226,7 @@ For a compact shell prompts, some people prefer a very condensed time format. Bu
>>> $PROMPT_FIELDS['shelldate'] = get_shelldate
Use the Nix Package manager with Xonsh
---------------------------------------
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
To users of the `Nix Package Manager <https://www.nixos.org/>`_ these few lines might be life-savers:
.. code-block:: xonshcon
diff --git a/news/is_3622.rst b/news/is_3622.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3c939e8ef7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/is_3622.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+**Added:**
+
+* Setup extras tag '[full]' to install prompt-toolkit and pygments in one fell swoop.
+ Full feature install can be ``pip install xonsh[full]``.
+
+**Changed:**
+
+* Rewrote Installation and Configuration sections of Getting Started doc
+ to clarify install from packages, and generally improve flow.
+
+**Deprecated:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Removed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* RST code-block:: xonshcon now works.
+
+**Security:**
+
+* <news item>
diff --git a/setup.cfg b/setup.cfg
index 6d97666733..ea607a14aa 100644
--- a/setup.cfg
+++ b/setup.cfg
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ exclude =
.vscode/,
feedstock,
rever,
- .venv,
+ .venv*/,
# remove later
pygments_cache.py
# lint nits that are acceptable in Xonsh project:
diff --git a/setup.py b/setup.py
index 6861e72172..a2e2dc535a 100755
--- a/setup.py
+++ b/setup.py
@@ -412,6 +412,7 @@ def main():
"linux": ["distro"],
"proctitle": ["setproctitle"],
"zipapp": ['importlib_resources; python_version < "3.7"'],
+ "full" : ["ptk", "pygments", "distro"]
}
skw["python_requires"] = ">=3.6"
setup(**skw)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Dependency Updates & Env Compatibility"
}
|
sympy__sympy-22211@6704d77
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 22,211
|
Fix handling of zoo in evalf
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #8242
Fixes #21147
Closes #21183
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Fix by allowing `evalf`s to return `zoo` in addition to mpf value tuple, as there's no equivalent mpc representation in mpmath. Check this return value in each `evalf`s and handle it.
#### Other comments
Some additional logics are added to `equals` and `is_constant` in order to fix newly broken tests. One case is leaving unfixed, which imho is acceptable because it’s a bit complicated and previously based on wrong evalf intermediate result.
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* core
* Evaluation of expressions involving zoo is now handled properly in evalf without raising obscure exceptions.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-10-03T04:54:09Z
|
(1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0}) produces 0
Here's how it looks like:
``` python
In [1]: sp.__version__
Out[1]: '0.7.5-git'
In [2]: x = sp.abc.x
In [3]: (1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0})
Out[3]: 0
In [4]: (1/x).subs({x: 0})
Out[4]: zoo
In [5]: (1/x).xreplace({x: 0})
Out[5]: zoo
```
I did investigate it some time ago and, AFAIR, it happens in `Pow` evaluation that short-circuits to 0 whenever the base is 0 while it should return infs if the exponent is negative.
Evalf and evaluate=False issues
`Mul(2, Pow(0,-1, evaluate=False), evaluate=False).evalf()` returns 0 instead of complex infinity.
|
Another interesting and related issue: while
``` python
In [3]: x = Symbol('x', real=True)
In [4]: (1/x).subs({x: 0.})
Out[4]: +inf
In [5]: (1/x).xreplace({x: 0.})
Out[5]: +inf
```
the following
``` python
(1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0.})
```
raises
``` pytb
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-6-226388149257>", line 1, in <module>
(1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0.})
File "sympy/core/evalf.py", line 1326, in evalf
result = evalf(self, prec + 4, options)
File "sympy/core/evalf.py", line 1220, in evalf
r = rf(x, prec, options)
File "sympy/core/evalf.py", line 622, in evalf_pow
return mpf_pow_int(re, p, target_prec), None, target_prec, None
File "sympy/mpmath/libmp/libmpf.py", line 1044, in mpf_pow_int
if n == -1: return mpf_div(fone, s, prec, rnd)
File "sympy/mpmath/libmp/libmpf.py", line 934, in mpf_div
raise ZeroDivisionError
ZeroDivisionError
```
Valid for sympy-1.0 and sympy-1.1-58-gd250ff0, too, as noted in #12904. There are many related issues:
#10662
#9807
#7867
#7192
#6974
I get these results
```
>>> (x*y).n(subs={y:0})
0
>>> log(x).evalf(subs={x: 0})
zoo
>>> (x-1).evalf(subs={x:1})
0.e-125
>>> (x**I).evalf(subs={x:0})
nan
```
with these mods (which are suggestive as to where the problem lies)
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/core/evalf.py b/sympy/core/evalf.py
index c794656..233bbe5 100644
--- a/sympy/core/evalf.py
+++ b/sympy/core/evalf.py
@@ -821,6 +821,8 @@ def evalf_log(expr, prec, options):
imaginary_term = (mpf_cmp(xre, fzero) < 0)
+ if xre == (0,)*4:
+ return S.ComplexInfinity
re = mpf_log(mpf_abs(xre), prec, rnd)
size = fastlog(re)
if prec - size > workprec and re != fzero:
@@ -1284,13 +1286,25 @@ def evalf(x, prec, options):
try:
rf = evalf_table[x.func]
r = rf(x, prec, options)
- except KeyError:
+ if r is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return r
+ if x and r[0] == r[1] == None:
+ assert not 'subs' in options
+ except (KeyError, AssertionError):
try:
# Fall back to ordinary evalf if possible
if 'subs' in options:
x = x.subs(evalf_subs(prec, options['subs']))
- xe = x._eval_evalf(prec)
- re, im = xe.as_real_imag()
+ if x is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return x
+ if x:
+ if not x.is_number:
+ return (None,)*4
+ x = evalf(x, prec, options)
+ xe = x._eval_evalf(prec)
+ re, im = xe.as_real_imag()
+ else:
+ return (0, 0, 0, 0), None, None, None
if re.has(re_) or im.has(im_):
raise NotImplementedError
if re == 0:
@@ -1306,6 +1320,8 @@ def evalf(x, prec, options):
im = im._to_mpmath(prec, allow_ints=False)._mpf_
imprec = prec
r = re, im, reprec, imprec
+ if re == im == None:
+ return (0, 0, 0, 0), None, None, None
except AttributeError:
raise NotImplementedError
if options.get("verbose"):
@@ -1392,6 +1408,8 @@ def evalf(self, n=15, subs=None, maxn=100, chop=False, strict=False, quad=None,
options['quad'] = quad
try:
result = evalf(self, prec + 4, options)
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return result
except NotImplementedError:
# Fall back to the ordinary evalf
v = self._eval_evalf(prec)
```
Whoever tackles this beware: there is the `evalf` method and the `evalf` function (which references the `evalf_table` (of special evalf functions) and the `_eval_evalf` method. This is not a beginner's issue...unless you are a special beginner!
I believe the problem is [here](https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/b42c1c6645cc1b0d8e8a6c9c9e86c6979ef2c76d/sympy/core/evalf.py#L673). `evalf_pow` assumes that 0 to an integer power is 0 (`None`s represent exact zeros). But this is only true if the exponent is > 0. The question is, what *should* it return. I guess we want it to give zoo, but what value to we return from that function to give that (there is no floating point version of zoo). I guess your patch is in that direction, although I don't like that it makes the evalf functions return just `zoo` instead of a tuple.
We could also make it return `inf` quite easily:
```patch
diff --git a/sympy/core/evalf.py b/sympy/core/evalf.py
index c79465651..9437c9c17 100644
--- a/sympy/core/evalf.py
+++ b/sympy/core/evalf.py
@@ -670,7 +670,12 @@ def evalf_pow(v, prec, options):
return None, mpf_neg(z), None, target_prec
# Zero raised to an integer power
if not re:
- return None, None, None, None
+ if exp > 0:
+ return None, None, None, None
+ elif exp < 0:
+ return mpmath_inf._mpf_, None, target_prec, None
+ else:
+ return mpf(1)._mpf_, None, target_prec, None
# General complex number to arbitrary integer power
re, im = libmp.mpc_pow_int((re, im), p, prec)
# Assumes full accuracy in input
```
Maybe we should apply the above as a simpler fix for now (`inf` is not as correct as zoo, but it's definitely less wrong than 0).
SO [reports this issue](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/45637615), too.
I want to work on this. Ideally mpmath should provide a tuple that represents `zoo`, but it doesn't. And there is no benefit that we assign a tuple as `zoo` then check this tuple everywhere, so I'd like to follow @smichr 's idea that directly return the `zoo` when appropriate.
|
[
{
"body": "Here's how it looks like:\n\n``` python\nIn [1]: sp.__version__\nOut[1]: '0.7.5-git'\n\nIn [2]: x = sp.abc.x\n\nIn [3]: (1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0})\nOut[3]: 0\n\nIn [4]: (1/x).subs({x: 0})\nOut[4]: zoo\n\nIn [5]: (1/x).xreplace({x: 0})\nOut[5]: zoo\n```\n\nI did investigate it some time ago and, AFAIR, it happens in `Pow` evaluation that short-circuits to 0 whenever the base is 0 while it should return infs if the exponent is negative.\n",
"number": 8242,
"title": "(1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0}) produces 0"
},
{
"body": "`Mul(2, Pow(0,-1, evaluate=False), evaluate=False).evalf()` returns 0 instead of complex infinity.",
"number": 21147,
"title": "Evalf and evaluate=False issues"
}
] |
d04fa46664c3aeda08fb41a2b2d62055056e8926
|
{
"head_commit": "6704d77acb7ce10349c5d87c0c2f30d14e35f8d3",
"head_commit_message": "fix issue 8242",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/evalf.py b/sympy/core/evalf.py\nindex c9313200a434..c39e52f4637b 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/evalf.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/evalf.py\n@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@\n make_mpc, make_mpf, mp, mpc, mpf, nsum, quadts, quadosc, workprec)\n from mpmath import inf as mpmath_inf\n from mpmath.libmp import (from_int, from_man_exp, from_rational, fhalf,\n- fnan, fnone, fone, fzero, mpf_abs, mpf_add,\n+ fnan, finf, fninf, fnone, fone, fzero, mpf_abs, mpf_add,\n mpf_atan, mpf_atan2, mpf_cmp, mpf_cos, mpf_e, mpf_exp, mpf_log, mpf_lt,\n mpf_mul, mpf_neg, mpf_pi, mpf_pow, mpf_pow_int, mpf_shift, mpf_sin,\n mpf_sqrt, normalize, round_nearest, to_int, to_str)\n@@ -206,6 +206,8 @@ def complex_accuracy(result):\n In the worst case (re and im equal), this is wrong by a factor\n sqrt(2), or by log2(sqrt(2)) = 0.5 bit.\n \"\"\"\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ return INF\n re, im, re_acc, im_acc = result\n if not im:\n if not re:\n@@ -221,8 +223,10 @@ def complex_accuracy(result):\n \n \n def get_abs(expr, prec, options):\n- re, im, re_acc, im_acc = evalf(expr, prec + 2, options)\n-\n+ result = evalf(expr, prec + 2, options)\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ return finf, None, prec, None\n+ re, im, re_acc, im_acc = result\n if not re:\n re, re_acc, im, im_acc = im, im_acc, re, re_acc\n if im:\n@@ -246,6 +250,8 @@ def get_complex_part(expr, no, prec, options):\n i = 0\n while 1:\n res = evalf(expr, workprec, options)\n+ if res is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ return fnan, None, prec, None\n value, accuracy = res[no::2]\n # XXX is the last one correct? Consider re((1+I)**2).n()\n if (not value) or accuracy >= prec or -value[2] > prec:\n@@ -289,6 +295,8 @@ def chop_parts(value, prec):\n \"\"\"\n Chop off tiny real or complex parts.\n \"\"\"\n+ if value is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ return value\n re, im, re_acc, im_acc = value\n # Method 1: chop based on absolute value\n if re and re not in _infs_nan and (fastlog(re) < -prec + 4):\n@@ -323,7 +331,10 @@ def get_integer_part(expr, no, options, return_ints=False):\n from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import re, im\n # The expression is likely less than 2^30 or so\n assumed_size = 30\n- ire, iim, ire_acc, iim_acc = evalf(expr, assumed_size, options)\n+ result = evalf(expr, assumed_size, options)\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Cannot get integer part of Complex Infinity\")\n+ ire, iim, ire_acc, iim_acc = result\n \n # We now know the size, so we can calculate how much extra precision\n # (if any) is needed to get within the nearest integer\n@@ -532,10 +543,17 @@ def evalf_add(v, prec, options):\n options['maxprec'] = min(oldmaxprec, 2*prec)\n \n terms = [evalf(arg, prec + 10, options) for arg in v.args]\n+ n = terms.count(S.ComplexInfinity)\n+ if n >= 2:\n+ return fnan, None, prec, None\n re, re_acc = add_terms(\n- [a[0::2] for a in terms if a[0]], prec, target_prec)\n+ [a[0::2] for a in terms if isinstance(a, tuple) and a[0]], prec, target_prec)\n im, im_acc = add_terms(\n- [a[1::2] for a in terms if a[1]], prec, target_prec)\n+ [a[1::2] for a in terms if isinstance(a, tuple) and a[1]], prec, target_prec)\n+ if n == 1:\n+ if re in (finf, fninf, fnan) or im in (finf, fninf, fnan):\n+ return fnan, None, prec, None\n+ return S.ComplexInfinity\n acc = complex_accuracy((re, im, re_acc, im_acc))\n if acc >= target_prec:\n if options.get('verbose'):\n@@ -568,19 +586,30 @@ def evalf_mul(v, prec, options):\n args = list(v.args)\n \n # see if any argument is NaN or oo and thus warrants a special return\n+ has_zero = False\n special = []\n from .numbers import Float\n for arg in args:\n- arg = evalf(arg, prec, options)\n- if arg[0] is None:\n+ result = evalf(arg, prec, options)\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ special.append(result)\n continue\n- arg = Float._new(arg[0], 1)\n- if arg is S.NaN or arg.is_infinite:\n- special.append(arg)\n+ if result[0] is None:\n+ if result[1] is None:\n+ has_zero = True\n+ continue\n+ num = Float._new(result[0], 1)\n+ if num is S.NaN:\n+ return fnan, None, prec, None\n+ if num.is_infinite:\n+ special.append(num)\n if special:\n+ if has_zero:\n+ return fnan, None, prec, None\n from .mul import Mul\n- special = Mul(*special)\n- return evalf(special, prec + 4, {})\n+ return evalf(Mul(*special), prec + 4, {})\n+ if has_zero:\n+ return None, None, None, None\n \n # With guard digits, multiplication in the real case does not destroy\n # accuracy. This is also true in the complex case when considering the\n@@ -688,7 +717,12 @@ def evalf_pow(v, prec, options):\n # Exponentiation by p magnifies relative error by |p|, so the\n # base must be evaluated with increased precision if p is large\n prec += int(math.log(abs(p), 2))\n- re, im, re_acc, im_acc = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)\n+ result = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ if p < 0:\n+ return None, None, None, None\n+ return result\n+ re, im, re_acc, im_acc = result\n # Real to integer power\n if re and not im:\n return mpf_pow_int(re, p, target_prec), None, target_prec, None\n@@ -706,15 +740,25 @@ def evalf_pow(v, prec, options):\n return None, mpf_neg(z), None, target_prec\n # Zero raised to an integer power\n if not re:\n+ if p < 0:\n+ return S.ComplexInfinity\n return None, None, None, None\n # General complex number to arbitrary integer power\n re, im = libmp.mpc_pow_int((re, im), p, prec)\n # Assumes full accuracy in input\n return finalize_complex(re, im, target_prec)\n \n+ result = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ if exp.is_Rational:\n+ if exp < 0:\n+ return None, None, None, None\n+ return result\n+ raise NotImplementedError\n+\n # Pure square root\n if exp is S.Half:\n- xre, xim, _, _ = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)\n+ xre, xim, _, _ = result\n # General complex square root\n if xim:\n re, im = libmp.mpc_sqrt((xre or fzero, xim), prec)\n@@ -730,7 +774,10 @@ def evalf_pow(v, prec, options):\n # We first evaluate the exponent to find its magnitude\n # This determines the working precision that must be used\n prec += 10\n- yre, yim, _, _ = evalf(exp, prec, options)\n+ result = evalf(exp, prec, options)\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ return fnan, None, prec, None\n+ yre, yim, _, _ = result\n # Special cases: x**0\n if not (yre or yim):\n return fone, None, prec, None\n@@ -752,6 +799,10 @@ def evalf_pow(v, prec, options):\n xre, xim, _, _ = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)\n # 0**y\n if not (xre or xim):\n+ if yim:\n+ return fnan, None, prec, None\n+ if yre[0] == 1: # y < 0\n+ return S.ComplexInfinity\n return None, None, None, None\n \n # (real ** complex) or (complex ** complex)\n@@ -846,7 +897,10 @@ def evalf_log(expr, prec, options):\n return evalf(expr, prec, options)\n arg = expr.args[0]\n workprec = prec + 10\n- xre, xim, xacc, _ = evalf(arg, workprec, options)\n+ result = evalf(arg, workprec, options)\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ return result\n+ xre, xim, xacc, _ = result\n \n # evalf can return NoneTypes if chop=True\n # issue 18516, 19623\n@@ -1203,11 +1257,11 @@ def summand(k, _term=[term0]):\n \n def evalf_prod(expr, prec, options):\n if all((l[1] - l[2]).is_Integer for l in expr.limits):\n- re, im, re_acc, im_acc = evalf(expr.doit(), prec=prec, options=options)\n+ result = evalf(expr.doit(), prec=prec, options=options)\n else:\n from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum\n- re, im, re_acc, im_acc = evalf(expr.rewrite(Sum), prec=prec, options=options)\n- return re, im, re_acc, im_acc\n+ result = evalf(expr.rewrite(Sum), prec=prec, options=options)\n+ return result\n \n \n def evalf_sum(expr, prec, options):\n@@ -1285,7 +1339,8 @@ def _create_evalf_table():\n from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum\n from .add import Add\n from .mul import Mul\n- from .numbers import Exp1, Float, Half, ImaginaryUnit, Integer, NaN, NegativeOne, One, Pi, Rational, Zero\n+ from .numbers import Exp1, Float, Half, ImaginaryUnit, Integer, NaN, NegativeOne, One, Pi, Rational, \\\n+ Zero, ComplexInfinity\n from .power import Pow\n from .symbol import Dummy, Symbol\n from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import Abs, im, re\n@@ -1307,6 +1362,7 @@ def _create_evalf_table():\n Exp1: lambda x, prec, options: (mpf_e(prec), None, prec, None),\n ImaginaryUnit: lambda x, prec, options: (None, fone, None, prec),\n NegativeOne: lambda x, prec, options: (fnone, None, prec, None),\n+ ComplexInfinity: lambda x, prec, options: S.ComplexInfinity,\n NaN: lambda x, prec, options: (fnan, None, prec, None),\n \n exp: lambda x, prec, options: evalf_pow(\n@@ -1405,7 +1461,7 @@ def evalf(x, prec, options):\n \n if options.get(\"verbose\"):\n print(\"### input\", x)\n- print(\"### output\", to_str(r[0] or fzero, 50))\n+ print(\"### output\", to_str(r[0] or fzero, 50) if isinstance(r, tuple) else r)\n print(\"### raw\", r) # r[0], r[2]\n print()\n chop = options.get('chop', False)\n@@ -1536,6 +1592,8 @@ def evalf(self, n=15, subs=None, maxn=100, chop=False, strict=False, quad=None,\n except NotImplementedError:\n # Probably contains symbols or unknown functions\n return v\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ return result\n re, im, re_acc, im_acc = result\n if re is S.NaN or im is S.NaN:\n return S.NaN\n@@ -1571,7 +1629,10 @@ def _to_mpmath(self, prec, allow_ints=True):\n if hasattr(self, '_as_mpf_val'):\n return make_mpf(self._as_mpf_val(prec))\n try:\n- re, im, _, _ = evalf(self, prec, {})\n+ result = evalf(self, prec, {})\n+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:\n+ raise NotImplementedError\n+ re, im, _, _ = result\n if im:\n if not re:\n re = fzero\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py\nindex c9c9e8150c6d..fb010a533183 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/expr.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py\n@@ -651,7 +651,7 @@ def check_denominator_zeros(expression):\n if expr.is_zero:\n return True\n \n- # Don't attempt subsitution or differentiation with non-number symbols\n+ # Don't attempt substitution or differentiation with non-number symbols\n wrt_number = {sym for sym in wrt if sym.kind is NumberKind}\n \n # try numerical evaluation to see if we get two different values\n@@ -700,9 +700,6 @@ def check_denominator_zeros(expression):\n if not (pure_complex(deriv, or_real=True)):\n if flags.get('failing_number', False):\n return failing_number\n- elif deriv.free_symbols:\n- # dead line provided _random returns None in such cases\n- return None\n return False\n cd = check_denominator_zeros(self)\n if cd is True:\n@@ -752,6 +749,12 @@ def equals(self, other, failing_expression=False):\n # then this can't be a zero\n return False\n \n+ factors = diff.as_coeff_mul()[1]\n+ if len(factors) > 1: # avoid infinity recursion\n+ fac_zero = [fac.equals(0) for fac in factors]\n+ if None not in fac_zero: # every part can be decided\n+ return any(fac_zero)\n+\n constant = diff.is_constant(simplify=False, failing_number=True)\n \n if constant is False:\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py\nindex cd099e7d05b8..af8667cf5f98 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py\n@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@\n+import math\n+\n from sympy.concrete.products import (Product, product)\n from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum\n from sympy.core.add import Add\n@@ -5,7 +7,7 @@\n from sympy.core.function import (Function, nfloat)\n from sympy.core.mul import Mul\n from sympy.core import (GoldenRatio)\n-from sympy.core.numbers import (E, I, Rational, oo, pi)\n+from sympy.core.numbers import (E, I, Rational, oo, zoo, nan, pi)\n from sympy.core.power import Pow\n from sympy.core.relational import Eq\n from sympy.core.singleton import S\n@@ -13,7 +15,7 @@\n from sympy.core.sympify import sympify\n from sympy.functions.combinatorial.factorials import factorial\n from sympy.functions.combinatorial.numbers import fibonacci\n-from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import Abs\n+from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import (Abs, re, im)\n from sympy.functions.elementary.exponential import (exp, log)\n from sympy.functions.elementary.hyperbolic import (acosh, cosh)\n from sympy.functions.elementary.integers import (ceiling, floor)\n@@ -38,6 +40,7 @@ def NS(e, n=15, **options):\n \n \n def test_evalf_helpers():\n+ from mpmath.libmp import finf\n assert complex_accuracy((from_float(2.0), None, 35, None)) == 35\n assert complex_accuracy((from_float(2.0), from_float(10.0), 35, 100)) == 37\n assert complex_accuracy(\n@@ -45,6 +48,9 @@ def test_evalf_helpers():\n assert complex_accuracy((from_float(2.0), from_float(10.0), 100, 35)) == 35\n assert complex_accuracy(\n (from_float(2.0), from_float(1000.0), 100, 35)) == 35\n+ assert complex_accuracy(finf) == math.inf\n+ assert complex_accuracy(zoo) == math.inf\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: get_integer_part(zoo, 1, {}))\n \n \n def test_evalf_basic():\n@@ -496,8 +502,7 @@ def test_issue_6632_evalf():\n \n def test_issue_4945():\n from sympy.abc import H\n- from sympy.core.numbers import zoo\n- assert (H/0).evalf(subs={H:1}) == zoo*H\n+ assert (H/0).evalf(subs={H:1}) == zoo\n \n \n def test_evalf_integral():\n@@ -628,3 +633,28 @@ def test_issue_20291():\n \n sol = Complement(Intersection(FiniteSet(-b/2 - sqrt(b**2-4*pi)/2), Reals), FiniteSet(0))\n assert sol.evalf(subs={b: 1}) == EmptySet\n+\n+\n+def test_evalf_with_zoo():\n+ assert (1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == zoo # issue 8242\n+ assert (-1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == zoo # PR 16150\n+ assert (0 ** x).evalf(subs={x: -1}) == zoo # PR 16150\n+ assert (0 ** x).evalf(subs={x: -1 + I}) == nan\n+ assert Mul(2, Pow(0, -1, evaluate=False), evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo # issue 21147\n+ assert Mul(x, 1/x, evaluate=False).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == Mul(x, 1/x, evaluate=False).subs(x, 0) == nan\n+ assert Mul(1/x, 1/x, evaluate=False).evalf(subs={x: 0})\n+ assert Mul(1/x, Abs(1/x), evaluate=False).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == zoo\n+ assert Abs(zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == oo\n+ assert re(zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan\n+ assert im(zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan\n+ assert Add(zoo, zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan\n+ assert Add(oo, zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan\n+ assert Pow(zoo, -1, evaluate=False).evalf() == 0\n+ assert Pow(zoo, Rational(-1, 3), evaluate=False).evalf() == 0\n+ assert Pow(zoo, Rational(1, 3), evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo\n+ assert Pow(zoo, S.Half, evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo\n+ assert Pow(zoo, 2, evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo\n+ assert Pow(0, zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan\n+ assert log(zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo\n+ assert zoo.evalf(chop=True) == zoo\n+ assert x.evalf(subs={x: zoo}) == zoo\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_expr.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_expr.py\nindex 6982c827e70a..19458f30c751 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_expr.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_expr.py\n@@ -1797,16 +1797,17 @@ def test_issue_5843():\n \n def test_is_constant():\n from sympy.solvers.solvers import checksol\n- Sum(x, (x, 1, 10)).is_constant() is True\n- Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant() is False\n- Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(y) is True\n- Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(n) is False\n- Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(x) is True\n+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, 10)).is_constant() is True\n+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant() is False\n+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(y) is True\n+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(n) is False\n+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(x) is True\n eq = a*cos(x)**2 + a*sin(x)**2 - a\n- eq.is_constant() is True\n+ assert eq.is_constant() is True\n assert eq.subs({x: pi, a: 2}) == eq.subs({x: pi, a: 3}) == 0\n assert x.is_constant() is False\n assert x.is_constant(y) is True\n+ assert log(x/y).is_constant() is False\n \n assert checksol(x, x, Sum(x, (x, 1, n))) is False\n assert checksol(x, x, Sum(x, (x, 1, n))) is False\n@@ -1852,7 +1853,7 @@ def test_equals():\n 2*sqrt(2)*x**(S(3)/2)*(1 + 1/(2*x))**(S(5)/2)/(-6 - 3/x)\n ans = sqrt(2*x + 1)*(6*x**2 + x - 1)/15\n diff = i - ans\n- assert diff.equals(0) is False\n+ assert diff.equals(0) is None # should be False, but previously this was False due to wrong intermediate result\n assert diff.subs(x, Rational(-1, 2)/2) == 7*sqrt(2)/120\n # there are regions for x for which the expression is True, for\n # example, when x < -1/2 or x > 0 the expression is zero\n@@ -2084,7 +2085,7 @@ def test_issue_6325():\n (a + b*t)**2 + (c + t*z)**2))/sqrt((a + b*t)**2 + (c + t*z)**2)\n e = sqrt((a + b*t)**2 + (c + z*t)**2)\n assert diff(e, t, 2) == ans\n- e.diff(t, 2) == ans\n+ assert e.diff(t, 2) == ans\n assert diff(e, t, 2, simplify=False) != ans\n \n \ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py\nindex 1b5dd7c27ba5..cc4aa6000730 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py\n@@ -1055,6 +1055,9 @@ def _eval_as_leading_term(self, x, logx=None, cdir=0):\n return self.func(x0) - 2*I*S.Pi\n return self.func(arg)\n \n+ def is_constant(self, *wrt, **flags):\n+ return self.args[0].is_constant(*wrt, **flags)\n+\n \n class LambertW(Function):\n r\"\"\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1055,6 +1055,9 @@ def _eval_as_leading_term(self, x, logx=None, cdir=0):\n return self.func(x0) - 2*I*S.Pi\n return self.func(arg)\n \n+ def is_constant(self, *wrt, **flags):\n+ return self.args[0].is_constant(*wrt, **flags)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1059,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhy is this needed for `log`? No other function class has this.\n\n@author:\nIt was imported when fixing test_issue_22020 in test_expr.py\r\nSeems without it that case can still pass now. I'll remove it to see what CI says."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -628,3 +633,28 @@ def test_issue_20291():\n \n sol = Complement(Intersection(FiniteSet(-b/2 - sqrt(b**2-4*pi)/2), Reals), FiniteSet(0))\n assert sol.evalf(subs={b: 1}) == EmptySet\n+\n+\n+def test_evalf_with_zoo():\n+ assert (1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == zoo # issue 8242\n+ assert (-1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == zoo # PR 16150\n+ assert (0 ** x).evalf(subs={x: -1}) == zoo # PR 16150\n+ assert (0 ** x).evalf(subs={x: -1 + I}) == nan\n+ assert Mul(2, Pow(0, -1, evaluate=False), evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo # issue 21147\n+ assert Mul(x, 1/x, evaluate=False).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == Mul(x, 1/x, evaluate=False).subs(x, 0) == nan\n+ assert Mul(1/x, 1/x, evaluate=False).evalf(subs={x: 0})",
"line": null,
"original_line": 645,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThere seems to be a missing `== zoo` here"
}
] |
20b5d8e4284d2aa1b8315905aebc91c37ec330ed
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/evalf.py b/sympy/core/evalf.py
index c9313200a434..c39e52f4637b 100644
--- a/sympy/core/evalf.py
+++ b/sympy/core/evalf.py
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
make_mpc, make_mpf, mp, mpc, mpf, nsum, quadts, quadosc, workprec)
from mpmath import inf as mpmath_inf
from mpmath.libmp import (from_int, from_man_exp, from_rational, fhalf,
- fnan, fnone, fone, fzero, mpf_abs, mpf_add,
+ fnan, finf, fninf, fnone, fone, fzero, mpf_abs, mpf_add,
mpf_atan, mpf_atan2, mpf_cmp, mpf_cos, mpf_e, mpf_exp, mpf_log, mpf_lt,
mpf_mul, mpf_neg, mpf_pi, mpf_pow, mpf_pow_int, mpf_shift, mpf_sin,
mpf_sqrt, normalize, round_nearest, to_int, to_str)
@@ -206,6 +206,8 @@ def complex_accuracy(result):
In the worst case (re and im equal), this is wrong by a factor
sqrt(2), or by log2(sqrt(2)) = 0.5 bit.
"""
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return INF
re, im, re_acc, im_acc = result
if not im:
if not re:
@@ -221,8 +223,10 @@ def complex_accuracy(result):
def get_abs(expr, prec, options):
- re, im, re_acc, im_acc = evalf(expr, prec + 2, options)
-
+ result = evalf(expr, prec + 2, options)
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return finf, None, prec, None
+ re, im, re_acc, im_acc = result
if not re:
re, re_acc, im, im_acc = im, im_acc, re, re_acc
if im:
@@ -246,6 +250,8 @@ def get_complex_part(expr, no, prec, options):
i = 0
while 1:
res = evalf(expr, workprec, options)
+ if res is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return fnan, None, prec, None
value, accuracy = res[no::2]
# XXX is the last one correct? Consider re((1+I)**2).n()
if (not value) or accuracy >= prec or -value[2] > prec:
@@ -289,6 +295,8 @@ def chop_parts(value, prec):
"""
Chop off tiny real or complex parts.
"""
+ if value is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return value
re, im, re_acc, im_acc = value
# Method 1: chop based on absolute value
if re and re not in _infs_nan and (fastlog(re) < -prec + 4):
@@ -323,7 +331,10 @@ def get_integer_part(expr, no, options, return_ints=False):
from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import re, im
# The expression is likely less than 2^30 or so
assumed_size = 30
- ire, iim, ire_acc, iim_acc = evalf(expr, assumed_size, options)
+ result = evalf(expr, assumed_size, options)
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ raise ValueError("Cannot get integer part of Complex Infinity")
+ ire, iim, ire_acc, iim_acc = result
# We now know the size, so we can calculate how much extra precision
# (if any) is needed to get within the nearest integer
@@ -532,10 +543,17 @@ def evalf_add(v, prec, options):
options['maxprec'] = min(oldmaxprec, 2*prec)
terms = [evalf(arg, prec + 10, options) for arg in v.args]
+ n = terms.count(S.ComplexInfinity)
+ if n >= 2:
+ return fnan, None, prec, None
re, re_acc = add_terms(
- [a[0::2] for a in terms if a[0]], prec, target_prec)
+ [a[0::2] for a in terms if isinstance(a, tuple) and a[0]], prec, target_prec)
im, im_acc = add_terms(
- [a[1::2] for a in terms if a[1]], prec, target_prec)
+ [a[1::2] for a in terms if isinstance(a, tuple) and a[1]], prec, target_prec)
+ if n == 1:
+ if re in (finf, fninf, fnan) or im in (finf, fninf, fnan):
+ return fnan, None, prec, None
+ return S.ComplexInfinity
acc = complex_accuracy((re, im, re_acc, im_acc))
if acc >= target_prec:
if options.get('verbose'):
@@ -568,19 +586,30 @@ def evalf_mul(v, prec, options):
args = list(v.args)
# see if any argument is NaN or oo and thus warrants a special return
+ has_zero = False
special = []
from .numbers import Float
for arg in args:
- arg = evalf(arg, prec, options)
- if arg[0] is None:
+ result = evalf(arg, prec, options)
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ special.append(result)
continue
- arg = Float._new(arg[0], 1)
- if arg is S.NaN or arg.is_infinite:
- special.append(arg)
+ if result[0] is None:
+ if result[1] is None:
+ has_zero = True
+ continue
+ num = Float._new(result[0], 1)
+ if num is S.NaN:
+ return fnan, None, prec, None
+ if num.is_infinite:
+ special.append(num)
if special:
+ if has_zero:
+ return fnan, None, prec, None
from .mul import Mul
- special = Mul(*special)
- return evalf(special, prec + 4, {})
+ return evalf(Mul(*special), prec + 4, {})
+ if has_zero:
+ return None, None, None, None
# With guard digits, multiplication in the real case does not destroy
# accuracy. This is also true in the complex case when considering the
@@ -688,7 +717,12 @@ def evalf_pow(v, prec, options):
# Exponentiation by p magnifies relative error by |p|, so the
# base must be evaluated with increased precision if p is large
prec += int(math.log(abs(p), 2))
- re, im, re_acc, im_acc = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)
+ result = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ if p < 0:
+ return None, None, None, None
+ return result
+ re, im, re_acc, im_acc = result
# Real to integer power
if re and not im:
return mpf_pow_int(re, p, target_prec), None, target_prec, None
@@ -706,15 +740,25 @@ def evalf_pow(v, prec, options):
return None, mpf_neg(z), None, target_prec
# Zero raised to an integer power
if not re:
+ if p < 0:
+ return S.ComplexInfinity
return None, None, None, None
# General complex number to arbitrary integer power
re, im = libmp.mpc_pow_int((re, im), p, prec)
# Assumes full accuracy in input
return finalize_complex(re, im, target_prec)
+ result = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ if exp.is_Rational:
+ if exp < 0:
+ return None, None, None, None
+ return result
+ raise NotImplementedError
+
# Pure square root
if exp is S.Half:
- xre, xim, _, _ = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)
+ xre, xim, _, _ = result
# General complex square root
if xim:
re, im = libmp.mpc_sqrt((xre or fzero, xim), prec)
@@ -730,7 +774,10 @@ def evalf_pow(v, prec, options):
# We first evaluate the exponent to find its magnitude
# This determines the working precision that must be used
prec += 10
- yre, yim, _, _ = evalf(exp, prec, options)
+ result = evalf(exp, prec, options)
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return fnan, None, prec, None
+ yre, yim, _, _ = result
# Special cases: x**0
if not (yre or yim):
return fone, None, prec, None
@@ -752,6 +799,10 @@ def evalf_pow(v, prec, options):
xre, xim, _, _ = evalf(base, prec + 5, options)
# 0**y
if not (xre or xim):
+ if yim:
+ return fnan, None, prec, None
+ if yre[0] == 1: # y < 0
+ return S.ComplexInfinity
return None, None, None, None
# (real ** complex) or (complex ** complex)
@@ -846,7 +897,10 @@ def evalf_log(expr, prec, options):
return evalf(expr, prec, options)
arg = expr.args[0]
workprec = prec + 10
- xre, xim, xacc, _ = evalf(arg, workprec, options)
+ result = evalf(arg, workprec, options)
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return result
+ xre, xim, xacc, _ = result
# evalf can return NoneTypes if chop=True
# issue 18516, 19623
@@ -1203,11 +1257,11 @@ def summand(k, _term=[term0]):
def evalf_prod(expr, prec, options):
if all((l[1] - l[2]).is_Integer for l in expr.limits):
- re, im, re_acc, im_acc = evalf(expr.doit(), prec=prec, options=options)
+ result = evalf(expr.doit(), prec=prec, options=options)
else:
from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum
- re, im, re_acc, im_acc = evalf(expr.rewrite(Sum), prec=prec, options=options)
- return re, im, re_acc, im_acc
+ result = evalf(expr.rewrite(Sum), prec=prec, options=options)
+ return result
def evalf_sum(expr, prec, options):
@@ -1285,7 +1339,8 @@ def _create_evalf_table():
from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum
from .add import Add
from .mul import Mul
- from .numbers import Exp1, Float, Half, ImaginaryUnit, Integer, NaN, NegativeOne, One, Pi, Rational, Zero
+ from .numbers import Exp1, Float, Half, ImaginaryUnit, Integer, NaN, NegativeOne, One, Pi, Rational, \
+ Zero, ComplexInfinity
from .power import Pow
from .symbol import Dummy, Symbol
from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import Abs, im, re
@@ -1307,6 +1362,7 @@ def _create_evalf_table():
Exp1: lambda x, prec, options: (mpf_e(prec), None, prec, None),
ImaginaryUnit: lambda x, prec, options: (None, fone, None, prec),
NegativeOne: lambda x, prec, options: (fnone, None, prec, None),
+ ComplexInfinity: lambda x, prec, options: S.ComplexInfinity,
NaN: lambda x, prec, options: (fnan, None, prec, None),
exp: lambda x, prec, options: evalf_pow(
@@ -1405,7 +1461,7 @@ def evalf(x, prec, options):
if options.get("verbose"):
print("### input", x)
- print("### output", to_str(r[0] or fzero, 50))
+ print("### output", to_str(r[0] or fzero, 50) if isinstance(r, tuple) else r)
print("### raw", r) # r[0], r[2]
print()
chop = options.get('chop', False)
@@ -1536,6 +1592,8 @@ def evalf(self, n=15, subs=None, maxn=100, chop=False, strict=False, quad=None,
except NotImplementedError:
# Probably contains symbols or unknown functions
return v
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ return result
re, im, re_acc, im_acc = result
if re is S.NaN or im is S.NaN:
return S.NaN
@@ -1571,7 +1629,10 @@ def _to_mpmath(self, prec, allow_ints=True):
if hasattr(self, '_as_mpf_val'):
return make_mpf(self._as_mpf_val(prec))
try:
- re, im, _, _ = evalf(self, prec, {})
+ result = evalf(self, prec, {})
+ if result is S.ComplexInfinity:
+ raise NotImplementedError
+ re, im, _, _ = result
if im:
if not re:
re = fzero
diff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py
index c9c9e8150c6d..fb010a533183 100644
--- a/sympy/core/expr.py
+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py
@@ -651,7 +651,7 @@ def check_denominator_zeros(expression):
if expr.is_zero:
return True
- # Don't attempt subsitution or differentiation with non-number symbols
+ # Don't attempt substitution or differentiation with non-number symbols
wrt_number = {sym for sym in wrt if sym.kind is NumberKind}
# try numerical evaluation to see if we get two different values
@@ -700,9 +700,6 @@ def check_denominator_zeros(expression):
if not (pure_complex(deriv, or_real=True)):
if flags.get('failing_number', False):
return failing_number
- elif deriv.free_symbols:
- # dead line provided _random returns None in such cases
- return None
return False
cd = check_denominator_zeros(self)
if cd is True:
@@ -752,6 +749,12 @@ def equals(self, other, failing_expression=False):
# then this can't be a zero
return False
+ factors = diff.as_coeff_mul()[1]
+ if len(factors) > 1: # avoid infinity recursion
+ fac_zero = [fac.equals(0) for fac in factors]
+ if None not in fac_zero: # every part can be decided
+ return any(fac_zero)
+
constant = diff.is_constant(simplify=False, failing_number=True)
if constant is False:
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py
index cd099e7d05b8..f2c429c3ea5c 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
+import math
+
from sympy.concrete.products import (Product, product)
from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum
from sympy.core.add import Add
@@ -5,7 +7,7 @@
from sympy.core.function import (Function, nfloat)
from sympy.core.mul import Mul
from sympy.core import (GoldenRatio)
-from sympy.core.numbers import (E, I, Rational, oo, pi)
+from sympy.core.numbers import (E, I, Rational, oo, zoo, nan, pi)
from sympy.core.power import Pow
from sympy.core.relational import Eq
from sympy.core.singleton import S
@@ -13,7 +15,7 @@
from sympy.core.sympify import sympify
from sympy.functions.combinatorial.factorials import factorial
from sympy.functions.combinatorial.numbers import fibonacci
-from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import Abs
+from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import (Abs, re, im)
from sympy.functions.elementary.exponential import (exp, log)
from sympy.functions.elementary.hyperbolic import (acosh, cosh)
from sympy.functions.elementary.integers import (ceiling, floor)
@@ -38,6 +40,7 @@ def NS(e, n=15, **options):
def test_evalf_helpers():
+ from mpmath.libmp import finf
assert complex_accuracy((from_float(2.0), None, 35, None)) == 35
assert complex_accuracy((from_float(2.0), from_float(10.0), 35, 100)) == 37
assert complex_accuracy(
@@ -45,6 +48,9 @@ def test_evalf_helpers():
assert complex_accuracy((from_float(2.0), from_float(10.0), 100, 35)) == 35
assert complex_accuracy(
(from_float(2.0), from_float(1000.0), 100, 35)) == 35
+ assert complex_accuracy(finf) == math.inf
+ assert complex_accuracy(zoo) == math.inf
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: get_integer_part(zoo, 1, {}))
def test_evalf_basic():
@@ -496,8 +502,7 @@ def test_issue_6632_evalf():
def test_issue_4945():
from sympy.abc import H
- from sympy.core.numbers import zoo
- assert (H/0).evalf(subs={H:1}) == zoo*H
+ assert (H/0).evalf(subs={H:1}) == zoo
def test_evalf_integral():
@@ -628,3 +633,28 @@ def test_issue_20291():
sol = Complement(Intersection(FiniteSet(-b/2 - sqrt(b**2-4*pi)/2), Reals), FiniteSet(0))
assert sol.evalf(subs={b: 1}) == EmptySet
+
+
+def test_evalf_with_zoo():
+ assert (1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == zoo # issue 8242
+ assert (-1/x).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == zoo # PR 16150
+ assert (0 ** x).evalf(subs={x: -1}) == zoo # PR 16150
+ assert (0 ** x).evalf(subs={x: -1 + I}) == nan
+ assert Mul(2, Pow(0, -1, evaluate=False), evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo # issue 21147
+ assert Mul(x, 1/x, evaluate=False).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == Mul(x, 1/x, evaluate=False).subs(x, 0) == nan
+ assert Mul(1/x, 1/x, evaluate=False).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == zoo
+ assert Mul(1/x, Abs(1/x), evaluate=False).evalf(subs={x: 0}) == zoo
+ assert Abs(zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == oo
+ assert re(zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan
+ assert im(zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan
+ assert Add(zoo, zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan
+ assert Add(oo, zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan
+ assert Pow(zoo, -1, evaluate=False).evalf() == 0
+ assert Pow(zoo, Rational(-1, 3), evaluate=False).evalf() == 0
+ assert Pow(zoo, Rational(1, 3), evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo
+ assert Pow(zoo, S.Half, evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo
+ assert Pow(zoo, 2, evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo
+ assert Pow(0, zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == nan
+ assert log(zoo, evaluate=False).evalf() == zoo
+ assert zoo.evalf(chop=True) == zoo
+ assert x.evalf(subs={x: zoo}) == zoo
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_expr.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_expr.py
index 6982c827e70a..19458f30c751 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_expr.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_expr.py
@@ -1797,16 +1797,17 @@ def test_issue_5843():
def test_is_constant():
from sympy.solvers.solvers import checksol
- Sum(x, (x, 1, 10)).is_constant() is True
- Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant() is False
- Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(y) is True
- Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(n) is False
- Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(x) is True
+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, 10)).is_constant() is True
+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant() is False
+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(y) is True
+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(n) is False
+ assert Sum(x, (x, 1, n)).is_constant(x) is True
eq = a*cos(x)**2 + a*sin(x)**2 - a
- eq.is_constant() is True
+ assert eq.is_constant() is True
assert eq.subs({x: pi, a: 2}) == eq.subs({x: pi, a: 3}) == 0
assert x.is_constant() is False
assert x.is_constant(y) is True
+ assert log(x/y).is_constant() is False
assert checksol(x, x, Sum(x, (x, 1, n))) is False
assert checksol(x, x, Sum(x, (x, 1, n))) is False
@@ -1852,7 +1853,7 @@ def test_equals():
2*sqrt(2)*x**(S(3)/2)*(1 + 1/(2*x))**(S(5)/2)/(-6 - 3/x)
ans = sqrt(2*x + 1)*(6*x**2 + x - 1)/15
diff = i - ans
- assert diff.equals(0) is False
+ assert diff.equals(0) is None # should be False, but previously this was False due to wrong intermediate result
assert diff.subs(x, Rational(-1, 2)/2) == 7*sqrt(2)/120
# there are regions for x for which the expression is True, for
# example, when x < -1/2 or x > 0 the expression is zero
@@ -2084,7 +2085,7 @@ def test_issue_6325():
(a + b*t)**2 + (c + t*z)**2))/sqrt((a + b*t)**2 + (c + t*z)**2)
e = sqrt((a + b*t)**2 + (c + z*t)**2)
assert diff(e, t, 2) == ans
- e.diff(t, 2) == ans
+ assert e.diff(t, 2) == ans
assert diff(e, t, 2, simplify=False) != ans
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-22097@c98bccd
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 22,097
|
21942: remove match from solve (master)
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
fixes #21942
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* solvers
* use of `match` was removed to make solving more reliable
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-09-14T00:59:10Z
|
Algebraic re-arrangement of exponential equations
Sympy version: 1.7.1
Environment: Google Colab
Python version: 3.7
I am trying to use Sympy 1.7.1 in a google Colab environment running python 3.7 to automate some tedious algebra in macroeconomic models, and I'm running into an issue when trying to re-arrange equations of the form:
```
mc = (a * r ** (1 - p) + (1 - a) * w ** (1 - p)) ** (1 / (1 - p))
```
With parameters 0 < a < 1, and p > 0, p != 1 given, and w, r > 0. I would like to be able to re-arrange this expression to obtain functions r(mc, w) or w(mc, r). In the case of r, my expected output is:
```
r = ((1 / a) * (mc ** (1 - p) - (1 - a) * w ** (1 - p))) ** (1 / (1 - p))
```
To solve this equation I am trying the following code:
```
import sympy as sp
a, p, mc, r, w = sp.symbols(['a', 'p', 'mc', 'r', 'w'], real=True, nonnegative=True)
eq = mc - (a * r ** (1 - p) + (1 - a) * w ** (1 - p)) ** (1 / (1 - p))
sp.solve(eq, r)
```
Which results in the following error and trace-back:
```
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-15-a95f68afce93> in <module>()
----> 1 sp.solve(eq, r)
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/sympy/solvers/solvers.py in _solve(f, *symbols, **flags)
1458 d = dgen.pop()
1459 w = Wild('g')
-> 1460 gen = f_num.match(D.xreplace({d: w}))[w]
1461 spart = gen.as_independent(symbol)[1].as_base_exp()[0]
1462 if spart == symbol:
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not subscriptable
```
When i define a new parameter q = (1 - p), however, so that:
```
mc = (a * r ** q + (1 - a) * w ** q) ** (1 / q)
```
Sympy.solve finds expressions for r or w without any problem. Indeed, it seems only the outside exponent, (1 / (1 - p)) is important to change: the system is able to solve `mc = (a * r ** (1 - p) + (1 - a) * w ** (1 - p)) ** (1 / p)` without any problem. Evidently, that (1 - p) in the denominator of the exponent is causing the problem, but I don't know enough about how the solve function works to understand why that would be the case.
Are there best practices for writing functions of exponents, such as the one I have presented here, in order to facilitate the solve function?
Thanks for any help in advance! This is my first time posting an issue on github, so I apologize if I did it wrong.
|
[
{
"body": "Sympy version: 1.7.1\r\nEnvironment: Google Colab\r\nPython version: 3.7\r\n\r\nI am trying to use Sympy 1.7.1 in a google Colab environment running python 3.7 to automate some tedious algebra in macroeconomic models, and I'm running into an issue when trying to re-arrange equations of the form:\r\n```\r\nmc = (a * r ** (1 - p) + (1 - a) * w ** (1 - p)) ** (1 / (1 - p))\r\n```\r\nWith parameters 0 < a < 1, and p > 0, p != 1 given, and w, r > 0. I would like to be able to re-arrange this expression to obtain functions r(mc, w) or w(mc, r). In the case of r, my expected output is:\r\n ```\r\nr = ((1 / a) * (mc ** (1 - p) - (1 - a) * w ** (1 - p))) ** (1 / (1 - p))\r\n```\r\n\r\nTo solve this equation I am trying the following code:\r\n\r\n```\r\nimport sympy as sp\r\n\r\na, p, mc, r, w = sp.symbols(['a', 'p', 'mc', 'r', 'w'], real=True, nonnegative=True)\r\neq = mc - (a * r ** (1 - p) + (1 - a) * w ** (1 - p)) ** (1 / (1 - p))\r\nsp.solve(eq, r)\r\n```\r\n\r\nWhich results in the following error and trace-back: \r\n\r\n```\r\nTypeError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n<ipython-input-15-a95f68afce93> in <module>()\r\n----> 1 sp.solve(eq, r)\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/sympy/solvers/solvers.py in _solve(f, *symbols, **flags)\r\n 1458 d = dgen.pop()\r\n 1459 w = Wild('g')\r\n-> 1460 gen = f_num.match(D.xreplace({d: w}))[w]\r\n 1461 spart = gen.as_independent(symbol)[1].as_base_exp()[0]\r\n 1462 if spart == symbol:\r\n\r\nTypeError: 'NoneType' object is not subscriptable\r\n```\r\n\r\nWhen i define a new parameter q = (1 - p), however, so that:\r\n```\r\nmc = (a * r ** q + (1 - a) * w ** q) ** (1 / q)\r\n```\r\n\r\nSympy.solve finds expressions for r or w without any problem. Indeed, it seems only the outside exponent, (1 / (1 - p)) is important to change: the system is able to solve `mc = (a * r ** (1 - p) + (1 - a) * w ** (1 - p)) ** (1 / p)` without any problem. Evidently, that (1 - p) in the denominator of the exponent is causing the problem, but I don't know enough about how the solve function works to understand why that would be the case.\r\n\r\nAre there best practices for writing functions of exponents, such as the one I have presented here, in order to facilitate the solve function? \r\n\r\nThanks for any help in advance! This is my first time posting an issue on github, so I apologize if I did it wrong. \r\n",
"number": 21942,
"title": "Algebraic re-arrangement of exponential equations"
}
] |
fd94b018b0266fa9a04f463218a0d424ee11ae10
|
{
"head_commit": "c98bccd22b7d40455cf79dc1cdfc97d0c2b37732",
"head_commit_message": "Initial fix for `matches`",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/add.py b/sympy/core/add.py\nindex 6b308069878a..0d3f574837ce 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/add.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/add.py\n@@ -518,8 +518,8 @@ def _combine_inverse(lhs, rhs):\n Returns lhs - rhs, but treats oo like a symbol so oo - oo\n returns 0, instead of a nan.\n \"\"\"\n- from sympy.simplify.simplify import signsimp\n from sympy.core.symbol import Dummy\n+ from sympy.simplify.simplify import signsimp\n inf = (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity)\n if lhs.has(*inf) or rhs.has(*inf):\n oo = Dummy('oo')\n@@ -527,14 +527,16 @@ def _combine_inverse(lhs, rhs):\n S.Infinity: oo,\n S.NegativeInfinity: -oo}\n ireps = {v: k for k, v in reps.items()}\n- eq = signsimp(lhs.xreplace(reps) - rhs.xreplace(reps))\n+ eq = lhs.xreplace(reps) - rhs.xreplace(reps)\n if eq.has(oo):\n eq = eq.replace(\n lambda x: x.is_Pow and x.base is oo,\n lambda x: x.base)\n return eq.xreplace(ireps)\n else:\n- return signsimp(lhs - rhs)\n+ rv = lhs - rhs\n+ srv = signsimp(rv)\n+ return srv if srv.is_Number else rv\n \n @cacheit\n def as_two_terms(self):\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/mul.py b/sympy/core/mul.py\nindex 1b3fc566ccf1..57a2175412ec 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/mul.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/mul.py\n@@ -1224,7 +1224,9 @@ def check(l, r):\n if len(b) != blen:\n lhs = Mul(*[k**v for k, v in a.items()]).xreplace(i_)\n rhs = Mul(*[k**v for k, v in b.items()]).xreplace(i_)\n- return signsimp(lhs/rhs)\n+ rv = lhs/rhs\n+ srv = signsimp(rv)\n+ return srv if srv.is_Number else rv\n \n def as_powers_dict(self):\n d = defaultdict(int)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_match.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_match.py\nindex 62c06c9f965a..c88cbb6b912e 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_match.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_match.py\n@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@\n from sympy import (abc, Add, cos, collect, Derivative, diff, exp, Float, Function,\n- I, Integer, log, Mul, oo, Poly, Rational, S, sin, sqrt, Symbol, symbols,\n+ I, Integer, log, Mul, oo, Poly, Rational, S, signsimp, sin, sqrt, Symbol, symbols,\n Wild, pi, meijerg, Sum\n )\n \n@@ -509,7 +509,7 @@ def test_issue_3883():\n a, b, c = symbols('a b c', cls=Wild, exclude=(gamma,))\n \n assert f.match(a * log(gamma) + b * gamma + c) == \\\n- {a: Rational(-1, 2), b: -(mu - x)**2/2, c: log(2*pi)/2}\n+ {a: Rational(-1, 2), b: -(-mu + x)**2/2, c: log(2*pi)/2}\n assert f.expand().collect(gamma).match(a * log(gamma) + b * gamma + c) == \\\n {a: Rational(-1, 2), b: (-(x - mu)**2/2).expand(), c: (log(2*pi)/2).expand()}\n g1 = Wild('g1', exclude=[gamma])\n@@ -647,7 +647,7 @@ def test_issue_4319():\n ans = {S.Zero, y - S.One/8}\n \n def ok(pat):\n- assert set(p.match(pat).values()) == ans\n+ assert set(p.match(pat).values()) == ans, set(p.match(pat).values())\n \n ok(Wild(\"coeff\", exclude=[x])*x + Wild(\"rest\"))\n ok(Wild(\"w\", exclude=[x])*x + Wild(\"rest\"))\n@@ -717,6 +717,18 @@ def test_match_issue_17397():\n assert r == {a3: x - 4 + 4/x, b3: 1 - 2/x, c3: x - 4}\n \n \n+def test_match_issue_21942():\n+ a, r, w = symbols('a, r, w', nonnegative=True)\n+ p = symbols('p', positive=True)\n+ g_ = Wild('g')\n+ pattern = g_ ** (1 / (1 - p))\n+ eq = (a * r ** (1 - p) + w ** (1 - p) * (1 - a)) ** (1 / (1 - p))\n+ m = {g_: a * r ** (1 - p) + w ** (1 - p) * (1 - a)}\n+ assert pattern.matches(eq) == m\n+ assert (-pattern).matches(-eq) == m\n+ assert pattern.matches(signsimp(eq)) is None\n+\n+\n def test_match_terms():\n X, Y = map(Wild, \"XY\")\n x, y, z = symbols('x y z')\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\nindex e2f69271119a..4459d1417f9d 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@\n default_sort_key)\n from sympy.core.sympify import sympify\n from sympy.core import (S, Add, Symbol, Equality, Dummy, Expr, Mul,\n- Pow, Unequality, Wild)\n+ Pow, Unequality)\n from sympy.core.exprtools import factor_terms\n from sympy.core.function import (expand_mul, expand_log,\n Derivative, AppliedUndef, UndefinedFunction, nfloat,\n@@ -1447,17 +1447,12 @@ def _solve(f, *symbols, **flags):\n return [sol]\n \n poly = None\n- # check for a single non-symbol generator\n- dums = f_num.atoms(Dummy)\n- D = f_num.replace(\n- lambda i: isinstance(i, Add) and symbol in i.free_symbols,\n- lambda i: Dummy())\n- if not D.is_Dummy:\n- dgen = D.atoms(Dummy) - dums\n- if len(dgen) == 1:\n- d = dgen.pop()\n- w = Wild('g')\n- gen = f_num.match(D.xreplace({d: w}))[w]\n+ # check for a single Add generator\n+ if not f_num.is_Add:\n+ add_args = [i for i in f_num.atoms(Add)\n+ if symbol in i.free_symbols]\n+ if len(add_args) == 1:\n+ gen = add_args[0]\n spart = gen.as_independent(symbol)[1].as_base_exp()[0]\n if spart == symbol:\n try:\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\nindex c2100197c640..21ffe5d65521 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\n@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@\n from sympy.testing.pytest import slow, XFAIL, SKIP, raises\n from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn\n \n-from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, k, h, p, x, y, z, t, q, m, R\n+from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, e, k, h, p, x, y, z, t, q, m, R\n \n \n def NS(e, n=15, **options):\n@@ -2390,3 +2390,9 @@ def test_issue_17454():\n def test_issue_21852():\n solution = [21 - 21*sqrt(2)/2]\n assert solve(2*x + sqrt(2*x**2) - 21) == solution\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_21942():\n+ eq = -d + (a*c**(1 - e) + b**(1 - e)*(1 - a))**(1/(1 - e))\n+ sol = solve(eq, c, simplify=False, check=False)\n+ assert sol == [(b/b**e - b/(a*b**e) + d**(1 - e)/a)**(1/(1 - e))]\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -518,23 +518,25 @@ def _combine_inverse(lhs, rhs):\n Returns lhs - rhs, but treats oo like a symbol so oo - oo\n returns 0, instead of a nan.\n \"\"\"\n- from sympy.simplify.simplify import signsimp\n from sympy.core.symbol import Dummy\n+ from sympy.simplify.simplify import signsimp\n inf = (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity)\n if lhs.has(*inf) or rhs.has(*inf):\n oo = Dummy('oo')\n reps = {\n S.Infinity: oo,\n S.NegativeInfinity: -oo}\n ireps = {v: k for k, v in reps.items()}\n- eq = signsimp(lhs.xreplace(reps) - rhs.xreplace(reps))\n+ eq = lhs.xreplace(reps) - rhs.xreplace(reps)\n if eq.has(oo):\n eq = eq.replace(\n lambda x: x.is_Pow and x.base is oo,\n lambda x: x.base)\n return eq.xreplace(ireps)\n else:\n- return signsimp(lhs - rhs)\n+ rv = lhs - rhs\n+ srv = signsimp(rv)\n+ return srv if srv.is_Number else rv",
"line": null,
"original_line": 539,
"original_start_line": 538,
"path": "sympy/core/add.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@author:\n```suggestion\r\n srv = signsimp(rv)\r\n return srv if srv.is_Number else rv\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -518,23 +518,25 @@ def _combine_inverse(lhs, rhs):\n Returns lhs - rhs, but treats oo like a symbol so oo - oo\n returns 0, instead of a nan.\n \"\"\"\n- from sympy.simplify.simplify import signsimp\n from sympy.core.symbol import Dummy\n+ from sympy.simplify.simplify import signsimp\n inf = (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity)\n if lhs.has(*inf) or rhs.has(*inf):\n oo = Dummy('oo')\n reps = {\n S.Infinity: oo,\n S.NegativeInfinity: -oo}\n ireps = {v: k for k, v in reps.items()}\n- eq = signsimp(lhs.xreplace(reps) - rhs.xreplace(reps))\n+ eq = lhs.xreplace(reps) - rhs.xreplace(reps)\n if eq.has(oo):\n eq = eq.replace(\n lambda x: x.is_Pow and x.base is oo,\n lambda x: x.base)\n return eq.xreplace(ireps)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 535,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/add.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@author:\n```suggestion\r\n rv = eq.xreplace(ireps)\r\n```"
}
] |
206da29ace24f88e4311906e26ac21019de6d2ee
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/add.py b/sympy/core/add.py
index 6b308069878a..697589271e89 100644
--- a/sympy/core/add.py
+++ b/sympy/core/add.py
@@ -527,14 +527,16 @@ def _combine_inverse(lhs, rhs):
S.Infinity: oo,
S.NegativeInfinity: -oo}
ireps = {v: k for k, v in reps.items()}
- eq = signsimp(lhs.xreplace(reps) - rhs.xreplace(reps))
+ eq = lhs.xreplace(reps) - rhs.xreplace(reps)
if eq.has(oo):
eq = eq.replace(
lambda x: x.is_Pow and x.base is oo,
lambda x: x.base)
- return eq.xreplace(ireps)
+ rv = eq.xreplace(ireps)
else:
- return signsimp(lhs - rhs)
+ rv = lhs - rhs
+ srv = signsimp(rv)
+ return srv if srv.is_Number else rv
@cacheit
def as_two_terms(self):
diff --git a/sympy/core/mul.py b/sympy/core/mul.py
index 1b3fc566ccf1..57a2175412ec 100644
--- a/sympy/core/mul.py
+++ b/sympy/core/mul.py
@@ -1224,7 +1224,9 @@ def check(l, r):
if len(b) != blen:
lhs = Mul(*[k**v for k, v in a.items()]).xreplace(i_)
rhs = Mul(*[k**v for k, v in b.items()]).xreplace(i_)
- return signsimp(lhs/rhs)
+ rv = lhs/rhs
+ srv = signsimp(rv)
+ return srv if srv.is_Number else rv
def as_powers_dict(self):
d = defaultdict(int)
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_match.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_match.py
index 62c06c9f965a..513eceda39c2 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_match.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_match.py
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
from sympy import (abc, Add, cos, collect, Derivative, diff, exp, Float, Function,
- I, Integer, log, Mul, oo, Poly, Rational, S, sin, sqrt, Symbol, symbols,
+ I, Integer, log, Mul, oo, Poly, Rational, S, signsimp, sin, sqrt, Symbol, symbols,
Wild, pi, meijerg, Sum
)
@@ -509,7 +509,7 @@ def test_issue_3883():
a, b, c = symbols('a b c', cls=Wild, exclude=(gamma,))
assert f.match(a * log(gamma) + b * gamma + c) == \
- {a: Rational(-1, 2), b: -(mu - x)**2/2, c: log(2*pi)/2}
+ {a: Rational(-1, 2), b: -(-mu + x)**2/2, c: log(2*pi)/2}
assert f.expand().collect(gamma).match(a * log(gamma) + b * gamma + c) == \
{a: Rational(-1, 2), b: (-(x - mu)**2/2).expand(), c: (log(2*pi)/2).expand()}
g1 = Wild('g1', exclude=[gamma])
@@ -717,6 +717,18 @@ def test_match_issue_17397():
assert r == {a3: x - 4 + 4/x, b3: 1 - 2/x, c3: x - 4}
+def test_match_issue_21942():
+ a, r, w = symbols('a, r, w', nonnegative=True)
+ p = symbols('p', positive=True)
+ g_ = Wild('g')
+ pattern = g_ ** (1 / (1 - p))
+ eq = (a * r ** (1 - p) + w ** (1 - p) * (1 - a)) ** (1 / (1 - p))
+ m = {g_: a * r ** (1 - p) + w ** (1 - p) * (1 - a)}
+ assert pattern.matches(eq) == m
+ assert (-pattern).matches(-eq) == m
+ assert pattern.matches(signsimp(eq)) is None
+
+
def test_match_terms():
X, Y = map(Wild, "XY")
x, y, z = symbols('x y z')
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index e2f69271119a..4459d1417f9d 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@
default_sort_key)
from sympy.core.sympify import sympify
from sympy.core import (S, Add, Symbol, Equality, Dummy, Expr, Mul,
- Pow, Unequality, Wild)
+ Pow, Unequality)
from sympy.core.exprtools import factor_terms
from sympy.core.function import (expand_mul, expand_log,
Derivative, AppliedUndef, UndefinedFunction, nfloat,
@@ -1447,17 +1447,12 @@ def _solve(f, *symbols, **flags):
return [sol]
poly = None
- # check for a single non-symbol generator
- dums = f_num.atoms(Dummy)
- D = f_num.replace(
- lambda i: isinstance(i, Add) and symbol in i.free_symbols,
- lambda i: Dummy())
- if not D.is_Dummy:
- dgen = D.atoms(Dummy) - dums
- if len(dgen) == 1:
- d = dgen.pop()
- w = Wild('g')
- gen = f_num.match(D.xreplace({d: w}))[w]
+ # check for a single Add generator
+ if not f_num.is_Add:
+ add_args = [i for i in f_num.atoms(Add)
+ if symbol in i.free_symbols]
+ if len(add_args) == 1:
+ gen = add_args[0]
spart = gen.as_independent(symbol)[1].as_base_exp()[0]
if spart == symbol:
try:
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
index c2100197c640..21ffe5d65521 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@
from sympy.testing.pytest import slow, XFAIL, SKIP, raises
from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn
-from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, k, h, p, x, y, z, t, q, m, R
+from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, e, k, h, p, x, y, z, t, q, m, R
def NS(e, n=15, **options):
@@ -2390,3 +2390,9 @@ def test_issue_17454():
def test_issue_21852():
solution = [21 - 21*sqrt(2)/2]
assert solve(2*x + sqrt(2*x**2) - 21) == solution
+
+
+def test_issue_21942():
+ eq = -d + (a*c**(1 - e) + b**(1 - e)*(1 - a))**(1/(1 - e))
+ sol = solve(eq, c, simplify=False, check=False)
+ assert sol == [(b/b**e - b/(a*b**e) + d**(1 - e)/a)**(1/(1 - e))]
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-9057@2fde552
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 9,057
|
Add MFCC Feature Extraction Algorithm
|
### Describe your change:
Added MFCC Audio Signal Feature Extraction Algorithm.
Fixes https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/issues/9026
* [x] Add an algorithm?
* [ ] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [ ] Documentation change?
### Checklist:
* [x] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [x] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [x] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [x] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [x] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [x] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [x] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [x] All new algorithms include at least one URL that points to Wikipedia or another similar explanation.
* [x] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the description above includes the issue number(s) with a [closing keyword](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue): "Fixes #ISSUE-NUMBER".
|
2023-09-12T08:24:30Z
|
Adding MFCC Audio Signal Feature Extraction Algorithm
### Feature description
**Issue Title:**
Adding MFCC Audio Signal Feature Extraction Algorithm
**Issue Description:**
I am planning to contribute to this repository by implementing the MFCC (Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients) audio signal feature extraction algorithm. MFCC is widely used in various applications, including speech recognition and audio analysis.
**Proposed Location:**
I would like to propose adding a new category or subcategory for signal processing or feature extraction. Specifically, I suggest:
- Creating a "Signal Processing" category if one does not exist, and placing the MFCC algorithm under it.
OR
- Creating a "Feature Extraction" subcategory under the "Machine Learning" section and placing MFCC under it.
**Contributor Request:**
I am opening this issue to let the community know about my intention to work on this algorithm. I also welcome suggestions and feedback from other contributors regarding the best location for this feature extraction algorithm and any considerations related to its implementation.
Looking forward to collaborating with the community to enhance this repository with the addition of the MFCC feature extraction algorithm.
|
check [audio_filters](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/tree/master/audio_filters) folder of this repo.
Thanks for your response. @rohan472000
I also checked the audio filter folder, but I didn't find an MFCC implementation there, so I will open a PR to add the MFCC Algorithm. MFCC is commonly categorized as a feature extraction algorithm in machine learning, rather than an audio filter. I'm open to community feedback, and if most agree, I'll add it to the audio filter category.
Yep.. it would be better to put this into machine_learning folder.
The automatic build keeps failing for other algorithm tests. Hey Rohan, What do you suggest I do? @rohan472000
Here is the error message:
=========================== short test summary info ============================
FAILED machine_learning/xgboost_regressor.py::machine_learning.xgboost_regressor.main
FAILED machine_learning/xgboost_regressor.py::machine_learning.xgboost_regressor.xgboost
============ 2 failed, 1473 passed, 16 warnings in 66.14s (0:01:06) ============
Error: Process completed with exit code 1.
I'm working to fix that issue...will raise PR for it...after getting merged your PR's build will be successful.
|
[
{
"body": "### Feature description\n\n**Issue Title:** \r\nAdding MFCC Audio Signal Feature Extraction Algorithm\r\n\r\n**Issue Description:**\r\nI am planning to contribute to this repository by implementing the MFCC (Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients) audio signal feature extraction algorithm. MFCC is widely used in various applications, including speech recognition and audio analysis.\r\n\r\n**Proposed Location:**\r\nI would like to propose adding a new category or subcategory for signal processing or feature extraction. Specifically, I suggest:\r\n- Creating a \"Signal Processing\" category if one does not exist, and placing the MFCC algorithm under it.\r\nOR\r\n- Creating a \"Feature Extraction\" subcategory under the \"Machine Learning\" section and placing MFCC under it.\r\n\r\n**Contributor Request:**\r\nI am opening this issue to let the community know about my intention to work on this algorithm. I also welcome suggestions and feedback from other contributors regarding the best location for this feature extraction algorithm and any considerations related to its implementation.\r\n\r\nLooking forward to collaborating with the community to enhance this repository with the addition of the MFCC feature extraction algorithm.",
"number": 9026,
"title": "Adding MFCC Audio Signal Feature Extraction Algorithm"
}
] |
b203150ac481743a6d8c1ef01091712a54dfbf6c
|
{
"head_commit": "2fde552cb2561114acf792dd1a8cbb979f4396a2",
"head_commit_message": "Update review issues\n* Remove types from docstring\n* Rename dct\n* Add mfcc docstring\n* Add typing to several functions",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/machine_learning/mfcc.py b/machine_learning/mfcc.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..c3d85b526112\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/machine_learning/mfcc.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,484 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) Calculation\n+\n+MFCC is a feature widely used in audio and speech processing to represent the\n+short-term power spectrum of a sound signal in a more compact and\n+discriminative way. It is particularly popular in speech and audio processing\n+tasks such as speech recognition and speaker identification.\n+\n+How MFCC is Calculated:\n+1. Preprocessing:\n+ - Load an audio signal and normalize it to ensure that the values fall\n+ within a specific range (e.g., between -1 and 1).\n+ - Frame the audio signal into overlapping, fixed-length segments, typically\n+ using a technique like windowing to reduce spectral leakage.\n+\n+2. Fourier Transform:\n+ - Apply a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to each audio frame to convert it\n+ from the time domain to the frequency domain. This results in a\n+ representation of the audio frame as a sequence of frequency components.\n+\n+3. Power Spectrum:\n+ - Calculate the power spectrum by taking the squared magnitude of each\n+ frequency component obtained from the FFT. This step measures the energy\n+ distribution across different frequency bands.\n+\n+4. Mel Filterbank:\n+ - Apply a set of triangular filterbanks spaced in the Mel frequency scale\n+ to the power spectrum. These filters mimic the human auditory system's\n+ frequency response. Each filterbank sums the power spectrum values within\n+ its band.\n+\n+5. Logarithmic Compression:\n+ - Take the logarithm (typically base 10) of the filterbank values to\n+ compress the dynamic range. This step mimics the logarithmic response of\n+ the human ear to sound intensity.\n+\n+6. Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT):\n+ - Apply the Discrete Cosine Transform to the log filterbank energies to\n+ obtain the MFCC coefficients. This transformation helps decorrelate the\n+ filterbank energies and captures the most important features of the audio\n+ signal.\n+\n+7. Feature Extraction:\n+ - Select a subset of the DCT coefficients to form the feature vector.\n+ Often, the first few coefficients (e.g., 12-13) are used for most\n+ applications.\n+\n+References:\n+- Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs):\n+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mel-frequency_cepstrum\n+- Speech and Language Processing by Daniel Jurafsky & James H. Martin:\n+ https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/\n+- Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) tutorial\n+ http://practicalcryptography.com/miscellaneous/machine-learning\n+ /guide-mel-frequency-cepstral-coefficients-mfccs/\n+\n+Author: Amir Lavasani\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+\n+import logging\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+import scipy.fftpack as fft\n+from scipy.signal import get_window\n+\n+logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARNING)\n+\n+\n+def mfcc(\n+ audio: np.ndarray,\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+ hop_length: int = 20,\n+ mel_filter_num: int = 10,\n+ dct_filter_num: int = 40,\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) from an audio signal.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal (in Hz).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).\n+ hop_length: The hop length for frame creation (default is 20ms).\n+ mel_filter_num: The number of Mel filters (default is 10).\n+ dct_filter_num: The number of DCT filters (default is 40).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ A matrix of MFCCs for the input audio.\n+\n+ Raises:\n+ ValueError: If the input audio is empty.\n+\n+ Example:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> sample_rate = 44100 # Sample rate of 44.1 kHz\n+ >>> duration = 2.0 # Duration of 1 second\n+ >>> t = np.linspace(0, duration, int(sample_rate * duration), endpoint=False)\n+ >>> audio = 0.5 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 440.0 * t) # Generate a 440 Hz sine wave\n+ >>> mfccs = mfcc(audio, sample_rate)\n+ >>> mfccs.shape\n+ (40, 101)\n+ \"\"\"\n+ logging.info(f\"Sample rate: {sample_rate}Hz\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio duration: {len(audio) / sample_rate}s\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio min: {np.min(audio)}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio max: {np.max(audio)}\")\n+\n+ # normalize audio\n+ audio_normalized = normalize(audio)\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Normalized audio min: {np.min(audio_normalized)}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Normalized audio max: {np.max(audio_normalized)}\")\n+\n+ # frame audio into\n+ audio_framed = audio_frames(\n+ audio_normalized, sample_rate, ftt_size=ftt_size, hop_length=hop_length\n+ )\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Framed audio shape: {audio_framed.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_framed[0]}\")\n+\n+ # convert to frequency domain\n+ # For simplicity we will choose the Hanning window.\n+ window = get_window(\"hann\", ftt_size, fftbins=True)\n+ audio_windowed = audio_framed * window\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Windowed audio shape: {audio_windowed.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_windowed[0]}\")\n+\n+ audio_fft = calculate_fft(audio_windowed, ftt_size)\n+ logging.info(f\"fft audio shape: {audio_fft.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_fft[0]}\")\n+\n+ audio_power = calculate_signal_power(audio_fft)\n+ logging.info(f\"power audio shape: {audio_power.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_power[0]}\")\n+\n+ filters = mel_spaced_filterbank(sample_rate, mel_filter_num, ftt_size)\n+ logging.info(f\"filters shape: {filters.shape}\")\n+\n+ audio_filtered = np.dot(filters, np.transpose(audio_power))\n+ audio_log = 10.0 * np.log10(audio_filtered)\n+ logging.info(f\"audio_log shape: {audio_log.shape}\")\n+\n+ dct_filters = discrete_cosine_transform(dct_filter_num, mel_filter_num)\n+ cepstral_coefficents = np.dot(dct_filters, audio_log)\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"cepstral_coefficents shape: {cepstral_coefficents.shape}\")\n+ return cepstral_coefficents\n+\n+\n+def normalize(audio: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Normalize an audio signal by scaling it to have values between -1 and 1.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The normalized audio signal.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> audio = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])\n+ >>> normalized_audio = normalize(audio)\n+ >>> np.max(normalized_audio)\n+ 1.0\n+ >>> np.min(normalized_audio)\n+ 0.2\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Find the maximum absolute value in the audio signal\n+ max_abs_value = np.max(np.abs(audio))\n+\n+ # Divide the entire audio signal by the maximum absolute value\n+ return audio / max_abs_value\n+\n+\n+def audio_frames(\n+ audio: np.ndarray,\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ hop_length: int = 20,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Split an audio signal into overlapping frames.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal.\n+ hop_length: The length of the hopping (default is 20ms).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ An array of overlapping frames.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> audio = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]*1000)\n+ >>> sample_rate = 8000\n+ >>> frames = audio_frames(audio, sample_rate, hop_length=10, ftt_size=512)\n+ >>> frames.shape\n+ (126, 512)\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ hop_size = np.round(sample_rate * hop_length / 1000).astype(int)\n+\n+ # Pad the audio signal to handle edge cases\n+ audio = np.pad(audio, int(ftt_size / 2), mode=\"reflect\")\n+\n+ # Calculate the number of frames\n+ frame_count = int((len(audio) - ftt_size) / hop_size) + 1\n+\n+ # Initialize an array to store the frames\n+ frames = np.zeros((frame_count, ftt_size))\n+\n+ # Split the audio signal into frames\n+ for n in range(frame_count):\n+ frames[n] = audio[n * hop_size : n * hop_size + ftt_size]\n+\n+ return frames\n+\n+\n+def calculate_fft(audio_windowed: np.ndarray, ftt_size: int = 1024) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of windowed audio data.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio_windowed: The windowed audio signal.\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT (default is 1024).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The FFT of the audio data.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> audio_windowed = np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]])\n+ >>> audio_fft = calculate_fft(audio_windowed, ftt_size=4)\n+ >>> np.allclose(audio_fft[0], np.array([6.0+0.j, -1.5+0.8660254j, -1.5-0.8660254j]))\n+ True\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Transpose the audio data to have time in rows and channels in columns\n+ audio_transposed = np.transpose(audio_windowed)\n+\n+ # Initialize an array to store the FFT results\n+ audio_fft = np.empty(\n+ (int(1 + ftt_size // 2), audio_transposed.shape[1]),\n+ dtype=np.complex64,\n+ order=\"F\",\n+ )\n+\n+ # Compute FFT for each channel\n+ for n in range(audio_fft.shape[1]):\n+ audio_fft[:, n] = fft.fft(audio_transposed[:, n], axis=0)[: audio_fft.shape[0]]\n+\n+ # Transpose the FFT results back to the original shape\n+ return np.transpose(audio_fft)\n+\n+\n+def calculate_signal_power(audio_fft: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate the power of the audio signal from its FFT.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio_fft: The FFT of the audio signal.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The power of the audio signal.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> audio_fft = np.array([1+2j, 2+3j, 3+4j, 4+5j])\n+ >>> power = calculate_signal_power(audio_fft)\n+ >>> np.allclose(power, np.array([5, 13, 25, 41]))\n+ True\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Calculate the power by squaring the absolute values of the FFT coefficients\n+ audio_power = np.square(np.abs(audio_fft))\n+\n+ return audio_power\n+\n+\n+def freq_to_mel(freq: float) -> float:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Convert a frequency in Hertz to the mel scale.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ freq: The frequency in Hertz.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The frequency in mel scale.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> round(freq_to_mel(1000), 2)\n+ 999.99\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Use the formula to convert frequency to the mel scale\n+ return 2595.0 * np.log10(1.0 + freq / 700.0)\n+\n+\n+def mel_to_freq(mels: float) -> float:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Convert a frequency in the mel scale to Hertz.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ mels: The frequency in mel scale.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The frequency in Hertz.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> round(mel_to_freq(999.99), 2)\n+ 1000.01\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Use the formula to convert mel scale to frequency\n+ return 700.0 * (10.0 ** (mels / 2595.0) - 1.0)\n+\n+\n+def mel_spaced_filterbank(\n+ sample_rate: int, mel_filter_num: int = 10, ftt_size: int = 1024\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Create a Mel-spaced filter bank for audio processing.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio.\n+ mel_filter_num: The number of mel filters (default is 10).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT (default is 1024).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ Mel-spaced filter bank.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> round(mel_spaced_filterbank(8000, 10, 1024)[0][1], 10)\n+ 0.0004603981\n+ \"\"\"\n+ freq_min = 0\n+ freq_high = sample_rate // 2\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Minimum frequency: {freq_min}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Maximum frequency: {freq_high}\")\n+\n+ # Calculate filter points and mel frequencies\n+ filter_points, mel_freqs = get_filter_points(\n+ sample_rate,\n+ freq_min,\n+ freq_high,\n+ mel_filter_num,\n+ ftt_size,\n+ )\n+\n+ filters = get_filters(filter_points, ftt_size)\n+\n+ # normalize filters\n+ # taken from the librosa library\n+ enorm = 2.0 / (mel_freqs[2 : mel_filter_num + 2] - mel_freqs[:mel_filter_num])\n+ return filters * enorm[:, np.newaxis]\n+\n+\n+def get_filters(filter_points: np.ndarray, ftt_size: int) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Generate filters for audio processing.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ filter_points: A list of filter points.\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ A matrix of filters.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> get_filters(np.array([0, 20, 51, 95, 161, 256], dtype=int), 512).shape\n+ (4, 257)\n+ \"\"\"\n+ num_filters = len(filter_points) - 2\n+ filters = np.zeros((num_filters, int(ftt_size / 2) + 1))\n+\n+ for n in range(num_filters):\n+ start = filter_points[n]\n+ mid = filter_points[n + 1]\n+ end = filter_points[n + 2]\n+\n+ # Linearly increase values from 0 to 1\n+ filters[n, start:mid] = np.linspace(0, 1, mid - start)\n+\n+ # Linearly decrease values from 1 to 0\n+ filters[n, mid:end] = np.linspace(1, 0, end - mid)\n+\n+ return filters\n+\n+\n+def get_filter_points(\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ freq_min: int,\n+ freq_high: int,\n+ mel_filter_num: int = 10,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate the filter points and frequencies for mel frequency filters.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio.\n+ freq_min: The minimum frequency in Hertz.\n+ freq_high: The maximum frequency in Hertz.\n+ mel_filter_num: The number of mel filters (default is 10).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT (default is 1024).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ Filter points and corresponding frequencies.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> get_filter_points(8000, 0, 4000, mel_filter_num=4, ftt_size=512)[0]\n+ array([ 0, 20, 51, 95, 161, 256])\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Convert minimum and maximum frequencies to mel scale\n+ fmin_mel = freq_to_mel(freq_min)\n+ fmax_mel = freq_to_mel(freq_high)\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"MEL min: {fmin_mel}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"MEL max: {fmax_mel}\")\n+\n+ # Generate equally spaced mel frequencies\n+ mels = np.linspace(fmin_mel, fmax_mel, num=mel_filter_num + 2)\n+\n+ # Convert mel frequencies back to Hertz\n+ freqs = mel_to_freq(mels)\n+\n+ # Calculate filter points as integer values\n+ filter_points = np.floor((ftt_size + 1) / sample_rate * freqs).astype(int)\n+\n+ return filter_points, freqs\n+\n+\n+def discrete_cosine_transform(dct_filter_num: int, filter_num: int) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Compute the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) basis matrix.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ dct_filter_num: The number of DCT filters to generate.\n+ filter_num: The number of the fbank filters.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The DCT basis matrix.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> round(discrete_cosine_transform(3, 5)[0][0], 5)\n+ 0.44721\n+ \"\"\"\n+ basis = np.empty((dct_filter_num, filter_num))\n+ basis[0, :] = 1.0 / np.sqrt(filter_num)\n+\n+ samples = np.arange(1, 2 * filter_num, 2) * np.pi / (2.0 * filter_num)\n+\n+ for i in range(1, dct_filter_num):\n+ basis[i, :] = np.cos(i * samples) * np.sqrt(2.0 / filter_num)\n+\n+ return basis\n+\n+\n+def example(wav_file_path: str = \"./path-to-file/sample.wav\") -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Example function to calculate Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients\n+ (MFCCs) from an audio file.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ wav_file_path: The path to the WAV audio file.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ np.ndarray: The computed MFCCs for the audio.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ from scipy.io import wavfile\n+\n+ # Load the audio from the WAV file\n+ sample_rate, audio = wavfile.read(wav_file_path)\n+\n+ # Calculate MFCCs\n+ return mfcc(audio, sample_rate)\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ import doctest\n+\n+ doctest.testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,484 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) Calculation\n+\n+MFCC is a feature widely used in audio and speech processing to represent the\n+short-term power spectrum of a sound signal in a more compact and\n+discriminative way. It is particularly popular in speech and audio processing\n+tasks such as speech recognition and speaker identification.\n+\n+How MFCC is Calculated:\n+1. Preprocessing:\n+ - Load an audio signal and normalize it to ensure that the values fall\n+ within a specific range (e.g., between -1 and 1).\n+ - Frame the audio signal into overlapping, fixed-length segments, typically\n+ using a technique like windowing to reduce spectral leakage.\n+\n+2. Fourier Transform:\n+ - Apply a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to each audio frame to convert it\n+ from the time domain to the frequency domain. This results in a\n+ representation of the audio frame as a sequence of frequency components.\n+\n+3. Power Spectrum:\n+ - Calculate the power spectrum by taking the squared magnitude of each\n+ frequency component obtained from the FFT. This step measures the energy\n+ distribution across different frequency bands.\n+\n+4. Mel Filterbank:\n+ - Apply a set of triangular filterbanks spaced in the Mel frequency scale\n+ to the power spectrum. These filters mimic the human auditory system's\n+ frequency response. Each filterbank sums the power spectrum values within\n+ its band.\n+\n+5. Logarithmic Compression:\n+ - Take the logarithm (typically base 10) of the filterbank values to\n+ compress the dynamic range. This step mimics the logarithmic response of\n+ the human ear to sound intensity.\n+\n+6. Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT):\n+ - Apply the Discrete Cosine Transform to the log filterbank energies to\n+ obtain the MFCC coefficients. This transformation helps decorrelate the\n+ filterbank energies and captures the most important features of the audio\n+ signal.\n+\n+7. Feature Extraction:\n+ - Select a subset of the DCT coefficients to form the feature vector.\n+ Often, the first few coefficients (e.g., 12-13) are used for most\n+ applications.\n+\n+References:\n+- Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs):\n+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mel-frequency_cepstrum\n+- Speech and Language Processing by Daniel Jurafsky & James H. Martin:\n+ https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/\n+- Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) tutorial\n+ http://practicalcryptography.com/miscellaneous/machine-learning\n+ /guide-mel-frequency-cepstral-coefficients-mfccs/\n+\n+Author: Amir Lavasani\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+\n+import logging\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+import scipy.fftpack as fft\n+from scipy.signal import get_window\n+\n+logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARNING)\n+\n+\n+def mfcc(\n+ audio: np.ndarray,\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+ hop_length: int = 20,\n+ mel_filter_num: int = 10,\n+ dct_filter_num: int = 40,\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) from an audio signal.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal (in Hz).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).\n+ hop_length: The hop length for frame creation (default is 20ms).\n+ mel_filter_num: The number of Mel filters (default is 10).\n+ dct_filter_num: The number of DCT filters (default is 40).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ A matrix of MFCCs for the input audio.\n+\n+ Raises:\n+ ValueError: If the input audio is empty.\n+\n+ Example:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> sample_rate = 44100 # Sample rate of 44.1 kHz\n+ >>> duration = 2.0 # Duration of 1 second\n+ >>> t = np.linspace(0, duration, int(sample_rate * duration), endpoint=False)\n+ >>> audio = 0.5 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 440.0 * t) # Generate a 440 Hz sine wave\n+ >>> mfccs = mfcc(audio, sample_rate)\n+ >>> mfccs.shape\n+ (40, 101)\n+ \"\"\"\n+ logging.info(f\"Sample rate: {sample_rate}Hz\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio duration: {len(audio) / sample_rate}s\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio min: {np.min(audio)}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio max: {np.max(audio)}\")\n+\n+ # normalize audio\n+ audio_normalized = normalize(audio)\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Normalized audio min: {np.min(audio_normalized)}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Normalized audio max: {np.max(audio_normalized)}\")\n+\n+ # frame audio into\n+ audio_framed = audio_frames(\n+ audio_normalized, sample_rate, ftt_size=ftt_size, hop_length=hop_length\n+ )\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Framed audio shape: {audio_framed.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_framed[0]}\")\n+\n+ # convert to frequency domain\n+ # For simplicity we will choose the Hanning window.\n+ window = get_window(\"hann\", ftt_size, fftbins=True)\n+ audio_windowed = audio_framed * window\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Windowed audio shape: {audio_windowed.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_windowed[0]}\")\n+\n+ audio_fft = calculate_fft(audio_windowed, ftt_size)\n+ logging.info(f\"fft audio shape: {audio_fft.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_fft[0]}\")\n+\n+ audio_power = calculate_signal_power(audio_fft)\n+ logging.info(f\"power audio shape: {audio_power.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_power[0]}\")\n+\n+ filters = mel_spaced_filterbank(sample_rate, mel_filter_num, ftt_size)\n+ logging.info(f\"filters shape: {filters.shape}\")\n+\n+ audio_filtered = np.dot(filters, np.transpose(audio_power))\n+ audio_log = 10.0 * np.log10(audio_filtered)\n+ logging.info(f\"audio_log shape: {audio_log.shape}\")\n+\n+ dct_filters = discrete_cosine_transform(dct_filter_num, mel_filter_num)\n+ cepstral_coefficents = np.dot(dct_filters, audio_log)\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"cepstral_coefficents shape: {cepstral_coefficents.shape}\")\n+ return cepstral_coefficents\n+\n+\n+def normalize(audio: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Normalize an audio signal by scaling it to have values between -1 and 1.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The normalized audio signal.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> audio = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])\n+ >>> normalized_audio = normalize(audio)\n+ >>> np.max(normalized_audio)\n+ 1.0\n+ >>> np.min(normalized_audio)\n+ 0.2\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Find the maximum absolute value in the audio signal\n+ max_abs_value = np.max(np.abs(audio))\n+\n+ # Divide the entire audio signal by the maximum absolute value\n+ return audio / max_abs_value\n+\n+\n+def audio_frames(\n+ audio: np.ndarray,\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ hop_length: int = 20,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Split an audio signal into overlapping frames.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal.\n+ hop_length: The length of the hopping (default is 20ms).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ An array of overlapping frames.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> audio = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]*1000)\n+ >>> sample_rate = 8000\n+ >>> frames = audio_frames(audio, sample_rate, hop_length=10, ftt_size=512)\n+ >>> frames.shape\n+ (126, 512)\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ hop_size = np.round(sample_rate * hop_length / 1000).astype(int)\n+\n+ # Pad the audio signal to handle edge cases\n+ audio = np.pad(audio, int(ftt_size / 2), mode=\"reflect\")\n+\n+ # Calculate the number of frames\n+ frame_count = int((len(audio) - ftt_size) / hop_size) + 1\n+\n+ # Initialize an array to store the frames\n+ frames = np.zeros((frame_count, ftt_size))\n+\n+ # Split the audio signal into frames\n+ for n in range(frame_count):\n+ frames[n] = audio[n * hop_size : n * hop_size + ftt_size]\n+\n+ return frames\n+\n+\n+def calculate_fft(audio_windowed: np.ndarray, ftt_size: int = 1024) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of windowed audio data.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio_windowed: The windowed audio signal.\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT (default is 1024).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The FFT of the audio data.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> import numpy as np",
"line": null,
"original_line": 236,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "machine_learning/mfcc.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis was already done on line 63\r\n```suggestion\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,484 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) Calculation\n+\n+MFCC is a feature widely used in audio and speech processing to represent the\n+short-term power spectrum of a sound signal in a more compact and\n+discriminative way. It is particularly popular in speech and audio processing\n+tasks such as speech recognition and speaker identification.\n+\n+How MFCC is Calculated:\n+1. Preprocessing:\n+ - Load an audio signal and normalize it to ensure that the values fall\n+ within a specific range (e.g., between -1 and 1).\n+ - Frame the audio signal into overlapping, fixed-length segments, typically\n+ using a technique like windowing to reduce spectral leakage.\n+\n+2. Fourier Transform:\n+ - Apply a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to each audio frame to convert it\n+ from the time domain to the frequency domain. This results in a\n+ representation of the audio frame as a sequence of frequency components.\n+\n+3. Power Spectrum:\n+ - Calculate the power spectrum by taking the squared magnitude of each\n+ frequency component obtained from the FFT. This step measures the energy\n+ distribution across different frequency bands.\n+\n+4. Mel Filterbank:\n+ - Apply a set of triangular filterbanks spaced in the Mel frequency scale\n+ to the power spectrum. These filters mimic the human auditory system's\n+ frequency response. Each filterbank sums the power spectrum values within\n+ its band.\n+\n+5. Logarithmic Compression:\n+ - Take the logarithm (typically base 10) of the filterbank values to\n+ compress the dynamic range. This step mimics the logarithmic response of\n+ the human ear to sound intensity.\n+\n+6. Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT):\n+ - Apply the Discrete Cosine Transform to the log filterbank energies to\n+ obtain the MFCC coefficients. This transformation helps decorrelate the\n+ filterbank energies and captures the most important features of the audio\n+ signal.\n+\n+7. Feature Extraction:\n+ - Select a subset of the DCT coefficients to form the feature vector.\n+ Often, the first few coefficients (e.g., 12-13) are used for most\n+ applications.\n+\n+References:\n+- Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs):\n+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mel-frequency_cepstrum\n+- Speech and Language Processing by Daniel Jurafsky & James H. Martin:\n+ https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/\n+- Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) tutorial\n+ http://practicalcryptography.com/miscellaneous/machine-learning\n+ /guide-mel-frequency-cepstral-coefficients-mfccs/\n+\n+Author: Amir Lavasani\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+\n+import logging\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+import scipy.fftpack as fft\n+from scipy.signal import get_window\n+\n+logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARNING)\n+\n+\n+def mfcc(\n+ audio: np.ndarray,\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+ hop_length: int = 20,\n+ mel_filter_num: int = 10,\n+ dct_filter_num: int = 40,\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) from an audio signal.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal (in Hz).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).\n+ hop_length: The hop length for frame creation (default is 20ms).\n+ mel_filter_num: The number of Mel filters (default is 10).\n+ dct_filter_num: The number of DCT filters (default is 40).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ A matrix of MFCCs for the input audio.\n+\n+ Raises:\n+ ValueError: If the input audio is empty.\n+\n+ Example:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> sample_rate = 44100 # Sample rate of 44.1 kHz\n+ >>> duration = 2.0 # Duration of 1 second\n+ >>> t = np.linspace(0, duration, int(sample_rate * duration), endpoint=False)\n+ >>> audio = 0.5 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 440.0 * t) # Generate a 440 Hz sine wave\n+ >>> mfccs = mfcc(audio, sample_rate)\n+ >>> mfccs.shape\n+ (40, 101)\n+ \"\"\"\n+ logging.info(f\"Sample rate: {sample_rate}Hz\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio duration: {len(audio) / sample_rate}s\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio min: {np.min(audio)}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio max: {np.max(audio)}\")\n+\n+ # normalize audio\n+ audio_normalized = normalize(audio)\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Normalized audio min: {np.min(audio_normalized)}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Normalized audio max: {np.max(audio_normalized)}\")\n+\n+ # frame audio into\n+ audio_framed = audio_frames(\n+ audio_normalized, sample_rate, ftt_size=ftt_size, hop_length=hop_length\n+ )\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Framed audio shape: {audio_framed.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_framed[0]}\")\n+\n+ # convert to frequency domain\n+ # For simplicity we will choose the Hanning window.\n+ window = get_window(\"hann\", ftt_size, fftbins=True)\n+ audio_windowed = audio_framed * window\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Windowed audio shape: {audio_windowed.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_windowed[0]}\")\n+\n+ audio_fft = calculate_fft(audio_windowed, ftt_size)\n+ logging.info(f\"fft audio shape: {audio_fft.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_fft[0]}\")\n+\n+ audio_power = calculate_signal_power(audio_fft)\n+ logging.info(f\"power audio shape: {audio_power.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_power[0]}\")\n+\n+ filters = mel_spaced_filterbank(sample_rate, mel_filter_num, ftt_size)\n+ logging.info(f\"filters shape: {filters.shape}\")\n+\n+ audio_filtered = np.dot(filters, np.transpose(audio_power))\n+ audio_log = 10.0 * np.log10(audio_filtered)\n+ logging.info(f\"audio_log shape: {audio_log.shape}\")\n+\n+ dct_filters = discrete_cosine_transform(dct_filter_num, mel_filter_num)\n+ cepstral_coefficents = np.dot(dct_filters, audio_log)\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"cepstral_coefficents shape: {cepstral_coefficents.shape}\")\n+ return cepstral_coefficents\n+\n+\n+def normalize(audio: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Normalize an audio signal by scaling it to have values between -1 and 1.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The normalized audio signal.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> audio = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])\n+ >>> normalized_audio = normalize(audio)\n+ >>> np.max(normalized_audio)\n+ 1.0\n+ >>> np.min(normalized_audio)\n+ 0.2\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Find the maximum absolute value in the audio signal\n+ max_abs_value = np.max(np.abs(audio))\n+\n+ # Divide the entire audio signal by the maximum absolute value\n+ return audio / max_abs_value\n+\n+\n+def audio_frames(\n+ audio: np.ndarray,\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ hop_length: int = 20,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Split an audio signal into overlapping frames.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal.\n+ hop_length: The length of the hopping (default is 20ms).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ An array of overlapping frames.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> import numpy as np",
"line": null,
"original_line": 198,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "machine_learning/mfcc.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis was already done on line 63\r\n```suggestion\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,484 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) Calculation\n+\n+MFCC is a feature widely used in audio and speech processing to represent the\n+short-term power spectrum of a sound signal in a more compact and\n+discriminative way. It is particularly popular in speech and audio processing\n+tasks such as speech recognition and speaker identification.\n+\n+How MFCC is Calculated:\n+1. Preprocessing:\n+ - Load an audio signal and normalize it to ensure that the values fall\n+ within a specific range (e.g., between -1 and 1).\n+ - Frame the audio signal into overlapping, fixed-length segments, typically\n+ using a technique like windowing to reduce spectral leakage.\n+\n+2. Fourier Transform:\n+ - Apply a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to each audio frame to convert it\n+ from the time domain to the frequency domain. This results in a\n+ representation of the audio frame as a sequence of frequency components.\n+\n+3. Power Spectrum:\n+ - Calculate the power spectrum by taking the squared magnitude of each\n+ frequency component obtained from the FFT. This step measures the energy\n+ distribution across different frequency bands.\n+\n+4. Mel Filterbank:\n+ - Apply a set of triangular filterbanks spaced in the Mel frequency scale\n+ to the power spectrum. These filters mimic the human auditory system's\n+ frequency response. Each filterbank sums the power spectrum values within\n+ its band.\n+\n+5. Logarithmic Compression:\n+ - Take the logarithm (typically base 10) of the filterbank values to\n+ compress the dynamic range. This step mimics the logarithmic response of\n+ the human ear to sound intensity.\n+\n+6. Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT):\n+ - Apply the Discrete Cosine Transform to the log filterbank energies to\n+ obtain the MFCC coefficients. This transformation helps decorrelate the\n+ filterbank energies and captures the most important features of the audio\n+ signal.\n+\n+7. Feature Extraction:\n+ - Select a subset of the DCT coefficients to form the feature vector.\n+ Often, the first few coefficients (e.g., 12-13) are used for most\n+ applications.\n+\n+References:\n+- Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs):\n+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mel-frequency_cepstrum\n+- Speech and Language Processing by Daniel Jurafsky & James H. Martin:\n+ https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/\n+- Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) tutorial\n+ http://practicalcryptography.com/miscellaneous/machine-learning\n+ /guide-mel-frequency-cepstral-coefficients-mfccs/\n+\n+Author: Amir Lavasani\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+\n+import logging\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+import scipy.fftpack as fft\n+from scipy.signal import get_window\n+\n+logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARNING)\n+\n+\n+def mfcc(\n+ audio: np.ndarray,\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+ hop_length: int = 20,\n+ mel_filter_num: int = 10,\n+ dct_filter_num: int = 40,\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) from an audio signal.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal (in Hz).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).\n+ hop_length: The hop length for frame creation (default is 20ms).\n+ mel_filter_num: The number of Mel filters (default is 10).\n+ dct_filter_num: The number of DCT filters (default is 40).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ A matrix of MFCCs for the input audio.\n+\n+ Raises:\n+ ValueError: If the input audio is empty.\n+\n+ Example:\n+ >>> import numpy as np",
"line": null,
"original_line": 96,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "machine_learning/mfcc.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis was already done on line 63\r\n```suggestion\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,484 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) Calculation\n+\n+MFCC is a feature widely used in audio and speech processing to represent the\n+short-term power spectrum of a sound signal in a more compact and\n+discriminative way. It is particularly popular in speech and audio processing\n+tasks such as speech recognition and speaker identification.\n+\n+How MFCC is Calculated:\n+1. Preprocessing:\n+ - Load an audio signal and normalize it to ensure that the values fall\n+ within a specific range (e.g., between -1 and 1).\n+ - Frame the audio signal into overlapping, fixed-length segments, typically\n+ using a technique like windowing to reduce spectral leakage.\n+\n+2. Fourier Transform:\n+ - Apply a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to each audio frame to convert it\n+ from the time domain to the frequency domain. This results in a\n+ representation of the audio frame as a sequence of frequency components.\n+\n+3. Power Spectrum:\n+ - Calculate the power spectrum by taking the squared magnitude of each\n+ frequency component obtained from the FFT. This step measures the energy\n+ distribution across different frequency bands.\n+\n+4. Mel Filterbank:\n+ - Apply a set of triangular filterbanks spaced in the Mel frequency scale\n+ to the power spectrum. These filters mimic the human auditory system's\n+ frequency response. Each filterbank sums the power spectrum values within\n+ its band.\n+\n+5. Logarithmic Compression:\n+ - Take the logarithm (typically base 10) of the filterbank values to\n+ compress the dynamic range. This step mimics the logarithmic response of\n+ the human ear to sound intensity.\n+\n+6. Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT):\n+ - Apply the Discrete Cosine Transform to the log filterbank energies to\n+ obtain the MFCC coefficients. This transformation helps decorrelate the\n+ filterbank energies and captures the most important features of the audio\n+ signal.\n+\n+7. Feature Extraction:\n+ - Select a subset of the DCT coefficients to form the feature vector.\n+ Often, the first few coefficients (e.g., 12-13) are used for most\n+ applications.\n+\n+References:\n+- Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs):\n+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mel-frequency_cepstrum\n+- Speech and Language Processing by Daniel Jurafsky & James H. Martin:\n+ https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/\n+- Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) tutorial\n+ http://practicalcryptography.com/miscellaneous/machine-learning\n+ /guide-mel-frequency-cepstral-coefficients-mfccs/\n+\n+Author: Amir Lavasani\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+\n+import logging\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+import scipy.fftpack as fft\n+from scipy.signal import get_window\n+\n+logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARNING)\n+\n+\n+def mfcc(\n+ audio: np.ndarray,\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+ hop_length: int = 20,\n+ mel_filter_num: int = 10,\n+ dct_filter_num: int = 40,\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) from an audio signal.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal (in Hz).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).\n+ hop_length: The hop length for frame creation (default is 20ms).\n+ mel_filter_num: The number of Mel filters (default is 10).\n+ dct_filter_num: The number of DCT filters (default is 40).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ A matrix of MFCCs for the input audio.\n+\n+ Raises:\n+ ValueError: If the input audio is empty.\n+\n+ Example:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> sample_rate = 44100 # Sample rate of 44.1 kHz\n+ >>> duration = 2.0 # Duration of 1 second\n+ >>> t = np.linspace(0, duration, int(sample_rate * duration), endpoint=False)\n+ >>> audio = 0.5 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 440.0 * t) # Generate a 440 Hz sine wave\n+ >>> mfccs = mfcc(audio, sample_rate)\n+ >>> mfccs.shape\n+ (40, 101)\n+ \"\"\"\n+ logging.info(f\"Sample rate: {sample_rate}Hz\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio duration: {len(audio) / sample_rate}s\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio min: {np.min(audio)}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Audio max: {np.max(audio)}\")\n+\n+ # normalize audio\n+ audio_normalized = normalize(audio)\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Normalized audio min: {np.min(audio_normalized)}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"Normalized audio max: {np.max(audio_normalized)}\")\n+\n+ # frame audio into\n+ audio_framed = audio_frames(\n+ audio_normalized, sample_rate, ftt_size=ftt_size, hop_length=hop_length\n+ )\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Framed audio shape: {audio_framed.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_framed[0]}\")\n+\n+ # convert to frequency domain\n+ # For simplicity we will choose the Hanning window.\n+ window = get_window(\"hann\", ftt_size, fftbins=True)\n+ audio_windowed = audio_framed * window\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"Windowed audio shape: {audio_windowed.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_windowed[0]}\")\n+\n+ audio_fft = calculate_fft(audio_windowed, ftt_size)\n+ logging.info(f\"fft audio shape: {audio_fft.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_fft[0]}\")\n+\n+ audio_power = calculate_signal_power(audio_fft)\n+ logging.info(f\"power audio shape: {audio_power.shape}\")\n+ logging.info(f\"First frame: {audio_power[0]}\")\n+\n+ filters = mel_spaced_filterbank(sample_rate, mel_filter_num, ftt_size)\n+ logging.info(f\"filters shape: {filters.shape}\")\n+\n+ audio_filtered = np.dot(filters, np.transpose(audio_power))\n+ audio_log = 10.0 * np.log10(audio_filtered)\n+ logging.info(f\"audio_log shape: {audio_log.shape}\")\n+\n+ dct_filters = discrete_cosine_transform(dct_filter_num, mel_filter_num)\n+ cepstral_coefficents = np.dot(dct_filters, audio_log)\n+\n+ logging.info(f\"cepstral_coefficents shape: {cepstral_coefficents.shape}\")\n+ return cepstral_coefficents\n+\n+\n+def normalize(audio: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Normalize an audio signal by scaling it to have values between -1 and 1.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The normalized audio signal.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> audio = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])\n+ >>> normalized_audio = normalize(audio)\n+ >>> np.max(normalized_audio)\n+ 1.0\n+ >>> np.min(normalized_audio)\n+ 0.2\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Find the maximum absolute value in the audio signal\n+ max_abs_value = np.max(np.abs(audio))\n+\n+ # Divide the entire audio signal by the maximum absolute value\n+ return audio / max_abs_value\n+\n+\n+def audio_frames(\n+ audio: np.ndarray,\n+ sample_rate: int,\n+ hop_length: int = 20,\n+ ftt_size: int = 1024,\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Split an audio signal into overlapping frames.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio: The input audio signal.\n+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal.\n+ hop_length: The length of the hopping (default is 20ms).\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ An array of overlapping frames.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> audio = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]*1000)\n+ >>> sample_rate = 8000\n+ >>> frames = audio_frames(audio, sample_rate, hop_length=10, ftt_size=512)\n+ >>> frames.shape\n+ (126, 512)\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ hop_size = np.round(sample_rate * hop_length / 1000).astype(int)\n+\n+ # Pad the audio signal to handle edge cases\n+ audio = np.pad(audio, int(ftt_size / 2), mode=\"reflect\")\n+\n+ # Calculate the number of frames\n+ frame_count = int((len(audio) - ftt_size) / hop_size) + 1\n+\n+ # Initialize an array to store the frames\n+ frames = np.zeros((frame_count, ftt_size))\n+\n+ # Split the audio signal into frames\n+ for n in range(frame_count):\n+ frames[n] = audio[n * hop_size : n * hop_size + ftt_size]\n+\n+ return frames\n+\n+\n+def calculate_fft(audio_windowed: np.ndarray, ftt_size: int = 1024) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of windowed audio data.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio_windowed: The windowed audio signal.\n+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT (default is 1024).\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The FFT of the audio data.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> import numpy as np\n+ >>> audio_windowed = np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]])\n+ >>> audio_fft = calculate_fft(audio_windowed, ftt_size=4)\n+ >>> np.allclose(audio_fft[0], np.array([6.0+0.j, -1.5+0.8660254j, -1.5-0.8660254j]))\n+ True\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Transpose the audio data to have time in rows and channels in columns\n+ audio_transposed = np.transpose(audio_windowed)\n+\n+ # Initialize an array to store the FFT results\n+ audio_fft = np.empty(\n+ (int(1 + ftt_size // 2), audio_transposed.shape[1]),\n+ dtype=np.complex64,\n+ order=\"F\",\n+ )\n+\n+ # Compute FFT for each channel\n+ for n in range(audio_fft.shape[1]):\n+ audio_fft[:, n] = fft.fft(audio_transposed[:, n], axis=0)[: audio_fft.shape[0]]\n+\n+ # Transpose the FFT results back to the original shape\n+ return np.transpose(audio_fft)\n+\n+\n+def calculate_signal_power(audio_fft: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Calculate the power of the audio signal from its FFT.\n+\n+ Args:\n+ audio_fft: The FFT of the audio signal.\n+\n+ Returns:\n+ The power of the audio signal.\n+\n+ Examples:\n+ >>> import numpy as np",
"line": null,
"original_line": 271,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "machine_learning/mfcc.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis was already done on line 63\r\n```suggestion\r\n```"
}
] |
e143e5b12f88742e3739fd76f5c4e1bd06ec79dd
|
diff --git a/machine_learning/mfcc.py b/machine_learning/mfcc.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..7ce8ceb50ff2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/machine_learning/mfcc.py
@@ -0,0 +1,479 @@
+"""
+Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) Calculation
+
+MFCC is an algorithm widely used in audio and speech processing to represent the
+short-term power spectrum of a sound signal in a more compact and
+discriminative way. It is particularly popular in speech and audio processing
+tasks such as speech recognition and speaker identification.
+
+How Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients are Calculated:
+1. Preprocessing:
+ - Load an audio signal and normalize it to ensure that the values fall
+ within a specific range (e.g., between -1 and 1).
+ - Frame the audio signal into overlapping, fixed-length segments, typically
+ using a technique like windowing to reduce spectral leakage.
+
+2. Fourier Transform:
+ - Apply a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to each audio frame to convert it
+ from the time domain to the frequency domain. This results in a
+ representation of the audio frame as a sequence of frequency components.
+
+3. Power Spectrum:
+ - Calculate the power spectrum by taking the squared magnitude of each
+ frequency component obtained from the FFT. This step measures the energy
+ distribution across different frequency bands.
+
+4. Mel Filterbank:
+ - Apply a set of triangular filterbanks spaced in the Mel frequency scale
+ to the power spectrum. These filters mimic the human auditory system's
+ frequency response. Each filterbank sums the power spectrum values within
+ its band.
+
+5. Logarithmic Compression:
+ - Take the logarithm (typically base 10) of the filterbank values to
+ compress the dynamic range. This step mimics the logarithmic response of
+ the human ear to sound intensity.
+
+6. Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT):
+ - Apply the Discrete Cosine Transform to the log filterbank energies to
+ obtain the MFCC coefficients. This transformation helps decorrelate the
+ filterbank energies and captures the most important features of the audio
+ signal.
+
+7. Feature Extraction:
+ - Select a subset of the DCT coefficients to form the feature vector.
+ Often, the first few coefficients (e.g., 12-13) are used for most
+ applications.
+
+References:
+- Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs):
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mel-frequency_cepstrum
+- Speech and Language Processing by Daniel Jurafsky & James H. Martin:
+ https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/
+- Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) tutorial
+ http://practicalcryptography.com/miscellaneous/machine-learning
+ /guide-mel-frequency-cepstral-coefficients-mfccs/
+
+Author: Amir Lavasani
+"""
+
+
+import logging
+
+import numpy as np
+import scipy.fftpack as fft
+from scipy.signal import get_window
+
+logging.basicConfig(filename=f"{__file__}.log", level=logging.INFO)
+
+
+def mfcc(
+ audio: np.ndarray,
+ sample_rate: int,
+ ftt_size: int = 1024,
+ hop_length: int = 20,
+ mel_filter_num: int = 10,
+ dct_filter_num: int = 40,
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Calculate Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) from an audio signal.
+
+ Args:
+ audio: The input audio signal.
+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal (in Hz).
+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).
+ hop_length: The hop length for frame creation (default is 20ms).
+ mel_filter_num: The number of Mel filters (default is 10).
+ dct_filter_num: The number of DCT filters (default is 40).
+
+ Returns:
+ A matrix of MFCCs for the input audio.
+
+ Raises:
+ ValueError: If the input audio is empty.
+
+ Example:
+ >>> sample_rate = 44100 # Sample rate of 44.1 kHz
+ >>> duration = 2.0 # Duration of 1 second
+ >>> t = np.linspace(0, duration, int(sample_rate * duration), endpoint=False)
+ >>> audio = 0.5 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 440.0 * t) # Generate a 440 Hz sine wave
+ >>> mfccs = mfcc(audio, sample_rate)
+ >>> mfccs.shape
+ (40, 101)
+ """
+ logging.info(f"Sample rate: {sample_rate}Hz")
+ logging.info(f"Audio duration: {len(audio) / sample_rate}s")
+ logging.info(f"Audio min: {np.min(audio)}")
+ logging.info(f"Audio max: {np.max(audio)}")
+
+ # normalize audio
+ audio_normalized = normalize(audio)
+
+ logging.info(f"Normalized audio min: {np.min(audio_normalized)}")
+ logging.info(f"Normalized audio max: {np.max(audio_normalized)}")
+
+ # frame audio into
+ audio_framed = audio_frames(
+ audio_normalized, sample_rate, ftt_size=ftt_size, hop_length=hop_length
+ )
+
+ logging.info(f"Framed audio shape: {audio_framed.shape}")
+ logging.info(f"First frame: {audio_framed[0]}")
+
+ # convert to frequency domain
+ # For simplicity we will choose the Hanning window.
+ window = get_window("hann", ftt_size, fftbins=True)
+ audio_windowed = audio_framed * window
+
+ logging.info(f"Windowed audio shape: {audio_windowed.shape}")
+ logging.info(f"First frame: {audio_windowed[0]}")
+
+ audio_fft = calculate_fft(audio_windowed, ftt_size)
+ logging.info(f"fft audio shape: {audio_fft.shape}")
+ logging.info(f"First frame: {audio_fft[0]}")
+
+ audio_power = calculate_signal_power(audio_fft)
+ logging.info(f"power audio shape: {audio_power.shape}")
+ logging.info(f"First frame: {audio_power[0]}")
+
+ filters = mel_spaced_filterbank(sample_rate, mel_filter_num, ftt_size)
+ logging.info(f"filters shape: {filters.shape}")
+
+ audio_filtered = np.dot(filters, np.transpose(audio_power))
+ audio_log = 10.0 * np.log10(audio_filtered)
+ logging.info(f"audio_log shape: {audio_log.shape}")
+
+ dct_filters = discrete_cosine_transform(dct_filter_num, mel_filter_num)
+ cepstral_coefficents = np.dot(dct_filters, audio_log)
+
+ logging.info(f"cepstral_coefficents shape: {cepstral_coefficents.shape}")
+ return cepstral_coefficents
+
+
+def normalize(audio: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Normalize an audio signal by scaling it to have values between -1 and 1.
+
+ Args:
+ audio: The input audio signal.
+
+ Returns:
+ The normalized audio signal.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> audio = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
+ >>> normalized_audio = normalize(audio)
+ >>> np.max(normalized_audio)
+ 1.0
+ >>> np.min(normalized_audio)
+ 0.2
+ """
+ # Divide the entire audio signal by the maximum absolute value
+ return audio / np.max(np.abs(audio))
+
+
+def audio_frames(
+ audio: np.ndarray,
+ sample_rate: int,
+ hop_length: int = 20,
+ ftt_size: int = 1024,
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Split an audio signal into overlapping frames.
+
+ Args:
+ audio: The input audio signal.
+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio signal.
+ hop_length: The length of the hopping (default is 20ms).
+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT window (default is 1024).
+
+ Returns:
+ An array of overlapping frames.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> audio = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]*1000)
+ >>> sample_rate = 8000
+ >>> frames = audio_frames(audio, sample_rate, hop_length=10, ftt_size=512)
+ >>> frames.shape
+ (126, 512)
+ """
+
+ hop_size = np.round(sample_rate * hop_length / 1000).astype(int)
+
+ # Pad the audio signal to handle edge cases
+ audio = np.pad(audio, int(ftt_size / 2), mode="reflect")
+
+ # Calculate the number of frames
+ frame_count = int((len(audio) - ftt_size) / hop_size) + 1
+
+ # Initialize an array to store the frames
+ frames = np.zeros((frame_count, ftt_size))
+
+ # Split the audio signal into frames
+ for n in range(frame_count):
+ frames[n] = audio[n * hop_size : n * hop_size + ftt_size]
+
+ return frames
+
+
+def calculate_fft(audio_windowed: np.ndarray, ftt_size: int = 1024) -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Calculate the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of windowed audio data.
+
+ Args:
+ audio_windowed: The windowed audio signal.
+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT (default is 1024).
+
+ Returns:
+ The FFT of the audio data.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> audio_windowed = np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]])
+ >>> audio_fft = calculate_fft(audio_windowed, ftt_size=4)
+ >>> np.allclose(audio_fft[0], np.array([6.0+0.j, -1.5+0.8660254j, -1.5-0.8660254j]))
+ True
+ """
+ # Transpose the audio data to have time in rows and channels in columns
+ audio_transposed = np.transpose(audio_windowed)
+
+ # Initialize an array to store the FFT results
+ audio_fft = np.empty(
+ (int(1 + ftt_size // 2), audio_transposed.shape[1]),
+ dtype=np.complex64,
+ order="F",
+ )
+
+ # Compute FFT for each channel
+ for n in range(audio_fft.shape[1]):
+ audio_fft[:, n] = fft.fft(audio_transposed[:, n], axis=0)[: audio_fft.shape[0]]
+
+ # Transpose the FFT results back to the original shape
+ return np.transpose(audio_fft)
+
+
+def calculate_signal_power(audio_fft: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Calculate the power of the audio signal from its FFT.
+
+ Args:
+ audio_fft: The FFT of the audio signal.
+
+ Returns:
+ The power of the audio signal.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> audio_fft = np.array([1+2j, 2+3j, 3+4j, 4+5j])
+ >>> power = calculate_signal_power(audio_fft)
+ >>> np.allclose(power, np.array([5, 13, 25, 41]))
+ True
+ """
+ # Calculate the power by squaring the absolute values of the FFT coefficients
+ return np.square(np.abs(audio_fft))
+
+
+def freq_to_mel(freq: float) -> float:
+ """
+ Convert a frequency in Hertz to the mel scale.
+
+ Args:
+ freq: The frequency in Hertz.
+
+ Returns:
+ The frequency in mel scale.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> round(freq_to_mel(1000), 2)
+ 999.99
+ """
+ # Use the formula to convert frequency to the mel scale
+ return 2595.0 * np.log10(1.0 + freq / 700.0)
+
+
+def mel_to_freq(mels: float) -> float:
+ """
+ Convert a frequency in the mel scale to Hertz.
+
+ Args:
+ mels: The frequency in mel scale.
+
+ Returns:
+ The frequency in Hertz.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> round(mel_to_freq(999.99), 2)
+ 1000.01
+ """
+ # Use the formula to convert mel scale to frequency
+ return 700.0 * (10.0 ** (mels / 2595.0) - 1.0)
+
+
+def mel_spaced_filterbank(
+ sample_rate: int, mel_filter_num: int = 10, ftt_size: int = 1024
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Create a Mel-spaced filter bank for audio processing.
+
+ Args:
+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio.
+ mel_filter_num: The number of mel filters (default is 10).
+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT (default is 1024).
+
+ Returns:
+ Mel-spaced filter bank.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> round(mel_spaced_filterbank(8000, 10, 1024)[0][1], 10)
+ 0.0004603981
+ """
+ freq_min = 0
+ freq_high = sample_rate // 2
+
+ logging.info(f"Minimum frequency: {freq_min}")
+ logging.info(f"Maximum frequency: {freq_high}")
+
+ # Calculate filter points and mel frequencies
+ filter_points, mel_freqs = get_filter_points(
+ sample_rate,
+ freq_min,
+ freq_high,
+ mel_filter_num,
+ ftt_size,
+ )
+
+ filters = get_filters(filter_points, ftt_size)
+
+ # normalize filters
+ # taken from the librosa library
+ enorm = 2.0 / (mel_freqs[2 : mel_filter_num + 2] - mel_freqs[:mel_filter_num])
+ return filters * enorm[:, np.newaxis]
+
+
+def get_filters(filter_points: np.ndarray, ftt_size: int) -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Generate filters for audio processing.
+
+ Args:
+ filter_points: A list of filter points.
+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT.
+
+ Returns:
+ A matrix of filters.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> get_filters(np.array([0, 20, 51, 95, 161, 256], dtype=int), 512).shape
+ (4, 257)
+ """
+ num_filters = len(filter_points) - 2
+ filters = np.zeros((num_filters, int(ftt_size / 2) + 1))
+
+ for n in range(num_filters):
+ start = filter_points[n]
+ mid = filter_points[n + 1]
+ end = filter_points[n + 2]
+
+ # Linearly increase values from 0 to 1
+ filters[n, start:mid] = np.linspace(0, 1, mid - start)
+
+ # Linearly decrease values from 1 to 0
+ filters[n, mid:end] = np.linspace(1, 0, end - mid)
+
+ return filters
+
+
+def get_filter_points(
+ sample_rate: int,
+ freq_min: int,
+ freq_high: int,
+ mel_filter_num: int = 10,
+ ftt_size: int = 1024,
+) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
+ """
+ Calculate the filter points and frequencies for mel frequency filters.
+
+ Args:
+ sample_rate: The sample rate of the audio.
+ freq_min: The minimum frequency in Hertz.
+ freq_high: The maximum frequency in Hertz.
+ mel_filter_num: The number of mel filters (default is 10).
+ ftt_size: The size of the FFT (default is 1024).
+
+ Returns:
+ Filter points and corresponding frequencies.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> filter_points = get_filter_points(8000, 0, 4000, mel_filter_num=4, ftt_size=512)
+ >>> filter_points[0]
+ array([ 0, 20, 51, 95, 161, 256])
+ >>> filter_points[1]
+ array([ 0. , 324.46707094, 799.33254207, 1494.30973963,
+ 2511.42581671, 4000. ])
+ """
+ # Convert minimum and maximum frequencies to mel scale
+ fmin_mel = freq_to_mel(freq_min)
+ fmax_mel = freq_to_mel(freq_high)
+
+ logging.info(f"MEL min: {fmin_mel}")
+ logging.info(f"MEL max: {fmax_mel}")
+
+ # Generate equally spaced mel frequencies
+ mels = np.linspace(fmin_mel, fmax_mel, num=mel_filter_num + 2)
+
+ # Convert mel frequencies back to Hertz
+ freqs = mel_to_freq(mels)
+
+ # Calculate filter points as integer values
+ filter_points = np.floor((ftt_size + 1) / sample_rate * freqs).astype(int)
+
+ return filter_points, freqs
+
+
+def discrete_cosine_transform(dct_filter_num: int, filter_num: int) -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Compute the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) basis matrix.
+
+ Args:
+ dct_filter_num: The number of DCT filters to generate.
+ filter_num: The number of the fbank filters.
+
+ Returns:
+ The DCT basis matrix.
+
+ Examples:
+ >>> round(discrete_cosine_transform(3, 5)[0][0], 5)
+ 0.44721
+ """
+ basis = np.empty((dct_filter_num, filter_num))
+ basis[0, :] = 1.0 / np.sqrt(filter_num)
+
+ samples = np.arange(1, 2 * filter_num, 2) * np.pi / (2.0 * filter_num)
+
+ for i in range(1, dct_filter_num):
+ basis[i, :] = np.cos(i * samples) * np.sqrt(2.0 / filter_num)
+
+ return basis
+
+
+def example(wav_file_path: str = "./path-to-file/sample.wav") -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Example function to calculate Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients
+ (MFCCs) from an audio file.
+
+ Args:
+ wav_file_path: The path to the WAV audio file.
+
+ Returns:
+ np.ndarray: The computed MFCCs for the audio.
+ """
+ from scipy.io import wavfile
+
+ # Load the audio from the WAV file
+ sample_rate, audio = wavfile.read(wav_file_path)
+
+ # Calculate MFCCs
+ return mfcc(audio, sample_rate)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import doctest
+
+ doctest.testmod()
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-9027@b5a4d22
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 9,027
|
Added Scaled Exponential Linear Unit Activation Function
|
Added Scaled Exponential Linear Unit Activation (SELU) Function under TheAlgorithms/Python/neural_network/activation_functions. Description of SELU taken from reference link provided in the top comment section in scaled_exponential_linear_unit.py
Fixes #9010
* [X] Add an algorithm?
### Checklist:
* [X] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [X] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [X] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [X] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [X] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [X] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [X] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [X] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [X] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [X] All new algorithms include at least one URL that points to Wikipedia or another similar explanation.
* [X] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the description above includes the issue number(s) with a [closing keyword](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue): "Fixes #ISSUE-NUMBER".
|
2023-09-02T13:46:27Z
|
Other Activation Functions
### Feature description
Hi, I'm relatively new to open source and found this repo friendly for early contributions. But is there a reason as to why there are only two activations (ELU and Leaky ReLU), under neural_network / activation_functions.? Also, can I contribute new activations into it?
|
> But is there a reason as to why there are only two activations (ELU and Leaky ReLU), under neural_network / activation_functions.?
People simply haven't contributed any more activation functions. That being said, I think there are some activation functions currently placed under different directories (such as sigmoid in the maths directory)—they should be moved to the activation functions directory IMO, so feel free to open a PR to do so if you wish.
> Also, can I contribute new activations into it?
Yes, you can simply open a PR to do so. We don't assign issues in this repo, so there's no need to ask or open an issue about it.
|
[
{
"body": "### Feature description\n\nHi, I'm relatively new to open source and found this repo friendly for early contributions. But is there a reason as to why there are only two activations (ELU and Leaky ReLU), under neural_network / activation_functions.? Also, can I contribute new activations into it?",
"number": 9010,
"title": "Other Activation Functions"
}
] |
421ace81edb0d9af3a173f4ca7e66cc900078c1d
|
{
"head_commit": "b5a4d22184e7bd251d213105e5367796465e78c2",
"head_commit_message": "Update scaled_exponential_linear_unit.py",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/neural_network/activation_functions/scaled_exponential_linear_unit.py b/neural_network/activation_functions/scaled_exponential_linear_unit.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..a9f272d8f294\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/neural_network/activation_functions/scaled_exponential_linear_unit.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Implements the Scaled Exponential Linear Unit or SELU function.\n+The function takes a vector of K real numbers and two real numbers\n+alpha(default = 1.6732) & lambda (default = 1.0507) as input and\n+then applies the SELU function to each element of the vector.\n+SELU is a self-normalizing activation function. It is a variant\n+of the ELU. The main advantage of SELU is that we can be sure\n+that the output will always be standardized due to its\n+self-normalizing behavior. That means there is no need to\n+include Batch-Normalization layers.\n+References :\n+https://iq.opengenus.org/scaled-exponential-linear-unit/\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+\n+\n+def scaled_exponential_linear_unit(\n+ vector: np.ndarray, alpha: float = 1.6732, _lambda: float = 1.0507\n+) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Applies the Scaled Exponential Linear Unit function to each element of the vector.\n+ Parameters :\n+ vector : np.ndarray\n+ alpha : float (default = 1.6732)\n+ _lambda : float (default = 1.0507)\n+\n+ Returns : np.ndarray\n+ Formula : f(x) = _lambda * x if x > 0\n+ _lambda * alpha * (e**x - 1) if x <= 0\n+ Examples :\n+ >>> scaled_exponential_linear_unit(vector=np.array([1.3, 3.7, 2.4]))\n+ array([1.36591, 3.88759, 2.52168])\n+\n+ >>> scaled_exponential_linear_unit(vector=np.array([1.3, 4.7, 8.2]))\n+ array([1.36591, 4.93829, 8.61574])\n+ \"\"\"\n+ return _lambda * np.where(vector > 0, vector, alpha * (np.exp(vector) - 1))\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ import doctest\n+\n+ doctest.testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Implements the Scaled Exponential Linear Unit or SELU function.\n+The function takes a vector of K real numbers and two real numbers\n+alpha(default = 1.6732) & lambda (default = 1.0507) as input and\n+then applies the SELU function to each element of the vector.\n+SELU is a self-normalizing activation function. It is a variant\n+of the ELU. The main advantage of SELU is that we can be sure\n+that the output will always be standardized due to its\n+self-normalizing behavior. That means there is no need to\n+include Batch-Normalization layers.\n+References :\n+https://iq.opengenus.org/scaled-exponential-linear-unit/\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+\n+\n+def scaled_exponential_linear_unit(\n+ vector: np.ndarray, alpha: float = 1.6732, _lambda: float = 1.0507",
"line": null,
"original_line": 19,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "neural_network/activation_functions/scaled_exponential_linear_unit.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIs there a reason why `_lambda` has an underscore? Is the user not meant to change this coefficient?\n\n@author:\nYes, firstly lambda is a reserved keyword in python. Secondly both alpha and lambda are fixed constants.\n\n@author:\nThe user can change these values, that may yield slightly different behaviour from the function, but the default values given to them are `alpha: float = 1.6732, _lambda: float = 1.0507`.\n\n@user1:\n> Yes, firstly lambda is a reserved keyword in python.\r\n\r\nOh yeah, duh 🤦\r\n\r\nCould you rename the variable to something like `lambda_` instead? Having an underscore at the start of a variable name generally signifies that the user isn't supposed to use it.\n\n@author:\nAh. Yes for sure, I'll get it done right away!\n\n@author:\nDone"
}
] |
76a11d1ff74c89ccf19b4b7684920d3978e2ceb9
|
diff --git a/neural_network/activation_functions/scaled_exponential_linear_unit.py b/neural_network/activation_functions/scaled_exponential_linear_unit.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..f91dc6852136
--- /dev/null
+++ b/neural_network/activation_functions/scaled_exponential_linear_unit.py
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+"""
+Implements the Scaled Exponential Linear Unit or SELU function.
+The function takes a vector of K real numbers and two real numbers
+alpha(default = 1.6732) & lambda (default = 1.0507) as input and
+then applies the SELU function to each element of the vector.
+SELU is a self-normalizing activation function. It is a variant
+of the ELU. The main advantage of SELU is that we can be sure
+that the output will always be standardized due to its
+self-normalizing behavior. That means there is no need to
+include Batch-Normalization layers.
+References :
+https://iq.opengenus.org/scaled-exponential-linear-unit/
+"""
+
+import numpy as np
+
+
+def scaled_exponential_linear_unit(
+ vector: np.ndarray, alpha: float = 1.6732, lambda_: float = 1.0507
+) -> np.ndarray:
+ """
+ Applies the Scaled Exponential Linear Unit function to each element of the vector.
+ Parameters :
+ vector : np.ndarray
+ alpha : float (default = 1.6732)
+ lambda_ : float (default = 1.0507)
+
+ Returns : np.ndarray
+ Formula : f(x) = lambda_ * x if x > 0
+ lambda_ * alpha * (e**x - 1) if x <= 0
+ Examples :
+ >>> scaled_exponential_linear_unit(vector=np.array([1.3, 3.7, 2.4]))
+ array([1.36591, 3.88759, 2.52168])
+
+ >>> scaled_exponential_linear_unit(vector=np.array([1.3, 4.7, 8.2]))
+ array([1.36591, 4.93829, 8.61574])
+ """
+ return lambda_ * np.where(vector > 0, vector, alpha * (np.exp(vector) - 1))
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import doctest
+
+ doctest.testmod()
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-3565@04ecb26
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 3,565
|
Fix column offset of unary operator AST node
|
Fixes #3564
|
2020-05-08T20:09:39Z
|
chaining other commands after `nix-store` causes "NameError: name 'nix' is not defined"
## xonfig
<details>
```
$ xonfig
+------------------+-----------------+
| xonsh | 0.9.17 |
| Python | 3.7.7 |
| PLY | 3.11 |
| have readline | True |
| prompt toolkit | 3.0.4 |
| shell type | prompt_toolkit2 |
| pygments | 2.5.2 |
| on posix | True |
| on linux | True |
| distro | unknown |
| on darwin | False |
| on windows | False |
| on cygwin | False |
| on msys2 | False |
| is superuser | False |
| default encoding | utf-8 |
| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |
| encoding errors | surrogateescape |
+------------------+-----------------+
```
</details>
## nix-info -m
<details>
- system: `"x86_64-linux"`
- host os: `Linux 5.4.35, NixOS, 20.09pre223023.fce7562cf46 (Nightingale)`
- multi-user?: `yes`
- sandbox: `yes`
- version: `nix-env (Nix) 2.3.4`
- channels(root): `"nixos-20.09pre223023.fce7562cf46, nixos-unstable-20.09pre218613.ae6bdcc5358"`
- channels(das-g): `""`
- nixpkgs: `/nix/var/nix/profiles/per-user/root/channels/nixos`
</details>
## Expected Behavior
If `nix-store` is in `$PATH`, it can be used as part of longer command lines, too, with other commands chained after it.
## Current Behavior
<!--- Tell us what happens instead of the expected behavior -->
If the command line continues after `nix-store` and its arguments, xonsh won't run `nix-store` and instead reports `NameError: name 'nix' is not defined`.
<!--- If part of your bug report is a traceback, please first enter debug mode before triggering the error
To enter debug mode, set the environment variable `XONSH_DEBUG=1` _before_ starting `xonsh`.
On Linux and OSX, an easy way to to do this is to run `env XONSH_DEBUG=1 xonsh` -->
### Traceback (if applicable)
<details>
```
xonsh: To log full traceback to a file set: $XONSH_TRACEBACK_LOGFILE = <filename>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/nix/store/y22pwfk39i9r22ga10c3ifbp345gdl0p-xonsh-0.9.17/lib/python3.7/site-packages/xonsh/base_shell.py", line 362, in default
run_compiled_code(code, self.ctx, None, "single")
File "/nix/store/y22pwfk39i9r22ga10c3ifbp345gdl0p-xonsh-0.9.17/lib/python3.7/site-packages/xonsh/codecache.py", line 67, in run_compiled_code
func(code, glb, loc)
File "<xonsh-code>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'nix' is not defined
```
</details>
## Steps to Reproduce
<!--- Please try to write out a minimal reproducible snippet to trigger the bug, it will help us fix it! -->
1. make sure `nix-store` is in `$PATH`
```xonsh
nix-store --version
```
You should get some output like
```
nix-store (Nix) 2.3.4
```
2. call the following command line
```xonsh
nix-store --version or true
```
|
This also occurs with aliases that contain a dash (`-`) if you pass a long option and chain some other command with `and` after that:
```xonsh
$ aliases['foo-bar'] = 'true'
$ foo-bar
$ foo-bar --version
true (GNU coreutils) 8.31
[...]
$ foo-bar and true
$ foo-bar --version and true
xonsh: To log full traceback to a file set: $XONSH_TRACEBACK_LOGFILE = <filename>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/nix/store/y22pwfk39i9r22ga10c3ifbp345gdl0p-xonsh-0.9.17/lib/python3.7/site-packages/xonsh/base_shell.py", line 362, in default
run_compiled_code(code, self.ctx, None, "single")
File "/nix/store/y22pwfk39i9r22ga10c3ifbp345gdl0p-xonsh-0.9.17/lib/python3.7/site-packages/xonsh/codecache.py", line 67, in run_compiled_code
func(code, glb, loc)
File "<xonsh-code>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'foo' is not defined
```
Workaround: use `$[...]`:
```xonsh
$ aliases['foo-bar'] = 'true'
$ $[foo-bar --version] and true
true (GNU coreutils) 8.31
[...]
$ $[nix-store --version] and true
nix-store (Nix) 2.3.4
```
("Workaround", because I don't think `$[...]` should be necessary here.)
Wow! Thanks for reporting @das-g.
It insists for some reason on executing `foo-bar` in python mode. This is also interresting:
```
$ aliases["foo"]="true"
$ foo --abc and echo a
a
$ foo --abcd and echo a
NameError: name 'foo' is not defined
```
> This is also interresting:
>
> ```
> $ aliases["foo"]="true"
> $ foo --abc and echo a
> a
> $ foo --abcd and echo a
> NameError: name 'foo' is not defined
> ```
Oh, so it doesn't even require a dash in the executable to trigger this problem. :thinking:
Another symptom:
```
$ aliases["showargs"] = lambda args: print(args)
$ showargs -a and echo a
['-a']
a
$ showargs --a and echo a
['--a', 'and']
a
```
The ultimate cause of the issue seems to be, that unary operator ({'+', '-', '~'}) AST nodes have incorrect column offset.
For `showargs -a and echo a` the relevant part of the AST looks like:
```
BoolOp(op=And(), values=[
BinOp(
left=Name(id='showargs', ctx=Load(), lineno=1, col_offset=0), op=Sub(),
right=Name(id='a', ctx=Load(), lineno=1, col_offset=10), lineno=1, col_offset=0)
```
The maximum col_offset here is the one of the "a" "Name" (that's what the parameter seems to be to the Python parser), which is indeed the position of the final token at the left side of the `and` operation.
For `showargs --a and echo a` the AST, however, is:
```
BoolOp(op=And(), values=[
BinOp(
left=Name(id='showargs', ctx=Load(), lineno=1, col_offset=0), op=Sub(),
right=UnaryOp(op=USub(), operand=Name(id='a', ctx=Load(), lineno=1, col_offset=11), lineno=1, col_offset=13), lineno=1, col_offset=0),
```
The maximum col_offset here - the one of the unary `USub()` operator - is 13, which is way behind the whole parameter construct.
|
[
{
"body": "## xonfig\r\n\r\n<details>\r\n\r\n```\r\n$ xonfig \r\n+------------------+-----------------+\r\n| xonsh | 0.9.17 |\r\n| Python | 3.7.7 |\r\n| PLY | 3.11 |\r\n| have readline | True |\r\n| prompt toolkit | 3.0.4 |\r\n| shell type | prompt_toolkit2 |\r\n| pygments | 2.5.2 |\r\n| on posix | True |\r\n| on linux | True |\r\n| distro | unknown |\r\n| on darwin | False |\r\n| on windows | False |\r\n| on cygwin | False |\r\n| on msys2 | False |\r\n| is superuser | False |\r\n| default encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| encoding errors | surrogateescape |\r\n+------------------+-----------------+\r\n```\r\n\r\n</details>\r\n\r\n## nix-info -m\r\n\r\n<details>\r\n\r\n - system: `\"x86_64-linux\"`\r\n - host os: `Linux 5.4.35, NixOS, 20.09pre223023.fce7562cf46 (Nightingale)`\r\n - multi-user?: `yes`\r\n - sandbox: `yes`\r\n - version: `nix-env (Nix) 2.3.4`\r\n - channels(root): `\"nixos-20.09pre223023.fce7562cf46, nixos-unstable-20.09pre218613.ae6bdcc5358\"`\r\n - channels(das-g): `\"\"`\r\n - nixpkgs: `/nix/var/nix/profiles/per-user/root/channels/nixos`\r\n\r\n</details>\r\n\r\n## Expected Behavior\r\nIf `nix-store` is in `$PATH`, it can be used as part of longer command lines, too, with other commands chained after it.\r\n\r\n## Current Behavior\r\n<!--- Tell us what happens instead of the expected behavior -->\r\nIf the command line continues after `nix-store` and its arguments, xonsh won't run `nix-store` and instead reports `NameError: name 'nix' is not defined`.\r\n\r\n<!--- If part of your bug report is a traceback, please first enter debug mode before triggering the error\r\nTo enter debug mode, set the environment variable `XONSH_DEBUG=1` _before_ starting `xonsh`.\r\nOn Linux and OSX, an easy way to to do this is to run `env XONSH_DEBUG=1 xonsh` -->\r\n\r\n### Traceback (if applicable)\r\n\r\n<details>\r\n\r\n```\r\nxonsh: To log full traceback to a file set: $XONSH_TRACEBACK_LOGFILE = <filename>\r\nTraceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"/nix/store/y22pwfk39i9r22ga10c3ifbp345gdl0p-xonsh-0.9.17/lib/python3.7/site-packages/xonsh/base_shell.py\", line 362, in default\r\n run_compiled_code(code, self.ctx, None, \"single\")\r\n File \"/nix/store/y22pwfk39i9r22ga10c3ifbp345gdl0p-xonsh-0.9.17/lib/python3.7/site-packages/xonsh/codecache.py\", line 67, in run_compiled_code\r\n func(code, glb, loc)\r\n File \"<xonsh-code>\", line 1, in <module>\r\nNameError: name 'nix' is not defined\r\n```\r\n\r\n</details>\r\n\r\n## Steps to Reproduce\r\n<!--- Please try to write out a minimal reproducible snippet to trigger the bug, it will help us fix it! -->\r\n\r\n1. make sure `nix-store` is in `$PATH`\r\n ```xonsh\r\n nix-store --version\r\n ```\r\n You should get some output like\r\n ```\r\n nix-store (Nix) 2.3.4\r\n ```\r\n2. call the following command line\r\n ```xonsh\r\n nix-store --version or true\r\n ```",
"number": 3564,
"title": "chaining other commands after `nix-store` causes \"NameError: name 'nix' is not defined\""
}
] |
debb98ceabab474233068384a0cbfb960b2a3a92
|
{
"head_commit": "04ecb2661f82612a32dd5a105b48da4aa2116e35",
"head_commit_message": "Fix unary operator AST node column offset\n\nThis acually fixes a bug in subprocess mode. Logical subrocess\noperators could not follow long subprocess arguments (e.g. --version).",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/xonsh/parsers/base.py b/xonsh/parsers/base.py\nindex 8d4c48286e..266a393071 100644\n--- a/xonsh/parsers/base.py\n+++ b/xonsh/parsers/base.py\n@@ -2153,12 +2153,13 @@ def p_factor_power(self, p):\n p[0] = p[1]\n \n def p_factor_unary(self, p):\n- \"\"\"factor : PLUS factor\n- | MINUS factor\n- | TILDE factor\n+ \"\"\"factor : plus_tok factor\n+ | minus_tok factor\n+ | tilde_tok factor\n \"\"\"\n- op = self._factor_ops[p[1]]()\n- p[0] = ast.UnaryOp(op=op, operand=p[2], lineno=self.lineno, col_offset=self.col)\n+ p1 = p[1]\n+ op = self._factor_ops[p1.value]()\n+ p[0] = ast.UnaryOp(op=op, operand=p[2], lineno=self.lineno, col_offset=p1.lexpos)\n \n def p_power_atom(self, p):\n \"\"\"power : atom_expr\"\"\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Changed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Deprecated:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Removed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Logical sobprocess operators now work after long arguments (e.g. --version).",
"line": null,
"original_line": 19,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "news/fix-unary-position.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n* Logical subprocess operators now work after long arguments (e.g. `--version`).\r\n```\n\n@author:\nThanks! New system - no proofreader :wink:"
}
] |
9654ba1d724b01097d637fc45e6b569a1b24b837
|
diff --git a/news/fix-unary-position.rst b/news/fix-unary-position.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..61e9a9a161
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/fix-unary-position.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+**Added:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Changed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Deprecated:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Removed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* Logical subprocess operators now work after long arguments (e.g. ``--version``).
+
+**Security:**
+
+* <news item>
diff --git a/tests/test_integrations.py b/tests/test_integrations.py
index cc104f1bf5..0f3677f9a3 100644
--- a/tests/test_integrations.py
+++ b/tests/test_integrations.py
@@ -415,6 +415,49 @@ def _echo(args):
"Var foo\n",
0,
),
+ #
+ # test logical subprocess operators
+ #
+ (
+ """
+def _echo(args):
+ print(' '.join(args))
+aliases['echo'] = _echo
+
+echo --version and echo a
+echo --version && echo a
+echo --version or echo a
+echo --version || echo a
+echo -+version and echo a
+echo -+version && echo a
+echo -+version or echo a
+echo -+version || echo a
+echo -~version and echo a
+echo -~version && echo a
+echo -~version or echo a
+echo -~version || echo a
+""",
+ """--version
+a
+--version
+a
+--version
+--version
+-+version
+a
+-+version
+a
+-+version
+-+version
+-~version
+a
+-~version
+a
+-~version
+-~version
+""",
+ 0,
+ ),
]
diff --git a/xonsh/parsers/base.py b/xonsh/parsers/base.py
index 8d4c48286e..9739222a05 100644
--- a/xonsh/parsers/base.py
+++ b/xonsh/parsers/base.py
@@ -2153,12 +2153,15 @@ def p_factor_power(self, p):
p[0] = p[1]
def p_factor_unary(self, p):
- """factor : PLUS factor
- | MINUS factor
- | TILDE factor
+ """factor : plus_tok factor
+ | minus_tok factor
+ | tilde_tok factor
"""
- op = self._factor_ops[p[1]]()
- p[0] = ast.UnaryOp(op=op, operand=p[2], lineno=self.lineno, col_offset=self.col)
+ p1 = p[1]
+ op = self._factor_ops[p1.value]()
+ p[0] = ast.UnaryOp(
+ op=op, operand=p[2], lineno=self.lineno, col_offset=p1.lexpos
+ )
def p_power_atom(self, p):
"""power : atom_expr"""
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21952@233e209
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,952
|
enhanced int/even/odd detection
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
fixes #8648
closes #12399 as alternate
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Consideration of the nominal multiplicity of 2 allows us to return True/False for queries on integer/odd/even as tests indicate.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* core
* better detection of odd/even/integer for expressions with symbolic powers of even bases
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-08-26T11:12:47Z
|
If n is even, n**2/2 should also be even
The following:
``` python
>>> n = Symbol('n', integer=True, even=True)
>>> (n**2/2).is_even
```
should return `True`, but it returns `None` (of course, this is also an enhancement).
That makes me think that perhaps symbolic integers should keep a more complex "assumptions" method, which generalizes "is_even" and "is_odd" to instead contain a dictionary of primes that are known to divide that integer, mapping to minimum and maximum known multiplicity.
I would like to think about it and post a proposition/plan, but I am not sure what is the correct github way of doing this.
|
I have added some handling for this instance in this [PR](https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/12320). I did put thought into generalizing this even more for any integer divisor, but because we don't have the factorizations for the symbols, this does not seem easily possible.
|
[
{
"body": "The following:\n\n``` python\n>>> n = Symbol('n', integer=True, even=True)\n>>> (n**2/2).is_even\n```\n\nshould return `True`, but it returns `None` (of course, this is also an enhancement).\n\nThat makes me think that perhaps symbolic integers should keep a more complex \"assumptions\" method, which generalizes \"is_even\" and \"is_odd\" to instead contain a dictionary of primes that are known to divide that integer, mapping to minimum and maximum known multiplicity.\n\nI would like to think about it and post a proposition/plan, but I am not sure what is the correct github way of doing this.\n",
"number": 8648,
"title": "If n is even, n**2/2 should also be even"
}
] |
b8156f36f0f3144c5e3b66002b9e8fcbe2ee66c4
|
{
"head_commit": "233e2091bf4eb5087575f4aca3bb9e32426555eb",
"head_commit_message": "document Rational gcd=1 arg",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/mul.py b/sympy/core/mul.py\nindex 2c1d3b1ec8e5..d37b950fbc63 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/mul.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/mul.py\n@@ -1334,6 +1334,7 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):\n #_eval_is_integer = lambda self: _fuzzy_group(\n # (a.is_integer for a in self.args), quick_exit=True)\n def _eval_is_integer(self):\n+ from sympy import trailing\n is_rational = self._eval_is_rational()\n if is_rational is False:\n return False\n@@ -1342,11 +1343,14 @@ def _eval_is_integer(self):\n denominators = []\n for a in self.args:\n if a.is_integer:\n- numerators.append(a)\n+ if abs(a) is not S.One:\n+ numerators.append(a)\n elif a.is_Rational:\n n, d = a.as_numer_denom()\n- numerators.append(n)\n- denominators.append(d)\n+ if abs(n) is not S.One:\n+ numerators.append(n)\n+ if d is not S.One:\n+ denominators.append(d)\n elif a.is_Pow:\n b, e = a.as_base_exp()\n if not b.is_integer or not e.is_integer: return\n@@ -1364,13 +1368,35 @@ def _eval_is_integer(self):\n if not denominators:\n return True\n \n- odd = lambda ints: all(i.is_odd for i in ints)\n- even = lambda ints: any(i.is_even for i in ints)\n+ odd = lambda ints: all(i.is_odd for i in ints) # ALL\n+ even = lambda ints: any(i.is_even for i in ints) # ANY\n \n if odd(numerators) and even(denominators):\n return False\n elif even(numerators) and denominators == [2]:\n return True\n+ elif all(i.is_even for i in numerators) and odd(denominators\n+ ) and (Mul(*denominators, evaluate=False) - 1\n+ ).is_positive:\n+ return False\n+ if len(denominators) == 1:\n+ d = denominators[0]\n+ if d.is_Integer and d.is_even:\n+ # if minimal power of 2 in num vs den is not\n+ # negative then we have an integer\n+ if (Add(*[i.as_base_exp()[1] for i in\n+ numerators if i.is_even]) - trailing(d.p)\n+ ).is_nonnegative:\n+ return True\n+ if len(numerators) == 1:\n+ n = numerators[0]\n+ if n.is_Integer and n.is_even:\n+ # if minimal power of 2 in den vs num is positive\n+ # then we have have a non-integer\n+ if (Add(*[i.as_base_exp()[1] for i in\n+ denominators if i.is_even]) - trailing(n.p)\n+ ).is_positive:\n+ return False\n \n def _eval_is_polar(self):\n has_polar = any(arg.is_polar for arg in self.args)\n@@ -1545,37 +1571,54 @@ def _eval_is_extended_negative(self):\n return self._eval_pos_neg(-1)\n \n def _eval_is_odd(self):\n+ from sympy import trailing, fraction\n is_integer = self.is_integer\n-\n if is_integer:\n+ if self.is_zero:\n+ return False\n+ n, d = fraction(self)\n+ if d.is_Integer and d.is_even:\n+ # if minimal power of 2 in num vs den is\n+ # positive then we have an even number\n+ if (Add(*[i.as_base_exp()[1] for i in\n+ Mul.make_args(n) if i.is_even]) - trailing(d.p)\n+ ).is_positive:\n+ return False\n+ return\n r, acc = True, 1\n for t in self.args:\n- if not t.is_integer:\n- return None\n- elif t.is_even:\n+ if abs(t) is S.One:\n+ continue\n+ assert t.is_integer\n+ if t.is_even:\n+ return False\n+ if r is False:\n+ pass\n+ elif acc != 1 and (acc + t).is_odd:\n r = False\n- elif t.is_integer:\n- if r is False:\n- pass\n- elif acc != 1 and (acc + t).is_odd:\n- r = False\n- elif t.is_odd is None:\n- r = None\n+ elif t.is_even is None:\n+ r = None\n acc = t\n return r\n-\n- # !integer -> !odd\n- elif is_integer is False:\n- return False\n+ return is_integer # !integer -> !odd\n \n def _eval_is_even(self):\n+ from sympy import trailing, fraction\n is_integer = self.is_integer\n \n if is_integer:\n return fuzzy_not(self.is_odd)\n \n- elif is_integer is False:\n- return False\n+ n, d = fraction(self)\n+ if n.is_Integer and n.is_even:\n+ # if minimal power of 2 in den vs num is not\n+ # negative then this is not an integer and\n+ # can't be even\n+ if (Add(*[i.as_base_exp()[1] for i in\n+ Mul.make_args(d) if i.is_even]) - trailing(n.p)\n+ ).is_nonnegative:\n+ return False\n+ return is_integer\n \n def _eval_is_composite(self):\n \"\"\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/numbers.py b/sympy/core/numbers.py\nindex 845260626e16..4e4373e9d238 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/numbers.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/numbers.py\n@@ -1572,6 +1572,16 @@ class Rational(Number):\n >>> r.p/r.q\n 0.75\n \n+ If an unevaluated Rational is desired, ``gcd=1`` can be passed and\n+ this will keep common divisors of the numerator and denominator\n+ from being eliminated. It is not possible, however, to leave a\n+ negative value in the denominator.\n+\n+ >>> Rational(2, 4, gcd=1)\n+ 2/4\n+ >>> Rational(2, -4, gcd=1).q\n+ 4\n+\n See Also\n ========\n sympy.core.sympify.sympify, sympy.simplify.simplify.nsimplify\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\nindex d12eeabe2db0..16580c14fa37 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\n@@ -512,6 +512,12 @@ def test_Mul_is_even_odd():\n assert (x*(x + k)).is_odd is False\n assert (x*(x + m)).is_odd is None\n \n+ # issue 8648\n+ assert (m**2/2).is_even\n+ assert (m**2/3).is_even is False\n+ assert (2/m**2).is_odd is False\n+ assert (2/m).is_odd is None\n+\n \n @XFAIL\n def test_evenness_in_ternary_integer_product_with_odd():\n@@ -1051,6 +1057,18 @@ def test_Pow_is_integer():\n assert (1/(x + 1)).is_integer is False\n assert (1/(-x - 1)).is_integer is False\n \n+ # issue 8648-like\n+ k = Symbol('k', even=True)\n+ assert (k**3/2).is_integer\n+ assert (k**3/8).is_integer\n+ assert (k**3/16).is_integer is None\n+ assert (2/k).is_integer is None\n+ assert (2/k**2).is_integer is False\n+ o = Symbol('o', odd=True)\n+ assert (k/o).is_integer is None\n+ o = Symbol('o', odd=True, prime=True)\n+ assert (k/o).is_integer is False\n+\n \n def test_Pow_is_real():\n x = Symbol('x', real=True)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_numbers.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_numbers.py\nindex 0b9abd816771..a288e4a64da2 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_numbers.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_numbers.py\n@@ -343,6 +343,11 @@ def test_Rational_new():\n assert Rational(mpq(2, 6)) == Rational(1, 3)\n assert Rational(PythonRational(2, 6)) == Rational(1, 3)\n \n+ assert Rational(2, 4, gcd=1).q == 4\n+ n = Rational(2, -4, gcd=1)\n+ assert n.q == 4\n+ assert n.p == -2\n+\n \n def test_Number_new():\n \"\"\"\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1364,13 +1368,35 @@ def _eval_is_integer(self):\n if not denominators:\n return True\n \n- odd = lambda ints: all(i.is_odd for i in ints)\n- even = lambda ints: any(i.is_even for i in ints)\n+ odd = lambda ints: all(i.is_odd for i in ints) # ALL\n+ even = lambda ints: any(i.is_even for i in ints) # ANY",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1372,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/mul.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think it would be slightly easier to understand if a third lambda `alleven` was introduced and the above was named `allodd` and `anyeven`. I was about to comment on the all below earlier.\r\n\r\nBut apart from that I think the changes really makes sense."
}
] |
7cc883ca13749f19c334d9a2125f9c81020d9a66
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/mul.py b/sympy/core/mul.py
index 2c1d3b1ec8e5..0d293e64d11c 100644
--- a/sympy/core/mul.py
+++ b/sympy/core/mul.py
@@ -1334,6 +1334,7 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):
#_eval_is_integer = lambda self: _fuzzy_group(
# (a.is_integer for a in self.args), quick_exit=True)
def _eval_is_integer(self):
+ from sympy import trailing
is_rational = self._eval_is_rational()
if is_rational is False:
return False
@@ -1342,11 +1343,14 @@ def _eval_is_integer(self):
denominators = []
for a in self.args:
if a.is_integer:
- numerators.append(a)
+ if abs(a) is not S.One:
+ numerators.append(a)
elif a.is_Rational:
n, d = a.as_numer_denom()
- numerators.append(n)
- denominators.append(d)
+ if abs(n) is not S.One:
+ numerators.append(n)
+ if d is not S.One:
+ denominators.append(d)
elif a.is_Pow:
b, e = a.as_base_exp()
if not b.is_integer or not e.is_integer: return
@@ -1364,13 +1368,36 @@ def _eval_is_integer(self):
if not denominators:
return True
- odd = lambda ints: all(i.is_odd for i in ints)
- even = lambda ints: any(i.is_even for i in ints)
+ allodd = lambda x: all(i.is_odd for i in x)
+ alleven = lambda x: all(i.is_even for i in x)
+ anyeven = lambda x: any(i.is_even for i in x)
- if odd(numerators) and even(denominators):
+ if allodd(numerators) and anyeven(denominators):
return False
- elif even(numerators) and denominators == [2]:
+ elif anyeven(numerators) and denominators == [2]:
return True
+ elif alleven(numerators) and allodd(denominators
+ ) and (Mul(*denominators, evaluate=False) - 1
+ ).is_positive:
+ return False
+ if len(denominators) == 1:
+ d = denominators[0]
+ if d.is_Integer and d.is_even:
+ # if minimal power of 2 in num vs den is not
+ # negative then we have an integer
+ if (Add(*[i.as_base_exp()[1] for i in
+ numerators if i.is_even]) - trailing(d.p)
+ ).is_nonnegative:
+ return True
+ if len(numerators) == 1:
+ n = numerators[0]
+ if n.is_Integer and n.is_even:
+ # if minimal power of 2 in den vs num is positive
+ # then we have have a non-integer
+ if (Add(*[i.as_base_exp()[1] for i in
+ denominators if i.is_even]) - trailing(n.p)
+ ).is_positive:
+ return False
def _eval_is_polar(self):
has_polar = any(arg.is_polar for arg in self.args)
@@ -1545,37 +1572,54 @@ def _eval_is_extended_negative(self):
return self._eval_pos_neg(-1)
def _eval_is_odd(self):
+ from sympy import trailing, fraction
is_integer = self.is_integer
-
if is_integer:
+ if self.is_zero:
+ return False
+ n, d = fraction(self)
+ if d.is_Integer and d.is_even:
+ # if minimal power of 2 in num vs den is
+ # positive then we have an even number
+ if (Add(*[i.as_base_exp()[1] for i in
+ Mul.make_args(n) if i.is_even]) - trailing(d.p)
+ ).is_positive:
+ return False
+ return
r, acc = True, 1
for t in self.args:
- if not t.is_integer:
- return None
- elif t.is_even:
+ if abs(t) is S.One:
+ continue
+ assert t.is_integer
+ if t.is_even:
+ return False
+ if r is False:
+ pass
+ elif acc != 1 and (acc + t).is_odd:
r = False
- elif t.is_integer:
- if r is False:
- pass
- elif acc != 1 and (acc + t).is_odd:
- r = False
- elif t.is_odd is None:
- r = None
+ elif t.is_even is None:
+ r = None
acc = t
return r
-
- # !integer -> !odd
- elif is_integer is False:
- return False
+ return is_integer # !integer -> !odd
def _eval_is_even(self):
+ from sympy import trailing, fraction
is_integer = self.is_integer
if is_integer:
return fuzzy_not(self.is_odd)
- elif is_integer is False:
- return False
+ n, d = fraction(self)
+ if n.is_Integer and n.is_even:
+ # if minimal power of 2 in den vs num is not
+ # negative then this is not an integer and
+ # can't be even
+ if (Add(*[i.as_base_exp()[1] for i in
+ Mul.make_args(d) if i.is_even]) - trailing(n.p)
+ ).is_nonnegative:
+ return False
+ return is_integer
def _eval_is_composite(self):
"""
diff --git a/sympy/core/numbers.py b/sympy/core/numbers.py
index 845260626e16..4e4373e9d238 100644
--- a/sympy/core/numbers.py
+++ b/sympy/core/numbers.py
@@ -1572,6 +1572,16 @@ class Rational(Number):
>>> r.p/r.q
0.75
+ If an unevaluated Rational is desired, ``gcd=1`` can be passed and
+ this will keep common divisors of the numerator and denominator
+ from being eliminated. It is not possible, however, to leave a
+ negative value in the denominator.
+
+ >>> Rational(2, 4, gcd=1)
+ 2/4
+ >>> Rational(2, -4, gcd=1).q
+ 4
+
See Also
========
sympy.core.sympify.sympify, sympy.simplify.simplify.nsimplify
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
index d12eeabe2db0..16580c14fa37 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
@@ -512,6 +512,12 @@ def test_Mul_is_even_odd():
assert (x*(x + k)).is_odd is False
assert (x*(x + m)).is_odd is None
+ # issue 8648
+ assert (m**2/2).is_even
+ assert (m**2/3).is_even is False
+ assert (2/m**2).is_odd is False
+ assert (2/m).is_odd is None
+
@XFAIL
def test_evenness_in_ternary_integer_product_with_odd():
@@ -1051,6 +1057,18 @@ def test_Pow_is_integer():
assert (1/(x + 1)).is_integer is False
assert (1/(-x - 1)).is_integer is False
+ # issue 8648-like
+ k = Symbol('k', even=True)
+ assert (k**3/2).is_integer
+ assert (k**3/8).is_integer
+ assert (k**3/16).is_integer is None
+ assert (2/k).is_integer is None
+ assert (2/k**2).is_integer is False
+ o = Symbol('o', odd=True)
+ assert (k/o).is_integer is None
+ o = Symbol('o', odd=True, prime=True)
+ assert (k/o).is_integer is False
+
def test_Pow_is_real():
x = Symbol('x', real=True)
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_numbers.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_numbers.py
index 0b9abd816771..a288e4a64da2 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_numbers.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_numbers.py
@@ -343,6 +343,11 @@ def test_Rational_new():
assert Rational(mpq(2, 6)) == Rational(1, 3)
assert Rational(PythonRational(2, 6)) == Rational(1, 3)
+ assert Rational(2, 4, gcd=1).q == 4
+ n = Rational(2, -4, gcd=1)
+ assert n.q == 4
+ assert n.p == -2
+
def test_Number_new():
""""
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-3277@c7e5b7b
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 3,277
|
Add autovox xontrib
|
Add a xontrib to support automatic vox xontribs (such as avox).
This deals with all the mechanics of handling events, searching up the directory tree for venvs, and dealing with multiple policies.
Example policy:
```python
@events.autovox_policy
def dotvenv_policy(path, **_):
venv = path / '.venv'
if venv.exists():
return venv
```
The user does need to invoke `xontrib load autovox` to enable this functionality.
Closes #3246
|
2019-08-19T01:20:45Z
|
Automatic Vox Policies?
One of the re-occuring feature requests for vox is automatic de/activation of venvs, based on various polices (avox is based on a concept of project directory, I think someone did it based on `.venv`, just saw one based on `pyenv-virtualenv` (which is based on the presence of a `.python-version` file).
Wondering if we should refactor `avox` into a generic framework bundled with xonsh, and have these different polices plug in to it.
|
Yeah, that seems like a nice approach.
|
[
{
"body": "One of the re-occuring feature requests for vox is automatic de/activation of venvs, based on various polices (avox is based on a concept of project directory, I think someone did it based on `.venv`, just saw one based on `pyenv-virtualenv` (which is based on the presence of a `.python-version` file).\r\n\r\nWondering if we should refactor `avox` into a generic framework bundled with xonsh, and have these different polices plug in to it.",
"number": 3246,
"title": "Automatic Vox Policies?"
}
] |
59a042010f95e62f3be91368bd866a8580273174
|
{
"head_commit": "c7e5b7b0f94bd55fce125538fc8dcc1d8c955f53",
"head_commit_message": "Add autovox xontrib to support automatic vox",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/xontrib/autovox.py b/xontrib/autovox.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..d7240205fd\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/xontrib/autovox.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+A framework for automatic vox.\n+\n+This coordinates multiple automatic vox policies and deals with some of the\n+mechanics of venv searching and chdir handling.\n+\n+This provides no interface for end users.\n+\n+Developers should look at events.autovox_policy\n+\"\"\"\n+import itertools\n+from pathlib import Path\n+import xontrib.voxapi as voxapi\n+import warnings\n+\n+__all__ = ()\n+\n+\n+_policies = []\n+\n+events.doc(\n+ \"autovox_policy\",\n+ \"\"\"\n+autovox_policy(path: pathlib.Path) -> Union[str, pathlib.Path, None]\n+\n+Register a policy with autovox.\n+\n+A policy is a function that takes a Path and returns the venv associated with it,\n+if any.\n+\n+NOTE: The policy should only return a venv for this path exactly, not for\n+parent paths. Parent walking is handled by autovox so that all policies can\n+be queried at each level.\n+\"\"\",\n+)\n+\n+\n+class MultipleVenvsWarning(RuntimeWarning):\n+ pass\n+\n+\n+def get_venv(vox, dirpath):\n+ # Search up the directory tree until a venv is found, or none\n+ for path in itertools.chain((dirpath,), dirpath.parents):\n+ print(f\"Checking {path}\")\n+ venvs = [\n+ vox[p]\n+ for p in events.autovox_policy.fire(path=path)\n+ if p is not None and p in vox # Filter out venvs that don't exist\n+ ]\n+ if len(venvs) == 0:\n+ continue\n+ else:\n+ if len(venvs) > 1:\n+ warnings.warn(\n+ MultipleVenvsWarning(\n+ f\"Found {len(venvs)} venvs for {path}; using the first\"\n+ )\n+ )\n+ return venvs[0]\n+\n+\n+def check_for_new_venv(curdir):\n+ vox = voxapi.Vox()\n+ try:\n+ oldve = vox[...]\n+ except KeyError:\n+ oldve = None\n+ newve = get_venv(vox, curdir)\n+\n+ if oldve != newve:\n+ if newve is None:\n+ vox.deactivate()\n+ else:\n+ vox.activate(newve)\n+\n+\n+# Core mechanism: Check for venv when the current directory changes\[email protected]_chdir\n+def cd_handler(newdir, **_):\n+ check_for_new_venv(Path(newdir))\n+\n+\n+# Recalculate when venvs are created or destroyed\n+\n+\[email protected]_on_create\n+def create_handler(**_):\n+ check_for_new_venv(Path.cwd())\n+\n+\[email protected]_on_destroy\n+def destroy_handler(**_):\n+ check_for_new_venv(Path.cwd())\n+\n+\n+# Initial activation before first prompt\n+\n+\[email protected]_post_init\n+def load_handler(**_):\n+ check_for_new_venv(Path.cwd())\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+A framework for automatic vox.\n+\n+This coordinates multiple automatic vox policies and deals with some of the\n+mechanics of venv searching and chdir handling.\n+\n+This provides no interface for end users.\n+\n+Developers should look at events.autovox_policy\n+\"\"\"\n+import itertools\n+from pathlib import Path\n+import xontrib.voxapi as voxapi\n+import warnings\n+\n+__all__ = ()\n+\n+\n+_policies = []\n+\n+events.doc(\n+ \"autovox_policy\",\n+ \"\"\"\n+autovox_policy(path: pathlib.Path) -> Union[str, pathlib.Path, None]\n+\n+Register a policy with autovox.\n+\n+A policy is a function that takes a Path and returns the venv associated with it,\n+if any.\n+\n+NOTE: The policy should only return a venv for this path exactly, not for\n+parent paths. Parent walking is handled by autovox so that all policies can\n+be queried at each level.\n+\"\"\",\n+)\n+\n+\n+class MultipleVenvsWarning(RuntimeWarning):\n+ pass\n+\n+\n+def get_venv(vox, dirpath):\n+ # Search up the directory tree until a venv is found, or none\n+ for path in itertools.chain((dirpath,), dirpath.parents):\n+ print(f\"Checking {path}\")",
"line": null,
"original_line": 45,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xontrib/autovox.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nAre we OK with f-strings in xontribs? I am not oppossed \n\n@author:\nDepends entirely on what versions of Python we're supporting.\r\n\r\nf-strings were added in 3.6.\r\n\r\nCurrent PSF status:\r\n* 3.5.7 final: March 18, 2019 (No further plans)\r\n* 3.6.9 final: 2019-07-02\r\n* 3.6.10 and beyond schedule: Security fixes only, as needed, until 2021-12\r\n* 3.7.8 final: 2020-06-27 (expected)\r\n* 3.8.0 final: Monday, 2019-10-21 (expected)\r\n\r\nXonsh is still running tests for 3.5, but that might be more a matter of \"hasn't been updated yet\" and less \"this is a thing we should/need to be doing\"\n\n@author:\nOh, and this is a debugging statement that shouldn't even be left in, so the point is moot.\n\n@author:\nOk, this is a debugging statement, but there's another f-string farther down."
}
] |
14cf2265eb9f8fad8386d7a94211f5b7937154e3
|
diff --git a/docs/python_virtual_environments.rst b/docs/python_virtual_environments.rst
index b744c11019..9ff824b3f0 100644
--- a/docs/python_virtual_environments.rst
+++ b/docs/python_virtual_environments.rst
@@ -102,3 +102,19 @@ Simply add the ``'{env_name}'`` variable to your ``$PROMPT``::
Note that you do **not** need to load the ``vox`` xontrib for this to work.
For more details see :ref:`customprompt`.
+
+
+Automatically Switching Environments
+------------------------------------
+
+Automatic environment switching based on the current directory is managed with the ``autovox`` xontrib (``xontrib load autovox``). Third-party xontribs may register various policies for use with autovox. Pick and choose xontribs that implement policies that match your work style.
+
+Implementing policies is easy! Just register with the ``autovox_policy`` event and return a ``Path`` if there is a matching venv. For example, this policy implements handling if there is a ``.venv`` directory in the project::
+
+ @events.autovox_policy
+ def dotvenv_policy(path, **_):
+ venv = path / '.venv'
+ if venv.exists():
+ return venv
+
+Note that you should only return if there is an environment for this directory exactly. Scanning parent directories is managed by autovox. You should also make the policy check relatively cheap. (Local IO is ok, but probably shouldn't call out to network services.)
diff --git a/news/autovox.rst b/news/autovox.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b7db759c41
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/autovox.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+**Added:**
+
+* Added ``autovox`` xontrib
+
+**Changed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Deprecated:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Removed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Security:**
+
+* <news item>
diff --git a/tests/test_vox.py b/tests/test_vox.py
index 80ee598033..7a1a1e0575 100644
--- a/tests/test_vox.py
+++ b/tests/test_vox.py
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
import pytest
from xontrib.voxapi import Vox
-from tools import skip_if_on_conda, skip_if_on_msys
+from tools import skip_if_on_conda, skip_if_on_msys, skip_if_lt_py36
from xonsh.platform import ON_WINDOWS
@@ -159,9 +159,9 @@ def test_crud_path(xonsh_builtins, tmpdir):
@skip_if_on_msys
@skip_if_on_conda
-def test_crud_subdir(xonsh_builtins, tmpdir):
+def test_reserved_names(xonsh_builtins, tmpdir):
"""
- Creates a virtual environment, gets it, enumerates it, and then deletes it.
+ Tests that reserved words are disallowed.
"""
xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env["VIRTUALENV_HOME"] = str(tmpdir)
@@ -177,3 +177,51 @@ def test_crud_subdir(xonsh_builtins, tmpdir):
vox.create("spameggs/Scripts")
else:
vox.create("spameggs/bin")
+
+
+@skip_if_on_msys
+@skip_if_on_conda
+@skip_if_lt_py36
+def test_autovox(xonsh_builtins, tmpdir):
+ """
+ Tests that autovox works
+ """
+ import importlib
+ from xonsh.lib import subprocess
+ import xonsh.dirstack
+
+ # Set up an isolated venv home
+ xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env["VIRTUALENV_HOME"] = str(tmpdir)
+
+ # Makes sure that event handlers are registered
+ import xontrib.autovox
+ importlib.reload(xontrib.autovox)
+
+ # Set up enough environment for xonsh to function
+ xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env['PWD'] = os.getcwd()
+ xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env['DIRSTACK_SIZE'] = 10
+ xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env['PATH'] = []
+
+ xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env['XONSH_SHOW_TRACEBACK'] = True
+
+ @xonsh_builtins.events.autovox_policy
+ def policy(path, **_):
+ print("Checking", repr(path), vox.active())
+ if str(path) == str(tmpdir):
+ return "myenv"
+
+ vox = Vox()
+
+ print(xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env['PWD'])
+ xonsh.dirstack.pushd([str(tmpdir)])
+ print(xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env['PWD'])
+ assert vox.active() is None
+ xonsh.dirstack.popd([])
+ print(xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env['PWD'])
+
+ vox.create('myenv')
+ xonsh.dirstack.pushd([str(tmpdir)])
+ print(xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env['PWD'])
+ assert vox.active() == 'myenv'
+ xonsh.dirstack.popd([])
+ print(xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env['PWD'])
diff --git a/tests/tools.py b/tests/tools.py
index 1956862e63..77de738e75 100644
--- a/tests/tools.py
+++ b/tests/tools.py
@@ -122,12 +122,17 @@ def detype(self):
return {k: str(v) for k, v in self._d.items()}
def __getitem__(self, k):
- return self._d[k]
+ if k is ...:
+ return self
+ else:
+ return self._d[k]
def __setitem__(self, k, v):
+ assert k is not ...
self._d[k] = v
def __delitem__(self, k):
+ assert k is not ...
del self._d[k]
def __len__(self):
@@ -156,6 +161,9 @@ def swap(self, other=None, **kwargs):
else:
self[k] = v
+ def is_manually_set(self, key):
+ return False
+
#
# Execer tools
diff --git a/xonsh/xontribs.json b/xonsh/xontribs.json
index 02c54da8a3..46cf5b16b8 100644
--- a/xonsh/xontribs.json
+++ b/xonsh/xontribs.json
@@ -9,6 +9,11 @@
"url": "https://github.com/sagartewari01/autojump-xonsh",
"description": ["autojump support for xonsh"]
},
+ {"name": "autovox",
+ "package": "xonsh",
+ "url": "http://xon.sh",
+ "description": ["Manages automatic activation of virtual environments."]
+ },
{"name": "autoxsh",
"package": "xonsh-autoxsh",
"url": "https://github.com/Granitas/xonsh-autoxsh",
diff --git a/xontrib/autovox.py b/xontrib/autovox.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2e76217657
--- /dev/null
+++ b/xontrib/autovox.py
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+"""
+A framework for automatic vox.
+
+This coordinates multiple automatic vox policies and deals with some of the
+mechanics of venv searching and chdir handling.
+
+This provides no interface for end users.
+
+Developers should look at events.autovox_policy
+"""
+import itertools
+from pathlib import Path
+import xontrib.voxapi as voxapi
+import warnings
+
+__all__ = ()
+
+
+_policies = []
+
+events.doc(
+ "autovox_policy",
+ """
+autovox_policy(path: pathlib.Path) -> Union[str, pathlib.Path, None]
+
+Register a policy with autovox.
+
+A policy is a function that takes a Path and returns the venv associated with it,
+if any.
+
+NOTE: The policy should only return a venv for this path exactly, not for
+parent paths. Parent walking is handled by autovox so that all policies can
+be queried at each level.
+""",
+)
+
+
+class MultipleVenvsWarning(RuntimeWarning):
+ pass
+
+
+def get_venv(vox, dirpath):
+ # Search up the directory tree until a venv is found, or none
+ for path in itertools.chain((dirpath,), dirpath.parents):
+ venvs = [
+ vox[p]
+ for p in events.autovox_policy.fire(path=path)
+ if p is not None and p in vox # Filter out venvs that don't exist
+ ]
+ if len(venvs) == 0:
+ continue
+ else:
+ if len(venvs) > 1:
+ warnings.warn(
+ MultipleVenvsWarning(
+ f"Found {len(venvs)} venvs for {path}; using the first"
+ )
+ )
+ return venvs[0]
+
+
+def check_for_new_venv(curdir):
+ vox = voxapi.Vox()
+ try:
+ oldve = vox[...]
+ except KeyError:
+ oldve = None
+ newve = get_venv(vox, curdir)
+
+ if oldve != newve:
+ if newve is None:
+ vox.deactivate()
+ else:
+ vox.activate(newve.env)
+
+
+# Core mechanism: Check for venv when the current directory changes
[email protected]_chdir
+def cd_handler(newdir, **_):
+ check_for_new_venv(Path(newdir))
+
+
+# Recalculate when venvs are created or destroyed
+
+
[email protected]_on_create
+def create_handler(**_):
+ check_for_new_venv(Path.cwd())
+
+
[email protected]_on_destroy
+def destroy_handler(**_):
+ check_for_new_venv(Path.cwd())
+
+
+# Initial activation before first prompt
+
+
[email protected]_post_init
+def load_handler(**_):
+ check_for_new_venv(Path.cwd())
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-3342@af2c094
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 3,342
|
👻 Spoooky! Ctrl+Z Fix!
|
This PR fixes the many job control issues we have had with suspending and presumably closes #1103, #2353, #2370, #2874, #3019, and #3216. I am writing this down so that we don't have to rediscover all of these points in the future.
TL;DR is that threadable subprocesses can't work with job suspension in their current form.
## The Problem
Pressing `Ctrl+Z` (`^Z`, or `b"\x1a"`) at the interactive terminal on posix would cause the subprocess to go into state T (or [stopped](https://linuxjourney.com/lesson/process-states)). This is because [`SIGTSTP`](https://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/Job-Control-Signals.html) is being issued (as it should be). However, this would cause xonsh / Python to deadlock until an *external* process sent a `SIGCONT` signal, **which is very bad**.
For example, let's look at the `sleep` command run in a thread (`PopenThread`) before `^Z` is pressed. The process status and heirarchy would look like:
**Before `^Z`:**
```
PID Status Command
10016 S |- xonsh # this is the parent xonsh process
10045 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10044 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10043 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10042 S |- sleep # the subprocess being run
```
They are all asleep like they should be. Oddly though, the threads that are spun up to monitor stdout, stderr, etc. each get their own process id and are children of original xonsh process at the same level as the subprocess we are running.
Now suposse that the user hits `^Z`. The status of the processes becomes:
**After `^Z`:**
```
PID Status Command
10016 S |- xonsh # this is the parent xonsh process
10045 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10044 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10043 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10042 T |- sleep # the subprocess being run
```
Because these extra xonsh threads exist that are waiting on the stopped process, xonsh itself is deadlocked and cannot act on any further input until the `SIGCONT` signal is recieved. Note that this situation is very different for subprocs that are not threaded (`Popen`). For example, let's look at `less` running on some file. **These procs behave normally with job control.**
**Before `^Z`:**
```
PID Status Command
10016 S |- xonsh # this is the parent xonsh process
10042 R |- less f.txt # the subprocess being run
```
**After `^Z`:**
```
PID Status Command
10016 S |- xonsh # this is the parent xonsh process
10042 T |- less f.txt # the subprocess being run
```
The example with `less` parallels what happens in Bash, where no subprocs are threadable.
## Strategies
There are so many options for how to try to resolve the deadlocking, I named them after character(s) in a [book series](https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/34403860-sufficiently-advanced-magic). Branches have the same name as strategy. The stratgies are outlined here, with sections going into their feasability below.
* **Keras:** Kill the extra threads before suspending.
* **Selyrian:** Kill the extra threads and ignore the suspending signal.
* **Talien:** Ignore the suspend signal and try to reimplement it by reading stdin
* **Salaris:** Ignore the suspend signal entriely and just continue on as if nothing happened.
* **Lydia:** The addition of an environment variable to allow the user to determine if subprocs should be run in threads or not.
The above (except for Lydia) apply only to `PopenThread`.
## Keras
The Keras strategy attempts to kill the threads prior to suspending. This means turning off the teeing of stdin, stdout, and stderr. In principle, this is a safe operations because we will be stopping the subprocess and returning control back to the terminal, and then rendering a new prompt.
However, this turns out to not be possible because the subproc seems to be stopped before the other processes and thus any signal handlers that have been installed by Python/xonsh to address `SIGTSTP` are never called and we are deadlocked. It may be that the signal handlers are never called just because the subprocess *always seems* to have a lower process id (PID) than the other xonsh threads, and thus is stopped first. However, even if were were able to manipulate the execution order to ensure that the threads have lower PIDs, this seems like a non-detrministic fix.
It is important to note, though, that SIGTSTP comes in on file descriptor 0 (fd0, stdin), which has been attached to the subprocess by this point. So the signal is first sent to the subprocess. We do not want to, and may not be able to, redirect stdin for all subprocs. Many commands rely on being attched to fd0 for stdin, or change their behavior if they think they are being piped a different input.
One way to get around this might have been to run the subprocess in a Python subprocess, adding a level to the Python process heirarchy. For example:
**Before `^Z`:**
```
PID Status Command
10016 S |- xonsh # this is the parent xonsh process
10046 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10045 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10044 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10042 S |- python -c "subprocess.run(['sleep', '2'])"
10043 S |- sleep 2 # the subprocess being run
```
You might think this is a reasonble cheat because unthreaded (`Popen`) subprocs have the correct job control behavior in xonsh. However, this tomfoolery doesn't trick anybody and the deadlock remains.
**After `^Z`:**
```
PID Status Command
10016 S |- xonsh # this is the parent xonsh process
10046 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10045 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10044 S |- xonsh # some xonsh i/o monitoring thread
10042 T |- python -c "subprocess.run(['sleep', '2'])"
10043 T |- sleep 2 # the subprocess being run
```
Thus, unfortunately, the Keras strategy is unviable.
## Selyrian
The Seylrian strategy is to kill the threads and the ignore any suspending that may happen. As discussed with the Keras strategy, we are not able to kill the threads. Thus, unfortunately, the Selyrian strategy is unviable.
## Taelien
The Taelien strategy is to ignore the `^Z`, kill the other threads, and then suspend the subprocess ourselves. The theory behind this is that it is possible to set suspends signal to be bound to a null key (`b"\x00"`, `stty susp "<undef>"`). In this case, when the user types `^Z`, the kernel does not send SIGTSTP to the subprocess. However, because `^Z` is a control character, it is still echoed to stdin/stdout/stderr. It should be possible to read the `^Z` from the relevant buffer `PopenThread` and hook into the proper next steps.
The good news is that unbinding the suspend action in this way does prevent `^Z` from sending SIGTSTP, and the subprocess continues executing as if nothing had happened. The bad news is that it is not possible to monitor the I/O buffers for the `^Z` (`b"\x1a"`) character because it written directly to that buffer (by the kernel) and does not go through the capture pipeline setup by `SubprocSpec` and `PopenThread`. Also because of this direct writting, we have no way of realizing that `^Z` has been typed and cannot issue a message to the user that it has been disabled.
Thus, unfortunately, the Taelien strategy is unviable.
## Salaris
The Salaris strategy is to just ignore all `^Z` input completely in `PopenThread`. Given the discussion in the Taelien strategy, this...actually works.
## Lydia
The Lydia strategy yields initial control over whether `Popen` or `PopenThread` is selected to the user. This is presumably done through an environment variable (`$THREAD_SUBPROCS`, because no one else in the world seems to be using it). This allows users to choose the behavior they want, both as a global configuration and in a small context with `${...}.swap(THREAD_SUBPROCS=False)`. This is effectively an easier-to-use alternative to saying,
```python
__xonsh__.commands_cache.threadable_predictors['cmd'] = lambda x: False
```
when testing if threading subprocs is causing problems. It also enables people to always have a working version of `^Z` if that is what they want. The trade off is that when `$THREAD_SUBPROCS = False`, the I/O streams may not be fully captured on the command pipeline in all cases.
The Lydia strategy is also workable.
## Solution
In the end, the only two viable strategies are Salaris + Lydia. This PR implements these both, `lydia` being branched off of `salaris`. This is not the ideal combination for all of the reasons above. However, it is the best that is achievable given the current state of the code base.
As discussed many other times, we can probably do a ground-up rewrite of this whole system and incorporate all of the lessons learned. This is probably best done in another library (slug) that xonsh then uses. However, it is not clear to me that the Python `subprocess` module is actually able to handle the kind of signal manipulation we want. We might need to move to an async system or write a low-level version of job control for proper handling of `^Z`.
|
2019-10-06T00:47:40Z
|
ctrl-z problem on Linux
Launching a command (like emacs) followed by ctrl-z suspends
the process but doesn't return keyboard control to xonsh. So there
is no way to detach the process with bg and continue typing. The
documentation only mentions that ctrl-z doesn't work on Windows.
xonfig
+------------------+----------+
| xonsh | 0.3.2 |
| Python | 3.4.3 |
| PLY | 3.7 |
| have readline | True |
| prompt toolkit | None |
| shell type | readline |
| pygments | None |
| on posix | True |
| on linux | True |
| distro | Fedora |
| on darwin | False |
| on windows | False |
| is superuser | False |
| default encoding | utf-8 |
+------------------+----------+
|
This one I can't reproduce. For me, the ctrl-z functionality is working just as I would expect (control goes back to the terminal).
Does this happen for all commands (e.g., `sleep 10`)? Or just for certain ones like `emacs`?
Okay, wait. I can reproduce this from within a graphical `emacs` window. I had been testing with text emacs (`emacs -nw`). This does indeed look like a bug.
For reference, just tested now...
In Bash, after opening emacs:
- hitting ctrl-z when the terminal has focus _stops the job and returns control to the terminal_ (correct)
- hitting ctrl-z when the emacs window has focus _does nothing_ (correct)
In xonsh, after opening emacs:
- hitting ctrl-z when the terminal has focus _stops the job and returns control to the terminal_ (correct)
- hitting ctrl-z when the emacs window has focus _stops the job and does not return control to the terminal_ (incorrect)
Again, thanks for reporting, @mburo!
Actually, @mburo, I'm not sure I can consider this a bug, as xonsh seems to exhibit the exact same behavior as bash in this situation. I think if anything, one could consider this to be a problem with emacs.
I tested this as well - it works fine for me, in both cases.
pbr@mongo:~$ emacs
(....text-based emacs takes over screen)
^Z
[1]+ Stopped emacs
pbr@mongo:~$ fg
emacs
^X^C
pbr@mongo:~$ emacs
^Z
[1]+ Stopped emacs
pbr@mongo:~$ fg
emacs
(...takes over screen again)
^Z
[1]+ Stopped emacs
pbr@mongo:~$ jobs
[1]+ Stopped emacs
pbr@mongo:~$ ls|cat /dev/tty
^Z
[2]+ Stopped ls --color=auto | cat /dev/tty
pbr@mongo:~$ fg
ls --color=auto | cat /dev/tty
^C
pbr@mongo:~$ fg
(...emacs takes over the screen again)
In the above, ^Z is working properly. When I tested with xonsh it worked exactly the same.
I just tested this again (this time with xonsh 0.3.4 and python 3.5.1). Seems to work now.
Okay! In that case, I'm going to go ahead and close this issue. If it crops up again, feel free to reopen.
issue is present again.
xonsh --version
xonsh/0.5.2
python --version
Python 3.5.2
(venv3.5) milez@dev-guy-automerge:~/AutoMerge$ lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS
Release: 16.04
Codename: xenial
hey @guyromm, thanks for reporting! We are aware of the issue and it's being addressed on #2071,
any more information is welcomed!
|
[
{
"body": "Launching a command (like emacs) followed by ctrl-z suspends\nthe process but doesn't return keyboard control to xonsh. So there\nis no way to detach the process with bg and continue typing. The\ndocumentation only mentions that ctrl-z doesn't work on Windows.\n\nxonfig\n+------------------+----------+\n| xonsh | 0.3.2 |\n| Python | 3.4.3 |\n| PLY | 3.7 |\n| have readline | True |\n| prompt toolkit | None |\n| shell type | readline |\n| pygments | None |\n| on posix | True |\n| on linux | True |\n| distro | Fedora |\n| on darwin | False |\n| on windows | False |\n| is superuser | False |\n| default encoding | utf-8 |\n+------------------+----------+\n",
"number": 1103,
"title": "ctrl-z problem on Linux"
}
] |
50155c66e3eb465c1bc328fad515220899acd361
|
{
"head_commit": "af2c094515a7dda2387df62980e6edfb41e51905",
"head_commit_message": "black",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/news/ctrlz.rst b/news/ctrlz.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..f9f43123e3\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/ctrlz.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* New ``$TRHEAD_SUBPROCS`` environment variable allows you to\n+ specify wheather threadable subprocesses should actually be\n+ run in a thread or not. Default ``True``.\n+\n+**Changed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Deprecated:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Removed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Pressing ``Ctrl+Z`` no longer deadlocks the terminal,\n+ allowing further input from the user, even for threaded\n+ subprocesses.\n+\n+**Security:**\n+\n+* <news item>\ndiff --git a/tests/test_builtins.py b/tests/test_builtins.py\nindex 29950df65d..36dcd2c594 100644\n--- a/tests/test_builtins.py\n+++ b/tests/test_builtins.py\n@@ -6,6 +6,7 @@\n import builtins\n import types\n from ast import AST, Module, Interactive, Expression\n+from subprocess import Popen\n \n import pytest\n \n@@ -25,8 +26,10 @@\n in_macro_call,\n call_macro,\n enter_macro,\n+ cmds_to_specs,\n )\n from xonsh.environ import Env\n+from xonsh.proc import PopenThread, ProcProxy, ProcProxyThread\n \n from tools import skip_if_on_windows\n \n@@ -388,3 +391,28 @@ def test_enter_macro():\n assert obj.macro_block == \"wakka\"\n assert obj.macro_globals\n assert obj.macro_locals\n+\n+\n+@skip_if_on_windows\n+def test_cmds_to_specs_thread_subproc(xonsh_builtins):\n+ env = xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env\n+ cmds = [[\"pwd\"]]\n+ # First check that threadable subprocs become threadable\n+ env['THREAD_SUBPROCS'] = True\n+ specs = cmds_to_specs(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')\n+ assert specs[0].cls is PopenThread\n+ # turn off threading and check we use Popen\n+ env['THREAD_SUBPROCS'] = False\n+ specs = cmds_to_specs(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')\n+ assert specs[0].cls is Popen\n+\n+ # now check the threadbility of callable aliases\n+ cmds = [[lambda: \"Keras Selyrian\"]]\n+ # check that threadable alias become threadable\n+ env['THREAD_SUBPROCS'] = True\n+ specs = cmds_to_specs(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')\n+ assert specs[0].cls is ProcProxyThread\n+ # turn off threading and check we use ProcProxy\n+ env['THREAD_SUBPROCS'] = False\n+ specs = cmds_to_specs(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')\n+ assert specs[0].cls is ProcProxy\ndiff --git a/xonsh/built_ins.py b/xonsh/built_ins.py\nindex 586c0ad993..2794a2263d 100644\n--- a/xonsh/built_ins.py\n+++ b/xonsh/built_ins.py\n@@ -738,7 +738,10 @@ def resolve_alias_cls(self):\n if not callable(alias):\n return\n self.is_proxy = True\n- thable = getattr(alias, \"__xonsh_threadable__\", True)\n+ env = builtins.__xonsh__.env\n+ thable = env.get(\"THREAD_SUBPROCS\") and getattr(\n+ alias, \"__xonsh_threadable__\", True\n+ )\n cls = ProcProxyThread if thable else ProcProxy\n self.cls = cls\n self.threadable = thable\n@@ -790,6 +793,7 @@ def _safe_pipe_properties(fd, use_tty=False):\n \n \n def _update_last_spec(last):\n+ env = builtins.__xonsh__.env\n captured = last.captured\n last.last_in_pipeline = True\n if not captured:\n@@ -799,9 +803,11 @@ def _update_last_spec(last):\n pass\n else:\n cmds_cache = builtins.__xonsh__.commands_cache\n- thable = cmds_cache.predict_threadable(\n- last.args\n- ) and cmds_cache.predict_threadable(last.cmd)\n+ thable = (\n+ env.get(\"THREAD_SUBPROCS\")\n+ and cmds_cache.predict_threadable(last.args)\n+ and cmds_cache.predict_threadable(last.cmd)\n+ )\n if captured and thable:\n last.cls = PopenThread\n elif not thable:\ndiff --git a/xonsh/environ.py b/xonsh/environ.py\nindex 500ce14ee3..e3dba35e0e 100644\n--- a/xonsh/environ.py\n+++ b/xonsh/environ.py\n@@ -571,6 +571,7 @@ def DEFAULT_ENSURERS():\n \"SUGGEST_MAX_NUM\": (is_int, int, str),\n \"SUGGEST_THRESHOLD\": (is_int, int, str),\n \"SUPPRESS_BRANCH_TIMEOUT_MESSAGE\": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),\n+ \"THREAD_SUBPROCS\": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),\n \"UPDATE_COMPLETIONS_ON_KEYPRESS\": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),\n \"UPDATE_OS_ENVIRON\": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),\n \"UPDATE_PROMPT_ON_KEYPRESS\": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),\n@@ -755,6 +756,7 @@ def DEFAULT_VALUES():\n \"SUGGEST_COMMANDS\": True,\n \"SUGGEST_MAX_NUM\": 5,\n \"SUGGEST_THRESHOLD\": 3,\n+ \"THREAD_SUBPROCS\": True,\n \"TITLE\": DEFAULT_TITLE,\n \"UPDATE_COMPLETIONS_ON_KEYPRESS\": False,\n \"UPDATE_OS_ENVIRON\": False,\n@@ -1159,6 +1161,26 @@ def DEFAULT_DOCS():\n \"not always happen.\",\n configurable=False,\n ),\n+ \"THREAD_SUBPROCS\": VarDocs(\n+ \"Whether or not to try to run subrocess mode in a Python thread, \"\n+ \"when applicable. There are various trade-offs, which normally \"\n+ \"affects only interactive sessions.\\n\\nWhen True:\\n\\n\"\n+ \"* Xonsh is able capture & store the stdin, stdout, and stderr \\n\"\n+ \" of threadable subprocesses.\\n\"\n+ \"* However, stopping threaded suprocs with ^Z (i.e. ``SIGTSTP``)\\n\"\n+ \" is disabled as it causes deadlocked terminals.\\n\"\n+ \" ``SIGTSTP`` may still be issued and only the physical pressing\\n\"\n+ \" of ``Ctrl+Z`` is ignored.\\n\"\n+ \"* Thredable commands are run with ``PopenThread`` and threadable \\n\"\n+ \" alias are run with ``ProcProxyThread``.\\n\\n\"\n+ \"When False:\\n\\n\"\n+ \"* Xonsh may not be able to capture stdin, stdout, and stderr streams \\n\"\n+ \" unless explicitly asked to do so.\\n\"\n+ \"* Stopping the thread with yields to job control.\\n\"\n+ \"* Thredable commands are run with ``Popen`` and threadable \\n\"\n+ \" alias are run with ``ProcProxy``.\\n\\n\"\n+ \"The desired effect is often up to the command, user, or use case.\"\n+ ),\n \"TITLE\": VarDocs(\n \"The title text for the window in which xonsh is running. Formatted \"\n \"in the same manner as ``$PROMPT``, see 'Customizing the Prompt' \"\ndiff --git a/xonsh/jobs.py b/xonsh/jobs.py\nindex ec984db1c4..7994119fa6 100644\n--- a/xonsh/jobs.py\n+++ b/xonsh/jobs.py\n@@ -202,7 +202,7 @@ def wait_for_active_job(last_task=None, backgrounded=False, return_error=False):\n last_task=active_task, backgrounded=backgrounded\n )\n if os.WIFSTOPPED(wcode):\n- print(\"^Z\")\n+ print()\n active_task[\"status\"] = \"stopped\"\n backgrounded = True\n elif os.WIFSIGNALED(wcode):\ndiff --git a/xonsh/proc.py b/xonsh/proc.py\nindex 9c778e9cff..3c2899fe59 100644\n--- a/xonsh/proc.py\n+++ b/xonsh/proc.py\n@@ -554,6 +554,8 @@ def __init__(self, *args, stdin=None, stdout=None, stderr=None, **kwargs):\n self.timeout = env.get(\"XONSH_PROC_FREQUENCY\")\n self.in_alt_mode = False\n self.stdin_mode = None\n+ self._tc_cc_vsusp = b\"\\x1a\" # default is usually ^Z\n+ self._disable_suspend_keybind()\n # stdout setup\n self.orig_stdout = stdout\n self.stdout_fd = 1 if stdout is None else stdout.fileno()\n@@ -820,6 +822,33 @@ def _restore_sigtstp(self, frame=None):\n self.old_tstp_handler = None\n if frame is not None:\n self._disable_cbreak_stdin()\n+ self._restore_suspend_keybind()\n+\n+ def _disable_suspend_keybind(self):\n+ if ON_WINDOWS:\n+ return\n+ try:\n+ mode = termios.tcgetattr(0) # only makes sense for stdin\n+ except termios.error:\n+ return\n+ self._tc_cc_vsusp = mode[CC][termios.VSUSP]\n+ mode[CC][termios.VSUSP] = b\"\\x00\" # set ^Z (ie SIGSTOP) to undefined\n+ termios.tcsetattr(0, termios.TCSANOW, mode)\n+\n+ def _restore_suspend_keybind(self):\n+ if ON_WINDOWS:\n+ return\n+ try:\n+ mode = termios.tcgetattr(0) # only makes sense for stdin\n+ except termios.error:\n+ return\n+ mode[CC][termios.VSUSP] = self._tc_cc_vsusp # set ^Z (ie SIGSTOP) to original\n+ try:\n+ # this usually doesn't work in interactive mode,\n+ # but we should try it anyway.\n+ termios.tcsetattr(0, termios.TCSANOW, mode)\n+ except termios.error:\n+ pass\n \n #\n # SIGQUIT handler\n@@ -1749,6 +1778,7 @@ def SIGNAL_MESSAGES():\n signal.SIGILL: \"Illegal instructions\",\n signal.SIGTERM: \"Terminated\",\n signal.SIGSEGV: \"Segmentation fault\",\n+ signal.SIGTSTP: \"Stopped\",\n }\n if ON_POSIX:\n sm.update(\ndiff --git a/xonsh/ptk2/key_bindings.py b/xonsh/ptk2/key_bindings.py\nindex c3e78dc0ad..c68f9acb9c 100644\n--- a/xonsh/ptk2/key_bindings.py\n+++ b/xonsh/ptk2/key_bindings.py\n@@ -350,3 +350,10 @@ def wrap_cursor_forward(event):\n @handle(Keys.ControlJ, filter=IsSearching())\n def accept_search(event):\n search.accept_search()\n+\n+ @handle(Keys.ControlZ)\n+ def skip_control_z(event):\n+ \"\"\"Prevents the writing of ^Z to the prompt, if Ctrl+Z was pressed\n+ during the previous command.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ pass\ndiff --git a/xonsh/ptk2/shell.py b/xonsh/ptk2/shell.py\nindex d8d699f507..ec8b3f26e9 100644\n--- a/xonsh/ptk2/shell.py\n+++ b/xonsh/ptk2/shell.py\n@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@\n # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-\n \"\"\"The prompt_toolkit based xonsh shell.\"\"\"\n+import os\n import sys\n import builtins\n from types import MethodType\n@@ -8,7 +9,7 @@\n from xonsh.base_shell import BaseShell\n from xonsh.shell import transform_command\n from xonsh.tools import print_exception, carriage_return\n-from xonsh.platform import HAS_PYGMENTS, ON_WINDOWS\n+from xonsh.platform import HAS_PYGMENTS, ON_WINDOWS, ON_POSIX\n from xonsh.style_tools import partial_color_tokenize, _TokenType, DEFAULT_STYLE_DICT\n from xonsh.lazyimps import pygments, pyghooks, winutils\n from xonsh.pygments_cache import get_all_styles\n@@ -366,3 +367,9 @@ def restore_tty_sanity(self):\n # if not ON_POSIX:\n # return\n # sys.stdout.write('\\033[9999999C\\n')\n+ if not ON_POSIX:\n+ return\n+ stty, _ = builtins.__xonsh__.commands_cache.lazyget(\"stty\", (None, None))\n+ if stty is None:\n+ return\n+ os.system(stty + \" sane\")\ndiff --git a/xontrib/bashisms.py b/xontrib/bashisms.py\nindex 567602aaca..9f620023aa 100644\n--- a/xontrib/bashisms.py\n+++ b/xontrib/bashisms.py\n@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@\n import shlex\n import sys\n import re\n+import builtins\n \n \n __all__ = ()\n@@ -62,3 +63,4 @@ def alias(args, stdin=None):\n \n \n aliases[\"alias\"] = alias\n+builtins.__xonsh__.env[\"THREAD_SUBPROCS\"] = False\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1159,6 +1161,26 @@ def DEFAULT_DOCS():\n \"not always happen.\",\n configurable=False,\n ),\n+ \"THREAD_SUBPROCS\": VarDocs(\n+ \"Whether or not to try to run subrocess mode in a Python thread, \"\n+ \"when applicable. There are various trade-offs, which normally \"\n+ \"affects only interactive sessions.\\n\\nWhen True:\\n\\n\"\n+ \"* Xonsh is able capture & store the stdin, stdout, and stderr \\n\"\n+ \" of threadable subprocesses.\\n\"\n+ \"* However, stopping threaded suprocs with ^Z (i.e. ``SIGTSTP``)\\n\"\n+ \" is disabled as it causes deadlocked terminals.\\n\"\n+ \" ``SIGTSTP`` may still be issued and only the physical pressing\\n\"\n+ \" of ``Ctrl+Z`` is ignored.\\n\"\n+ \"* Thredable commands are run with ``PopenThread`` and threadable \\n\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1174,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/environ.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n \"* Threadable commands are run with ``PopenThread`` and threadable \\n\"\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1159,6 +1161,26 @@ def DEFAULT_DOCS():\n \"not always happen.\",\n configurable=False,\n ),\n+ \"THREAD_SUBPROCS\": VarDocs(\n+ \"Whether or not to try to run subrocess mode in a Python thread, \"\n+ \"when applicable. There are various trade-offs, which normally \"\n+ \"affects only interactive sessions.\\n\\nWhen True:\\n\\n\"\n+ \"* Xonsh is able capture & store the stdin, stdout, and stderr \\n\"\n+ \" of threadable subprocesses.\\n\"\n+ \"* However, stopping threaded suprocs with ^Z (i.e. ``SIGTSTP``)\\n\"\n+ \" is disabled as it causes deadlocked terminals.\\n\"\n+ \" ``SIGTSTP`` may still be issued and only the physical pressing\\n\"\n+ \" of ``Ctrl+Z`` is ignored.\\n\"\n+ \"* Thredable commands are run with ``PopenThread`` and threadable \\n\"\n+ \" alias are run with ``ProcProxyThread``.\\n\\n\"\n+ \"When False:\\n\\n\"\n+ \"* Xonsh may not be able to capture stdin, stdout, and stderr streams \\n\"\n+ \" unless explicitly asked to do so.\\n\"\n+ \"* Stopping the thread with yields to job control.\\n\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1179,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/environ.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThere's a word missing here, I think..."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1159,6 +1161,26 @@ def DEFAULT_DOCS():\n \"not always happen.\",\n configurable=False,\n ),\n+ \"THREAD_SUBPROCS\": VarDocs(\n+ \"Whether or not to try to run subrocess mode in a Python thread, \"\n+ \"when applicable. There are various trade-offs, which normally \"\n+ \"affects only interactive sessions.\\n\\nWhen True:\\n\\n\"\n+ \"* Xonsh is able capture & store the stdin, stdout, and stderr \\n\"\n+ \" of threadable subprocesses.\\n\"\n+ \"* However, stopping threaded suprocs with ^Z (i.e. ``SIGTSTP``)\\n\"\n+ \" is disabled as it causes deadlocked terminals.\\n\"\n+ \" ``SIGTSTP`` may still be issued and only the physical pressing\\n\"\n+ \" of ``Ctrl+Z`` is ignored.\\n\"\n+ \"* Thredable commands are run with ``PopenThread`` and threadable \\n\"\n+ \" alias are run with ``ProcProxyThread``.\\n\\n\"\n+ \"When False:\\n\\n\"\n+ \"* Xonsh may not be able to capture stdin, stdout, and stderr streams \\n\"\n+ \" unless explicitly asked to do so.\\n\"\n+ \"* Stopping the thread with yields to job control.\\n\"\n+ \"* Thredable commands are run with ``Popen`` and threadable \\n\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1180,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/environ.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n \"* Threadable commands are run with ``Popen`` and threadable \\n\"\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -202,7 +202,7 @@ def wait_for_active_job(last_task=None, backgrounded=False, return_error=False):\n last_task=active_task, backgrounded=backgrounded\n )\n if os.WIFSTOPPED(wcode):\n- print(\"^Z\")\n+ print()",
"line": null,
"original_line": 205,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/jobs.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIs this flushing something out? Or can it be removed altogether?\n\n@author:\nI think it could be removed potentially."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* New ``$TRHEAD_SUBPROCS`` environment variable allows you to",
"line": null,
"original_line": 3,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "news/ctrlz.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n* New ``$THREAD_SUBPROCS`` environment variable allows you to\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1159,6 +1161,26 @@ def DEFAULT_DOCS():\n \"not always happen.\",\n configurable=False,\n ),\n+ \"THREAD_SUBPROCS\": VarDocs(\n+ \"Whether or not to try to run subrocess mode in a Python thread, \"\n+ \"when applicable. There are various trade-offs, which normally \"\n+ \"affects only interactive sessions.\\n\\nWhen True:\\n\\n\"\n+ \"* Xonsh is able capture & store the stdin, stdout, and stderr \\n\"\n+ \" of threadable subprocesses.\\n\"\n+ \"* However, stopping threaded suprocs with ^Z (i.e. ``SIGTSTP``)\\n\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1170,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/environ.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n \"* However, stopping threaded subprocs with ^Z (i.e. ``SIGTSTP``)\\n\"\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* New ``$TRHEAD_SUBPROCS`` environment variable allows you to\n+ specify wheather threadable subprocesses should actually be",
"line": null,
"original_line": 4,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "news/ctrlz.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n specify whether threadable subprocesses should actually be\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1159,6 +1161,26 @@ def DEFAULT_DOCS():\n \"not always happen.\",\n configurable=False,\n ),\n+ \"THREAD_SUBPROCS\": VarDocs(\n+ \"Whether or not to try to run subrocess mode in a Python thread, \"\n+ \"when applicable. There are various trade-offs, which normally \"\n+ \"affects only interactive sessions.\\n\\nWhen True:\\n\\n\"\n+ \"* Xonsh is able capture & store the stdin, stdout, and stderr \\n\"\n+ \" of threadable subprocesses.\\n\"\n+ \"* However, stopping threaded suprocs with ^Z (i.e. ``SIGTSTP``)\\n\"\n+ \" is disabled as it causes deadlocked terminals.\\n\"\n+ \" ``SIGTSTP`` may still be issued and only the physical pressing\\n\"\n+ \" of ``Ctrl+Z`` is ignored.\\n\"\n+ \"* Thredable commands are run with ``PopenThread`` and threadable \\n\"\n+ \" alias are run with ``ProcProxyThread``.\\n\\n\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1175,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/environ.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n \" aliases are run with ``ProcProxyThread``.\\n\\n\"\r\n```"
}
] |
f5948f44d2415d1367594338adb07f1e90c7fbaa
|
diff --git a/news/ctrlz.rst b/news/ctrlz.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fa8c5d3828
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/ctrlz.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+**Added:**
+
+* New ``$THREAD_SUBPROCS`` environment variable allows you to
+ specify whether threadable subprocesses should actually be
+ run in a thread or not. Default ``True``.
+
+**Changed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Deprecated:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Removed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* Pressing ``Ctrl+Z`` no longer deadlocks the terminal,
+ allowing further input from the user, even for threaded
+ subprocesses.
+
+**Security:**
+
+* <news item>
diff --git a/tests/test_builtins.py b/tests/test_builtins.py
index 29950df65d..36dcd2c594 100644
--- a/tests/test_builtins.py
+++ b/tests/test_builtins.py
@@ -6,6 +6,7 @@
import builtins
import types
from ast import AST, Module, Interactive, Expression
+from subprocess import Popen
import pytest
@@ -25,8 +26,10 @@
in_macro_call,
call_macro,
enter_macro,
+ cmds_to_specs,
)
from xonsh.environ import Env
+from xonsh.proc import PopenThread, ProcProxy, ProcProxyThread
from tools import skip_if_on_windows
@@ -388,3 +391,28 @@ def test_enter_macro():
assert obj.macro_block == "wakka"
assert obj.macro_globals
assert obj.macro_locals
+
+
+@skip_if_on_windows
+def test_cmds_to_specs_thread_subproc(xonsh_builtins):
+ env = xonsh_builtins.__xonsh__.env
+ cmds = [["pwd"]]
+ # First check that threadable subprocs become threadable
+ env['THREAD_SUBPROCS'] = True
+ specs = cmds_to_specs(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')
+ assert specs[0].cls is PopenThread
+ # turn off threading and check we use Popen
+ env['THREAD_SUBPROCS'] = False
+ specs = cmds_to_specs(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')
+ assert specs[0].cls is Popen
+
+ # now check the threadbility of callable aliases
+ cmds = [[lambda: "Keras Selyrian"]]
+ # check that threadable alias become threadable
+ env['THREAD_SUBPROCS'] = True
+ specs = cmds_to_specs(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')
+ assert specs[0].cls is ProcProxyThread
+ # turn off threading and check we use ProcProxy
+ env['THREAD_SUBPROCS'] = False
+ specs = cmds_to_specs(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')
+ assert specs[0].cls is ProcProxy
diff --git a/xonsh/built_ins.py b/xonsh/built_ins.py
index 586c0ad993..2794a2263d 100644
--- a/xonsh/built_ins.py
+++ b/xonsh/built_ins.py
@@ -738,7 +738,10 @@ def resolve_alias_cls(self):
if not callable(alias):
return
self.is_proxy = True
- thable = getattr(alias, "__xonsh_threadable__", True)
+ env = builtins.__xonsh__.env
+ thable = env.get("THREAD_SUBPROCS") and getattr(
+ alias, "__xonsh_threadable__", True
+ )
cls = ProcProxyThread if thable else ProcProxy
self.cls = cls
self.threadable = thable
@@ -790,6 +793,7 @@ def _safe_pipe_properties(fd, use_tty=False):
def _update_last_spec(last):
+ env = builtins.__xonsh__.env
captured = last.captured
last.last_in_pipeline = True
if not captured:
@@ -799,9 +803,11 @@ def _update_last_spec(last):
pass
else:
cmds_cache = builtins.__xonsh__.commands_cache
- thable = cmds_cache.predict_threadable(
- last.args
- ) and cmds_cache.predict_threadable(last.cmd)
+ thable = (
+ env.get("THREAD_SUBPROCS")
+ and cmds_cache.predict_threadable(last.args)
+ and cmds_cache.predict_threadable(last.cmd)
+ )
if captured and thable:
last.cls = PopenThread
elif not thable:
diff --git a/xonsh/environ.py b/xonsh/environ.py
index 500ce14ee3..6bc3e2d350 100644
--- a/xonsh/environ.py
+++ b/xonsh/environ.py
@@ -571,6 +571,7 @@ def DEFAULT_ENSURERS():
"SUGGEST_MAX_NUM": (is_int, int, str),
"SUGGEST_THRESHOLD": (is_int, int, str),
"SUPPRESS_BRANCH_TIMEOUT_MESSAGE": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),
+ "THREAD_SUBPROCS": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),
"UPDATE_COMPLETIONS_ON_KEYPRESS": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),
"UPDATE_OS_ENVIRON": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),
"UPDATE_PROMPT_ON_KEYPRESS": (is_bool, to_bool, bool_to_str),
@@ -755,6 +756,7 @@ def DEFAULT_VALUES():
"SUGGEST_COMMANDS": True,
"SUGGEST_MAX_NUM": 5,
"SUGGEST_THRESHOLD": 3,
+ "THREAD_SUBPROCS": True,
"TITLE": DEFAULT_TITLE,
"UPDATE_COMPLETIONS_ON_KEYPRESS": False,
"UPDATE_OS_ENVIRON": False,
@@ -1159,6 +1161,26 @@ def DEFAULT_DOCS():
"not always happen.",
configurable=False,
),
+ "THREAD_SUBPROCS": VarDocs(
+ "Whether or not to try to run subrocess mode in a Python thread, "
+ "when applicable. There are various trade-offs, which normally "
+ "affects only interactive sessions.\n\nWhen True:\n\n"
+ "* Xonsh is able capture & store the stdin, stdout, and stderr \n"
+ " of threadable subprocesses.\n"
+ "* However, stopping threaded subprocs with ^Z (i.e. ``SIGTSTP``)\n"
+ " is disabled as it causes deadlocked terminals.\n"
+ " ``SIGTSTP`` may still be issued and only the physical pressing\n"
+ " of ``Ctrl+Z`` is ignored.\n"
+ "* Threadable commands are run with ``PopenThread`` and threadable \n"
+ " aliases are run with ``ProcProxyThread``.\n\n"
+ "When False:\n\n"
+ "* Xonsh may not be able to capture stdin, stdout, and stderr streams \n"
+ " unless explicitly asked to do so.\n"
+ "* Stopping the thread with ``Ctrl+Z`` yields to job control.\n"
+ "* Threadable commands are run with ``Popen`` and threadable \n"
+ " alias are run with ``ProcProxy``.\n\n"
+ "The desired effect is often up to the command, user, or use case."
+ ),
"TITLE": VarDocs(
"The title text for the window in which xonsh is running. Formatted "
"in the same manner as ``$PROMPT``, see 'Customizing the Prompt' "
diff --git a/xonsh/jobs.py b/xonsh/jobs.py
index ec984db1c4..20d5923b57 100644
--- a/xonsh/jobs.py
+++ b/xonsh/jobs.py
@@ -202,7 +202,6 @@ def wait_for_active_job(last_task=None, backgrounded=False, return_error=False):
last_task=active_task, backgrounded=backgrounded
)
if os.WIFSTOPPED(wcode):
- print("^Z")
active_task["status"] = "stopped"
backgrounded = True
elif os.WIFSIGNALED(wcode):
diff --git a/xonsh/proc.py b/xonsh/proc.py
index 9c778e9cff..3c2899fe59 100644
--- a/xonsh/proc.py
+++ b/xonsh/proc.py
@@ -554,6 +554,8 @@ def __init__(self, *args, stdin=None, stdout=None, stderr=None, **kwargs):
self.timeout = env.get("XONSH_PROC_FREQUENCY")
self.in_alt_mode = False
self.stdin_mode = None
+ self._tc_cc_vsusp = b"\x1a" # default is usually ^Z
+ self._disable_suspend_keybind()
# stdout setup
self.orig_stdout = stdout
self.stdout_fd = 1 if stdout is None else stdout.fileno()
@@ -820,6 +822,33 @@ def _restore_sigtstp(self, frame=None):
self.old_tstp_handler = None
if frame is not None:
self._disable_cbreak_stdin()
+ self._restore_suspend_keybind()
+
+ def _disable_suspend_keybind(self):
+ if ON_WINDOWS:
+ return
+ try:
+ mode = termios.tcgetattr(0) # only makes sense for stdin
+ except termios.error:
+ return
+ self._tc_cc_vsusp = mode[CC][termios.VSUSP]
+ mode[CC][termios.VSUSP] = b"\x00" # set ^Z (ie SIGSTOP) to undefined
+ termios.tcsetattr(0, termios.TCSANOW, mode)
+
+ def _restore_suspend_keybind(self):
+ if ON_WINDOWS:
+ return
+ try:
+ mode = termios.tcgetattr(0) # only makes sense for stdin
+ except termios.error:
+ return
+ mode[CC][termios.VSUSP] = self._tc_cc_vsusp # set ^Z (ie SIGSTOP) to original
+ try:
+ # this usually doesn't work in interactive mode,
+ # but we should try it anyway.
+ termios.tcsetattr(0, termios.TCSANOW, mode)
+ except termios.error:
+ pass
#
# SIGQUIT handler
@@ -1749,6 +1778,7 @@ def SIGNAL_MESSAGES():
signal.SIGILL: "Illegal instructions",
signal.SIGTERM: "Terminated",
signal.SIGSEGV: "Segmentation fault",
+ signal.SIGTSTP: "Stopped",
}
if ON_POSIX:
sm.update(
diff --git a/xonsh/ptk2/key_bindings.py b/xonsh/ptk2/key_bindings.py
index c3e78dc0ad..c68f9acb9c 100644
--- a/xonsh/ptk2/key_bindings.py
+++ b/xonsh/ptk2/key_bindings.py
@@ -350,3 +350,10 @@ def wrap_cursor_forward(event):
@handle(Keys.ControlJ, filter=IsSearching())
def accept_search(event):
search.accept_search()
+
+ @handle(Keys.ControlZ)
+ def skip_control_z(event):
+ """Prevents the writing of ^Z to the prompt, if Ctrl+Z was pressed
+ during the previous command.
+ """
+ pass
diff --git a/xonsh/ptk2/shell.py b/xonsh/ptk2/shell.py
index d8d699f507..ec8b3f26e9 100644
--- a/xonsh/ptk2/shell.py
+++ b/xonsh/ptk2/shell.py
@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""The prompt_toolkit based xonsh shell."""
+import os
import sys
import builtins
from types import MethodType
@@ -8,7 +9,7 @@
from xonsh.base_shell import BaseShell
from xonsh.shell import transform_command
from xonsh.tools import print_exception, carriage_return
-from xonsh.platform import HAS_PYGMENTS, ON_WINDOWS
+from xonsh.platform import HAS_PYGMENTS, ON_WINDOWS, ON_POSIX
from xonsh.style_tools import partial_color_tokenize, _TokenType, DEFAULT_STYLE_DICT
from xonsh.lazyimps import pygments, pyghooks, winutils
from xonsh.pygments_cache import get_all_styles
@@ -366,3 +367,9 @@ def restore_tty_sanity(self):
# if not ON_POSIX:
# return
# sys.stdout.write('\033[9999999C\n')
+ if not ON_POSIX:
+ return
+ stty, _ = builtins.__xonsh__.commands_cache.lazyget("stty", (None, None))
+ if stty is None:
+ return
+ os.system(stty + " sane")
diff --git a/xontrib/bashisms.py b/xontrib/bashisms.py
index 567602aaca..9f620023aa 100644
--- a/xontrib/bashisms.py
+++ b/xontrib/bashisms.py
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
import shlex
import sys
import re
+import builtins
__all__ = ()
@@ -62,3 +63,4 @@ def alias(args, stdin=None):
aliases["alias"] = alias
+builtins.__xonsh__.env["THREAD_SUBPROCS"] = False
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-8825@2f19c85
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 8,825
|
Simplex algorithm
|
### Describe your change:
Fixes: #8820
Implements the simplex algorithm for solving linear programs.
Adds `linear_programming` folder.
* [x] Add an algorithm?
* [ ] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [ ] Documentation change?
### Checklist:
* [x] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [x] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [ ] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [x] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [x] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [x] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [x] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [x] All new algorithms include at least one URL that points to Wikipedia or another similar explanation.
* [x] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the commit message contains `Fixes: #{$ISSUE_NO}`.
|
2023-06-16T20:39:49Z
|
Create optimization folder
### Feature description
I have implemented the simplex algorithm in Python, but I can’t find the appropriate category to place it in.
The simplex algorithm finds the best value of a function, while restricted by inequality constraints. It enters the linear programming sub-field of mathematical optimisation.
Other linear programming algorithms include the:
- Criss-cross,
- Ellipsoid,
- Projective, and
- Input sparsity time
algorithms.
I considered putting simplex in `other`, `math`, and `machine learning`:
For `other`, mathematical optimisation is an organised discipline and has many algorithms which could be implemented in Python, deserving its own folder.
For `math`, it is too applied to fit in with the pure math algorithms there.
For `machine learning`, while simplex finds use in ML, so it does in operations research, engineering and physics. It would be false to say simplex is an ML algorithm.
|
@cclauss @dhruvmanila
What are your opinions on the creation of this directory?
Let's go with `linear_programming`. Thanks.
|
[
{
"body": "### Feature description\n\nI have implemented the simplex algorithm in Python, but I can’t find the appropriate category to place it in.\r\n\r\nThe simplex algorithm finds the best value of a function, while restricted by inequality constraints. It enters the linear programming sub-field of mathematical optimisation. \r\n\r\nOther linear programming algorithms include the:\r\n- Criss-cross,\r\n- Ellipsoid,\r\n- Projective, and\r\n- Input sparsity time \r\nalgorithms.\r\n\r\nI considered putting simplex in `other`, `math`, and `machine learning`:\r\n\r\nFor `other`, mathematical optimisation is an organised discipline and has many algorithms which could be implemented in Python, deserving its own folder.\r\n\r\nFor `math`, it is too applied to fit in with the pure math algorithms there.\r\n\r\nFor `machine learning`, while simplex finds use in ML, so it does in operations research, engineering and physics. It would be false to say simplex is an ML algorithm.",
"number": 8820,
"title": "Create optimization folder"
}
] |
46379861257d43bb7140d261094bf17dc414950f
|
{
"head_commit": "2f19c85c779cd0d93bcc2cfbca88f8546e308e16",
"head_commit_message": "added docstrings",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/linear_programming/simplex.py b/linear_programming/simplex.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..f6c17136da9a\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/linear_programming/simplex.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,327 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Python implementation of the simplex algorithm for solving linear programs in\n+tabular form with\n+- `>=`, `<=`, and `=` constraints and\n+- each variable `x1, x2, ...>= 0`.\n+\n+See https://gist.github.com/imengus/f9619a568f7da5bc74eaf20169a24d98 for how\n+to convert linear programs to simplex tableaus, and the steps taken in the\n+simplex algorithm.\n+\n+Resources:\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_programming\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simplex_algorithm\n+\n+https://towardsdatascience.com/ \\\n+ a-beginners-guide-to-linear-programming-and-the-simplex-algorithm \\\n+ -87db017e92b4\n+\"\"\"\n+from typing import Any\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+\n+\n+class Tableau:\n+ \"\"\"Operate on simplex tableaus\"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, tableau: np.ndarray, n_vars: int) -> None:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,-1],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: RHS must be > 0\n+ \"\"\"\n+ rhs = tableau[:, -1]\n+ if np.any(rhs, where=rhs < 0):\n+ raise ValueError(\"RHS must be > 0\")\n+\n+ if tableau is None:\n+ return\n+\n+ self.tableau = tableau\n+ self.n_rows = len(tableau[:, 0])\n+ self.n_cols = len(tableau[0])\n+\n+ # Number of decision variables x1, x2, x3...\n+ self.n_vars = n_vars\n+\n+ # Number of artificial variables to be minimised\n+ self.n_art_vars = len(np.where(tableau[self.n_vars : -1] == -1)[0])\n+\n+ # 2 if there are >= or == constraints (nonstandard), 1 otherwise (std)\n+ self.n_stages = (self.n_art_vars > 0) + 1\n+\n+ # Number of slack variables added to make inequalities into equalities\n+ self.n_slack = self.n_rows - self.n_stages\n+\n+ # Objectives for each stage\n+ self.objectives = [\"max\"]\n+\n+ # In two stage simplex, first minimise then maximise\n+ if self.n_art_vars:\n+ self.objectives.append(\"min\")\n+\n+ self.col_titles = [\"\"]\n+\n+ # Index of current pivot row and column\n+ self.row_idx = None\n+ self.col_idx = None\n+\n+ # Does objective row only contain (non)-negative values?\n+ self.stop_iter = False\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def generate_col_titles(*args: int) -> list[str]:\n+ \"\"\"Generate column titles for tableau of specific dimensions\n+\n+ >>> Tableau.generate_col_titles(2, 3, 1)\n+ ['x1', 'x2', 's1', 's2', 's3', 'a1', 'RHS']\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # decision | slack | artificial\n+ string_starts = [\"x\", \"s\", \"a\"]\n+ titles = []\n+ for i in range(3):\n+ for j in range(args[i]):\n+ titles.append(string_starts[i] + str(j + 1))\n+ titles.append(\"RHS\")\n+ return titles\n+\n+ def find_pivot(self, tableau: np.ndarray) -> tuple[Any, Any]:\n+ \"\"\"Finds the pivot row and column.\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [-2,-1,0,0,0],\n+ ... [3,1,1,0,6],\n+ ... [1,2,0,1,7.]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.find_pivot(t.tableau)\n+ (1, 0)\n+ \"\"\"\n+ objective = self.objectives[-1]\n+\n+ # Find entries of highest magnitude in objective rows\n+ sign = (objective == \"min\") - (objective == \"max\")\n+ col_idx = np.argmax(sign * tableau[0, : self.n_vars])\n+\n+ # Choice is only valid if below 0 for maximise, and above for minimise\n+ if sign * self.tableau[0, col_idx] <= 0:\n+ self.stop_iter = True\n+ return 0, 0\n+\n+ # Pivot row is chosen as having the lowest quotient when elements of\n+ # the pivot column divide the right-hand side\n+\n+ # Slice excluding the objective rows\n+ s = slice(self.n_stages, self.n_rows)\n+\n+ # RHS\n+ dividend = tableau[s, -1]\n+\n+ # Elements of pivot column within slice\n+ divisor = tableau[s, col_idx]\n+\n+ # Array filled with nans\n+ nans = np.full(self.n_rows - self.n_stages, np.nan)\n+\n+ # If element in pivot column is greater than zeron_stages, return\n+ # quotient or nan otherwise\n+ quotients = np.divide(dividend, divisor, out=nans, where=divisor > 0)\n+\n+ # Arg of minimum quotient excluding the nan values. n_stages is added\n+ # to compensate for earlier exclusion of objective columns\n+ row_idx = np.nanargmin(quotients) + self.n_stages\n+ return row_idx, col_idx\n+\n+ def pivot(self, tableau: np.ndarray, row_idx: int, col_idx: int) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"Pivots on value on the intersection of pivot row and column.\n+\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([[-2,-3,0,0,0],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.pivot(t.tableau, 1, 0).tolist()\n+ ... # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE\n+ [[0.0, 3.0, 2.0, 0.0, 8.0],\n+ [1.0, 3.0, 1.0, 0.0, 4.0],\n+ [0.0, -8.0, -3.0, 1.0, -8.0]]\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Avoid changes to original tableau\n+ piv_row = tableau[row_idx].copy()\n+\n+ piv_val = piv_row[col_idx]\n+\n+ # Entry becomes 1\n+ piv_row *= 1 / piv_val\n+\n+ # Variable in pivot column becomes basic, ie the only non-zero entry\n+ for idx, coeff in enumerate(tableau[:, col_idx]):\n+ tableau[idx] += -coeff * piv_row\n+ tableau[row_idx] = piv_row\n+ return tableau\n+\n+ def change_stage(self, tableau: np.ndarray, objectives: list[Any]) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"Exits first phase of the two-stage method by deleting artificial\n+ rows and columns, or completes the algorithm if exiting the standard\n+ case.\n+\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [3,3,-1,-1,0,0,4],\n+ ... [2,1,0,0,0,0,0.],\n+ ... [1,2,-1,0,1,0,2],\n+ ... [2,1,0,-1,0,1,2]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.change_stage(t.tableau, t.objectives).tolist()\n+ ... # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE\n+ [[2.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],\n+ [1.0, 2.0, -1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0],\n+ [2.0, 1.0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, 2.0]]\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Objective of original objective row remains\n+ objectives.pop()\n+\n+ if not objectives:\n+ return tableau\n+\n+ # Slice containing ids for artificial columns\n+ s = slice(-self.n_art_vars - 1, -1)\n+\n+ # Delete the artificial variable columns\n+ tableau = np.delete(tableau, s, axis=1)\n+\n+ # Delete the objective row of the first stage\n+ tableau = np.delete(tableau, 0, axis=0)\n+\n+ self.n_stages = 1\n+ self.n_rows -= 1\n+ self.n_art_vars = 0\n+ self.stop_iter = False\n+ self.objectives = objectives\n+ return tableau\n+\n+ def run_simplex(self) -> dict[Any, Any]:\n+ \"\"\"Operate on tableau until objective function cannot be\n+ improved further.\n+\n+ # Standard linear program:\n+ Max: x1 + x2\n+ ST: x1 + 3x2 <= 4\n+ 3x1 + x2 <= 4\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,0],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.run_simplex()\n+ {'P': 2.0, 'x1': 1.0, 'x2': 1.0}\n+\n+ # Optimal tableau input:\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [0,0,0.25,0.25,2],\n+ ... [0,1,0.375,-0.125,1],\n+ ... [1,0,-0.125,0.375,1]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.run_simplex()\n+ {'P': 2.0, 'x1': 1.0, 'x2': 1.0}\n+\n+ # Non-standard: >= constraints\n+ Max: 2x1 + 3x2 + x3\n+ ST: x1 + x2 + x3 <= 40\n+ 2x1 + x2 - x3 >= 10\n+ - x2 + x3 >= 10\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [2,0,0,0,-1,-1,0,0,20],\n+ ... [-2,-3,-1,0,0,0,0,0,0],\n+ ... [1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,40],\n+ ... [2,1,-1,0,-1,0,1,0,10],\n+ ... [0,-1,1,0,0,-1,0,1,10.]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 3)\n+ >>> t.run_simplex()\n+ {'P': 70.0, 'x1': 10.0, 'x2': 10.0, 'x3': 20.0}\n+\n+ # Non standard: minimisation and equalities\n+ Min: x1 + x2\n+ ST: 2x1 + x2 = 12\n+ 6x1 + 5x2 = 40\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [8,6,0,-1,0,-1,0,0,52],\n+ ... [1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],\n+ ... [2,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,12],\n+ ... [2,1,0,-1,0,0,1,0,12],\n+ ... [6,5,0,0,1,0,0,0,40],\n+ ... [6,5,0,0,0,-1,0,1,40.]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.run_simplex()\n+ {'P': 7.0, 'x1': 5.0, 'x2': 2.0}\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Stop simplex algorithm from cycling.\n+ iter_num = 0\n+\n+ while iter_num < 100:\n+ # Completion of each stage removes an objective. If both stages\n+ # are complete, then no objectives are left\n+ if not self.objectives:\n+ self.col_titles = self.generate_col_titles(\n+ self.n_vars, self.n_slack, self.n_art_vars\n+ )\n+\n+ # Find the values of each variable at optimal solution\n+ return self.interpret_tableau(self.tableau, self.col_titles)\n+\n+ row_idx, col_idx = self.find_pivot(self.tableau)\n+\n+ # If there are no more negative values in objective row\n+ if self.stop_iter:\n+ # Delete artificial variable columns and rows. Update attributes\n+ self.tableau = self.change_stage(self.tableau, self.objectives)\n+\n+ # Pivot again\n+ continue\n+\n+ self.tableau = self.pivot(self.tableau, row_idx, col_idx)\n+ iter_num += 1\n+ return {}\n+\n+ def interpret_tableau(\n+ self, tableau: np.ndarray, col_titles: list[str]\n+ ) -> dict[str, float]:\n+ \"\"\"Given the final tableau, add the corresponding values of the basic\n+ decision variables to the `output_dict`\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [0,0,0.875,0.375,5],\n+ ... [0,1,0.375,-0.125,1],\n+ ... [1,0,-0.125,0.375,1]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.interpret_tableau(tableau, [\"x1\", \"x2\", \"s1\", \"s2\", \"RHS\"])\n+ {'P': 5.0, 'x1': 1.0, 'x2': 1.0}\n+ \"\"\"\n+ output_dict = {}\n+\n+ # P = RHS of final tableau\n+ output_dict[\"P\"] = abs(tableau[0, -1])\n+\n+ for i in range(self.n_vars):\n+ # Gives ids of nonzero entries in the ith column\n+ nonzero = np.nonzero(tableau[:, i])\n+ n_nonzero = len(nonzero[0])\n+\n+ # First entry in the nonzero ids\n+ nonzero_rowidx = nonzero[0][0]\n+ nonzero_val = tableau[nonzero_rowidx, i]\n+\n+ # If there is only one nonzero value in column, which is one\n+ if n_nonzero == nonzero_val == 1:\n+ rhs_val = tableau[nonzero_rowidx, -1]\n+ output_dict[col_titles[i]] = rhs_val\n+ # Check for basic variables\n+ for title in col_titles:\n+ # Don't add RHS or slack variables to output dict\n+ if title[0] not in \"R-s\":\n+ output_dict.setdefault(title, 0)\n+ return output_dict\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ import doctest\n+\n+ doctest.testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,327 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Python implementation of the simplex algorithm for solving linear programs in\n+tabular form with\n+- `>=`, `<=`, and `=` constraints and\n+- each variable `x1, x2, ...>= 0`.\n+\n+See https://gist.github.com/imengus/f9619a568f7da5bc74eaf20169a24d98 for how\n+to convert linear programs to simplex tableaus, and the steps taken in the\n+simplex algorithm.\n+\n+Resources:\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_programming\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simplex_algorithm\n+\n+https://towardsdatascience.com/ \\\n+ a-beginners-guide-to-linear-programming-and-the-simplex-algorithm \\\n+ -87db017e92b4",
"line": null,
"original_line": 17,
"original_start_line": 15,
"path": "linear_programming/simplex.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI can't click this link, either use a shortener or put it all on one line"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,327 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Python implementation of the simplex algorithm for solving linear programs in\n+tabular form with\n+- `>=`, `<=`, and `=` constraints and\n+- each variable `x1, x2, ...>= 0`.\n+\n+See https://gist.github.com/imengus/f9619a568f7da5bc74eaf20169a24d98 for how\n+to convert linear programs to simplex tableaus, and the steps taken in the\n+simplex algorithm.\n+\n+Resources:\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_programming\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simplex_algorithm\n+\n+https://towardsdatascience.com/ \\\n+ a-beginners-guide-to-linear-programming-and-the-simplex-algorithm \\\n+ -87db017e92b4\n+\"\"\"\n+from typing import Any\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+\n+\n+class Tableau:\n+ \"\"\"Operate on simplex tableaus\"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, tableau: np.ndarray, n_vars: int) -> None:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,-1],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: RHS must be > 0\n+ \"\"\"\n+ rhs = tableau[:, -1]\n+ if np.any(rhs, where=rhs < 0):\n+ raise ValueError(\"RHS must be > 0\")\n+\n+ if tableau is None:\n+ return",
"line": null,
"original_line": 40,
"original_start_line": 39,
"path": "linear_programming/simplex.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhat's supposed to happen here? No tableau is entered so the program will mysteriously crash? Note that tableau is typed to `np.ndarray` so therefore *should* never be None\r\n\r\n```suggestion\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,327 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Python implementation of the simplex algorithm for solving linear programs in\n+tabular form with\n+- `>=`, `<=`, and `=` constraints and\n+- each variable `x1, x2, ...>= 0`.\n+\n+See https://gist.github.com/imengus/f9619a568f7da5bc74eaf20169a24d98 for how\n+to convert linear programs to simplex tableaus, and the steps taken in the\n+simplex algorithm.\n+\n+Resources:\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_programming\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simplex_algorithm\n+\n+https://towardsdatascience.com/ \\\n+ a-beginners-guide-to-linear-programming-and-the-simplex-algorithm \\\n+ -87db017e92b4\n+\"\"\"\n+from typing import Any\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+\n+\n+class Tableau:\n+ \"\"\"Operate on simplex tableaus\"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, tableau: np.ndarray, n_vars: int) -> None:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,-1],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: RHS must be > 0\n+ \"\"\"\n+ rhs = tableau[:, -1]\n+ if np.any(rhs, where=rhs < 0):\n+ raise ValueError(\"RHS must be > 0\")\n+\n+ if tableau is None:\n+ return\n+\n+ self.tableau = tableau\n+ self.n_rows = len(tableau[:, 0])\n+ self.n_cols = len(tableau[0])\n+\n+ # Number of decision variables x1, x2, x3...\n+ self.n_vars = n_vars\n+\n+ # Number of artificial variables to be minimised\n+ self.n_art_vars = len(np.where(tableau[self.n_vars : -1] == -1)[0])\n+\n+ # 2 if there are >= or == constraints (nonstandard), 1 otherwise (std)\n+ self.n_stages = (self.n_art_vars > 0) + 1\n+\n+ # Number of slack variables added to make inequalities into equalities\n+ self.n_slack = self.n_rows - self.n_stages\n+\n+ # Objectives for each stage\n+ self.objectives = [\"max\"]\n+\n+ # In two stage simplex, first minimise then maximise\n+ if self.n_art_vars:\n+ self.objectives.append(\"min\")\n+\n+ self.col_titles = [\"\"]\n+\n+ # Index of current pivot row and column\n+ self.row_idx = None\n+ self.col_idx = None\n+\n+ # Does objective row only contain (non)-negative values?\n+ self.stop_iter = False\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def generate_col_titles(*args: int) -> list[str]:\n+ \"\"\"Generate column titles for tableau of specific dimensions\n+\n+ >>> Tableau.generate_col_titles(2, 3, 1)\n+ ['x1', 'x2', 's1', 's2', 's3', 'a1', 'RHS']\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # decision | slack | artificial\n+ string_starts = [\"x\", \"s\", \"a\"]\n+ titles = []\n+ for i in range(3):\n+ for j in range(args[i]):\n+ titles.append(string_starts[i] + str(j + 1))\n+ titles.append(\"RHS\")\n+ return titles\n+\n+ def find_pivot(self, tableau: np.ndarray) -> tuple[Any, Any]:\n+ \"\"\"Finds the pivot row and column.\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [-2,-1,0,0,0],\n+ ... [3,1,1,0,6],\n+ ... [1,2,0,1,7.]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 97,
"original_start_line": 91,
"path": "linear_programming/simplex.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n Finds the pivot row and column.\r\n \r\n >>> t = Tableau(np.array([[-2,-1,0,0,0], [3,1,1,0,6], [1,2,0,1,7.]]), 2)\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,327 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Python implementation of the simplex algorithm for solving linear programs in\n+tabular form with\n+- `>=`, `<=`, and `=` constraints and\n+- each variable `x1, x2, ...>= 0`.\n+\n+See https://gist.github.com/imengus/f9619a568f7da5bc74eaf20169a24d98 for how\n+to convert linear programs to simplex tableaus, and the steps taken in the\n+simplex algorithm.\n+\n+Resources:\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_programming\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simplex_algorithm\n+\n+https://towardsdatascience.com/ \\\n+ a-beginners-guide-to-linear-programming-and-the-simplex-algorithm \\\n+ -87db017e92b4\n+\"\"\"\n+from typing import Any\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+\n+\n+class Tableau:\n+ \"\"\"Operate on simplex tableaus\"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, tableau: np.ndarray, n_vars: int) -> None:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,-1],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: RHS must be > 0\n+ \"\"\"\n+ rhs = tableau[:, -1]\n+ if np.any(rhs, where=rhs < 0):\n+ raise ValueError(\"RHS must be > 0\")\n+\n+ if tableau is None:\n+ return\n+\n+ self.tableau = tableau\n+ self.n_rows = len(tableau[:, 0])\n+ self.n_cols = len(tableau[0])\n+\n+ # Number of decision variables x1, x2, x3...\n+ self.n_vars = n_vars\n+\n+ # Number of artificial variables to be minimised\n+ self.n_art_vars = len(np.where(tableau[self.n_vars : -1] == -1)[0])\n+\n+ # 2 if there are >= or == constraints (nonstandard), 1 otherwise (std)\n+ self.n_stages = (self.n_art_vars > 0) + 1\n+\n+ # Number of slack variables added to make inequalities into equalities\n+ self.n_slack = self.n_rows - self.n_stages\n+\n+ # Objectives for each stage\n+ self.objectives = [\"max\"]\n+\n+ # In two stage simplex, first minimise then maximise\n+ if self.n_art_vars:\n+ self.objectives.append(\"min\")\n+\n+ self.col_titles = [\"\"]\n+\n+ # Index of current pivot row and column\n+ self.row_idx = None\n+ self.col_idx = None\n+\n+ # Does objective row only contain (non)-negative values?\n+ self.stop_iter = False\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def generate_col_titles(*args: int) -> list[str]:\n+ \"\"\"Generate column titles for tableau of specific dimensions\n+\n+ >>> Tableau.generate_col_titles(2, 3, 1)\n+ ['x1', 'x2', 's1', 's2', 's3', 'a1', 'RHS']\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # decision | slack | artificial\n+ string_starts = [\"x\", \"s\", \"a\"]\n+ titles = []\n+ for i in range(3):\n+ for j in range(args[i]):\n+ titles.append(string_starts[i] + str(j + 1))\n+ titles.append(\"RHS\")\n+ return titles\n+\n+ def find_pivot(self, tableau: np.ndarray) -> tuple[Any, Any]:\n+ \"\"\"Finds the pivot row and column.\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [-2,-1,0,0,0],\n+ ... [3,1,1,0,6],\n+ ... [1,2,0,1,7.]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.find_pivot(t.tableau)\n+ (1, 0)\n+ \"\"\"\n+ objective = self.objectives[-1]\n+\n+ # Find entries of highest magnitude in objective rows\n+ sign = (objective == \"min\") - (objective == \"max\")\n+ col_idx = np.argmax(sign * tableau[0, : self.n_vars])\n+\n+ # Choice is only valid if below 0 for maximise, and above for minimise\n+ if sign * self.tableau[0, col_idx] <= 0:\n+ self.stop_iter = True\n+ return 0, 0\n+\n+ # Pivot row is chosen as having the lowest quotient when elements of\n+ # the pivot column divide the right-hand side\n+\n+ # Slice excluding the objective rows\n+ s = slice(self.n_stages, self.n_rows)\n+\n+ # RHS\n+ dividend = tableau[s, -1]\n+\n+ # Elements of pivot column within slice\n+ divisor = tableau[s, col_idx]\n+\n+ # Array filled with nans\n+ nans = np.full(self.n_rows - self.n_stages, np.nan)\n+\n+ # If element in pivot column is greater than zeron_stages, return\n+ # quotient or nan otherwise\n+ quotients = np.divide(dividend, divisor, out=nans, where=divisor > 0)\n+\n+ # Arg of minimum quotient excluding the nan values. n_stages is added\n+ # to compensate for earlier exclusion of objective columns\n+ row_idx = np.nanargmin(quotients) + self.n_stages\n+ return row_idx, col_idx\n+\n+ def pivot(self, tableau: np.ndarray, row_idx: int, col_idx: int) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"Pivots on value on the intersection of pivot row and column.\n+\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([[-2,-3,0,0,0],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.pivot(t.tableau, 1, 0).tolist()\n+ ... # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE\n+ [[0.0, 3.0, 2.0, 0.0, 8.0],\n+ [1.0, 3.0, 1.0, 0.0, 4.0],\n+ [0.0, -8.0, -3.0, 1.0, -8.0]]\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Avoid changes to original tableau\n+ piv_row = tableau[row_idx].copy()\n+\n+ piv_val = piv_row[col_idx]\n+\n+ # Entry becomes 1\n+ piv_row *= 1 / piv_val\n+\n+ # Variable in pivot column becomes basic, ie the only non-zero entry\n+ for idx, coeff in enumerate(tableau[:, col_idx]):\n+ tableau[idx] += -coeff * piv_row\n+ tableau[row_idx] = piv_row\n+ return tableau\n+\n+ def change_stage(self, tableau: np.ndarray, objectives: list[Any]) -> np.ndarray:\n+ \"\"\"Exits first phase of the two-stage method by deleting artificial\n+ rows and columns, or completes the algorithm if exiting the standard\n+ case.\n+\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [3,3,-1,-1,0,0,4],\n+ ... [2,1,0,0,0,0,0.],\n+ ... [1,2,-1,0,1,0,2],\n+ ... [2,1,0,-1,0,1,2]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.change_stage(t.tableau, t.objectives).tolist()\n+ ... # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE\n+ [[2.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],\n+ [1.0, 2.0, -1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0],\n+ [2.0, 1.0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, 2.0]]\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Objective of original objective row remains\n+ objectives.pop()\n+\n+ if not objectives:\n+ return tableau\n+\n+ # Slice containing ids for artificial columns\n+ s = slice(-self.n_art_vars - 1, -1)\n+\n+ # Delete the artificial variable columns\n+ tableau = np.delete(tableau, s, axis=1)\n+\n+ # Delete the objective row of the first stage\n+ tableau = np.delete(tableau, 0, axis=0)\n+\n+ self.n_stages = 1\n+ self.n_rows -= 1\n+ self.n_art_vars = 0\n+ self.stop_iter = False\n+ self.objectives = objectives\n+ return tableau\n+\n+ def run_simplex(self) -> dict[Any, Any]:\n+ \"\"\"Operate on tableau until objective function cannot be\n+ improved further.\n+\n+ # Standard linear program:\n+ Max: x1 + x2\n+ ST: x1 + 3x2 <= 4\n+ 3x1 + x2 <= 4\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,0],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.run_simplex()\n+ {'P': 2.0, 'x1': 1.0, 'x2': 1.0}\n+\n+ # Optimal tableau input:\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [0,0,0.25,0.25,2],\n+ ... [0,1,0.375,-0.125,1],\n+ ... [1,0,-0.125,0.375,1]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.run_simplex()\n+ {'P': 2.0, 'x1': 1.0, 'x2': 1.0}\n+\n+ # Non-standard: >= constraints\n+ Max: 2x1 + 3x2 + x3\n+ ST: x1 + x2 + x3 <= 40\n+ 2x1 + x2 - x3 >= 10\n+ - x2 + x3 >= 10\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [2,0,0,0,-1,-1,0,0,20],\n+ ... [-2,-3,-1,0,0,0,0,0,0],\n+ ... [1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,40],\n+ ... [2,1,-1,0,-1,0,1,0,10],\n+ ... [0,-1,1,0,0,-1,0,1,10.]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 3)\n+ >>> t.run_simplex()\n+ {'P': 70.0, 'x1': 10.0, 'x2': 10.0, 'x3': 20.0}\n+\n+ # Non standard: minimisation and equalities\n+ Min: x1 + x2\n+ ST: 2x1 + x2 = 12\n+ 6x1 + 5x2 = 40\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [8,6,0,-1,0,-1,0,0,52],\n+ ... [1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],\n+ ... [2,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,12],\n+ ... [2,1,0,-1,0,0,1,0,12],\n+ ... [6,5,0,0,1,0,0,0,40],\n+ ... [6,5,0,0,0,-1,0,1,40.]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.run_simplex()\n+ {'P': 7.0, 'x1': 5.0, 'x2': 2.0}\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # Stop simplex algorithm from cycling.\n+ iter_num = 0\n+\n+ while iter_num < 100:\n+ # Completion of each stage removes an objective. If both stages\n+ # are complete, then no objectives are left\n+ if not self.objectives:\n+ self.col_titles = self.generate_col_titles(\n+ self.n_vars, self.n_slack, self.n_art_vars\n+ )\n+\n+ # Find the values of each variable at optimal solution\n+ return self.interpret_tableau(self.tableau, self.col_titles)\n+\n+ row_idx, col_idx = self.find_pivot(self.tableau)\n+\n+ # If there are no more negative values in objective row\n+ if self.stop_iter:\n+ # Delete artificial variable columns and rows. Update attributes\n+ self.tableau = self.change_stage(self.tableau, self.objectives)\n+\n+ # Pivot again\n+ continue\n+\n+ self.tableau = self.pivot(self.tableau, row_idx, col_idx)\n+ iter_num += 1\n+ return {}\n+\n+ def interpret_tableau(\n+ self, tableau: np.ndarray, col_titles: list[str]\n+ ) -> dict[str, float]:\n+ \"\"\"Given the final tableau, add the corresponding values of the basic\n+ decision variables to the `output_dict`\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([\n+ ... [0,0,0.875,0.375,5],\n+ ... [0,1,0.375,-0.125,1],\n+ ... [1,0,-0.125,0.375,1]\n+ ... ])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ >>> t.interpret_tableau(tableau, [\"x1\", \"x2\", \"s1\", \"s2\", \"RHS\"])\n+ {'P': 5.0, 'x1': 1.0, 'x2': 1.0}\n+ \"\"\"\n+ output_dict = {}\n+\n+ # P = RHS of final tableau\n+ output_dict[\"P\"] = abs(tableau[0, -1])",
"line": null,
"original_line": 301,
"original_start_line": 298,
"path": "linear_programming/simplex.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n # P = RHS of final tableau\r\n output_dict = {\"P\": abs(tableau[0, -1])}\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,327 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Python implementation of the simplex algorithm for solving linear programs in\n+tabular form with\n+- `>=`, `<=`, and `=` constraints and\n+- each variable `x1, x2, ...>= 0`.\n+\n+See https://gist.github.com/imengus/f9619a568f7da5bc74eaf20169a24d98 for how\n+to convert linear programs to simplex tableaus, and the steps taken in the\n+simplex algorithm.\n+\n+Resources:\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_programming\n+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simplex_algorithm\n+\n+https://towardsdatascience.com/ \\\n+ a-beginners-guide-to-linear-programming-and-the-simplex-algorithm \\\n+ -87db017e92b4\n+\"\"\"\n+from typing import Any\n+\n+import numpy as np\n+\n+\n+class Tableau:\n+ \"\"\"Operate on simplex tableaus\"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, tableau: np.ndarray, n_vars: int) -> None:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ >>> tableau = np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,-1],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\n+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: RHS must be > 0\n+ \"\"\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 34,
"original_start_line": 24,
"path": "linear_programming/simplex.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nDocstrings don't go within the `__init__`\r\n```suggestion\r\nclass Tableau:\r\n \"\"\"Operate on simplex tableaus\r\n \r\n >>> tableau = np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,-1],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]])\r\n >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)\r\n Traceback (most recent call last):\r\n ...\r\n ValueError: RHS must be > 0\r\n \"\"\"\r\n\r\n def __init__(self, tableau: np.ndarray, n_vars: int) -> None:\r\n```"
}
] |
7593cbbb713a53e17261e17dab682824e4dac701
|
diff --git a/linear_programming/simplex.py b/linear_programming/simplex.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..ba64add40b5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/linear_programming/simplex.py
@@ -0,0 +1,311 @@
+"""
+Python implementation of the simplex algorithm for solving linear programs in
+tabular form with
+- `>=`, `<=`, and `=` constraints and
+- each variable `x1, x2, ...>= 0`.
+
+See https://gist.github.com/imengus/f9619a568f7da5bc74eaf20169a24d98 for how to
+convert linear programs to simplex tableaus, and the steps taken in the simplex
+algorithm.
+
+Resources:
+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simplex_algorithm
+https://tinyurl.com/simplex4beginners
+"""
+from typing import Any
+
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class Tableau:
+ """Operate on simplex tableaus
+
+ >>> t = Tableau(np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,-1],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]]), 2)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: RHS must be > 0
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self, tableau: np.ndarray, n_vars: int) -> None:
+ # Check if RHS is negative
+ if np.any(tableau[:, -1], where=tableau[:, -1] < 0):
+ raise ValueError("RHS must be > 0")
+
+ self.tableau = tableau
+ self.n_rows, _ = tableau.shape
+
+ # Number of decision variables x1, x2, x3...
+ self.n_vars = n_vars
+
+ # Number of artificial variables to be minimised
+ self.n_art_vars = len(np.where(tableau[self.n_vars : -1] == -1)[0])
+
+ # 2 if there are >= or == constraints (nonstandard), 1 otherwise (std)
+ self.n_stages = (self.n_art_vars > 0) + 1
+
+ # Number of slack variables added to make inequalities into equalities
+ self.n_slack = self.n_rows - self.n_stages
+
+ # Objectives for each stage
+ self.objectives = ["max"]
+
+ # In two stage simplex, first minimise then maximise
+ if self.n_art_vars:
+ self.objectives.append("min")
+
+ self.col_titles = [""]
+
+ # Index of current pivot row and column
+ self.row_idx = None
+ self.col_idx = None
+
+ # Does objective row only contain (non)-negative values?
+ self.stop_iter = False
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def generate_col_titles(*args: int) -> list[str]:
+ """Generate column titles for tableau of specific dimensions
+
+ >>> Tableau.generate_col_titles(2, 3, 1)
+ ['x1', 'x2', 's1', 's2', 's3', 'a1', 'RHS']
+
+ >>> Tableau.generate_col_titles()
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Must provide n_vars, n_slack, and n_art_vars
+ >>> Tableau.generate_col_titles(-2, 3, 1)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: All arguments must be non-negative integers
+ """
+ if len(args) != 3:
+ raise ValueError("Must provide n_vars, n_slack, and n_art_vars")
+
+ if not all(x >= 0 and isinstance(x, int) for x in args):
+ raise ValueError("All arguments must be non-negative integers")
+
+ # decision | slack | artificial
+ string_starts = ["x", "s", "a"]
+ titles = []
+ for i in range(3):
+ for j in range(args[i]):
+ titles.append(string_starts[i] + str(j + 1))
+ titles.append("RHS")
+ return titles
+
+ def find_pivot(self, tableau: np.ndarray) -> tuple[Any, Any]:
+ """Finds the pivot row and column.
+ >>> t = Tableau(np.array([[-2,1,0,0,0], [3,1,1,0,6], [1,2,0,1,7.]]), 2)
+ >>> t.find_pivot(t.tableau)
+ (1, 0)
+ """
+ objective = self.objectives[-1]
+
+ # Find entries of highest magnitude in objective rows
+ sign = (objective == "min") - (objective == "max")
+ col_idx = np.argmax(sign * tableau[0, : self.n_vars])
+
+ # Choice is only valid if below 0 for maximise, and above for minimise
+ if sign * self.tableau[0, col_idx] <= 0:
+ self.stop_iter = True
+ return 0, 0
+
+ # Pivot row is chosen as having the lowest quotient when elements of
+ # the pivot column divide the right-hand side
+
+ # Slice excluding the objective rows
+ s = slice(self.n_stages, self.n_rows)
+
+ # RHS
+ dividend = tableau[s, -1]
+
+ # Elements of pivot column within slice
+ divisor = tableau[s, col_idx]
+
+ # Array filled with nans
+ nans = np.full(self.n_rows - self.n_stages, np.nan)
+
+ # If element in pivot column is greater than zeron_stages, return
+ # quotient or nan otherwise
+ quotients = np.divide(dividend, divisor, out=nans, where=divisor > 0)
+
+ # Arg of minimum quotient excluding the nan values. n_stages is added
+ # to compensate for earlier exclusion of objective columns
+ row_idx = np.nanargmin(quotients) + self.n_stages
+ return row_idx, col_idx
+
+ def pivot(self, tableau: np.ndarray, row_idx: int, col_idx: int) -> np.ndarray:
+ """Pivots on value on the intersection of pivot row and column.
+
+ >>> t = Tableau(np.array([[-2,-3,0,0,0],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]]), 2)
+ >>> t.pivot(t.tableau, 1, 0).tolist()
+ ... # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE
+ [[0.0, 3.0, 2.0, 0.0, 8.0],
+ [1.0, 3.0, 1.0, 0.0, 4.0],
+ [0.0, -8.0, -3.0, 1.0, -8.0]]
+ """
+ # Avoid changes to original tableau
+ piv_row = tableau[row_idx].copy()
+
+ piv_val = piv_row[col_idx]
+
+ # Entry becomes 1
+ piv_row *= 1 / piv_val
+
+ # Variable in pivot column becomes basic, ie the only non-zero entry
+ for idx, coeff in enumerate(tableau[:, col_idx]):
+ tableau[idx] += -coeff * piv_row
+ tableau[row_idx] = piv_row
+ return tableau
+
+ def change_stage(self, tableau: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
+ """Exits first phase of the two-stage method by deleting artificial
+ rows and columns, or completes the algorithm if exiting the standard
+ case.
+
+ >>> t = Tableau(np.array([
+ ... [3, 3, -1, -1, 0, 0, 4],
+ ... [2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.],
+ ... [1, 2, -1, 0, 1, 0, 2],
+ ... [2, 1, 0, -1, 0, 1, 2]
+ ... ]), 2)
+ >>> t.change_stage(t.tableau).tolist()
+ ... # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE
+ [[2.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
+ [1.0, 2.0, -1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0],
+ [2.0, 1.0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, 2.0]]
+ """
+ # Objective of original objective row remains
+ self.objectives.pop()
+
+ if not self.objectives:
+ return tableau
+
+ # Slice containing ids for artificial columns
+ s = slice(-self.n_art_vars - 1, -1)
+
+ # Delete the artificial variable columns
+ tableau = np.delete(tableau, s, axis=1)
+
+ # Delete the objective row of the first stage
+ tableau = np.delete(tableau, 0, axis=0)
+
+ self.n_stages = 1
+ self.n_rows -= 1
+ self.n_art_vars = 0
+ self.stop_iter = False
+ return tableau
+
+ def run_simplex(self) -> dict[Any, Any]:
+ """Operate on tableau until objective function cannot be
+ improved further.
+
+ # Standard linear program:
+ Max: x1 + x2
+ ST: x1 + 3x2 <= 4
+ 3x1 + x2 <= 4
+ >>> Tableau(np.array([[-1,-1,0,0,0],[1,3,1,0,4],[3,1,0,1,4.]]),
+ ... 2).run_simplex()
+ {'P': 2.0, 'x1': 1.0, 'x2': 1.0}
+
+ # Optimal tableau input:
+ >>> Tableau(np.array([
+ ... [0, 0, 0.25, 0.25, 2],
+ ... [0, 1, 0.375, -0.125, 1],
+ ... [1, 0, -0.125, 0.375, 1]
+ ... ]), 2).run_simplex()
+ {'P': 2.0, 'x1': 1.0, 'x2': 1.0}
+
+ # Non-standard: >= constraints
+ Max: 2x1 + 3x2 + x3
+ ST: x1 + x2 + x3 <= 40
+ 2x1 + x2 - x3 >= 10
+ - x2 + x3 >= 10
+ >>> Tableau(np.array([
+ ... [2, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0, 0, 20],
+ ... [-2, -3, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
+ ... [1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 40],
+ ... [2, 1, -1, 0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 10],
+ ... [0, -1, 1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 1, 10.]
+ ... ]), 3).run_simplex()
+ {'P': 70.0, 'x1': 10.0, 'x2': 10.0, 'x3': 20.0}
+
+ # Non standard: minimisation and equalities
+ Min: x1 + x2
+ ST: 2x1 + x2 = 12
+ 6x1 + 5x2 = 40
+ >>> Tableau(np.array([
+ ... [8, 6, 0, -1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 52],
+ ... [1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
+ ... [2, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 12],
+ ... [2, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 12],
+ ... [6, 5, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 40],
+ ... [6, 5, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 1, 40.]
+ ... ]), 2).run_simplex()
+ {'P': 7.0, 'x1': 5.0, 'x2': 2.0}
+ """
+ # Stop simplex algorithm from cycling.
+ for _ in range(100):
+ # Completion of each stage removes an objective. If both stages
+ # are complete, then no objectives are left
+ if not self.objectives:
+ self.col_titles = self.generate_col_titles(
+ self.n_vars, self.n_slack, self.n_art_vars
+ )
+
+ # Find the values of each variable at optimal solution
+ return self.interpret_tableau(self.tableau, self.col_titles)
+
+ row_idx, col_idx = self.find_pivot(self.tableau)
+
+ # If there are no more negative values in objective row
+ if self.stop_iter:
+ # Delete artificial variable columns and rows. Update attributes
+ self.tableau = self.change_stage(self.tableau)
+ else:
+ self.tableau = self.pivot(self.tableau, row_idx, col_idx)
+ return {}
+
+ def interpret_tableau(
+ self, tableau: np.ndarray, col_titles: list[str]
+ ) -> dict[str, float]:
+ """Given the final tableau, add the corresponding values of the basic
+ decision variables to the `output_dict`
+ >>> tableau = np.array([
+ ... [0,0,0.875,0.375,5],
+ ... [0,1,0.375,-0.125,1],
+ ... [1,0,-0.125,0.375,1]
+ ... ])
+ >>> t = Tableau(tableau, 2)
+ >>> t.interpret_tableau(tableau, ["x1", "x2", "s1", "s2", "RHS"])
+ {'P': 5.0, 'x1': 1.0, 'x2': 1.0}
+ """
+ # P = RHS of final tableau
+ output_dict = {"P": abs(tableau[0, -1])}
+
+ for i in range(self.n_vars):
+ # Gives ids of nonzero entries in the ith column
+ nonzero = np.nonzero(tableau[:, i])
+ n_nonzero = len(nonzero[0])
+
+ # First entry in the nonzero ids
+ nonzero_rowidx = nonzero[0][0]
+ nonzero_val = tableau[nonzero_rowidx, i]
+
+ # If there is only one nonzero value in column, which is one
+ if n_nonzero == nonzero_val == 1:
+ rhs_val = tableau[nonzero_rowidx, -1]
+ output_dict[col_titles[i]] = rhs_val
+
+ # Check for basic variables
+ for title in col_titles:
+ # Don't add RHS or slack variables to output dict
+ if title[0] not in "R-s-a":
+ output_dict.setdefault(title, 0)
+ return output_dict
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import doctest
+
+ doctest.testmod()
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-3200@344671b
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 3,200
|
Fix `cat` can't read pseudo files with zero size
|
<!--- Thanks for opening a PR on xonsh! Please include a news entry with your PR
to help keep our changelog up to date! There are instructions available here:
https://xon.sh/devguide.html#changelog -->
<!--- If there is specific issue / feature request that this PR is addressing,
please link to the corresponding issue by using the `#issuenumber` syntax.
Thanks again! -->
I hope this patch will fix #3182 and #3199.
I tried `cat /proc/cpuinfo` in my machine.
|
2019-07-05T16:49:06Z
|
coreutils cat can't read /proc/*
Hey ! cat from coreutils doesn't return anything when reading files from `/proc` :
```
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo
$ /usr/bin/cat /proc/cpuinfo
processor : 0
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 60
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4590 CPU @ 3.30GHz
```
Here is my config :
```
+------------------+---------------------+
| xonsh | 0.9.6 |
| Git SHA | dabd4bd3 |
| Commit Date | Jun 6 09:44:17 2019 |
| Python | 3.7.3 |
| PLY | 3.11 |
| have readline | True |
| prompt toolkit | 2.0.9 |
| shell type | prompt_toolkit2 |
| pygments | 2.4.2 |
| on posix | True |
| on linux | True |
| distro | unknown |
| on darwin | False |
| on windows | False |
| on cygwin | False |
| on msys2 | False |
| is superuser | False |
| default encoding | utf-8 |
| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |
| encoding errors | surrogateescape |
+------------------+---------------------+
```
|
[
{
"body": "Hey ! cat from coreutils doesn't return anything when reading files from `/proc` :\r\n```\r\n$ cat /proc/cpuinfo \r\n$ /usr/bin/cat /proc/cpuinfo \r\nprocessor : 0\r\nvendor_id : GenuineIntel\r\ncpu family : 6\r\nmodel : 60\r\nmodel name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4590 CPU @ 3.30GHz\r\n```\r\n\r\nHere is my config :\r\n```\r\n+------------------+---------------------+\r\n| xonsh | 0.9.6 |\r\n| Git SHA | dabd4bd3 |\r\n| Commit Date | Jun 6 09:44:17 2019 |\r\n| Python | 3.7.3 |\r\n| PLY | 3.11 |\r\n| have readline | True |\r\n| prompt toolkit | 2.0.9 |\r\n| shell type | prompt_toolkit2 |\r\n| pygments | 2.4.2 |\r\n| on posix | True |\r\n| on linux | True |\r\n| distro | unknown |\r\n| on darwin | False |\r\n| on windows | False |\r\n| on cygwin | False |\r\n| on msys2 | False |\r\n| is superuser | False |\r\n| default encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| encoding errors | surrogateescape |\r\n+------------------+---------------------+\r\n```",
"number": 3182,
"title": "coreutils cat can't read /proc/*"
}
] |
cb485817ea4fad44138b4e4b9d573fbd9cee60b0
|
{
"head_commit": "344671ba42562cc4e52ebd10c06432d75c78d211",
"head_commit_message": "add to restore the deleted new line",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/news/3182-fix-cat-proc-file.rst b/news/3182-fix-cat-proc-file.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..c26c588255\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/3182-fix-cat-proc-file.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Changed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Deprecated:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Removed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Fix ``cat`` can't read pseudo files with zero size such as /proc/\\* or /sys/\\* (#3182, #3199)\n+\n+**Security:**\n+\n+* <news item>\ndiff --git a/tests/test_xoreutils.py b/tests/test_xoreutils.py\nindex 34642e2046..2253b77b76 100644\n--- a/tests/test_xoreutils.py\n+++ b/tests/test_xoreutils.py\n@@ -191,6 +191,24 @@ def test_cat_single_file_work_exist_content(self, cat_env_fixture):\n assert stdout_buf.getvalue() == bytes(expected_content, \"utf-8\")\n assert stderr_buf.getvalue() == b''\n \n+ def test_cat_single_file_with_end_newline(self, cat_env_fixture):\n+ content = \"this is a content withe \\\\n\\nfor testing xoreutil's cat\\n\"\n+ with open(self.tempfile, \"w\") as f:\n+ f.write(content)\n+ expected_content = content.replace(\"\\n\", os.linesep)\n+\n+ stdin = io.StringIO()\n+ stdout_buf = io.BytesIO()\n+ stderr_buf = io.BytesIO()\n+ stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(stdout_buf)\n+ stderr = io.TextIOWrapper(stderr_buf)\n+ opts = cat._cat_parse_args([])\n+ cat._cat_single_file(opts, self.tempfile, stdin, stdout, stderr)\n+ stdout.flush()\n+ stderr.flush()\n+ assert stdout_buf.getvalue() == bytes(expected_content, \"utf-8\")\n+ assert stderr_buf.getvalue() == b''\n+\n def test_cat_empty_file(self, cat_env_fixture):\n with open(self.tempfile, \"w\") as f:\n f.write(\"\")\ndiff --git a/xonsh/xoreutils/cat.py b/xonsh/xoreutils/cat.py\nindex 2a89f14193..4f1a5c5984 100644\n--- a/xonsh/xoreutils/cat.py\n+++ b/xonsh/xoreutils/cat.py\n@@ -1,6 +1,5 @@\n \"\"\"Implements a cat command for xonsh.\"\"\"\n import os\n-import stat\n import time\n import builtins\n \n@@ -12,15 +11,17 @@ def _cat_line(\n f, sep, last_was_blank, line_count, opts, out, enc, enc_errors, read_size\n ):\n _r = r = f.readline(size=80)\n+ restore_newline = False\n if isinstance(_r, str):\n _r = r = _r.encode(enc, enc_errors)\n if r == b\"\":\n- last_was_blank, line_count, read_size, True\n+ return last_was_blank, line_count, read_size, True\n if r.endswith(sep):\n _r = _r[: -len(sep)]\n+ restore_newline = True\n this_one_blank = _r == b\"\"\n if last_was_blank and this_one_blank and opts[\"squeeze_blank\"]:\n- last_was_blank, line_count, read_size, False\n+ return last_was_blank, line_count, read_size, False\n last_was_blank = this_one_blank\n if opts[\"number_all\"] or (opts[\"number_nonblank\"] and not this_one_blank):\n start = (\"%6d \" % line_count).encode(enc, enc_errors)\n@@ -28,6 +29,8 @@ def _cat_line(\n line_count += 1\n if opts[\"show_ends\"]:\n _r = _r + b\"$\"\n+ if restore_newline:\n+ _r = _r + sep\n out.buffer.write(_r)\n out.flush()\n read_size += len(r)\n@@ -39,7 +42,7 @@ def _cat_single_file(opts, fname, stdin, out, err, line_count=1):\n enc = env.get(\"XONSH_ENCODING\")\n enc_errors = env.get(\"XONSH_ENCODING_ERRORS\")\n read_size = 0\n- file_size = fobj = None\n+ fobj = None\n if fname == \"-\":\n f = stdin\n elif os.path.isdir(fname):\n@@ -49,15 +52,11 @@ def _cat_single_file(opts, fname, stdin, out, err, line_count=1):\n print(\"cat: No such file or directory: {}\".format(fname), file=err)\n return True, line_count\n else:\n- fstat = os.stat(fname)\n- file_size = fstat.st_size\n- if file_size == 0 and not stat.S_ISREG(fstat.st_mode):\n- file_size = None\n fobj = open(fname, \"rb\")\n f = xproc.NonBlockingFDReader(fobj.fileno(), timeout=0.1)\n sep = os.linesep.encode(enc, enc_errors)\n last_was_blank = False\n- while file_size is None or read_size < file_size:\n+ while True:\n try:\n last_was_blank, line_count, read_size, endnow = _cat_line(\n f,\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -49,15 +52,11 @@ def _cat_single_file(opts, fname, stdin, out, err, line_count=1):\n print(\"cat: No such file or directory: {}\".format(fname), file=err)\n return True, line_count\n else:\n- fstat = os.stat(fname)\n- file_size = fstat.st_size\n- if file_size == 0 and not stat.S_ISREG(fstat.st_mode):\n- file_size = None\n fobj = open(fname, \"rb\")\n f = xproc.NonBlockingFDReader(fobj.fileno(), timeout=0.1)\n sep = os.linesep.encode(enc, enc_errors)\n last_was_blank = False\n- while file_size is None or read_size < file_size:\n+ while True:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 59,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/xoreutils/cat.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think some of these conditions might need to be implemented in the body for safety\n\n@user1:\npinginf this again @author\n\n@author:\nThanks for reviewing and sorry for the delayed response.\r\nI think you are right but I don't know what is the good condition for safety...\r\nDoes checking `endnow` meet safety?\n\n@user1:\nIs there a reason the original check doesn't apply anymore is what I was asking. I think it could be restored.\n\n@author:\nThe original check ( 344671ba ) caused #3182 because `stat.S_ISREG(os.stat(\"/proc/cpuinfo\").st_mode)` returns 0 and the file size of `/proc/cpuinfo` is 0.\r\nBut the previous of original check( 7b7a9a30 ) works fine, so I think it can be restored. I will try it."
}
] |
585a0e4d24c34354ef72184d779421f687de3889
|
diff --git a/news/3182-fix-cat-proc-file.rst b/news/3182-fix-cat-proc-file.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c26c588255
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/3182-fix-cat-proc-file.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+**Added:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Changed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Deprecated:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Removed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* Fix ``cat`` can't read pseudo files with zero size such as /proc/\* or /sys/\* (#3182, #3199)
+
+**Security:**
+
+* <news item>
diff --git a/tests/test_xoreutils.py b/tests/test_xoreutils.py
index 34642e2046..2253b77b76 100644
--- a/tests/test_xoreutils.py
+++ b/tests/test_xoreutils.py
@@ -191,6 +191,24 @@ def test_cat_single_file_work_exist_content(self, cat_env_fixture):
assert stdout_buf.getvalue() == bytes(expected_content, "utf-8")
assert stderr_buf.getvalue() == b''
+ def test_cat_single_file_with_end_newline(self, cat_env_fixture):
+ content = "this is a content withe \\n\nfor testing xoreutil's cat\n"
+ with open(self.tempfile, "w") as f:
+ f.write(content)
+ expected_content = content.replace("\n", os.linesep)
+
+ stdin = io.StringIO()
+ stdout_buf = io.BytesIO()
+ stderr_buf = io.BytesIO()
+ stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(stdout_buf)
+ stderr = io.TextIOWrapper(stderr_buf)
+ opts = cat._cat_parse_args([])
+ cat._cat_single_file(opts, self.tempfile, stdin, stdout, stderr)
+ stdout.flush()
+ stderr.flush()
+ assert stdout_buf.getvalue() == bytes(expected_content, "utf-8")
+ assert stderr_buf.getvalue() == b''
+
def test_cat_empty_file(self, cat_env_fixture):
with open(self.tempfile, "w") as f:
f.write("")
diff --git a/xonsh/xoreutils/cat.py b/xonsh/xoreutils/cat.py
index 2a89f14193..73f172bf68 100644
--- a/xonsh/xoreutils/cat.py
+++ b/xonsh/xoreutils/cat.py
@@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
"""Implements a cat command for xonsh."""
import os
-import stat
import time
import builtins
@@ -12,15 +11,17 @@ def _cat_line(
f, sep, last_was_blank, line_count, opts, out, enc, enc_errors, read_size
):
_r = r = f.readline(size=80)
+ restore_newline = False
if isinstance(_r, str):
_r = r = _r.encode(enc, enc_errors)
if r == b"":
- last_was_blank, line_count, read_size, True
+ return last_was_blank, line_count, read_size, True
if r.endswith(sep):
_r = _r[: -len(sep)]
+ restore_newline = True
this_one_blank = _r == b""
if last_was_blank and this_one_blank and opts["squeeze_blank"]:
- last_was_blank, line_count, read_size, False
+ return last_was_blank, line_count, read_size, False
last_was_blank = this_one_blank
if opts["number_all"] or (opts["number_nonblank"] and not this_one_blank):
start = ("%6d " % line_count).encode(enc, enc_errors)
@@ -28,6 +29,8 @@ def _cat_line(
line_count += 1
if opts["show_ends"]:
_r = _r + b"$"
+ if restore_newline:
+ _r = _r + sep
out.buffer.write(_r)
out.flush()
read_size += len(r)
@@ -49,9 +52,8 @@ def _cat_single_file(opts, fname, stdin, out, err, line_count=1):
print("cat: No such file or directory: {}".format(fname), file=err)
return True, line_count
else:
- fstat = os.stat(fname)
- file_size = fstat.st_size
- if file_size == 0 and not stat.S_ISREG(fstat.st_mode):
+ file_size = os.stat(fname).st_size
+ if file_size == 0:
file_size = None
fobj = open(fname, "rb")
f = xproc.NonBlockingFDReader(fobj.fileno(), timeout=0.1)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
xonsh__xonsh-2957@79da918
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 2,957
|
fix extra newlines in ptk2
|
Weird that this is needed, but it does fix the problem. Closes #2910
|
2018-12-12T00:01:56Z
|
An extra newline character gets printed in Python mode
## xonfig
```
+------------------+----------------------+
| xonsh | 0.8.2 |
| Git SHA | 6159f449 |
| Commit Date | Sep 21 02:39:43 2018 |
| Python | 3.7.1 |
| PLY | 3.11 |
| have readline | True |
| prompt toolkit | 2.0.4 |
| shell type | prompt_toolkit2 |
| pygments | 2.2.0 |
| on posix | True |
| on linux | True |
| distro | arch |
| on darwin | False |
| on windows | False |
| on cygwin | False |
| on msys2 | False |
| is superuser | False |
| default encoding | utf-8 |
| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |
| encoding errors | surrogateescape |
+------------------+----------------------+
```
## Expected Behavior
Prompt should be rendered immediately after the last command's output.
## Current Behavior
PTK2 shell adds an extra newline to the output of commands executed in Python mode.
## Steps to Reproduce
```
laloch@uriel ~ $ echo @(1+1)
2
laloch@uriel ~ $ 1+1
2
laloch@uriel ~ $
```
|
If I understood him right, @scopatz suggested that the extra newline gets there from
https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/blob/dca4a477150b55a7011078daba9da8bb0e95ceae/xonsh/base_shell.py#L382, but no, unfortunately that's not the case.
The extra EOL seems to be printed from within `exec()` call in codecache.py:run_compiled_code(). If I replace the call at [line 67](https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/blob/f409a020387c6e73a58fbac5191675f0d519591e/xonsh/codecache.py#L67) by
```
print("<")
func(code, glb, loc)
print(">")
```
I get
from `xonsh --shell-type=rl --no-rc`:
```
$ 1+1
<
2
>
$
```
from `xonsh --shell-type=ptk2 --no-rc`:
```
$ 1+1
<
2
>
$
```
|
[
{
"body": "## xonfig\r\n```\r\n+------------------+----------------------+\r\n| xonsh | 0.8.2 |\r\n| Git SHA | 6159f449 |\r\n| Commit Date | Sep 21 02:39:43 2018 |\r\n| Python | 3.7.1 |\r\n| PLY | 3.11 |\r\n| have readline | True |\r\n| prompt toolkit | 2.0.4 |\r\n| shell type | prompt_toolkit2 |\r\n| pygments | 2.2.0 |\r\n| on posix | True |\r\n| on linux | True |\r\n| distro | arch |\r\n| on darwin | False |\r\n| on windows | False |\r\n| on cygwin | False |\r\n| on msys2 | False |\r\n| is superuser | False |\r\n| default encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| encoding errors | surrogateescape |\r\n+------------------+----------------------+\r\n```\r\n## Expected Behavior\r\nPrompt should be rendered immediately after the last command's output.\r\n\r\n## Current Behavior\r\nPTK2 shell adds an extra newline to the output of commands executed in Python mode.\r\n\r\n## Steps to Reproduce\r\n```\r\nlaloch@uriel ~ $ echo @(1+1)\r\n2\r\nlaloch@uriel ~ $ 1+1\r\n2\r\n\r\nlaloch@uriel ~ $\r\n```",
"number": 2910,
"title": "An extra newline character gets printed in Python mode"
}
] |
6d1b5e0842779dad1094e6c6c849cc68b196535a
|
{
"head_commit": "79da918e72bd6a3897d172bd341e82188295b75f",
"head_commit_message": "fix extra newlines in ptk2",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/news/extranl.rst b/news/extranl.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..73f7f346d5\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/extranl.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Changed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Deprecated:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Removed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Fixed issues where the prompt-toolkit v2 shell would print an extra newline\n+ after Python evalutions in interactive mode.\n+\n+**Security:**\n+\n+* <news item>\ndiff --git a/xonsh/main.py b/xonsh/main.py\nindex ae9e857d0c..854005e2f2 100644\n--- a/xonsh/main.py\n+++ b/xonsh/main.py\n@@ -257,7 +257,8 @@ def _pprint_displayhook(value):\n printed_val = repr(value)\n if HAS_PYGMENTS and env.get(\"COLOR_RESULTS\"):\n tokens = list(pygments.lex(printed_val, lexer=pyghooks.XonshLexer()))\n- print_color(tokens)\n+ end = \"\" if env.get(\"SHELL_TYPE\") == \"prompt_toolkit2\" else \"\\n\"\n+ print_color(tokens, end=end)\n else:\n print(printed_val) # black & white case\n builtins._ = value\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Changed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Deprecated:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Removed:**\n+\n+* <news item>\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Fixed issues where the prompt-toolkit v2 shell would print an extra newline\n+ after Python evalutions in interactive mode.",
"line": null,
"original_line": 20,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "news/extranl.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThere's a typo in 'evaluations'.\r\n```suggestion\r\n after Python evaluations in interactive mode.\r\n```\n\n@author:\nThanks!"
}
] |
f7ff9724210c5b468b80474b8fe1b0095bfd1f96
|
diff --git a/news/extranl.rst b/news/extranl.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..586f5af4fc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/extranl.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+**Added:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Changed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Deprecated:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Removed:**
+
+* <news item>
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* Fixed issues where the prompt-toolkit v2 shell would print an extra newline
+ after Python evaluations in interactive mode.
+
+**Security:**
+
+* <news item>
diff --git a/xonsh/main.py b/xonsh/main.py
index ae9e857d0c..854005e2f2 100644
--- a/xonsh/main.py
+++ b/xonsh/main.py
@@ -257,7 +257,8 @@ def _pprint_displayhook(value):
printed_val = repr(value)
if HAS_PYGMENTS and env.get("COLOR_RESULTS"):
tokens = list(pygments.lex(printed_val, lexer=pyghooks.XonshLexer()))
- print_color(tokens)
+ end = "" if env.get("SHELL_TYPE") == "prompt_toolkit2" else "\n"
+ print_color(tokens, end=end)
else:
print(printed_val) # black & white case
builtins._ = value
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21883@418efae
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,883
|
fix(solvers): split separable systems of equations properly
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #21882
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* solvers
* A bug when splitting separable systems of equations in solve was fixed.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-08-16T22:44:36Z
|
Incorrect solutions given by `solve`
The following code tries to find the solutions of a system of (multivariate quadratic) equations. However, the single solution returned by `solve` is not correct.
It seems like `f = 0` should be part of the solution but is not.
```python
from sympy import solve, sympify
equations = [
"-k*a + b + 5*f/6 + 2*c/9 + 5*d/6 + 4*a/3",
"-k*f + 4*f/3 + d/2",
"-k*d + f/6 + d",
"13*b/18 + 13*c/18 + 13*a/18",
"-k*c + b/2 + 20*c/9 + a",
"-k*b + b + c/18 + a/6",
"5*b/3 + c/3 + a",
"2*b/3 + 2*c + 4*a/3",
"-g"
]
equations = [sympify(e) for e in equations]
unknowns = {s for e in equations for s in e.free_symbols}
solutions = solve(equations, unknowns, dict=True)
# Should all be zero but are not:
for solution in solutions:
for e in equations:
print(e.subs(solution).simplify())
```
Output:
```
0
f*(-12*k**2 + 28*k - 15)/(12*(k - 1))
0
65*f*(5 - 6*k)/(108*(3*k**2 - 5*k + 2))
5*f*(6*k - 5)*(9*k - 17)/(36*(k - 1)*(3*k - 2))
0
0
35*f*(5 - 6*k)/(18*(3*k**2 - 5*k + 2))
0
```
Expected Output:
```
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
```
The bug exists in sympy versions `1.8` and `1.7` but NOT in version `1.6`.
In the meantime, is there a way to circumvent this problem until the issue is fixed? We thought about calling `solve` again on the equations of the output but are not sure if that is the best way.
|
I've bisected this to 67fbbe670dbf2e77b4fdebf6493ee4f32f9c8a79 from #18844.
A simple diff that fixes this is:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index fd9e6a5fc8..aea9652aa2 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -1737,7 +1737,7 @@ def _solve_system(exprs, symbols, **flags):
if not exprs:
return []
- if flags.pop('_split', True):
+ if flags.pop('_split', False):
# Split the system into connected components
V = exprs
symsset = set(symbols)
```
However it should be possible to split the system so there must be a bug somehow that was introduced by the changes in that commit.
This is a better fix but I'm not quite sure why it works:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index fd9e6a5fc8..dbe97dd12a 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -1757,18 +1757,7 @@ def _solve_system(exprs, symbols, **flags):
subsyms = set()
for e in subexpr:
subsyms |= exprsyms[e]
- subsyms = list(sorted(subsyms, key = lambda x: sym_indices[x]))
- # use canonical subset to solve these equations
- # since there may be redundant equations in the set:
- # take the first equation of several that may have the
- # same sub-maximal free symbols of interest; the
- # other equations that weren't used should be checked
- # to see that they did not fail -- does the solver
- # take care of that?
- choices = sift(subexpr, lambda x: tuple(ordered(exprsyms[x])))
- subexpr = choices.pop(tuple(ordered(subsyms)), [])
- for k in choices:
- subexpr.append(next(ordered(choices[k])))
+ subsyms = sorted(subsyms, key=default_sort_key)
flags['_split'] = False # skip split step
subsol = _solve_system(subexpr, subsyms, **flags)
if not isinstance(subsol, list):
```
Apparently that comment was committed by me in 67fbbe670dbf2e77b4fdebf6493ee4f32f9c8a79 but the code in that commit doesn't look like something that I would write and I don't understand what the comment means...
@smichr do you understand what this is doing?
> This is a better fix but I'm not quite sure why it works:
That diff gives three test failures in the solvers tests:
```
test_issue_5849
test_issue_5849_matrix
test_issue_18208
```
I think that in the the #5849 case the tests might just be wrong. #18208 seems related and made a change to the ordering here. Actually seeing that a better fix here is:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index fd9e6a5fc8..acb12eb421 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -1758,17 +1758,6 @@ def _solve_system(exprs, symbols, **flags):
for e in subexpr:
subsyms |= exprsyms[e]
subsyms = list(sorted(subsyms, key = lambda x: sym_indices[x]))
- # use canonical subset to solve these equations
- # since there may be redundant equations in the set:
- # take the first equation of several that may have the
- # same sub-maximal free symbols of interest; the
- # other equations that weren't used should be checked
- # to see that they did not fail -- does the solver
- # take care of that?
- choices = sift(subexpr, lambda x: tuple(ordered(exprsyms[x])))
- subexpr = choices.pop(tuple(ordered(subsyms)), [])
- for k in choices:
- subexpr.append(next(ordered(choices[k])))
flags['_split'] = False # skip split step
subsol = _solve_system(subexpr, subsyms, **flags)
if not isinstance(subsol, list):
```
I'm still not sure what the removed code does. With that diff though `test_issue_18208` passes but the other two for #5849 still fail.
Fix plus update to tests:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index fd9e6a5fc8..acb12eb421 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -1758,17 +1758,6 @@ def _solve_system(exprs, symbols, **flags):
for e in subexpr:
subsyms |= exprsyms[e]
subsyms = list(sorted(subsyms, key = lambda x: sym_indices[x]))
- # use canonical subset to solve these equations
- # since there may be redundant equations in the set:
- # take the first equation of several that may have the
- # same sub-maximal free symbols of interest; the
- # other equations that weren't used should be checked
- # to see that they did not fail -- does the solver
- # take care of that?
- choices = sift(subexpr, lambda x: tuple(ordered(exprsyms[x])))
- subexpr = choices.pop(tuple(ordered(subsyms)), [])
- for k in choices:
- subexpr.append(next(ordered(choices[k])))
flags['_split'] = False # skip split step
subsol = _solve_system(subexpr, subsyms, **flags)
if not isinstance(subsol, list):
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
index ef5a4176c7..9c9ea50e81 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
@@ -1316,6 +1316,11 @@ def test_issue_5114_solvers():
def test_issue_5849():
+ #
+ # XXX: This system does not have a solution for most values of the
+ # parameters. Generally solve returns the empty set for systems that are
+ # generically inconsistent.
+ #
I1, I2, I3, I4, I5, I6 = symbols('I1:7')
dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4, Q2, Q4 = symbols('dI1,dI4,dQ2,dQ4,Q2,Q4')
@@ -1332,21 +1337,24 @@ def test_issue_5849():
)
ans = [{
- I1: I2 + I6,
- dI1: -4*I2 - 4*I3 - 4*I5 - 10*I6 + 24,
- I4: -I5 + I6,
- dQ4: -I5 + I6,
- Q4: 3*I5/2 - I6/2 - dI4/2,
+ I1: I2 + I3,
+ dI1: -4*I2 - 8*I3 - 4*I5 - 6*I6 + 24,
+ I4: I3 - I5,
+ dQ4: I3 - I5,
+ Q4: -I3/2 + 3*I5/2 - dI4/2,
dQ2: I2,
Q2: 2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6}]
v = I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4
assert solve(e, *v, manual=True, check=False, dict=True) == ans
- assert solve(e, *v, manual=True) == ans[0]
+ assert solve(e, *v, manual=True, check=False) == ans[0]
+ assert solve(e, *v, manual=True) == []
+ assert solve(e, *v) == []
+
# the matrix solver (tested below) doesn't like this because it produces
# a zero row in the matrix. Is this related to issue 4551?
assert [ei.subs(
- ans[0]) for ei in e] == [-I3 + I6, I3 - I6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
+ ans[0]) for ei in e] == [0, 0, I3 - I6, -I3 + I6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
def test_issue_5849_matrix():
@@ -1373,14 +1381,7 @@ def test_issue_5849_matrix():
2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6 - Q2,
I4 - 2*I5 + 2*Q4 + dI4
)
- assert solve(e, I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4) == {
- I1: I2 + I6,
- dI1: -4*I2 - 4*I3 - 4*I5 - 10*I6 + 24,
- I4: -I5 + I6,
- dQ4: -I5 + I6,
- Q4: 3*I5/2 - I6/2 - dI4/2,
- dQ2: I2,
- Q2: 2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6}
+ assert solve(e, I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4) == []
def test_issue_5901():
```
I've opened a PR for this: #21883
@oscarbenjamin We tried out your solution and it seems to resolve the issue mentioned at the beginning but introduces a new problem: Renaming the symbols appearing in the equations changes the solutions (also the number of solutions) we get. For example the following code solves two identical systems then just contains the symbol "_k" instead of "k":
```python
from sympy import solve, sympify, Symbol
equations = [
"-k*a + b + 5*f/6 + 2*c/9 + 5*d/6 + 4*a/3",
"-k*f + 4*f/3 + d/2",
"-k*d + f/6 + d",
"13*b/18 + 13*c/18 + 13*a/18",
"-k*c + b/2 + 20*c/9 + a",
"-k*b + b + c/18 + a/6",
"5*b/3 + c/3 + a",
"2*b/3 + 2*c + 4*a/3",
"-g"
]
equations = [sympify(e) for e in equations]
unknowns = {s for e in equations for s in e.free_symbols}
solutions = solve(equations, unknowns, dict=True)
print(solutions)
equations = [e.subs({Symbol("k"): Symbol("_k")}) for e in equations]
unknowns = {s for e in equations for s in e.free_symbols}
solutions = solve(equations, unknowns, dict=True)
print(solutions)
```
Output:
```
[{a: 0, d: 0, b: 0, f: 0, c: 0, g: 0}, {a: 0, d: -f, b: 0, k: 5/6, c: 0, g: 0}, {a: -2*c, d: 0, b: c, f: 0, k: 13/18, g: 0}, {a: 0, d: 0, b: 0, k: 3/2, c: 0, f: 0, g: 0}]
[{a: 0, _k: 5/6, b: 0, d: -f, c: 0, g: 0}, {a: 0, _k: 3/2, b: 0, d: 0, c: 0, f: 0, g: 0}]
```
> We tried out your solution and it seems to resolve the issue mentioned at the beginning but introduces a new problem:
When you say that this introduces a new problem what do you mean?
I get the same output you showed when testing with master so I don't think it is caused by the change I suggested but is rather a different issue with `solve`. With master:
```
[{a: 0, d: 0, b: 0, f: 0, c: 0, g: 0}, {a: 0, d: -f, b: 0, k: 5/6, c: 0, g: 0}, {a: -2*c, d: 0, b: c, f: 0, k: 13/18, g: 0}, {a: 0, d: 0, b: 0, k: 3/2, c: 0, f: 0, g: 0}]
[{a: 0, _k: 5/6, b: 0, d: -f, c: 0, g: 0}, {a: 0, _k: 3/2, b: 0, d: 0, c: 0, f: 0, g: 0}]
```
With master I get the following output:
```
[{a: 5*f*(6*k - 5)/(12*(k - 1)*(3*k - 2)), b: 0, c: -5*f*(6*k - 5)/(4*(k - 1)*(3*k - 2)), d: f/(6*(k - 1)), g: 0}]
[{_k: (6*d + f)/(6*d), a: 5*d*(d + f)/(2*d + f), b: 0, c: -15*d*(d + f)/(2*d + f), g: 0}]
```
One solution in both cases, although incorrect solutions in both cases for reasons this issue is about, but at least they have the same cardinality.
> With master I get the following output:
Oh, yes I get that now. I must have gotten confused and thought I was testing master when I wasn't.
There's clearly something fishy going on somewhere but it shouldn't be to do with the diff I showed. Those outputs on master are both incorrect. Let's try to work out what the correct answer should be from the Groebner basis:
```python
In [7]: for eq in equations: print(eq)
-a*k + 4*a/3 + b + 2*c/9 + 5*d/6 + 5*f/6
d/2 - f*k + 4*f/3
-d*k + d + f/6
13*a/18 + 13*b/18 + 13*c/18
a + b/2 - c*k + 20*c/9
a/6 - b*k + b + c/18
a + 5*b/3 + c/3
4*a/3 + 2*b/3 + 2*c
-g
In [8]: for eq in groebner(equations).exprs: print(eq)
a + 2*c
b - c
c*f
c*k - 13*c/18
d + f
f*k - 5*f/6
g
```
So we can see that `g=0`, `d=-f`, `b=c` and `a=-2*c`. The remaining unknowns are `c`, `f` and `k` and the remaining equations are
```python
c*f
c*(k - 13/18)
f*(k - 5/6)
```
Now either `c=0` or `f=0`:
Case 1: `c=0`. The final equation is
```python
f*(k - 5/6)
```
and either `f=0` and `k` is anything (case 1a) or `k=5/6` and `f` is anything (case 1b)
Case 2: `f=0`. The final equation is
```python
c*(k - 13/18)
```
and either `c=0` and `k` is anything (case 2a) or `k=13/18` and `c` is anything (case 2b).
The 4 cases given by solve with the diff above are:
```python
{a: 0, d: 0, b: 0, f: 0, c: 0, g: 0} # case 1a and 2a (same)
{a: 0, d: -f, b: 0, k: 5/6, c: 0, g: 0} # case 1b
{a: -2*c, d: 0, b: c, f: 0, k: 13/18, g: 0} # case 2b
{a: 0, d: 0, b: 0, k: 3/2, c: 0, f: 0, g: 0} # other
```
Now the "other" case is a valid solution but it is in fact a special case of the first solution which has the same zeros but allows `k` to be arbitrary - that case could be eliminated without losing anything from the full solution set since it is implied by the first case.
So the correct result to return should be:
```python
{a: 0, d: 0, b: 0, f: 0, c: 0, g: 0} # case 1a and 2a (same)
{a: 0, d: -f, b: 0, k: 5/6, c: 0, g: 0} # case 1b
{a: -2*c, d: 0, b: c, f: 0, k: 13/18, g: 0} # case 2b
```
Each of these is a valid solution. None are redundant since each solution allows a different symbol ('k', 'f', 'c') to be anything while the other solutions require a particular value for the same symbol. Also I think that the argument above shows that this is a comprehensive set of solutions.
So the diff I showed means that we get correct (although redundant) output for the equations with `k` but not for `k_` so there must be a bug somewhere to do with ordering the symbols. I'm not sure why the output is incorrect on master or why the diff above changes this but there must be a bug.
This seems to make the results for `k` and `k_` consistent:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index 17540efcc3..a7a6f5beba 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -1886,7 +1886,7 @@ def _ok_syms(e, sort=False):
rv = (e.free_symbols - solved_syms) & legal
if sort:
rv = list(rv)
- rv.sort(key=default_sort_key)
+ rv.sort(key=lambda s: s.name.replace('_', ''))
return rv
solved_syms = set(solved_syms) # set of symbols we have solved for
```
There must be a bug somewhere in this:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/801b1045d714686fe1baec6ece94815fe43c003a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py#L1890-L1961
That code is called when `solve_poly_system` fails. I'm not sure why `solve_poly_system` would fail here but there's a clearly a bug in the code to handle the failure.
|
[
{
"body": "The following code tries to find the solutions of a system of (multivariate quadratic) equations. However, the single solution returned by `solve` is not correct.\r\nIt seems like `f = 0` should be part of the solution but is not.\r\n\r\n```python\r\nfrom sympy import solve, sympify\r\n\r\nequations = [\r\n \"-k*a + b + 5*f/6 + 2*c/9 + 5*d/6 + 4*a/3\",\r\n \"-k*f + 4*f/3 + d/2\",\r\n \"-k*d + f/6 + d\",\r\n \"13*b/18 + 13*c/18 + 13*a/18\",\r\n \"-k*c + b/2 + 20*c/9 + a\",\r\n \"-k*b + b + c/18 + a/6\",\r\n \"5*b/3 + c/3 + a\",\r\n \"2*b/3 + 2*c + 4*a/3\",\r\n \"-g\"\r\n]\r\nequations = [sympify(e) for e in equations]\r\nunknowns = {s for e in equations for s in e.free_symbols}\r\n\r\nsolutions = solve(equations, unknowns, dict=True)\r\n# Should all be zero but are not:\r\nfor solution in solutions:\r\n for e in equations:\r\n print(e.subs(solution).simplify())\r\n\r\n```\r\n\r\nOutput:\r\n```\r\n0\r\nf*(-12*k**2 + 28*k - 15)/(12*(k - 1))\r\n0\r\n65*f*(5 - 6*k)/(108*(3*k**2 - 5*k + 2))\r\n5*f*(6*k - 5)*(9*k - 17)/(36*(k - 1)*(3*k - 2))\r\n0\r\n0\r\n35*f*(5 - 6*k)/(18*(3*k**2 - 5*k + 2))\r\n0\r\n```\r\n\r\nExpected Output:\r\n```\r\n0\r\n0\r\n0\r\n0\r\n0\r\n0\r\n0\r\n0\r\n0\r\n```\r\n\r\nThe bug exists in sympy versions `1.8` and `1.7` but NOT in version `1.6`.\r\n\r\nIn the meantime, is there a way to circumvent this problem until the issue is fixed? We thought about calling `solve` again on the equations of the output but are not sure if that is the best way.",
"number": 21882,
"title": "Incorrect solutions given by `solve` "
}
] |
ad4cbf280c381a08601405b4453e4a60a73b7e52
|
{
"head_commit": "418efaea73e6eed5282a92ab96c066474369eaa4",
"head_commit_message": "fix(solvers): fix doctest after change to solve_system",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/doc/src/tutorial/solvers.rst b/doc/src/tutorial/solvers.rst\nindex f41f1d9f5979..7091ee6a0af1 100644\n--- a/doc/src/tutorial/solvers.rst\n+++ b/doc/src/tutorial/solvers.rst\n@@ -142,9 +142,9 @@ In the ``solveset`` module, the non linear system of equations is solved using\n ``solve`` can be used for such cases:\n \n >>> solve([x**2 - y**2/exp(x)], [x, y], dict=True)\n- ⎡⎧ ⎛-y ⎞⎫ ⎧ ⎛y⎞⎫⎤\n- ⎢⎨x: 2⋅W⎜───⎟⎬, ⎨x: 2⋅W⎜─⎟⎬⎥\n- ⎣⎩ ⎝ 2 ⎠⎭ ⎩ ⎝2⎠⎭⎦\n+ ⎡⎧ ____⎫ ⎧ ____⎫⎤\n+ ⎢⎨ ╱ x ⎬ ⎨ ╱ x ⎬⎥\n+ ⎣⎩y: -x⋅╲╱ ℯ ⎭, ⎩y: x⋅╲╱ ℯ ⎭⎦\n \n 3. Currently ``nonlinsolve`` is not properly capable of solving the system of equations\n having trigonometric functions.\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\nindex fd9e6a5fc83f..f5c109c0a0f2 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@\n from sympy.utilities.lambdify import lambdify\n from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import (cartes, connected_components,\n- generate_bell, uniq, sift)\n+ generate_bell, uniq)\n from sympy.utilities.decorator import conserve_mpmath_dps\n \n from mpmath import findroot\n@@ -1758,17 +1758,6 @@ def _solve_system(exprs, symbols, **flags):\n for e in subexpr:\n subsyms |= exprsyms[e]\n subsyms = list(sorted(subsyms, key = lambda x: sym_indices[x]))\n- # use canonical subset to solve these equations\n- # since there may be redundant equations in the set:\n- # take the first equation of several that may have the\n- # same sub-maximal free symbols of interest; the\n- # other equations that weren't used should be checked\n- # to see that they did not fail -- does the solver\n- # take care of that?\n- choices = sift(subexpr, lambda x: tuple(ordered(exprsyms[x])))\n- subexpr = choices.pop(tuple(ordered(subsyms)), [])\n- for k in choices:\n- subexpr.append(next(ordered(choices[k])))\n flags['_split'] = False # skip split step\n subsol = _solve_system(subexpr, subsyms, **flags)\n if not isinstance(subsol, list):\n@@ -1895,9 +1884,22 @@ def _solve_system(exprs, symbols, **flags):\n # be solved.\n def _ok_syms(e, sort=False):\n rv = (e.free_symbols - solved_syms) & legal\n+\n+ # Solve first for symbols that have lower degree in the equation.\n+ # Ideally we want to solve firstly for symbols that appear linearly\n+ # with rational coefficients e.g. if e = x*y + z then we should\n+ # solve for z first.\n+ def key(sym):\n+ ep = e.as_poly(sym)\n+ if ep is None:\n+ complexity = (S.Infinity, S.Infinity, S.Infinity)\n+ else:\n+ coeff_syms = ep.LC().free_symbols\n+ complexity = (ep.degree(), len(coeff_syms & rv), len(coeff_syms))\n+ return complexity + (default_sort_key(sym),)\n+\n if sort:\n- rv = list(rv)\n- rv.sort(key=default_sort_key)\n+ rv = sorted(rv, key=key)\n return rv\n \n solved_syms = set(solved_syms) # set of symbols we have solved for\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\nindex ef5a4176c719..9ea118021c9f 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\n@@ -870,12 +870,12 @@ def test_issue_5132():\n {(log(-sin(2)), -S(2)), (log(sin(2)), S(2))}\n eqs = [exp(x)**2 - sin(y) + z**2, 1/exp(y) - 3]\n assert solve(eqs, set=True) == \\\n- ([x, y], {\n- (log(-sqrt(-z**2 - sin(log(3)))), -log(3)),\n- (log(-z**2 - sin(log(3)))/2, -log(3))})\n+ ([y, z], {\n+ (-log(3), sqrt(-exp(2*x) - sin(log(3)))),\n+ (-log(3), -sqrt(-exp(2*x) - sin(log(3))))})\n assert solve(eqs, x, z, set=True) == (\n [x, z],\n- {(log(-z**2 + sin(y))/2, z), (log(-sqrt(-z**2 + sin(y))), z)})\n+ {(x, sqrt(-exp(2*x) + sin(y))), (x, -sqrt(-exp(2*x) + sin(y)))})\n assert set(solve(eqs, x, y)) == \\\n {\n (log(-sqrt(-z**2 - sin(log(3)))), -log(3)),\n@@ -885,12 +885,10 @@ def test_issue_5132():\n (-log(3), -sqrt(-exp(2*x) - sin(log(3)))),\n (-log(3), sqrt(-exp(2*x) - sin(log(3))))}\n eqs = [exp(x)**2 - sin(y) + z, 1/exp(y) - 3]\n- assert solve(eqs, set=True) == ([x, y], {\n- (log(-sqrt(-z - sin(log(3)))), -log(3)),\n- (log(-z - sin(log(3)))/2, -log(3))})\n+ assert solve(eqs, set=True) == ([y, z], {\n+ (-log(3), -exp(2*x) - sin(log(3)))})\n assert solve(eqs, x, z, set=True) == (\n- [x, z],\n- {(log(-sqrt(-z + sin(y))), z), (log(-z + sin(y))/2, z)})\n+ [x, z], {(x, -exp(2*x) + sin(y))})\n assert set(solve(eqs, x, y)) == {\n (log(-sqrt(-z - sin(log(3)))), -log(3)),\n (log(-z - sin(log(3)))/2, -log(3))}\n@@ -1316,6 +1314,11 @@ def test_issue_5114_solvers():\n \n \n def test_issue_5849():\n+ #\n+ # XXX: This system does not have a solution for most values of the\n+ # parameters. Generally solve returns the empty set for systems that are\n+ # generically inconsistent.\n+ #\n I1, I2, I3, I4, I5, I6 = symbols('I1:7')\n dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4, Q2, Q4 = symbols('dI1,dI4,dQ2,dQ4,Q2,Q4')\n \n@@ -1332,21 +1335,24 @@ def test_issue_5849():\n )\n \n ans = [{\n- I1: I2 + I6,\n- dI1: -4*I2 - 4*I3 - 4*I5 - 10*I6 + 24,\n- I4: -I5 + I6,\n- dQ4: -I5 + I6,\n- Q4: 3*I5/2 - I6/2 - dI4/2,\n+ I1: I2 + I3,\n+ dI1: -4*I2 - 8*I3 - 4*I5 - 6*I6 + 24,\n+ I4: I3 - I5,\n+ dQ4: I3 - I5,\n+ Q4: -I3/2 + 3*I5/2 - dI4/2,\n dQ2: I2,\n Q2: 2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6}]\n \n v = I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4\n assert solve(e, *v, manual=True, check=False, dict=True) == ans\n- assert solve(e, *v, manual=True) == ans[0]\n+ assert solve(e, *v, manual=True, check=False) == ans[0]\n+ assert solve(e, *v, manual=True) == []\n+ assert solve(e, *v) == []\n+\n # the matrix solver (tested below) doesn't like this because it produces\n # a zero row in the matrix. Is this related to issue 4551?\n assert [ei.subs(\n- ans[0]) for ei in e] == [-I3 + I6, I3 - I6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]\n+ ans[0]) for ei in e] == [0, 0, I3 - I6, -I3 + I6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]\n \n \n def test_issue_5849_matrix():\n@@ -1373,14 +1379,33 @@ def test_issue_5849_matrix():\n 2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6 - Q2,\n I4 - 2*I5 + 2*Q4 + dI4\n )\n- assert solve(e, I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4) == {\n- I1: I2 + I6,\n- dI1: -4*I2 - 4*I3 - 4*I5 - 10*I6 + 24,\n- I4: -I5 + I6,\n- dQ4: -I5 + I6,\n- Q4: 3*I5/2 - I6/2 - dI4/2,\n- dQ2: I2,\n- Q2: 2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6}\n+ assert solve(e, I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4) == []\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_21882():\n+\n+ a, b, c, d, f, g, k = unknowns = symbols('a, b, c, d, f, g, k')\n+\n+ equations = [\n+ -k*a + b + 5*f/6 + 2*c/9 + 5*d/6 + 4*a/3,\n+ -k*f + 4*f/3 + d/2,\n+ -k*d + f/6 + d,\n+ 13*b/18 + 13*c/18 + 13*a/18,\n+ -k*c + b/2 + 20*c/9 + a,\n+ -k*b + b + c/18 + a/6,\n+ 5*b/3 + c/3 + a,\n+ 2*b/3 + 2*c + 4*a/3,\n+ -g,\n+ ]\n+\n+ answer = [\n+ {a: 0, f: 0, b: 0, d: 0, c: 0, g: 0},\n+ {a: 0, f: -d, b: 0, k: S(5)/6, c: 0, g: 0},\n+ {a: -2*c, f: 0, b: c, d: 0, k: S(13)/18, g: 0},\n+ {a: 0, f: 0, b: 0, k: S(3)/2, c: 0, d: 0, g: 0}\n+ ]\n+\n+ assert solve(equations, unknowns, dict=True) == answer\n \n \n def test_issue_5901():\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1373,14 +1379,33 @@ def test_issue_5849_matrix():\n 2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6 - Q2,\n I4 - 2*I5 + 2*Q4 + dI4\n )\n- assert solve(e, I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4) == {\n- I1: I2 + I6,\n- dI1: -4*I2 - 4*I3 - 4*I5 - 10*I6 + 24,\n- I4: -I5 + I6,\n- dQ4: -I5 + I6,\n- Q4: 3*I5/2 - I6/2 - dI4/2,\n- dQ2: I2,\n- Q2: 2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6}\n+ assert solve(e, I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4) == []\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_21882():\n+\n+ a, b, c, d, f, g, k = unknowns = symbols('a, b, c, d, f, g, k')\n+\n+ equations = [\n+ -k*a + b + 5*f/6 + 2*c/9 + 5*d/6 + 4*a/3,\n+ -k*f + 4*f/3 + d/2,\n+ -k*d + f/6 + d,\n+ 13*b/18 + 13*c/18 + 13*a/18,\n+ -k*c + b/2 + 20*c/9 + a,\n+ -k*b + b + c/18 + a/6,\n+ 5*b/3 + c/3 + a,\n+ 2*b/3 + 2*c + 4*a/3,\n+ -g,\n+ ]\n+\n+ answer = [\n+ {a: 0, f: 0, b: 0, d: 0, c: 0, g: 0},\n+ {a: 0, f: -d, b: 0, k: S(5)/6, c: 0, g: 0},\n+ {a: -2*c, f: 0, b: c, d: 0, k: S(13)/18, g: 0},\n+ {a: 0, f: 0, b: 0, k: S(3)/2, c: 0, d: 0, g: 0}",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1405,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n```"
}
] |
a8adad61b6edf0ec5e6cd775819d96e89286c3a4
|
diff --git a/doc/src/tutorial/solvers.rst b/doc/src/tutorial/solvers.rst
index f41f1d9f5979..91a054a57e3a 100644
--- a/doc/src/tutorial/solvers.rst
+++ b/doc/src/tutorial/solvers.rst
@@ -142,6 +142,10 @@ In the ``solveset`` module, the non linear system of equations is solved using
``solve`` can be used for such cases:
>>> solve([x**2 - y**2/exp(x)], [x, y], dict=True)
+ ⎡⎧ ____⎫ ⎧ ____⎫⎤
+ ⎢⎨ ╱ x ⎬ ⎨ ╱ x ⎬⎥
+ ⎣⎩y: -x⋅╲╱ ℯ ⎭, ⎩y: x⋅╲╱ ℯ ⎭⎦
+ >>> solve(x**2 - y**2/exp(x), x, dict=True)
⎡⎧ ⎛-y ⎞⎫ ⎧ ⎛y⎞⎫⎤
⎢⎨x: 2⋅W⎜───⎟⎬, ⎨x: 2⋅W⎜─⎟⎬⎥
⎣⎩ ⎝ 2 ⎠⎭ ⎩ ⎝2⎠⎭⎦
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index fd9e6a5fc83f..bc1baaf74245 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@
from sympy.utilities.lambdify import lambdify
from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent
from sympy.utilities.iterables import (cartes, connected_components,
- generate_bell, uniq, sift)
+ generate_bell, uniq)
from sympy.utilities.decorator import conserve_mpmath_dps
from mpmath import findroot
@@ -1758,17 +1758,6 @@ def _solve_system(exprs, symbols, **flags):
for e in subexpr:
subsyms |= exprsyms[e]
subsyms = list(sorted(subsyms, key = lambda x: sym_indices[x]))
- # use canonical subset to solve these equations
- # since there may be redundant equations in the set:
- # take the first equation of several that may have the
- # same sub-maximal free symbols of interest; the
- # other equations that weren't used should be checked
- # to see that they did not fail -- does the solver
- # take care of that?
- choices = sift(subexpr, lambda x: tuple(ordered(exprsyms[x])))
- subexpr = choices.pop(tuple(ordered(subsyms)), [])
- for k in choices:
- subexpr.append(next(ordered(choices[k])))
flags['_split'] = False # skip split step
subsol = _solve_system(subexpr, subsyms, **flags)
if not isinstance(subsol, list):
@@ -1895,9 +1884,22 @@ def _solve_system(exprs, symbols, **flags):
# be solved.
def _ok_syms(e, sort=False):
rv = (e.free_symbols - solved_syms) & legal
+
+ # Solve first for symbols that have lower degree in the equation.
+ # Ideally we want to solve firstly for symbols that appear linearly
+ # with rational coefficients e.g. if e = x*y + z then we should
+ # solve for z first.
+ def key(sym):
+ ep = e.as_poly(sym)
+ if ep is None:
+ complexity = (S.Infinity, S.Infinity, S.Infinity)
+ else:
+ coeff_syms = ep.LC().free_symbols
+ complexity = (ep.degree(), len(coeff_syms & rv), len(coeff_syms))
+ return complexity + (default_sort_key(sym),)
+
if sort:
- rv = list(rv)
- rv.sort(key=default_sort_key)
+ rv = sorted(rv, key=key)
return rv
solved_syms = set(solved_syms) # set of symbols we have solved for
@@ -1949,7 +1951,16 @@ def _ok_syms(e, sort=False):
rnew[k] = v.subs(s, sol)
# and add this new solution
rnew[s] = sol
- newresult.append(rnew)
+ # check that it is independent of previous solutions
+ iset = set(rnew.items())
+ for i in newresult:
+ if len(i) < len(iset) and not set(i.items()) - iset:
+ # this is a superset of a known solution that
+ # is smaller
+ break
+ else:
+ # keep it
+ newresult.append(rnew)
hit = True
got_s.add(s)
if not hit:
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
index ef5a4176c719..7dbc09582be9 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
@@ -870,12 +870,12 @@ def test_issue_5132():
{(log(-sin(2)), -S(2)), (log(sin(2)), S(2))}
eqs = [exp(x)**2 - sin(y) + z**2, 1/exp(y) - 3]
assert solve(eqs, set=True) == \
- ([x, y], {
- (log(-sqrt(-z**2 - sin(log(3)))), -log(3)),
- (log(-z**2 - sin(log(3)))/2, -log(3))})
+ ([y, z], {
+ (-log(3), sqrt(-exp(2*x) - sin(log(3)))),
+ (-log(3), -sqrt(-exp(2*x) - sin(log(3))))})
assert solve(eqs, x, z, set=True) == (
[x, z],
- {(log(-z**2 + sin(y))/2, z), (log(-sqrt(-z**2 + sin(y))), z)})
+ {(x, sqrt(-exp(2*x) + sin(y))), (x, -sqrt(-exp(2*x) + sin(y)))})
assert set(solve(eqs, x, y)) == \
{
(log(-sqrt(-z**2 - sin(log(3)))), -log(3)),
@@ -885,12 +885,10 @@ def test_issue_5132():
(-log(3), -sqrt(-exp(2*x) - sin(log(3)))),
(-log(3), sqrt(-exp(2*x) - sin(log(3))))}
eqs = [exp(x)**2 - sin(y) + z, 1/exp(y) - 3]
- assert solve(eqs, set=True) == ([x, y], {
- (log(-sqrt(-z - sin(log(3)))), -log(3)),
- (log(-z - sin(log(3)))/2, -log(3))})
+ assert solve(eqs, set=True) == ([y, z], {
+ (-log(3), -exp(2*x) - sin(log(3)))})
assert solve(eqs, x, z, set=True) == (
- [x, z],
- {(log(-sqrt(-z + sin(y))), z), (log(-z + sin(y))/2, z)})
+ [x, z], {(x, -exp(2*x) + sin(y))})
assert set(solve(eqs, x, y)) == {
(log(-sqrt(-z - sin(log(3)))), -log(3)),
(log(-z - sin(log(3)))/2, -log(3))}
@@ -1316,6 +1314,11 @@ def test_issue_5114_solvers():
def test_issue_5849():
+ #
+ # XXX: This system does not have a solution for most values of the
+ # parameters. Generally solve returns the empty set for systems that are
+ # generically inconsistent.
+ #
I1, I2, I3, I4, I5, I6 = symbols('I1:7')
dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4, Q2, Q4 = symbols('dI1,dI4,dQ2,dQ4,Q2,Q4')
@@ -1332,21 +1335,24 @@ def test_issue_5849():
)
ans = [{
- I1: I2 + I6,
- dI1: -4*I2 - 4*I3 - 4*I5 - 10*I6 + 24,
- I4: -I5 + I6,
- dQ4: -I5 + I6,
- Q4: 3*I5/2 - I6/2 - dI4/2,
+ I1: I2 + I3,
+ dI1: -4*I2 - 8*I3 - 4*I5 - 6*I6 + 24,
+ I4: I3 - I5,
+ dQ4: I3 - I5,
+ Q4: -I3/2 + 3*I5/2 - dI4/2,
dQ2: I2,
Q2: 2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6}]
v = I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4
assert solve(e, *v, manual=True, check=False, dict=True) == ans
- assert solve(e, *v, manual=True) == ans[0]
+ assert solve(e, *v, manual=True, check=False) == ans[0]
+ assert solve(e, *v, manual=True) == []
+ assert solve(e, *v) == []
+
# the matrix solver (tested below) doesn't like this because it produces
# a zero row in the matrix. Is this related to issue 4551?
assert [ei.subs(
- ans[0]) for ei in e] == [-I3 + I6, I3 - I6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
+ ans[0]) for ei in e] == [0, 0, I3 - I6, -I3 + I6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
def test_issue_5849_matrix():
@@ -1373,14 +1379,32 @@ def test_issue_5849_matrix():
2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6 - Q2,
I4 - 2*I5 + 2*Q4 + dI4
)
- assert solve(e, I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4) == {
- I1: I2 + I6,
- dI1: -4*I2 - 4*I3 - 4*I5 - 10*I6 + 24,
- I4: -I5 + I6,
- dQ4: -I5 + I6,
- Q4: 3*I5/2 - I6/2 - dI4/2,
- dQ2: I2,
- Q2: 2*I3 + 2*I5 + 3*I6}
+ assert solve(e, I1, I4, Q2, Q4, dI1, dI4, dQ2, dQ4) == []
+
+
+def test_issue_21882():
+
+ a, b, c, d, f, g, k = unknowns = symbols('a, b, c, d, f, g, k')
+
+ equations = [
+ -k*a + b + 5*f/6 + 2*c/9 + 5*d/6 + 4*a/3,
+ -k*f + 4*f/3 + d/2,
+ -k*d + f/6 + d,
+ 13*b/18 + 13*c/18 + 13*a/18,
+ -k*c + b/2 + 20*c/9 + a,
+ -k*b + b + c/18 + a/6,
+ 5*b/3 + c/3 + a,
+ 2*b/3 + 2*c + 4*a/3,
+ -g,
+ ]
+
+ answer = [
+ {a: 0, f: 0, b: 0, d: 0, c: 0, g: 0},
+ {a: 0, f: -d, b: 0, k: S(5)/6, c: 0, g: 0},
+ {a: -2*c, f: 0, b: c, d: 0, k: S(13)/18, g: 0},
+ ]
+
+ assert solve(equations, unknowns, dict=True) == answer
def test_issue_5901():
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-2221@edadbca
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 2,221
|
fixes OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument
|
closes #2220
|
2017-02-19T04:54:19Z
|
Potential OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument
In current `proc.py:CommandPipeline` implementation, we built and run procs first, then give controlling terminal to them. There are cases that all the processes have finished, then the "give terminal to them" will raise errors.
```
$ ls
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/base_shell.py", line 322, in default
run_compiled_code(code, self.ctx, None, 'single')
File "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/codecache.py", line 65, in run_compiled_code
func(code, glb, loc)
File "<xonsh-code>", line 1, in <module>
File "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/built_ins.py", line 858, in subproc_captured_hiddenobject
return run_subproc(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')
File "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/built_ins.py", line 799, in run_subproc
command = HiddenCommandPipeline(specs)
File "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/proc.py", line 1756, in __init__
if update_fg_process_group(pipeline_group, background):
File "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/proc.py", line 1691, in update_fg_process_group
return give_terminal_to(pipeline_group)
File "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/jobs.py", line 138, in give_terminal_to
os.tcsetpgrp(FD_STDERR, pgid)
OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument
```
|
I think this just needs a try-except. Thanks for reporting @mitnk
@scopatz yes, PR is coming.
|
[
{
"body": "In current `proc.py:CommandPipeline` implementation, we built and run procs first, then give controlling terminal to them. There are cases that all the processes have finished, then the \"give terminal to them\" will raise errors.\r\n\r\n```\r\n$ ls\r\nTraceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/base_shell.py\", line 322, in default\r\n run_compiled_code(code, self.ctx, None, 'single')\r\n File \"/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/codecache.py\", line 65, in run_compiled_code\r\n func(code, glb, loc)\r\n File \"<xonsh-code>\", line 1, in <module>\r\n File \"/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/built_ins.py\", line 858, in subproc_captured_hiddenobject\r\n return run_subproc(cmds, captured='hiddenobject')\r\n File \"/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/built_ins.py\", line 799, in run_subproc\r\n command = HiddenCommandPipeline(specs)\r\n File \"/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/proc.py\", line 1756, in __init__\r\n if update_fg_process_group(pipeline_group, background):\r\n File \"/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/proc.py\", line 1691, in update_fg_process_group\r\n return give_terminal_to(pipeline_group)\r\n File \"/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/site-packages/xonsh/jobs.py\", line 138, in give_terminal_to\r\n os.tcsetpgrp(FD_STDERR, pgid)\r\nOSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument\r\n```",
"number": 2220,
"title": "Potential OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument"
}
] |
684dce97da0c9a3c96293ca10833ceca4f48a53b
|
{
"head_commit": "edadbcab64f6e1b827e49836a5bb61eb6e85635a",
"head_commit_message": "fixes OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/news/give-term-to-none.rst b/news/give-term-to-none.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..59016251c7\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/give-term-to-none.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@\n+**Added:** None\n+\n+**Changed:** None\n+\n+**Deprecated:** None\n+\n+**Removed:** None\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Fixed a potential \"OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument\" to increase job\n+ control stability.\n+\n+**Security:** None\ndiff --git a/xonsh/jobs.py b/xonsh/jobs.py\nindex 5cd849cda1..7c38364f93 100644\n--- a/xonsh/jobs.py\n+++ b/xonsh/jobs.py\n@@ -135,9 +135,19 @@ def give_terminal_to(pgid):\n def give_terminal_to(pgid):\n oldmask = signal.pthread_sigmask(signal.SIG_BLOCK,\n _block_when_giving)\n- os.tcsetpgrp(FD_STDERR, pgid)\n- signal.pthread_sigmask(signal.SIG_SETMASK, oldmask)\n- return True\n+ try:\n+ os.tcsetpgrp(FD_STDERR, pgid)\n+ return True\n+ except OSError as e:\n+ if getattr(e, 'errno') == 22: # [Errno 22] Invalid argument\n+ # there are cases that all the processes of pgid have\n+ # finished, then we don't need to do anything here, see\n+ # issue #2220\n+ return False\n+ else:\n+ raise\n+ finally:\n+ signal.pthread_sigmask(signal.SIG_SETMASK, oldmask)\n \n def wait_for_active_job(last_task=None, backgrounded=False):\n \"\"\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -135,9 +135,19 @@ def give_terminal_to(pgid):\n def give_terminal_to(pgid):\n oldmask = signal.pthread_sigmask(signal.SIG_BLOCK,\n _block_when_giving)\n- os.tcsetpgrp(FD_STDERR, pgid)\n- signal.pthread_sigmask(signal.SIG_SETMASK, oldmask)\n- return True\n+ try:\n+ os.tcsetpgrp(FD_STDERR, pgid)\n+ return True\n+ except OSError as e:\n+ if getattr(e, 'errno') == 22: # [Errno 22] Invalid argument",
"line": null,
"original_line": null,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/jobs.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think the getattr() call should either have a default value or it should be `e.errno`. The current method doesn't add any safety and OSErrors should always have the `errno` attribute.\n\n@author:\nAh, right! :)"
}
] |
caa4b89954d79212fc0ac6d87fa07ed0c10803c5
|
diff --git a/news/give-term-to-none.rst b/news/give-term-to-none.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..59016251c7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/give-term-to-none.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+**Added:** None
+
+**Changed:** None
+
+**Deprecated:** None
+
+**Removed:** None
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* Fixed a potential "OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument" to increase job
+ control stability.
+
+**Security:** None
diff --git a/xonsh/jobs.py b/xonsh/jobs.py
index 5cd849cda1..e46f2e5a38 100644
--- a/xonsh/jobs.py
+++ b/xonsh/jobs.py
@@ -135,9 +135,19 @@ def give_terminal_to(pgid):
def give_terminal_to(pgid):
oldmask = signal.pthread_sigmask(signal.SIG_BLOCK,
_block_when_giving)
- os.tcsetpgrp(FD_STDERR, pgid)
- signal.pthread_sigmask(signal.SIG_SETMASK, oldmask)
- return True
+ try:
+ os.tcsetpgrp(FD_STDERR, pgid)
+ return True
+ except OSError as e:
+ if e.errno == 22: # [Errno 22] Invalid argument
+ # there are cases that all the processes of pgid have
+ # finished, then we don't need to do anything here, see
+ # issue #2220
+ return False
+ else:
+ raise
+ finally:
+ signal.pthread_sigmask(signal.SIG_SETMASK, oldmask)
def wait_for_active_job(last_task=None, backgrounded=False):
"""
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-2172@2b6119b
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 2,172
|
fix tcsetattr: Interrupted system call
|
try fixes #2170
|
2017-02-08T15:03:21Z
|
script that calls ssh gets interrupted
```
laerus@xonsh$ cat autossh
ssh [email protected]
laerus@xonsh$ ./autossh
^Z <--- didn't press anything here, this comes from xonsh or ssh
```
tried again with a non-lan remote
```
laerus@xonsh$ ./autossh
^Z
tcsetattr: Interrupted system call
```
|
[
{
"body": "```\r\nlaerus@xonsh$ cat autossh \r\nssh [email protected]\r\nlaerus@xonsh$ ./autossh \r\n^Z <--- didn't press anything here, this comes from xonsh or ssh\r\n```\r\n\r\ntried again with a non-lan remote\r\n```\r\nlaerus@xonsh$ ./autossh\r\n^Z\r\ntcsetattr: Interrupted system call\r\n```",
"number": 2170,
"title": "script that calls ssh gets interrupted"
}
] |
ff9d890846e01e81edbd0610e9acd70a042d9446
|
{
"head_commit": "2b6119bf0ec62074664efbd51b7548636129380e",
"head_commit_message": "fix tcsetattr: Interrupted system call",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/news/xonsh-script-fix.rst b/news/xonsh-script-fix.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..e42eeec3ed\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/xonsh-script-fix.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@\n+**Added:** None\n+\n+**Changed:** None\n+\n+**Deprecated:** None\n+\n+**Removed:** None\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Fixed a ``tcsetattr: Interrupted system call`` issue when run xonsh scripts.\n+\n+**Security:** None\ndiff --git a/xonsh/built_ins.py b/xonsh/built_ins.py\nindex 032e197614..e0ef5f68ad 100644\n--- a/xonsh/built_ins.py\n+++ b/xonsh/built_ins.py\n@@ -535,6 +535,9 @@ def prep_preexec_fn(self, kwargs, pipeline_group=None):\n \"\"\"Prepares the 'preexec_fn' keyword argument\"\"\"\n if not (ON_POSIX and self.cls is subprocess.Popen):\n return\n+ env = builtins.__xonsh_env__\n+ if not env['XONSH_INTERACTIVE']:\n+ return\n if pipeline_group is None:\n xonsh_preexec_fn = no_pg_xonsh_preexec_fn\n else:\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -535,6 +535,9 @@ def prep_preexec_fn(self, kwargs, pipeline_group=None):\n \"\"\"Prepares the 'preexec_fn' keyword argument\"\"\"\n if not (ON_POSIX and self.cls is subprocess.Popen):\n return\n+ env = builtins.__xonsh_env__\n+ if not env['XONSH_INTERACTIVE']:",
"line": null,
"original_line": null,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/built_ins.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis might need to be env.get('XONSH_INTERACTIVE')\n\n@user2:\n`'XONSH_INTERACTIVE' in env`?\n\n@author:\nI think this is safe. this env is always set during the start up phase, and here is a run-sub-proc phase. But I could update a bit :)\n\n@author:\nOk, I see the points. CI was failing because of this. In tests we may only mock part of the ENVs."
}
] |
3586a3580ac683ed3bd76a453e667613680231af
|
diff --git a/news/xonsh-script-fix.rst b/news/xonsh-script-fix.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e42eeec3ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/xonsh-script-fix.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+**Added:** None
+
+**Changed:** None
+
+**Deprecated:** None
+
+**Removed:** None
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* Fixed a ``tcsetattr: Interrupted system call`` issue when run xonsh scripts.
+
+**Security:** None
diff --git a/xonsh/built_ins.py b/xonsh/built_ins.py
index 032e197614..b21c9d4cb1 100644
--- a/xonsh/built_ins.py
+++ b/xonsh/built_ins.py
@@ -535,6 +535,8 @@ def prep_preexec_fn(self, kwargs, pipeline_group=None):
"""Prepares the 'preexec_fn' keyword argument"""
if not (ON_POSIX and self.cls is subprocess.Popen):
return
+ if not builtins.__xonsh_env__.get('XONSH_INTERACTIVE'):
+ return
if pipeline_group is None:
xonsh_preexec_fn = no_pg_xonsh_preexec_fn
else:
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-8163@255e4b7
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 8,163
|
docs: add the other/miscellaneous form
|
### Describe your change
- Add the other/miscellaneous form.
- Closes #8133.
### Checklist:
* [x] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [ ] ~This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.~
* [ ] ~All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.~
* [ ] ~All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.~
* [ ] ~All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.~
* [ ] ~All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).~
* [ ] ~All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.~
* [ ] ~All new algorithms include at least one URL that points to Wikipedia or another similar explanation.~
* [x] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the commit message contains `Fixes: #{$ISSUE_NO}`.
|
2023-03-02T04:50:59Z
|
[DOCS] Add a miscellaneous issue form
### Feature description
By adding a miscellaneous/other issue template/form, we can make other types of issues that do not fit any of the provided templates.
The benefits of adding this would include the ability to:
- Create good first issues, which are beginner-friendly opportunities.
- Create GitHub repository discussion issues, such as the Code of Conduct, licenses, and other community files.
- Make to-do lists for improving the repository or such.
- Prevent blank issues to be created with no information. The miscellaneous template can have a required field that asks for a description.
What do you think about this? Thanks. 🙂
|
Can you please specify that "adding miscellaneous/other issue template or form" means to add it to the repo or add it to one of the particular repo folders? And what type of output do you expect from the form?
I mean to the repository itself when reporting an issue.
What do you mean exactly by output? 🤔
By output I mean that what do you want that form to do mean to categorize the issues with the help of description to avoid unnecessary and unsubscribed issues or any thing else?
> By output I mean that what do you want that form to do mean to categorize the issues with the help of description to avoid unnecessary and unsubscribed issues or any thing else?
I'm not sure I understand well. 😅
nah my fault I was just getting too deep in the issue; I might solve it, and I'll let you know if I do.Thanks for replying to my queries 😊
In addition, having a miscellaneous template could also facilitate the creation of to-do lists for repository improvements, which can help to organize and prioritize tasks more effectively. By requiring a description in the miscellaneous issue template, it can also help to prevent blank or incomplete issues from being created.
CC: @cclauss, @dhruvmanila, what do you think about this?
Should I create a pull request for this or?
I have no opinion on this. If you think it's useful, you can go ahead with the PR :)
|
[
{
"body": "### Feature description\n\nBy adding a miscellaneous/other issue template/form, we can make other types of issues that do not fit any of the provided templates.\r\nThe benefits of adding this would include the ability to:\r\n\r\n- Create good first issues, which are beginner-friendly opportunities.\r\n- Create GitHub repository discussion issues, such as the Code of Conduct, licenses, and other community files.\r\n- Make to-do lists for improving the repository or such.\r\n- Prevent blank issues to be created with no information. The miscellaneous template can have a required field that asks for a description.\r\n\r\nWhat do you think about this? Thanks. 🙂\r\n",
"number": 8133,
"title": "[DOCS] Add a miscellaneous issue form"
}
] |
64543faa980b526f79d287a073ebb7554749faf9
|
{
"head_commit": "255e4b7e1bfdfffe1147fbdf9cf43a86fc36898d",
"head_commit_message": "docs: add the other/miscellaneous form",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/other.yml b/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/other.yml\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..f32dadef93be\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/other.yml\n@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@\n+name: Other\n+description: Use this for any other issues. PLEASE do not create blank issues\n+title: \"[OTHER]\"\n+labels: [\"awaiting triage\"]\n+body:\n+ - type: markdown\n+ attributes:\n+ value: \"# Other issue\"\n+ - type: textarea\n+ id: issuedescription\n+ attributes:\n+ label: What would you like to share?\n+ description: Provide a clear and concise explanation of your issue.\n+ validations:\n+ required: true\n+ - type: textarea\n+ id: extrainfo\n+ attributes:\n+ label: Additional information\n+ description: Is there anything else we should know about this issue?\n+ validations:\n+ required: false\n+ - type: checkboxes\n+ id: consent\n+ attributes:\n+ label: Would you like to work on this issue?\n+ options:\n+ - label: Yes, I want to work on this issue!\n+ required: false\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@\n+name: Other\n+description: Use this for any other issues. PLEASE do not create blank issues\n+title: \"[OTHER]\"\n+labels: [\"awaiting triage\"]\n+body:\n+ - type: markdown\n+ attributes:\n+ value: \"# Other issue\"\n+ - type: textarea\n+ id: issuedescription\n+ attributes:\n+ label: What would you like to share?\n+ description: Provide a clear and concise explanation of your issue.\n+ validations:\n+ required: true\n+ - type: textarea\n+ id: extrainfo\n+ attributes:\n+ label: Additional information\n+ description: Is there anything else we should know about this issue?\n+ validations:\n+ required: false\n+ - type: checkboxes\n+ id: consent\n+ attributes:\n+ label: Would you like to work on this issue?\n+ options:\n+ - label: Yes, I want to work on this issue!\n+ required: false",
"line": null,
"original_line": 29,
"original_start_line": 23,
"path": ".github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/other.yml",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n```\r\n\r\nLet's lose this. This repo does not reserve issues. Instead, we encourage visitors to submit pull requests. If multiple contributors submit a pull request for the same algorithm then it is almost always a learning experience (or plagiarism).\n\n@user2:\nI agree with this 👍"
}
] |
b93fd4535adb879bb34c603768d638c10772fe18
|
diff --git a/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/other.yml b/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/other.yml
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..44d6ff541506
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/other.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+name: Other
+description: Use this for any other issues. PLEASE do not create blank issues
+labels: ["awaiting triage"]
+body:
+ - type: textarea
+ id: issuedescription
+ attributes:
+ label: What would you like to share?
+ description: Provide a clear and concise explanation of your issue.
+ validations:
+ required: true
+
+ - type: textarea
+ id: extrainfo
+ attributes:
+ label: Additional information
+ description: Is there anything else we should know about this issue?
+ validations:
+ required: false
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 1,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-2136@27ef724
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 2,136
|
ignore vc aliases in command_cache
|
I don't *think* this will have any side effects.
When we build the ``$PROMPT``, we lazily check for ``git`` and ``hg``
binaries to see if we should generate a ``<branch>`` field.
At the same time ``lazy_locate_binary`` doesn't return the path to a
command if it detects that that command is an alias (since aliases won't
have a path).
In the case that ``git`` or ``hg`` is aliased (the specific case here
was replacing ``git`` with ``hub``), ``lazy_locate_binary`` will return
``None`` because the command is an alias.
This breaks the logic in the branch detection. We don't want to change
the logic in the branch detection since there are many potential impacts
on prompt generation speed, which makes for a bad user experience.
So, this is a mildly ugly hack, but it's the best option I could come up
with in order to preserve prompt speed and still keep the branch
information available for this slightly weird edge case.
I'm all ears to alternative solutions.
Should resolve #2135
|
2017-01-31T23:16:50Z
|
Branch not shown if 'git' is aliased to 'hub'
I you do `brew install hub` and add `aliases['git'] = ['hub']` to ~/.xonshrc, git branches will no longer be shown in directories.
This is very strange since Hub is just a wrapper around git, and `hub branch` yields exactly the same output as `git branch`. In fact the former just invokes the latter.
|
Hey @moigagoo -- thanks for reporting.
Quick question: does the same behavior occur if you set `aliases['git'] = 'hub'`?
hmmm, interesting. I can duplicate this by setting `aliases['git'] = 'git'`
Yes, the same behavior occurs with `aliases['git'] = 'hub'`.
the `curr_branch` function in `$PROMPT_FIELDS` that fetches the branch for the current git repo calls the git binary through python's subprocess module, same for the `gistatus` prompt field.
@laerus invoking `hub branch` with subprocess works just fine:
```python
>>> subprocess.run("git branch", shell=True)
* develop
master
CompletedProcess(args='git branch', returncode=0)
>>> subprocess.run("hub branch", shell=True)
* develop
master
CompletedProcess(args='hub branch', returncode=0)
```
Ok, I think I have an idea about what's going on.
Aliasing `git` to something, even itself, is throwing off something in `locate_binary`. It's not finding a binary for `git` since it's an alias and then the branch info isn't returned.
yeah, ok, in `commands_cache.py` line 165
`return path if not is_alias else None`
similar issue if you try, for instance, to do a `locate_binary('ls')`
|
[
{
"body": "I you do `brew install hub` and add `aliases['git'] = ['hub']` to ~/.xonshrc, git branches will no longer be shown in directories.\r\n\r\nThis is very strange since Hub is just a wrapper around git, and `hub branch` yields exactly the same output as `git branch`. In fact the former just invokes the latter.\r\n",
"number": 2135,
"title": "Branch not shown if 'git' is aliased to 'hub'"
}
] |
cb62c0c3c336095fafd7dbf1f9767650bcc9ac73
|
{
"head_commit": "27ef724927efebe2a8299dab244d1dfec281baff",
"head_commit_message": "remove special case ugliness\n\nReplace with something better.\nNo more special casing, now `allcmds` is a tuple of path and also alias\nif it exists (otherwise `None`). `locate_binary` and\n`lazy_locate_binary` also not take an additional option kwarg to force\nreturning the path to a binary even if an alias exists",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/news/vc_alias_fix.rst b/news/vc_alias_fix.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..9469b4d785\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/vc_alias_fix.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@\n+**Added:** None\n+\n+**Changed:** None\n+\n+**Deprecated:** None\n+\n+**Removed:** None\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Fixed issue wherein if ``git`` or (presumably) ``hg`` are aliased, then branch\n+ information no longer appears in the ``$PROMPT``\n+\n+**Security:** None\ndiff --git a/xonsh/commands_cache.py b/xonsh/commands_cache.py\nindex aa08b59ed6..9af7b8f223 100644\n--- a/xonsh/commands_cache.py\n+++ b/xonsh/commands_cache.py\n@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ def all_commands(self):\n cache_valid = path_hash == self._path_checksum\n self._path_checksum = path_hash\n # did aliases change?\n- alss = getattr(builtins, 'aliases', set())\n+ alss = getattr(builtins, 'aliases', dict())\n al_hash = hash(frozenset(alss))\n cache_valid = cache_valid and al_hash == self._alias_checksum\n self._alias_checksum = al_hash\n@@ -99,11 +99,11 @@ def all_commands(self):\n # entries at the back.\n for cmd in executables_in(path):\n key = cmd.upper() if ON_WINDOWS else cmd\n- allcmds[key] = (os.path.join(path, cmd), cmd in alss)\n+ allcmds[key] = (os.path.join(path, cmd), alss.get(key, None))\n for cmd in alss:\n if cmd not in allcmds:\n key = cmd.upper() if ON_WINDOWS else cmd\n- allcmds[key] = (cmd, True)\n+ allcmds[key] = (cmd, None)\n self._cmds_cache = allcmds\n return allcmds\n \n@@ -142,14 +142,32 @@ def lazyget(self, key, default=None):\n \"\"\"A lazy value getter.\"\"\"\n return self._cmds_cache.get(self.cached_name(key), default)\n \n- def locate_binary(self, name):\n- \"\"\"Locates an executable on the file system using the cache.\"\"\"\n+ def locate_binary(self, name, ignore_alias=False):\n+ \"\"\"Locates an executable on the file system using the cache.\n+\n+ Arguments\n+ ---------\n+ name : str\n+ name of binary to search for\n+ ignore_alias : bool, optional\n+ Force return of binary path even if alias of ``name`` exists\n+ (default ``False``)\n+ \"\"\"\n # make sure the cache is up to date by accessing the property\n _ = self.all_commands\n- return self.lazy_locate_binary(name)\n-\n- def lazy_locate_binary(self, name):\n- \"\"\"Locates an executable in the cache, without checking its validity.\"\"\"\n+ return self.lazy_locate_binary(name, ignore_alias)\n+\n+ def lazy_locate_binary(self, name, ignore_alias=False):\n+ \"\"\"Locates an executable in the cache, without checking its validity.\n+\n+ Arguments\n+ ---------\n+ name : str\n+ name of binary to search for\n+ ignore_alias : bool, optional\n+ Force return of binary path even if alias of ``name`` exists\n+ (default ``False``)\n+ \"\"\"\n possibilities = self.get_possible_names(name)\n if ON_WINDOWS:\n # Windows users expect to be able to execute files in the same\n@@ -161,8 +179,11 @@ def lazy_locate_binary(self, name):\n cached = next((cmd for cmd in possibilities if cmd in self._cmds_cache),\n None)\n if cached:\n- (path, is_alias) = self._cmds_cache[cached]\n- return path if not is_alias else None\n+ (path, alias) = self._cmds_cache[cached]\n+ if not alias or ignore_alias:\n+ return path\n+ else:\n+ return None\n elif os.path.isfile(name) and name != pathbasename(name):\n return name\n \ndiff --git a/xonsh/prompt/vc.py b/xonsh/prompt/vc.py\nindex 54636547e2..0a62b5cc90 100644\n--- a/xonsh/prompt/vc.py\n+++ b/xonsh/prompt/vc.py\n@@ -123,11 +123,11 @@ def current_branch():\n cmds = builtins.__xonsh_commands_cache__\n # check for binary only once\n if cmds.is_empty():\n- has_git = bool(cmds.locate_binary('git'))\n- has_hg = bool(cmds.locate_binary('hg'))\n+ has_git = bool(cmds.locate_binary('git', ignore_alias=True))\n+ has_hg = bool(cmds.locate_binary('hg', ignore_alias=True))\n else:\n- has_git = bool(cmds.lazy_locate_binary('git'))\n- has_hg = bool(cmds.lazy_locate_binary('hg'))\n+ has_git = bool(cmds.lazy_locate_binary('git', ignore_alias=True))\n+ has_hg = bool(cmds.lazy_locate_binary('hg', ignore_alias=True))\n if has_git:\n branch = get_git_branch()\n if not branch and has_hg:\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -99,11 +99,11 @@ def all_commands(self):\n # entries at the back.\n for cmd in executables_in(path):\n key = cmd.upper() if ON_WINDOWS else cmd\n- allcmds[key] = (os.path.join(path, cmd), cmd in alss)\n+ allcmds[key] = (os.path.join(path, cmd), alss.get(key, None))\n for cmd in alss:\n if cmd not in allcmds:\n key = cmd.upper() if ON_WINDOWS else cmd\n- allcmds[key] = (cmd, True)\n+ allcmds[key] = (cmd, None)",
"line": null,
"original_line": null,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/commands_cache.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhy? Would this indicate that this is not an alias? \n\n@author:\nAhh, that's an interesting point. In this case, there's an alias that doesn't exist in `allcmds` for some reason -- the second value of the tuple is (now) the name of the alias if it exists and the first value is the full string path of the command, so in this case, the \"alias\" value is the same as the cmd value. I just set it to None, but it could be `(cmd, cmd)`\n\n@user1:\nBut on line 183 you check: \r\n```\r\n(path, alias) = self._cmds_cache[cached]\r\n if not alias or ignore_alias:\r\n...\r\n```\r\nWhich would evaluate to True since `alias` would be `None`. \n\n@author:\nAhh, gotcha. Yes, I agree. I'll change it."
}
] |
21d05918aede6beb6edfd730c52e1721dae2e8c9
|
diff --git a/news/vc_alias_fix.rst b/news/vc_alias_fix.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9469b4d785
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/vc_alias_fix.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+**Added:** None
+
+**Changed:** None
+
+**Deprecated:** None
+
+**Removed:** None
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* Fixed issue wherein if ``git`` or (presumably) ``hg`` are aliased, then branch
+ information no longer appears in the ``$PROMPT``
+
+**Security:** None
diff --git a/xonsh/commands_cache.py b/xonsh/commands_cache.py
index aa08b59ed6..e37d6dd72a 100644
--- a/xonsh/commands_cache.py
+++ b/xonsh/commands_cache.py
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ def all_commands(self):
cache_valid = path_hash == self._path_checksum
self._path_checksum = path_hash
# did aliases change?
- alss = getattr(builtins, 'aliases', set())
+ alss = getattr(builtins, 'aliases', dict())
al_hash = hash(frozenset(alss))
cache_valid = cache_valid and al_hash == self._alias_checksum
self._alias_checksum = al_hash
@@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ def all_commands(self):
# entries at the back.
for cmd in executables_in(path):
key = cmd.upper() if ON_WINDOWS else cmd
- allcmds[key] = (os.path.join(path, cmd), cmd in alss)
+ allcmds[key] = (os.path.join(path, cmd), alss.get(key, None))
for cmd in alss:
if cmd not in allcmds:
key = cmd.upper() if ON_WINDOWS else cmd
@@ -142,14 +142,32 @@ def lazyget(self, key, default=None):
"""A lazy value getter."""
return self._cmds_cache.get(self.cached_name(key), default)
- def locate_binary(self, name):
- """Locates an executable on the file system using the cache."""
+ def locate_binary(self, name, ignore_alias=False):
+ """Locates an executable on the file system using the cache.
+
+ Arguments
+ ---------
+ name : str
+ name of binary to search for
+ ignore_alias : bool, optional
+ Force return of binary path even if alias of ``name`` exists
+ (default ``False``)
+ """
# make sure the cache is up to date by accessing the property
_ = self.all_commands
- return self.lazy_locate_binary(name)
-
- def lazy_locate_binary(self, name):
- """Locates an executable in the cache, without checking its validity."""
+ return self.lazy_locate_binary(name, ignore_alias)
+
+ def lazy_locate_binary(self, name, ignore_alias=False):
+ """Locates an executable in the cache, without checking its validity.
+
+ Arguments
+ ---------
+ name : str
+ name of binary to search for
+ ignore_alias : bool, optional
+ Force return of binary path even if alias of ``name`` exists
+ (default ``False``)
+ """
possibilities = self.get_possible_names(name)
if ON_WINDOWS:
# Windows users expect to be able to execute files in the same
@@ -161,8 +179,11 @@ def lazy_locate_binary(self, name):
cached = next((cmd for cmd in possibilities if cmd in self._cmds_cache),
None)
if cached:
- (path, is_alias) = self._cmds_cache[cached]
- return path if not is_alias else None
+ (path, alias) = self._cmds_cache[cached]
+ if not alias or ignore_alias:
+ return path
+ else:
+ return None
elif os.path.isfile(name) and name != pathbasename(name):
return name
diff --git a/xonsh/prompt/vc.py b/xonsh/prompt/vc.py
index 54636547e2..0a62b5cc90 100644
--- a/xonsh/prompt/vc.py
+++ b/xonsh/prompt/vc.py
@@ -123,11 +123,11 @@ def current_branch():
cmds = builtins.__xonsh_commands_cache__
# check for binary only once
if cmds.is_empty():
- has_git = bool(cmds.locate_binary('git'))
- has_hg = bool(cmds.locate_binary('hg'))
+ has_git = bool(cmds.locate_binary('git', ignore_alias=True))
+ has_hg = bool(cmds.locate_binary('hg', ignore_alias=True))
else:
- has_git = bool(cmds.lazy_locate_binary('git'))
- has_hg = bool(cmds.lazy_locate_binary('hg'))
+ has_git = bool(cmds.lazy_locate_binary('git', ignore_alias=True))
+ has_hg = bool(cmds.lazy_locate_binary('hg', ignore_alias=True))
if has_git:
branch = get_git_branch()
if not branch and has_hg:
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-2756@a1c5b46
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 2,756
|
Jupyter Xernel
|
This fixes #2712, in so far as that issue is actually addressable.
I have completely removed the dependence on `ipykernel`, and instead forked the pyzmq-based [simple kernel](https://github.com/dsblank/simple_kernel/blob/master/simple_kernel.py). I needed to do this in order to avoid some of the AST transformations that were interfering with xonsh's syntax.
Things should more or less be working now.
|
2018-08-02T22:48:19Z
|
Issues with the Jupyter kernel
The Jupyter kernel seems nice, but it doesn't seem to work too well in a notebook:
- Output isn't printed until the command exits
- Commands like a git clone that clear the line aren't cleared (compare this to the standard IPython `!git clone`)
- It doesn't know that the output isn't a tty. So something like `git log` will not work, and it messes up the terminal that the notebook is running from
|
Ok, so I think the issue might be that we are subclassing from `ipykernel`, which is leading to all sorts of wrong assumptions about the code being valid Python. We probably shouldn't be doing that anymore, but maybe @Carreau can weight in with his thoughts
> It doesn't know that the output isn't a tty. So something like git log will not work, and it messes up the terminal that the notebook is running from
This actually isn't possible, given my reading of [the docs](http://jupyter-client.readthedocs.io/en/stable/messaging.html#messages-on-the-stdin-router-dealer-channel). Even the Bash kernel messes up in such cases. CC @takluyver
|
[
{
"body": "The Jupyter kernel seems nice, but it doesn't seem to work too well in a notebook:\r\n\r\n- Output isn't printed until the command exits\r\n- Commands like a git clone that clear the line aren't cleared (compare this to the standard IPython `!git clone`)\r\n- It doesn't know that the output isn't a tty. So something like `git log` will not work, and it messes up the terminal that the notebook is running from",
"number": 2712,
"title": "Issues with the Jupyter kernel"
}
] |
483591308c77a1def45df638d6b5be5b280c1778
|
{
"head_commit": "a1c5b46a6961340b23eebfae7a7beff4c14885e4",
"head_commit_message": "fixed flake issue",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/docs/api/jupyter_shell.rst b/docs/api/jupyter_shell.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..dc2f277000\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/docs/api/jupyter_shell.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@\n+.. _xonsh_jupyter_shell:\n+\n+******************************************\n+Jupyter Shell (``xonsh.jupyter_shell``)\n+******************************************\n+\n+.. automodule:: xonsh.jupyter_shell\n+ :members:\n+ :undoc-members:\n+\ndiff --git a/news/xernel.rst b/news/xernel.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..0f2dbc6ed9\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/xernel.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@\n+**Added:**\n+\n+* New ``JupyterShell`` for interactive interfacing with Jupyter.\n+\n+**Changed:** None\n+\n+**Deprecated:** None\n+\n+**Removed:** None\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* The JupyterKernel has been fixed from a rather broken state.\n+\n+**Security:** None\ndiff --git a/requirements-docs.txt b/requirements-docs.txt\nindex 1cdc198684..610f47ee97 100644\n--- a/requirements-docs.txt\n+++ b/requirements-docs.txt\n@@ -5,6 +5,6 @@ prompt_toolkit\n pygments\n ply\n psutil\n-ipykernel\n+pyzmq\n matplotlib\n doctr\ndiff --git a/xonsh/__init__.py b/xonsh/__init__.py\nindex ceeaaee274..f68c68cbf2 100644\n--- a/xonsh/__init__.py\n+++ b/xonsh/__init__.py\n@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@\n \n # amalgamate exclude jupyter_kernel parser_table parser_test_table pyghooks\n # amalgamate exclude winutils wizard pytest_plugin fs macutils pygments_cache\n+# amalgamate exclude jupyter_shell\n import os as _os\n if _os.getenv('XONSH_DEBUG', ''):\n pass\ndiff --git a/xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py b/xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py\nindex 93433dc8d1..99e6166993 100644\n--- a/xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py\n+++ b/xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py\n@@ -1,72 +1,398 @@\n # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-\n \"\"\"Hooks for Jupyter Xonsh Kernel.\"\"\"\n+import sys\n+import json\n+import hmac\n+import uuid\n+import errno\n+import hashlib\n+import datetime\n import builtins\n+import threading\n from pprint import pformat\n+from argparse import ArgumentParser\n+from collections.abc import Set\n \n-from ipykernel.kernelbase import Kernel\n+import zmq\n+from zmq.eventloop import ioloop, zmqstream\n+from zmq.error import ZMQError\n \n from xonsh import __version__ as version\n-from xonsh.main import main_context\n+from xonsh.main import setup\n from xonsh.completer import Completer\n \n \n MAX_SIZE = 8388608 # 8 Mb\n+DELIM = b\"<IDS|MSG>\"\n \n \n-class XonshKernel(Kernel):\n+def dump_bytes(*args, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"Converts an object to JSON and returns the bytes.\"\"\"\n+ return json.dumps(*args, **kwargs).encode(\"ascii\")\n+\n+\n+def load_bytes(b):\n+ \"\"\"Converts bytes of JSON to an object.\"\"\"\n+ return json.loads(b.decode(\"ascii\"))\n+\n+\n+def bind(socket, connection, port):\n+ \"\"\"Binds a socket to a port, or a random port if needed. Returns the port.\"\"\"\n+ if port <= 0:\n+ return socket.bind_to_random_port(connection)\n+ else:\n+ socket.bind(\"{}:{}\".format(connection, port))\n+ return port\n+\n+\n+class XonshKernel:\n \"\"\"Xonsh xernal for Jupyter\"\"\"\n- implementation = 'Xonsh ' + version\n+\n+ implementation = \"Xonsh \" + version\n implementation_version = version\n- language = 'xonsh'\n- language_version = version\n- banner = 'Xonsh - Python-powered, cross-platform shell'\n- language_info = {'name': 'xonsh',\n- 'version': version,\n- 'pygments_lexer': 'xonsh',\n- 'codemirror_mode': 'shell',\n- 'mimetype': 'text/x-sh',\n- 'file_extension': '.xsh',\n- }\n-\n- def __init__(self, **kwargs):\n+ language = \"xonsh\"\n+ language_version = version.split(\".\")[:3]\n+ banner = \"Xonsh - Python-powered, cross-platform shell\"\n+ language_info = {\n+ \"name\": \"xonsh\",\n+ \"version\": version,\n+ \"pygments_lexer\": \"xonsh\",\n+ \"codemirror_mode\": \"shell\",\n+ \"mimetype\": \"text/x-sh\",\n+ \"file_extension\": \".xsh\",\n+ }\n+ signature_schemes = {\"hmac-sha256\": hashlib.sha256}\n+\n+ def __init__(self, debug_level=0, session_id=None, config=None, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Parameters\n+ ----------\n+ debug_level : int, optional\n+ Integer from 0 (no debugging) to 3 (all debugging), default: 0.\n+ session_id : str or None, optional\n+ Unique string id representing the kernel session. If None, this will\n+ be replaced with a random UUID.\n+ config : dict or None, optional\n+ Configuration dictionary to start server with. BY default will\n+ search the command line for options (if given) or use default\n+ configuration.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ self.debug_level = debug_level\n+ self.session_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) if session_id is None else session_id\n+ self._parser = None\n+ self.config = self.make_default_config() if config is None else config\n+\n+ self.exiting = False\n+ self.execution_count = 1\n self.completer = Completer()\n- super().__init__(**kwargs)\n \n- def do_execute(self, code, silent, store_history=True, user_expressions=None,\n- allow_stdin=False):\n+ @property\n+ def parser(self):\n+ if self._parser is None:\n+ p = ArgumentParser(\"jupyter_kerenel\")\n+ p.add_argument(\"-f\", dest=\"config_file\", default=None)\n+ self._parser = p\n+ return self._parser\n+\n+ def make_default_config(self):\n+ \"\"\"Provides default configuration\"\"\"\n+ ns, unknown = self.parser.parse_known_args(sys.argv)\n+ if ns.config_file is None:\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Starting xonsh kernel with default args...\")\n+ config = {\n+ \"control_port\": 0,\n+ \"hb_port\": 0,\n+ \"iopub_port\": 0,\n+ \"ip\": \"127.0.0.1\",\n+ \"key\": str(uuid.uuid4()),\n+ \"shell_port\": 0,\n+ \"signature_scheme\": \"hmac-sha256\",\n+ \"stdin_port\": 0,\n+ \"transport\": \"tcp\",\n+ }\n+ else:\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Loading simple_kernel with args:\", sys.argv)\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Reading config file {!r}...\".format(ns.config_file))\n+ with open(ns.config_file) as f:\n+ config = json.load(f)\n+ return config\n+\n+ def iopub_handler(self, message):\n+ \"\"\"Handles iopub requests.\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(2, \"iopub received:\", message)\n+\n+ def control_handler(self, wire_message):\n+ \"\"\"Handles control requests\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(1, \"control received:\", wire_message)\n+ identities, msg = self.deserialize_wire_message(wire_message)\n+ if msg[\"header\"][\"msg_type\"] == \"shutdown_request\":\n+ self.shutdown()\n+\n+ def stdin_handler(self, message):\n+ dprint(2, \"stdin received:\", message)\n+\n+ def start(self):\n+ \"\"\"Starts the server\"\"\"\n+ ioloop.install()\n+ connection = self.config[\"transport\"] + \"://\" + self.config[\"ip\"]\n+ secure_key = self.config[\"key\"].encode()\n+ digestmod = self.signature_schemes[self.config[\"signature_scheme\"]]\n+ self.auth = hmac.HMAC(secure_key, digestmod=digestmod)\n+\n+ # Heartbeat\n+ ctx = zmq.Context()\n+ self.heartbeat_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.REP)\n+ self.config[\"hb_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.heartbeat_socket, connection, self.config[\"hb_port\"]\n+ )\n+\n+ # IOPub/Sub, aslo called SubSocketChannel in IPython sources\n+ self.iopub_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.PUB)\n+ self.config[\"iopub_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.iopub_socket, connection, self.config[\"iopub_port\"]\n+ )\n+ self.iopub_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.iopub_socket)\n+ self.iopub_stream.on_recv(self.iopub_handler)\n+\n+ # Control\n+ self.control_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.ROUTER)\n+ self.config[\"control_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.control_socket, connection, self.config[\"control_port\"]\n+ )\n+ self.control_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.control_socket)\n+ self.control_stream.on_recv(self.control_handler)\n+\n+ # Stdin:\n+ self.stdin_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.ROUTER)\n+ self.config[\"stdin_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.stdin_socket, connection, self.config[\"stdin_port\"]\n+ )\n+ self.stdin_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.stdin_socket)\n+ self.stdin_stream.on_recv(self.stdin_handler)\n+\n+ # Shell\n+ self.shell_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.ROUTER)\n+ self.config[\"shell_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.shell_socket, connection, self.config[\"shell_port\"]\n+ )\n+ self.shell_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.shell_socket)\n+ self.shell_stream.on_recv(self.shell_handler)\n+\n+ # start up configurtation\n+ self.dprint(2, \"Config:\", json.dumps(self.config))\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Starting loops...\")\n+ self.hb_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.heartbeat_loop)\n+ self.hb_thread.daemon = True\n+ self.hb_thread.start()\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Ready! Listening...\")\n+ ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()\n+\n+ def shutdown(self):\n+ \"\"\"Shutsdown the kernel\"\"\"\n+ self.exiting = True\n+ ioloop.IOLoop.instance().stop()\n+\n+ def dprint(self, level, *args, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"Print but with debug information.\"\"\"\n+ if level <= self.debug_level:\n+ print(\"DEBUG\" + str(level) + \":\", file=sys.__stdout__, *args, **kwargs)\n+ sys.__stdout__.flush()\n+\n+ def sign(self, messages):\n+ \"\"\"Sign a message list with a secure signature.\"\"\"\n+ h = self.auth.copy()\n+ for m in messages:\n+ h.update(m)\n+ return h.hexdigest().encode(\"ascii\")\n+\n+ def new_header(self, message_type):\n+ \"\"\"Make a new header\"\"\"\n+ return {\n+ \"date\": datetime.datetime.now().isoformat(),\n+ \"msg_id\": str(uuid.uuid4()),\n+ \"username\": \"kernel\",\n+ \"session\": self.session_id,\n+ \"msg_type\": message_type,\n+ \"version\": \"5.0\",\n+ }\n+\n+ def send(\n+ self,\n+ stream,\n+ message_type,\n+ content=None,\n+ parent_header=None,\n+ metadata=None,\n+ identities=None,\n+ ):\n+ \"\"\"Send data to the client via a stream\"\"\"\n+ header = self.new_header(message_type)\n+ if content is None:\n+ content = {}\n+ if parent_header is None:\n+ parent_header = {}\n+ if metadata is None:\n+ metadata = {}\n+\n+ messages = list(map(dump_bytes, [header, parent_header, metadata, content]))\n+ signature = self.sign(messages)\n+ parts = [DELIM, signature] + messages\n+ if identities:\n+ parts = identities + parts\n+ self.dprint(3, \"send parts:\", parts)\n+ stream.send_multipart(parts)\n+ if isinstance(stream, zmqstream.ZMQStream):\n+ stream.flush()\n+\n+ def deserialize_wire_message(self, wire_message):\n+ \"\"\"Split the routing prefix and message frames from a message on the wire\"\"\"\n+ delim_idx = wire_message.index(DELIM)\n+ identities = wire_message[:delim_idx]\n+ m_signature = wire_message[delim_idx + 1]\n+ msg_frames = wire_message[delim_idx + 2 :]\n+\n+ keys = (\"header\", \"parent_header\", \"metadata\", \"content\")\n+ m = {k: load_bytes(v) for k, v in zip(keys, msg_frames)}\n+ check_sig = self.sign(msg_frames)\n+ if check_sig != m_signature:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Signatures do not match\")\n+ return identities, m\n+\n+ def run_thread(self, loop, name):\n+ \"\"\"Run main thread\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(2, \"Starting loop for {name!r}...\".format(name=name))\n+ while not self.exiting:\n+ self.dprint(2, \"{} Loop!\".format(name))\n+ try:\n+ loop.start()\n+ except ZMQError as e:\n+ self.dprint(1, \"{} ZMQError!\\n {}\".format(name, e))\n+ if e.errno == errno.EINTR:\n+ continue\n+ else:\n+ raise\n+ except Exception:\n+ self.dprint(2, \"{} Exception!\".format(name))\n+ if self.exiting:\n+ break\n+ else:\n+ raise\n+ else:\n+ self.dprint(2, \"{} Break!\".format(name))\n+ break\n+\n+ def heartbeat_loop(self):\n+ \"\"\"Run heartbeat\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(2, \"Starting heartbeat loop...\")\n+ while not self.exiting:\n+ self.dprint(3, \".\", end=\"\")\n+ try:\n+ zmq.device(zmq.FORWARDER, self.heartbeat_socket, self.heartbeat_socket)\n+ except zmq.ZMQError as e:\n+ if e.errno == errno.EINTR:\n+ continue\n+ else:\n+ raise\n+ else:\n+ break\n+\n+ def shell_handler(self, message):\n+ \"\"\"Dispatch shell messages to their handlers\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(1, \"received:\", message)\n+ position = 0\n+ identities, msg = self.deserialize_wire_message(message)\n+ handler = getattr(self, \"handle_\" + msg[\"header\"][\"msg_type\"], None)\n+ if handler is None:\n+ self.dprint(0, \"unknown message type:\", msg[\"header\"][\"msg_type\"])\n+ return\n+ handler(msg, identities)\n+\n+ def handle_execute_request(self, message, identities):\n+ \"\"\"Handle execute request messages.\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(2, \"Xonsh Kernel Executing:\", pformat(message[\"content\"][\"code\"]))\n+ # Start by sending busy signal\n+ content = {\"execution_state\": \"busy\"}\n+ self.send(self.iopub_stream, \"status\", content, parent_header=message[\"header\"])\n+\n+ # confirm the input that we are executing\n+ content = {\n+ \"execution_count\": self.execution_count,\n+ \"code\": message[\"content\"][\"code\"],\n+ }\n+ self.send(\n+ self.iopub_stream, \"execute_input\", content, parent_header=message[\"header\"]\n+ )\n+\n+ # execute the code\n+ metadata = {\n+ \"dependencies_met\": True,\n+ \"engine\": self.session_id,\n+ \"status\": \"ok\",\n+ \"started\": datetime.datetime.now().isoformat(),\n+ }\n+ content = self.do_execute(parent_header=message[\"header\"], **message[\"content\"])\n+ self.send(\n+ self.shell_stream,\n+ \"execute_reply\",\n+ content,\n+ metadata=metadata,\n+ parent_header=message[\"header\"],\n+ identities=identities,\n+ )\n+ self.execution_count += 1\n+\n+ # once we are done, send a signal that we are idle\n+ content = {\"execution_state\": \"idle\"}\n+ self.send(self.iopub_stream, \"status\", content, parent_header=message[\"header\"])\n+\n+ def do_execute(\n+ self,\n+ code=\"\",\n+ silent=False,\n+ store_history=True,\n+ user_expressions=None,\n+ allow_stdin=False,\n+ parent_header=None,\n+ **kwargs\n+ ):\n \"\"\"Execute user code.\"\"\"\n if len(code.strip()) == 0:\n- return {'status': 'ok', 'execution_count': self.execution_count,\n- 'payload': [], 'user_expressions': {}}\n+ return {\n+ \"status\": \"ok\",\n+ \"execution_count\": self.execution_count,\n+ \"payload\": [],\n+ \"user_expressions\": {},\n+ }\n shell = builtins.__xonsh_shell__\n hist = builtins.__xonsh_history__\n try:\n- shell.default(code)\n+ shell.default(code, self, parent_header)\n interrupted = False\n except KeyboardInterrupt:\n interrupted = True\n \n- if not silent: # stdout response\n- if hasattr(builtins, '_') and builtins._ is not None:\n- # rely on sys.displayhook functionality\n- self._respond_in_chunks('stdout', pformat(builtins._))\n- builtins._ = None\n- if hist is not None and len(hist) > 0:\n- self._respond_in_chunks('stdout', hist.outs[-1])\n-\n if interrupted:\n- return {'status': 'abort', 'execution_count': self.execution_count}\n+ return {\"status\": \"abort\", \"execution_count\": self.execution_count}\n \n rtn = 0 if (hist is None or len(hist) == 0) else hist.rtns[-1]\n if 0 < rtn:\n- message = {'status': 'error', 'execution_count': self.execution_count,\n- 'ename': '', 'evalue': str(rtn), 'traceback': []}\n+ message = {\n+ \"status\": \"error\",\n+ \"execution_count\": self.execution_count,\n+ \"ename\": \"\",\n+ \"evalue\": str(rtn),\n+ \"traceback\": [],\n+ }\n else:\n- message = {'status': 'ok', 'execution_count': self.execution_count,\n- 'payload': [], 'user_expressions': {}}\n+ message = {\n+ \"status\": \"ok\",\n+ \"execution_count\": self.execution_count,\n+ \"payload\": [],\n+ \"user_expressions\": {},\n+ }\n return message\n \n- def _respond_in_chunks(self, name, s, chunksize=1024):\n+ def _respond_in_chunks(self, name, s, chunksize=1024, parent_header=None):\n if s is None:\n return\n n = len(s)\n@@ -75,26 +401,67 @@ def _respond_in_chunks(self, name, s, chunksize=1024):\n lower = range(0, n, chunksize)\n upper = range(chunksize, n + chunksize, chunksize)\n for l, u in zip(lower, upper):\n- response = {'name': name, 'text': s[l:u], }\n- self.send_response(self.iopub_socket, 'stream', response)\n+ response = {\"name\": name, \"text\": s[l:u]}\n+ self.send(\n+ self.iopub_socket, \"stream\", response, parent_header=parent_header\n+ )\n+\n+ def handle_complete_request(self, message, identities):\n+ \"\"\"Handles kernel info requests.\"\"\"\n+ content = self.do_complete(\n+ message[\"content\"][\"code\"], message[\"content\"][\"cursor_pos\"]\n+ )\n+ self.send(\n+ self.shell_stream,\n+ \"complete_reply\",\n+ content,\n+ parent_header=message[\"header\"],\n+ identities=identities,\n+ )\n \n def do_complete(self, code, pos):\n \"\"\"Get completions.\"\"\"\n shell = builtins.__xonsh_shell__\n- line = code.split('\\n')[-1]\n+ line = code.split(\"\\n\")[-1]\n line = builtins.aliases.expand_alias(line)\n- prefix = line.split(' ')[-1]\n+ prefix = line.split(\" \")[-1]\n endidx = pos\n begidx = pos - len(prefix)\n- rtn, _ = self.completer.complete(prefix, line, begidx,\n- endidx, shell.ctx)\n- message = {'matches': rtn, 'cursor_start': begidx, 'cursor_end': endidx,\n- 'metadata': {}, 'status': 'ok'}\n+ rtn, _ = self.completer.complete(prefix, line, begidx, endidx, shell.ctx)\n+ if isinstance(rtn, Set):\n+ rtn = list(rtn)\n+ message = {\n+ \"matches\": rtn,\n+ \"cursor_start\": begidx,\n+ \"cursor_end\": endidx,\n+ \"metadata\": {},\n+ \"status\": \"ok\",\n+ }\n return message\n \n+ def handle_kernel_info_request(self, message, identities):\n+ \"\"\"Handles kernel info requests.\"\"\"\n+ content = {\n+ \"protocol_version\": \"5.0\",\n+ \"ipython_version\": [1, 1, 0, \"\"],\n+ \"language\": self.language,\n+ \"language_version\": self.language_version,\n+ \"implementation\": self.implementation,\n+ \"implementation_version\": self.implementation_version,\n+ \"language_info\": self.language_info,\n+ \"banner\": self.banner,\n+ }\n+ self.send(\n+ self.shell_stream,\n+ \"kernel_info_reply\",\n+ content,\n+ parent_header=message[\"header\"],\n+ identities=identities,\n+ )\n+\n \n-if __name__ == '__main__':\n- from ipykernel.kernelapp import IPKernelApp\n- # must manually pass in args to avoid interfering w/ Jupyter arg parsing\n- with main_context(argv=['--shell-type=readline']):\n- IPKernelApp.launch_instance(kernel_class=XonshKernel)\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ setup(shell_type=\"jupyter\", env={})\n+ shell = builtins.__xonsh_shell__\n+ kernel = shell.kernel = XonshKernel()\n+ kernel.start()\ndiff --git a/xonsh/jupyter_shell.py b/xonsh/jupyter_shell.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..52943469be\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/xonsh/jupyter_shell.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@\n+\"\"\"An interactive shell for the Jupyter kernel.\"\"\"\n+import io\n+import sys\n+import builtins\n+\n+from xonsh.base_shell import BaseShell\n+\n+\n+class StdJupyterRedirectBuf(io.RawIOBase):\n+ \"\"\"Redirects standard I/O buffers to the Jupyter kernel.\"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, redirect):\n+ self.redirect = redirect\n+ self.encoding = redirect.encoding\n+ self.errors = redirect.errors\n+\n+ def fileno(self):\n+ \"\"\"Returns the file descriptor of the std buffer.\"\"\"\n+ return self.redirect.fileno()\n+\n+ def seek(self, offset, whence=io.SEEK_SET):\n+ \"\"\"Sets the location in both the stdbuf and the membuf.\"\"\"\n+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot seek Jupyter redirect')\n+\n+ def truncate(self, size=None):\n+ \"\"\"Truncate both buffers.\"\"\"\n+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot truncate Jupyter redirect')\n+\n+ def readinto(self, b):\n+ \"\"\"Read bytes into buffer from both streams.\"\"\"\n+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot read into Jupyter redirect')\n+\n+ def write(self, b):\n+ \"\"\"Write bytes to kernel.\"\"\"\n+ s = b if isinstance(b, str) else b.decode(self.encoding, self.errors)\n+ self.redirect.write(s)\n+\n+\n+class StdJupyterRedirect(io.TextIOBase):\n+ \"\"\"Redirects a standard I/O stream to the Jupyter kernel.\"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, name, kernel, parent_header=None):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Parameters\n+ ----------\n+ name : str\n+ The name of the buffer in the sys module, e.g. 'stdout'.\n+ kernel : XonshKernel\n+ Instance of a Jupyter kernel\n+ parent_header : dict or None, optional\n+ parent header information to pass along with the kernel\n+ \"\"\"\n+ self._name = name\n+ self.kernel = kernel\n+ self.parent_header = parent_header\n+\n+ self.std = getattr(sys, name)\n+ self.buffer = StdJupyterRedirectBuf(self)\n+ setattr(sys, name, self)\n+\n+ @property\n+ def encoding(self):\n+ \"\"\"The encoding of the stream\"\"\"\n+ env = builtins.__xonsh_env__\n+ return getattr(self.std, 'encoding', env.get('XONSH_ENCODING'))\n+\n+ @property\n+ def errors(self):\n+ \"\"\"The encoding errors of the stream\"\"\"\n+ env = builtins.__xonsh_env__\n+ return getattr(self.std, 'errors', env.get('XONSH_ENCODING_ERRORS'))\n+\n+ @property\n+ def newlines(self):\n+ \"\"\"The newlines of the standard buffer.\"\"\"\n+ return self.std.newlines\n+\n+ def _replace_std(self):\n+ std = self.std\n+ if std is None:\n+ return\n+ setattr(sys, self._name, std)\n+ self.std = None\n+\n+ def __del__(self):\n+ self._replace_std()\n+\n+ def close(self):\n+ \"\"\"Restores the original std stream.\"\"\"\n+ self._replace_std()\n+\n+ def __enter__(self):\n+ return self\n+\n+ def __exit__(self, *args, **kwargs):\n+ self.close()\n+\n+ def write(self, s):\n+ \"\"\"Writes data to the original kernel stream.\"\"\"\n+ self.kernel._respond_in_chunks(self._name, s,\n+ parent_header=self.parent_header)\n+\n+ def flush(self):\n+ \"\"\"Flushes kernel iopub_stream.\"\"\"\n+ self.kernel.iopub_stream.flush()\n+\n+ def fileno(self):\n+ \"\"\"Tunnel fileno() calls to the std stream.\"\"\"\n+ return self.std.fileno()\n+\n+ def seek(self, offset, whence=io.SEEK_SET):\n+ \"\"\"Seek to a location.\"\"\"\n+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot seek Jupyter redirect')\n+\n+ def truncate(self, size=None):\n+ \"\"\"Truncate the streams.\"\"\"\n+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot truncate Jupyter redirect')\n+\n+ def detach(self):\n+ \"\"\"This operation is not supported.\"\"\"\n+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot detach a Jupyter redirect')\n+\n+ def read(self, size=None):\n+ \"\"\"Read from the stream\"\"\"\n+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot read a Jupyter redirect')\n+\n+ def readline(self, size=-1):\n+ \"\"\"Read a line.\"\"\"\n+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot read a line from a Jupyter redirect')\n+\n+\n+class JupyterShell(BaseShell):\n+ \"\"\"A shell for the Jupyter kernel.\"\"\"\n+\n+ def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):\n+ super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)\n+ self.kernel = None\n+\n+ def default(self, line, kernel, parent_header=None):\n+ \"\"\"Executes code, but redirects output to Jupyter client\"\"\"\n+ stdout = StdJupyterRedirect('stdout', kernel, parent_header)\n+ stderr = StdJupyterRedirect('stderr', kernel, parent_header)\n+ with stdout, stderr:\n+ rtn = super().default(line)\n+ return rtn\ndiff --git a/xonsh/main.py b/xonsh/main.py\nindex 9d59c0bbb1..e9043a5b2f 100644\n--- a/xonsh/main.py\n+++ b/xonsh/main.py\n@@ -436,6 +436,6 @@ def setup(ctx=None, shell_type='none', env=(('RAISE_SUBPROC_ERROR', True),)):\n builtins.__xonsh_execer__ = Execer(xonsh_ctx=ctx)\n builtins.__xonsh_shell__ = Shell(builtins.__xonsh_execer__,\n ctx=ctx,\n- shell_type='none')\n+ shell_type=shell_type)\n builtins.__xonsh_env__.update(env)\n install_import_hooks()\ndiff --git a/xonsh/shell.py b/xonsh/shell.py\nindex 2c1e79c525..74a35978e9 100644\n--- a/xonsh/shell.py\n+++ b/xonsh/shell.py\n@@ -166,6 +166,8 @@ def __init__(self, execer, ctx=None, shell_type=None, **kwargs):\n from xonsh.ptk.shell import PromptToolkitShell as shell_class\n elif shell_type == 'readline':\n from xonsh.readline_shell import ReadlineShell as shell_class\n+ elif shell_type == 'jupyter':\n+ from xonsh.jupyter_shell import JupyterShell as shell_class\n else:\n raise XonshError('{} is not recognized as a shell type'.format(\n shell_type))\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1,72 +1,398 @@\n # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-\n \"\"\"Hooks for Jupyter Xonsh Kernel.\"\"\"\n+import sys\n+import json\n+import hmac\n+import uuid\n+import errno\n+import hashlib\n+import datetime\n import builtins\n+import threading\n from pprint import pformat\n+from argparse import ArgumentParser\n+from collections.abc import Set\n \n-from ipykernel.kernelbase import Kernel\n+import zmq\n+from zmq.eventloop import ioloop, zmqstream\n+from zmq.error import ZMQError\n \n from xonsh import __version__ as version\n-from xonsh.main import main_context\n+from xonsh.main import setup\n from xonsh.completer import Completer\n \n \n MAX_SIZE = 8388608 # 8 Mb\n+DELIM = b\"<IDS|MSG>\"\n \n \n-class XonshKernel(Kernel):\n+def dump_bytes(*args, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"Converts an object to JSON and returns the bytes.\"\"\"\n+ return json.dumps(*args, **kwargs).encode(\"ascii\")\n+\n+\n+def load_bytes(b):\n+ \"\"\"Converts bytes of JSON to an object.\"\"\"\n+ return json.loads(b.decode(\"ascii\"))\n+\n+\n+def bind(socket, connection, port):\n+ \"\"\"Binds a socket to a port, or a random port if needed. Returns the port.\"\"\"\n+ if port <= 0:\n+ return socket.bind_to_random_port(connection)\n+ else:\n+ socket.bind(\"{}:{}\".format(connection, port))\n+ return port\n+\n+\n+class XonshKernel:\n \"\"\"Xonsh xernal for Jupyter\"\"\"\n- implementation = 'Xonsh ' + version\n+\n+ implementation = \"Xonsh \" + version\n implementation_version = version\n- language = 'xonsh'\n- language_version = version\n- banner = 'Xonsh - Python-powered, cross-platform shell'\n- language_info = {'name': 'xonsh',\n- 'version': version,\n- 'pygments_lexer': 'xonsh',\n- 'codemirror_mode': 'shell',\n- 'mimetype': 'text/x-sh',\n- 'file_extension': '.xsh',\n- }\n-\n- def __init__(self, **kwargs):\n+ language = \"xonsh\"\n+ language_version = version.split(\".\")[:3]\n+ banner = \"Xonsh - Python-powered, cross-platform shell\"\n+ language_info = {\n+ \"name\": \"xonsh\",\n+ \"version\": version,\n+ \"pygments_lexer\": \"xonsh\",\n+ \"codemirror_mode\": \"shell\",\n+ \"mimetype\": \"text/x-sh\",\n+ \"file_extension\": \".xsh\",\n+ }\n+ signature_schemes = {\"hmac-sha256\": hashlib.sha256}\n+\n+ def __init__(self, debug_level=0, session_id=None, config=None, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Parameters\n+ ----------\n+ debug_level : int, optional\n+ Integer from 0 (no debugging) to 3 (all debugging), default: 0.\n+ session_id : str or None, optional\n+ Unique string id representing the kernel session. If None, this will\n+ be replaced with a random UUID.\n+ config : dict or None, optional\n+ Configuration dictionary to start server with. BY default will\n+ search the command line for options (if given) or use default\n+ configuration.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ self.debug_level = debug_level\n+ self.session_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) if session_id is None else session_id\n+ self._parser = None\n+ self.config = self.make_default_config() if config is None else config\n+\n+ self.exiting = False\n+ self.execution_count = 1\n self.completer = Completer()\n- super().__init__(**kwargs)\n \n- def do_execute(self, code, silent, store_history=True, user_expressions=None,\n- allow_stdin=False):\n+ @property\n+ def parser(self):\n+ if self._parser is None:\n+ p = ArgumentParser(\"jupyter_kerenel\")\n+ p.add_argument(\"-f\", dest=\"config_file\", default=None)\n+ self._parser = p\n+ return self._parser\n+\n+ def make_default_config(self):\n+ \"\"\"Provides default configuration\"\"\"\n+ ns, unknown = self.parser.parse_known_args(sys.argv)\n+ if ns.config_file is None:\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Starting xonsh kernel with default args...\")\n+ config = {\n+ \"control_port\": 0,\n+ \"hb_port\": 0,\n+ \"iopub_port\": 0,\n+ \"ip\": \"127.0.0.1\",\n+ \"key\": str(uuid.uuid4()),\n+ \"shell_port\": 0,\n+ \"signature_scheme\": \"hmac-sha256\",\n+ \"stdin_port\": 0,\n+ \"transport\": \"tcp\",\n+ }\n+ else:\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Loading simple_kernel with args:\", sys.argv)\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Reading config file {!r}...\".format(ns.config_file))\n+ with open(ns.config_file) as f:\n+ config = json.load(f)\n+ return config\n+\n+ def iopub_handler(self, message):\n+ \"\"\"Handles iopub requests.\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(2, \"iopub received:\", message)\n+\n+ def control_handler(self, wire_message):\n+ \"\"\"Handles control requests\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(1, \"control received:\", wire_message)\n+ identities, msg = self.deserialize_wire_message(wire_message)\n+ if msg[\"header\"][\"msg_type\"] == \"shutdown_request\":\n+ self.shutdown()\n+\n+ def stdin_handler(self, message):\n+ dprint(2, \"stdin received:\", message)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 132,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis should be `self.dprint`"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1,72 +1,398 @@\n # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-\n \"\"\"Hooks for Jupyter Xonsh Kernel.\"\"\"\n+import sys\n+import json\n+import hmac\n+import uuid\n+import errno\n+import hashlib\n+import datetime\n import builtins\n+import threading\n from pprint import pformat\n+from argparse import ArgumentParser\n+from collections.abc import Set\n \n-from ipykernel.kernelbase import Kernel\n+import zmq\n+from zmq.eventloop import ioloop, zmqstream\n+from zmq.error import ZMQError\n \n from xonsh import __version__ as version\n-from xonsh.main import main_context\n+from xonsh.main import setup\n from xonsh.completer import Completer\n \n \n MAX_SIZE = 8388608 # 8 Mb\n+DELIM = b\"<IDS|MSG>\"\n \n \n-class XonshKernel(Kernel):\n+def dump_bytes(*args, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"Converts an object to JSON and returns the bytes.\"\"\"\n+ return json.dumps(*args, **kwargs).encode(\"ascii\")\n+\n+\n+def load_bytes(b):\n+ \"\"\"Converts bytes of JSON to an object.\"\"\"\n+ return json.loads(b.decode(\"ascii\"))\n+\n+\n+def bind(socket, connection, port):\n+ \"\"\"Binds a socket to a port, or a random port if needed. Returns the port.\"\"\"\n+ if port <= 0:\n+ return socket.bind_to_random_port(connection)\n+ else:\n+ socket.bind(\"{}:{}\".format(connection, port))\n+ return port\n+\n+\n+class XonshKernel:\n \"\"\"Xonsh xernal for Jupyter\"\"\"\n- implementation = 'Xonsh ' + version\n+\n+ implementation = \"Xonsh \" + version\n implementation_version = version\n- language = 'xonsh'\n- language_version = version\n- banner = 'Xonsh - Python-powered, cross-platform shell'\n- language_info = {'name': 'xonsh',\n- 'version': version,\n- 'pygments_lexer': 'xonsh',\n- 'codemirror_mode': 'shell',\n- 'mimetype': 'text/x-sh',\n- 'file_extension': '.xsh',\n- }\n-\n- def __init__(self, **kwargs):\n+ language = \"xonsh\"\n+ language_version = version.split(\".\")[:3]\n+ banner = \"Xonsh - Python-powered, cross-platform shell\"\n+ language_info = {\n+ \"name\": \"xonsh\",\n+ \"version\": version,\n+ \"pygments_lexer\": \"xonsh\",\n+ \"codemirror_mode\": \"shell\",\n+ \"mimetype\": \"text/x-sh\",\n+ \"file_extension\": \".xsh\",\n+ }\n+ signature_schemes = {\"hmac-sha256\": hashlib.sha256}\n+\n+ def __init__(self, debug_level=0, session_id=None, config=None, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Parameters\n+ ----------\n+ debug_level : int, optional\n+ Integer from 0 (no debugging) to 3 (all debugging), default: 0.\n+ session_id : str or None, optional\n+ Unique string id representing the kernel session. If None, this will\n+ be replaced with a random UUID.\n+ config : dict or None, optional\n+ Configuration dictionary to start server with. BY default will\n+ search the command line for options (if given) or use default\n+ configuration.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ self.debug_level = debug_level\n+ self.session_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) if session_id is None else session_id\n+ self._parser = None\n+ self.config = self.make_default_config() if config is None else config\n+\n+ self.exiting = False\n+ self.execution_count = 1\n self.completer = Completer()\n- super().__init__(**kwargs)\n \n- def do_execute(self, code, silent, store_history=True, user_expressions=None,\n- allow_stdin=False):\n+ @property\n+ def parser(self):\n+ if self._parser is None:\n+ p = ArgumentParser(\"jupyter_kerenel\")\n+ p.add_argument(\"-f\", dest=\"config_file\", default=None)\n+ self._parser = p\n+ return self._parser\n+\n+ def make_default_config(self):\n+ \"\"\"Provides default configuration\"\"\"\n+ ns, unknown = self.parser.parse_known_args(sys.argv)\n+ if ns.config_file is None:\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Starting xonsh kernel with default args...\")\n+ config = {\n+ \"control_port\": 0,\n+ \"hb_port\": 0,\n+ \"iopub_port\": 0,\n+ \"ip\": \"127.0.0.1\",\n+ \"key\": str(uuid.uuid4()),\n+ \"shell_port\": 0,\n+ \"signature_scheme\": \"hmac-sha256\",\n+ \"stdin_port\": 0,\n+ \"transport\": \"tcp\",\n+ }\n+ else:\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Loading simple_kernel with args:\", sys.argv)\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Reading config file {!r}...\".format(ns.config_file))\n+ with open(ns.config_file) as f:\n+ config = json.load(f)\n+ return config\n+\n+ def iopub_handler(self, message):\n+ \"\"\"Handles iopub requests.\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(2, \"iopub received:\", message)\n+\n+ def control_handler(self, wire_message):\n+ \"\"\"Handles control requests\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(1, \"control received:\", wire_message)\n+ identities, msg = self.deserialize_wire_message(wire_message)\n+ if msg[\"header\"][\"msg_type\"] == \"shutdown_request\":\n+ self.shutdown()\n+\n+ def stdin_handler(self, message):\n+ dprint(2, \"stdin received:\", message)\n+\n+ def start(self):\n+ \"\"\"Starts the server\"\"\"\n+ ioloop.install()\n+ connection = self.config[\"transport\"] + \"://\" + self.config[\"ip\"]\n+ secure_key = self.config[\"key\"].encode()\n+ digestmod = self.signature_schemes[self.config[\"signature_scheme\"]]\n+ self.auth = hmac.HMAC(secure_key, digestmod=digestmod)\n+\n+ # Heartbeat\n+ ctx = zmq.Context()\n+ self.heartbeat_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.REP)\n+ self.config[\"hb_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.heartbeat_socket, connection, self.config[\"hb_port\"]\n+ )\n+\n+ # IOPub/Sub, aslo called SubSocketChannel in IPython sources\n+ self.iopub_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.PUB)\n+ self.config[\"iopub_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.iopub_socket, connection, self.config[\"iopub_port\"]\n+ )\n+ self.iopub_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.iopub_socket)\n+ self.iopub_stream.on_recv(self.iopub_handler)\n+\n+ # Control\n+ self.control_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.ROUTER)\n+ self.config[\"control_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.control_socket, connection, self.config[\"control_port\"]\n+ )\n+ self.control_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.control_socket)\n+ self.control_stream.on_recv(self.control_handler)\n+\n+ # Stdin:\n+ self.stdin_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.ROUTER)\n+ self.config[\"stdin_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.stdin_socket, connection, self.config[\"stdin_port\"]\n+ )\n+ self.stdin_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.stdin_socket)\n+ self.stdin_stream.on_recv(self.stdin_handler)\n+\n+ # Shell\n+ self.shell_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.ROUTER)\n+ self.config[\"shell_port\"] = bind(\n+ self.shell_socket, connection, self.config[\"shell_port\"]\n+ )\n+ self.shell_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.shell_socket)\n+ self.shell_stream.on_recv(self.shell_handler)\n+\n+ # start up configurtation\n+ self.dprint(2, \"Config:\", json.dumps(self.config))\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Starting loops...\")\n+ self.hb_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.heartbeat_loop)\n+ self.hb_thread.daemon = True\n+ self.hb_thread.start()\n+ self.dprint(1, \"Ready! Listening...\")\n+ ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()\n+\n+ def shutdown(self):\n+ \"\"\"Shutsdown the kernel\"\"\"\n+ self.exiting = True\n+ ioloop.IOLoop.instance().stop()\n+\n+ def dprint(self, level, *args, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"Print but with debug information.\"\"\"\n+ if level <= self.debug_level:\n+ print(\"DEBUG\" + str(level) + \":\", file=sys.__stdout__, *args, **kwargs)\n+ sys.__stdout__.flush()\n+\n+ def sign(self, messages):\n+ \"\"\"Sign a message list with a secure signature.\"\"\"\n+ h = self.auth.copy()\n+ for m in messages:\n+ h.update(m)\n+ return h.hexdigest().encode(\"ascii\")\n+\n+ def new_header(self, message_type):\n+ \"\"\"Make a new header\"\"\"\n+ return {\n+ \"date\": datetime.datetime.now().isoformat(),\n+ \"msg_id\": str(uuid.uuid4()),\n+ \"username\": \"kernel\",\n+ \"session\": self.session_id,\n+ \"msg_type\": message_type,\n+ \"version\": \"5.0\",\n+ }\n+\n+ def send(\n+ self,\n+ stream,\n+ message_type,\n+ content=None,\n+ parent_header=None,\n+ metadata=None,\n+ identities=None,\n+ ):\n+ \"\"\"Send data to the client via a stream\"\"\"\n+ header = self.new_header(message_type)\n+ if content is None:\n+ content = {}\n+ if parent_header is None:\n+ parent_header = {}\n+ if metadata is None:\n+ metadata = {}\n+\n+ messages = list(map(dump_bytes, [header, parent_header, metadata, content]))\n+ signature = self.sign(messages)\n+ parts = [DELIM, signature] + messages\n+ if identities:\n+ parts = identities + parts\n+ self.dprint(3, \"send parts:\", parts)\n+ stream.send_multipart(parts)\n+ if isinstance(stream, zmqstream.ZMQStream):\n+ stream.flush()\n+\n+ def deserialize_wire_message(self, wire_message):\n+ \"\"\"Split the routing prefix and message frames from a message on the wire\"\"\"\n+ delim_idx = wire_message.index(DELIM)\n+ identities = wire_message[:delim_idx]\n+ m_signature = wire_message[delim_idx + 1]\n+ msg_frames = wire_message[delim_idx + 2 :]\n+\n+ keys = (\"header\", \"parent_header\", \"metadata\", \"content\")\n+ m = {k: load_bytes(v) for k, v in zip(keys, msg_frames)}\n+ check_sig = self.sign(msg_frames)\n+ if check_sig != m_signature:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Signatures do not match\")\n+ return identities, m\n+\n+ def run_thread(self, loop, name):\n+ \"\"\"Run main thread\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(2, \"Starting loop for {name!r}...\".format(name=name))\n+ while not self.exiting:\n+ self.dprint(2, \"{} Loop!\".format(name))\n+ try:\n+ loop.start()\n+ except ZMQError as e:\n+ self.dprint(1, \"{} ZMQError!\\n {}\".format(name, e))\n+ if e.errno == errno.EINTR:\n+ continue\n+ else:\n+ raise\n+ except Exception:\n+ self.dprint(2, \"{} Exception!\".format(name))\n+ if self.exiting:\n+ break\n+ else:\n+ raise\n+ else:\n+ self.dprint(2, \"{} Break!\".format(name))\n+ break\n+\n+ def heartbeat_loop(self):\n+ \"\"\"Run heartbeat\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(2, \"Starting heartbeat loop...\")\n+ while not self.exiting:\n+ self.dprint(3, \".\", end=\"\")\n+ try:\n+ zmq.device(zmq.FORWARDER, self.heartbeat_socket, self.heartbeat_socket)\n+ except zmq.ZMQError as e:\n+ if e.errno == errno.EINTR:\n+ continue\n+ else:\n+ raise\n+ else:\n+ break\n+\n+ def shell_handler(self, message):\n+ \"\"\"Dispatch shell messages to their handlers\"\"\"\n+ self.dprint(1, \"received:\", message)\n+ position = 0",
"line": null,
"original_line": 302,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n`position` is unused"
}
] |
abd568fcccdb2fc223b7a773c7b7b07655d8b78c
|
diff --git a/docs/api/index.rst b/docs/api/index.rst
index 50aa585c16..b659117709 100644
--- a/docs/api/index.rst
+++ b/docs/api/index.rst
@@ -77,6 +77,7 @@ For those of you who want the gritty details.
color_tools
pyghooks
jupyter_kernel
+ jupyter_shell
wizard
xonfig
codecache
diff --git a/docs/api/jupyter_shell.rst b/docs/api/jupyter_shell.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dc2f277000
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/api/jupyter_shell.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+.. _xonsh_jupyter_shell:
+
+******************************************
+Jupyter Shell (``xonsh.jupyter_shell``)
+******************************************
+
+.. automodule:: xonsh.jupyter_shell
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+
diff --git a/news/xernel.rst b/news/xernel.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0f2dbc6ed9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/xernel.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+**Added:**
+
+* New ``JupyterShell`` for interactive interfacing with Jupyter.
+
+**Changed:** None
+
+**Deprecated:** None
+
+**Removed:** None
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* The JupyterKernel has been fixed from a rather broken state.
+
+**Security:** None
diff --git a/requirements-docs.txt b/requirements-docs.txt
index 1cdc198684..610f47ee97 100644
--- a/requirements-docs.txt
+++ b/requirements-docs.txt
@@ -5,6 +5,6 @@ prompt_toolkit
pygments
ply
psutil
-ipykernel
+pyzmq
matplotlib
doctr
diff --git a/setup.cfg b/setup.cfg
index 08564869c0..3c63d2e3db 100644
--- a/setup.cfg
+++ b/setup.cfg
@@ -11,6 +11,7 @@ flake8-ignore =
xonsh/built_ins.py F821 E721
xonsh/commands_cache.py F841
xonsh/history.py F821
+ xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py E203
xonsh/pyghooks.py F821
xonsh/style_tools.py F821
xonsh/readline_shell.py F401
diff --git a/xonsh/__init__.py b/xonsh/__init__.py
index ceeaaee274..f68c68cbf2 100644
--- a/xonsh/__init__.py
+++ b/xonsh/__init__.py
@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@
# amalgamate exclude jupyter_kernel parser_table parser_test_table pyghooks
# amalgamate exclude winutils wizard pytest_plugin fs macutils pygments_cache
+# amalgamate exclude jupyter_shell
import os as _os
if _os.getenv('XONSH_DEBUG', ''):
pass
diff --git a/xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py b/xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py
index 93433dc8d1..aeb956bec3 100644
--- a/xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py
+++ b/xonsh/jupyter_kernel.py
@@ -1,72 +1,397 @@
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""Hooks for Jupyter Xonsh Kernel."""
+import sys
+import json
+import hmac
+import uuid
+import errno
+import hashlib
+import datetime
import builtins
+import threading
from pprint import pformat
+from argparse import ArgumentParser
+from collections.abc import Set
-from ipykernel.kernelbase import Kernel
+import zmq
+from zmq.eventloop import ioloop, zmqstream
+from zmq.error import ZMQError
from xonsh import __version__ as version
-from xonsh.main import main_context
+from xonsh.main import setup
from xonsh.completer import Completer
MAX_SIZE = 8388608 # 8 Mb
+DELIM = b"<IDS|MSG>"
-class XonshKernel(Kernel):
+def dump_bytes(*args, **kwargs):
+ """Converts an object to JSON and returns the bytes."""
+ return json.dumps(*args, **kwargs).encode("ascii")
+
+
+def load_bytes(b):
+ """Converts bytes of JSON to an object."""
+ return json.loads(b.decode("ascii"))
+
+
+def bind(socket, connection, port):
+ """Binds a socket to a port, or a random port if needed. Returns the port."""
+ if port <= 0:
+ return socket.bind_to_random_port(connection)
+ else:
+ socket.bind("{}:{}".format(connection, port))
+ return port
+
+
+class XonshKernel:
"""Xonsh xernal for Jupyter"""
- implementation = 'Xonsh ' + version
+
+ implementation = "Xonsh " + version
implementation_version = version
- language = 'xonsh'
- language_version = version
- banner = 'Xonsh - Python-powered, cross-platform shell'
- language_info = {'name': 'xonsh',
- 'version': version,
- 'pygments_lexer': 'xonsh',
- 'codemirror_mode': 'shell',
- 'mimetype': 'text/x-sh',
- 'file_extension': '.xsh',
- }
-
- def __init__(self, **kwargs):
+ language = "xonsh"
+ language_version = version.split(".")[:3]
+ banner = "Xonsh - Python-powered, cross-platform shell"
+ language_info = {
+ "name": "xonsh",
+ "version": version,
+ "pygments_lexer": "xonsh",
+ "codemirror_mode": "shell",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-sh",
+ "file_extension": ".xsh",
+ }
+ signature_schemes = {"hmac-sha256": hashlib.sha256}
+
+ def __init__(self, debug_level=0, session_id=None, config=None, **kwargs):
+ """
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ debug_level : int, optional
+ Integer from 0 (no debugging) to 3 (all debugging), default: 0.
+ session_id : str or None, optional
+ Unique string id representing the kernel session. If None, this will
+ be replaced with a random UUID.
+ config : dict or None, optional
+ Configuration dictionary to start server with. BY default will
+ search the command line for options (if given) or use default
+ configuration.
+ """
+ self.debug_level = debug_level
+ self.session_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) if session_id is None else session_id
+ self._parser = None
+ self.config = self.make_default_config() if config is None else config
+
+ self.exiting = False
+ self.execution_count = 1
self.completer = Completer()
- super().__init__(**kwargs)
- def do_execute(self, code, silent, store_history=True, user_expressions=None,
- allow_stdin=False):
+ @property
+ def parser(self):
+ if self._parser is None:
+ p = ArgumentParser("jupyter_kerenel")
+ p.add_argument("-f", dest="config_file", default=None)
+ self._parser = p
+ return self._parser
+
+ def make_default_config(self):
+ """Provides default configuration"""
+ ns, unknown = self.parser.parse_known_args(sys.argv)
+ if ns.config_file is None:
+ self.dprint(1, "Starting xonsh kernel with default args...")
+ config = {
+ "control_port": 0,
+ "hb_port": 0,
+ "iopub_port": 0,
+ "ip": "127.0.0.1",
+ "key": str(uuid.uuid4()),
+ "shell_port": 0,
+ "signature_scheme": "hmac-sha256",
+ "stdin_port": 0,
+ "transport": "tcp",
+ }
+ else:
+ self.dprint(1, "Loading simple_kernel with args:", sys.argv)
+ self.dprint(1, "Reading config file {!r}...".format(ns.config_file))
+ with open(ns.config_file) as f:
+ config = json.load(f)
+ return config
+
+ def iopub_handler(self, message):
+ """Handles iopub requests."""
+ self.dprint(2, "iopub received:", message)
+
+ def control_handler(self, wire_message):
+ """Handles control requests"""
+ self.dprint(1, "control received:", wire_message)
+ identities, msg = self.deserialize_wire_message(wire_message)
+ if msg["header"]["msg_type"] == "shutdown_request":
+ self.shutdown()
+
+ def stdin_handler(self, message):
+ self.dprint(2, "stdin received:", message)
+
+ def start(self):
+ """Starts the server"""
+ ioloop.install()
+ connection = self.config["transport"] + "://" + self.config["ip"]
+ secure_key = self.config["key"].encode()
+ digestmod = self.signature_schemes[self.config["signature_scheme"]]
+ self.auth = hmac.HMAC(secure_key, digestmod=digestmod)
+
+ # Heartbeat
+ ctx = zmq.Context()
+ self.heartbeat_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.REP)
+ self.config["hb_port"] = bind(
+ self.heartbeat_socket, connection, self.config["hb_port"]
+ )
+
+ # IOPub/Sub, aslo called SubSocketChannel in IPython sources
+ self.iopub_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.PUB)
+ self.config["iopub_port"] = bind(
+ self.iopub_socket, connection, self.config["iopub_port"]
+ )
+ self.iopub_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.iopub_socket)
+ self.iopub_stream.on_recv(self.iopub_handler)
+
+ # Control
+ self.control_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.ROUTER)
+ self.config["control_port"] = bind(
+ self.control_socket, connection, self.config["control_port"]
+ )
+ self.control_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.control_socket)
+ self.control_stream.on_recv(self.control_handler)
+
+ # Stdin:
+ self.stdin_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.ROUTER)
+ self.config["stdin_port"] = bind(
+ self.stdin_socket, connection, self.config["stdin_port"]
+ )
+ self.stdin_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.stdin_socket)
+ self.stdin_stream.on_recv(self.stdin_handler)
+
+ # Shell
+ self.shell_socket = ctx.socket(zmq.ROUTER)
+ self.config["shell_port"] = bind(
+ self.shell_socket, connection, self.config["shell_port"]
+ )
+ self.shell_stream = zmqstream.ZMQStream(self.shell_socket)
+ self.shell_stream.on_recv(self.shell_handler)
+
+ # start up configurtation
+ self.dprint(2, "Config:", json.dumps(self.config))
+ self.dprint(1, "Starting loops...")
+ self.hb_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.heartbeat_loop)
+ self.hb_thread.daemon = True
+ self.hb_thread.start()
+ self.dprint(1, "Ready! Listening...")
+ ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
+
+ def shutdown(self):
+ """Shutsdown the kernel"""
+ self.exiting = True
+ ioloop.IOLoop.instance().stop()
+
+ def dprint(self, level, *args, **kwargs):
+ """Print but with debug information."""
+ if level <= self.debug_level:
+ print("DEBUG" + str(level) + ":", file=sys.__stdout__, *args, **kwargs)
+ sys.__stdout__.flush()
+
+ def sign(self, messages):
+ """Sign a message list with a secure signature."""
+ h = self.auth.copy()
+ for m in messages:
+ h.update(m)
+ return h.hexdigest().encode("ascii")
+
+ def new_header(self, message_type):
+ """Make a new header"""
+ return {
+ "date": datetime.datetime.now().isoformat(),
+ "msg_id": str(uuid.uuid4()),
+ "username": "kernel",
+ "session": self.session_id,
+ "msg_type": message_type,
+ "version": "5.0",
+ }
+
+ def send(
+ self,
+ stream,
+ message_type,
+ content=None,
+ parent_header=None,
+ metadata=None,
+ identities=None,
+ ):
+ """Send data to the client via a stream"""
+ header = self.new_header(message_type)
+ if content is None:
+ content = {}
+ if parent_header is None:
+ parent_header = {}
+ if metadata is None:
+ metadata = {}
+
+ messages = list(map(dump_bytes, [header, parent_header, metadata, content]))
+ signature = self.sign(messages)
+ parts = [DELIM, signature] + messages
+ if identities:
+ parts = identities + parts
+ self.dprint(3, "send parts:", parts)
+ stream.send_multipart(parts)
+ if isinstance(stream, zmqstream.ZMQStream):
+ stream.flush()
+
+ def deserialize_wire_message(self, wire_message):
+ """Split the routing prefix and message frames from a message on the wire"""
+ delim_idx = wire_message.index(DELIM)
+ identities = wire_message[:delim_idx]
+ m_signature = wire_message[delim_idx + 1]
+ msg_frames = wire_message[delim_idx + 2 :]
+
+ keys = ("header", "parent_header", "metadata", "content")
+ m = {k: load_bytes(v) for k, v in zip(keys, msg_frames)}
+ check_sig = self.sign(msg_frames)
+ if check_sig != m_signature:
+ raise ValueError("Signatures do not match")
+ return identities, m
+
+ def run_thread(self, loop, name):
+ """Run main thread"""
+ self.dprint(2, "Starting loop for {name!r}...".format(name=name))
+ while not self.exiting:
+ self.dprint(2, "{} Loop!".format(name))
+ try:
+ loop.start()
+ except ZMQError as e:
+ self.dprint(1, "{} ZMQError!\n {}".format(name, e))
+ if e.errno == errno.EINTR:
+ continue
+ else:
+ raise
+ except Exception:
+ self.dprint(2, "{} Exception!".format(name))
+ if self.exiting:
+ break
+ else:
+ raise
+ else:
+ self.dprint(2, "{} Break!".format(name))
+ break
+
+ def heartbeat_loop(self):
+ """Run heartbeat"""
+ self.dprint(2, "Starting heartbeat loop...")
+ while not self.exiting:
+ self.dprint(3, ".", end="")
+ try:
+ zmq.device(zmq.FORWARDER, self.heartbeat_socket, self.heartbeat_socket)
+ except zmq.ZMQError as e:
+ if e.errno == errno.EINTR:
+ continue
+ else:
+ raise
+ else:
+ break
+
+ def shell_handler(self, message):
+ """Dispatch shell messages to their handlers"""
+ self.dprint(1, "received:", message)
+ identities, msg = self.deserialize_wire_message(message)
+ handler = getattr(self, "handle_" + msg["header"]["msg_type"], None)
+ if handler is None:
+ self.dprint(0, "unknown message type:", msg["header"]["msg_type"])
+ return
+ handler(msg, identities)
+
+ def handle_execute_request(self, message, identities):
+ """Handle execute request messages."""
+ self.dprint(2, "Xonsh Kernel Executing:", pformat(message["content"]["code"]))
+ # Start by sending busy signal
+ content = {"execution_state": "busy"}
+ self.send(self.iopub_stream, "status", content, parent_header=message["header"])
+
+ # confirm the input that we are executing
+ content = {
+ "execution_count": self.execution_count,
+ "code": message["content"]["code"],
+ }
+ self.send(
+ self.iopub_stream, "execute_input", content, parent_header=message["header"]
+ )
+
+ # execute the code
+ metadata = {
+ "dependencies_met": True,
+ "engine": self.session_id,
+ "status": "ok",
+ "started": datetime.datetime.now().isoformat(),
+ }
+ content = self.do_execute(parent_header=message["header"], **message["content"])
+ self.send(
+ self.shell_stream,
+ "execute_reply",
+ content,
+ metadata=metadata,
+ parent_header=message["header"],
+ identities=identities,
+ )
+ self.execution_count += 1
+
+ # once we are done, send a signal that we are idle
+ content = {"execution_state": "idle"}
+ self.send(self.iopub_stream, "status", content, parent_header=message["header"])
+
+ def do_execute(
+ self,
+ code="",
+ silent=False,
+ store_history=True,
+ user_expressions=None,
+ allow_stdin=False,
+ parent_header=None,
+ **kwargs
+ ):
"""Execute user code."""
if len(code.strip()) == 0:
- return {'status': 'ok', 'execution_count': self.execution_count,
- 'payload': [], 'user_expressions': {}}
+ return {
+ "status": "ok",
+ "execution_count": self.execution_count,
+ "payload": [],
+ "user_expressions": {},
+ }
shell = builtins.__xonsh_shell__
hist = builtins.__xonsh_history__
try:
- shell.default(code)
+ shell.default(code, self, parent_header)
interrupted = False
except KeyboardInterrupt:
interrupted = True
- if not silent: # stdout response
- if hasattr(builtins, '_') and builtins._ is not None:
- # rely on sys.displayhook functionality
- self._respond_in_chunks('stdout', pformat(builtins._))
- builtins._ = None
- if hist is not None and len(hist) > 0:
- self._respond_in_chunks('stdout', hist.outs[-1])
-
if interrupted:
- return {'status': 'abort', 'execution_count': self.execution_count}
+ return {"status": "abort", "execution_count": self.execution_count}
rtn = 0 if (hist is None or len(hist) == 0) else hist.rtns[-1]
if 0 < rtn:
- message = {'status': 'error', 'execution_count': self.execution_count,
- 'ename': '', 'evalue': str(rtn), 'traceback': []}
+ message = {
+ "status": "error",
+ "execution_count": self.execution_count,
+ "ename": "",
+ "evalue": str(rtn),
+ "traceback": [],
+ }
else:
- message = {'status': 'ok', 'execution_count': self.execution_count,
- 'payload': [], 'user_expressions': {}}
+ message = {
+ "status": "ok",
+ "execution_count": self.execution_count,
+ "payload": [],
+ "user_expressions": {},
+ }
return message
- def _respond_in_chunks(self, name, s, chunksize=1024):
+ def _respond_in_chunks(self, name, s, chunksize=1024, parent_header=None):
if s is None:
return
n = len(s)
@@ -75,26 +400,67 @@ def _respond_in_chunks(self, name, s, chunksize=1024):
lower = range(0, n, chunksize)
upper = range(chunksize, n + chunksize, chunksize)
for l, u in zip(lower, upper):
- response = {'name': name, 'text': s[l:u], }
- self.send_response(self.iopub_socket, 'stream', response)
+ response = {"name": name, "text": s[l:u]}
+ self.send(
+ self.iopub_socket, "stream", response, parent_header=parent_header
+ )
+
+ def handle_complete_request(self, message, identities):
+ """Handles kernel info requests."""
+ content = self.do_complete(
+ message["content"]["code"], message["content"]["cursor_pos"]
+ )
+ self.send(
+ self.shell_stream,
+ "complete_reply",
+ content,
+ parent_header=message["header"],
+ identities=identities,
+ )
def do_complete(self, code, pos):
"""Get completions."""
shell = builtins.__xonsh_shell__
- line = code.split('\n')[-1]
+ line = code.split("\n")[-1]
line = builtins.aliases.expand_alias(line)
- prefix = line.split(' ')[-1]
+ prefix = line.split(" ")[-1]
endidx = pos
begidx = pos - len(prefix)
- rtn, _ = self.completer.complete(prefix, line, begidx,
- endidx, shell.ctx)
- message = {'matches': rtn, 'cursor_start': begidx, 'cursor_end': endidx,
- 'metadata': {}, 'status': 'ok'}
+ rtn, _ = self.completer.complete(prefix, line, begidx, endidx, shell.ctx)
+ if isinstance(rtn, Set):
+ rtn = list(rtn)
+ message = {
+ "matches": rtn,
+ "cursor_start": begidx,
+ "cursor_end": endidx,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "status": "ok",
+ }
return message
+ def handle_kernel_info_request(self, message, identities):
+ """Handles kernel info requests."""
+ content = {
+ "protocol_version": "5.0",
+ "ipython_version": [1, 1, 0, ""],
+ "language": self.language,
+ "language_version": self.language_version,
+ "implementation": self.implementation,
+ "implementation_version": self.implementation_version,
+ "language_info": self.language_info,
+ "banner": self.banner,
+ }
+ self.send(
+ self.shell_stream,
+ "kernel_info_reply",
+ content,
+ parent_header=message["header"],
+ identities=identities,
+ )
+
-if __name__ == '__main__':
- from ipykernel.kernelapp import IPKernelApp
- # must manually pass in args to avoid interfering w/ Jupyter arg parsing
- with main_context(argv=['--shell-type=readline']):
- IPKernelApp.launch_instance(kernel_class=XonshKernel)
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ setup(shell_type="jupyter", env={})
+ shell = builtins.__xonsh_shell__
+ kernel = shell.kernel = XonshKernel()
+ kernel.start()
diff --git a/xonsh/jupyter_shell.py b/xonsh/jupyter_shell.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..52943469be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/xonsh/jupyter_shell.py
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+"""An interactive shell for the Jupyter kernel."""
+import io
+import sys
+import builtins
+
+from xonsh.base_shell import BaseShell
+
+
+class StdJupyterRedirectBuf(io.RawIOBase):
+ """Redirects standard I/O buffers to the Jupyter kernel."""
+
+ def __init__(self, redirect):
+ self.redirect = redirect
+ self.encoding = redirect.encoding
+ self.errors = redirect.errors
+
+ def fileno(self):
+ """Returns the file descriptor of the std buffer."""
+ return self.redirect.fileno()
+
+ def seek(self, offset, whence=io.SEEK_SET):
+ """Sets the location in both the stdbuf and the membuf."""
+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot seek Jupyter redirect')
+
+ def truncate(self, size=None):
+ """Truncate both buffers."""
+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot truncate Jupyter redirect')
+
+ def readinto(self, b):
+ """Read bytes into buffer from both streams."""
+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot read into Jupyter redirect')
+
+ def write(self, b):
+ """Write bytes to kernel."""
+ s = b if isinstance(b, str) else b.decode(self.encoding, self.errors)
+ self.redirect.write(s)
+
+
+class StdJupyterRedirect(io.TextIOBase):
+ """Redirects a standard I/O stream to the Jupyter kernel."""
+
+ def __init__(self, name, kernel, parent_header=None):
+ """
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ name : str
+ The name of the buffer in the sys module, e.g. 'stdout'.
+ kernel : XonshKernel
+ Instance of a Jupyter kernel
+ parent_header : dict or None, optional
+ parent header information to pass along with the kernel
+ """
+ self._name = name
+ self.kernel = kernel
+ self.parent_header = parent_header
+
+ self.std = getattr(sys, name)
+ self.buffer = StdJupyterRedirectBuf(self)
+ setattr(sys, name, self)
+
+ @property
+ def encoding(self):
+ """The encoding of the stream"""
+ env = builtins.__xonsh_env__
+ return getattr(self.std, 'encoding', env.get('XONSH_ENCODING'))
+
+ @property
+ def errors(self):
+ """The encoding errors of the stream"""
+ env = builtins.__xonsh_env__
+ return getattr(self.std, 'errors', env.get('XONSH_ENCODING_ERRORS'))
+
+ @property
+ def newlines(self):
+ """The newlines of the standard buffer."""
+ return self.std.newlines
+
+ def _replace_std(self):
+ std = self.std
+ if std is None:
+ return
+ setattr(sys, self._name, std)
+ self.std = None
+
+ def __del__(self):
+ self._replace_std()
+
+ def close(self):
+ """Restores the original std stream."""
+ self._replace_std()
+
+ def __enter__(self):
+ return self
+
+ def __exit__(self, *args, **kwargs):
+ self.close()
+
+ def write(self, s):
+ """Writes data to the original kernel stream."""
+ self.kernel._respond_in_chunks(self._name, s,
+ parent_header=self.parent_header)
+
+ def flush(self):
+ """Flushes kernel iopub_stream."""
+ self.kernel.iopub_stream.flush()
+
+ def fileno(self):
+ """Tunnel fileno() calls to the std stream."""
+ return self.std.fileno()
+
+ def seek(self, offset, whence=io.SEEK_SET):
+ """Seek to a location."""
+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot seek Jupyter redirect')
+
+ def truncate(self, size=None):
+ """Truncate the streams."""
+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot truncate Jupyter redirect')
+
+ def detach(self):
+ """This operation is not supported."""
+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot detach a Jupyter redirect')
+
+ def read(self, size=None):
+ """Read from the stream"""
+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot read a Jupyter redirect')
+
+ def readline(self, size=-1):
+ """Read a line."""
+ raise io.UnsupportedOperation('cannot read a line from a Jupyter redirect')
+
+
+class JupyterShell(BaseShell):
+ """A shell for the Jupyter kernel."""
+
+ def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
+ super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
+ self.kernel = None
+
+ def default(self, line, kernel, parent_header=None):
+ """Executes code, but redirects output to Jupyter client"""
+ stdout = StdJupyterRedirect('stdout', kernel, parent_header)
+ stderr = StdJupyterRedirect('stderr', kernel, parent_header)
+ with stdout, stderr:
+ rtn = super().default(line)
+ return rtn
diff --git a/xonsh/main.py b/xonsh/main.py
index 9d59c0bbb1..e9043a5b2f 100644
--- a/xonsh/main.py
+++ b/xonsh/main.py
@@ -436,6 +436,6 @@ def setup(ctx=None, shell_type='none', env=(('RAISE_SUBPROC_ERROR', True),)):
builtins.__xonsh_execer__ = Execer(xonsh_ctx=ctx)
builtins.__xonsh_shell__ = Shell(builtins.__xonsh_execer__,
ctx=ctx,
- shell_type='none')
+ shell_type=shell_type)
builtins.__xonsh_env__.update(env)
install_import_hooks()
diff --git a/xonsh/shell.py b/xonsh/shell.py
index 2c1e79c525..74a35978e9 100644
--- a/xonsh/shell.py
+++ b/xonsh/shell.py
@@ -166,6 +166,8 @@ def __init__(self, execer, ctx=None, shell_type=None, **kwargs):
from xonsh.ptk.shell import PromptToolkitShell as shell_class
elif shell_type == 'readline':
from xonsh.readline_shell import ReadlineShell as shell_class
+ elif shell_type == 'jupyter':
+ from xonsh.jupyter_shell import JupyterShell as shell_class
else:
raise XonshError('{} is not recognized as a shell type'.format(
shell_type))
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21864@723fd13
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,864
|
iterables - fixes issue 21863 and now multiset_permutations can handle []
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Fixes #21863 and now multiset_permutations can handle null/empty sets and also added regression tests in test_iterables.py
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* utilities
* Fixed bug in iterables.py and now multiset_permutations can handle []
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-08-12T19:02:26Z
|
multiset_permutations needs to handle []
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
index 83fc2f48d2..0a91615dde 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
@@ -1419,7 +1419,7 @@ def multiset_permutations(m, size=None, g=None):
do = [gi for gi in g if gi[1] > 0]
SUM = sum([gi[1] for gi in do])
if not do or size is not None and (size > SUM or size < 1):
- if size < 1:
+ if not do and size is None or size < 1:
yield []
return
elif size == 1:
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py
index 221b03f618..b405ac37f5 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py
@@ -423,6 +423,9 @@ def test_multiset_permutations():
[0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 0], [1, 2], [2, 0], [2, 1]]
assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 0))) == 1
assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 3))) == 0
+ for nul in ([], {}, ''):
+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul)) == [[]], list(multiset_permutations(nul))
+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, 1)) == []
def test():
for i in range(1, 7):
```
|
[
{
"body": "```diff\r\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\r\nindex 83fc2f48d2..0a91615dde 100644\r\n--- a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\r\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\r\n@@ -1419,7 +1419,7 @@ def multiset_permutations(m, size=None, g=None):\r\n do = [gi for gi in g if gi[1] > 0]\r\n SUM = sum([gi[1] for gi in do])\r\n if not do or size is not None and (size > SUM or size < 1):\r\n- if size < 1:\r\n+ if not do and size is None or size < 1:\r\n yield []\r\n return\r\n elif size == 1:\r\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py\r\nindex 221b03f618..b405ac37f5 100644\r\n--- a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py\r\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py\r\n@@ -423,6 +423,9 @@ def test_multiset_permutations():\r\n [0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 0], [1, 2], [2, 0], [2, 1]]\r\n assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 0))) == 1\r\n assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 3))) == 0\r\n+ for nul in ([], {}, ''):\r\n+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul)) == [[]], list(multiset_permutations(nul))\r\n+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, 1)) == []\r\n \r\n def test():\r\n for i in range(1, 7):\r\n```",
"number": 21863,
"title": "multiset_permutations needs to handle []"
}
] |
ec0fe8c5f3e59840e8aa5d3d6a7c976e40f76b64
|
{
"head_commit": "723fd1320c3d6c5473ae6bd69dc47fef9f6f9024",
"head_commit_message": "fixed issue 21863",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\nindex 83fc2f48d2e9..0a91615ddedd 100644\n--- a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\n@@ -1419,7 +1419,7 @@ def multiset_permutations(m, size=None, g=None):\n do = [gi for gi in g if gi[1] > 0]\n SUM = sum([gi[1] for gi in do])\n if not do or size is not None and (size > SUM or size < 1):\n- if size < 1:\n+ if not do and size is None or size < 1:\n yield []\n return\n elif size == 1:\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py\nindex 221b03f61883..b405ac37f5ad 100644\n--- a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py\n@@ -423,6 +423,9 @@ def test_multiset_permutations():\n [0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 0], [1, 2], [2, 0], [2, 1]]\n assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 0))) == 1\n assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 3))) == 0\n+ for nul in ([], {}, ''):\n+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul)) == [[]], list(multiset_permutations(nul))\n+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, 1)) == []\n \n def test():\n for i in range(1, 7):\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1419,7 +1419,7 @@ def multiset_permutations(m, size=None, g=None):\n do = [gi for gi in g if gi[1] > 0]\n SUM = sum([gi[1] for gi in do])\n if not do or size is not None and (size > SUM or size < 1):\n- if size < 1:\n+ if not do and size is None or size < 1:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1422,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/utilities/iterables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n if not do and size is None or size == 0:\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -423,6 +423,9 @@ def test_multiset_permutations():\n [0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 0], [1, 2], [2, 0], [2, 1]]\n assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 0))) == 1\n assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 3))) == 0\n+ for nul in ([], {}, ''):\n+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul)) == [[]], list(multiset_permutations(nul))\n+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, 1)) == []",
"line": null,
"original_line": 428,
"original_start_line": 427,
"path": "sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n assert list(multiset_permutations(nul)) == [[]]\r\n assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, 0)) == [[]]\r\n # impossible requests give no result\r\n assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, 1)) == []\r\n assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, -1)) == []\r\n```"
}
] |
581ec835bb1be83d7d22d9eb929e5dc827b1134b
|
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
index 83fc2f48d2e9..77ccd453bd69 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
@@ -1419,7 +1419,7 @@ def multiset_permutations(m, size=None, g=None):
do = [gi for gi in g if gi[1] > 0]
SUM = sum([gi[1] for gi in do])
if not do or size is not None and (size > SUM or size < 1):
- if size < 1:
+ if not do and size is None or size == 0:
yield []
return
elif size == 1:
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py
index 221b03f61883..77dadbf429f5 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_iterables.py
@@ -423,6 +423,12 @@ def test_multiset_permutations():
[0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 0], [1, 2], [2, 0], [2, 1]]
assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 0))) == 1
assert len(list(multiset_permutations('a', 3))) == 0
+ for nul in ([], {}, ''):
+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul)) == [[]]
+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, 0)) == [[]]
+ # impossible requests give no result
+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, 1)) == []
+ assert list(multiset_permutations(nul, -1)) == []
def test():
for i in range(1, 7):
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-7790@16ad3be
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 7,790
|
Added Manhattan distance algorithm
|
### Describe your change:
Added an algorithm to calculate Manhattan distance,
Added the algorithm twice, one in a mor traditional way and other using a one-liner.
Fixes: #7776
* [x] Add an algorithm?
* [ ] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [ ] Documentation change?
### Checklist:
* [X] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [x] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [x] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [x] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [x] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [x] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [x] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [x] All new algorithms have a URL in its comments that points to Wikipedia or other similar explanation.
* [x] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the commit message contains `Fixes: #{$ISSUE_NO}`.
|
2022-10-28T16:38:29Z
|
Add the calculation of Manhattan Distance
### Feature description
The Manhattan distance (also known as taxicab distance) measures the distance between two points in a n-dimensional grid only taking into account the diference between each coordinate point instead of using the Euclidean distance.
For example, you want to go by taxi from point a to b in a city with a grid layout like Manhattan, the shortest path should be a straight line but it would require the cab going through buildings, the real distance requires going along the streets and making turns utntil you reach the destination.
The function must receive two points in the same n-dimensional space and each component is a real number, but the output shall be the calculated with the Manhattan distance instead of the Euclidean one.
### Example
```
manhattan_distance([1,1], [2,2]) -> 2
manhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2,2]) -> 1
manhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2.5,2]) -> 1.5
```
### Would you like to work on this feature?
- [X] Yes, I want to work on this feature!
|
Please, assing it to me, as soon as I finish at work, I'll commit and make the PR
|
[
{
"body": "### Feature description\r\n\r\nThe Manhattan distance (also known as taxicab distance) measures the distance between two points in a n-dimensional grid only taking into account the diference between each coordinate point instead of using the Euclidean distance.\r\n\r\nFor example, you want to go by taxi from point a to b in a city with a grid layout like Manhattan, the shortest path should be a straight line but it would require the cab going through buildings, the real distance requires going along the streets and making turns utntil you reach the destination.\r\n\r\nThe function must receive two points in the same n-dimensional space and each component is a real number, but the output shall be the calculated with the Manhattan distance instead of the Euclidean one.\r\n\r\n### Example\r\n```\r\nmanhattan_distance([1,1], [2,2]) -> 2\r\nmanhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2,2]) -> 1\r\nmanhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2.5,2]) -> 1.5\r\n```\r\n\r\n### Would you like to work on this feature?\r\n\r\n- [X] Yes, I want to work on this feature!",
"number": 7776,
"title": "Add the calculation of Manhattan Distance"
}
] |
26cecea27198848e2c1c0bc6d7f887d4ed7adb87
|
{
"head_commit": "16ad3be296f51d31530cf1c764970649b2a5a664",
"head_commit_message": "Added Manhattan distance algorithm, Fixes: #7776",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/maths/manhattan_distance.py b/maths/manhattan_distance.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..f0508d34d959\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/maths/manhattan_distance.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@\n+from typing import Any\n+\n+\n+def manhattan_distance(point_a: list, point_b: list) -> float:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Expectts two list of numbers representing two points in the same\n+ n-dimensional space\n+\n+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taxicab_geometry\n+\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], [2,2])\n+ 2.0\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2,2])\n+ 1.0\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2.5,2])\n+ 1.5\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([-3, -3, -3], [0, 0, 0])\n+ 9.0\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], None)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Missing an input\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], [2, 2, 2])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,\"one\"], [2, 2, 2])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ >>> manhattan_distance(1, [2, 2, 2])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found int\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], \"not_a_list\")\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ _validate_point(point_a)\n+ _validate_point(point_b)\n+ if len(point_a) != len(point_b):\n+ raise ValueError(\"Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space\")\n+\n+ total_distance = 0.0\n+ for i in range(len(point_a)):\n+ total_distance += abs(point_a[i] - point_b[i])\n+\n+ return total_distance\n+\n+\n+def _validate_point(point: Any) -> None:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ >>> _validate_point(None)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Missing an input\n+ >>> _validate_point([1,\"one\"])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ >>> _validate_point(1)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found int\n+ >>> _validate_point(\"not_a_list\")\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if point:\n+ if isinstance(point, list):\n+ for item in point:\n+ if not (isinstance(item, int) or isinstance(item, float)):\n+ raise TypeError(\n+ f\"Expected a list of numbers as input, \"\n+ f\"found {type(item).__name__}\"\n+ )\n+ else:\n+ raise TypeError(\n+ f\"Expected a list of numbers as input, found {type(point).__name__}\"\n+ )\n+ else:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Missing an input\")\n+\n+\n+def manhattan_distance_one_liner(point_a: list, point_b: list) -> float:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Version with one liner\n+\n+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,1], [2,2])\n+ 2.0\n+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1.5,1.5], [2,2])\n+ 1.0\n+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1.5,1.5], [2.5,2])\n+ 1.5\n+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([-3, -3, -3], [0, 0, 0])\n+ 9.0\n+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,1], None)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Missing an input\n+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,1], [2, 2, 2])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space\n+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,\"one\"], [2, 2, 2])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner(1, [2, 2, 2])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found int\n+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,1], \"not_a_list\")\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ _validate_point(point_a)\n+ _validate_point(point_b)\n+ if len(point_a) != len(point_b):\n+ raise ValueError(\"Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space\")\n+\n+ return float(sum(abs(x - y) for x, y in zip(point_a, point_b)))\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ import doctest\n+\n+ doctest.testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@\n+from typing import Any\n+\n+\n+def manhattan_distance(point_a: list, point_b: list) -> float:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Expectts two list of numbers representing two points in the same\n+ n-dimensional space\n+\n+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taxicab_geometry\n+\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], [2,2])\n+ 2.0\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2,2])\n+ 1.0\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2.5,2])\n+ 1.5\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([-3, -3, -3], [0, 0, 0])\n+ 9.0\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], None)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Missing an input\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], [2, 2, 2])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,\"one\"], [2, 2, 2])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ >>> manhattan_distance(1, [2, 2, 2])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found int\n+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], \"not_a_list\")\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ _validate_point(point_a)\n+ _validate_point(point_b)\n+ if len(point_a) != len(point_b):\n+ raise ValueError(\"Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space\")\n+\n+ total_distance = 0.0\n+ for i in range(len(point_a)):\n+ total_distance += abs(point_a[i] - point_b[i])\n+\n+ return total_distance\n+\n+\n+def _validate_point(point: Any) -> None:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ >>> _validate_point(None)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Missing an input\n+ >>> _validate_point([1,\"one\"])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ >>> _validate_point(1)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found int\n+ >>> _validate_point(\"not_a_list\")\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if point:\n+ if isinstance(point, list):\n+ for item in point:\n+ if not (isinstance(item, int) or isinstance(item, float)):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 75,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "maths/manhattan_distance.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n if not isinstance(item, (int, float)):\r\n```\n\n@author:\nForgot that it can accept a tuple, fixed"
}
] |
ae57a5a8513826770292e5eed642073c7ff9446a
|
diff --git a/maths/manhattan_distance.py b/maths/manhattan_distance.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..2711d4c8ccd6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/maths/manhattan_distance.py
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+def manhattan_distance(point_a: list, point_b: list) -> float:
+ """
+ Expectts two list of numbers representing two points in the same
+ n-dimensional space
+
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taxicab_geometry
+
+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], [2,2])
+ 2.0
+ >>> manhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2,2])
+ 1.0
+ >>> manhattan_distance([1.5,1.5], [2.5,2])
+ 1.5
+ >>> manhattan_distance([-3, -3, -3], [0, 0, 0])
+ 9.0
+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], None)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Missing an input
+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], [2, 2, 2])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space
+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,"one"], [2, 2, 2])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str
+ >>> manhattan_distance(1, [2, 2, 2])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found int
+ >>> manhattan_distance([1,1], "not_a_list")
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str
+ """
+
+ _validate_point(point_a)
+ _validate_point(point_b)
+ if len(point_a) != len(point_b):
+ raise ValueError("Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space")
+
+ return float(sum(abs(a - b) for a, b in zip(point_a, point_b)))
+
+
+def _validate_point(point: list[float]) -> None:
+ """
+ >>> _validate_point(None)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Missing an input
+ >>> _validate_point([1,"one"])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str
+ >>> _validate_point(1)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found int
+ >>> _validate_point("not_a_list")
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str
+ """
+ if point:
+ if isinstance(point, list):
+ for item in point:
+ if not isinstance(item, (int, float)):
+ raise TypeError(
+ f"Expected a list of numbers as input, "
+ f"found {type(item).__name__}"
+ )
+ else:
+ raise TypeError(
+ f"Expected a list of numbers as input, found {type(point).__name__}"
+ )
+ else:
+ raise ValueError("Missing an input")
+
+
+def manhattan_distance_one_liner(point_a: list, point_b: list) -> float:
+ """
+ Version with one liner
+
+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,1], [2,2])
+ 2.0
+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1.5,1.5], [2,2])
+ 1.0
+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1.5,1.5], [2.5,2])
+ 1.5
+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([-3, -3, -3], [0, 0, 0])
+ 9.0
+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,1], None)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Missing an input
+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,1], [2, 2, 2])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space
+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,"one"], [2, 2, 2])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str
+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner(1, [2, 2, 2])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found int
+ >>> manhattan_distance_one_liner([1,1], "not_a_list")
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: Expected a list of numbers as input, found str
+ """
+
+ _validate_point(point_a)
+ _validate_point(point_b)
+ if len(point_a) != len(point_b):
+ raise ValueError("Both points must be in the same n-dimensional space")
+
+ return float(sum(abs(x - y) for x, y in zip(point_a, point_b)))
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import doctest
+
+ doctest.testmod()
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-2560@289af91
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 2,560
|
tutorial for subproc strings
|
Hopefully this closes #621 and #1432
|
2017-12-09T06:35:40Z
|
quote removal in subprocess mode does not behave as expected
Please have a look at the following two examples::
```
xonsh$ /bin/echo 'foo'
foo
xonsh$ /bin/echo 'foo'bar
'foo'bar
```
In the first case quotes are stripped from the second argument; in the
second, quotes are kept.
This is not consistent with what other shells do, and makes it quite
inconvenient to pass option arguments containing spaces. For example,
the following would include the quotes in the commit message::
```
svn commit --message='A short description here.'
```
|
Hi @riccardomurri, you are correct that we are not consistent with how other shells treat string. Xonsh makes a willful departure from what other shells do, in part because what other shells do is not self-consistent. Rather, xonsh's literal string syntax sticks as close as possible to Python string behaviour, which we believe to be cleaner and more consistent.
The only departure from Python strings in subproc mode is that literal strings are globbed and have their environment variables expanded, as one would expect from other shells.
The examples that you give of echo and svn are not entirely consistent themselves. It is generally the responsibility of each program to parse its own arguments. So if svn is including quotes this is svn fault. As an demonstration, consider the following Bash script which simply prints its arguments:
**temp.sh**
``` bash
#!/bin/bash
echo $*
```
Now let's run this with multiple arguments.
``` console
scopatz@localhost ~ $ chmod 755 temp.sh
# see bash keeps the quotes
scopatz@localhost ~ $ ./temp.sh --message='hello mom'
--message='hello mom'
# bash keeps the quotes even when running though bash directly
scopatz@localhost ~ $ bash temp.sh --message='hello mom'
--message='hello mom'
# same thing with double quotes
scopatz@localhost ~ $ bash temp.sh --message="hello mom"
--message="hello mom"
# Let's add a 'foo'bar argument, and see that the quotes remain.
scopatz@localhost ~ $ bash temp.sh 'foo'bar --message="hello mom"
'foo'bar --message="hello mom"
```
So bash is doing something strange here with echo and a literal string + characters that I don't think is worth replicating.
As per getting the SVN example to work in a natural way, recall that arguments are whitespace separated. Thus, I would leave off the `=` and you have two distinct tokens:
``` console
$ svn commit --message 'A short description here.'
```
Alternatively, if you truly must have the equals sign and want xonsh to group the internal whitespace, I believe that you can put the whole token in quotes.
``` console
$ svn commit '--message=A short description here.'
```
This is probably less satisfying, but works because your original command is actually equivalent to:
``` console
$ svn commit "--message='A short description here.'"
```
In general for xonsh, if a subprocess argument does not start _and_ end with quote characters or other known syntax like `$()`, `$[]`, or `@()` then that argument is interpreted as being wrapped in Python-like quotes.
I hope this helps clear things up.
Hello @scopatz, thank for looking into this!
Actually, I cannot replicate the "temp.sh" example you showed. (Did
you run that from windows?) My bash (and zsh too) removes the quotes,
both single and double, wherever they are in the argument being
processed, which is consistent with what the [bash man page
states](https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/manual/bashref.html#Quote-Removal)::
```
rmurri@xenia:~$ cat /tmp/test.sh
#! /bin/sh
echo $*
rmurri@xenia:~$ /tmp/test.sh foo'bar'
foobar
rmurri@xenia:~$ /tmp/test.sh --message='foo'
--message=foo
rmurri@xenia:~$ /tmp/test.sh --message="foo"
--message=foo
```
I understand Xonsh does not need to retain compatibility; actually, I
would go as far as to argue that, since Xonsh does not do
word-splitting after variable substitution, it does not need quote
removal _at all_::
```
xonsh$ def cnt(args, stdin=None):
print(len(args))
xonsh$ aliases['cnt'] = cnt
# three separate arguments
xonsh$ cnt a b c
3
# when coming from a var, this is one argument instead
xonsh$ $var='a b c'
xonsh$ cnt $var
1
```
Instead sh/bash needs quote removal to control whether variables are
expanded into one or several arguments:
```
bash$ cnt () { echo $#; }
# three args
bash$ cnt a b c
3
# still three args because of word splitting
bash$ var='a b c'
bash$ cnt $var
3
bash$ cnt "$var"
1
```
Still, if you keep quote removal, I think it should behave like
sh/bash does, for the principle of least surprise. (And because
rewriting simple cases of quote removal using Xonsh' `@(...)` is too
verbose.)
I stand corrected: of course we need quote removal in order to have
arguments with embedded spaces.
So, to sum up, there are two styles of quote removal:
- What Xonsh currently implements (Windows-style?): remove quotes only
if an argument starts and ends with them.
- UNIX shell style: remove quotes anywhere in an argument as the last
step of command-line processing.
Being used to UNIX shells, I would like to see the latter style
implemented, at least as an option.
Hi @riccardomurri, I think I got the bash behaviour wrong myself. temp.sh does act as you describe if I am in a Bash interactive instance.
On the subject of what to do about it, I would really call the first one "Python-style." My personal opinion is that the way the sh-lang spec is written is rather arcane and not up to modern notions of how strings should work. (Though I am not saying that what we have now is perfect.)
Now, I may be wrong about this, but I believe that adding in optional Unix-sh-style strings would touch the parser. I am a little wary of having option-dependent syntax. This means that xonsh code could not be universally parsed.
On the flipside, adding in the behvaiour for strings you are suggesting would have overlapping syntax some Python literals, namely `b"x"`, `r"x"`, `u"x"`, and in v3.6 now `f"x"`. Whatever would be done would have to avoid these specific cases.
Now, that said, I am open to suggestions - though for something like this I would also like for it to be vetted by @adqm, @gforsyth, and the mailing list. A suggestion backed by a PR would be even more compelling. Here are a couple of thoughts that I had that might be more or less compelling:
1. Use double quotes. I don't believe that Python uses double quote so `foo""bar""` and `foo''bar''` may be fair game.
2. Match a backtick and a single quote, like in LaTeX.
3. Make `=""` and `=''` an operator in subproc mode that removes the quote characters and keeps the equals sign. This doesn't cover the `foo'bar'` case, and therefore not as hard to understand or implement.
4. Come up with some other crazy syntax that is better than the above.
In any event, I guess I'd like folks to weigh in with their thoughts.
Hey @scopatz,
I agree that Python doesn't use double-up quotes -- are you envisioning something along the lines of
```
> echo foo""bar""
foo"bar"
```
?
That doesn't seem too terribly hard, but I'm also at a loss for an actual use-case. @riccardomurri -- did you have a specific idea in mind that led you to this example? If it's the `svn` case, then my inclination is to go with number 3 above and create the subproc operators.
Hi @gforsyth, sorry to be clear, I am envisioning double quotes as the following:
``` console
$ echo foo""bar""
foobar
```
Which would mirror Bash's quoting behaviour. However, I don't think that this makes anyone happy because it isn't as concise as the sh-lang syntax for the people that want it and it makes something possible that should not be possible for the people who don't want it (and are generally anti-arcana).
Also, I am most pro option 3 as well.
|
[
{
"body": "Please have a look at the following two examples::\n\n```\n xonsh$ /bin/echo 'foo'\n foo\n\n xonsh$ /bin/echo 'foo'bar\n 'foo'bar\n```\n\nIn the first case quotes are stripped from the second argument; in the\nsecond, quotes are kept.\n\nThis is not consistent with what other shells do, and makes it quite\ninconvenient to pass option arguments containing spaces. For example,\nthe following would include the quotes in the commit message::\n\n```\n svn commit --message='A short description here.'\n```\n",
"number": 621,
"title": "quote removal in subprocess mode does not behave as expected"
}
] |
c4e2ec5815ffb44eb449953743fb07398b3041cf
|
{
"head_commit": "289af915e1d04f3ac0867da1767691953d5e2f16",
"head_commit_message": "Thanks to @melund, tailing",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/docs/guides.rst b/docs/guides.rst\nindex c402ba016b..0f42e1f32a 100644\n--- a/docs/guides.rst\n+++ b/docs/guides.rst\n@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@ Guides\n tutorial_events\n tutorial_completers\n tutorial_history_backend\n+ tutorial_subproc_strings\n tutorial_ptk\n bash_to_xsh\n python_virtual_environments\n\\ No newline at end of file\ndiff --git a/docs/tutorial_subproc_strings.rst b/docs/tutorial_subproc_strings.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..ce4f3f1426\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/docs/tutorial_subproc_strings.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@\n+.. _tutorial_subproc_strings:\n+\n+************************************\n+Tutorial: Subprocess Strings\n+************************************\n+Strings in xonsh follow two simple rules:\n+\n+1. Strings in xonsh are always parsed in the same way, and\n+2. Python always wins!\n+\n+Together these rules mean that **even strings in subprocess mode are treated\n+like Python strings!** This will (help) preserve your sanity.\n+\n+No Escape\n+=========\n+Xonsh strings are exactly like Python strings everywhere. Xonsh uses\n+exactly the same escape characters that Python dones; no more and no less.\n+This is different from other shells, which have a different set of escape\n+sequences than Python has. Notably, many sh-langs allow you to escape\n+spaces with ``\\ `` (backslash-space).\n+\n+**bash**\n+\n+.. code-block:: bash\n+\n+ $ echo A\\ Single\\ Argument\n+ A Single Argument\n+\n+In the above example, since the spaces are escaped, the ``echo`` command\n+only receves a single argument. Xonsh does not allow this. If you were\n+to try this in xonsh, you'd see:\n+\n+**xonsh**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo Actually\\ Three\\ Arguments\n+ Actually\\ Three\\ Arguments\n+\n+In this example, echo recives three arguments:: ``\"Actually\\\\\"``, ``\"Three\\\\\"``,\n+and ``\"Arguments\"``. Instead, xonsh requires you to use quotes in order to\n+pass in a single argument:\n+\n+**xonsh** or **bash**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo \"A Single Argument\"\n+ A Single Argument\n+\n+Using quotes is arguably what should have been done in sh-lang in the\n+first place.\n+\n+.. note::\n+\n+ When in doubt in subprocess mode, use quotes!\n+\n+\n+Justification\n+=============\n+The reasons for not having additional escape sequences, as in sh-langs, are:\n+\n+1. Escape charaters can get overwhemlingly ugly, fast.\n+2. We have escape characters, they are called quotes :)\n+3. We have literal input in subprocess mode via macros.\n+\n+On this last point, if you don't already know about\n+`Subprocess Macros <tutorial_macros.html#subprocess-macros>`_,\n+these allow all input following an ``!`` to be treated as a single argument.\n+For example,\n+\n+**xonsh**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo! A Single Argument\n+ A Single Argument\n+\n+Subprocess macros are the ultimate escape mechanism.\n+\n+The Quotes Stay\n+===============\n+In sh-langs, internal quote characters are removed. For instance:\n+\n+.. code-block:: bash\n+\n+ $ echo foo\"bar\"baz\n+ foobarbaz\n+\n+ $ echo --key=\"value\"\n+ --key=value\n+\n+Xonsh considers this behaviour insane. Instead, xonsh treats these\n+arguments as if they were surrounded in another, outer level of\n+quotation (``'foo\"bar\"baz'``). Xonsh will keep the quotation marks\n+when leading and trailing quotes are not matched.\n+\n+**xonsh**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo foo\"bar\"baz\n+ foo\"bar\"baz\n+\n+ $ echo --key=\"value\"\n+ --key=\"value\"\n+\n+You can think of these being equivalent to,\n+\n+\n+**xonsh**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo 'foo\"bar\"baz'\n+ foo\"bar\"baz\n+\n+ $ echo '--key=\"value\"'\n+ --key=\"value\"\n+\n+This is yet-another major point of departure for xonsh from traditional\n+shells. However, the xonsh subprocess string handling is\n+consistent and predictable.\n+\n+Further Reading\n+===============\n+For deeper details on the great string debate, please feel free to read\n+and comment at:\n+\n+* `To Quote or Not Quote <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/issues/1432>`_\n+* `Quote removal in subprocess mode does not behave as expected <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/issues/621>`_\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@\n+.. _tutorial_subproc_strings:\n+\n+************************************\n+Tutorial: Subprocess Strings\n+************************************\n+Strings in xonsh follow two simple rules:\n+\n+1. Strings in xonsh are always parsed in the same way, and\n+2. Python always wins!\n+\n+Together these rules mean that **even strings in subprocess mode are treated\n+like Python strings!** This will (help) preserve your sanity.\n+\n+No Escape\n+=========\n+Xonsh strings are exactly like Python strings everywhere. Xonsh uses\n+exactly the same escape characters that Python dones; no more and no less.",
"line": null,
"original_line": 17,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "docs/tutorial_subproc_strings.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n*dones -> does"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@\n+.. _tutorial_subproc_strings:\n+\n+************************************\n+Tutorial: Subprocess Strings\n+************************************\n+Strings in xonsh follow two simple rules:\n+\n+1. Strings in xonsh are always parsed in the same way, and\n+2. Python always wins!\n+\n+Together these rules mean that **even strings in subprocess mode are treated\n+like Python strings!** This will (help) preserve your sanity.\n+\n+No Escape\n+=========\n+Xonsh strings are exactly like Python strings everywhere. Xonsh uses\n+exactly the same escape characters that Python dones; no more and no less.\n+This is different from other shells, which have a different set of escape\n+sequences than Python has. Notably, many sh-langs allow you to escape\n+spaces with ``\\ `` (backslash-space).\n+\n+**bash**\n+\n+.. code-block:: bash\n+\n+ $ echo A\\ Single\\ Argument\n+ A Single Argument\n+\n+In the above example, since the spaces are escaped, the ``echo`` command\n+only receves a single argument. Xonsh does not allow this. If you were\n+to try this in xonsh, you'd see:\n+\n+**xonsh**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo Actually\\ Three\\ Arguments\n+ Actually\\ Three\\ Arguments\n+\n+In this example, echo recives three arguments:: ``\"Actually\\\\\"``, ``\"Three\\\\\"``,\n+and ``\"Arguments\"``. Instead, xonsh requires you to use quotes in order to\n+pass in a single argument:\n+\n+**xonsh** or **bash**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo \"A Single Argument\"\n+ A Single Argument\n+\n+Using quotes is arguably what should have been done in sh-lang in the\n+first place.\n+\n+.. note::\n+\n+ When in doubt in subprocess mode, use quotes!\n+\n+\n+Justification\n+=============\n+The reasons for not having additional escape sequences, as in sh-langs, are:\n+\n+1. Escape charaters can get overwhemlingly ugly, fast.\n+2. We have escape characters, they are called quotes :)\n+3. We have literal input in subprocess mode via macros.\n+\n+On this last point, if you don't already know about\n+`Subprocess Macros <tutorial_macros.html#subprocess-macros>`_,\n+these allow all input following an ``!`` to be treated as a single argument.\n+For example,\n+\n+**xonsh**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo! A Single Argument\n+ A Single Argument\n+\n+Subprocess macros are the ultimate escape mechanism.\n+\n+The Quotes Stay\n+===============\n+In sh-langs, internal quote characters are removed. For instance:\n+\n+.. code-block:: bash\n+\n+ $ echo foo\"bar\"baz\n+ foobarbaz\n+\n+ $ echo --key=\"value\"\n+ --key=value\n+\n+Xonsh considers this behaviour insane. Instead, xonsh treats these\n+arguments as if they were surrounded in another, outer level of\n+quotation (``'foo\"bar\"baz'``). Xonsh will keep the quotation marks\n+when leading and trailing quotes are not matched.\n+\n+**xonsh**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo foo\"bar\"baz\n+ foo\"bar\"baz\n+\n+ $ echo --key=\"value\"\n+ --key=\"value\"\n+\n+You can think of these being equivalent to,\n+\n+\n+**xonsh**\n+\n+.. code-block:: xonsh\n+\n+ $ echo 'foo\"bar\"baz'\n+ foo\"bar\"baz\n+\n+ $ echo '--key=\"value\"'\n+ --key=\"value\"\n+\n+This is yet-another major point of departure for xonsh from traditional",
"line": null,
"original_line": 121,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "docs/tutorial_subproc_strings.rst",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nNo hyphen"
}
] |
503c40c66ca10ce6298f0cbc03ddb78628f34766
|
diff --git a/docs/guides.rst b/docs/guides.rst
index c402ba016b..0f42e1f32a 100644
--- a/docs/guides.rst
+++ b/docs/guides.rst
@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@ Guides
tutorial_events
tutorial_completers
tutorial_history_backend
+ tutorial_subproc_strings
tutorial_ptk
bash_to_xsh
python_virtual_environments
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/tutorial_subproc_strings.rst b/docs/tutorial_subproc_strings.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b53cd01a20
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/tutorial_subproc_strings.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
+.. _tutorial_subproc_strings:
+
+************************************
+Tutorial: Subprocess Strings
+************************************
+Strings in xonsh follow two simple rules:
+
+1. Strings in xonsh are always parsed in the same way, and
+2. Python always wins!
+
+Together these rules mean that **even strings in subprocess mode are treated
+like Python strings!** This will (help) preserve your sanity.
+
+No Escape
+=========
+Xonsh strings are exactly like Python strings everywhere. Xonsh uses
+exactly the same escape characters that Python does; no more and no less.
+This is different from other shells, which have a different set of escape
+sequences than Python has. Notably, many sh-langs allow you to escape
+spaces with ``\ `` (backslash-space).
+
+**bash**
+
+.. code-block:: bash
+
+ $ echo A\ Single\ Argument
+ A Single Argument
+
+In the above example, since the spaces are escaped, the ``echo`` command
+only receves a single argument. Xonsh does not allow this. If you were
+to try this in xonsh, you'd see:
+
+**xonsh**
+
+.. code-block:: xonsh
+
+ $ echo Actually\ Three\ Arguments
+ Actually\ Three\ Arguments
+
+In this example, echo recives three arguments:: ``"Actually\\"``, ``"Three\\"``,
+and ``"Arguments"``. Instead, xonsh requires you to use quotes in order to
+pass in a single argument:
+
+**xonsh** or **bash**
+
+.. code-block:: xonsh
+
+ $ echo "A Single Argument"
+ A Single Argument
+
+Using quotes is arguably what should have been done in sh-lang in the
+first place.
+
+.. note::
+
+ When in doubt in subprocess mode, use quotes!
+
+
+Justification
+=============
+The reasons for not having additional escape sequences, as in sh-langs, are:
+
+1. Escape charaters can get overwhemlingly ugly, fast.
+2. We have escape characters, they are called quotes :)
+3. We have literal input in subprocess mode via macros.
+
+On this last point, if you don't already know about
+`Subprocess Macros <tutorial_macros.html#subprocess-macros>`_,
+these allow all input following an ``!`` to be treated as a single argument.
+For example,
+
+**xonsh**
+
+.. code-block:: xonsh
+
+ $ echo! A Single Argument
+ A Single Argument
+
+Subprocess macros are the ultimate escape mechanism.
+
+The Quotes Stay
+===============
+In sh-langs, internal quote characters are removed. For instance:
+
+.. code-block:: bash
+
+ $ echo foo"bar"baz
+ foobarbaz
+
+ $ echo --key="value"
+ --key=value
+
+Xonsh considers this behavior insane. Instead, xonsh treats these
+arguments as if they were surrounded in another, outer level of
+quotation (``'foo"bar"baz'``). Xonsh will keep the quotation marks
+when leading and trailing quotes are not matched.
+
+**xonsh**
+
+.. code-block:: xonsh
+
+ $ echo foo"bar"baz
+ foo"bar"baz
+
+ $ echo --key="value"
+ --key="value"
+
+You can think of these being equivalent to,
+
+
+**xonsh**
+
+.. code-block:: xonsh
+
+ $ echo 'foo"bar"baz'
+ foo"bar"baz
+
+ $ echo '--key="value"'
+ --key="value"
+
+This is yet another major point of departure for xonsh from traditional
+shells. However, the xonsh subprocess string handling is
+consistent and predictable.
+
+Further Reading
+===============
+For deeper details on the great string debate, please feel free to read
+and comment at:
+
+* `To Quote or Not Quote <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/issues/1432>`_
+* `Quote removal in subprocess mode does not behave as expected <https://github.com/xonsh/xonsh/issues/621>`_
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-7547@60e5156
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 7,547
|
Add Cramer's rule for solving system of linear equations in two variables
|
### Describe your change:
Fixes #7122
* [x] Add an algorithm?
* [ ] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [] Documentation change?
### Checklist:
* [x] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [x] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [x] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [x] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [x] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [x] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [x] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [x] All new algorithms have a URL in its comments that points to Wikipedia or other similar explanation.
* [x] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the commit message contains `Fixes: #{$ISSUE_NO}`.
|
2022-10-23T09:10:03Z
|
System of linear equation in 2 variable.
### Feature description
I want to implement a new module inside the matrix ... To solve the System of linear equations in 2 variables using Cramer's Rule.
### Would you like to work on this feature?
- [X] Yes, I want to work on this feature!
|
Please, assign me this, I want to work on this.
Bro, I want to work on this that's why I CREATED THIS ISSUE 🥲🥲 I m not maintainer ... I m contributor.
Please leave this, try other issues.
Please assign me this issue.
|
[
{
"body": "### Feature description\n\nI want to implement a new module inside the matrix ... To solve the System of linear equations in 2 variables using Cramer's Rule. \n\n### Would you like to work on this feature?\n\n- [X] Yes, I want to work on this feature!",
"number": 7122,
"title": "System of linear equation in 2 variable."
}
] |
ed127032b303d06f2c1ceefd58a8680bb4c2ce50
|
{
"head_commit": "60e5156b0756ce1e39bc48a53f9aea91a45f9158",
"head_commit_message": "added script for solving system of linear equations in two variables",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py b/matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..aac84ce60072\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Solves the system of linear equation in 2 variables.\n+ :param: eq1: list of 3 numbers\n+ :param: eq2: list of 3 numbers\n+ :return: String of result\n+ Theory:-\n+ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/systems-linear-equations-matrices.html\n+ Cramer's rule for 2x2 matrix:-\n+ https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/cramers-rule-with-two-variables\n+ a1x + b1y = = d1\n+ a2x + b2y = = d2\n+ input format : [a1, b1, d1], [a2, b2, d2]\n+ d_matrix = [[a1, b1], [a2, b2]]\n+ d is determinant of matrix d_matrix\n+ dx_matrix = [[d1, b1], [d2, b2]]\n+ dx is determinant of matrix dx_matrix\n+ dy_matrix = [[a1, d1], [a2, d2]]\n+ dy is determinant of matrix dy_matrix\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 7])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [11, 22])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Please enter a valid equation.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([11, 2, 30], [1, 0, 4])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 4.0, y = -7.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 1, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 0, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([4, 7, 1], [1, 2, 0])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 2.0, y = -1.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([2, 3, 0], [5, 1, 0])\n+ 'Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [2, 0, 26])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 13.0, y = 12.5'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [0, 3, 99])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Checking if the input is valid\n+ if len(eq1) != 3 or len(eq2) != 3:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Please enter a valid equation.\")\n+ elif (eq1[0] == 0 and eq1[1] == 0) and (eq2[0] == 0 and eq2[1] == 0):\n+ print(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\")\n+ else:\n+ # Extracting the coefficients\n+ a1, b1, c1 = eq1\n+ a2, b2, c2 = eq2\n+\n+ # Calculating the determinant of matrix d_matrix, dx_matrix and dy_matrix\n+ d = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1\n+ dx = c1 * b2 - c2 * b1\n+ dy = a1 * c2 - a2 * c1\n+\n+ # Checking if the system of linear equation has a solution (Using Cramer's rule)\n+ if d == 0:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return \"Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)\"\n+ else:\n+ return \"No solution. (Inconsistent system)\"\n+ else:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return f\"Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = {0} and y = {0}\"\n+ else:\n+ x = dx / d\n+ y = dy / d\n+ return f\"Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = {x}, y = {y}\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Solves the system of linear equation in 2 variables.\n+ :param: eq1: list of 3 numbers\n+ :param: eq2: list of 3 numbers\n+ :return: String of result\n+ Theory:-\n+ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/systems-linear-equations-matrices.html\n+ Cramer's rule for 2x2 matrix:-\n+ https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/cramers-rule-with-two-variables\n+ a1x + b1y = = d1\n+ a2x + b2y = = d2\n+ input format : [a1, b1, d1], [a2, b2, d2]\n+ d_matrix = [[a1, b1], [a2, b2]]\n+ d is determinant of matrix d_matrix\n+ dx_matrix = [[d1, b1], [d2, b2]]\n+ dx is determinant of matrix dx_matrix\n+ dy_matrix = [[a1, d1], [a2, d2]]\n+ dy is determinant of matrix dy_matrix\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 7])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [11, 22])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Please enter a valid equation.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([11, 2, 30], [1, 0, 4])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 4.0, y = -7.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 1, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 0, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([4, 7, 1], [1, 2, 0])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 2.0, y = -1.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([2, 3, 0], [5, 1, 0])\n+ 'Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [2, 0, 26])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 13.0, y = 12.5'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [0, 3, 99])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Checking if the input is valid\n+ if len(eq1) != 3 or len(eq2) != 3:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Please enter a valid equation.\")\n+ elif (eq1[0] == 0 and eq1[1] == 0) and (eq2[0] == 0 and eq2[1] == 0):\n+ print(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\")\n+ else:\n+ # Extracting the coefficients\n+ a1, b1, c1 = eq1\n+ a2, b2, c2 = eq2\n+\n+ # Calculating the determinant of matrix d_matrix, dx_matrix and dy_matrix\n+ d = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1\n+ dx = c1 * b2 - c2 * b1\n+ dy = a1 * c2 - a2 * c1\n+\n+ # Checking if the system of linear equation has a solution (Using Cramer's rule)\n+ if d == 0:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return \"Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)\"\n+ else:\n+ return \"No solution. (Inconsistent system)\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 77,
"original_start_line": 76,
"path": "matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\n raise RuntimeError(\"No solution. (Inconsistent system)\")\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Solves the system of linear equation in 2 variables.\n+ :param: eq1: list of 3 numbers\n+ :param: eq2: list of 3 numbers\n+ :return: String of result\n+ Theory:-\n+ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/systems-linear-equations-matrices.html\n+ Cramer's rule for 2x2 matrix:-\n+ https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/cramers-rule-with-two-variables\n+ a1x + b1y = = d1\n+ a2x + b2y = = d2\n+ input format : [a1, b1, d1], [a2, b2, d2]\n+ d_matrix = [[a1, b1], [a2, b2]]\n+ d is determinant of matrix d_matrix\n+ dx_matrix = [[d1, b1], [d2, b2]]\n+ dx is determinant of matrix dx_matrix\n+ dy_matrix = [[a1, d1], [a2, d2]]\n+ dy is determinant of matrix dy_matrix\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 7])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [11, 22])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Please enter a valid equation.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([11, 2, 30], [1, 0, 4])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 4.0, y = -7.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 1, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 0, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([4, 7, 1], [1, 2, 0])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 2.0, y = -1.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([2, 3, 0], [5, 1, 0])\n+ 'Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [2, 0, 26])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 13.0, y = 12.5'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [0, 3, 99])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Checking if the input is valid\n+ if len(eq1) != 3 or len(eq2) != 3:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Please enter a valid equation.\")\n+ elif (eq1[0] == 0 and eq1[1] == 0) and (eq2[0] == 0 and eq2[1] == 0):\n+ print(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\")\n+ else:\n+ # Extracting the coefficients\n+ a1, b1, c1 = eq1\n+ a2, b2, c2 = eq2\n+\n+ # Calculating the determinant of matrix d_matrix, dx_matrix and dy_matrix\n+ d = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1\n+ dx = c1 * b2 - c2 * b1\n+ dy = a1 * c2 - a2 * c1\n+\n+ # Checking if the system of linear equation has a solution (Using Cramer's rule)\n+ if d == 0:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return \"Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)\"\n+ else:\n+ return \"No solution. (Inconsistent system)\"\n+ else:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return f\"Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = {0} and y = {0}\"\n+ else:\n+ x = dx / d\n+ y = dy / d\n+ return f\"Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = {x}, y = {y}\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 84,
"original_start_line": 81,
"path": "matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\n x = dx / d\n y = dy / d\n raise RuntimeError(f\"Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = {x}, y = {y}\")\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\ndef calculate_x_and_y(eq1: list[int], eq2: list[int]) -> str:\r\n```\n\n@author:\nwhat should I type in place of str if it will raise only runtime error (according to @user2 's changes) ??\n\n@user2:\n> what should I type in place of str if it will raise only runtime error (according to @user2 's changes) ??\n\nRuntime error doesnt count as a return type, it implies a return type of `None`\n\n@user1:\nExceptions that are raised are NOT return values. The way to think about this is that if the function succeeds (no Exceptions are raised) then the caller should expect to receive a str."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Solves the system of linear equation in 2 variables.\n+ :param: eq1: list of 3 numbers\n+ :param: eq2: list of 3 numbers\n+ :return: String of result\n+ Theory:-\n+ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/systems-linear-equations-matrices.html\n+ Cramer's rule for 2x2 matrix:-\n+ https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/cramers-rule-with-two-variables\n+ a1x + b1y = = d1\n+ a2x + b2y = = d2\n+ input format : [a1, b1, d1], [a2, b2, d2]\n+ d_matrix = [[a1, b1], [a2, b2]]\n+ d is determinant of matrix d_matrix\n+ dx_matrix = [[d1, b1], [d2, b2]]\n+ dx is determinant of matrix dx_matrix\n+ dy_matrix = [[a1, d1], [a2, d2]]\n+ dy is determinant of matrix dy_matrix\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 7])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [11, 22])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Please enter a valid equation.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([11, 2, 30], [1, 0, 4])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 4.0, y = -7.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 1, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 0, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([4, 7, 1], [1, 2, 0])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 2.0, y = -1.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([2, 3, 0], [5, 1, 0])\n+ 'Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [2, 0, 26])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 13.0, y = 12.5'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [0, 3, 99])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Checking if the input is valid\n+ if len(eq1) != 3 or len(eq2) != 3:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Please enter a valid equation.\")\n+ elif (eq1[0] == 0 and eq1[1] == 0) and (eq2[0] == 0 and eq2[1] == 0):\n+ print(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\")",
"line": null,
"original_line": 61,
"original_start_line": 58,
"path": "matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n if not len(eq1) == len(eq2) == 3:\r\n raise ValueError(\"Please enter a valid equation.\")\r\n elif eq1[0] == eq1[1] == eq2[0] == eq2[1] == 0:\r\n print(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\") # This should raise a ValueError()\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Solves the system of linear equation in 2 variables.\n+ :param: eq1: list of 3 numbers\n+ :param: eq2: list of 3 numbers\n+ :return: String of result\n+ Theory:-\n+ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/systems-linear-equations-matrices.html\n+ Cramer's rule for 2x2 matrix:-\n+ https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/cramers-rule-with-two-variables\n+ a1x + b1y = = d1\n+ a2x + b2y = = d2\n+ input format : [a1, b1, d1], [a2, b2, d2]\n+ d_matrix = [[a1, b1], [a2, b2]]\n+ d is determinant of matrix d_matrix\n+ dx_matrix = [[d1, b1], [d2, b2]]\n+ dx is determinant of matrix dx_matrix\n+ dy_matrix = [[a1, d1], [a2, d2]]\n+ dy is determinant of matrix dy_matrix\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 7])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [11, 22])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Please enter a valid equation.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([11, 2, 30], [1, 0, 4])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 4.0, y = -7.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 1, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 0, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([4, 7, 1], [1, 2, 0])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 2.0, y = -1.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([2, 3, 0], [5, 1, 0])\n+ 'Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [2, 0, 26])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 13.0, y = 12.5'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [0, 3, 99])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Checking if the input is valid\n+ if len(eq1) != 3 or len(eq2) != 3:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Please enter a valid equation.\")\n+ elif (eq1[0] == 0 and eq1[1] == 0) and (eq2[0] == 0 and eq2[1] == 0):\n+ print(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\")\n+ else:\n+ # Extracting the coefficients\n+ a1, b1, c1 = eq1\n+ a2, b2, c2 = eq2\n+\n+ # Calculating the determinant of matrix d_matrix, dx_matrix and dy_matrix\n+ d = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1\n+ dx = c1 * b2 - c2 * b1\n+ dy = a1 * c2 - a2 * c1\n+\n+ # Checking if the system of linear equation has a solution (Using Cramer's rule)\n+ if d == 0:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return \"Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)\"\n+ else:\n+ return \"No solution. (Inconsistent system)\"\n+ else:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return f\"Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = {0} and y = {0}\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 80,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\n raise RuntimeError(f\"Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = {0} and y = {0}\")\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Solves the system of linear equation in 2 variables.\n+ :param: eq1: list of 3 numbers\n+ :param: eq2: list of 3 numbers\n+ :return: String of result\n+ Theory:-\n+ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/systems-linear-equations-matrices.html\n+ Cramer's rule for 2x2 matrix:-\n+ https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/cramers-rule-with-two-variables\n+ a1x + b1y = = d1\n+ a2x + b2y = = d2\n+ input format : [a1, b1, d1], [a2, b2, d2]\n+ d_matrix = [[a1, b1], [a2, b2]]\n+ d is determinant of matrix d_matrix\n+ dx_matrix = [[d1, b1], [d2, b2]]\n+ dx is determinant of matrix dx_matrix\n+ dy_matrix = [[a1, d1], [a2, d2]]\n+ dy is determinant of matrix dy_matrix\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 7])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [11, 22])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Please enter a valid equation.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([11, 2, 30], [1, 0, 4])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 4.0, y = -7.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 1, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 0, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([4, 7, 1], [1, 2, 0])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 2.0, y = -1.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([2, 3, 0], [5, 1, 0])\n+ 'Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [2, 0, 26])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 13.0, y = 12.5'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [0, 3, 99])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Checking if the input is valid\n+ if len(eq1) != 3 or len(eq2) != 3:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Please enter a valid equation.\")\n+ elif (eq1[0] == 0 and eq1[1] == 0) and (eq2[0] == 0 and eq2[1] == 0):\n+ print(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\")\n+ else:\n+ # Extracting the coefficients\n+ a1, b1, c1 = eq1\n+ a2, b2, c2 = eq2\n+\n+ # Calculating the determinant of matrix d_matrix, dx_matrix and dy_matrix\n+ d = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1\n+ dx = c1 * b2 - c2 * b1\n+ dy = a1 * c2 - a2 * c1\n+\n+ # Checking if the system of linear equation has a solution (Using Cramer's rule)\n+ if d == 0:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return \"Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)\"\n+ else:\n+ return \"No solution. (Inconsistent system)\"\n+ else:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return f\"Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = {0} and y = {0}\"\n+ else:\n+ x = dx / d\n+ y = dy / d\n+ return f\"Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = {x}, y = {y}\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 84,
"original_start_line": 74,
"path": "matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n if dx == dy == 0:\r\n return \"Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)\" # This should raise a ValueError()\r\n else:\r\n return \"No solution. (Inconsistent system)\" # This should raise a ValueError()\r\n else:\r\n if dx == dy == 0:\r\n return \"Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0\"\r\n else:\r\n return f\"Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = {dx / d}, y = {dy / d}\"\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Solves the system of linear equation in 2 variables.\n+ :param: eq1: list of 3 numbers\n+ :param: eq2: list of 3 numbers\n+ :return: String of result\n+ Theory:-\n+ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/systems-linear-equations-matrices.html\n+ Cramer's rule for 2x2 matrix:-\n+ https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/cramers-rule-with-two-variables\n+ a1x + b1y = = d1\n+ a2x + b2y = = d2\n+ input format : [a1, b1, d1], [a2, b2, d2]\n+ d_matrix = [[a1, b1], [a2, b2]]\n+ d is determinant of matrix d_matrix\n+ dx_matrix = [[d1, b1], [d2, b2]]\n+ dx is determinant of matrix dx_matrix\n+ dy_matrix = [[a1, d1], [a2, d2]]\n+ dy is determinant of matrix dy_matrix\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 7])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [11, 22])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Please enter a valid equation.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([11, 2, 30], [1, 0, 4])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 4.0, y = -7.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 1, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 0, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([4, 7, 1], [1, 2, 0])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 2.0, y = -1.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([2, 3, 0], [5, 1, 0])\n+ 'Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [2, 0, 26])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 13.0, y = 12.5'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [0, 3, 99])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Checking if the input is valid\n+ if len(eq1) != 3 or len(eq2) != 3:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Please enter a valid equation.\")\n+ elif (eq1[0] == 0 and eq1[1] == 0) and (eq2[0] == 0 and eq2[1] == 0):\n+ print(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\")\n+ else:\n+ # Extracting the coefficients\n+ a1, b1, c1 = eq1\n+ a2, b2, c2 = eq2\n+\n+ # Calculating the determinant of matrix d_matrix, dx_matrix and dy_matrix\n+ d = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1\n+ dx = c1 * b2 - c2 * b1\n+ dy = a1 * c2 - a2 * c1\n+\n+ # Checking if the system of linear equation has a solution (Using Cramer's rule)\n+ if d == 0:\n+ if dx == 0 and dy == 0:\n+ return \"Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 75,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\n raise RuntimeError(\"Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)\")\n```\n\n\n@author:\ndone"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nPlease provide return type hint for the function: `calculate_x_and_y`. **If the function does not return a value, please provide the type hint as:** `def function() -> None:`\n\nPlease provide type hint for the parameter: `eq1`\n\nPlease provide type hint for the parameter: `eq2`\n\n@author:\nok \n\n@author:\nDone"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@\n+def calculate_x_and_y(eq1, eq2):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Solves the system of linear equation in 2 variables.\n+ :param: eq1: list of 3 numbers\n+ :param: eq2: list of 3 numbers\n+ :return: String of result\n+ Theory:-\n+ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/systems-linear-equations-matrices.html\n+ Cramer's rule for 2x2 matrix:-\n+ https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/cramers-rule-with-two-variables\n+ a1x + b1y = = d1\n+ a2x + b2y = = d2\n+ input format : [a1, b1, d1], [a2, b2, d2]\n+ d_matrix = [[a1, b1], [a2, b2]]\n+ d is determinant of matrix d_matrix\n+ dx_matrix = [[d1, b1], [d2, b2]]\n+ dx is determinant of matrix dx_matrix\n+ dy_matrix = [[a1, d1], [a2, d2]]\n+ dy is determinant of matrix dy_matrix\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 7])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [11, 22])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Please enter a valid equation.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([11, 2, 30], [1, 0, 4])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 4.0, y = -7.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 1, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 0, 6], [0, 0, 3])\n+ Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([4, 7, 1], [1, 2, 0])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 2.0, y = -1.0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])\n+ 'Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([2, 3, 0], [5, 1, 0])\n+ 'Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [2, 0, 26])\n+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 13.0, y = 12.5'\n+\n+ >>> calculate_x_and_y([0, 4, 50], [0, 3, 99])\n+ 'No solution. (Inconsistent system)'\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Checking if the input is valid\n+ if len(eq1) != 3 or len(eq2) != 3:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Please enter a valid equation.\")\n+ elif (eq1[0] == 0 and eq1[1] == 0) and (eq2[0] == 0 and eq2[1] == 0):\n+ print(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\")",
"line": null,
"original_line": 61,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "matrix/system_of_linear_equation_in_2_variables.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\n raise ValueError(\"Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.\")\n```\n\n\n@author:\nokie, done"
}
] |
a832ad864ed079d78195ac9c6787186b13f77844
|
diff --git a/matrix/cramers_rule_2x2.py b/matrix/cramers_rule_2x2.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..a635d66fbb6c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/matrix/cramers_rule_2x2.py
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+# https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/cramers-rule-with-two-variables
+# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cramer%27s_rule
+
+
+def cramers_rule_2x2(equation1: list[int], equation2: list[int]) -> str:
+ """
+ Solves the system of linear equation in 2 variables.
+ :param: equation1: list of 3 numbers
+ :param: equation2: list of 3 numbers
+ :return: String of result
+ input format : [a1, b1, d1], [a2, b2, d2]
+ determinant = [[a1, b1], [a2, b2]]
+ determinant_x = [[d1, b1], [d2, b2]]
+ determinant_y = [[a1, d1], [a2, d2]]
+
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([2, 3, 0], [5, 1, 0])
+ 'Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0'
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([0, 4, 50], [2, 0, 26])
+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 13.0, y = 12.5'
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([11, 2, 30], [1, 0, 4])
+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 4.0, y = -7.0'
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([4, 7, 1], [1, 2, 0])
+ 'Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = 2.0, y = -1.0'
+
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 7])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: No solution. (Inconsistent system)
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([1, 2, 3], [11, 22])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Please enter a valid equation.
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([0, 1, 6], [0, 0, 3])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: No solution. (Inconsistent system)
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([0, 0, 6], [0, 0, 3])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)
+ >>> cramers_rule_2x2([0, 4, 50], [0, 3, 99])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: No solution. (Inconsistent system)
+ """
+
+ # Check if the input is valid
+ if not len(equation1) == len(equation2) == 3:
+ raise ValueError("Please enter a valid equation.")
+ if equation1[0] == equation1[1] == equation2[0] == equation2[1] == 0:
+ raise ValueError("Both a & b of two equations can't be zero.")
+
+ # Extract the coefficients
+ a1, b1, c1 = equation1
+ a2, b2, c2 = equation2
+
+ # Calculate the determinants of the matrices
+ determinant = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1
+ determinant_x = c1 * b2 - c2 * b1
+ determinant_y = a1 * c2 - a2 * c1
+
+ # Check if the system of linear equations has a solution (using Cramer's rule)
+ if determinant == 0:
+ if determinant_x == determinant_y == 0:
+ raise ValueError("Infinite solutions. (Consistent system)")
+ else:
+ raise ValueError("No solution. (Inconsistent system)")
+ else:
+ if determinant_x == determinant_y == 0:
+ return "Trivial solution. (Consistent system) x = 0 and y = 0"
+ else:
+ x = determinant_x / determinant
+ y = determinant_y / determinant
+ return f"Non-Trivial Solution (Consistent system) x = {x}, y = {y}"
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21817@ec2b195
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,817
|
stats - fixes issue#21057 by change value check to positive semi-definite
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Fixes #21057 and now joint normal distribution with a positive semi-definite covariance matrix
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* stats
* Added support for positive semi-definite covariance matrix in joint Multivariate normal distribution.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-08-03T13:07:24Z
|
Cannot create joint normal distribution with positive semidefinite covariance matrix
I want to create a joint normal distributed random variable with a covariance matrix that is positive semidefinite but not positive definite. This seems to be impossible:
```python
import sympy.stats
sympy.stats.Normal("x", [0, 0], [[0,0], [0,0]])
```
gives
```
File "<ipython-input-28-3bd23a2d609a>", line 1, in <module>
sympy.stats.Normal("x", [0, 0], [[0,0], [0,0]])
File "/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/crv_types.py", line 2966, in Normal
return MultivariateNormal(name, mean, std)
File "/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py", line 209, in MultivariateNormal
return multivariate_rv(MultivariateNormalDistribution, name, mu, sigma)
File "/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py", line 28, in multivariate_rv
dist.check(*args)
File "/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py", line 143, in check
_value_check(sigma.is_positive_definite,
File "/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/rv.py", line 1487, in _value_check
raise ValueError(message)
ValueError: The covariance matrix must be positive definite.
```
I don't know if there is some implementation reason for this, but mathematically any positive semidefinite matrix should be accepted. I checked numpy and there it works to do:
```python
import numpy as np
np.random.multivariate_normal([0, 0], [[0, 0], [0, 0]])
```
with the expected output:
```
Out[30]: array([0., 0.])
```
|
It seems like the fix is simply changing `sigma.is_positive_definite` to `sigma.is_positive_semidefinite` in https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/2346054bb4888ef7eec2f6dad6c3dd52bf1fe927/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py#L138-L144
Reminds me of [this](https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/19935) PR. I haven't checked the code for the multivariate distributions but I suspect `pdf`, `cdf` and a whole lot of other functions would have to be changed as well.
It might be simpler just to work with constants (since I think their `pdf` and `cdf` are defined somewhere).
@Maelstrom6 Hey , I am bit new to open source contribution and would like to work on this issue, Could you give me an headstart on how to start working on this issue?
I don't have any experience with the random vectors part of SymPy but there would probably be at least 4 things that need to change:
- The assertion to check if the covariance Matrix is positive should be changed to positive semidefinite.
- The pdf should also change. According to Wikipedia:
> In the degenerate case where the covariance matrix is singular, the corresponding distribution has no density; see the section below for details. This case arises frequently in statistics; for example, in the distribution of the vector of residuals in the ordinary least squares regression.
This means that we should probably have a piecewise or if statement in the pdf function. Considering that a piecewise expression is not what people are expecting and it slows things down a bit, an if statement to return some kind of SymPy object representing a Nan would be good.
- cdf should similarly be changed if the code defines the cdf.
- The sampling which would be the main reason why people use a positive semidefinite matrix should be changed. I'm not sure how the code looks so that could either require no change or it could be more complicated.
- Testing should be done on every applicable function for random vectors.
There are probably other things to figure out along the way.
A normal distribution with zero variance is also not permitted:
```python
In [1]: from sympy.stats import *
In [2]: X = Normal('X', 0, 0)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError: Standard deviation must be positive
```
> A normal distribution with zero variance is also not permitted
The scalar normal distribution did have a PR for zero variance but it was closed because we couldn't reach an agreement on what the PDF and CDF should be and because the Wikipedia page says that the variance must be strictly positive.
The user could also replace `X = Normal('X', mu, sigma)` with `X = mu` to get the same functionality (except for sampling capabilities).
The case of zero variance for a single variate normal distribution is analogous to the case of positive semi-definite but not positive definite for the joint normal distribution. In my opinion sympy should allow it. Some arguments as for why it should:
1. Numpy allows it
```
np.random.normal(1, 0)
Out[1]: 1.0
```
2. It arises naturally from numerical situations. For example if you have two datasets like for example
```
a = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
b = [1, 1, 1, 1, 2]
```
The sample variance would be 0 for ```a``` and 0.16 for ```b```. If we want to model both as normally distributed (this assumption might be wrong but it might also be correct) in sympy we only do it directly for b and not for a, which would lead to an unnecessary special case.
3. Mathematically the 0 variance case or perhaps the limit when the variance approaching zero is usually considered to be the dirac distribution.
Perhaps sympy could support it by letting `Normal('X', 1 , 0)` return a dirac distribution.
Given that SymPy represents random variables as expressions wouldn't a dirac distribution just be `mu`?
Not really. Let's say we want to calculate the probability of the random variable falling in some range: `P(a < X < b)` This would then be the integral from `a` to `b` of the pdf of the distribution. If the range includes `mu` the integral should become 1 else 0. A constant expression really cannot capture this. I think the dirac distribution needs to implemented as a distribution.
It seems to work as far as I can tell:
```python
In [19]: mu = Symbol('mu')
In [20]: density(mu)
Out[20]: x ↦ δ(-μ + x)
In [21]: E(mu)
Out[21]: μ
In [22]: integrate(density(mu)(z), (z, 0, 1))
Out[22]: -θ(-μ) + θ(1 - μ)
In [23]: integrate(density(mu)(z), (z, mu-1, mu+1))
Out[23]: 1
In [24]: integrate(density(mu)(z), (z, mu-1, mu-0.5))
Out[24]: 0
```
Apart from these:
```python
In [25]: variance(mu) # <--- incorrect
Out[25]: μ
In [26]: E(mu**2) - E(mu)**2
Out[26]: 0
In [27]: P(mu < 1)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError: Expression containing Random Variable expected, not mu < 1
In [28]: P(mu < mu+1)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError: Expression containing Random Variable expected, not mu < mu + 1
```
> I think the dirac distribution needs to implemented as a distribution.
I'm not sure what this means. SymPy's stats module does not really provide for working with distributions rather than expressions involving random variables e.g. https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/20643#issuecomment-749473694 https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/20560#issuecomment-740792093
|
[
{
"body": "I want to create a joint normal distributed random variable with a covariance matrix that is positive semidefinite but not positive definite. This seems to be impossible:\r\n\r\n```python\r\nimport sympy.stats\r\n\r\nsympy.stats.Normal(\"x\", [0, 0], [[0,0], [0,0]])\r\n```\r\ngives\r\n\r\n```\r\n File \"<ipython-input-28-3bd23a2d609a>\", line 1, in <module>\r\n sympy.stats.Normal(\"x\", [0, 0], [[0,0], [0,0]])\r\n\r\n File \"/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/crv_types.py\", line 2966, in Normal\r\n return MultivariateNormal(name, mean, std)\r\n\r\n File \"/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py\", line 209, in MultivariateNormal\r\n return multivariate_rv(MultivariateNormalDistribution, name, mu, sigma)\r\n\r\n File \"/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py\", line 28, in multivariate_rv\r\n dist.check(*args)\r\n\r\n File \"/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py\", line 143, in check\r\n _value_check(sigma.is_positive_definite,\r\n\r\n File \"/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/stats/rv.py\", line 1487, in _value_check\r\n raise ValueError(message)\r\n\r\nValueError: The covariance matrix must be positive definite. \r\n```\r\n\r\nI don't know if there is some implementation reason for this, but mathematically any positive semidefinite matrix should be accepted. I checked numpy and there it works to do:\r\n\r\n```python\r\nimport numpy as np\r\n\r\nnp.random.multivariate_normal([0, 0], [[0, 0], [0, 0]])\r\n```\r\n\r\nwith the expected output:\r\n\r\n```\r\nOut[30]: array([0., 0.])\r\n```",
"number": 21057,
"title": "Cannot create joint normal distribution with positive semidefinite covariance matrix"
}
] |
746d7e5640fdeae864505eba8e9ce0a1ba7a1d52
|
{
"head_commit": "ec2b195a43bb51d38156295b4a5b0423ded37fda",
"head_commit_message": "changed docstrings",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py b/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py\nindex 51ccb7089ba5..57b2ab20bd84 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py\n@@ -139,10 +139,10 @@ def set(self):\n def check(mu, sigma):\n _value_check(mu.shape[0] == sigma.shape[0],\n \"Size of the mean vector and covariance matrix are incorrect.\")\n- #check if covariance matrix is positive definite or not.\n+ #check if covariance matrix is positive semi definite or not.\n if not isinstance(sigma, MatrixSymbol):\n- _value_check(sigma.is_positive_definite,\n- \"The covariance matrix must be positive definite. \")\n+ _value_check(sigma.is_positive_semidefinite,\n+ \"The covariance matrix must be positive semi definite. \")\n \n def pdf(self, *args):\n mu, sigma = self.mu, self.sigma\n@@ -182,6 +182,7 @@ def MultivariateNormal(name, mu, sigma):\n mu : List representing the mean or the mean vector\n sigma : Positive definite square matrix\n Represents covariance Matrix\n+ If `sigma` is noninvertible then only sampling is supported currently\n \n Returns\n =======\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_joint_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_joint_rv.py\nindex c05161c5bad6..2f9339c08a59 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_joint_rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_joint_rv.py\n@@ -25,8 +25,6 @@ def test_Normal():\n assert density(m)(1, 2) == 1/(2*pi)\n assert m.pspace.distribution.set == ProductSet(S.Reals, S.Reals)\n raises (ValueError, lambda:m[2])\n- raises (ValueError,\\\n- lambda: Normal('M',[1, 2], [[0, 0], [0, 1]]))\n n = Normal('B', [1, 2, 3], [[1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]])\n p = Normal('C', Matrix([1, 2]), Matrix([[1, 0], [0, 1]]))\n assert density(m)(x, y) == density(p)(x, y)\n@@ -354,3 +352,19 @@ def test_sample_seed():\n assert all(s1 != s2)\n except NotImplementedError:\n continue\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_21057():\n+ m = Normal(\"x\", [0, 0], [[0, 0], [0, 0]])\n+ n = MultivariateNormal(\"x\", [0, 0], [[0, 0], [0, 0]])\n+ assert m == n\n+ libraries = ['scipy', 'numpy', 'pymc3']\n+ for library in libraries:\n+ try:\n+ imported_lib = import_module(library)\n+ if imported_lib:\n+ s1 = sample(m, size=8)\n+ s2 = sample(n, size=8)\n+ assert tuple(s1.flatten()) == tuple(s2.flatten())\n+ except NotImplementedError:\n+ continue\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -182,6 +182,7 @@ def MultivariateNormal(name, mu, sigma):\n mu : List representing the mean or the mean vector\n sigma : Positive definite square matrix",
"line": null,
"original_line": 183,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nShould it say `sigma : Positive semidefinite square matrix` instead? \n\n@author:\nWell , yes i guess since all Positive definite square matrix are subset of Positive semidefinite square matrix's , I'll update the change."
}
] |
ffab691c0aa47000b632e5381b7a46f3eef2f5a7
|
diff --git a/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py b/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py
index 51ccb7089ba5..26e1d84a5d73 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py
@@ -139,10 +139,10 @@ def set(self):
def check(mu, sigma):
_value_check(mu.shape[0] == sigma.shape[0],
"Size of the mean vector and covariance matrix are incorrect.")
- #check if covariance matrix is positive definite or not.
+ #check if covariance matrix is positive semi definite or not.
if not isinstance(sigma, MatrixSymbol):
- _value_check(sigma.is_positive_definite,
- "The covariance matrix must be positive definite. ")
+ _value_check(sigma.is_positive_semidefinite,
+ "The covariance matrix must be positive semi definite. ")
def pdf(self, *args):
mu, sigma = self.mu, self.sigma
@@ -180,8 +180,9 @@ def MultivariateNormal(name, mu, sigma):
==========
mu : List representing the mean or the mean vector
- sigma : Positive definite square matrix
+ sigma : Positive semidefinite square matrix
Represents covariance Matrix
+ If `sigma` is noninvertible then only sampling is supported currently
Returns
=======
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_joint_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_joint_rv.py
index c05161c5bad6..72c7086a435f 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_joint_rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_joint_rv.py
@@ -25,8 +25,6 @@ def test_Normal():
assert density(m)(1, 2) == 1/(2*pi)
assert m.pspace.distribution.set == ProductSet(S.Reals, S.Reals)
raises (ValueError, lambda:m[2])
- raises (ValueError,\
- lambda: Normal('M',[1, 2], [[0, 0], [0, 1]]))
n = Normal('B', [1, 2, 3], [[1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]])
p = Normal('C', Matrix([1, 2]), Matrix([[1, 0], [0, 1]]))
assert density(m)(x, y) == density(p)(x, y)
@@ -354,3 +352,23 @@ def test_sample_seed():
assert all(s1 != s2)
except NotImplementedError:
continue
+
+
+def test_issue_21057():
+ m = Normal("x", [0, 0], [[0, 0], [0, 0]])
+ n = MultivariateNormal("x", [0, 0], [[0, 0], [0, 0]])
+ p = Normal("x", [0, 0], [[0, 0], [0, 1]])
+ assert m == n
+ libraries = ['scipy', 'numpy', 'pymc3']
+ for library in libraries:
+ try:
+ imported_lib = import_module(library)
+ if imported_lib:
+ s1 = sample(m, size=8)
+ s2 = sample(n, size=8)
+ s3 = sample(p, size=8)
+ assert tuple(s1.flatten()) == tuple(s2.flatten())
+ for s in s3:
+ assert tuple(s.flatten()) in p.pspace.distribution.set
+ except NotImplementedError:
+ continue
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-7034@5e69a3b
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 7,034
|
Convert snake_case to camelCase or PascalCase (#7028)
|
### Describe your change:
Fixes #7028
* [X] Add an algorithm?
* [ ] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [ ] Documentation change?
### Checklist:
* [X] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [X] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [X] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [X] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [X] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [X] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [X] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [X] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [X] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [X] All new algorithms have a URL in its comments that points to Wikipedia or other similar explanation.
* [X] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the commit message contains `Fixes: #{$ISSUE_NO}`.
|
2022-10-12T09:48:09Z
|
Convert snake_case to camelCase or PascalCase
### Feature description
An algorithm that given a string formatted as snake_case returns it as camelCase or PascalCase depending on Boolean parameter.
Examples:
`def snake_to_camel_case(input: str, use_pascal: bool = False) -> str`
`snake_to_camel_case('some_string_in_snake_case') -> 'someStringInSnakeCase'`
`snake_to_camel_case('some_string_in_snake_case', True) -> 'SomeStringInSnakeCase'`
### Would you like to work on this feature?
- [X] Yes, I want to work on this feature!
|
Please assign it to me, I have almost finished it
|
[
{
"body": "### Feature description\n\nAn algorithm that given a string formatted as snake_case returns it as camelCase or PascalCase depending on Boolean parameter.\r\n\r\nExamples:\r\n\r\n`def snake_to_camel_case(input: str, use_pascal: bool = False) -> str`\r\n`snake_to_camel_case('some_string_in_snake_case') -> 'someStringInSnakeCase'`\r\n`snake_to_camel_case('some_string_in_snake_case', True) -> 'SomeStringInSnakeCase'`\n\n### Would you like to work on this feature?\n\n- [X] Yes, I want to work on this feature!",
"number": 7028,
"title": "Convert snake_case to camelCase or PascalCase"
}
] |
f0d1a42deb146bebcdf7b1b2ec788c815ede452a
|
{
"head_commit": "5e69a3b7992e7fa63e91c587d39c3f1c5e70e11c",
"head_commit_message": "Added snake_case to Camel or Pascal case Fixes: #7028",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/strings/snake_case_to_camel_pascal_case.py b/strings/snake_case_to_camel_pascal_case.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..614cb841fd18\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/strings/snake_case_to_camel_pascal_case.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@\n+def snake_to_camel_case(input: str, use_pascal: bool = False) -> str:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Transforms a snake_case fiven string to camelCase (or PascalCase if indicated)\n+ (defaults to not use Pascal)\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string\")\n+ 'someRandomString'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string\", use_pascal=True)\n+ 'SomeRandomString'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string_with_numbers_123\")\n+ 'someRandomStringWithNumbers123'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string_with_numbers_123\", use_pascal=True)\n+ 'SomeRandomStringWithNumbers123'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(123)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Expected string as input, found <class 'int'>\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_string\", use_pascal=\"True\")\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Expected boolean as use_pascal parameter, found <class 'str'>\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not isinstance(input, str):\n+ raise ValueError(f\"Expected string as input, found {type(input)}\")\n+ if not isinstance(use_pascal, bool):\n+ raise ValueError(\n+ f\"Expected boolean as use_pascal parameter, found {type(use_pascal)}\"\n+ )\n+\n+ words = input.split(\"_\")\n+\n+ start_index = 0 if use_pascal else 1\n+\n+ words_to_capitalize = words[start_index:]\n+\n+ capitalized_words = []\n+\n+ for word in words_to_capitalize:\n+ capitalized_words.append(word[0].upper() + word[1:])\n+\n+ result = \"\" if use_pascal else words[0]\n+\n+ for word in capitalized_words:\n+ result += word\n+\n+ return result\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ from doctest import testmod\n+\n+ testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@\n+def snake_to_camel_case(input: str, use_pascal: bool = False) -> str:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Transforms a snake_case fiven string to camelCase (or PascalCase if indicated)\n+ (defaults to not use Pascal)\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string\")\n+ 'someRandomString'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string\", use_pascal=True)\n+ 'SomeRandomString'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string_with_numbers_123\")\n+ 'someRandomStringWithNumbers123'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string_with_numbers_123\", use_pascal=True)\n+ 'SomeRandomStringWithNumbers123'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(123)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Expected string as input, found <class 'int'>\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_string\", use_pascal=\"True\")\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Expected boolean as use_pascal parameter, found <class 'str'>\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not isinstance(input, str):\n+ raise ValueError(f\"Expected string as input, found {type(input)}\")\n+ if not isinstance(use_pascal, bool):\n+ raise ValueError(\n+ f\"Expected boolean as use_pascal parameter, found {type(use_pascal)}\"\n+ )\n+\n+ words = input.split(\"_\")\n+\n+ start_index = 0 if use_pascal else 1\n+\n+ words_to_capitalize = words[start_index:]\n+\n+ capitalized_words = []\n+\n+ for word in words_to_capitalize:\n+ capitalized_words.append(word[0].upper() + word[1:])",
"line": null,
"original_line": 45,
"original_start_line": 42,
"path": "strings/snake_case_to_camel_pascal_case.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n capitalized_words = [(word[0].upper() + word[1:]) for word in words_to_capitalize]\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@\n+def snake_to_camel_case(input: str, use_pascal: bool = False) -> str:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Transforms a snake_case fiven string to camelCase (or PascalCase if indicated)\n+ (defaults to not use Pascal)\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string\")\n+ 'someRandomString'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string\", use_pascal=True)\n+ 'SomeRandomString'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string_with_numbers_123\")\n+ 'someRandomStringWithNumbers123'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_random_string_with_numbers_123\", use_pascal=True)\n+ 'SomeRandomStringWithNumbers123'\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(123)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Expected string as input, found <class 'int'>\n+\n+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(\"some_string\", use_pascal=\"True\")\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ ValueError: Expected boolean as use_pascal parameter, found <class 'str'>\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not isinstance(input, str):\n+ raise ValueError(f\"Expected string as input, found {type(input)}\")\n+ if not isinstance(use_pascal, bool):\n+ raise ValueError(\n+ f\"Expected boolean as use_pascal parameter, found {type(use_pascal)}\"\n+ )\n+\n+ words = input.split(\"_\")\n+\n+ start_index = 0 if use_pascal else 1\n+\n+ words_to_capitalize = words[start_index:]\n+\n+ capitalized_words = []\n+\n+ for word in words_to_capitalize:\n+ capitalized_words.append(word[0].upper() + word[1:])\n+\n+ result = \"\" if use_pascal else words[0]\n+\n+ for word in capitalized_words:\n+ result += word",
"line": null,
"original_line": 50,
"original_start_line": 47,
"path": "strings/snake_case_to_camel_pascal_case.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nHere instead of adding it to a string you can just use the `\"\".join(...)` method"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@\n+def snake_to_camel_case(input: str, use_pascal: bool = False) -> str:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Transforms a snake_case fiven string to camelCase (or PascalCase if indicated)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 3,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "strings/snake_case_to_camel_pascal_case.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n Transforms a snake_case given string to camelCase (or PascalCase if indicated)\r\n```"
}
] |
80dc427a5b9b82a04eda68f283778b67ac37b739
|
diff --git a/strings/snake_case_to_camel_pascal_case.py b/strings/snake_case_to_camel_pascal_case.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..7b2b61d1d1cf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/strings/snake_case_to_camel_pascal_case.py
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+def snake_to_camel_case(input: str, use_pascal: bool = False) -> str:
+ """
+ Transforms a snake_case given string to camelCase (or PascalCase if indicated)
+ (defaults to not use Pascal)
+
+ >>> snake_to_camel_case("some_random_string")
+ 'someRandomString'
+
+ >>> snake_to_camel_case("some_random_string", use_pascal=True)
+ 'SomeRandomString'
+
+ >>> snake_to_camel_case("some_random_string_with_numbers_123")
+ 'someRandomStringWithNumbers123'
+
+ >>> snake_to_camel_case("some_random_string_with_numbers_123", use_pascal=True)
+ 'SomeRandomStringWithNumbers123'
+
+ >>> snake_to_camel_case(123)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Expected string as input, found <class 'int'>
+
+ >>> snake_to_camel_case("some_string", use_pascal="True")
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ ValueError: Expected boolean as use_pascal parameter, found <class 'str'>
+ """
+
+ if not isinstance(input, str):
+ raise ValueError(f"Expected string as input, found {type(input)}")
+ if not isinstance(use_pascal, bool):
+ raise ValueError(
+ f"Expected boolean as use_pascal parameter, found {type(use_pascal)}"
+ )
+
+ words = input.split("_")
+
+ start_index = 0 if use_pascal else 1
+
+ words_to_capitalize = words[start_index:]
+
+ capitalized_words = [word[0].upper() + word[1:] for word in words_to_capitalize]
+
+ initial_word = "" if use_pascal else words[0]
+
+ return "".join([initial_word] + capitalized_words)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ from doctest import testmod
+
+ testmod()
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-5882@966fe8d
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 5,882
|
Minmum path sum
|
### Describe your change:
Added an algorithm that takes a 2 dimensional grid of numbers, and finds the path starting from the top left and ending at the bottom right with the lowest possible sum of numbers along the path. It then returns the sum of all numbers along that path.
For Example:
Input: [
[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]
]
Expected output: 7
* [x] Add an algorithm?
* [ ] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [ ] Documentation change?
### Checklist:
* [x] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [x] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [x] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [x] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [x] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [x] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [x] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [x] All new algorithms have a URL in its comments that points to Wikipedia or other similar explanation.
* [x] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the commit message contains `Fixes: #{$ISSUE_NO}`.
fixes #4796
|
2021-12-24T22:40:15Z
|
DSA-Matrix-Python- Minimum Path sum
Hey there, I'm participating in #hactoberfest2k21, Please assign me the issue. Good day!
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right, which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example:
Input: grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
Output: 7
|
Please assign me this issue. I am a good programmer and a beginner at open source. I would give it my best!
Please assign me this issue. I want to take my first steps towards contributing in open-source.
Hello please assigne me this issue.I am a beginner at open source and want to hone my skills.
`I can do this! please assign me this issue`
I can complete this Pythagoras Generator, Please assign this to me
I am new to opensource and I am willing to learn and contribute.
|
[
{
"body": "Hey there, I'm participating in #hactoberfest2k21, Please assign me the issue. Good day!\r\nGiven a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right, which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.You can only move either down or right at any point in time.\r\nExample:\r\nInput: grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]\r\nOutput: 7\r\n",
"number": 4796,
"title": "DSA-Matrix-Python- Minimum Path sum"
}
] |
9af2eef9b3761bf51580dedfb6fa7136ca0c5c2c
|
{
"head_commit": "966fe8d6dda81e2376dbc10e5754e677973d6f36",
"head_commit_message": "added description to minimum_path_sum",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/graphs/minimum_path_sum.py b/graphs/minimum_path_sum.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..faf104c2e107\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/graphs/minimum_path_sum.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@\n+def min_path(grid):\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Find the path from top left to bottom right of array of numbers\n+ with the lowest possible sum and return the sum along this path.\n+ >>> min_path([\n+ ... [1, 3, 1],\n+ ... [1, 5, 1],\n+ ... [4, 2, 1],\n+ ... ])\n+ 7\n+\n+ >>> min_path([\n+ ... [1, 0, 5, 6, 7],\n+ ... [8, 9, 0, 4, 2],\n+ ... [4, 4, 4, 5, 1],\n+ ... [9, 6, 3, 1, 0],\n+ ... [8, 4, 3, 2, 7],\n+ ... ])\n+ 20\n+\n+ >>> min_path(None)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: The grid does not contain the appropriate information\n+\n+ >>> min_path([[]])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: The grid does not contain the appropriate information\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not grid or not grid[0]:\n+ raise TypeError(\"The grid does not contain the appropriate information\")\n+\n+ for cell_n in range(1, len(grid[0])):\n+ grid[0][cell_n] += grid[0][cell_n - 1]\n+ row_above = grid[0]\n+\n+ for row_n in range(1, len(grid)):\n+ current_row = grid[row_n]\n+ grid[row_n] = fill_row(current_row, row_above)\n+ row_above = grid[row_n]\n+\n+ return grid[-1][-1]\n+\n+\n+def fill_row(current_row, row_above):\n+\n+ current_row[0] += row_above[0]\n+ for cell_n in range(1, len(current_row)):\n+ current_row[cell_n] += min(current_row[cell_n - 1], row_above[cell_n])\n+\n+ return current_row\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ import doctest\n+\n+ doctest.testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@\n+def min_path(grid):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "graphs/minimum_path_sum.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@unknown:\nPlease provide return type hint for the function: `min_path`. **If the function does not return a value, please provide the type hint as:** `def function() -> None:`\n\nPlease provide type hint for the parameter: `grid`"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@\n+def min_path(grid):\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Find the path from top left to bottom right of array of numbers\n+ with the lowest possible sum and return the sum along this path.\n+ >>> min_path([\n+ ... [1, 3, 1],\n+ ... [1, 5, 1],\n+ ... [4, 2, 1],\n+ ... ])\n+ 7\n+\n+ >>> min_path([\n+ ... [1, 0, 5, 6, 7],\n+ ... [8, 9, 0, 4, 2],\n+ ... [4, 4, 4, 5, 1],\n+ ... [9, 6, 3, 1, 0],\n+ ... [8, 4, 3, 2, 7],\n+ ... ])\n+ 20\n+\n+ >>> min_path(None)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: The grid does not contain the appropriate information\n+\n+ >>> min_path([[]])\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: The grid does not contain the appropriate information\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not grid or not grid[0]:\n+ raise TypeError(\"The grid does not contain the appropriate information\")\n+\n+ for cell_n in range(1, len(grid[0])):\n+ grid[0][cell_n] += grid[0][cell_n - 1]\n+ row_above = grid[0]\n+\n+ for row_n in range(1, len(grid)):\n+ current_row = grid[row_n]\n+ grid[row_n] = fill_row(current_row, row_above)\n+ row_above = grid[row_n]\n+\n+ return grid[-1][-1]\n+\n+\n+def fill_row(current_row, row_above):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 48,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "graphs/minimum_path_sum.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@unknown:\nAs there is no test file in this pull request nor any test function or class in the file `graphs/minimum_path_sum.py`, please provide doctest for the function `fill_row`\n\nPlease provide return type hint for the function: `fill_row`. **If the function does not return a value, please provide the type hint as:** `def function() -> None:`\n\nPlease provide type hint for the parameter: `current_row`\n\nPlease provide type hint for the parameter: `row_above`"
}
] |
a77cb2f41ca1a9e184aa65d364f77ba0f90eb53f
|
diff --git a/graphs/minimum_path_sum.py b/graphs/minimum_path_sum.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..df1e545df3d0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/graphs/minimum_path_sum.py
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+def min_path_sum(grid: list) -> int:
+ """
+ Find the path from top left to bottom right of array of numbers
+ with the lowest possible sum and return the sum along this path.
+ >>> min_path_sum([
+ ... [1, 3, 1],
+ ... [1, 5, 1],
+ ... [4, 2, 1],
+ ... ])
+ 7
+
+ >>> min_path_sum([
+ ... [1, 0, 5, 6, 7],
+ ... [8, 9, 0, 4, 2],
+ ... [4, 4, 4, 5, 1],
+ ... [9, 6, 3, 1, 0],
+ ... [8, 4, 3, 2, 7],
+ ... ])
+ 20
+
+ >>> min_path_sum(None)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: The grid does not contain the appropriate information
+
+ >>> min_path_sum([[]])
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: The grid does not contain the appropriate information
+ """
+
+ if not grid or not grid[0]:
+ raise TypeError("The grid does not contain the appropriate information")
+
+ for cell_n in range(1, len(grid[0])):
+ grid[0][cell_n] += grid[0][cell_n - 1]
+ row_above = grid[0]
+
+ for row_n in range(1, len(grid)):
+ current_row = grid[row_n]
+ grid[row_n] = fill_row(current_row, row_above)
+ row_above = grid[row_n]
+
+ return grid[-1][-1]
+
+
+def fill_row(current_row: list, row_above: list) -> list:
+ """
+ >>> fill_row([2, 2, 2], [1, 2, 3])
+ [3, 4, 5]
+ """
+
+ current_row[0] += row_above[0]
+ for cell_n in range(1, len(current_row)):
+ current_row[cell_n] += min(current_row[cell_n - 1], row_above[cell_n])
+
+ return current_row
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import doctest
+
+ doctest.testmod()
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
xonsh__xonsh-2530@534f496
|
xonsh/xonsh
|
Python
| 2,530
|
Fixes spaces in readline tab completer
|
Should fix #2485
|
2017-11-10T02:40:52Z
|
Tab completion breaks on paths with spaces
```
de3lxl-106789 /tmp $ xonfig
+------------------+----------------------+
| xonsh | 0.5.12.dev47.dev102 |
| Git SHA | c787f9ab |
| Commit Date | Aug 16 00:10:57 2017 |
| Python | 3.4.3 |
| PLY | 3.8 |
| have readline | True |
| prompt toolkit | 1.0.0 |
| shell type | readline |
| pygments | 1.6 |
| on posix | True |
| on linux | True |
| distro | Ubuntu |
| on darwin | False |
| on windows | False |
| on cygwin | False |
| is superuser | False |
| default encoding | utf-8 |
| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |
| encoding errors | surrogateescape |
+------------------+----------------------+
de3lxl-106789 /tmp $ mkdir 'a space'
de3lxl-106789 /tmp $ touch 'a space/test.txt'
de3lxl-106789 /tmp $ cat 'a space'<tab>
de3lxl-106789 /tmp $ cat 'a 'a space/test.txt'
```
The last two lines demonstrate the problem: Pressing <tab> in the second-to-last line at the where indicated produces the last line (note the double 'a), this doesn't seem to be a mere visual/refreshing issue, the produced command is actually not understood by xonsh (pressing return prompts for more input because of the resulting uneven number of ').
OS is Ubuntu 14.04.5 LTS, terminal is rxvt-unicode-256color.
|
Thanks for reporting @Droggelbecher ! This seems like a regression.
I've occasionally seen similar issues with partial completes not substituting correctly.
I had the same issue but it was fixed when I upgraded to prompt_toolkit version 1.0.15
Ok! I am not seeing this issue anymore on PTK v1.015, however, I am still seeing it on readline.
Should be fixed by #2530
|
[
{
"body": "```\r\nde3lxl-106789 /tmp $ xonfig\r\n+------------------+----------------------+\r\n| xonsh | 0.5.12.dev47.dev102 |\r\n| Git SHA | c787f9ab |\r\n| Commit Date | Aug 16 00:10:57 2017 |\r\n| Python | 3.4.3 |\r\n| PLY | 3.8 |\r\n| have readline | True |\r\n| prompt toolkit | 1.0.0 |\r\n| shell type | readline |\r\n| pygments | 1.6 |\r\n| on posix | True |\r\n| on linux | True |\r\n| distro | Ubuntu |\r\n| on darwin | False |\r\n| on windows | False |\r\n| on cygwin | False |\r\n| is superuser | False |\r\n| default encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| xonsh encoding | utf-8 |\r\n| encoding errors | surrogateescape |\r\n+------------------+----------------------+\r\nde3lxl-106789 /tmp $ mkdir 'a space'\r\n\r\nde3lxl-106789 /tmp $ touch 'a space/test.txt'\r\nde3lxl-106789 /tmp $ cat 'a space'<tab>\r\nde3lxl-106789 /tmp $ cat 'a 'a space/test.txt'\r\n```\r\nThe last two lines demonstrate the problem: Pressing <tab> in the second-to-last line at the where indicated produces the last line (note the double 'a), this doesn't seem to be a mere visual/refreshing issue, the produced command is actually not understood by xonsh (pressing return prompts for more input because of the resulting uneven number of ').\r\n\r\nOS is Ubuntu 14.04.5 LTS, terminal is rxvt-unicode-256color.\r\n\r\n",
"number": 2485,
"title": "Tab completion breaks on paths with spaces"
}
] |
20dfda5d59a4d109e9c19bc73119c3cd6870d703
|
{
"head_commit": "534f4967c2c4164fa3cfc9db5f05108842f2729c",
"head_commit_message": "indents",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/docs/intro.rst b/docs/intro.rst\nindex 6bc36d9bb8..43aec33c65 100644\n--- a/docs/intro.rst\n+++ b/docs/intro.rst\n@@ -42,6 +42,7 @@ the xonsh shell\n \"Conches for the xonsh god!\",\n \"Python-powered, cross-platform, Unix-gazing shell\",\n \"Tab completion in Alderaan places\",\n+ \"This fix was trickier expected\",\n \"Exploiting the workers and hanging on to outdated imperialist dogma since 2015.\"\n ];\n document.write(taglines[Math.floor(Math.random() * taglines.length)]);\ndiff --git a/news/aspace.rst b/news/aspace.rst\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 0000000000..42d66abcf8\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/news/aspace.rst\n@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@\n+**Added:** None\n+\n+**Changed:** None\n+\n+**Deprecated:** None\n+\n+**Removed:** None\n+\n+**Fixed:**\n+\n+* Fixed issues with readline completer tab completing entries\n+ with spaces.\n+* Fixed ``xonsh.tools.columnize()`` bug the prevented single-row\n+ input from being columnized correctly.\n+\n+**Security:** None\ndiff --git a/xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py b/xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py\nindex 77550bead0..f5f50b61cc 100644\n--- a/xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py\n+++ b/xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py\n@@ -190,7 +190,7 @@ def _bash_quote_paths(paths, start, end):\n if end in s:\n s = s.replace(end, ''.join('\\\\%s' % i for i in end))\n out.add(start + s + end)\n- return out\n+ return out, need_quotes\n \n \n BASH_COMPLETE_SCRIPT = r\"\"\"\n@@ -270,7 +270,8 @@ def bash_completions(prefix, line, begidx, endidx, env=None, paths=None,\n from the environment and platform.\n quote_paths : callable, optional\n A functions that quotes file system paths. You shouldn't normally need\n- this as the default is acceptable 99+% of the time.\n+ this as the default is acceptable 99+% of the time. This function should\n+ a set of the new paths and a boolean for whether the paths were quoted.\n \n Returns\n -------\n@@ -335,7 +336,8 @@ def bash_completions(prefix, line, begidx, endidx, env=None, paths=None,\n strip_len += 1\n \n if '-o noquote' not in complete_stmt:\n- out = quote_paths(out, '', '')\n+ out, need_qoutes = quote_paths(out, '', '')\n+ strip_len += int(need_qoutes)\n if '-o nospace' in complete_stmt:\n out = set([x.rstrip() for x in out])\n \ndiff --git a/xonsh/completers/path.py b/xonsh/completers/path.py\nindex 373e8317dc..268a623516 100644\n--- a/xonsh/completers/path.py\n+++ b/xonsh/completers/path.py\n@@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ def _quote_paths(paths, start, end, append_end=True):\n s = s.replace(end, ''.join('\\\\%s' % i for i in end))\n s = start + s + end if append_end else start + s\n out.add(s)\n- return out\n+ return out, need_quotes\n \n \n def _joinpath(path):\n@@ -298,10 +298,10 @@ def complete_path(prefix, line, start, end, ctx, cdpath=True, filtfunc=None):\n if cdpath:\n _add_cdpaths(paths, prefix)\n paths = set(filter(filtfunc, paths))\n- paths = _quote_paths({_normpath(s) for s in paths},\n- path_str_start,\n- path_str_end,\n- append_end)\n+ paths, _ = _quote_paths({_normpath(s) for s in paths},\n+ path_str_start,\n+ path_str_end,\n+ append_end)\n paths.update(filter(filtfunc, _dots(prefix)))\n paths.update(filter(filtfunc, _env(prefix)))\n return paths, lprefix\ndiff --git a/xonsh/readline_shell.py b/xonsh/readline_shell.py\nindex 849055a1ef..bb76391e76 100644\n--- a/xonsh/readline_shell.py\n+++ b/xonsh/readline_shell.py\n@@ -268,6 +268,43 @@ def __init__(self, completekey='tab', stdin=None, stdout=None, **kwargs):\n self._current_indent = ''\n self._current_prompt = ''\n self._force_hide = None\n+ self._complete_only_last_table = {\n+ # Truth table for completions, keys are:\n+ # (prefix_begs_quote, prefix_ends_quote, i_ends_quote,\n+ # last_starts_with_prefix, i_has_space)\n+ (True, True, True, True, True): True,\n+ (True, True, True, True, False): True,\n+ (True, True, True, False, True): False,\n+ (True, True, True, False, False): True,\n+ (True, True, False, True, True): False,\n+ (True, True, False, True, False): False,\n+ (True, True, False, False, True): False,\n+ (True, True, False, False, False): False,\n+ (True, False, True, True, True): True,\n+ (True, False, True, True, False): False,\n+ (True, False, True, False, True): False,\n+ (True, False, True, False, False): True,\n+ (True, False, False, True, True): False,\n+ (True, False, False, True, False): False,\n+ (True, False, False, False, True): False,\n+ (True, False, False, False, False): False,\n+ (False, True, True, True, True): True,\n+ (False, True, True, True, False): True,\n+ (False, True, True, False, True): True,\n+ (False, True, True, False, False): True,\n+ (False, True, False, True, True): False,\n+ (False, True, False, True, False): False,\n+ (False, True, False, False, True): False,\n+ (False, True, False, False, False): False,\n+ (False, False, True, True, True): True,\n+ (False, False, True, True, False): False,\n+ (False, False, True, False, True): False,\n+ (False, False, True, False, False): True,\n+ (False, False, False, True, True): True,\n+ (False, False, False, True, False): False,\n+ (False, False, False, False, True): False,\n+ (False, False, False, False, False): False,\n+ }\n self.cmdqueue = collections.deque()\n \n def __del__(self):\n@@ -296,11 +333,15 @@ def parseline(self, line):\n return '', line, line\n \n def _querycompletions(self, completions, loc):\n- \"\"\"Returns whether or not we should show completions\"\"\"\n+ \"\"\"Returns whether or not we should show completions. 0 means that prefixes\n+ should not be shown, 1 means that there is a common prefix among all completions\n+ and they should be shown, while 2 means that there is no common prefix but\n+ we are under the query limit and they should be shown.\n+ \"\"\"\n if os.path.commonprefix([c[loc:] for c in completions]):\n- return True\n+ return 1\n elif len(completions) <= builtins.__xonsh_env__.get('COMPLETION_QUERY_LIMIT'):\n- return True\n+ return 2\n msg = '\\nDisplay all {} possibilities? '.format(len(completions))\n msg += '({GREEN}y{NO_COLOR} or {RED}n{NO_COLOR})'\n self.print_color(msg, end='', flush=True, file=sys.stderr)\n@@ -311,7 +352,7 @@ def _querycompletions(self, completions, loc):\n print()\n if not show_completions:\n rl_on_new_line()\n- return False\n+ return 0\n w, h = shutil.get_terminal_size()\n lines = columnize(completions, width=w)\n more_msg = self.format_color('{YELLOW}==={NO_COLOR} more or '\n@@ -325,10 +366,10 @@ def _querycompletions(self, completions, loc):\n print(flush=True, file=sys.stderr)\n if q == 'q':\n rl_on_new_line()\n- return False\n+ return 0\n print(''.join(lines), end='', flush=True, file=sys.stderr)\n rl_on_new_line()\n- return False\n+ return 0\n \n def completedefault(self, prefix, line, begidx, endidx):\n \"\"\"Implements tab-completion for text.\"\"\"\n@@ -341,9 +382,31 @@ def completedefault(self, prefix, line, begidx, endidx):\n begidx, endidx,\n ctx=self.ctx)\n chopped = prefix[:-l]\n- rtn_completions = [chopped + i for i in completions]\n+ if chopped:\n+ rtn_completions = [chopped + i for i in completions]\n+ else:\n+ rtn_completions = completions\n+ rtn = []\n+ prefix_begs_quote = prefix.startswith(\"'\") or prefix.startswith('\"')\n+ prefix_ends_quote = prefix.endswith(\"'\") or prefix.endswith('\"')\n+ for i in rtn_completions:\n+ i_ends_quote = i.endswith(\"'\") or i.endswith('\"')\n+ last = i.rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]\n+ last_starts_prefix = last.startswith(prefix)\n+ i_has_space = ' ' in i\n+ key = (prefix_begs_quote, prefix_ends_quote, i_ends_quote,\n+ last_starts_prefix, i_has_space)\n+ rtn.append(last if self._complete_only_last_table[key] else i)\n+ # return based on show completions\n show_completions = self._querycompletions(completions, endidx - begidx)\n- return rtn_completions if show_completions else []\n+ if show_completions == 0:\n+ return []\n+ elif show_completions == 1:\n+ return rtn\n+ elif show_completions == 2:\n+ return completions\n+ else:\n+ raise ValueError('query compeltions flag not understood.')\n \n # tab complete on first index too\n completenames = completedefault\ndiff --git a/xonsh/tools.py b/xonsh/tools.py\nindex 1c2338f174..2001ab63fe 100644\n--- a/xonsh/tools.py\n+++ b/xonsh/tools.py\n@@ -1923,12 +1923,21 @@ def columnize(elems, width=80, newline='\\n'):\n The newline character will be appended to the end of each line.\n \"\"\"\n sizes = [len(e) + 1 for e in elems]\n+ total = sum(sizes)\n nelem = len(elems)\n- ncols = 1\n- nrows = len(sizes)\n- columns = [sizes]\n- last_longest_row = max(sizes)\n- while True:\n+ if total - 1 <= width:\n+ ncols = len(sizes)\n+ nrows = 1\n+ columns = [sizes]\n+ last_longest_row = total\n+ enter_loop = False\n+ else:\n+ ncols = 1\n+ nrows = len(sizes)\n+ columns = [sizes]\n+ last_longest_row = max(sizes)\n+ enter_loop = True\n+ while enter_loop:\n longest_row = sum(map(max, columns))\n if longest_row - 1 <= width:\n # we might be able to fit another column.\ndiff --git a/xonsh/xonfig.py b/xonsh/xonfig.py\nindex b457a77ffe..ed2da45e87 100644\n--- a/xonsh/xonfig.py\n+++ b/xonsh/xonfig.py\n@@ -577,6 +577,7 @@ def TAGLINES():\n \"Conches for the xonsh god!\",\n \"Python-powered, cross-platform, Unix-gazing shell\",\n \"Tab completion in Alderaan places\",\n+ \"This fix was trickier expected\",\n ]\n \n \n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -335,7 +336,8 @@ def bash_completions(prefix, line, begidx, endidx, env=None, paths=None,\n strip_len += 1\n \n if '-o noquote' not in complete_stmt:\n- out = quote_paths(out, '', '')\n+ out, need_qoutes = quote_paths(out, '', '')\n+ strip_len += int(need_qoutes)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 340,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n`need_quotes`"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -335,7 +336,8 @@ def bash_completions(prefix, line, begidx, endidx, env=None, paths=None,\n strip_len += 1\n \n if '-o noquote' not in complete_stmt:\n- out = quote_paths(out, '', '')\n+ out, need_qoutes = quote_paths(out, '', '')",
"line": null,
"original_line": 339,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n`need_quotes`"
}
] |
60365ff00c59f5e712bda98e889cd1987c9c625f
|
diff --git a/docs/intro.rst b/docs/intro.rst
index 56cf68a2b8..d946437ba6 100644
--- a/docs/intro.rst
+++ b/docs/intro.rst
@@ -42,6 +42,7 @@ the xonsh shell
"Conches for the xonsh god!",
"Python-powered, cross-platform, Unix-gazing shell",
"Tab completion in Alderaan places",
+ "This fix was trickier than expected",
"Exploiting the workers and hanging on to outdated imperialist dogma since 2015."
];
document.write(taglines[Math.floor(Math.random() * taglines.length)]);
diff --git a/news/aspace.rst b/news/aspace.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..42d66abcf8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/news/aspace.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+**Added:** None
+
+**Changed:** None
+
+**Deprecated:** None
+
+**Removed:** None
+
+**Fixed:**
+
+* Fixed issues with readline completer tab completing entries
+ with spaces.
+* Fixed ``xonsh.tools.columnize()`` bug the prevented single-row
+ input from being columnized correctly.
+
+**Security:** None
diff --git a/xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py b/xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py
index 48b4774464..d27bad7097 100644
--- a/xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py
+++ b/xonsh/completers/bash_completion.py
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@
import functools
import subprocess
-__version__ = '0.1.0'
+__version__ = '0.2.1'
@functools.lru_cache(1)
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ def _bash_quote_paths(paths, start, end):
if end in s:
s = s.replace(end, ''.join('\\%s' % i for i in end))
out.add(start + s + end)
- return out
+ return out, need_quotes
BASH_COMPLETE_SCRIPT = r"""
@@ -283,7 +283,8 @@ def bash_completions(prefix, line, begidx, endidx, env=None, paths=None,
from the environment and platform.
quote_paths : callable, optional
A functions that quotes file system paths. You shouldn't normally need
- this as the default is acceptable 99+% of the time.
+ this as the default is acceptable 99+% of the time. This function should
+ a set of the new paths and a boolean for whether the paths were quoted.
Returns
-------
@@ -348,7 +349,8 @@ def bash_completions(prefix, line, begidx, endidx, env=None, paths=None,
strip_len += 1
if '-o noquote' not in complete_stmt:
- out = quote_paths(out, '', '')
+ out, need_quotes = quote_paths(out, '', '')
+ strip_len += int(need_quotes)
if '-o nospace' in complete_stmt:
out = set([x.rstrip() for x in out])
diff --git a/xonsh/completers/path.py b/xonsh/completers/path.py
index b96fe1a7b4..0da08335f2 100644
--- a/xonsh/completers/path.py
+++ b/xonsh/completers/path.py
@@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ def _quote_paths(paths, start, end, append_end=True):
s = s.replace(end, ''.join('\\%s' % i for i in end))
s = start + s + end if append_end else start + s
out.add(s)
- return out
+ return out, need_quotes
def _joinpath(path):
@@ -298,10 +298,10 @@ def complete_path(prefix, line, start, end, ctx, cdpath=True, filtfunc=None):
if cdpath:
_add_cdpaths(paths, prefix)
paths = set(filter(filtfunc, paths))
- paths = _quote_paths({_normpath(s) for s in paths},
- path_str_start,
- path_str_end,
- append_end)
+ paths, _ = _quote_paths({_normpath(s) for s in paths},
+ path_str_start,
+ path_str_end,
+ append_end)
paths.update(filter(filtfunc, _dots(prefix)))
paths.update(filter(filtfunc, _env(prefix)))
return paths, lprefix
diff --git a/xonsh/readline_shell.py b/xonsh/readline_shell.py
index bcfed37c49..6c704230ed 100644
--- a/xonsh/readline_shell.py
+++ b/xonsh/readline_shell.py
@@ -269,6 +269,43 @@ def __init__(self, completekey='tab', stdin=None, stdout=None, **kwargs):
self._current_indent = ''
self._current_prompt = ''
self._force_hide = None
+ self._complete_only_last_table = {
+ # Truth table for completions, keys are:
+ # (prefix_begs_quote, prefix_ends_quote, i_ends_quote,
+ # last_starts_with_prefix, i_has_space)
+ (True, True, True, True, True): True,
+ (True, True, True, True, False): True,
+ (True, True, True, False, True): False,
+ (True, True, True, False, False): True,
+ (True, True, False, True, True): False,
+ (True, True, False, True, False): False,
+ (True, True, False, False, True): False,
+ (True, True, False, False, False): False,
+ (True, False, True, True, True): True,
+ (True, False, True, True, False): False,
+ (True, False, True, False, True): False,
+ (True, False, True, False, False): True,
+ (True, False, False, True, True): False,
+ (True, False, False, True, False): False,
+ (True, False, False, False, True): False,
+ (True, False, False, False, False): False,
+ (False, True, True, True, True): True,
+ (False, True, True, True, False): True,
+ (False, True, True, False, True): True,
+ (False, True, True, False, False): True,
+ (False, True, False, True, True): False,
+ (False, True, False, True, False): False,
+ (False, True, False, False, True): False,
+ (False, True, False, False, False): False,
+ (False, False, True, True, True): True,
+ (False, False, True, True, False): False,
+ (False, False, True, False, True): False,
+ (False, False, True, False, False): True,
+ (False, False, False, True, True): True,
+ (False, False, False, True, False): False,
+ (False, False, False, False, True): False,
+ (False, False, False, False, False): False,
+ }
self.cmdqueue = collections.deque()
def __del__(self):
@@ -297,11 +334,15 @@ def parseline(self, line):
return '', line, line
def _querycompletions(self, completions, loc):
- """Returns whether or not we should show completions"""
+ """Returns whether or not we should show completions. 0 means that prefixes
+ should not be shown, 1 means that there is a common prefix among all completions
+ and they should be shown, while 2 means that there is no common prefix but
+ we are under the query limit and they should be shown.
+ """
if os.path.commonprefix([c[loc:] for c in completions]):
- return True
+ return 1
elif len(completions) <= builtins.__xonsh_env__.get('COMPLETION_QUERY_LIMIT'):
- return True
+ return 2
msg = '\nDisplay all {} possibilities? '.format(len(completions))
msg += '({GREEN}y{NO_COLOR} or {RED}n{NO_COLOR})'
self.print_color(msg, end='', flush=True, file=sys.stderr)
@@ -312,7 +353,7 @@ def _querycompletions(self, completions, loc):
print()
if not show_completions:
rl_on_new_line()
- return False
+ return 0
w, h = shutil.get_terminal_size()
lines = columnize(completions, width=w)
more_msg = self.format_color('{YELLOW}==={NO_COLOR} more or '
@@ -326,10 +367,10 @@ def _querycompletions(self, completions, loc):
print(flush=True, file=sys.stderr)
if q == 'q':
rl_on_new_line()
- return False
+ return 0
print(''.join(lines), end='', flush=True, file=sys.stderr)
rl_on_new_line()
- return False
+ return 0
def completedefault(self, prefix, line, begidx, endidx):
"""Implements tab-completion for text."""
@@ -342,9 +383,31 @@ def completedefault(self, prefix, line, begidx, endidx):
begidx, endidx,
ctx=self.ctx)
chopped = prefix[:-l]
- rtn_completions = [chopped + i for i in completions]
+ if chopped:
+ rtn_completions = [chopped + i for i in completions]
+ else:
+ rtn_completions = completions
+ rtn = []
+ prefix_begs_quote = prefix.startswith("'") or prefix.startswith('"')
+ prefix_ends_quote = prefix.endswith("'") or prefix.endswith('"')
+ for i in rtn_completions:
+ i_ends_quote = i.endswith("'") or i.endswith('"')
+ last = i.rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]
+ last_starts_prefix = last.startswith(prefix)
+ i_has_space = ' ' in i
+ key = (prefix_begs_quote, prefix_ends_quote, i_ends_quote,
+ last_starts_prefix, i_has_space)
+ rtn.append(last if self._complete_only_last_table[key] else i)
+ # return based on show completions
show_completions = self._querycompletions(completions, endidx - begidx)
- return rtn_completions if show_completions else []
+ if show_completions == 0:
+ return []
+ elif show_completions == 1:
+ return rtn
+ elif show_completions == 2:
+ return completions
+ else:
+ raise ValueError('query compeltions flag not understood.')
# tab complete on first index too
completenames = completedefault
diff --git a/xonsh/tools.py b/xonsh/tools.py
index a8f9fbed01..c74f368f2d 100644
--- a/xonsh/tools.py
+++ b/xonsh/tools.py
@@ -1925,12 +1925,21 @@ def columnize(elems, width=80, newline='\n'):
The newline character will be appended to the end of each line.
"""
sizes = [len(e) + 1 for e in elems]
+ total = sum(sizes)
nelem = len(elems)
- ncols = 1
- nrows = len(sizes)
- columns = [sizes]
- last_longest_row = max(sizes)
- while True:
+ if total - 1 <= width:
+ ncols = len(sizes)
+ nrows = 1
+ columns = [sizes]
+ last_longest_row = total
+ enter_loop = False
+ else:
+ ncols = 1
+ nrows = len(sizes)
+ columns = [sizes]
+ last_longest_row = max(sizes)
+ enter_loop = True
+ while enter_loop:
longest_row = sum(map(max, columns))
if longest_row - 1 <= width:
# we might be able to fit another column.
diff --git a/xonsh/xonfig.py b/xonsh/xonfig.py
index 334a538f74..4f17358a5c 100644
--- a/xonsh/xonfig.py
+++ b/xonsh/xonfig.py
@@ -652,6 +652,7 @@ def TAGLINES():
"Conches for the xonsh god!",
"Python-powered, cross-platform, Unix-gazing shell",
"Tab completion in Alderaan places",
+ "This fix was trickier than expected",
]
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21547@4e8d1c1
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,547
|
Fix: Bug in MinMax which returned an incorrect simplication which is not true for all ranges of the variables
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #21399
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
earlier, Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c)) returned Min(a,b,c)
now, Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c)) returns Min(a,b)
- Add test for the above fix
- Add the above example in doc
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* functions
* Fixed a bug in MaxMin of elementary functions
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-05-30T17:07:52Z
|
nested Max and Min give incorrect result
While working with different types of nested Max and Min expressions, I have encountered a problem in the following expression:
```
from sympy import sympify
sympify( "Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c))" )
```
output: `Min(a, b, c)`
This simplification is not correct for all possible values of a, b, and c.
I have not found any problems with other similar expressions, and I cannot find the specific reason why this one evaluates incorrectly.
|
The issue isn't to do with sympify because it happens if you use Max/Min directly:
```python
In [1]: a, b, c = symbols('a, b, c')
In [2]: Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c))
Out[2]: Min(a, b, c)
```
The logic for handling this is here:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/d43e9dc5aed4d2b695a3176cdf8ad4e3c79f0e5b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py#L515-L542
At the end here we have
```
(Pdb) p sets
[c]
(Pdb) p common
{b, a}
(Pdb) p cls
Max
(Pdb) p other
Min
(Pdb) p args
[Min(a, b, c)]
```
Thanks for pointing that out.
From my understanding, the code you quoted refactors `Max(Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c))` into `Min(a, b, Max(c))`, which then becomes `Min(a, b, c)`
A correct refactoring would be `Min(a, b)`, though I'm not sure how the code could be adapted to take this specific case into account.
I suppose one way to get there would be to realise that `Min(a, b) >= Min(a, b, c)` although that comparison isn't implemented. There must be a bug in here though to get this wrong result.
I'm just trying to get my head round how this `Max/Min` algebra works. The rule described in the code is
```
Min(Max(x, y), Max(x, z)) -> Max(x, Min(y, z))
```
which seems to be valid. Now we want to generalise to handle this:
```
Min(Max(a, b, c, d), Max(a, b, d, e))
```
The current implementation turns this into:
```python
In [4]: Min(Max(a, b, c, d), Max(a, b, e, f))
Out[4]: Max(a, b, Min(Max(c, d), Max(e, f)))
```
Applying that kind of reasoning to your case gives:
```
Max(Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c)) -> Min(a, b, Max(Min(), Min(c)))
```
Now the question is what a no arg `Min()` should be. If we suppose that `Min(a, b, c) <= Min(a, b)` then `Min(a) <= Min() = oo`. The simplification would then be:
```
Min(a, b, Max(Min(), Min(c))) -> Min(a, b, Max(oo, c)) -> Min(a, b, oo) -> Min(a, b)
```
The current code filters out a `Min` whose args are equal to the common subset so it simply removes `Min()`. Actually if any `Min` has args equal to common then I think it means that *all* `Min`s can be removed and the result is just `Min(*common)`.
Here is a diff that will fix this:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py
index 85b606e754..c4d341501e 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
+from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift
from sympy.core import Function, S, sympify
from sympy.core.add import Add
from sympy.core.containers import Tuple
@@ -518,28 +519,34 @@ def do(ai, a):
# easy case where all functions contain something in common;
# trying to find some optimal subset of args to modify takes
# too long
+
+ def factor_minmax(args):
+ is_other = lambda arg: isinstance(arg, other)
+ other_args, remaining_args = sift(args, is_other, binary=True)
+ if not other_args:
+ return args
+
+ # Min(Max(x, y, z), Max(x, y, u, v)) -> {x,y}, ({z}, {u,v})
+ arg_sets = [set(arg.args) for arg in other_args]
+ common = set.intersection(*arg_sets)
+ if not common:
+ return args
+
+ new_other_args = list(common)
+ arg_sets_diff = [arg_set - common for arg_set in arg_sets]
+
+ # If any set is empty after removing common then all can be
+ # discarded e.g. Min(Max(a, b, c), Max(a, b)) -> Max(a, b)
+ if all(arg_sets_diff):
+ other_args_diff = [other(*s, evaluate=False) for s in arg_sets_diff]
+ new_other_args.append(cls(*other_args_diff, evaluate=False))
+
+ other_args_factored = other(*new_other_args, evaluate=False)
+ return remaining_args + [other_args_factored]
+
+
if len(args) > 1:
- common = None
- remove = []
- sets = []
- for i in range(len(args)):
- a = args[i]
- if not isinstance(a, other):
- continue
- s = set(a.args)
- common = s if common is None else (common & s)
- if not common:
- break
- sets.append(s)
- remove.append(i)
- if common:
- sets = filter(None, [s - common for s in sets])
- sets = [other(*s, evaluate=False) for s in sets]
- for i in reversed(remove):
- args.pop(i)
- oargs = [cls(*sets)] if sets else []
- oargs.extend(common)
- args.append(other(*oargs, evaluate=False))
+ args = factor_minmax(args)
return args
```
|
[
{
"body": "While working with different types of nested Max and Min expressions, I have encountered a problem in the following expression:\r\n```\r\nfrom sympy import sympify \r\nsympify( \"Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c))\" )\r\n```\r\n\r\noutput: `Min(a, b, c)`\r\n\r\nThis simplification is not correct for all possible values of a, b, and c.\r\nI have not found any problems with other similar expressions, and I cannot find the specific reason why this one evaluates incorrectly.\r\n\r\n",
"number": 21399,
"title": "nested Max and Min give incorrect result"
}
] |
b4736a507d0158a2a09a15bc61907a063d5fa674
|
{
"head_commit": "4e8d1c1506cdbcad835bf36b030f90b35fbf134d",
"head_commit_message": "Fix: Bug in MinMax which returned an incorrect simplication which is not true for all ranges of the variables\nearlier, Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c)) returned Min(a,b,c)\nnow, Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c)) returns Min(a,b)\n\n- Add test for the above fix\n- Add the above example in doc",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py\nindex 85b606e754bc..94067844ee0e 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py\n@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@\n from sympy.core import Function, S, sympify\n+from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift\n from sympy.core.add import Add\n from sympy.core.containers import Tuple\n from sympy.core.compatibility import ordered\n@@ -432,7 +433,8 @@ def _collapse_arguments(cls, args, **assumptions):\n \n >>> Min(a, Max(b, Min(c, d, Max(a, e))))\n Min(a, Max(b, Min(a, c, d)))\n-\n+ >>> Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c))\n+ Min(a,b)\n \"\"\"\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import ordered\n from sympy.simplify.simplify import walk\n@@ -518,28 +520,33 @@ def do(ai, a):\n # easy case where all functions contain something in common;\n # trying to find some optimal subset of args to modify takes\n # too long\n+\n+ def factor_minmax(args):\n+ is_other = lambda arg: isinstance(arg, other)\n+ other_args, remaining_args = sift(args, is_other, binary=True)\n+ if not other_args:\n+ return args\n+\n+ # Min(Max(x, y, z), Max(x, y, u, v)) -> {x,y}, ({z}, {u,v})\n+ arg_sets = [set(arg.args) for arg in other_args]\n+ common = set.intersection(*arg_sets)\n+ if not common:\n+ return args\n+\n+ new_other_args = list(common)\n+ arg_sets_diff = [arg_set - common for arg_set in arg_sets]\n+\n+ # If any set is empty after removing common then all can be\n+ # discarded e.g. Min(Max(a, b, c), Max(a, b)) -> Max(a, b)\n+ if all(arg_sets_diff):\n+ other_args_diff = [other(*s, evaluate=False) for s in arg_sets_diff]\n+ new_other_args.append(cls(*other_args_diff, evaluate=False))\n+\n+ other_args_factored = other(*new_other_args, evaluate=False)\n+ return remaining_args + [other_args_factored]\n+\n if len(args) > 1:\n- common = None\n- remove = []\n- sets = []\n- for i in range(len(args)):\n- a = args[i]\n- if not isinstance(a, other):\n- continue\n- s = set(a.args)\n- common = s if common is None else (common & s)\n- if not common:\n- break\n- sets.append(s)\n- remove.append(i)\n- if common:\n- sets = filter(None, [s - common for s in sets])\n- sets = [other(*s, evaluate=False) for s in sets]\n- for i in reversed(remove):\n- args.pop(i)\n- oargs = [cls(*sets)] if sets else []\n- oargs.extend(common)\n- args.append(other(*oargs, evaluate=False))\n+ args = factor_minmax(args)\n \n return args\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py\nindex 0e1a5b1d08ce..2f6e16977967 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py\n@@ -410,6 +410,10 @@ def test_issue_12638():\n assert Min(a, b, Max(a, b, c)) == Min(a, b)\n assert Min(a, b, Max(a, c)) == Min(a, b)\n \n+def test_issue_21399():\n+ from sympy.abc import a, b, c\n+ assert Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c)) == Min(a,b)\n+\n \n def test_instantiation_evaluation():\n from sympy.abc import v, w, x, y, z\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -432,7 +433,8 @@ def _collapse_arguments(cls, args, **assumptions):\n \n >>> Min(a, Max(b, Min(c, d, Max(a, e))))\n Min(a, Max(b, Min(a, c, d)))\n-\n+ >>> Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c))\n+ Min(a,b)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 437,
"original_start_line": 436,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -432,7 +433,8 @@ def _collapse_arguments(cls, args, **assumptions):\n \n >>> Min(a, Max(b, Min(c, d, Max(a, e))))\n Min(a, Max(b, Min(a, c, d)))\n-\n+ >>> Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c))\n+ Min(a,b)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 437,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI don't think that an example needs to be added here."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -410,6 +410,10 @@ def test_issue_12638():\n assert Min(a, b, Max(a, b, c)) == Min(a, b)\n assert Min(a, b, Max(a, c)) == Min(a, b)\n \n+def test_issue_21399():\n+ from sympy.abc import a, b, c\n+ assert Max( Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c)) == Min(a,b)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 415,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n assert Max(Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c)) == Min(a, b)\r\n```"
}
] |
2598335352740227c85857ac2b07d00200a98858
|
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py
index 85b606e754bc..b458bd2af7c6 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
from sympy.core import Function, S, sympify
+from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift
from sympy.core.add import Add
from sympy.core.containers import Tuple
from sympy.core.compatibility import ordered
@@ -432,7 +433,6 @@ def _collapse_arguments(cls, args, **assumptions):
>>> Min(a, Max(b, Min(c, d, Max(a, e))))
Min(a, Max(b, Min(a, c, d)))
-
"""
from sympy.utilities.iterables import ordered
from sympy.simplify.simplify import walk
@@ -518,28 +518,33 @@ def do(ai, a):
# easy case where all functions contain something in common;
# trying to find some optimal subset of args to modify takes
# too long
+
+ def factor_minmax(args):
+ is_other = lambda arg: isinstance(arg, other)
+ other_args, remaining_args = sift(args, is_other, binary=True)
+ if not other_args:
+ return args
+
+ # Min(Max(x, y, z), Max(x, y, u, v)) -> {x,y}, ({z}, {u,v})
+ arg_sets = [set(arg.args) for arg in other_args]
+ common = set.intersection(*arg_sets)
+ if not common:
+ return args
+
+ new_other_args = list(common)
+ arg_sets_diff = [arg_set - common for arg_set in arg_sets]
+
+ # If any set is empty after removing common then all can be
+ # discarded e.g. Min(Max(a, b, c), Max(a, b)) -> Max(a, b)
+ if all(arg_sets_diff):
+ other_args_diff = [other(*s, evaluate=False) for s in arg_sets_diff]
+ new_other_args.append(cls(*other_args_diff, evaluate=False))
+
+ other_args_factored = other(*new_other_args, evaluate=False)
+ return remaining_args + [other_args_factored]
+
if len(args) > 1:
- common = None
- remove = []
- sets = []
- for i in range(len(args)):
- a = args[i]
- if not isinstance(a, other):
- continue
- s = set(a.args)
- common = s if common is None else (common & s)
- if not common:
- break
- sets.append(s)
- remove.append(i)
- if common:
- sets = filter(None, [s - common for s in sets])
- sets = [other(*s, evaluate=False) for s in sets]
- for i in reversed(remove):
- args.pop(i)
- oargs = [cls(*sets)] if sets else []
- oargs.extend(common)
- args.append(other(*oargs, evaluate=False))
+ args = factor_minmax(args)
return args
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py
index 0e1a5b1d08ce..bc6f2e2762ee 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_miscellaneous.py
@@ -410,6 +410,10 @@ def test_issue_12638():
assert Min(a, b, Max(a, b, c)) == Min(a, b)
assert Min(a, b, Max(a, c)) == Min(a, b)
+def test_issue_21399():
+ from sympy.abc import a, b, c
+ assert Max(Min(a, b), Min(a, b, c)) == Min(a, b)
+
def test_instantiation_evaluation():
from sympy.abc import v, w, x, y, z
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py
index 1833939f5ee2..cb977261be2d 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_piecewise.py
@@ -233,38 +233,40 @@ def test_piecewise_integrate1ca():
assert g.integrate((x, 1, -2)) == g1y.subs(y, -2)
assert g.integrate((x, 0, 1)) == gy1.subs(y, 0)
assert g.integrate((x, 1, 0)) == g1y.subs(y, 0)
- # XXX Make test pass without simplify
- assert g.integrate((x, 2, 1)) == gy1.subs(y, 2).simplify()
- assert g.integrate((x, 1, 2)) == g1y.subs(y, 2).simplify()
-
+ # since xreplace is followed by doit with deep=False
+ # to Min/Max don't get resolved so doit is needed
+ assert g.integrate((x, 2, 1)) == gy1.subs(y, 2).doit()
+ assert g.integrate((x, 1, 2)) == g1y.subs(y, 2).doit()
assert piecewise_fold(gy1.rewrite(Piecewise)) == \
Piecewise(
- (1, y <= -1),
- (-y**2/2 - y + S.Half, y <= 0),
- (y**2/2 - y + S.Half, y < 1),
+ (-y**2/2 - y + S.Half, (y >= -1) & (y <= 0)),
+ (y**2/2 - y + S.Half, (y >= -1) & (y < 1)),
+ (1, y <= 0),
+ (y**2 + 1, y < 1),
(0, True))
assert piecewise_fold(g1y.rewrite(Piecewise)) == \
Piecewise(
- (-1, y <= -1),
- (y**2/2 + y - S.Half, y <= 0),
- (-y**2/2 + y - S.Half, y < 1),
+ (y**2/2 + y - S.Half, (y >= -1) & (y <= 0)),
+ (-y**2/2 + y - S.Half, (y >= -1) & (y < 1)),
+ (-1, y <= 0),
+ (-y**2 - 1, y < 1),
(0, True))
- # g1y and gy1 should simplify if the condition that y < 1
+ # g1y and gy1 simplify if the condition that y < 1
# is applied, e.g. Min(1, Max(-1, y)) --> Max(-1, y)
- # XXX Make test pass without simplify
- assert gy1.simplify() == Piecewise(
+ assert gy1.doit() == Piecewise(
(
-Min(1, Max(-1, y))**2/2 - Min(1, Max(-1, y)) +
Min(1, Max(0, y))**2 + S.Half, y < 1),
(0, True)
)
- assert g1y.simplify() == Piecewise(
+ assert g1y.doit() == Piecewise(
(
Min(1, Max(-1, y))**2/2 + Min(1, Max(-1, y)) -
Min(1, Max(0, y))**2 - S.Half, y < 1),
(0, True))
+
@slow
def test_piecewise_integrate1cb():
y = symbols('y', real=True)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-2467@0984075
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 2,467
|
Add Python type hints and doctests to other/two_sum.py
|
Fixes #2465
### **Describe your change:**
* [ ] Add an algorithm?
* [x] Fix a bug or typo in an existing algorithm?
* [ ] Documentation change?
### **Checklist:**
* [x] I have read [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
* [x] This pull request is all my own work -- I have not plagiarized.
* [x] I know that pull requests will not be merged if they fail the automated tests.
* [x] This PR only changes one algorithm file. To ease review, please open separate PRs for separate algorithms.
* [x] All new Python files are placed inside an existing directory.
* [x] All filenames are in all lowercase characters with no spaces or dashes.
* [x] All functions and variable names follow Python naming conventions.
* [x] All function parameters and return values are annotated with Python [type hints](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
* [x] All functions have [doctests](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) that pass the automated testing.
* [x] All new algorithms have a URL in its comments that points to Wikipedia or other similar explanation.
* [x] If this pull request resolves one or more open issues then the commit message contains `Fixes: #{$ISSUE_NO}`.
|
2020-09-23T19:20:09Z
|
Add Python type hints and doctests to other/two_sum.py
@tonydelanuez Would you be willing to add Python type hints and doctests to [`other/two_sum.py`](../blob/master/other/two_sum.py)? The function comments say that it will return a `list[int]` but instead it either returns a `list[list[int]]` or `False`.
|
[
{
"body": "@tonydelanuez Would you be willing to add Python type hints and doctests to [`other/two_sum.py`](../blob/master/other/two_sum.py)? The function comments say that it will return a `list[int]` but instead it either returns a `list[list[int]]` or `False`.",
"number": 2465,
"title": "Add Python type hints and doctests to other/two_sum.py"
}
] |
9200a2e54362ecd6be6cfc7e257a37e7a4f16013
|
{
"head_commit": "09840756e3fd95eb21c4ea1ced077aac89929953",
"head_commit_message": "Add Python type hints and doctests to other/two_sum.py\n\n#2465",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/other/two_sum.py b/other/two_sum.py\nindex 8ac7a18ba9a4..7011ba049756 100644\n--- a/other/two_sum.py\n+++ b/other/two_sum.py\n@@ -11,21 +11,36 @@\n Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,\n return [0, 1].\n \"\"\"\n+from typing import List\n \n \n-def twoSum(nums, target):\n+def two_sum(nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:\n \"\"\"\n- :type nums: List[int]\n- :type target: int\n- :rtype: List[int]\n+ >>> two_sum([2, 7, 11, 15], 9)\n+ [0, 1]\n+ >>> two_sum([15, 2, 11, 7], 13)\n+ [1, 2]\n+ >>> two_sum([2, 7, 11, 15], 17)\n+ [0, 3]\n+ >>> two_sum([7, 15, 11, 2], 18)\n+ [0, 2]\n+ >>> two_sum([2, 7, 11, 15], 26)\n+ [2, 3]\n+ >>> two_sum([2, 7, 11, 15], 8)\n+ []\n+ >>> two_sum([3 * i for i in range(10)], 19)\n+ []\n \"\"\"\n chk_map = {}\n for index, val in enumerate(nums):\n compl = target - val\n if compl in chk_map:\n- indices = [chk_map[compl], index]\n- print(indices)\n- return [indices]\n- else:\n- chk_map[val] = index\n- return False\n+ return [chk_map[compl], index]\n+ chk_map[val] = index\n+ return []\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+ import doctest\n+\n+ doctest.testmod()\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -11,21 +11,36 @@\n Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,\n return [0, 1].\n \"\"\"\n+from typing import List",
"line": null,
"original_line": 14,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "other/two_sum.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\nfrom __future__ import annotations\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -11,21 +11,36 @@\n Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,\n return [0, 1].\n \"\"\"\n+from typing import List\n \n \n-def twoSum(nums, target):\n+def two_sum(nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 17,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "other/two_sum.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\ndef two_sum(nums: list[int], target: int) -> list[int]:\r\n```\n\n@user1:\nTravis tests fail without this change.\n\n@author:\nI clicked \"Commit suggestion\" but I guess it didn't work.\n\n@author:\nI committed it manually below, still waiting for Travis to kick in.\n\n@user1:\nYou can `Add suggestion to batch` on all suggestions that then they will commit all at once.\n\n@author:\nOh! Didn't know that! Thanks. Github is so confusing! It should be good now."
}
] |
4203f373d15a52aecf360a96994bc0477a0097e7
|
diff --git a/other/two_sum.py b/other/two_sum.py
index 8ac7a18ba9a4..5209acbc7e44 100644
--- a/other/two_sum.py
+++ b/other/two_sum.py
@@ -11,21 +11,37 @@
Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
return [0, 1].
"""
+from __future__ import annotations
-def twoSum(nums, target):
+def two_sum(nums: list[int], target: int) -> list[int]:
"""
- :type nums: List[int]
- :type target: int
- :rtype: List[int]
+ >>> two_sum([2, 7, 11, 15], 9)
+ [0, 1]
+ >>> two_sum([15, 2, 11, 7], 13)
+ [1, 2]
+ >>> two_sum([2, 7, 11, 15], 17)
+ [0, 3]
+ >>> two_sum([7, 15, 11, 2], 18)
+ [0, 2]
+ >>> two_sum([2, 7, 11, 15], 26)
+ [2, 3]
+ >>> two_sum([2, 7, 11, 15], 8)
+ []
+ >>> two_sum([3 * i for i in range(10)], 19)
+ []
"""
chk_map = {}
for index, val in enumerate(nums):
compl = target - val
if compl in chk_map:
- indices = [chk_map[compl], index]
- print(indices)
- return [indices]
- else:
- chk_map[val] = index
- return False
+ return [chk_map[compl], index]
+ chk_map[val] = index
+ return []
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import doctest
+
+ doctest.testmod()
+ print(f"{two_sum([2, 7, 11, 15], 9) = }")
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Documentation Updates"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-21527@bd2aad4
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,527
|
fix(matrices): Don't use DomainMatrix.rref for RR in linsolve
|
The DomainMatrix.rref method as implemented by the sdm_irref function
has not been well designed for handling matrices of floats as it does
not have a pivoting strategy that can mitigate errors arising from
erroneously choosing a zero pivot (that is nonzero only because of
roundoff). This commit makes linsolve use the `ddm_irref()` for the case of
pure RR or CC matrices. The behaviour of sdm_rref for floats should be
improved. Until then it is better not to use `sdm_rref` in these
cases.
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #21520
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* solvers
* Some bugs in the new implementation of linsolve are fixed by the dense RREF implementation instead of the sparse implemention. These bugs previously led to incorrect results being returned linsolve.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-05-26T23:53:16Z
|
linsolve fails simple system of two equations
```
import sympy
x,y = sympy.symbols('x, y')
sympy.linsolve([sympy.Eq(y, x), sympy.Eq(y, 0.0215 * x)], (x, y))
>> FiniteSet((0, 0))
sympy.linsolve([sympy.Eq(y, x), sympy.Eq(y, 0.0216 * x)], (x, y))
>> FiniteSet((-4.07992766242527e+17*y, 1.0*y))
sympy.linsolve([sympy.Eq(y, x), sympy.Eq(y, 0.0217 * x)], (x, y))
>> FiniteSet((0, 0))
```
Any thoughts on why these don't all return the same solution? Thanks!
|
It seems that in rref the pivot is not fully cancelled due to a rounding error so e.g. we have something like:
```python
In [1]: M = Matrix([[1.0, 1.0], [3.1, 1.0]])
In [2]: M
Out[2]:
⎡1.0 1.0⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎣3.1 1.0⎦
```
Then one step of row reduction gives:
```python
In [3]: M = Matrix([[1.0, 1.0], [1e-16, -2.1]])
In [4]: M
Out[4]:
⎡ 1.0 1.0 ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎣1.0e-16 -2.1⎦
```
With exact arithmetic the 1e-16 would have been 0 but the rounding error makes it not zero and then it throws off subsequent steps. I think that the solution is to make it exactly zero:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py
index cfa624185a..647eb6af3d 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py
@@ -904,6 +904,8 @@ def sdm_irref(A):
Ajnz = set(Aj)
for k in Ajnz - Ainz:
Ai[k] = - Aij * Aj[k]
+ Ai.pop(j)
+ Ainz.remove(j)
for k in Ajnz & Ainz:
Aik = Ai[k] - Aij * Aj[k]
if Aik:
```
That gives:
```python
In [1]: import sympy
In [2]: sympy.linsolve([sympy.Eq(y, x), sympy.Eq(y, 0.0215 * x)], (x, y))
Out[2]: {(0, 0)}
In [3]: sympy.linsolve([sympy.Eq(y, x), sympy.Eq(y, 0.0216 * x)], (x, y))
Out[3]: {(0, 0)}
In [4]: sympy.linsolve([sympy.Eq(y, x), sympy.Eq(y, 0.0217 * x)], (x, y))
Out[4]: {(0, 0)}
```
@tyler-herzer-volumetric can you try out that diff?
Haven't been able to replicate the issue after making that change. Thanks a lot @oscarbenjamin!
This example still fails with the diff:
```python
In [1]: linsolve([0.4*x + 0.3*y + 0.2, 0.4*x + 0.3*y + 0.3], [x, y])
Out[1]: {(1.35107988821115e+15, -1.8014398509482e+15)}
```
In this case although the pivot is set to zero actually the matrix is singular but row reduction leads to something like:
```python
In [3]: Matrix([[1, 1], [0, 1e-17]])
Out[3]:
⎡1 1 ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎣0 1.0e-17⎦
```
That's a trickier case. It seems that numpy can pick up on it e.g.:
```python
In [52]: M = np.array([[0.4, 0.3], [0.4, 0.3]])
In [53]: b = np.array([0.2, 0.3])
In [54]: np.linalg.solve(M, b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
LinAlgError: Singular matrix
```
A slight modification or rounding error leads to the same large result though:
```python
In [55]: M = np.array([[0.4, 0.3], [0.4, 0.3-3e-17]])
In [56]: np.linalg.solve(M, b)
Out[56]: array([ 1.35107989e+15, -1.80143985e+15])
```
I'm not sure it's possible to arrange the floating point calculation so that cases like this are picked up as being singular without introducing some kind of heuristic threshold for the determinant. This fails in numpy with even fairly simple examples:
```python
In [83]: b
Out[83]: array([0.2, 0.3, 0.5])
In [84]: M
Out[84]:
array([[0.1, 0.2, 0.3],
[0.4, 0.5, 0.6],
[0.7, 0.8, 0.9]])
In [85]: np.linalg.solve(M, b)
Out[85]: array([-4.50359963e+14, 9.00719925e+14, -4.50359963e+14])
In [86]: np.linalg.det(M)
Out[86]: 6.661338147750926e-18
```
Maybe the not full-rank case for float matrices isn't so important since it can't be done reliably with floats. I guess that the diff shown above is good enough then since it fixes the calculation in the full rank case.
There is another problematic case. This should have a unique solution but a parametric solution is returned instead:
```python
In [21]: eqs = [0.8*x + 0.8*z + 0.2, 0.9*x + 0.7*y + 0.2*z + 0.9, 0.7*x + 0.2*y + 0.2*z + 0.5]
In [22]: linsolve(eqs, [x, y, z])
Out[22]: {(-0.32258064516129⋅z - 0.548387096774194, 1.22033022161007e+16⋅z - 5.37526407137769e+15, 1.0⋅z)}
```
That seems to be another bug in the sparse rref routine somehow:
```python
In [34]: M = Matrix([
...: [0.8, 0, 0.8, -0.2],
...: [0.9, 0.7, 0.2, -0.9],
...: [0.7, 0.2, 0.2, -0.5]])
In [35]: from sympy.polys.matrices import DomainMatrix
In [36]: dM = DomainMatrix.from_Matrix(M)
In [37]: M.rref()
Out[37]:
⎛⎡1 0 0 -0.690476190476191⎤ ⎞
⎜⎢ ⎥ ⎟
⎜⎢0 1 0 -0.523809523809524⎥, (0, 1, 2)⎟
⎜⎢ ⎥ ⎟
⎝⎣0 0 1 0.440476190476191 ⎦ ⎠
In [38]: dM.rref()[0].to_Matrix()
Out[38]:
⎡1.0 5.55111512312578e-17 0.32258064516129 -0.548387096774194 ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢0.0 1.0 -1.22033022161007e+16 -5.37526407137769e+15⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ⎦
In [39]: dM.to_dense().rref()[0].to_Matrix()
Out[39]:
⎡1.0 0.0 0.0 -0.69047619047619 ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢0.0 1.0 0.0 -0.523809523809524⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣0.0 0.0 1.0 0.44047619047619 ⎦
```
The last one was a similar problem to do with cancelling above the pivot:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py
index cfa624185a..7c4ad43660 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py
@@ -904,6 +904,8 @@ def sdm_irref(A):
Ajnz = set(Aj)
for k in Ajnz - Ainz:
Ai[k] = - Aij * Aj[k]
+ Ai.pop(j)
+ Ainz.remove(j)
for k in Ajnz & Ainz:
Aik = Ai[k] - Aij * Aj[k]
if Aik:
@@ -938,6 +940,8 @@ def sdm_irref(A):
for l in Ainz - Aknz:
Ak[l] = - Akj * Ai[l]
nonzero_columns[l].add(k)
+ Ak.pop(j)
+ Aknz.remove(j)
for l in Ainz & Aknz:
Akl = Ak[l] - Akj * Ai[l]
if Akl:
diff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py
index eda4cdbdf3..6b79842fa7 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
from sympy import S, Eq, I
-from sympy.abc import x, y
+from sympy.abc import x, y, z
from sympy.polys.matrices.linsolve import _linsolve
from sympy.polys.solvers import PolyNonlinearError
@@ -23,6 +23,14 @@ def test__linsolve():
raises(PolyNonlinearError, lambda: _linsolve([x*(1 + x)], [x]))
+def test__linsolve_float():
+ assert _linsolve([Eq(y, x), Eq(y, 0.0216 * x)], (x, y)) == {x:0, y:0}
+
+ eqs = [0.8*x + 0.8*z + 0.2, 0.9*x + 0.7*y + 0.2*z + 0.9, 0.7*x + 0.2*y + 0.2*z + 0.5]
+ sol = {x:-0.69047619047619047, y:-0.52380952380952395, z:0.44047619047619047}
+ assert _linsolve(eqs, [x,y,z]) == sol
+
+
def test__linsolve_deprecated():
assert _linsolve([Eq(x**2, x**2+y)], [x, y]) == {x:x, y:S.Zero}
assert _linsolve([(x+y)**2-x**2], [x]) == {x:-y/2}
```
Another problem has emerged though:
```python
In [1]: eqs = [0.9*x + 0.3*y + 0.4*z + 0.6, 0.6*x + 0.9*y + 0.1*z + 0.7, 0.4*x + 0.6*y + 0.9*z + 0.5]
In [2]: linsolve(eqs, [x, y, z])
Out[2]: {(-0.5, -0.4375, -0.0400000000000001)}
In [3]: solve(eqs, [x, y, z])
Out[3]: {x: -0.502857142857143, y: -0.438095238095238, z: -0.04}
```
> Another problem has emerged though:
>
> ```python
> In [1]: eqs = [0.9*x + 0.3*y + 0.4*z + 0.6, 0.6*x + 0.9*y + 0.1*z + 0.7, 0.4*x + 0.6*y + 0.9*z + 0.5]
> ```
In this case the problem is that something like `1e-17` is chosen (incorrectly) as a pivot. It doesn't look easy to resolve this because the `sdm_rref` routine doesn't have an easy way of incorporating pivoting and is really designed for exact domains.
Probably float matrices should be handled by mpmath or at least a separate routine.
|
[
{
"body": "```\r\nimport sympy\r\nx,y = sympy.symbols('x, y')\r\n\r\nsympy.linsolve([sympy.Eq(y, x), sympy.Eq(y, 0.0215 * x)], (x, y))\r\n>> FiniteSet((0, 0))\r\n\r\nsympy.linsolve([sympy.Eq(y, x), sympy.Eq(y, 0.0216 * x)], (x, y))\r\n>> FiniteSet((-4.07992766242527e+17*y, 1.0*y))\r\n\r\nsympy.linsolve([sympy.Eq(y, x), sympy.Eq(y, 0.0217 * x)], (x, y))\r\n>> FiniteSet((0, 0))\r\n```\r\n\r\nAny thoughts on why these don't all return the same solution? Thanks!",
"number": 21520,
"title": "linsolve fails simple system of two equations"
}
] |
31d469a5335c81ec4a437e36a861945a6b43d916
|
{
"head_commit": "bd2aad45a6ab782e7e4f8fe08cabfa8836a25227",
"head_commit_message": "fix(matrices): Don't use DomainMatrix.rref for RR in linsolve\n\nThe DomainMatrix.rref method as implemented by the sdm_irref function\nhas not been well designed for handling matrices of floats as it does\nnot have a pivoting strategy that can mitigate errors arising from\nerroneously choosing a zero pivot (that is nonzero only because of\nroundoff). This commit makes linsolve use Matrix.rref() for the case of\npure float matrices. The behaviour of sdm_rref for floats should be\nimproved. Until then it is better not to use DomainMatrix in these\ncases.",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/linsolve.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/linsolve.py\nindex 62e6d90aae36..387ea9c79cc6 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/linsolve.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/linsolve.py\n@@ -35,6 +35,7 @@\n from sympy.polys.constructor import construct_domain\n from sympy.polys.solvers import PolyNonlinearError\n \n+from .domainmatrix import DomainMatrix\n from .sdm import (\n SDM,\n sdm_irref,\n@@ -73,6 +74,13 @@ def _linsolve(eqs, syms):\n Aaug = sympy_dict_to_dm(eqsdict, rhs, syms)\n K = Aaug.domain\n \n+ # sdm_irref has issues with float matrices. This uses the Matrix.rref()\n+ # method. When DomainMatrix.rref() can handle float matrices reasonably\n+ # this should be removed...\n+ if K.is_RealField:\n+ Aaug_Matrix = DomainMatrix.from_rep(Aaug).to_Matrix().rref()[0]\n+ Aaug = DomainMatrix.from_Matrix(Aaug_Matrix).to_field().to_sparse().rep\n+\n # Compute reduced-row echelon form (RREF)\n Arref, pivots, nzcols = sdm_irref(Aaug)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py\nindex cfa624185a5d..7c4ad43660cc 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py\n@@ -904,6 +904,8 @@ def sdm_irref(A):\n Ajnz = set(Aj)\n for k in Ajnz - Ainz:\n Ai[k] = - Aij * Aj[k]\n+ Ai.pop(j)\n+ Ainz.remove(j)\n for k in Ajnz & Ainz:\n Aik = Ai[k] - Aij * Aj[k]\n if Aik:\n@@ -938,6 +940,8 @@ def sdm_irref(A):\n for l in Ainz - Aknz:\n Ak[l] = - Akj * Ai[l]\n nonzero_columns[l].add(k)\n+ Ak.pop(j)\n+ Aknz.remove(j)\n for l in Ainz & Aknz:\n Akl = Ak[l] - Akj * Ai[l]\n if Akl:\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py\nindex eda4cdbdf3fa..354801a83816 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py\n@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n \n from sympy import S, Eq, I\n-from sympy.abc import x, y\n+from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n \n from sympy.polys.matrices.linsolve import _linsolve\n from sympy.polys.solvers import PolyNonlinearError\n@@ -23,6 +23,33 @@ def test__linsolve():\n raises(PolyNonlinearError, lambda: _linsolve([x*(1 + x)], [x]))\n \n \n+def test__linsolve_float():\n+ eqs = [\n+ y - x,\n+ y - 0.0216 * x\n+ ]\n+ sol = {x:0, y:0}\n+ assert _linsolve(eqs, (x, y)) == sol\n+\n+ eqs = [\n+ 0.8*x + 0.8*z + 0.2,\n+ 0.9*x + 0.7*y + 0.2*z + 0.9,\n+ 0.7*x + 0.2*y + 0.2*z + 0.5\n+ ]\n+ #sol = {x:-0.69047619047619047, y:-0.52380952380952395, z:0.44047619047619047}\n+ sol = {x:-0.69047619047619069, y:-0.52380952380952361, z:0.44047619047619069}\n+ assert _linsolve(eqs, [x,y,z]) == sol\n+\n+ eqs = [\n+ 0.9*x + 0.3*y + 0.4*z + 0.6,\n+ 0.6*x + 0.9*y + 0.1*z + 0.7,\n+ 0.4*x + 0.6*y + 0.9*z + 0.5\n+ ]\n+ #sol = {x:-0.50285714285714289, y:-0.43809523809523804, z:-0.040000000000000063}\n+ sol = {x:-0.50285714285714278, y:-0.43809523809523798, z:-0.040000000000000022}\n+ assert _linsolve(eqs, [x,y,z]) == sol\n+\n+\n def test__linsolve_deprecated():\n assert _linsolve([Eq(x**2, x**2+y)], [x, y]) == {x:x, y:S.Zero}\n assert _linsolve([(x+y)**2-x**2], [x]) == {x:-y/2}\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -73,6 +74,13 @@ def _linsolve(eqs, syms):\n Aaug = sympy_dict_to_dm(eqsdict, rhs, syms)\n K = Aaug.domain\n \n+ # sdm_irref has issues with float matrices. This uses the Matrix.rref()\n+ # method. When DomainMatrix.rref() can handle float matrices reasonably\n+ # this should be removed...\n+ if K.is_RealField:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 80,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/polys/matrices/linsolve.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nComplex field should treated similarly.\n\n@author:\nYes, it should although it isn't actually used here since it always goes to EX:\r\n```python\r\nIn [2]: construct_domain([1.0+1.0*I])\r\nOut[2]: (EX, [EX(1.0 + 1.0*I)])\r\n\r\nIn [3]: Poly(1.0+1.0*I, x)\r\nOut[3]: Poly(1.0 + 1.0*I, x, domain='EX')\r\n```\r\nI think the only way to get CC is by unifying `ZZ_I/QQ_I` with `RR`:\r\n```python\r\nIn [4]: ZZ_I.unify(RR)\r\nOut[4]: CC\r\n```\n\n@author:\nI've changed it so that `construct_domain` can identify `CC`. I would have expected to see some test failures from that but there don't seem to be any which means that there is not good test coverage for Poly/linsolve etc over CC.\r\n\r\nIt should be possible to test `if K.is_Exact` here but that apparently fails for a polynomial ring:\r\n```python\r\nIn [1]: RR.frac_field(x).is_Exact\r\nOut[1]: False\r\n\r\nIn [2]: RR[x].is_Exact\r\nOut[2]: True\r\n```"
}
] |
e49bddb241b36b34d0a9ebc8e11b5b8995cff57c
|
diff --git a/sympy/polys/constructor.py b/sympy/polys/constructor.py
index adcfd13dc3cc..3ae1babce9c0 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/constructor.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/constructor.py
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ def _construct_simple(coeffs, opt):
float_numbers.append(x)
if y.is_Float:
float_numbers.append(y)
- if is_algebraic(coeff):
+ elif is_algebraic(coeff):
if floats:
# there are both algebraics and reals -> EX
return False
diff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/ddm.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/ddm.py
index 7b98cc16f4d8..d1770b21b832 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/ddm.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/ddm.py
@@ -284,7 +284,9 @@ def applyfunc(self, func, domain):
def rref(a):
"""Reduced-row echelon form of a and list of pivots"""
b = a.copy()
- pivots = ddm_irref(b)
+ K = a.domain
+ partial_pivot = K.is_RealField or K.is_ComplexField
+ pivots = ddm_irref(b, _partial_pivot=partial_pivot)
return b, pivots
def nullspace(a):
diff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/dense.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/dense.py
index bf6908805f20..dfaff42a2969 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/dense.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/dense.py
@@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ def ddm_imatmul(a, b, c):
ai[j] = sum(map(mul, bi, cTj), ai[j])
-def ddm_irref(a):
+def ddm_irref(a, _partial_pivot=False):
"""a <-- rref(a)"""
# a is (m x n)
m = len(a)
@@ -97,6 +97,15 @@ def ddm_irref(a):
pivots = []
for j in range(n):
+ # Proper pivoting should be used for all domains for performance
+ # reasons but it is only strictly needed for RR and CC (and possibly
+ # other domains like RR(x)). This path is used by DDM.rref() if the
+ # domain is RR or CC. It uses partial (row) pivoting based on the
+ # absolute value of the pivot candidates.
+ if _partial_pivot:
+ ip = max(range(i, m), key=lambda ip: abs(a[ip][j]))
+ a[i], a[ip] = a[ip], a[i]
+
# pivot
aij = a[i][j]
diff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/linsolve.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/linsolve.py
index 62e6d90aae36..337a9939ae39 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/linsolve.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/linsolve.py
@@ -73,6 +73,12 @@ def _linsolve(eqs, syms):
Aaug = sympy_dict_to_dm(eqsdict, rhs, syms)
K = Aaug.domain
+ # sdm_irref has issues with float matrices. This uses the ddm_rref()
+ # function. When sdm_rref() can handle float matrices reasonably this
+ # should be removed...
+ if K.is_RealField or K.is_ComplexField:
+ Aaug = Aaug.to_ddm().rref()[0].to_sdm()
+
# Compute reduced-row echelon form (RREF)
Arref, pivots, nzcols = sdm_irref(Aaug)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py
index cfa624185a5d..7c4ad43660cc 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/sdm.py
@@ -904,6 +904,8 @@ def sdm_irref(A):
Ajnz = set(Aj)
for k in Ajnz - Ainz:
Ai[k] = - Aij * Aj[k]
+ Ai.pop(j)
+ Ainz.remove(j)
for k in Ajnz & Ainz:
Aik = Ai[k] - Aij * Aj[k]
if Aik:
@@ -938,6 +940,8 @@ def sdm_irref(A):
for l in Ainz - Aknz:
Ak[l] = - Akj * Ai[l]
nonzero_columns[l].add(k)
+ Ak.pop(j)
+ Aknz.remove(j)
for l in Ainz & Aknz:
Akl = Ak[l] - Akj * Ai[l]
if Akl:
diff --git a/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py b/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py
index eda4cdbdf3fa..a77beebdbab7 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/matrices/tests/test_linsolve.py
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
from sympy import S, Eq, I
-from sympy.abc import x, y
+from sympy.abc import x, y, z
from sympy.polys.matrices.linsolve import _linsolve
from sympy.polys.solvers import PolyNonlinearError
@@ -23,6 +23,83 @@ def test__linsolve():
raises(PolyNonlinearError, lambda: _linsolve([x*(1 + x)], [x]))
+def test__linsolve_float():
+
+ # This should give the exact answer:
+ eqs = [
+ y - x,
+ y - 0.0216 * x
+ ]
+ sol = {x:0.0, y:0.0}
+ assert _linsolve(eqs, (x, y)) == sol
+
+ # Other cases should be close to eps
+
+ def all_close(sol1, sol2, eps=1e-15):
+ close = lambda a, b: abs(a - b) < eps
+ assert sol1.keys() == sol2.keys()
+ return all(close(sol1[s], sol2[s]) for s in sol1)
+
+ eqs = [
+ 0.8*x + 0.8*z + 0.2,
+ 0.9*x + 0.7*y + 0.2*z + 0.9,
+ 0.7*x + 0.2*y + 0.2*z + 0.5
+ ]
+ sol_exact = {x:-29/42, y:-11/21, z:37/84}
+ sol_linsolve = _linsolve(eqs, [x,y,z])
+ assert all_close(sol_exact, sol_linsolve)
+
+ eqs = [
+ 0.9*x + 0.3*y + 0.4*z + 0.6,
+ 0.6*x + 0.9*y + 0.1*z + 0.7,
+ 0.4*x + 0.6*y + 0.9*z + 0.5
+ ]
+ sol_exact = {x:-88/175, y:-46/105, z:-1/25}
+ sol_linsolve = _linsolve(eqs, [x,y,z])
+ assert all_close(sol_exact, sol_linsolve)
+
+ eqs = [
+ 0.4*x + 0.3*y + 0.6*z + 0.7,
+ 0.4*x + 0.3*y + 0.9*z + 0.9,
+ 0.7*x + 0.9*y,
+ ]
+ sol_exact = {x:-9/5, y:7/5, z:-2/3}
+ sol_linsolve = _linsolve(eqs, [x,y,z])
+ assert all_close(sol_exact, sol_linsolve)
+
+ eqs = [
+ x*(0.7 + 0.6*I) + y*(0.4 + 0.7*I) + z*(0.9 + 0.1*I) + 0.5,
+ 0.2*I*x + 0.2*I*y + z*(0.9 + 0.2*I) + 0.1,
+ x*(0.9 + 0.7*I) + y*(0.9 + 0.7*I) + z*(0.9 + 0.4*I) + 0.4,
+ ]
+ sol_exact = {
+ x:-6157/7995 - 411/5330*I,
+ y:8519/15990 + 1784/7995*I,
+ z:-34/533 + 107/1599*I,
+ }
+ sol_linsolve = _linsolve(eqs, [x,y,z])
+ assert all_close(sol_exact, sol_linsolve)
+
+ # XXX: This system for x and y over RR(z) is problematic.
+ #
+ # eqs = [
+ # x*(0.2*z + 0.9) + y*(0.5*z + 0.8) + 0.6,
+ # 0.1*x*z + y*(0.1*z + 0.6) + 0.9,
+ # ]
+ #
+ # linsolve(eqs, [x, y])
+ # The solution for x comes out as
+ #
+ # -3.9e-5*z**2 - 3.6e-5*z - 8.67361737988404e-20
+ # x = ----------------------------------------------
+ # 3.0e-6*z**3 - 1.3e-5*z**2 - 5.4e-5*z
+ #
+ # The 8e-20 in the numerator should be zero which would allow z to cancel
+ # from top and bottom. It should be possible to avoid this somehow because
+ # the inverse of the matrix only has a quadratic factor (the determinant)
+ # in the denominator.
+
+
def test__linsolve_deprecated():
assert _linsolve([Eq(x**2, x**2+y)], [x, y]) == {x:x, y:S.Zero}
assert _linsolve([(x+y)**2-x**2], [x]) == {x:-y/2}
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py
index 0f2c747202fe..0feb681d26ba 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py
@@ -27,6 +27,9 @@ def test_construct_domain():
assert isinstance(result[0], ComplexField)
assert result[1] == [CC(3.14), CC(1.0j), CC(0.5)]
+ assert construct_domain([1.0+I]) == (CC, [CC(1.0, 1.0)])
+ assert construct_domain([2.0+3.0*I]) == (CC, [CC(2.0, 3.0)])
+
assert construct_domain([1, I]) == (ZZ_I, [ZZ_I(1, 0), ZZ_I(0, 1)])
assert construct_domain([1, I/2]) == (QQ_I, [QQ_I(1, 0), QQ_I(0, S.Half)])
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
index c6b7a5c126c5..790c62ba8abb 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
@@ -51,6 +51,7 @@
from sympy.polys.fields import field
from sympy.polys.domains import FF, ZZ, QQ, ZZ_I, QQ_I, RR, EX
from sympy.polys.domains.realfield import RealField
+from sympy.polys.domains.complexfield import ComplexField
from sympy.polys.orderings import lex, grlex, grevlex
from sympy import (
@@ -387,6 +388,7 @@ def test_Poly__new__():
modulus=65537, symmetric=False)
assert isinstance(Poly(x**2 + x + 1.0).get_domain(), RealField)
+ assert isinstance(Poly(x**2 + x + I + 1.0).get_domain(), ComplexField)
def test_Poly__args():
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-2032@ab151ba
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 2,032
|
Merge sort Update variable names
|
Fixes #2023
Merge sort variable name updated along with some comments are added
|
2020-05-23T19:28:59Z
|
Mergesort Update Variable Names
I was looking over the mergesort.py file in the divide_and_conquer directory when I saw that all of the variable names are a single letter and there is not much documentation. Does anyone know enough about this file to improve the variable names and make the code more understandable?
|
Can I improve the file?
No need to wait for permission. Just go for it. Pull requests will be reviewed.
Only our competitors think that we should wait.
Can I Modify the Variables to Clarify There Meanings ?
What I can do
Hello folks @Robinson-Arivan @aditya-190 @avitomar12, welcome to the community and before you contribute, please read our [CONTRIBUTION.md](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md). It resolves most of the doubts you may have! You can go to the file and see if there's a problem as OP has noted. If you want to take the issue, remember to notify our community here as well to avoid conflicts.
|
[
{
"body": "I was looking over the mergesort.py file in the divide_and_conquer directory when I saw that all of the variable names are a single letter and there is not much documentation. Does anyone know enough about this file to improve the variable names and make the code more understandable?",
"number": 2023,
"title": "Mergesort Update Variable Names"
}
] |
d8a4faf96d940737ddc488aa8817bc3563ab1a82
|
{
"head_commit": "ab151baa0dd3d5913b5248d53523141a50a13ef1",
"head_commit_message": "Update Merge sort variable names",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/divide_and_conquer/mergesort.py b/divide_and_conquer/mergesort.py\nindex 328e3dca316f..51da8ba716e3 100644\n--- a/divide_and_conquer/mergesort.py\n+++ b/divide_and_conquer/mergesort.py\n@@ -1,45 +1,48 @@\n-def merge(a, b, m, e):\n- l = a[b : m + 1] # noqa: E741\n- r = a[m + 1 : e + 1]\n- k = b\n+def merge(arr, left, mid, right): \n+ # overall array will divided into 2 array\n+ # l contain left portion of array from left to mid of array\n+ # r contain right portion of array from mid+1 to till last of array\n+ l = arr[left : mid + 1] # noqa: E741\n+ r = arr[mid + 1 : right + 1]\n+ k = left\n i = 0\n j = 0\n while i < len(l) and j < len(r):\n # change sign for Descending order\n if l[i] < r[j]:\n- a[k] = l[i]\n+ arr[k] = l[i]\n i += 1\n else:\n- a[k] = r[j]\n+ arr[k] = r[j]\n j += 1\n k += 1\n while i < len(l):\n- a[k] = l[i]\n+ arr[k] = l[i]\n i += 1\n k += 1\n while j < len(r):\n- a[k] = r[j]\n+ arr[k] = r[j]\n j += 1\n k += 1\n- return a\n+ return arr\n \n \n-def mergesort(a, b, e):\n+def mergesort(arr, left, right):\n \"\"\"\n >>> mergesort([3,2,1],0,2)\n [1, 2, 3]\n >>> mergesort([3,2,1,0,1,2,3,5,4],0,8)\n [0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5]\n \"\"\"\n- if b < e:\n- m = (b + e) // 2\n+ if left < right:\n+ mid = (left + right) // 2\n # print(\"ms1\",a,b,m)\n- mergesort(a, b, m)\n+ mergesort(arr, left, mid)\n # print(\"ms2\",a,m+1,e)\n- mergesort(a, m + 1, e)\n+ mergesort(arr, mid + 1, right)\n # print(\"m\",a,b,m,e)\n- merge(a, b, m, e)\n- return a\n+ merge(arr, left, mid, right)\n+ return arr\n \n \n if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1,45 +1,48 @@\n-def merge(a, b, m, e):\n- l = a[b : m + 1] # noqa: E741\n- r = a[m + 1 : e + 1]\n- k = b\n+def merge(arr, left, mid, right): \n+ # overall array will divided into 2 array\n+ # l contain left portion of array from left to mid of array\n+ # r contain right portion of array from mid+1 to till last of array\n+ l = arr[left : mid + 1] # noqa: E741\n+ r = arr[mid + 1 : right + 1]",
"line": null,
"original_line": 6,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "divide_and_conquer/mergesort.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nPlease change `l` to `new_left` and `r` to `new_right`. The # noqa comment can also be removed. Thanks!\n\n@user1:\nOr `left_arr` and `right_arr` might be better.\n\n@author:\nHello @user1 sir, I have updated variable name. \r\nPlease go through it.\r\nThanks!"
}
] |
d1c3e55cb788b62953cf7b92618618fcd4714782
|
diff --git a/divide_and_conquer/mergesort.py b/divide_and_conquer/mergesort.py
index 328e3dca316f..f31a57251ce6 100644
--- a/divide_and_conquer/mergesort.py
+++ b/divide_and_conquer/mergesort.py
@@ -1,45 +1,48 @@
-def merge(a, b, m, e):
- l = a[b : m + 1] # noqa: E741
- r = a[m + 1 : e + 1]
- k = b
+def merge(arr, left, mid, right):
+ # overall array will divided into 2 array
+ # left_arr contains the left portion of array from left to mid
+ # right_arr contains the right portion of array from mid + 1 to right
+ left_arr = arr[left : mid + 1]
+ right_arr = arr[mid + 1 : right + 1]
+ k = left
i = 0
j = 0
- while i < len(l) and j < len(r):
+ while i < len(left_arr) and j < len(right_arr):
# change sign for Descending order
- if l[i] < r[j]:
- a[k] = l[i]
+ if left_arr[i] < right_arr[j]:
+ arr[k] = left_arr[i]
i += 1
else:
- a[k] = r[j]
+ arr[k] = right_arr[j]
j += 1
k += 1
- while i < len(l):
- a[k] = l[i]
+ while i < len(left_arr):
+ arr[k] = left_arr[i]
i += 1
k += 1
- while j < len(r):
- a[k] = r[j]
+ while j < len(right_arr):
+ arr[k] = right_arr[j]
j += 1
k += 1
- return a
+ return arr
-def mergesort(a, b, e):
+def mergesort(arr, left, right):
"""
- >>> mergesort([3,2,1],0,2)
+ >>> mergesort([3, 2, 1], 0, 2)
[1, 2, 3]
- >>> mergesort([3,2,1,0,1,2,3,5,4],0,8)
+ >>> mergesort([3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 4], 0, 8)
[0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5]
"""
- if b < e:
- m = (b + e) // 2
+ if left < right:
+ mid = (left + right) // 2
# print("ms1",a,b,m)
- mergesort(a, b, m)
+ mergesort(arr, left, mid)
# print("ms2",a,m+1,e)
- mergesort(a, m + 1, e)
+ mergesort(arr, mid + 1, right)
# print("m",a,b,m,e)
- merge(a, b, m, e)
- return a
+ merge(arr, left, mid, right)
+ return arr
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 1,
"problem_domain": "Code Refactoring / Architectural Improvement"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21476@ecab539
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,476
|
fix(diffgeom): fix indirect transformation
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #20742
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Allow indirect transformation
Change signature of relation in order to allow indirect transformation
#### Other comments
Before #21464, transformation relation for `CoordSystem` used `Lambda` e.g. `Lambda((x, y), (y, -x))`.
In #21464, the signature was changed to use only the expression, e.g. `(y, -x)`.
However, to allow indirect transformation it is crucial to store the original symbol and transformed expression altogether. Therefore, the signature is now `((x, y), (y, -x))`. Old signature with `Lambda` is still supported, so it won't break backwards compatibility.
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* diffgeom
* Bug in indirect transformation between coordinate systems is fixed.
* Transform relation between coordinate systems now consists of two tuples instead of `Lambda`.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-05-16T07:53:41Z
|
diffgeom.CoordSystem.transform with indirect relation raises KeyError
Below code is a minimal example for an indirect transform via a temporary intermediate coordinate system. `parabolic2D.transform(poloidal)` raises a KeyError.
MWE:
```
"""
2D manifold coordinate systems
"""
import sympy
import sympy.diffgeom
CARTESIAN2D = "cartesian2D"
POLOIDAL = "poloidal"
PARABOLIC2D = "parabolic2D"
m = sympy.diffgeom.Manifold("M", 2)
p = sympy.diffgeom.Patch("P", m)
RELATIONS = {}
# #########
# cartesian
# #########
x, y = sympy.symbols("x y")
# #########
# poloidal
# #########
r, theta = sympy.symbols("r theta", nonnegative=True)
RELATIONS[(CARTESIAN2D, POLOIDAL)] = sympy.Lambda(
(x, y),
sympy.Matrix(
[
sympy.sqrt(x ** 2 + y ** 2),
sympy.atan2(y, x)
]
)
)
RELATIONS[(POLOIDAL, CARTESIAN2D)] = sympy.Lambda(
(r, theta),
sympy.Matrix(
[
r * sympy.cos(theta),
r * sympy.sin(theta)
]
)
)
# #########
# parabolic
# #########
sigma, tau = sympy.symbols("sigma tau")
RELATIONS[(PARABOLIC2D, CARTESIAN2D)] = sympy.Lambda(
(sigma, tau),
sympy.Matrix(
[
sigma * tau,
1 / 2 * (tau**2 - sigma**2)
]
)
)
cartesian2D = sympy.diffgeom.CoordSystem(CARTESIAN2D, p, [x, y], RELATIONS)
poloidal = sympy.diffgeom.CoordSystem(POLOIDAL, p, [r, theta], RELATIONS)
parabolic2D = sympy.diffgeom.CoordSystem(PARABOLIC2D, p, [sigma, tau], RELATIONS)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(parabolic2D.transform(poloidal)) # raises a KeyError
print(poloidal.transform(parabolic2D)) # raises a KeyError
```
This raises a KeyError.
> Traceback (most recent call last):
> File "/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/pdb.py", line 1703, in main
> pdb._runscript(mainpyfile)
> File "/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/pdb.py", line 1572, in _runscript
> self.run(statement)
> File "/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/bdb.py", line 580, in run
> exec(cmd, globals, locals)
> File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
> File "/home/IPP-HGW/dboe/git/tfields/tfields/bases/manifold_2.py", line 1, in <module>
> """
> File "/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py", line 480, in transform
> transf = self.transformation(sys)
> File "/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py", line 354, in transformation
> return self._indirect_transformation(self, sys)
> File "/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/core/cache.py", line 72, in wrapper
> retval = cfunc(*args, **kwargs)
> File "/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py", line 376, in _indirect_transformation
> path = cls._dijkstra(sys1, sys2)
> File "/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py", line 414, in _dijkstra
> visit(sys1)
> File "/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py", line 406, in visit
> path_dict[sys][2] = 1
> KeyError: parabolic2D
>
I think I found the reson already: In dijkstra routing the comparison is done between a CoordSystem and sympy.Str
DEBUGGING:
```
Uncaught exception. Entering post mortem debugging
Running 'cont' or 'step' will restart the program
> /opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py(406)visit()
-> path_dict[sys][2] = 1
(Pdb) path_dict
{cartesian2D: [0, [], 0], poloidal: [0, [], 0], parabolic2D: [0, [], 0]}
(Pdb) sys
parabolic2D
(Pdb) hash(sys)
-2150956724454717966
(Pdb) [hash(k) for k in path_dict]
[6233656281303402583, 5480353473597806494, -1340528192013030397]
(Pdb) type(sys)
<class 'sympy.diffgeom.diffgeom.CoordSystem'>
(Pdb) [type(k) for k in path_dict]
[<class 'sympy.core.symbol.Str'>, <class 'sympy.core.symbol.Str'>, <class 'sympy.core.symbol.Str'>]
```
|
I started looking into this, I noticed another bug in addition to the type mismatch in the Dijkstra algorithm. Your example only gives the forward transformation from parabolic2D to cartesian2D, so in order to solve `poloidal.transform(parabolic2D)` the `transform `method will need to calculate the inverse transformation from cartesian2D to parabolic2D, which will raise an exception, see https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/21356
|
[
{
"body": "Below code is a minimal example for an indirect transform via a temporary intermediate coordinate system. `parabolic2D.transform(poloidal)` raises a KeyError.\r\n\r\nMWE:\r\n```\r\n\"\"\"\r\n2D manifold coordinate systems\r\n\"\"\"\r\nimport sympy\r\nimport sympy.diffgeom\r\n\r\nCARTESIAN2D = \"cartesian2D\"\r\nPOLOIDAL = \"poloidal\"\r\nPARABOLIC2D = \"parabolic2D\"\r\n\r\nm = sympy.diffgeom.Manifold(\"M\", 2)\r\np = sympy.diffgeom.Patch(\"P\", m)\r\nRELATIONS = {}\r\n\r\n# #########\r\n# cartesian\r\n# #########\r\nx, y = sympy.symbols(\"x y\")\r\n\r\n# #########\r\n# poloidal\r\n# #########\r\nr, theta = sympy.symbols(\"r theta\", nonnegative=True)\r\nRELATIONS[(CARTESIAN2D, POLOIDAL)] = sympy.Lambda(\r\n (x, y),\r\n sympy.Matrix(\r\n [\r\n sympy.sqrt(x ** 2 + y ** 2),\r\n sympy.atan2(y, x)\r\n ]\r\n )\r\n)\r\nRELATIONS[(POLOIDAL, CARTESIAN2D)] = sympy.Lambda(\r\n (r, theta),\r\n sympy.Matrix(\r\n [\r\n r * sympy.cos(theta),\r\n r * sympy.sin(theta)\r\n ]\r\n )\r\n)\r\n\r\n# #########\r\n# parabolic\r\n# #########\r\nsigma, tau = sympy.symbols(\"sigma tau\")\r\nRELATIONS[(PARABOLIC2D, CARTESIAN2D)] = sympy.Lambda(\r\n (sigma, tau),\r\n sympy.Matrix(\r\n [\r\n sigma * tau,\r\n 1 / 2 * (tau**2 - sigma**2)\r\n ]\r\n )\r\n)\r\n\r\ncartesian2D = sympy.diffgeom.CoordSystem(CARTESIAN2D, p, [x, y], RELATIONS)\r\npoloidal = sympy.diffgeom.CoordSystem(POLOIDAL, p, [r, theta], RELATIONS)\r\nparabolic2D = sympy.diffgeom.CoordSystem(PARABOLIC2D, p, [sigma, tau], RELATIONS)\r\n\r\n\r\nif __name__ == \"__main__\":\r\n print(parabolic2D.transform(poloidal)) # raises a KeyError\r\n print(poloidal.transform(parabolic2D)) # raises a KeyError\r\n```\r\n\r\nThis raises a KeyError.\r\n\r\n> Traceback (most recent call last):\r\n> File \"/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/pdb.py\", line 1703, in main\r\n> pdb._runscript(mainpyfile)\r\n> File \"/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/pdb.py\", line 1572, in _runscript\r\n> self.run(statement)\r\n> File \"/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/bdb.py\", line 580, in run\r\n> exec(cmd, globals, locals)\r\n> File \"<string>\", line 1, in <module>\r\n> File \"/home/IPP-HGW/dboe/git/tfields/tfields/bases/manifold_2.py\", line 1, in <module>\r\n> \"\"\"\r\n> File \"/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\", line 480, in transform\r\n> transf = self.transformation(sys)\r\n> File \"/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\", line 354, in transformation\r\n> return self._indirect_transformation(self, sys)\r\n> File \"/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/core/cache.py\", line 72, in wrapper\r\n> retval = cfunc(*args, **kwargs)\r\n> File \"/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\", line 376, in _indirect_transformation\r\n> path = cls._dijkstra(sys1, sys2)\r\n> File \"/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\", line 414, in _dijkstra\r\n> visit(sys1)\r\n> File \"/opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\", line 406, in visit\r\n> path_dict[sys][2] = 1\r\n> KeyError: parabolic2D\r\n> \r\n\r\nI think I found the reson already: In dijkstra routing the comparison is done between a CoordSystem and sympy.Str\r\nDEBUGGING:\r\n\r\n```\r\nUncaught exception. Entering post mortem debugging\r\nRunning 'cont' or 'step' will restart the program\r\n> /opt/anaconda/envs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py(406)visit()\r\n-> path_dict[sys][2] = 1\r\n(Pdb) path_dict\r\n{cartesian2D: [0, [], 0], poloidal: [0, [], 0], parabolic2D: [0, [], 0]}\r\n(Pdb) sys\r\nparabolic2D\r\n(Pdb) hash(sys)\r\n-2150956724454717966\r\n(Pdb) [hash(k) for k in path_dict]\r\n[6233656281303402583, 5480353473597806494, -1340528192013030397]\r\n(Pdb) type(sys)\r\n<class 'sympy.diffgeom.diffgeom.CoordSystem'>\r\n(Pdb) [type(k) for k in path_dict]\r\n[<class 'sympy.core.symbol.Str'>, <class 'sympy.core.symbol.Str'>, <class 'sympy.core.symbol.Str'>]\r\n```\r\n",
"number": 20742,
"title": "diffgeom.CoordSystem.transform with indirect relation raises KeyError"
}
] |
f6b0190377be37f93f5e431951e66b562ef5dc35
|
{
"head_commit": "ecab539228b95d9dd9de48f035daa5da377aa1fc",
"head_commit_message": "fix(diffgeom): fix indirect transformation\n\nAllow indirect transformation\nChange signature of relation in order to allow indirect transformation",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\nindex ba82beebbab6..1e7b04be4c95 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\n@@ -193,8 +193,9 @@ class CoordSystem(Basic):\n \n relations : dict, optional\n Key is a tuple of two strings, who are the names of the systems where\n- the coordinates transform from and transform to. Value is a tuple of\n- transformed coordinates.\n+ the coordinates transform from and transform to.\n+ Value is a tuple of the symbols before transformation and a tuple of\n+ the expressions after transformation.\n \n Examples\n ========\n@@ -209,8 +210,8 @@ class CoordSystem(Basic):\n >>> x, y = symbols('x y', real=True)\n >>> r, theta = symbols('r theta', nonnegative=True)\n >>> relation_dict = {\n- ... ('Car2D', 'Pol'): (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)),\n- ... ('Pol', 'Car2D'): (r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta))\n+ ... ('Car2D', 'Pol'): [(x, y), (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x))],\n+ ... ('Pol', 'Car2D'): [(r, theta), (r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta))]\n ... }\n >>> Car2D = CoordSystem('Car2D', p, (x, y), relation_dict)\n >>> Pol = CoordSystem('Pol', p, (r, theta), relation_dict)\n@@ -314,8 +315,12 @@ def __new__(cls, name, patch, symbols=None, relations={}, **kwargs):\n if not isinstance(s2, Str):\n s2 = Str(s2)\n key = Tuple(s1, s2)\n+\n+ # Old version used Lambda as a value.\n if isinstance(v, Lambda):\n- v = tuple(v(*symbols))\n+ v = (tuple(v.signature), tuple(v.expr))\n+ else:\n+ v = (tuple(v[0]), tuple(v[1]))\n rel_temp[key] = v\n relations = Dict(rel_temp)\n \n@@ -396,7 +401,7 @@ def transformation(self, sys):\n if self == sys:\n expr = Matrix(self.symbols)\n elif key in self.relations:\n- expr = Matrix(self.relations[key])\n+ expr = Matrix(self.relations[key][1])\n elif key[::-1] in self.relations:\n expr = Matrix(self._inverse_transformation(sys, self))\n else:\n@@ -404,44 +409,58 @@ def transformation(self, sys):\n return Lambda(signature, expr)\n \n @staticmethod\n- def _inverse_transformation(sys1, sys2):\n- # Find the transformation relation from sys2 to sys1\n- forward_transform_expressions = sys1.transform(sys2)\n-\n- inv_results = solve(\n- [t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(sys2.symbols, forward_transform_expressions)],\n- list(sys1.symbols), dict=True)\n- if len(inv_results) == 0:\n- raise NotImplementedError(\n- \"Cannot solve inverse of transformation from {} to {}\".format(sys1, sys2))\n- elif len(inv_results) > 1:\n- raise ValueError(\n- \"Obtained multiple results for inverse of transformation from {} to {}\".format(sys1, sys2)\n- )\n+ def _solve_inverse(sym1, sym2, exprs, sys1_name, sys2_name):\n+ ret = solve(\n+ [t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(sym2, exprs)],\n+ list(sym1), dict=True)\n+\n+ if len(ret) == 0:\n+ temp = \"Cannot solve inverse relation from {} to {}.\"\n+ raise NotImplementedError(temp.format(sys1_name, sys2_name))\n+ elif len(ret) > 1:\n+ temp = \"Obtained multiple inverse relation from {} to {}.\"\n+ raise ValueError(temp.format(sys1_name, sys2_name))\n+\n+ return ret[0]\n \n- inv_results = inv_results[0]\n+ @classmethod\n+ def _inverse_transformation(cls, sys1, sys2):\n+ # Find the transformation relation from sys2 to sys1\n+ forward = sys1.transform(sys2)\n+ inv_results = cls._solve_inverse(sys1.symbols, sys2.symbols, forward,\n+ sys1.name, sys2.name)\n signature = tuple(sys1.symbols)\n return [inv_results[s] for s in signature]\n \n @classmethod\n @cacheit\n def _indirect_transformation(cls, sys1, sys2):\n- # Find the transformation relation between two indirectly connected coordinate systems\n+ # Find the transformation relation betweentwo indirectly connected\n+ # coordinate systems\n+ rel = sys1.relations\n path = cls._dijkstra(sys1, sys2)\n- Lambdas = []\n- for i in range(len(path) - 1):\n- s1, s2 = path[i], path[i + 1]\n- Lambdas.append(s1.transformation(s2))\n- syms = Lambdas[-1].signature\n- expr = syms\n- for l in reversed(Lambdas):\n- expr = l(*expr)\n- return Lambda(syms, expr)\n+\n+ transforms = []\n+ for s1, s2 in zip(path, path[1:]):\n+ if (s1, s2) in rel:\n+ transforms.append(rel[(s1, s2)])\n+ else:\n+ sym2, inv_exprs = rel[(s2, s1)]\n+ sym1 = tuple(Dummy() for i in sym2)\n+ ret = cls._solve_inverse(sym2, sym1, inv_exprs, s2, s1)\n+ ret = tuple(ret[s] for s in sym2)\n+ transforms.append((sym1, ret))\n+ syms = sys1.args[2]\n+ exprs = syms\n+ for newsyms, newexprs in transforms:\n+ exprs = tuple(e.subs(zip(newsyms, exprs)) for e in newexprs)\n+ return exprs\n \n @staticmethod\n def _dijkstra(sys1, sys2):\n # Use Dijkstra algorithm to find the shortest path between two indirectly-connected\n # coordinate systems\n+ # return value is the list of the names of the systems.\n relations = sys1.relations\n graph = {}\n for s1, s2 in relations.keys():\n@@ -465,7 +484,7 @@ def visit(sys):\n path_dict[newsys][1] = [i for i in path_dict[sys][1]]\n path_dict[newsys][1].append(sys)\n \n- visit(sys1)\n+ visit(sys1.name)\n \n while True:\n min_distance = max(path_dict.values(), key=lambda x:x[0])[0]\n@@ -478,10 +497,10 @@ def visit(sys):\n break\n visit(newsys)\n \n- result = path_dict[sys2][1]\n- result.append(sys2)\n+ result = path_dict[sys2.name][1]\n+ result.append(sys2.name)\n \n- if result == [sys2]:\n+ if result == [sys2.name]:\n raise KeyError(\"Two coordinate systems are not connected.\")\n return result\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py b/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py\nindex 635e85f7365a..c6254734f4da 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py\n@@ -30,8 +30,8 @@\n r, theta = symbols('rho theta', nonnegative=True)\n \n relations_2d = {\n- ('rectangular', 'polar'): (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)),\n- ('polar', 'rectangular'): (r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)),\n+ ('rectangular', 'polar'): [(x, y), (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x))],\n+ ('polar', 'rectangular'): [(r, theta), (r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta))],\n }\n \n R2_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R2_origin, (x, y), relations_2d) # type: Any\n@@ -74,18 +74,24 @@\n rho, psi, r, theta, phi = symbols('rho psi r theta phi', nonnegative=True)\n \n relations_3d = {\n- ('rectangular', 'cylindrical'): (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z),\n- ('cylindrical', 'rectangular'): (rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z),\n- ('rectangular', 'spherical'): (sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2),\n- acos(z/sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)),\n- atan2(y, x)),\n- ('spherical', 'rectangular'): (r*sin(theta)*cos(phi),\n- r*sin(theta)*sin(phi),\n- r*cos(theta)),\n- ('cylindrical', 'spherical'): (sqrt(rho**2 + z**2),\n- acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)),\n- psi),\n- ('spherical', 'cylindrical'): (r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta)),\n+ ('rectangular', 'cylindrical'): [(x, y, z),\n+ (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z)],\n+ ('cylindrical', 'rectangular'): [(rho, psi, z),\n+ (rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z)],\n+ ('rectangular', 'spherical'): [(x, y, z),\n+ (sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2),\n+ acos(z/sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)),\n+ atan2(y, x))],\n+ ('spherical', 'rectangular'): [(r, theta, phi),\n+ (r*sin(theta)*cos(phi),\n+ r*sin(theta)*sin(phi),\n+ r*cos(theta))],\n+ ('cylindrical', 'spherical'): [(rho, psi, z),\n+ (sqrt(rho**2 + z**2),\n+ acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)),\n+ psi)],\n+ ('spherical', 'cylindrical'): [(r, theta, phi),\n+ (r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta))],\n }\n \n R3_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R3_origin, (x, y, z), relations_3d) # type: Any\ndiff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py\nindex f5c1209702d4..dc36547e87eb 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py\n@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@\n+from sympy.core import Lambda, Symbol, symbols\n from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_p, R2_r, R3_r, R3_c, R3_s, R2_origin\n from sympy.diffgeom import (CoordSystem, Commutator, Differential, TensorProduct,\n WedgeProduct, BaseCovarDerivativeOp, CovarDerivativeOp, LieDerivative,\n covariant_order, contravariant_order, twoform_to_matrix, metric_to_Christoffel_1st,\n metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, metric_to_Riemann_components,\n metric_to_Ricci_components, intcurve_diffequ, intcurve_series)\n-from sympy.core import Symbol, symbols\n from sympy.simplify import trigsimp, simplify\n from sympy.functions import sqrt, atan2, sin\n from sympy.matrices import Matrix\n@@ -14,6 +14,78 @@\n TP = TensorProduct\n \n \n+def test_coordsys_transform():\n+ # test inverse transforms\n+ p, q, r, s = symbols('p q r s')\n+ rel = {('first', 'second'): [(p, q), (q, -p)]}\n+ R2_pq = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [p, q], rel)\n+ R2_rs = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [r, s], rel)\n+ r, s = R2_rs.symbols\n+ assert R2_rs.transform(R2_pq) == Matrix([[-s], [r]])\n+\n+ # inverse transform impossible case\n+ a, b = symbols('a b', positive=True)\n+ rel = {('first', 'second'): [(a,), (-a,)]}\n+ R2_a = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [a], rel)\n+ R2_b = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [b], rel)\n+ # This transformation is uninvertible because there is no positive a, b satisfying a = -b\n+ with raises(NotImplementedError):\n+ R2_b.transform(R2_a)\n+\n+ # inverse transform ambiguous case\n+ c, d = symbols('c d')\n+ rel = {('first', 'second'): [(c,), (c**2,)]}\n+ R2_c = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [c], rel)\n+ R2_d = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [d], rel)\n+ # The transform method should throw if it finds multiple inverses for a coordinate transformation.\n+ with raises(ValueError):\n+ R2_d.transform(R2_c)\n+\n+ # test indirect transformation\n+ a, b, c, d, e, f = symbols('a, b, c, d, e, f')\n+ rel = {('C1', 'C2'): [(a, b), (2*a, 3*b)],\n+ ('C2', 'C3'): [(c, d), (3*c, 2*d)]}\n+ C1 = CoordSystem('C1', R2_origin, (a, b), rel)\n+ C2 = CoordSystem('C2', R2_origin, (c, d), rel)\n+ C3 = CoordSystem('C3', R2_origin, (e, f), rel)\n+ a, b = C1.symbols\n+ c, d = C2.symbols\n+ e, f = C3.symbols\n+ assert C2.transform(C1) == Matrix([c/2, d/3])\n+ assert C1.transform(C3) == Matrix([6*a, 6*b])\n+ assert C3.transform(C1) == Matrix([e/6, f/6])\n+ assert C3.transform(C2) == Matrix([e/3, f/2])\n+\n+ a, b, c, d, e, f = symbols('a, b, c, d, e, f')\n+ rel = {('C1', 'C2'): [(a, b), (2*a, 3*b + 1)],\n+ ('C3', 'C2'): [(e, f), (-e - 2, 2*f)]}\n+ C1 = CoordSystem('C1', R2_origin, (a, b), rel)\n+ C2 = CoordSystem('C2', R2_origin, (c, d), rel)\n+ C3 = CoordSystem('C3', R2_origin, (e, f), rel)\n+ a, b = C1.symbols\n+ c, d = C2.symbols\n+ e, f = C3.symbols\n+ assert C2.transform(C1) == Matrix([c/2, (d - 1)/3])\n+ assert C1.transform(C3) == Matrix([-2*a - 2, (3*b + 1)/2])\n+ assert C3.transform(C1) == Matrix([-e/2 - 1, (2*f - 1)/3])\n+ assert C3.transform(C2) == Matrix([-e - 2, 2*f])\n+\n+ # old signature uses Lambda\n+ a, b, c, d, e, f = symbols('a, b, c, d, e, f')\n+ rel = {('C1', 'C2'): Lambda((a, b), (2*a, 3*b + 1)),\n+ ('C3', 'C2'): Lambda((e, f), (-e - 2, 2*f))}\n+ C1 = CoordSystem('C1', R2_origin, (a, b), rel)\n+ C2 = CoordSystem('C2', R2_origin, (c, d), rel)\n+ C3 = CoordSystem('C3', R2_origin, (e, f), rel)\n+ a, b = C1.symbols\n+ c, d = C2.symbols\n+ e, f = C3.symbols\n+ assert C2.transform(C1) == Matrix([c/2, (d - 1)/3])\n+ assert C1.transform(C3) == Matrix([-2*a - 2, (3*b + 1)/2])\n+ assert C3.transform(C1) == Matrix([-e/2 - 1, (2*f - 1)/3])\n+ assert C3.transform(C2) == Matrix([-e - 2, 2*f])\n+\n+\n def test_R2():\n x0, y0, r0, theta0 = symbols('x0, y0, r0, theta0', real=True)\n point_r = R2_r.point([x0, y0])\n@@ -37,45 +109,6 @@ def test_R2():\n R2_r, R2_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_p, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n \n \n-def test_inverse_transformations():\n- p, q, r, s = symbols('p q r s')\n-\n- relations_quarter_rotation = {\n- ('first', 'second'): (q, -p)\n- }\n-\n- R2_pq = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [p, q], relations_quarter_rotation)\n- R2_rs = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [r, s], relations_quarter_rotation)\n-\n- # The transform method should derive the inverse transformation if not given explicitly\n- assert R2_rs.transform(R2_pq) == Matrix([[-R2_rs.symbols[1]], [R2_rs.symbols[0]]])\n-\n- a, b = symbols('a b', positive=True)\n- relations_uninvertible_transformation = {\n- ('first', 'second'): (-a,)\n- }\n-\n- R2_a = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [a], relations_uninvertible_transformation)\n- R2_b = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [b], relations_uninvertible_transformation)\n-\n- # The transform method should throw if it cannot invert the coordinate transformation.\n- # This transformation is uninvertible because there is no positive a, b satisfying a = -b\n- with raises(NotImplementedError):\n- R2_b.transform(R2_a)\n-\n- c, d = symbols('c d')\n- relations_ambiguous_inverse = {\n- ('first', 'second'): (c**2,)\n- }\n-\n- R2_c = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [c], relations_ambiguous_inverse)\n- R2_d = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [d], relations_ambiguous_inverse)\n-\n- # The transform method should throw if it finds multiple inverses for a coordinate transformation.\n- with raises(ValueError):\n- R2_d.transform(R2_c)\n-\n-\n def test_R3():\n a, b, c = symbols('a b c', positive=True)\n m = Matrix([[a], [b], [c]])\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -396,52 +401,66 @@ def transformation(self, sys):\n if self == sys:\n expr = Matrix(self.symbols)\n elif key in self.relations:\n- expr = Matrix(self.relations[key])\n+ expr = Matrix(self.relations[key][1])\n elif key[::-1] in self.relations:\n expr = Matrix(self._inverse_transformation(sys, self))\n else:\n expr = Matrix(self._indirect_transformation(self, sys))\n return Lambda(signature, expr)\n \n @staticmethod\n- def _inverse_transformation(sys1, sys2):\n- # Find the transformation relation from sys2 to sys1\n- forward_transform_expressions = sys1.transform(sys2)\n-\n- inv_results = solve(\n- [t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(sys2.symbols, forward_transform_expressions)],\n- list(sys1.symbols), dict=True)\n- if len(inv_results) == 0:\n- raise NotImplementedError(\n- \"Cannot solve inverse of transformation from {} to {}\".format(sys1, sys2))\n- elif len(inv_results) > 1:\n- raise ValueError(\n- \"Obtained multiple results for inverse of transformation from {} to {}\".format(sys1, sys2)\n- )\n+ def _solve_inverse(sym1, sym2, exprs, sys1_name, sys2_name):\n+ ret = solve(\n+ [t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(sym2, exprs)],\n+ list(sym1), dict=True)\n+\n+ if len(ret) == 0:\n+ temp = \"Cannot solve inverse relation from {} to {}.\"\n+ raise NotImplementedError(temp.format(sys1_name, sys2_name))\n+ elif len(ret) > 1:\n+ temp = \"Obtained multiple inverse relation from {} to {}.\"\n+ raise ValueError(temp.format(sys1_name, sys2_name))\n+\n+ return ret[0]\n \n- inv_results = inv_results[0]\n+ @classmethod\n+ def _inverse_transformation(cls, sys1, sys2):\n+ # Find the transformation relation from sys2 to sys1\n+ forward = sys1.transform(sys2)\n+ inv_results = cls._solve_inverse(sys1.symbols, sys2.symbols, forward,\n+ sys1.name, sys2.name)\n signature = tuple(sys1.symbols)\n return [inv_results[s] for s in signature]\n \n @classmethod\n @cacheit\n def _indirect_transformation(cls, sys1, sys2):\n- # Find the transformation relation between two indirectly connected coordinate systems\n+ # Find the transformation relation betweentwo indirectly connected",
"line": null,
"original_line": 438,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n # Find the transformation relation between two indirectly connected\r\n```"
}
] |
d76f3b9abe2d417d8f27f6b5dfa4c40c95bc001c
|
diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py
index ba82beebbab6..f4f1aa444d41 100644
--- a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py
+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py
@@ -193,8 +193,9 @@ class CoordSystem(Basic):
relations : dict, optional
Key is a tuple of two strings, who are the names of the systems where
- the coordinates transform from and transform to. Value is a tuple of
- transformed coordinates.
+ the coordinates transform from and transform to.
+ Value is a tuple of the symbols before transformation and a tuple of
+ the expressions after transformation.
Examples
========
@@ -209,8 +210,8 @@ class CoordSystem(Basic):
>>> x, y = symbols('x y', real=True)
>>> r, theta = symbols('r theta', nonnegative=True)
>>> relation_dict = {
- ... ('Car2D', 'Pol'): (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)),
- ... ('Pol', 'Car2D'): (r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta))
+ ... ('Car2D', 'Pol'): [(x, y), (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x))],
+ ... ('Pol', 'Car2D'): [(r, theta), (r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta))]
... }
>>> Car2D = CoordSystem('Car2D', p, (x, y), relation_dict)
>>> Pol = CoordSystem('Pol', p, (r, theta), relation_dict)
@@ -314,8 +315,12 @@ def __new__(cls, name, patch, symbols=None, relations={}, **kwargs):
if not isinstance(s2, Str):
s2 = Str(s2)
key = Tuple(s1, s2)
+
+ # Old version used Lambda as a value.
if isinstance(v, Lambda):
- v = tuple(v(*symbols))
+ v = (tuple(v.signature), tuple(v.expr))
+ else:
+ v = (tuple(v[0]), tuple(v[1]))
rel_temp[key] = v
relations = Dict(rel_temp)
@@ -396,7 +401,7 @@ def transformation(self, sys):
if self == sys:
expr = Matrix(self.symbols)
elif key in self.relations:
- expr = Matrix(self.relations[key])
+ expr = Matrix(self.relations[key][1])
elif key[::-1] in self.relations:
expr = Matrix(self._inverse_transformation(sys, self))
else:
@@ -404,44 +409,58 @@ def transformation(self, sys):
return Lambda(signature, expr)
@staticmethod
- def _inverse_transformation(sys1, sys2):
- # Find the transformation relation from sys2 to sys1
- forward_transform_expressions = sys1.transform(sys2)
-
- inv_results = solve(
- [t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(sys2.symbols, forward_transform_expressions)],
- list(sys1.symbols), dict=True)
- if len(inv_results) == 0:
- raise NotImplementedError(
- "Cannot solve inverse of transformation from {} to {}".format(sys1, sys2))
- elif len(inv_results) > 1:
- raise ValueError(
- "Obtained multiple results for inverse of transformation from {} to {}".format(sys1, sys2)
- )
+ def _solve_inverse(sym1, sym2, exprs, sys1_name, sys2_name):
+ ret = solve(
+ [t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(sym2, exprs)],
+ list(sym1), dict=True)
+
+ if len(ret) == 0:
+ temp = "Cannot solve inverse relation from {} to {}."
+ raise NotImplementedError(temp.format(sys1_name, sys2_name))
+ elif len(ret) > 1:
+ temp = "Obtained multiple inverse relation from {} to {}."
+ raise ValueError(temp.format(sys1_name, sys2_name))
+
+ return ret[0]
- inv_results = inv_results[0]
+ @classmethod
+ def _inverse_transformation(cls, sys1, sys2):
+ # Find the transformation relation from sys2 to sys1
+ forward = sys1.transform(sys2)
+ inv_results = cls._solve_inverse(sys1.symbols, sys2.symbols, forward,
+ sys1.name, sys2.name)
signature = tuple(sys1.symbols)
return [inv_results[s] for s in signature]
@classmethod
@cacheit
def _indirect_transformation(cls, sys1, sys2):
- # Find the transformation relation between two indirectly connected coordinate systems
+ # Find the transformation relation between two indirectly connected
+ # coordinate systems
+ rel = sys1.relations
path = cls._dijkstra(sys1, sys2)
- Lambdas = []
- for i in range(len(path) - 1):
- s1, s2 = path[i], path[i + 1]
- Lambdas.append(s1.transformation(s2))
- syms = Lambdas[-1].signature
- expr = syms
- for l in reversed(Lambdas):
- expr = l(*expr)
- return Lambda(syms, expr)
+
+ transforms = []
+ for s1, s2 in zip(path, path[1:]):
+ if (s1, s2) in rel:
+ transforms.append(rel[(s1, s2)])
+ else:
+ sym2, inv_exprs = rel[(s2, s1)]
+ sym1 = tuple(Dummy() for i in sym2)
+ ret = cls._solve_inverse(sym2, sym1, inv_exprs, s2, s1)
+ ret = tuple(ret[s] for s in sym2)
+ transforms.append((sym1, ret))
+ syms = sys1.args[2]
+ exprs = syms
+ for newsyms, newexprs in transforms:
+ exprs = tuple(e.subs(zip(newsyms, exprs)) for e in newexprs)
+ return exprs
@staticmethod
def _dijkstra(sys1, sys2):
# Use Dijkstra algorithm to find the shortest path between two indirectly-connected
# coordinate systems
+ # return value is the list of the names of the systems.
relations = sys1.relations
graph = {}
for s1, s2 in relations.keys():
@@ -465,7 +484,7 @@ def visit(sys):
path_dict[newsys][1] = [i for i in path_dict[sys][1]]
path_dict[newsys][1].append(sys)
- visit(sys1)
+ visit(sys1.name)
while True:
min_distance = max(path_dict.values(), key=lambda x:x[0])[0]
@@ -478,10 +497,10 @@ def visit(sys):
break
visit(newsys)
- result = path_dict[sys2][1]
- result.append(sys2)
+ result = path_dict[sys2.name][1]
+ result.append(sys2.name)
- if result == [sys2]:
+ if result == [sys2.name]:
raise KeyError("Two coordinate systems are not connected.")
return result
diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py b/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py
index 635e85f7365a..c6254734f4da 100644
--- a/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py
+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py
@@ -30,8 +30,8 @@
r, theta = symbols('rho theta', nonnegative=True)
relations_2d = {
- ('rectangular', 'polar'): (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)),
- ('polar', 'rectangular'): (r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)),
+ ('rectangular', 'polar'): [(x, y), (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x))],
+ ('polar', 'rectangular'): [(r, theta), (r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta))],
}
R2_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R2_origin, (x, y), relations_2d) # type: Any
@@ -74,18 +74,24 @@
rho, psi, r, theta, phi = symbols('rho psi r theta phi', nonnegative=True)
relations_3d = {
- ('rectangular', 'cylindrical'): (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z),
- ('cylindrical', 'rectangular'): (rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z),
- ('rectangular', 'spherical'): (sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2),
- acos(z/sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)),
- atan2(y, x)),
- ('spherical', 'rectangular'): (r*sin(theta)*cos(phi),
- r*sin(theta)*sin(phi),
- r*cos(theta)),
- ('cylindrical', 'spherical'): (sqrt(rho**2 + z**2),
- acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)),
- psi),
- ('spherical', 'cylindrical'): (r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta)),
+ ('rectangular', 'cylindrical'): [(x, y, z),
+ (sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z)],
+ ('cylindrical', 'rectangular'): [(rho, psi, z),
+ (rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z)],
+ ('rectangular', 'spherical'): [(x, y, z),
+ (sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2),
+ acos(z/sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)),
+ atan2(y, x))],
+ ('spherical', 'rectangular'): [(r, theta, phi),
+ (r*sin(theta)*cos(phi),
+ r*sin(theta)*sin(phi),
+ r*cos(theta))],
+ ('cylindrical', 'spherical'): [(rho, psi, z),
+ (sqrt(rho**2 + z**2),
+ acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)),
+ psi)],
+ ('spherical', 'cylindrical'): [(r, theta, phi),
+ (r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta))],
}
R3_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R3_origin, (x, y, z), relations_3d) # type: Any
diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py
index f5c1209702d4..dc36547e87eb 100644
--- a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py
+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
+from sympy.core import Lambda, Symbol, symbols
from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_p, R2_r, R3_r, R3_c, R3_s, R2_origin
from sympy.diffgeom import (CoordSystem, Commutator, Differential, TensorProduct,
WedgeProduct, BaseCovarDerivativeOp, CovarDerivativeOp, LieDerivative,
covariant_order, contravariant_order, twoform_to_matrix, metric_to_Christoffel_1st,
metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, metric_to_Riemann_components,
metric_to_Ricci_components, intcurve_diffequ, intcurve_series)
-from sympy.core import Symbol, symbols
from sympy.simplify import trigsimp, simplify
from sympy.functions import sqrt, atan2, sin
from sympy.matrices import Matrix
@@ -14,6 +14,78 @@
TP = TensorProduct
+def test_coordsys_transform():
+ # test inverse transforms
+ p, q, r, s = symbols('p q r s')
+ rel = {('first', 'second'): [(p, q), (q, -p)]}
+ R2_pq = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [p, q], rel)
+ R2_rs = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [r, s], rel)
+ r, s = R2_rs.symbols
+ assert R2_rs.transform(R2_pq) == Matrix([[-s], [r]])
+
+ # inverse transform impossible case
+ a, b = symbols('a b', positive=True)
+ rel = {('first', 'second'): [(a,), (-a,)]}
+ R2_a = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [a], rel)
+ R2_b = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [b], rel)
+ # This transformation is uninvertible because there is no positive a, b satisfying a = -b
+ with raises(NotImplementedError):
+ R2_b.transform(R2_a)
+
+ # inverse transform ambiguous case
+ c, d = symbols('c d')
+ rel = {('first', 'second'): [(c,), (c**2,)]}
+ R2_c = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [c], rel)
+ R2_d = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [d], rel)
+ # The transform method should throw if it finds multiple inverses for a coordinate transformation.
+ with raises(ValueError):
+ R2_d.transform(R2_c)
+
+ # test indirect transformation
+ a, b, c, d, e, f = symbols('a, b, c, d, e, f')
+ rel = {('C1', 'C2'): [(a, b), (2*a, 3*b)],
+ ('C2', 'C3'): [(c, d), (3*c, 2*d)]}
+ C1 = CoordSystem('C1', R2_origin, (a, b), rel)
+ C2 = CoordSystem('C2', R2_origin, (c, d), rel)
+ C3 = CoordSystem('C3', R2_origin, (e, f), rel)
+ a, b = C1.symbols
+ c, d = C2.symbols
+ e, f = C3.symbols
+ assert C2.transform(C1) == Matrix([c/2, d/3])
+ assert C1.transform(C3) == Matrix([6*a, 6*b])
+ assert C3.transform(C1) == Matrix([e/6, f/6])
+ assert C3.transform(C2) == Matrix([e/3, f/2])
+
+ a, b, c, d, e, f = symbols('a, b, c, d, e, f')
+ rel = {('C1', 'C2'): [(a, b), (2*a, 3*b + 1)],
+ ('C3', 'C2'): [(e, f), (-e - 2, 2*f)]}
+ C1 = CoordSystem('C1', R2_origin, (a, b), rel)
+ C2 = CoordSystem('C2', R2_origin, (c, d), rel)
+ C3 = CoordSystem('C3', R2_origin, (e, f), rel)
+ a, b = C1.symbols
+ c, d = C2.symbols
+ e, f = C3.symbols
+ assert C2.transform(C1) == Matrix([c/2, (d - 1)/3])
+ assert C1.transform(C3) == Matrix([-2*a - 2, (3*b + 1)/2])
+ assert C3.transform(C1) == Matrix([-e/2 - 1, (2*f - 1)/3])
+ assert C3.transform(C2) == Matrix([-e - 2, 2*f])
+
+ # old signature uses Lambda
+ a, b, c, d, e, f = symbols('a, b, c, d, e, f')
+ rel = {('C1', 'C2'): Lambda((a, b), (2*a, 3*b + 1)),
+ ('C3', 'C2'): Lambda((e, f), (-e - 2, 2*f))}
+ C1 = CoordSystem('C1', R2_origin, (a, b), rel)
+ C2 = CoordSystem('C2', R2_origin, (c, d), rel)
+ C3 = CoordSystem('C3', R2_origin, (e, f), rel)
+ a, b = C1.symbols
+ c, d = C2.symbols
+ e, f = C3.symbols
+ assert C2.transform(C1) == Matrix([c/2, (d - 1)/3])
+ assert C1.transform(C3) == Matrix([-2*a - 2, (3*b + 1)/2])
+ assert C3.transform(C1) == Matrix([-e/2 - 1, (2*f - 1)/3])
+ assert C3.transform(C2) == Matrix([-e - 2, 2*f])
+
+
def test_R2():
x0, y0, r0, theta0 = symbols('x0, y0, r0, theta0', real=True)
point_r = R2_r.point([x0, y0])
@@ -37,45 +109,6 @@ def test_R2():
R2_r, R2_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_p, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
-def test_inverse_transformations():
- p, q, r, s = symbols('p q r s')
-
- relations_quarter_rotation = {
- ('first', 'second'): (q, -p)
- }
-
- R2_pq = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [p, q], relations_quarter_rotation)
- R2_rs = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [r, s], relations_quarter_rotation)
-
- # The transform method should derive the inverse transformation if not given explicitly
- assert R2_rs.transform(R2_pq) == Matrix([[-R2_rs.symbols[1]], [R2_rs.symbols[0]]])
-
- a, b = symbols('a b', positive=True)
- relations_uninvertible_transformation = {
- ('first', 'second'): (-a,)
- }
-
- R2_a = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [a], relations_uninvertible_transformation)
- R2_b = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [b], relations_uninvertible_transformation)
-
- # The transform method should throw if it cannot invert the coordinate transformation.
- # This transformation is uninvertible because there is no positive a, b satisfying a = -b
- with raises(NotImplementedError):
- R2_b.transform(R2_a)
-
- c, d = symbols('c d')
- relations_ambiguous_inverse = {
- ('first', 'second'): (c**2,)
- }
-
- R2_c = CoordSystem('first', R2_origin, [c], relations_ambiguous_inverse)
- R2_d = CoordSystem('second', R2_origin, [d], relations_ambiguous_inverse)
-
- # The transform method should throw if it finds multiple inverses for a coordinate transformation.
- with raises(ValueError):
- R2_d.transform(R2_c)
-
-
def test_R3():
a, b, c = symbols('a b c', positive=True)
m = Matrix([[a], [b], [c]])
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
TheAlgorithms__Python-1203@79531e5
|
TheAlgorithms/Python
|
Python
| 1,203
|
Added Matrix Exponentiation
|
Fixes #1180 Added the **matrix_exponentiation.py** file in **maths directory**
|
2019-09-25T08:51:44Z
|
Adding Matrix Exponentiation
I was just browsing through the algorithms and data structures but couldn't find Matrix Exponentiation, which is useful for solving linear recurrences in logarithmic time. So, is this something you guys think should be added? If yes then I can work on it and submit a PR. Thanks
|
👍 Go for it!
sure
Please show us side-by-sige benchmarks (using [timeit](https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/timeit.html) or similar) of the two methods running on the same square matrices so we can see the performance.
Initially I thought of using the simple problem of finding the nth element of fibonacci series in O(logn) using Matrix Exponentiation as the base example to use because this is the most common problem in competitive programing sites to introduce matrix exponentiation. So, do you think this problem is enough or do I go for some more general linear recurrence?
@cclauss I used the example of finding the nth element in the Fibonacci series in O(logn) to demonstrate Matrix Exponentiation. For performance evaluation, I compared the simple linear method of finding the nth element with the same using Matrix Exponentiation for random numbers in range of 10**4. Is anything else you would like me to add? otherwise I will submit the PR. Thanks
https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python/issues/1180#issuecomment-531466471 submit the PR
|
[
{
"body": "I was just browsing through the algorithms and data structures but couldn't find Matrix Exponentiation, which is useful for solving linear recurrences in logarithmic time. So, is this something you guys think should be added? If yes then I can work on it and submit a PR. Thanks",
"number": 1180,
"title": "Adding Matrix Exponentiation"
}
] |
01601e6382e92b5a3806fb3a44357460dff97ee7
|
{
"head_commit": "79531e5bc8ffd94cb10d72fc370bef1761bc152c",
"head_commit_message": "Added the matrix_exponentiation.py file in maths directory",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/maths/matrix_exponentiation.py b/maths/matrix_exponentiation.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..17b243baf7ca\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/maths/matrix_exponentiation.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@\n+\"\"\"Matrix Exponentiation\"\"\"\n+\n+import timeit\n+\n+\"\"\"\n+Matrix Exponentiation is a technique to solve linear recurrences in logarithmic time.\n+You read more about it here: \n+http://zobayer.blogspot.com/2010/11/matrix-exponentiation.html\n+https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/notes/matrix-exponentiation-1/\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+\n+class Matrix(object):\n+\tdef __init__(self, arg):\n+\t\tif isinstance(arg,list): #Initialzes a matrix identical to the one provided.\n+\t\t\tself.t = arg\n+\t\t\tself.n = len(arg)\n+\n+\t\telse: #Initializes a square matrix of the given size and set the values to zero.\n+\t\t\tself.n = arg\n+\t\t\tself.t = [[0 for _ in range(self.n)] for _ in range(self.n)]\n+\n+\tdef __mul__(self, b):\n+\t\tc = Matrix(self.n)\n+\n+\t\tfor i in range(self.n):\n+\t\t\tfor j in range(self.n):\n+\t\t\t\tfor k in range(self.n):\n+\t\t\t\t\tc.t[i][j] += self.t[i][k]*b.t[k][j]\n+\n+\t\treturn c\n+\n+def modular_exponentiation(a, b):\n+\tret = Matrix([[1,0], [0,1]])\n+\n+\twhile b > 0:\n+\t\tif b&1:\n+\t\t\tret = ret*a\n+\n+\t\ta = a*a\n+\t\tb >>= 1\n+\n+\treturn ret\n+\n+def fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation(n, f1, f2):\n+\t\n+\t#Trivial Cases\n+\tif n == 1:\n+\t\treturn f1\n+\n+\tif n == 2:\n+\t\treturn f2\n+\n+\ta = Matrix([[1,1], [1,0]])\n+\n+\tm = modular_exponentiation(a, n-2)\n+\n+\treturn f2*m.t[0][0] + f1*m.t[0][1]\n+\n+def simple_fibonacci(n, f1, f2):\n+\n+\t#Trival Cases\n+\tif n == 1:\n+\t\treturn f1\n+\n+\tif n == 2:\n+\t\treturn f2\n+\n+\tfn_1 = f1\n+\tfn_2 = f2\n+\n+\tn -= 2\n+\n+\twhile n > 0:\n+\t\tfn = fn_1 + fn_2\n+\n+\t\tfn_2 = fn_1\n+\t\tfn_1 = fn\n+\n+\t\tn -= 1\n+\n+\treturn fn\n+\n+def matrix_exponentiation_time():\n+\tsetup = '''\n+from random import randint\n+from __main__ import fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation\n+'''\n+\n+\tcode = '''\n+n = randint(1,70000)\n+\n+f1 = 1\n+f2 = 1\n+\n+\n+fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation(n, f1, f2)\n+'''\n+\texec_time = timeit.timeit(setup = setup,\n+\t\t\t\t\t\t stmt = code,\n+\t\t\t\t\t\t number = 100)\n+\n+\tprint (\"With matrix exponentiation the average execution time is \", exec_time/100)\n+\n+\n+def simple_fibonacci_time():\n+\tsetup = '''\n+from random import randint\n+from __main__ import simple_fibonacci\n+'''\n+\n+\tcode = '''\n+n = randint(1,70000)\n+\n+f1 = 1\n+f2 = 1\n+\n+\n+simple_fibonacci(n, f1, f2)\n+'''\n+\texec_time = timeit.timeit(setup = setup,\n+\t\t\t\t\t\t stmt = code,\n+\t\t\t\t\t\t number = 100)\n+\n+\tprint (\"Without matrix exponentiation the average execution time is \", exec_time/100)\n+\n+\t\n+def main():\n+\tmatrix_exponentiation_time()\n+\tsimple_fibonacci_time()\n+\n+\n+if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n+\tmain()\n\\ No newline at end of file\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@\n+\"\"\"Matrix Exponentiation\"\"\"\n+\n+import timeit\n+\n+\"\"\"\n+Matrix Exponentiation is a technique to solve linear recurrences in logarithmic time.\n+You read more about it here: \n+http://zobayer.blogspot.com/2010/11/matrix-exponentiation.html\n+https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/notes/matrix-exponentiation-1/\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+\n+class Matrix(object):\n+\tdef __init__(self, arg):\n+\t\tif isinstance(arg,list): #Initialzes a matrix identical to the one provided.\n+\t\t\tself.t = arg\n+\t\t\tself.n = len(arg)\n+\n+\t\telse: #Initializes a square matrix of the given size and set the values to zero.\n+\t\t\tself.n = arg\n+\t\t\tself.t = [[0 for _ in range(self.n)] for _ in range(self.n)]\n+\n+\tdef __mul__(self, b):\n+\t\tc = Matrix(self.n)\n+\n+\t\tfor i in range(self.n):\n+\t\t\tfor j in range(self.n):\n+\t\t\t\tfor k in range(self.n):\n+\t\t\t\t\tc.t[i][j] += self.t[i][k]*b.t[k][j]\n+\n+\t\treturn c\n+\n+def modular_exponentiation(a, b):\n+\tret = Matrix([[1,0], [0,1]])\n+\n+\twhile b > 0:\n+\t\tif b&1:\n+\t\t\tret = ret*a\n+\n+\t\ta = a*a\n+\t\tb >>= 1\n+\n+\treturn ret\n+\n+def fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation(n, f1, f2):\n+\t\n+\t#Trivial Cases\n+\tif n == 1:\n+\t\treturn f1\n+\n+\tif n == 2:\n+\t\treturn f2\n+\n+\ta = Matrix([[1,1], [1,0]])\n+\n+\tm = modular_exponentiation(a, n-2)\n+\n+\treturn f2*m.t[0][0] + f1*m.t[0][1]\n+\n+def simple_fibonacci(n, f1, f2):\n+\n+\t#Trival Cases\n+\tif n == 1:\n+\t\treturn f1\n+\n+\tif n == 2:\n+\t\treturn f2\n+\n+\tfn_1 = f1\n+\tfn_2 = f2\n+\n+\tn -= 2\n+\n+\twhile n > 0:\n+\t\tfn = fn_1 + fn_2\n+\n+\t\tfn_2 = fn_1\n+\t\tfn_1 = fn\n+\n+\t\tn -= 1\n+\n+\treturn fn\n+\n+def matrix_exponentiation_time():\n+\tsetup = '''\n+from random import randint\n+from __main__ import fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation\n+'''\n+\n+\tcode = '''\n+n = randint(1,70000)\n+\n+f1 = 1\n+f2 = 1\n+\n+\n+fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation(n, f1, f2)\n+'''",
"line": null,
"original_line": 98,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "maths/matrix_exponentiation.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nFor readability, simplify this to:\r\n__code = \"fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation(randint(1,70000), 1, 1)\"__"
}
] |
8e64f021cc0ad35494bb130f77ec7a46d24f65b0
|
diff --git a/maths/matrix_exponentiation.py b/maths/matrix_exponentiation.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..ee9e1757687c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/maths/matrix_exponentiation.py
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+"""Matrix Exponentiation"""
+
+import timeit
+
+"""
+Matrix Exponentiation is a technique to solve linear recurrences in logarithmic time.
+You read more about it here:
+http://zobayer.blogspot.com/2010/11/matrix-exponentiation.html
+https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/notes/matrix-exponentiation-1/
+"""
+
+
+class Matrix(object):
+ def __init__(self, arg):
+ if isinstance(arg, list): # Initialzes a matrix identical to the one provided.
+ self.t = arg
+ self.n = len(arg)
+ else: # Initializes a square matrix of the given size and set the values to zero.
+ self.n = arg
+ self.t = [[0 for _ in range(self.n)] for _ in range(self.n)]
+
+ def __mul__(self, b):
+ matrix = Matrix(self.n)
+ for i in range(self.n):
+ for j in range(self.n):
+ for k in range(self.n):
+ matrix.t[i][j] += self.t[i][k] * b.t[k][j]
+ return matrix
+
+
+def modular_exponentiation(a, b):
+ matrix = Matrix([[1, 0], [0, 1]])
+ while b > 0:
+ if b & 1:
+ matrix *= a
+ a *= a
+ b >>= 1
+ return matrix
+
+
+def fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation(n, f1, f2):
+ # Trivial Cases
+ if n == 1:
+ return f1
+ elif n == 2:
+ return f2
+ matrix = Matrix([[1, 1], [1, 0]])
+ matrix = modular_exponentiation(matrix, n - 2)
+ return f2 * matrix.t[0][0] + f1 * matrix.t[0][1]
+
+
+def simple_fibonacci(n, f1, f2):
+ # Trival Cases
+ if n == 1:
+ return f1
+ elif n == 2:
+ return f2
+
+ fn_1 = f1
+ fn_2 = f2
+ n -= 2
+
+ while n > 0:
+ fn_1, fn_2 = fn_1 + fn_2, fn_1
+ n -= 1
+
+ return fn
+
+
+def matrix_exponentiation_time():
+ setup = """
+from random import randint
+from __main__ import fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation
+"""
+ code = "fibonacci_with_matrix_exponentiation(randint(1,70000), 1, 1)"
+ exec_time = timeit.timeit(setup=setup, stmt=code, number=100)
+ print("With matrix exponentiation the average execution time is ", exec_time / 100)
+ return exec_time
+
+
+def simple_fibonacci_time():
+ setup = """
+from random import randint
+from __main__ import simple_fibonacci
+"""
+ code = "simple_fibonacci(randint(1,70000), 1, 1)"
+ exec_time = timeit.timeit(setup=setup, stmt=code, number=100)
+ print("Without matrix exponentiation the average execution time is ",
+ exec_time / 100)
+ return exec_time
+
+
+def main():
+ matrix_exponentiation_time()
+ simple_fibonacci_time()
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ main()
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21436@02ee02f
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,436
|
Raise warning if relation of frames is looped.
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #21036
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Do bfs to find loop and raise warning.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* physics.vector
* Warning is raised if orientation of frames is looped.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-05-06T06:38:29Z
|
Support orienting adjacent reference frames in arbitrary orders
Suppose you want to establish relative orientation among frames A, B, C, D, and E as such:
```
A ----- B
|
|-------C----D
|
|----E
```
A is the root of the tree, B, D, and E are leaves. You do this now with code that looks like:
```python
B.orient(A)
C.orient(A)
D.orient(C)
E.orient(C)
```
This will establish rotation matrices for each connection in the above graph. But a user may, for whatever reason, do something like (call this the alternative use case):
```python
B.orient(A)
A.orient(C)
C.orient(D)
E.orient(C)
```
This currently does not work because with every call of `X.orient()` all adjacent relationships to `X` will be cleared. That is, calling `.orient()` assumes `self`'s orientation relationships should be overwritten. This is sometimes needed, for example if I do:
```python
B.orient(A, ...)
A.orient(B, ...)
```
Anything that was defined in `B.orient(A, ...)` should be fully replaced with the relationships established with `A.orient(B, ...)` because they may be inconsistent with each other. Or if a user tries to do a loop:
```python
B.orient(A)
C.orient(B)
A.orient(C)
```
The last line should raise an error and say something like "Loops in graph not allowed", but what it does is overwrites all relationships to `A` in the last line, effectively undoing the first line.
The alternative use case should work. There is no reason we shouldn't allow construction of the graph in any sequence. Overwriting the relationships to `self` in calls to `orient()` is unnecessary. I think it was implemented like that because it was easier than checking the graph for consistency in a more thorough way.
I think the relationships between points do not have this issue and you can establish them in any order you like. It would be nice if frames also allowed that.
Here is some code that shows how the method `ReferenceFrame._dcm()` wipes relationships of `self`:
```ipython
IPython 7.21.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: import sympy as sm
In [2]: import sympy.physics.mechanics as me
In [3]: A, B, C = sm.symbols("A, B, C", cls=me.ReferenceFrame)
In [4]: a, b, c = sm.symbols('a, b, c')
In [5]: B.orient(A, 'Axis', (a, A.x))
In [6]: A._dcm_dict
Out[6]:
{B: Matrix([
[1, 0, 0],
[0, cos(a), -sin(a)],
[0, sin(a), cos(a)]])}
In [7]: B._dcm_dict
Out[7]:
{A: Matrix([
[1, 0, 0],
[0, cos(a), sin(a)],
[0, -sin(a), cos(a)]])}
In [8]: C._dcm_dict
Out[8]: {}
In [9]: B.orient(C, 'Axis', (b, C.x))
In [10]: A._dcm_dict
Out[10]: {}
In [11]: B._dcm_dict
Out[11]:
{C: Matrix([
[1, 0, 0],
[0, cos(b), sin(b)],
[0, -sin(b), cos(b)]])}
In [12]: C._dcm_dict
Out[12]:
{B: Matrix([
[1, 0, 0],
[0, cos(b), -sin(b)],
[0, sin(b), cos(b)]])}
In [13]: sm.__version__
Out[13]: '1.7.1'
```
|
@angadhn I've opened an issue for this topic that we discussed last night.
A minimum enhancement here would be to explain in the various `.orient*()` documentation that any call to `X.orient*()` will remove any prior relationships to `X` and that to construct a chain or tree of relative oriented reference frames requires that only un-oriented frames can be added to the ends of the chain/branches.
I'm adding a reference to a previously closed/rejected pull request here. #13824
It is very similar, however, the solution there was to allow loops in a graph.
> Or if a user tries to do a loop:
>
> ```python
> B.orient(A)
> C.orient(B)
> A.orient(C)
> ```
>
> The last line should raise an error and say something like "Loops in graph not allowed", but what it does is overwrites all relationships to `A` in the last line, effectively undoing the first line.
>
> The alternative use case should work. There is no reason we shouldn't allow construction of the graph in any sequence. Overwriting the relationships to `self` in calls to `orient()` is unnecessary. I think it was implemented like that because it was easier than checking the graph for consistency in a more thorough way.
>
> I think the relationships between points do not have this issue and you can establish them in any order you like. It would be nice if frames also allowed that.
#21271 fixed almost all of the problems mentioned here. Only this part is left to be done.
@moorepants I was wondering if instead of giving error in case of loops in frames, shouldn't we raise `warning` as we did in velocity.
> @moorepants I was wondering if instead of giving error in case of loops in frames, shouldn't we raise `warning` as we did in velocity.
@moorepants So it should be a warning or an error?
I guess we should be consistent with what we did with point relationships.
On #21436 I suggested using `topological_sort` for detection of loops. But given the issues described here, is there any reason to not have a helper function to which one passes the orientation information and then the function works out the order -- perhaps through a topological sort -- that orientations should be applied so you don't run into the issues?
I think something like that is needed. We may even need a graph object to manage these things in these modules.
|
[
{
"body": "Suppose you want to establish relative orientation among frames A, B, C, D, and E as such:\r\n\r\n```\r\nA ----- B\r\n|\r\n|-------C----D\r\n |\r\n |----E\r\n```\r\n\r\nA is the root of the tree, B, D, and E are leaves. You do this now with code that looks like:\r\n\r\n```python\r\nB.orient(A)\r\nC.orient(A)\r\nD.orient(C)\r\nE.orient(C)\r\n```\r\n\r\nThis will establish rotation matrices for each connection in the above graph. But a user may, for whatever reason, do something like (call this the alternative use case):\r\n\r\n```python\r\nB.orient(A)\r\nA.orient(C)\r\nC.orient(D)\r\nE.orient(C)\r\n```\r\nThis currently does not work because with every call of `X.orient()` all adjacent relationships to `X` will be cleared. That is, calling `.orient()` assumes `self`'s orientation relationships should be overwritten. This is sometimes needed, for example if I do:\r\n\r\n```python\r\nB.orient(A, ...)\r\nA.orient(B, ...)\r\n```\r\n\r\nAnything that was defined in `B.orient(A, ...)` should be fully replaced with the relationships established with `A.orient(B, ...)` because they may be inconsistent with each other. Or if a user tries to do a loop:\r\n\r\n```python\r\nB.orient(A)\r\nC.orient(B)\r\nA.orient(C)\r\n```\r\n\r\nThe last line should raise an error and say something like \"Loops in graph not allowed\", but what it does is overwrites all relationships to `A` in the last line, effectively undoing the first line.\r\n\r\nThe alternative use case should work. There is no reason we shouldn't allow construction of the graph in any sequence. Overwriting the relationships to `self` in calls to `orient()` is unnecessary. I think it was implemented like that because it was easier than checking the graph for consistency in a more thorough way.\r\n\r\nI think the relationships between points do not have this issue and you can establish them in any order you like. It would be nice if frames also allowed that.\r\n\r\nHere is some code that shows how the method `ReferenceFrame._dcm()` wipes relationships of `self`:\r\n\r\n```ipython\r\nIPython 7.21.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.\r\n\r\nIn [1]: import sympy as sm\r\n\r\nIn [2]: import sympy.physics.mechanics as me\r\n\r\nIn [3]: A, B, C = sm.symbols(\"A, B, C\", cls=me.ReferenceFrame)\r\n\r\nIn [4]: a, b, c = sm.symbols('a, b, c')\r\n\r\nIn [5]: B.orient(A, 'Axis', (a, A.x))\r\n\r\nIn [6]: A._dcm_dict\r\nOut[6]: \r\n{B: Matrix([\r\n [1, 0, 0],\r\n [0, cos(a), -sin(a)],\r\n [0, sin(a), cos(a)]])}\r\n\r\nIn [7]: B._dcm_dict\r\nOut[7]: \r\n{A: Matrix([\r\n [1, 0, 0],\r\n [0, cos(a), sin(a)],\r\n [0, -sin(a), cos(a)]])}\r\n\r\nIn [8]: C._dcm_dict\r\nOut[8]: {}\r\n\r\nIn [9]: B.orient(C, 'Axis', (b, C.x))\r\n\r\nIn [10]: A._dcm_dict\r\nOut[10]: {}\r\n\r\nIn [11]: B._dcm_dict\r\nOut[11]: \r\n{C: Matrix([\r\n [1, 0, 0],\r\n [0, cos(b), sin(b)],\r\n [0, -sin(b), cos(b)]])}\r\n\r\nIn [12]: C._dcm_dict\r\nOut[12]: \r\n{B: Matrix([\r\n [1, 0, 0],\r\n [0, cos(b), -sin(b)],\r\n [0, sin(b), cos(b)]])}\r\n\r\nIn [13]: sm.__version__\r\nOut[13]: '1.7.1'\r\n```",
"number": 21036,
"title": "Support orienting adjacent reference frames in arbitrary orders"
}
] |
45d4e5f7fe1ac8bcdfa425bbac722481d2ec183f
|
{
"head_commit": "02ee02ffd64f86addf136dffb52ef0f023f7d551",
"head_commit_message": "Add `Warns` section to all orient functions' docstring",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py b/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py\nindex aa9e21e4b561..b3c7a1547ea0 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py\n@@ -4,6 +4,8 @@\n from sympy.physics.vector.vector import Vector, _check_vector\n from sympy.utilities.misc import translate\n \n+from warnings import warn\n+\n __all__ = ['CoordinateSym', 'ReferenceFrame']\n \n \n@@ -554,6 +556,25 @@ def _dcm(self, parent, parent_orient):\n self._dcm_dict = self._dlist[0] = {}\n # Reset the _dcm_cache\n self._dcm_cache = {}\n+\n+ else:\n+ #Check for loops and raise warning accordingly.\n+ visited = []\n+ queue = list(frames)\n+ cont = True #Flag to control queue loop.\n+ while queue and cont:\n+ node = queue.pop(0)\n+ if node not in visited:\n+ visited.append(node)\n+ neighbors = node._dcm_dict.keys()\n+ for neighbor in neighbors:\n+ if neighbor == parent:\n+ warn('Loops are defined among the orientation of frames.' + \\\n+ ' This is likely not desired and may cause errors in your calculations.')\n+ cont = False\n+ break\n+ queue.append(neighbor)\n+\n # Add the dcm relationship to _dcm_dict\n self._dcm_dict.update({parent: parent_orient.T})\n parent._dcm_dict.update({self: parent_orient})\n@@ -579,6 +600,12 @@ def orient_axis(self, parent, axis, angle):\n angle : sympifiable\n Angle in radians by which it the frame is to be rotated.\n \n+ Warns\n+ ======\n+\n+ UserWarning\n+ If frames are looped.\n+\n Examples\n ========\n \n@@ -657,6 +684,12 @@ def orient_explicit(self, parent, dcm):\n Direction cosine matrix that specifies the relative rotation\n between the two reference frames.\n \n+ Warns\n+ ======\n+\n+ UserWarning\n+ If frames are looped.\n+\n Examples\n ========\n \n@@ -761,6 +794,12 @@ def orient_body_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):\n Tait-Bryan): zxz, xyx, yzy, zyz, xzx, yxy, xyz, yzx, zxy, xzy, zyx,\n and yxz.\n \n+ Warns\n+ ======\n+\n+ UserWarning\n+ If frames are looped.\n+\n Examples\n ========\n \n@@ -773,6 +812,7 @@ def orient_body_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):\n >>> B = ReferenceFrame('B')\n >>> B1 = ReferenceFrame('B1')\n >>> B2 = ReferenceFrame('B2')\n+ >>> B3 = ReferenceFrame('B3')\n \n For example, a classic Euler Angle rotation can be done by:\n \n@@ -790,8 +830,8 @@ def orient_body_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):\n \n >>> B1.orient_axis(N, N.x, q1)\n >>> B2.orient_axis(B1, B1.y, q2)\n- >>> B.orient_axis(B2, B2.x, q3)\n- >>> B.dcm(N)\n+ >>> B3.orient_axis(B2, B2.x, q3)\n+ >>> B3.dcm(N)\n Matrix([\n [ cos(q2), sin(q1)*sin(q2), -sin(q2)*cos(q1)],\n [sin(q2)*sin(q3), -sin(q1)*sin(q3)*cos(q2) + cos(q1)*cos(q3), sin(q1)*cos(q3) + sin(q3)*cos(q1)*cos(q2)],\n@@ -871,6 +911,12 @@ def orient_space_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):\n ``'131'``, or the integer ``131``. There are 12 unique valid\n rotation orders.\n \n+ Warns\n+ ======\n+\n+ UserWarning\n+ If frames are looped.\n+\n Examples\n ========\n \n@@ -883,6 +929,7 @@ def orient_space_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):\n >>> B = ReferenceFrame('B')\n >>> B1 = ReferenceFrame('B1')\n >>> B2 = ReferenceFrame('B2')\n+ >>> B3 = ReferenceFrame('B3')\n \n >>> B.orient_space_fixed(N, (q1, q2, q3), '312')\n >>> B.dcm(N)\n@@ -895,8 +942,8 @@ def orient_space_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):\n \n >>> B1.orient_axis(N, N.z, q1)\n >>> B2.orient_axis(B1, N.x, q2)\n- >>> B.orient_axis(B2, N.y, q3)\n- >>> B.dcm(N).simplify()\n+ >>> B3.orient_axis(B2, N.y, q3)\n+ >>> B3.dcm(N).simplify()\n Matrix([\n [ sin(q1)*sin(q2)*sin(q3) + cos(q1)*cos(q3), sin(q1)*cos(q2), sin(q1)*sin(q2)*cos(q3) - sin(q3)*cos(q1)],\n [-sin(q1)*cos(q3) + sin(q2)*sin(q3)*cos(q1), cos(q1)*cos(q2), sin(q1)*sin(q3) + sin(q2)*cos(q1)*cos(q3)],\n@@ -992,6 +1039,12 @@ def orient_quaternion(self, parent, numbers):\n The four quaternion scalar numbers as defined above: ``q0``,\n ``q1``, ``q2``, ``q3``.\n \n+ Warns\n+ ======\n+\n+ UserWarning\n+ If frames are looped.\n+\n Examples\n ========\n \n@@ -1098,6 +1151,12 @@ def orient(self, parent, rot_type, amounts, rot_order=''):\n ``'123'`` and integer ``123`` are equivalent, for example. Required\n for ``'Body'`` and ``'Space'``.\n \n+ Warns\n+ ======\n+\n+ UserWarning\n+ If frames are looped.\n+\n \"\"\"\n \n _check_frame(parent)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_frame.py b/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_frame.py\nindex 61fe2030bbe2..819ba0cb54b2 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_frame.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_frame.py\n@@ -6,6 +6,7 @@\n from sympy.physics.vector.frame import _check_frame\n from sympy.physics.vector.vector import VectorTypeError\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n+import warnings\n \n Vector.simp = True\n \n@@ -472,6 +473,22 @@ def test_orient_quaternion():\n B.orient_quaternion(A, (0,0,0,0))\n assert B.dcm(A) == Matrix([[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]])\n \n+def test_looped_frame_warning():\n+ A = ReferenceFrame('A')\n+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')\n+ C = ReferenceFrame('C')\n+\n+ a, b, c = symbols('a b c')\n+ B.orient_axis(A, A.x, a)\n+ C.orient_axis(B, B.x, b)\n+\n+ with warnings.catch_warnings(record = True) as w:\n+ warnings.simplefilter(\"always\")\n+ A.orient_axis(C, C.x, c)\n+ assert issubclass(w[-1].category, UserWarning)\n+ assert 'Loops are defined among the orientation of frames. ' + \\\n+ 'This is likely not desired and may cause errors in your calculations.' in str(w[-1].message)\n+\n def test_frame_dict():\n A = ReferenceFrame('A')\n B = ReferenceFrame('B')\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -579,6 +600,12 @@ def orient_axis(self, parent, axis, angle):\n angle : sympifiable\n Angle in radians by which it the frame is to be rotated.\n \n+ Warns\n+ ======\n+\n+ UserWarning\n+ If frames are looped.",
"line": null,
"original_line": 607,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/vector/frame.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIf the orientation creates a kinematic loop."
}
] |
a2b81fb9e4ab650bf8d0259787adaeaff5ee1279
|
diff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py b/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py
index aa9e21e4b561..e181a7d36701 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py
@@ -4,6 +4,8 @@
from sympy.physics.vector.vector import Vector, _check_vector
from sympy.utilities.misc import translate
+from warnings import warn
+
__all__ = ['CoordinateSym', 'ReferenceFrame']
@@ -554,6 +556,25 @@ def _dcm(self, parent, parent_orient):
self._dcm_dict = self._dlist[0] = {}
# Reset the _dcm_cache
self._dcm_cache = {}
+
+ else:
+ #Check for loops and raise warning accordingly.
+ visited = []
+ queue = list(frames)
+ cont = True #Flag to control queue loop.
+ while queue and cont:
+ node = queue.pop(0)
+ if node not in visited:
+ visited.append(node)
+ neighbors = node._dcm_dict.keys()
+ for neighbor in neighbors:
+ if neighbor == parent:
+ warn('Loops are defined among the orientation of frames.' + \
+ ' This is likely not desired and may cause errors in your calculations.')
+ cont = False
+ break
+ queue.append(neighbor)
+
# Add the dcm relationship to _dcm_dict
self._dcm_dict.update({parent: parent_orient.T})
parent._dcm_dict.update({self: parent_orient})
@@ -579,6 +600,12 @@ def orient_axis(self, parent, axis, angle):
angle : sympifiable
Angle in radians by which it the frame is to be rotated.
+ Warns
+ ======
+
+ UserWarning
+ If the orientation creates a kinematic loop.
+
Examples
========
@@ -657,6 +684,12 @@ def orient_explicit(self, parent, dcm):
Direction cosine matrix that specifies the relative rotation
between the two reference frames.
+ Warns
+ ======
+
+ UserWarning
+ If the orientation creates a kinematic loop.
+
Examples
========
@@ -761,6 +794,12 @@ def orient_body_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):
Tait-Bryan): zxz, xyx, yzy, zyz, xzx, yxy, xyz, yzx, zxy, xzy, zyx,
and yxz.
+ Warns
+ ======
+
+ UserWarning
+ If the orientation creates a kinematic loop.
+
Examples
========
@@ -773,6 +812,7 @@ def orient_body_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):
>>> B = ReferenceFrame('B')
>>> B1 = ReferenceFrame('B1')
>>> B2 = ReferenceFrame('B2')
+ >>> B3 = ReferenceFrame('B3')
For example, a classic Euler Angle rotation can be done by:
@@ -790,8 +830,8 @@ def orient_body_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):
>>> B1.orient_axis(N, N.x, q1)
>>> B2.orient_axis(B1, B1.y, q2)
- >>> B.orient_axis(B2, B2.x, q3)
- >>> B.dcm(N)
+ >>> B3.orient_axis(B2, B2.x, q3)
+ >>> B3.dcm(N)
Matrix([
[ cos(q2), sin(q1)*sin(q2), -sin(q2)*cos(q1)],
[sin(q2)*sin(q3), -sin(q1)*sin(q3)*cos(q2) + cos(q1)*cos(q3), sin(q1)*cos(q3) + sin(q3)*cos(q1)*cos(q2)],
@@ -871,6 +911,12 @@ def orient_space_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):
``'131'``, or the integer ``131``. There are 12 unique valid
rotation orders.
+ Warns
+ ======
+
+ UserWarning
+ If the orientation creates a kinematic loop.
+
Examples
========
@@ -883,6 +929,7 @@ def orient_space_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):
>>> B = ReferenceFrame('B')
>>> B1 = ReferenceFrame('B1')
>>> B2 = ReferenceFrame('B2')
+ >>> B3 = ReferenceFrame('B3')
>>> B.orient_space_fixed(N, (q1, q2, q3), '312')
>>> B.dcm(N)
@@ -895,8 +942,8 @@ def orient_space_fixed(self, parent, angles, rotation_order):
>>> B1.orient_axis(N, N.z, q1)
>>> B2.orient_axis(B1, N.x, q2)
- >>> B.orient_axis(B2, N.y, q3)
- >>> B.dcm(N).simplify()
+ >>> B3.orient_axis(B2, N.y, q3)
+ >>> B3.dcm(N).simplify()
Matrix([
[ sin(q1)*sin(q2)*sin(q3) + cos(q1)*cos(q3), sin(q1)*cos(q2), sin(q1)*sin(q2)*cos(q3) - sin(q3)*cos(q1)],
[-sin(q1)*cos(q3) + sin(q2)*sin(q3)*cos(q1), cos(q1)*cos(q2), sin(q1)*sin(q3) + sin(q2)*cos(q1)*cos(q3)],
@@ -992,6 +1039,12 @@ def orient_quaternion(self, parent, numbers):
The four quaternion scalar numbers as defined above: ``q0``,
``q1``, ``q2``, ``q3``.
+ Warns
+ ======
+
+ UserWarning
+ If the orientation creates a kinematic loop.
+
Examples
========
@@ -1098,6 +1151,12 @@ def orient(self, parent, rot_type, amounts, rot_order=''):
``'123'`` and integer ``123`` are equivalent, for example. Required
for ``'Body'`` and ``'Space'``.
+ Warns
+ ======
+
+ UserWarning
+ If the orientation creates a kinematic loop.
+
"""
_check_frame(parent)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_frame.py b/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_frame.py
index 61fe2030bbe2..819ba0cb54b2 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_frame.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_frame.py
@@ -6,6 +6,7 @@
from sympy.physics.vector.frame import _check_frame
from sympy.physics.vector.vector import VectorTypeError
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
+import warnings
Vector.simp = True
@@ -472,6 +473,22 @@ def test_orient_quaternion():
B.orient_quaternion(A, (0,0,0,0))
assert B.dcm(A) == Matrix([[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]])
+def test_looped_frame_warning():
+ A = ReferenceFrame('A')
+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')
+ C = ReferenceFrame('C')
+
+ a, b, c = symbols('a b c')
+ B.orient_axis(A, A.x, a)
+ C.orient_axis(B, B.x, b)
+
+ with warnings.catch_warnings(record = True) as w:
+ warnings.simplefilter("always")
+ A.orient_axis(C, C.x, c)
+ assert issubclass(w[-1].category, UserWarning)
+ assert 'Loops are defined among the orientation of frames. ' + \
+ 'This is likely not desired and may cause errors in your calculations.' in str(w[-1].message)
+
def test_frame_dict():
A = ReferenceFrame('A')
B = ReferenceFrame('B')
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Code Refactoring / Architectural Improvement"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21452@7f98847
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,452
|
Modified Heaviside(t) to have a standard value at Heaviside(0)=1/2
|
#### References to other Issues or PRs
related to https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/20411
fixes #21392
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Modified Heaviside(t) to have a standard value at Heaviside(0)=1/2 with all tests adapted.
The test_issue_15923() are removed, they are not necessary anymore.
See discussion in https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/20411 for more details.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* functions
* Heaviside(0) now returns 1/2 instead of being undefined.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-05-10T14:31:10Z
|
get_points() generates error when used with Heaviside() function
The following code used to work with older versions of sympy (e.g. 1.3) but generates an error with 1.7.1
```
import sympy as sym
t = sym.symbols('t')
p = sym.plot(sym.Heaviside(t), (t, -5, 5), show=False)
points = p[0].get_points()
```
results in
`AttributeError: 'ImmutableDenseNDimArray' object has no attribute 'as_coefficient'`
|
[
{
"body": "The following code used to work with older versions of sympy (e.g. 1.3) but generates an error with 1.7.1\r\n\r\n```\r\nimport sympy as sym\r\n\r\nt = sym.symbols('t')\r\np = sym.plot(sym.Heaviside(t), (t, -5, 5), show=False)\r\npoints = p[0].get_points()\r\n```\r\n\r\nresults in\r\n\r\n`AttributeError: 'ImmutableDenseNDimArray' object has no attribute 'as_coefficient'`",
"number": 21392,
"title": "get_points() generates error when used with Heaviside() function"
}
] |
92e7cb0b27bb810d67013a2cdbbd1f8e7f7aba45
|
{
"head_commit": "7f9884733f767dc032d7f95e310f224803f5f02b",
"head_commit_message": "Post-review changes:\n* Heaviside(0,nan) now evaluates and returns nan\n* Tests tidied up\n* Documentation improved",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py\nindex f4cdfc9f9791..3c3e8d21b3cf 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py\n@@ -442,7 +442,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Piecewise(self, arg, **kwargs):\n def _eval_rewrite_as_Heaviside(self, arg, **kwargs):\n from sympy.functions.special.delta_functions import Heaviside\n if arg.is_extended_real:\n- return Heaviside(arg, H0=S(1)/2) * 2 - 1\n+ return Heaviside(arg) * 2 - 1\n \n def _eval_rewrite_as_Abs(self, arg, **kwargs):\n return Piecewise((0, Eq(arg, 0)), (arg / Abs(arg), True))\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_trigonometric.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_trigonometric.py\nindex 65b068349b09..61b63a319899 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_trigonometric.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_trigonometric.py\n@@ -1049,7 +1049,7 @@ def test_atan2():\n assert atan2(0, u) == pi\n \n assert atan2(y, oo) == 0\n- assert atan2(y, -oo)== 2*pi*Heaviside(re(y)) - pi\n+ assert atan2(y, -oo)== 2*pi*Heaviside(re(y), S.Half) - pi\n \n assert atan2(y, x).rewrite(log) == -I*log((x + I*y)/sqrt(x**2 + y**2))\n assert atan2(0, 0) is S.NaN\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py\nindex e5315e181d51..480f76fe525f 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py\n@@ -404,8 +404,11 @@ def _sage_(self):\n \n \n class Heaviside(Function):\n- r\"\"\"\n- Heaviside Piecewise function.\n+ r\"\"\"Heaviside step function.\n+\n+ .. versionchanged:: 1.9\n+ ``Heaviside(0)`` now returns 1/2; previously, the default was that\n+ the value at 0 was undefined.\n \n Explanation\n ===========\n@@ -413,35 +416,34 @@ class Heaviside(Function):\n Heaviside function has the following properties:\n \n 1) $\\frac{d}{d x} \\theta(x) = \\delta(x)$\n- 2) $\\theta(x) = \\begin{cases} 0 & \\text{for}\\: x < 0 \\\\ \\text{undefined} &\n+ 2) $\\theta(x) = \\begin{cases} 0 & \\text{for}\\: x < 0 \\\\ \\frac{1}{2} &\n \\text{for}\\: x = 0 \\\\1 & \\text{for}\\: x > 0 \\end{cases}$\n 3) $\\frac{d}{d x} \\max(x, 0) = \\theta(x)$\n \n Heaviside(x) is printed as $\\theta(x)$ with the SymPy LaTeX printer.\n \n- Regarding to the value at 0, Mathematica defines $\\theta(0)=1$, but Maple\n- uses $\\theta(0) = \\text{undefined}$. Different application areas may have\n- specific conventions. For example, in control theory, it is common practice\n- to assume $\\theta(0) = 0$ to match the Laplace transform of a DiracDelta\n- distribution.\n+ The value at 0 is set differently in different fields. SymPy uses 1/2,\n+ which is a convention from electronics and signal processing, and is\n+ consistent with solving improper integrals by Fourier transform and\n+ convolution.\n \n- To specify the value of Heaviside at ``x=0``, a second argument can be\n- given. Omit this 2nd argument or pass ``None`` to recover the default\n- behavior.\n+ To specify a different value of Heaviside at ``x=0``, a second argument\n+ can be given. Using ``Heaviside(x, nan)`` gives an expression that will\n+ evaluate to nan for x=0.\n \n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Heaviside, S\n+ >>> from sympy import Heaviside, nan\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> Heaviside(9)\n 1\n >>> Heaviside(-9)\n 0\n >>> Heaviside(0)\n- Heaviside(0)\n- >>> Heaviside(0, S.Half)\n 1/2\n+ >>> Heaviside(0, nan)\n+ nan\n >>> (Heaviside(x) + 1).replace(Heaviside(x), Heaviside(x, 1))\n Heaviside(x, 1) + 1\n \n@@ -487,21 +489,17 @@ def fdiff(self, argindex=1):\n \n \"\"\"\n if argindex == 1:\n- # property number 1\n return DiracDelta(self.args[0])\n else:\n raise ArgumentIndexError(self, argindex)\n \n- def __new__(cls, arg, H0=None, **options):\n+ def __new__(cls, arg, H0=S.Half, **options):\n if isinstance(H0, Heaviside) and len(H0.args) == 1:\n- H0 = None\n-\n- if H0 is None:\n- return super(cls, cls).__new__(cls, arg, **options)\n+ H0 = S.Half\n return super(cls, cls).__new__(cls, arg, H0, **options)\n \n @classmethod\n- def eval(cls, arg, H0=None):\n+ def eval(cls, arg, H0=S.Half):\n \"\"\"\n Returns a simplified form or a value of Heaviside depending on the\n argument passed by the Heaviside object.\n@@ -528,7 +526,7 @@ class is about to be instantiated and it returns either some simplified\n 1\n \n >>> Heaviside(0)\n- Heaviside(0)\n+ 1/2\n \n >>> Heaviside(0, 1)\n 1\n@@ -539,7 +537,7 @@ class is about to be instantiated and it returns either some simplified\n >>> Heaviside(S.NaN)\n nan\n \n- >>> Heaviside(x).eval(100)\n+ >>> Heaviside(x).eval(42)\n 1\n \n >>> Heaviside(x - 100).subs(x, 5)\n@@ -551,8 +549,9 @@ class is about to be instantiated and it returns either some simplified\n Parameters\n ==========\n \n- arg : argument passed by HeaviSide object\n- HO : boolean flag for HeaviSide Object is set to True\n+ arg : argument passed by Heaviside object\n+\n+ H0 : value of Heaviside(0)\n \n \"\"\"\n H0 = sympify(H0)\n@@ -575,58 +574,61 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Piecewise(self, arg, H0=None, **kwargs):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Piecewise, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Piecewise, Symbol, nan\n >>> x = Symbol('x')\n \n >>> Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise)\n- Piecewise((0, x < 0), (Heaviside(0), Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0))\n+ Piecewise((0, x < 0), (1/2, Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0))\n+\n+ >>> Heaviside(x,nan).rewrite(Piecewise)\n+ Piecewise((0, x < 0), (nan, Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0))\n \n >>> Heaviside(x - 5).rewrite(Piecewise)\n- Piecewise((0, x - 5 < 0), (Heaviside(0), Eq(x - 5, 0)), (1, x - 5 > 0))\n+ Piecewise((0, x - 5 < 0), (1/2, Eq(x - 5, 0)), (1, x - 5 > 0))\n \n >>> Heaviside(x**2 - 1).rewrite(Piecewise)\n- Piecewise((0, x**2 - 1 < 0), (Heaviside(0), Eq(x**2 - 1, 0)), (1, x**2 - 1 > 0))\n+ Piecewise((0, x**2 - 1 < 0), (1/2, Eq(x**2 - 1, 0)), (1, x**2 - 1 > 0))\n \n \"\"\"\n- if H0 is None:\n- return Piecewise((0, arg < 0), (Heaviside(0), Eq(arg, 0)), (1, arg > 0))\n if H0 == 0:\n return Piecewise((0, arg <= 0), (1, arg > 0))\n if H0 == 1:\n return Piecewise((0, arg < 0), (1, arg >= 0))\n return Piecewise((0, arg < 0), (H0, Eq(arg, 0)), (1, arg > 0))\n \n- def _eval_rewrite_as_sign(self, arg, H0=None, **kwargs):\n+ def _eval_rewrite_as_sign(self, arg, H0=S.Half, **kwargs):\n \"\"\"\n Represents the Heaviside function in the form of sign function.\n \n Explanation\n ===========\n \n- The value of the second argument of Heaviside must specify Heaviside(0)\n- = 1/2 for rewritting as sign to be strictly equivalent. For easier\n- usage, we also allow this rewriting when Heaviside(0) is undefined.\n+ The value of Heaviside(0) must be 1/2 for rewritting as sign to be\n+ strictly equivalent. For easier usage, we also allow this rewriting\n+ when Heaviside(0) is undefined.\n \n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Symbol, sign, S\n+ >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Symbol, sign, nan\n >>> x = Symbol('x', real=True)\n+ >>> y = Symbol('y')\n \n- >>> Heaviside(x, H0=S.Half).rewrite(sign)\n+ >>> Heaviside(x).rewrite(sign)\n sign(x)/2 + 1/2\n \n >>> Heaviside(x, 0).rewrite(sign)\n Piecewise((sign(x)/2 + 1/2, Ne(x, 0)), (0, True))\n \n- >>> Heaviside(x - 2, H0=S.Half).rewrite(sign)\n+ >>> Heaviside(x, nan).rewrite(sign)\n+ Piecewise((sign(x)/2 + 1/2, Ne(x, 0)), (nan, True))\n+\n+ >>> Heaviside(x - 2).rewrite(sign)\n sign(x - 2)/2 + 1/2\n \n- >>> Heaviside(x**2 - 2*x + 1, H0=S.Half).rewrite(sign)\n+ >>> Heaviside(x**2 - 2*x + 1).rewrite(sign)\n sign(x**2 - 2*x + 1)/2 + 1/2\n \n- >>> y = Symbol('y')\n-\n >>> Heaviside(y).rewrite(sign)\n Heaviside(y)\n \n@@ -648,7 +650,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_sign(self, arg, H0=None, **kwargs):\n (pw1, True))\n return pw2\n \n- def _eval_rewrite_as_SingularityFunction(self, args, **kwargs):\n+ def _eval_rewrite_as_SingularityFunction(self, args, H0=S.Half, **kwargs):\n \"\"\"\n Returns the Heaviside expression written in the form of Singularity\n Functions.\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_delta_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_delta_functions.py\nindex 72ba93e2c96e..69722eac1bc8 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_delta_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_delta_functions.py\n@@ -6,6 +6,8 @@\n \n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, warns_deprecated_sympy\n \n+from sympy.core.expr import unchanged\n+\n from sympy.core.function import ArgumentIndexError\n \n \n@@ -80,19 +82,13 @@ def test_DiracDelta():\n \n \n def test_heaviside():\n- assert Heaviside(0).func == Heaviside\n assert Heaviside(-5) == 0\n assert Heaviside(1) == 1\n- assert Heaviside(nan) is nan\n+ assert Heaviside(0) == S.Half\n \n assert Heaviside(0, x) == x\n- assert Heaviside(0, nan) is nan\n- assert Heaviside(x, None) == Heaviside(x)\n- assert Heaviside(0, None) == Heaviside(0)\n-\n- # we do not want None and Heaviside(0) in the args:\n- assert Heaviside(x, H0=None).args == (x,)\n- assert Heaviside(x, H0=Heaviside(0)).args == (x,)\n+ assert unchanged(Heaviside,x, nan)\n+ assert Heaviside(0, nan) == nan\n \n assert adjoint(Heaviside(x)) == Heaviside(x)\n assert adjoint(Heaviside(x - y)) == Heaviside(x - y)\n@@ -122,6 +118,8 @@ def test_rewrite():\n Piecewise((0, x <= 0), (1, x > 0)))\n assert Heaviside(x, 1).rewrite(Piecewise) == (\n Piecewise((0, x < 0), (1, x >= 0)))\n+ assert Heaviside(x, nan).rewrite(Piecewise) == (\n+ Piecewise((0, x < 0), (nan, Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0)))\n \n assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(sign) == \\\n Heaviside(x, H0=Heaviside(0)).rewrite(sign) == \\\n@@ -153,13 +151,4 @@ def test_rewrite():\n assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == SingularityFunction(x, 0, 0)\n assert 5*x*y*Heaviside(y + 1).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == 5*x*y*SingularityFunction(y, -1, 0)\n assert ((x - 3)**3*Heaviside(x - 3)).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == (x - 3)**3*SingularityFunction(x, 3, 0)\n- assert Heaviside(0).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == SingularityFunction(0, 0, 0)\n-\n-def test_issue_15923():\n- x = Symbol('x', real=True)\n- assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise, H0=0) == (\n- Piecewise((0, x <= 0), (1, True)))\n- assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise, H0=1) == (\n- Piecewise((0, x < 0), (1, True)))\n- assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise, H0=S.Half) == (\n- Piecewise((0, x < 0), (S.Half, Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0)))\n+ assert Heaviside(0).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == S.Half\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/transforms.py b/sympy/integrals/transforms.py\nindex 739450dd9391..4f5218052bab 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/transforms.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/transforms.py\n@@ -1234,17 +1234,17 @@ def pw_simp(*args):\n \n u = Dummy('u')\n \n- def simp_heaviside(arg):\n+ def simp_heaviside(arg, H0=S.Half):\n a = arg.subs(exp(-t), u)\n if a.has(t):\n- return Heaviside(arg)\n+ return Heaviside(arg,H0)\n rel = _solve_inequality(a > 0, u)\n if rel.lts == u:\n k = log(rel.gts)\n- return Heaviside(t + k)\n+ return Heaviside(t + k,H0)\n else:\n k = log(rel.lts)\n- return Heaviside(-(t + k))\n+ return Heaviside(-(t + k),H0)\n f = f.replace(Heaviside, simp_heaviside)\n \n def simp_exp(arg):\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py\nindex 42fae775d346..eaede3c00c44 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py\n@@ -7224,8 +7224,8 @@ def test_pretty_misc_functions():\n assert upretty(fresnelc(x)) == 'C(x)'\n assert pretty(fresnels(x)) == 'S(x)'\n assert upretty(fresnels(x)) == 'S(x)'\n- assert pretty(Heaviside(x)) == 'Heaviside(x)'\n- assert upretty(Heaviside(x)) == 'θ(x)'\n+ assert pretty(Heaviside(x)) == 'Heaviside(x, 1/2)'\n+ assert upretty(Heaviside(x)) == 'θ(x, 1/2)'\n assert pretty(Heaviside(x, y)) == 'Heaviside(x, y)'\n assert upretty(Heaviside(x, y)) == 'θ(x, y)'\n assert pretty(dirichlet_eta(x)) == 'dirichlet_eta(x)'\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_mathml.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_mathml.py\nindex ffd59826093d..a2404718a911 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_mathml.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_mathml.py\n@@ -1530,7 +1530,7 @@ def test_print_different_functions():\n assert mpp.doprint(primeomega(x)) == '<mrow><mi>Ω</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi></mfenced></mrow>'\n assert mpp.doprint(fresnels(x)) == '<mrow><mi>S</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi></mfenced></mrow>'\n assert mpp.doprint(fresnelc(x)) == '<mrow><mi>C</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi></mfenced></mrow>'\n- assert mpp.doprint(Heaviside(x)) == '<mrow><mi>Θ</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi></mfenced></mrow>'\n+ assert mpp.doprint(Heaviside(x)) == '<mrow><mi>Θ</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi><mfrac><mn>1</mn><mn>2</mn></mfrac></mfenced></mrow>'\n \n \n def test_mathml_builtins():\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_octave.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_octave.py\nindex bdd0dca02e12..b39116d4606d 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_octave.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_octave.py\n@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ def test_Function_change_name():\n assert mcode(RisingFactorial(x, y)) == \"pochhammer(x, y)\"\n assert mcode(DiracDelta(x)) == \"dirac(x)\"\n assert mcode(DiracDelta(x, 3)) == \"dirac(3, x)\"\n- assert mcode(Heaviside(x)) == \"heaviside(x)\"\n+ assert mcode(Heaviside(x)) == \"heaviside(x, 1/2)\"\n assert mcode(Heaviside(x, y)) == \"heaviside(x, y)\"\n assert mcode(binomial(x, y)) == \"bincoeff(x, y)\"\n assert mcode(Mod(x, y)) == \"mod(x, y)\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -7224,8 +7224,8 @@ def test_pretty_misc_functions():\n assert upretty(fresnelc(x)) == 'C(x)'\n assert pretty(fresnels(x)) == 'S(x)'\n assert upretty(fresnels(x)) == 'S(x)'\n- assert pretty(Heaviside(x)) == 'Heaviside(x)'\n- assert upretty(Heaviside(x)) == 'θ(x)'\n+ assert pretty(Heaviside(x)) == 'Heaviside(x, 1/2)'\n+ assert upretty(Heaviside(x)) == 'θ(x, 1/2)'",
"line": null,
"original_line": 7228,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI wonder if the extra arg should be omitted in the printing for the default value of `1/2`.\n\n@author:\nThat would be a very good idea, but I do not know where to do it. Would I need to write a `def _print_Function` in the `class Heaviside`?\n\n@user1:\nIt's the other way round. You add a `_print_Heaviside` method to the pretty printer:\r\nhttps://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/92e7cb0b27bb810d67013a2cdbbd1f8e7f7aba45/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py#L1574-L1576\n\n@author:\nOK, I did it ;) Push comes as soon as I have run all checks I think I need to run locally.\n\n@author:\nI wondered whether we should also change the normal printer, but I think we should just leave it as it is, such that people using this will see immediately that `Heaviside` has changed. Is that OK?\n\n@user1:\nWhat do you mean by the normal printer? SymPy has so many printers...\n\n@author:\nThe printer that activates for in-line documentation and is tested through `bin/doctest`. I don't actually know which one that is ;)\r\n\r\nP.S. It is the same that does `print(Heaviside(x))`\r\n\r\nSince all went through now, I suggest to take what we have now, proceed with DiracDelta, and later return to Heaviside if necessary."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -404,44 +404,46 @@ def _sage_(self):\n \n \n class Heaviside(Function):\n- r\"\"\"\n- Heaviside Piecewise function.\n+ r\"\"\"Heaviside step function.\n+\n+ .. versionchanged:: 1.9\n+ ``Heaviside(0)`` now returns 1/2; previously, the default was that\n+ the value at 0 was undefined.",
"line": null,
"original_line": 411,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWe don't have anything about this in the style guide but I wouldn't put the versionchanged at the top of the docstring. Probably it should go at the bottom.\n\n@author:\nWill be moved ;)"
}
] |
8247a096aca4d9f8cf9def4307a0f90bd0a8cc67
|
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
index 1c3b4e50c4ef..66a96335ebc5 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
@@ -442,7 +442,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Piecewise(self, arg, **kwargs):
def _eval_rewrite_as_Heaviside(self, arg, **kwargs):
from sympy.functions.special.delta_functions import Heaviside
if arg.is_extended_real:
- return Heaviside(arg, H0=S(1)/2) * 2 - 1
+ return Heaviside(arg) * 2 - 1
def _eval_rewrite_as_Abs(self, arg, **kwargs):
return Piecewise((0, Eq(arg, 0)), (arg / Abs(arg), True))
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_trigonometric.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_trigonometric.py
index 65b068349b09..61b63a319899 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_trigonometric.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_trigonometric.py
@@ -1049,7 +1049,7 @@ def test_atan2():
assert atan2(0, u) == pi
assert atan2(y, oo) == 0
- assert atan2(y, -oo)== 2*pi*Heaviside(re(y)) - pi
+ assert atan2(y, -oo)== 2*pi*Heaviside(re(y), S.Half) - pi
assert atan2(y, x).rewrite(log) == -I*log((x + I*y)/sqrt(x**2 + y**2))
assert atan2(0, 0) is S.NaN
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py
index e5315e181d51..e3ffc481f28c 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py
@@ -405,43 +405,44 @@ def _sage_(self):
class Heaviside(Function):
r"""
- Heaviside Piecewise function.
+ Heaviside step function.
Explanation
===========
- Heaviside function has the following properties:
+ The Heaviside step function has the following properties:
1) $\frac{d}{d x} \theta(x) = \delta(x)$
- 2) $\theta(x) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{for}\: x < 0 \\ \text{undefined} &
+ 2) $\theta(x) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{for}\: x < 0 \\ \frac{1}{2} &
\text{for}\: x = 0 \\1 & \text{for}\: x > 0 \end{cases}$
3) $\frac{d}{d x} \max(x, 0) = \theta(x)$
Heaviside(x) is printed as $\theta(x)$ with the SymPy LaTeX printer.
- Regarding to the value at 0, Mathematica defines $\theta(0)=1$, but Maple
- uses $\theta(0) = \text{undefined}$. Different application areas may have
- specific conventions. For example, in control theory, it is common practice
- to assume $\theta(0) = 0$ to match the Laplace transform of a DiracDelta
- distribution.
+ The value at 0 is set differently in different fields. SymPy uses 1/2,
+ which is a convention from electronics and signal processing, and is
+ consistent with solving improper integrals by Fourier transform and
+ convolution.
- To specify the value of Heaviside at ``x=0``, a second argument can be
- given. Omit this 2nd argument or pass ``None`` to recover the default
- behavior.
+ To specify a different value of Heaviside at ``x=0``, a second argument
+ can be given. Using ``Heaviside(x, nan)`` gives an expression that will
+ evaluate to nan for x=0.
+
+ .. versionchanged:: 1.9 ``Heaviside(0)`` now returns 1/2 (before: undefined)
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Heaviside, S
+ >>> from sympy import Heaviside, nan
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> Heaviside(9)
1
>>> Heaviside(-9)
0
>>> Heaviside(0)
- Heaviside(0)
- >>> Heaviside(0, S.Half)
1/2
+ >>> Heaviside(0, nan)
+ nan
>>> (Heaviside(x) + 1).replace(Heaviside(x), Heaviside(x, 1))
Heaviside(x, 1) + 1
@@ -487,21 +488,17 @@ def fdiff(self, argindex=1):
"""
if argindex == 1:
- # property number 1
return DiracDelta(self.args[0])
else:
raise ArgumentIndexError(self, argindex)
- def __new__(cls, arg, H0=None, **options):
+ def __new__(cls, arg, H0=S.Half, **options):
if isinstance(H0, Heaviside) and len(H0.args) == 1:
- H0 = None
-
- if H0 is None:
- return super(cls, cls).__new__(cls, arg, **options)
+ H0 = S.Half
return super(cls, cls).__new__(cls, arg, H0, **options)
@classmethod
- def eval(cls, arg, H0=None):
+ def eval(cls, arg, H0=S.Half):
"""
Returns a simplified form or a value of Heaviside depending on the
argument passed by the Heaviside object.
@@ -522,13 +519,13 @@ class is about to be instantiated and it returns either some simplified
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> Heaviside(x)
- Heaviside(x)
+ Heaviside(x, 1/2)
>>> Heaviside(19)
1
>>> Heaviside(0)
- Heaviside(0)
+ 1/2
>>> Heaviside(0, 1)
1
@@ -539,7 +536,7 @@ class is about to be instantiated and it returns either some simplified
>>> Heaviside(S.NaN)
nan
- >>> Heaviside(x).eval(100)
+ >>> Heaviside(x).eval(42)
1
>>> Heaviside(x - 100).subs(x, 5)
@@ -551,8 +548,9 @@ class is about to be instantiated and it returns either some simplified
Parameters
==========
- arg : argument passed by HeaviSide object
- HO : boolean flag for HeaviSide Object is set to True
+ arg : argument passed by Heaviside object
+
+ H0 : value of Heaviside(0)
"""
H0 = sympify(H0)
@@ -575,63 +573,66 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Piecewise(self, arg, H0=None, **kwargs):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Piecewise, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Piecewise, Symbol, nan
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise)
- Piecewise((0, x < 0), (Heaviside(0), Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0))
+ Piecewise((0, x < 0), (1/2, Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0))
+
+ >>> Heaviside(x,nan).rewrite(Piecewise)
+ Piecewise((0, x < 0), (nan, Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0))
>>> Heaviside(x - 5).rewrite(Piecewise)
- Piecewise((0, x - 5 < 0), (Heaviside(0), Eq(x - 5, 0)), (1, x - 5 > 0))
+ Piecewise((0, x - 5 < 0), (1/2, Eq(x - 5, 0)), (1, x - 5 > 0))
>>> Heaviside(x**2 - 1).rewrite(Piecewise)
- Piecewise((0, x**2 - 1 < 0), (Heaviside(0), Eq(x**2 - 1, 0)), (1, x**2 - 1 > 0))
+ Piecewise((0, x**2 - 1 < 0), (1/2, Eq(x**2 - 1, 0)), (1, x**2 - 1 > 0))
"""
- if H0 is None:
- return Piecewise((0, arg < 0), (Heaviside(0), Eq(arg, 0)), (1, arg > 0))
if H0 == 0:
return Piecewise((0, arg <= 0), (1, arg > 0))
if H0 == 1:
return Piecewise((0, arg < 0), (1, arg >= 0))
return Piecewise((0, arg < 0), (H0, Eq(arg, 0)), (1, arg > 0))
- def _eval_rewrite_as_sign(self, arg, H0=None, **kwargs):
+ def _eval_rewrite_as_sign(self, arg, H0=S.Half, **kwargs):
"""
Represents the Heaviside function in the form of sign function.
Explanation
===========
- The value of the second argument of Heaviside must specify Heaviside(0)
- = 1/2 for rewritting as sign to be strictly equivalent. For easier
- usage, we also allow this rewriting when Heaviside(0) is undefined.
+ The value of Heaviside(0) must be 1/2 for rewritting as sign to be
+ strictly equivalent. For easier usage, we also allow this rewriting
+ when Heaviside(0) is undefined.
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Symbol, sign, S
+ >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Symbol, sign, nan
>>> x = Symbol('x', real=True)
+ >>> y = Symbol('y')
- >>> Heaviside(x, H0=S.Half).rewrite(sign)
+ >>> Heaviside(x).rewrite(sign)
sign(x)/2 + 1/2
>>> Heaviside(x, 0).rewrite(sign)
Piecewise((sign(x)/2 + 1/2, Ne(x, 0)), (0, True))
- >>> Heaviside(x - 2, H0=S.Half).rewrite(sign)
+ >>> Heaviside(x, nan).rewrite(sign)
+ Piecewise((sign(x)/2 + 1/2, Ne(x, 0)), (nan, True))
+
+ >>> Heaviside(x - 2).rewrite(sign)
sign(x - 2)/2 + 1/2
- >>> Heaviside(x**2 - 2*x + 1, H0=S.Half).rewrite(sign)
+ >>> Heaviside(x**2 - 2*x + 1).rewrite(sign)
sign(x**2 - 2*x + 1)/2 + 1/2
- >>> y = Symbol('y')
-
>>> Heaviside(y).rewrite(sign)
- Heaviside(y)
+ Heaviside(y, 1/2)
>>> Heaviside(y**2 - 2*y + 1).rewrite(sign)
- Heaviside(y**2 - 2*y + 1)
+ Heaviside(y**2 - 2*y + 1, 1/2)
See Also
========
@@ -648,7 +649,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_sign(self, arg, H0=None, **kwargs):
(pw1, True))
return pw2
- def _eval_rewrite_as_SingularityFunction(self, args, **kwargs):
+ def _eval_rewrite_as_SingularityFunction(self, args, H0=S.Half, **kwargs):
"""
Returns the Heaviside expression written in the form of Singularity
Functions.
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/singularity_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/singularity_functions.py
index 69695de60111..d568c28a1f43 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/singularity_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/singularity_functions.py
@@ -65,11 +65,11 @@ class SingularityFunction(Function):
>>> expr = SingularityFunction(x, 4, 5) + SingularityFunction(x, -3, -1) - SingularityFunction(x, 0, -2)
>>> expr.rewrite(Heaviside)
- (x - 4)**5*Heaviside(x - 4) + DiracDelta(x + 3) - DiracDelta(x, 1)
+ (x - 4)**5*Heaviside(x - 4, 1/2) + DiracDelta(x + 3) - DiracDelta(x, 1)
>>> expr.rewrite(DiracDelta)
- (x - 4)**5*Heaviside(x - 4) + DiracDelta(x + 3) - DiracDelta(x, 1)
+ (x - 4)**5*Heaviside(x - 4, 1/2) + DiracDelta(x + 3) - DiracDelta(x, 1)
>>> expr.rewrite('HeavisideDiracDelta')
- (x - 4)**5*Heaviside(x - 4) + DiracDelta(x + 3) - DiracDelta(x, 1)
+ (x - 4)**5*Heaviside(x - 4, 1/2) + DiracDelta(x + 3) - DiracDelta(x, 1)
See Also
========
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_delta_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_delta_functions.py
index 72ba93e2c96e..69722eac1bc8 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_delta_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_delta_functions.py
@@ -6,6 +6,8 @@
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, warns_deprecated_sympy
+from sympy.core.expr import unchanged
+
from sympy.core.function import ArgumentIndexError
@@ -80,19 +82,13 @@ def test_DiracDelta():
def test_heaviside():
- assert Heaviside(0).func == Heaviside
assert Heaviside(-5) == 0
assert Heaviside(1) == 1
- assert Heaviside(nan) is nan
+ assert Heaviside(0) == S.Half
assert Heaviside(0, x) == x
- assert Heaviside(0, nan) is nan
- assert Heaviside(x, None) == Heaviside(x)
- assert Heaviside(0, None) == Heaviside(0)
-
- # we do not want None and Heaviside(0) in the args:
- assert Heaviside(x, H0=None).args == (x,)
- assert Heaviside(x, H0=Heaviside(0)).args == (x,)
+ assert unchanged(Heaviside,x, nan)
+ assert Heaviside(0, nan) == nan
assert adjoint(Heaviside(x)) == Heaviside(x)
assert adjoint(Heaviside(x - y)) == Heaviside(x - y)
@@ -122,6 +118,8 @@ def test_rewrite():
Piecewise((0, x <= 0), (1, x > 0)))
assert Heaviside(x, 1).rewrite(Piecewise) == (
Piecewise((0, x < 0), (1, x >= 0)))
+ assert Heaviside(x, nan).rewrite(Piecewise) == (
+ Piecewise((0, x < 0), (nan, Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0)))
assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(sign) == \
Heaviside(x, H0=Heaviside(0)).rewrite(sign) == \
@@ -153,13 +151,4 @@ def test_rewrite():
assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == SingularityFunction(x, 0, 0)
assert 5*x*y*Heaviside(y + 1).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == 5*x*y*SingularityFunction(y, -1, 0)
assert ((x - 3)**3*Heaviside(x - 3)).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == (x - 3)**3*SingularityFunction(x, 3, 0)
- assert Heaviside(0).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == SingularityFunction(0, 0, 0)
-
-def test_issue_15923():
- x = Symbol('x', real=True)
- assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise, H0=0) == (
- Piecewise((0, x <= 0), (1, True)))
- assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise, H0=1) == (
- Piecewise((0, x < 0), (1, True)))
- assert Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise, H0=S.Half) == (
- Piecewise((0, x < 0), (S.Half, Eq(x, 0)), (1, x > 0)))
+ assert Heaviside(0).rewrite(SingularityFunction) == S.Half
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py b/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py
index e0acdab905ad..dd9086757518 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py
@@ -123,9 +123,9 @@ def deltaintegrate(f, x):
>>> from sympy.integrals.deltafunctions import deltaintegrate
>>> from sympy import sin, cos, DiracDelta
>>> deltaintegrate(x*sin(x)*cos(x)*DiracDelta(x - 1), x)
- sin(1)*cos(1)*Heaviside(x - 1)
+ sin(1)*cos(1)*Heaviside(x - 1, 1/2)
>>> deltaintegrate(y**2*DiracDelta(x - z)*DiracDelta(y - z), y)
- z**2*DiracDelta(x - z)*Heaviside(y - z)
+ z**2*DiracDelta(x - z)*Heaviside(y - z, 1/2)
See Also
========
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py b/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py
index 86cecddb33ce..3acab5cac7d9 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py
@@ -2087,7 +2087,7 @@ def meijerint_inversion(f, x, t):
>>> from sympy.abc import x, t
>>> from sympy.integrals.meijerint import meijerint_inversion
>>> meijerint_inversion(1/x, x, t)
- Heaviside(t)
+ Heaviside(t, 1/2)
"""
from sympy import exp, expand, log, Add, Mul, Heaviside
f_ = f
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/transforms.py b/sympy/integrals/transforms.py
index 739450dd9391..f1be3131dd7a 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/transforms.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/transforms.py
@@ -893,11 +893,11 @@ def inverse_mellin_transform(F, s, x, strip, **hints):
>>> f = 1/(s**2 - 1)
>>> inverse_mellin_transform(f, s, x, (-oo, -1))
- x*(1 - 1/x**2)*Heaviside(x - 1)/2
+ x*(1 - 1/x**2)*Heaviside(x - 1, 1/2)/2
>>> inverse_mellin_transform(f, s, x, (-1, 1))
- -x*Heaviside(1 - x)/2 - Heaviside(x - 1)/(2*x)
+ -x*Heaviside(1 - x, 1/2)/2 - Heaviside(x - 1, 1/2)/(2*x)
>>> inverse_mellin_transform(f, s, x, (1, oo))
- (1/2 - x**2/2)*Heaviside(1 - x)/x
+ (1/2 - x**2/2)*Heaviside(1 - x, 1/2)/x
See Also
========
@@ -1234,17 +1234,17 @@ def pw_simp(*args):
u = Dummy('u')
- def simp_heaviside(arg):
+ def simp_heaviside(arg, H0=S.Half):
a = arg.subs(exp(-t), u)
if a.has(t):
- return Heaviside(arg)
+ return Heaviside(arg,H0)
rel = _solve_inequality(a > 0, u)
if rel.lts == u:
k = log(rel.gts)
- return Heaviside(t + k)
+ return Heaviside(t + k,H0)
else:
k = log(rel.lts)
- return Heaviside(-(t + k))
+ return Heaviside(-(t + k),H0)
f = f.replace(Heaviside, simp_heaviside)
def simp_exp(arg):
@@ -1328,7 +1328,7 @@ def inverse_laplace_transform(F, s, t, plane=None, **hints):
>>> from sympy.abc import s, t
>>> a = Symbol('a', positive=True)
>>> inverse_laplace_transform(exp(-a*s)/s, s, t)
- Heaviside(-a + t)
+ Heaviside(-a + t, 1/2)
See Also
========
diff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py
index 917b70382148..06bd23478734 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py
@@ -1573,7 +1573,12 @@ def _print_dirichlet_eta(self, e):
def _print_Heaviside(self, e):
func_name = greek_unicode['theta'] if self._use_unicode else 'Heaviside'
- return self._print_Function(e, func_name=func_name)
+ if e.args[1]==1/2:
+ pform = prettyForm(*self._print(e.args[0]).parens())
+ pform = prettyForm(*pform.left(func_name))
+ return pform
+ else:
+ return self._print_Function(e, func_name=func_name)
def _print_fresnels(self, e):
return self._print_Function(e, func_name="S")
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_mathml.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_mathml.py
index ffd59826093d..a2404718a911 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_mathml.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_mathml.py
@@ -1530,7 +1530,7 @@ def test_print_different_functions():
assert mpp.doprint(primeomega(x)) == '<mrow><mi>Ω</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi></mfenced></mrow>'
assert mpp.doprint(fresnels(x)) == '<mrow><mi>S</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi></mfenced></mrow>'
assert mpp.doprint(fresnelc(x)) == '<mrow><mi>C</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi></mfenced></mrow>'
- assert mpp.doprint(Heaviside(x)) == '<mrow><mi>Θ</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi></mfenced></mrow>'
+ assert mpp.doprint(Heaviside(x)) == '<mrow><mi>Θ</mi><mfenced><mi>x</mi><mfrac><mn>1</mn><mn>2</mn></mfrac></mfenced></mrow>'
def test_mathml_builtins():
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_octave.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_octave.py
index bdd0dca02e12..b39116d4606d 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_octave.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_octave.py
@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ def test_Function_change_name():
assert mcode(RisingFactorial(x, y)) == "pochhammer(x, y)"
assert mcode(DiracDelta(x)) == "dirac(x)"
assert mcode(DiracDelta(x, 3)) == "dirac(3, x)"
- assert mcode(Heaviside(x)) == "heaviside(x)"
+ assert mcode(Heaviside(x)) == "heaviside(x, 1/2)"
assert mcode(Heaviside(x, y)) == "heaviside(x, y)"
assert mcode(binomial(x, y)) == "bincoeff(x, y)"
assert mcode(Mod(x, y)) == "mod(x, y)"
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-21286@5bf16b4
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,286
|
corrections for symbolic Range
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
fixes #21269
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
#### Other comments
* to return or to raise
Symbolic Range is tricky because you can't assume that it isn't EmptSet when making queries like `.inf`, e.g. neither `Range(x,y,z).inf` nor Range(x,y,z)[0] can return `x` unless we know that (y - x)*z > 0
And, technically, even `Range(x, x + 2, 1)[0]` should not return `x` unless we know that it is an integer.
- [x] this now raises an error
* the relational form
cf #21285 For better protection, a two more Mods could be added to give: `And(Eq(Mod(x,1),a%s), Eq(Mod(a,1),0), Eq(Mod(s,1),0))` where `a` is a representative point in the Range that is not infinite, `s` is the step and `x` is the relational variable. We should also make sure that there is not a clash between the symbols of the Range and the relational variable as in `Range(x, x + 5, 2).as_relational(x)`.
- [x] this is done but the user can clash symbols if they want to
```python
>>> var('x')
x
>>> Range(x, x + 3, 2).as_relational(x)
(x >= x) & Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0) & (x <= x + 2)
>>> var('x',real=True)
x
>>> Range(x, x + 3, 2).as_relational(x)
Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0)
>>> var('x',integer=1)
x
>>> Range(x, x + 3, 2).as_relational(x)
True
>>> var('x')
x
>>> Range(1, 1+ 2*x, x).as_relational(x)
Eq(Mod(-1, x), 0) & Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0) & (((x >= 1) & (x <= x + 1)) | ((x <= -1) &
(x <= 1) & (x >= x + 1)))
>>> var('x',real=1)
x
>>> Range(1, 1+ 2*x, x).as_relational(x)
(x >= 1) & Eq(Mod(-1, x), 0) & Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0)
>>> var('x',integer=1)
x
>>> Range(1, 1+ 2*x, x).as_relational(x)
(x >= 1) & Eq(Mod(-1, x), 0)
```
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* sets
* Range involving symbols will be made more canonical (correcting a bug in calculation of `sup`) and errors will be raised when trying to compute attributes that are not known due to limitations of assumptions on the arguments.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-04-10T12:15:40Z
|
make symbolic Range more canonical
Whereas a Range with numerical args is canonical, the Range containing symbols is not:
```python
>>> [Range(3,j,2) for j in range(4,10)]
[Range(3, 5, 2), Range(3, 5, 2), Range(3, 7, 2), Range(3, 7, 2), Range(3, 9, 2), Range(3, 9, 2)]
vs
>>> [Range(i,i+j,5) for j in range(1,6)]
[Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 2, 5), Range(i, i + 3, 5), Range(i, i + 4, 5), Range(i, i + 5, 5)]
which could be
[Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 1, 5)]
```
The incorrect results are based on the assumption that the instantiated Range is canonical:
```python
>> r=Range(2, 2 + 3, 5)
>>> r.inf,r.reversed.sup
(2, 2)
>>> r = Range(k, k + 3, 5)
>>> r.inf,r.reversed.sup
(k, k - 2)
```
|
[
{
"body": "Whereas a Range with numerical args is canonical, the Range containing symbols is not:\r\n```python\r\n>>> [Range(3,j,2) for j in range(4,10)]\r\n[Range(3, 5, 2), Range(3, 5, 2), Range(3, 7, 2), Range(3, 7, 2), Range(3, 9, 2), Range(3, 9, 2)]\r\n\r\nvs\r\n\r\n>>> [Range(i,i+j,5) for j in range(1,6)]\r\n[Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 2, 5), Range(i, i + 3, 5), Range(i, i + 4, 5), Range(i, i + 5, 5)]\r\n\r\nwhich could be\r\n\r\n[Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 1, 5), Range(i, i + 1, 5)]\r\n\r\n```\r\nThe incorrect results are based on the assumption that the instantiated Range is canonical:\r\n```python\r\n>> r=Range(2, 2 + 3, 5)\r\n>>> r.inf,r.reversed.sup\r\n(2, 2)\r\n>>> r = Range(k, k + 3, 5)\r\n>>> r.inf,r.reversed.sup\r\n(k, k - 2)\r\n```",
"number": 21269,
"title": "make symbolic Range more canonical"
}
] |
546e10799fe55b3e59dea8fa6b3a6d6e71843d33
|
{
"head_commit": "5bf16b49c0029f307a74bc5eaae0303b7b27930f",
"head_commit_message": "enforce step range with condition",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/sets/fancysets.py b/sympy/sets/fancysets.py\nindex 45404f2862ae..0eae37f619b9 100644\n--- a/sympy/sets/fancysets.py\n+++ b/sympy/sets/fancysets.py\n@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@\n from sympy.core.singleton import Singleton, S\n from sympy.core.symbol import Dummy, symbols, Symbol\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify, sympify, converter\n-from sympy.logic.boolalg import And\n+from sympy.logic.boolalg import And, Or\n from sympy.sets.sets import (Set, Interval, Union, FiniteSet,\n ProductSet)\n from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent\n@@ -571,7 +571,7 @@ class Range(Set):\n >>> r.inf\n n\n >>> pprint(r)\n- {n, n + 3, ..., n + 17}\n+ {n, n + 3, ..., n + 18}\n \"\"\"\n \n is_iterable = True\n@@ -598,6 +598,8 @@ def __new__(cls, *args):\n w.has(Symbol) and w.is_integer != False):\n ok.append(w)\n elif not w.is_Integer:\n+ if w.is_infinite:\n+ raise ValueError('infinite symbols not allowed')\n raise ValueError\n else:\n ok.append(w)\n@@ -610,10 +612,25 @@ def __new__(cls, *args):\n \n null = False\n if any(i.has(Symbol) for i in (start, stop, step)):\n- if start == stop:\n+ dif = stop - start\n+ n = dif/step\n+ if n.is_Rational:\n+ from sympy import floor\n+ if dif == 0:\n+ null = True\n+ else: # (x, x + 5, 2) or (x, 3*x, x)\n+ n = floor(n)\n+ end = start + n*step\n+ if dif.is_Rational: # (x, x + 5, 2)\n+ if (end - stop).is_negative:\n+ end += step\n+ else: # (x, 3*x, x)\n+ if (end/stop - 1).is_negative:\n+ end += step\n+ elif n.is_extended_negative:\n null = True\n else:\n- end = stop\n+ end = stop # other methods like sup and reversed must fail\n elif start.is_infinite:\n span = step*(stop - start)\n if span is S.NaN or span <= 0:\n@@ -631,8 +648,8 @@ def __new__(cls, *args):\n if n <= 0:\n null = True\n elif oostep:\n- end = start + 1\n- step = S.One # make it a canonical single step\n+ step = S.One # make it canonical\n+ end = start + step\n else:\n end = start + n*step\n if null:\n@@ -656,7 +673,10 @@ def reversed(self):\n Range(9, -1, -1)\n \"\"\"\n if self.has(Symbol):\n- _ = self.size # validate\n+ n = (self.stop - self.start)/self.step\n+ if not n.is_extended_positive or not all(\n+ i.is_integer or i.is_infinite for i in self.args):\n+ raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')\n if not self:\n return self\n return self.func(\n@@ -670,20 +690,25 @@ def _contains(self, other):\n if not other.is_integer:\n return other.is_integer\n if self.has(Symbol):\n- try:\n- _ = self.size # validate\n- except ValueError:\n+ n = (self.stop - self.start)/self.step\n+ if not n.is_extended_positive or not all(\n+ i.is_integer or i.is_infinite for i in self.args):\n return\n+ else:\n+ n = self.size\n if self.start.is_finite:\n ref = self.start\n elif self.stop.is_finite:\n ref = self.stop\n else: # both infinite; step is +/- 1 (enforced by __new__)\n return S.true\n- if self.size == 1:\n+ if n == 1:\n return Eq(other, self[0])\n res = (ref - other) % self.step\n if res == S.Zero:\n+ if self.has(Symbol):\n+ d = Dummy('i')\n+ return self.as_relational(d).subs(d, other)\n return And(other >= self.inf, other <= self.sup)\n elif res.is_Integer: # off sequence\n return S.false\n@@ -691,20 +716,19 @@ def _contains(self, other):\n return None\n \n def __iter__(self):\n- if self.has(Symbol):\n- _ = self.size # validate\n+ n = self.size # validate\n if self.start in [S.NegativeInfinity, S.Infinity]:\n raise TypeError(\"Cannot iterate over Range with infinite start\")\n elif self:\n i = self.start\n- step = self.step\n-\n- while True:\n- if (step > 0 and not (self.start <= i < self.stop)) or \\\n- (step < 0 and not (self.stop < i <= self.start)):\n- break\n- yield i\n- i += step\n+ if n.is_infinite:\n+ while True:\n+ yield i\n+ i += self.step\n+ else:\n+ for j in range(n):\n+ yield i\n+ i += self.step\n \n def __len__(self):\n rv = self.size\n@@ -717,12 +741,12 @@ def size(self):\n if not self:\n return S.Zero\n dif = self.stop - self.start\n- n = abs(dif // self.step)\n- if not n.is_Integer:\n- if n.is_infinite:\n- return S.Infinity\n+ n = dif/self.step\n+ if n.is_infinite:\n+ return S.Infinity\n+ if not n.is_Integer or not all(i.is_integer for i in self.args):\n raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')\n- return n\n+ return abs(n)\n \n @property\n def is_finite_set(self):\n@@ -731,6 +755,9 @@ def is_finite_set(self):\n return self.size.is_finite\n \n def __bool__(self):\n+ # this only distinguishes between definite null range\n+ # and non-null/unknown null; getting True doesn't mean\n+ # that it actually is not null\n return self.start != self.stop\n \n def __getitem__(self, i):\n@@ -745,6 +772,8 @@ def __getitem__(self, i):\n \"with an infinite value\"\n if isinstance(i, slice):\n if self.size.is_finite: # validates, too\n+ if not self:\n+ return Range(0)\n start, stop, step = i.indices(self.size)\n n = ceiling((stop - start)/step)\n if n <= 0:\n@@ -847,42 +876,38 @@ def __getitem__(self, i):\n else:\n if not self:\n raise IndexError('Range index out of range')\n+ if not (all(i.is_integer or i.is_infinite\n+ for i in self.args) and ((self.stop - self.start)/\n+ self.step).is_extended_positive):\n+ raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')\n if i == 0:\n if self.start.is_infinite:\n raise ValueError(ooslice)\n- if self.has(Symbol):\n- if (self.stop > self.start) == self.step.is_positive and self.step.is_positive is not None:\n- pass\n- else:\n- _ = self.size # validate\n return self.start\n if i == -1:\n if self.stop.is_infinite:\n raise ValueError(ooslice)\n- n = self.stop - self.step\n- if n.is_Integer or (\n- n.is_integer and (\n- (n - self.start).is_nonnegative ==\n- self.step.is_positive)):\n- return n\n- _ = self.size # validate\n+ return self.stop - self.step\n+ n = self.size # must be known for any other index\n rv = (self.stop if i < 0 else self.start) + i*self.step\n if rv.is_infinite:\n raise ValueError(ooslice)\n- if rv < self.inf or rv > self.sup:\n- raise IndexError(\"Range index out of range\")\n- return rv\n+ if 0 <= (rv - self.start)/self.step <= n:\n+ return rv\n+ raise IndexError(\"Range index out of range\")\n \n @property\n def _inf(self):\n if not self:\n- raise NotImplementedError\n+ return S.EmptySet.inf\n if self.has(Symbol):\n- if self.step.is_positive:\n- return self[0]\n- elif self.step.is_negative:\n- return self[-1]\n- _ = self.size # validate\n+ if all(i.is_integer or i.is_infinite for i in self.args):\n+ dif = self.stop - self.start\n+ if self.step.is_positive and dif.is_positive:\n+ return self.start\n+ elif self.step.is_negative and dif.is_negative:\n+ return self.stop - self.step\n+ raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')\n if self.step > 0:\n return self.start\n else:\n@@ -891,13 +916,15 @@ def _inf(self):\n @property\n def _sup(self):\n if not self:\n- raise NotImplementedError\n+ return S.EmptySet.sup\n if self.has(Symbol):\n- if self.step.is_positive:\n- return self[-1]\n- elif self.step.is_negative:\n- return self[0]\n- _ = self.size # validate\n+ if all(i.is_integer or i.is_infinite for i in self.args):\n+ dif = self.stop - self.start\n+ if self.step.is_positive and dif.is_positive:\n+ return self.stop - self.step\n+ elif self.step.is_negative and dif.is_negative:\n+ return self.start\n+ raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')\n if self.step > 0:\n return self.stop - self.step\n else:\n@@ -909,27 +936,34 @@ def _boundary(self):\n \n def as_relational(self, x):\n \"\"\"Rewrite a Range in terms of equalities and logic operators. \"\"\"\n- if self.size == 1:\n- return Eq(x, self[0])\n- elif self.size == 0:\n- return S.false\n+ from sympy.core.mod import Mod\n+ if self.start.is_infinite:\n+ assert not self.stop.is_infinite # by instantiation\n+ a = self.reversed.start\n else:\n- from sympy.core.mod import Mod\n- cond = None\n- if self.start.is_infinite:\n- if self.stop.is_infinite:\n- cond = S.true\n- else:\n- a = self.reversed.start\n- elif self.start == self.stop:\n- cond = S.false # null range\n- else:\n- a = self.start\n- step = abs(self.step)\n- cond = Eq(Mod(x, step), a % step) if cond is None else cond\n- return And(cond,\n- x >= self.inf if self.inf in self else x > self.inf,\n- x <= self.sup if self.sup in self else x < self.sup)\n+ a = self.start\n+ step = self.step\n+ in_seq = Eq(Mod(x - a, step), 0)\n+ ints = And(Eq(Mod(a, 1), 0), Eq(Mod(step, 1), 0))\n+ n = (self.stop - self.start)/self.step\n+ try:\n+ if n == 0:\n+ return S.EmptySet.as_relational(x)\n+ if n == 1:\n+ return And(Eq(x, a), ints)\n+ a, b = self.inf, self.sup\n+ range_cond = And(\n+ x > a if a.is_infinite else x >= a,\n+ x < b if b.is_infinite else x <= b)\n+ except ValueError: # inf/sup unknown\n+ a, b = self.start, self.stop - self.step\n+ range_cond = Or(\n+ And(self.step >= 1, x > a if a.is_infinite else x >= a,\n+ x < b if b.is_infinite else x <= b),\n+ And(self.step <= -1, x < a if a.is_infinite else x <= a,\n+ x > b if b.is_infinite else x >= b))\n+ return And(in_seq, ints, range_cond)\n+\n \n converter[range] = lambda r: Range(r.start, r.stop, r.step)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/sets/tests/test_fancysets.py b/sympy/sets/tests/test_fancysets.py\nindex 6b2cf51aeb2b..9fbdc2ecfa50 100644\n--- a/sympy/sets/tests/test_fancysets.py\n+++ b/sympy/sets/tests/test_fancysets.py\n@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@\n Dummy, floor, And, Eq)\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import cartes\n from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, raises\n-from sympy.abc import x, y, t\n+from sympy.abc import x, y, t, z\n from sympy.core.mod import Mod\n \n import itertools\n@@ -174,8 +174,6 @@ def test_inf_Range_len():\n assert Range(0, -oo, -2).size is S.Infinity\n assert Range(oo, 0, -2).size is S.Infinity\n assert Range(-oo, 0, 2).size is S.Infinity\n- i = Symbol('i', integer=True)\n- assert Range(0, 4 * i, i).size == 4\n \n \n def test_Range_set():\n@@ -209,6 +207,9 @@ def test_Range_set():\n assert Range(1, oo, -1) == empty\n assert Range(1, -oo, 1) == empty\n assert Range(1, -4, oo) == empty\n+ ip = symbols('ip', positive=True)\n+ assert Range(0, ip, -1) == empty\n+ assert Range(0, -ip, 1) == empty\n assert Range(1, -4, -oo) == Range(1, 2)\n assert Range(1, 4, oo) == Range(1, 2)\n assert Range(-oo, oo).size == oo\n@@ -231,13 +232,8 @@ def test_Range_set():\n assert Range(-oo, 1, 1)[-1] is S.Zero\n assert Range(oo, 1, -1)[-1] == 2\n assert inf not in Range(oo)\n- inf = symbols('inf', infinite=True)\n- assert inf not in Range(oo)\n- assert Range(-oo, 1, 1)[-1] is S.Zero\n- assert Range(oo, 1, -1)[-1] == 2\n assert Range(1, 10, 1)[-1] == 9\n assert all(i.is_Integer for i in Range(0, -1, 1))\n-\n it = iter(Range(-oo, 0, 2))\n raises(TypeError, lambda: next(it))\n \n@@ -278,6 +274,7 @@ def test_Range_set():\n raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(-oo, 4, 2)[2::-1])\n assert Range(-oo, 4, 2)[-2::2] == Range(0, 4, 4)\n assert Range(oo, 0, -2)[-10:0:2] == empty\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(oo, 0, -2)[0])\n raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(oo, 0, -2)[-10:10:2])\n raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(oo, 0, -2)[0::-2])\n assert Range(oo, 0, -2)[0:-4:-2] == empty\n@@ -297,6 +294,7 @@ def test_Range_set():\n assert empty[:0] == empty\n raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: empty.inf)\n raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: empty.sup)\n+ assert empty.as_relational(x) is S.false\n \n AB = [None] + list(range(12))\n for R in [\n@@ -330,45 +328,85 @@ def test_Range_set():\n \n # test Range.as_relational\n assert Range(1, 4).as_relational(x) == (x >= 1) & (x <= 3) & Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0)\n- assert Range(oo, 1, -2).as_relational(x) == (x >= 3) & (x < oo) & Eq(Mod(x, 2), 1)\n+ assert Range(oo, 1, -2).as_relational(x) == (x >= 3) & (x < oo) & Eq(Mod(x + 1, -2), 0)\n \n \n def test_Range_symbolic():\n # symbolic Range\n+ xr = Range(x, x + 4, 5)\n sr = Range(x, y, t)\n i = Symbol('i', integer=True)\n ip = Symbol('i', integer=True, positive=True)\n- ir = Range(i, i + 20, 2)\n+ ipr = Range(ip)\n+ inr = Range(0, -ip, -1)\n+ ir = Range(i, i + 19, 2)\n+ ir2 = Range(i, i*8, 3*i)\n+ i = Symbol('i', integer=True)\n inf = symbols('inf', infinite=True)\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(inf))\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(inf, 0, -1))\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(inf, inf, 1))\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(1, 1, inf))\n # args\n+ assert xr.args == (x, x + 5, 5)\n assert sr.args == (x, y, t)\n assert ir.args == (i, i + 20, 2)\n+ assert ir2.args == (i, 10*i, 3*i)\n # reversed\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr.reversed)\n raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.reversed)\n- assert ir.reversed == Range(i + 18, i - 2, -2)\n+ assert ipr.reversed.args == (ip - 1, -1, -1)\n+ assert inr.reversed.args == (-ip + 1, 1, 1)\n+ assert ir.reversed.args == (i + 18, i - 2, -2)\n+ assert ir2.reversed.args == (7*i, -2*i, -3*i)\n # contains\n assert inf not in sr\n assert inf not in ir\n+ assert 0 in ipr\n+ assert 0 in inr\n+ raises(TypeError, lambda: 1 in ipr)\n+ raises(TypeError, lambda: -1 in inr)\n assert .1 not in sr\n assert .1 not in ir\n assert i + 1 not in ir\n assert i + 2 in ir\n+ raises(TypeError, lambda: x in xr) # XXX is this what contains is supposed to do?\n raises(TypeError, lambda: 1 in sr) # XXX is this what contains is supposed to do?\n # iter\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: next(iter(xr)))\n raises(ValueError, lambda: next(iter(sr)))\n assert next(iter(ir)) == i\n+ assert next(iter(ir2)) == i\n assert sr.intersect(S.Integers) == sr\n assert sr.intersect(FiniteSet(x)) == Intersection({x}, sr)\n raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[:2])\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr[0])\n raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[0])\n- raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.as_relational(x))\n # len\n assert len(ir) == ir.size == 10\n+ assert len(ir2) == ir2.size == 3\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: len(xr))\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr.size)\n raises(ValueError, lambda: len(sr))\n raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.size)\n # bool\n- assert bool(ir) == bool(sr) == True\n+ assert bool(ir) == bool(sr) == bool(xr) == True\n+ # inf\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr.inf)\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.inf)\n+ assert ipr.inf == 0\n+ assert inr.inf == -ip + 1\n+ assert ir.inf == i\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: ir2.inf)\n+ # sup\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr.sup)\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.sup)\n+ assert ipr.sup == ip - 1\n+ assert inr.sup == 0\n+ assert ir.inf == i\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: ir2.sup)\n # getitem\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr[0])\n raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[0])\n raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[-1])\n raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[:2])\n@@ -376,17 +414,33 @@ def test_Range_symbolic():\n assert ir[0] == i\n assert ir[-2] == i + 16\n assert ir[-1] == i + 18\n+ assert ir2[:2] == Range(i, 7*i, 3*i)\n+ assert ir2[0] == i\n+ assert ir2[-2] == 4*i\n+ assert ir2[-1] == 7*i\n raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(i)[-1])\n- assert Range(ip)[-1] == ip - 1\n+ assert ipr[0] == ipr.inf == 0\n+ assert ipr[-1] == ipr.sup == ip - 1\n+ assert inr[0] == inr.sup == 0\n+ assert inr[-1] == inr.inf == -ip + 1\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda: ipr[-2])\n assert ir.inf == i\n assert ir.sup == i + 18\n- assert Range(ip).inf == 0\n- assert Range(ip).sup == ip - 1\n raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(i).inf)\n # as_relational\n- raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.as_relational(x))\n- assert ir.as_relational(x) == (x >= i) & (x <= i + 18) & Eq(Mod(x, 2), Mod(i, 2))\n+ assert ir.as_relational(x) == ((x >= i) & (x <= i + 18) &\n+ Eq(Mod(-i + x, 2), 0))\n+ assert ir2.as_relational(x) == Eq(\n+ Mod(-i + x, 3*i), 0) & (((x >= i) & (x <= 7*i) & (3*i >= 1)) |\n+ ((x <= i) & (x >= 7*i) & (3*i <= -1)))\n assert Range(i, i + 1).as_relational(x) == Eq(x, i)\n+ assert sr.as_relational(z) == Eq(\n+ Mod(t, 1), 0) & Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0) & Eq(Mod(-x + z, t), 0\n+ ) & (((z >= x) & (z <= -t + y) & (t >= 1)) |\n+ ((z <= x) & (z >= -t + y) & (t <= -1)))\n+ assert xr.as_relational(z) == Eq(z, x) & Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0)\n+ # symbols can clash if user wants (but it must be integer)\n+ assert xr.as_relational(x) == Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0)\n # contains() for symbolic values (issue #18146)\n e = Symbol('e', integer=True, even=True)\n o = Symbol('o', integer=True, odd=True)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -731,6 +755,9 @@ def is_finite_set(self):\n return self.size.is_finite\n \n def __bool__(self):\n+ # this only distinguishes between definite null range\n+ # and non-null/unknown null; getting True doesn't mean\n+ # that it actually is not null\n return self.start != self.stop",
"line": null,
"original_line": 761,
"original_start_line": 757,
"path": "sympy/sets/fancysets.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think it would be better if this returned something like `is_eq(self.start, self.stop)` and raised an exception in the None case."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -909,27 +936,34 @@ def _boundary(self):\n \n def as_relational(self, x):\n \"\"\"Rewrite a Range in terms of equalities and logic operators. \"\"\"\n- if self.size == 1:\n- return Eq(x, self[0])\n- elif self.size == 0:\n- return S.false\n+ from sympy.core.mod import Mod\n+ if self.start.is_infinite:\n+ assert not self.stop.is_infinite # by instantiation\n+ a = self.reversed.start\n else:\n- from sympy.core.mod import Mod\n- cond = None\n- if self.start.is_infinite:\n- if self.stop.is_infinite:\n- cond = S.true\n- else:\n- a = self.reversed.start\n- elif self.start == self.stop:\n- cond = S.false # null range\n- else:\n- a = self.start\n- step = abs(self.step)\n- cond = Eq(Mod(x, step), a % step) if cond is None else cond\n- return And(cond,\n- x >= self.inf if self.inf in self else x > self.inf,\n- x <= self.sup if self.sup in self else x < self.sup)\n+ a = self.start\n+ step = self.step\n+ in_seq = Eq(Mod(x - a, step), 0)\n+ ints = And(Eq(Mod(a, 1), 0), Eq(Mod(step, 1), 0))\n+ n = (self.stop - self.start)/self.step\n+ try:\n+ if n == 0:\n+ return S.EmptySet.as_relational(x)\n+ if n == 1:\n+ return And(Eq(x, a), ints)\n+ a, b = self.inf, self.sup\n+ range_cond = And(\n+ x > a if a.is_infinite else x >= a,\n+ x < b if b.is_infinite else x <= b)\n+ except ValueError: # inf/sup unknown",
"line": null,
"original_line": 958,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/sets/fancysets.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIt would be better not to catch `ValueError`. Lots of things can raise `ValueError`. Ideally it would not be explicitly raised in sympy code when a sympy-specific exception could be used instead.\n\n@author:\nI wrapped only the sup/inf part in the try/except clause. This is the only error arising from these routines under the condition of working with a set for which n not in (0,1)."
}
] |
b3a2a7bbbac0281314fecfa64c2d06a2e1c413bd
|
diff --git a/sympy/sets/fancysets.py b/sympy/sets/fancysets.py
index 45404f2862ae..861737b25760 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/fancysets.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/fancysets.py
@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
from sympy.core.function import Lambda
from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_not, fuzzy_or, fuzzy_and
from sympy.core.numbers import oo
-from sympy.core.relational import Eq
+from sympy.core.relational import Eq, is_eq
from sympy.core.singleton import Singleton, S
from sympy.core.symbol import Dummy, symbols, Symbol
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify, sympify, converter
-from sympy.logic.boolalg import And
+from sympy.logic.boolalg import And, Or
from sympy.sets.sets import (Set, Interval, Union, FiniteSet,
ProductSet)
from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent
@@ -571,7 +571,7 @@ class Range(Set):
>>> r.inf
n
>>> pprint(r)
- {n, n + 3, ..., n + 17}
+ {n, n + 3, ..., n + 18}
"""
is_iterable = True
@@ -598,6 +598,8 @@ def __new__(cls, *args):
w.has(Symbol) and w.is_integer != False):
ok.append(w)
elif not w.is_Integer:
+ if w.is_infinite:
+ raise ValueError('infinite symbols not allowed')
raise ValueError
else:
ok.append(w)
@@ -610,10 +612,25 @@ def __new__(cls, *args):
null = False
if any(i.has(Symbol) for i in (start, stop, step)):
- if start == stop:
+ dif = stop - start
+ n = dif/step
+ if n.is_Rational:
+ from sympy import floor
+ if dif == 0:
+ null = True
+ else: # (x, x + 5, 2) or (x, 3*x, x)
+ n = floor(n)
+ end = start + n*step
+ if dif.is_Rational: # (x, x + 5, 2)
+ if (end - stop).is_negative:
+ end += step
+ else: # (x, 3*x, x)
+ if (end/stop - 1).is_negative:
+ end += step
+ elif n.is_extended_negative:
null = True
else:
- end = stop
+ end = stop # other methods like sup and reversed must fail
elif start.is_infinite:
span = step*(stop - start)
if span is S.NaN or span <= 0:
@@ -631,8 +648,8 @@ def __new__(cls, *args):
if n <= 0:
null = True
elif oostep:
- end = start + 1
- step = S.One # make it a canonical single step
+ step = S.One # make it canonical
+ end = start + step
else:
end = start + n*step
if null:
@@ -656,34 +673,42 @@ def reversed(self):
Range(9, -1, -1)
"""
if self.has(Symbol):
- _ = self.size # validate
- if not self:
+ n = (self.stop - self.start)/self.step
+ if not n.is_extended_positive or not all(
+ i.is_integer or i.is_infinite for i in self.args):
+ raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')
+ if self.start == self.stop:
return self
return self.func(
self.stop - self.step, self.start - self.step, -self.step)
def _contains(self, other):
- if not self:
+ if self.start == self.stop:
return S.false
if other.is_infinite:
return S.false
if not other.is_integer:
return other.is_integer
if self.has(Symbol):
- try:
- _ = self.size # validate
- except ValueError:
+ n = (self.stop - self.start)/self.step
+ if not n.is_extended_positive or not all(
+ i.is_integer or i.is_infinite for i in self.args):
return
+ else:
+ n = self.size
if self.start.is_finite:
ref = self.start
elif self.stop.is_finite:
ref = self.stop
else: # both infinite; step is +/- 1 (enforced by __new__)
return S.true
- if self.size == 1:
+ if n == 1:
return Eq(other, self[0])
res = (ref - other) % self.step
if res == S.Zero:
+ if self.has(Symbol):
+ d = Dummy('i')
+ return self.as_relational(d).subs(d, other)
return And(other >= self.inf, other <= self.sup)
elif res.is_Integer: # off sequence
return S.false
@@ -691,20 +716,19 @@ def _contains(self, other):
return None
def __iter__(self):
- if self.has(Symbol):
- _ = self.size # validate
+ n = self.size # validate
if self.start in [S.NegativeInfinity, S.Infinity]:
raise TypeError("Cannot iterate over Range with infinite start")
- elif self:
+ elif self.start != self.stop:
i = self.start
- step = self.step
-
- while True:
- if (step > 0 and not (self.start <= i < self.stop)) or \
- (step < 0 and not (self.stop < i <= self.start)):
- break
- yield i
- i += step
+ if n.is_infinite:
+ while True:
+ yield i
+ i += self.step
+ else:
+ for j in range(n):
+ yield i
+ i += self.step
def __len__(self):
rv = self.size
@@ -714,15 +738,15 @@ def __len__(self):
@property
def size(self):
- if not self:
+ if self.start == self.stop:
return S.Zero
dif = self.stop - self.start
- n = abs(dif // self.step)
- if not n.is_Integer:
- if n.is_infinite:
- return S.Infinity
+ n = dif/self.step
+ if n.is_infinite:
+ return S.Infinity
+ if not n.is_Integer or not all(i.is_integer for i in self.args):
raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')
- return n
+ return abs(n)
@property
def is_finite_set(self):
@@ -731,7 +755,13 @@ def is_finite_set(self):
return self.size.is_finite
def __bool__(self):
- return self.start != self.stop
+ # this only distinguishes between definite null range
+ # and non-null/unknown null; getting True doesn't mean
+ # that it actually is not null
+ b = is_eq(self.start, self.stop)
+ if b is None:
+ raise ValueError('cannot tell if Range is null or not')
+ return not bool(b)
def __getitem__(self, i):
from sympy.functions.elementary.integers import ceiling
@@ -745,6 +775,8 @@ def __getitem__(self, i):
"with an infinite value"
if isinstance(i, slice):
if self.size.is_finite: # validates, too
+ if self.start == self.stop:
+ return Range(0)
start, stop, step = i.indices(self.size)
n = ceiling((stop - start)/step)
if n <= 0:
@@ -845,44 +877,40 @@ def __getitem__(self, i):
elif start > 0:
raise ValueError(ooslice)
else:
- if not self:
+ if self.start == self.stop:
raise IndexError('Range index out of range')
+ if not (all(i.is_integer or i.is_infinite
+ for i in self.args) and ((self.stop - self.start)/
+ self.step).is_extended_positive):
+ raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')
if i == 0:
if self.start.is_infinite:
raise ValueError(ooslice)
- if self.has(Symbol):
- if (self.stop > self.start) == self.step.is_positive and self.step.is_positive is not None:
- pass
- else:
- _ = self.size # validate
return self.start
if i == -1:
if self.stop.is_infinite:
raise ValueError(ooslice)
- n = self.stop - self.step
- if n.is_Integer or (
- n.is_integer and (
- (n - self.start).is_nonnegative ==
- self.step.is_positive)):
- return n
- _ = self.size # validate
+ return self.stop - self.step
+ n = self.size # must be known for any other index
rv = (self.stop if i < 0 else self.start) + i*self.step
if rv.is_infinite:
raise ValueError(ooslice)
- if rv < self.inf or rv > self.sup:
- raise IndexError("Range index out of range")
- return rv
+ if 0 <= (rv - self.start)/self.step <= n:
+ return rv
+ raise IndexError("Range index out of range")
@property
def _inf(self):
if not self:
- raise NotImplementedError
+ return S.EmptySet.inf
if self.has(Symbol):
- if self.step.is_positive:
- return self[0]
- elif self.step.is_negative:
- return self[-1]
- _ = self.size # validate
+ if all(i.is_integer or i.is_infinite for i in self.args):
+ dif = self.stop - self.start
+ if self.step.is_positive and dif.is_positive:
+ return self.start
+ elif self.step.is_negative and dif.is_negative:
+ return self.stop - self.step
+ raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')
if self.step > 0:
return self.start
else:
@@ -891,13 +919,15 @@ def _inf(self):
@property
def _sup(self):
if not self:
- raise NotImplementedError
+ return S.EmptySet.sup
if self.has(Symbol):
- if self.step.is_positive:
- return self[-1]
- elif self.step.is_negative:
- return self[0]
- _ = self.size # validate
+ if all(i.is_integer or i.is_infinite for i in self.args):
+ dif = self.stop - self.start
+ if self.step.is_positive and dif.is_positive:
+ return self.stop - self.step
+ elif self.step.is_negative and dif.is_negative:
+ return self.start
+ raise ValueError('invalid method for symbolic range')
if self.step > 0:
return self.stop - self.step
else:
@@ -909,27 +939,37 @@ def _boundary(self):
def as_relational(self, x):
"""Rewrite a Range in terms of equalities and logic operators. """
- if self.size == 1:
- return Eq(x, self[0])
- elif self.size == 0:
- return S.false
+ from sympy.core.mod import Mod
+ if self.start.is_infinite:
+ assert not self.stop.is_infinite # by instantiation
+ a = self.reversed.start
else:
- from sympy.core.mod import Mod
- cond = None
- if self.start.is_infinite:
- if self.stop.is_infinite:
- cond = S.true
- else:
- a = self.reversed.start
- elif self.start == self.stop:
- cond = S.false # null range
- else:
- a = self.start
- step = abs(self.step)
- cond = Eq(Mod(x, step), a % step) if cond is None else cond
- return And(cond,
- x >= self.inf if self.inf in self else x > self.inf,
- x <= self.sup if self.sup in self else x < self.sup)
+ a = self.start
+ step = self.step
+ in_seq = Eq(Mod(x - a, step), 0)
+ ints = And(Eq(Mod(a, 1), 0), Eq(Mod(step, 1), 0))
+ n = (self.stop - self.start)/self.step
+ if n == 0:
+ return S.EmptySet.as_relational(x)
+ if n == 1:
+ return And(Eq(x, a), ints)
+ try:
+ a, b = self.inf, self.sup
+ except ValueError:
+ a = None
+ if a is not None:
+ range_cond = And(
+ x > a if a.is_infinite else x >= a,
+ x < b if b.is_infinite else x <= b)
+ else:
+ a, b = self.start, self.stop - self.step
+ range_cond = Or(
+ And(self.step >= 1, x > a if a.is_infinite else x >= a,
+ x < b if b.is_infinite else x <= b),
+ And(self.step <= -1, x < a if a.is_infinite else x <= a,
+ x > b if b.is_infinite else x >= b))
+ return And(in_seq, ints, range_cond)
+
converter[range] = lambda r: Range(r.start, r.stop, r.step)
diff --git a/sympy/sets/tests/test_fancysets.py b/sympy/sets/tests/test_fancysets.py
index 6b2cf51aeb2b..07d9529e9e3a 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/tests/test_fancysets.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/tests/test_fancysets.py
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
Dummy, floor, And, Eq)
from sympy.utilities.iterables import cartes
from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, raises
-from sympy.abc import x, y, t
+from sympy.abc import x, y, t, z
from sympy.core.mod import Mod
import itertools
@@ -174,8 +174,6 @@ def test_inf_Range_len():
assert Range(0, -oo, -2).size is S.Infinity
assert Range(oo, 0, -2).size is S.Infinity
assert Range(-oo, 0, 2).size is S.Infinity
- i = Symbol('i', integer=True)
- assert Range(0, 4 * i, i).size == 4
def test_Range_set():
@@ -209,6 +207,9 @@ def test_Range_set():
assert Range(1, oo, -1) == empty
assert Range(1, -oo, 1) == empty
assert Range(1, -4, oo) == empty
+ ip = symbols('ip', positive=True)
+ assert Range(0, ip, -1) == empty
+ assert Range(0, -ip, 1) == empty
assert Range(1, -4, -oo) == Range(1, 2)
assert Range(1, 4, oo) == Range(1, 2)
assert Range(-oo, oo).size == oo
@@ -231,13 +232,8 @@ def test_Range_set():
assert Range(-oo, 1, 1)[-1] is S.Zero
assert Range(oo, 1, -1)[-1] == 2
assert inf not in Range(oo)
- inf = symbols('inf', infinite=True)
- assert inf not in Range(oo)
- assert Range(-oo, 1, 1)[-1] is S.Zero
- assert Range(oo, 1, -1)[-1] == 2
assert Range(1, 10, 1)[-1] == 9
assert all(i.is_Integer for i in Range(0, -1, 1))
-
it = iter(Range(-oo, 0, 2))
raises(TypeError, lambda: next(it))
@@ -278,6 +274,7 @@ def test_Range_set():
raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(-oo, 4, 2)[2::-1])
assert Range(-oo, 4, 2)[-2::2] == Range(0, 4, 4)
assert Range(oo, 0, -2)[-10:0:2] == empty
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(oo, 0, -2)[0])
raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(oo, 0, -2)[-10:10:2])
raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(oo, 0, -2)[0::-2])
assert Range(oo, 0, -2)[0:-4:-2] == empty
@@ -297,6 +294,7 @@ def test_Range_set():
assert empty[:0] == empty
raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: empty.inf)
raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: empty.sup)
+ assert empty.as_relational(x) is S.false
AB = [None] + list(range(12))
for R in [
@@ -330,45 +328,91 @@ def test_Range_set():
# test Range.as_relational
assert Range(1, 4).as_relational(x) == (x >= 1) & (x <= 3) & Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0)
- assert Range(oo, 1, -2).as_relational(x) == (x >= 3) & (x < oo) & Eq(Mod(x, 2), 1)
+ assert Range(oo, 1, -2).as_relational(x) == (x >= 3) & (x < oo) & Eq(Mod(x + 1, -2), 0)
def test_Range_symbolic():
# symbolic Range
+ xr = Range(x, x + 4, 5)
sr = Range(x, y, t)
i = Symbol('i', integer=True)
ip = Symbol('i', integer=True, positive=True)
- ir = Range(i, i + 20, 2)
+ ipr = Range(ip)
+ inr = Range(0, -ip, -1)
+ ir = Range(i, i + 19, 2)
+ ir2 = Range(i, i*8, 3*i)
+ i = Symbol('i', integer=True)
inf = symbols('inf', infinite=True)
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(inf))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(inf, 0, -1))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(inf, inf, 1))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(1, 1, inf))
# args
+ assert xr.args == (x, x + 5, 5)
assert sr.args == (x, y, t)
assert ir.args == (i, i + 20, 2)
+ assert ir2.args == (i, 10*i, 3*i)
# reversed
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr.reversed)
raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.reversed)
- assert ir.reversed == Range(i + 18, i - 2, -2)
+ assert ipr.reversed.args == (ip - 1, -1, -1)
+ assert inr.reversed.args == (-ip + 1, 1, 1)
+ assert ir.reversed.args == (i + 18, i - 2, -2)
+ assert ir2.reversed.args == (7*i, -2*i, -3*i)
# contains
assert inf not in sr
assert inf not in ir
+ assert 0 in ipr
+ assert 0 in inr
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: 1 in ipr)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: -1 in inr)
assert .1 not in sr
assert .1 not in ir
assert i + 1 not in ir
assert i + 2 in ir
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: x in xr) # XXX is this what contains is supposed to do?
raises(TypeError, lambda: 1 in sr) # XXX is this what contains is supposed to do?
# iter
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: next(iter(xr)))
raises(ValueError, lambda: next(iter(sr)))
assert next(iter(ir)) == i
+ assert next(iter(ir2)) == i
assert sr.intersect(S.Integers) == sr
assert sr.intersect(FiniteSet(x)) == Intersection({x}, sr)
raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[:2])
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr[0])
raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[0])
- raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.as_relational(x))
# len
assert len(ir) == ir.size == 10
+ assert len(ir2) == ir2.size == 3
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: len(xr))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr.size)
raises(ValueError, lambda: len(sr))
raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.size)
# bool
- assert bool(ir) == bool(sr) == True
+ assert bool(Range(0)) == False
+ assert bool(xr)
+ assert bool(ir)
+ assert bool(ipr)
+ assert bool(inr)
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: bool(sr))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: bool(ir2))
+ # inf
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr.inf)
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.inf)
+ assert ipr.inf == 0
+ assert inr.inf == -ip + 1
+ assert ir.inf == i
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: ir2.inf)
+ # sup
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr.sup)
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.sup)
+ assert ipr.sup == ip - 1
+ assert inr.sup == 0
+ assert ir.inf == i
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: ir2.sup)
# getitem
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: xr[0])
raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[0])
raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[-1])
raises(ValueError, lambda: sr[:2])
@@ -376,17 +420,33 @@ def test_Range_symbolic():
assert ir[0] == i
assert ir[-2] == i + 16
assert ir[-1] == i + 18
+ assert ir2[:2] == Range(i, 7*i, 3*i)
+ assert ir2[0] == i
+ assert ir2[-2] == 4*i
+ assert ir2[-1] == 7*i
raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(i)[-1])
- assert Range(ip)[-1] == ip - 1
+ assert ipr[0] == ipr.inf == 0
+ assert ipr[-1] == ipr.sup == ip - 1
+ assert inr[0] == inr.sup == 0
+ assert inr[-1] == inr.inf == -ip + 1
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: ipr[-2])
assert ir.inf == i
assert ir.sup == i + 18
- assert Range(ip).inf == 0
- assert Range(ip).sup == ip - 1
raises(ValueError, lambda: Range(i).inf)
# as_relational
- raises(ValueError, lambda: sr.as_relational(x))
- assert ir.as_relational(x) == (x >= i) & (x <= i + 18) & Eq(Mod(x, 2), Mod(i, 2))
+ assert ir.as_relational(x) == ((x >= i) & (x <= i + 18) &
+ Eq(Mod(-i + x, 2), 0))
+ assert ir2.as_relational(x) == Eq(
+ Mod(-i + x, 3*i), 0) & (((x >= i) & (x <= 7*i) & (3*i >= 1)) |
+ ((x <= i) & (x >= 7*i) & (3*i <= -1)))
assert Range(i, i + 1).as_relational(x) == Eq(x, i)
+ assert sr.as_relational(z) == Eq(
+ Mod(t, 1), 0) & Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0) & Eq(Mod(-x + z, t), 0
+ ) & (((z >= x) & (z <= -t + y) & (t >= 1)) |
+ ((z <= x) & (z >= -t + y) & (t <= -1)))
+ assert xr.as_relational(z) == Eq(z, x) & Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0)
+ # symbols can clash if user wants (but it must be integer)
+ assert xr.as_relational(x) == Eq(Mod(x, 1), 0)
# contains() for symbolic values (issue #18146)
e = Symbol('e', integer=True, even=True)
o = Symbol('o', integer=True, odd=True)
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Code Refactoring / Architectural Improvement"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-21326@d19a52e
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,326
|
Fix irrational exponent case in solveset._invert_real
|
Fixes #21236
Original code would raise ValueError on 'not base.is_positive'
assuming that the only situation for this case is when the
exponent is irrational. Issue 21236 showed that this case is
reached even when exponent is a Float. Also, the 'not base.is_positive'
is invalid for three-valued logic. solveset removes assumptions before
calling invert causing 'not base.is_positive' to be True regardless.
- [x] change odd/even tests for numer and denom to be accurate for rational -- they are currently written for Rational cases. The `rational` case tests should be something like
```
numer, denom = expo.as_numer_denom()
denom.is_odd and numer.is_even # for numer % 2 == 0 case
denom.is_even and numer.is_odd # for denom % 2 == 0 case
else: # unknown
```
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* solvers
* Fixed bug in solveset
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-04-15T17:47:56Z
|
computing probability involving a weibull distribution raises ValueError
OS: Linux Ubuntu 20.04
Python: 3.9.3
SymPy: 1.7.1
```python
>>> import sympy
>>> sympy.__version__
'1.7.1'
>>> from sympy.stats import Weibull, P
>>> X = Weibull("x", 8000, 1.5)
>>> P(X <= 4000)
...
ValueError: x**w where w is irrational is not defined for negative x
```
The problem appears to be with the shape factor being a floating point value causing SymPy to interpret the value 1.5 as an irrational number. Forcing the shape factor to be Rational gives the expected result.
```python
>>> from sympy import Rational, N
>>> X = Weibull("x", 8000, Rational(3, 2))
>>> P(X <= 4000)
1 - exp(-sqrt(2)/4)
>>> N(_)
0.297811498673440
```
Working directly with the cdf also gives the expected result.
```python
>>> from sympy.stats import cdf
>>> X = Weibull("x", 8000, 1.5)
>>> cdf(X)(4000)
0.297811498673440
```
This problem does not appear in SymPy version 1.5.1.
```python
>>> import sympy
>>> sympy.__version__
'1.5.1'
>>> from sympy.stats import Weibull, P
>>> X = Weibull("x", 8000, 1.5)
>>> P(X <= 4000)
0.297811498673440
```
|
I'd like to work on this issue.
The particular issue described here could be fixed by this diff:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
index 17da5ae025..786041be5e 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
@@ -258,7 +258,7 @@ def _invert_real(f, g_ys, symbol):
else:
return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
else:
- if not base.is_positive:
+ if base.is_positive is False:
raise ValueError("x**w where w is irrational is not "
"defined for negative x")
return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
```
The problem is that in this case `base` is a `Symbol` with `real=True` and it is not known to be positive:
```python
In [1]: base = Symbol('base', real=True)
In [2]: print(base.is_positive)
None
```
The `is_positive` property is part of the core assumptions and uses three-valued logic: True, False or None with None meaning unknown. It is not usually valid to use the plain Python `not` operator with a three-valued bool because `not None` gives `True`. In this case that means that an error is raised if the `base` is not known to be positive which is probably not correct.
A simpler way to see the error is:
```python
In [13]: solveset(x**1.5, x, Reals)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError: x**w where w is irrational is not defined for negative x
```
@oscarbenjamin , as usual things are more complicated. `solveset` strips assumptions so that `base.is_positive` is always `None` no matter what the end user provides to `solveset`. While the change you propose works for the original problem, it breaks the existing test suite and does not allow for the case where `base` is explicitly non-positive.
So we're trying to rearrange
```
f(x)**w in B
```
into
```
f(x) in {real_root(b, w) where b in B}
```
where `x`, `f(x)`, `w`, are real and `B` is a subset of the Reals and `w` is irrational.
If `f(x)` is positive (for every real value of x) then that's simple. If `f(x)`.
Now consider if `f(x)` is negative for some x. We can write `f(x)` as `|f(x)| * exp(I*pi)` and hence
```
f(x)**w = |f(x)|**w * exp(I*pi)**w
```
Here `exp(I*pi)**w` can never be real if `w` is irrational because it has argument `pi*w + 2*n*pi`. That means that there can be no solutions where `f(x) < 0`.
So maybe the solution is something like
```
f(x) in {real_root(b, w), b in B} & Interval(0, oo)
```
In other words rather than raising an error we can adjoin this condition on `f(x)` to the rhs set `res`.
I think this does it:
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
index aecdb2c2cb..6c654cf708 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
@@ -257,10 +257,9 @@ def _invert_real(f, g_ys, symbol):
else:
return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
- else:
- if not base.is_positive:
- raise ValueError("x**w where w is irrational is not "
- "defined for negative x")
+ elif expo.is_irrational or expo.is_Float:
+ g_ys_pos = g_ys & Interval(0, oo)
+ res = imageset(Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo)), g_ys_pos)
return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
if not base_has_sym:
```
That gives e.g.:
```python
In [7]: solveset(x**pi-E, x, Reals)
Out[7]:
⎧ 1⎫
⎪ ─⎪
⎨ π⎬
⎪ℯ ⎪
⎩ ⎭
```
@oscarbenjamin, well not quite. What about the case when `expo=1.0`? With your proposed solution:
```python
>>> solveset(x**1.0 + 1, x, Reals)
EmptySet
>>> solveset(x**1 + 1, x, Reals)
FiniteSet(-1)
```
@oscarbenjamin, moving the `Float` case up appears to resolve the previous issue:
```diff
diff --git a/a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py b/b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
index 4eb82a9..40683a7 100644
--- a/a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
+++ b/b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
@@ -240,7 +240,7 @@ def _invert_real(f, g_ys, symbol):
if not expo_has_sym:
res = imageset(Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo)), g_ys)
- if expo.is_rational:
+ if expo.is_rational or expo.is_Float:
numer, denom = expo.as_numer_denom()
if denom % 2 == 0:
base_positive = solveset(base >= 0, symbol, S.Reals)
@@ -257,10 +257,9 @@ def _invert_real(f, g_ys, symbol):
else:
return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
- else:
- if not base.is_positive:
- raise ValueError("x**w where w is irrational is not "
- "defined for negative x")
+ elif expo.is_irrational:
+ g_ys_pos = g_ys & Interval(0, oo)
+ res = imageset(Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo)), g_ys_pos)
return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
if not base_has_sym:
```
```python
>>> solveset(x**1.0 + 1, x, Reals)
FiniteSet(-1.0)
```
@oscarbenjamin I have made your most recent suggested changes on my build and
solveset(x ** 1.0 + 1, x, Reals) -> FiniteSet(-1.0)
solveset(x ** pi-E, x, Reals) -> FiniteSet(exp(1/pi))
solveset(x ** 1.5, x, Reals) -> FiniteSet(0)
all of these tests appears to return the correct answer.
Is there anything I can do to make this change happen? This is my first issue and I'd like to make a contribution somehow. I could potentially add these tests and a few more into the regression test suite.
You can send a pull request with these changes. It would be good to have some tests for cases with either a non-trivial base or a non-trivial rhs e.g. if the rhs is always/sometimes negative or something like that. I expect that there are already tests for this somewhere so these can be added to those test functions along with a comment pointing to this issue e.g.:
```
# https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/21236
```
Alright, was testing out the fix with some less trivial functions.
@l-johnston , I've found a test that your last fix does not pass:
```
solveset(sin(x) ** 1.0, x, Reals) -> ImageSet(Lambda(_n, 2*_n*pi), Integers)
```
If we change 1.0 to an int we get:
```
solveset(sin(x) ** 1, x, Reals) -> Union(ImageSet(Lambda(_n, 2*_n*pi + pi), Integers), ImageSet(Lambda(_n, 2*_n*pi), Integers))
```
Which is the correct answer
Not sure what is happening here though.
|
[
{
"body": "OS: Linux Ubuntu 20.04\r\nPython: 3.9.3\r\nSymPy: 1.7.1\r\n\r\n```python\r\n>>> import sympy\r\n>>> sympy.__version__\r\n'1.7.1'\r\n>>> from sympy.stats import Weibull, P\r\n>>> X = Weibull(\"x\", 8000, 1.5)\r\n>>> P(X <= 4000)\r\n...\r\nValueError: x**w where w is irrational is not defined for negative x\r\n```\r\nThe problem appears to be with the shape factor being a floating point value causing SymPy to interpret the value 1.5 as an irrational number. Forcing the shape factor to be Rational gives the expected result.\r\n\r\n```python\r\n>>> from sympy import Rational, N\r\n>>> X = Weibull(\"x\", 8000, Rational(3, 2))\r\n>>> P(X <= 4000)\r\n1 - exp(-sqrt(2)/4)\r\n>>> N(_)\r\n0.297811498673440\r\n```\r\nWorking directly with the cdf also gives the expected result.\r\n\r\n```python\r\n>>> from sympy.stats import cdf\r\n>>> X = Weibull(\"x\", 8000, 1.5)\r\n>>> cdf(X)(4000)\r\n0.297811498673440\r\n```\r\n\r\nThis problem does not appear in SymPy version 1.5.1.\r\n\r\n```python\r\n>>> import sympy\r\n>>> sympy.__version__\r\n'1.5.1'\r\n>>> from sympy.stats import Weibull, P\r\n>>> X = Weibull(\"x\", 8000, 1.5)\r\n>>> P(X <= 4000)\r\n0.297811498673440\r\n```\r\n\r\n",
"number": 21236,
"title": "computing probability involving a weibull distribution raises ValueError"
}
] |
0a2f378e73f6e1f1f992aab63b2516b12439b728
|
{
"head_commit": "d19a52e01fdc6be0155a4ed3dda079a9700b842e",
"head_commit_message": "Refactor and add test",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\nindex 17da5ae0255d..bbfbb47a5494 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\n@@ -239,29 +239,27 @@ def _invert_real(f, g_ys, symbol):\n expo_has_sym = expo.has(symbol)\n \n if not expo_has_sym:\n- res = imageset(Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo)), g_ys)\n+ root = Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo))\n if expo.is_rational:\n- numer, denom = expo.as_numer_denom()\n- if denom % 2 == 0:\n+ n, d = expo.as_numer_denom()\n+ if d % 2 == 0 and n % 2 == 1 and d.is_zero is False:\n+ g_ys_pos = g_ys & Interval(0, oo)\n+ res = imageset(root, g_ys_pos)\n base_positive = solveset(base >= 0, symbol, S.Reals)\n- res = imageset(Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo)\n- ), g_ys.intersect(\n- Interval.Ropen(S.Zero, S.Infinity)))\n _inv, _set = _invert_real(base, res, symbol)\n return (_inv, _set.intersect(base_positive))\n-\n- elif numer % 2 == 0:\n- n = Dummy('n')\n- neg_res = imageset(Lambda(n, -n), res)\n- return _invert_real(base, res + neg_res, symbol)\n-\n- else:\n- return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)\n- else:\n- if not base.is_positive:\n- raise ValueError(\"x**w where w is irrational is not \"\n- \"defined for negative x\")\n+ if n % 2 == 0 and d % 2 == 1:\n+ res = imageset(root, g_ys)\n+ n = Dummy(\"n\")\n+ neg_res = imageset(Lambda(n, -n), res)\n+ return _invert_real(base, res + neg_res, symbol)\n+ return _invert_real(base, imageset(root, g_ys), symbol)\n+ if expo.is_irrational:\n+ g_ys_pos = g_ys & Interval(0, oo)\n+ res = imageset(root, g_ys_pos)\n return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)\n+ # indeterminate exponent, e.g. Float\n+ return (f, g_ys)\n \n if not base_has_sym:\n rhs = g_ys.args[0]\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\nindex b30d370c383c..97befcded6d7 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\n@@ -92,7 +92,13 @@ def ireal(x, s=S.Reals):\n assert invert_real(x**S.Half, y, x) == (x, FiniteSet(y**2))\n \n raises(ValueError, lambda: invert_real(x, x, x))\n- raises(ValueError, lambda: invert_real(x**pi, y, x))\n+\n+ # issue 21236\n+ assert invert_real(x**pi, y, x) == (x, FiniteSet(y**(1/pi)))\n+ assert invert_real(x**pi, -E, x) == (x, EmptySet())\n+ assert invert_real(x**Rational(3/2), 1000, x) == (x, FiniteSet(100))\n+ assert invert_real(x**1.0, 1, x) == (x**1.0, FiniteSet(1))\n+\n raises(ValueError, lambda: invert_real(S.One, y, x))\n \n assert invert_real(x**31 + x, y, x) == (x**31 + x, FiniteSet(y))\n@@ -2811,3 +2817,7 @@ def test_substitution_with_infeasible_solution():\n (0, Complement(FiniteSet(p01), FiniteSet(0)), 0, p11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -l2*p11/p01, -l3*p11/p01, l2, l3),\n )\n assert sol != nonlinsolve(system, solvefor)\n+\n+def test_issue_21236():\n+ x, y, z = symbols(\"x y z\")\n+ assert solveset(x**y - z, x, S.Reals) == ConditionSet(x, Eq(x**y - z, 0), S.Reals)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2811,3 +2817,7 @@ def test_substitution_with_infeasible_solution():\n (0, Complement(FiniteSet(p01), FiniteSet(0)), 0, p11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -l2*p11/p01, -l3*p11/p01, l2, l3),\n )\n assert sol != nonlinsolve(system, solvefor)\n+\n+def test_issue_21236():\n+ x, y, z = symbols(\"x y z\")",
"line": null,
"original_line": 2822,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n x, z = symbols(\"x z\")\r\n y = symbols('y', rational=True)\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2811,3 +2817,7 @@ def test_substitution_with_infeasible_solution():\n (0, Complement(FiniteSet(p01), FiniteSet(0)), 0, p11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -l2*p11/p01, -l3*p11/p01, l2, l3),\n )\n assert sol != nonlinsolve(system, solvefor)\n+\n+def test_issue_21236():\n+ x, y, z = symbols(\"x y z\")\n+ assert solveset(x**y - z, x, S.Reals) == ConditionSet(x, Eq(x**y - z, 0), S.Reals)",
"line": 2827,
"original_line": 2823,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n assert solveset(x**y - z, x, S.Reals) == ConditionSet(x, Eq(x**y - z, 0), S.Reals)\r\n e1, e2 = symbols('e1 e2', even=True)\r\n y = e1/e2 # don't know if num or den will be odd and the other even\r\n assert solveset(x**y - z, x, S.Reals) == ConditionSet(x, Eq(x**y - z, 0), S.Reals)\r\n```"
}
] |
2c1a01652547c31ca7eaff81753178ffd5bab8ce
|
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
index 17da5ae0255d..f02b58af8043 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
@@ -239,30 +239,38 @@ def _invert_real(f, g_ys, symbol):
expo_has_sym = expo.has(symbol)
if not expo_has_sym:
- res = imageset(Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo)), g_ys)
+
if expo.is_rational:
- numer, denom = expo.as_numer_denom()
- if denom % 2 == 0:
+ num, den = expo.as_numer_denom()
+
+ if den % 2 == 0 and num % 2 == 1 and den.is_zero is False:
+ root = Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo))
+ g_ys_pos = g_ys & Interval(0, oo)
+ res = imageset(root, g_ys_pos)
base_positive = solveset(base >= 0, symbol, S.Reals)
- res = imageset(Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo)
- ), g_ys.intersect(
- Interval.Ropen(S.Zero, S.Infinity)))
_inv, _set = _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
return (_inv, _set.intersect(base_positive))
- elif numer % 2 == 0:
- n = Dummy('n')
+ if den % 2 == 1:
+ root = Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo))
+ res = imageset(root, g_ys)
+ if num % 2 == 0:
neg_res = imageset(Lambda(n, -n), res)
return _invert_real(base, res + neg_res, symbol)
+ if num % 2 == 1:
+ return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
- else:
- return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
- else:
- if not base.is_positive:
- raise ValueError("x**w where w is irrational is not "
- "defined for negative x")
+ elif expo.is_irrational:
+ root = Lambda(n, real_root(n, expo))
+ g_ys_pos = g_ys & Interval(0, oo)
+ res = imageset(root, g_ys_pos)
return _invert_real(base, res, symbol)
+ else:
+ # indeterminate exponent, e.g. Float or parity of
+ # num, den of rational could not be determined
+ pass # use default return
+
if not base_has_sym:
rhs = g_ys.args[0]
if base.is_positive:
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
index b30d370c383c..3a137b87ef2a 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
@@ -92,7 +92,13 @@ def ireal(x, s=S.Reals):
assert invert_real(x**S.Half, y, x) == (x, FiniteSet(y**2))
raises(ValueError, lambda: invert_real(x, x, x))
- raises(ValueError, lambda: invert_real(x**pi, y, x))
+
+ # issue 21236
+ assert invert_real(x**pi, y, x) == (x, FiniteSet(y**(1/pi)))
+ assert invert_real(x**pi, -E, x) == (x, EmptySet())
+ assert invert_real(x**Rational(3/2), 1000, x) == (x, FiniteSet(100))
+ assert invert_real(x**1.0, 1, x) == (x**1.0, FiniteSet(1))
+
raises(ValueError, lambda: invert_real(S.One, y, x))
assert invert_real(x**31 + x, y, x) == (x**31 + x, FiniteSet(y))
@@ -2811,3 +2817,11 @@ def test_substitution_with_infeasible_solution():
(0, Complement(FiniteSet(p01), FiniteSet(0)), 0, p11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -l2*p11/p01, -l3*p11/p01, l2, l3),
)
assert sol != nonlinsolve(system, solvefor)
+
+def test_issue_21236():
+ x, z = symbols("x z")
+ y = symbols('y', rational=True)
+ assert solveset(x**y - z, x, S.Reals) == ConditionSet(x, Eq(x**y - z, 0), S.Reals)
+ e1, e2 = symbols('e1 e2', even=True)
+ y = e1/e2 # don't know if num or den will be odd and the other even
+ assert solveset(x**y - z, x, S.Reals) == ConditionSet(x, Eq(x**y - z, 0), S.Reals)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21279@1c3b514
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,279
|
feat(assumptions): reorganize facts for new assumptions
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #21228
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
* `Q.positive_infinite()` and `Q.negative_infinite()` predicates are introduced.
* `Q.extended_positive()`, `Q.extended_negative()`, `Q.extended_nonzero()`, `Q.extended_nonpositive()`, and `Q.extended_nonnegative()` predicates are introduced.
* `Q.positive()` and `Q.negative()` now correctly implies the argument being finite.
* Incorrect results from `Q.hermitian()` and `Q.antihermitian()` are fixed.
* In order to reduce the complexity of sat solver, some predicates are now decomposed into a combination of primitive predicates.
* Facts are now defined in `assumptions/facts.py`, instead of in `assumptions/ask.py`.
#### Other comments
Benchmark showed no slowdown.
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* assumptions
* `Q.positive_infinite()` and `Q.negative_infinite()` predicates are introduced.
* `Q.extended_positive()`, `Q.extended_negative()`, `Q.extended_nonzero()`, `Q.extended_nonpositive()`, and `Q.extended_nonnegative()` predicates are introduced.
* `Q.positive()` and `Q.negative()` now correctly implies the argument being finite.
* Incorrect results from `Q.hermitian()` and `Q.antihermitian()` are fixed.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-04-09T15:38:42Z
|
Incorrect assumption for is_hermitian
An object being antihermitian implies it being not hermitian in new assumption system. (and vice versa)
```python
>>> ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.antihermitian(x))
False
```
But in old assumptions system, it does not.
```python
>>> x = Symbol('x', antihermitian=True)
>>> print(x.is_hermitian)
None
```
Is this an error of core/assumptions module?
|
A matrix or operator can be neither hermitian nor antihermitian so that's a bug in the new assumptions.
I don't think that hermitian/antihermitian should be part of the old assumptions.
It is true that an operator being not hermitian does not mean that it is antihermitian. But doesn't an operator ***being hermitian*** means that it is ***not antihermitian***?
The zero operator is an operator which is hermitian and antihermitian, and it is the only such operator (unless the characteristic of the ground field is 2).
Hence this is an error and `None` would be the correct output. Maybe there should be a `nonzero` assumption for operators.
It would also make sense to introduce `positive` and `negative` assumptions for operators etc.
Thanks. Didn't notice that!
|
[
{
"body": "An object being antihermitian implies it being not hermitian in new assumption system. (and vice versa)\r\n\r\n```python\r\n>>> ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.antihermitian(x))\r\nFalse\r\n```\r\n\r\nBut in old assumptions system, it does not.\r\n\r\n```python\r\n>>> x = Symbol('x', antihermitian=True)\r\n>>> print(x.is_hermitian)\r\nNone\r\n```\r\n\r\nIs this an error of core/assumptions module?",
"number": 21228,
"title": "Incorrect assumption for is_hermitian"
}
] |
e4e840ca8e83c0e206a8bf17525a6490d89665d4
|
{
"head_commit": "1c3b514896cb2720b261b73687fedc7e1f4c9dc1",
"head_commit_message": "feat(assumptions) : reorganize new assumption fact\n\nFix test_known_facts_consistent()",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/bin/ask_update.py b/bin/ask_update.py\nindex 97d0485b3682..345d0e4759e8 100755\n--- a/bin/ask_update.py\n+++ b/bin/ask_update.py\n@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@\n if os.path.isdir(sympy_dir):\n sys.path.insert(0, sympy_top)\n \n-from sympy.assumptions.ask import (compute_known_facts,\n+from sympy.assumptions.facts import (compute_known_facts,\n get_known_facts, get_known_facts_keys)\n \n with open('sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py', 'w') as f:\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/ask.py b/sympy/assumptions/ask.py\nindex 8e2f85ec2ba1..2069eba52327 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/ask.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/ask.py\n@@ -4,10 +4,9 @@\n AppliedPredicate)\n from sympy.assumptions.cnf import CNF, EncodedCNF, Literal\n from sympy.core import sympify\n-from sympy.core.cache import cacheit\n from sympy.core.kind import BooleanKind\n from sympy.core.relational import Eq, Ne, Gt, Lt, Ge, Le\n-from sympy.logic.boolalg import (to_cnf, And, Not, Implies, Equivalent)\n+from sympy.logic.boolalg import Not\n from sympy.logic.inference import satisfiable\n from sympy.utilities.decorator import memoize_property\n from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning\n@@ -91,9 +90,19 @@ def finite(self):\n \n @memoize_property\n def infinite(self):\n- from .predicates.calculus import InfinitePredicate\n+ from .handlers.calculus import InfinitePredicate\n return InfinitePredicate()\n \n+ @memoize_property\n+ def positive_infinite(self):\n+ from .handlers.calculus import PositiveInfinitePredicate\n+ return PositiveInfinitePredicate()\n+\n+ @memoize_property\n+ def negative_infinite(self):\n+ from .handlers.calculus import NegativeInfinitePredicate\n+ return NegativeInfinitePredicate()\n+\n @memoize_property\n def positive(self):\n from .handlers.order import PositivePredicate\n@@ -109,6 +118,16 @@ def zero(self):\n from .handlers.order import ZeroPredicate\n return ZeroPredicate()\n \n+ @memoize_property\n+ def extended_positive(self):\n+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedPositivePredicate\n+ return ExtendedPositivePredicate()\n+\n+ @memoize_property\n+ def extended_negative(self):\n+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedNegativePredicate\n+ return ExtendedNegativePredicate()\n+\n @memoize_property\n def nonzero(self):\n from .handlers.order import NonZeroPredicate\n@@ -124,6 +143,21 @@ def nonnegative(self):\n from .handlers.order import NonNegativePredicate\n return NonNegativePredicate()\n \n+ @memoize_property\n+ def extended_nonzero(self):\n+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedNonZeroPredicate\n+ return ExtendedNonZeroPredicate()\n+\n+ @memoize_property\n+ def extended_nonpositive(self):\n+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedNonPositivePredicate\n+ return ExtendedNonPositivePredicate()\n+\n+ @memoize_property\n+ def extended_nonnegative(self):\n+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedNonNegativePredicate\n+ return ExtendedNonNegativePredicate()\n+\n @memoize_property\n def even(self):\n from .handlers.ntheory import EvenPredicate\n@@ -407,16 +441,14 @@ def ask(proposition, assumptions=True, context=global_assumptions):\n key, args = Q.is_true, (proposition,)\n \n # convert local and global assumptions to CNF\n- assump = CNF.from_prop(assumptions)\n- assump.extend(context)\n+ assump_cnf = CNF.from_prop(assumptions)\n+ assump_cnf.extend(context)\n \n # extract the relevant facts from assumptions with respect to args\n- local_facts = _extract_all_facts(assump, args)\n-\n- known_facts_cnf = get_all_known_facts()\n- known_facts_dict = get_known_facts_dict()\n+ local_facts = _extract_all_facts(assump_cnf, args)\n \n # convert default facts and assumed facts to encoded CNF\n+ known_facts_cnf = get_all_known_facts()\n enc_cnf = EncodedCNF()\n enc_cnf.from_cnf(CNF(known_facts_cnf))\n enc_cnf.add_from_cnf(local_facts)\n@@ -425,10 +457,11 @@ def ask(proposition, assumptions=True, context=global_assumptions):\n if local_facts.clauses and satisfiable(enc_cnf) is False:\n raise ValueError(\"inconsistent assumptions %s\" % assumptions)\n \n+ known_facts_dict = get_known_facts_dict()\n if local_facts.clauses:\n \n # quick exit if the prerequisite of proposition is not true\n- # e.g. proposition = Q.odd(x), assumptions = ~Q.integer(x)\n+ # e.g. proposition = Q.zero(x), assumptions = ~Q.even(x)\n if len(local_facts.clauses) == 1:\n cl, = local_facts.clauses\n if len(cl) == 1:\n@@ -444,7 +477,7 @@ def ask(proposition, assumptions=True, context=global_assumptions):\n pass\n elif key in fdict:\n # quick exit if proposition is directly satisfied by assumption\n- # e.g. proposition = Q.integer(x), assumptions = Q.odd(x)\n+ # e.g. proposition = Q.even(x), assumptions = Q.zero(x)\n return True\n elif Not(key) in fdict:\n # quick exit if proposition is directly rejected by assumption\n@@ -457,23 +490,12 @@ def ask(proposition, assumptions=True, context=global_assumptions):\n res = key(*args)._eval_ask(assumptions)\n if res is not None:\n return bool(res)\n+\n # using satask (still costly)\n res = satask(proposition, assumptions=assumptions, context=context)\n return res\n \n \n-def ask_full_inference(proposition, assumptions, known_facts_cnf):\n- \"\"\"\n- Method for inferring properties about objects.\n-\n- \"\"\"\n- if not satisfiable(And(known_facts_cnf, assumptions, proposition)):\n- return False\n- if not satisfiable(And(known_facts_cnf, assumptions, Not(proposition))):\n- return True\n- return None\n-\n-\n def register_handler(key, handler):\n \"\"\"\n Register a handler in the ask system. key must be a string and handler a\n@@ -517,148 +539,5 @@ def remove_handler(key, handler):\n getattr(Q, key).remove_handler(handler)\n \n \n-def single_fact_lookup(known_facts_keys, known_facts_cnf):\n- # Compute the quick lookup for single facts\n- mapping = {}\n- for key in known_facts_keys:\n- mapping[key] = {key}\n- for other_key in known_facts_keys:\n- if other_key != key:\n- if ask_full_inference(other_key, key, known_facts_cnf):\n- mapping[key].add(other_key)\n- return mapping\n-\n-\n-def compute_known_facts(known_facts, known_facts_keys):\n- \"\"\"Compute the various forms of knowledge compilation used by the\n- assumptions system.\n-\n- Explanation\n- ===========\n-\n- This function is typically applied to the results of the ``get_known_facts``\n- and ``get_known_facts_keys`` functions defined at the bottom of\n- this file.\n- \"\"\"\n- from textwrap import dedent, wrap\n-\n- fact_string = dedent('''\\\n- \"\"\"\n- The contents of this file are the return value of\n- ``sympy.assumptions.ask.compute_known_facts``.\n-\n- Do NOT manually edit this file.\n- Instead, run ./bin/ask_update.py.\n- \"\"\"\n-\n- from sympy.core.cache import cacheit\n- from sympy.logic.boolalg import And\n- from sympy.assumptions.cnf import Literal\n- from sympy.assumptions.ask import Q\n-\n- # -{ Known facts as a set }-\n- @cacheit\n- def get_all_known_facts():\n- return {\n- %s\n- }\n-\n- # -{ Known facts in Conjunctive Normal Form }-\n- @cacheit\n- def get_known_facts_cnf():\n- return And(\n- %s\n- )\n-\n- # -{ Known facts in compressed sets }-\n- @cacheit\n- def get_known_facts_dict():\n- return {\n- %s\n- }\n- ''')\n- # Compute the known facts in CNF form for logical inference\n- LINE = \",\\n \"\n- HANG = ' '*8\n- cnf = to_cnf(known_facts)\n- cnf_ = CNF.to_CNF(known_facts)\n- c = LINE.join([str(a) for a in cnf.args])\n-\n- p = LINE.join(sorted(['frozenset((' + ', '.join(str(lit) for lit in sorted(clause, key=str)) +'))' for clause in cnf_.clauses]))\n- mapping = single_fact_lookup(known_facts_keys, cnf)\n- items = sorted(mapping.items(), key=str)\n- keys = [str(i[0]) for i in items]\n- values = ['set(%s)' % sorted(i[1], key=str) for i in items]\n- m = LINE.join(['\\n'.join(\n- wrap(\"{}: {}\".format(k, v),\n- subsequent_indent=HANG,\n- break_long_words=False))\n- for k, v in zip(keys, values)]) + ','\n- return fact_string % (p, c, m)\n-\n-@cacheit\n-def get_known_facts_keys():\n- return [\n- getattr(Q, attr)\n- for attr in Q.__class__.__dict__\n- if not attr.startswith('__')]\n-\n-@cacheit\n-def get_known_facts():\n- return And(\n- Implies(Q.infinite, ~Q.finite),\n- Implies(Q.real, Q.complex),\n- Implies(Q.real, Q.hermitian),\n- Equivalent(Q.extended_real, Q.real | Q.infinite),\n- Equivalent(Q.even | Q.odd, Q.integer),\n- Implies(Q.even, ~Q.odd),\n- Implies(Q.prime, Q.integer & Q.positive & ~Q.composite),\n- Implies(Q.integer, Q.rational),\n- Implies(Q.rational, Q.algebraic),\n- Implies(Q.algebraic, Q.complex),\n- Implies(Q.algebraic, Q.finite),\n- Equivalent(Q.transcendental | Q.algebraic, Q.complex & Q.finite),\n- Implies(Q.transcendental, ~Q.algebraic),\n- Implies(Q.transcendental, Q.finite),\n- Implies(Q.imaginary, Q.complex & ~Q.real),\n- Implies(Q.imaginary, Q.antihermitian),\n- Implies(Q.antihermitian, ~Q.hermitian),\n- Equivalent(Q.irrational | Q.rational, Q.real & Q.finite),\n- Implies(Q.irrational, ~Q.rational),\n- Implies(Q.zero, Q.even),\n-\n- Equivalent(Q.real, Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive),\n- Implies(Q.zero, ~Q.negative & ~Q.positive),\n- Implies(Q.negative, ~Q.positive),\n- Equivalent(Q.nonnegative, Q.zero | Q.positive),\n- Equivalent(Q.nonpositive, Q.zero | Q.negative),\n- Equivalent(Q.nonzero, Q.negative | Q.positive),\n-\n- Implies(Q.orthogonal, Q.positive_definite),\n- Implies(Q.orthogonal, Q.unitary),\n- Implies(Q.unitary & Q.real, Q.orthogonal),\n- Implies(Q.unitary, Q.normal),\n- Implies(Q.unitary, Q.invertible),\n- Implies(Q.normal, Q.square),\n- Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.normal),\n- Implies(Q.positive_definite, Q.invertible),\n- Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.upper_triangular),\n- Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.lower_triangular),\n- Implies(Q.lower_triangular, Q.triangular),\n- Implies(Q.upper_triangular, Q.triangular),\n- Implies(Q.triangular, Q.upper_triangular | Q.lower_triangular),\n- Implies(Q.upper_triangular & Q.lower_triangular, Q.diagonal),\n- Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.symmetric),\n- Implies(Q.unit_triangular, Q.triangular),\n- Implies(Q.invertible, Q.fullrank),\n- Implies(Q.invertible, Q.square),\n- Implies(Q.symmetric, Q.square),\n- Implies(Q.fullrank & Q.square, Q.invertible),\n- Equivalent(Q.invertible, ~Q.singular),\n- Implies(Q.integer_elements, Q.real_elements),\n- Implies(Q.real_elements, Q.complex_elements),\n- )\n-\n-\n from sympy.assumptions.ask_generated import (\n get_known_facts_dict, get_all_known_facts)\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py b/sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py\nindex 1eb45b4cd9b2..536757a223b8 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py\n@@ -15,75 +15,68 @@\n @cacheit\n def get_all_known_facts():\n return {\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.complex, True), Literal(Q.finite, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.rational, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, True), Literal(Q.complex, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.transcendental, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, True), Literal(Q.finite, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.antihermitian, False), Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.antihermitian, False), Literal(Q.imaginary, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.antihermitian, True), Literal(Q.hermitian, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.complex, False), Literal(Q.imaginary, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.complex, False), Literal(Q.real, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.complex, False), Literal(Q.transcendental, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.commutative, False), Literal(Q.finite, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.commutative, False), Literal(Q.infinite, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.complex_elements, False), Literal(Q.real_elements, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.composite, False), Literal(Q.even, True), Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.prime, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.composite, True), Literal(Q.even, False), Literal(Q.odd, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.composite, True), Literal(Q.positive, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.composite, True), Literal(Q.prime, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, False), Literal(Q.lower_triangular, True), Literal(Q.upper_triangular, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, True), Literal(Q.lower_triangular, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, True), Literal(Q.normal, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, True), Literal(Q.symmetric, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, True), Literal(Q.upper_triangular, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.even, False), Literal(Q.integer, True), Literal(Q.odd, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.even, False), Literal(Q.odd, False), Literal(Q.prime, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.even, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.even, True), Literal(Q.integer, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.even, True), Literal(Q.odd, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.extended_real, False), Literal(Q.infinite, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.extended_real, False), Literal(Q.real, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.extended_real, True), Literal(Q.infinite, False), Literal(Q.real, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, False), Literal(Q.irrational, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, False), Literal(Q.rational, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.even, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, False), Literal(Q.transcendental, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, True), Literal(Q.infinite, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, True), Literal(Q.irrational, False), Literal(Q.rational, False), Literal(Q.real, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.fullrank, False), Literal(Q.invertible, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.fullrank, True), Literal(Q.invertible, False), Literal(Q.square, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.real, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.real, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.integer, False), Literal(Q.odd, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.integer, False), Literal(Q.prime, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.integer, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.negative, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.positive, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.negative, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.positive, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.infinite, False), Literal(Q.negative_infinite, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.infinite, False), Literal(Q.positive_infinite, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.integer_elements, True), Literal(Q.real_elements, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, False), Literal(Q.positive_definite, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, False), Literal(Q.singular, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, False), Literal(Q.unitary, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, True), Literal(Q.singular, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, True), Literal(Q.square, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, False), Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, False), Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, False), Literal(Q.rational, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, True), Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.zero, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, True), Literal(Q.rational, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, True), Literal(Q.real, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.lower_triangular, False), Literal(Q.triangular, True), Literal(Q.upper_triangular, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.lower_triangular, True), Literal(Q.triangular, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.nonpositive, True), Literal(Q.zero, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.nonzero, True), Literal(Q.positive, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.real, True), Literal(Q.zero, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.nonpositive, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.nonzero, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.rational, True), Literal(Q.zero, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.positive, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.real, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonnegative, False), Literal(Q.positive, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonnegative, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonnegative, True), Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.zero, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonpositive, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonzero, False), Literal(Q.positive, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.negative_infinite, True), Literal(Q.positive_infinite, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.normal, False), Literal(Q.unitary, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.normal, True), Literal(Q.square, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.orthogonal, False), Literal(Q.real, True), Literal(Q.unitary, True))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.odd, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),\n+ frozenset((Literal(Q.orthogonal, False), Literal(Q.real_elements, True), Literal(Q.unitary, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.orthogonal, True), Literal(Q.positive_definite, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.orthogonal, True), Literal(Q.unitary, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.prime, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.real, False))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.rational, True), Literal(Q.real, False))),\n- frozenset((Literal(Q.real, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.square, False), Literal(Q.symmetric, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.triangular, False), Literal(Q.unit_triangular, True))),\n frozenset((Literal(Q.triangular, False), Literal(Q.upper_triangular, True)))\n@@ -96,43 +89,29 @@ def get_known_facts_cnf():\n Q.invertible | Q.singular,\n Q.algebraic | ~Q.rational,\n Q.antihermitian | ~Q.imaginary,\n+ Q.commutative | ~Q.finite,\n+ Q.commutative | ~Q.infinite,\n Q.complex_elements | ~Q.real_elements,\n- Q.complex | ~Q.algebraic,\n- Q.complex | ~Q.imaginary,\n- Q.complex | ~Q.real,\n- Q.complex | ~Q.transcendental,\n Q.even | ~Q.zero,\n- Q.extended_real | ~Q.infinite,\n- Q.extended_real | ~Q.real,\n Q.finite | ~Q.algebraic,\n- Q.finite | ~Q.irrational,\n- Q.finite | ~Q.rational,\n Q.finite | ~Q.transcendental,\n Q.fullrank | ~Q.invertible,\n- Q.hermitian | ~Q.real,\n- Q.integer | ~Q.even,\n- Q.integer | ~Q.odd,\n- Q.integer | ~Q.prime,\n+ Q.hermitian | ~Q.negative,\n+ Q.hermitian | ~Q.positive,\n+ Q.hermitian | ~Q.zero,\n+ Q.infinite | ~Q.negative_infinite,\n+ Q.infinite | ~Q.positive_infinite,\n Q.invertible | ~Q.positive_definite,\n Q.invertible | ~Q.unitary,\n Q.lower_triangular | ~Q.diagonal,\n- Q.nonnegative | ~Q.positive,\n- Q.nonnegative | ~Q.zero,\n- Q.nonpositive | ~Q.negative,\n- Q.nonpositive | ~Q.zero,\n- Q.nonzero | ~Q.negative,\n- Q.nonzero | ~Q.positive,\n Q.normal | ~Q.diagonal,\n Q.normal | ~Q.unitary,\n Q.positive_definite | ~Q.orthogonal,\n+ Q.positive | ~Q.composite,\n Q.positive | ~Q.prime,\n- Q.rational | ~Q.integer,\n+ Q.rational | ~Q.even,\n+ Q.rational | ~Q.odd,\n Q.real_elements | ~Q.integer_elements,\n- Q.real | ~Q.irrational,\n- Q.real | ~Q.negative,\n- Q.real | ~Q.positive,\n- Q.real | ~Q.rational,\n- Q.real | ~Q.zero,\n Q.square | ~Q.invertible,\n Q.square | ~Q.normal,\n Q.square | ~Q.symmetric,\n@@ -143,99 +122,98 @@ def get_known_facts_cnf():\n Q.unitary | ~Q.orthogonal,\n Q.upper_triangular | ~Q.diagonal,\n ~Q.algebraic | ~Q.transcendental,\n- ~Q.antihermitian | ~Q.hermitian,\n ~Q.composite | ~Q.prime,\n ~Q.even | ~Q.odd,\n ~Q.finite | ~Q.infinite,\n- ~Q.imaginary | ~Q.real,\n+ ~Q.imaginary | ~Q.negative,\n+ ~Q.imaginary | ~Q.positive,\n+ ~Q.imaginary | ~Q.zero,\n ~Q.invertible | ~Q.singular,\n ~Q.irrational | ~Q.rational,\n+ ~Q.negative_infinite | ~Q.positive_infinite,\n ~Q.negative | ~Q.positive,\n ~Q.negative | ~Q.zero,\n ~Q.positive | ~Q.zero,\n- Q.even | Q.odd | ~Q.integer,\n- Q.infinite | Q.real | ~Q.extended_real,\n+ Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.imaginary,\n+ Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.negative,\n+ Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.positive,\n+ Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.zero,\n+ Q.antihermitian | Q.hermitian | ~Q.zero,\n+ Q.even | Q.odd | ~Q.composite,\n+ Q.even | Q.odd | ~Q.prime,\n+ Q.irrational | Q.rational | ~Q.negative,\n+ Q.irrational | Q.rational | ~Q.positive,\n+ Q.irrational | Q.rational | ~Q.zero,\n Q.lower_triangular | Q.upper_triangular | ~Q.triangular,\n- Q.negative | Q.positive | ~Q.nonzero,\n- Q.negative | Q.zero | ~Q.nonpositive,\n- Q.positive | Q.zero | ~Q.nonnegative,\n Q.diagonal | ~Q.lower_triangular | ~Q.upper_triangular,\n Q.invertible | ~Q.fullrank | ~Q.square,\n- Q.orthogonal | ~Q.real | ~Q.unitary,\n- Q.negative | Q.positive | Q.zero | ~Q.real,\n- Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.complex | ~Q.finite,\n- Q.irrational | Q.rational | ~Q.finite | ~Q.real\n+ Q.orthogonal | ~Q.real_elements | ~Q.unitary,\n+ Q.negative | Q.positive | Q.zero | ~Q.irrational,\n+ Q.negative | Q.positive | Q.zero | ~Q.rational,\n+ Q.composite | Q.prime | ~Q.even | ~Q.positive\n )\n \n # -{ Known facts in compressed sets }-\n+# This dictionary means that if a key is True, every item in its value is True.\n @cacheit\n def get_known_facts_dict():\n return {\n- Q.algebraic: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.finite]),\n+ Q.algebraic: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.finite]),\n Q.antihermitian: set([Q.antihermitian]),\n Q.commutative: set([Q.commutative]),\n- Q.complex: set([Q.complex]),\n Q.complex_elements: set([Q.complex_elements]),\n- Q.composite: set([Q.composite]),\n+ Q.composite: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.composite, Q.finite,\n+ Q.hermitian, Q.positive, Q.rational]),\n Q.diagonal: set([Q.diagonal, Q.lower_triangular, Q.normal, Q.square,\n Q.symmetric, Q.triangular, Q.upper_triangular]),\n Q.eq: set([Q.eq]),\n- Q.even: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.even, Q.extended_real,\n- Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.rational, Q.real]),\n- Q.extended_real: set([Q.extended_real]),\n- Q.finite: set([Q.finite]),\n+ Q.even: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.even, Q.finite,\n+ Q.hermitian, Q.rational]),\n+ Q.finite: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite]),\n Q.fullrank: set([Q.fullrank]),\n Q.ge: set([Q.ge]),\n Q.gt: set([Q.gt]),\n Q.hermitian: set([Q.hermitian]),\n- Q.imaginary: set([Q.antihermitian, Q.complex, Q.imaginary]),\n- Q.infinite: set([Q.extended_real, Q.infinite]),\n- Q.integer: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite,\n- Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.rational, Q.real]),\n+ Q.imaginary: set([Q.antihermitian, Q.commutative, Q.finite,\n+ Q.imaginary]),\n+ Q.infinite: set([Q.commutative, Q.infinite]),\n Q.integer_elements: set([Q.complex_elements, Q.integer_elements,\n Q.real_elements]),\n Q.invertible: set([Q.fullrank, Q.invertible, Q.square]),\n- Q.irrational: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite, Q.hermitian,\n- Q.irrational, Q.nonzero, Q.real]),\n+ Q.irrational: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian,\n+ Q.irrational]),\n Q.is_true: set([Q.is_true]),\n Q.le: set([Q.le]),\n Q.lower_triangular: set([Q.lower_triangular, Q.triangular]),\n Q.lt: set([Q.lt]),\n Q.ne: set([Q.ne]),\n- Q.negative: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian, Q.negative,\n- Q.nonpositive, Q.nonzero, Q.real]),\n- Q.nonnegative: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian,\n- Q.nonnegative, Q.real]),\n- Q.nonpositive: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian,\n- Q.nonpositive, Q.real]),\n- Q.nonzero: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian, Q.nonzero,\n- Q.real]),\n+ Q.negative: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.negative]),\n+ Q.negative_infinite: set([Q.commutative, Q.infinite,\n+ Q.negative_infinite]),\n Q.normal: set([Q.normal, Q.square]),\n- Q.odd: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite,\n- Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.nonzero, Q.odd, Q.rational, Q.real]),\n+ Q.odd: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.odd,\n+ Q.rational]),\n Q.orthogonal: set([Q.fullrank, Q.invertible, Q.normal, Q.orthogonal,\n Q.positive_definite, Q.square, Q.unitary]),\n- Q.positive: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian,\n- Q.nonnegative, Q.nonzero, Q.positive, Q.real]),\n+ Q.positive: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.positive]),\n Q.positive_definite: set([Q.fullrank, Q.invertible,\n Q.positive_definite, Q.square]),\n- Q.prime: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite,\n- Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.nonnegative, Q.nonzero, Q.positive,\n- Q.prime, Q.rational, Q.real]),\n- Q.rational: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite,\n- Q.hermitian, Q.rational, Q.real]),\n- Q.real: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian, Q.real]),\n+ Q.positive_infinite: set([Q.commutative, Q.infinite,\n+ Q.positive_infinite]),\n+ Q.prime: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian,\n+ Q.positive, Q.prime, Q.rational]),\n+ Q.rational: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian,\n+ Q.rational]),\n Q.real_elements: set([Q.complex_elements, Q.real_elements]),\n Q.singular: set([Q.singular]),\n Q.square: set([Q.square]),\n Q.symmetric: set([Q.square, Q.symmetric]),\n- Q.transcendental: set([Q.complex, Q.finite, Q.transcendental]),\n+ Q.transcendental: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.transcendental]),\n Q.triangular: set([Q.triangular]),\n Q.unit_triangular: set([Q.triangular, Q.unit_triangular]),\n Q.unitary: set([Q.fullrank, Q.invertible, Q.normal, Q.square,\n Q.unitary]),\n Q.upper_triangular: set([Q.triangular, Q.upper_triangular]),\n- Q.zero: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.even, Q.extended_real,\n- Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.nonnegative,\n- Q.nonpositive, Q.rational, Q.real, Q.zero]),\n+ Q.zero: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.even, Q.finite,\n+ Q.hermitian, Q.rational, Q.zero]),\n }\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/cnf.py b/sympy/assumptions/cnf.py\nindex f5fb466d5768..f957f03fc52e 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/cnf.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/cnf.py\n@@ -143,7 +143,27 @@ def to_NNF(expr):\n \"\"\"\n Generates the Negation Normal Form of any boolean expression in terms\n of AND, OR, and Literal objects.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import Q\n+ >>> from sympy.assumptions.cnf import to_NNF\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n+ >>> expr = Q.even(x) & ~Q.positive(x)\n+ >>> to_NNF(expr)\n+ (Literal(Q.even(x), False) & Literal(Q.positive(x), True))\n+\n+ ``to_NNF`` decomposes the predicate into a combination of primitive\n+ predicates if possible.\n+\n+ >>> to_NNF(Q.nonpositive)\n+ (Literal(Q.negative, False) | Literal(Q.zero, False))\n+ >>> to_NNF(Q.nonpositive(x))\n+ (Literal(Q.negative(x), False) | Literal(Q.zero(x), False))\n \"\"\"\n+ from sympy.assumptions.assume import AppliedPredicate, Predicate\n+ from sympy.assumptions.facts import get_composite_predicates\n \n if isinstance(expr, Not):\n arg = expr.args[0]\n@@ -200,8 +220,20 @@ def to_NNF(expr):\n R = to_NNF(expr.args[2])\n return AND(OR(~L, M), OR(L, R))\n \n- else:\n- return Literal(expr)\n+ if isinstance(expr, AppliedPredicate):\n+ comp_dct = get_composite_predicates()\n+ pred, args = expr.function, expr.arguments\n+ newpred = comp_dct.get(pred, None)\n+ if newpred is not None:\n+ return to_NNF(newpred.rcall(*args))\n+\n+ if isinstance(expr, Predicate):\n+ comp_dct = get_composite_predicates()\n+ newpred = comp_dct.get(expr, None)\n+ if newpred is not None:\n+ return to_NNF(newpred)\n+\n+ return Literal(expr)\n \n \n def distribute_AND_over_OR(expr):\n@@ -238,7 +270,9 @@ class CNF:\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> cnf = CNF.from_prop(Q.real(x) & ~Q.zero(x))\n >>> cnf.clauses\n- {frozenset({Literal(Q.real(x), False)}), frozenset({Literal(Q.zero(x), True)})}\n+ {frozenset({Literal(Q.zero(x), True)}),\n+ frozenset({Literal(Q.negative(x), False),\n+ Literal(Q.positive(x), False), Literal(Q.zero(x), False)})}\n \"\"\"\n def __init__(self, clauses=None):\n if not clauses:\n@@ -318,8 +352,6 @@ def rcall(self, expr):\n expr = AND(*clause_list)\n return distribute_AND_over_OR(expr)\n \n-\n-\n @classmethod\n def all_or(cls, *cnfs):\n b = cnfs[0].copy()\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/facts.py b/sympy/assumptions/facts.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..3fd3d7ed247d\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/facts.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@\n+\"\"\"\n+Known facts in assumptions module.\n+\n+This module defines the facts in ``get_known_facts()``, and supports functions\n+to generate the contents in ``sympy.assumptions.ask_generated`` file.\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+from sympy.core.cache import cacheit\n+from sympy.assumptions import Q\n+from sympy.assumptions.cnf import CNF\n+from sympy.logic.boolalg import (to_cnf, And, Not, Implies, Equivalent)\n+from sympy.logic.inference import satisfiable\n+\n+\n+@cacheit\n+def get_composite_predicates():\n+ # To reduce the complexity of sat solver, these predicates never goes into facts\n+ # but are transformed into the combination of primitive predicates.\n+ return {\n+ Q.real : Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive,\n+ Q.integer : Q.even | Q.odd,\n+ Q.nonpositive : Q.negative | Q.zero,\n+ Q.nonzero : Q.negative | Q.positive,\n+ Q.nonnegative : Q.zero | Q.positive,\n+ Q.extended_real : Q.negative_infinite | Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive | Q.positive_infinite,\n+ Q.extended_positive: Q.positive | Q.positive_infinite,\n+ Q.extended_negative: Q.negative | Q.negative_infinite,\n+ Q.extended_nonzero: Q.negative_infinite | Q.negative | Q.positive | Q.positive_infinite,\n+ Q.extended_nonpositive: Q.negative_infinite | Q.negative | Q.zero,\n+ Q.extended_nonnegative: Q.zero | Q.positive | Q.positive_infinite,\n+ Q.complex : Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental\n+ }\n+\n+\n+@cacheit\n+def get_known_facts():\n+ # We build the facts starting with primitive predicates.\n+ # DO NOT include the predicates in get_composite_predicates()'s keys here!\n+ return And(\n+\n+ # primitive predicates exclude each other\n+ Implies(Q.negative_infinite, ~Q.positive_infinite),\n+ Implies(Q.negative, ~Q.zero & ~Q.positive),\n+ Implies(Q.positive, ~Q.zero),\n+\n+ # build real line and complex plane\n+ Implies(Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive, ~Q.imaginary),\n+ Implies(Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive | Q.imaginary, Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental),\n+\n+ # other subsets of complex\n+ Implies(Q.transcendental, ~Q.algebraic),\n+ Implies(Q.irrational, ~Q.rational),\n+ Equivalent(Q.rational | Q.irrational, Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive),\n+ Implies(Q.rational, Q.algebraic),\n+\n+ # integers\n+ Implies(Q.even, ~Q.odd),\n+ Implies(Q.even | Q.odd, Q.rational),\n+ Implies(Q.zero, Q.even),\n+ Implies(Q.composite, ~Q.prime),\n+ Implies(Q.composite | Q.prime, (Q.even | Q.odd) & Q.positive),\n+ Implies(Q.even & Q.positive & ~Q.prime, Q.composite),\n+\n+ # hermitian and antihermitian\n+ Implies(Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive, Q.hermitian),\n+ Implies(Q.imaginary, Q.antihermitian),\n+ Implies(Q.zero, Q.hermitian | Q.antihermitian),\n+\n+ # define finity and infinity, and build extended real line\n+ Implies(Q.infinite, ~Q.finite),\n+ Implies(Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental, Q.finite),\n+ Implies(Q.negative_infinite | Q.positive_infinite, Q.infinite),\n+\n+ # commutativity\n+ Implies(Q.finite | Q.infinite, Q.commutative),\n+\n+ # matrices\n+ Implies(Q.orthogonal, Q.positive_definite),\n+ Implies(Q.orthogonal, Q.unitary),\n+ Implies(Q.unitary & Q.real_elements, Q.orthogonal),\n+ Implies(Q.unitary, Q.normal),\n+ Implies(Q.unitary, Q.invertible),\n+ Implies(Q.normal, Q.square),\n+ Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.normal),\n+ Implies(Q.positive_definite, Q.invertible),\n+ Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.upper_triangular),\n+ Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.lower_triangular),\n+ Implies(Q.lower_triangular, Q.triangular),\n+ Implies(Q.upper_triangular, Q.triangular),\n+ Implies(Q.triangular, Q.upper_triangular | Q.lower_triangular),\n+ Implies(Q.upper_triangular & Q.lower_triangular, Q.diagonal),\n+ Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.symmetric),\n+ Implies(Q.unit_triangular, Q.triangular),\n+ Implies(Q.invertible, Q.fullrank),\n+ Implies(Q.invertible, Q.square),\n+ Implies(Q.symmetric, Q.square),\n+ Implies(Q.fullrank & Q.square, Q.invertible),\n+ Equivalent(Q.invertible, ~Q.singular),\n+ Implies(Q.integer_elements, Q.real_elements),\n+ Implies(Q.real_elements, Q.complex_elements),\n+ )\n+\n+\n+@cacheit\n+def get_known_facts_keys():\n+ result = []\n+ exclude = get_composite_predicates()\n+ for attr in Q.__class__.__dict__:\n+ if attr.startswith('__'):\n+ continue\n+ pred = getattr(Q, attr)\n+ if pred in exclude:\n+ continue\n+ result.append(pred)\n+ return result\n+\n+\n+def compute_known_facts(known_facts, known_facts_keys):\n+ \"\"\"Compute the various forms of knowledge compilation used by the\n+ assumptions system.\n+\n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n+ This function is typically applied to the results of the ``get_known_facts``\n+ and ``get_known_facts_keys`` functions defined at the bottom of\n+ this file.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ from textwrap import dedent, wrap\n+\n+ fact_string = dedent('''\\\n+ \"\"\"\n+ The contents of this file are the return value of\n+ ``sympy.assumptions.ask.compute_known_facts``.\n+\n+ Do NOT manually edit this file.\n+ Instead, run ./bin/ask_update.py.\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ from sympy.core.cache import cacheit\n+ from sympy.logic.boolalg import And\n+ from sympy.assumptions.cnf import Literal\n+ from sympy.assumptions.ask import Q\n+\n+ # -{ Known facts as a set }-\n+ @cacheit\n+ def get_all_known_facts():\n+ return {\n+ %s\n+ }\n+\n+ # -{ Known facts in Conjunctive Normal Form }-\n+ @cacheit\n+ def get_known_facts_cnf():\n+ return And(\n+ %s\n+ )\n+\n+ # -{ Known facts in compressed sets }-\n+ # This dictionary means that if a key is True, every item in its value is True.\n+ @cacheit\n+ def get_known_facts_dict():\n+ return {\n+ %s\n+ }\n+ ''')\n+ # Compute the known facts in CNF form for logical inference\n+ LINE = \",\\n \"\n+ HANG = ' '*8\n+ cnf = to_cnf(known_facts)\n+ cnf_ = CNF.to_CNF(known_facts)\n+ c = LINE.join([str(a) for a in cnf.args])\n+\n+ p = LINE.join(sorted(['frozenset((' + ', '.join(str(lit) for lit in sorted(clause, key=str)) +'))' for clause in cnf_.clauses]))\n+ mapping = single_fact_lookup(known_facts_keys, cnf)\n+ items = sorted(mapping.items(), key=str)\n+ keys = [str(i[0]) for i in items]\n+ values = ['set(%s)' % sorted(i[1], key=str) for i in items]\n+ m = LINE.join(['\\n'.join(\n+ wrap(\"{}: {}\".format(k, v),\n+ subsequent_indent=HANG,\n+ break_long_words=False))\n+ for k, v in zip(keys, values)]) + ','\n+ return fact_string % (p, c, m)\n+\n+\n+def single_fact_lookup(known_facts_keys, known_facts_cnf):\n+ # Compute the quick lookup for single facts\n+ mapping = {}\n+ for key in known_facts_keys:\n+ mapping[key] = {key}\n+ for other_key in known_facts_keys:\n+ if other_key != key:\n+ if ask_full_inference(other_key, key, known_facts_cnf):\n+ mapping[key].add(other_key)\n+ return mapping\n+\n+\n+def ask_full_inference(proposition, assumptions, known_facts_cnf):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Method for inferring properties about objects.\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if not satisfiable(And(known_facts_cnf, assumptions, proposition)):\n+ return False\n+ if not satisfiable(And(known_facts_cnf, assumptions, Not(proposition))):\n+ return True\n+ return None\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py\nindex 4ae13d71a80d..71293b58afe5 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py\n@@ -10,7 +10,8 @@\n from sympy.functions import cos, exp, log, sign, sin\n from sympy.logic.boolalg import conjuncts\n \n-from ..predicates.calculus import FinitePredicate, InfinitePredicate\n+from ..predicates.calculus import (FinitePredicate, InfinitePredicate,\n+ PositiveInfinitePredicate, NegativeInfinitePredicate)\n \n \n # FinitePredicate\n@@ -95,7 +96,7 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):\n _bounded = ask(Q.finite(arg), assumptions)\n if _bounded:\n continue\n- s = ask(Q.positive(arg), assumptions)\n+ s = ask(Q.extended_positive(arg), assumptions)\n # if there has been more than one sign or if the sign of this arg\n # is None and Bounded is None or there was already\n # an unknown sign, return None\n@@ -228,3 +229,29 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):\n @InfinitePredicate.register_many(ComplexInfinity, Infinity, NegativeInfinity)\n def _(expr, assumptions):\n return True\n+\n+\n+# PositiveInfinitePredicate\n+\n+\[email protected](Infinity)\n+def _(expr, assumptions):\n+ return True\n+\n+\[email protected]_many(NegativeInfinity, ComplexInfinity)\n+def _(expr, assumptions):\n+ return False\n+\n+\n+# NegativeInfinitePredicate\n+\n+\[email protected](NegativeInfinity)\n+def _(expr, assumptions):\n+ return True\n+\n+\[email protected]_many(Infinity, ComplexInfinity)\n+def _(expr, assumptions):\n+ return False\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/order.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/order.py\nindex 7b3bc758974c..6f2581e606a3 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/order.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/order.py\n@@ -13,7 +13,10 @@\n from sympy.multipledispatch import MDNotImplementedError\n \n from ..predicates.order import (NegativePredicate, NonNegativePredicate,\n- NonZeroPredicate, ZeroPredicate, NonPositivePredicate, PositivePredicate)\n+ NonZeroPredicate, ZeroPredicate, NonPositivePredicate, PositivePredicate,\n+ ExtendedNegativePredicate, ExtendedNonNegativePredicate,\n+ ExtendedNonPositivePredicate, ExtendedNonZeroPredicate,\n+ ExtendedPositivePredicate,)\n \n \n # NegativePredicate\n@@ -392,3 +395,44 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):\n @PositivePredicate.register(NaN)\n def _(expr, assumptions):\n return None\n+\n+\n+# ExtendedNegativePredicate\n+\[email protected](object)\n+def _(expr, assumptions):\n+ return ask(Q.negative(expr) | Q.negative_infinite(expr), assumptions)\n+\n+\n+# ExtendedPositivePredicate\n+\[email protected](object)\n+def _(expr, assumptions):\n+ return ask(Q.positive(expr) | Q.positive_infinite(expr), assumptions)\n+\n+\n+# ExtendedNonZeroPredicate\n+\[email protected](object)\n+def _(expr, assumptions):\n+ return ask(\n+ Q.negative_infinite(expr) | Q.negative(expr) | Q.positive(expr) | Q.positive_infinite(expr),\n+ assumptions)\n+\n+\n+# ExtendedNonPositivePredicate\n+\[email protected](object)\n+def _(expr, assumptions):\n+ return ask(\n+ Q.negative_infinite(expr) | Q.negative(expr) | Q.zero(expr),\n+ assumptions)\n+\n+\n+# ExtendedNonNegativePredicate\n+\[email protected](object)\n+def _(expr, assumptions):\n+ return ask(\n+ Q.zero(expr) | Q.positive(expr) | Q.positive_infinite(expr),\n+ assumptions)\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/sets.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/sets.py\nindex bc1487960cf6..8911bc0f1d95 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/sets.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/sets.py\n@@ -638,6 +638,8 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):\n def _(expr, assumptions):\n if isinstance(expr, MatrixBase):\n return None\n+ if ask(Q.zero(expr), assumptions):\n+ return True\n return ask(Q.imaginary(expr), assumptions)\n \n @AntihermitianPredicate.register(Add)\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/predicates/calculus.py b/sympy/assumptions/predicates/calculus.py\nindex d0ad129bef48..f30070378868 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/predicates/calculus.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/predicates/calculus.py\n@@ -27,8 +27,8 @@ class FinitePredicate(Predicate):\n True\n >>> ask(Q.finite(2 + 3*I))\n True\n- >>> print(ask(Q.finite(x), Q.positive(x)))\n- None\n+ >>> ask(Q.finite(x), Q.positive(x))\n+ True\n >>> print(ask(Q.finite(S.NaN)))\n None\n \n@@ -60,3 +60,23 @@ class InfinitePredicate(Predicate):\n \"InfiniteHandler\",\n doc=\"\"\"Handler for Q.infinite key.\"\"\"\n )\n+\n+\n+class PositiveInfinitePredicate(Predicate):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Positive infinity predicate.\n+\n+ ``Q.positive_infinite(x)`` is true iff ``x`` is positive infinity ``oo``.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ name = 'positive_infinite'\n+ handler = Dispatcher(\"PositiveInfiniteHandler\")\n+\n+\n+class NegativeInfinitePredicate(Predicate):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Negative infinity predicate.\n+\n+ ``Q.negative_infinite(x)`` is true iff ``x`` is negative infinity ``-oo``.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ name = 'negative_infinite'\n+ handler = Dispatcher(\"NegativeInfiniteHandler\")\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/predicates/order.py b/sympy/assumptions/predicates/order.py\nindex e183ecc8d57d..372eda329325 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/predicates/order.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/predicates/order.py\n@@ -254,3 +254,137 @@ class PositivePredicate(Predicate):\n doc=(\"Handler for key 'positive'. Test that an expression is strictly\"\n \" greater than zero.\")\n )\n+\n+\n+class ExtendedPositivePredicate(Predicate):\n+ r\"\"\"\n+ Positive extended real number predicate.\n+\n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n+ ``Q.extended_positive(x)`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and\n+ `x > 0`, that is if ``x`` is in the interval `(0, \\infty]`.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_positive(1))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_positive(oo))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_positive(I))\n+ False\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ name = 'extended_positive'\n+ handler = Dispatcher(\"ExtendedPositiveHandler\")\n+\n+\n+class ExtendedNegativePredicate(Predicate):\n+ r\"\"\"\n+ Negative extended real number predicate.\n+\n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n+ ``Q.extended_negative(x)`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and\n+ `x < 0`, that is if ``x`` is in the interval `[-\\infty, 0)`.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_negative(-1))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_negative(-oo))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_negative(-I))\n+ False\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ name = 'extended_negative'\n+ handler = Dispatcher(\"ExtendedNegativeHandler\")\n+\n+\n+class ExtendedNonZeroPredicate(Predicate):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Nonzero extended real number predicate.\n+\n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n+ ``ask(Q.extended_nonzero(x))`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and\n+ ``x`` is not zero.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonzero(-1))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonzero(oo))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonzero(I))\n+ False\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ name = 'extended_nonzero'\n+ handler = Dispatcher(\"ExtendedNonZeroHandler\")\n+\n+\n+class ExtendedNonPositivePredicate(Predicate):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Nonpositive extended real number predicate.\n+\n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n+ ``ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(x))`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and\n+ ``x`` is not positive.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(-1))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(oo))\n+ False\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(0))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(I))\n+ False\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ name = 'extended_nonpositive'\n+ handler = Dispatcher(\"ExtendedNonPositiveHandler\")\n+\n+\n+class ExtendedNonNegativePredicate(Predicate):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Nonnegative extended real number predicate.\n+\n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n+ ``ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(x))`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and\n+ ``x`` is not negative.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(-1))\n+ False\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(oo))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(0))\n+ True\n+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(I))\n+ False\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ name = 'extended_nonnegative'\n+ handler = Dispatcher(\"ExtendedNonNegativeHandler\")\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_query.py b/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_query.py\nindex 4e010cca0b20..2189ef93c557 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_query.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_query.py\n@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@\n from sympy.assumptions import (ask, AssumptionsContext, Q, register_handler,\n remove_handler)\n from sympy.assumptions.assume import assuming, global_assumptions, Predicate\n-from sympy.assumptions.ask import compute_known_facts, single_fact_lookup\n+from sympy.assumptions.facts import compute_known_facts, single_fact_lookup\n from sympy.assumptions.handlers import AskHandler\n from sympy.core.add import Add\n from sympy.core.numbers import (I, Integer, Rational, oo, zoo, pi)\n@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ def test_zero_0():\n assert ask(Q.prime(z)) is False\n assert ask(Q.composite(z)) is False\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(z)) is True\n- assert ask(Q.antihermitian(z)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(z)) is True\n \n \n def test_negativeone():\n@@ -176,7 +176,7 @@ def test_infinity():\n assert ask(Q.irrational(oo)) is False\n assert ask(Q.imaginary(oo)) is False\n assert ask(Q.positive(oo)) is False\n- #assert ask(Q.extended_positive(oo)) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.extended_positive(oo)) is True\n assert ask(Q.negative(oo)) is False\n assert ask(Q.even(oo)) is False\n assert ask(Q.odd(oo)) is False\n@@ -186,6 +186,8 @@ def test_infinity():\n assert ask(Q.composite(oo)) is False\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(oo)) is False\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(oo)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.positive_infinite(oo)) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.negative_infinite(oo)) is False\n \n \n def test_neg_infinity():\n@@ -201,7 +203,7 @@ def test_neg_infinity():\n assert ask(Q.imaginary(mm)) is False\n assert ask(Q.positive(mm)) is False\n assert ask(Q.negative(mm)) is False\n- #assert ask(Q.extended_negative(mm)) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.extended_negative(mm)) is True\n assert ask(Q.even(mm)) is False\n assert ask(Q.odd(mm)) is False\n assert ask(Q.finite(mm)) is False\n@@ -210,6 +212,8 @@ def test_neg_infinity():\n assert ask(Q.composite(mm)) is False\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(mm)) is False\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(mm)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.positive_infinite(-oo)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.negative_infinite(-oo)) is True\n \n \n def test_complex_infinity():\n@@ -234,6 +238,8 @@ def test_complex_infinity():\n assert ask(Q.composite(zoo)) is False\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(zoo)) is False\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(zoo)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.positive_infinite(zoo)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.negative_infinite(zoo)) is False\n \n \n def test_nan():\n@@ -595,13 +601,13 @@ def test_I():\n assert ask(Q.real(z)) is True\n \n \n-\n+@XFAIL # definition for boundedness fixed! will be changed in next commit\n def test_bounded():\n x, y, z = symbols('x,y,z')\n assert ask(Q.finite(x)) is None\n assert ask(Q.finite(x), Q.finite(x)) is True\n assert ask(Q.finite(x), Q.finite(y)) is None\n- assert ask(Q.finite(x), Q.complex(x)) is None\n+ assert ask(Q.finite(x), Q.complex(x)) is True\n \n assert ask(Q.finite(x + 1)) is None\n assert ask(Q.finite(x + 1), Q.finite(x)) is True\n@@ -610,7 +616,7 @@ def test_bounded():\n # B + B\n assert ask(Q.finite(a), Q.finite(x) & Q.finite(y)) is True\n assert ask(\n- Q.finite(a), Q.finite(x) & Q.finite(y) & Q.positive(x)) is True\n+ Q.finite(a), Q.positive(x) & Q.finite(y)) is True\n assert ask(\n Q.finite(a), Q.finite(x) & Q.finite(y) & Q.positive(y)) is True\n assert ask(Q.finite(a),\n@@ -1354,12 +1360,13 @@ def test_rational():\n \n def test_hermitian():\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x)) is None\n- assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.antihermitian(x)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.antihermitian(x)) is None\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.imaginary(x)) is False\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.prime(x)) is True\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.real(x)) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.zero(x)) is True\n \n- assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.antihermitian(x)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.antihermitian(x)) is None\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.complex(x)) is None\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.hermitian(x)) is True\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.imaginary(x)) is False\n@@ -1373,9 +1380,9 @@ def test_hermitian():\n Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.antihermitian(y)) is None\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None\n assert ask(\n- Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is False\n+ Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is None\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is None\n- assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.real(y)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.real(y)) is None\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is True\n assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is False\n@@ -1410,12 +1417,13 @@ def test_hermitian():\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.complex(x)) is None\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.hermitian(x)) is None\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.imaginary(x)) is False\n- assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.real(x)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.real(x)) is None\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.antihermitian(x)) is True\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.complex(x)) is None\n- assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.hermitian(x)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.hermitian(x)) is None\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.imaginary(x)) is True\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.real(x)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x), Q.zero(x)) is True\n \n assert ask(\n Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.antihermitian(y)\n@@ -1423,7 +1431,7 @@ def test_hermitian():\n assert ask(\n Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None\n assert ask(\n- Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is False\n+ Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is None\n assert ask(\n Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is True\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.real(y)\n@@ -1432,13 +1440,13 @@ def test_hermitian():\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)\n ) is None\n assert ask(\n- Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is False\n+ Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is None\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.real(y)) is None\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.imaginary(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.imaginary(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is True\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.imaginary(x) & Q.real(y)) is False\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.real(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None\n- assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.real(x) & Q.real(y)) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.real(x) & Q.real(y)) is None\n \n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(I*x), Q.real(x)) is True\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(I*x), Q.antihermitian(x)) is False\n@@ -1446,7 +1454,7 @@ def test_hermitian():\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x*y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.real(y)) is True\n \n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y + z),\n- Q.real(x) & Q.real(y) & Q.real(z)) is False\n+ Q.real(x) & Q.real(y) & Q.real(z)) is None\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y + z),\n Q.real(x) & Q.real(y) & Q.imaginary(z)) is None\n assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y + z),\n@@ -2130,7 +2138,7 @@ def test_compute_known_facts():\n @slow\n def test_known_facts_consistent():\n \"\"\"\"Test that ask_generated.py is up-to-date\"\"\"\n- from sympy.assumptions.ask import get_known_facts, get_known_facts_keys\n+ from sympy.assumptions.facts import get_known_facts, get_known_facts_keys\n from os.path import abspath, dirname, join\n filename = join(dirname(dirname(abspath(__file__))), 'ask_generated.py')\n with open(filename) as f:\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py\nindex 6ce543c84f1d..8066fd527e3e 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py\n@@ -96,7 +96,6 @@ def _test_args(obj):\n \n def test_sympy__assumptions__assume__AppliedPredicate():\n from sympy.assumptions.assume import AppliedPredicate, Predicate\n- from sympy import Q\n assert _test_args(AppliedPredicate(Predicate(\"test\"), 2))\n assert _test_args(Q.is_true(True))\n \n@@ -105,8 +104,10 @@ def test_sympy__assumptions__assume__Predicate():\n pass\n \n def test_predicates():\n- from sympy.assumptions.ask import get_known_facts_keys\n- predicates = get_known_facts_keys()\n+ predicates = [\n+ getattr(Q, attr)\n+ for attr in Q.__class__.__dict__\n+ if not attr.startswith('__')]\n for p in predicates:\n assert _test_args(p)\n \n@@ -123,38 +124,31 @@ def test_sympy__assumptions__relation__binrel__AppliedBinaryRelation():\n \n def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__UnevaluatedOnFree():\n from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import UnevaluatedOnFree\n- from sympy import Q\n assert _test_args(UnevaluatedOnFree(Q.positive))\n \n def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__AllArgs():\n from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import AllArgs\n- from sympy import Q\n assert _test_args(AllArgs(Q.positive))\n \n def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__AnyArgs():\n from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import AnyArgs\n- from sympy import Q\n assert _test_args(AnyArgs(Q.positive))\n \n def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__ExactlyOneArg():\n from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import ExactlyOneArg\n- from sympy import Q\n assert _test_args(ExactlyOneArg(Q.positive))\n \n def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__CheckOldAssump():\n from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import CheckOldAssump\n- from sympy import Q\n assert _test_args(CheckOldAssump(Q.positive))\n \n def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__CheckIsPrime():\n from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import CheckIsPrime\n- from sympy import Q\n # Input must be a number\n assert _test_args(CheckIsPrime(Q.positive))\n \n def test_sympy__assumptions__wrapper__AssumptionsWrapper():\n from sympy.assumptions.wrapper import AssumptionsWrapper\n- from sympy import Q\n assert _test_args(AssumptionsWrapper(x, Q.positive(x)))\n \n \n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -143,7 +143,27 @@ def to_NNF(expr):\n \"\"\"\n Generates the Negation Normal Form of any boolean expression in terms\n of AND, OR, and Literal objects.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import Q\n+ >>> from sympy.assumptions.cnf import to_NNF\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n+ >>> expr = Q.even(x) & ~Q.positive(x)\n+ >>> to_NNF(expr)\n+ (Literal(Q.even(x), False) & Literal(Q.positive(x), True))\n+\n+ ``to_NNF`` decomposes the predicate into a combination of primitive\n+ predicates if possible.",
"line": null,
"original_line": 158,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/assumptions/cnf.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIt doesn't seem like this belongs as part of the `to_NNF` function.\n\n@author:\nDo you mean that predicate decomposition should be done by some other function?\n\n@user1:\nIt just seems messy to me to do it as part of this function which has a clearly defined purpose: take a logical expression and convert it to NNF (without applying any interpretation to the meaning of the literals).\n\n@author:\nWhat about giving keyword argument `decompose=True/False` to this function?\n\n@user1:\nPerhaps it could take a `composite_map` argument or something like that.\n\n@author:\nDone."
}
] |
d9eb7850ad8eac45df07113de6b5347a80481f6e
|
diff --git a/bin/ask_update.py b/bin/ask_update.py
index 97d0485b3682..345d0e4759e8 100755
--- a/bin/ask_update.py
+++ b/bin/ask_update.py
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@
if os.path.isdir(sympy_dir):
sys.path.insert(0, sympy_top)
-from sympy.assumptions.ask import (compute_known_facts,
+from sympy.assumptions.facts import (compute_known_facts,
get_known_facts, get_known_facts_keys)
with open('sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py', 'w') as f:
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/ask.py b/sympy/assumptions/ask.py
index 8e2f85ec2ba1..2069eba52327 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/ask.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/ask.py
@@ -4,10 +4,9 @@
AppliedPredicate)
from sympy.assumptions.cnf import CNF, EncodedCNF, Literal
from sympy.core import sympify
-from sympy.core.cache import cacheit
from sympy.core.kind import BooleanKind
from sympy.core.relational import Eq, Ne, Gt, Lt, Ge, Le
-from sympy.logic.boolalg import (to_cnf, And, Not, Implies, Equivalent)
+from sympy.logic.boolalg import Not
from sympy.logic.inference import satisfiable
from sympy.utilities.decorator import memoize_property
from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning
@@ -91,9 +90,19 @@ def finite(self):
@memoize_property
def infinite(self):
- from .predicates.calculus import InfinitePredicate
+ from .handlers.calculus import InfinitePredicate
return InfinitePredicate()
+ @memoize_property
+ def positive_infinite(self):
+ from .handlers.calculus import PositiveInfinitePredicate
+ return PositiveInfinitePredicate()
+
+ @memoize_property
+ def negative_infinite(self):
+ from .handlers.calculus import NegativeInfinitePredicate
+ return NegativeInfinitePredicate()
+
@memoize_property
def positive(self):
from .handlers.order import PositivePredicate
@@ -109,6 +118,16 @@ def zero(self):
from .handlers.order import ZeroPredicate
return ZeroPredicate()
+ @memoize_property
+ def extended_positive(self):
+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedPositivePredicate
+ return ExtendedPositivePredicate()
+
+ @memoize_property
+ def extended_negative(self):
+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedNegativePredicate
+ return ExtendedNegativePredicate()
+
@memoize_property
def nonzero(self):
from .handlers.order import NonZeroPredicate
@@ -124,6 +143,21 @@ def nonnegative(self):
from .handlers.order import NonNegativePredicate
return NonNegativePredicate()
+ @memoize_property
+ def extended_nonzero(self):
+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedNonZeroPredicate
+ return ExtendedNonZeroPredicate()
+
+ @memoize_property
+ def extended_nonpositive(self):
+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedNonPositivePredicate
+ return ExtendedNonPositivePredicate()
+
+ @memoize_property
+ def extended_nonnegative(self):
+ from .handlers.order import ExtendedNonNegativePredicate
+ return ExtendedNonNegativePredicate()
+
@memoize_property
def even(self):
from .handlers.ntheory import EvenPredicate
@@ -407,16 +441,14 @@ def ask(proposition, assumptions=True, context=global_assumptions):
key, args = Q.is_true, (proposition,)
# convert local and global assumptions to CNF
- assump = CNF.from_prop(assumptions)
- assump.extend(context)
+ assump_cnf = CNF.from_prop(assumptions)
+ assump_cnf.extend(context)
# extract the relevant facts from assumptions with respect to args
- local_facts = _extract_all_facts(assump, args)
-
- known_facts_cnf = get_all_known_facts()
- known_facts_dict = get_known_facts_dict()
+ local_facts = _extract_all_facts(assump_cnf, args)
# convert default facts and assumed facts to encoded CNF
+ known_facts_cnf = get_all_known_facts()
enc_cnf = EncodedCNF()
enc_cnf.from_cnf(CNF(known_facts_cnf))
enc_cnf.add_from_cnf(local_facts)
@@ -425,10 +457,11 @@ def ask(proposition, assumptions=True, context=global_assumptions):
if local_facts.clauses and satisfiable(enc_cnf) is False:
raise ValueError("inconsistent assumptions %s" % assumptions)
+ known_facts_dict = get_known_facts_dict()
if local_facts.clauses:
# quick exit if the prerequisite of proposition is not true
- # e.g. proposition = Q.odd(x), assumptions = ~Q.integer(x)
+ # e.g. proposition = Q.zero(x), assumptions = ~Q.even(x)
if len(local_facts.clauses) == 1:
cl, = local_facts.clauses
if len(cl) == 1:
@@ -444,7 +477,7 @@ def ask(proposition, assumptions=True, context=global_assumptions):
pass
elif key in fdict:
# quick exit if proposition is directly satisfied by assumption
- # e.g. proposition = Q.integer(x), assumptions = Q.odd(x)
+ # e.g. proposition = Q.even(x), assumptions = Q.zero(x)
return True
elif Not(key) in fdict:
# quick exit if proposition is directly rejected by assumption
@@ -457,23 +490,12 @@ def ask(proposition, assumptions=True, context=global_assumptions):
res = key(*args)._eval_ask(assumptions)
if res is not None:
return bool(res)
+
# using satask (still costly)
res = satask(proposition, assumptions=assumptions, context=context)
return res
-def ask_full_inference(proposition, assumptions, known_facts_cnf):
- """
- Method for inferring properties about objects.
-
- """
- if not satisfiable(And(known_facts_cnf, assumptions, proposition)):
- return False
- if not satisfiable(And(known_facts_cnf, assumptions, Not(proposition))):
- return True
- return None
-
-
def register_handler(key, handler):
"""
Register a handler in the ask system. key must be a string and handler a
@@ -517,148 +539,5 @@ def remove_handler(key, handler):
getattr(Q, key).remove_handler(handler)
-def single_fact_lookup(known_facts_keys, known_facts_cnf):
- # Compute the quick lookup for single facts
- mapping = {}
- for key in known_facts_keys:
- mapping[key] = {key}
- for other_key in known_facts_keys:
- if other_key != key:
- if ask_full_inference(other_key, key, known_facts_cnf):
- mapping[key].add(other_key)
- return mapping
-
-
-def compute_known_facts(known_facts, known_facts_keys):
- """Compute the various forms of knowledge compilation used by the
- assumptions system.
-
- Explanation
- ===========
-
- This function is typically applied to the results of the ``get_known_facts``
- and ``get_known_facts_keys`` functions defined at the bottom of
- this file.
- """
- from textwrap import dedent, wrap
-
- fact_string = dedent('''\
- """
- The contents of this file are the return value of
- ``sympy.assumptions.ask.compute_known_facts``.
-
- Do NOT manually edit this file.
- Instead, run ./bin/ask_update.py.
- """
-
- from sympy.core.cache import cacheit
- from sympy.logic.boolalg import And
- from sympy.assumptions.cnf import Literal
- from sympy.assumptions.ask import Q
-
- # -{ Known facts as a set }-
- @cacheit
- def get_all_known_facts():
- return {
- %s
- }
-
- # -{ Known facts in Conjunctive Normal Form }-
- @cacheit
- def get_known_facts_cnf():
- return And(
- %s
- )
-
- # -{ Known facts in compressed sets }-
- @cacheit
- def get_known_facts_dict():
- return {
- %s
- }
- ''')
- # Compute the known facts in CNF form for logical inference
- LINE = ",\n "
- HANG = ' '*8
- cnf = to_cnf(known_facts)
- cnf_ = CNF.to_CNF(known_facts)
- c = LINE.join([str(a) for a in cnf.args])
-
- p = LINE.join(sorted(['frozenset((' + ', '.join(str(lit) for lit in sorted(clause, key=str)) +'))' for clause in cnf_.clauses]))
- mapping = single_fact_lookup(known_facts_keys, cnf)
- items = sorted(mapping.items(), key=str)
- keys = [str(i[0]) for i in items]
- values = ['set(%s)' % sorted(i[1], key=str) for i in items]
- m = LINE.join(['\n'.join(
- wrap("{}: {}".format(k, v),
- subsequent_indent=HANG,
- break_long_words=False))
- for k, v in zip(keys, values)]) + ','
- return fact_string % (p, c, m)
-
-@cacheit
-def get_known_facts_keys():
- return [
- getattr(Q, attr)
- for attr in Q.__class__.__dict__
- if not attr.startswith('__')]
-
-@cacheit
-def get_known_facts():
- return And(
- Implies(Q.infinite, ~Q.finite),
- Implies(Q.real, Q.complex),
- Implies(Q.real, Q.hermitian),
- Equivalent(Q.extended_real, Q.real | Q.infinite),
- Equivalent(Q.even | Q.odd, Q.integer),
- Implies(Q.even, ~Q.odd),
- Implies(Q.prime, Q.integer & Q.positive & ~Q.composite),
- Implies(Q.integer, Q.rational),
- Implies(Q.rational, Q.algebraic),
- Implies(Q.algebraic, Q.complex),
- Implies(Q.algebraic, Q.finite),
- Equivalent(Q.transcendental | Q.algebraic, Q.complex & Q.finite),
- Implies(Q.transcendental, ~Q.algebraic),
- Implies(Q.transcendental, Q.finite),
- Implies(Q.imaginary, Q.complex & ~Q.real),
- Implies(Q.imaginary, Q.antihermitian),
- Implies(Q.antihermitian, ~Q.hermitian),
- Equivalent(Q.irrational | Q.rational, Q.real & Q.finite),
- Implies(Q.irrational, ~Q.rational),
- Implies(Q.zero, Q.even),
-
- Equivalent(Q.real, Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive),
- Implies(Q.zero, ~Q.negative & ~Q.positive),
- Implies(Q.negative, ~Q.positive),
- Equivalent(Q.nonnegative, Q.zero | Q.positive),
- Equivalent(Q.nonpositive, Q.zero | Q.negative),
- Equivalent(Q.nonzero, Q.negative | Q.positive),
-
- Implies(Q.orthogonal, Q.positive_definite),
- Implies(Q.orthogonal, Q.unitary),
- Implies(Q.unitary & Q.real, Q.orthogonal),
- Implies(Q.unitary, Q.normal),
- Implies(Q.unitary, Q.invertible),
- Implies(Q.normal, Q.square),
- Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.normal),
- Implies(Q.positive_definite, Q.invertible),
- Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.upper_triangular),
- Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.lower_triangular),
- Implies(Q.lower_triangular, Q.triangular),
- Implies(Q.upper_triangular, Q.triangular),
- Implies(Q.triangular, Q.upper_triangular | Q.lower_triangular),
- Implies(Q.upper_triangular & Q.lower_triangular, Q.diagonal),
- Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.symmetric),
- Implies(Q.unit_triangular, Q.triangular),
- Implies(Q.invertible, Q.fullrank),
- Implies(Q.invertible, Q.square),
- Implies(Q.symmetric, Q.square),
- Implies(Q.fullrank & Q.square, Q.invertible),
- Equivalent(Q.invertible, ~Q.singular),
- Implies(Q.integer_elements, Q.real_elements),
- Implies(Q.real_elements, Q.complex_elements),
- )
-
-
from sympy.assumptions.ask_generated import (
get_known_facts_dict, get_all_known_facts)
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py b/sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py
index 1eb45b4cd9b2..536757a223b8 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/ask_generated.py
@@ -15,75 +15,68 @@
@cacheit
def get_all_known_facts():
return {
- frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.complex, True), Literal(Q.finite, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.rational, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, True), Literal(Q.complex, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, False), Literal(Q.transcendental, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, True), Literal(Q.finite, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.algebraic, True), Literal(Q.transcendental, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.antihermitian, False), Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.antihermitian, False), Literal(Q.imaginary, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.antihermitian, True), Literal(Q.hermitian, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.complex, False), Literal(Q.imaginary, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.complex, False), Literal(Q.real, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.complex, False), Literal(Q.transcendental, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.commutative, False), Literal(Q.finite, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.commutative, False), Literal(Q.infinite, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.complex_elements, False), Literal(Q.real_elements, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.composite, False), Literal(Q.even, True), Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.prime, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.composite, True), Literal(Q.even, False), Literal(Q.odd, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.composite, True), Literal(Q.positive, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.composite, True), Literal(Q.prime, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, False), Literal(Q.lower_triangular, True), Literal(Q.upper_triangular, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, True), Literal(Q.lower_triangular, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, True), Literal(Q.normal, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, True), Literal(Q.symmetric, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.diagonal, True), Literal(Q.upper_triangular, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.even, False), Literal(Q.integer, True), Literal(Q.odd, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.even, False), Literal(Q.odd, False), Literal(Q.prime, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.even, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.even, True), Literal(Q.integer, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.even, True), Literal(Q.odd, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.extended_real, False), Literal(Q.infinite, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.extended_real, False), Literal(Q.real, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.extended_real, True), Literal(Q.infinite, False), Literal(Q.real, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, False), Literal(Q.irrational, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, False), Literal(Q.rational, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.even, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, False), Literal(Q.transcendental, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, True), Literal(Q.infinite, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.finite, True), Literal(Q.irrational, False), Literal(Q.rational, False), Literal(Q.real, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.fullrank, False), Literal(Q.invertible, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.fullrank, True), Literal(Q.invertible, False), Literal(Q.square, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.real, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.real, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.integer, False), Literal(Q.odd, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.integer, False), Literal(Q.prime, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.integer, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.negative, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.positive, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.hermitian, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.negative, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.positive, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.imaginary, True), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.infinite, False), Literal(Q.negative_infinite, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.infinite, False), Literal(Q.positive_infinite, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.integer_elements, True), Literal(Q.real_elements, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, False), Literal(Q.positive_definite, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, False), Literal(Q.singular, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, False), Literal(Q.unitary, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, True), Literal(Q.singular, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.invertible, True), Literal(Q.square, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, False), Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, False), Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, False), Literal(Q.rational, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, True), Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.zero, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, True), Literal(Q.rational, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.irrational, True), Literal(Q.real, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.lower_triangular, False), Literal(Q.triangular, True), Literal(Q.upper_triangular, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.lower_triangular, True), Literal(Q.triangular, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.nonpositive, True), Literal(Q.zero, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.nonzero, True), Literal(Q.positive, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.real, True), Literal(Q.zero, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.nonpositive, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.nonzero, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, False), Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.rational, True), Literal(Q.zero, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.positive, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.real, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.negative, True), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonnegative, False), Literal(Q.positive, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonnegative, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonnegative, True), Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.zero, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonpositive, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.nonzero, False), Literal(Q.positive, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.negative_infinite, True), Literal(Q.positive_infinite, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.normal, False), Literal(Q.unitary, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.normal, True), Literal(Q.square, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.orthogonal, False), Literal(Q.real, True), Literal(Q.unitary, True))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.odd, True), Literal(Q.rational, False))),
+ frozenset((Literal(Q.orthogonal, False), Literal(Q.real_elements, True), Literal(Q.unitary, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.orthogonal, True), Literal(Q.positive_definite, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.orthogonal, True), Literal(Q.unitary, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.positive, False), Literal(Q.prime, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.real, False))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.positive, True), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.rational, True), Literal(Q.real, False))),
- frozenset((Literal(Q.real, False), Literal(Q.zero, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.square, False), Literal(Q.symmetric, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.triangular, False), Literal(Q.unit_triangular, True))),
frozenset((Literal(Q.triangular, False), Literal(Q.upper_triangular, True)))
@@ -96,43 +89,29 @@ def get_known_facts_cnf():
Q.invertible | Q.singular,
Q.algebraic | ~Q.rational,
Q.antihermitian | ~Q.imaginary,
+ Q.commutative | ~Q.finite,
+ Q.commutative | ~Q.infinite,
Q.complex_elements | ~Q.real_elements,
- Q.complex | ~Q.algebraic,
- Q.complex | ~Q.imaginary,
- Q.complex | ~Q.real,
- Q.complex | ~Q.transcendental,
Q.even | ~Q.zero,
- Q.extended_real | ~Q.infinite,
- Q.extended_real | ~Q.real,
Q.finite | ~Q.algebraic,
- Q.finite | ~Q.irrational,
- Q.finite | ~Q.rational,
Q.finite | ~Q.transcendental,
Q.fullrank | ~Q.invertible,
- Q.hermitian | ~Q.real,
- Q.integer | ~Q.even,
- Q.integer | ~Q.odd,
- Q.integer | ~Q.prime,
+ Q.hermitian | ~Q.negative,
+ Q.hermitian | ~Q.positive,
+ Q.hermitian | ~Q.zero,
+ Q.infinite | ~Q.negative_infinite,
+ Q.infinite | ~Q.positive_infinite,
Q.invertible | ~Q.positive_definite,
Q.invertible | ~Q.unitary,
Q.lower_triangular | ~Q.diagonal,
- Q.nonnegative | ~Q.positive,
- Q.nonnegative | ~Q.zero,
- Q.nonpositive | ~Q.negative,
- Q.nonpositive | ~Q.zero,
- Q.nonzero | ~Q.negative,
- Q.nonzero | ~Q.positive,
Q.normal | ~Q.diagonal,
Q.normal | ~Q.unitary,
Q.positive_definite | ~Q.orthogonal,
+ Q.positive | ~Q.composite,
Q.positive | ~Q.prime,
- Q.rational | ~Q.integer,
+ Q.rational | ~Q.even,
+ Q.rational | ~Q.odd,
Q.real_elements | ~Q.integer_elements,
- Q.real | ~Q.irrational,
- Q.real | ~Q.negative,
- Q.real | ~Q.positive,
- Q.real | ~Q.rational,
- Q.real | ~Q.zero,
Q.square | ~Q.invertible,
Q.square | ~Q.normal,
Q.square | ~Q.symmetric,
@@ -143,99 +122,98 @@ def get_known_facts_cnf():
Q.unitary | ~Q.orthogonal,
Q.upper_triangular | ~Q.diagonal,
~Q.algebraic | ~Q.transcendental,
- ~Q.antihermitian | ~Q.hermitian,
~Q.composite | ~Q.prime,
~Q.even | ~Q.odd,
~Q.finite | ~Q.infinite,
- ~Q.imaginary | ~Q.real,
+ ~Q.imaginary | ~Q.negative,
+ ~Q.imaginary | ~Q.positive,
+ ~Q.imaginary | ~Q.zero,
~Q.invertible | ~Q.singular,
~Q.irrational | ~Q.rational,
+ ~Q.negative_infinite | ~Q.positive_infinite,
~Q.negative | ~Q.positive,
~Q.negative | ~Q.zero,
~Q.positive | ~Q.zero,
- Q.even | Q.odd | ~Q.integer,
- Q.infinite | Q.real | ~Q.extended_real,
+ Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.imaginary,
+ Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.negative,
+ Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.positive,
+ Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.zero,
+ Q.antihermitian | Q.hermitian | ~Q.zero,
+ Q.even | Q.odd | ~Q.composite,
+ Q.even | Q.odd | ~Q.prime,
+ Q.irrational | Q.rational | ~Q.negative,
+ Q.irrational | Q.rational | ~Q.positive,
+ Q.irrational | Q.rational | ~Q.zero,
Q.lower_triangular | Q.upper_triangular | ~Q.triangular,
- Q.negative | Q.positive | ~Q.nonzero,
- Q.negative | Q.zero | ~Q.nonpositive,
- Q.positive | Q.zero | ~Q.nonnegative,
Q.diagonal | ~Q.lower_triangular | ~Q.upper_triangular,
Q.invertible | ~Q.fullrank | ~Q.square,
- Q.orthogonal | ~Q.real | ~Q.unitary,
- Q.negative | Q.positive | Q.zero | ~Q.real,
- Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental | ~Q.complex | ~Q.finite,
- Q.irrational | Q.rational | ~Q.finite | ~Q.real
+ Q.orthogonal | ~Q.real_elements | ~Q.unitary,
+ Q.negative | Q.positive | Q.zero | ~Q.irrational,
+ Q.negative | Q.positive | Q.zero | ~Q.rational,
+ Q.composite | Q.prime | ~Q.even | ~Q.positive
)
# -{ Known facts in compressed sets }-
+# This dictionary means that if a key is True, every item in its value is True.
@cacheit
def get_known_facts_dict():
return {
- Q.algebraic: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.finite]),
+ Q.algebraic: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.finite]),
Q.antihermitian: set([Q.antihermitian]),
Q.commutative: set([Q.commutative]),
- Q.complex: set([Q.complex]),
Q.complex_elements: set([Q.complex_elements]),
- Q.composite: set([Q.composite]),
+ Q.composite: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.composite, Q.finite,
+ Q.hermitian, Q.positive, Q.rational]),
Q.diagonal: set([Q.diagonal, Q.lower_triangular, Q.normal, Q.square,
Q.symmetric, Q.triangular, Q.upper_triangular]),
Q.eq: set([Q.eq]),
- Q.even: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.even, Q.extended_real,
- Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.rational, Q.real]),
- Q.extended_real: set([Q.extended_real]),
- Q.finite: set([Q.finite]),
+ Q.even: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.even, Q.finite,
+ Q.hermitian, Q.rational]),
+ Q.finite: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite]),
Q.fullrank: set([Q.fullrank]),
Q.ge: set([Q.ge]),
Q.gt: set([Q.gt]),
Q.hermitian: set([Q.hermitian]),
- Q.imaginary: set([Q.antihermitian, Q.complex, Q.imaginary]),
- Q.infinite: set([Q.extended_real, Q.infinite]),
- Q.integer: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite,
- Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.rational, Q.real]),
+ Q.imaginary: set([Q.antihermitian, Q.commutative, Q.finite,
+ Q.imaginary]),
+ Q.infinite: set([Q.commutative, Q.infinite]),
Q.integer_elements: set([Q.complex_elements, Q.integer_elements,
Q.real_elements]),
Q.invertible: set([Q.fullrank, Q.invertible, Q.square]),
- Q.irrational: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite, Q.hermitian,
- Q.irrational, Q.nonzero, Q.real]),
+ Q.irrational: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian,
+ Q.irrational]),
Q.is_true: set([Q.is_true]),
Q.le: set([Q.le]),
Q.lower_triangular: set([Q.lower_triangular, Q.triangular]),
Q.lt: set([Q.lt]),
Q.ne: set([Q.ne]),
- Q.negative: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian, Q.negative,
- Q.nonpositive, Q.nonzero, Q.real]),
- Q.nonnegative: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian,
- Q.nonnegative, Q.real]),
- Q.nonpositive: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian,
- Q.nonpositive, Q.real]),
- Q.nonzero: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian, Q.nonzero,
- Q.real]),
+ Q.negative: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.negative]),
+ Q.negative_infinite: set([Q.commutative, Q.infinite,
+ Q.negative_infinite]),
Q.normal: set([Q.normal, Q.square]),
- Q.odd: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite,
- Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.nonzero, Q.odd, Q.rational, Q.real]),
+ Q.odd: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.odd,
+ Q.rational]),
Q.orthogonal: set([Q.fullrank, Q.invertible, Q.normal, Q.orthogonal,
Q.positive_definite, Q.square, Q.unitary]),
- Q.positive: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian,
- Q.nonnegative, Q.nonzero, Q.positive, Q.real]),
+ Q.positive: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.positive]),
Q.positive_definite: set([Q.fullrank, Q.invertible,
Q.positive_definite, Q.square]),
- Q.prime: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite,
- Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.nonnegative, Q.nonzero, Q.positive,
- Q.prime, Q.rational, Q.real]),
- Q.rational: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.finite,
- Q.hermitian, Q.rational, Q.real]),
- Q.real: set([Q.complex, Q.extended_real, Q.hermitian, Q.real]),
+ Q.positive_infinite: set([Q.commutative, Q.infinite,
+ Q.positive_infinite]),
+ Q.prime: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian,
+ Q.positive, Q.prime, Q.rational]),
+ Q.rational: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.hermitian,
+ Q.rational]),
Q.real_elements: set([Q.complex_elements, Q.real_elements]),
Q.singular: set([Q.singular]),
Q.square: set([Q.square]),
Q.symmetric: set([Q.square, Q.symmetric]),
- Q.transcendental: set([Q.complex, Q.finite, Q.transcendental]),
+ Q.transcendental: set([Q.commutative, Q.finite, Q.transcendental]),
Q.triangular: set([Q.triangular]),
Q.unit_triangular: set([Q.triangular, Q.unit_triangular]),
Q.unitary: set([Q.fullrank, Q.invertible, Q.normal, Q.square,
Q.unitary]),
Q.upper_triangular: set([Q.triangular, Q.upper_triangular]),
- Q.zero: set([Q.algebraic, Q.complex, Q.even, Q.extended_real,
- Q.finite, Q.hermitian, Q.integer, Q.nonnegative,
- Q.nonpositive, Q.rational, Q.real, Q.zero]),
+ Q.zero: set([Q.algebraic, Q.commutative, Q.even, Q.finite,
+ Q.hermitian, Q.rational, Q.zero]),
}
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/cnf.py b/sympy/assumptions/cnf.py
index f5fb466d5768..55c7ebd7a230 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/cnf.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/cnf.py
@@ -139,36 +139,56 @@ def __str__(self):
__repr__ = __str__
-def to_NNF(expr):
+def to_NNF(expr, composite_map={}):
"""
Generates the Negation Normal Form of any boolean expression in terms
of AND, OR, and Literal objects.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import Q
+ >>> from sympy.assumptions.cnf import to_NNF
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
+ >>> expr = Q.even(x) & ~Q.positive(x)
+ >>> to_NNF(expr)
+ (Literal(Q.even(x), False) & Literal(Q.positive(x), True))
+
+ If ``composite_map`` argument is given, ``to_NNF`` decomposes the
+ specified predicate into a combination of primitive predicates.
+
+ >>> cmap = {Q.nonpositive: Q.negative | Q.zero}
+ >>> to_NNF(Q.nonpositive, cmap)
+ (Literal(Q.negative, False) | Literal(Q.zero, False))
+ >>> to_NNF(Q.nonpositive(x), cmap)
+ (Literal(Q.negative(x), False) | Literal(Q.zero(x), False))
"""
+ from sympy.assumptions.assume import AppliedPredicate, Predicate
if isinstance(expr, Not):
arg = expr.args[0]
- tmp = to_NNF(arg) # Strategy: negate the NNF of expr
+ tmp = to_NNF(arg, composite_map) # Strategy: negate the NNF of expr
return ~tmp
if isinstance(expr, Or):
- return OR(*[to_NNF(x) for x in Or.make_args(expr)])
+ return OR(*[to_NNF(x, composite_map) for x in Or.make_args(expr)])
if isinstance(expr, And):
- return AND(*[to_NNF(x) for x in And.make_args(expr)])
+ return AND(*[to_NNF(x, composite_map) for x in And.make_args(expr)])
if isinstance(expr, Nand):
- tmp = AND(*[to_NNF(x) for x in expr.args])
+ tmp = AND(*[to_NNF(x, composite_map) for x in expr.args])
return ~tmp
if isinstance(expr, Nor):
- tmp = OR(*[to_NNF(x) for x in expr.args])
+ tmp = OR(*[to_NNF(x, composite_map) for x in expr.args])
return ~tmp
if isinstance(expr, Xor):
cnfs = []
for i in range(0, len(expr.args) + 1, 2):
for neg in combinations(expr.args, i):
- clause = [~to_NNF(s) if s in neg else to_NNF(s)
+ clause = [~to_NNF(s, composite_map) if s in neg else to_NNF(s, composite_map)
for s in expr.args]
cnfs.append(OR(*clause))
return AND(*cnfs)
@@ -177,31 +197,41 @@ def to_NNF(expr):
cnfs = []
for i in range(0, len(expr.args) + 1, 2):
for neg in combinations(expr.args, i):
- clause = [~to_NNF(s) if s in neg else to_NNF(s)
+ clause = [~to_NNF(s, composite_map) if s in neg else to_NNF(s, composite_map)
for s in expr.args]
cnfs.append(OR(*clause))
return ~AND(*cnfs)
if isinstance(expr, Implies):
- L, R = to_NNF(expr.args[0]), to_NNF(expr.args[1])
+ L, R = to_NNF(expr.args[0], composite_map), to_NNF(expr.args[1], composite_map)
return OR(~L, R)
if isinstance(expr, Equivalent):
cnfs = []
for a, b in zip_longest(expr.args, expr.args[1:], fillvalue=expr.args[0]):
- a = to_NNF(a)
- b = to_NNF(b)
+ a = to_NNF(a, composite_map)
+ b = to_NNF(b, composite_map)
cnfs.append(OR(~a, b))
return AND(*cnfs)
if isinstance(expr, ITE):
- L = to_NNF(expr.args[0])
- M = to_NNF(expr.args[1])
- R = to_NNF(expr.args[2])
+ L = to_NNF(expr.args[0], composite_map)
+ M = to_NNF(expr.args[1], composite_map)
+ R = to_NNF(expr.args[2], composite_map)
return AND(OR(~L, M), OR(L, R))
- else:
- return Literal(expr)
+ if isinstance(expr, AppliedPredicate):
+ pred, args = expr.function, expr.arguments
+ newpred = composite_map.get(pred, None)
+ if newpred is not None:
+ return to_NNF(newpred.rcall(*args), composite_map)
+
+ if isinstance(expr, Predicate):
+ newpred = composite_map.get(expr, None)
+ if newpred is not None:
+ return to_NNF(newpred, composite_map)
+
+ return Literal(expr)
def distribute_AND_over_OR(expr):
@@ -238,7 +268,9 @@ class CNF:
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> cnf = CNF.from_prop(Q.real(x) & ~Q.zero(x))
>>> cnf.clauses
- {frozenset({Literal(Q.real(x), False)}), frozenset({Literal(Q.zero(x), True)})}
+ {frozenset({Literal(Q.zero(x), True)}),
+ frozenset({Literal(Q.negative(x), False),
+ Literal(Q.positive(x), False), Literal(Q.zero(x), False)})}
"""
def __init__(self, clauses=None):
if not clauses:
@@ -318,8 +350,6 @@ def rcall(self, expr):
expr = AND(*clause_list)
return distribute_AND_over_OR(expr)
-
-
@classmethod
def all_or(cls, *cnfs):
b = cnfs[0].copy()
@@ -336,7 +366,8 @@ def all_and(cls, *cnfs):
@classmethod
def to_CNF(cls, expr):
- expr = to_NNF(expr)
+ from sympy.assumptions.facts import get_composite_predicates
+ expr = to_NNF(expr, get_composite_predicates())
expr = distribute_AND_over_OR(expr)
return expr
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/facts.py b/sympy/assumptions/facts.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..3fd3d7ed247d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/facts.py
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+"""
+Known facts in assumptions module.
+
+This module defines the facts in ``get_known_facts()``, and supports functions
+to generate the contents in ``sympy.assumptions.ask_generated`` file.
+"""
+
+from sympy.core.cache import cacheit
+from sympy.assumptions import Q
+from sympy.assumptions.cnf import CNF
+from sympy.logic.boolalg import (to_cnf, And, Not, Implies, Equivalent)
+from sympy.logic.inference import satisfiable
+
+
+@cacheit
+def get_composite_predicates():
+ # To reduce the complexity of sat solver, these predicates never goes into facts
+ # but are transformed into the combination of primitive predicates.
+ return {
+ Q.real : Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive,
+ Q.integer : Q.even | Q.odd,
+ Q.nonpositive : Q.negative | Q.zero,
+ Q.nonzero : Q.negative | Q.positive,
+ Q.nonnegative : Q.zero | Q.positive,
+ Q.extended_real : Q.negative_infinite | Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive | Q.positive_infinite,
+ Q.extended_positive: Q.positive | Q.positive_infinite,
+ Q.extended_negative: Q.negative | Q.negative_infinite,
+ Q.extended_nonzero: Q.negative_infinite | Q.negative | Q.positive | Q.positive_infinite,
+ Q.extended_nonpositive: Q.negative_infinite | Q.negative | Q.zero,
+ Q.extended_nonnegative: Q.zero | Q.positive | Q.positive_infinite,
+ Q.complex : Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental
+ }
+
+
+@cacheit
+def get_known_facts():
+ # We build the facts starting with primitive predicates.
+ # DO NOT include the predicates in get_composite_predicates()'s keys here!
+ return And(
+
+ # primitive predicates exclude each other
+ Implies(Q.negative_infinite, ~Q.positive_infinite),
+ Implies(Q.negative, ~Q.zero & ~Q.positive),
+ Implies(Q.positive, ~Q.zero),
+
+ # build real line and complex plane
+ Implies(Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive, ~Q.imaginary),
+ Implies(Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive | Q.imaginary, Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental),
+
+ # other subsets of complex
+ Implies(Q.transcendental, ~Q.algebraic),
+ Implies(Q.irrational, ~Q.rational),
+ Equivalent(Q.rational | Q.irrational, Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive),
+ Implies(Q.rational, Q.algebraic),
+
+ # integers
+ Implies(Q.even, ~Q.odd),
+ Implies(Q.even | Q.odd, Q.rational),
+ Implies(Q.zero, Q.even),
+ Implies(Q.composite, ~Q.prime),
+ Implies(Q.composite | Q.prime, (Q.even | Q.odd) & Q.positive),
+ Implies(Q.even & Q.positive & ~Q.prime, Q.composite),
+
+ # hermitian and antihermitian
+ Implies(Q.negative | Q.zero | Q.positive, Q.hermitian),
+ Implies(Q.imaginary, Q.antihermitian),
+ Implies(Q.zero, Q.hermitian | Q.antihermitian),
+
+ # define finity and infinity, and build extended real line
+ Implies(Q.infinite, ~Q.finite),
+ Implies(Q.algebraic | Q.transcendental, Q.finite),
+ Implies(Q.negative_infinite | Q.positive_infinite, Q.infinite),
+
+ # commutativity
+ Implies(Q.finite | Q.infinite, Q.commutative),
+
+ # matrices
+ Implies(Q.orthogonal, Q.positive_definite),
+ Implies(Q.orthogonal, Q.unitary),
+ Implies(Q.unitary & Q.real_elements, Q.orthogonal),
+ Implies(Q.unitary, Q.normal),
+ Implies(Q.unitary, Q.invertible),
+ Implies(Q.normal, Q.square),
+ Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.normal),
+ Implies(Q.positive_definite, Q.invertible),
+ Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.upper_triangular),
+ Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.lower_triangular),
+ Implies(Q.lower_triangular, Q.triangular),
+ Implies(Q.upper_triangular, Q.triangular),
+ Implies(Q.triangular, Q.upper_triangular | Q.lower_triangular),
+ Implies(Q.upper_triangular & Q.lower_triangular, Q.diagonal),
+ Implies(Q.diagonal, Q.symmetric),
+ Implies(Q.unit_triangular, Q.triangular),
+ Implies(Q.invertible, Q.fullrank),
+ Implies(Q.invertible, Q.square),
+ Implies(Q.symmetric, Q.square),
+ Implies(Q.fullrank & Q.square, Q.invertible),
+ Equivalent(Q.invertible, ~Q.singular),
+ Implies(Q.integer_elements, Q.real_elements),
+ Implies(Q.real_elements, Q.complex_elements),
+ )
+
+
+@cacheit
+def get_known_facts_keys():
+ result = []
+ exclude = get_composite_predicates()
+ for attr in Q.__class__.__dict__:
+ if attr.startswith('__'):
+ continue
+ pred = getattr(Q, attr)
+ if pred in exclude:
+ continue
+ result.append(pred)
+ return result
+
+
+def compute_known_facts(known_facts, known_facts_keys):
+ """Compute the various forms of knowledge compilation used by the
+ assumptions system.
+
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
+ This function is typically applied to the results of the ``get_known_facts``
+ and ``get_known_facts_keys`` functions defined at the bottom of
+ this file.
+ """
+ from textwrap import dedent, wrap
+
+ fact_string = dedent('''\
+ """
+ The contents of this file are the return value of
+ ``sympy.assumptions.ask.compute_known_facts``.
+
+ Do NOT manually edit this file.
+ Instead, run ./bin/ask_update.py.
+ """
+
+ from sympy.core.cache import cacheit
+ from sympy.logic.boolalg import And
+ from sympy.assumptions.cnf import Literal
+ from sympy.assumptions.ask import Q
+
+ # -{ Known facts as a set }-
+ @cacheit
+ def get_all_known_facts():
+ return {
+ %s
+ }
+
+ # -{ Known facts in Conjunctive Normal Form }-
+ @cacheit
+ def get_known_facts_cnf():
+ return And(
+ %s
+ )
+
+ # -{ Known facts in compressed sets }-
+ # This dictionary means that if a key is True, every item in its value is True.
+ @cacheit
+ def get_known_facts_dict():
+ return {
+ %s
+ }
+ ''')
+ # Compute the known facts in CNF form for logical inference
+ LINE = ",\n "
+ HANG = ' '*8
+ cnf = to_cnf(known_facts)
+ cnf_ = CNF.to_CNF(known_facts)
+ c = LINE.join([str(a) for a in cnf.args])
+
+ p = LINE.join(sorted(['frozenset((' + ', '.join(str(lit) for lit in sorted(clause, key=str)) +'))' for clause in cnf_.clauses]))
+ mapping = single_fact_lookup(known_facts_keys, cnf)
+ items = sorted(mapping.items(), key=str)
+ keys = [str(i[0]) for i in items]
+ values = ['set(%s)' % sorted(i[1], key=str) for i in items]
+ m = LINE.join(['\n'.join(
+ wrap("{}: {}".format(k, v),
+ subsequent_indent=HANG,
+ break_long_words=False))
+ for k, v in zip(keys, values)]) + ','
+ return fact_string % (p, c, m)
+
+
+def single_fact_lookup(known_facts_keys, known_facts_cnf):
+ # Compute the quick lookup for single facts
+ mapping = {}
+ for key in known_facts_keys:
+ mapping[key] = {key}
+ for other_key in known_facts_keys:
+ if other_key != key:
+ if ask_full_inference(other_key, key, known_facts_cnf):
+ mapping[key].add(other_key)
+ return mapping
+
+
+def ask_full_inference(proposition, assumptions, known_facts_cnf):
+ """
+ Method for inferring properties about objects.
+
+ """
+ if not satisfiable(And(known_facts_cnf, assumptions, proposition)):
+ return False
+ if not satisfiable(And(known_facts_cnf, assumptions, Not(proposition))):
+ return True
+ return None
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py
index 4ae13d71a80d..55386e298787 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py
@@ -10,7 +10,8 @@
from sympy.functions import cos, exp, log, sign, sin
from sympy.logic.boolalg import conjuncts
-from ..predicates.calculus import FinitePredicate, InfinitePredicate
+from ..predicates.calculus import (FinitePredicate, InfinitePredicate,
+ PositiveInfinitePredicate, NegativeInfinitePredicate)
# FinitePredicate
@@ -95,7 +96,7 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):
_bounded = ask(Q.finite(arg), assumptions)
if _bounded:
continue
- s = ask(Q.positive(arg), assumptions)
+ s = ask(Q.extended_positive(arg), assumptions)
# if there has been more than one sign or if the sign of this arg
# is None and Bounded is None or there was already
# an unknown sign, return None
@@ -156,7 +157,7 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):
elif _bounded is None:
if result is None:
return None
- if ask(Q.nonzero(arg), assumptions) is None:
+ if ask(Q.extended_nonzero(arg), assumptions) is None:
return None
if result is not False:
result = None
@@ -184,13 +185,13 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):
exp_bounded = ask(Q.finite(expr.exp), assumptions)
if base_bounded is None and exp_bounded is None: # Common Case
return None
- if base_bounded is False and ask(Q.nonzero(expr.exp), assumptions):
+ if base_bounded is False and ask(Q.extended_nonzero(expr.exp), assumptions):
return False
if base_bounded and exp_bounded:
return True
- if (abs(expr.base) <= 1) == True and ask(Q.positive(expr.exp), assumptions):
+ if (abs(expr.base) <= 1) == True and ask(Q.extended_positive(expr.exp), assumptions):
return True
- if (abs(expr.base) >= 1) == True and ask(Q.negative(expr.exp), assumptions):
+ if (abs(expr.base) >= 1) == True and ask(Q.extended_negative(expr.exp), assumptions):
return True
if (abs(expr.base) >= 1) == True and exp_bounded is False:
return False
@@ -206,7 +207,7 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):
# querying Q.infinite may be removed.
if ask(Q.infinite(expr.args[0]), assumptions):
return False
- return ask(Q.nonzero(expr.args[0]), assumptions)
+ return ask(~Q.zero(expr.args[0]), assumptions)
@FinitePredicate.register_many(cos, sin, Number, Pi, Exp1, GoldenRatio,
TribonacciConstant, ImaginaryUnit, sign)
@@ -228,3 +229,29 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):
@InfinitePredicate.register_many(ComplexInfinity, Infinity, NegativeInfinity)
def _(expr, assumptions):
return True
+
+
+# PositiveInfinitePredicate
+
+
[email protected](Infinity)
+def _(expr, assumptions):
+ return True
+
+
[email protected]_many(NegativeInfinity, ComplexInfinity)
+def _(expr, assumptions):
+ return False
+
+
+# NegativeInfinitePredicate
+
+
[email protected](NegativeInfinity)
+def _(expr, assumptions):
+ return True
+
+
[email protected]_many(Infinity, ComplexInfinity)
+def _(expr, assumptions):
+ return False
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/order.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/order.py
index 7b3bc758974c..6f2581e606a3 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/order.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/order.py
@@ -13,7 +13,10 @@
from sympy.multipledispatch import MDNotImplementedError
from ..predicates.order import (NegativePredicate, NonNegativePredicate,
- NonZeroPredicate, ZeroPredicate, NonPositivePredicate, PositivePredicate)
+ NonZeroPredicate, ZeroPredicate, NonPositivePredicate, PositivePredicate,
+ ExtendedNegativePredicate, ExtendedNonNegativePredicate,
+ ExtendedNonPositivePredicate, ExtendedNonZeroPredicate,
+ ExtendedPositivePredicate,)
# NegativePredicate
@@ -392,3 +395,44 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):
@PositivePredicate.register(NaN)
def _(expr, assumptions):
return None
+
+
+# ExtendedNegativePredicate
+
[email protected](object)
+def _(expr, assumptions):
+ return ask(Q.negative(expr) | Q.negative_infinite(expr), assumptions)
+
+
+# ExtendedPositivePredicate
+
[email protected](object)
+def _(expr, assumptions):
+ return ask(Q.positive(expr) | Q.positive_infinite(expr), assumptions)
+
+
+# ExtendedNonZeroPredicate
+
[email protected](object)
+def _(expr, assumptions):
+ return ask(
+ Q.negative_infinite(expr) | Q.negative(expr) | Q.positive(expr) | Q.positive_infinite(expr),
+ assumptions)
+
+
+# ExtendedNonPositivePredicate
+
[email protected](object)
+def _(expr, assumptions):
+ return ask(
+ Q.negative_infinite(expr) | Q.negative(expr) | Q.zero(expr),
+ assumptions)
+
+
+# ExtendedNonNegativePredicate
+
[email protected](object)
+def _(expr, assumptions):
+ return ask(
+ Q.zero(expr) | Q.positive(expr) | Q.positive_infinite(expr),
+ assumptions)
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/sets.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/sets.py
index bc1487960cf6..8911bc0f1d95 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/sets.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/sets.py
@@ -638,6 +638,8 @@ def _(expr, assumptions):
def _(expr, assumptions):
if isinstance(expr, MatrixBase):
return None
+ if ask(Q.zero(expr), assumptions):
+ return True
return ask(Q.imaginary(expr), assumptions)
@AntihermitianPredicate.register(Add)
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/predicates/calculus.py b/sympy/assumptions/predicates/calculus.py
index d0ad129bef48..f30070378868 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/predicates/calculus.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/predicates/calculus.py
@@ -27,8 +27,8 @@ class FinitePredicate(Predicate):
True
>>> ask(Q.finite(2 + 3*I))
True
- >>> print(ask(Q.finite(x), Q.positive(x)))
- None
+ >>> ask(Q.finite(x), Q.positive(x))
+ True
>>> print(ask(Q.finite(S.NaN)))
None
@@ -60,3 +60,23 @@ class InfinitePredicate(Predicate):
"InfiniteHandler",
doc="""Handler for Q.infinite key."""
)
+
+
+class PositiveInfinitePredicate(Predicate):
+ """
+ Positive infinity predicate.
+
+ ``Q.positive_infinite(x)`` is true iff ``x`` is positive infinity ``oo``.
+ """
+ name = 'positive_infinite'
+ handler = Dispatcher("PositiveInfiniteHandler")
+
+
+class NegativeInfinitePredicate(Predicate):
+ """
+ Negative infinity predicate.
+
+ ``Q.negative_infinite(x)`` is true iff ``x`` is negative infinity ``-oo``.
+ """
+ name = 'negative_infinite'
+ handler = Dispatcher("NegativeInfiniteHandler")
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/predicates/order.py b/sympy/assumptions/predicates/order.py
index e183ecc8d57d..372eda329325 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/predicates/order.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/predicates/order.py
@@ -254,3 +254,137 @@ class PositivePredicate(Predicate):
doc=("Handler for key 'positive'. Test that an expression is strictly"
" greater than zero.")
)
+
+
+class ExtendedPositivePredicate(Predicate):
+ r"""
+ Positive extended real number predicate.
+
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
+ ``Q.extended_positive(x)`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and
+ `x > 0`, that is if ``x`` is in the interval `(0, \infty]`.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_positive(1))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_positive(oo))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_positive(I))
+ False
+
+ """
+ name = 'extended_positive'
+ handler = Dispatcher("ExtendedPositiveHandler")
+
+
+class ExtendedNegativePredicate(Predicate):
+ r"""
+ Negative extended real number predicate.
+
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
+ ``Q.extended_negative(x)`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and
+ `x < 0`, that is if ``x`` is in the interval `[-\infty, 0)`.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_negative(-1))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_negative(-oo))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_negative(-I))
+ False
+
+ """
+ name = 'extended_negative'
+ handler = Dispatcher("ExtendedNegativeHandler")
+
+
+class ExtendedNonZeroPredicate(Predicate):
+ """
+ Nonzero extended real number predicate.
+
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
+ ``ask(Q.extended_nonzero(x))`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and
+ ``x`` is not zero.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonzero(-1))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonzero(oo))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonzero(I))
+ False
+
+ """
+ name = 'extended_nonzero'
+ handler = Dispatcher("ExtendedNonZeroHandler")
+
+
+class ExtendedNonPositivePredicate(Predicate):
+ """
+ Nonpositive extended real number predicate.
+
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
+ ``ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(x))`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and
+ ``x`` is not positive.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(-1))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(oo))
+ False
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(0))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonpositive(I))
+ False
+
+ """
+ name = 'extended_nonpositive'
+ handler = Dispatcher("ExtendedNonPositiveHandler")
+
+
+class ExtendedNonNegativePredicate(Predicate):
+ """
+ Nonnegative extended real number predicate.
+
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
+ ``ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(x))`` is true iff ``x`` is extended real and
+ ``x`` is not negative.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import ask, I, oo, Q
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(-1))
+ False
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(oo))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(0))
+ True
+ >>> ask(Q.extended_nonnegative(I))
+ False
+
+ """
+ name = 'extended_nonnegative'
+ handler = Dispatcher("ExtendedNonNegativeHandler")
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/sathandlers.py b/sympy/assumptions/sathandlers.py
index 175d0fe431f2..de5e7e69f4d2 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/sathandlers.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/sathandlers.py
@@ -4,6 +4,7 @@
from sympy.assumptions.ask import Q
from sympy.assumptions.assume import Predicate, AppliedPredicate
from sympy.assumptions.cnf import AND, OR, to_NNF
+from sympy.assumptions.facts import get_composite_predicates
from sympy.core import (Add, Mul, Pow, Integer, Number, NumberSymbol,)
from sympy.core.numbers import ImaginaryUnit
from sympy.core.rules import Transform
@@ -76,7 +77,7 @@ def __new__(cls, arg):
def apply(self, expr=None):
if expr is None:
return
- pred = to_NNF(self.pred)
+ pred = to_NNF(self.pred, get_composite_predicates())
return self._eval_apply(expr, pred)
def _eval_apply(self, expr, pred):
@@ -231,7 +232,7 @@ class CheckOldAssump(UnevaluatedOnFree):
def apply(self, expr=None, is_Not=False):
arg = self.args[0](expr) if callable(self.args[0]) else self.args[0]
res = Equivalent(arg, evaluate_old_assump(arg))
- return to_NNF(res)
+ return to_NNF(res, get_composite_predicates())
class CheckIsPrime(UnevaluatedOnFree):
@@ -239,7 +240,7 @@ def apply(self, expr=None, is_Not=False):
from sympy import isprime
arg = self.args[0](expr) if callable(self.args[0]) else self.args[0]
res = Equivalent(arg, isprime(expr))
- return to_NNF(res)
+ return to_NNF(res, get_composite_predicates())
class CustomLambda:
"""
@@ -251,7 +252,7 @@ def __init__(self, lamda):
self.lamda = lamda
def apply(self, *args):
- return to_NNF(self.lamda(*args))
+ return to_NNF(self.lamda(*args), get_composite_predicates())
class ClassFactRegistry(MutableMapping):
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_query.py b/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_query.py
index 4e010cca0b20..2189ef93c557 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_query.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_query.py
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
from sympy.assumptions import (ask, AssumptionsContext, Q, register_handler,
remove_handler)
from sympy.assumptions.assume import assuming, global_assumptions, Predicate
-from sympy.assumptions.ask import compute_known_facts, single_fact_lookup
+from sympy.assumptions.facts import compute_known_facts, single_fact_lookup
from sympy.assumptions.handlers import AskHandler
from sympy.core.add import Add
from sympy.core.numbers import (I, Integer, Rational, oo, zoo, pi)
@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ def test_zero_0():
assert ask(Q.prime(z)) is False
assert ask(Q.composite(z)) is False
assert ask(Q.hermitian(z)) is True
- assert ask(Q.antihermitian(z)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(z)) is True
def test_negativeone():
@@ -176,7 +176,7 @@ def test_infinity():
assert ask(Q.irrational(oo)) is False
assert ask(Q.imaginary(oo)) is False
assert ask(Q.positive(oo)) is False
- #assert ask(Q.extended_positive(oo)) is True
+ assert ask(Q.extended_positive(oo)) is True
assert ask(Q.negative(oo)) is False
assert ask(Q.even(oo)) is False
assert ask(Q.odd(oo)) is False
@@ -186,6 +186,8 @@ def test_infinity():
assert ask(Q.composite(oo)) is False
assert ask(Q.hermitian(oo)) is False
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(oo)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.positive_infinite(oo)) is True
+ assert ask(Q.negative_infinite(oo)) is False
def test_neg_infinity():
@@ -201,7 +203,7 @@ def test_neg_infinity():
assert ask(Q.imaginary(mm)) is False
assert ask(Q.positive(mm)) is False
assert ask(Q.negative(mm)) is False
- #assert ask(Q.extended_negative(mm)) is True
+ assert ask(Q.extended_negative(mm)) is True
assert ask(Q.even(mm)) is False
assert ask(Q.odd(mm)) is False
assert ask(Q.finite(mm)) is False
@@ -210,6 +212,8 @@ def test_neg_infinity():
assert ask(Q.composite(mm)) is False
assert ask(Q.hermitian(mm)) is False
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(mm)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.positive_infinite(-oo)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.negative_infinite(-oo)) is True
def test_complex_infinity():
@@ -234,6 +238,8 @@ def test_complex_infinity():
assert ask(Q.composite(zoo)) is False
assert ask(Q.hermitian(zoo)) is False
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(zoo)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.positive_infinite(zoo)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.negative_infinite(zoo)) is False
def test_nan():
@@ -595,13 +601,13 @@ def test_I():
assert ask(Q.real(z)) is True
-
+@XFAIL # definition for boundedness fixed! will be changed in next commit
def test_bounded():
x, y, z = symbols('x,y,z')
assert ask(Q.finite(x)) is None
assert ask(Q.finite(x), Q.finite(x)) is True
assert ask(Q.finite(x), Q.finite(y)) is None
- assert ask(Q.finite(x), Q.complex(x)) is None
+ assert ask(Q.finite(x), Q.complex(x)) is True
assert ask(Q.finite(x + 1)) is None
assert ask(Q.finite(x + 1), Q.finite(x)) is True
@@ -610,7 +616,7 @@ def test_bounded():
# B + B
assert ask(Q.finite(a), Q.finite(x) & Q.finite(y)) is True
assert ask(
- Q.finite(a), Q.finite(x) & Q.finite(y) & Q.positive(x)) is True
+ Q.finite(a), Q.positive(x) & Q.finite(y)) is True
assert ask(
Q.finite(a), Q.finite(x) & Q.finite(y) & Q.positive(y)) is True
assert ask(Q.finite(a),
@@ -1354,12 +1360,13 @@ def test_rational():
def test_hermitian():
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x)) is None
- assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.antihermitian(x)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.antihermitian(x)) is None
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.imaginary(x)) is False
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.prime(x)) is True
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.real(x)) is True
+ assert ask(Q.hermitian(x), Q.zero(x)) is True
- assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.antihermitian(x)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.antihermitian(x)) is None
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.complex(x)) is None
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.hermitian(x)) is True
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + 1), Q.imaginary(x)) is False
@@ -1373,9 +1380,9 @@ def test_hermitian():
Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.antihermitian(y)) is None
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None
assert ask(
- Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is False
+ Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is None
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is None
- assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.real(y)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.real(y)) is None
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is True
assert ask(Q.hermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is False
@@ -1410,12 +1417,13 @@ def test_hermitian():
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.complex(x)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.hermitian(x)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.imaginary(x)) is False
- assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.real(x)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + 1), Q.real(x)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.antihermitian(x)) is True
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.complex(x)) is None
- assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.hermitian(x)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.hermitian(x)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.imaginary(x)) is True
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + I), Q.real(x)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x), Q.zero(x)) is True
assert ask(
Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.antihermitian(y)
@@ -1423,7 +1431,7 @@ def test_hermitian():
assert ask(
Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None
assert ask(
- Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is False
+ Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)) is None
assert ask(
Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is True
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.real(y)
@@ -1432,13 +1440,13 @@ def test_hermitian():
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.hermitian(y)
) is None
assert ask(
- Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is False
+ Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.hermitian(x) & Q.real(y)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.imaginary(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.imaginary(x) & Q.imaginary(y)) is True
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.imaginary(x) & Q.real(y)) is False
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.real(x) & Q.complex(y)) is None
- assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.real(x) & Q.real(y)) is False
+ assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y), Q.real(x) & Q.real(y)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(I*x), Q.real(x)) is True
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(I*x), Q.antihermitian(x)) is False
@@ -1446,7 +1454,7 @@ def test_hermitian():
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x*y), Q.antihermitian(x) & Q.real(y)) is True
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y + z),
- Q.real(x) & Q.real(y) & Q.real(z)) is False
+ Q.real(x) & Q.real(y) & Q.real(z)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y + z),
Q.real(x) & Q.real(y) & Q.imaginary(z)) is None
assert ask(Q.antihermitian(x + y + z),
@@ -2130,7 +2138,7 @@ def test_compute_known_facts():
@slow
def test_known_facts_consistent():
""""Test that ask_generated.py is up-to-date"""
- from sympy.assumptions.ask import get_known_facts, get_known_facts_keys
+ from sympy.assumptions.facts import get_known_facts, get_known_facts_keys
from os.path import abspath, dirname, join
filename = join(dirname(dirname(abspath(__file__))), 'ask_generated.py')
with open(filename) as f:
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py
index 6ce543c84f1d..8066fd527e3e 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py
@@ -96,7 +96,6 @@ def _test_args(obj):
def test_sympy__assumptions__assume__AppliedPredicate():
from sympy.assumptions.assume import AppliedPredicate, Predicate
- from sympy import Q
assert _test_args(AppliedPredicate(Predicate("test"), 2))
assert _test_args(Q.is_true(True))
@@ -105,8 +104,10 @@ def test_sympy__assumptions__assume__Predicate():
pass
def test_predicates():
- from sympy.assumptions.ask import get_known_facts_keys
- predicates = get_known_facts_keys()
+ predicates = [
+ getattr(Q, attr)
+ for attr in Q.__class__.__dict__
+ if not attr.startswith('__')]
for p in predicates:
assert _test_args(p)
@@ -123,38 +124,31 @@ def test_sympy__assumptions__relation__binrel__AppliedBinaryRelation():
def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__UnevaluatedOnFree():
from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import UnevaluatedOnFree
- from sympy import Q
assert _test_args(UnevaluatedOnFree(Q.positive))
def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__AllArgs():
from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import AllArgs
- from sympy import Q
assert _test_args(AllArgs(Q.positive))
def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__AnyArgs():
from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import AnyArgs
- from sympy import Q
assert _test_args(AnyArgs(Q.positive))
def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__ExactlyOneArg():
from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import ExactlyOneArg
- from sympy import Q
assert _test_args(ExactlyOneArg(Q.positive))
def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__CheckOldAssump():
from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import CheckOldAssump
- from sympy import Q
assert _test_args(CheckOldAssump(Q.positive))
def test_sympy__assumptions__sathandlers__CheckIsPrime():
from sympy.assumptions.sathandlers import CheckIsPrime
- from sympy import Q
# Input must be a number
assert _test_args(CheckIsPrime(Q.positive))
def test_sympy__assumptions__wrapper__AssumptionsWrapper():
from sympy.assumptions.wrapper import AssumptionsWrapper
- from sympy import Q
assert _test_args(AssumptionsWrapper(x, Q.positive(x)))
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21459@382ea94
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,459
|
[WIP] Rational Riccati solver
|
This PR introduces a Rational Riccati ODE solver. This code can also be used to solve a subclass of 2nd order ODEs solvable by [Kovacic's Algorithm](https://cs.uwaterloo.ca/research/tr/1984/CS-84-35.pdf)
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Partial Fix #19183, #21503
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
The algorithm present [here](https://www3.risc.jku.at/publications/download/risc_5387/PhDThesisThieu.pdf) is implemented. The examples used to test are [here](https://www3.risc.jku.at/publications/download/risc_5197/RISCReport15-19.pdf).
#### Other comments
I will soon add the Kovacic solver.
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* solvers
* ode: Added a new solver for Riccati equation
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-05-11T16:56:48Z
|
Riccati's equation
Hello
I have a question regarding using Sympy for solving Riccati's equation:
y’ = -y**2 + x*y + 1
It seems that Sympy is not able to solve this equation, while a closed-formed solution in terms of the error function exists (Mathematica has no problem finding this solution).
Would someone have any advice?
Thanks a lot for your time.
Stay safe,
Elie.
|
Sympy currently gives a series solution:
```
In [3]: dsolve(Eq(f(x).diff(x), -f(x)**2 + f(x)*x + 1))
Out[3]:
3 ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎛ 2 ⎞ ⎞ 5 ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎛ 2 ⎞ ⎛
⎛ 2⎞ x ⋅⎝- 3⋅C₁ + ⎝1 - C₁ ⎠⋅⎝6⋅C₁ - 1⎠ + 1⎠ x ⋅⎝8⋅C₁ ⋅⎝1 - 3⋅C₁ ⎠ - 14⋅C₁ + ⎝1 - C₁ ⎠⋅⎝36⋅C₁ - 5⎠ + ⎝1 - C
f(x) = x⋅⎝1 - C₁ ⎠ + ──────────────────────────────────────── + ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
6
2⎞ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ⎞ 2 ⎛ 2 ⎞ 4 ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞
₁ ⎠⋅⎝- 16⋅C₁ ⋅⎝1 - 3⋅C₁ ⎠ + 36⋅C₁ + 8⋅⎝1 - 9⋅C₁ ⎠⋅⎝1 - C₁ ⎠ - 5⎠ + 2⎠ C₁⋅x ⋅⎝2⋅C₁ - 1⎠ C₁⋅x ⋅⎝12⋅C₁ + 8⋅⎝1 - 3⋅C₁ ⎠⋅
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── + C₁ + ───────────────── + ──────────────────────────────
120 2 24
⎛ 2⎞ ⎞
⎝1 - C₁ ⎠ - 5⎠ ⎛ 6⎞
────────────── + O⎝x ⎠
```
There is a solver for one type of Ricatti equation but maybe this is a different one.
Thanks. But a solution in terms of a series is not really useful when a closed-form solution exists
y(x) = E^(-x^2/2)/ (Sqrt(Pi/2) Erf(x/Sqrt(2)) + c)) + x
(with Erf the error function, and c an arbitrary constant).
> a solution in terms of a series is not really useful
I agree. In fact I don't think dsolve should return series solutions at all (#15916).
There is a handler for one type of Riccati ODE. I'm not sure if should handle this case or if another solver should be added.
The solver 'Riccati_special_minus2' is of no help in our case. Maybe there is another one, but I was not able to find it.
This is a special type of Riccati ODE, and it can be solved by finding a rational transformation to a Bernoulli ODE. This has not been implemented in sympy as far as I know. The Lie group is [0,exp((x^2)/2)*(y-x)^2] and this group can also not be found with the current implementations.
Another alternative is transforming it to a second order linear ode and use kovacic algorithm to solve second order linear ODEs with Liouvillian solutions. But it seems that this method is also not implemented in sympy? You could try the jupyter implementation of the maxima cas, the Kovacic algorithm as well as Lie's algorithm work for this ODE.
Interesting. How exactly would you transform this to a linear 2nd order ODE?
I had a quick look at the Kovacic algorithm and that definitely seems like something that should be added to sympy:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0747717186800104
Q. How exactly would you transform this to a linear 2nd order ODE?
A. Let’s start from the Riccati’s equation (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riccati_equation)
$y'(x) = a(x) + b(x) y(x) + c(x) y^2(x)$
with $a(x) \not= 0$ and $c(x) \not= 0$. (Note: If $a(x) = 0$ the equation reduces to a Bernoulli equation, while if $c(x) = 0$ the equation becomes a 1st oder linear ODE)
Let us define $S(x) = a(x) c(x)$ and R(x) = b(x) + c'(x)/c(x)$.
One can show (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riccati_equation) that if $u(x)$ is a solution of the 2nd order linear ODE:
$u''(x) - R(x) u'(x) + S(x) u(x) = 0$,
then $y(x) = -u'(x)/(c(x) u(x)$ is a solution of the original Riccati equation.
> Le 27 avr. 2020 à 02:31, Oscar Benjamin <[email protected]> a écrit :
>
>
> Interesting. How exactly would you transform this to a linear 2nd order ODE?
>
> I had a quick look at the Kovacic algorithm and that definitely seems like something that should be added to sympy:
> https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0747717186800104 <https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0747717186800104>
> —
> You are receiving this because you authored the thread.
> Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub <https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/19183#issuecomment-619650042>, or unsubscribe <https://github.com/notifications/unsubscribe-auth/APKF3JCQOFGONBZOKAKZWATROTG5ZANCNFSM4MP3R4WQ>.
>
Thanks so it's basically the substitution `y = u'/cu` i.e.:
```julia
In [19]: a, b, c, y, u = symbols('a, b, c, y, u', cls=Function)
In [20]: x = Symbol('x')
In [21]: eq_y = Eq(Derivative(y(x), x), a(x) + b(x)*y(x) + c(x)*y(x)**2)
In [22]: eq_y
Out[22]:
d 2
──(y(x)) = a(x) + b(x)⋅y(x) + c(x)⋅y (x)
dx
In [23]: eq_u_subs = eq_y.subs(y(x), -Derivative(u(x), x)/(c(x)*u(x)))
In [24]: eq_u_subs
Out[24]:
2
⎛ d ⎞ d ⎛d ⎞
⎜-──(u(x)) ⎟ b(x)⋅──(u(x)) ⎜──(u(x))⎟
d ⎜ dx ⎟ dx ⎝dx ⎠
──⎜──────────⎟ = a(x) - ───────────── + ───────────
dx⎝c(x)⋅u(x) ⎠ c(x)⋅u(x) 2
c(x)⋅u (x)
In [25]: eq_u = Eq(Derivative(u(x), x, 2), solve(eq_u_subs.doit(), Derivative(u(x), x, 2))[0].collect(u(x)))
In [26]: eq_u
Out[26]:
⎛ d ⎞
2 ⎜ ──(c(x))⎟
d ⎜ dx ⎟ d
───(u(x)) = ⎜b(x) + ────────⎟⋅──(u(x)) - a(x)⋅c(x)⋅u(x)
2 ⎝ c(x) ⎠ dx
dx
```
Yes, your calculation is correct.
(Note that there is a small typo in the first line of your message: the substitution is y = - u’/(c u) )
> Le 27 avr. 2020 à 11:58, Oscar Benjamin <[email protected]> a écrit :
>
>
> Thanks so it's basically the substitution y = u'/cu i.e.:
>
> In [19]: a, b, c, y, u = symbols('a, b, c, y, u', cls=Function)
>
> In [20]: x = Symbol('x')
>
> In [21]: eq_y = Eq(Derivative(y(x), x), a(x) + b(x)*y(x) + c(x)*y(x)**2)
>
> In [22]: eq_y
> Out[22]:
> d 2
> ──(y(x)) = a(x) + b(x)⋅y(x) + c(x)⋅y (x)
> dx
>
> In [23]: eq_u_subs = eq_y.subs(y(x), -Derivative(u(x), x)/(c(x)*u(x)))
>
> In [24]: eq_u_subs
> Out[24]:
> 2
> ⎛ d ⎞ d ⎛d ⎞
> ⎜-──(u(x)) ⎟ b(x)⋅──(u(x)) ⎜──(u(x))⎟
> d ⎜ dx ⎟ dx ⎝dx ⎠
> ──⎜──────────⎟ = a(x) - ───────────── + ───────────
> dx⎝c(x)⋅u(x) ⎠ c(x)⋅u(x) 2
> c(x)⋅u (x)
>
> In [25]: eq_u = Eq(Derivative(u(x), x, 2), solve(eq_u_subs.doit(), Derivative(u(x), x, 2))[0].collect(u(x)))
>
> In [26]: eq_u
> Out[26]:
> ⎛ d ⎞
> 2 ⎜ ──(c(x))⎟
> d ⎜ dx ⎟ d
> ───(u(x)) = ⎜b(x) + ────────⎟⋅──(u(x)) - a(x)⋅c(x)⋅u(x)
> 2 ⎝ c(x) ⎠ dx
> dx
> —
> You are receiving this because you authored the thread.
> Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub <https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/19183#issuecomment-619872552>, or unsubscribe <https://github.com/notifications/unsubscribe-auth/APKF3JFSGBWW76462BXP7DDROVJLDANCNFSM4MP3R4WQ>.
>
|
[
{
"body": "Hello\r\nI have a question regarding using Sympy for solving Riccati's equation:\r\ny’ = -y**2 + x*y + 1 \r\nIt seems that Sympy is not able to solve this equation, while a closed-formed solution in terms of the error function exists (Mathematica has no problem finding this solution).\r\nWould someone have any advice?\r\nThanks a lot for your time.\r\nStay safe,\r\nElie.",
"number": 19183,
"title": "Riccati's equation"
}
] |
49470f4c02543337647b9dd37ac900c40e208b0c
|
{
"head_commit": "382ea94adcef2474e7578701fb248e7a25300766",
"head_commit_message": "Added riccati submodule",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py\nindex 98bad219834d..d97d155371fe 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py\n@@ -332,6 +332,7 @@\n \"Liouville_Integral\",\n \"2nd_nonlinear_autonomous_conserved\",\n \"2nd_nonlinear_autonomous_conserved_Integral\",\n+ \"1st_rational_riccati\",\n )\n \n lie_heuristics = (\n@@ -1053,6 +1054,7 @@ class in it. Note that a hint may do this anyway if\n Factorable: ('factorable',),\n RiccatiSpecial: ('Riccati_special_minus2',),\n SecondNonlinearAutonomousConserved: ('2nd_nonlinear_autonomous_conserved',),\n+ RationalRiccati: ('1st_rational_riccati',),\n }\n for solvercls in solvers:\n solver = solvercls(ode)\n@@ -7096,3 +7098,4 @@ def _nonlinear_3eq_order1_type5(x, y, z, t, eq):\n from .single import (NthAlgebraic, Factorable, FirstLinear, AlmostLinear,\n Bernoulli, SingleODEProblem, SingleODESolver, RiccatiSpecial,\n SecondNonlinearAutonomousConserved)\n+from .riccati import RationalRiccati\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/riccati.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/riccati.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..dd8cba72e0e4\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/riccati.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,500 @@\n+r\"\"\"\n+This module contains :py:meth:`~sympy.solvers.ode.riccati.RationalRiccati`,\n+a solver class which gives rational solutions to first order Riccati ODEs.\n+A general first order Riccati ODE is given by\n+\n+.. math:: y' = b_0(x) + b_1(x)w + b_2(x)w^2\n+\n+where `b_0, b_1` and `b_2` can be arbitrary functions of `x` with `b_2 \\ne 0`.\n+\n+Background\n+==========\n+\n+A Riccati equation can be transformed to its normal form\n+\n+.. math:: y' + y^2 = a(x)\n+\n+using the transformation\n+\n+.. math:: y = -b_2(x) - \\frac{b'_2(x)}{2 b_2(x)} - \\frac{b_1(x)}{2}\n+\n+where `a(x)` is given by\n+\n+.. math:: a(x) = \\frac{1}{4}\\left(\\frac{b_2'}{b_2} + b_1\\right)^2 - \\frac{1}{2}\\left(\\frac{b_2'}{b_2} + b_1\\right)' - b_0 b_2\n+\n+Thus, we can develop an algorithm to solve for the Riccati equation\n+in its normal form, which would in turn give us the solution for\n+the original Riccati equation.\n+\n+Algorithm\n+=========\n+\n+The algorithm implemented here was presented in a Ph.D thesis by\n+N. Thieu Vo. The entire thesis can be found here -\n+https://www3.risc.jku.at/publications/download/risc_5387/PhDThesisThieu.pdf\n+\n+We have only implemented the Rational Riccati solver (Pg 78 in Thesis).\n+Before we proceed towards the implementation of the algorithm, a\n+few definitions to understand -\n+\n+1. Valuation of a Rational Function at `\\infty`:\n+ The valuation of a rational function `p(x)` at `\\infty` is equal\n+ to the difference between the degree of the denominator and the\n+ numerator of `p(x)`.\n+\n+ Note: A general definition of valuation of a rational function\n+ at any value of `x` can be found in Pg 63 of the thesis, but\n+ is not of any interest for this algorithm.\n+\n+2. Zeros and Poles of a Rational Function:\n+ Let `a(x) = \\frac{S(x)}{T(x)}, T \\ne 0` be a rational function\n+ of `x`. Then -\n+\n+ a. The Zeros of `a(x)` are the roots of `S(x)`.\n+ b. The Poles of `a(x)` are the roots of `T(x)`. However, `\\infty`\n+ can also be a pole of a(x). We say that `a(x)` has a pole at\n+ `\\infty` if `a(\\frac{1}{x})` has a pole at 0.\n+\n+Every pole is associated with an order that is equal to the multiplicity\n+of its appearence as a root of `T(x)`. A pole is called a simple pole if\n+it has an order 1. Similarly, a pole is called a multiple pole if it has\n+an order `\\ge` 2.\n+\n+Necessary Conditions\n+====================\n+\n+For a Riccati equation in its normal form,\n+\n+.. math:: y' + y^2 = a(x)\n+\n+we can define\n+\n+a. A pole is called a movable pole if it is a pole of `y(x)` and is not\n+a pole of `a(x)`.\n+b. Similarly, a pole is called a non-movable pole if it is a pole of both\n+`y(x)` and `a(x)`.\n+\n+Then, the algorithm states that a rational solution exists only if -\n+\n+a. Every pole of `a(x)` must be either a simple pole or a multiple pole\n+of even order.\n+b. The valuation of `a(x)` at `\\infty` must be even or be `\\ge` 2.\n+\n+Implementation\n+==============\n+\n+The code is written to match the steps given in the thesis (Pg 82)\n+\n+Step 0 : Match the equation -\n+Find `b_0, b_1` and `b_2`. If `b_2 = 0` or no such functions exist, raise\n+an error\n+\n+Step 1 : Transform the equation to its normal form as explained in the\n+theory section.\n+\n+Step 2 : Initialize 2 empty set of solutions, ``sol`` and ``presol``.\n+\n+Step 3 : If `a(x) = 0`, append `\\frac{1}/{(x - C1)}` to ``presol``.\n+\n+Step 4 : If `a(x)` is a rational non-zero number, append `\\pm \\sqrt{a}`\n+to ``presol``.\n+\n+Step 5 : Find the poles and their multiplicities of `a(x)` using\n+``find_poles``. Let the number of poles be `n`. Also find the\n+valuation of `a(x)` at `\\infty` using ``val_at_inf``.\n+\n+Step 6 : Find `n` c-vectors (one for each pole) and 1 d-vector using\n+``construct_c`` and ``construct_d``. Now, determine all the ``2**(n + 1)``\n+combinations of choosing between 2 choices for each of the `n` c-vectors\n+and 1 d-vector.\n+\n+For each of these above combinations, do\n+\n+Step 8 : Compute `m` in ``compute_degree``\n+\n+Step 9 : In ``compute_degree``, compute ybar as well. If ybar contains any\n+term like `\\frac{c_{ij}}{(x - oo)^j}` where `c_{ij}` is non-zero, discard\n+this solution.\n+\n+Step 10 : If `m` is a non-negative integer -\n+\n+Step 11: Find a polynomial solution of degree `m` for the auxiliary equation.\n+\n+There are 2 cases possible -\n+\n+ a. `m` is a non-negative integer: We can solve for the coefficients\n+ in `p(x)` using Undetermined Coefficients.\n+\n+ b. `m` is an expression: In this case, we may not be able to determine\n+ if it is possible for `m` to be a non-negative integer. However, the\n+ solution to the auxiliary equation always seems to be x**m + C1 (where\n+ C1 is an arbitrary constant). This has been confirmed by testing many\n+ examples. NOTE that this is NOT mentioned in the thesis and is an\n+ assumption made by me. If any failing test cases are found, this case\n+ must be removed.\n+\n+Step 12 : For each `p(x)` that exists, append `ybar + \\frac{p'(x)}{p(x)}`\n+to ``presol``.\n+\n+Step 13 : For each solution in ``presol``, apply an inverse transformation\n+and append them to ``sol``, so that the solutions of the original equation\n+are found using the solutions of the equation in its normal form.\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+from .single import SinglePatternODESolver\n+\n+from sympy.core import S\n+from sympy.core.add import Add\n+from sympy.core.function import Function\n+from sympy.core.numbers import oo\n+from sympy.core.relational import Eq\n+from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol, Wild\n+from sympy.functions import sqrt\n+from sympy.polys.polytools import cancel, degree\n+from sympy.polys.polyroots import roots\n+from sympy.simplify.radsimp import numer, denom\n+from sympy.series.limits import limit\n+from sympy.solvers.solvers import solve\n+\n+class RationalRiccati(SinglePatternODESolver):\n+ r\"\"\"\n+ Gives all rational solutions to the first\n+ order Riccati Differential Equation\n+\n+ .. math :: y' = b_0(x) + b_1(x) y + b_2(x) y^2\n+\n+ where `b_0`, `b_1` and `b_2` are rational functions of `x`\n+ with `b_2 \\ne 0` (`b_2 = 0` would make it a Bernoulli equation).\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, Function, dsolve, checkodesol\n+ >>> f = Function('f')\n+ >>> x = Symbol('x')\n+\n+ >>> eq = x**3*f(x).diff(x) - x**2*f(x) - f(x)**2\n+ >>> sols = dsolve(eq, hint=\"1st_rational_riccati\")\n+ >>> sols\n+ Eq(f(x), x**2*(-x/(C1 + x) + 1))\n+ >>> checkodesol(eq, sols)\n+ (True, 0)\n+\n+ >>> eq = -x**4*f(x)**2 + x**3*f(x).diff(x) + x**2*f(x) + 20\n+ >>> sols = dsolve(eq, hint=\"1st_rational_riccati\")\n+ >>> sols\n+ [Eq(f(x), (-9*x**8/(C1 + x**9) + 4/x)/x), Eq(f(x), 4/x**2)]\n+ >>> checkodesol(eq, sols)\n+ [(True, 0), (True, 0)]\n+\n+ >>> eq = x**3*f(x).diff(x) - x**2*(f(x) + f(x).diff(x)) + 2*x*f(x) - f(x)**2\n+ >>> sols = dsolve(eq, hint=\"1st_rational_riccati\")\n+ >>> sols\n+ Eq(f(x), x**2*(1 - (x - 1)/(C1 + x)))\n+ >>> checkodesol(eq, sols)\n+ (True, 0)\n+\n+ References\n+ ==========\n+\n+ .. [1] Algorithm (Pg 78) - https://www3.risc.jku.at/publications/download/risc_5387/PhDThesisThieu.pdf\n+ .. [2] Examples - https://www3.risc.jku.at/publications/download/risc_5197/RISCReport15-19.pdf\n+ \"\"\"\n+ has_integral = False\n+ hint = \"1st_rational_riccati\"\n+ order = [1]\n+\n+ def _wilds(self, f, x, order):\n+ b0 = Wild('b0', exclude=[f(x), f(x).diff(x)])\n+ b1 = Wild('b1', exclude=[f(x), f(x).diff(x)])\n+ b2 = Wild('b2', exclude=[f(x), f(x).diff(x)])\n+ return (b0, b1, b2)\n+\n+ def _equation(self, fx, x, order):\n+ b0, b1, b2 = self.wilds()\n+ return fx.diff(x) - b0 - b1*fx - b2*fx**2\n+\n+ def _matches(self):\n+ eq = self.ode_problem.eq_expanded\n+ f = self.ode_problem.func.func\n+ x = self.ode_problem.sym\n+ order = self.ode_problem.order\n+\n+ if order != 1:\n+ return False\n+\n+ eq = eq.collect(f(x))\n+ cf = eq.coeff(f(x).diff(x))\n+\n+ # There must be an f(x).diff(x) term.\n+ # eq must be an Add object since we are using the expanded\n+ # equation and it must have atleast 2 terms (b2 != 0)\n+ if cf != 0 and isinstance(eq, Add):\n+\n+ # Divide all coefficients by the coefficient of f(x).diff(x)\n+ # and add the terms again to get the same equation\n+ eq = Add(*map(lambda x: cancel(x/cf), eq.args)).collect(f(x))\n+\n+ # Get the pattern for the Riccati equation\n+ pattern = self._equation(f(x), x, order)\n+\n+ # Match the equation with the pattern\n+ self._wilds_match = match = eq.match(pattern)\n+\n+ # If there is a match, verify it\n+ if match is not None:\n+ return self._verify(f(x))\n+ return False\n+\n+ def _verify(self, fx):\n+ b0, b1, b2 = self.wilds_match()\n+ x = self.ode_problem.sym\n+\n+ # b0, b1 and b2 must all be rational functions of x, with b2 != 0\n+ return all([b2 != 0, b0.is_rational_function(x), b1.is_rational_function(x), b2.is_rational_function(x)])\n+\n+ def solve_aux_eq(self, a, x, m, ybar):\n+ p = Function('p')\n+ # Eq (5.16) in Thesis - Pg 81\n+ auxeq = numer((p(x).diff(x, 2) + 2*ybar*p(x).diff(x) + (ybar.diff(x) + ybar**2 - a)*p(x)).together())\n+\n+ # Assume that the solution is of the type\n+ # p(x) = C0 + C1*x + ... + Cm*x**m\n+ psyms = get_numbered_constants(auxeq, m)\n+ if type(psyms) != tuple:\n+ psyms = (psyms, )\n+ psol = x**m\n+ for i in range(m):\n+ psol += psyms[i]*x**i\n+ if m != 0:\n+ # m is a non-zero integer. Find the constant terms using undetermined coefficients\n+ return psol, solve(auxeq.subs(p(x), psol).doit().expand(), psyms, dict=True), True\n+ else:\n+ # m ==0 . Check if 1 (x**0) is a solution to the auxiliary equation\n+ cf = auxeq.subs(p(x), psol).doit().expand()\n+ return S(1), cf, cf == 0\n+\n+ def compute_degree(self, x, poles, choice, c, d, N):\n+ ybar = 0\n+ m = S(d[choice[0]][-1])\n+\n+ # Calculate the first (nested) summation for ybar\n+ # as given in Step 9 of the Thesis (Pg 82)\n+ for i in range(len(poles)):\n+ for j in range(len(c[i][choice[i + 1]])):\n+ # If one of the poles is infinity and its coefficient is\n+ # not zero, the given solution is invalid as there will be\n+ # a c/(x - oo)^j term in ybar for some c and j\n+ if poles[i] == oo and c[i][choice[i + 1]][j] != 0:\n+ return m, ybar, False\n+ ybar += c[i][choice[i + 1]][j]/(x - poles[i])**(j+1)\n+ m -= c[i][choice[i + 1]][0]\n+\n+ # Calculate the second summation for ybar\n+ for i in range(N+1):\n+ ybar += d[choice[0]][i]*x**i\n+ return m, ybar, True\n+\n+ def construct_d(self, a, x, val_inf):\n+ ser = a.series(x, oo)\n+ N = -val_inf//2\n+\n+ # Case 4\n+ if val_inf < 0:\n+ temp = [0 for i in range(N+2)]\n+ temp[N] = sqrt(ser.coeff(x, 2*N))\n+ for s in range(N-1, -2, -1):\n+ sm = 0\n+ for j in range(s+1, N):\n+ sm += temp[j]*temp[N+s-j]\n+ if s != -1:\n+ temp[s] = (ser.coeff(x, N+s) - sm)/(2*temp[N])\n+ temp1 = list(map(lambda x: -x, temp))\n+ temp[-1] = (ser.coeff(x, N+s) - temp[N] - sm)/(2*temp[N])\n+ temp1[-1] = (ser.coeff(x, N+s) - temp1[N] - sm)/(2*temp1[N])\n+ d = [temp, temp1]\n+\n+ # Case 5\n+ elif val_inf == 0:\n+ # List to store coefficients for plus case\n+ temp = [0, 0]\n+\n+ # d_0 = sqrt(a_0)\n+ temp[0] = sqrt(ser.coeff(x, 0))\n+\n+ # d_(-1) = a_(-1)/(2*d_0)\n+ temp[-1] = ser.coeff(x, -1)/(2*temp[0])\n+\n+ # Coefficients for the minus case are just the negative\n+ # of the coefficients for the positive case. Append both.\n+ d = [temp, list(map(lambda x: -x, temp))]\n+\n+ # Case 6\n+ else:\n+ # s_oo = lim x->0 1/x**2 * a(1/x) which is equivalent to\n+ # s_oo = lim x->oo x**2 * a(x)\n+ s_inf = limit(x**2*a, x, oo)\n+\n+ # d_(-1) = (1 +- sqrt(1 + 4*s_oo))/2\n+ d = [[(1 + sqrt(1 + 4*s_inf))/2], [(1 - sqrt(1 + 4*s_inf))/2]]\n+ return d\n+\n+ def construct_c(self, a, x, poles, muls):\n+ c = []\n+ for pole, mul in zip(poles, muls):\n+ c.append([])\n+\n+ # Case 3\n+ if mul == 1:\n+ # If multiplicity is 1, the coefficient to be added\n+ # in the c-vector is 1 (no choice)\n+ c[-1].extend([[1], [1]])\n+\n+ # Case 1\n+ elif mul == 2:\n+ # Find the coefficient of 1/(x - pole)**2 in the\n+ # Laurent series expansion of a(x) about pole.\n+ r = a.series(x, pole).coeff(x - pole, -2)\n+\n+ # If multiplicity is 2, the coefficient to be added\n+ # in the c-vector is c = (1 +- sqrt(1 + 4*r))/2\n+ c[-1].extend([[(1 + sqrt(1 + 4*r))/2], [(1 - sqrt(1 + 4*r))/2]])\n+\n+ # Case 2\n+ else:\n+ # Generate the coefficients using the recurrence\n+ # relation mentioned in (5.14) in the thesis (Pg 80)\n+\n+ # r_i = mul/2\n+ ri = mul//2\n+\n+ # Find the Laurent series about the pole\n+ ser = a.series(x, pole)\n+\n+ # Start with an empty memo to store the coefficients\n+ # This is for the plus case\n+ temp = [0 for i in range(ri)]\n+\n+ # Base Case\n+ temp[ri-1] = sqrt(ser.coeff(x - pole, -mul))\n+\n+ # Iterate backwards to find all coefficients\n+ for s in range(ri-1, 0, -1):\n+ sm = 0\n+ for j in range(s+1, ri):\n+ sm += temp[j-1]*temp[ri+s-j-1]\n+ if s!= 1:\n+ temp[s-1] = (ser.coeff(x - pole, -ri-s) - sm)/(2*temp[ri-1])\n+\n+ # Memo for the minus case\n+ temp1 = list(map(lambda x: -x, temp))\n+\n+ # Find the 0th coefficient in the recurrence\n+ temp[0] = (ser.coeff(x - pole, -ri-s) - sm + ri*temp[ri-1])/(2*temp[ri-1])\n+ temp1[0] = (ser.coeff(x - pole, -ri-s) - sm + ri*temp1[ri-1])/(2*temp1[ri-1])\n+\n+ # Add both the plus and minus cases' coefficients\n+ c[-1].extend([temp, temp1])\n+ return c\n+\n+ def find_poles(self, a, x):\n+ # All roots of denominator are poles of a(x)\n+ p = roots(denom(a), x)\n+\n+ # Substitute 1/x for x and check if oo is a pole\n+ a = cancel(a.subs(x, 1/x).together())\n+\n+ # Find the poles of a(1/x)\n+ p_inv = roots(denom(a))\n+\n+ # If 0 is a pole of a(1/x), oo is a pole of a(x)\n+ if 0 in p_inv:\n+ p.update({oo: p_inv[0]})\n+ return p\n+\n+ def val_at_inf(self, a, x):\n+ numer, denom = a.as_numer_denom()\n+ # Valuation of a rational function at oo = deg(denom) - deg(numer)\n+ return degree(denom, x) - degree(numer, x)\n+\n+ def _get_general_solution(self, *, simplify: bool = True):\n+ # Step 0 :Match the equation\n+ b0, b1, b2 = self.wilds_match()\n+ fx = self.ode_problem.func\n+ x = self.ode_problem.sym\n+\n+ # Step 1 : Convert to Normal Form\n+ a = -b0*b2 + b1**2/4 - b1.diff(x)/2 + 3*b2.diff(x)**2/(4*b2**2) + b1*b2.diff(x)/(2*b2) - b2.diff(x, 2)/(2*b2)\n+ a_t = cancel(a.together())\n+\n+ # Step 2\n+ presol = []\n+\n+ # Step 3 : a(x) is 0\n+ if a_t == 0:\n+ presol.append(1/(x + self.ode_problem.get_numbered_constants(num=1)[0]))\n+\n+ # Step 4 : a(x) is a non-zero constant\n+ elif x not in a_t.free_symbols:\n+ presol.extend([sqrt(a), -sqrt(a)])\n+\n+ # Step 5 : Find poles and valuation at infinity\n+ poles = self.find_poles(a_t, x)\n+ poles, muls = list(poles.keys()), list(poles.values())\n+ val_inf = self.val_at_inf(a_t, x)\n+\n+ if len(poles):\n+ # Check necessary conditions (outlined in the module docstring)\n+ if val_inf%2 != 0 or not all(map(lambda mul: (mul == 1 or (mul%2 == 0 and mul >= 2)), muls)):\n+ raise ValueError(\"Rational Solution doesn't exist\")\n+\n+ # Step 6\n+ # Construct c-vectors for each singular point\n+ c = self.construct_c(a, x, poles, muls)\n+\n+ # Construct d vectors for each singular point\n+ d = self.construct_d(a, x, val_inf)\n+\n+ # Step 7 : Iterate over all possible combinations and return solutions\n+ for it in range(2**(len(poles) + 1)):\n+ # For each possible combination, generate an array of 0's and 1's\n+ # where 0 means pick 1st choice and 1 means pick the second choice.\n+ choice = list(map(lambda x: int(x), bin(it)[2:].zfill(len(poles) + 1)))\n+\n+ # Step 8 and 9 : Compute m and ybar\n+ m, ybar, exists = self.compute_degree(x, poles, choice, c, d, -val_inf//2)\n+\n+ # Step 10 : Check if a valid solution exists. If yes, also check\n+ # if m is a non-negative integer\n+ if exists and S(m).is_nonnegative == True and S(m).is_integer == True:\n+\n+ # Step 11 : Find polynomial solutions of degree m for the auxiliary equation\n+ psol, coeffs, exists = self.solve_aux_eq(a, x, m, ybar)\n+\n+ # Step 12 : If valid polynomial solution exists, append solution.\n+ if exists:\n+ # m == 0 case\n+ if psol == 1 and coeffs == 0:\n+ # p(x) = 1, so p'(x)/p(x) term need not be added\n+ presol.append(ybar)\n+ # m is a positive integer and there are valid coefficients\n+ elif len(coeffs):\n+ # Substitute the valid coefficients to get p(x)\n+ psol = psol.subs(coeffs[0])\n+ # y(x) = ybar(x) + p'(x)/p(x)\n+ presol.append(ybar + psol.diff(x)/psol)\n+\n+ # If m is an expression with symbols, we generate a Piecewise solution where\n+ # the solution will exist only if the expression is a nonnegative integer.\n+ # NOTE: In this case, it seems like x**m + C1 is always a solution\n+ # for the auxiliary equation. It is however NOT mentioned in the thesis.\n+ elif len(m.free_symbols):\n+ C1 = Symbol('C1')\n+ psol = x**m + C1\n+ presol.append(ybar + psol.diff(x)/psol)\n+ # Step 15 : Inverse transform the solutions of the equation in normal form\n+ sol = list(map(lambda y: Eq(fx, -y/b2 - b2.diff(x)/(2*b2**2) - b1/(2*b2)), presol))\n+ return sol\n+\n+# Avoid circular import:\n+from .ode import get_numbered_constants\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py\nindex 8dd5f00c28d0..127c3a9e2dbb 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py\n@@ -528,6 +528,10 @@ def test_Riccati_special_minus2():\n _ode_solver_test(_get_examples_ode_sol_riccati)\n \n \n+def test_1st_rational_riccati():\n+ _ode_solver_test(_get_examples_ode_sol_1st_rational_riccati)\n+\n+\n def test_Bernoulli():\n _ode_solver_test(_get_examples_ode_sol_bernoulli)\n \n@@ -780,6 +784,115 @@ def _get_examples_ode_sol_riccati():\n }\n \n \n+@_add_example_keys\n+def _get_examples_ode_sol_1st_rational_riccati():\n+ a, b, c, k = symbols('a b c k')\n+ # Type: 1st Order Rational Riccati, dy/dx = a + b*y + c*y**2,\n+ # a, b, c are rational functions of x\n+ return {\n+ 'hint': \"1st_rational_riccati\",\n+ 'func': f(x),\n+ 'examples':{\n+ \"rational_riccati_01\": {\n+ \"eq\": x**2 - (2*x + 1/x)*f(x) + f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), 2*x/(C1 + x**2) + (2*x**2 + 1)/(2*x) - 1/(2*x)), Eq(f(x), x)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_02\": {\n+ \"eq\": f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) - (4*x**6 - 8*x**5 + 12*x**4 + 4*x**3 + 7*x**2 - 20*x + 4)/(4*x**4),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), x + 2*x/(x**2 - 1) - 1 - 3/(2*x) + x**(-2))]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_03\": {\n+ \"eq\": -x*f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) - 2*f(x)/x,\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), -4*x**2/(C1 + x**4)), Eq(f(x), 0)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_04\": {\n+ \"eq\": -f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) + (15*x**2 - 20*x + 7)/((x - 1)**2*(2*x - 1)**2),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), Mul(-2, (2*x**3 - 5*x**2 + 4*x - 1), evaluate=False)/(C1 + x**4 - 10*x**3/3 + 4*x**2 - 2*x) +\n+ (S(1)/2)*(1/(x - S(1)/2)) + 1/(x - 1)), Eq(f(x), (S(1)/2)*(1/(x - S(1)/2)) + 1/(x - 1))]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_05\": {\n+ \"eq\": 9*x**2/4 - f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) - S(21)/2,\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), 3*x/2 - (3*x**2 - 1)/(x*(x**2 - 1)))]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_06\": {\n+ \"eq\": Derivative(f(x), x) + (3*x**2 + 1)*f(x)**2/x + (6*x**2 - x + 3)*f(x)/(x*(x - 1)) + (3*x**2 - 2*x + 2)/(x*(x - 1)**2),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), (-x**2*(-6 + (3*x**2 + 1)/x**2)/Mul(2, (3*x**2 + 1), evaluate=False) - x*(-3/Mul(2, (x + sqrt(3)*I/3), \\\n+ evaluate=False) + 1/Mul(2, (x - sqrt(3)*I/3), evaluate=False) - 1/(x - 2*sqrt(3)*I/3)) - (6*x**2 - x + 3)/Mul(2, (x - 1), \\\n+ evaluate=False))/(3*x**2 + 1)), Eq(f(x), (-x**2*(-6 + (3*x**2 + 1)/x**2)/Mul(2, (3*x**2 + 1), evaluate=False) - \\\n+ x*(-1/(x + 2*sqrt(3)*I/3) + 1/Mul(2, (x + sqrt(3)*I/3), evaluate=False) - 3/Mul(2, (x - sqrt(3)*I/3), evaluate=False)) \\\n+ - (6*x**2 - x + 3)/Mul(2, (x - 1), evaluate=False))/(3*x**2 + 1)), Eq(f(x), (-x**2*(-6 + (3*x**2 + 1)/x**2)/Mul(2, \\\n+ (3*x**2 + 1), evaluate=False) - x*(Mul(-1, (3*x**2 + 1), evaluate=False)/(C1 + x**3 + x) + 1/Mul(2, (x + sqrt(3)*I/3), \\\n+ evaluate=False) + 1/Mul(2, (x - sqrt(3)*I/3), evaluate=False)) - (6*x**2 - x + 3)/Mul(2, (x - 1), evaluate=False)) \\\n+ /(3*x**2 + 1)), Eq(f(x), (-x**2*(-6 + (3*x**2 + 1)/x**2)/(3*x**2 + 1) - x*(1/(x + sqrt(3)*I/3) + 1/(x - sqrt(3)*I/3)) \\\n+ - (6*x**2 - x + 3)/(x - 1))/Mul(2, (3*x**2 + 1), evaluate=False))]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_07\": {\n+ \"eq\": f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) - 15/(4*x**2),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), 4*x**3/(C1 + x**4) - 3/(2*x)), Eq(f(x), -3/(2*x))]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_08\": {\n+ \"eq\": 3*f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) - 2/x**2,\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), 5*x**4/Mul(3, (C1 + x**5), evaluate=False) - 2/(3*x)), Eq(f(x), -2/(3*x))]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_09\": {\n+ \"eq\": -a*b*k**2*f(x)**2 + 2*a*b*k*f(x) - a*b + Derivative(f(x), x),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), (1 - 1/(a*b*k*(C1 + x)))/k)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_10\": {\n+ \"eq\": Derivative(f(x), x) - 2*I*(f(x)**2 + 1)/x,\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), -I*x*(-4*x**3/(C1 + x**4) + 3/(2*x))/2 - I/4), Eq(f(x), -I)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_11\": {\n+ \"eq\": Derivative(f(x), x) - f(x)**2/x + 1/x,\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), x*(-2*x/(C1 + x**2) + 1/(2*x)) + S(1)/2), Eq(f(x), 1)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_12\": {\n+ \"eq\": a*f(x)**2 + c + x*Derivative(f(x), x),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), sqrt(-a*c)*(2*x**(2*sqrt(-a*c))/(C1 + x**(2*sqrt(-a*c))) - 1)/a), Eq(f(x), -sqrt(-a*c)/a)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_13\": {\n+ \"eq\": a*f(x)**2/x - b*f(x)/x - c/x + Derivative(f(x), x),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), (b/2 + x**(sqrt(4*a*c + b**2))*sqrt(4*a*c + b**2)/(C1 + x**(sqrt(4*a*c + b**2))) - \\\n+ sqrt(4*a*c + b**2)/2)/a), Eq(f(x), (b - sqrt(4*a*c + b**2))/(2*a))]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_14\": {\n+ \"eq\": f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) - f(x)/x,\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), 2*x/(C1 + x**2)), Eq(f(x), 0)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_15\": {\n+ \"eq\": -x**2 - (2*x + 1/x)*f(x) - f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), -2*x/(C1 + x**2) - (2*x**2 + 1)/(2*x) + 1/(2*x)), Eq(f(x), -x)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_16\": {\n+ \"eq\": f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) + 4*f(x)/x + 2/x**2,\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), 1/(C1 + x) - 2/x)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_17\": {\n+ \"eq\": a*f(x)**2 - b/x**2 + Derivative(f(x), x),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), Mul(-1, (-x**(sqrt(4*a*b + 1))*sqrt(4*a*b + 1)/(C1 + x**(sqrt(4*a*b + 1))) + \\\n+ sqrt(4*a*b + 1)/2 - S(1)/2), evaluate=False)/(a*x)), Eq(f(x), (1 - sqrt(4*a*b + 1))/(2*a*x))]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_18\": {\n+ \"eq\": a*f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) + (b + c)/x**2,\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), Mul(-1, (-x**(sqrt(-4*a*(b + c) + 1)/2 + sqrt(-4*a*b - 4*a*c + 1)/2)*(sqrt(-4*a*(b + c) + 1) \\\n+ + sqrt(-4*a*b - 4*a*c + 1))/(C1 + x**(sqrt(-4*a*(b + c) + 1)/2 + sqrt(-4*a*b - 4*a*c + 1)/2)) + sqrt(-4*a*b \\\n+ - 4*a*c + 1) - 1), evaluate=False)/(2*a*x)), Eq(f(x), Mul(-1, (-x**(-sqrt(-4*a*(b + c) + 1)/2 + sqrt(-4*a*b \\\n+ - 4*a*c + 1)/2)*(-sqrt(-4*a*(b + c) + 1) + sqrt(-4*a*b - 4*a*c + 1))/(C1 + x**(-sqrt(-4*a*(b + c) + 1)/2 + \\\n+ sqrt(-4*a*b - 4*a*c + 1)/2)) + sqrt(-4*a*b - 4*a*c + 1) - 1), evaluate=False)/(2*a*x))]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_19\": {\n+ \"eq\": 2*x**2*Derivative(f(x), x) - x*(4*f(x) + Derivative(f(x), x) - 4) + (f(x) - 1)*f(x),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), -x*(1 - 2*x)/(C1 + x) - 2*x - (S(1)/2 - x)*(4*x + 1)/(2*x - 1) + S(1)/2)]\n+ },\n+ \"rational_riccati_20\": {\n+ \"eq\": x**4*Derivative(f(x), x) + x**2 - x*(2*f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x)) + f(x),\n+ \"sol\": [Eq(f(x), 3*x**2/4 + (x**3 - 1)*(-2*x/(C1 + x**2) + 1/(2*x))/2 + 1/(4*x)), \\\n+ Eq(f(x), 3*x**2/4 + (x**3 - 1)/(4*x) + 1/(4*x))]\n+ }\n+ }\n+ }\n+\n+\n @_add_example_keys\n def _get_examples_ode_sol_1st_linear():\n # Type: first order linear form f'(x)+p(x)f(x)=q(x)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,500 @@\n+r\"\"\"\n+This module contains :py:meth:`~sympy.solvers.ode.riccati.RationalRiccati`,\n+a solver class which gives rational solutions to first order Riccati ODEs.\n+A general first order Riccati ODE is given by\n+\n+.. math:: y' = b_0(x) + b_1(x)w + b_2(x)w^2\n+\n+where `b_0, b_1` and `b_2` can be arbitrary functions of `x` with `b_2 \\ne 0`.\n+\n+Background\n+==========\n+\n+A Riccati equation can be transformed to its normal form\n+\n+.. math:: y' + y^2 = a(x)\n+\n+using the transformation\n+\n+.. math:: y = -b_2(x) - \\frac{b'_2(x)}{2 b_2(x)} - \\frac{b_1(x)}{2}\n+\n+where `a(x)` is given by\n+\n+.. math:: a(x) = \\frac{1}{4}\\left(\\frac{b_2'}{b_2} + b_1\\right)^2 - \\frac{1}{2}\\left(\\frac{b_2'}{b_2} + b_1\\right)' - b_0 b_2\n+\n+Thus, we can develop an algorithm to solve for the Riccati equation\n+in its normal form, which would in turn give us the solution for\n+the original Riccati equation.\n+\n+Algorithm\n+=========\n+\n+The algorithm implemented here was presented in a Ph.D thesis by\n+N. Thieu Vo. The entire thesis can be found here -\n+https://www3.risc.jku.at/publications/download/risc_5387/PhDThesisThieu.pdf\n+\n+We have only implemented the Rational Riccati solver (Pg 78 in Thesis).\n+Before we proceed towards the implementation of the algorithm, a\n+few definitions to understand -\n+\n+1. Valuation of a Rational Function at `\\infty`:\n+ The valuation of a rational function `p(x)` at `\\infty` is equal\n+ to the difference between the degree of the denominator and the\n+ numerator of `p(x)`.\n+\n+ Note: A general definition of valuation of a rational function\n+ at any value of `x` can be found in Pg 63 of the thesis, but\n+ is not of any interest for this algorithm.\n+\n+2. Zeros and Poles of a Rational Function:\n+ Let `a(x) = \\frac{S(x)}{T(x)}, T \\ne 0` be a rational function\n+ of `x`. Then -\n+\n+ a. The Zeros of `a(x)` are the roots of `S(x)`.\n+ b. The Poles of `a(x)` are the roots of `T(x)`. However, `\\infty`\n+ can also be a pole of a(x). We say that `a(x)` has a pole at\n+ `\\infty` if `a(\\frac{1}{x})` has a pole at 0.\n+\n+Every pole is associated with an order that is equal to the multiplicity\n+of its appearence as a root of `T(x)`. A pole is called a simple pole if\n+it has an order 1. Similarly, a pole is called a multiple pole if it has\n+an order `\\ge` 2.\n+\n+Necessary Conditions\n+====================\n+\n+For a Riccati equation in its normal form,\n+\n+.. math:: y' + y^2 = a(x)\n+\n+we can define\n+\n+a. A pole is called a movable pole if it is a pole of `y(x)` and is not\n+a pole of `a(x)`.\n+b. Similarly, a pole is called a non-movable pole if it is a pole of both\n+`y(x)` and `a(x)`.\n+\n+Then, the algorithm states that a rational solution exists only if -\n+\n+a. Every pole of `a(x)` must be either a simple pole or a multiple pole\n+of even order.\n+b. The valuation of `a(x)` at `\\infty` must be even or be `\\ge` 2.\n+\n+Implementation\n+==============\n+\n+The code is written to match the steps given in the thesis (Pg 82)\n+\n+Step 0 : Match the equation -\n+Find `b_0, b_1` and `b_2`. If `b_2 = 0` or no such functions exist, raise\n+an error\n+\n+Step 1 : Transform the equation to its normal form as explained in the\n+theory section.\n+\n+Step 2 : Initialize 2 empty set of solutions, ``sol`` and ``presol``.\n+\n+Step 3 : If `a(x) = 0`, append `\\frac{1}/{(x - C1)}` to ``presol``.\n+\n+Step 4 : If `a(x)` is a rational non-zero number, append `\\pm \\sqrt{a}`\n+to ``presol``.\n+\n+Step 5 : Find the poles and their multiplicities of `a(x)` using\n+``find_poles``. Let the number of poles be `n`. Also find the\n+valuation of `a(x)` at `\\infty` using ``val_at_inf``.\n+\n+Step 6 : Find `n` c-vectors (one for each pole) and 1 d-vector using\n+``construct_c`` and ``construct_d``. Now, determine all the ``2**(n + 1)``\n+combinations of choosing between 2 choices for each of the `n` c-vectors\n+and 1 d-vector.\n+\n+For each of these above combinations, do\n+\n+Step 8 : Compute `m` in ``compute_degree``\n+\n+Step 9 : In ``compute_degree``, compute ybar as well. If ybar contains any\n+term like `\\frac{c_{ij}}{(x - oo)^j}` where `c_{ij}` is non-zero, discard\n+this solution.\n+\n+Step 10 : If `m` is a non-negative integer -\n+\n+Step 11: Find a polynomial solution of degree `m` for the auxiliary equation.\n+\n+There are 2 cases possible -\n+\n+ a. `m` is a non-negative integer: We can solve for the coefficients\n+ in `p(x)` using Undetermined Coefficients.\n+\n+ b. `m` is an expression: In this case, we may not be able to determine\n+ if it is possible for `m` to be a non-negative integer. However, the\n+ solution to the auxiliary equation always seems to be x**m + C1 (where\n+ C1 is an arbitrary constant). This has been confirmed by testing many\n+ examples. NOTE that this is NOT mentioned in the thesis and is an\n+ assumption made by me. If any failing test cases are found, this case\n+ must be removed.\n+\n+Step 12 : For each `p(x)` that exists, append `ybar + \\frac{p'(x)}{p(x)}`\n+to ``presol``.\n+\n+Step 13 : For each solution in ``presol``, apply an inverse transformation\n+and append them to ``sol``, so that the solutions of the original equation\n+are found using the solutions of the equation in its normal form.\n+\"\"\"\n+\n+from .single import SinglePatternODESolver\n+\n+from sympy.core import S\n+from sympy.core.add import Add\n+from sympy.core.function import Function\n+from sympy.core.numbers import oo\n+from sympy.core.relational import Eq\n+from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol, Wild\n+from sympy.functions import sqrt\n+from sympy.polys.polytools import cancel, degree\n+from sympy.polys.polyroots import roots\n+from sympy.simplify.radsimp import numer, denom\n+from sympy.series.limits import limit\n+from sympy.solvers.solvers import solve\n+\n+class RationalRiccati(SinglePatternODESolver):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 159,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/solvers/ode/riccati.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI don't think this should use SinglePatternODESolver.\r\n\r\nRather the code here should just be a bunch of functions for doing the different parts of the algorithm. Then we can make a Solve class in single.py that wraps this for the current dsolve framework.\n\n@author:\nSo we don't need the `RationalRiccati` class? What would the `Solve` class constitute?\n\n@user1:\nThe solver class would basically be this one except that it wouldn't have all of these methods. Instead it would just call the functions from the ricatti module.\r\n\r\nThese classes exist just for the current pattern-matching structure of dsolve but we might want to move beyond that to a different structure later so an algorithm like this should not be tied to that structure."
}
] |
b74008ab706238dede78b5cef12060aa65371820
|
diff --git a/doc/src/modules/solvers/ode.rst b/doc/src/modules/solvers/ode.rst
index 8f9c74fe856c..2076a36ba830 100644
--- a/doc/src/modules/solvers/ode.rst
+++ b/doc/src/modules/solvers/ode.rst
@@ -100,6 +100,11 @@ factorable
.. autoclass:: sympy.solvers.ode.single::FirstLinear
:members:
+1st_rational_riccati
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autoclass:: sympy.solvers.ode.single::RationalRiccati
+ :members:
+
2nd_linear_airy
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
.. autoclass:: sympy.solvers.ode.single::SecondLinearAiry
@@ -248,6 +253,56 @@ linear
^^^^^^
.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.ode::lie_heuristic_linear
+Rational Riccati Solver
+-----------------------
+These functions are intended for internal use to solve
+a first order Riccati differential equation with atleast
+one rational particular solution.
+
+riccati_normal
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::riccati_normal
+
+riccati_inverse_normal
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::riccati_inverse_normal
+
+riccati_reduced
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::riccati_reduced
+
+construct_c
+^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::construct_c
+
+construct_d
+^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::construct_d
+
+rational_laurent_series
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::rational_laurent_series
+
+compute_m_ybar
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::compute_m_ybar
+
+solve_aux_eq
+^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::solve_aux_eq
+
+remove_redundant_sols
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::remove_redundant_sols
+
+get_gen_sol_from_part_sol
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::get_gen_sol_from_part_sol
+
+solve_riccati
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+.. autofunction:: sympy.solvers.ode.riccati::solve_riccati
+
System of ODEs
--------------
These functions are intended for internal use by
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py
index 438336c3263f..22db13ff22f7 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py
@@ -283,6 +283,7 @@
"1st_exact",
"1st_linear",
"Bernoulli",
+ "1st_rational_riccati",
"Riccati_special_minus2",
"1st_homogeneous_coeff_best",
"1st_homogeneous_coeff_subs_indep_div_dep",
@@ -1035,6 +1036,7 @@ class in it. Note that a hint may do this anyway if
# d^3/dx^3(x y) = F(x)
ode = SingleODEProblem(eq_orig, func, x, prep=prep)
solvers = {
+ RationalRiccati: ('1st_rational_riccati',),
NthAlgebraic: ('nth_algebraic',),
FirstExact:('1st_exact',),
FirstLinear: ('1st_linear',),
@@ -4765,7 +4767,7 @@ def _nonlinear_3eq_order1_type5(x, y, z, t, eq):
#This import is written at the bottom to avoid circular imports.
-from .single import (NthAlgebraic, Factorable, FirstLinear, AlmostLinear,
+from .single import (NthAlgebraic, Factorable, FirstLinear, AlmostLinear, RationalRiccati,
Bernoulli, SingleODEProblem, SingleODESolver, RiccatiSpecial,
SecondNonlinearAutonomousConserved, FirstExact, Liouville, Separable,
SeparableReduced, HomogeneousCoeffSubsDepDivIndep, HomogeneousCoeffSubsIndepDivDep,
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/riccati.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/riccati.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..3842d0f9f159
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/riccati.py
@@ -0,0 +1,891 @@
+r"""
+This module contains :py:meth:`~sympy.solvers.ode.riccati.solve_riccati`,
+a function which gives all rational particular solutions to first order
+Riccati ODEs. A general first order Riccati ODE is given by -
+
+.. math:: y' = b_0(x) + b_1(x)w + b_2(x)w^2
+
+where `b_0, b_1` and `b_2` can be arbitrary rational functions of `x`
+with `b_2 \ne 0`. When `b_2 = 0`, the equation is not a Riccati ODE
+anymore and becomes a Linear ODE. Similarly, when `b_0 = 0`, the equation
+is a Bernoulli ODE. The algorithm presented below can find rational
+solution(s) to all ODEs with `b_2 \ne 0` that have a rational solution,
+or prove that no rational solution exists for the equation.
+
+Background
+==========
+
+A Riccati equation can be transformed to its normal form
+
+.. math:: y' + y^2 = a(x)
+
+using the transformation
+
+.. math:: y = -b_2(x) - \frac{b'_2(x)}{2 b_2(x)} - \frac{b_1(x)}{2}
+
+where `a(x)` is given by
+
+.. math:: a(x) = \frac{1}{4}\left(\frac{b_2'}{b_2} + b_1\right)^2 - \frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{b_2'}{b_2} + b_1\right)' - b_0 b_2
+
+Thus, we can develop an algorithm to solve for the Riccati equation
+in its normal form, which would in turn give us the solution for
+the original Riccati equation.
+
+Algorithm
+=========
+
+The algorithm implemented here is presented in the Ph.D thesis
+"Rational and Algebraic Solutions of First-Order Algebraic ODEs"
+by N. Thieu Vo. The entire thesis can be found here -
+https://www3.risc.jku.at/publications/download/risc_5387/PhDThesisThieu.pdf
+
+We have only implemented the Rational Riccati solver (Algorithm 11,
+Pg 78-82 in Thesis). Before we proceed towards the implementation
+of the algorithm, a few definitions to understand are -
+
+1. Valuation of a Rational Function at `\infty`:
+ The valuation of a rational function `p(x)` at `\infty` is equal
+ to the difference between the degree of the denominator and the
+ numerator of `p(x)`.
+
+ NOTE: A general definition of valuation of a rational function
+ at any value of `x` can be found in Pg 63 of the thesis, but
+ is not of any interest for this algorithm.
+
+2. Zeros and Poles of a Rational Function:
+ Let `a(x) = \frac{S(x)}{T(x)}, T \ne 0` be a rational function
+ of `x`. Then -
+
+ a. The Zeros of `a(x)` are the roots of `S(x)`.
+ b. The Poles of `a(x)` are the roots of `T(x)`. However, `\infty`
+ can also be a pole of a(x). We say that `a(x)` has a pole at
+ `\infty` if `a(\frac{1}{x})` has a pole at 0.
+
+Every pole is associated with an order that is equal to the multiplicity
+of its appearence as a root of `T(x)`. A pole is called a simple pole if
+it has an order 1. Similarly, a pole is called a multiple pole if it has
+an order `\ge` 2.
+
+Necessary Conditions
+====================
+
+For a Riccati equation in its normal form,
+
+.. math:: y' + y^2 = a(x)
+
+we can define
+
+a. A pole is called a movable pole if it is a pole of `y(x)` and is not
+a pole of `a(x)`.
+b. Similarly, a pole is called a non-movable pole if it is a pole of both
+`y(x)` and `a(x)`.
+
+Then, the algorithm states that a rational solution exists only if -
+
+a. Every pole of `a(x)` must be either a simple pole or a multiple pole
+of even order.
+b. The valuation of `a(x)` at `\infty` must be even or be `\ge` 2.
+
+This algorithm finds all possible rational solutions for the Riccati ODE.
+If no rational solutions are found, it means that no rational solutions
+exist.
+
+The algorithm works for Riccati ODEs where the coefficients are rational
+functions in the independent variable `x` with rational number coefficients
+i.e. in `Q(x)`. The coefficients in the rational function cannot be floats,
+irrational numbers, symbols or any other kind of expression. The reasons
+for this are -
+
+1. When using symbols, different symbols could take the same value and this
+would affect the multiplicity of poles if symbols are present here.
+
+2. An integer degree bound is required to calculate a polynomial solution
+to an auxiliary differential equation, which in turn gives the particular
+solution for the original ODE. If symbols/floats/irrational numbers are
+present, we cannot determine if the expression for the degree bound is an
+integer or not.
+
+Solution
+========
+
+With these definitions, we can state a general form for the solution of
+the equation. `y(x)` must have the form -
+
+.. math:: y(x) = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \sum_{j=1}^{r_i} \frac{c_{ij}}{(x - x_i)^j} + \sum_{i=1}^{m} \frac{1}{x - \chi_i} + \sum_{i=0}^{N} d_i x^i
+
+where `x_1, x_2, ..., x_n` are non-movable poles of `a(x)`,
+`\chi_1, \chi_2, ..., \chi_m` are movable poles of `a(x)`, and the values
+of `N, n, r_1, r_2, ..., r_n` can be determined from `a(x)`. The
+coefficient vectors `(d_0, d_1, ..., d_N)` and `(c_{i1}, c_{i2}, ..., c_{i r_i})`
+can be determined from `a(x)`. We will have 2 choices each of these vectors
+and part of the procedure is figuring out which of the 2 should be used
+to get the solution correctly.
+
+Implementation
+==============
+
+In this implementatin, we use ``Poly`` to represent a rational function
+rather than using ``Expr`` since ``Poly`` is much faster. Since we cannot
+represent rational functions directly using ``Poly``, we instead represent
+a rational function with 2 ``Poly`` objects - one for its numerator and
+the other for its denominator.
+
+The code is written to match the steps given in the thesis (Pg 82)
+
+Step 0 : Match the equation -
+Find `b_0, b_1` and `b_2`. If `b_2 = 0` or no such functions exist, raise
+an error
+
+Step 1 : Transform the equation to its normal form as explained in the
+theory section.
+
+Step 2 : Initialize an empty set of solutions, ``sol``.
+
+Step 3 : If `a(x) = 0`, append `\frac{1}/{(x - C1)}` to ``sol``.
+
+Step 4 : If `a(x)` is a rational non-zero number, append `\pm \sqrt{a}`
+to ``sol``.
+
+Step 5 : Find the poles and their multiplicities of `a(x)`. Let
+the number of poles be `n`. Also find the valuation of `a(x)` at
+`\infty` using ``val_at_inf``.
+
+NOTE: Although the algorithm considers `\infty` as a pole, it is
+not mentioned if it a part of the set of finite poles. `\infty`
+is NOT a part of the set of finite poles. If a pole exists at
+`\infty`, we use its multiplicty to find the laurent series of
+`a(x)` about `\infty`.
+
+Step 6 : Find `n` c-vectors (one for each pole) and 1 d-vector using
+``construct_c`` and ``construct_d``. Now, determine all the ``2**(n + 1)``
+combinations of choosing between 2 choices for each of the `n` c-vectors
+and 1 d-vector.
+
+NOTE: The equation for `d_{-1}` in Case 4 (Pg 80) has a printinig
+mistake. The term `- d_N` must be replaced with `-N d_N`. The same
+has been explained in the code as well.
+
+For each of these above combinations, do
+
+Step 8 : Compute `m` in ``compute_m_ybar``. `m` is the degree bound of
+the polynomial solution we must find for the auxiliary equation.
+
+Step 9 : In ``compute_m_ybar``, compute ybar as well where ``ybar`` is
+one part of y(x) -
+
+.. math:: \overline{y}(x) = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \sum_{j=1}^{r_i} \frac{c_{ij}}{(x - x_i)^j} + \sum_{i=0}^{N} d_i x^i
+
+Step 10 : If `m` is a non-negative integer -
+
+Step 11: Find a polynomial solution of degree `m` for the auxiliary equation.
+
+There are 2 cases possible -
+
+ a. `m` is a non-negative integer: We can solve for the coefficients
+ in `p(x)` using Undetermined Coefficients.
+
+ b. `m` is not a non-negative integer: In this case, we cannot find
+ a polynomial solution to the auxiliary equation, and hence, we ignore
+ this value of `m`.
+
+Step 12 : For each `p(x)` that exists, append `ybar + \frac{p'(x)}{p(x)}`
+to ``sol``.
+
+Step 13 : For each solution in ``sol``, apply an inverse transformation,
+so that the solutions of the original equation are found using the
+solutions of the equation in its normal form.
+"""
+
+
+from itertools import product
+from sympy.core import S
+from sympy.core.add import Add
+from sympy.core.numbers import oo, Float
+from sympy.core.function import count_ops
+from sympy.core.relational import Eq
+from sympy.core.symbol import symbols, Symbol, Dummy
+from sympy.functions import sqrt, exp
+from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import sign
+from sympy.integrals.integrals import Integral
+from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ
+from sympy.polys.polytools import Poly
+from sympy.polys.polyroots import roots
+from sympy.solvers.solveset import linsolve
+
+
+def riccati_normal(w, x, b1, b2):
+ """
+ Given a solution `w(x)` to the equation
+
+ .. math:: w'(x) = b_0(x) + b_1(x)*w(x) + b_2(x)*w(x)^2
+
+ and rational function coefficients `b_1(x)` and
+ `b_2(x)`, this function transforms the solution to
+ give a solution `y(x)` for its corresponding normal
+ Riccati ODE
+
+ .. math:: y'(x) + y(x)^2 = a(x)
+
+ using the transformation
+
+ .. math:: y(x) = -b_2(x)*w(x) - b'_2(x)/(2*b_2(x)) - b_1(x)/2
+ """
+ return -b2*w - b2.diff(x)/(2*b2) - b1/2
+
+
+def riccati_inverse_normal(y, x, b1, b2, bp=None):
+ """
+ Inverse transforming the solution to the normal
+ Riccati ODE to get the solution to the Riccati ODE.
+ """
+ # bp is the expression which is independent of the solution
+ # and hence, it need not be computed again
+ if bp is None:
+ bp = -b2.diff(x)/(2*b2**2) - b1/(2*b2)
+ # w(x) = -y(x)/b2(x) - b2'(x)/(2*b2(x)^2) - b1(x)/(2*b2(x))
+ return -y/b2 + bp
+
+
+def riccati_reduced(eq, f, x):
+ """
+ Convert a Riccati ODE into its corresponding
+ normal Riccati ODE.
+ """
+ match, funcs = match_riccati(eq, f, x)
+ # If equation is not a Riccati ODE, exit
+ if not match:
+ return False
+ # Using the rational functions, find the expression for a(x)
+ b0, b1, b2 = funcs
+ a = -b0*b2 + b1**2/4 - b1.diff(x)/2 + 3*b2.diff(x)**2/(4*b2**2) + b1*b2.diff(x)/(2*b2) - \
+ b2.diff(x, 2)/(2*b2)
+ # Normal form of Riccati ODE is f'(x) + f(x)^2 = a(x)
+ return f(x).diff(x) + f(x)**2 - a
+
+def linsolve_dict(eq, syms):
+ """
+ Get the output of linsolve as a dict
+ """
+ # Convert tuple type return value of linsolve
+ # to a dictionary for ease of use
+ sol = linsolve(eq, syms)
+ if not sol:
+ return {}
+ return {k:v for k, v in zip(syms, list(sol)[0])}
+
+
+def match_riccati(eq, f, x):
+ """
+ A function that matches and returns the coefficients
+ if an equation is a Riccati ODE
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ eq: Equation to be matched
+ f: Dependent variable
+ x: Independent variable
+
+ Returns
+ =======
+
+ match: True if equation is a Riccati ODE, False otherwise
+ funcs: [b0, b1, b2] if match is True, [] otherwise. Here,
+ b0, b1 and b2 are rational functions which match the equation.
+ """
+ # Group terms based on f(x)
+ if isinstance(eq, Eq):
+ eq = eq.lhs - eq.rhs
+ eq = eq.expand().collect(f(x))
+ cf = eq.coeff(f(x).diff(x))
+
+ # There must be an f(x).diff(x) term.
+ # eq must be an Add object since we are using the expanded
+ # equation and it must have atleast 2 terms (b2 != 0)
+ if cf != 0 and isinstance(eq, Add):
+
+ # Divide all coefficients by the coefficient of f(x).diff(x)
+ # and add the terms again to get the same equation
+ eq = Add(*((x/cf).cancel() for x in eq.args)).collect(f(x))
+
+ # Match the equation with the pattern
+ b1 = -eq.coeff(f(x))
+ b2 = -eq.coeff(f(x)**2)
+ b0 = (f(x).diff(x) - b1*f(x) - b2*f(x)**2 - eq).expand()
+ funcs = [b0, b1, b2]
+
+ # Check if coefficients are not symbols and floats
+ if any([len(x.atoms(Symbol)) > 1 or len(x.atoms(Float)) for x in [b0, b1, b2]]):
+ return False, []
+
+ # If b_0(x) contains f(x), it is not a Riccati ODE
+ if len(b0.atoms(f)) or not all([b2 != 0, b0.is_rational_function(x), \
+ b1.is_rational_function(x), b2.is_rational_function(x)]):
+ return False, []
+ return True, funcs
+ return False, []
+
+
+def val_at_inf(num, den, x):
+ # Valuation of a rational function at oo = deg(denom) - deg(numer)
+ return den.degree(x) - num.degree(x)
+
+
+def check_necessary_conds(val_inf, muls):
+ """
+ The necessary conditions for a rational solution
+ to exist are as follows -
+
+ i) Every pole of a(x) must be either a simple pole
+ or a multiple pole of even order.
+
+ ii) The valuation of a(x) at infinity must be even
+ or be greater than or equal to 2.
+
+ Here, a simple pole is a pole with multiplicity 1
+ and a multiple pole is a pole with multiplicity
+ greater than 1.
+ """
+ return (val_inf >= 2 or (val_inf <= 0 and val_inf%2 == 0)) and \
+ all([mul == 1 or (mul%2 == 0 and mul >= 2) for mul in muls])
+
+
+def inverse_transform_poly(num, den, x):
+ """
+ A function to make the substitution
+ x -> 1/x in a rational function that
+ is represented using Poly objects for
+ numerator and denominator.
+ """
+ # Declare for reuse
+ one = Poly(1, x)
+ xpoly = Poly(x, x)
+
+ # Check if degree of numerator is same as denominator
+ pwr = val_at_inf(num, den, x)
+ if pwr >= 0:
+ # Denominator has greater degree. Substituting x with
+ # 1/x would make the extra power go to the numerator
+ if num.expr != 0:
+ num = num.transform(one, xpoly) * x**pwr
+ den = den.transform(one, xpoly)
+ else:
+ # Numerator has greater degree. Substituting x with
+ # 1/x would make the extra power go to the denominator
+ num = num.transform(one, xpoly)
+ den = den.transform(one, xpoly) * x**(-pwr)
+ return num.cancel(den, include=True)
+
+
+def limit_at_inf(num, den, x):
+ """
+ Find the limit of a rational function
+ at oo
+ """
+ # pwr = degree(num) - degree(den)
+ pwr = -val_at_inf(num, den, x)
+ # Numerator has a greater degree than denominator
+ # Limit at infinity would depend on the sign of the
+ # leading coefficients of numerator and denominator
+ if pwr > 0:
+ return oo*sign(num.LC()/den.LC())
+ # Degree of numerator is equal to that of denominator
+ # Limit at infinity is just the ratio of leading coeffs
+ elif pwr == 0:
+ return num.LC()/den.LC()
+ # Degree of numerator is less than that of denominator
+ # Limit at infinity is just 0
+ else:
+ return 0
+
+
+def construct_c_case_1(num, den, x, pole):
+ # Find the coefficient of 1/(x - pole)**2 in the
+ # Laurent series expansion of a(x) about pole.
+ num1, den1 = (num*Poly((x - pole)**2, x, extension=True)).cancel(den, include=True)
+ r = (num1.subs(x, pole))/(den1.subs(x, pole))
+
+ # If multiplicity is 2, the coefficient to be added
+ # in the c-vector is c = (1 +- sqrt(1 + 4*r))/2
+ if r != -S(1)/4:
+ return [[(1 + sqrt(1 + 4*r))/2], [(1 - sqrt(1 + 4*r))/2]]
+ return [[S(1)/2]]
+
+
+def construct_c_case_2(num, den, x, pole, mul):
+ # Generate the coefficients using the recurrence
+ # relation mentioned in (5.14) in the thesis (Pg 80)
+
+ # r_i = mul/2
+ ri = mul//2
+
+ # Find the Laurent series coefficients about the pole
+ ser = rational_laurent_series(num, den, x, pole, mul, 6)
+
+ # Start with an empty memo to store the coefficients
+ # This is for the plus case
+ cplus = [0 for i in range(ri)]
+
+ # Base Case
+ cplus[ri-1] = sqrt(ser[2*ri])
+
+ # Iterate backwards to find all coefficients
+ s = ri - 1
+ sm = 0
+ for s in range(ri-1, 0, -1):
+ sm = 0
+ for j in range(s+1, ri):
+ sm += cplus[j-1]*cplus[ri+s-j-1]
+ if s!= 1:
+ cplus[s-1] = (ser[ri+s] - sm)/(2*cplus[ri-1])
+
+ # Memo for the minus case
+ cminus = [-x for x in cplus]
+
+ # Find the 0th coefficient in the recurrence
+ cplus[0] = (ser[ri+s] - sm - ri*cplus[ri-1])/(2*cplus[ri-1])
+ cminus[0] = (ser[ri+s] - sm - ri*cminus[ri-1])/(2*cminus[ri-1])
+
+ # Add both the plus and minus cases' coefficients
+ if cplus != cminus:
+ return [cplus, cminus]
+ return cplus
+
+
+def construct_c_case_3():
+ # If multiplicity is 1, the coefficient to be added
+ # in the c-vector is 1 (no choice)
+ return [[1]]
+
+
+def construct_c(num, den, x, poles, muls):
+ """
+ Helper function to calculate the coefficients
+ in the c-vector for each pole.
+ """
+ c = []
+ for pole, mul in zip(poles, muls):
+ c.append([])
+
+ # Case 3
+ if mul == 1:
+ # Add the coefficients from Case 3
+ c[-1].extend(construct_c_case_3())
+
+ # Case 1
+ elif mul == 2:
+ # Add the coefficients from Case 1
+ c[-1].extend(construct_c_case_1(num, den, x, pole))
+
+ # Case 2
+ else:
+ # Add the coefficients from Case 2
+ c[-1].extend(construct_c_case_2(num, den, x, pole, mul))
+
+ return c
+
+
+def construct_d_case_4(ser, N):
+ # Initialize an empty vector
+ dplus = [0 for i in range(N+2)]
+ # d_N = sqrt(a_{2*N})
+ dplus[N] = sqrt(ser[2*N])
+
+ # Use the recurrence relations to find
+ # the value of d_s
+ for s in range(N-1, -2, -1):
+ sm = 0
+ for j in range(s+1, N):
+ sm += dplus[j]*dplus[N+s-j]
+ if s != -1:
+ dplus[s] = (ser[N+s] - sm)/(2*dplus[N])
+
+ # Coefficients for the case of d_N = -sqrt(a_{2*N})
+ dminus = [-x for x in dplus]
+
+ # The third equation in Eq 5.15 of the thesis is WRONG!
+ # d_N must be replaced with N*d_N in that equation.
+ dplus[-1] = (ser[N+s] - N*dplus[N] - sm)/(2*dplus[N])
+ dminus[-1] = (ser[N+s] - N*dminus[N] - sm)/(2*dminus[N])
+
+ if dplus != dminus:
+ return [dplus, dminus]
+ return dplus
+
+
+def construct_d_case_5(ser):
+ # List to store coefficients for plus case
+ dplus = [0, 0]
+
+ # d_0 = sqrt(a_0)
+ dplus[0] = sqrt(ser[0])
+
+ # d_(-1) = a_(-1)/(2*d_0)
+ dplus[-1] = ser[-1]/(2*dplus[0])
+
+ # Coefficients for the minus case are just the negative
+ # of the coefficients for the positive case.
+ dminus = [-x for x in dplus]
+
+ if dplus != dminus:
+ return [dplus, dminus]
+ return dplus
+
+
+def construct_d_case_6(num, den, x):
+ # s_oo = lim x->0 1/x**2 * a(1/x) which is equivalent to
+ # s_oo = lim x->oo x**2 * a(x)
+ s_inf = limit_at_inf(Poly(x**2, x)*num, den, x)
+
+ # d_(-1) = (1 +- sqrt(1 + 4*s_oo))/2
+ if s_inf != -S(1)/4:
+ return [[(1 + sqrt(1 + 4*s_inf))/2], [(1 - sqrt(1 + 4*s_inf))/2]]
+ return [[S(1)/2]]
+
+
+def construct_d(num, den, x, val_inf):
+ """
+ Helper function to calculate the coefficients
+ in the d-vector based on the valuation of the
+ function at oo.
+ """
+ N = -val_inf//2
+ # Multiplicity of oo as a pole
+ mul = -val_inf if val_inf < 0 else 0
+ ser = rational_laurent_series(num, den, x, oo, mul, 1)
+
+ # Case 4
+ if val_inf < 0:
+ d = construct_d_case_4(ser, N)
+
+ # Case 5
+ elif val_inf == 0:
+ d = construct_d_case_5(ser)
+
+ # Case 6
+ else:
+ d = construct_d_case_6(num, den, x)
+
+ return d
+
+
+def rational_laurent_series(num, den, x, r, m, n):
+ r"""
+ The function computes the Laurent series coefficients
+ of a rational function.
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ num: A Poly object that is the numerator of `f(x)`.
+ den: A Poly object that is the denominator of `f(x)`.
+ x: The variable of expansion of the series.
+ r: The point of expansion of the series.
+ m: Multiplicity of r if r is a pole of `f(x)`. Should
+ be zero otherwise.
+ n: Order of the term upto which the series is expanded.
+
+ Returns
+ =======
+
+ series: A dictionary that has power of the term as key
+ and coefficient of that term as value.
+
+ Below is a basic outline of how the Laurent series of a
+ rational function `f(x)` about `x_0` is being calculated -
+
+ 1. Substitute `x + x_0` in place of `x`. If `x_0`
+ is a pole of `f(x)`, multiply the expression by `x^m`
+ where `m` is the multiplicity of `x_0`. Denote the
+ the resulting expression as g(x). We do this substitution
+ so that we can now find the Laurent series of g(x) about
+ `x = 0`.
+
+ 2. We can then assume that the Laurent series of `g(x)`
+ takes the following form -
+
+ .. math:: g(x) = \frac{num(x)}{den(x)} = \sum_{m = 0}^{\infty} a_m x^m
+
+ where `a_m` denotes the Laurent series coefficients.
+
+ 3. Multiply the denominator to the RHS of the equation
+ and form a recurrence relation for the coefficients `a_m`.
+ """
+ one = Poly(1, x, extension=True)
+
+ if r == oo:
+ # Series at x = oo is equal to first transforming
+ # the function from x -> 1/x and finding the
+ # series at x = 0
+ num, den = inverse_transform_poly(num, den, x)
+ r = S(0)
+
+ if r:
+ # For an expansion about a non-zero point, a
+ # transformation from x -> x + r must be made
+ num = num.transform(Poly(x + r, x, extension=True), one)
+ den = den.transform(Poly(x + r, x, extension=True), one)
+
+ # Remove the pole from the denominator if the series
+ # expansion is about one of the poles
+ num, den = (num*x**m).cancel(den, include=True)
+
+ # Equate coefficients for the first terms (base case)
+ maxdegree = 1 + max(num.degree(), den.degree())
+ syms = symbols(f'a:{maxdegree}', cls=Dummy)
+ diff = num - den * Poly(syms[::-1], x)
+ coeff_diffs = diff.all_coeffs()[::-1][:maxdegree]
+ (coeffs, ) = linsolve(coeff_diffs, syms)
+
+ # Use the recursion relation for the rest
+ recursion = den.all_coeffs()[::-1]
+ div, rec_rhs = recursion[0], recursion[1:]
+ series = list(coeffs)
+ while len(series) < n:
+ next_coeff = Add(*(c*series[-1-n] for n, c in enumerate(rec_rhs))) / div
+ series.append(-next_coeff)
+ series = {m - i: val for i, val in enumerate(series)}
+ return series
+
+def compute_m_ybar(x, poles, choice, N):
+ """
+ Helper function to calculate -
+
+ 1. m - The degree bound for the polynomial
+ solution that must be found for the auxiliary
+ differential equation.
+
+ 2. ybar - Part of the solution which can be
+ computed using the poles, c and d vectors.
+ """
+ ybar = 0
+ m = Poly(choice[-1][-1], x, extension=True)
+
+ # Calculate the first (nested) summation for ybar
+ # as given in Step 9 of the Thesis (Pg 82)
+ for i in range(len(poles)):
+ for j in range(len(choice[i])):
+ ybar += choice[i][j]/(x - poles[i])**(j+1)
+ m -= Poly(choice[i][0], x, extension=True)
+
+ # Calculate the second summation for ybar
+ for i in range(N+1):
+ ybar += choice[-1][i]*x**i
+ return (m.expr, ybar)
+
+
+def solve_aux_eq(numa, dena, numy, deny, x, m):
+ """
+ Helper function to find a polynomial solution
+ of degree m for the auxiliary differential
+ equation.
+ """
+ # Assume that the solution is of the type
+ # p(x) = C_0 + C_1*x + ... + C_{m-1}*x**(m-1) + x**m
+ psyms = symbols(f'C0:{m}', cls=Dummy)
+ K = ZZ[psyms]
+ psol = Poly(K.gens, x, domain=K) + Poly(x**m, x, domain=K)
+
+ # Eq (5.16) in Thesis - Pg 81
+ auxeq = (dena*(numy.diff(x)*deny - numy*deny.diff(x) + numy**2) - numa*deny**2)*psol
+ if m >= 1:
+ px = psol.diff(x)
+ auxeq += px*(2*numy*deny*dena)
+ if m >= 2:
+ auxeq += px.diff(x)*(deny**2*dena)
+ if m != 0:
+ # m is a non-zero integer. Find the constant terms using undetermined coefficients
+ return psol, linsolve_dict(auxeq.all_coeffs(), psyms), True
+ else:
+ # m == 0 . Check if 1 (x**0) is a solution to the auxiliary equation
+ return S(1), auxeq, auxeq == 0
+
+
+def remove_redundant_sols(sol1, sol2, x):
+ """
+ Helper function to remove redundant
+ solutions to the differential equation.
+ """
+ # If y1 and y2 are redundant solutions, there is
+ # some value of the arbitrary constant for which
+ # they will be equal
+
+ syms1 = sol1.atoms(Symbol, Dummy)
+ syms2 = sol2.atoms(Symbol, Dummy)
+ num1, den1 = [Poly(e, x, extension=True) for e in sol1.together().as_numer_denom()]
+ num2, den2 = [Poly(e, x, extension=True) for e in sol2.together().as_numer_denom()]
+ # Cross multiply
+ e = num1*den2 - den1*num2
+ # Check if there are any constants
+ syms = list(e.atoms(Symbol, Dummy))
+ if len(syms):
+ # Find values of constants for which solutions are equal
+ redn = linsolve(e.all_coeffs(), syms)
+ if len(redn):
+ # Return the general solution over a particular solution
+ if len(syms1) > len(syms2):
+ return sol2
+ # If both have constants, return the lesser complex solution
+ elif len(syms1) == len(syms2):
+ return sol1 if count_ops(syms1) >= count_ops(syms2) else sol2
+ else:
+ return sol1
+
+
+def get_gen_sol_from_part_sol(part_sols, a, x):
+ """"
+ Helper function which computes the general
+ solution for a Riccati ODE from its particular
+ solutions.
+
+ There are 3 cases to find the general solution
+ from the particular solutions for a Riccati ODE
+ depending on the number of particular solution(s)
+ we have - 1, 2 or 3.
+
+ For more information, see Section 6 of
+ "Methods of Solution of the Riccati Differential Equation"
+ by D. R. Haaheim and F. M. Stein
+ """
+
+ # If no particular solutions are found, a general
+ # solution cannot be found
+ if len(part_sols) == 0:
+ return []
+
+ # In case of a single particular solution, the general
+ # solution can be found by using the substitution
+ # y = y1 + 1/z and solving a Bernoulli ODE to find z.
+ elif len(part_sols) == 1:
+ y1 = part_sols[0]
+ i = exp(Integral(2*y1, x))
+ z = i * Integral(a/i, x)
+ z = z.doit()
+ if a == 0 or z == 0:
+ return y1
+ return y1 + 1/z
+
+ # In case of 2 particular solutions, the general solution
+ # can be found by solving a separable equation. This is
+ # the most common case, i.e. most Riccati ODEs have 2
+ # rational particular solutions.
+ elif len(part_sols) == 2:
+ y1, y2 = part_sols
+ # One of them already has a constant
+ if len(y1.atoms(Dummy)) + len(y2.atoms(Dummy)) > 0:
+ u = exp(Integral(y2 - y1, x)).doit()
+ # Introduce a constant
+ else:
+ C1 = Dummy('C1')
+ u = C1*exp(Integral(y2 - y1, x)).doit()
+ if u == 1:
+ return y2
+ return (y2*u - y1)/(u - 1)
+
+ # In case of 3 particular solutions, a closed form
+ # of the general solution can be obtained directly
+ else:
+ y1, y2, y3 = part_sols[:3]
+ C1 = Dummy('C1')
+ return (C1 + 1)*y2*(y1 - y3)/(C1*y1 + y2 - (C1 + 1)*y3)
+
+
+def solve_riccati(fx, x, b0, b1, b2, gensol=False):
+ """
+ The main function that gives particular/general
+ solutions to Riccati ODEs that have atleast 1
+ rational particular solution.
+ """
+ # Step 1 : Convert to Normal Form
+ a = -b0*b2 + b1**2/4 - b1.diff(x)/2 + 3*b2.diff(x)**2/(4*b2**2) + b1*b2.diff(x)/(2*b2) - \
+ b2.diff(x, 2)/(2*b2)
+ a_t = a.together()
+ num, den = [Poly(e, x, extension=True) for e in a_t.as_numer_denom()]
+ num, den = num.cancel(den, include=True)
+
+ # Step 2
+ presol = []
+
+ # Step 3 : a(x) is 0
+ if num == 0:
+ presol.append(1/(x + Dummy('C1')))
+
+ # Step 4 : a(x) is a non-zero constant
+ elif x not in num.free_symbols.union(den.free_symbols):
+ presol.extend([sqrt(a), -sqrt(a)])
+
+ # Step 5 : Find poles and valuation at infinity
+ poles = roots(den, x)
+ poles, muls = list(poles.keys()), list(poles.values())
+ val_inf = val_at_inf(num, den, x)
+
+ if len(poles):
+ # Check necessary conditions (outlined in the module docstring)
+ if not check_necessary_conds(val_inf, muls):
+ raise ValueError("Rational Solution doesn't exist")
+
+ # Step 6
+ # Construct c-vectors for each singular point
+ c = construct_c(num, den, x, poles, muls)
+
+ # Construct d vectors for each singular point
+ d = construct_d(num, den, x, val_inf)
+
+ # Step 7 : Iterate over all possible combinations and return solutions
+ # For each possible combination, generate an array of 0's and 1's
+ # where 0 means pick 1st choice and 1 means pick the second choice.
+
+ # NOTE: We could exit from the loop if we find 3 particular solutions,
+ # but it is not implemented here as -
+ # a. Finding 3 particular solutions is very rare. Most of the time,
+ # only 2 particular solutions are found.
+ # b. In case we exit after finding 3 particular solutions, it might
+ # happen that 1 or 2 of them are redundant solutions. So, instead of
+ # spending some more time in computing the particular solutions,
+ # we will end up computing the general solution from a single
+ # particular solution which is usually slower than computing the
+ # general solution from 2 or 3 particular solutions.
+ c.append(d)
+ choices = product(*c)
+ for choice in choices:
+ m, ybar = compute_m_ybar(x, poles, choice, -val_inf//2)
+ numy, deny = [Poly(e, x, extension=True) for e in ybar.together().as_numer_denom()]
+ # Step 10 : Check if a valid solution exists. If yes, also check
+ # if m is a non-negative integer
+ if m.is_nonnegative == True and m.is_integer == True:
+
+ # Step 11 : Find polynomial solutions of degree m for the auxiliary equation
+ psol, coeffs, exists = solve_aux_eq(num, den, numy, deny, x, m)
+
+ # Step 12 : If valid polynomial solution exists, append solution.
+ if exists:
+ # m == 0 case
+ if psol == 1 and coeffs == 0:
+ # p(x) = 1, so p'(x)/p(x) term need not be added
+ presol.append(ybar)
+ # m is a positive integer and there are valid coefficients
+ elif len(coeffs):
+ # Substitute the valid coefficients to get p(x)
+ psol = psol.xreplace(coeffs)
+ # y(x) = ybar(x) + p'(x)/p(x)
+ presol.append(ybar + psol.diff(x)/psol)
+
+ # Remove redundant solutions from the list of existing solutions
+ remove = set()
+ for i in range(len(presol)):
+ for j in range(i+1, len(presol)):
+ rem = remove_redundant_sols(presol[i], presol[j], x)
+ if rem is not None:
+ remove.add(rem)
+ sols = [x for x in presol if x not in remove]
+
+ # Step 15 : Inverse transform the solutions of the equation in normal form
+ bp = -b2.diff(x)/(2*b2**2) - b1/(2*b2)
+
+ # If general solution is required, compute it from the particular solutions
+ if gensol:
+ sols = [get_gen_sol_from_part_sol(sols, a, x)]
+
+ # Inverse transform the particular solutions
+ presol = [Eq(fx, riccati_inverse_normal(y, x, b1, b2, bp).cancel(extension=True)) for y in sols]
+ return presol
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
index efdc382e530c..e58df5fac4ce 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
@@ -5,9 +5,9 @@
import typing
if typing.TYPE_CHECKING:
from typing import ClassVar
-from typing import Dict, Type
+from typing import Dict, Type, Iterator, List, Optional
-from typing import Iterator, List, Optional
+from .riccati import match_riccati, solve_riccati
from sympy.core import Add, S, Pow, Rational
from sympy.core.exprtools import factor_terms
from sympy.core.expr import Expr
@@ -945,7 +945,7 @@ class RiccatiSpecial(SinglePatternODESolver):
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> y = f(x)
>>> genform = a*y.diff(x) - (b*y**2 + c*y/x + d/x**2)
- >>> sol = dsolve(genform, y)
+ >>> sol = dsolve(genform, y, hint="Riccati_special_minus2")
>>> pprint(sol, wrap_line=False)
/ / __________________ \\
| __________________ | / 2 ||
@@ -961,9 +961,9 @@ class RiccatiSpecial(SinglePatternODESolver):
References
==========
- 1. http://www.maplesoft.com/support/help/Maple/view.aspx?path=odeadvisor/Riccati
- 2. http://eqworld.ipmnet.ru/en/solutions/ode/ode0106.pdf -
- http://eqworld.ipmnet.ru/en/solutions/ode/ode0123.pdf
+ - http://www.maplesoft.com/support/help/Maple/view.aspx?path=odeadvisor/Riccati
+ - http://eqworld.ipmnet.ru/en/solutions/ode/ode0106.pdf -
+ http://eqworld.ipmnet.ru/en/solutions/ode/ode0123.pdf
"""
hint = "Riccati_special_minus2"
has_integral = False
@@ -991,6 +991,76 @@ def _get_general_solution(self, *, simplify_flag: bool = True):
return [gensol]
+class RationalRiccati(SinglePatternODESolver):
+ r"""
+ Gives general solutions to the first order Riccati differential
+ equations that have atleast one rational particular solution.
+
+ .. math :: y' = b_0(x) + b_1(x) y + b_2(x) y^2
+
+ where `b_0`, `b_1` and `b_2` are rational functions of `x`
+ with `b_2 \ne 0` (`b_2 = 0` would make it a Bernoulli equation).
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, Function, dsolve, checkodesol
+ >>> f = Function('f')
+ >>> x = Symbol('x')
+
+ >>> eq = -x**4*f(x)**2 + x**3*f(x).diff(x) + x**2*f(x) + 20
+ >>> sol = dsolve(eq, hint="1st_rational_riccati")
+ >>> sol
+ Eq(f(x), (4*C1 - 5*x**9 - 4)/(x**2*(C1 + x**9 - 1)))
+ >>> checkodesol(eq, sol)
+ (True, 0)
+
+ References
+ ==========
+
+ - Riccati ODE: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riccati_equation
+ - N. Thieu Vo - Rational and Algebraic Solutions of First-Order Algebraic ODEs:
+ Algorithm 11, pp. 78 - https://www3.risc.jku.at/publications/download/risc_5387/PhDThesisThieu.pdf
+ """
+ has_integral = False
+ hint = "1st_rational_riccati"
+ order = [1]
+
+ def _wilds(self, f, x, order):
+ b0 = Wild('b0', exclude=[f(x), f(x).diff(x)])
+ b1 = Wild('b1', exclude=[f(x), f(x).diff(x)])
+ b2 = Wild('b2', exclude=[f(x), f(x).diff(x)])
+ return (b0, b1, b2)
+
+ def _equation(self, fx, x, order):
+ b0, b1, b2 = self.wilds()
+ return fx.diff(x) - b0 - b1*fx - b2*fx**2
+
+ def _matches(self):
+ eq = self.ode_problem.eq_expanded
+ f = self.ode_problem.func.func
+ x = self.ode_problem.sym
+ order = self.ode_problem.order
+
+ if order != 1:
+ return False
+
+ match, funcs = match_riccati(eq, f, x)
+ if not match:
+ return False
+ _b0, _b1, _b2 = funcs
+ b0, b1, b2 = self.wilds()
+ self._wilds_match = match = {b0: _b0, b1: _b1, b2: _b2}
+ return True
+
+ def _get_general_solution(self, *, simplify_flag: bool = True):
+ # Match the equation
+ b0, b1, b2 = self.wilds_match()
+ fx = self.ode_problem.func
+ x = self.ode_problem.sym
+ return solve_riccati(fx, x, b0, b1, b2, gensol=True)
+
+
class SecondNonlinearAutonomousConserved(SinglePatternODESolver):
r"""
Gives solution for the autonomous second order nonlinear
@@ -1023,7 +1093,7 @@ class SecondNonlinearAutonomousConserved(SinglePatternODESolver):
References
==========
- http://eqworld.ipmnet.ru/en/solutions/ode/ode0301.pdf
+ - http://eqworld.ipmnet.ru/en/solutions/ode/ode0301.pdf
"""
hint = "2nd_nonlinear_autonomous_conserved"
has_integral = True
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..fdce01f3a2dd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_riccati.py
@@ -0,0 +1,866 @@
+from random import randint
+from sympy import (S, symbols, Function, Rational, Poly, Eq, ratsimp,
+ checkodesol, sqrt, Dummy, oo, I, Mul, sin, exp, log, tanh)
+from sympy.testing.pytest import slow
+from sympy.solvers.ode.riccati import (riccati_normal, riccati_inverse_normal,
+ riccati_reduced, match_riccati, inverse_transform_poly, limit_at_inf,
+ check_necessary_conds, val_at_inf, construct_c_case_1,
+ construct_c_case_2, construct_c_case_3, construct_d_case_4,
+ construct_d_case_5, construct_d_case_6, rational_laurent_series,
+ solve_riccati)
+
+f = Function('f')
+x = symbols('x')
+
+# These are the functions used to generate the tests
+# SHOULD NOT BE USED DIRECTLY IN TESTS
+
+def rand_rational(maxint):
+ return Rational(randint(-maxint, maxint), randint(1, maxint))
+
+
+def rand_poly(x, degree, maxint):
+ return Poly([rand_rational(maxint) for _ in range(degree+1)], x)
+
+
+def rand_rational_function(x, degree, maxint):
+ degnum = randint(1, degree)
+ degden = randint(1, degree)
+ num = rand_poly(x, degnum, maxint)
+ den = rand_poly(x, degden, maxint)
+ while den == Poly(0, x):
+ den = rand_poly(x, degden, maxint)
+ return num / den
+
+
+def find_riccati_ode(ratfunc, x, yf):
+ y = ratfunc
+ yp = y.diff(x)
+ q1 = rand_rational_function(x, 1, 3)
+ q2 = rand_rational_function(x, 1, 3)
+ while q2 == 0:
+ q2 = rand_rational_function(x, 1, 3)
+ q0 = ratsimp(yp - q1*y - q2*y**2)
+ eq = Eq(yf.diff(), q0 + q1*yf + q2*yf**2)
+ sol = Eq(yf, y)
+ assert checkodesol(eq, sol) == (True, 0)
+ return eq, q0, q1, q2
+
+
+# Testing functions start
+
+def test_riccati_transformation():
+ """
+ This function tests the transformation of the
+ solution of a Riccati ODE to the solution of
+ its corresponding normal Riccati ODE.
+
+ Each test case 4 values -
+
+ 1. w - The solution to be transformed
+ 2. b1 - The coefficient of f(x) in the ODE.
+ 3. b2 - The coefficient of f(x)**2 in the ODE.
+ 4. y - The solution to the normal Riccati ODE.
+ """
+ tests = [
+ (
+ x/(x - 1),
+ (x**2 + 7)/3*x,
+ x,
+ -x**2/(x - 1) - x*(x**2/3 + S(7)/3)/2 - 1/(2*x)
+ ),
+ (
+ (2*x + 3)/(2*x + 2),
+ (3 - 3*x)/(x + 1),
+ 5*x,
+ -5*x*(2*x + 3)/(2*x + 2) - (3 - 3*x)/(Mul(2, x + 1, evaluate=False)) - 1/(2*x)
+ ),
+ (
+ -1/(2*x**2 - 1),
+ 0,
+ (2 - x)/(4*x - 2),
+ (2 - x)/((4*x - 2)*(2*x**2 - 1)) - (4*x - 2)*(Mul(-4, 2 - x, evaluate=False)/(4*x - \
+ 2)**2 - 1/(4*x - 2))/(Mul(2, 2 - x, evaluate=False))
+ ),
+ (
+ x,
+ (8*x - 12)/(12*x + 9),
+ x**3/(6*x - 9),
+ -x**4/(6*x - 9) - (8*x - 12)/(Mul(2, 12*x + 9, evaluate=False)) - (6*x - 9)*(-6*x**3/(6*x \
+ - 9)**2 + 3*x**2/(6*x - 9))/(2*x**3)
+ )]
+ for w, b1, b2, y in tests:
+ assert y == riccati_normal(w, x, b1, b2)
+ assert w == riccati_inverse_normal(y, x, b1, b2).cancel()
+
+ # Test bp parameter in riccati_inverse_normal
+ tests = [
+ (
+ (-2*x - 1)/(2*x**2 + 2*x - 2),
+ -2/x,
+ (-x - 1)/(4*x),
+ 8*x**2*(1/(4*x) + (-x - 1)/(4*x**2))/(-x - 1)**2 + 4/(-x - 1),
+ -2*x*(-1/(4*x) - (-x - 1)/(4*x**2))/(-x - 1) - (-2*x - 1)*(-x - 1)/(4*x*(2*x**2 + 2*x \
+ - 2)) + 1/x
+ ),
+ (
+ 3/(2*x**2),
+ -2/x,
+ (-x - 1)/(4*x),
+ 8*x**2*(1/(4*x) + (-x - 1)/(4*x**2))/(-x - 1)**2 + 4/(-x - 1),
+ -2*x*(-1/(4*x) - (-x - 1)/(4*x**2))/(-x - 1) + 1/x - Mul(3, -x - 1, evaluate=False)/(8*x**3)
+ )]
+ for w, b1, b2, bp, y in tests:
+ assert y == riccati_normal(w, x, b1, b2)
+ assert w == riccati_inverse_normal(y, x, b1, b2, bp).cancel()
+
+
+def test_riccati_reduced():
+ """
+ This function tests the transformation of a
+ Riccati ODE to its normal Riccati ODE.
+
+ Each test case 2 values -
+
+ 1. eq - A Riccati ODE.
+ 2. normal_eq - The normal Riccati ODE of eq.
+ """
+ tests = [
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) - x**2 - x*f(x) - x*f(x)**2,
+
+ f(x).diff(x) + f(x)**2 + x**3 - x**2/4 - 3/(4*x**2)
+ ),
+ (
+ 6*x/(2*x + 9) + f(x).diff(x) - (x + 1)*f(x)**2/x,
+
+ -3*x**2*(1/x + (-x - 1)/x**2)**2/(4*(-x - 1)**2) + Mul(6, \
+ -x - 1, evaluate=False)/(2*x + 9) + f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x) \
+ - (-1 + (x + 1)/x)/(x*(-x - 1))
+ ),
+ (
+ f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x) - (x - 1)*f(x)/(-x - S(1)/2),
+
+ -(2*x - 2)**2/(4*(2*x + 1)**2) + (2*x - 2)/(2*x + 1)**2 + \
+ f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x) - 1/(2*x + 1)
+ ),
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) - f(x)**2/x,
+
+ f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x) + 1/(4*x**2)
+ ),
+ (
+ -3*(-x**2 - x + 1)/(x**2 + 6*x + 1) + f(x).diff(x) + f(x)**2/x,
+
+ f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x) + (3*x**2/(x**2 + 6*x + 1) + 3*x/(x**2 \
+ + 6*x + 1) - 3/(x**2 + 6*x + 1))/x + 1/(4*x**2)
+ ),
+ (
+ 6*x/(2*x + 9) + f(x).diff(x) - (x + 1)*f(x)/x,
+
+ False
+ ),
+ (
+ f(x)*f(x).diff(x) - 1/x + f(x)/3 + f(x)**2/(x**2 - 2),
+
+ False
+ )]
+ for eq, normal_eq in tests:
+ assert normal_eq == riccati_reduced(eq, f, x)
+
+
+def test_match_riccati():
+ """
+ This function tests if an ODE is Riccati or not.
+
+ Each test case has 5 values -
+
+ 1. eq - The Riccati ODE.
+ 2. match - Boolean indicating if eq is a Riccati ODE.
+ 3. b0 -
+ 4. b1 - Coefficient of f(x) in eq.
+ 5. b2 - Coefficient of f(x)**2 in eq.
+ """
+ tests = [
+ # Test Rational Riccati ODEs
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) - (405*x**3 - 882*x**2 - 78*x + 92)/(243*x**4 \
+ - 945*x**3 + 846*x**2 + 180*x - 72) - 2 - f(x)**2/(3*x + 1) \
+ - (S(1)/3 - x)*f(x)/(S(1)/3 - 3*x/2),
+
+ True,
+
+ 45*x**3/(27*x**4 - 105*x**3 + 94*x**2 + 20*x - 8) - 98*x**2/ \
+ (27*x**4 - 105*x**3 + 94*x**2 + 20*x - 8) - 26*x/(81*x**4 - \
+ 315*x**3 + 282*x**2 + 60*x - 24) + 2 + 92/(243*x**4 - 945*x**3 \
+ + 846*x**2 + 180*x - 72),
+
+ Mul(-1, 2 - 6*x, evaluate=False)/(9*x - 2),
+
+ 1/(3*x + 1)
+ ),
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) + 4*x/27 - (x/3 - 1)*f(x)**2 - (2*x/3 + \
+ 1)*f(x)/(3*x + 2) - S(10)/27 - (265*x**2 + 423*x + 162) \
+ /(324*x**3 + 216*x**2),
+
+ True,
+
+ -4*x/27 + S(10)/27 + 3/(6*x**3 + 4*x**2) + 47/(36*x**2 \
+ + 24*x) + 265/(324*x + 216),
+
+ Mul(-1, -2*x - 3, evaluate=False)/(9*x + 6),
+
+ x/3 - 1
+ ),
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) - (304*x**5 - 745*x**4 + 631*x**3 - 876*x**2 \
+ + 198*x - 108)/(36*x**6 - 216*x**5 + 477*x**4 - 567*x**3 + \
+ 360*x**2 - 108*x) - S(17)/9 - (x - S(3)/2)*f(x)/(x/2 - \
+ S(3)/2) - (x/3 - 3)*f(x)**2/(3*x),
+
+ True,
+
+ 304*x**4/(36*x**5 - 216*x**4 + 477*x**3 - 567*x**2 + 360*x - \
+ 108) - 745*x**3/(36*x**5 - 216*x**4 + 477*x**3 - 567*x**2 + \
+ 360*x - 108) + 631*x**2/(36*x**5 - 216*x**4 + 477*x**3 - 567* \
+ x**2 + 360*x - 108) - 292*x/(12*x**5 - 72*x**4 + 159*x**3 - \
+ 189*x**2 + 120*x - 36) + S(17)/9 - 12/(4*x**6 - 24*x**5 + \
+ 53*x**4 - 63*x**3 + 40*x**2 - 12*x) + 22/(4*x**5 - 24*x**4 \
+ + 53*x**3 - 63*x**2 + 40*x - 12),
+
+ Mul(-1, 3 - 2*x, evaluate=False)/(x - 3),
+
+ Mul(-1, 9 - x, evaluate=False)/(9*x)
+ ),
+ # Test Non-Rational Riccati ODEs
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) - x**(S(3)/2)/(x**(S(1)/2) - 2) + x**2*f(x) + \
+ x*f(x)**2/(x**(S(3)/4)),
+ False, 0, 0, 0
+ ),
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) - sin(x**2) + exp(x)*f(x) + log(x)*f(x)**2,
+ False, 0, 0, 0
+ ),
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) - tanh(x + sqrt(x)) + f(x) + x**4*f(x)**2,
+ False, 0, 0, 0
+ ),
+ # Test Non-Riccati ODEs
+ (
+ (1 - x**2)*f(x).diff(x, 2) - 2*x*f(x).diff(x) + 20*f(x),
+ False, 0, 0, 0
+ ),
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) - x**2 + x**3*f(x) + (x**2/(x + 1))*f(x)**3,
+ False, 0, 0, 0
+ ),
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x)*f(x)**2 + (x**2 - 1)/(x**3 + 1)*f(x) + 1/(2*x \
+ + 3) + f(x)**2,
+ False, 0, 0, 0
+ )]
+ for eq, res, b0, b1, b2 in tests:
+ match, funcs = match_riccati(eq, f, x)
+ assert match == res
+ if res:
+ assert [b0, b1, b2] == funcs
+
+
+def test_val_at_inf():
+ """
+ This function tests the valuation of rational
+ function at oo.
+
+ Each test case has 3 values -
+
+ 1. num - Numerator of rational function.
+ 2. den - Denominator of rational function.
+ 3. val_inf - Valuation of rational function at oo
+ """
+ tests = [
+ # degree(denom) > degree(numer)
+ (
+ Poly(10*x**3 + 8*x**2 - 13*x + 6, x),
+ Poly(-13*x**10 - x**9 + 5*x**8 + 7*x**7 + 10*x**6 + 6*x**5 - 7*x**4 + 11*x**3 - 8*x**2 + 5*x + 13, x),
+ 7
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(1, x),
+ Poly(-9*x**4 + 3*x**3 + 15*x**2 - 6*x - 14, x),
+ 4
+ ),
+ # degree(denom) == degree(numer)
+ (
+ Poly(-6*x**3 - 8*x**2 + 8*x - 6, x),
+ Poly(-5*x**3 + 12*x**2 - 6*x - 9, x),
+ 0
+ ),
+ # degree(denom) < degree(numer)
+ (
+ Poly(12*x**8 - 12*x**7 - 11*x**6 + 8*x**5 + 3*x**4 - x**3 + x**2 - 11*x, x),
+ Poly(-14*x**2 + x, x),
+ -6
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(5*x**6 + 9*x**5 - 11*x**4 - 9*x**3 + x**2 - 4*x + 4, x),
+ Poly(15*x**4 + 3*x**3 - 8*x**2 + 15*x + 12, x),
+ -2
+ )]
+ for num, den, val in tests:
+ assert val_at_inf(num, den, x) == val
+
+
+def test_necessary_conds():
+ """
+ This function tests the necessary conditions for
+ a Riccati ODE to have a rational particular solution.
+ """
+ # Valuation at Infinity is an odd negative integer
+ assert check_necessary_conds(-3, [1, 2, 4]) == False
+ # Valuation at Infinity is a positive integer lesser than 2
+ assert check_necessary_conds(1, [1, 2, 4]) == False
+ # Multiplicity of a pole is an odd integer greater than 1
+ assert check_necessary_conds(2, [3, 1, 6]) == False
+ # All values are correct
+ assert check_necessary_conds(-10, [1, 2, 8, 12]) == True
+
+
+def test_inverse_transform_poly():
+ """
+ This function tests the substitution x -> 1/x
+ in rational functions represented using Poly.
+ """
+ fns = [
+ (15*x**3 - 8*x**2 - 2*x - 6)/(18*x + 6),
+
+ (180*x**5 + 40*x**4 + 80*x**3 + 30*x**2 - 60*x - 80)/(180*x**3 - 150*x**2 + 75*x + 12),
+
+ (-15*x**5 - 36*x**4 + 75*x**3 - 60*x**2 - 80*x - 60)/(80*x**4 + 60*x**3 + 60*x**2 + 60*x - 80),
+
+ (60*x**7 + 24*x**6 - 15*x**5 - 20*x**4 + 30*x**2 + 100*x - 60)/(240*x**2 - 20*x - 30),
+
+ (30*x**6 - 12*x**5 + 15*x**4 - 15*x**2 + 10*x + 60)/(3*x**10 - 45*x**9 + 15*x**5 + 15*x**4 - 5*x**3 \
+ + 15*x**2 + 45*x - 15)
+ ]
+ for f in fns:
+ num, den = [Poly(e, x) for e in f.as_numer_denom()]
+ num, den = inverse_transform_poly(num, den, x)
+ assert f.subs(x, 1/x).cancel() == num/den
+
+
+def test_limit_at_inf():
+ """
+ This function tests the limit at oo of a
+ rational function.
+
+ Each test case has 3 values -
+
+ 1. num - Numerator of rational function.
+ 2. den - Denominator of rational function.
+ 3. limit_at_inf - Limit of rational function at oo
+ """
+ tests = [
+ # deg(denom) > deg(numer)
+ (
+ Poly(-12*x**2 + 20*x + 32, x),
+ Poly(32*x**3 + 72*x**2 + 3*x - 32, x),
+ 0
+ ),
+ # deg(denom) < deg(numer)
+ (
+ Poly(1260*x**4 - 1260*x**3 - 700*x**2 - 1260*x + 1400, x),
+ Poly(6300*x**3 - 1575*x**2 + 756*x - 540, x),
+ oo
+ ),
+ # deg(denom) < deg(numer), one of the leading coefficients is negative
+ (
+ Poly(-735*x**8 - 1400*x**7 + 1680*x**6 - 315*x**5 - 600*x**4 + 840*x**3 - 525*x**2 \
+ + 630*x + 3780, x),
+ Poly(1008*x**7 - 2940*x**6 - 84*x**5 + 2940*x**4 - 420*x**3 + 1512*x**2 + 105*x + 168, x),
+ -oo
+ ),
+ # deg(denom) == deg(numer)
+ (
+ Poly(105*x**7 - 960*x**6 + 60*x**5 + 60*x**4 - 80*x**3 + 45*x**2 + 120*x + 15, x),
+ Poly(735*x**7 + 525*x**6 + 720*x**5 + 720*x**4 - 8400*x**3 - 2520*x**2 + 2800*x + 280, x),
+ S(1)/7
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(288*x**4 - 450*x**3 + 280*x**2 - 900*x - 90, x),
+ Poly(607*x**4 + 840*x**3 - 1050*x**2 + 420*x + 420, x),
+ S(288)/607
+ )]
+ for num, den, lim in tests:
+ assert limit_at_inf(num, den, x) == lim
+
+
+def test_construct_c_case_1():
+ """
+ This function tests the Case 1 in the step
+ to calculate coefficients of c-vectors.
+
+ Each test case has 4 values -
+
+ 1. num - Numerator of the rational function a(x).
+ 2. den - Denominator of the rational function a(x).
+ 3. pole - Pole of a(x) for which c-vector is being
+ calculated.
+ 4. c - The c-vector for the pole.
+ """
+ tests = [
+ (
+ Poly(-3*x**3 + 3*x**2 + 4*x - 5, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(4*x**8 + 16*x**7 + 9*x**5 + 12*x**4 + 6*x**3 + 12*x**2, x, extension=True),
+ S(0),
+ [[S(1)/2 + sqrt(6)*I/6], [S(1)/2 - sqrt(6)*I/6]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(1200*x**3 + 1440*x**2 + 816*x + 560, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(128*x**5 - 656*x**4 + 1264*x**3 - 1125*x**2 + 385*x + 49, x, extension=True),
+ S(7)/4,
+ [[S(1)/2 + sqrt(16367978)/634], [S(1)/2 - sqrt(16367978)/634]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(4*x + 2, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(18*x**4 + (2 - 18*sqrt(3))*x**3 + (14 - 11*sqrt(3))*x**2 + (4 - 6*sqrt(3))*x \
+ + 8*sqrt(3) + 16, x, domain='QQ<sqrt(3)>'),
+ (S(1) + sqrt(3))/2,
+ [[S(1)/2 + sqrt(Mul(4, 2*sqrt(3) + 4, evaluate=False)/(19*sqrt(3) + 44) + 1)/2], \
+ [S(1)/2 - sqrt(Mul(4, 2*sqrt(3) + 4, evaluate=False)/(19*sqrt(3) + 44) + 1)/2]]
+ )]
+ for num, den, pole, c in tests:
+ assert construct_c_case_1(num, den, x, pole) == c
+
+
+def test_construct_c_case_2():
+ """
+ This function tests the Case 2 in the step
+ to calculate coefficients of c-vectors.
+
+ Each test case has 5 values -
+
+ 1. num - Numerator of the rational function a(x).
+ 2. den - Denominator of the rational function a(x).
+ 3. pole - Pole of a(x) for which c-vector is being
+ calculated.
+ 4. mul - The multiplicity of the pole.
+ 5. c - The c-vector for the pole.
+ """
+ tests = [
+ # Testing poles with multiplicity 2
+ (
+ Poly(1, x, extension=True),
+ Poly((x - 1)**2*(x - 2), x, extension=True),
+ 1, 2,
+ [[-I*(-1 - I)/2], [I*(-1 + I)/2]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(3*x**5 - 12*x**4 - 7*x**3 + 1, x, extension=True),
+ Poly((3*x - 1)**2*(x + 2)**2, x, extension=True),
+ S(1)/3, 2,
+ [[-S(89)/98], [-S(9)/98]]
+ ),
+ # Testing poles with multiplicity 4
+ (
+ Poly(x**3 - x**2 + 4*x, x, extension=True),
+ Poly((x - 2)**4*(x + 5)**2, x, extension=True),
+ 2, 4,
+ [[7*sqrt(3)*(S(60)/343 - 4*sqrt(3)/7)/12, 2*sqrt(3)/7], \
+ [-7*sqrt(3)*(S(60)/343 + 4*sqrt(3)/7)/12, -2*sqrt(3)/7]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(3*x**5 + x**4 + 3, x, extension=True),
+ Poly((4*x + 1)**4*(x + 2), x, extension=True),
+ -S(1)/4, 4,
+ [[128*sqrt(439)*(-sqrt(439)/128 - S(55)/14336)/439, sqrt(439)/256], \
+ [-128*sqrt(439)*(sqrt(439)/128 - S(55)/14336)/439, -sqrt(439)/256]]
+ ),
+ # Testing poles with multiplicity 6
+ (
+ Poly(x**3 + 2, x, extension=True),
+ Poly((3*x - 1)**6*(x**2 + 1), x, extension=True),
+ S(1)/3, 6,
+ [[27*sqrt(66)*(-sqrt(66)/54 - S(131)/267300)/22, -2*sqrt(66)/1485, sqrt(66)/162], \
+ [-27*sqrt(66)*(sqrt(66)/54 - S(131)/267300)/22, 2*sqrt(66)/1485, -sqrt(66)/162]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(x**2 + 12, x, extension=True),
+ Poly((x - sqrt(2))**6, x, extension=True),
+ sqrt(2), 6,
+ [[sqrt(14)*(S(6)/7 - 3*sqrt(14))/28, sqrt(7)/7, sqrt(14)], \
+ [-sqrt(14)*(S(6)/7 + 3*sqrt(14))/28, -sqrt(7)/7, -sqrt(14)]]
+ )]
+ for num, den, pole, mul, c in tests:
+ assert construct_c_case_2(num, den, x, pole, mul) == c
+
+
+def test_construct_c_case_3():
+ """
+ This function tests the Case 3 in the step
+ to calculate coefficients of c-vectors.
+ """
+ assert construct_c_case_3() == [[1]]
+
+
+def test_construct_d_case_4():
+ """
+ This function tests the Case 4 in the step
+ to calculate coefficients of the d-vector.
+
+ Each test case has 4 values -
+
+ 1. num - Numerator of the rational function a(x).
+ 2. den - Denominator of the rational function a(x).
+ 3. mul - Multiplicity of oo as a pole.
+ 4. d - The d-vector.
+ """
+ tests = [
+ # Tests with multiplicity at oo = 2
+ (
+ Poly(-x**5 - 2*x**4 + 4*x**3 + 2*x + 5, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(9*x**3 - 2*x**2 + 10*x - 2, x, extension=True),
+ 2,
+ [[10*I/27, I/3, -3*I*(S(158)/243 - I/3)/2], \
+ [-10*I/27, -I/3, 3*I*(S(158)/243 + I/3)/2]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(-x**6 + 9*x**5 + 5*x**4 + 6*x**3 + 5*x**2 + 6*x + 7, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(x**4 + 3*x**3 + 12*x**2 - x + 7, x, extension=True),
+ 2,
+ [[-6*I, I, -I*(17 - I)/2], [6*I, -I, I*(17 + I)/2]]
+ ),
+ # Tests with multiplicity at oo = 4
+ (
+ Poly(-2*x**6 - x**5 - x**4 - 2*x**3 - x**2 - 3*x - 3, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(3*x**2 + 10*x + 7, x, extension=True),
+ 4,
+ [[269*sqrt(6)*I/288, -17*sqrt(6)*I/36, sqrt(6)*I/3, -sqrt(6)*I*(S(16969)/2592 \
+ - 2*sqrt(6)*I/3)/4], [-269*sqrt(6)*I/288, 17*sqrt(6)*I/36, -sqrt(6)*I/3, \
+ sqrt(6)*I*(S(16969)/2592 + 2*sqrt(6)*I/3)/4]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(-3*x**5 - 3*x**4 - 3*x**3 - x**2 - 1, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(12*x - 2, x, extension=True),
+ 4,
+ [[41*I/192, 7*I/24, I/2, -I*(-S(59)/6912 - I)], \
+ [-41*I/192, -7*I/24, -I/2, I*(-S(59)/6912 + I)]]
+ ),
+ # Tests with multiplicity at oo = 4
+ (
+ Poly(-x**7 - x**5 - x**4 - x**2 - x, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(x + 2, x, extension=True),
+ 6,
+ [[-5*I/2, 2*I, -I, I, -I*(-9 - 3*I)/2], [5*I/2, -2*I, I, -I, I*(-9 + 3*I)/2]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(-x**7 - x**6 - 2*x**5 - 2*x**4 - x**3 - x**2 + 2*x - 2, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(2*x - 2, x, extension=True),
+ 6,
+ [[3*sqrt(2)*I/4, 3*sqrt(2)*I/4, sqrt(2)*I/2, sqrt(2)*I/2, -sqrt(2)*I*(-S(7)/8 - \
+ 3*sqrt(2)*I/2)/2], [-3*sqrt(2)*I/4, -3*sqrt(2)*I/4, -sqrt(2)*I/2, -sqrt(2)*I/2, \
+ sqrt(2)*I*(-S(7)/8 + 3*sqrt(2)*I/2)/2]]
+ )]
+ for num, den, mul, d in tests:
+ ser = rational_laurent_series(num, den, x, oo, mul, 1)
+ assert construct_d_case_4(ser, mul//2) == d
+
+
+def test_construct_d_case_5():
+ """
+ This function tests the Case 5 in the step
+ to calculate coefficients of the d-vector.
+
+ Each test case has 3 values -
+
+ 1. num - Numerator of the rational function a(x).
+ 2. den - Denominator of the rational function a(x).
+ 3. d - The d-vector.
+ """
+ tests = [
+ (
+ Poly(2*x**3 + x**2 + x - 2, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(9*x**3 + 5*x**2 + 2*x - 1, x, extension=True),
+ [[sqrt(2)/3, -sqrt(2)/108], [-sqrt(2)/3, sqrt(2)/108]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(3*x**5 + x**4 - x**3 + x**2 - 2*x - 2, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ Poly(9*x**5 + 7*x**4 + 3*x**3 + 2*x**2 + 5*x + 7, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ [[sqrt(3)/3, -2*sqrt(3)/27], [-sqrt(3)/3, 2*sqrt(3)/27]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(x**2 - x + 1, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ Poly(3*x**2 + 7*x + 3, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ [[sqrt(3)/3, -5*sqrt(3)/9], [-sqrt(3)/3, 5*sqrt(3)/9]]
+ )]
+ for num, den, d in tests:
+ # Multiplicity of oo is 0
+ ser = rational_laurent_series(num, den, x, oo, 0, 1)
+ assert construct_d_case_5(ser) == d
+
+
+def test_construct_d_case_6():
+ """
+ This function tests the Case 6 in the step
+ to calculate coefficients of the d-vector.
+
+ Each test case has 3 values -
+
+ 1. num - Numerator of the rational function a(x).
+ 2. den - Denominator of the rational function a(x).
+ 3. d - The d-vector.
+ """
+ tests = [
+ (
+ Poly(-2*x**2 - 5, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ Poly(4*x**4 + 2*x**2 + 10*x + 2, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ [[S(1)/2 + I/2], [S(1)/2 - I/2]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(-2*x**3 - 4*x**2 - 2*x - 5, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ Poly(x**6 - x**5 + 2*x**4 - 4*x**3 - 5*x**2 - 5*x + 9, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ [[1], [0]]
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(-5*x**3 + x**2 + 11*x + 12, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ Poly(6*x**8 - 26*x**7 - 27*x**6 - 10*x**5 - 44*x**4 - 46*x**3 - 34*x**2 \
+ - 27*x - 42, x, domain='ZZ'),
+ [[1], [0]]
+ )]
+ for num, den, d in tests:
+ assert construct_d_case_6(num, den, x) == d
+
+
+def test_rational_laurent_series():
+ """
+ This function tests the computation of coefficients
+ of Laurent series of a rational function.
+
+ Each test case has 5 values -
+
+ 1. num - Numerator of the rational function.
+ 2. den - Denominator of the rational function.
+ 3. x0 - Point about which Laurent series is to
+ be calculated.
+ 4. mul - Multiplicity of x0 if x0 is a pole of
+ the rational function (0 otherwise).
+ 5. n - Number of terms upto which the series
+ is to be calcuated.
+ """
+ tests = [
+ # Laurent series about simple pole (Multiplicity = 1)
+ (
+ Poly(x**2 - 3*x + 9, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(x**2 - x, x, extension=True),
+ S(1), 1, 6,
+ {1: 7, 0: -8, -1: 9, -2: -9, -3: 9, -4: -9}
+ ),
+ # Laurent series about multiple pole (Multiplicty > 1)
+ (
+ Poly(64*x**3 - 1728*x + 1216, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(64*x**4 - 80*x**3 - 831*x**2 + 1809*x - 972, x, extension=True),
+ S(9)/8, 2, 3,
+ {0: S(32177152)/46521675, 2: S(1019)/984, -1: S(11947565056)/28610830125, \
+ 1: S(209149)/75645}
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(1, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(x**5 + (-4*sqrt(2) - 1)*x**4 + (4*sqrt(2) + 12)*x**3 + (-12 - 8*sqrt(2))*x**2 \
+ + (4 + 8*sqrt(2))*x - 4, x, extension=True),
+ sqrt(2), 4, 6,
+ {4: 1 + sqrt(2), 3: -3 - 2*sqrt(2), 2: Mul(-1, -3 - 2*sqrt(2), evaluate=False)/(-1 \
+ + sqrt(2)), 1: (-3 - 2*sqrt(2))/(-1 + sqrt(2))**2, 0: Mul(-1, -3 - 2*sqrt(2), evaluate=False \
+ )/(-1 + sqrt(2))**3, -1: (-3 - 2*sqrt(2))/(-1 + sqrt(2))**4}
+ ),
+ # Laurent series about oo
+ (
+ Poly(x**5 - 4*x**3 + 6*x**2 + 10*x - 13, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(x**2 - 5, x, extension=True),
+ oo, 3, 6,
+ {3: 1, 2: 0, 1: 1, 0: 6, -1: 15, -2: 17}
+ ),
+ # Laurent series at x0 where x0 is not a pole of the function
+ # Using multiplicity as 0 (as x0 will not be a pole)
+ (
+ Poly(3*x**3 + 6*x**2 - 2*x + 5, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(9*x**4 - x**3 - 3*x**2 + 4*x + 4, x, extension=True),
+ S(2)/5, 0, 1,
+ {0: S(3345)/3304, -1: S(399325)/2729104, -2: S(3926413375)/4508479808, \
+ -3: S(-5000852751875)/1862002160704, -4: S(-6683640101653125)/6152055138966016}
+ ),
+ (
+ Poly(-7*x**2 + 2*x - 4, x, extension=True),
+ Poly(7*x**5 + 9*x**4 + 8*x**3 + 3*x**2 + 6*x + 9, x, extension=True),
+ oo, 0, 6,
+ {0: 0, -2: 0, -5: -S(71)/49, -1: 0, -3: -1, -4: S(11)/7}
+ )]
+ for num, den, x0, mul, n, ser in tests:
+ assert ser == rational_laurent_series(num, den, x, x0, mul, n)
+
+
+def check_dummy_sol(eq, solse, dummy_sym):
+ """
+ Helper function to check if actual solution
+ matches expected solution if actual solution
+ contains dummy symbols.
+ """
+ if isinstance(eq, Eq):
+ eq = eq.lhs - eq.rhs
+ _, funcs = match_riccati(eq, f, x)
+
+ sols = solve_riccati(f(x), x, *funcs)
+ C1 = Dummy('C1')
+ sols = [sol.subs(C1, dummy_sym) for sol in sols]
+
+ assert all([x[0] for x in checkodesol(eq, sols)])
+ assert all([s1.dummy_eq(s2, dummy_sym) for s1, s2 in zip(sols, solse)])
+
+
+def test_solve_riccati():
+ """
+ This function tests the computation of rational
+ particular solutions for a Riccati ODE.
+
+ Each test case has 2 values -
+
+ 1. eq - Riccati ODE to be solved.
+ 2. sol - Expected solution to the equation.
+
+ Some examples have been taken from the paper - "Statistical Investigation of
+ First-Order Algebraic ODEs and their Rational General Solutions" by
+ Georg Grasegger, N. Thieu Vo, Franz Winkler
+
+ https://www3.risc.jku.at/publications/download/risc_5197/RISCReport15-19.pdf
+ """
+ C0 = Dummy('C0')
+ # Type: 1st Order Rational Riccati, dy/dx = a + b*y + c*y**2,
+ # a, b, c are rational functions of x
+
+ tests = [
+ # a(x) is a constant
+ (
+ Eq(f(x).diff(x) + f(x)**2 - 2, 0),
+ [Eq(f(x), sqrt(2)), Eq(f(x), -sqrt(2))]
+ ),
+ # a(x) is a constant
+ (
+ f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x) + 4*f(x)/x + 2/x**2,
+ [Eq(f(x), (-2*C0 - x)/(C0*x + x**2))]
+ ),
+ # a(x) is a constant
+ (
+ 2*x**2*f(x).diff(x) - x*(4*f(x) + f(x).diff(x) - 4) + (f(x) - 1)*f(x),
+ [Eq(f(x), (C0 + 2*x**2)/(C0 + x))]
+ ),
+ # Pole with multiplicity 1
+ (
+ Eq(f(x).diff(x), -f(x)**2 - 2/(x**3 - x**2)),
+ [Eq(f(x), 1/(x**2 - x))]
+ ),
+ # One pole of multiplicity 2
+ (
+ x**2 - (2*x + 1/x)*f(x) + f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x),
+ [Eq(f(x), (C0*x + x**3 + 2*x)/(C0 + x**2)), Eq(f(x), x)]
+ ),
+ (
+ x**4*f(x).diff(x) + x**2 - x*(2*f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x)) + f(x),
+ [Eq(f(x), (C0*x**2 + x)/(C0 + x**2)), Eq(f(x), x**2)]
+ ),
+ # Multiple poles of multiplicity 2
+ (
+ -f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x) + (15*x**2 - 20*x + 7)/((x - 1)**2*(2*x \
+ - 1)**2),
+ [Eq(f(x), (9*C0*x - 6*C0 - 15*x**5 + 60*x**4 - 94*x**3 + 72*x**2 \
+ - 30*x + 6)/(6*C0*x**2 - 9*C0*x + 3*C0 + 6*x**6 - 29*x**5 + \
+ 57*x**4 - 58*x**3 + 30*x**2 - 6*x)), Eq(f(x), (3*x - 2)/(2*x**2 \
+ - 3*x + 1))]
+ ),
+ # Regression: Poles with even multiplicity > 2 fixed
+ (
+ f(x)**2 + f(x).diff(x) - (4*x**6 - 8*x**5 + 12*x**4 + 4*x**3 + \
+ 7*x**2 - 20*x + 4)/(4*x**4),
+ [Eq(f(x), (2*x**5 - 2*x**4 - x**3 + 4*x**2 + 3*x - 2)/(2*x**4 \
+ - 2*x**2))]
+ ),
+ # Regression: Poles with even multiplicity > 2 fixed
+ (
+ Eq(f(x).diff(x), (-x**6 + 15*x**4 - 40*x**3 + 45*x**2 - 24*x + 4)/\
+ (x**12 - 12*x**11 + 66*x**10 - 220*x**9 + 495*x**8 - 792*x**7 + 924*x**6 - \
+ 792*x**5 + 495*x**4 - 220*x**3 + 66*x**2 - 12*x + 1) + f(x)**2 + f(x)),
+ [Eq(f(x), 1/(x**6 - 6*x**5 + 15*x**4 - 20*x**3 + 15*x**2 - 6*x + 1))]
+ ),
+ # More than 2 poles with multiplicity 2
+ # Regression: Fixed mistake in necessary conditions
+ (
+ Eq(f(x).diff(x), x*f(x) + 2*x + (3*x - 2)*f(x)**2/(4*x + 2) + \
+ (8*x**2 - 7*x + 26)/(16*x**3 - 24*x**2 + 8) - S(3)/2),
+ [Eq(f(x), (1 - 4*x)/(2*x - 2))]
+ ),
+ # Regression: Fixed mistake in necessary conditions
+ (
+ Eq(f(x).diff(x), (-12*x**2 - 48*x - 15)/(24*x**3 - 40*x**2 + 8*x + 8) \
+ + 3*f(x)**2/(6*x + 2)),
+ [Eq(f(x), (2*x + 1)/(2*x - 2))]
+ ),
+ # Imaginary poles
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) + (3*x**2 + 1)*f(x)**2/x + (6*x**2 - x + 3)*f(x)/(x*(x \
+ - 1)) + (3*x**2 - 2*x + 2)/(x*(x - 1)**2),
+ [Eq(f(x), (-C0 - x**3 + x**2 - 2*x)/(C0*x - C0 + x**4 - x**3 + x**2 \
+ - x)), Eq(f(x), -1/(x - 1))],
+ ),
+ # Imaginary coefficients in equation
+ (
+ f(x).diff(x) - 2*I*(f(x)**2 + 1)/x,
+ [Eq(f(x), (-I*C0 + I*x**4)/(C0 + x**4)), Eq(f(x), -I)]
+ ),
+ # Regression: linsolve returning empty solution
+ # Large value of m (> 10)
+ (
+ Eq(f(x).diff(x), x*f(x)/(S(3)/2 - 2*x) + (x/2 - S(1)/3)*f(x)**2/\
+ (2*x/3 - S(1)/2) - S(5)/4 + (281*x**2 - 1260*x + 756)/(16*x**3 - 12*x**2)),
+ [Eq(f(x), (9 - x)/x), Eq(f(x), (40*x**14 + 28*x**13 + 420*x**12 + 2940*x**11 + \
+ 18480*x**10 + 103950*x**9 + 519750*x**8 + 2286900*x**7 + 8731800*x**6 + 28378350*\
+ x**5 + 76403250*x**4 + 163721250*x**3 + 261954000*x**2 + 278326125*x + 147349125)/\
+ ((24*x**14 + 140*x**13 + 840*x**12 + 4620*x**11 + 23100*x**10 + 103950*x**9 + \
+ 415800*x**8 + 1455300*x**7 + 4365900*x**6 + 10914750*x**5 + 21829500*x**4 + 32744250\
+ *x**3 + 32744250*x**2 + 16372125*x)))]
+ ),
+ # Regression: Fixed bug due to a typo in paper
+ (
+ Eq(f(x).diff(x), 18*x**3 + 18*x**2 + (-x/2 - S(1)/2)*f(x)**2 + 6),
+ [Eq(f(x), 6*x)]
+ ),
+ # Regression: Fixed bug due to a typo in paper
+ (
+ Eq(f(x).diff(x), -3*x**3/4 + 15*x/2 + (x/3 - S(4)/3)*f(x)**2 \
+ + 9 + (1 - x)*f(x)/x + 3/x),
+ [Eq(f(x), -3*x/2 - 3)]
+ )]
+ for eq, sol in tests:
+ check_dummy_sol(eq, sol, C0)
+
+
+@slow
+def test_solve_riccati_slow():
+ """
+ This function tests the computation of rational
+ particular solutions for a Riccati ODE.
+
+ Each test case has 2 values -
+
+ 1. eq - Riccati ODE to be solved.
+ 2. sol - Expected solution to the equation.
+ """
+ C0 = Dummy('C0')
+ tests = [
+ # Very large values of m (989 and 991)
+ (
+ Eq(f(x).diff(x), (1 - x)*f(x)/(x - 3) + (2 - 12*x)*f(x)**2/(2*x - 9) + \
+ (54924*x**3 - 405264*x**2 + 1084347*x - 1087533)/(8*x**4 - 132*x**3 + 810*x**2 - \
+ 2187*x + 2187) + 495),
+ [Eq(f(x), (18*x + 6)/(2*x - 9))]
+ )]
+ for eq, sol in tests:
+ check_dummy_sol(eq, sol, C0)
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py
index feb7eacf9c07..7ef52d08b290 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py
@@ -530,6 +530,10 @@ def test_Riccati_special_minus2():
_ode_solver_test(_get_examples_ode_sol_riccati)
+def test_1st_rational_riccati():
+ _ode_solver_test(_get_examples_ode_sol_1st_rational_riccati)
+
+
def test_Bernoulli():
_ode_solver_test(_get_examples_ode_sol_bernoulli)
@@ -782,6 +786,83 @@ def _get_examples_ode_sol_riccati():
}
+@_add_example_keys
+def _get_examples_ode_sol_1st_rational_riccati():
+ # Type: 1st Order Rational Riccati, dy/dx = a + b*y + c*y**2,
+ # a, b, c are rational functions of x
+ return {
+ 'hint': "1st_rational_riccati",
+ 'func': f(x),
+ 'examples':{
+ # a(x) is a constant
+ "rational_riccati_01": {
+ "eq": Eq(f(x).diff(x) + f(x)**2 - 2, 0),
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), sqrt(2)*(-C1 - exp(2*sqrt(2)*x))/(C1 - exp(2*sqrt(2)*x)))]
+ },
+ # a(x) is a constant
+ "rational_riccati_02": {
+ "eq": f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) + 4*f(x)/x + 2/x**2,
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), (-2*C1 - x)/(x*(C1 + x)))]
+ },
+ # a(x) is a constant
+ "rational_riccati_03": {
+ "eq": 2*x**2*Derivative(f(x), x) - x*(4*f(x) + Derivative(f(x), x) - 4) + (f(x) - 1)*f(x),
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), (C1 + 2*x**2)/(C1 + x))]
+ },
+ # Constant coefficients
+ "rational_riccati_04": {
+ "eq": f(x).diff(x) - 6 - 5*f(x) - f(x)**2,
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), (-2*C1 + 3*exp(x))/(C1 - exp(x)))]
+ },
+ # One pole of multiplicity 2
+ "rational_riccati_05": {
+ "eq": x**2 - (2*x + 1/x)*f(x) + f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x),
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), x*(C1 + x**2 + 1)/(C1 + x**2 - 1))]
+ },
+ # One pole of multiplicity 2
+ "rational_riccati_06": {
+ "eq": x**4*Derivative(f(x), x) + x**2 - x*(2*f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x)) + f(x),
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), x*(C1*x - x + 1)/(C1 + x**2 - 1))]
+ },
+ # Multiple poles of multiplicity 2
+ "rational_riccati_07": {
+ "eq": -f(x)**2 + Derivative(f(x), x) + (15*x**2 - 20*x + 7)/((x - 1)**2*(2*x \
+ - 1)**2),
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), (9*C1*x - 6*C1 - 15*x**5 + 60*x**4 - 94*x**3 + 72*x**2 - \
+ 33*x + 8)/(6*C1*x**2 - 9*C1*x + 3*C1 + 6*x**6 - 29*x**5 + 57*x**4 - \
+ 58*x**3 + 28*x**2 - 3*x - 1))]
+ },
+ # Imaginary poles
+ "rational_riccati_08": {
+ "eq": Derivative(f(x), x) + (3*x**2 + 1)*f(x)**2/x + (6*x**2 - x + 3)*f(x)/(x*(x \
+ - 1)) + (3*x**2 - 2*x + 2)/(x*(x - 1)**2),
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), (-C1 - x**3 + x**2 - 2*x + 1)/(C1*x - C1 + x**4 - x**3 + x**2 - \
+ 2*x + 1))],
+ },
+ # Imaginary coefficients in equation
+ "rational_riccati_09": {
+ "eq": Derivative(f(x), x) - 2*I*(f(x)**2 + 1)/x,
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), (-I*C1 + I*x**4 + I)/(C1 + x**4 - 1))]
+ },
+ # Regression: linsolve returning empty solution
+ # Large value of m (> 10)
+ "rational_riccati_10": {
+ "eq": Eq(Derivative(f(x), x), x*f(x)/(S(3)/2 - 2*x) + (x/2 - S(1)/3)*f(x)**2/\
+ (2*x/3 - S(1)/2) - S(5)/4 + (281*x**2 - 1260*x + 756)/(16*x**3 - 12*x**2)),
+ "sol": [Eq(f(x), (40*C1*x**14 + 28*C1*x**13 + 420*C1*x**12 + 2940*C1*x**11 + \
+ 18480*C1*x**10 + 103950*C1*x**9 + 519750*C1*x**8 + 2286900*C1*x**7 + \
+ 8731800*C1*x**6 + 28378350*C1*x**5 + 76403250*C1*x**4 + 163721250*C1*x**3 \
+ + 261954000*C1*x**2 + 278326125*C1*x + 147349125*C1 + x*exp(2*x) - 9*exp(2*x) \
+ )/(x*(24*C1*x**13 + 140*C1*x**12 + 840*C1*x**11 + 4620*C1*x**10 + 23100*C1*x**9 \
+ + 103950*C1*x**8 + 415800*C1*x**7 + 1455300*C1*x**6 + 4365900*C1*x**5 + \
+ 10914750*C1*x**4 + 21829500*C1*x**3 + 32744250*C1*x**2 + 32744250*C1*x + \
+ 16372125*C1 - exp(2*x))))]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+
+
@_add_example_keys
def _get_examples_ode_sol_1st_linear():
# Type: first order linear form f'(x)+p(x)f(x)=q(x)
@@ -2766,6 +2847,7 @@ def _get_all_examples():
_get_examples_ode_sol_nth_linear_undetermined_coefficients + \
_get_examples_ode_sol_liouville + \
_get_examples_ode_sol_separable + \
+ _get_examples_ode_sol_1st_rational_riccati + \
_get_examples_ode_sol_nth_linear_var_of_parameters + \
_get_examples_ode_sol_2nd_linear_bessel + \
_get_examples_ode_sol_2nd_2F1_hypergeometric + \
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21171@bd5489e
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,171
|
Patched the latex printing error in _print_SingularityFunction()
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #21127
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Latex printer for singularity function threw TypeError because of an additional functional parameter for exponent (exp) which was lacking in the function signature. Moreover, there was no provision for printing angle brackets with an exponent which was also fixed.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below between the BEGIN and END
statements. The basic format is a bulleted list with the name of the subpackage
and the release note for this PR. For example:
* solvers
* Added a new solver for logarithmic equations.
* functions
* Fixed a bug with log of integers.
or if no release note(s) should be included use:
NO ENTRY
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more
information on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release
notes automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* printing
* Fixed a bug which led to latex printing error in singularity function expressions.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-03-26T07:48:35Z
|
_print_SingularityFunction() got an unexpected keyword argument 'exp'
On a Jupyter Notebook cell, type the following:
```python
from sympy import *
from sympy.physics.continuum_mechanics import Beam
# Young's modulus
E = symbols("E")
# length of the beam
L = symbols("L")
# concentrated load at the end tip of the beam
F = symbols("F")
# square cross section
B, H = symbols("B, H")
I = B * H**3 / 12
# numerical values (material: steel)
d = {B: 1e-02, H: 1e-02, E: 210e09, L: 0.2, F: 100}
b2 = Beam(L, E, I)
b2.apply_load(-F, L / 2, -1)
b2.apply_support(0, "fixed")
R0, M0 = symbols("R_0, M_0")
b2.solve_for_reaction_loads(R0, M0)
```
Then:
```
b2.shear_force()
```
The following error appears:
```
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py in __call__(self, obj)
343 method = get_real_method(obj, self.print_method)
344 if method is not None:
--> 345 return method()
346 return None
347 else:
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/interactive/printing.py in _print_latex_png(o)
184 """
185 if _can_print(o):
--> 186 s = latex(o, mode=latex_mode, **settings)
187 if latex_mode == 'plain':
188 s = '$\\displaystyle %s$' % s
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in __call__(self, *args, **kwargs)
371
372 def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
--> 373 return self.__wrapped__(*args, **kwargs)
374
375 @property
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in latex(expr, **settings)
2913
2914 """
-> 2915 return LatexPrinter(settings).doprint(expr)
2916
2917
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in doprint(self, expr)
252
253 def doprint(self, expr):
--> 254 tex = Printer.doprint(self, expr)
255
256 if self._settings['mode'] == 'plain':
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in doprint(self, expr)
289 def doprint(self, expr):
290 """Returns printer's representation for expr (as a string)"""
--> 291 return self._str(self._print(expr))
292
293 def _print(self, expr, **kwargs):
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)
327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__
328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):
--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)
330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.
331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Add(self, expr, order)
381 else:
382 tex += " + "
--> 383 term_tex = self._print(term)
384 if self._needs_add_brackets(term):
385 term_tex = r"\left(%s\right)" % term_tex
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)
327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__
328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):
--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)
330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.
331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Mul(self, expr)
565 # use the original expression here, since fraction() may have
566 # altered it when producing numer and denom
--> 567 tex += convert(expr)
568
569 else:
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in convert(expr)
517 isinstance(x.base, Quantity)))
518
--> 519 return convert_args(args)
520
521 def convert_args(args):
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in convert_args(args)
523
524 for i, term in enumerate(args):
--> 525 term_tex = self._print(term)
526
527 if self._needs_mul_brackets(term, first=(i == 0),
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)
327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__
328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):
--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)
330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.
331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Add(self, expr, order)
381 else:
382 tex += " + "
--> 383 term_tex = self._print(term)
384 if self._needs_add_brackets(term):
385 term_tex = r"\left(%s\right)" % term_tex
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)
327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__
328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):
--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)
330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.
331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Mul(self, expr)
569 else:
570 snumer = convert(numer)
--> 571 sdenom = convert(denom)
572 ldenom = len(sdenom.split())
573 ratio = self._settings['long_frac_ratio']
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in convert(expr)
505 def convert(expr):
506 if not expr.is_Mul:
--> 507 return str(self._print(expr))
508 else:
509 if self.order not in ('old', 'none'):
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)
327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__
328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):
--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)
330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.
331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Add(self, expr, order)
381 else:
382 tex += " + "
--> 383 term_tex = self._print(term)
384 if self._needs_add_brackets(term):
385 term_tex = r"\left(%s\right)" % term_tex
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)
327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__
328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):
--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)
330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.
331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Pow(self, expr)
649 else:
650 if expr.base.is_Function:
--> 651 return self._print(expr.base, exp=self._print(expr.exp))
652 else:
653 tex = r"%s^{%s}"
/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)
327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__
328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):
--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)
330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.
331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)
TypeError: _print_SingularityFunction() got an unexpected keyword argument 'exp'
```
|
Could you provide a fully working example? Copying and pasting your code leaves a number of non-defined variables. Thanks for the report.
@moorepants Sorry for that, I've just updated the code in the original post.
This is the string printed version from `b2..shear_force()`:
```
Out[5]: -F*SingularityFunction(x, L/2, 0) + (F*SingularityFunction(L, 0, -1)*SingularityFunction(L, L/2, 1)/(SingularityFunction(L, 0, -1)*SingularityFunction(L, 0, 1) - SingularityFunction(L, 0, 0)**2) - F*SingularityFunction(L, 0, 0)*SingularityFunction(L, L/2, 0)/(SingularityFunction(L, 0, -1)*SingularityFunction(L, 0, 1) - SingularityFunction(L, 0, 0)**2))*SingularityFunction(x, 0, 0) + (-F*SingularityFunction(L, 0, 0)*SingularityFunction(L, L/2, 1)/(SingularityFunction(L, 0, -1)*SingularityFunction(L, 0, 1) - SingularityFunction(L, 0, 0)**2) + F*SingularityFunction(L, 0, 1)*SingularityFunction(L, L/2, 0)/(SingularityFunction(L, 0, -1)*SingularityFunction(L, 0, 1) - SingularityFunction(L, 0, 0)**2))*SingularityFunction(x, 0, -1)
```
Yes works correctly if you print the string. It throws the error when you display the expression on a jupyter notebook with latex
It errors on this term: `SingularityFunction(L, 0, 0)**2`. For some reasons the latex printer fails on printing a singularity function raised to a power.
|
[
{
"body": "On a Jupyter Notebook cell, type the following:\r\n\r\n```python\r\nfrom sympy import *\r\nfrom sympy.physics.continuum_mechanics import Beam\r\n# Young's modulus\r\nE = symbols(\"E\")\r\n# length of the beam\r\nL = symbols(\"L\")\r\n# concentrated load at the end tip of the beam\r\nF = symbols(\"F\")\r\n# square cross section\r\nB, H = symbols(\"B, H\")\r\nI = B * H**3 / 12\r\n# numerical values (material: steel)\r\nd = {B: 1e-02, H: 1e-02, E: 210e09, L: 0.2, F: 100}\r\n\r\nb2 = Beam(L, E, I)\r\nb2.apply_load(-F, L / 2, -1)\r\nb2.apply_support(0, \"fixed\")\r\nR0, M0 = symbols(\"R_0, M_0\")\r\nb2.solve_for_reaction_loads(R0, M0)\r\n```\r\n\r\nThen:\r\n\r\n```\r\nb2.shear_force()\r\n```\r\n\r\nThe following error appears:\r\n```\r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nTypeError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py in __call__(self, obj)\r\n 343 method = get_real_method(obj, self.print_method)\r\n 344 if method is not None:\r\n--> 345 return method()\r\n 346 return None\r\n 347 else:\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/interactive/printing.py in _print_latex_png(o)\r\n 184 \"\"\"\r\n 185 if _can_print(o):\r\n--> 186 s = latex(o, mode=latex_mode, **settings)\r\n 187 if latex_mode == 'plain':\r\n 188 s = '$\\\\displaystyle %s$' % s\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in __call__(self, *args, **kwargs)\r\n 371 \r\n 372 def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):\r\n--> 373 return self.__wrapped__(*args, **kwargs)\r\n 374 \r\n 375 @property\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in latex(expr, **settings)\r\n 2913 \r\n 2914 \"\"\"\r\n-> 2915 return LatexPrinter(settings).doprint(expr)\r\n 2916 \r\n 2917 \r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in doprint(self, expr)\r\n 252 \r\n 253 def doprint(self, expr):\r\n--> 254 tex = Printer.doprint(self, expr)\r\n 255 \r\n 256 if self._settings['mode'] == 'plain':\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in doprint(self, expr)\r\n 289 def doprint(self, expr):\r\n 290 \"\"\"Returns printer's representation for expr (as a string)\"\"\"\r\n--> 291 return self._str(self._print(expr))\r\n 292 \r\n 293 def _print(self, expr, **kwargs):\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)\r\n 327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__\r\n 328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):\r\n--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)\r\n 330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.\r\n 331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Add(self, expr, order)\r\n 381 else:\r\n 382 tex += \" + \"\r\n--> 383 term_tex = self._print(term)\r\n 384 if self._needs_add_brackets(term):\r\n 385 term_tex = r\"\\left(%s\\right)\" % term_tex\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)\r\n 327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__\r\n 328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):\r\n--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)\r\n 330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.\r\n 331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Mul(self, expr)\r\n 565 # use the original expression here, since fraction() may have\r\n 566 # altered it when producing numer and denom\r\n--> 567 tex += convert(expr)\r\n 568 \r\n 569 else:\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in convert(expr)\r\n 517 isinstance(x.base, Quantity)))\r\n 518 \r\n--> 519 return convert_args(args)\r\n 520 \r\n 521 def convert_args(args):\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in convert_args(args)\r\n 523 \r\n 524 for i, term in enumerate(args):\r\n--> 525 term_tex = self._print(term)\r\n 526 \r\n 527 if self._needs_mul_brackets(term, first=(i == 0),\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)\r\n 327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__\r\n 328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):\r\n--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)\r\n 330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.\r\n 331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Add(self, expr, order)\r\n 381 else:\r\n 382 tex += \" + \"\r\n--> 383 term_tex = self._print(term)\r\n 384 if self._needs_add_brackets(term):\r\n 385 term_tex = r\"\\left(%s\\right)\" % term_tex\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)\r\n 327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__\r\n 328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):\r\n--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)\r\n 330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.\r\n 331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Mul(self, expr)\r\n 569 else:\r\n 570 snumer = convert(numer)\r\n--> 571 sdenom = convert(denom)\r\n 572 ldenom = len(sdenom.split())\r\n 573 ratio = self._settings['long_frac_ratio']\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in convert(expr)\r\n 505 def convert(expr):\r\n 506 if not expr.is_Mul:\r\n--> 507 return str(self._print(expr))\r\n 508 else:\r\n 509 if self.order not in ('old', 'none'):\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)\r\n 327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__\r\n 328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):\r\n--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)\r\n 330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.\r\n 331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Add(self, expr, order)\r\n 381 else:\r\n 382 tex += \" + \"\r\n--> 383 term_tex = self._print(term)\r\n 384 if self._needs_add_brackets(term):\r\n 385 term_tex = r\"\\left(%s\\right)\" % term_tex\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)\r\n 327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__\r\n 328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):\r\n--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)\r\n 330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.\r\n 331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/latex.py in _print_Pow(self, expr)\r\n 649 else:\r\n 650 if expr.base.is_Function:\r\n--> 651 return self._print(expr.base, exp=self._print(expr.exp))\r\n 652 else:\r\n 653 tex = r\"%s^{%s}\"\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/sympy/printing/printer.py in _print(self, expr, **kwargs)\r\n 327 printmethod = '_print_' + cls.__name__\r\n 328 if hasattr(self, printmethod):\r\n--> 329 return getattr(self, printmethod)(expr, **kwargs)\r\n 330 # Unknown object, fall back to the emptyPrinter.\r\n 331 return self.emptyPrinter(expr)\r\n\r\nTypeError: _print_SingularityFunction() got an unexpected keyword argument 'exp'\r\n```",
"number": 21127,
"title": "_print_SingularityFunction() got an unexpected keyword argument 'exp'"
}
] |
aa22709cb7df2d7503803d4b2c0baa7aa21440b6
|
{
"head_commit": "bd5489ee747e40084c44989b526ea891dafb0846",
"head_commit_message": "remove trailing whitespace",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/printing/latex.py b/sympy/printing/latex.py\nindex 43f9e6ad8d93..6a713e8098ec 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/latex.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/latex.py\n@@ -1968,10 +1968,12 @@ def _print_DiracDelta(self, expr, exp=None):\n tex = r\"\\left(%s\\right)^{%s}\" % (tex, exp)\n return tex\n \n- def _print_SingularityFunction(self, expr):\n+ def _print_SingularityFunction(self, expr, exp=None):\n shift = self._print(expr.args[0] - expr.args[1])\n power = self._print(expr.args[2])\n tex = r\"{\\left\\langle %s \\right\\rangle}^{%s}\" % (shift, power)\n+ if exp:\n+ tex = r\"{\\left({\\langle %s \\rangle}^{%s}\\right)}^{%s}\" % (shift, power, exp)\n return tex\n \n def _print_Heaviside(self, expr, exp=None):\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py\nindex 84227a1785f6..f04d04c404a9 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py\n@@ -214,6 +214,19 @@ def test_latex_SingularityFunction():\n assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, 4, -1)) == \\\n r\"{\\left\\langle x - 4 \\right\\rangle}^{-1}\"\n \n+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, 4, 5)**3) == \\\n+ r\"{\\left({\\langle x - 4 \\rangle}^{5}\\right)}^{3}\"\n+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, -3, 4)**3) == \\\n+ r\"{\\left({\\langle x + 3 \\rangle}^{4}\\right)}^{3}\"\n+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, 0, 4)**3) == \\\n+ r\"{\\left({\\langle x \\rangle}^{4}\\right)}^{3}\"\n+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, a, n)**3) == \\\n+ r\"{\\left({\\langle - a + x \\rangle}^{n}\\right)}^{3}\"\n+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, 4, -2)**3) == \\\n+ r\"{\\left({\\langle x - 4 \\rangle}^{-2}\\right)}^{3}\"\n+ assert latex((SingularityFunction(x, 4, -1)**3)**3) == \\\n+ r\"{\\left({\\langle x - 4 \\rangle}^{-1}\\right)}^{9}\"\n+\n \n def test_latex_cycle():\n assert latex(Cycle(1, 2, 4)) == r\"\\left( 1\\; 2\\; 4\\right)\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1968,10 +1968,12 @@ def _print_DiracDelta(self, expr, exp=None):\n tex = r\"\\left(%s\\right)^{%s}\" % (tex, exp)\n return tex\n \n- def _print_SingularityFunction(self, expr):\n+ def _print_SingularityFunction(self, expr, exp=None):\n shift = self._print(expr.args[0] - expr.args[1])\n power = self._print(expr.args[2])\n tex = r\"{\\left\\langle %s \\right\\rangle}^{%s}\" % (shift, power)\n+ if exp:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1975,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/latex.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n if exp is not None:\r\n```"
}
] |
f24da7a32face8a0858fabbb0ade82a8d0d937ca
|
diff --git a/sympy/printing/latex.py b/sympy/printing/latex.py
index 43f9e6ad8d93..e9d404021ecc 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/latex.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/latex.py
@@ -1968,10 +1968,12 @@ def _print_DiracDelta(self, expr, exp=None):
tex = r"\left(%s\right)^{%s}" % (tex, exp)
return tex
- def _print_SingularityFunction(self, expr):
+ def _print_SingularityFunction(self, expr, exp=None):
shift = self._print(expr.args[0] - expr.args[1])
power = self._print(expr.args[2])
tex = r"{\left\langle %s \right\rangle}^{%s}" % (shift, power)
+ if exp is not None:
+ tex = r"{\left({\langle %s \rangle}^{%s}\right)}^{%s}" % (shift, power, exp)
return tex
def _print_Heaviside(self, expr, exp=None):
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py
index 84227a1785f6..f04d04c404a9 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py
@@ -214,6 +214,19 @@ def test_latex_SingularityFunction():
assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, 4, -1)) == \
r"{\left\langle x - 4 \right\rangle}^{-1}"
+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, 4, 5)**3) == \
+ r"{\left({\langle x - 4 \rangle}^{5}\right)}^{3}"
+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, -3, 4)**3) == \
+ r"{\left({\langle x + 3 \rangle}^{4}\right)}^{3}"
+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, 0, 4)**3) == \
+ r"{\left({\langle x \rangle}^{4}\right)}^{3}"
+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, a, n)**3) == \
+ r"{\left({\langle - a + x \rangle}^{n}\right)}^{3}"
+ assert latex(SingularityFunction(x, 4, -2)**3) == \
+ r"{\left({\langle x - 4 \rangle}^{-2}\right)}^{3}"
+ assert latex((SingularityFunction(x, 4, -1)**3)**3) == \
+ r"{\left({\langle x - 4 \rangle}^{-1}\right)}^{9}"
+
def test_latex_cycle():
assert latex(Cycle(1, 2, 4)) == r"\left( 1\; 2\; 4\right)"
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-21165@9eebefe
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 21,165
|
Fixes 21079 issue, periodicity, solvify for piecewise
|
`solvify` is now able to solve `piecewise` expressions.
Fixes #21079 as it was giving an error due to a bug in `periodicity`.
Hence, periodicity for `piecewise` is fixed as `None` as the period of `piecewise` should also be `piecewise`.(which is an inconsistent return type)
```
>>> p = Piecewise((0, x < -10), (x**2 + 5*x - 6, x >= -9))
>>> solvify(p, x, S.Reals)
[-6, 1]
>>> periodicity(p, x) is None
True
```
Closes & Fixes #21079
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-03-25T14:38:04Z
|
Solvify cannot solve Piecewise
```
>>> p = Piecewise((0, x < -1), (x**2, x <= 1), (log(x), True))
>>> solvify(p,x,S.Reals)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/home/sayandip/sympy/sympy/solvers/solveset.py", line 2446, in solvify
period = periodicity(f, symbol)
File "/home/sayandip/sympy/sympy/calculus/util.py", line 516, in periodicity
g_s = decompogen(f, symbol)
File "/home/sayandip/sympy/sympy/solvers/decompogen.py", line 47, in decompogen
result += [f.subs(f.args[0], symbol)] + decompogen(f.args[0], symbol)
File "/home/sayandip/sympy/sympy/solvers/decompogen.py", line 37, in decompogen
raise TypeError('expecting Expr but got: `%s`' % func_name(f))
TypeError: expecting Expr but got: `ExprCondPair`
>>> solveset(p,x,S.Reals)
Union(FiniteSet(0), Interval.open(-oo, -1))
```
|
Related: #20881.
|
[
{
"body": "```\r\n>>> p = Piecewise((0, x < -1), (x**2, x <= 1), (log(x), True))\r\n>>> solvify(p,x,S.Reals)\r\nTraceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"<stdin>\", line 1, in <module>\r\n File \"/home/sayandip/sympy/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\", line 2446, in solvify\r\n period = periodicity(f, symbol)\r\n File \"/home/sayandip/sympy/sympy/calculus/util.py\", line 516, in periodicity\r\n g_s = decompogen(f, symbol)\r\n File \"/home/sayandip/sympy/sympy/solvers/decompogen.py\", line 47, in decompogen\r\n result += [f.subs(f.args[0], symbol)] + decompogen(f.args[0], symbol)\r\n File \"/home/sayandip/sympy/sympy/solvers/decompogen.py\", line 37, in decompogen\r\n raise TypeError('expecting Expr but got: `%s`' % func_name(f))\r\nTypeError: expecting Expr but got: `ExprCondPair`\r\n>>> solveset(p,x,S.Reals)\r\nUnion(FiniteSet(0), Interval.open(-oo, -1))\r\n\r\n```\r\n\r\n",
"number": 21079,
"title": "Solvify cannot solve Piecewise"
}
] |
aa22709cb7df2d7503803d4b2c0baa7aa21440b6
|
{
"head_commit": "9eebefe313809e0d95fa07b3adff652c04d99163",
"head_commit_message": "docs",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/calculus/tests/test_util.py b/sympy/calculus/tests/test_util.py\nindex 510fb12741ba..d29f1edfbe55 100644\n--- a/sympy/calculus/tests/test_util.py\n+++ b/sympy/calculus/tests/test_util.py\n@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@\n from sympy import (Symbol, S, exp, log, sqrt, oo, E, zoo, pi, tan, sin, cos,\n cot, sec, csc, Abs, symbols, I, re, simplify,\n- expint, Rational)\n+ expint, Rational, Piecewise)\n from sympy.calculus.util import (function_range, continuous_domain, not_empty_in,\n periodicity, lcim, AccumBounds, is_convex,\n stationary_points, minimum, maximum)\n@@ -171,6 +171,9 @@ def test_periodicity():\n assert periodicity((E**x)%3, x) is None\n \n assert periodicity(sin(expint(1, x))/expint(1, x), x) is None\n+ # returning `None` for any Piecewise\n+ p = Piecewise((0, x < -1), (x**2, x <= 1), (log(x), True))\n+ assert periodicity(p, x) is None\n \n \n def test_periodicity_check():\ndiff --git a/sympy/calculus/util.py b/sympy/calculus/util.py\nindex 81cdec0d18cc..fad8e13f05df 100644\n--- a/sympy/calculus/util.py\n+++ b/sympy/calculus/util.py\n@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@\n-from sympy import Order, S, log, limit, lcm_list, im, re, Dummy\n+from sympy import Order, S, log, limit, lcm_list, im, re, Dummy, Piecewise\n from sympy.core import Add, Mul, Pow\n from sympy.core.basic import Basic\n from sympy.core.compatibility import iterable\n@@ -511,6 +511,11 @@ def _check(orig_f, period):\n symbol not in n.free_symbols):\n period = Abs(n / a.diff(symbol))\n \n+ elif isinstance(f, Piecewise):\n+ # Returning None, as the return type, period of the `piecewise`\n+ # also should be a piecewise. (i.e. the return type is not favorable)\n+ return None\n+\n elif period is None:\n from sympy.solvers.decompogen import compogen\n g_s = decompogen(f, symbol)\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\nindex c0d2616a9be4..c39aaea5f7f8 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\n@@ -2318,6 +2318,8 @@ def solvify(f, symbol, domain):\n ImageSet, | list (if `f` is periodic)\n Union |\n \n+ Union | list (with FiniteSet)\n+\n EmptySet | empty list\n \n Others | None\n@@ -2377,7 +2379,16 @@ def solvify(f, symbol, domain):\n \n else:\n solution = solution_set.intersect(domain)\n- if isinstance(solution, FiniteSet):\n+ if isinstance(solution, Union):\n+ # concerned about only FiniteSet with Union but not about ImageSet\n+ # if required could be extend\n+ if any(isinstance(i, FiniteSet) for i in solution.args):\n+ result = [sol for soln in solution.args \\\n+ for sol in soln.args if isinstance(soln,FiniteSet)]\n+ else:\n+ return None\n+\n+ elif isinstance(solution, FiniteSet):\n result += solution\n \n return result\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\nindex 08d989363dce..5cc2d3746c27 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\n@@ -1320,7 +1320,24 @@ def test_solvify():\n raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: solvify(sin(exp(x)), x, S.Complexes))\n \n \n+def test_solvify_piecewise():\n+ p1 = Piecewise((0, x < -1), (x**2, x <= 1), (log(x), True))\n+ p2 = Piecewise((0, x < -10), (x**2 + 5*x - 6, x >= -9))\n+ p3 = Piecewise((0, Eq(x, 0)), (x**2/Abs(x), True))\n+ p4 = Piecewise((0, Eq(x, pi)), ((x - pi)/sin(x), True))\n+\n+ # issue 21079\n+ assert solvify(p1, x, S.Reals) == [0]\n+ assert solvify(p2, x, S.Reals) == [-6, 1]\n+ assert solvify(p3, x, S.Reals) == [0]\n+ assert solvify(p4, x, S.Reals) == [pi]\n+\n+\n def test_abs_invert_solvify():\n+\n+ x = Symbol('x',positive=True)\n+ assert solvify(sin(Abs(x)), x, S.Reals) == [0, pi]\n+ x = Symbol('x')\n assert solvify(sin(Abs(x)), x, S.Reals) is None\n \n \n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -511,6 +511,11 @@ def _check(orig_f, period):\n symbol not in n.free_symbols):\n period = Abs(n / a.diff(symbol))\n \n+ elif isinstance(f, Piecewise):\n+ # Returning None, as the return type, period of the `piecewise`\n+ # also should be a piecewise. (i.e. the return type is not favorable)\n+ return None",
"line": null,
"original_line": 517,
"original_start_line": 515,
"path": "sympy/calculus/util.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n pass # not handling Piecewise yet\r\n```"
}
] |
7856abc70ad9657afb0a068e6cb3ef199f2395bf
|
diff --git a/sympy/calculus/tests/test_util.py b/sympy/calculus/tests/test_util.py
index 510fb12741ba..d29f1edfbe55 100644
--- a/sympy/calculus/tests/test_util.py
+++ b/sympy/calculus/tests/test_util.py
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
from sympy import (Symbol, S, exp, log, sqrt, oo, E, zoo, pi, tan, sin, cos,
cot, sec, csc, Abs, symbols, I, re, simplify,
- expint, Rational)
+ expint, Rational, Piecewise)
from sympy.calculus.util import (function_range, continuous_domain, not_empty_in,
periodicity, lcim, AccumBounds, is_convex,
stationary_points, minimum, maximum)
@@ -171,6 +171,9 @@ def test_periodicity():
assert periodicity((E**x)%3, x) is None
assert periodicity(sin(expint(1, x))/expint(1, x), x) is None
+ # returning `None` for any Piecewise
+ p = Piecewise((0, x < -1), (x**2, x <= 1), (log(x), True))
+ assert periodicity(p, x) is None
def test_periodicity_check():
diff --git a/sympy/calculus/util.py b/sympy/calculus/util.py
index 81cdec0d18cc..4a5e72a80c2d 100644
--- a/sympy/calculus/util.py
+++ b/sympy/calculus/util.py
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-from sympy import Order, S, log, limit, lcm_list, im, re, Dummy
+from sympy import Order, S, log, limit, lcm_list, im, re, Dummy, Piecewise
from sympy.core import Add, Mul, Pow
from sympy.core.basic import Basic
from sympy.core.compatibility import iterable
@@ -511,6 +511,9 @@ def _check(orig_f, period):
symbol not in n.free_symbols):
period = Abs(n / a.diff(symbol))
+ elif isinstance(f, Piecewise):
+ pass # not handling Piecewise yet as the return type is not favorable
+
elif period is None:
from sympy.solvers.decompogen import compogen
g_s = decompogen(f, symbol)
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
index c0d2616a9be4..c39aaea5f7f8 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
@@ -2318,6 +2318,8 @@ def solvify(f, symbol, domain):
ImageSet, | list (if `f` is periodic)
Union |
+ Union | list (with FiniteSet)
+
EmptySet | empty list
Others | None
@@ -2377,7 +2379,16 @@ def solvify(f, symbol, domain):
else:
solution = solution_set.intersect(domain)
- if isinstance(solution, FiniteSet):
+ if isinstance(solution, Union):
+ # concerned about only FiniteSet with Union but not about ImageSet
+ # if required could be extend
+ if any(isinstance(i, FiniteSet) for i in solution.args):
+ result = [sol for soln in solution.args \
+ for sol in soln.args if isinstance(soln,FiniteSet)]
+ else:
+ return None
+
+ elif isinstance(solution, FiniteSet):
result += solution
return result
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
index 08d989363dce..5cc2d3746c27 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
@@ -1320,7 +1320,24 @@ def test_solvify():
raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: solvify(sin(exp(x)), x, S.Complexes))
+def test_solvify_piecewise():
+ p1 = Piecewise((0, x < -1), (x**2, x <= 1), (log(x), True))
+ p2 = Piecewise((0, x < -10), (x**2 + 5*x - 6, x >= -9))
+ p3 = Piecewise((0, Eq(x, 0)), (x**2/Abs(x), True))
+ p4 = Piecewise((0, Eq(x, pi)), ((x - pi)/sin(x), True))
+
+ # issue 21079
+ assert solvify(p1, x, S.Reals) == [0]
+ assert solvify(p2, x, S.Reals) == [-6, 1]
+ assert solvify(p3, x, S.Reals) == [0]
+ assert solvify(p4, x, S.Reals) == [pi]
+
+
def test_abs_invert_solvify():
+
+ x = Symbol('x',positive=True)
+ assert solvify(sin(Abs(x)), x, S.Reals) == [0, pi]
+ x = Symbol('x')
assert solvify(sin(Abs(x)), x, S.Reals) is None
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20925@27e8652
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,925
|
added _eval_derivative for products
|
This PR adds the `_eval_derivative` method based on the `Leibniz rule`.
Fixes #20848
Added `_eval_derivative` method based on the `Leibniz rule`.
Also added test cases for the same.
Credits to @Maelstrom6 and @asmeurer
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-02-08T11:18:32Z
|
diff(Product(...)) does not evaluate the derivative
Usually Derivative gives an unevaluated derivative and doit is used to evaluate it:
```python
In [4]: Derivative(x**2, x)
Out[4]:
d ⎛ 2⎞
──⎝x ⎠
dx
In [5]: Derivative(x**2, x).doit()
Out[5]: 2⋅x
In [6]: diff(x**2, x)
Out[6]: 2⋅x
```
The diff function is used to create the derivative and call doit but it doesn't work with a Product:
```python
In [8]: Derivative(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x)
Out[8]:
⎛ z ⎞
∂ ⎜─┬─┬─ ⎟
──⎜ │ │ x⎟
∂x⎜ │ │ ⎟
⎝y = 1 ⎠
In [9]: Derivative(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x).doit()
Out[9]:
z
x ⋅z
────
x
In [10]: diff(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x)
Out[10]:
⎛ z ⎞
∂ ⎜─┬─┬─ ⎟
──⎜ │ │ x⎟
∂x⎜ │ │ ⎟
⎝y = 1 ⎠
```
Here `Out[10]` should be the same as `Out[9]`.
|
Probably because it doesn't actually know how to differentiate a Product. [9] only works because the original Product evaluates first and then the derivative does. We could implement the general Leibniz rule (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Product_rule#A_product_of_more_than_two_factors). I'm not sure if there are concerns with that formula if the product is infinite.
Outside of this, I'm not sure if Derivative.doit() should recursively call doit() before evaluating.
> We could implement the general Leibniz rule (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Product_rule#A_product_of_more_than_two_factors). I'm not sure if there are concerns with that formula if the product is infinite.
I think it does work for infinite products if they converge. [Wiki Proof](https://proofwiki.org/wiki/Derivative_of_Infinite_Product_of_Analytic_Functions).
@Maelstrom6, is this issue open, can I take it?
Thanks.
Feel free to work on it👍. #20851 is working on this but the author is fairly busy at the moment. Maybe have a look at the discussion there for some ideas on how to tackle the problem.
@Maelstrom6 I tried something like with the code you suggested with respect to the discussions:
```
def _eval_derivative(self, x):
from sympy import Sum
limits = list(self.limits)
if any(x in limit[1:].free_symbols for limit in reversed(limits)):
return None
return self * Sum(self.function.diff(x) / self.function, self._args[1:], **self.assumptions0)
```
It covers if `x` is in the free symbols of any of the lower or upper limits, it returns unevaluated.
Looks good. You can open up a PR for it and we can do a few finishing touches there.
Sure, thanks a lot!
|
[
{
"body": "Usually Derivative gives an unevaluated derivative and doit is used to evaluate it:\r\n```python\r\nIn [4]: Derivative(x**2, x)\r\nOut[4]: \r\nd ⎛ 2⎞\r\n──⎝x ⎠\r\ndx \r\n\r\nIn [5]: Derivative(x**2, x).doit()\r\nOut[5]: 2⋅x\r\n\r\nIn [6]: diff(x**2, x)\r\nOut[6]: 2⋅x\r\n```\r\nThe diff function is used to create the derivative and call doit but it doesn't work with a Product:\r\n```python\r\nIn [8]: Derivative(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x)\r\nOut[8]: \r\n ⎛ z ⎞\r\n∂ ⎜─┬─┬─ ⎟\r\n──⎜ │ │ x⎟\r\n∂x⎜ │ │ ⎟\r\n ⎝y = 1 ⎠\r\n\r\nIn [9]: Derivative(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x).doit()\r\nOut[9]: \r\n z \r\nx ⋅z\r\n────\r\n x \r\n\r\nIn [10]: diff(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x)\r\nOut[10]: \r\n ⎛ z ⎞\r\n∂ ⎜─┬─┬─ ⎟\r\n──⎜ │ │ x⎟\r\n∂x⎜ │ │ ⎟\r\n ⎝y = 1 ⎠\r\n```\r\nHere `Out[10]` should be the same as `Out[9]`.",
"number": 20848,
"title": "diff(Product(...)) does not evaluate the derivative"
}
] |
ef14666d718f147878b51ed7ba9a5192e16c04f3
|
{
"head_commit": "27e86526a175ca44aa23faf581bc5013b4b6548a",
"head_commit_message": "added test cases",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/concrete/products.py b/sympy/concrete/products.py\nindex 6ff6a06f66b9..3ea873c8d6e9 100644\n--- a/sympy/concrete/products.py\n+++ b/sympy/concrete/products.py\n@@ -399,6 +399,18 @@ def _eval_product_direct(self, term, limits):\n (k, a, n) = limits\n return Mul(*[term.subs(k, a + i) for i in range(n - a + 1)])\n \n+ def _eval_derivative(self, x):\n+ if self.is_zero:\n+ return S.Zero\n+ from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum, Dummy\n+ i = Dummy('i')\n+ f = self.function\n+ limits = list(self.limits)\n+ _, a, b = limits[0]\n+ if any(x in limit[1:].free_symbols for limit in limits):\n+ return None\n+ return Sum(f.subs(_, i).diff(x) * Product(f, (_, a, i - 1)) * Product(f, (_, i + 1, b)), (i, a, b), **self.assumptions0)\n+\n def is_convergent(self):\n r\"\"\"\n See docs of :obj:`.Sum.is_convergent()` for explanation of convergence\ndiff --git a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_products.py b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_products.py\nindex 0d2de4a45109..b6d759210509 100644\n--- a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_products.py\n+++ b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_products.py\n@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@\n from sympy import (symbols, Symbol, product, combsimp, factorial, rf, sqrt, cos,\n Function, Product, Rational, Sum, oo, exp, log, S, pi,\n- KroneckerDelta)\n+ KroneckerDelta, Derivative, diff, sin, polygamma, gamma, Dummy)\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n from sympy import simplify\n \n@@ -382,3 +382,13 @@ def test_rewrite_Sum():\n def test_KroneckerDelta_Product():\n y = Symbol('y')\n assert Product(x*KroneckerDelta(x, y), (x, 0, 1)).doit() == 0\n+\n+def test_issue_20848():\n+ _i = Dummy('_i')\n+ t, y, z = symbols('t y z')\n+ assert diff(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x).as_dummy() == Sum(Product(x, (y, 1, _i - 1))*Product(x, (y, _i + 1, z)), (_i, 1, z)).as_dummy()\n+ assert diff(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x).doit() == x**z*z/x\n+ assert diff(Product(x, (y, x, z)), x) == Derivative(Product(x, (y, x, z)), x)\n+ assert diff(Product(t, (x, 1, z)), x) == S(0)\n+ assert Product(sin(n*x), (n, -1, 1)).diff(x).doit() == S(0)\n+ assert Product(x*y, (x, 1, z), (y, 1, m)).diff(z).doit() == m*factorial(m)**z*factorial(z)**m*gamma(z + 1)*polygamma(0, z + 1)/factorial(z) + log(factorial(m))*factorial(m)**z*factorial(z)**m\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -382,3 +382,13 @@ def test_rewrite_Sum():\n def test_KroneckerDelta_Product():\n y = Symbol('y')\n assert Product(x*KroneckerDelta(x, y), (x, 0, 1)).doit() == 0\n+\n+def test_issue_20848():\n+ _i = Dummy('_i')",
"line": null,
"original_line": 387,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/concrete/tests/test_products.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThe underscore in `'_i'` is not needed. `Dummy` automatically appends the underscore for the string representation.\n\n@author:\nSure will change.\r\nThanks."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -399,6 +399,18 @@ def _eval_product_direct(self, term, limits):\n (k, a, n) = limits\n return Mul(*[term.subs(k, a + i) for i in range(n - a + 1)])\n \n+ def _eval_derivative(self, x):\n+ if self.is_zero:\n+ return S.Zero\n+ from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum, Dummy\n+ i = Dummy('i')\n+ f = self.function\n+ limits = list(self.limits)\n+ _, a, b = limits[0]\n+ if any(x in limit[1:].free_symbols for limit in limits):\n+ return None\n+ return Sum(f.subs(_, i).diff(x) * Product(f, (_, a, i - 1)) * Product(f, (_, i + 1, b)), (i, a, b), **self.assumptions0)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 412,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/concrete/products.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis would produce wrong answers if `limits` has more than one element. I thought that `Sum` had a similar problem but it does not. Looking at the code of `Sum`: \r\n- it pops `limits[0]` from the stack\r\n- checks if there are still limits remaining\r\n * if there are limits remaining, then it replaces `f` with `Sum(f, remaining_limits)`\r\n- it calls `Derivative(f, ...)` instead of `f.diff(x)`\r\n\r\nThis way, it would keep all the sums as required. \r\n\r\nI think a similar mechanism should be a adopted here. It might even be better to copy the code and change it as you need to. That way, if there is a bug in `Sum.diff` then there will be a similar bug in `Product.diff` and they can be fixed in a similar way. I think it might help with maintainability.\n\n@author:\n> This would produce wrong answers if `limits` has more than one element.\r\n>\r\nCan you please provide an example?\r\nI ran it for:\r\n```\r\nIn [2]: Product(x*y, (x, 1, z), (y, 1, m)).diff(z).doit()\r\nOut[2]:\r\n z m\r\nm⋅m! ⋅z! ⋅Γ(z + 1)⋅polygamma(0, z + 1) z m\r\n────────────────────────────────────── + log(m!)⋅m! ⋅z!\r\n z!\r\n\r\nIn [3]: Product(x*y, (x, 1, z), (y, 1, m)).doit().diff(z)\r\nOut[3]:\r\n z m\r\nm⋅m! ⋅z! ⋅Γ(z + 1)⋅polygamma(0, z + 1) z m\r\n────────────────────────────────────── + log(m!)⋅m! ⋅z!\r\n z!\r\n```\r\nThis seems to work though.\r\nThanks.\r\n\n\n@user1:\nWith this, you are differentiating with respect to one of the indexes of the summation. So the `_eval_derivaitve` returns `None` and the value becomes `Derivative(Product(x*y, (x, 1, z), (y, 1, m)), z)` and calling doit will simplify the product and then it takes the derivative. \r\n\r\nI'll quickly come up with an example that shows this issue.\n\n@user1:\n```python\r\nfrom sympy import *\r\nx, y = symbols(\"x y\")\r\ni, j, m, n = symbols(\"i, j, m, n\", integer=True)\r\n\r\nexpr = Product(sin(x*i/j), (i, 1, m), (j, 1, n))\r\nprint(expr.diff(x))\r\n# output:\r\n# Sum(_i*cos(_i*x/j)*Product(sin(i*x/j), (i, 1, _i - 1))*Product(sin(i*x/j), (i, _i + 1, m))/j, (_i, 1, m))\r\n```\r\nAs you can see, the `(j, 1, n)` part has completely disappeared from the output.\n\n@author:\n@user1 Thank you for correcting, I went ahead as you suggested to start with code in `Sum`.\r\nThe implementation below seems to works for the case you gave and for the previous cases:\r\n\r\n```\r\ndef _eval_derivative(self, x):\r\n from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum, Dummy, Symbol, Derivative\r\n if isinstance(x, Symbol) and x not in self.free_symbols:\r\n return S.Zero\r\n f, limits = self.function, list(self.limits)\r\n limit = limits.pop(-1)\r\n if limits:\r\n f = self.func(f, *limits)\r\n _, a, b = limit\r\n if x in a.free_symbols or x in b.free_symbols:\r\n return None\r\n h = Dummy()\r\n rv = Sum( Product(f, (_, a, h - 1)) * Product(f, (_, h + 1, b)) * Derivative(f, x, evaluate=True).subs(_, h), (h, a, b))\r\n return rv\r\n```\r\n\r\n```\r\nIn [1]: i,j=symbols('i j')\r\n\r\nIn [2]: expr = Product(sin(x*i/j), (i, 1, n), (j, 1, m))\r\n\r\nIn [3]: print(expr.diff(x))\r\nSum(Product(sin(i*x/j), (i, 1, n), (j, 1, _Dummy_23 - 1))*Product(sin(i*x/j), (i, 1, n), (j, _Dummy_23 + 1, m))*Sum(_Dummy_24*cos(_Dummy_24*x/_Dummy_23)*Product(sin(i*x/_Dummy_23), (i, 1, _Dummy_24 - 1))*Product(sin(i*x/_Dummy_23), (i, _Dummy_24 + 1, n))/_Dummy_23, (_Dummy_24, 1, n)), (_Dummy_23, 1, m))\r\n```\r\nKindly give your opinion.\r\nThanks."
}
] |
de93c0379e4db59a0dbcd709f4673f4defe77eb4
|
diff --git a/sympy/concrete/products.py b/sympy/concrete/products.py
index 6ff6a06f66b9..90b193352a0d 100644
--- a/sympy/concrete/products.py
+++ b/sympy/concrete/products.py
@@ -5,6 +5,8 @@
from sympy.functions.elementary.exponential import exp, log
from sympy.polys import quo, roots
from sympy.simplify import powsimp
+from sympy.core.function import Derivative
+from sympy.core.symbol import Dummy, Symbol
class Product(ExprWithIntLimits):
@@ -399,6 +401,21 @@ def _eval_product_direct(self, term, limits):
(k, a, n) = limits
return Mul(*[term.subs(k, a + i) for i in range(n - a + 1)])
+ def _eval_derivative(self, x):
+ from sympy.concrete.summations import Sum
+ if isinstance(x, Symbol) and x not in self.free_symbols:
+ return S.Zero
+ f, limits = self.function, list(self.limits)
+ limit = limits.pop(-1)
+ if limits:
+ f = self.func(f, *limits)
+ i, a, b = limit
+ if x in a.free_symbols or x in b.free_symbols:
+ return None
+ h = Dummy()
+ rv = Sum( Product(f, (i, a, h - 1)) * Product(f, (i, h + 1, b)) * Derivative(f, x, evaluate=True).subs(i, h), (h, a, b))
+ return rv
+
def is_convergent(self):
r"""
See docs of :obj:`.Sum.is_convergent()` for explanation of convergence
diff --git a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_products.py b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_products.py
index 0d2de4a45109..801f34799d7c 100644
--- a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_products.py
+++ b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_products.py
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
from sympy import (symbols, Symbol, product, combsimp, factorial, rf, sqrt, cos,
Function, Product, Rational, Sum, oo, exp, log, S, pi,
- KroneckerDelta)
+ KroneckerDelta, Derivative, diff, sin, Dummy)
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
from sympy import simplify
@@ -382,3 +382,12 @@ def test_rewrite_Sum():
def test_KroneckerDelta_Product():
y = Symbol('y')
assert Product(x*KroneckerDelta(x, y), (x, 0, 1)).doit() == 0
+
+def test_issue_20848():
+ _i = Dummy('i')
+ t, y, z = symbols('t y z')
+ assert diff(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x).as_dummy() == Sum(Product(x, (y, 1, _i - 1))*Product(x, (y, _i + 1, z)), (_i, 1, z)).as_dummy()
+ assert diff(Product(x, (y, 1, z)), x).doit() == x**z*z/x
+ assert diff(Product(x, (y, x, z)), x) == Derivative(Product(x, (y, x, z)), x)
+ assert diff(Product(t, (x, 1, z)), x) == S(0)
+ assert Product(sin(n*x), (n, -1, 1)).diff(x).doit() == S(0)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20663@018c18e
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,663
|
core: fixed _eval_is_zero() and added test
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #17130
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
_eval_is_zero() would give wrong result with imaginary numbers,
resolved as directed by @oscarbenjamin, and added
appropriate test.
#### Other comments
Please suggest any extra tests I should add to it.
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* core
* Fixed `_eval_is_zero()` functionality when imaginary numbers are involved.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-12-25T18:17:15Z
|
IndexError from jordan_form
I get an error computing the Jordan form of this Matrix:
```julia
In [6]: M = Matrix([
...: [exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 + exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2, exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 - exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2],
...: [exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 - exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2, exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 + exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2]])
In [7]: M
Out[7]:
⎡ 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2⎤
⎢ t t t t t t t t ⎥
⎢ ── - ── ── + ── ── - ── ── + ──⎥
⎢ 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 ⎥
⎢ℯ ℯ ℯ ℯ ⎥
⎢──────── + ──────── ──────── - ────────⎥
⎢ 2 2 2 2 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2⎥
⎢ t t t t t t t t ⎥
⎢ ── - ── ── + ── ── - ── ── + ──⎥
⎢ 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 ⎥
⎢ℯ ℯ ℯ ℯ ⎥
⎢──────── - ──────── ──────── + ────────⎥
⎣ 2 2 2 2 ⎦
In [8]: M.jordan_form()
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
IndexError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-8-192ccf6137fc> in <module>
----> 1 M.jordan_form()
~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/matrices/matrices.py in jordan_form(self, calc_transform, **kwargs)
1806 if not calc_transform:
1807 return restore_floats(jordan_mat)
-> 1808 jordan_basis = [eig_mat(eig, 1).nullspace()[0] for eig in blocks]
1809 basis_mat = mat.hstack(*jordan_basis)
1810 return restore_floats(basis_mat, jordan_mat)
~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/matrices/matrices.py in <listcomp>(.0)
1806 if not calc_transform:
1807 return restore_floats(jordan_mat)
-> 1808 jordan_basis = [eig_mat(eig, 1).nullspace()[0] for eig in blocks]
1809 basis_mat = mat.hstack(*jordan_basis)
1810 return restore_floats(basis_mat, jordan_mat)
IndexError: list index out of range
```
Looks like nullspace returns an empty list:
```julia
In [17]: M = Matrix([
...: [sqrt((exp(2*t**2) - 2*exp(t**2) + 1)*exp(t**2*(2*t/3 - 1)))/2 - (exp(t**2) + 1)*exp(t**2*(2*t - 3)/6)/2 + exp(t**3/3 - t
...: **2/2)/2 + exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2,
...: exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 - exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2],
...: [ exp(t**3/3 - t
...: **2/2)/2 - exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2, sqrt((exp(2*t**2) - 2*exp(t**2) + 1)*exp(t**2*(2*t/3 - 1)))/2 - (exp(t**2) + 1)*exp(t*
...: *2*(2*t - 3)/6)/2 + exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 + exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2]])
In [18]: M
Out[18]:
⎡ _____________________________________ 2 3 2 3 2
⎢ ╱ 2 ⎛2⋅t ⎞ t ⋅(2⋅t - 3) t t t t
⎢ ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ t ⋅⎜─── - 1⎟ ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──────────── ── - ── ── + ──
⎢ ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ ⎝ 3 ⎠ ⎜ ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 6 3 2 3 2
⎢╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎝ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ℯ ℯ
⎢────────────────────────────────────────── - ───────────────────────── + ──────── + ────────
⎢ 2 2 2 2
⎢
⎢ 3 2 3 2 ____________________________
⎢ t t t t ╱ 2 ⎛
⎢ ── - ── ── + ── ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ t ⋅⎜
⎢ 3 2 3 2 ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ ⎝
⎢ ℯ ℯ ╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ
⎢ ──────── - ──────── ─────────────────────────────────
⎣ 2 2 2
3 2 3 2 ⎤
t t t t ⎥
── - ── ── + ── ⎥
3 2 3 2 ⎥
ℯ ℯ ⎥
──────── - ──────── ⎥
2 2 ⎥
⎥
_________ 2 3 2 3 2⎥
2⋅t ⎞ t ⋅(2⋅t - 3) t t t t ⎥
─── - 1⎟ ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──────────── ── - ── ── + ──⎥
3 ⎠ ⎜ ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 6 3 2 3 2 ⎥
⎝ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ℯ ℯ ⎥
───────── - ───────────────────────── + ──────── + ────────⎥
2 2 2 ⎦
In [19]: M.nullspace()
Out[19]: []
```
After simplifying the nullspace is found:
```julia
In [20]: M.simplify()
In [21]: M
Out[21]:
⎡ __________________________________ ⎤
⎢ ╱ 3 3 2 ⎥
⎢ ╱ 2⋅t 2 t t ⎥
⎢ ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──── - t ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞⎞ ── - ── ⎥
⎢ ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 3 ⎜ ⎝t ⎠⎟ 3 2 ⎥
⎢╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎝1 - ℯ ⎠⋅ℯ ⎥
⎢──────────────────────────────────────── ──────────────────── ⎥
⎢ 2 2 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢ __________________________________⎥
⎢ 3 2 ╱ 3 ⎥
⎢ t t ╱ 2⋅t 2 ⎥
⎢ ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞⎞ ── - ── ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──── - t ⎥
⎢ ⎜ ⎝t ⎠⎟ 3 2 ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 3 ⎥
⎢ ⎝1 - ℯ ⎠⋅ℯ ╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎥
⎢ ──────────────────── ────────────────────────────────────────⎥
⎣ 2 2 ⎦
In [22]: M.nullspace()
Out[22]:
⎡⎡ 3 2 ⎤⎤
⎢⎢ t t ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞⎞ ── - ── ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ⎜ ⎝t ⎠⎟ 3 2 ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ -⎝1 - ℯ ⎠⋅ℯ ⎥⎥
⎢⎢────────────────────────────────────────⎥⎥
⎢⎢ __________________________________⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ╱ 3 ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ╱ 2⋅t 2 ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──── - t ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 3 ⎥⎥
⎢⎢╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ⎥⎥
⎣⎣ 1 ⎦⎦
```
I guess this is a problem in nullspace then.
|
Same here, with much simplier matrix. Consider
```
from numpy import array
from sympy import Matrix, pprint
S0 = array([ [-0.7, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5],
[0.5, -0.2, 0.0, 0.25],
[0.0, 0.2, -0.2, 0.0],
[0.2, 0.0, 0.2, -0.75]
])
S1 = array([ [-1.25, 0.5, 0., 0.],
[1., -0.5, 0., 0.5],
[0.25, 0., -1., 0.5],
[0., 0., 1., -1.]
])
m_s = Matrix(S0)
pprint(m_s.nullspace())
```
For other matrices with det=0 (such as S1) it prints column of nullspace elements. For matrix S0 it prints '[]'. Broken nullspace() breaks jordan_form(), which in turn breaks dsolve() for the equivalent system of ODEs.
I'm using sympy 1.6.2.
EDIT: _iszero() problem? Pull #15169 maybe related, custom iszerofunc=my_iszero from that pull can't help. At least with iszerofunc like:
```
def my_iszero():
return True
```
nullspace() returns entire identity matrix ;)
UPDATE: For those who want to use dsolve() || Matrix.jordan_form() || Matrix.nullspace() with constant quotitent matrices I suggest to use this workaround:
```
from sympy import Matrix
from scipy.linalg import null_space
from numpy import array, cdouble
def nullspace_sci(matrix):
''' SciPy version of nullspace() '''
return [Matrix(null_space(array(matrix).astype(cdouble)))]
Matrix.nullspace = nullspace_sci
```
Very fragile, but works with S0.
Using `nsimplify` to convert the floats to rational works for your case:
```
In [4]: m_s.applyfunc(nsimplify).nullspace()
Out[4]:
⎡⎡5/7⎤⎤
⎢⎢ ⎥⎥
⎢⎢85 ⎥⎥
⎢⎢── ⎥⎥
⎢⎢28 ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ⎥⎥
⎢⎢85 ⎥⎥
⎢⎢── ⎥⎥
⎢⎢28 ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ⎥⎥
⎣⎣ 1 ⎦⎦
```
It's ok with nullspace() but I wonder how can I propagate this behaviour up to dsolve().
AFAIK, dsolve() deals with list of Eq's. Currently I'm preparing ICs and Eq's by hand with given matrix. And dsolve() decomposes it back to matrix...
Also this Issue #17218 definitely related with my problem, because
```
pprint(Matrix(S0).rref())
pprint(Matrix(S0).rref(iszerofunc=lambda x: abs(x) < 10**-10)) # Different, more plausible output
```
So to fix dsolve() I need to just set iszerofunc in Matrix.nullspace() (which will passed to .rref()) to deal with it w/o SciPy.
You can use `nsimplify` on your original equations. It is generally better to avoid floats especially for something like `nullspace`:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_(linear_algebra)#Floating_point_computation
Even if I apply nsimplify to every equation in system (with rational=True, checking results after that with pprint()), aforementioned IndexError in dsolve()->jordan_form()->nullspace()[0] still persists.
Also, replacing iszerofunc default value not a solution since dsolve() calls it from different contexts and subtle errors appear.
Do you have an example where this happens with rational numbers? I think that the original matrix in the OP is also something that came up from `dsolve`.
The OP examples seem to work fine now for `jordan_form` and `nullspace`.
I think that this issue is fixed and the new example you've introduced is really another case of #17218 which is about matrices with floats.
This is somewhat truncated example (S0 and S1 same as above):
```
from numpy import array
from sympy import Eq, Derivative, symbols, Function, sympify, Add, dsolve, nsimplify
from sympy import pprint
S0 = array([ [-0.7, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5],
[0.5, -0.2, 0.0, 0.25],
[0.0, 0.2, -0.2, 0.0],
[0.2, 0.0, 0.2, -0.75]
])
S1 = array([ [-1.25, 0.5, 0., 0.],
[1., -0.5, 0., 0.5],
[0.25, 0., -1., 0.5],
[0., 0., 1., -1.]
])
S = S0 # S1 OK, S0 FAIL
ICS = sympify('{P1(0):0, P2(0):0, P3(0):0, P4(0):1}')
def sym_sol():
dim = S.shape[0]
t_s = symbols('t')
p_i_syms = symbols('P1, P2, P3, P4', cls=Function)
eq_sys = [None] * S.shape[0]
for i, p_i in enumerate(p_i_syms):
rhs_i = 0
for j in range(dim):
rhs_i = Add(rhs_i, S[i][j]*p_i_syms[j](t_s))
eq_sys[i] = nsimplify(Eq(Derivative(p_i(t_s)), rhs_i), rational=True)
eq_sys = tuple(eq_sys)
#pprint(eq_sys)
# Hint obtained by benchmarking
sol = dsolve(eq_sys, ics=ICS, hint='1st_power_series')
print('Solution:')
for equ in sol:
pprint(equ)
sym_sol()
```
Okay so the matrix there is
```python
M = Matrix([
[-7/10, 0, 0, 1/2],
[ 1/2, -1/5, 0, 1/4],
[ 0, 1/5, -1/5, 0],
[ 1/5, 0, 1/5, -3/4]]).applyfunc(nsimplify)
```
That does not have floats and gives:
```python
In [20]: M
Out[20]:
⎡-7/10 0 0 1/2 ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 1/2 -1/5 0 1/4 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 0 1/5 -1/5 0 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣ 1/5 0 1/5 -3/4⎦
In [21]: M.jordan_form()
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
IndexError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-21-192ccf6137fc> in <module>
----> 1 M.jordan_form()
~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/matrices/matrices.py in jordan_form(self, calc_transform, **kwargs)
410
411 def jordan_form(self, calc_transform=True, **kwargs):
--> 412 return _jordan_form(self, calc_transform=calc_transform, **kwargs)
413
414 def left_eigenvects(self, **flags):
~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/matrices/eigen.py in _jordan_form(M, calc_transform, chop)
1185 return restore_floats(jordan_mat)
1186
-> 1187 jordan_basis = [eig_mat(eig, 1).nullspace()[0]
1188 for eig in blocks]
1189 basis_mat = mat.hstack(*jordan_basis)
~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/matrices/eigen.py in <listcomp>(.0)
1185 return restore_floats(jordan_mat)
1186
-> 1187 jordan_basis = [eig_mat(eig, 1).nullspace()[0]
1188 for eig in blocks]
1189 basis_mat = mat.hstack(*jordan_basis)
IndexError: list index out of range
> /Users/enojb/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/matrices/eigen.py(1187)<listcomp>()
1185 return restore_floats(jordan_mat)
1186
-> 1187 jordan_basis = [eig_mat(eig, 1).nullspace()[0]
1188 for eig in blocks]
1189 basis_mat = mat.hstack(*jordan_basis)
```
Internally this computes nullspaces e.g.:
```python
In [29]: [len((M - e*eye(4)).nullspace()) for e in M.eigenvals()]
Out[29]: [1, 0, 0, 1]
```
So it looks like it fails for the 2nd and 3rd eigenvalues. Note these have complicated expressions from the cubic formula:
```python
In [30]: e1, e2, e3, e4 = M.eigenvals()
In [31]: e2
Out[31]:
______________
⎛ 1 √3⋅ⅈ⎞ ╱ 69⋅√165 23
⎜- ─ + ────⎟⋅3 ╱ ─────── + ──
37 ⎝ 2 2 ⎠ ╲╱ 1600 40 23
- ── - ─────────────────────────────── - ───────────────────────────────────
60 3 ______________
⎛ 1 √3⋅ⅈ⎞ ╱ 69⋅√165 23
240⋅⎜- ─ + ────⎟⋅3 ╱ ─────── + ──
⎝ 2 2 ⎠ ╲╱ 1600 40
In [32]: e3
Out[32]:
______________
⎛ 1 √3⋅ⅈ⎞ ╱ 69⋅√165 23
⎜- ─ - ────⎟⋅3 ╱ ─────── + ──
37 23 ⎝ 2 2 ⎠ ╲╱ 1600 40
- ── - ─────────────────────────────────── - ───────────────────────────────
60 ______________ 3
⎛ 1 √3⋅ⅈ⎞ ╱ 69⋅√165 23
240⋅⎜- ─ - ────⎟⋅3 ╱ ─────── + ──
⎝ 2 2 ⎠ ╲╱ 1600 40
```
There is I guess a bug somewhere in zero detection during nullspace.
Note that there is a new implementation of eigenvectors on the master branch (not yet released) that can calculate the eigenvectors much faster and correctly:
```python
In [58]: %time M.eigenvects()
CPU times: user 29.9 ms, sys: 274 µs, total: 30.2 ms
Wall time: 30.5 ms
```
That implementation should also be extended to `jordan_form` although it is still a work in progress.
The bug in the old implementation still warrants investigation.
The bug is that zero testing fails on this pivot:
```python
expr = (
(
-512109718324422794624654112703630525511*2645**(S(1)/3)*sqrt(3) +
512109718324422794624654112703630525511*23**(S(2)/3)*sqrt(3)*5**(S(1)/3) -
512109718324422794624654112703630525511*23**(S(2)/3)*5**(S(1)/3)*I +
512109718324422794624654112703630525511*2645**(S(1)/3)*I)
/(11232853364312579514316204343197764426240000*sqrt(3)*5**(S(2)/3)*(3*sqrt(165)
+ 40)**(S(1)/3) +
13117146726057831427621087078765368441868800*sqrt(11)*5**(1/6)*(3*sqrt(165)
+ 40)**(S(1)/3) +
4372382242019277142540362359588456147289600*sqrt(33)*5**(1/6)*I*(3*sqrt(165)
+ 40)**(S(1)/3) +
11232853364312579514316204343197764426240000*5**(S(2)/3)*I*(3*sqrt(165) +
40)**(S(1)/3))
)
print('expr.n():', expr.n())
print('expr.is_zero:', expr.is_zero)
```
That outputs:
```python
expr.n(): 0.e-144 - 0.e-146*I
expr.is_zero: False
```
That in turn boils down to this:
```python
In [8]: e = parse_expr('-2645**(1/3)*sqrt(3) + 23**(2/3)*sqrt(3)*5**(1/3) - 23**(2/3)*5**(1/3)*I + 2645**(1/3)*I')
In [9]: e
Out[9]:
3 ______ 2/3 3 ___ 2/3 3 ___ 3 ______
- ╲╱ 2645 ⋅√3 + 23 ⋅√3⋅╲╱ 5 - 23 ⋅╲╱ 5 ⋅ⅈ + ╲╱ 2645 ⋅ⅈ
In [10]: e.n()
Out[10]: 0.e-124 + 0.e-124⋅ⅈ
In [11]: e.is_zero
Out[11]: False
```
The faulty logic is here:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/c9dbb014993f6248be0a4a3d514545cbf7d4c1c1/sympy/core/add.py#L610-L615
Looking at the code suggests a simpler way to show the bug:
```python
In [1]: x = Symbol('x', positive=True)
In [2]: e = Add(x, -x, I, -I, evaluate=False)
In [3]: e.is_zero
Out[3]: False
In [4]: e
Out[4]: -x + x - ⅈ + ⅈ
```
The fix is
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/core/add.py b/sympy/core/add.py
index 772def1604..aab9e3f5b8 100644
--- a/sympy/core/add.py
+++ b/sympy/core/add.py
@@ -588,7 +588,7 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):
nz = []
z = 0
im_or_z = False
- im = False
+ im = 0
for a in self.args:
if a.is_extended_real:
if a.is_zero:
@@ -598,7 +598,7 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):
else:
return
elif a.is_imaginary:
- im = True
+ im += 1
elif (S.ImaginaryUnit*a).is_extended_real:
im_or_z = True
else:
@@ -609,10 +609,11 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):
return None
b = self.func(*nz)
if b.is_zero:
- if not im_or_z and not im:
- return True
- if im and not im_or_z:
- return False
+ if not im_or_z:
+ if im == 0:
+ return True
+ elif im == 1:
+ return False
if b.is_zero is False:
return False
```
With that diff it seems that `jordan_form` takes a two minutes to complete but comes up with a presumably correct answer (it's slow because it's trying really hard to simplfy the expressions to figure out whether or not they are zero).
The newer implementation of `jordan_form` would presumably finish in milliseconds like the newer eigenvects implementation so that's a fixable problem.
|
[
{
"body": "I get an error computing the Jordan form of this Matrix:\r\n```julia\r\nIn [6]: M = Matrix([ \r\n ...: [exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 + exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2, exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 - exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2], \r\n ...: [exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 - exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2, exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 + exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2]]) \r\n\r\nIn [7]: M \r\nOut[7]: \r\n⎡ 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2⎤\r\n⎢ t t t t t t t t ⎥\r\n⎢ ── - ── ── + ── ── - ── ── + ──⎥\r\n⎢ 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 ⎥\r\n⎢ℯ ℯ ℯ ℯ ⎥\r\n⎢──────── + ──────── ──────── - ────────⎥\r\n⎢ 2 2 2 2 ⎥\r\n⎢ ⎥\r\n⎢ 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2⎥\r\n⎢ t t t t t t t t ⎥\r\n⎢ ── - ── ── + ── ── - ── ── + ──⎥\r\n⎢ 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 ⎥\r\n⎢ℯ ℯ ℯ ℯ ⎥\r\n⎢──────── - ──────── ──────── + ────────⎥\r\n⎣ 2 2 2 2 ⎦\r\n\r\nIn [8]: M.jordan_form() \r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nIndexError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n<ipython-input-8-192ccf6137fc> in <module>\r\n----> 1 M.jordan_form()\r\n\r\n~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/matrices/matrices.py in jordan_form(self, calc_transform, **kwargs)\r\n 1806 if not calc_transform:\r\n 1807 return restore_floats(jordan_mat)\r\n-> 1808 jordan_basis = [eig_mat(eig, 1).nullspace()[0] for eig in blocks]\r\n 1809 basis_mat = mat.hstack(*jordan_basis)\r\n 1810 return restore_floats(basis_mat, jordan_mat)\r\n\r\n~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/matrices/matrices.py in <listcomp>(.0)\r\n 1806 if not calc_transform:\r\n 1807 return restore_floats(jordan_mat)\r\n-> 1808 jordan_basis = [eig_mat(eig, 1).nullspace()[0] for eig in blocks]\r\n 1809 basis_mat = mat.hstack(*jordan_basis)\r\n 1810 return restore_floats(basis_mat, jordan_mat)\r\n\r\nIndexError: list index out of range\r\n```\r\nLooks like nullspace returns an empty list:\r\n```julia\r\nIn [17]: M = Matrix([ \r\n ...: [sqrt((exp(2*t**2) - 2*exp(t**2) + 1)*exp(t**2*(2*t/3 - 1)))/2 - (exp(t**2) + 1)*exp(t**2*(2*t - 3)/6)/2 + exp(t**3/3 - t\r\n ...: **2/2)/2 + exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2, \r\n ...: exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 - exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2], \r\n ...: [ exp(t**3/3 - t\r\n ...: **2/2)/2 - exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2, sqrt((exp(2*t**2) - 2*exp(t**2) + 1)*exp(t**2*(2*t/3 - 1)))/2 - (exp(t**2) + 1)*exp(t*\r\n ...: *2*(2*t - 3)/6)/2 + exp(t**3/3 - t**2/2)/2 + exp(t**3/3 + t**2/2)/2]]) \r\n\r\nIn [18]: M \r\nOut[18]: \r\n⎡ _____________________________________ 2 3 2 3 2 \r\n⎢ ╱ 2 ⎛2⋅t ⎞ t ⋅(2⋅t - 3) t t t t \r\n⎢ ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ t ⋅⎜─── - 1⎟ ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──────────── ── - ── ── + ── \r\n⎢ ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ ⎝ 3 ⎠ ⎜ ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 6 3 2 3 2 \r\n⎢╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎝ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ℯ ℯ \r\n⎢────────────────────────────────────────── - ───────────────────────── + ──────── + ──────── \r\n⎢ 2 2 2 2 \r\n⎢ \r\n⎢ 3 2 3 2 ____________________________\r\n⎢ t t t t ╱ 2 ⎛\r\n⎢ ── - ── ── + ── ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ t ⋅⎜\r\n⎢ 3 2 3 2 ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ ⎝\r\n⎢ ℯ ℯ ╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ \r\n⎢ ──────── - ──────── ─────────────────────────────────\r\n⎣ 2 2 2 \r\n\r\n 3 2 3 2 ⎤\r\n t t t t ⎥\r\n ── - ── ── + ── ⎥\r\n 3 2 3 2 ⎥\r\n ℯ ℯ ⎥\r\n ──────── - ──────── ⎥\r\n 2 2 ⎥\r\n ⎥\r\n_________ 2 3 2 3 2⎥\r\n2⋅t ⎞ t ⋅(2⋅t - 3) t t t t ⎥\r\n─── - 1⎟ ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──────────── ── - ── ── + ──⎥\r\n 3 ⎠ ⎜ ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 6 3 2 3 2 ⎥\r\n ⎝ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ℯ ℯ ⎥\r\n───────── - ───────────────────────── + ──────── + ────────⎥\r\n 2 2 2 ⎦\r\n\r\nIn [19]: M.nullspace() \r\nOut[19]: []\r\n```\r\nAfter simplifying the nullspace is found:\r\n```julia\r\nIn [20]: M.simplify() \r\n\r\nIn [21]: M \r\nOut[21]: \r\n⎡ __________________________________ ⎤\r\n⎢ ╱ 3 3 2 ⎥\r\n⎢ ╱ 2⋅t 2 t t ⎥\r\n⎢ ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──── - t ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞⎞ ── - ── ⎥\r\n⎢ ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 3 ⎜ ⎝t ⎠⎟ 3 2 ⎥\r\n⎢╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎝1 - ℯ ⎠⋅ℯ ⎥\r\n⎢──────────────────────────────────────── ──────────────────── ⎥\r\n⎢ 2 2 ⎥\r\n⎢ ⎥\r\n⎢ __________________________________⎥\r\n⎢ 3 2 ╱ 3 ⎥\r\n⎢ t t ╱ 2⋅t 2 ⎥\r\n⎢ ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞⎞ ── - ── ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──── - t ⎥\r\n⎢ ⎜ ⎝t ⎠⎟ 3 2 ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 3 ⎥\r\n⎢ ⎝1 - ℯ ⎠⋅ℯ ╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎥\r\n⎢ ──────────────────── ────────────────────────────────────────⎥\r\n⎣ 2 2 ⎦\r\n\r\nIn [22]: M.nullspace() \r\nOut[22]: \r\n⎡⎡ 3 2 ⎤⎤\r\n⎢⎢ t t ⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢ ⎛ ⎛ 2⎞⎞ ── - ── ⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢ ⎜ ⎝t ⎠⎟ 3 2 ⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢ -⎝1 - ℯ ⎠⋅ℯ ⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢────────────────────────────────────────⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢ __________________________________⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢ ╱ 3 ⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢ ╱ 2⋅t 2 ⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢ ╱ ⎛ 2 ⎛ 2⎞ ⎞ ──── - t ⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢ ╱ ⎜ 2⋅t ⎝t ⎠ ⎟ 3 ⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢╲╱ ⎝ℯ - 2⋅ℯ + 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎥⎥\r\n⎢⎢ ⎥⎥\r\n⎣⎣ 1 ⎦⎦\r\n```\r\nI guess this is a problem in nullspace then.",
"number": 17130,
"title": "IndexError from jordan_form"
}
] |
dd9188277caada7161b64bfb56cf900b5480772b
|
{
"head_commit": "018c18e3051290a4d2b05103138f7ffbce3d966a",
"head_commit_message": "core: fixed _eval_is_zero() and added test, fixing issue #17130\n\n_eval_is_zero() would give wrong result with imaginary numbers,\nresolved as directed by @oscarbenjamin, and added\nappropriate test.",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/add.py b/sympy/core/add.py\nindex 6a3d10ac0e66..301d0132c5ea 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/add.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/add.py\n@@ -604,7 +604,7 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):\n nz = []\n z = 0\n im_or_z = False\n- im = False\n+ im = 0\n for a in self.args:\n if a.is_extended_real:\n if a.is_zero:\n@@ -614,7 +614,7 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):\n else:\n return\n elif a.is_imaginary:\n- im = True\n+ im += 1\n elif (S.ImaginaryUnit*a).is_extended_real:\n im_or_z = True\n else:\n@@ -625,10 +625,12 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):\n return None\n b = self.func(*nz)\n if b.is_zero:\n- if not im_or_z and not im:\n- return True\n- if im and not im_or_z:\n- return False\n+ if not im_or_z:\n+ if im == 0:\n+ return True\n+ elif im == 1:\n+ return False\n+ return True\n if b.is_zero is False:\n return False\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\nindex 2cd5e484bb98..27d40ffcf432 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\n@@ -2307,3 +2307,8 @@ def test__neg__():\n \n def test_issue_18507():\n assert Mul(zoo, zoo, 0) is nan\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_17130():\n+ e = Add(b, -b, I, -I, evaluate=False)\n+ assert e._eval_is_zero() == True\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -625,10 +625,12 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):\n return None\n b = self.func(*nz)\n if b.is_zero:\n- if not im_or_z and not im:\n- return True\n- if im and not im_or_z:\n- return False\n+ if not im_or_z:\n+ if im == 0:\n+ return True\n+ elif im == 1:\n+ return False\n+ return True",
"line": null,
"original_line": 633,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/add.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis return True was not there in my suggestion in https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/17130#issuecomment-749117670\r\nWhy is it needed?\n\n@author:\nI tried doing it without this `return True` line, but then the test I wrote as suggested by you in #17130 was failing.\r\n\r\nSince this function was not returning anything when `b.is_zero` is true and `im_or_z` is true, I added this line so as to return true when `b.is_zero` is true and `im_or_z` is true.\r\n\n\n@user1:\nWhat test was failing?\r\n\r\nThe return True here will give erroneous results:\r\n```python\r\nIn [2]: Add(1, -1, I, -I, I, evaluate=False).is_zero\r\nOut[2]: True\r\n```\n\n@author:\nIt was failing the test you suggested in the [comment](https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/17130#issuecomment-749117670). \r\nIt is:\r\n```python\r\ndef test_issue_17130():\r\n e = Add(b, -b, I, -I, evaluate=False)\r\n assert e._eval_is_zero() == True\r\n```\n\n@user1:\nIt's fine if that case gives `None`. In the assumptions system we just need to make sure that we don't incorrectly return True or False. There will always be cases that are not resolvable because an assumptions check like `is_zero` needs to be efficient.\r\n\r\nThe test could just be for None but with a comment indicating why:\r\n```\r\n assert e._eval_is_zero() is None # ideally this would be True\r\n```\n\n@author:\nI see, thanks for the help. I will change the code accordingly."
}
] |
a5737ebc45cd4446f9cc4048a3ef5d4062e3855b
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/add.py b/sympy/core/add.py
index 6a3d10ac0e66..209020649430 100644
--- a/sympy/core/add.py
+++ b/sympy/core/add.py
@@ -604,7 +604,7 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):
nz = []
z = 0
im_or_z = False
- im = False
+ im = 0
for a in self.args:
if a.is_extended_real:
if a.is_zero:
@@ -614,7 +614,7 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):
else:
return
elif a.is_imaginary:
- im = True
+ im += 1
elif (S.ImaginaryUnit*a).is_extended_real:
im_or_z = True
else:
@@ -625,10 +625,11 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):
return None
b = self.func(*nz)
if b.is_zero:
- if not im_or_z and not im:
- return True
- if im and not im_or_z:
- return False
+ if not im_or_z:
+ if im == 0:
+ return True
+ elif im == 1:
+ return False
if b.is_zero is False:
return False
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
index 2cd5e484bb98..bdc1a1223f86 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
@@ -2307,3 +2307,8 @@ def test__neg__():
def test_issue_18507():
assert Mul(zoo, zoo, 0) is nan
+
+
+def test_issue_17130():
+ e = Add(b, -b, I, -I, evaluate=False)
+ assert e.is_zero is None # ideally this would be True
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20573@bbd941a
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,573
|
Added test for sin(x + a) - sin(x) (for a)
|
References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #10426
Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Here we added tests to address the above issue by comparing the given equation with the specified answer for a. In the solution, we found out a can be dependent on x also, so we covered all the possible solutions in the test.
Verified on Sympy Live
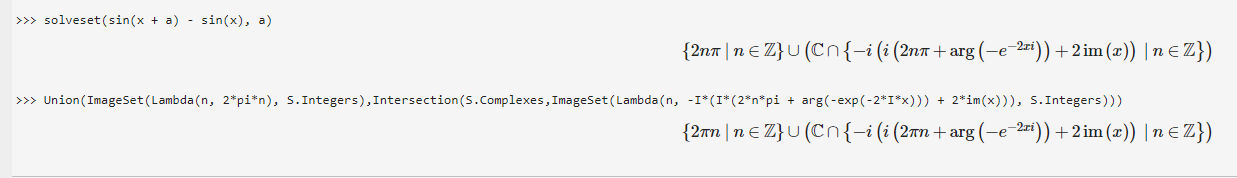
Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-12-10T17:08:28Z
|
Can't solve sin(x + a) - sin(x) (for a)
```
In [9]: solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a)
Out[9]: {a | a ∊ ℂ ∧ -sin(x) + sin(a + x) = 0}
In [10]: solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a, domain=S.Reals)
Out[10]:
⎧ ⎛ ⎛ ⅈ⋅(-a - x) ⅈ⋅(a + x)⎞ ⅈ⋅x 2⋅ⅈ⋅x ⎞ -ⅈ⋅x ⎫
⎪ ⅈ⋅⎝- ⎝- ℯ + ℯ ⎠⋅ℯ + ℯ - 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎪
⎨a | a ∊ ℝ ∧ ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── = 0⎬
⎪ 2 ⎪
⎩ ⎭
In [11]: solve(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a)
Out[11]: [-x + asin(sin(x)), -x - asin(sin(x)) + π]
```
The solution should be `a=2*pi*n`. I believe the first solution from solve is equivalent to that.
|
For a start, `a = 2*pi*n` is not the complete solution to the equation. Since `sin(x+a) - sin(x) = 2*cos(x+a/2)*sin(a/2)`, `a = 2*pi*n` corresponds only to the part of solution where `sin(a/2) = 0`, whereas `cos(x + a/2) = 0` gives `a = (2*n + 1) * pi - 2*x`.
SymPy seems to give the correct answer if we assume `x` to be real, but fails if it is a general complex variable. Perhaps this is due to the different implementation of `solveset_real` and `solveset_complex`?
``` Python
>>> x = symbols('x', real=True)
... z = symbols('z')
... a = Dummy('a')
...
>>> solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a, domain=S.Reals)
⎧ ⎛ -2⋅ⅈ⋅x⎞ ⎫
{2⋅n⋅π | n ∊ ℤ} ∪ ⎨2⋅n⋅π + arg⎝-ℯ ⎠ | n ∊ ℤ⎬
⎩ ⎭
>>> solveset(sin(z + a) - sin(z), a, domain=S.Reals)
⎧ ⎛ ⎛ ⅈ⋅(-a - z) ⅈ⋅(a + z)⎞ ⅈ⋅z 2⋅ⅈ⋅z ⎞ -ⅈ⋅z ⎫
⎪ ⅈ⋅⎝- ⎝- ℯ + ℯ ⎠⋅ℯ + ℯ - 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎪
⎨a | a ∊ ℝ ∧ ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── = 0⎬
⎪ 2 ⎪
⎩ ⎭
```
Having said that, I believe `solveset` does needs improvement regarding trigonometric equations. For instance it doesn't know how to solve `sin(a/2) = 0`:
``` Python
>>> solveset(sin(a/2), a, domain=S.Reals)
⎧ -a⋅ⅈ ⎫
⎪ ───── ⎪
⎪ ⎛ a⋅ⅈ ⎞ 2 ⎪
⎨ -ⅈ⋅⎝ℯ - 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎬
⎪a | a ∊ ℝ ∧ ───────────────────── = 0⎪
⎪ 2 ⎪
⎩ ⎭
```
I think you are right. My goal here is specifically to find a solution that does not depend on x, so as to show that sine is periodic. Hence, although the solutions from solve are probably correct (plus `2*pi*n`) the second one is not useful as written because it is not easy to see that it doesn't depend on x.
solution should be :
`a = 4πn, a = 4πn + 2π, a = 4πn + π − 2x, a = 4πn + 3π − 2x`
because using this formula :
`sin s − sin t = 2cos((s+t)/2)sin((s-t)/2)`
we get this `2cos((2x+a)/2)sin(a/2) = 0`
Getting the solution to reduce to just `2*pi*n` would also be helpful (since that would be the period of sine). This is just a matter of getting `solveset(sin(x))` to give `pi*n` instead of `2*pi*n` and `2*pi*n + pi`.
Currently solveset gives
```
In [62]: solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a)
Out[62]:
⎧ ⎛ ⎛ ⎛ -2⋅ⅈ⋅x⎞⎞ ⎞ ⎫
{2⋅n⋅π | n ∊ ℤ} ∪ ⎨-ⅈ⋅⎝ⅈ⋅⎝2⋅n⋅π + arg⎝-ℯ ⎠⎠ + 2⋅im(x)⎠ | n ∊ ℤ⎬
⎩
```
The first part of that is that the `2*n*pi` as requested. I guess that the other part shows that the solution depends on x in some way. For example if x is zero then we should have:
```
In [63]: solveset(sin(0 + a) - sin(0), a)
Out[63]: {2⋅n⋅π | n ∊ ℤ} ∪ {2⋅n⋅π + π | n ∊ ℤ}
```
which gives `a = n*pi`. The solutions from solveset matches up with this for zero x
```
In [64]: solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a).subs(x, 0)
Out[64]: {2⋅n⋅π | n ∊ ℤ} ∪ {2⋅n⋅π + π | n ∊ ℤ}
```
It also works for some other values:
```
In [67]: solveset(sin(1 + a) - sin(1), a).simplify()
Out[67]: {2⋅n⋅π | n ∊ ℤ} ∪ {2⋅n⋅π - 2 + π | n ∊ ℤ}
In [68]: solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a).subs(x, 1).simplify()
Out[68]: {2⋅n⋅π | n ∊ ℤ} ∪ {2⋅n⋅π - 2 + π | n ∊ ℤ}
```
I think this is correct so closing.
This can be closed if a test is added for solveset to prevent future regressions.
A test should also be added for solve
The original motivation for this was for the `periodicity` function. It looks like `periodicity` currently works without making use of solve.
Hi @asmeurer @oscarbenjamin, I would like to know if this issue is resolved or I can add test cases for solveset. Kindly guide me through the process if it's still open.
I think that the solution is correct although potentially it could be simplified. This issue could be closed if the tests were added.
|
[
{
"body": "```\nIn [9]: solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a)\nOut[9]: {a | a ∊ ℂ ∧ -sin(x) + sin(a + x) = 0}\n\nIn [10]: solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a, domain=S.Reals)\nOut[10]:\n⎧ ⎛ ⎛ ⅈ⋅(-a - x) ⅈ⋅(a + x)⎞ ⅈ⋅x 2⋅ⅈ⋅x ⎞ -ⅈ⋅x ⎫\n⎪ ⅈ⋅⎝- ⎝- ℯ + ℯ ⎠⋅ℯ + ℯ - 1⎠⋅ℯ ⎪\n⎨a | a ∊ ℝ ∧ ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── = 0⎬\n⎪ 2 ⎪\n⎩ ⎭\n\nIn [11]: solve(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a)\nOut[11]: [-x + asin(sin(x)), -x - asin(sin(x)) + π]\n\n```\n\nThe solution should be `a=2*pi*n`. I believe the first solution from solve is equivalent to that. \n",
"number": 10426,
"title": "Can't solve sin(x + a) - sin(x) (for a)"
}
] |
e5c901e5f30bcc9bd0cb91f03d0696815b96bd1a
|
{
"head_commit": "bbd941a94c724f11df2ce6017ad84a286b63fd9f",
"head_commit_message": "Added test for sin(x + a) - sin(x) (for a)",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\nindex cb91957b79bd..9335f0596773 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py\n@@ -2472,6 +2472,14 @@ def test_issue_17276():\n FiniteSet((5**(S(1)/5), 25*5**(S(3)/10)))\n \n \n+def test_issue_10426():\n+ x=Dummy('x')\n+ a=Symbol('a')\n+ n=Symbol('n')\n+ assert solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a) == \\\n+ Union(ImageSet(Lambda(n, 2*pi*n), S.Integers),Intersection(S.Complexes,ImageSet(Lambda(n, -I*(I*(2*n*pi + arg(-exp(-2*I*x))) + 2*im(x))), S.Integers)))\n+\n+\n @XFAIL\n def test_substitution_with_infeasible_solution():\n a00, a01, a10, a11, l0, l1, l2, l3, m0, m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, m6, m7, c00, c01, c10, c11, p00, p01, p10, p11 = symbols(\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2472,6 +2472,14 @@ def test_issue_17276():\n FiniteSet((5**(S(1)/5), 25*5**(S(3)/10)))\n \n \n+def test_issue_10426():\n+ x=Dummy('x')\n+ a=Symbol('a')\n+ n=Symbol('n')\n+ assert solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a) == \\\n+ Union(ImageSet(Lambda(n, 2*pi*n), S.Integers),Intersection(S.Complexes,ImageSet(Lambda(n, -I*(I*(2*n*pi + arg(-exp(-2*I*x))) + 2*im(x))), S.Integers)))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 2480,
"original_start_line": 2476,
"path": "sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWould be more readable as\r\n```suggestion\r\n x = Dummy('x')\r\n a = Symbol('a')\r\n n = Symbol('n')\r\n assert solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a) == Union(\r\n ImageSet(Lambda(n, 2*pi*n), S.Integers),\r\n Intersection(S.Complexes, ImageSet(Lambda(n, -I*(I*(2*n*pi + arg(-exp(-2*I*x))) + 2*im(x))), S.Integers)))\r\n```\n\n@author:\nThank you for the suggestion, I tried it running locally, it shows an assertion error. I guess it is coming because of the order of n and pi in both are different. Can you provide me a confirmation on that."
}
] |
675ab8eefba302f7de7d49cac5b531934e09afaf
|
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
index cb91957b79bd..fb7e360b002c 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solveset.py
@@ -2472,6 +2472,16 @@ def test_issue_17276():
FiniteSet((5**(S(1)/5), 25*5**(S(3)/10)))
+def test_issue_10426():
+ x=Dummy('x')
+ a=Symbol('a')
+ n=Dummy('n')
+ assert (solveset(sin(x + a) - sin(x), a)).dummy_eq(Dummy('x')) == (Union(
+ ImageSet(Lambda(n, 2*n*pi), S.Integers),
+ Intersection(S.Complexes, ImageSet(Lambda(n, -I*(I*(2*n*pi + arg(-exp(-2*I*x))) + 2*im(x))),
+ S.Integers)))).dummy_eq(Dummy('x,n'))
+
+
@XFAIL
def test_substitution_with_infeasible_solution():
a00, a01, a10, a11, l0, l1, l2, l3, m0, m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, m6, m7, c00, c01, c10, c11, p00, p01, p10, p11 = symbols(
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20618@ef99c69
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,618
|
Make complex exponential algebraic
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #20617
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
I've modified the _eval_is_algebraic to accept rational multiples of `I*pi` as algebraic numbers, but I'd first see if this passes the tests.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
- functions
- Fixed assumption `is_algebraic` for exponentials with rational multiples of `I*pi` to be `True`.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-12-16T23:59:25Z
|
Complex exponentials are not recognized by domains
```python3
>>> from sympy import *
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> w = exp(I*2*pi/3)
>>> Poly([w**2, w, 1], x, extension=True)
Poly(exp(-2*I*pi/3)*x**2 + exp(2*I*pi/3)*x + 1, x, domain='ZZ(exp(I*pi/3))')
>>> w = w.expand(complex=True)
>>> Poly([w**2, w, 1], x, extension=True)
Poly((-1/2 - sqrt(3)*I/2)*x**2 + (-1/2 + sqrt(3)*I/2)*x + 1, x, domain='QQ<sqrt(3) + I>')
```
Only the second one gets recognized as algebraic extension
|
I think it's because `_eval_is_algebraic` gives None
|
[
{
"body": "```python3\r\n>>> from sympy import *\r\n\r\n>>> x = Symbol('x')\r\n>>> w = exp(I*2*pi/3)\r\n>>> Poly([w**2, w, 1], x, extension=True)\r\nPoly(exp(-2*I*pi/3)*x**2 + exp(2*I*pi/3)*x + 1, x, domain='ZZ(exp(I*pi/3))')\r\n>>> w = w.expand(complex=True)\r\n>>> Poly([w**2, w, 1], x, extension=True)\r\nPoly((-1/2 - sqrt(3)*I/2)*x**2 + (-1/2 + sqrt(3)*I/2)*x + 1, x, domain='QQ<sqrt(3) + I>')\r\n```\r\n\r\nOnly the second one gets recognized as algebraic extension",
"number": 20617,
"title": "Complex exponentials are not recognized by domains"
}
] |
989300eda95d4a7661479d64bb7dac44240c036d
|
{
"head_commit": "ef99c69f2edf35c7846f9d0c81ddfe0a126d73fe",
"head_commit_message": "Make complex exponential algebraic",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py\nindex fd360934c67c..a035927e2a22 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py\n@@ -445,15 +445,15 @@ def complex_extended_negative(arg):\n return fuzzy_or(complex_extended_negative(self.args[0]))\n \n def _eval_is_algebraic(self):\n- s = self.func(*self.args)\n- if s.func == self.func:\n- if fuzzy_not(self.exp.is_zero):\n- if self.exp.is_algebraic:\n- return False\n- elif (self.exp/S.Pi).is_rational:\n- return False\n- else:\n- return s.is_algebraic\n+ if fuzzy_not(self.exp.is_zero):\n+ if (self.exp / S.Pi / S.ImaginaryUnit).is_rational:\n+ return True\n+ if self.exp.is_algebraic:\n+ return False\n+ elif (self.exp / S.Pi).is_rational:\n+ return False\n+ elif self.exp.is_zero:\n+ return True\n \n def _eval_is_extended_positive(self):\n if self.args[0].is_extended_real:\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -445,15 +445,15 @@ def complex_extended_negative(arg):\n return fuzzy_or(complex_extended_negative(self.args[0]))\n \n def _eval_is_algebraic(self):\n- s = self.func(*self.args)\n- if s.func == self.func:\n- if fuzzy_not(self.exp.is_zero):\n- if self.exp.is_algebraic:\n- return False\n- elif (self.exp/S.Pi).is_rational:\n- return False\n- else:\n- return s.is_algebraic\n+ if fuzzy_not(self.exp.is_zero):\n+ if (self.exp / S.Pi / S.ImaginaryUnit).is_rational:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 449,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nHow about taking this test first? It would also cover the `exp.is_zero` test."
}
] |
86fa5d6440e2dbd63150af19de229dd4cbedc72e
|
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py
index fd360934c67c..c4b0231395d5 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py
@@ -445,15 +445,13 @@ def complex_extended_negative(arg):
return fuzzy_or(complex_extended_negative(self.args[0]))
def _eval_is_algebraic(self):
- s = self.func(*self.args)
- if s.func == self.func:
- if fuzzy_not(self.exp.is_zero):
- if self.exp.is_algebraic:
- return False
- elif (self.exp/S.Pi).is_rational:
- return False
- else:
- return s.is_algebraic
+ if (self.exp / S.Pi / S.ImaginaryUnit).is_rational:
+ return True
+ if fuzzy_not(self.exp.is_zero):
+ if self.exp.is_algebraic:
+ return False
+ elif (self.exp / S.Pi).is_rational:
+ return False
def _eval_is_extended_positive(self):
if self.args[0].is_extended_real:
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_exponential.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_exponential.py
index bad76c2b169d..d2718c70fdd9 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_exponential.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_exponential.py
@@ -382,6 +382,10 @@ def test_exp_assumptions():
assert exp(pi*r).is_algebraic is None
assert exp(pi*rn).is_algebraic is False
+ assert exp(0, evaluate=False).is_algebraic is True
+ assert exp(I*pi/3, evaluate=False).is_algebraic is True
+ assert exp(I*pi*r, evaluate=False).is_algebraic is True
+
def test_exp_AccumBounds():
assert exp(AccumBounds(1, 2)) == AccumBounds(E, E**2)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py
index 33e2ede9dca5..0f2c747202fe 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py
@@ -5,7 +5,8 @@
from sympy.polys.domains.realfield import RealField
from sympy.polys.domains.complexfield import ComplexField
-from sympy import S, sqrt, sin, Float, E, I, GoldenRatio, pi, Catalan, Rational
+from sympy import (
+ S, sqrt, sin, exp, Float, E, I, GoldenRatio, pi, Catalan, Rational)
from sympy.abc import x, y
@@ -149,6 +150,17 @@ def test_construct_domain():
assert construct_domain({}) == (ZZ, {})
+def test_complex_exponential():
+ w = exp(-I*2*pi/3, evaluate=False)
+ alg = QQ.algebraic_field(w)
+ assert construct_domain([w**2, w, 1], extension=True) == (
+ alg,
+ [alg.convert(w**2),
+ alg.convert(w),
+ alg.convert(1)]
+ )
+
+
def test_composite_option():
assert construct_domain({(1,): sin(y)}, composite=False) == \
(EX, {(1,): EX(sin(y))})
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20639@3127e5e
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,639
|
Pretty printing bug fix
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #17616
Closes https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/17620
Closes https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/17628
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Earlier,
```
>>> pprint(pi**(1/exp(1)))
-1___
╲╱ π
```
Now,
```
>>> pprint(pi**(1/exp(1)))
⎛ -1⎞
⎝ℯ ⎠
π
```
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* printing
* irrational powers are no longer printed with square root sign, they are printed as fractional powers
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-12-21T07:42:53Z
|
inaccurate rendering of pi**(1/E)
This claims to be version 1.5.dev; I just merged from the project master, so I hope this is current. I didn't notice this bug among others in printing.pretty.
```
In [52]: pi**(1/E)
Out[52]:
-1___
╲╱ π
```
LaTeX and str not fooled:
```
In [53]: print(latex(pi**(1/E)))
\pi^{e^{-1}}
In [54]: str(pi**(1/E))
Out[54]: 'pi**exp(-1)'
```
|
I can confirm this bug on master. Looks like it's been there a while
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/2d700c4b3c0871a26741456787b0555eed9d5546/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py#L1814
`1/E` is `exp(-1)` which has totally different arg structure than something like `1/pi`:
```
>>> (1/E).args
(-1,)
>>> (1/pi).args
(pi, -1)
```
@ethankward nice! Also, the use of `str` there isn't correct:
```
>>> pprint(7**(1/(pi)))
pi___
╲╱ 7
>>> pprint(pi**(1/(pi)))
pi___
╲╱ π
>>> pprint(pi**(1/(EulerGamma)))
EulerGamma___
╲╱ π
```
(`pi` and `EulerGamma` were not pretty printed)
I guess str is used because it's hard to put 2-D stuff in the corner of the radical like that. But I think it would be better to recursively call the pretty printer, and if it is multiline, or maybe even if it is a more complicated expression than just a single number or symbol name, then print it without the radical like
```
1
─
e
π
```
or
```
⎛ -1⎞
⎝e ⎠
π
For this https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/eb926a1d0c1158bf43f01eaf673dc84416b5ebb1/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py#L5945
I think it should also be changed to
```
1
--
pi
x
```
|
[
{
"body": "This claims to be version 1.5.dev; I just merged from the project master, so I hope this is current. I didn't notice this bug among others in printing.pretty.\r\n\r\n```\r\nIn [52]: pi**(1/E) \r\nOut[52]: \r\n-1___\r\n╲╱ π \r\n\r\n```\r\nLaTeX and str not fooled:\r\n```\r\nIn [53]: print(latex(pi**(1/E))) \r\n\\pi^{e^{-1}}\r\n\r\nIn [54]: str(pi**(1/E)) \r\nOut[54]: 'pi**exp(-1)'\r\n```\r\n",
"number": 17616,
"title": "inaccurate rendering of pi**(1/E)"
}
] |
eb926a1d0c1158bf43f01eaf673dc84416b5ebb1
|
{
"head_commit": "3127e5ec0b7b34e1f59586a50040f67674c36582",
"head_commit_message": "Removed use of assumptions in pretty printing",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py\nindex df7452ee873f..b0b297d93103 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py\n@@ -1902,7 +1902,7 @@ def _print_Mul(self, product):\n return prettyForm.__mul__(*a)/prettyForm.__mul__(*b)\n \n # A helper function for _print_Pow to print x**(1/n)\n- def _print_nth_root(self, base, expt):\n+ def _print_nth_root(self, base, expt, den_p):\n bpretty = self._print(base)\n \n # In very simple cases, use a single-char root sign\n@@ -1916,12 +1916,15 @@ def _print_nth_root(self, base, expt):\n _zZ = xobj('/', 1)\n rootsign = xobj('\\\\', 1) + _zZ\n # Make exponent number to put above it\n+ #print(dir(expt))\n if isinstance(expt, Rational):\n exp = str(expt.q)\n if exp == '2':\n exp = ''\n else:\n- exp = str(expt.args[0])\n+ if den_p.height() > 1 or den_p.width() > 1:\n+ return self._print(base)**self._print(expt)\n+ exp = str(den_p)\n exp = exp.ljust(2)\n if len(exp) > 2:\n rootsign = ' '*(len(exp) - 2) + rootsign\n@@ -1954,8 +1957,10 @@ def _print_Pow(self, power):\n if e is S.NegativeOne:\n return prettyForm(\"1\")/self._print(b)\n n, d = fraction(e)\n- if n is S.One and d.is_Atom and not e.is_Integer and self._settings['root_notation']:\n- return self._print_nth_root(b, e)\n+ if n is S.One and d.is_Atom and not e.is_Integer and (e.is_Rational or d.is_Symbol)\\\n+ and self._settings['root_notation']:\n+ den_p = self._print(d)\n+ return self._print_nth_root(b, e, den_p)\n if e.is_Rational and e < 0:\n return prettyForm(\"1\")/self._print(Pow(b, -e, evaluate=False))\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py\nindex d33795d155cf..3f0ec100d7c8 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py\n@@ -5942,7 +5942,11 @@ def test_PrettyPoly():\n \n def test_issue_6285():\n assert pretty(Pow(2, -5, evaluate=False)) == '1 \\n--\\n 5\\n2 '\n- assert pretty(Pow(x, (1/pi))) == 'pi___\\n\\\\/ x '\n+ assert pretty(Pow(x, (1/pi))) == \\\n+ ' 1 \\n'\\\n+ ' --\\n'\\\n+ ' pi\\n'\\\n+ 'x '\n \n \n def test_issue_6359():\n@@ -7250,3 +7254,51 @@ def test_diffgeom():\n assert pretty(rect) == \"rect\"\n b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n assert pretty(b) == \"x\"\n+\n+def test_issue_17616():\n+ assert pretty(pi**(1/exp(1))) == \\\n+ ' / -1\\\\\\n'\\\n+ ' \\e /\\n'\\\n+ 'pi '\n+\n+ assert upretty(pi**(1/exp(1))) == \\\n+ ' ⎛ -1⎞\\n'\\\n+ ' ⎝ℯ ⎠\\n'\\\n+ 'π '\n+\n+ assert pretty(pi**(1/pi)) == \\\n+ ' 1 \\n'\\\n+ ' --\\n'\\\n+ ' pi\\n'\\\n+ 'pi '\n+\n+ assert upretty(pi**(1/pi)) == \\\n+ ' 1\\n'\\\n+ ' ─\\n'\\\n+ ' π\\n'\\\n+ 'π '\n+\n+ assert pretty(pi**(1/EulerGamma)) == \\\n+ ' 1 \\n'\\\n+ ' ----------\\n'\\\n+ ' EulerGamma\\n'\\\n+ 'pi '\n+\n+ assert upretty(pi**(1/EulerGamma)) == \\\n+ ' 1\\n'\\\n+ ' ─\\n'\\\n+ ' γ\\n'\\\n+ 'π '\n+\n+ z = Symbol(\"x_17\")\n+ assert upretty(7**(1/z)) == \\\n+ ' 1 \\n'\\\n+ ' ───\\n'\\\n+ ' x₁₇\\n'\\\n+ '7 '\n+\n+ assert pretty(7**(1/z)) == \\\n+ ' 1 \\n'\\\n+ ' ----\\n'\\\n+ ' x_17\\n'\\\n+ '7 '\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1916,12 +1916,15 @@ def _print_nth_root(self, base, expt):\n _zZ = xobj('/', 1)\n rootsign = xobj('\\\\', 1) + _zZ\n # Make exponent number to put above it\n+ #print(dir(expt))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1919,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis change should not be here"
}
] |
336f93fe0b4e7cf18e1b520f21487ba0b534ba75
|
diff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py
index df7452ee873f..fbe9edb63229 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py
@@ -1902,12 +1902,12 @@ def _print_Mul(self, product):
return prettyForm.__mul__(*a)/prettyForm.__mul__(*b)
# A helper function for _print_Pow to print x**(1/n)
- def _print_nth_root(self, base, expt):
+ def _print_nth_root(self, base, root):
bpretty = self._print(base)
# In very simple cases, use a single-char root sign
if (self._settings['use_unicode_sqrt_char'] and self._use_unicode
- and expt is S.Half and bpretty.height() == 1
+ and root == 2 and bpretty.height() == 1
and (bpretty.width() == 1
or (base.is_Integer and base.is_nonnegative))):
return prettyForm(*bpretty.left('\N{SQUARE ROOT}'))
@@ -1915,14 +1915,13 @@ def _print_nth_root(self, base, expt):
# Construct root sign, start with the \/ shape
_zZ = xobj('/', 1)
rootsign = xobj('\\', 1) + _zZ
- # Make exponent number to put above it
- if isinstance(expt, Rational):
- exp = str(expt.q)
- if exp == '2':
- exp = ''
- else:
- exp = str(expt.args[0])
- exp = exp.ljust(2)
+ # Constructing the number to put on root
+ rpretty = self._print(root)
+ # roots look bad if they are not a single line
+ if rpretty.height() != 1:
+ return self._print(base)**self._print(1/root)
+ # If power is half, no number should appear on top of root sign
+ exp = '' if root == 2 else str(rpretty).ljust(2)
if len(exp) > 2:
rootsign = ' '*(len(exp) - 2) + rootsign
# Stack the exponent
@@ -1954,8 +1953,9 @@ def _print_Pow(self, power):
if e is S.NegativeOne:
return prettyForm("1")/self._print(b)
n, d = fraction(e)
- if n is S.One and d.is_Atom and not e.is_Integer and self._settings['root_notation']:
- return self._print_nth_root(b, e)
+ if n is S.One and d.is_Atom and not e.is_Integer and (e.is_Rational or d.is_Symbol) \
+ and self._settings['root_notation']:
+ return self._print_nth_root(b, d)
if e.is_Rational and e < 0:
return prettyForm("1")/self._print(Pow(b, -e, evaluate=False))
diff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py
index d33795d155cf..64d6831c5746 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py
@@ -5942,7 +5942,11 @@ def test_PrettyPoly():
def test_issue_6285():
assert pretty(Pow(2, -5, evaluate=False)) == '1 \n--\n 5\n2 '
- assert pretty(Pow(x, (1/pi))) == 'pi___\n\\/ x '
+ assert pretty(Pow(x, (1/pi))) == \
+ ' 1 \n'\
+ ' --\n'\
+ ' pi\n'\
+ 'x '
def test_issue_6359():
@@ -7205,6 +7209,51 @@ def test_is_combining():
[False, True, False, False]
+def test_issue_17616():
+ assert pretty(pi**(1/exp(1))) == \
+ ' / -1\\\n'\
+ ' \e /\n'\
+ 'pi '
+
+ assert upretty(pi**(1/exp(1))) == \
+ ' ⎛ -1⎞\n'\
+ ' ⎝ℯ ⎠\n'\
+ 'π '
+
+ assert pretty(pi**(1/pi)) == \
+ ' 1 \n'\
+ ' --\n'\
+ ' pi\n'\
+ 'pi '
+
+ assert upretty(pi**(1/pi)) == \
+ ' 1\n'\
+ ' ─\n'\
+ ' π\n'\
+ 'π '
+
+ assert pretty(pi**(1/EulerGamma)) == \
+ ' 1 \n'\
+ ' ----------\n'\
+ ' EulerGamma\n'\
+ 'pi '
+
+ assert upretty(pi**(1/EulerGamma)) == \
+ ' 1\n'\
+ ' ─\n'\
+ ' γ\n'\
+ 'π '
+
+ z = Symbol("x_17")
+ assert upretty(7**(1/z)) == \
+ 'x₁₇___\n'\
+ ' ╲╱ 7 '
+
+ assert pretty(7**(1/z)) == \
+ 'x_17___\n'\
+ ' \\/ 7 '
+
+
def test_issue_17857():
assert pretty(Range(-oo, oo)) == '{..., -1, 0, 1, ...}'
assert pretty(Range(oo, -oo, -1)) == '{..., 1, 0, -1, ...}'
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20390@e7617d3
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,390
|
Correct the -oo case in degree.
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #20389
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Added a check in `polytools.degree` to see if the polygon degree is infinite, and provide the correct result.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* polys
* Solve a bug in polytools.degree.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-11-06T20:57:16Z
|
TypeError: Argument of Integer should be of numeric type, got -oo.
The present expression generates the previous error.
```python
sp.degree(sp.sympify('_R*_X34*(_X35**2*_X26 - _X26*_X35*(_X35 + 1) + 2*_X26*_X35 - _X26*(_X35 + 1) + _X26 - _X29*_X32*_X35 + _X29*_X32*(_X35 + 1) - _X29*_X32)'), sp.Symbol('_R'))
```
The return statement does not take into account the `p.degree(gen)` returns and -oo.
|
A simpler way to reproduce this:
```python
In [32]: degree(x*(x + 1) - x**2 - x, x)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/core/numbers.py in __new__(cls, i)
2101 try:
-> 2102 ival = int(i)
2103 except TypeError:
~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/core/expr.py in __int__(self)
323 if r in (S.NaN, S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity):
--> 324 raise TypeError("can't convert %s to int" % r)
325 i = int(r)
TypeError: can't convert -oo to int
...
TypeError: Argument of Integer should be of numeric type, got -oo.
```
|
[
{
"body": "The present expression generates the previous error.\r\n\r\n```python\r\nsp.degree(sp.sympify('_R*_X34*(_X35**2*_X26 - _X26*_X35*(_X35 + 1) + 2*_X26*_X35 - _X26*(_X35 + 1) + _X26 - _X29*_X32*_X35 + _X29*_X32*(_X35 + 1) - _X29*_X32)'), sp.Symbol('_R'))\r\n```\r\n\r\nThe return statement does not take into account the `p.degree(gen)` returns and -oo.",
"number": 20389,
"title": "TypeError: Argument of Integer should be of numeric type, got -oo."
}
] |
579929113f2d663c2d69846ded0b0b19cf7dbbaf
|
{
"head_commit": "e7617d3e3d7a42c758d0b87fd13d766dd94ed706",
"head_commit_message": "Solve and check the issue #20389\n\nAdded a check to see if the polygon degree is infinite, and provide the correct result.",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/polys/polytools.py b/sympy/polys/polytools.py\nindex 70112de3b65f..c4a9c0b13e42 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/polytools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/polytools.py\n@@ -4480,8 +4480,8 @@ def degree(f, gen=0):\n expression like func = %s, e.g. degree(func, gen = %s) instead of\n degree(func, gen = %s).\n ''' % (f, next(ordered(f.free_symbols)), gen)))\n-\n- return Integer(p.degree(gen))\n+ result = p.degree(gen)\n+ return Integer(result) if result is int else S.NegativeInfinity\n \n \n @public\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py\nindex c774fc41e294..48916f4afbd8 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py\n@@ -3441,3 +3441,8 @@ def test_deserialized_poly_equals_original():\n \"Deserialized polynomial not equal to original.\")\n assert poly.gens == deserialized.gens, (\n \"Deserialized polynomial has different generators than original.\")\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_20389():\n+ result = degree(x * (x + 1) - x ** 2 - x, x)\n+ assert result == -oo\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -4480,8 +4480,8 @@ def degree(f, gen=0):\n expression like func = %s, e.g. degree(func, gen = %s) instead of\n degree(func, gen = %s).\n ''' % (f, next(ordered(f.free_symbols)), gen)))\n-\n- return Integer(p.degree(gen))\n+ result = p.degree(gen)\n+ return Integer(result) if result is int else S.NegativeInfinity",
"line": null,
"original_line": 4484,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/polys/polytools.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n`result is int` doesn't check if result is an integer. This should be\r\n```suggestion\r\n return Integer(result) if isinstance(result, int) else S.NegativeInfinity\r\n```\r\n\r\nAlthough it would be simpler to just return a SymPy type, like `return sympify(result)`. \n\n@user1:\nActually it would make more sense for Poly.degree to return an `Integer`. It already returns -oo, so I think it should always return a SymPy type. Then no conversion would be needed in this function. \n\n@author:\nYou are right. Corrected the isinstance. I have left the hardcoded conversion to reduce overhead."
}
] |
6eaa11873aa9abb93558c8bed92608f826666f1d
|
diff --git a/sympy/polys/polytools.py b/sympy/polys/polytools.py
index 70112de3b65f..18655988a8dc 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/polytools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/polytools.py
@@ -4480,8 +4480,8 @@ def degree(f, gen=0):
expression like func = %s, e.g. degree(func, gen = %s) instead of
degree(func, gen = %s).
''' % (f, next(ordered(f.free_symbols)), gen)))
-
- return Integer(p.degree(gen))
+ result = p.degree(gen)
+ return Integer(result) if isinstance(result, int) else S.NegativeInfinity
@public
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
index c774fc41e294..48916f4afbd8 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
@@ -3441,3 +3441,8 @@ def test_deserialized_poly_equals_original():
"Deserialized polynomial not equal to original.")
assert poly.gens == deserialized.gens, (
"Deserialized polynomial has different generators than original.")
+
+
+def test_issue_20389():
+ result = degree(x * (x + 1) - x ** 2 - x, x)
+ assert result == -oo
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20353@5cd584c
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,353
|
Added test case for GramSchimdt
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #9488
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Added required test case.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-10-29T10:35:07Z
|
FiniteSets can be filled with other objects than numbers, but this is not supported by other classes.
```
>>> FiniteSet([Matrix([1,2,0]), Matrix([1,3,0])])
{Matrix([
[1],
[2],
[0]]), Matrix([
[1],
[3],
[0]])}
```
But
```
>>> L= FiniteSet([Matrix([1,2,0]), Matrix([1,3,0])])
>>> GramSchmidt(L)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sympy/matrices/dense.py", line 1531, in GramSchmidt
tmp = vlist[i]
TypeError: 'FiniteSet' object does not support indexing
>>>
```
In my opinion a set is a storage for all mathematical objects, and therefore it should also fulfill this job in sympy, or am I wrong ?
So (in my opinion), there should be added an exception to the FiniteSet class, so that it only can be filled with numbers for the moment, and, as an other issue, the set class should be improved, so that it could contain all kind of mathematical objects.
|
I agree about adding the exception, since it's clearly not supported yet in other classes.
Hi,
in the tests_sets.py the following line can be found:
```
s = FiniteSet((1, 2), Float, A, -5, x, 'eggs', x**2, Interval)
```
so this should be fixed, too, and we should test if
```
FiniteSet(3,2,complex('5+j'), Number(3), 3.47342, Symbol('a'), Matrix([3,4]), 'eggs')
```
raises TypeError,
or am I wrong?
Edit/PS:
In my opinion subclasses of int, float, complex (since the FiniteSet constructor sympyfies his arguments), sympy.numbers.Number and sympy.symbols.Symbol should be allowed, but nothing else for the moment.
I don't think the issue here is that of objects other than numbers:
```
>>> from sympy import FiniteSet, GramSchmidt
>>> s = FiniteSet(1, 2, 3)
>>> s
{1, 2, 3}
>>> GramSchmidt(s)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/lib/python3.4/site-packages/sympy/matrices/dense.py", line 1483, in GramSchmidt
tmp = vlist[i]
TypeError: 'FiniteSet' object does not support indexing
```
Ok,
then the Problem lies in GramSchmidt. Sorry, I should have seen that.
In my opinion applying GramSchmidt on sets is very natural, since Bases are sets.
However, iterating trough a set, by mapping elements of a set to definite integer numbers, not really makes sense (since there is no canonic isomorphism :D).
Therefore i would suggest, that we should (if you share my opinion, that GramSchmidt should work with sets, too) improve the GramSchmidt algorithm by iterating in the sense "for i in FiniteSet(...)", since this works with sets:
```
>>> for i in FiniteSet(Matrix([3,4,5]), Matrix([0,8,15])):
... print(i)
...
Matrix([
[ 0],
[ 8],
[15]])
Matrix([
[3],
[4],
[5]])
```
For the case of `FiniteSets`, another possible solution can be implementing `__getitem__`. I tried it and I seem to get an answer.
Oops, but args are not ordered. That could be a problem. I don't really have much knowledge about `GramSchmidt`.
The documentation of `GramSchmidt` is a bit confusing.
```
def GramSchmidt(vlist, orthog=False):
"""
Apply the Gram-Schmidt process to a set of vectors.
```
The docstring speaks of a set of vectors, but the argument is called `vlist` and a list is also returned.
Thus one is expected to call with a list argument (`GramSchmidt(list(L))`).
I think this is a better solution than changing `GramSchmidt` to work with sets, since the Gram-Schmidt process relies on the order of vectors in the sequence. Otherwise the result would be unpredictable and possibly implementation dependent.
The expression in the original post here raises now. I think that's because the signature of FiniteSet has changed so:
```
In [13]: L = FiniteSet(Matrix([1,2,0]), Matrix([1,3,0]))
In [14]: L
Out[14]:
⎧⎡1⎤ ⎡1⎤⎫
⎪⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥⎪
⎨⎢2⎥, ⎢3⎥⎬
⎪⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥⎪
⎩⎣0⎦ ⎣0⎦⎭
In [15]: GramSchmidt(L)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-15-e1ef40d009e6> in <module>
----> 1 GramSchmidt(L)
~/current/sympy/sympy.git/sympy/matrices/dense.py in GramSchmidt(vlist, orthonormal)
1212 m = len(vlist)
1213 for i in range(m):
-> 1214 tmp = vlist[i]
1215 for j in range(i):
1216 tmp -= vlist[i].project(out[j])
TypeError: 'FiniteSet' object does not support indexing
In [16]: GramSchmidt(list(L))
Out[16]:
⎡⎡1⎤ ⎡-2/5⎤⎤
⎢⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥⎥
⎢⎢2⎥, ⎢1/5 ⎥⎥
⎢⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥⎥
⎣⎣0⎦ ⎣ 0 ⎦⎦
```
Everything is fine then except the docstring for Gram-Schmidt which should be updated to say that the input vectors should be in a sequence and that it returns a list (rather than unordered sets).
Marking as easy to fix
On the current master I get:
```
>>> from sympy import *
>>> L = FiniteSet(Matrix([1,2,0]), Matrix([1,3,0]))
>>> L
FiniteSet(Matrix([
[1],
[2],
[0]]), Matrix([
[1],
[3],
[0]]))
>>> GramSchmidt(L)
[Matrix([
[1],
[2],
[0]]), Matrix([
[-2/5],
[ 1/5],
[ 0]])]
```
Should this closed with a test case? @oscarbenjamin
|
[
{
"body": "```\n>>> FiniteSet([Matrix([1,2,0]), Matrix([1,3,0])])\n{Matrix([\n[1],\n[2],\n[0]]), Matrix([\n[1],\n[3],\n[0]])}\n```\n\nBut\n\n```\n>>> L= FiniteSet([Matrix([1,2,0]), Matrix([1,3,0])])\n>>> GramSchmidt(L)\nTraceback (most recent call last):\n File \"<stdin>\", line 1, in <module>\n File \"/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sympy/matrices/dense.py\", line 1531, in GramSchmidt\n tmp = vlist[i]\nTypeError: 'FiniteSet' object does not support indexing\n>>>\n```\n\nIn my opinion a set is a storage for all mathematical objects, and therefore it should also fulfill this job in sympy, or am I wrong ?\n\nSo (in my opinion), there should be added an exception to the FiniteSet class, so that it only can be filled with numbers for the moment, and, as an other issue, the set class should be improved, so that it could contain all kind of mathematical objects.\n",
"number": 9488,
"title": "FiniteSets can be filled with other objects than numbers, but this is not supported by other classes."
}
] |
153864a6ed7432256022a13c78499e558d04fa31
|
{
"head_commit": "5cd584c2f1519a1d98f24376e90bb08a940011e7",
"head_commit_message": "Added test case for GramSchimdt",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/matrices/tests/test_matrices.py b/sympy/matrices/tests/test_matrices.py\nindex 101a16d977d3..8e3b9ae2d16f 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/tests/test_matrices.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/tests/test_matrices.py\n@@ -2276,6 +2276,11 @@ def test_GramSchmidt():\n assert GramSchmidt([Matrix([3, 1]), Matrix([2, 2])], True) == [\n Matrix([3*sqrt(10)/10, sqrt(10)/10]),\n Matrix([-sqrt(10)/10, 3*sqrt(10)/10])]\n+ # Issue #9488\n+ from sympy import FiniteSet\n+ L = FiniteSet(Matrix([1]))\n+ print(GramSchmidt(L))\n+ assert GramSchmidt(L) == [Matrix([[1]])]\n \n \n def test_casoratian():\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2276,6 +2276,11 @@ def test_GramSchmidt():\n assert GramSchmidt([Matrix([3, 1]), Matrix([2, 2])], True) == [\n Matrix([3*sqrt(10)/10, sqrt(10)/10]),\n Matrix([-sqrt(10)/10, 3*sqrt(10)/10])]\n+ # Issue #9488\n+ from sympy import FiniteSet\n+ L = FiniteSet(Matrix([1]))\n+ print(GramSchmidt(L))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 2282,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/matrices/tests/test_matrices.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nImports should go at the top of the file.\r\n\r\nThere should be no print here.\r\n\r\nI think it's better to include a link to the issue in a comment rather than just the issue number.\n\n@author:\nOkay"
}
] |
b5fc055507b8bb28f95c2dd20f58be0101bb53a6
|
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/tests/test_matrices.py b/sympy/matrices/tests/test_matrices.py
index 101a16d977d3..eeb5fc1c90c4 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/tests/test_matrices.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/tests/test_matrices.py
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
from sympy import (
Abs, Add, E, Float, I, Integer, Max, Min, Poly, Pow, PurePoly, Rational,
S, Symbol, cos, exp, log, oo, pi, signsimp, simplify, sin,
- sqrt, symbols, sympify, trigsimp, tan, sstr, diff, Function, expand)
+ sqrt, symbols, sympify, trigsimp, tan, sstr, diff, Function, expand, FiniteSet)
from sympy.matrices.matrices import (ShapeError, MatrixError,
NonSquareMatrixError, DeferredVector, _find_reasonable_pivot_naive,
_simplify)
@@ -2276,6 +2276,9 @@ def test_GramSchmidt():
assert GramSchmidt([Matrix([3, 1]), Matrix([2, 2])], True) == [
Matrix([3*sqrt(10)/10, sqrt(10)/10]),
Matrix([-sqrt(10)/10, 3*sqrt(10)/10])]
+ # https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/9488
+ L = FiniteSet(Matrix([1]))
+ assert GramSchmidt(L) == [Matrix([[1]])]
def test_casoratian():
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20322@23490db
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,322
|
fixed is_integer of Mul by not using fraction but collecting numerators and denominators directly
|
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #20161
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
In Mul._eval_is_integer instead of using the function fraction the args are scanned for contributions to the numerator and denominator.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* core
* Fixed a few broken cases of expr.is_integer
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-10-22T20:39:24Z
|
Inconsistent behavior for sympify/simplify with ceiling
In sympy v1.5.1:
```python
In [16]: sympy.sympify('4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)', evaluate=False).simplify()
Out[16]: 4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)
In [17]: sympy.sympify('4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)', evaluate=True).simplify()
Out[17]: 4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)
```
In sympy v.1.6.2:
```python
In [16]: sympy.sympify('4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)', evaluate=False).simplify()
Out[16]: 4*ceiling(x/4) - 3
In [17]: sympy.sympify('4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)', evaluate=True).simplify()
Out [17]: 4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)
```
Is there a way to ensure that the behavior is consistent, even though evaluate is equal to `False` when parsing?
|
`4*ceiling(x/4) - 3` is simply wrong:
```python
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> (4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)).subs({x:0})
0
>>> (4*ceiling(x/4) - 3).subs({x:0})
-3
```
Boiling the problem further down we find that already a simpler expression is evaluated/transformed incorrectly:
```python
>>> sympy.sympify('ceiling(x-1/2)', evaluate=False)
ceiling(x) + (-1)*1*1/2
```
The `-1/2` is (under `evaluate=False`) constructed as `Mul(-1, Mul(1, Pow(2, -1)))`, for which the attribute `is_integer` is set incorrectly:
```python
>>> Mul(-1,Mul(1,Pow(2,-1,evaluate=False),evaluate=False),evaluate=False).is_integer
True
```
Since `ceiling` takes out all integer summands from its argument, it also takes out `(-1)*1*1/2`. Maybe somebody else can look into the problem, why `is_integer` is set wrongly for this expression.
The reason `is_integer` is incorrect for the expression is because it returns here:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/1b4529a95ef641c2fc15889091b281644069d20e/sympy/core/mul.py#L1274-L1277
That is due to
```julia
In [1]: e = Mul(-1,Mul(1,Pow(2,-1,evaluate=False),evaluate=False),evaluate=False)
In [2]: fraction(e)
Out[2]: (-1/2, 1)
```
It seems that the `1/2` is carried into the numerator by fraction giving a denominator of one.
You can see the fraction function here:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/1b4529a95ef641c2fc15889091b281644069d20e/sympy/simplify/radsimp.py#L1071-L1098
The check `term.is_Rational` will not match an unevaluated `Mul(1, Rational(1, 2), evaluate=False)` so that gets carried into the numerator.
Perhaps the root of the problem is the fact that we have unflattened args and `Mul.make_args` hasn't extracted them:
```julia
In [3]: Mul.make_args(e)
Out[3]:
⎛ 1⎞
⎜-1, 1⋅─⎟
⎝ 2⎠
```
The `make_args` function does not recurse into the args:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/1b4529a95ef641c2fc15889091b281644069d20e/sympy/core/operations.py#L425-L428
I'm not sure if `make_args` should recurse. An easier fix would be to recurse into any nested Muls in `fraction`.
What about not setting `is_integer` if `evaluate=False` is set on an expression or one of its sub-expressions? Actually I think one cannot expect `is_integer` to be set correctly without evaluating.
That sounds like a good solution. As a safeguard, another one is to not remove the integer summands from `ceiling` if `evaluate=False`; it could be considered as an evaluation of ceiling w.r.t. its arguments.
There is no way to tell if `evaluate=False` was used in general when creating the `Mul`. It's also not possible in general to know if evaluating the Muls would lead to a different result without evaluating them. We should *not* evaluate the Muls as part of an assumptions query. If they are unevaluated then the user did that deliberately and it is not up to `_eval_is_integer` to evaluate them.
This was discussed when changing this to `fraction(..., exact=True)`: https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/19182#issuecomment-619398889
I think that using `fraction` at all is probably too much but we should certainly not replace that with something that evaluates the object.
Hm, does one really need to know whether `evaluate=False` was used? It looks like all we need is the expression tree to decide if `is_integer` is set to `True`. What about setting `is_integer=True` in a conservative way, i.e. only for these expression nodes:
- atoms: type `Integer`, constants `Zero` and `One` and symbols with appropriate assumptions
- `Add` and `Mul` if all args have `is_integer==True`
- `Pow` if base and exponent have `is_integer==True` and exponent is non-negative
I probably missed some cases, but you get the general idea. Would that work? The current implementation would only change in a few places, I guess - to a simpler form. Then also for `ceiling` we do not need to check for `evaluate=False`; its implementation could remain unchanged.
What you describe is more or less the way that it already works. You can find more detail in the (unmerged) #20090
The code implementing this is in the `Mul._eval_is_integer` function I linked to above.
@oscarbenjamin @coproc Sorry for bugging, but are there any plans about this? We cannot use sympy with Python 3.8 anymore in our package because of this...
I explained a possible solution above:
> An easier fix would be to recurse into any nested Muls in `fraction`.
I think this just needs someone to make a PR for that. If the PR comes *very* quickly it can be included in the 1.7 release (I'm going to put out the RC just as soon as #20307 is fixed).
|
[
{
"body": "In sympy v1.5.1:\r\n```python\r\nIn [16]: sympy.sympify('4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)', evaluate=False).simplify()\r\nOut[16]: 4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)\r\n\r\nIn [17]: sympy.sympify('4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)', evaluate=True).simplify()\r\nOut[17]: 4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)\r\n```\r\n\r\nIn sympy v.1.6.2:\r\n```python\r\nIn [16]: sympy.sympify('4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)', evaluate=False).simplify()\r\nOut[16]: 4*ceiling(x/4) - 3\r\n\r\nIn [17]: sympy.sympify('4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)', evaluate=True).simplify()\r\nOut [17]: 4*ceiling(x/4 - 3/4)\r\n```\r\n\r\nIs there a way to ensure that the behavior is consistent, even though evaluate is equal to `False` when parsing?",
"number": 20161,
"title": "Inconsistent behavior for sympify/simplify with ceiling"
}
] |
ab864967e71c950a15771bb6c3723636026ba876
|
{
"head_commit": "23490db348daa38b7f53faf09f7dbbdf196cc482",
"head_commit_message": "convention: make symbol name equal to variable name",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/mul.py b/sympy/core/mul.py\nindex 46f310b122a3..94a0ba8a0aca 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/mul.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/mul.py\n@@ -1262,7 +1262,11 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):\n zero = None\n return zero\n \n+ #_eval_is_integer = lambda self: _fuzzy_group(\n+ # (a.is_integer for a in self.args), quick_exit=True)\n def _eval_is_integer(self):\n+ #return _fuzzy_group(\n+ # (a.is_integer for a in self.args), quick_exit=True)\n from sympy import fraction\n from sympy.core.numbers import Float\n \n@@ -1270,19 +1274,35 @@ def _eval_is_integer(self):\n if is_rational is False:\n return False\n \n- # use exact=True to avoid recomputing num or den\n- n, d = fraction(self, exact=True)\n- if is_rational:\n- if d is S.One:\n- return True\n- if d.is_even:\n- if d.is_prime: # literal or symbolic 2\n- return n.is_even\n- if n.is_odd:\n- return False # true even if d = 0\n- if n == d:\n- return fuzzy_and([not bool(self.atoms(Float)),\n- fuzzy_not(d.is_zero)])\n+ numerators = []\n+ denominators = []\n+ for a in self.args:\n+ if a.is_integer:\n+ numerators.append(a)\n+ elif a.is_Rational:\n+ n, d = a.as_numer_denom()\n+ numerators.append(n)\n+ denominators.append(d)\n+ elif a.is_Pow:\n+ b, e = a.as_base_exp()\n+ if not b.is_integer or not e.is_integer: return\n+ if e.is_negative:\n+ denominators.append(b)\n+ elif e.is_positive:\n+ denominators.append(b)\n+ else:\n+ return\n+\n+ if not denominators:\n+ return True\n+\n+ odd = lambda ints: all(i.is_odd for i in ints)\n+ even = lambda ints: any(i.is_even for i in ints)\n+\n+ if odd(numerators) and even(denominators):\n+ return False\n+ elif even(numerators) and denominators == [2]:\n+ return True\n \n def _eval_is_polar(self):\n has_polar = any(arg.is_polar for arg in self.args)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\nindex e05cdf6ac190..c4554ce1d6d4 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py\n@@ -374,7 +374,6 @@ def test_Mul_doesnt_expand_exp():\n assert (x**(-log(5)/log(3))*x)/(x*x**( - log(5)/log(3))) == sympify(1)\n \n def test_Mul_is_integer():\n-\n k = Symbol('k', integer=True)\n n = Symbol('n', integer=True)\n nr = Symbol('nr', rational=False)\n@@ -388,18 +387,27 @@ def test_Mul_is_integer():\n assert (nz/3).is_integer is None\n assert (nr/3).is_integer is False\n assert (x*k*n).is_integer is None\n+ assert (e/2).is_integer is True\n+ assert (e**2/2).is_integer is True\n+ assert ((-1)**k*n).is_integer is True\n+ assert (3*k*e/2).is_integer is True\n+ assert (2*k*e/3).is_integer is None\n assert (e/o).is_integer is None\n assert (o/e).is_integer is False\n assert (o/i2).is_integer is False\n- assert Mul(o, 1/o, evaluate=False).is_integer is True\n assert Mul(k, 1/k, evaluate=False).is_integer is None\n- assert Mul(nze, 1/nze, evaluate=False).is_integer is True\n- assert Mul(2., S.Half, evaluate=False).is_integer is False\n+ assert Mul(2., S.Half, evaluate=False).is_integer is None\n \n s = 2**2**2**Pow(2, 1000, evaluate=False)\n m = Mul(s, s, evaluate=False)\n assert m.is_integer\n \n+ # broken in 1.6 and before, see #20161\n+ xq = Symbol('xq', rational=True)\n+ yq = Symbol('yq', rational=True)\n+ assert (xq*yq).is_integer is None\n+ e_20161 = Mul(-1,Mul(1,Pow(2,-1,evaluate=False),evaluate=False),evaluate=False)\n+ assert e_20161.is_integer is not True # expand(e_20161) -> -1/2, but no need to see that in the assumption without evaluation\n \n def test_Add_Mul_is_integer():\n x = Symbol('x')\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1262,27 +1262,47 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):\n zero = None\n return zero\n \n+ #_eval_is_integer = lambda self: _fuzzy_group(\n+ # (a.is_integer for a in self.args), quick_exit=True)\n def _eval_is_integer(self):\n+ #return _fuzzy_group(\n+ # (a.is_integer for a in self.args), quick_exit=True)\n from sympy import fraction\n from sympy.core.numbers import Float\n \n is_rational = self._eval_is_rational()\n if is_rational is False:\n return False\n \n- # use exact=True to avoid recomputing num or den\n- n, d = fraction(self, exact=True)\n- if is_rational:\n- if d is S.One:\n- return True\n- if d.is_even:\n- if d.is_prime: # literal or symbolic 2\n- return n.is_even\n- if n.is_odd:\n- return False # true even if d = 0\n- if n == d:\n- return fuzzy_and([not bool(self.atoms(Float)),\n- fuzzy_not(d.is_zero)])\n+ numerators = []\n+ denominators = []\n+ for a in self.args:\n+ if a.is_integer:\n+ numerators.append(a)\n+ elif a.is_Rational:\n+ n, d = a.as_numer_denom()\n+ numerators.append(n)\n+ denominators.append(d)\n+ elif a.is_Pow:\n+ b, e = a.as_base_exp()\n+ if not b.is_integer or not e.is_integer: return\n+ if e.is_negative:\n+ denominators.append(b)\n+ elif e.is_positive:\n+ denominators.append(b)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1292,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/mul.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think this needs an `else: return`. If we don't know whether e is positive or negative then we don't know if b is in the numerator or denominator so the subsequent logic is not valid.\n\n@author:\nYou are right. I was implicitely assuming e.is_zero. Also the case e.is_positive is not needed - a.is_integer would already be triggered. (and the command inside was wrong: 'numerators.append(b)` would be needed)"
}
] |
de4cc9624ecaabd405fd2c938beed293c3f2fc3a
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/mul.py b/sympy/core/mul.py
index 46f310b122a3..251b7fa4c731 100644
--- a/sympy/core/mul.py
+++ b/sympy/core/mul.py
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
from .singleton import S
from .operations import AssocOp, AssocOpDispatcher
from .cache import cacheit
-from .logic import fuzzy_not, _fuzzy_group, fuzzy_and
+from .logic import fuzzy_not, _fuzzy_group
from .compatibility import reduce
from .expr import Expr
from .parameters import global_parameters
@@ -1262,27 +1262,47 @@ def _eval_is_zero(self):
zero = None
return zero
+ # without involving odd/even checks this code would suffice:
+ #_eval_is_integer = lambda self: _fuzzy_group(
+ # (a.is_integer for a in self.args), quick_exit=True)
def _eval_is_integer(self):
- from sympy import fraction
- from sympy.core.numbers import Float
-
is_rational = self._eval_is_rational()
if is_rational is False:
return False
- # use exact=True to avoid recomputing num or den
- n, d = fraction(self, exact=True)
- if is_rational:
- if d is S.One:
- return True
- if d.is_even:
- if d.is_prime: # literal or symbolic 2
- return n.is_even
- if n.is_odd:
- return False # true even if d = 0
- if n == d:
- return fuzzy_and([not bool(self.atoms(Float)),
- fuzzy_not(d.is_zero)])
+ numerators = []
+ denominators = []
+ for a in self.args:
+ if a.is_integer:
+ numerators.append(a)
+ elif a.is_Rational:
+ n, d = a.as_numer_denom()
+ numerators.append(n)
+ denominators.append(d)
+ elif a.is_Pow:
+ b, e = a.as_base_exp()
+ if not b.is_integer or not e.is_integer: return
+ if e.is_negative:
+ denominators.append(b)
+ else:
+ # for integer b and positive integer e: a = b**e would be integer
+ assert not e.is_positive
+ # for self being rational and e equal to zero: a = b**e would be 1
+ assert not e.is_zero
+ return # sign of e unknown -> self.is_integer cannot be decided
+ else:
+ return
+
+ if not denominators:
+ return True
+
+ odd = lambda ints: all(i.is_odd for i in ints)
+ even = lambda ints: any(i.is_even for i in ints)
+
+ if odd(numerators) and even(denominators):
+ return False
+ elif even(numerators) and denominators == [2]:
+ return True
def _eval_is_polar(self):
has_polar = any(arg.is_polar for arg in self.args)
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
index e05cdf6ac190..2cd5e484bb98 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_arit.py
@@ -374,12 +374,10 @@ def test_Mul_doesnt_expand_exp():
assert (x**(-log(5)/log(3))*x)/(x*x**( - log(5)/log(3))) == sympify(1)
def test_Mul_is_integer():
-
k = Symbol('k', integer=True)
n = Symbol('n', integer=True)
nr = Symbol('nr', rational=False)
nz = Symbol('nz', integer=True, zero=False)
- nze = Symbol('nze', even=True, zero=False)
e = Symbol('e', even=True)
o = Symbol('o', odd=True)
i2 = Symbol('2', prime=True, even=True)
@@ -388,18 +386,31 @@ def test_Mul_is_integer():
assert (nz/3).is_integer is None
assert (nr/3).is_integer is False
assert (x*k*n).is_integer is None
+ assert (e/2).is_integer is True
+ assert (e**2/2).is_integer is True
+ assert (2/k).is_integer is None
+ assert (2/k**2).is_integer is None
+ assert ((-1)**k*n).is_integer is True
+ assert (3*k*e/2).is_integer is True
+ assert (2*k*e/3).is_integer is None
assert (e/o).is_integer is None
assert (o/e).is_integer is False
assert (o/i2).is_integer is False
- assert Mul(o, 1/o, evaluate=False).is_integer is True
assert Mul(k, 1/k, evaluate=False).is_integer is None
- assert Mul(nze, 1/nze, evaluate=False).is_integer is True
- assert Mul(2., S.Half, evaluate=False).is_integer is False
+ assert Mul(2., S.Half, evaluate=False).is_integer is None
+ assert (2*sqrt(k)).is_integer is None
+ assert (2*k**n).is_integer is None
s = 2**2**2**Pow(2, 1000, evaluate=False)
m = Mul(s, s, evaluate=False)
assert m.is_integer
+ # broken in 1.6 and before, see #20161
+ xq = Symbol('xq', rational=True)
+ yq = Symbol('yq', rational=True)
+ assert (xq*yq).is_integer is None
+ e_20161 = Mul(-1,Mul(1,Pow(2,-1,evaluate=False),evaluate=False),evaluate=False)
+ assert e_20161.is_integer is not True # expand(e_20161) -> -1/2, but no need to see that in the assumption without evaluation
def test_Add_Mul_is_integer():
x = Symbol('x')
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20806@773d7fa
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,806
|
printing: Remove curly braces from subscripted variables in python() and pycode()
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #20762
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Added handling for subscripted variables in `python` and `pycode`. Subscripted variables only become an issue when using a parsed latex expression, since latex wraps them in curly braces. `python` and `pycode` were creating variable names with curly braces in them, resulting in syntax errors. Added a simple check and modification in `python`, but redefined inherited `_print_Symbol` in `pycode`'s `PythonCodePrinter`.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* printing
* Remove curly braces from subscripted variables in python() and pycode()
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2021-01-15T17:22:21Z
|
pycode of latex expression with subscript leads to syntax error
Hey guys, while generating python code from a simple latex expression works
```python
expr = parse_latex(r'a \cdot b')
print(sympy.pycode(expr))
`>>> a*b
print(sympy.python(expr))
>>> a = Symbol('a')
>>> b = Symbol('b')
>>> e = a*b
```
for anything with a subscript the code generated by `pycode` or `.python` will lead to a syntax error due to the non-compliant variable name.
```python
expr = parse_latex(r'a_b \cdot b')
print(sympy.pycode(expr))
>>> a_{b}*b
print(sympy.python(expr))
>>> a_{b} = Symbol('a_{b}') # this will generate a syntax error
>>> b = Symbol('b')
>>> e = a_{b}*b # and this as well
```
Cheers and thanks for the great work!
-------
versions
python = "3.9.1"
sympy = '1.7.1'
ANTLR runtime = "4.9.1"
|
Would something like this fix the issue in `python`?
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/printing/python.py b/sympy/printing/python.py
index ac6d95a06c..f60719b497 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/python.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/python.py
@@ -51,7 +51,13 @@ def python(expr, **settings):
# Returning found symbols and functions
renamings = {}
for symbolname in printer.symbols:
- newsymbolname = symbolname
+ # Remove curly braces from subscripted variables
+ if '{' in symbolname:
+ newsymbolname = ''.join([s if s != '{' and s != '}' else '' for s in symbolname])
+ renamings[sympy.Symbol(symbolname)] = newsymbolname
+ else:
+ newsymbolname = symbolname
+
# Escape symbol names that are reserved python keywords
if kw.iskeyword(newsymbolname):
while True:
```
|
[
{
"body": "Hey guys, while generating python code from a simple latex expression works\r\n\r\n```python\r\nexpr = parse_latex(r'a \\cdot b')\r\nprint(sympy.pycode(expr))\r\n`>>> a*b\r\nprint(sympy.python(expr))\r\n>>> a = Symbol('a')\r\n>>> b = Symbol('b')\r\n>>> e = a*b\r\n```\r\nfor anything with a subscript the code generated by `pycode` or `.python` will lead to a syntax error due to the non-compliant variable name.\r\n\r\n```python\r\nexpr = parse_latex(r'a_b \\cdot b')\r\nprint(sympy.pycode(expr))\r\n>>> a_{b}*b\r\nprint(sympy.python(expr))\r\n>>> a_{b} = Symbol('a_{b}') # this will generate a syntax error\r\n>>> b = Symbol('b')\r\n>>> e = a_{b}*b # and this as well \r\n```\r\n\r\nCheers and thanks for the great work!\r\n\r\n-------\r\nversions\r\npython = \"3.9.1\"\r\nsympy = '1.7.1'\r\nANTLR runtime = \"4.9.1\"",
"number": 20762,
"title": "pycode of latex expression with subscript leads to syntax error"
}
] |
c181470266243ffdefa3c4129165e0e1e009195f
|
{
"head_commit": "773d7fa818464b19e13c16ca3ec9de1151f4d710",
"head_commit_message": "Add tests",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/printing/pycode.py b/sympy/printing/pycode.py\nindex b7315a4c559c..7c7898612407 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/pycode.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/pycode.py\n@@ -456,6 +456,21 @@ def _print_frac(self, expr):\n from sympy import Mod\n return self._print_Mod(Mod(expr.args[0], 1))\n \n+ def _print_Symbol(self, expr):\n+\n+ name = super()._print_Symbol(expr)\n+\n+ if name in self.reserved_words:\n+ if self._settings['error_on_reserved']:\n+ msg = ('This expression includes the symbol \"{}\" which is a '\n+ 'reserved keyword in this language.')\n+ raise ValueError(msg.format(name))\n+ return name + self._settings['reserved_word_suffix']\n+ elif '{' in name: # Remove curly braces from subscripted variables\n+ return ''.join([s if s != '{' and s != '}' else '' for s in name])\n+ else:\n+ return name\n+\n _print_lowergamma = CodePrinter._print_not_supported\n _print_uppergamma = CodePrinter._print_not_supported\n _print_fresnelc = CodePrinter._print_not_supported\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/python.py b/sympy/printing/python.py\nindex ac6d95a06ca5..f60719b49778 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/python.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/python.py\n@@ -51,7 +51,13 @@ def python(expr, **settings):\n # Returning found symbols and functions\n renamings = {}\n for symbolname in printer.symbols:\n- newsymbolname = symbolname\n+ # Remove curly braces from subscripted variables\n+ if '{' in symbolname:\n+ newsymbolname = ''.join([s if s != '{' and s != '}' else '' for s in symbolname])\n+ renamings[sympy.Symbol(symbolname)] = newsymbolname\n+ else:\n+ newsymbolname = symbolname\n+\n # Escape symbol names that are reserved python keywords\n if kw.iskeyword(newsymbolname):\n while True:\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py\nindex a8f6f97a8fa2..362bdd27680b 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py\n@@ -18,6 +18,7 @@\n from sympy.testing.pytest import skip\n from sympy.external import import_module\n from sympy.functions.special.gamma_functions import loggamma\n+from sympy.parsing.latex import parse_latex\n \n x, y, z = symbols('x y z')\n p = IndexedBase(\"p\")\n@@ -166,6 +167,11 @@ def test_pycode_reserved_words():\n py_str = pycode(s1 + s2)\n assert py_str in ('else_ + if_', 'if_ + else_')\n \n+def test_issue_20762():\n+ # Make sure pycode removes curly braces from subscripted variables\n+ expr = parse_latex(r'a_b \\cdot b')\n+ assert pycode(expr) == 'a_b*b'\n+\n \n def test_sqrt():\n prntr = PythonCodePrinter()\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_python.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_python.py\nindex 89a2e48a3b87..7071d56c2094 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_python.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_python.py\n@@ -6,6 +6,8 @@\n \n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, XFAIL\n \n+from sympy.parsing.latex import parse_latex\n+\n x, y = symbols('x,y')\n th = Symbol('theta')\n ph = Symbol('phi')\n@@ -183,6 +185,11 @@ def test_python_limits():\n assert python(limit(x, x, oo)) == 'e = oo'\n assert python(limit(x**2, x, 0)) == 'e = 0'\n \n+def test_issue_20762():\n+ # Make sure python removes curly braces from subscripted variables\n+ expr = parse_latex(r'a_b \\cdot b')\n+ assert python(expr) == \"a_b = Symbol('a_{b}')\\nb = Symbol('b')\\ne = a_b*b\"\n+\n \n def test_settings():\n raises(TypeError, lambda: python(x, method=\"garbage\"))\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -51,7 +51,13 @@ def python(expr, **settings):\n # Returning found symbols and functions\n renamings = {}\n for symbolname in printer.symbols:\n- newsymbolname = symbolname\n+ # Remove curly braces from subscripted variables\n+ if '{' in symbolname:\n+ newsymbolname = ''.join([s if s != '{' and s != '}' else '' for s in symbolname])",
"line": null,
"original_line": 56,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/python.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhat about `newsymbolname = symbolname.replace('{', '').replace('}', '')`?"
}
] |
29ff5424ac78361dcdf5bc25c079441e60ead5cf
|
diff --git a/sympy/printing/pycode.py b/sympy/printing/pycode.py
index 63ccfec7517d..b669a2c783d2 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/pycode.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/pycode.py
@@ -456,6 +456,21 @@ def _print_frac(self, expr):
from sympy import Mod
return self._print_Mod(Mod(expr.args[0], 1))
+ def _print_Symbol(self, expr):
+
+ name = super()._print_Symbol(expr)
+
+ if name in self.reserved_words:
+ if self._settings['error_on_reserved']:
+ msg = ('This expression includes the symbol "{}" which is a '
+ 'reserved keyword in this language.')
+ raise ValueError(msg.format(name))
+ return name + self._settings['reserved_word_suffix']
+ elif '{' in name: # Remove curly braces from subscripted variables
+ return name.replace('{', '').replace('}', '')
+ else:
+ return name
+
_print_lowergamma = CodePrinter._print_not_supported
_print_uppergamma = CodePrinter._print_not_supported
_print_fresnelc = CodePrinter._print_not_supported
diff --git a/sympy/printing/python.py b/sympy/printing/python.py
index ac6d95a06ca5..51c602b259d5 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/python.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/python.py
@@ -51,7 +51,13 @@ def python(expr, **settings):
# Returning found symbols and functions
renamings = {}
for symbolname in printer.symbols:
- newsymbolname = symbolname
+ # Remove curly braces from subscripted variables
+ if '{' in symbolname:
+ newsymbolname = symbolname.replace('{', '').replace('}', '')
+ renamings[sympy.Symbol(symbolname)] = newsymbolname
+ else:
+ newsymbolname = symbolname
+
# Escape symbol names that are reserved python keywords
if kw.iskeyword(newsymbolname):
while True:
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py
index 42518f652fa2..cf18825eb1b6 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py
@@ -13,11 +13,12 @@
MpmathPrinter, PythonCodePrinter, pycode, SymPyPrinter
)
from sympy.printing.numpy import NumPyPrinter, SciPyPrinter
-from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
+from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, skip
from sympy.tensor import IndexedBase
-from sympy.testing.pytest import skip
from sympy.external import import_module
from sympy.functions.special.gamma_functions import loggamma
+from sympy.parsing.latex import parse_latex
+
x, y, z = symbols('x y z')
p = IndexedBase("p")
@@ -166,6 +167,16 @@ def test_pycode_reserved_words():
py_str = pycode(s1 + s2)
assert py_str in ('else_ + if_', 'if_ + else_')
+def test_issue_20762():
+ antlr4 = import_module("antlr4")
+ if not antlr4:
+ skip('antlr not installed.')
+ # Make sure pycode removes curly braces from subscripted variables
+ expr = parse_latex(r'a_b \cdot b')
+ assert pycode(expr) == 'a_b*b'
+ expr = parse_latex(r'a_{11} \cdot b')
+ assert pycode(expr) == 'a_11*b'
+
def test_sqrt():
prntr = PythonCodePrinter()
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_python.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_python.py
index 89a2e48a3b87..800b8bc75215 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_python.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_python.py
@@ -4,7 +4,13 @@
from sympy.printing.python import python
-from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, XFAIL
+from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, XFAIL, skip
+
+from sympy.parsing.latex import parse_latex
+from sympy.external import import_module
+
+# To test latex to python printing
+antlr4 = import_module("antlr4")
x, y = symbols('x,y')
th = Symbol('theta')
@@ -183,6 +189,13 @@ def test_python_limits():
assert python(limit(x, x, oo)) == 'e = oo'
assert python(limit(x**2, x, 0)) == 'e = 0'
+def test_issue_20762():
+ if not antlr4:
+ skip('antlr not installed')
+ # Make sure python removes curly braces from subscripted variables
+ expr = parse_latex(r'a_b \cdot b')
+ assert python(expr) == "a_b = Symbol('a_{b}')\nb = Symbol('b')\ne = a_b*b"
+
def test_settings():
raises(TypeError, lambda: python(x, method="garbage"))
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20348@a3ebdad
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,348
|
Support for Symbolic Queries in Discrete and Continuous Markov Chains
|
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #19012
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Added code to process symbolic queries of the type `P(Eq(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))`, `P(Gt(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))`, `P(Ge(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))`, `P(Lt(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))` and `P(Le(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))`.
#### Other comments
We should be able to add the same for multivariate queries like `P(Eq(Y[a], Y[b]), Eq(Y[c], d))`, `P(Gt(Y[a], Y[b]), Eq(Y[c], d))`, etc.
I tried to do this but there is some issue with using nested summations.
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-10-28T04:44:55Z
|
How to generate results for queries like `P(Eq(X(j), 2), Eq(X(1), i))`?
In the query, `P(Eq(X(j), 2), Eq(X(1), i))`, X represents a Markov chain(discrete/continuous). Here, i and j are symbols.
Currently,
```python
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> i, j = symbols('i, j', integer=True)
>>> P(Eq(X[j], 2), Eq(X[1], i))
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py", line 196, in __getitem__
if time not in self.index_set:
File "/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/sets/sets.py", line 672, in __contains__
raise TypeError('did not evaluate to a bool: %r' % c)
TypeError: did not evaluate to a bool: None
```
This issue should discuss what all needs to be done to support such queries.
|
`X` is which process?
> X represents a Markov chain(discrete/continuous).
I understand how discreet markov chains work and I can see that you want after the j-1th "jump" a person lands on the state "2" given that currently they're sitting on state "i", what I dont get is what sort of input and output formats are you looking for. Do you want the code to produce j x i matrix with indices containing corresponding solutions or do you want sympy to churn out a general trinomial type function. I cant fully visualize what your expectation from the above expression is. Please elaborate. We can create a function that takes definite values for i and j ,return probabilities accordingly. Knowing j is crucial as if we dont know the number of instances(j) an infinte number of permutations is possible hence the errors
The number of values that "i" can take are restricted by the transition matrix used to define the discreet markov chain. Hence, for a transition matrix of order 3 one must ensure that the value assigned to i corresponds to any one of three space states.
I think the idea is that it would be a symbolic expression involving the symbols i and j.
Well, we can return a Matrix in case of discrete Markov chains but in continuous that won't be possible. In fact in discrete time Markov chains we don't know the upper bound of `j`. Any how, would it be possible to return half done result and then allowing substitution of i and j to continue from that half done result.
For queries of this type, I am thinking of the following appoach - `P(Eq(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))` would be returned as it is if `a` or `c` is not substituted, else a matrix (P^(a-c)) can be returned. How do we handle it for `ContinuousMarkovChain`?
> How do we handle it for `ContinuousMarkovChain`?
As far as I remember in `ContinuousMarkovChain` the algorithm for queries is the same but the transition probabilities are generated from generator matrix and are time dependent in which we pass the difference `t = (a-c)` and `P` becomes `exp(t*gen_mat)` and `P[next_state, curr_state]` will be the direct answer. So, I think even if `a`, `b`, `c` and `d` all are symbols, may be we can return `P[next_state, curr_state]`, though only if `P` supports symbolic indices which is supported,
```python
In [1]: M = Matrix([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
In [2]: M[x, y]
Out[2]:
⎛⎡1 2⎤⎞
⎜⎢ ⎥⎟[x, y]
⎝⎣3 4⎦⎠
In [4]: _.subs({x: 1, y: 1})
Out[4]: 4
```
That looks good, I'll start implementing this then
I'm having a problem using indices in matrices raised to power a-c. Its directly getting evaluated leading to a messy output. Can you suggest anything? @czgdp1807
``` python
>>> from sympy import *
>>> from sympy.stats import *
>>> a,b,c,d = symbols('a b c d')
>>> T = Matrix([[Rational(1,10), Rational(4, 10), Rational(5, 10)], [Rational(3,10), Rational(4,10), Rational(3,10)], [Rational(7,10), Rational(2,10), Rational(1,10)]])
>>> T**(a-c)[d, b]
Long evaluated matrix...
>>> Pow(T, a-c)[d, b]
Long evaluated matrix...
>>> Pow(T, a-c, evaluate=False)[d,b]
TypeError: 'Pow' object is not subscriptable
```
|
[
{
"body": "In the query, `P(Eq(X(j), 2), Eq(X(1), i))`, X represents a Markov chain(discrete/continuous). Here, i and j are symbols.\r\nCurrently,\r\n```python\r\n>>> from sympy import symbols\r\n>>> i, j = symbols('i, j', integer=True)\r\n>>> P(Eq(X[j], 2), Eq(X[1], i))\r\nTraceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"<stdin>\", line 1, in <module>\r\n File \"/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\", line 196, in __getitem__\r\n if time not in self.index_set:\r\n File \"/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/sets/sets.py\", line 672, in __contains__\r\n raise TypeError('did not evaluate to a bool: %r' % c)\r\nTypeError: did not evaluate to a bool: None\r\n```\r\nThis issue should discuss what all needs to be done to support such queries.",
"number": 19012,
"title": "How to generate results for queries like `P(Eq(X(j), 2), Eq(X(1), i))`?"
}
] |
b3cae120dad022dd83e338df69c45f60dd95efd9
|
{
"head_commit": "a3ebdadf8cf540ff5e9166381c61b537b3cb16ca",
"head_commit_message": "Removed unused import",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\nindex 446d417c1887..ffa3fc5a5537 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@\n Union, Expr, Function, exp, cacheit, sqrt, pi, gamma,\n Ge, Piecewise, Symbol, NonSquareMatrixError, EmptySet,\n ceiling, MatrixBase, ConditionSet, ones, zeros, Identity,\n- Rational, Lt, Gt, Ne, BlockMatrix)\n+ Rational, Lt, Gt, Le, Ne, BlockMatrix, Sum)\n from sympy.core.relational import Relational\n from sympy.logic.boolalg import Boolean\n from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning\n@@ -250,7 +250,8 @@ def __getitem__(self, time):\n \n RandomIndexedSymbol\n \"\"\"\n- if time not in self.index_set:\n+ time = sympify(time)\n+ if not time.is_symbol and time not in self.index_set:\n raise IndexError(\"%s is not in the index set of %s\"%(time, self.symbol))\n idx_obj = Indexed(self.symbol, time)\n pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self, self.distribution)\n@@ -269,7 +270,8 @@ def __call__(self, time):\n \n RandomIndexedSymbol\n \"\"\"\n- if time not in self.index_set:\n+ time = sympify(time)\n+ if not time.is_symbol and time not in self.index_set:\n raise IndexError(\"%s is not in the index set of %s\"%(time, self.symbol))\n func_obj = Function(self.symbol)(time)\n pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self, self.distribution)\n@@ -509,6 +511,13 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n check, mat, state_index, new_given_condition = \\\n self._preprocess(given_condition, evaluate)\n \n+ rv = list(condition.atoms(RandomIndexedSymbol))\n+ symbolic = False\n+ for sym in rv:\n+ if sym.key.is_symbol:\n+ symbolic = True\n+ break\n+\n if check:\n return Probability(condition, new_given_condition)\n \n@@ -526,21 +535,34 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n else:\n gcs = (new_given_condition, )\n min_key_rv = list(new_given_condition.atoms(RandomIndexedSymbol))\n- rv = list(condition.atoms(RandomIndexedSymbol))\n \n if len(min_key_rv):\n min_key_rv = min_key_rv[0]\n for r in rv:\n+ if min_key_rv.key.is_symbol or r.key.is_symbol:\n+ continue\n if min_key_rv.key > r.key:\n return Probability(condition)\n else:\n min_key_rv = None\n return Probability(condition)\n \n+ if symbolic:\n+ return self.symbolic_probability(condition, new_given_condition, rv, min_key_rv)\n+\n if len(rv) > 1:\n- rv = rv[:2]\n+ rv[0] = condition.lhs\n+ rv[1] = condition.rhs\n if rv[0].key < rv[1].key:\n rv[0], rv[1] = rv[1], rv[0]\n+ if isinstance(condition, Gt):\n+ condition = Lt(condition.lhs, condition.rhs)\n+ elif isinstance(condition, Lt):\n+ condition = Lt(condition.lhs, condition.rhs)\n+ elif isinstance(condition, Ge):\n+ condition = Le(condition.lhs, condition.rhs)\n+ elif isinstance(condition, Le):\n+ condition = Ge(condition.lhs, condition.rhs)\n s = Rational(0, 1)\n n = len(self.state_space)\n \n@@ -658,6 +680,37 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Mechanism for handling (%s, %s) queries hasn't been \"\n \"implemented yet.\"%(condition, given_condition))\n \n+ def symbolic_probability(self, condition, new_given_condition, rv, min_key_rv):\n+ #Function to calculate probability for queries with symbols\n+ if isinstance(condition, Relational):\n+ curr_state = new_given_condition.rhs if isinstance(new_given_condition.lhs, RandomIndexedSymbol) \\\n+ else new_given_condition.lhs\n+ next_state = condition.rhs if isinstance(condition.lhs, RandomIndexedSymbol) \\\n+ else condition.lhs\n+\n+ if isinstance(condition, Eq) or isinstance(condition, Ne):\n+ if isinstance(self, DiscreteMarkovChain):\n+ P = self.transition_probabilities**(rv[0].key - min_key_rv.key)\n+ else:\n+ P = exp(self.generator_matrix*(rv[0].key - min_key_rv.key))\n+ prob = P[curr_state, next_state] if isinstance(condition, Eq) else 1 - P[curr_state, next_state]\n+ return Piecewise((prob, rv[0].key > min_key_rv.key), (Probability(condition), True))\n+ else:\n+ upper = 1\n+ greater = False\n+ if isinstance(condition, Ge) or isinstance(condition, Lt):\n+ upper = 0\n+ if isinstance(condition, Gt) or isinstance(condition, Ge):\n+ greater = True\n+ k = Dummy('k')\n+ condition = Eq(condition.lhs, k) if isinstance(condition.lhs, RandomIndexedSymbol)\\\n+ else Eq(condition.rhs, k)\n+ total = Sum(self.probability(condition, new_given_condition), (k, next_state + upper, self.state_space._sup))\n+ return Piecewise((total, rv[0].key > min_key_rv.key), (Probability(condition), True)) if greater\\\n+ else Piecewise((1 - total, rv[0].key > min_key_rv.key), (Probability(condition), True))\n+ else:\n+ return Probability(condition, new_given_condition)\n+\n def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n \"\"\"\n Handles expectation queries for markov process.\n@@ -806,6 +859,24 @@ class DiscreteMarkovChain(DiscreteTimeStochasticProcess, MarkovProcess):\n >>> P(Le(Y[15], Y[10]), Eq(Y[8], 2)).round(7)\n 0.6963328\n \n+ Symbolic probability queries are also supported\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Matrix, Rational, Eq, Gt\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import P, DiscreteMarkovChain\n+ >>> a,b,c,d = symbols('a b c d')\n+ >>> T = Matrix([[Rational(1,10), Rational(4, 10), Rational(5, 10)], [Rational(3,10), Rational(4,10), Rational(3,10)], [Rational(7,10), Rational(2,10), Rational(1,10)]])\n+ >>> Y = DiscreteMarkovChain(\"Y\", [0,1,2], T)\n+ >>> query=P(Eq(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))\n+ >>> query.subs({a:10 ,b:2, c:5, d:1}).round(4)\n+ 0.3096\n+ >>> P(Eq(Y[10], 2), Eq(Y[5], 1)).evalf().round(4)\n+ 0.3096\n+ >>> query_gt=P(Gt(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))\n+ >>> query_gt.subs({a:21 ,b:0, c:5, d:0}).evalf().round(5)\n+ 0.64705\n+ >>> P(Gt(Y[21], 0), Eq(Y[5], 0)).round(5)\n+ 0.64705\n+\n There is limited support for arbitrarily sized states:\n \n >>> n = symbols('n', nonnegative=True, integer=True)\n@@ -813,6 +884,9 @@ class DiscreteMarkovChain(DiscreteTimeStochasticProcess, MarkovProcess):\n >>> Y = DiscreteMarkovChain(\"Y\", trans_probs=T)\n >>> Y.state_space\n Range(0, n, 1)\n+ >>> query=P(Eq(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))\n+ >>> query.subs({a:10 ,b:2, c:5, d:1})\n+ (T**5)[1, 2]\n \n References\n ==========\n@@ -1405,12 +1479,59 @@ class ContinuousMarkovChain(ContinuousTimeStochasticProcess, MarkovProcess):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import ContinuousMarkovChain\n- >>> from sympy import Matrix, S\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import ContinuousMarkovChain, P\n+ >>> from sympy import Matrix, S, Eq, Gt\n >>> G = Matrix([[-S(1), S(1)], [S(1), -S(1)]])\n >>> C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1], gen_mat=G)\n >>> C.limiting_distribution()\n Matrix([[1/2, 1/2]])\n+ >>> C.state_space\n+ FiniteSet(0, 1)\n+ >>> C.generator_matrix\n+ Matrix([\n+ [-1, 1],\n+ [ 1, -1]])\n+\n+ Probability queries are supported\n+\n+ >>> P(Eq(C(1.96), 0), Eq(C(0.78), 1)).round(5)\n+ 0.45279\n+ >>> P(Gt(C(1.7), 0), Eq(C(0.82), 1)).round(5)\n+ 0.58602\n+\n+ Probability of expressions with multiple RandomIndexedSymbols\n+ can also be calculated provided there is only 1 RandomIndexedSymbol\n+ in the given condition. It is always better to use Rational instead\n+ of floating point numbers for the probabilities in the\n+ generator matrix to avoid errors.\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import Gt, Le, Rational\n+ >>> G = Matrix([[-S(1), Rational(1, 10), Rational(9, 10)], [Rational(2, 5), -S(1), Rational(3, 5)], [Rational(1, 2), Rational(1, 2), -S(1)]])\n+ >>> C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1, 2], gen_mat=G)\n+ >>> P(Eq(C(3.92), C(1.75)), Eq(C(0.46), 0)).round(5)\n+ 0.37933\n+ >>> P(Gt(C(3.92), C(1.75)), Eq(C(0.46), 0)).round(5)\n+ 0.34211\n+ >>> P(Le(C(1.57), C(3.14)), Eq(C(1.22), 1)).round(4)\n+ 0.7143\n+\n+ Symbolic probability queries are also supported\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import S, symbols, Matrix, Rational, Eq, Gt\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import P, ContinuousMarkovChain\n+ >>> a,b,c,d = symbols('a b c d')\n+ >>> G = Matrix([[-S(1), Rational(1, 10), Rational(9, 10)], [Rational(2, 5), -S(1), Rational(3, 5)], [Rational(1, 2), Rational(1, 2), -S(1)]])\n+ >>> C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1, 2], gen_mat=G)\n+ >>> query=P(Eq(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))\n+ >>> query.subs({a:3.65 ,b:2, c:1.78, d:1}).evalf().round(10)\n+ 0.4002723175\n+ >>> P(Eq(C(3.65), 2), Eq(C(1.78), 1)).round(10)\n+ 0.4002723175\n+ >>> query_gt=P(Gt(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))\n+ >>> query_gt.subs({a:43.2 ,b:0, c:3.29, d:2}).evalf().round(10)\n+ 0.6832579186\n+ >>> P(Gt(C(43.2), 0), Eq(C(3.29), 2)).round(10)\n+ 0.6832579186\n \n References\n ==========\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\nindex 67acba4a0741..b2749312a820 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\n@@ -264,10 +264,29 @@ def test_DiscreteMarkovChain():\n Y = DiscreteMarkovChain(\"Y\", [0, 1, 2], T)\n assert P(Eq(Y[7], Y[5]), Eq(Y[2], 0)).round(5) == Float(0.44428, 5)\n assert P(Gt(Y[3], Y[1]), Eq(Y[0], 0)).round(2) == Float(0.36, 2)\n- assert P(Le(Y[5], Y[10]), Eq(Y[4], 2)).round(6) == Float(0.739072, 6)\n+ assert P(Le(Y[5], Y[10]), Eq(Y[4], 2)).round(6) == Float(0.583120, 6)\n assert Float(P(Eq(Y[500], Y[240]), Eq(Y[120], 1)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ne(Y[500], Y[240]), Eq(Y[120], 1)), 14)\n assert Float(P(Gt(Y[350], Y[100]), Eq(Y[75], 2)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Le(Y[350], Y[100]), Eq(Y[75], 2)), 14)\n assert Float(P(Lt(Y[400], Y[210]), Eq(Y[161], 0)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ge(Y[400], Y[210]), Eq(Y[161], 0)), 14)\n+ assert P(Eq(Y[5], Y[10]), Eq(Y[2], 1)) == P(Eq(Y[10], Y[5]), Eq(Y[2], 1))\n+ assert P(Gt(Y[23], Y[100]), Eq(Y[19], 1)) == P(Lt(Y[100], Y[23]), Eq(Y[19], 1))\n+ assert P(Ge(Y[78], Y[111]), Eq(Y[29], 1)) == P(Le(Y[111], Y[78]), Eq(Y[29], 1))\n+ assert (P(Lt(Y[295], Y[201]), Eq(Y[173], 1)) + P(Gt(Y[295], Y[201]), Eq(Y[173], 0)) + P(Eq(Y[295], Y[201]), Eq(Y[173], 0))).round(10) == 1\n+ assert (P(Le(Y[531], Y[367]), Eq(Y[279], 1)) + P(Ge(Y[531], Y[367]), Eq(Y[279], 0)) - P(Eq(Y[531], Y[367]), Eq(Y[279], 0))).round(10) == 1\n+\n+ #test symbolic queries\n+ a,b,c,d = symbols('a b c d')\n+ T = Matrix([[Rational(1,10), Rational(4, 10), Rational(5, 10)], [Rational(3,10), Rational(4,10), Rational(3,10)], [Rational(7,10), Rational(2,10), Rational(1,10)]])\n+ Y = DiscreteMarkovChain(\"Y\", [0,1,2], T)\n+ query=P(Eq(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))\n+ assert(query.subs({a:48 ,b:2, c:23, d:1}).evalf().round(4) == P(Eq(Y[48], 2), Eq(Y[23], 1)).round(4))\n+ assert(query.subs({a:191 ,b:0, c:87, d:1}).evalf().round(4) == P(Eq(Y[191], 0), Eq(Y[87], 1)).round(4))\n+ query_gt=P(Gt(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))\n+ query_le=P(Le(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))\n+ assert((query_gt.subs({a:432 ,b:2, c:329, d:0}) + query_le.subs({a:432 ,b:2, c:329, d:0})).evalf() == 1)\n+ query_ge=P(Ge(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))\n+ query_lt=P(Lt(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))\n+ assert((query_ge.subs({a:287 ,b:1, c:0, d:0}) + query_lt.subs({a:287 ,b:1, c:0, d:0})).evalf() == 1)\n \n def test_sample_stochastic_process():\n if not import_module('scipy'):\n@@ -331,6 +350,32 @@ def test_ContinuousMarkovChain():\n assert P(Eq(C3(1), 1), Eq(C3(0), 1)) == exp(-2)/2 + S.Half\n assert P(Eq(C3(1), Symbol('1')), Eq(C3(0), Symbol('1'))) == exp(-2)/2 + S.Half\n \n+ #test probability queries\n+ G = Matrix([[-S(1), Rational(1, 10), Rational(9, 10)], [Rational(2, 5), -S(1), Rational(3, 5)], [Rational(1, 2), Rational(1, 2), -S(1)]])\n+ C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1, 2], gen_mat=G)\n+ assert P(Eq(C(7.385), C(3.19)), Eq(C(0.862), 0)).round(5) == Float(0.35469, 5)\n+ assert P(Gt(C(98.715), C(19.807)), Eq(C(11.314), 2)).round(5) == Float(0.32452, 5)\n+ assert P(Le(C(5.9), C(10.112)), Eq(C(4), 1)).round(6) == Float(0.675214, 6)\n+ assert Float(P(Eq(C(771.32), C(291.65)), Eq(C(290.63), 1)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ne(C(771.32), C(291.65)), Eq(C(290.63), 1)), 14)\n+ assert Float(P(Gt(C(365.36), C(100.101)), Eq(C(75.992), 2)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Le(C(365.36), C(100.101)), Eq(C(75.992), 2)), 14)\n+ assert Float(P(Lt(C(400.90), C(243.79)), Eq(C(161.54), 0)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ge(C(400.90), C(243.79)), Eq(C(161.54), 0)), 14)\n+ assert P(Eq(C(5.243), C(10.912)), Eq(C(2.174), 1)) == P(Eq(C(10.912), C(5.243)), Eq(C(2.174), 1))\n+ assert P(Gt(C(23.44), C(99.99)), Eq(C(19.102), 1)) == P(Lt(C(99.99), C(23.44)), Eq(C(19.102), 1))\n+ assert P(Ge(C(71.87), C(111.008)), Eq(C(29.153), 1)) == P(Le(C(111.008), C(71.87)), Eq(C(29.153), 1))\n+ assert (P(Lt(C(295.706), C(201.98)), Eq(C(173.767), 1)) + P(Gt(C(295.706), C(201.98)), Eq(C(173.767), 0)) + P(Eq(C(295.706), C(201.98)), Eq(C(173.767), 0))).round(10) == 1\n+ assert (P(Le(C(531.12), C(367.8)), Eq(C(279.64), 1)) + P(Ge(C(531.12), C(367.8)), Eq(C(279.64), 0)) - P(Eq(C(531.12), C(367.8)), Eq(C(279.64), 0))).round(10) == 1\n+\n+ #test symbolic queries\n+ a,b,c,d = symbols('a b c d')\n+ query=P(Eq(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))\n+ assert(query.subs({a:3.65 ,b:2, c:1.78, d:1}).evalf().round(10) == P(Eq(C(3.65), 2), Eq(C(1.78), 1)).round(10))\n+ query_gt=P(Gt(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))\n+ query_le=P(Le(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))\n+ assert((query_gt.subs({a:143.2 ,b:0, c:31.29, d:2}) + query_le.subs({a:143.2 ,b:0, c:31.29, d:2})).evalf() == 1)\n+ query_ge=P(Ge(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))\n+ query_lt=P(Lt(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))\n+ assert((query_ge.subs({a:287.43 ,b:1, c:121.45, d:0}) + query_lt.subs({a:287.43 ,b:1, c:121.45, d:0})).evalf() == 1)\n+\n def test_BernoulliProcess():\n \n B = BernoulliProcess(\"B\", p=0.6, success=1, failure=0)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -658,6 +680,37 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Mechanism for handling (%s, %s) queries hasn't been \"\n \"implemented yet.\"%(condition, given_condition))\n \n+ def symbolic_probability(self, condition, new_given_condition, rv, min_key_rv):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 683,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nShouldn't it be private? I mean `_symbolic_probability`. \n\n@author:\nI'll change that"
}
] |
13ffdf4890c3301d8f2eed7854e5c76071496fd8
|
diff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
index e40774553df7..de912f97638f 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
Union, Expr, Function, exp, cacheit, sqrt, pi, gamma,
Ge, Piecewise, Symbol, NonSquareMatrixError, EmptySet,
ceiling, MatrixBase, ConditionSet, ones, zeros, Identity,
- Rational, Lt, Gt, Ne, BlockMatrix)
+ Rational, Lt, Gt, Le, Ne, BlockMatrix, Sum)
from sympy.core.relational import Relational
from sympy.logic.boolalg import Boolean
from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning
@@ -250,7 +250,8 @@ def __getitem__(self, time):
RandomIndexedSymbol
"""
- if time not in self.index_set:
+ time = sympify(time)
+ if not time.is_symbol and time not in self.index_set:
raise IndexError("%s is not in the index set of %s"%(time, self.symbol))
idx_obj = Indexed(self.symbol, time)
pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self, self.distribution)
@@ -269,7 +270,8 @@ def __call__(self, time):
RandomIndexedSymbol
"""
- if time not in self.index_set:
+ time = sympify(time)
+ if not time.is_symbol and time not in self.index_set:
raise IndexError("%s is not in the index set of %s"%(time, self.symbol))
func_obj = Function(self.symbol)(time)
pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self, self.distribution)
@@ -509,6 +511,13 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
check, mat, state_index, new_given_condition = \
self._preprocess(given_condition, evaluate)
+ rv = list(condition.atoms(RandomIndexedSymbol))
+ symbolic = False
+ for sym in rv:
+ if sym.key.is_symbol:
+ symbolic = True
+ break
+
if check:
return Probability(condition, new_given_condition)
@@ -526,21 +535,34 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
else:
gcs = (new_given_condition, )
min_key_rv = list(new_given_condition.atoms(RandomIndexedSymbol))
- rv = list(condition.atoms(RandomIndexedSymbol))
if len(min_key_rv):
min_key_rv = min_key_rv[0]
for r in rv:
+ if min_key_rv.key.is_symbol or r.key.is_symbol:
+ continue
if min_key_rv.key > r.key:
return Probability(condition)
else:
min_key_rv = None
return Probability(condition)
+ if symbolic:
+ return self._symbolic_probability(condition, new_given_condition, rv, min_key_rv)
+
if len(rv) > 1:
- rv = rv[:2]
+ rv[0] = condition.lhs
+ rv[1] = condition.rhs
if rv[0].key < rv[1].key:
rv[0], rv[1] = rv[1], rv[0]
+ if isinstance(condition, Gt):
+ condition = Lt(condition.lhs, condition.rhs)
+ elif isinstance(condition, Lt):
+ condition = Gt(condition.lhs, condition.rhs)
+ elif isinstance(condition, Ge):
+ condition = Le(condition.lhs, condition.rhs)
+ elif isinstance(condition, Le):
+ condition = Ge(condition.lhs, condition.rhs)
s = Rational(0, 1)
n = len(self.state_space)
@@ -658,6 +680,37 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
raise NotImplementedError("Mechanism for handling (%s, %s) queries hasn't been "
"implemented yet."%(condition, given_condition))
+ def _symbolic_probability(self, condition, new_given_condition, rv, min_key_rv):
+ #Function to calculate probability for queries with symbols
+ if isinstance(condition, Relational):
+ curr_state = new_given_condition.rhs if isinstance(new_given_condition.lhs, RandomIndexedSymbol) \
+ else new_given_condition.lhs
+ next_state = condition.rhs if isinstance(condition.lhs, RandomIndexedSymbol) \
+ else condition.lhs
+
+ if isinstance(condition, Eq) or isinstance(condition, Ne):
+ if isinstance(self, DiscreteMarkovChain):
+ P = self.transition_probabilities**(rv[0].key - min_key_rv.key)
+ else:
+ P = exp(self.generator_matrix*(rv[0].key - min_key_rv.key))
+ prob = P[curr_state, next_state] if isinstance(condition, Eq) else 1 - P[curr_state, next_state]
+ return Piecewise((prob, rv[0].key > min_key_rv.key), (Probability(condition), True))
+ else:
+ upper = 1
+ greater = False
+ if isinstance(condition, Ge) or isinstance(condition, Lt):
+ upper = 0
+ if isinstance(condition, Gt) or isinstance(condition, Ge):
+ greater = True
+ k = Dummy('k')
+ condition = Eq(condition.lhs, k) if isinstance(condition.lhs, RandomIndexedSymbol)\
+ else Eq(condition.rhs, k)
+ total = Sum(self.probability(condition, new_given_condition), (k, next_state + upper, self.state_space._sup))
+ return Piecewise((total, rv[0].key > min_key_rv.key), (Probability(condition), True)) if greater\
+ else Piecewise((1 - total, rv[0].key > min_key_rv.key), (Probability(condition), True))
+ else:
+ return Probability(condition, new_given_condition)
+
def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
"""
Handles expectation queries for markov process.
@@ -806,6 +859,24 @@ class DiscreteMarkovChain(DiscreteTimeStochasticProcess, MarkovProcess):
>>> P(Le(Y[15], Y[10]), Eq(Y[8], 2)).round(7)
0.6963328
+ Symbolic probability queries are also supported
+
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Matrix, Rational, Eq, Gt
+ >>> from sympy.stats import P, DiscreteMarkovChain
+ >>> a, b, c, d = symbols('a b c d')
+ >>> T = Matrix([[Rational(1, 10), Rational(4, 10), Rational(5, 10)], [Rational(3, 10), Rational(4, 10), Rational(3, 10)], [Rational(7, 10), Rational(2, 10), Rational(1, 10)]])
+ >>> Y = DiscreteMarkovChain("Y", [0, 1, 2], T)
+ >>> query = P(Eq(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))
+ >>> query.subs({a:10 ,b:2, c:5, d:1}).round(4)
+ 0.3096
+ >>> P(Eq(Y[10], 2), Eq(Y[5], 1)).evalf().round(4)
+ 0.3096
+ >>> query_gt = P(Gt(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))
+ >>> query_gt.subs({a:21, b:0, c:5, d:0}).evalf().round(5)
+ 0.64705
+ >>> P(Gt(Y[21], 0), Eq(Y[5], 0)).round(5)
+ 0.64705
+
There is limited support for arbitrarily sized states:
>>> n = symbols('n', nonnegative=True, integer=True)
@@ -813,6 +884,9 @@ class DiscreteMarkovChain(DiscreteTimeStochasticProcess, MarkovProcess):
>>> Y = DiscreteMarkovChain("Y", trans_probs=T)
>>> Y.state_space
Range(0, n, 1)
+ >>> query = P(Eq(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))
+ >>> query.subs({a:10, b:2, c:5, d:1})
+ (T**5)[1, 2]
References
==========
@@ -1418,12 +1492,59 @@ class ContinuousMarkovChain(ContinuousTimeStochasticProcess, MarkovProcess):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import ContinuousMarkovChain
- >>> from sympy import Matrix, S
+ >>> from sympy.stats import ContinuousMarkovChain, P
+ >>> from sympy import Matrix, S, Eq, Gt
>>> G = Matrix([[-S(1), S(1)], [S(1), -S(1)]])
>>> C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1], gen_mat=G)
>>> C.limiting_distribution()
Matrix([[1/2, 1/2]])
+ >>> C.state_space
+ FiniteSet(0, 1)
+ >>> C.generator_matrix
+ Matrix([
+ [-1, 1],
+ [ 1, -1]])
+
+ Probability queries are supported
+
+ >>> P(Eq(C(1.96), 0), Eq(C(0.78), 1)).round(5)
+ 0.45279
+ >>> P(Gt(C(1.7), 0), Eq(C(0.82), 1)).round(5)
+ 0.58602
+
+ Probability of expressions with multiple RandomIndexedSymbols
+ can also be calculated provided there is only 1 RandomIndexedSymbol
+ in the given condition. It is always better to use Rational instead
+ of floating point numbers for the probabilities in the
+ generator matrix to avoid errors.
+
+ >>> from sympy import Gt, Le, Rational
+ >>> G = Matrix([[-S(1), Rational(1, 10), Rational(9, 10)], [Rational(2, 5), -S(1), Rational(3, 5)], [Rational(1, 2), Rational(1, 2), -S(1)]])
+ >>> C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1, 2], gen_mat=G)
+ >>> P(Eq(C(3.92), C(1.75)), Eq(C(0.46), 0)).round(5)
+ 0.37933
+ >>> P(Gt(C(3.92), C(1.75)), Eq(C(0.46), 0)).round(5)
+ 0.34211
+ >>> P(Le(C(1.57), C(3.14)), Eq(C(1.22), 1)).round(4)
+ 0.7143
+
+ Symbolic probability queries are also supported
+
+ >>> from sympy import S, symbols, Matrix, Rational, Eq, Gt
+ >>> from sympy.stats import P, ContinuousMarkovChain
+ >>> a,b,c,d = symbols('a b c d')
+ >>> G = Matrix([[-S(1), Rational(1, 10), Rational(9, 10)], [Rational(2, 5), -S(1), Rational(3, 5)], [Rational(1, 2), Rational(1, 2), -S(1)]])
+ >>> C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1, 2], gen_mat=G)
+ >>> query = P(Eq(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))
+ >>> query.subs({a:3.65 ,b:2, c:1.78, d:1}).evalf().round(10)
+ 0.4002723175
+ >>> P(Eq(C(3.65), 2), Eq(C(1.78), 1)).round(10)
+ 0.4002723175
+ >>> query_gt = P(Gt(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))
+ >>> query_gt.subs({a:43.2 ,b:0, c:3.29, d:2}).evalf().round(10)
+ 0.6832579186
+ >>> P(Gt(C(43.2), 0), Eq(C(3.29), 2)).round(10)
+ 0.6832579186
References
==========
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
index 7b3af9d9ab14..444210c7e3e3 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
@@ -315,10 +315,27 @@ def test_DiscreteMarkovChain():
Y = DiscreteMarkovChain("Y", [0, 1, 2], T)
assert P(Eq(Y[7], Y[5]), Eq(Y[2], 0)).round(5) == Float(0.44428, 5)
assert P(Gt(Y[3], Y[1]), Eq(Y[0], 0)).round(2) == Float(0.36, 2)
- assert P(Le(Y[5], Y[10]), Eq(Y[4], 2)).round(6) == Float(0.739072, 6)
- assert Float(P(Eq(Y[500], Y[240]), Eq(Y[120], 1)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ne(Y[500], Y[240]), Eq(Y[120], 1)), 14)
- assert Float(P(Gt(Y[350], Y[100]), Eq(Y[75], 2)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Le(Y[350], Y[100]), Eq(Y[75], 2)), 14)
- assert Float(P(Lt(Y[400], Y[210]), Eq(Y[161], 0)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ge(Y[400], Y[210]), Eq(Y[161], 0)), 14)
+ assert P(Le(Y[5], Y[10]), Eq(Y[4], 2)).round(6) == Float(0.583120, 6)
+ assert Float(P(Eq(Y[10], Y[5]), Eq(Y[4], 1)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ne(Y[10], Y[5]), Eq(Y[4], 1)), 14)
+ assert Float(P(Gt(Y[8], Y[9]), Eq(Y[3], 2)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Le(Y[8], Y[9]), Eq(Y[3], 2)), 14)
+ assert Float(P(Lt(Y[1], Y[4]), Eq(Y[0], 0)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ge(Y[1], Y[4]), Eq(Y[0], 0)), 14)
+ assert P(Eq(Y[5], Y[10]), Eq(Y[2], 1)) == P(Eq(Y[10], Y[5]), Eq(Y[2], 1))
+ assert P(Gt(Y[1], Y[2]), Eq(Y[0], 1)) == P(Lt(Y[2], Y[1]), Eq(Y[0], 1))
+ assert P(Ge(Y[7], Y[6]), Eq(Y[4], 1)) == P(Le(Y[6], Y[7]), Eq(Y[4], 1))
+
+ #test symbolic queries
+ a, b, c, d = symbols('a b c d')
+ T = Matrix([[Rational(1, 10), Rational(4, 10), Rational(5, 10)], [Rational(3, 10), Rational(4, 10), Rational(3, 10)], [Rational(7, 10), Rational(2, 10), Rational(1, 10)]])
+ Y = DiscreteMarkovChain("Y", [0, 1, 2], T)
+ query = P(Eq(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))
+ assert query.subs({a:10, b:2, c:5, d:1}).evalf().round(4) == P(Eq(Y[10], 2), Eq(Y[5], 1)).round(4)
+ assert query.subs({a:15, b:0, c:10, d:1}).evalf().round(4) == P(Eq(Y[15], 0), Eq(Y[10], 1)).round(4)
+ query_gt = P(Gt(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))
+ query_le = P(Le(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))
+ assert query_gt.subs({a:5, b:2, c:1, d:0}).evalf() + query_le.subs({a:5, b:2, c:1, d:0}).evalf() == 1
+ query_ge = P(Ge(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))
+ query_lt = P(Lt(Y[a], b), Eq(Y[c], d))
+ assert query_ge.subs({a:4, b:1, c:0, d:2}).evalf() + query_lt.subs({a:4, b:1, c:0, d:2}).evalf() == 1
def test_sample_stochastic_process():
if not import_module('scipy'):
@@ -382,6 +399,30 @@ def test_ContinuousMarkovChain():
assert P(Eq(C3(1), 1), Eq(C3(0), 1)) == exp(-2)/2 + S.Half
assert P(Eq(C3(1), Symbol('1')), Eq(C3(0), Symbol('1'))) == exp(-2)/2 + S.Half
+ #test probability queries
+ G = Matrix([[-S(1), Rational(1, 10), Rational(9, 10)], [Rational(2, 5), -S(1), Rational(3, 5)], [Rational(1, 2), Rational(1, 2), -S(1)]])
+ C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1, 2], gen_mat=G)
+ assert P(Eq(C(7.385), C(3.19)), Eq(C(0.862), 0)).round(5) == Float(0.35469, 5)
+ assert P(Gt(C(98.715), C(19.807)), Eq(C(11.314), 2)).round(5) == Float(0.32452, 5)
+ assert P(Le(C(5.9), C(10.112)), Eq(C(4), 1)).round(6) == Float(0.675214, 6)
+ assert Float(P(Eq(C(7.32), C(2.91)), Eq(C(2.63), 1)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ne(C(7.32), C(2.91)), Eq(C(2.63), 1)), 14)
+ assert Float(P(Gt(C(3.36), C(1.101)), Eq(C(0.8), 2)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Le(C(3.36), C(1.101)), Eq(C(0.8), 2)), 14)
+ assert Float(P(Lt(C(4.9), C(2.79)), Eq(C(1.61), 0)), 14) == Float(1 - P(Ge(C(4.9), C(2.79)), Eq(C(1.61), 0)), 14)
+ assert P(Eq(C(5.243), C(10.912)), Eq(C(2.174), 1)) == P(Eq(C(10.912), C(5.243)), Eq(C(2.174), 1))
+ assert P(Gt(C(2.344), C(9.9)), Eq(C(1.102), 1)) == P(Lt(C(9.9), C(2.344)), Eq(C(1.102), 1))
+ assert P(Ge(C(7.87), C(1.008)), Eq(C(0.153), 1)) == P(Le(C(1.008), C(7.87)), Eq(C(0.153), 1))
+
+ #test symbolic queries
+ a, b, c, d = symbols('a b c d')
+ query = P(Eq(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))
+ assert query.subs({a:3.65, b:2, c:1.78, d:1}).evalf().round(10) == P(Eq(C(3.65), 2), Eq(C(1.78), 1)).round(10)
+ query_gt = P(Gt(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))
+ query_le = P(Le(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))
+ assert query_gt.subs({a:13.2, b:0, c:3.29, d:2}).evalf() + query_le.subs({a:13.2, b:0, c:3.29, d:2}).evalf() == 1
+ query_ge = P(Ge(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))
+ query_lt = P(Lt(C(a), b), Eq(C(c), d))
+ assert query_ge.subs({a:7.43, b:1, c:1.45, d:0}).evalf() + query_lt.subs({a:7.43, b:1, c:1.45, d:0}).evalf() == 1
+
def test_BernoulliProcess():
B = BernoulliProcess("B", p=0.6, success=1, failure=0)
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20212@e676833
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,212
|
zero raised to power -infinity gives zoo
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19572
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Earlier 0 ** -oo gave 0 instead of zoo
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
- core
- Zero raised to power Negative Infinity gives ComplexInfinity(zoo) instead of zero
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-10-06T11:34:13Z
|
0**-oo produces 0, the documentation says it should produce zoo
Using SymPy 1.5.1, evaluate `0**-oo` produces `0`.
The documentation for the Pow class states that it should return `ComplexInfinity`, aka `zoo`
| expr | value | reason |
| :-- | :-- | :--|
| `0**-oo` | `zoo` | This is not strictly true, as 0**oo may be oscillating between positive and negative values or rotating in the complex plane. It is convenient, however, when the base is positive.|
|
[
{
"body": "Using SymPy 1.5.1, evaluate `0**-oo` produces `0`.\r\n\r\nThe documentation for the Pow class states that it should return `ComplexInfinity`, aka `zoo`\r\n\r\n| expr | value | reason |\r\n| :-- | :-- | :--|\r\n| `0**-oo` | `zoo` | This is not strictly true, as 0**oo may be oscillating between positive and negative values or rotating in the complex plane. It is convenient, however, when the base is positive.|\r\n",
"number": 19572,
"title": "0**-oo produces 0, the documentation says it should produce zoo"
}
] |
a106f4782a9dbe7f8fd16030f15401d977e03ae9
|
{
"head_commit": "e676833404bb19c01482b098331c31dd4d5cbf5b",
"head_commit_message": "zero raised to power -infinity gives zoo",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/power.py b/sympy/core/power.py\nindex 984398c760e0..85d1d2e892a9 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/power.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/power.py\n@@ -291,6 +291,8 @@ def __new__(cls, b, e, evaluate=None):\n ).warn()\n \n if evaluate:\n+ if b is S.Zero and e is S.NegativeInfinity:\n+ return S.ComplexInfinity\n if e is S.ComplexInfinity:\n return S.NaN\n if e is S.Zero:\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py\nindex 413fbd453217..060b2428d83d 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py\n@@ -579,3 +579,7 @@ def _(a, b):\n assert power(a, b) == NewPow(a, b)\n assert power(b, a) == NewPow(b, a)\n assert power(b, b) == NewPow(b, b)\n+\n+def test_issue_19572():\n+ assert 0 ** -oo is zoo\n+ assert power(0, -oo) is zoo\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -579,3 +579,7 @@ def _(a, b):\n assert power(a, b) == NewPow(a, b)\n assert power(b, a) == NewPow(b, a)\n assert power(b, b) == NewPow(b, b)\n+\n+def test_issue_19572():\n+ assert 0 ** -oo is zoo\n+ assert power(0, -oo) is zoo",
"line": null,
"original_line": 585,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/tests/test_power.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nCan you add this to `test_zero` above rather than a new test function? You can include the url for the issue in a comment.\n\n@author:\nYes sure"
}
] |
7e10ac3987817107408433840298f4450171b6c0
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/power.py b/sympy/core/power.py
index 984398c760e0..85d1d2e892a9 100644
--- a/sympy/core/power.py
+++ b/sympy/core/power.py
@@ -291,6 +291,8 @@ def __new__(cls, b, e, evaluate=None):
).warn()
if evaluate:
+ if b is S.Zero and e is S.NegativeInfinity:
+ return S.ComplexInfinity
if e is S.ComplexInfinity:
return S.NaN
if e is S.Zero:
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py
index 413fbd453217..2f8a7aece434 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py
@@ -266,6 +266,9 @@ def test_zero():
assert 0**(2*x*y) == 0**(x*y)
assert 0**(-2*x*y) == S.ComplexInfinity**(x*y)
+ #Test issue 19572
+ assert 0 ** -oo is zoo
+ assert power(0, -oo) is zoo
def test_pow_as_base_exp():
x = Symbol('x')
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 1,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-20208@540dfc8
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,208
|
Fixed set is equal to set only
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #20089
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Earlier #in #subset gave wrong output due to inconsistency of #Eq with sets and expr
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
- sets
- Earlier expr and sets were treated equal which gave incorrect output for some set functions(mainly : - in, is_subset), made sets and expr not to be equal
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-10-05T12:25:27Z
|
FiniteSet not Value False
A=FiniteSet(1,2)
B=(FiniteSet(1,2),FiniteSet(1))
{1} in A
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-80-becd25ec8a42> in <module>()
----> 1 {1} in A
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/sets/sets.py in __contains__(self, other)
577
578 def __contains__(self, other):
--> 579 symb = sympify(self.contains(other))
580 if not (symb is S.true or symb is S.false):
581 raise TypeError('contains did not evaluate to a bool: %r' % symb)
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/sets/sets.py in contains(self, other)
305 """
306 other = sympify(other, strict=True)
--> 307 ret = sympify(self._contains(other))
308 if ret is None:
309 ret = Contains(other, self, evaluate=False)
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/sets/sets.py in _contains(self, other)
2001 r = false
2002 for e in self._elements:
-> 2003 t = Eq(e, other, evaluate=True)
2004 if isinstance(t, Eq):
2005 t = t.simplify()
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/core/relational.py in __new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)
302 return r
303 if hasattr(rhs, '_eval_Eq'):
--> 304 r = rhs._eval_Eq(lhs)
305 if r is not None:
306 return r
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/sets/sets.py in _eval_Eq(self, other)
1899
1900 def _eval_Eq(self, other):
-> 1901 if not other.is_FiniteSet:
1902 if (other.is_Union or other.is_Complement or
1903 other.is_Intersection or other.is_Produ
|

Hi! Can you please clarify the issue further?
This is what I get with sympy 1.6.2:
```julia
In [8]: A = FiniteSet(1, 2)
In [9]: B = FiniteSet(FiniteSet(1, 2), FiniteSet(1))
In [10]: A
Out[10]: {1, 2}
In [11]: B
Out[11]: {{1}, {1, 2}}
In [12]: A in B
Out[12]: True
In [15]: 1 in A
Out[15]: True
In [13]: print(A.issubset(B)) # should be False
None
In [14]: 1 in B # should be False
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-14-858aaa7d4c4d> in <module>
----> 1 1 in B
~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/sets/sets.py in __contains__(self, other)
673 # x in y must evaluate to T or F; to entertain a None
674 # result with Set use y.contains(x)
--> 675 raise TypeError('did not evaluate to a bool: %r' % c)
676 return b
677
TypeError: did not evaluate to a bool: None
```
These would evaluate correctly if `Eq` could recognise that a Set is never equal to an Expr:
```julia
In [11]: Eq(1, FiniteSet(1, 2))
Out[11]: 1 = {1, 2}
In [12]: Eq(1, FiniteSet(1))
Out[12]: 1 = {1}
```
|
[
{
"body": "A=FiniteSet(1,2)\r\nB=(FiniteSet(1,2),FiniteSet(1))\r\n\r\n{1} in A\r\nAttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n<ipython-input-80-becd25ec8a42> in <module>()\r\n----> 1 {1} in A\r\n\r\n/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/sets/sets.py in __contains__(self, other)\r\n 577 \r\n 578 def __contains__(self, other):\r\n--> 579 symb = sympify(self.contains(other))\r\n 580 if not (symb is S.true or symb is S.false):\r\n 581 raise TypeError('contains did not evaluate to a bool: %r' % symb)\r\n\r\n/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/sets/sets.py in contains(self, other)\r\n 305 \"\"\"\r\n 306 other = sympify(other, strict=True)\r\n--> 307 ret = sympify(self._contains(other))\r\n 308 if ret is None:\r\n 309 ret = Contains(other, self, evaluate=False)\r\n\r\n/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/sets/sets.py in _contains(self, other)\r\n 2001 r = false\r\n 2002 for e in self._elements:\r\n-> 2003 t = Eq(e, other, evaluate=True)\r\n 2004 if isinstance(t, Eq):\r\n 2005 t = t.simplify()\r\n\r\n/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/core/relational.py in __new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)\r\n 302 return r\r\n 303 if hasattr(rhs, '_eval_Eq'):\r\n--> 304 r = rhs._eval_Eq(lhs)\r\n 305 if r is not None:\r\n 306 return r\r\n\r\n/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/sympy/sets/sets.py in _eval_Eq(self, other)\r\n 1899 \r\n 1900 def _eval_Eq(self, other):\r\n-> 1901 if not other.is_FiniteSet:\r\n 1902 if (other.is_Union or other.is_Complement or\r\n 1903 other.is_Intersection or other.is_Produ",
"number": 20089,
"title": "FiniteSet not Value False"
}
] |
a106f4782a9dbe7f8fd16030f15401d977e03ae9
|
{
"head_commit": "540dfc8e3029c263c876d0b91770663f1db75c61",
"head_commit_message": "Fixed sets eq function('in' , 'subset')",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py b/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py\nindex e21ab30b4312..6f7a19fccfaf 100644\n--- a/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py\n+++ b/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py\n@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@\n from sympy.core.relational import Eq, is_eq\n+from sympy.core.basic import Basic\n from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool\n from sympy.logic.boolalg import And\n from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n-from sympy.sets.sets import tfn, ProductSet, Interval, FiniteSet\n+from sympy.sets.sets import tfn, ProductSet, Interval, FiniteSet, Set\n \n \n @dispatch(Interval, FiniteSet) # type:ignore\n@@ -46,3 +47,13 @@ def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n \n eqs = (is_eq(x, y) for x, y in zip(lhs.sets, rhs.sets))\n return tfn[fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, eqs))]\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Set, Basic) # type:ignore\n+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ return False\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Set, Set) # type:ignore\n+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ return None\ndiff --git a/sympy/sets/tests/test_sets.py b/sympy/sets/tests/test_sets.py\nindex e92cb1f23f6a..2fb976156e9e 100644\n--- a/sympy/sets/tests/test_sets.py\n+++ b/sympy/sets/tests/test_sets.py\n@@ -1581,3 +1581,11 @@ def test_DisjointUnion_len():\n assert len(DisjointUnion(FiniteSet(3, 5, 7, 9), FiniteSet(x, y, z))) == 7\n assert len(DisjointUnion(S.EmptySet, S.EmptySet, FiniteSet(x, y, z), S.EmptySet)) == 3\n raises(ValueError, lambda: len(DisjointUnion(Interval(0, 1), S.EmptySet)))\n+\n+def test_issue_20089():\n+ B = FiniteSet(FiniteSet(1, 2), FiniteSet(1))\n+ assert not 1 in B\n+ assert Eq(1, FiniteSet(1, 2)) == False\n+ assert FiniteSet(1) in B\n+ A = FiniteSet(1, 2)\n+ assert not A.issubset(B)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1581,3 +1581,11 @@ def test_DisjointUnion_len():\n assert len(DisjointUnion(FiniteSet(3, 5, 7, 9), FiniteSet(x, y, z))) == 7\n assert len(DisjointUnion(S.EmptySet, S.EmptySet, FiniteSet(x, y, z), S.EmptySet)) == 3\n raises(ValueError, lambda: len(DisjointUnion(Interval(0, 1), S.EmptySet)))\n+\n+def test_issue_20089():\n+ B = FiniteSet(FiniteSet(1, 2), FiniteSet(1))\n+ assert not 1 in B\n+ assert Eq(1, FiniteSet(1, 2)) == False",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1588,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/sets/tests/test_sets.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis should be `is S.false` rather than `== False`."
}
] |
387c3cf37f367188107587bf59f0769472794535
|
diff --git a/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py b/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py
index e21ab30b4312..6f7a19fccfaf 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
from sympy.core.relational import Eq, is_eq
+from sympy.core.basic import Basic
from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool
from sympy.logic.boolalg import And
from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
-from sympy.sets.sets import tfn, ProductSet, Interval, FiniteSet
+from sympy.sets.sets import tfn, ProductSet, Interval, FiniteSet, Set
@dispatch(Interval, FiniteSet) # type:ignore
@@ -46,3 +47,13 @@ def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
eqs = (is_eq(x, y) for x, y in zip(lhs.sets, rhs.sets))
return tfn[fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, eqs))]
+
+
+@dispatch(Set, Basic) # type:ignore
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+ return False
+
+
+@dispatch(Set, Set) # type:ignore
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+ return None
diff --git a/sympy/sets/tests/test_sets.py b/sympy/sets/tests/test_sets.py
index e92cb1f23f6a..f20860a462ed 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/tests/test_sets.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/tests/test_sets.py
@@ -1581,3 +1581,18 @@ def test_DisjointUnion_len():
assert len(DisjointUnion(FiniteSet(3, 5, 7, 9), FiniteSet(x, y, z))) == 7
assert len(DisjointUnion(S.EmptySet, S.EmptySet, FiniteSet(x, y, z), S.EmptySet)) == 3
raises(ValueError, lambda: len(DisjointUnion(Interval(0, 1), S.EmptySet)))
+
+def test_issue_20089():
+ B = FiniteSet(FiniteSet(1, 2), FiniteSet(1))
+ assert not 1 in B
+ assert not 1.0 in B
+ assert not Eq(1, FiniteSet(1, 2))
+ assert FiniteSet(1) in B
+ A = FiniteSet(1, 2)
+ assert A in B
+ assert B.issubset(B)
+ assert not A.issubset(B)
+ assert 1 in A
+ C = FiniteSet(FiniteSet(1, 2), FiniteSet(1), 1, 2)
+ assert A.issubset(C)
+ assert B.issubset(C)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20159@0de3dae
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,159
|
NotImplemented for matrix and tensor addition
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #18956
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Added not implemented for tensor + matrix, and matrix + tensor.
#### Other comments
Earlier Matrix + Array gave result as a matrix and Array + Matrix gave Type Error . Now both functs would return Not Implemented.
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* matrices
* Adding an array and a matrix now consistently gives TypeError.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-09-28T07:19:19Z
|
Addition of tensor and matrix with same shape
Little example:
```
import sympy as sp
A = sp.Array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
B = sp.eye(2)
```
```
A + B
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-32-151064de832d> in <module>
----> 1 A + B
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py in __add__(self, other)
370
371 if not isinstance(other, NDimArray):
--> 372 raise TypeError(str(other))
373
374 if self.shape != other.shape:
TypeError: Matrix([[1, 0], [0, 1]])
```
Whereas:
```
B + A
```
works as expected.
|
Instead of raising `TypeError` it should return `NotImplemented`. Both examples should raise though so `Matrix.__add__` should also return `NotImplemented`.
I think that one of the problem in the sympy codebase are there are so many different array classes inter-operating badly.
I may have different ideas like `Matrix + Array` should always return `Array` if it is two dimensional.
> Instead of raising `TypeError` it should return `NotImplemented`. Both examples should raise though so `Matrix.__add__` should also return `NotImplemented`.
It should return NotImplemented or shall give NotImplementedError?
NotImplemented is a reserved error for builtin operator overrides and cannot be used interchangably with NotImplementedError
https://docs.python.org/3/library/constants.html#NotImplemented
In matrix __add__ method it shows matrix like objects can be added which implies matrix + array = matrix
Then similarly array + matrix shouldn't be array?
|
[
{
"body": "Little example:\r\n\r\n```\r\nimport sympy as sp\r\nA = sp.Array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])\r\nB = sp.eye(2)\r\n```\r\n\r\n```\r\nA + B\r\n\r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nTypeError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n<ipython-input-32-151064de832d> in <module>\r\n----> 1 A + B\r\n\r\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py in __add__(self, other)\r\n 370 \r\n 371 if not isinstance(other, NDimArray):\r\n--> 372 raise TypeError(str(other))\r\n 373 \r\n 374 if self.shape != other.shape:\r\n\r\nTypeError: Matrix([[1, 0], [0, 1]])\r\n```\r\n\r\nWhereas:\r\n\r\n```\r\nB + A\r\n```\r\n\r\nworks as expected.",
"number": 18956,
"title": "Addition of tensor and matrix with same shape"
}
] |
7566e6db93738ea3145082d7071e5d5816d00cf8
|
{
"head_commit": "0de3daee8b2687a205fae0d8a2e68c103a2e94d1",
"head_commit_message": "NotImplemented for matrix and tensor addition and vice versa",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/matrices/common.py b/sympy/matrices/common.py\nindex 44a3cdc795cf..bbe1c4a69ddf 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/common.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/common.py\n@@ -26,6 +26,7 @@\n from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import flatten\n from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent\n+from sympy.tensor.array import NDimArray\n \n from .utilities import _get_intermediate_simp_bool\n \n@@ -2535,6 +2536,8 @@ def __abs__(self):\n \n @call_highest_priority('__radd__')\n def __add__(self, other):\n+ if isinstance(other, NDimArray):\n+ return NotImplemented\n \"\"\"Return self + other, raising ShapeError if shapes don't match.\"\"\"\n other = _matrixify(other)\n # matrix-like objects can have shapes. This is\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/tests/test_commonmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/tests/test_commonmatrix.py\nindex 811d9cd96200..84e8378e0934 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/tests/test_commonmatrix.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/tests/test_commonmatrix.py\n@@ -20,6 +20,7 @@\n from sympy.polys.polytools import Poly\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import flatten\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, XFAIL, warns_deprecated_sympy\n+from sympy import Array\n \n from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n \n@@ -1059,3 +1060,8 @@ class Foo(ImmutableDenseMatrix):\n \n assert isinstance(c, Foo)\n assert c == Matrix([[7, 10], [15, 22]])\n+\n+def test_issue_18956():\n+ A = Array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])\n+ B = Matrix([[1,2],[3,4]])\n+ raises(TypeError, lambda: B + A)\ndiff --git a/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py b/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py\nindex b2288b9e942a..d7b63776344f 100644\n--- a/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py\n+++ b/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py\n@@ -315,8 +315,11 @@ def f(sh, shape_left, i, j):\n \n def __add__(self, other):\n from sympy.tensor.array.arrayop import Flatten\n+ from sympy.matrices import Matrix\n \n if not isinstance(other, NDimArray):\n+ if isinstance(other, Matrix):\n+ return NotImplemented\n raise TypeError(str(other))\n \n if self.shape != other.shape:\ndiff --git a/sympy/tensor/array/tests/test_ndim_array.py b/sympy/tensor/array/tests/test_ndim_array.py\nindex 9a097a3fb86b..2aa1b92e73a6 100644\n--- a/sympy/tensor/array/tests/test_ndim_array.py\n+++ b/sympy/tensor/array/tests/test_ndim_array.py\n@@ -6,6 +6,7 @@\n )\n from sympy.abc import x, y\n \n+from sympy.matrices import Matrix\n \n array_types = [\n ImmutableDenseNDimArray,\n@@ -42,3 +43,8 @@ def test_issue_18361():\n assert simplify(A) == Array([0])\n assert simplify(B) == Array([1, 0])\n assert simplify(C) == Array([x + 1, sin(2*x)])\n+\n+def test_issue_18956():\n+ A = Array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])\n+ B = Matrix([[1,2],[3,4]])\n+ raises(TypeError, lambda: A+B)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2535,6 +2536,8 @@ def __abs__(self):\n \n @call_highest_priority('__radd__')\n def __add__(self, other):\n+ if isinstance(other, NDimArray):\n+ return NotImplemented\n \"\"\"Return self + other, raising ShapeError if shapes don't match.\"\"\"",
"line": 2539,
"original_line": 2541,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/matrices/common.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThere should not be code before the docstring.\r\n\r\nAlso this should be phrased as:\r\n```\r\nif not isinstance(other, ...):\r\n return NotImplemented\r\n```\r\nThe method should return `NotImplemented` unless it explicitly knows how to interoperate with other object.\n\n@author:\nIn this case I think it should be if isinstance(other, NdimArray) because matrix class is meant to work work with all objects having similar shape, if not isinstance will make matrix class work only with matrix not any other object of similar shape. I think only Matrix and Array addition should return NotImplemented\n\n@user1:\nWhat does \"other object of similar shape\" mean?\r\n\r\nIn general `NotImplemented` should be returned except for a specific list of allowed types.\n\n@author:\nCan you please list the allowed types?\n\n\n\n@author:\n> What does \"other object of similar shape\" mean?\r\n\r\nMatrix like object"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -315,8 +315,11 @@ def f(sh, shape_left, i, j):\n \n def __add__(self, other):\n from sympy.tensor.array.arrayop import Flatten\n+ from sympy.matrices import Matrix\n \n if not isinstance(other, NDimArray):\n+ if isinstance(other, Matrix):\n+ return NotImplemented\n raise TypeError(str(other))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 323,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis should always return `NotImplemented`. We shouldn't raise `TypeError` in methods like `__add__` because then it's impossible to define other classes that can interact with this class.\n\n@author:\nI didn't add TypeError , fixed it anyway."
}
] |
f8042703c0fe965e2bafbdbb1572168e63dd5b92
|
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/common.py b/sympy/matrices/common.py
index 44a3cdc795cf..d2f6dcb9f930 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/common.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/common.py
@@ -26,6 +26,7 @@
from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning
from sympy.utilities.iterables import flatten
from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent
+from sympy.tensor.array import NDimArray
from .utilities import _get_intermediate_simp_bool
@@ -2536,6 +2537,8 @@ def __abs__(self):
@call_highest_priority('__radd__')
def __add__(self, other):
"""Return self + other, raising ShapeError if shapes don't match."""
+ if isinstance(other, NDimArray): # Matrix and array addition is currently not implemented
+ return NotImplemented
other = _matrixify(other)
# matrix-like objects can have shapes. This is
# our first sanity check.
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/tests/test_commonmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/tests/test_commonmatrix.py
index 811d9cd96200..b50b11eda48e 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/tests/test_commonmatrix.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/tests/test_commonmatrix.py
@@ -20,6 +20,7 @@
from sympy.polys.polytools import Poly
from sympy.utilities.iterables import flatten
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, XFAIL, warns_deprecated_sympy
+from sympy import Array
from sympy.abc import x, y, z
@@ -1059,3 +1060,9 @@ class Foo(ImmutableDenseMatrix):
assert isinstance(c, Foo)
assert c == Matrix([[7, 10], [15, 22]])
+
+def test_issue_18956():
+ A = Array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
+ B = Matrix([[1,2],[3,4]])
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: B + A)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: A + B)
diff --git a/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py b/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py
index b2288b9e942a..0836dcf6962b 100644
--- a/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py
+++ b/sympy/tensor/array/ndim_array.py
@@ -317,7 +317,7 @@ def __add__(self, other):
from sympy.tensor.array.arrayop import Flatten
if not isinstance(other, NDimArray):
- raise TypeError(str(other))
+ return NotImplemented
if self.shape != other.shape:
raise ValueError("array shape mismatch")
diff --git a/sympy/tensor/array/tests/test_ndim_array.py b/sympy/tensor/array/tests/test_ndim_array.py
index 9a097a3fb86b..5fa14822bc0e 100644
--- a/sympy/tensor/array/tests/test_ndim_array.py
+++ b/sympy/tensor/array/tests/test_ndim_array.py
@@ -6,7 +6,6 @@
)
from sympy.abc import x, y
-
array_types = [
ImmutableDenseNDimArray,
ImmutableSparseNDimArray,
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20321@adb756b
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,321
|
Fixed `FiniteSet.evalf(...)` with a subs argument
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #20291
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
`FiniteSet(a).evalf(subs={a: 1})` would return `FiniteSet(a)` instead of `FiniteSet(1)`. This PR fixes this and similar issues.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* sets
* `FiniteSet.evalf` with a subs argument now does the substitution. Previously, the argument was ignored.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-10-22T13:04:52Z
|
[bug] subs option to evalf isn't working for sets
Evalf does not seem to work on solveset.
Code to replicate:
```
from sympy.stats import Uniform, cdf
from sympy import Symbol, Eq, solveset, solve
x = Symbol("x")
a = Symbol("a")
b = Symbol("b")
D = Uniform("d", a, b)
F_x = cdf(D)(x)
u = Symbol("u")
expr = solveset(Eq(F_x, u), x)
expr.evalf(subs={u:0.6, a: 0, b: 2})
>> returns {a - u*(a - b)}
```
If instead I use solve, it works:
```
expr = solve(Eq(F_x, u), x)[0]
expr.evalf(subs={u:0.6, a: 0, b: 2})
>> returns 1.20000000000000
```
|
Looks like `Set.evalf` with a subs argument does not work. That is, `FiniteSet(a).evalf(subs={a: 1})` returns `FiniteSet(a)`. As a workaround for now, I suggest you do `expr.subs({u: 0.6, a: 0, b: 2}).evalf()`.
I'll have a PR out as soon as I know my changes don't break the build somewhere else.
Note that between your version and master, that cdf has become piecewise. SymPy is unable to solve for `x` and just throws an error. Hopefully by 1.8, there will be no more piecewise pdf's, pmf's and cdf's.
|
[
{
"body": "Evalf does not seem to work on solveset. \r\n\r\nCode to replicate:\r\n```\r\nfrom sympy.stats import Uniform, cdf\r\nfrom sympy import Symbol, Eq, solveset, solve\r\n\r\nx = Symbol(\"x\")\r\na = Symbol(\"a\")\r\nb = Symbol(\"b\")\r\n\r\nD = Uniform(\"d\", a, b)\r\nF_x = cdf(D)(x)\r\n\r\nu = Symbol(\"u\")\r\nexpr = solveset(Eq(F_x, u), x)\r\nexpr.evalf(subs={u:0.6, a: 0, b: 2})\r\n>> returns {a - u*(a - b)}\r\n```\r\n\r\nIf instead I use solve, it works:\r\n\r\n```\r\nexpr = solve(Eq(F_x, u), x)[0]\r\nexpr.evalf(subs={u:0.6, a: 0, b: 2})\r\n>> returns 1.20000000000000\r\n```",
"number": 20291,
"title": "[bug] subs option to evalf isn't working for sets"
}
] |
07a6388bc237a2c43e65dc3cf932373e4d06d91b
|
{
"head_commit": "adb756b913c0fb28876067a58bdade966941aa5a",
"head_commit_message": "Added `isinstance(self, Basic)` check",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/evalf.py b/sympy/core/evalf.py\nindex 812e9de5f8d6..862d7385e4ee 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/evalf.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/evalf.py\n@@ -1473,7 +1473,11 @@ def evalf(self, n=15, subs=None, maxn=100, chop=False, strict=False, quad=None,\n result = evalf(self, prec + 4, options)\n except NotImplementedError:\n # Fall back to the ordinary evalf\n- v = self._eval_evalf(prec)\n+ from sympy.core.basic import Basic\n+ if isinstance(self, Basic) and subs is not None: # issue 20291\n+ v = self.subs(subs)._eval_evalf(prec)\n+ else:\n+ v = self._eval_evalf(prec)\n if v is None:\n return self\n elif not v.is_number:\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py\nindex dc3a1663ca75..564893ec4edf 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py\n@@ -579,3 +579,13 @@ def test_issue_13425():\n \n def test_issue_17421():\n assert N(acos(-I + acosh(cosh(cosh(1) + I)))) == 1.0*I\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_20291():\n+ from sympy import FiniteSet\n+ a = Symbol('a')\n+ b = Symbol('b')\n+ A = FiniteSet(a, b)\n+ assert A.evalf(subs={a: 1, b: 2}) == FiniteSet(1, 2)\n+ B = FiniteSet(a-b, 1)\n+ assert B.evalf(subs={a: 1, b: 2}) == FiniteSet(-1, 1)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1473,7 +1473,11 @@ def evalf(self, n=15, subs=None, maxn=100, chop=False, strict=False, quad=None,\n result = evalf(self, prec + 4, options)\n except NotImplementedError:\n # Fall back to the ordinary evalf\n- v = self._eval_evalf(prec)\n+ from sympy.core.basic import Basic\n+ if isinstance(self, Basic) and subs is not None: # issue 20291",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1477,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/evalf.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhat is the purpose of this change? Won't `self` always be `Basic`?\n\n@author:\n`EvalfMixin` is not an instance of `Basic`. I think all its children are instances of `Basic` but I am not 100% sure. That's why I added it in. Should I remove the `Basic` check?"
}
] |
66edfc65d8d0a000d80ffed2a19ee3f2ff47c726
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/evalf.py b/sympy/core/evalf.py
index 812e9de5f8d6..5901d06fa2f3 100644
--- a/sympy/core/evalf.py
+++ b/sympy/core/evalf.py
@@ -1473,7 +1473,10 @@ def evalf(self, n=15, subs=None, maxn=100, chop=False, strict=False, quad=None,
result = evalf(self, prec + 4, options)
except NotImplementedError:
# Fall back to the ordinary evalf
- v = self._eval_evalf(prec)
+ if hasattr(self, 'subs') and subs is not None: # issue 20291
+ v = self.subs(subs)._eval_evalf(prec)
+ else:
+ v = self._eval_evalf(prec)
if v is None:
return self
elif not v.is_number:
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py
index dc3a1663ca75..8e3b655990bc 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_evalf.py
@@ -579,3 +579,16 @@ def test_issue_13425():
def test_issue_17421():
assert N(acos(-I + acosh(cosh(cosh(1) + I)))) == 1.0*I
+
+
+def test_issue_20291():
+ from sympy import FiniteSet, Complement, Intersection, Reals, EmptySet
+ a = Symbol('a')
+ b = Symbol('b')
+ A = FiniteSet(a, b)
+ assert A.evalf(subs={a: 1, b: 2}) == FiniteSet(1.0, 2.0)
+ B = FiniteSet(a-b, 1)
+ assert B.evalf(subs={a: 1, b: 2}) == FiniteSet(-1.0, 1.0)
+
+ sol = Complement(Intersection(FiniteSet(-b/2 - sqrt(b**2-4*pi)/2), Reals), FiniteSet(0))
+ assert sol.evalf(subs={b: 1}) == EmptySet
diff --git a/sympy/sets/sets.py b/sympy/sets/sets.py
index 72b2fa4a0a45..4ea90f2f0dd0 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/sets.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/sets.py
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@
@sympify_method_args
-class Set(Basic):
+class Set(Basic, EvalfMixin):
"""
The base class for any kind of set.
@@ -648,6 +648,9 @@ def _boundary(self):
def _measure(self):
raise NotImplementedError("(%s)._measure" % self)
+ def _eval_evalf(self, prec):
+ return self.func(*[arg.evalf(n=prec_to_dps(prec)) for arg in self.args])
+
@sympify_return([('other', 'Set')], NotImplemented)
def __add__(self, other):
return self.union(other)
@@ -866,7 +869,7 @@ def __bool__(self):
return all([bool(s) for s in self.sets])
-class Interval(Set, EvalfMixin):
+class Interval(Set):
"""
Represents a real interval as a Set.
@@ -1133,7 +1136,7 @@ def _eval_Eq(self, other):
return false
-class Union(Set, LatticeOp, EvalfMixin):
+class Union(Set, LatticeOp):
"""
Represents a union of sets as a :class:`Set`.
@@ -1293,15 +1296,6 @@ def as_relational(self, symbol):
def is_iterable(self):
return all(arg.is_iterable for arg in self.args)
- def _eval_evalf(self, prec):
- try:
- return Union(*(set._eval_evalf(prec) for set in self.args))
- except (TypeError, ValueError, NotImplementedError):
- import sys
- raise (TypeError("Not all sets are evalf-able"),
- None,
- sys.exc_info()[2])
-
def __iter__(self):
return roundrobin(*(iter(arg) for arg in self.args))
@@ -1526,7 +1520,7 @@ def as_relational(self, symbol):
return And(*[set.as_relational(symbol) for set in self.args])
-class Complement(Set, EvalfMixin):
+class Complement(Set):
r"""Represents the set difference or relative complement of a set with
another set.
@@ -1731,7 +1725,7 @@ def _boundary(self):
return S.EmptySet
-class FiniteSet(Set, EvalfMixin):
+class FiniteSet(Set):
"""
Represents a finite set of discrete numbers.
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20049@97e9aa8
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,049
|
point.vel() calculates velocity
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
fixes #17761
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Update vel() in point , now it calculates velocity if position vector is given.
#### Other comments
If appropriate position vectors are given , calculates velocity
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
- physics.vector
- Point.vel() now attempts to calculate the velocity using the relative position from other points if it has not been already set by the user. This behavior mimics the existing behavior in ReferenceFrame.ang_vel_in().
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-09-05T09:37:44Z
|
Point.vel() should calculate the velocity if possible
If you specify the orientation of two reference frames and then ask for the angular velocity between the two reference frames the angular velocity will be calculated. But if you try to do the same thing with velocities, this doesn't work. See below:
```
In [1]: import sympy as sm
In [2]: import sympy.physics.mechanics as me
In [3]: A = me.ReferenceFrame('A')
In [5]: q = me.dynamicsymbols('q')
In [6]: B = A.orientnew('B', 'Axis', (q, A.x))
In [7]: B.ang_vel_in(A)
Out[7]: q'*A.x
In [9]: P = me.Point('P')
In [10]: Q = me.Point('Q')
In [11]: r = q*A.x + 2*q*A.y
In [12]: Q.set_pos(P, r)
In [13]: Q.vel(A)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-13-0fc8041904cc> in <module>
----> 1 Q.vel(A)
~/miniconda3/lib/python3.6/site-packages/sympy/physics/vector/point.py in vel(self, frame)
453 if not (frame in self._vel_dict):
454 raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'
--> 455 ' defined in ReferenceFrame ' + frame.name)
456 return self._vel_dict[frame]
457
ValueError: Velocity of point Q has not been defined in ReferenceFrame A
```
The expected result of the `Q.vel(A)` should be:
```
In [14]: r.dt(A)
Out[14]: q'*A.x + 2*q'*A.y
```
I think that this is possible. Maybe there is a reason it isn't implemented. But we should try to implement it because it is confusing why this works for orientations and not positions.
|
Hi @moorepants, I think I could fix this. It would be implemented as a part of `ReferenceFrame` in `sympy/physics/vector/frame.py`, right?
No, it is part of Point. There are some nuances here and likely not a trivial PR to tackle. I'd recommend some simpler ones first if you are new to sympy and dynamics.
Sure, understood. Thank you @moorepants .
> No, it is part of Point. There are some nuances here and likely not a trivial PR to tackle. I'd recommend some simpler ones first if you are new to sympy and dynamics.
I would like to work on this issue.
The current Point.vel() returns velocity already defined in a reference frame , it doesn't calculate velocity between two points , so it would require a new function to calculate velocity between two points this would make it fully automatic.
So I propose , a change in vel() function to set velocity of particle from r and a new function to which calculates and returns velocity by calculating displacement vector , this function wouldn't set the velocity of particle but would return it on being called.
The idea is that if there is sufficient information about the relative position of points, that Point.vel() can determine there is sufficient information and calculate the velocity. You should study how ReferenceFrame does this with ang_vel().
> The idea is that if there is sufficient information about the relative position of points, that Point.vel() can determine there is sufficient information and calculate the velocity. You should study how ReferenceFrame does this with ang_vel().
Okay on it!!
@moorepants pls check my PR and tell if something's missing or wrong.
|
[
{
"body": "If you specify the orientation of two reference frames and then ask for the angular velocity between the two reference frames the angular velocity will be calculated. But if you try to do the same thing with velocities, this doesn't work. See below:\r\n\r\n```\r\nIn [1]: import sympy as sm \r\n\r\nIn [2]: import sympy.physics.mechanics as me \r\n\r\nIn [3]: A = me.ReferenceFrame('A') \r\n\r\nIn [5]: q = me.dynamicsymbols('q') \r\n\r\nIn [6]: B = A.orientnew('B', 'Axis', (q, A.x)) \r\n\r\nIn [7]: B.ang_vel_in(A) \r\nOut[7]: q'*A.x\r\n\r\nIn [9]: P = me.Point('P') \r\n\r\nIn [10]: Q = me.Point('Q') \r\n\r\nIn [11]: r = q*A.x + 2*q*A.y \r\n\r\nIn [12]: Q.set_pos(P, r) \r\n\r\nIn [13]: Q.vel(A) \r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nValueError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n<ipython-input-13-0fc8041904cc> in <module>\r\n----> 1 Q.vel(A)\r\n\r\n~/miniconda3/lib/python3.6/site-packages/sympy/physics/vector/point.py in vel(self, frame)\r\n 453 if not (frame in self._vel_dict):\r\n 454 raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'\r\n--> 455 ' defined in ReferenceFrame ' + frame.name)\r\n 456 return self._vel_dict[frame]\r\n 457 \r\n\r\nValueError: Velocity of point Q has not been defined in ReferenceFrame A\r\n```\r\n\r\nThe expected result of the `Q.vel(A)` should be:\r\n\r\n```\r\nIn [14]: r.dt(A) \r\nOut[14]: q'*A.x + 2*q'*A.y\r\n```\r\n\r\nI think that this is possible. Maybe there is a reason it isn't implemented. But we should try to implement it because it is confusing why this works for orientations and not positions.\r\n\r\n",
"number": 17761,
"title": "Point.vel() should calculate the velocity if possible"
}
] |
d57aaf064041fe52c0fa357639b069100f8b28e1
|
{
"head_commit": "97e9aa872cbbf4032c82ef6861f620b747e08a11",
"head_commit_message": "Added Comments",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/point.py b/sympy/physics/vector/point.py\nindex ddb3a4d09265..7a3b44764d11 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/vector/point.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/point.py\n@@ -56,6 +56,7 @@ def __init__(self, name):\n self._pos_dict = {}\n self._vel_dict = {}\n self._acc_dict = {}\n+ self._vel_dict_pos = {}\n self._pdlist = [self._pos_dict, self._vel_dict, self._acc_dict]\n \n def __str__(self):\n@@ -471,6 +472,44 @@ def v2pt_theory(self, otherpoint, outframe, fixedframe):\n self.set_vel(outframe, v + (omega ^ dist))\n return self.vel(outframe)\n \n+ def _calc_vel(self, frame, pos_vect):\n+ # Helper Function for velocty\n+ if len(self._pos_dict) == 1:\n+ #If len of post_dict is one it implies it only has that point from which it's being called\n+ #Stops infinite recursion\n+ return False\n+ #Copies vel_dict of current point(the one through which it's called, self for this function)\n+ self._vel_dict_pos = self._vel_dict.copy()\n+ #Loop 1 for checking all points at same level in self's pos_dict(to find nearest point in Tree)\n+ for p, p_pos in self._pos_dict.items():\n+ try:\n+ p_vel = p._vel_dict[frame] #Checks if the point's velocity is defined wrt req frame, if not throws Keyerror\n+ p_pos.dt(frame) #Checks if pos vector in defined with req frame, if not throws ValueError\n+ except KeyError:\n+ continue\n+ except ValueError:\n+ continue\n+ self._vel_dict_pos[frame] = p_vel + p_pos.dt(frame) #Updates current point's copied dict\n+ return True #Returns True, this point has it's velocity defined in appropriate ref frame\n+ for p, p_pos in self._pos_dict.items():\n+ #Loop 2 for searching in next level, if not found in same level\n+ if p_pos == -pos_vect:\n+ #If pos of this point is equal and negative of pos passed, this implies, referring back to point through which funct is called.\n+ #Prevents infinite recursion\n+ continue\n+ try:\n+ p_pos.dt(frame) #Checks if pos vector in defined with req frame, if not throws ValueError\n+ cond = p._calc_vel(frame, p_pos) # IF pos vector's condition is satisfied, calls helper function(recursive call)\n+ if not cond: # If funct returns False, next iteration takes place\n+ continue\n+ else: #If funct returned True , upto current point velocities have been calculated in Tree(not of current point)\n+ p_vel = p._vel_dict_pos[frame]\n+ except ValueError:\n+ continue\n+ self._vel_dict_pos[frame] = p_vel + p_pos.dt(frame) # Updates Velocity of current point in copied dict\n+ return True # Returns True to main funt, implies using current points calculated velocity thr req point's velocity can be calculated.\n+ return False #Return False to main funct for next iteration\n+\n def vel(self, frame):\n \"\"\"The velocity Vector of this Point in the ReferenceFrame.\n \n@@ -483,19 +522,54 @@ def vel(self, frame):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame, dynamicsymbols\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> p1 = Point('p1')\n >>> p1.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n >>> p1.vel(N)\n 10*N.x\n+ >>> p = Point('p')\n+ >>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')\n+ >>> p.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n+ >>> p2 = Point('p2')\n+ >>> p2.set_pos(p, q*N.x)\n+ >>> p2.vel(N)\n+ (Derivative(q(t), t) + 10)*N.x\n \n \"\"\"\n \n _check_frame(frame)\n- if not (frame in self._vel_dict):\n- raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'\n- ' defined in ReferenceFrame ' + frame.name)\n+ if not (frame in self._vel_dict):#If required point doesn't have its velocity defined in req frame.\n+ #Copies vel_dict so that velocity calculation doesn't affect user defined velocity.\n+ self._vel_dict_pos = self._vel_dict.copy()\n+ # p being point in pos_dit and p_pos being pos vector\n+ for p, p_pos in self._pos_dict.items():\n+ #Loop 1 for checking all points at same level in self's pos_dict(to find nearest point in Tree)\n+ try:\n+ p_vel = p._vel_dict[frame] #Checks if the point's velocity is defined wrt req frame, if not throws Keyerror\n+ p_pos.dt(frame) #Checks if pos vector in defined with req frame, if not throws ValueError\n+ except KeyError:\n+ continue\n+ except ValueError:\n+ continue\n+ self._vel_dict_pos[frame] = p_vel + p_pos.dt(frame) #Updates new dict(copied one)\n+ return self._vel_dict_pos[frame]\n+ #Loop 2 for searching in next level, if not found in same level\n+ for p, p_pos in self._pos_dict.items():\n+ try:\n+ p_pos.dt(frame) #Checks if pos vector in defined with req frame, if not throws ValueError\n+ p_vel_check = p._calc_vel(frame, p_pos) #If position vector is satisfied calls helper funct\n+ if not p_vel_check:\n+ continue # If helper function returns False next point is iterated\n+ else:\n+ p_vel = p._vel_dict_pos[frame] #If helper function returns True, velocity upto this particle(p) is calculated.\n+ except ValueError:\n+ continue\n+ self._vel_dict_pos[frame] = p_vel + p_pos.dt(frame) # Self's Copied dict is updated with the required velocity value.\n+ return self._vel_dict_pos[frame]\n+ else: #If no point satisfies condition\n+ raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'\n+ ' defined in ReferenceFrame ' + frame.name)\n return self._vel_dict[frame]\n \n def partial_velocity(self, frame, *gen_speeds):\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_point.py b/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_point.py\nindex 052b5c3af7d8..c6c1226c6795 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_point.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_point.py\n@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@\n from sympy.physics.vector import dynamicsymbols, Point, ReferenceFrame\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n+from sympy import Derivative\n \n \n def test_point_v1pt_theorys():\n@@ -82,6 +83,7 @@ def test_point_funcs():\n assert P.vel(B) == qd * B.x + q2d * B.y\n O.set_vel(N, 0)\n assert O.vel(N) == 0\n+\n assert P.a1pt_theory(O, N, B) == ((-25 * q + qdd) * B.x + (q2dd) * B.y +\n (-10 * qd) * B.z)\n \n@@ -126,3 +128,67 @@ def test_point_partial_velocity():\n assert p.partial_velocity(N, u1) == A.x\n assert p.partial_velocity(N, u1, u2) == (A.x, N.y)\n raises(ValueError, lambda: p.partial_velocity(A, u1))\n+\n+def test_point_vel():\n+ q1, q2 = dynamicsymbols('q1 q2')\n+ N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')\n+ S = ReferenceFrame('S')\n+ O = Point('O')\n+ Q = Point('Q')\n+ Q.set_pos(O, q1 * N.x)\n+ raises(ValueError , lambda : Q.vel(N)) #Velocity of Q is not defined\n+ O.set_vel(N, q2 * N.y)\n+ assert Q.vel(N) == Derivative(q1) * N.x + q2 * N.y # Velocity of Q using O\n+ P1 = Point('P1')\n+ P1.set_pos(O, q1 * B.x)\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P1.vel(B)) # O's velocity is defined in different frame\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P1.vel(N)) # Pos vector is defined in different frame\n+ P2 = Point('P2')\n+ P2.set_pos(P1, q2 * B.z)\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P2.vel(B)) # O's velocity is defined in different frame, and no\n+ #point in between has its velocity defined\n+ P3 = Point('P3')\n+ P3.set_pos(P2, q1 * B.x)\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P3.vel(B)) # O's velocity is defined in different frame, and no\n+ #point in between has its velocity defined\n+ P1.set_vel(B, 10 * q1 * B.x) #Defined P1's velocity\n+ assert P3.vel(B) == (10 * q1 + Derivative(q1)) * B.x + Derivative(q2) * B.z # Tree traversal upto P1\n+ # Vel of P3 = Vel of P1 + Calculated Vel of P2 + time derivative of pos vector\n+ P5 = Point('P5')\n+ P5.set_vel(B, q1 * B.x)\n+ P3.set_pos(P5, q2 * B.y)\n+ assert P3.vel(B) == q1 * B.x + Derivative(q2) * B.y # P5 closer in tree than P1\n+ Q1 = Point('Q1')\n+ Q1.set_vel(N, q1 * N.x)\n+ Q2 = Point('Q2')\n+ Q3 = Point('Q3')\n+ Q4 = Point('Q4')\n+ Q2.set_pos(Q1, q2 * N.x)\n+ Q3.set_pos(Q2, q1 * N.x)\n+ Q4.set_pos(Q3, q2 * N.x)\n+ assert Q4.vel(N) == (q1 + Derivative(q1) + 2 * Derivative(q2)) * N.x # Calculated velocity using\n+ # Q1, Q2, Q3\n+ Q3.set_vel(N, q1 * N.x)\n+ assert Q3.vel(N) == q1 * N.x # Outputs user defined velocity\n+ assert Q4.vel(N) == (q1 + Derivative(q2)) * N.x # If vel of one point in tree is changed the\n+ # resulting velocity is changed\n+ assert Q3.vel(N) == q1 * N.x # Automated vel calculation doesnt overwrite user defined vel\n+ #Complex Operations\n+ T1 = Point('T1')\n+ T1.set_vel(S, q1 * S.x)\n+ T2 = Point('T2')\n+ T2.set_pos(T1, q2 * S.x)\n+ T2.set_vel(N, q1 * N.y)\n+ T3 = Point('T3')\n+ T3.set_vel(B, q1 * B.z)\n+ T3.set_pos(T2, q1 * B.x + q2 * B.y)\n+ T3.set_pos(T1, q2 * S.x)\n+ T4 = Point('T4')\n+ T4.set_pos(T3, q1 * S.z)\n+ T5 = Point('T5')\n+ T5.set_pos(T4, q2 * S.y)\n+ T6 = Point('T6')\n+ T6.set_pos(T3, q1 * B.z)\n+ T6.set_pos(T2, q1 * S.z)\n+ assert T6.vel(S) + T6.vel(B) + T5.vel(S) + T2.vel(N) == q1*N.y + (q1 + Derivative(q1))*B.z + (2*q1 + 2*Derivative(q2))*S.x + Derivative(q2)*S.y + 2*Derivative(q1)*S.z\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -483,19 +522,54 @@ def vel(self, frame):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame, dynamicsymbols\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> p1 = Point('p1')\n >>> p1.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n >>> p1.vel(N)\n 10*N.x\n+ >>> p = Point('p')\n+ >>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')\n+ >>> p.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n+ >>> p2 = Point('p2')\n+ >>> p2.set_pos(p, q*N.x)\n+ >>> p2.vel(N)\n+ (Derivative(q(t), t) + 10)*N.x\n \n \"\"\"\n \n _check_frame(frame)\n- if not (frame in self._vel_dict):\n- raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'\n- ' defined in ReferenceFrame ' + frame.name)\n+ if not (frame in self._vel_dict):#If required point doesn't have its velocity defined in req frame.\n+ #Copies vel_dict so that velocity calculation doesn't affect user defined velocity.\n+ self._vel_dict_pos = self._vel_dict.copy()\n+ # p being point in pos_dit and p_pos being pos vector\n+ for p, p_pos in self._pos_dict.items():\n+ #Loop 1 for checking all points at same level in self's pos_dict(to find nearest point in Tree)\n+ try:\n+ p_vel = p._vel_dict[frame] #Checks if the point's velocity is defined wrt req frame, if not throws Keyerror\n+ p_pos.dt(frame) #Checks if pos vector in defined with req frame, if not throws ValueError",
"line": null,
"original_line": 550,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/vector/point.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhy is this code duplicated here and in the helper method?"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -483,19 +483,56 @@ def vel(self, frame):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame, dynamicsymbols\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> p1 = Point('p1')\n >>> p1.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n >>> p1.vel(N)\n 10*N.x\n+ >>> p = Point('p')\n+ >>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')\n+ >>> p.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n+ >>> p2 = Point('p2')\n+ >>> p2.set_pos(p, q*N.x)\n+ >>> p2.vel(N)\n+ (Derivative(q(t), t) + 10)*N.x\n \n \"\"\"\n \n _check_frame(frame)\n if not (frame in self._vel_dict):\n- raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'\n+ starting_node = self\n+ visited = []\n+ queue = [starting_node]",
"line": null,
"original_line": 506,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/vector/point.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n queue = [self]\r\n```\r\nAnd delete 504."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -471,6 +472,44 @@ def v2pt_theory(self, otherpoint, outframe, fixedframe):\n self.set_vel(outframe, v + (omega ^ dist))\n return self.vel(outframe)\n \n+ def _calc_vel(self, frame, pos_vect):\n+ # Helper Function for velocty\n+ if len(self._pos_dict) == 1:\n+ #If len of post_dict is one it implies it only has that point from which it's being called\n+ #Stops infinite recursion\n+ return False\n+ #Copies vel_dict of current point(the one through which it's called, self for this function)\n+ self._vel_dict_pos = self._vel_dict.copy()\n+ #Loop 1 for checking all points at same level in self's pos_dict(to find nearest point in Tree)\n+ for p, p_pos in self._pos_dict.items():\n+ try:\n+ p_vel = p._vel_dict[frame] #Checks if the point's velocity is defined wrt req frame, if not throws Keyerror\n+ p_pos.dt(frame) #Checks if pos vector in defined with req frame, if not throws ValueError",
"line": null,
"original_line": 487,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/vector/point.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI've already commented that this is bad practice catching different errors from two lines, you don't know what lines the errors come from and why."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -483,19 +483,56 @@ def vel(self, frame):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame, dynamicsymbols\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> p1 = Point('p1')\n >>> p1.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n >>> p1.vel(N)\n 10*N.x\n+ >>> p = Point('p')\n+ >>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')\n+ >>> p.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n+ >>> p2 = Point('p2')\n+ >>> p2.set_pos(p, q*N.x)\n+ >>> p2.vel(N)\n+ (Derivative(q(t), t) + 10)*N.x\n \n \"\"\"\n \n _check_frame(frame)\n if not (frame in self._vel_dict):\n- raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'\n+ starting_node = self\n+ visited = []\n+ queue = [starting_node]\n+ req_point = None\n+ while queue: #BFS to find nearest point\n+ node = queue.pop(0)\n+ if node not in visited:\n+ visited.append(node)\n+ for neighbor, neighbor_pos in node._pos_dict.items():\n+ try:\n+ neighbor_pos.dt(frame) #Checks if pos vector is valid\n+ except ValueError:\n+ continue",
"line": 517,
"original_line": 514,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/vector/point.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nA `ValueErrror` could be returned from this for multiple reasons. I think the check you are after here is whether or not `neighbor_pos` can be expressed in the frame. I think checking `neighbor_pos.express(frame)` is the more direct check."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -126,3 +128,67 @@ def test_point_partial_velocity():\n assert p.partial_velocity(N, u1) == A.x\n assert p.partial_velocity(N, u1, u2) == (A.x, N.y)\n raises(ValueError, lambda: p.partial_velocity(A, u1))\n+\n+def test_point_vel():\n+ q1, q2 = dynamicsymbols('q1 q2')\n+ N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')\n+ S = ReferenceFrame('S')\n+ O = Point('O')\n+ Q = Point('Q')\n+ Q.set_pos(O, q1 * N.x)\n+ raises(ValueError , lambda : Q.vel(N)) #Velocity of Q is not defined\n+ O.set_vel(N, q2 * N.y)\n+ assert Q.vel(N) == Derivative(q1) * N.x + q2 * N.y # Velocity of Q using O\n+ P1 = Point('P1')\n+ P1.set_pos(O, q1 * B.x)\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P1.vel(B)) # O's velocity is defined in different frame\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P1.vel(N)) # Pos vector is defined in different frame\n+ P2 = Point('P2')\n+ P2.set_pos(P1, q2 * B.z)\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P2.vel(B)) # O's velocity is defined in different frame, and no\n+ #point in between has its velocity defined\n+ P3 = Point('P3')\n+ P3.set_pos(P2, q1 * B.x)\n+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P3.vel(B)) # O's velocity is defined in different frame, and no\n+ #point in between has its velocity defined\n+ P1.set_vel(B, 10 * q1 * B.x) #Defined P1's velocity\n+ assert P3.vel(B) == (10 * q1 + Derivative(q1)) * B.x + Derivative(q2) * B.z # Tree traversal upto P1\n+ # Vel of P3 = Vel of P1 + Calculated Vel of P2 + time derivative of pos vector\n+ P5 = Point('P5')\n+ P5.set_vel(B, q1 * B.x)\n+ P3.set_pos(P5, q2 * B.y)\n+ assert P3.vel(B) == q1 * B.x + Derivative(q2) * B.y # P5 closer in tree than P1\n+ Q1 = Point('Q1')\n+ Q1.set_vel(N, q1 * N.x)\n+ Q2 = Point('Q2')\n+ Q3 = Point('Q3')\n+ Q4 = Point('Q4')\n+ Q2.set_pos(Q1, q2 * N.x)\n+ Q3.set_pos(Q2, q1 * N.x)\n+ Q4.set_pos(Q3, q2 * N.x)\n+ assert Q4.vel(N) == (q1 + Derivative(q1) + 2 * Derivative(q2)) * N.x # Calculated velocity using\n+ # Q1, Q2, Q3\n+ Q3.set_vel(N, q1 * N.x)\n+ assert Q3.vel(N) == q1 * N.x # Outputs user defined velocity\n+ assert Q4.vel(N) == (q1 + Derivative(q2)) * N.x # If vel of one point in tree is changed the\n+ # resulting velocity is changed\n+ assert Q3.vel(N) == q1 * N.x # Automated vel calculation doesnt overwrite user defined vel\n+ #Complex Operations",
"line": null,
"original_line": 177,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_point.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhat specifically are you testing here? For a long multi-branch tree, you should be checking that the shortest path is properly selected. The code here certainly looks complex, but is it testing anything that isn't already tested above?\n\n@author:\nIn line 174 , i'm checking that that if user changes any velocity in path then that should affect the calculated velocity as calculated velocity doesn't update _vel_dict\n\n@user1:\nThis comment refers to line 177 and below.\n\n@author:\nI'll break the test cases"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -483,19 +483,47 @@ def vel(self, frame):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame, dynamicsymbols\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> p1 = Point('p1')\n >>> p1.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n >>> p1.vel(N)\n 10*N.x\n+ >>> p = Point('p')\n+ >>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')\n+ >>> p.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)\n+ >>> p2 = Point('p2')\n+ >>> p2.set_pos(p, q*N.x)\n+ >>> p2.vel(N)\n+ (Derivative(q(t), t) + 10)*N.x\n \n \"\"\"\n \n _check_frame(frame)\n if not (frame in self._vel_dict):\n- raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'\n+ visited = []\n+ queue = [self]\n+ while queue: #BFS to find nearest point\n+ node = queue.pop(0)\n+ if node not in visited:\n+ visited.append(node)\n+ for neighbor, neighbor_pos in node._pos_dict.items():\n+ try:\n+ neighbor_pos.express(frame) #Checks if pos vector is valid\n+ except ValueError:\n+ continue\n+ else:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 515,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/vector/point.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nNo need for this `else` since the `except` has a `continue`. Removing it will save you a level of indentation, which is almost always a good ideas\n\n@author:\nDone"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -56,6 +56,7 @@ def __init__(self, name):\n self._pos_dict = {}\n self._vel_dict = {}\n self._acc_dict = {}\n+ self._vel_dict_pos = {}",
"line": null,
"original_line": 59,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/vector/point.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI don't see why this new attribute is needed to solve this issue."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -471,6 +472,44 @@ def v2pt_theory(self, otherpoint, outframe, fixedframe):\n self.set_vel(outframe, v + (omega ^ dist))\n return self.vel(outframe)\n \n+ def _calc_vel(self, frame, pos_vect):\n+ # Helper Function for velocty\n+ if len(self._pos_dict) == 1:\n+ #If len of post_dict is one it implies it only has that point from which it's being called\n+ #Stops infinite recursion\n+ return False\n+ #Copies vel_dict of current point(the one through which it's called, self for this function)\n+ self._vel_dict_pos = self._vel_dict.copy()\n+ #Loop 1 for checking all points at same level in self's pos_dict(to find nearest point in Tree)\n+ for p, p_pos in self._pos_dict.items():\n+ try:\n+ p_vel = p._vel_dict[frame] #Checks if the point's velocity is defined wrt req frame, if not throws Keyerror\n+ p_pos.dt(frame) #Checks if pos vector in defined with req frame, if not throws ValueError\n+ except KeyError:\n+ continue\n+ except ValueError:\n+ continue\n+ self._vel_dict_pos[frame] = p_vel + p_pos.dt(frame) #Updates current point's copied dict\n+ return True #Returns True, this point has it's velocity defined in appropriate ref frame\n+ for p, p_pos in self._pos_dict.items():\n+ #Loop 2 for searching in next level, if not found in same level",
"line": null,
"original_line": 495,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/vector/point.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis isn't clearly if this works for a tree depth of 100 or 1000. How can two loops do the breath first search of the entire tree?"
}
] |
c57dd28b995cb4d1d35d4d11c8d199a60c93b0cd
|
diff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/point.py b/sympy/physics/vector/point.py
index ddb3a4d09265..3b6e3fe2ad80 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/vector/point.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/point.py
@@ -483,19 +483,49 @@ def vel(self, frame):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame
+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame, dynamicsymbols
>>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')
>>> p1 = Point('p1')
>>> p1.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)
>>> p1.vel(N)
10*N.x
+ Velocities will be automatically calculated if possible, otherwise a ``ValueError`` will be returned. If it is possible to calculate multiple different velocities from the relative points, the points defined most directly relative to this point will be used. In the case of inconsistent relative positions of points, incorrect velocities may be returned. It is up to the user to define prior relative positions and velocities of points in a self-consistent way.
+
+ >>> p = Point('p')
+ >>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')
+ >>> p.set_vel(N, 10 * N.x)
+ >>> p2 = Point('p2')
+ >>> p2.set_pos(p, q*N.x)
+ >>> p2.vel(N)
+ (Derivative(q(t), t) + 10)*N.x
+
"""
_check_frame(frame)
if not (frame in self._vel_dict):
- raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'
+ visited = []
+ queue = [self]
+ while queue: #BFS to find nearest point
+ node = queue.pop(0)
+ if node not in visited:
+ visited.append(node)
+ for neighbor, neighbor_pos in node._pos_dict.items():
+ try:
+ neighbor_pos.express(frame) #Checks if pos vector is valid
+ except ValueError:
+ continue
+ try :
+ neighbor_velocity = neighbor._vel_dict[frame] #Checks if point has its vel defined in req frame
+ except KeyError:
+ queue.append(neighbor)
+ continue
+ self.set_vel(frame, self.pos_from(neighbor).dt(frame) + neighbor_velocity)
+ return self._vel_dict[frame]
+ else:
+ raise ValueError('Velocity of point ' + self.name + ' has not been'
' defined in ReferenceFrame ' + frame.name)
+
return self._vel_dict[frame]
def partial_velocity(self, frame, *gen_speeds):
diff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_point.py b/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_point.py
index 052b5c3af7d8..617d0bddd8c1 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_point.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/tests/test_point.py
@@ -126,3 +126,107 @@ def test_point_partial_velocity():
assert p.partial_velocity(N, u1) == A.x
assert p.partial_velocity(N, u1, u2) == (A.x, N.y)
raises(ValueError, lambda: p.partial_velocity(A, u1))
+
+def test_point_vel(): #Basic functionality
+ q1, q2 = dynamicsymbols('q1 q2')
+ N = ReferenceFrame('N')
+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')
+ Q = Point('Q')
+ O = Point('O')
+ Q.set_pos(O, q1 * N.x)
+ raises(ValueError , lambda: Q.vel(N)) # Velocity of O in N is not defined
+ O.set_vel(N, q2 * N.y)
+ assert O.vel(N) == q2 * N.y
+ raises(ValueError , lambda : O.vel(B)) #Velocity of O is not defined in B
+
+def test_auto_point_vel():
+ t = dynamicsymbols._t
+ q1, q2 = dynamicsymbols('q1 q2')
+ N = ReferenceFrame('N')
+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')
+ O = Point('O')
+ Q = Point('Q')
+ Q.set_pos(O, q1 * N.x)
+ O.set_vel(N, q2 * N.y)
+ assert Q.vel(N) == q1.diff(t) * N.x + q2 * N.y # Velocity of Q using O
+ P1 = Point('P1')
+ P1.set_pos(O, q1 * B.x)
+ P2 = Point('P2')
+ P2.set_pos(P1, q2 * B.z)
+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P2.vel(B)) # O's velocity is defined in different frame, and no
+ #point in between has its velocity defined
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: P2.vel(N)) # Velocity of O not defined in N
+
+def test_auto_point_vel_multiple_point_path():
+ t = dynamicsymbols._t
+ q1, q2 = dynamicsymbols('q1 q2')
+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')
+ P = Point('P')
+ P.set_vel(B, q1 * B.x)
+ P1 = Point('P1')
+ P1.set_pos(P, q2 * B.y)
+ P1.set_vel(B, q1 * B.z)
+ P2 = Point('P2')
+ P2.set_pos(P1, q1 * B.z)
+ P3 = Point('P3')
+ P3.set_pos(P2, 10 * q1 * B.y)
+ assert P3.vel(B) == 10 * q1.diff(t) * B.y + (q1 + q1.diff(t)) * B.z
+
+def test_auto_vel_dont_overwrite():
+ t = dynamicsymbols._t
+ q1, q2, u1 = dynamicsymbols('q1, q2, u1')
+ N = ReferenceFrame('N')
+ P = Point('P1')
+ P.set_vel(N, u1 * N.x)
+ P1 = Point('P1')
+ P1.set_pos(P, q2 * N.y)
+ assert P1.vel(N) == q2.diff(t) * N.y + u1 * N.x
+ assert P.vel(N) == u1 * N.x
+ P1.set_vel(N, u1 * N.z)
+ assert P1.vel(N) == u1 * N.z
+
+def test_auto_point_vel_if_tree_has_vel_but_inappropriate_pos_vector():
+ q1, q2 = dynamicsymbols('q1 q2')
+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')
+ S = ReferenceFrame('S')
+ P = Point('P')
+ P.set_vel(B, q1 * B.x)
+ P1 = Point('P1')
+ P1.set_pos(P, S.y)
+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P1.vel(B)) # P1.pos_from(P) can't be expressed in B
+ raises(ValueError, lambda : P1.vel(S)) # P.vel(S) not defined
+
+def test_auto_point_vel_shortest_path():
+ t = dynamicsymbols._t
+ q1, q2, u1, u2 = dynamicsymbols('q1 q2 u1 u2')
+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')
+ P = Point('P')
+ P.set_vel(B, u1 * B.x)
+ P1 = Point('P1')
+ P1.set_pos(P, q2 * B.y)
+ P1.set_vel(B, q1 * B.z)
+ P2 = Point('P2')
+ P2.set_pos(P1, q1 * B.z)
+ P3 = Point('P3')
+ P3.set_pos(P2, 10 * q1 * B.y)
+ P4 = Point('P4')
+ P4.set_pos(P3, q1 * B.x)
+ O = Point('O')
+ O.set_vel(B, u2 * B.y)
+ O1 = Point('O1')
+ O1.set_pos(O, q2 * B.z)
+ P4.set_pos(O1, q1 * B.x + q2 * B.z)
+ assert P4.vel(B) == q1.diff(t) * B.x + u2 * B.y + 2 * q2.diff(t) * B.z
+
+def test_auto_point_vel_connected_frames():
+ t = dynamicsymbols._t
+ q, q1, q2, u = dynamicsymbols('q q1 q2 u')
+ N = ReferenceFrame('N')
+ B = ReferenceFrame('B')
+ O = Point('O')
+ O.set_vel(N, u * N.x)
+ P = Point('P')
+ P.set_pos(O, q1 * N.x + q2 * B.y)
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: P.vel(N))
+ N.orient(B, 'Axis', (q, B.x))
+ assert P.vel(N) == (u + q1.diff(t)) * N.x + q2.diff(t) * B.y - q2 * q.diff(t) * B.z
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19990@dfd9c21
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,990
|
[GSoC] Functions: Fixes limit evaluations related to uppergamma and besselk function
|
Fixes: #13571
Fixes: #14874
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
1) Adds `_eval_is_meromorphic` method and `_eval_aseries` to `class lowergamma`
2) Adds `_eval_is_meromorphic` method and `_eval_rewrite_as_tractable` method to `class uppergamma`
3) Rectifies `eval` method of `class besselk`
#### Other Comments
Regression Tests have been added.
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* functions
* Adds `_eval_is_meromorphic` method and `_eval_aseries` to `class lowergamma`
* Adds `_eval_is_meromorphic` method and `_eval_rewrite_as_tractable` method to `class uppergamma`
* Rectifies `eval` method of `class besselk`
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-08-20T07:14:07Z
|
Incorrect limit of uppergamma(n, 1) / gamma(n)
>>> from sympy import *
>>> from sympy.abc import n
>>> limit(uppergamma(n, 1) / gamma(n), n, oo)
0
The answer should be 1.
Limit x --> oo for besselk
When I try
from sympy import symbols, besselk, limit, oo
x = symbols("x", real=True)
limit(besselk(0, x), x, oo)
I obtain the following
besselk(0, oo)
instead of obtaining 0.
|
How can I help in this issue ?
|
[
{
"body": " >>> from sympy import *\r\n >>> from sympy.abc import n\r\n >>> limit(uppergamma(n, 1) / gamma(n), n, oo)\r\n 0\r\n\r\nThe answer should be 1.",
"number": 13571,
"title": "Incorrect limit of uppergamma(n, 1) / gamma(n)"
},
{
"body": "When I try\r\n\r\n from sympy import symbols, besselk, limit, oo\r\n x = symbols(\"x\", real=True)\r\n limit(besselk(0, x), x, oo)\r\n\r\nI obtain the following\r\n\r\n besselk(0, oo)\r\n\r\ninstead of obtaining 0.",
"number": 14874,
"title": "Limit x --> oo for besselk"
}
] |
ba43dda5be251e6ea9834f15e99b939fa1065670
|
{
"head_commit": "dfd9c217ddd425e9c23d3ab5c0794c930dd31833",
"head_commit_message": "Fixes limit evaluations related to uppergamma and besselk function",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py b/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py\nindex ab04eeea24cf..aba153792479 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py\n@@ -464,6 +464,8 @@ def eval(cls, nu, z):\n return S.Zero\n \n if nu.is_integer:\n+ if z is S.Infinity:\n+ return S.Zero\n if nu.could_extract_minus_sign():\n return besselk(-nu, z)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py\nindex 888a02b2e9dd..f5ef7a0f914a 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py\n@@ -364,6 +364,16 @@ def _eval_conjugate(self):\n if x not in (S.Zero, S.NegativeInfinity):\n return self.func(self.args[0].conjugate(), x.conjugate())\n \n+ def _eval_aseries(self, n, args0, x, logx):\n+ from sympy import O\n+ s, z = self.args\n+ if args0[0] is S.Infinity and not z.has(x):\n+ coeff = z**s*exp(-z)\n+ sum_expr = sum(z**k/rf(s, k + 1) for k in range(n - 1))\n+ o = O(s**(-n - 1))\n+ return coeff*sum_expr + o\n+ return super()._eval_aseries(n, args0, x, logx)\n+\n def _eval_rewrite_as_uppergamma(self, s, x, **kwargs):\n return gamma(s) - uppergamma(s, x)\n \n@@ -526,6 +536,9 @@ def _eval_conjugate(self):\n def _eval_rewrite_as_lowergamma(self, s, x, **kwargs):\n return gamma(s) - lowergamma(s, x)\n \n+ def _eval_rewrite_as_tractable(self, s, x, **kwargs):\n+ return exp(loggamma(s)) - lowergamma(s, x)\n+\n def _eval_rewrite_as_expint(self, s, x, **kwargs):\n from sympy import expint\n return expint(1 - s, x)*x**s\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py\nindex 14ceb5c1aece..b38ad111bfdc 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py\n@@ -140,6 +140,9 @@ def test_lowergamma():\n assert conjugate(lowergamma(x, 0)) == 0\n assert unchanged(conjugate, lowergamma(x, -oo))\n \n+ assert lowergamma(x, 1).series(x, oo, 3) == \\\n+ (1 + 1/(x + 1))*exp(-1)/x + O(x**(-3), (x, oo))\n+\n assert lowergamma(\n x, y).rewrite(expint) == -y**x*expint(-x + 1, y) + gamma(x)\n k = Symbol('k', integer=True)\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\nindex cca634856f93..61ed840506bc 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\n@@ -5,8 +5,8 @@\n atan, Abs, gamma, Symbol, S, pi, Integral, Rational, I,\n tan, cot, integrate, Sum, sign, Function, subfactorial, symbols,\n binomial, simplify, frac, Float, sec, zoo, fresnelc, fresnels,\n- acos, erf, erfc, erfi, LambertW, factorial, digamma, Ei, EulerGamma,\n- asin, atanh, acot, acoth, asec, acsc, cbrt)\n+ acos, erf, erfc, erfi, LambertW, factorial, digamma, uppergamma,\n+ Ei, EulerGamma, asin, atanh, acot, acoth, asec, acsc, cbrt, besselk)\n \n from sympy.calculus.util import AccumBounds\n from sympy.core.add import Add\n@@ -705,6 +705,10 @@ def test_issue_15984():\n assert limit((-x + log(exp(x) + 1))/x, x, oo, dir='-').doit() == 0\n \n \n+def test_issue_13571():\n+ assert limit(uppergamma(x, 1) / gamma(x), x, oo) == 1\n+\n+\n def test_issue_13575():\n assert limit(acos(erfi(x)), x, 1).cancel() == acos(-I*erf(I))\n \n@@ -752,6 +756,10 @@ def test_issue_14811():\n assert limit(((1 + ((S(2)/3)**(x + 1)))**(2**x))/(2**((S(4)/3)**(x - 1))), x, oo) == oo\n \n \n+def test_issue_14874():\n+ assert limit(besselk(0, x), x, oo) == 0\n+\n+\n def test_issue_16222():\n assert limit(exp(x), x, 1000000000) == exp(1000000000)\n \n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -464,6 +464,8 @@ def eval(cls, nu, z):\n return S.Zero\n \n if nu.is_integer:\n+ if z is S.Infinity:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 467,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/special/bessel.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIt is not necessary that nu be an integer, the limit at oo is 0 for all nu.\n\n@author:\nYeah, will make the required change."
}
] |
f7d6d05428df8096d4b0ab56a0c4037067894ff8
|
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py b/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py
index ab04eeea24cf..37d99648d2c1 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py
@@ -460,7 +460,7 @@ def eval(cls, nu, z):
return S.ComplexInfinity
elif re(nu).is_zero:
return S.NaN
- if im(z) is S.Infinity or im(z) is S.NegativeInfinity:
+ if z in (S.Infinity, I*S.Infinity, I*S.NegativeInfinity):
return S.Zero
if nu.is_integer:
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py
index 888a02b2e9dd..baa6a5a5ac28 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py
@@ -364,6 +364,33 @@ def _eval_conjugate(self):
if x not in (S.Zero, S.NegativeInfinity):
return self.func(self.args[0].conjugate(), x.conjugate())
+ def _eval_is_meromorphic(self, x, a):
+ # By https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Incomplete_gamma_function#Holomorphic_extension,
+ # lowergamma(s, z) = z**s*gamma(s)*gammastar(s, z),
+ # where gammastar(s, z) is holomorphic for all s and z.
+ # Hence the singularities of lowergamma are z = 0 (branch
+ # point) and nonpositive integer values of s (poles of gamma(s)).
+ s, z = self.args
+ args_merom = fuzzy_and([z._eval_is_meromorphic(x, a),
+ s._eval_is_meromorphic(x, a)])
+ if not args_merom:
+ return args_merom
+ z0 = z.subs(x, a)
+ if s.is_integer:
+ return fuzzy_and([s.is_positive, z0.is_finite])
+ s0 = s.subs(x, a)
+ return fuzzy_and([s0.is_finite, z0.is_finite, fuzzy_not(z0.is_zero)])
+
+ def _eval_aseries(self, n, args0, x, logx):
+ from sympy import O
+ s, z = self.args
+ if args0[0] is S.Infinity and not z.has(x):
+ coeff = z**s*exp(-z)
+ sum_expr = sum(z**k/rf(s, k + 1) for k in range(n - 1))
+ o = O(z**s*s**(-n))
+ return coeff*sum_expr + o
+ return super()._eval_aseries(n, args0, x, logx)
+
def _eval_rewrite_as_uppergamma(self, s, x, **kwargs):
return gamma(s) - uppergamma(s, x)
@@ -523,9 +550,15 @@ def _eval_conjugate(self):
if not z in (S.Zero, S.NegativeInfinity):
return self.func(self.args[0].conjugate(), z.conjugate())
+ def _eval_is_meromorphic(self, x, a):
+ return lowergamma._eval_is_meromorphic(self, x, a)
+
def _eval_rewrite_as_lowergamma(self, s, x, **kwargs):
return gamma(s) - lowergamma(s, x)
+ def _eval_rewrite_as_tractable(self, s, x, **kwargs):
+ return exp(loggamma(s)) - lowergamma(s, x)
+
def _eval_rewrite_as_expint(self, s, x, **kwargs):
from sympy import expint
return expint(1 - s, x)*x**s
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py
index 14ceb5c1aece..68d883fdaebc 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/tests/test_gamma_functions.py
@@ -140,6 +140,28 @@ def test_lowergamma():
assert conjugate(lowergamma(x, 0)) == 0
assert unchanged(conjugate, lowergamma(x, -oo))
+ assert lowergamma(0, x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(S(1)/3, x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(1, x, evaluate=False)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == True
+ assert lowergamma(x, x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(x + 1, x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(1/x, x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(0, x + 1)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(S(1)/3, x + 1)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == True
+ assert lowergamma(1, x + 1, evaluate=False)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == True
+ assert lowergamma(x, x + 1)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == True
+ assert lowergamma(x + 1, x + 1)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == True
+ assert lowergamma(1/x, x + 1)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(0, 1/x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(S(1)/3, 1/x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(1, 1/x, evaluate=False)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(x, 1/x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(x + 1, 1/x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+ assert lowergamma(1/x, 1/x)._eval_is_meromorphic(x, 0) == False
+
+ assert lowergamma(x, 2).series(x, oo, 3) == \
+ 2**x*(1 + 2/(x + 1))*exp(-2)/x + O(exp(x*log(2))/x**3, (x, oo))
+
assert lowergamma(
x, y).rewrite(expint) == -y**x*expint(-x + 1, y) + gamma(x)
k = Symbol('k', integer=True)
diff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
index cca634856f93..61ed840506bc 100644
--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
@@ -5,8 +5,8 @@
atan, Abs, gamma, Symbol, S, pi, Integral, Rational, I,
tan, cot, integrate, Sum, sign, Function, subfactorial, symbols,
binomial, simplify, frac, Float, sec, zoo, fresnelc, fresnels,
- acos, erf, erfc, erfi, LambertW, factorial, digamma, Ei, EulerGamma,
- asin, atanh, acot, acoth, asec, acsc, cbrt)
+ acos, erf, erfc, erfi, LambertW, factorial, digamma, uppergamma,
+ Ei, EulerGamma, asin, atanh, acot, acoth, asec, acsc, cbrt, besselk)
from sympy.calculus.util import AccumBounds
from sympy.core.add import Add
@@ -705,6 +705,10 @@ def test_issue_15984():
assert limit((-x + log(exp(x) + 1))/x, x, oo, dir='-').doit() == 0
+def test_issue_13571():
+ assert limit(uppergamma(x, 1) / gamma(x), x, oo) == 1
+
+
def test_issue_13575():
assert limit(acos(erfi(x)), x, 1).cancel() == acos(-I*erf(I))
@@ -752,6 +756,10 @@ def test_issue_14811():
assert limit(((1 + ((S(2)/3)**(x + 1)))**(2**x))/(2**((S(4)/3)**(x - 1))), x, oo) == oo
+def test_issue_14874():
+ assert limit(besselk(0, x), x, oo) == 0
+
+
def test_issue_16222():
assert limit(exp(x), x, 1000000000) == exp(1000000000)
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-20190@3bd28f7
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 20,190
|
Fix for fundamental matrix of markov chains
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #20189
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
I have updated ``` fundamental_matrix()``` function so that we can now calculate the fundamental matrix for regular markov chains.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* stats
* added support for fundamental matrix for regular markov chains
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-10-02T19:56:43Z
|
Unable to find fundamental matrix for regular markov chains
Currently, it is not possible to calculate the fundamental matrix for regular markov chains as of now ``` fundamental_matrix()``` was only implemented for the absorbing Markov chains.
For example
```python
>>> T = Matrix([[0.5, 0.25, 0.25], [0.5, 0, 0.5], [0.25, 0.25, 0.5]])
>>> Y = DiscreteMarkovChain("Y", [0, 1, 2], T)
>>> Y.is_regular()
True
>>> Y.fundamental_matrix()
DiscreteMarkovChain(Y, FiniteSet(0, 1, 2), Matrix([
[ 0.5, 0.25, 0.25],
[ 0.5, 0, 0.5],
[0.25, 0.25, 0.5]]))
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-5-bd1859c21b86> in <module>
----> 1 Y.fundamental_matrix()
~/project/sympy(main)/sympy/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py in fundamental_matrix(self)
638 I = eye(Q.shape[0])
639 if (I - Q).det() == 0:
--> 640 raise ValueError("Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.")
641 return ImmutableMatrix((I - Q).inv().tolist())
642
ValueError: Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.
```
But correct answer should be
```
Matrix([
[ 1.14666666666667, 0.04, -0.186666666666667],
[ 0.08, 0.84, 0.0799999999999999],
[-0.186666666666667, 0.04, 1.14666666666667]])
```
|
[
{
"body": "Currently, it is not possible to calculate the fundamental matrix for regular markov chains as of now ``` fundamental_matrix()``` was only implemented for the absorbing Markov chains. \r\nFor example\r\n```python\r\n>>> T = Matrix([[0.5, 0.25, 0.25], [0.5, 0, 0.5], [0.25, 0.25, 0.5]])\r\n>>> Y = DiscreteMarkovChain(\"Y\", [0, 1, 2], T)\r\n>>> Y.is_regular()\r\nTrue\r\n>>> Y.fundamental_matrix()\r\nDiscreteMarkovChain(Y, FiniteSet(0, 1, 2), Matrix([\r\n[ 0.5, 0.25, 0.25],\r\n[ 0.5, 0, 0.5],\r\n[0.25, 0.25, 0.5]]))\r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nValueError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n<ipython-input-5-bd1859c21b86> in <module>\r\n----> 1 Y.fundamental_matrix()\r\n\r\n~/project/sympy(main)/sympy/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py in fundamental_matrix(self)\r\n 638 I = eye(Q.shape[0])\r\n 639 if (I - Q).det() == 0:\r\n--> 640 raise ValueError(\"Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.\")\r\n 641 return ImmutableMatrix((I - Q).inv().tolist())\r\n 642 \r\n\r\nValueError: Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.\r\n```\r\nBut correct answer should be\r\n``` \r\nMatrix([\r\n[ 1.14666666666667, 0.04, -0.186666666666667],\r\n[ 0.08, 0.84, 0.0799999999999999],\r\n[-0.186666666666667, 0.04, 1.14666666666667]])\r\n```",
"number": 20189,
"title": "Unable to find fundamental matrix for regular markov chains"
}
] |
1e5d400c948b85647f953abcdb87457b7bc53ff7
|
{
"head_commit": "3bd28f7528b163cacb9033d02fbf6e8e76fd2570",
"head_commit_message": "added support for fundamental matrix for regular markov chains",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\nindex 0e84402c3964..8775b0c1e497 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n@@ -846,9 +846,16 @@ def fundamental_matrix(self):\n if Q == None:\n return None\n I = eye(Q.shape[0])\n- if (I - Q).det() == 0:\n- raise ValueError(\"Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.\")\n- return ImmutableMatrix((I - Q).inv().tolist())\n+ if (self.is_absorbing_chain()):\n+ if (I - Q).det() == 0:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.\")\n+ return ImmutableMatrix((I - Q).inv().tolist())\n+ else:\n+ w = self.fixed_row_vector()\n+ W = Matrix([list(w) for i in range(0, Q.shape[0])])\n+ if (I - Q + W).det() == 0:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.\")\n+ return ImmutableMatrix((I - Q + W).inv().tolist())\n \n def absorbing_probabilities(self):\n \"\"\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\nindex 2d621e4901ee..20b6da78513d 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\n@@ -123,7 +123,6 @@ def test_DiscreteMarkovChain():\n Y2 = DiscreteMarkovChain('Y', trans_probs=TO2)\n Y3 = DiscreteMarkovChain('Y', trans_probs=TO3)\n assert Y3._transient2absorbing() == None\n- raises (ValueError, lambda: Y3.fundamental_matrix())\n assert Y2.is_absorbing_chain() == True\n assert Y3.is_absorbing_chain() == False\n TO4 = Matrix([[Rational(1, 5), Rational(2, 5), Rational(2, 5)], [Rational(1, 10), S.Half, Rational(2, 5)], [Rational(3, 5), Rational(3, 10), Rational(1, 10)]])\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -846,9 +846,16 @@ def fundamental_matrix(self):\n if Q == None:\n return None\n I = eye(Q.shape[0])\n- if (I - Q).det() == 0:\n- raise ValueError(\"Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.\")\n- return ImmutableMatrix((I - Q).inv().tolist())\n+ if (self.is_absorbing_chain()):\n+ if (I - Q).det() == 0:\n+ raise ValueError(\"Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.\")\n+ return ImmutableMatrix((I - Q).inv().tolist())",
"line": null,
"original_line": 852,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nhave you tried `(I - Q).inv().as_immutable()`?\n\n@author:\nI am not familiar with the matrix module so can you please tell what this `as_immutable` function does exactly.\r\nI tried modified my function by using the above lines, and it gives the same output and also passed all the test\n\n@user2:\nThe changes you have made may still not work for chains which are both absorbing and regular. What should be done in that case? For this patch, absorbing chain will be preferred and even if the regular chain property is true, `ValueError` will be raised if (I - Q)^-1 doesn't exist.\n\n@user2:\nThe shape of W may not always be the same as I and Q. \r\n```python\r\n____________________________________________________ sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py:test_DiscreteMarkovChain _____________________________________________________\r\nTraceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\", line 140, in test_DiscreteMarkovChain\r\n assert Y6.fundamental_matrix() == ImmutableMatrix([[Rational(3, 2), S.One, S.Half], [S.One, S(2), S.One], [S.Half, S.One, Rational(3, 2)]])\r\n File \"/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\", line 857, in fundamental_matrix\r\n if (I - Q + W).det() == 0:\r\n File \"/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/core/decorators.py\", line 136, in binary_op_wrapper\r\n return f(self)\r\n File \"/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/core/decorators.py\", line 137, in binary_op_wrapper\r\n return func(self, other)\r\n File \"/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/matrices/common.py\", line 2779, in __radd__\r\n return self + other\r\n File \"/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/core/decorators.py\", line 137, in binary_op_wrapper\r\n return func(self, other)\r\n File \"/home/czgdp1807ssd/sympy_project/sympy/sympy/matrices/common.py\", line 2545, in __add__\r\n self.shape, other.shape))\r\nsympy.matrices.common.ShapeError: Matrix size mismatch: (3, 5) + (3, 3)\r\n```\n\n@author:\n> The changes you have made may still not work for chains which are both absorbing and regular. What should be done in that case?\r\n\r\nThis case is not possible as chains cannot be absorbing and regular at the same time as regular matrix is a subset of ergodic chains, and also by the definition of regular chains, for some power of transition matrix it only has positive elements. \r\n\r\nIf any example is there of this type of chains then we should add a new condition to tackle it.\r\n\r\n\n\n@author:\n> The shape of W may not always be the same as I and Q.\r\n\r\nWhat I thought regarding the shape of W is that as this is for regular chains so it will have no absorbing state, so the size of W is just the sum of all the transient and recurrent state of the chains which is the shape of Q.\r\n\r\nI have explicitly formed a W matrix from a fixed row vector just by repeating. Is there any other way of using only a fixed row vector to calculate the output i.e. something like numpy broadcasting feature?\n\n@user2:\nSo, I think there shouldn't be any problem in keeping both the definitions in a single function as with any chain only one will be used? Or is there any example of a chain which is both ergodic and absorbing, though I don't think so that there should be one but in case. \n\n@user3:\nThere are chains that are neither absorbing nor ergodic. \n```\n0 1 0\n1 0 0\n1 0 0\n```\n\nBut for all possible chains, the typical definition of the fundamental matrix is needed. This is used to calculate first exit probabilities, limiting transient->recurrent probabilities, and expected number of steps within transient states.\n\nThere are cases where there are no transient states (an ergodic chain is one such instance). In this case the above 3 calculations are fairly trivial because they contain 0x0 matrices in their calculations. However, I do not believe a special exception for ergodic chains is needed (especially since there are other chains that are not ergodic that also have no transient states). I think a different function is needed for this different definition. \n\nThis new definition is applicable only for ergodic chains while the typical definition is needed for all chains. \n\n@user4:\n> I think there shouldn't be any problem in keeping both the definitions in a single function\r\n\r\nIs it useful to do that though? If you were going to use the matrix for something is there a use case where either definition would be suitable?\n\n@user2:\nAt most, only one definition will be used for an object, so I think, there won't be much ambiguity. The use case depends on the user, they can interpret the fundamental matrix in whatever way they want depending upon the type of the chain. If the chain is neither absorbing nor ergodic value error should be raised. It's not a good idea IMHO to change the public APIs for this task since things are very deterministic and involve no or very little ambiguity."
}
] |
f28f833171646e00b09f1dc3f186f6d7a7a6e6ee
|
diff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
index 0de4d3eeaa63..fdac9cb8cc1f 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
@@ -1055,13 +1055,32 @@ def communication_classes(self) -> tList[tTuple[tList[Basic], Boolean, Integer]]
return sympify(list(zip(classes, recurrence, periods)))
def fundamental_matrix(self):
+ """
+ Each entry fundamental matrix can be interpreted as
+ the expected number of times the chains is in state j
+ if it started in state i.
+
+ References
+ ==========
+
+ .. [1] https://lips.cs.princeton.edu/the-fundamental-matrix-of-a-finite-markov-chain/
+
+ """
_, _, _, Q = self.decompose()
- if Q == None:
- return None
- I = eye(Q.shape[0])
- if Q.shape[0]*Q.shape[1] == 0 or (I - Q).det() == 0:
- raise ValueError("Fundamental matrix doesn't exists.")
- return ImmutableMatrix((I - Q).inv().tolist())
+
+ if Q.shape[0] > 0: # if non-ergodic
+ I = eye(Q.shape[0])
+ if (I - Q).det() == 0:
+ raise ValueError("The fundamental matrix doesn't exist.")
+ return (I - Q).inv().as_immutable()
+ else: # if ergodic
+ P = self.transition_probabilities
+ I = eye(P.shape[0])
+ w = self.fixed_row_vector()
+ W = Matrix([list(w) for i in range(0, P.shape[0])])
+ if (I - P + W).det() == 0:
+ raise ValueError("The fundamental matrix doesn't exist.")
+ return (I - P + W).inv().as_immutable()
def absorbing_probabilities(self):
"""
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
index 24ae6db694c7..50511d9dea7a 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ def test_DiscreteMarkovChain():
TO3 = Matrix([[Rational(1, 4), Rational(3, 4), 0],[Rational(1, 3), Rational(1, 3), Rational(1, 3)], [0, Rational(1, 4), Rational(3, 4)]])
Y2 = DiscreteMarkovChain('Y', trans_probs=TO2)
Y3 = DiscreteMarkovChain('Y', trans_probs=TO3)
- raises (ValueError, lambda: Y3.fundamental_matrix())
+ assert Y3.fundamental_matrix() == ImmutableMatrix([[176, 81, -132], [36, 141, -52], [-44, -39, 208]])/125
assert Y2.is_absorbing_chain() == True
assert Y3.is_absorbing_chain() == False
assert Y2.canonical_form() == ([0, 1, 2], TO2)
@@ -141,6 +141,12 @@ def test_DiscreteMarkovChain():
Y6 = DiscreteMarkovChain('Y', trans_probs=TO6)
assert Y6.fundamental_matrix() == ImmutableMatrix([[Rational(3, 2), S.One, S.Half], [S.One, S(2), S.One], [S.Half, S.One, Rational(3, 2)]])
assert Y6.absorbing_probabilities() == ImmutableMatrix([[Rational(3, 4), Rational(1, 4)], [S.Half, S.Half], [Rational(1, 4), Rational(3, 4)]])
+ TO7 = Matrix([[Rational(1, 2), Rational(1, 4), Rational(1, 4)], [Rational(1, 2), 0, Rational(1, 2)], [Rational(1, 4), Rational(1, 4), Rational(1, 2)]])
+ Y7 = DiscreteMarkovChain('Y', trans_probs=TO7)
+ assert Y7.is_absorbing_chain() == False
+ assert Y7.fundamental_matrix() == ImmutableDenseMatrix([[Rational(86, 75), Rational(1, 25), Rational(-14, 75)],
+ [Rational(2, 25), Rational(21, 25), Rational(2, 25)],
+ [Rational(-14, 75), Rational(1, 25), Rational(86, 75)]])
# test for zero-sized matrix functionality
X = DiscreteMarkovChain('X', trans_probs=Matrix([[]]))
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-19819@b3c369f
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,819
|
[GSoC]Change return type of `P` and `E` with `evaluate=False`
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19798
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Change in the return types of P and E with `evaluate=False`. Examples:
```py
>>> from sympy.stats import *
>>> X = Normal('X',1,2)
>>> P(X > 1, evaluate=False)
Probability(X > 1)
>>> E(X, evaluate=False)
Expectation(X)
```
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* stats
* Change in return type of `P` and `E` with `evaluate=False`. With `evaluate=False`, `P` and `E` are made to return `Probability` and `Expectation` object respectively.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
ping @czgdp1807 @Upabjojr @jmig5776
|
2020-07-22T11:00:18Z
|
stats: Should `P(X > 1, evaluate=False)` return `Probability(X > 1)` or unevaluated Integral?
On current master, `P(X > 1, evaluate=False)` produces unevaluated Integral. However, according to the discussions on Gitter, it was suggested by @czgdp1807 that we should make `P(X > 1, evaluate=False)` to return a Symbolic probability object as `Probability(X > 1)`. Symbolic `Probability` class has been added with `doit` method recently and so, `P(X > 1, evaluate=True)` should return `Probability(X > 1).doit()`.
More clearly the current scenario is:
```py
In [1]: from sympy.stats import *
In [2]: X = Normal('X', 1, 2)
In [3]: P(X > 1, evaluate=False)
Out[3]:
∞
⌠
⎮ 2
⎮ -(z - 1)
⎮ ──────────
⎮ 8
⎮ √2⋅ℯ
⎮ ────────────── dz
⎮ 4⋅√π
⌡
1
```
Proposal to change the behavior to:
```py
In [5]: P(X > 1, evaluate=False)
Out[5]: Probability(X > 1)
```
ping @czgdp1807 @Upabjojr
|
What about:
1. `P(X > 1, evaluate=False)` ==> return `Probability` object,
2. `P(X > 1).doit(evaluate=False)` ==> return unevaluated integral.
Agreed with @Upabjojr , seems like a good idea and will also help in making APIs unambiguous.
> `P(X > 1).doit(evaluate=False)` ==> return unevaluated integral.
Do you mean `Probability(X > 1).doit(evaluate=False)` ==> return unevaluated integral ?
as `P(X > 1)` will already be evaluated(as `evaluate=True` is by default) in `P`
I think he meant to say what you are suggesting. What `doit` does is a different issue, what we need right now is `evaluate=False` to return `Probability(X > 1)`. Output of `doit` depends on how much the input can be processed before giving results and return type is variable so we cannot do much about it.
Maybe we don't need to deal with `.doit()` at all. We already have `Probability(X > 1).rewrite(Integral)`... which is supposed to return the `Integral` object.
Maybe `P(X > 1, evaluate=False)` should raise a warning about the change.
|
[
{
"body": "On current master, `P(X > 1, evaluate=False)` produces unevaluated Integral. However, according to the discussions on Gitter, it was suggested by @czgdp1807 that we should make `P(X > 1, evaluate=False)` to return a Symbolic probability object as `Probability(X > 1)`. Symbolic `Probability` class has been added with `doit` method recently and so, `P(X > 1, evaluate=True)` should return `Probability(X > 1).doit()`.\r\nMore clearly the current scenario is:\r\n```py\r\nIn [1]: from sympy.stats import *\r\n\r\nIn [2]: X = Normal('X', 1, 2)\r\n\r\nIn [3]: P(X > 1, evaluate=False)\r\nOut[3]:\r\n\r\n∞\r\n⌠\r\n⎮ 2\r\n⎮ -(z - 1)\r\n⎮ ──────────\r\n⎮ 8\r\n⎮ √2⋅ℯ\r\n⎮ ────────────── dz\r\n⎮ 4⋅√π\r\n⌡\r\n1\r\n\r\n```\r\nProposal to change the behavior to:\r\n\r\n```py\r\nIn [5]: P(X > 1, evaluate=False)\r\nOut[5]: Probability(X > 1)\r\n```\r\nping @czgdp1807 @Upabjojr ",
"number": 19798,
"title": "stats: Should `P(X > 1, evaluate=False)` return `Probability(X > 1)` or unevaluated Integral?"
}
] |
7389f1959f56e416a9f6c8060a4cbf5d98f830a8
|
{
"head_commit": "b3c369fb2e018b39c7871edacffe2ae5e173394b",
"head_commit_message": "remove import Integral",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/stats/rv.py b/sympy/stats/rv.py\nindex 2d2c6f67ada1..b84c6a895b5c 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/rv.py\n@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@\n \n from sympy import (Basic, S, Expr, Symbol, Tuple, And, Add, Eq, lambdify, Or,\n Equality, Lambda, sympify, Dummy, Ne, KroneckerDelta,\n- DiracDelta, Mul, Indexed, MatrixSymbol, Function, Integral)\n+ DiracDelta, Mul, Indexed, MatrixSymbol, Function)\n from sympy.core.relational import Relational\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n from sympy.sets.sets import FiniteSet, ProductSet, Intersection\n@@ -757,7 +757,11 @@ def expectation(expr, condition=None, numsamples=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Expectation\n if evaluate:\n return Expectation(expr, condition).doit(**kwargs)\n- return Expectation(expr, condition).rewrite(Integral) # will return Sum in case of discrete RV\n+ message = (\"Using `evaluate=False` now returns `Expectation` object \"\n+ \"since version 1.7. If you want unevaluated Integral/Sum use \"\n+ \"`E(expr, condition, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)`\")\n+ warnings.warn(filldedent(message))\n+ return Expectation(expr, condition)\n \n \n def probability(condition, given_condition=None, numsamples=None,\n@@ -796,7 +800,11 @@ def probability(condition, given_condition=None, numsamples=None,\n from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability\n if evaluate:\n return Probability(condition, given_condition).doit(**kwargs)\n- return Probability(condition, given_condition).rewrite(Integral) # will return Sum in case of discrete RV\n+ message = (\"Using `evaluate=False` returns `Probability` object since version 1.7. \"\n+ \"If you want unevaluated Integral/Sum use \"\n+ \"`P(condition, given_condition, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)`\")\n+ warnings.warn(filldedent(message))\n+ return Probability(condition, given_condition)\n \n \n class Density(Basic):\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_compound_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_compound_rv.py\nindex 5b32abeb1e45..3b88bb1a1344 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_compound_rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_compound_rv.py\n@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@\n from sympy.stats.crv_types import NormalDistribution\n from sympy.stats.drv_types import PoissonDistribution\n from sympy.stats.frv_types import BernoulliDistribution\n-from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n+from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, ignore_warnings\n from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import MultivariateNormalDistribution\n \n \n@@ -66,7 +66,8 @@ def test_unevaluated_CompoundDist():\n expre = Integral(Piecewise((_k*exp(S(3)/4 - _k/4)/8, 2*Abs(arg(_k - 3)) <= pi/2),\n (sqrt(2)*_k*Integral(exp(-(_k**4 + 16*(_k - 3)**2)/(32*_k**2)),\n (_k, 0, oo))/(32*sqrt(pi)), True)), (_k, -oo, oo))\n- assert (E(X, evaluate=False).simplify()).dummy_eq(expre.simplify())\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ assert (E(X, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).simplify()).dummy_eq(expre.simplify())\n \n \n def test_Compound_Distribution():\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py\nindex 1e249c68eaa8..a978c17e2f95 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py\n@@ -25,6 +25,7 @@\n from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import MultivariateLaplaceDistribution, MultivariateNormalDistribution\n from sympy.stats.crv import SingleContinuousPSpace, SingleContinuousDomain\n from sympy.stats.compound_rv import CompoundPSpace\n+from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, XFAIL, slow, skip, ignore_warnings\n from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn\n \n@@ -643,12 +644,12 @@ def test_exponential():\n _z = Dummy('_z')\n b = SingleContinuousPSpace(x, ExponentialDistribution(2))\n \n- expected1 = Integral(2*exp(-2*_z), (_z, 3, oo))\n- assert b.probability(x > 3, evaluate=False).dummy_eq(expected1) is True\n-\n- expected2 = Integral(2*exp(-2*_z), (_z, 0, 4))\n- assert b.probability(x < 4, evaluate=False).dummy_eq(expected2) is True\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ expected1 = Integral(2*exp(-2*_z), (_z, 3, oo))\n+ assert b.probability(x > 3, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).dummy_eq(expected1)\n \n+ expected2 = Integral(2*exp(-2*_z), (_z, 0, 4))\n+ assert b.probability(x < 4, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).dummy_eq(expected2)\n Y = Exponential('y', 2*rate)\n assert coskewness(X, X, X) == skewness(X)\n assert coskewness(X, Y + rate*X, Y + 2*rate*X) == \\\n@@ -1342,21 +1343,23 @@ def test_input_value_assertions():\n \n def test_unevaluated():\n X = Normal('x', 0, 1)\n- assert str(E(X, evaluate=False)) == (\"Integral(sqrt(2)*x*exp(-x**2/2)/\"\n- \"(2*sqrt(pi)), (x, -oo, oo))\")\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ assert str(E(X, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)) == (\"Integral(sqrt(2)*x*exp(-x**2/2)/\"\n+ \"(2*sqrt(pi)), (x, -oo, oo))\")\n \n- assert str(E(X + 1, evaluate=False)) == (\"Integral(sqrt(2)*x*exp(-x**2/2)/\"\n- \"(2*sqrt(pi)), (x, -oo, oo)) + 1\")\n+ assert str(E(X + 1, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)) == (\"Integral(sqrt(2)*x*exp(-x**2/2)/\"\n+ \"(2*sqrt(pi)), (x, -oo, oo)) + 1\")\n \n- assert str(P(X > 0, evaluate=False)) == (\"Integral(sqrt(2)*exp(-_z**2/2)/\"\n- \"(2*sqrt(pi)), (_z, 0, oo))\")\n+ assert str(P(X > 0, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)) == (\"Integral(sqrt(2)*exp(-_z**2/2)/\"\n+ \"(2*sqrt(pi)), (_z, 0, oo))\")\n \n- assert P(X > 0, X**2 < 1, evaluate=False) == S.Half\n+ assert P(X > 0, X**2 < 1) == S.Half\n \n \n def test_probability_unevaluated():\n T = Normal('T', 30, 3)\n- assert type(P(T > 33, evaluate=False)) == Integral\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ assert type(P(T > 33, evaluate=False)) == Probability\n \n \n def test_density_unevaluated():\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_discrete_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_discrete_rv.py\nindex b03b67c4686b..1c4e94070b29 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_discrete_rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_discrete_rv.py\n@@ -15,6 +15,7 @@\n from sympy.stats.rv import sample\n from sympy.testing.pytest import slow, nocache_fail, raises, skip, ignore_warnings\n from sympy.external import import_module\n+from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Expectation\n \n x = Symbol('x')\n \n@@ -33,8 +34,9 @@ def test_Poisson():\n assert E(x) == l\n assert variance(x) == l\n assert density(x) == PoissonDistribution(l)\n- assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Sum)\n- assert isinstance(E(2*x, evaluate=False), Sum)\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Expectation)\n+ assert isinstance(E(2*x, evaluate=False), Expectation)\n # issue 8248\n assert x.pspace.compute_expectation(1) == 1\n \n@@ -82,7 +84,8 @@ def test_Logarithmic():\n assert E(x) == -p / ((1 - p) * log(1 - p))\n assert variance(x) == -1/log(2)**2 + 2/log(2)\n assert E(2*x**2 + 3*x + 4) == 4 + 7 / log(2)\n- assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Sum)\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Expectation)\n \n \n @nocache_fail\n@@ -94,7 +97,8 @@ def test_negative_binomial():\n # This hangs when run with the cache disabled:\n assert variance(x) == p*r / (1-p)**2\n assert E(x**5 + 2*x + 3) == Rational(9207, 4)\n- assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Sum)\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Expectation)\n \n \n def test_skellam():\n@@ -121,7 +125,8 @@ def test_yule_simon():\n x = YuleSimon('x', rho)\n assert simplify(E(x)) == rho / (rho - 1)\n assert simplify(variance(x)) == rho**2 / ((rho - 1)**2 * (rho - 2))\n- assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Sum)\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Expectation)\n # To test the cdf function\n assert cdf(x)(x) == Piecewise((-beta(floor(x), 4)*floor(x) + 1, x >= 1), (0, True))\n \n@@ -272,7 +277,8 @@ def test_product_spaces():\n #assert str(P(X1 + X2 < 3, evaluate=False)) == \"\"\"Sum(Piecewise((2**(X2 - n - 2)*(2/3)**(X2 - 1)/6, \"\"\"\\\n # + \"\"\"(-X2 + n + 3 >= 1) & (-X2 + n + 3 < oo)), (0, True)), (X2, 1, oo), (n, -oo, -1))\"\"\"\n n = Dummy('n')\n- assert P(X1 + X2 < 3, evaluate=False).dummy_eq(Sum(Piecewise((2**(-n)/4,\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ assert P(X1 + X2 < 3, evaluate=False).rewrite(Sum).dummy_eq(Sum(Piecewise((2**(-n)/4,\n n + 2 >= 1), (0, True)), (n, -oo, -1))/3)\n #assert str(P(X1 + X2 > 3)) == \"\"\"Sum(Piecewise((2**(X2 - n - 2)*(2/3)**(X2 - 1)/6, \"\"\" +\\\n # \"\"\"(-X2 + n + 3 >= 1) & (-X2 + n + 3 < oo)), (0, True)), (X2, 1, oo), (n, 1, oo))\"\"\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_mix.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_mix.py\nindex 9cbd336646b5..b2686f26093e 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_mix.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_mix.py\n@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@\n from sympy import (Symbol, Eq, Ne, simplify, sqrt, exp, pi, symbols,\n Piecewise, factorial, gamma, IndexedBase, Add, Pow, Mul,\n- Indexed, Integer)\n+ Indexed, Integer, Integral)\n from sympy.functions.elementary.piecewise import ExprCondPair\n from sympy.stats import (Poisson, Beta, Exponential, P,\n Multinomial, MultivariateBeta)\n@@ -9,6 +9,7 @@\n from sympy.stats.compound_rv import CompoundPSpace, CompoundDistribution\n from sympy.stats.joint_rv import MarginalDistribution\n from sympy.stats.rv import pspace, density\n+from sympy.testing.pytest import ignore_warnings\n \n def test_density():\n x = Symbol('x')\n@@ -58,7 +59,8 @@ def test_mix_expression():\n Y, E = Poisson('Y', 1), Exponential('E', 1)\n assert P(Eq(Y + E, 1)) == 0\n assert P(Ne(Y + E, 2)) == 1\n- assert str(P(E + Y < 2, evaluate=False)) == \"\"\"Integral(Sum(exp(-1)*Integral\"\"\"\\\n-+\"\"\"(exp(-E)*DiracDelta(-_z + E + Y - 2), (E, 0, oo))/factorial(Y), (Y, 0, oo)), (_z, -oo, 0))\"\"\"\n- assert str(P(E + Y > 2, evaluate=False)) == \"\"\"Integral(Sum(exp(-1)*Integral\"\"\"\\\n-+\"\"\"(exp(-E)*DiracDelta(-_z + E + Y - 2), (E, 0, oo))/factorial(Y), (Y, 0, oo)), (_z, 0, oo))\"\"\"\n+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):\n+ assert str(P(E + Y < 2, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)) == \"\"\"Integral(Sum(exp(-1)*Integral\"\"\"\\\n+ +\"\"\"(exp(-E)*DiracDelta(-_z + E + Y - 2), (E, 0, oo))/factorial(Y), (Y, 0, oo)), (_z, -oo, 0))\"\"\"\n+ assert str(P(E + Y > 2, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)) == \"\"\"Integral(Sum(exp(-1)*Integral\"\"\"\\\n+ +\"\"\"(exp(-E)*DiracDelta(-_z + E + Y - 2), (E, 0, oo))/factorial(Y), (Y, 0, oo)), (_z, 0, oo))\"\"\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\nindex f4ff19a0e14d..a3c281c92c65 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py\n@@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ def test_ContinuousMarkovChain():\n assert C2.transition_probabilities(A)(t) == Matrix([[S.Half + exp(-2*t)/2, S.Half - exp(-2*t)/2, 0],\n [S.Half - exp(-2*t)/2, S.Half + exp(-2*t)/2, 0],\n [S.Half - exp(-t) + exp(-2*t)/2, S.Half - exp(-2*t)/2, exp(-t)]])\n- assert P(Eq(C2(1), 1), Eq(C2(0), 1), evaluate=False) == Probability(Eq(C2(1), 1))\n+ assert P(Eq(C2(1), 1), Eq(C2(0), 1), evaluate=False) == Probability(Eq(C2(1), 1), Eq(C2(0), 1))\n assert P(Eq(C2(1), 1), Eq(C2(0), 1)) == exp(-2)/2 + S.Half\n assert P(Eq(C2(1), 0) & Eq(C2(2), 1) & Eq(C2(3), 1),\n Eq(P(Eq(C2(1), 0)), S.Half)) == (Rational(1, 4) - exp(-2)/4)*(exp(-2)/2 + S.Half)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -757,7 +757,11 @@ def expectation(expr, condition=None, numsamples=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Expectation\n if evaluate:\n return Expectation(expr, condition).doit(**kwargs)\n- return Expectation(expr, condition).rewrite(Integral) # will return Sum in case of discrete RV\n+ message = (\"Using `evaluate=False` now returns `Expectation` object \"\n+ \"since version 1.7. If you want unevaluated Integral/Sum use \"\n+ \"`E(expr, condition, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)`\")",
"line": null,
"original_line": 762,
"original_start_line": 760,
"path": "sympy/stats/rv.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n message = (\"Since version 1.7, using `evaluate=False` returns `Expectation` object. \"\r\n \"If you want unevaluated Integral/Sum use \"\r\n \"`E(expr, condition, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)`\")\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -796,7 +800,11 @@ def probability(condition, given_condition=None, numsamples=None,\n from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability\n if evaluate:\n return Probability(condition, given_condition).doit(**kwargs)\n- return Probability(condition, given_condition).rewrite(Integral) # will return Sum in case of discrete RV\n+ message = (\"Using `evaluate=False` returns `Probability` object since version 1.7. \"\n+ \"If you want unevaluated Integral/Sum use \"\n+ \"`P(condition, given_condition, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)`\")",
"line": null,
"original_line": 805,
"original_start_line": 803,
"path": "sympy/stats/rv.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n message = (\"Since version version 1.7, using `evaluate=False` returns `Probability` object. \"\r\n \"If you want unevaluated Integral/Sum use \"\r\n \"`P(condition, given_condition, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)`\")\r\n```"
}
] |
b2db510dd36af5a031d2d9dd7a118242910bee59
|
diff --git a/sympy/stats/rv.py b/sympy/stats/rv.py
index 2d2c6f67ada1..c1bc92676621 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/rv.py
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@
from sympy import (Basic, S, Expr, Symbol, Tuple, And, Add, Eq, lambdify, Or,
Equality, Lambda, sympify, Dummy, Ne, KroneckerDelta,
- DiracDelta, Mul, Indexed, MatrixSymbol, Function, Integral)
+ DiracDelta, Mul, Indexed, MatrixSymbol, Function)
from sympy.core.relational import Relational
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
from sympy.sets.sets import FiniteSet, ProductSet, Intersection
@@ -757,7 +757,12 @@ def expectation(expr, condition=None, numsamples=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Expectation
if evaluate:
return Expectation(expr, condition).doit(**kwargs)
- return Expectation(expr, condition).rewrite(Integral) # will return Sum in case of discrete RV
+ ### TODO: Remove the user warnings in the future releases
+ message = ("Since version 1.7, using `evaluate=False` returns `Expectation` "
+ "object. If you want unevaluated Integral/Sum use "
+ "`E(expr, condition, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)`")
+ warnings.warn(filldedent(message))
+ return Expectation(expr, condition)
def probability(condition, given_condition=None, numsamples=None,
@@ -796,7 +801,12 @@ def probability(condition, given_condition=None, numsamples=None,
from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability
if evaluate:
return Probability(condition, given_condition).doit(**kwargs)
- return Probability(condition, given_condition).rewrite(Integral) # will return Sum in case of discrete RV
+ ### TODO: Remove the user warnings in the future releases
+ message = ("Since version 1.7, using `evaluate=False` returns `Probability` "
+ "object. If you want unevaluated Integral/Sum use "
+ "`P(condition, given_condition, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral)`")
+ warnings.warn(filldedent(message))
+ return Probability(condition, given_condition)
class Density(Basic):
@@ -1048,6 +1058,7 @@ def sample(expr, condition=None, size=(), library='scipy', numsamples=1,
iterator object containing the sample/samples of given expr
"""
+ ### TODO: Remove the user warnings in the future releases
message = ("The return type of sample has been changed to return an "
"iterator object since version 1.7. For more information see "
"https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/19061")
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_compound_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_compound_rv.py
index 5b32abeb1e45..40b661659468 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_compound_rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_compound_rv.py
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
from sympy.stats.crv_types import NormalDistribution
from sympy.stats.drv_types import PoissonDistribution
from sympy.stats.frv_types import BernoulliDistribution
-from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
+from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, ignore_warnings
from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import MultivariateNormalDistribution
@@ -66,7 +66,8 @@ def test_unevaluated_CompoundDist():
expre = Integral(Piecewise((_k*exp(S(3)/4 - _k/4)/8, 2*Abs(arg(_k - 3)) <= pi/2),
(sqrt(2)*_k*Integral(exp(-(_k**4 + 16*(_k - 3)**2)/(32*_k**2)),
(_k, 0, oo))/(32*sqrt(pi)), True)), (_k, -oo, oo))
- assert (E(X, evaluate=False).simplify()).dummy_eq(expre.simplify())
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ assert (E(X, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).simplify()).dummy_eq(expre.simplify())
def test_Compound_Distribution():
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py
index 1e249c68eaa8..5b32b68878a0 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_continuous_rv.py
@@ -25,6 +25,7 @@
from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import MultivariateLaplaceDistribution, MultivariateNormalDistribution
from sympy.stats.crv import SingleContinuousPSpace, SingleContinuousDomain
from sympy.stats.compound_rv import CompoundPSpace
+from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, XFAIL, slow, skip, ignore_warnings
from sympy.testing.randtest import verify_numerically as tn
@@ -327,7 +328,7 @@ def test_sample_continuous():
scipy = import_module('scipy')
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy is not installed. Abort tests')
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
assert next(sample(Z)) in Z.pspace.domain.set
sym, val = list(Z.pspace.sample().items())[0]
assert sym == Z and val in Interval(0, oo)
@@ -643,12 +644,12 @@ def test_exponential():
_z = Dummy('_z')
b = SingleContinuousPSpace(x, ExponentialDistribution(2))
- expected1 = Integral(2*exp(-2*_z), (_z, 3, oo))
- assert b.probability(x > 3, evaluate=False).dummy_eq(expected1) is True
-
- expected2 = Integral(2*exp(-2*_z), (_z, 0, 4))
- assert b.probability(x < 4, evaluate=False).dummy_eq(expected2) is True
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ expected1 = Integral(2*exp(-2*_z), (_z, 3, oo))
+ assert b.probability(x > 3, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).dummy_eq(expected1)
+ expected2 = Integral(2*exp(-2*_z), (_z, 0, 4))
+ assert b.probability(x < 4, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).dummy_eq(expected2)
Y = Exponential('y', 2*rate)
assert coskewness(X, X, X) == skewness(X)
assert coskewness(X, Y + rate*X, Y + 2*rate*X) == \
@@ -758,7 +759,7 @@ def test_sampling_gamma_inverse():
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy not installed. Abort tests for sampling of gamma inverse.')
X = GammaInverse("x", 1, 1)
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
assert next(sample(X)) in X.pspace.domain.set
def test_gompertz():
@@ -885,13 +886,13 @@ def test_lognormal():
scipy = import_module('scipy')
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy is not installed. Abort tests')
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
for i in range(3):
X = LogNormal('x', i, 1)
assert next(sample(X)) in X.pspace.domain.set
size = 5
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
samps = next(sample(X, size=size))
for samp in samps:
assert samp in X.pspace.domain.set
@@ -1014,7 +1015,7 @@ def test_sampling_gaussian_inverse():
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy not installed. Abort tests for sampling of Gaussian inverse.')
X = GaussianInverse("x", 1, 1)
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
assert next(sample(X, library='scipy')) in X.pspace.domain.set
def test_pareto():
@@ -1316,7 +1317,7 @@ def test_prefab_sampling():
variables = [N, L, E, P, W, U, B, G]
niter = 10
size = 5
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
for var in variables:
for i in range(niter):
assert next(sample(var)) in var.pspace.domain.set
@@ -1342,21 +1343,21 @@ def test_input_value_assertions():
def test_unevaluated():
X = Normal('x', 0, 1)
- assert str(E(X, evaluate=False)) == ("Integral(sqrt(2)*x*exp(-x**2/2)/"
- "(2*sqrt(pi)), (x, -oo, oo))")
-
- assert str(E(X + 1, evaluate=False)) == ("Integral(sqrt(2)*x*exp(-x**2/2)/"
- "(2*sqrt(pi)), (x, -oo, oo)) + 1")
-
- assert str(P(X > 0, evaluate=False)) == ("Integral(sqrt(2)*exp(-_z**2/2)/"
- "(2*sqrt(pi)), (_z, 0, oo))")
+ k = Dummy('k')
+ expr1 = Integral(sqrt(2)*k*exp(-k**2/2)/(2*sqrt(pi)), (k, -oo, oo))
+ expr2 = Integral(sqrt(2)*exp(-k**2/2)/(2*sqrt(pi)), (k, 0, oo))
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ assert E(X, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).dummy_eq(expr1)
+ assert E(X + 1, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).dummy_eq(expr1 + 1)
+ assert P(X > 0, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).dummy_eq(expr2)
- assert P(X > 0, X**2 < 1, evaluate=False) == S.Half
+ assert P(X > 0, X**2 < 1) == S.Half
def test_probability_unevaluated():
T = Normal('T', 30, 3)
- assert type(P(T > 33, evaluate=False)) == Integral
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ assert type(P(T > 33, evaluate=False)) == Probability
def test_density_unevaluated():
@@ -1583,7 +1584,7 @@ def test_sample_numpy():
if not numpy:
skip('Numpy is not installed. Abort tests for _sample_numpy.')
else:
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
for X in distribs_numpy:
samps = next(sample(X, size=size, library='numpy'))
for sam in samps:
@@ -1616,7 +1617,7 @@ def test_sample_scipy():
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy is not installed. Abort tests for _sample_scipy.')
else:
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
g_sample = list(sample(Gamma("G", 2, 7), size=size, numsamples=numsamples))
assert len(g_sample) == numsamples
for X in distribs_scipy:
@@ -1646,7 +1647,7 @@ def test_sample_pymc3():
if not pymc3:
skip('PyMC3 is not installed. Abort tests for _sample_pymc3.')
else:
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
for X in distribs_pymc3:
samps = next(sample(X, size=size, library='pymc3'))
for sam in samps:
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_discrete_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_discrete_rv.py
index b03b67c4686b..30388483e671 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_discrete_rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_discrete_rv.py
@@ -15,6 +15,7 @@
from sympy.stats.rv import sample
from sympy.testing.pytest import slow, nocache_fail, raises, skip, ignore_warnings
from sympy.external import import_module
+from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Expectation
x = Symbol('x')
@@ -33,8 +34,9 @@ def test_Poisson():
assert E(x) == l
assert variance(x) == l
assert density(x) == PoissonDistribution(l)
- assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Sum)
- assert isinstance(E(2*x, evaluate=False), Sum)
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Expectation)
+ assert isinstance(E(2*x, evaluate=False), Expectation)
# issue 8248
assert x.pspace.compute_expectation(1) == 1
@@ -82,7 +84,8 @@ def test_Logarithmic():
assert E(x) == -p / ((1 - p) * log(1 - p))
assert variance(x) == -1/log(2)**2 + 2/log(2)
assert E(2*x**2 + 3*x + 4) == 4 + 7 / log(2)
- assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Sum)
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Expectation)
@nocache_fail
@@ -94,7 +97,8 @@ def test_negative_binomial():
# This hangs when run with the cache disabled:
assert variance(x) == p*r / (1-p)**2
assert E(x**5 + 2*x + 3) == Rational(9207, 4)
- assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Sum)
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Expectation)
def test_skellam():
@@ -121,7 +125,8 @@ def test_yule_simon():
x = YuleSimon('x', rho)
assert simplify(E(x)) == rho / (rho - 1)
assert simplify(variance(x)) == rho**2 / ((rho - 1)**2 * (rho - 2))
- assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Sum)
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ assert isinstance(E(x, evaluate=False), Expectation)
# To test the cdf function
assert cdf(x)(x) == Piecewise((-beta(floor(x), 4)*floor(x) + 1, x >= 1), (0, True))
@@ -140,7 +145,7 @@ def test_sample_discrete():
scipy = import_module('scipy')
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy not installed. Abort tests')
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
assert next(sample(X)) in X.pspace.domain.set
samps = next(sample(X, size=2)) # This takes long time if ran without scipy
for samp in samps:
@@ -272,7 +277,8 @@ def test_product_spaces():
#assert str(P(X1 + X2 < 3, evaluate=False)) == """Sum(Piecewise((2**(X2 - n - 2)*(2/3)**(X2 - 1)/6, """\
# + """(-X2 + n + 3 >= 1) & (-X2 + n + 3 < oo)), (0, True)), (X2, 1, oo), (n, -oo, -1))"""
n = Dummy('n')
- assert P(X1 + X2 < 3, evaluate=False).dummy_eq(Sum(Piecewise((2**(-n)/4,
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ assert P(X1 + X2 < 3, evaluate=False).rewrite(Sum).dummy_eq(Sum(Piecewise((2**(-n)/4,
n + 2 >= 1), (0, True)), (n, -oo, -1))/3)
#assert str(P(X1 + X2 > 3)) == """Sum(Piecewise((2**(X2 - n - 2)*(2/3)**(X2 - 1)/6, """ +\
# """(-X2 + n + 3 >= 1) & (-X2 + n + 3 < oo)), (0, True)), (X2, 1, oo), (n, 1, oo))"""
@@ -295,7 +301,7 @@ def test_sample_numpy():
if not numpy:
skip('Numpy is not installed. Abort tests for _sample_numpy.')
else:
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
for X in distribs_numpy:
samps = next(sample(X, size=size, library='numpy'))
for sam in samps:
@@ -325,7 +331,7 @@ def test_sample_scipy():
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy is not installed. Abort tests for _sample_scipy.')
else:
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
z_sample = list(sample(Zeta("G", 7), size=size, numsamples=numsamples))
assert len(z_sample) == numsamples
for X in distribs_scipy:
@@ -348,7 +354,7 @@ def test_sample_pymc3():
if not pymc3:
skip('PyMC3 is not installed. Abort tests for _sample_pymc3.')
else:
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
for X in distribs_pymc3:
samps = next(sample(X, size=size, library='pymc3'))
for sam in samps:
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py
index 92f774913225..5598df07b4cb 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py
@@ -149,7 +149,7 @@ def test_given():
scipy = import_module('scipy')
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy is not installed. Abort tests')
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
assert next(sample(X, X > 5)) == 6
@@ -452,7 +452,7 @@ def test_sample_numpy():
if not numpy:
skip('Numpy is not installed. Abort tests for _sample_numpy.')
else:
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
for X in distribs_numpy:
samps = next(sample(X, size=size, library='numpy'))
for sam in samps:
@@ -480,7 +480,7 @@ def test_sample_scipy():
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy not installed. Abort tests for _sample_scipy.')
else:
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
h_sample = list(sample(Hypergeometric("H", 1, 1, 1), size=size, numsamples=numsamples))
assert len(h_sample) == numsamples
for X in distribs_scipy:
@@ -503,7 +503,7 @@ def test_sample_pymc3():
if not pymc3:
skip('PyMC3 is not installed. Abort tests for _sample_pymc3.')
else:
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
for X in distribs_pymc3:
samps = next(sample(X, size=size, library='pymc3'))
for sam in samps:
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_mix.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_mix.py
index 9cbd336646b5..a47f7beae8e6 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_mix.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_mix.py
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
from sympy import (Symbol, Eq, Ne, simplify, sqrt, exp, pi, symbols,
Piecewise, factorial, gamma, IndexedBase, Add, Pow, Mul,
- Indexed, Integer)
+ Indexed, Integer, Integral, DiracDelta, Dummy, Sum, oo)
from sympy.functions.elementary.piecewise import ExprCondPair
from sympy.stats import (Poisson, Beta, Exponential, P,
Multinomial, MultivariateBeta)
@@ -9,6 +9,7 @@
from sympy.stats.compound_rv import CompoundPSpace, CompoundDistribution
from sympy.stats.joint_rv import MarginalDistribution
from sympy.stats.rv import pspace, density
+from sympy.testing.pytest import ignore_warnings
def test_density():
x = Symbol('x')
@@ -56,9 +57,13 @@ def test_compound_distribution():
def test_mix_expression():
Y, E = Poisson('Y', 1), Exponential('E', 1)
+ k = Dummy('k')
+ expr1 = Integral(Sum(exp(-1)*Integral(exp(-k)*DiracDelta(k - 2), (k, 0, oo)
+ )/factorial(k), (k, 0, oo)), (k, -oo, 0))
+ expr2 = Integral(Sum(exp(-1)*Integral(exp(-k)*DiracDelta(k - 2), (k, 0, oo)
+ )/factorial(k), (k, 0, oo)), (k, 0, oo))
assert P(Eq(Y + E, 1)) == 0
assert P(Ne(Y + E, 2)) == 1
- assert str(P(E + Y < 2, evaluate=False)) == """Integral(Sum(exp(-1)*Integral"""\
-+"""(exp(-E)*DiracDelta(-_z + E + Y - 2), (E, 0, oo))/factorial(Y), (Y, 0, oo)), (_z, -oo, 0))"""
- assert str(P(E + Y > 2, evaluate=False)) == """Integral(Sum(exp(-1)*Integral"""\
-+"""(exp(-E)*DiracDelta(-_z + E + Y - 2), (E, 0, oo))/factorial(Y), (Y, 0, oo)), (_z, 0, oo))"""
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
+ assert P(E + Y < 2, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).dummy_eq(expr1)
+ assert P(E + Y > 2, evaluate=False).rewrite(Integral).dummy_eq(expr2)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py
index 2c50fdedc94d..26071dbc6f4d 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py
@@ -191,7 +191,7 @@ def test_Sample():
scipy = import_module('scipy')
if not scipy:
skip('Scipy is not installed. Abort tests')
- with ignore_warnings(UserWarning):
+ with ignore_warnings(UserWarning): ### TODO: Restore tests once warnings are removed
assert next(sample(X)) in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
assert isinstance(next(sample(X + Y)), float)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
index f4ff19a0e14d..a3c281c92c65 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
@@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ def test_ContinuousMarkovChain():
assert C2.transition_probabilities(A)(t) == Matrix([[S.Half + exp(-2*t)/2, S.Half - exp(-2*t)/2, 0],
[S.Half - exp(-2*t)/2, S.Half + exp(-2*t)/2, 0],
[S.Half - exp(-t) + exp(-2*t)/2, S.Half - exp(-2*t)/2, exp(-t)]])
- assert P(Eq(C2(1), 1), Eq(C2(0), 1), evaluate=False) == Probability(Eq(C2(1), 1))
+ assert P(Eq(C2(1), 1), Eq(C2(0), 1), evaluate=False) == Probability(Eq(C2(1), 1), Eq(C2(0), 1))
assert P(Eq(C2(1), 1), Eq(C2(0), 1)) == exp(-2)/2 + S.Half
assert P(Eq(C2(1), 0) & Eq(C2(2), 1) & Eq(C2(3), 1),
Eq(P(Eq(C2(1), 0)), S.Half)) == (Rational(1, 4) - exp(-2)/4)*(exp(-2)/2 + S.Half)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19913@d466e06
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,913
|
lambdify loggamma now works for mpmath
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixed #17411
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Lambdifying an expression with loggamma doesn't work for mpmath previously but I made some fixes so that it works. File changed are pycode and test_pycode.
#### Other comments
Nan
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* printing
* The mpmath code printer now correctly prints the `loggamma` function.
* utilities
* Lambdifying an expression with `loggamma` using mpmath no longer raises `ImportError`.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-08-07T05:06:19Z
|
lambdify loggamma doesn't work for mpmath
Lambdifying an expression with loggamma doesn't work for mpmath
```julia
In [6]: lambdify(x, loggamma(x), 'mpmath')
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ImportError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-6-02428e0a17ae> in <module>
----> 1 lambdify(x, loggamma(x), 'mpmath')
~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py in lambdify(args, expr, modules, printer, use_imps, dummify)
766 imp_mod_lines.append("from %s import %s" % (mod, k))
767 for ln in imp_mod_lines:
--> 768 exec_(ln, {}, namespace)
769
770 # Provide lambda expression with builtins, and compatible implementation of range
<string> in <module>
ImportError: cannot import name 'lgamma'
```
I think this is because it's called loggamma rather than lgamma:
```julia
In [7]: import mpmath
In [8]: mpmath.loggamma(1)
Out[8]: mpf('0.0')
```
I originally got this error from
```julia
In [11]: nsolve(im(loggamma(I*x)), x, 3.439*I)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ImportError
...
```
|
`lgamma` is the name in `math`. There seems to be some code to harvest all mpmath names and add them, but it doesn't seem to work (or some other magic happens, see "Other comments" in #17394, the printer does one thing, but lambdify another...).
Is it possible to write a test that automatically tries to import everything in these `_known_functions_*` lists?
Whatever, just adding `loggamma` to `knwon_functions_mpmath` can swiftly fix the problem.
```
diff --git a/sympy/printing/pycode.py b/sympy/printing/pycode.py
index 3270a171df..4bac55f1cc 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/pycode.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/pycode.py
@@ -491,6 +491,7 @@ def pycode(expr, **settings):
_in_mpmath = [(k, v) for k, v in _known_functions_math.items() if k not in _not_in_mpmath]
_known_functions_mpmath = dict(_in_mpmath, **{
'sign': 'sign',
+ 'loggamma': 'loggamma',
})
_known_constants_mpmath = {
'Pi': 'pi'
```
Ahh, it wasn't defined there. Not strange then.
```
In [23]: MpmathPrinter().doprint(loggamma(x))
Out[23]: 'mpmath.lgamma(x)'
```
I thought it was related to this behaviour:
```
In [36]: F =lambdify([x, y], beta(x, y), modules=['numpy'])
In [37]: F?
Signature: F(x, y)
Docstring:
Created with lambdify. Signature:
func(x, y)
Expression:
beta(x, y)
Source code:
def _lambdifygenerated(x, y):
return (beta(x, y))
Imported modules:
File: /nobackup/data/sympy/sympy/<lambdifygenerated-5>
Type: function
In [38]: NumPyPrinter().doprint(beta(x, y))
Out[38]: 'math.gamma(x)*math.gamma(y)/math.gamma(x + y)'
```
Yes, if the name is the same, it works automatically. Otherwise it has to be added to that list in lambdify. Actually I think the correct list is MPMATH_TRANSLATIONS in lambdify.py. That way it also works with the evalf mapping.
Is there a reason this was on the release milestone? I removed it, but if it should be there please explain and readd it.
I don't see any reason why this needs a milestone
If no one is working on this issue can I start contributing on it?
This issue is open for contributions. Please feel free to raise a PR. Thanks.
|
[
{
"body": "Lambdifying an expression with loggamma doesn't work for mpmath\r\n```julia\r\nIn [6]: lambdify(x, loggamma(x), 'mpmath') \r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nImportError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n<ipython-input-6-02428e0a17ae> in <module>\r\n----> 1 lambdify(x, loggamma(x), 'mpmath')\r\n\r\n~/current/sympy/sympy/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py in lambdify(args, expr, modules, printer, use_imps, dummify)\r\n 766 imp_mod_lines.append(\"from %s import %s\" % (mod, k))\r\n 767 for ln in imp_mod_lines:\r\n--> 768 exec_(ln, {}, namespace)\r\n 769 \r\n 770 # Provide lambda expression with builtins, and compatible implementation of range\r\n\r\n<string> in <module>\r\n\r\nImportError: cannot import name 'lgamma'\r\n```\r\nI think this is because it's called loggamma rather than lgamma:\r\n```julia\r\nIn [7]: import mpmath \r\n\r\nIn [8]: mpmath.loggamma(1) \r\nOut[8]: mpf('0.0')\r\n```\r\n\r\nI originally got this error from\r\n```julia\r\nIn [11]: nsolve(im(loggamma(I*x)), x, 3.439*I) \r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nImportError\r\n...\r\n```",
"number": 17411,
"title": "lambdify loggamma doesn't work for mpmath"
}
] |
1b9a569fd62ca548149705652dfd6eefcba0ef38
|
{
"head_commit": "d466e06844dd3c6558e20e5ed621d50e631c1aa3",
"head_commit_message": "Added testcase for loggamma",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/printing/pycode.py b/sympy/printing/pycode.py\nindex 5862c8fb514e..c35def62cdd2 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/pycode.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/pycode.py\n@@ -502,6 +502,7 @@ def pycode(expr, **settings):\n 'fresnelc': 'fresnelc',\n 'fresnels': 'fresnels',\n 'sign': 'sign',\n+ 'loggamma': 'loggamma',\n })\n _known_constants_mpmath = {\n 'Exp1': 'e',\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py\nindex 48fb134da5ef..a1cbbf7a9032 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py\n@@ -17,6 +17,7 @@\n from sympy.tensor import IndexedBase\n from sympy.testing.pytest import skip\n from sympy.external import import_module\n+from sympy.functions.special.gamma_functions import loggamma\n \n x, y, z = symbols('x y z')\n p = IndexedBase(\"p\")\n@@ -75,6 +76,7 @@ def test_MpmathPrinter():\n assert p.doprint(S.NaN) == 'mpmath.nan'\n assert p.doprint(S.Infinity) == 'mpmath.inf'\n assert p.doprint(S.NegativeInfinity) == 'mpmath.ninf'\n+ assert p.doprint(loggamma(x)) == 'mpmath.lgamma(x)'\n \n \n def test_NumPyPrinter():\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -75,6 +76,7 @@ def test_MpmathPrinter():\n assert p.doprint(S.NaN) == 'mpmath.nan'\n assert p.doprint(S.Infinity) == 'mpmath.inf'\n assert p.doprint(S.NegativeInfinity) == 'mpmath.ninf'\n+ assert p.doprint(loggamma(x)) == 'mpmath.lgamma(x)'",
"line": null,
"original_line": 79,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n assert p.doprint(loggamma(x)) == 'mpmath.loggamma(x)'\r\n```"
}
] |
adf1b437bc3671c8340515acd6e2167011b6ce0f
|
diff --git a/sympy/printing/pycode.py b/sympy/printing/pycode.py
index 5862c8fb514e..c35def62cdd2 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/pycode.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/pycode.py
@@ -502,6 +502,7 @@ def pycode(expr, **settings):
'fresnelc': 'fresnelc',
'fresnels': 'fresnels',
'sign': 'sign',
+ 'loggamma': 'loggamma',
})
_known_constants_mpmath = {
'Exp1': 'e',
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py
index 48fb134da5ef..486d208c93b6 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_pycode.py
@@ -17,6 +17,7 @@
from sympy.tensor import IndexedBase
from sympy.testing.pytest import skip
from sympy.external import import_module
+from sympy.functions.special.gamma_functions import loggamma
x, y, z = symbols('x y z')
p = IndexedBase("p")
@@ -75,6 +76,7 @@ def test_MpmathPrinter():
assert p.doprint(S.NaN) == 'mpmath.nan'
assert p.doprint(S.Infinity) == 'mpmath.inf'
assert p.doprint(S.NegativeInfinity) == 'mpmath.ninf'
+ assert p.doprint(loggamma(x)) == 'mpmath.loggamma(x)'
def test_NumPyPrinter():
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_lambdify.py b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_lambdify.py
index 4b61384becd1..7889244209bd 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/tests/test_lambdify.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/tests/test_lambdify.py
@@ -905,6 +905,19 @@ def intervalrepr(expr):
assert isinstance(func1(), mpi)
assert isinstance(func2(), mpi)
+ # To check Is lambdify loggamma works for mpmath or not
+ exp1 = lambdify(x, loggamma(x), 'mpmath')(5)
+ exp2 = lambdify(x, loggamma(x), 'mpmath')(1.8)
+ exp3 = lambdify(x, loggamma(x), 'mpmath')(15)
+ exp_ls = [exp1, exp2, exp3]
+
+ sol1 = mpmath.loggamma(5)
+ sol2 = mpmath.loggamma(1.8)
+ sol3 = mpmath.loggamma(15)
+ sol_ls = [sol1, sol2, sol3]
+
+ assert exp_ls == sol_ls
+
def test_true_false():
# We want exact is comparison here, not just ==
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19783@bfb4989
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,783
|
Dagger() * IdentityOperator() now simplifies by default
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #19747
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
```
from sympy.physics.quantum.dagger import Dagger
from sympy.physics.quantum.operator import Operator
from sympy.physics.quantum import IdentityOperator
A = Operator('A')
Identity = IdentityOperator()
print(B * Identity)
print(Identity * B)
```
now gives
```
Dagger(A)
Dagger(A)
```
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* physics.quantum
* Simplification of Dagger() * IdentityOperator()
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-07-16T09:40:38Z
|
Dagger() * IdentityOperator() is not simplified
As discussed on the mailing list the following does not work.
```
from sympy.physics.quantum.dagger import Dagger
from sympy.physics.quantum.operator import Operator
from sympy.physics.quantum import IdentityOperator
A = Operators('A')
Identity = IdentityOperator()
A * Identity #This gives A, correctly
B = Dagger(A)
B * Identity #This returns A^\dagger I
```
|
[
{
"body": "As discussed on the mailing list the following does not work.\r\n```\r\nfrom sympy.physics.quantum.dagger import Dagger\r\nfrom sympy.physics.quantum.operator import Operator\r\nfrom sympy.physics.quantum import IdentityOperator\r\nA = Operators('A')\r\nIdentity = IdentityOperator()\r\nA * Identity #This gives A, correctly\r\nB = Dagger(A)\r\nB * Identity #This returns A^\\dagger I \r\n```\r\n",
"number": 19747,
"title": "Dagger() * IdentityOperator() is not simplified"
}
] |
586a43201d0357e92e8c93548d69a9f42bf548f4
|
{
"head_commit": "bfb49895171b7e73d2a56028d3cde8079f77c130",
"head_commit_message": "Dagger() * IdentityOperator() now simplifies by default\n\nFixes #19747",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py\nindex 17da3cfd2c5c..9e3435165c48 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py\n@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@\n \n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n-from sympy.core import Expr\n+from sympy.core import Expr, Mul\n from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import adjoint\n \n __all__ = [\n@@ -85,5 +85,13 @@ def __new__(cls, arg):\n return obj\n return Expr.__new__(cls, arg)\n \n+ def __mul__(self, other):\n+ from sympy.physics.quantum import IdentityOperator\n+\n+ if isinstance(other, IdentityOperator):\n+ return self\n+\n+ return Mul(self,other)\n+\n adjoint.__name__ = \"Dagger\"\n adjoint._sympyrepr = lambda a, b: \"Dagger(%s)\" % b._print(a.args[0])\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py\nindex 306bfee64fde..9c50fe05a51d 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py\n@@ -307,7 +307,7 @@ def _print_contents_latex(self, printer, *args):\n \n def __mul__(self, other):\n \n- if isinstance(other, Operator):\n+ if isinstance(other, Operator) or isinstance(other, Dagger):\n return other\n \n return Mul(self, other)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_operator.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_operator.py\nindex 7c8574fe148e..a00bd8cf9f30 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_operator.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_operator.py\n@@ -94,6 +94,8 @@ def test_identity():\n \n assert I * O == O\n assert O * I == O\n+ assert I * Dagger(O) == Dagger(O)\n+ assert Dagger(O) * I == Dagger(O)\n assert isinstance(I * I, IdentityOperator)\n assert isinstance(3 * I, Mul)\n assert isinstance(I * x, Mul)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -85,5 +85,13 @@ def __new__(cls, arg):\n return obj\n return Expr.__new__(cls, arg)\n \n+ def __mul__(self, other):\n+ from sympy.physics.quantum import IdentityOperator\n+\n+ if isinstance(other, IdentityOperator):\n+ return self\n+\n+ return Mul(self,other)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 94,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n return Mul(self, other)\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@\n \n from __future__ import print_function, division",
"line": null,
"original_line": 3,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nCan you also remove this line and the blank line below it?? Future imports are no longer needed."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -307,7 +307,7 @@ def _print_contents_latex(self, printer, *args):\n \n def __mul__(self, other):\n \n- if isinstance(other, Operator):\n+ if isinstance(other, Operator) or isinstance(other, Dagger):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 310,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n if isinstance(other, (Operator, Dagger)):\r\n```"
}
] |
d91e3fe121b13d81cd74838e324fc51e87be80b1
|
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py
index 17da3cfd2c5c..a557073a0f07 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/dagger.py
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
"""Hermitian conjugation."""
-from __future__ import print_function, division
-
-from sympy.core import Expr
+from sympy.core import Expr, Mul
from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import adjoint
__all__ = [
@@ -85,5 +83,12 @@ def __new__(cls, arg):
return obj
return Expr.__new__(cls, arg)
+ def __mul__(self, other):
+ from sympy.physics.quantum import IdentityOperator
+ if isinstance(other, IdentityOperator):
+ return self
+
+ return Mul(self, other)
+
adjoint.__name__ = "Dagger"
adjoint._sympyrepr = lambda a, b: "Dagger(%s)" % b._print(a.args[0])
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py
index 306bfee64fde..81460db5c9d8 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py
@@ -307,7 +307,7 @@ def _print_contents_latex(self, printer, *args):
def __mul__(self, other):
- if isinstance(other, Operator):
+ if isinstance(other, (Operator, Dagger)):
return other
return Mul(self, other)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_dagger.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_dagger.py
index bcc8a28f58f4..ed93087790c1 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_dagger.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_dagger.py
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
-from sympy import I, Matrix, symbols, conjugate, Expr, Integer
+from sympy import I, Matrix, symbols, conjugate, Expr, Integer, Mul
from sympy.physics.quantum.dagger import adjoint, Dagger
from sympy.external import import_module
from sympy.testing.pytest import skip
+from sympy.physics.quantum.operator import Operator, IdentityOperator
def test_scalars():
@@ -29,6 +30,15 @@ def test_matrix():
assert Dagger(m) == m.H
+def test_dagger_mul():
+ O = Operator('O')
+ I = IdentityOperator()
+ assert Dagger(O)*O == Dagger(O)*O
+ assert Dagger(O)*O*I == Mul(Dagger(O), O)*I
+ assert Dagger(O)*Dagger(O) == Dagger(O)**2
+ assert Dagger(O)*Dagger(I) == Dagger(O)
+
+
class Foo(Expr):
def _eval_adjoint(self):
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_operator.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_operator.py
index 7c8574fe148e..a00bd8cf9f30 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_operator.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/tests/test_operator.py
@@ -94,6 +94,8 @@ def test_identity():
assert I * O == O
assert O * I == O
+ assert I * Dagger(O) == Dagger(O)
+ assert Dagger(O) * I == Dagger(O)
assert isinstance(I * I, IdentityOperator)
assert isinstance(3 * I, Mul)
assert isinstance(I * x, Mul)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-19993@e148ef8
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,993
|
upgrades to manualintegrate
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19983 #14329
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
I dunno why no one has implemented this yet 😕
#### Other comments
I've added screenshots of results and verifications. after initial scrutiny I'll add tests and finalise it.
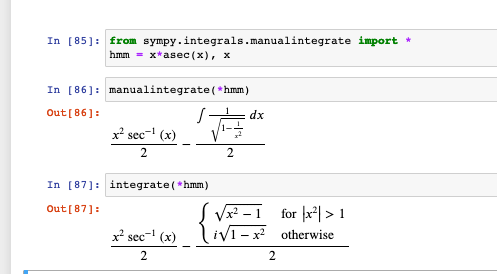
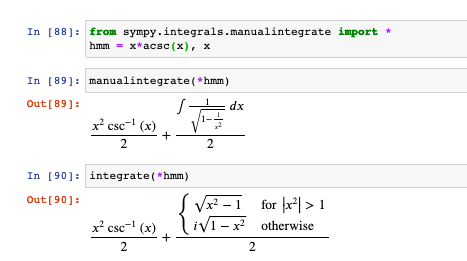
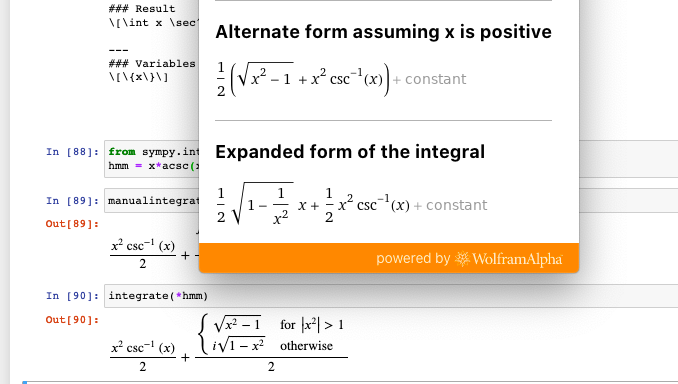
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* integrals
* upgrades to manualintegrate to support inverse trig functions!
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-08-21T10:00:38Z
|
Sympy doesn't Integrate when expr contains asec / acsc
```python3
>>> integrate(asin(x))
x*asin(x) + sqrt(1 - x**2)
>>> integrate(x*asin(x))
x**2*asin(x)/2 + x*sqrt(1 - x**2)/4 - asin(x)/4
>>> integrate(acos(x))
x*acos(x) - sqrt(1 - x**2)
>>> integrate(x*acos(x))
x**2*acos(x)/2 - x*sqrt(1 - x**2)/4 - acos(x)/4
>>> integrate(atan(x))
x*atan(x) - log(x**2 + 1)/2
>>> integrate(x*atan(x))
x**2*atan(x)/2 - x/2 + atan(x)/2
>>> integrate(asec(x)) # Secant inverse isn't evaluated
Integral(asec(x), x)
>>> integrate(x*asec(x)) # isn't evaluated
Integral(x*asec(x), x)
>>> integrate(acot(x))
x*acot(x) + log(x**2 + 1)/2
>>> integrate(x*acot(x))
x**2*acot(x)/2 + x/2 + acot(x)/2
>>> integrate(acsc(x)) # Cosecant inverse isn't evaluated
Integral(acsc(x), x)
>>> integrate(x*acsc(x)) # isn't evaluated
Integral(x*acsc(x), x)
>>>
```
|
346d9f1f34ce1f729f860fd98c188a5a38efe12a I've tried to implement this in manual-integrate
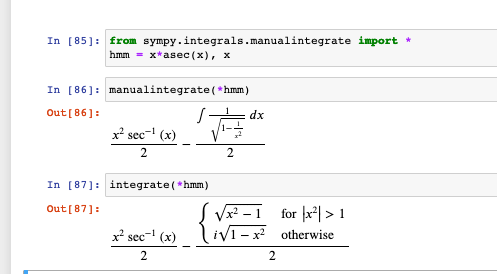

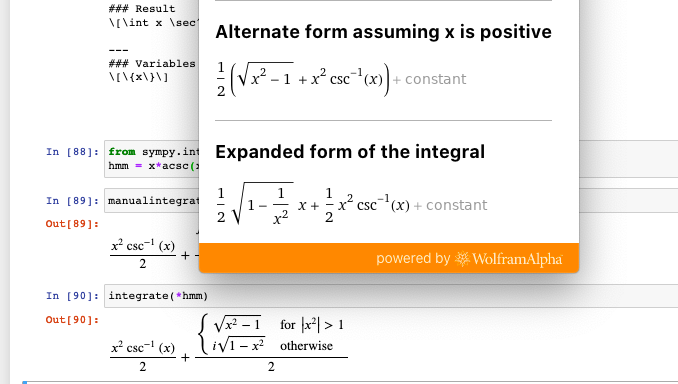
|
[
{
"body": "```python3\r\n>>> integrate(asin(x))\r\nx*asin(x) + sqrt(1 - x**2)\r\n>>> integrate(x*asin(x))\r\nx**2*asin(x)/2 + x*sqrt(1 - x**2)/4 - asin(x)/4\r\n>>> integrate(acos(x))\r\nx*acos(x) - sqrt(1 - x**2)\r\n>>> integrate(x*acos(x))\r\nx**2*acos(x)/2 - x*sqrt(1 - x**2)/4 - acos(x)/4\r\n>>> integrate(atan(x))\r\nx*atan(x) - log(x**2 + 1)/2\r\n>>> integrate(x*atan(x))\r\nx**2*atan(x)/2 - x/2 + atan(x)/2\r\n>>> integrate(asec(x)) # Secant inverse isn't evaluated\r\nIntegral(asec(x), x)\r\n>>> integrate(x*asec(x)) # isn't evaluated\r\nIntegral(x*asec(x), x)\r\n>>> integrate(acot(x))\r\nx*acot(x) + log(x**2 + 1)/2\r\n>>> integrate(x*acot(x))\r\nx**2*acot(x)/2 + x/2 + acot(x)/2\r\n>>> integrate(acsc(x)) # Cosecant inverse isn't evaluated\r\nIntegral(acsc(x), x)\r\n>>> integrate(x*acsc(x)) # isn't evaluated\r\nIntegral(x*acsc(x), x)\r\n>>>\r\n```",
"number": 19983,
"title": "Sympy doesn't Integrate when expr contains asec / acsc "
}
] |
e975b8a7b339ee2e209f6d92e8ac58ee278ad5d9
|
{
"head_commit": "e148ef8740d8eca19de2a51c4ff20bcef99445da",
"head_commit_message": "upgrades to manualintegrate",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py b/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py\nindex d1d61fb96250..5633db7d8867 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py\n@@ -535,14 +535,14 @@ def pull_out_u_rl(integrand):\n \n return pull_out_u_rl\n \n- liate_rules = [pull_out_u(sympy.log), pull_out_u(sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos),\n+ liate_rules = [pull_out_u(sympy.log), pull_out_u(sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos, sympy.acot, sympy.acsc, sympy.asec),\n pull_out_algebraic, pull_out_u(sympy.sin, sympy.cos),\n pull_out_u(sympy.exp)]\n \n \n dummy = sympy.Dummy(\"temporary\")\n # we can integrate log(x) and atan(x) by setting dv = 1\n- if isinstance(integrand, (sympy.log, sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos)):\n+ if isinstance(integrand, (sympy.log, sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos, sympy.acsc, sympy.asec, sympy.acot)):\n integrand = dummy * integrand\n \n for index, rule in enumerate(liate_rules):\n@@ -1272,6 +1272,7 @@ def key(integral):\n else:\n for cls in (sympy.Pow, sympy.Symbol, sympy.exp, sympy.log,\n sympy.Add, sympy.Mul, sympy.atan, sympy.asin,\n+ sympy.asec, sympy.acsc, sympy.acot,\n sympy.acos, sympy.Heaviside, OrthogonalPolynomial):\n if isinstance(integrand, cls):\n return cls\n@@ -1312,7 +1313,9 @@ def _integral_is_subclass(integral):\n integral_is_subclass(sympy.Mul, sympy.Pow),\n cancel_rule),\n condition(\n- integral_is_subclass(sympy.Mul, sympy.log, sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos),\n+ integral_is_subclass(sympy.Mul, sympy.log,\n+ sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos,\n+ sympy.acsc, sympy.asec, sympy.acot),\n parts_rule),\n condition(\n integral_is_subclass(sympy.Mul, sympy.Pow),\n@@ -1430,6 +1433,8 @@ def eval_piecewise(substeps, integrand, symbol):\n @evaluates(TrigSubstitutionRule)\n def eval_trigsubstitution(theta, func, rewritten, substep, restriction, integrand, symbol):\n func = func.subs(sympy.sec(theta), 1/sympy.cos(theta))\n+ func = func.subs(sympy.csc(theta), 1/sympy.sin(theta))\n+ func = func.subs(sympy.cot(theta), 1/sympy.tan(theta))\n \n trig_function = list(func.find(TrigonometricFunction))\n assert len(trig_function) == 1\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -535,14 +535,14 @@ def pull_out_u_rl(integrand):\n \n return pull_out_u_rl\n \n- liate_rules = [pull_out_u(sympy.log), pull_out_u(sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos),\n+ liate_rules = [pull_out_u(sympy.log), pull_out_u(sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos, sympy.acot, sympy.acsc, sympy.asec),",
"line": null,
"original_line": 538,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nMaybe it makes sense to define a list like\r\n```\r\ninverse_trig_functions = [sympy.atan, ...]\r\n```\r\nsomewhere so that it can be reused in lots of places.\n\n@author:\nHmm yeah that would make sense"
}
] |
d3719efcceb175acfa7bd82cf56806f0507b4467
|
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py b/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py
index d1d61fb96250..5c89088058c6 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py
@@ -174,6 +174,9 @@ def manual_subs(expr, *args):
# Method based on that on SIN, described in "Symbolic Integration: The
# Stormy Decade"
+inverse_trig_functions = (sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos, sympy.acot, sympy.acsc, sympy.asec)
+
+
def find_substitutions(integrand, symbol, u_var):
results = []
@@ -213,7 +216,7 @@ def test_subterm(u, u_diff):
def possible_subterms(term):
if isinstance(term, (TrigonometricFunction,
- sympy.asin, sympy.acos, sympy.atan,
+ *inverse_trig_functions,
sympy.exp, sympy.log, sympy.Heaviside)):
return [term.args[0]]
elif isinstance(term, (sympy.chebyshevt, sympy.chebyshevu,
@@ -535,14 +538,14 @@ def pull_out_u_rl(integrand):
return pull_out_u_rl
- liate_rules = [pull_out_u(sympy.log), pull_out_u(sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos),
+ liate_rules = [pull_out_u(sympy.log), pull_out_u(*inverse_trig_functions),
pull_out_algebraic, pull_out_u(sympy.sin, sympy.cos),
pull_out_u(sympy.exp)]
dummy = sympy.Dummy("temporary")
# we can integrate log(x) and atan(x) by setting dv = 1
- if isinstance(integrand, (sympy.log, sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos)):
+ if isinstance(integrand, (sympy.log, *inverse_trig_functions)):
integrand = dummy * integrand
for index, rule in enumerate(liate_rules):
@@ -1271,8 +1274,8 @@ def key(integral):
return sympy.Number
else:
for cls in (sympy.Pow, sympy.Symbol, sympy.exp, sympy.log,
- sympy.Add, sympy.Mul, sympy.atan, sympy.asin,
- sympy.acos, sympy.Heaviside, OrthogonalPolynomial):
+ sympy.Add, sympy.Mul, *inverse_trig_functions,
+ sympy.Heaviside, OrthogonalPolynomial):
if isinstance(integrand, cls):
return cls
@@ -1312,7 +1315,8 @@ def _integral_is_subclass(integral):
integral_is_subclass(sympy.Mul, sympy.Pow),
cancel_rule),
condition(
- integral_is_subclass(sympy.Mul, sympy.log, sympy.atan, sympy.asin, sympy.acos),
+ integral_is_subclass(sympy.Mul, sympy.log,
+ *inverse_trig_functions),
parts_rule),
condition(
integral_is_subclass(sympy.Mul, sympy.Pow),
@@ -1430,6 +1434,8 @@ def eval_piecewise(substeps, integrand, symbol):
@evaluates(TrigSubstitutionRule)
def eval_trigsubstitution(theta, func, rewritten, substep, restriction, integrand, symbol):
func = func.subs(sympy.sec(theta), 1/sympy.cos(theta))
+ func = func.subs(sympy.csc(theta), 1/sympy.sin(theta))
+ func = func.subs(sympy.cot(theta), 1/sympy.tan(theta))
trig_function = list(func.find(TrigonometricFunction))
assert len(trig_function) == 1
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_manual.py b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_manual.py
index 58804c5f9fba..a364bf4c70e7 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_manual.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_manual.py
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
Function, jacobi, gegenbauer, chebyshevt, chebyshevu,
legendre, hermite, laguerre, assoc_laguerre, uppergamma, li,
Ei, Ci, Si, Chi, Shi, fresnels, fresnelc, polylog, erfi,
- sinh, cosh, elliptic_f, elliptic_e)
+ sinh, cosh, elliptic_f, elliptic_e ,asec, acsc, acot )
from sympy.integrals.manualintegrate import (manualintegrate, find_substitutions,
_parts_rule, integral_steps, contains_dont_know, manual_subs)
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, slow
@@ -160,6 +160,32 @@ def test_manualintegrate_inversetrig():
assert manualintegrate(1/sqrt(-a + 4*x**2), x) == \
Piecewise((asinh(2*x*sqrt(-1/a))/2, -a > 0), (acosh(2*x*sqrt(1/a))/2, -a < 0))
+ # From https://www.wikiwand.com/en/List_of_integrals_of_inverse_trigonometric_functions
+ # asin
+ assert manualintegrate(asin(x), x) == x*asin(x) + sqrt(1 - x**2)
+ assert manualintegrate(asin(a*x), x) == Piecewise(((a*x*asin(a*x) + sqrt(-a**2*x**2 + 1))/a, Ne(a, 0)), (0, True))
+ assert manualintegrate(x*asin(a*x), x) == -a*Integral(x**2/sqrt(-a**2*x**2 + 1), x)/2 + x**2*asin(a*x)/2
+ # acos
+ assert manualintegrate(acos(x), x) == x*acos(x) - sqrt(1 - x**2)
+ assert manualintegrate(acos(a*x), x) == Piecewise(((a*x*acos(a*x) - sqrt(-a**2*x**2 + 1))/a, Ne(a, 0)), (pi*x/2, True))
+ assert manualintegrate(x*acos(a*x), x) == a*Integral(x**2/sqrt(-a**2*x**2 + 1), x)/2 + x**2*acos(a*x)/2
+ # atan
+ assert manualintegrate(atan(x), x) == x*atan(x) - log(x**2 + 1)/2
+ assert manualintegrate(atan(a*x), x) == Piecewise(((a*x*atan(a*x) - log(a**2*x**2 + 1)/2)/a, Ne(a, 0)), (0, True))
+ assert manualintegrate(x*atan(a*x), x) == -a*(x/a**2 - atan(x/sqrt(a**(-2)))/(a**4*sqrt(a**(-2))))/2 + x**2*atan(a*x)/2
+ # acsc
+ assert manualintegrate(acsc(x), x) == x*acsc(x) + Integral(1/(x*sqrt(1 - 1/x**2)), x)
+ assert manualintegrate(acsc(a*x), x) == x*acsc(a*x) + Integral(1/(x*sqrt(1 - 1/(a**2*x**2))), x)/a
+ assert manualintegrate(x*acsc(a*x), x) == x**2*acsc(a*x)/2 + Integral(1/sqrt(1 - 1/(a**2*x**2)), x)/(2*a)
+ # asec
+ assert manualintegrate(asec(x), x) == x*asec(x) - Integral(1/(x*sqrt(1 - 1/x**2)), x)
+ assert manualintegrate(asec(a*x), x) == x*asec(a*x) - Integral(1/(x*sqrt(1 - 1/(a**2*x**2))), x)/a
+ assert manualintegrate(x*asec(a*x), x) == x**2*asec(a*x)/2 - Integral(1/sqrt(1 - 1/(a**2*x**2)), x)/(2*a)
+ # acot
+ assert manualintegrate(acot(x), x) == x*acot(x) + log(x**2 + 1)/2
+ assert manualintegrate(acot(a*x), x) == Piecewise(((a*x*acot(a*x) + log(a**2*x**2 + 1)/2)/a, Ne(a, 0)), (pi*x/2, True))
+ assert manualintegrate(x*acot(a*x), x) == a*(x/a**2 - atan(x/sqrt(a**(-2)))/(a**4*sqrt(a**(-2))))/2 + x**2*acot(a*x)/2
+
# piecewise
assert manualintegrate(1/sqrt(a-b*x**2), x) == \
Piecewise((sqrt(a/b)*asin(x*sqrt(b/a))/sqrt(a), And(-b < 0, a > 0)),
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19753@71618fc
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,753
|
Added examples for hyper.appellf1 and Znm
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #17887
#19591
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Updated Functions.special submodule :
- Added examples for hyper.appellf1 in hyper.py
- Added examples for Znm in spherical_harmonics.py
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-07-12T17:10:07Z
|
Add missing docstring sections in Special submodule
As part of my Google Season of Docs project with SymPy, I copy edited all of the docstrings in the Special submodule to reflect the new SymPy Docstring Style Guide. While editing, I came across some docstrings that were missing sections or had other issues that need to be addressed. Here is a list of all of the functions in the Special submodule that had an issue and what needs to be fixed:
1. Jn_zeros
Parameters listed but does not have a parameters section
2. Bspline_basis, bspline_basis_set
In bspline_basis, parameters not pulling into HTML site
Both have parameters listed but do not have a parameters section
3. Interpolating_spline
Parameters listed but does not have a parameters section
4. Fdiff, eval (under DiracDelta)
Parameters listed but do not have a parameters section
5. Fdiff, eval (under Heaviside)
Parameters listed but do not have a parameters section
6. E1(z)
Missing examples section
7. Li (in error functions)
In the Examples section, the example for under the text “Defining the ``li`` function via an integral:” is missing
8. Hyper
Lists properties as part of this class that need to be their own docstrings with their own examples
9. Meijerg
Lists properties as part of this class that need to be their own docstrings with their own examples
10. Appellf1
Missing examples section
11. Jacobi_normalized
Parameters listed but does not have a parameters section
12. Ynm_c
Missing examples section
Parameters listed but does not have a parameters section
13. Znm
Missing examples section
CC @sympy/gsod
|
For anyone fixing this be sure to follow the documentation style guide https://docs.sympy.org/dev/documentation-style-guide.html
Hey can you assign me this issue? Also, where can I reach out for questions?
Contributors are not assigned with issues here. Anyone can start working and send a relevant PR solving that issue! Also, you can ask questions on this thread or on the mailing list.
I am facing an error when i run ```make html``` after installing prerequisites. Should I state my problem here or create an issue?
Just state it here. We can open an new issue if we determine there is a bug in the build process, but most likely there is some issue on your system.
I am facing this error when I run ```make html``` inside doc:
```
rm -rf _build/logo
mkdir -p _build/logo
python ./generate_logos.py -d
INFO:root: File saved: ./_build/logo/sympy-notail.svg
INFO:root: File saved: ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext.svg
INFO:root: File saved: ./_build/logo/sympy-notext.svg
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./src/logo/sympy.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-160px.png -h 160 -w 160
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./src/logo/sympy.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-500px.png -h 500 -w 500
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notail.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notail-160px.png -h 160 -w 160
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notail.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notail-500px.png -h 500 -w 500
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext-160px.png -h 160 -w 160
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext-500px.png -h 500 -w 500
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notext-160px.png -h 160 -w 160
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notext-500px.png -h 500 -w 500
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./src/logo/sympy.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-16px.png -h 16 -w 16
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./src/logo/sympy.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-32px.png -h 32 -w 32
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./src/logo/sympy.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-48px.png -h 48 -w 48
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./src/logo/sympy.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-64px.png -h 64 -w 64
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notail.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notail-16px.png -h 16 -w 16
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notail.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notail-32px.png -h 32 -w 32
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notail.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notail-48px.png -h 48 -w 48
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notail.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notail-64px.png -h 64 -w 64
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext-16px.png -h 16 -w 16
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext-32px.png -h 32 -w 32
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext-48px.png -h 48 -w 48
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notailtext-64px.png -h 64 -w 64
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notext-16px.png -h 16 -w 16
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notext-32px.png -h 32 -w 32
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notext-48px.png -h 48 -w 48
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
DEBUG:root:command: rsvg-convert ./_build/logo/sympy-notext.svg -f png -o ./_build/logo/sympy-notext-64px.png -h 64 -w 64
DEBUG:root:return code: 0
ERROR:root:Return code is not 0: Command: convert ./_build/logo/sympy-16px.png ./_build/logo/sympy-32px.png ./_build/logo/sympy-48px.png ./_build/logo/sympy-64px.png ./_build/logo/sympy-favicon.ico
ERROR:root:return code: 1
Makefile:143: recipe for target 'logo' failed
make: *** [logo] Error 1
```
Here are the commands I ran from the start to build:
```
git clone git://github.com/sympy/sympy.git
cd sympy
git remote add github [email protected]:Soumi7/sympy.git
conda create -n sympy-dev-py35 python=3.5 mpmath flake8
source activate sympy-dev-py35
flake8 sympy
python setup.py install
git branch branch1
git checkout branch1
sudo apt-get install python-sphinx texlive-latex-recommended dvipng librsvg2-bin imagemagick docbook2x graphviz
sudo apt-get update
python -m pip install sphinx-math-dollar
ls
cd doc
make html
```
It looks like the generate logos script doesn't print the stdout and stderr when there is an error, so we can't tell what the problem is. This should be fixed.
What is the output if you run
```
cd doc
convert ./_build/logo/sympy-16px.png ./_build/logo/sympy-32px.png ./_build/logo/sympy-48px.png ./_build/logo/sympy-64px.png ./_build/logo/sympy-favicon.ico
```
I installed `imagemagick` with apt-get. However , I was unable to convert the PG delegate to yes after configuring:
```
./configure --with-png=yes
```
I reinstalled **imagemagick from source** and that error has **gone**!
The logo generated but i got this error:
```
Running Sphinx v3.0.3
Exception occurred:
File "/home/soumi/anaconda3/envs/sympy-dev-py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages/matplotlib/sphinxext/plot_directive.py", line 262, in setup
app.add_directive('plot', plot_directive, True, (0, 2, False), **options)
TypeError: add_directive() got an unexpected keyword argument 'format'
The full traceback has been saved in /tmp/sphinx-err-arpru3bc.log, if you want to report the issue to the developers.
Please also report this if it was a user error, so that a better error message can be provided next time.
A bug report can be filed in the tracker at <https://github.com/sphinx-doc/sphinx/issues>. Thanks!
Makefile:49: recipe for target 'html' failed
make: *** [html] Error 2
```
It gives different error messages everytime I run it:
```
Exception occurred:
File "/home/soumi/anaconda3/envs/sympy-dev-py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages/matplotlib/sphinxext/plot_directive.py", line 262, in setup
app.add_directive('plot', plot_directive, True, (0, 2, False), **options)
TypeError: add_directive() got an unexpected keyword argument 'height'
The full traceback has been saved in /tmp/sphinx-err-s1h2y1is.log, if you want to report the issue to the developers.
Please also report this if it was a user error, so that a better error message can be provided next time.
A bug report can be filed in the tracker at <https://github.com/sphinx-doc/sphinx/issues>. Thanks!
Makefile:49: recipe for target 'html' failed
make: *** [html] Error 2
```
My Matplotlib version is
```
>>> matplotlib.__version__
'3.0.3'
```
My python version is :
```
Python 3.5.6 :: Anaconda, Inc.
```
My guess is that the matplotlib version is too old. The latest version is 3.2.1.
|
[
{
"body": "As part of my Google Season of Docs project with SymPy, I copy edited all of the docstrings in the Special submodule to reflect the new SymPy Docstring Style Guide. While editing, I came across some docstrings that were missing sections or had other issues that need to be addressed. Here is a list of all of the functions in the Special submodule that had an issue and what needs to be fixed:\r\n\r\n1. Jn_zeros \r\nParameters listed but does not have a parameters section\r\n\r\n2. Bspline_basis, bspline_basis_set\r\nIn bspline_basis, parameters not pulling into HTML site\r\nBoth have parameters listed but do not have a parameters section\r\n\r\n3. Interpolating_spline\r\nParameters listed but does not have a parameters section\r\n\r\n4. Fdiff, eval (under DiracDelta)\r\nParameters listed but do not have a parameters section\r\n\r\n5. Fdiff, eval (under Heaviside)\r\nParameters listed but do not have a parameters section\r\n\r\n6. E1(z)\r\nMissing examples section\r\n\r\n7. Li (in error functions)\r\nIn the Examples section, the example for under the text “Defining the ``li`` function via an integral:” is missing\r\n\r\n8. Hyper\r\nLists properties as part of this class that need to be their own docstrings with their own examples\r\n\r\n9. Meijerg\r\nLists properties as part of this class that need to be their own docstrings with their own examples\r\n\r\n10. Appellf1\r\nMissing examples section\r\n\r\n11. Jacobi_normalized\r\nParameters listed but does not have a parameters section\r\n\r\n12. Ynm_c\r\nMissing examples section\r\nParameters listed but does not have a parameters section\r\n\r\n13. Znm\r\nMissing examples section\r\n\r\n\r\nCC @sympy/gsod",
"number": 17887,
"title": "Add missing docstring sections in Special submodule"
}
] |
1eaefeb714cc05d87ea2f938813e5e859caa2b32
|
{
"head_commit": "71618fc94b43297fb320c96fe5ee784937587001",
"head_commit_message": "Added examples for hyper.appellf1 and Znm",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/hyper.py b/sympy/functions/special/hyper.py\nindex 51d9507f76ed..ad4ef38e5965 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/hyper.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/hyper.py\n@@ -1100,6 +1100,16 @@ class appellf1(Function):\n \\frac{(a)_{m+n} (b_1)_m (b_2)_n}{(c)_{m+n}}\n \\frac{x^m y^n}{m! n!}.\n \n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+ >>> from sympy.functions.special.hyper import appellf1\n+ >>> appellf1(2., 1., 6., 4., 5., 6.)\n+ 0.0063339426292673\n+ >>> appellf1(1,2,3,5,0.5,0.25)\n+ appellf1(1, 2, 3, 5, 0.5, 0.25)\n+ >>> appellf1(1,2,3,5,0.5,0.25)\n+ appellf1(1, 2, 3, 5, 0.5, 0.25)\n+\n References\n ==========\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/spherical_harmonics.py b/sympy/functions/special/spherical_harmonics.py\nindex fe210f5a0bfd..cf6a4d7f73f4 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/spherical_harmonics.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/spherical_harmonics.py\n@@ -262,6 +262,24 @@ def Ynm_c(n, m, theta, phi):\n \n Ynm, Znm\n \n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+ >>> from sympy import Znm, Symbol, simplify\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import n,m\n+ >>> theta = Symbol(\"theta\")\n+ >>> phi = Symbol(\"phi\")\n+ >>> Znm(n, m, theta, phi)\n+ Znm(n, m, theta, phi)\n+\n+ For specific integers n and m we can evaluate the harmonics\n+ to more useful expressions:\n+ >>> simplify(Znm(0, 0, theta, phi).expand(func=True))\n+ 1/(2*sqrt(pi))\n+ >>> simplify(Znm(1, 1, theta, phi).expand(func=True))\n+ -sqrt(3)*sin(theta)*cos(phi)/(2*sqrt(pi))\n+ >>> simplify(Znm(2, 1, theta, phi).expand(func=True))\n+ -sqrt(15)*sin(2*theta)*cos(phi)/(4*sqrt(pi))\n+\n References\n ==========\n \n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1100,6 +1100,16 @@ class appellf1(Function):\n \\frac{(a)_{m+n} (b_1)_m (b_2)_n}{(c)_{m+n}}\n \\frac{x^m y^n}{m! n!}.\n \n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+ >>> from sympy.functions.special.hyper import appellf1\n+ >>> appellf1(2., 1., 6., 4., 5., 6.)\n+ 0.0063339426292673\n+ >>> appellf1(1,2,3,5,0.5,0.25)\n+ appellf1(1, 2, 3, 5, 0.5, 0.25)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1109,
"original_start_line": 1108,
"path": "sympy/functions/special/hyper.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n >>> appellf1(1, 2, 3, 5, 0.5, 0.25)\r\n appellf1(1, 2, 3, 5, 0.5, 0.25)\r\n```\n\n@author:\nChanged."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -262,6 +262,24 @@ def Ynm_c(n, m, theta, phi):\n \n Ynm, Znm\n \n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+ >>> from sympy import Znm, Symbol, simplify\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import n,m\n+ >>> theta = Symbol(\"theta\")\n+ >>> phi = Symbol(\"phi\")\n+ >>> Znm(n, m, theta, phi)\n+ Znm(n, m, theta, phi)\n+\n+ For specific integers n and m we can evaluate the harmonics\n+ to more useful expressions:\n+ >>> simplify(Znm(0, 0, theta, phi).expand(func=True))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 276,
"original_start_line": 275,
"path": "sympy/functions/special/spherical_harmonics.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n to more useful expressions:\r\n\r\n >>> simplify(Znm(0, 0, theta, phi).expand(func=True))\r\n```\n\n@author:\nDone."
}
] |
9bdf5960a623e3619182bbfbf66079db16f926ad
|
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/hyper.py b/sympy/functions/special/hyper.py
index 51d9507f76ed..469299059985 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/hyper.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/hyper.py
@@ -1100,6 +1100,25 @@ class appellf1(Function):
\frac{(a)_{m+n} (b_1)_m (b_2)_n}{(c)_{m+n}}
\frac{x^m y^n}{m! n!}.
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.functions.special.hyper import appellf1
+ >>> from sympy import symbols
+ >>> x, y, a, b1, b2, c = symbols('x y a b1 b2 c')
+ >>> appellf1(2., 1., 6., 4., 5., 6.)
+ 0.0063339426292673
+ >>> appellf1(12., 12., 6., 4., 0.5, 0.12)
+ 172870711.659936
+ >>> appellf1(40, 2, 6, 4, 15, 60)
+ appellf1(40, 2, 6, 4, 15, 60)
+ >>> appellf1(20., 12., 10., 3., 0.5, 0.12)
+ 15605338197184.4
+ >>> appellf1(40, 2, 6, 4, x, y)
+ appellf1(40, 2, 6, 4, x, y)
+ >>> appellf1(a, b1, b2, c, x, y)
+ appellf1(a, b1, b2, c, x, y)
+
References
==========
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/spherical_harmonics.py b/sympy/functions/special/spherical_harmonics.py
index fe210f5a0bfd..8370c81ec336 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/spherical_harmonics.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/spherical_harmonics.py
@@ -298,6 +298,26 @@ class Znm(Function):
\frac{Y_n^m(\theta, \varphi) - (-1)^m Y_n^{-m}(\theta, \varphi)}{i \sqrt{2}} &\quad m < 0 \\
\end{cases}
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import Znm, Symbol, simplify
+ >>> from sympy.abc import n, m
+ >>> theta = Symbol("theta")
+ >>> phi = Symbol("phi")
+ >>> Znm(n, m, theta, phi)
+ Znm(n, m, theta, phi)
+
+ For specific integers n and m we can evaluate the harmonics
+ to more useful expressions:
+
+ >>> simplify(Znm(0, 0, theta, phi).expand(func=True))
+ 1/(2*sqrt(pi))
+ >>> simplify(Znm(1, 1, theta, phi).expand(func=True))
+ -sqrt(3)*sin(theta)*cos(phi)/(2*sqrt(pi))
+ >>> simplify(Znm(2, 1, theta, phi).expand(func=True))
+ -sqrt(15)*sin(2*theta)*cos(phi)/(4*sqrt(pi))
+
See Also
========
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 1,
"problem_domain": "Documentation Updates"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19730@8cb7282
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,730
|
Added tests for issue 16735
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #16735
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Adds tests to `concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py` and `series/tests/test_limitseq.py`
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-07-09T14:18:55Z
|
Sum.is_convergent uses the incorrect results from limit_seq
`limit_seq` gives the following wrong results:
```
In [1]: limit_seq(5**n/factorial(n),n)
Out[1]: ∞
```
```
In [2]: limit_seq(5**n/gamma(n+1),n)
Out[2]: ∞
```
Remarkably, this ends up being correct:
```
In [3]: limit_seq(5**n/gamma(n-1),n)
Out[3]: 0
```
Even though `gruntz` can compute both these limits, `Sum.is_convergent` uses the incorrect results from `limit_seq` to wrongly conclude that
```
In [4]: Sum(5**n/gamma(n+1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()
Out[4]: False
```
|
On current master:
```
In [1]: limit_seq(5**n/factorial(n),n)
Out[1]: 0
In [2]: limit_seq(5**n/gamma(n+1),n)
Out[2]: 0
In [3]: Sum(5**n/gamma(n+1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()
Out[3]: True
```
This issue seems fixed. Only requires a test in order to be closed.
Will adding the lines
```python
def test_issue_16735():
assert limit_seq(5**n/factorial(n),n) == 0
assert limit_seq(5**n/gamma(n+1),n) == 0
assert Sum(5**n/gamma(n+1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is True
```
to `concrete/test_sums_products.py` close the issue?
Should I go for it?
> assert limit_seq(5**n/factorial(n),n) == 0
Should be added to `series/test_limitseq.py`. No need to add the `gamma` testcase, both are essentially the same.
> assert Sum(5**n/gamma(n+1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is True
Add this one to `concrete/test_sums_products.py`.
|
[
{
"body": "`limit_seq` gives the following wrong results:\r\n```\r\nIn [1]: limit_seq(5**n/factorial(n),n) \r\nOut[1]: ∞\r\n```\r\n```\r\nIn [2]: limit_seq(5**n/gamma(n+1),n) \r\nOut[2]: ∞\r\n```\r\nRemarkably, this ends up being correct:\r\n```\r\nIn [3]: limit_seq(5**n/gamma(n-1),n) \r\nOut[3]: 0\r\n```\r\nEven though `gruntz` can compute both these limits, `Sum.is_convergent` uses the incorrect results from `limit_seq` to wrongly conclude that \r\n```\r\nIn [4]: Sum(5**n/gamma(n+1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent() \r\nOut[4]: False\r\n```",
"number": 16735,
"title": "Sum.is_convergent uses the incorrect results from limit_seq"
}
] |
c0bfc81f3ffee97c6d6732ac5e5ccf399e5ab3e2
|
{
"head_commit": "8cb7282cf58d1b6f0043850e8df1d6d926ece85a",
"head_commit_message": "Added tests for issue 16735",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py\nindex 18a9f850d573..7c8aa5e92258 100644\n--- a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py\n+++ b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py\n@@ -1317,6 +1317,11 @@ def test_issue_14313():\n assert Sum(S.Half**floor(n/2), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()\n \n \n+@XFAIL\n+def test_issue_16735():\n+ assert Sum(5**n/gamma(n+1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is True\n+\n+\n @XFAIL\n def test_issue_14871():\n assert Sum((Rational(1, 10))**x*RisingFactorial(0, x)/factorial(x), (x, 0, oo)).rewrite(factorial).doit() == 1\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limitseq.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limitseq.py\nindex 870c6c5d8da0..1300b4b98f31 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limitseq.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limitseq.py\n@@ -125,6 +125,10 @@ def test_issue_10382():\n assert limit_seq(fibonacci(n+1)/fibonacci(n), n) == S.GoldenRatio\n \n \n+def test_issue_16735():\n+ assert limit_seq(5**n/factorial(n),n) == 0\n+\n+\n @XFAIL\n def test_limit_seq_fail():\n # improve Summation algorithm or add ad-hoc criteria\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1317,6 +1317,11 @@ def test_issue_14313():\n assert Sum(S.Half**floor(n/2), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()\n \n \n+@XFAIL",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1320,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis should be removed. This is not a test which fails."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1317,6 +1317,11 @@ def test_issue_14313():\n assert Sum(S.Half**floor(n/2), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()\n \n \n+@XFAIL\n+def test_issue_16735():\n+ assert Sum(5**n/gamma(n+1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is True",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1322,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis can be `S.true` rather than `True`.\n\n@author:\nI see that S.true issue. When it is True, the test fails and hence I added `@user2`\n\n@author:\nPlease review the changes now."
}
] |
2bd9171c226c827ba9f9a4c90da8033ff3f4f68c
|
diff --git a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py
index 18a9f850d573..90b6f8aecec9 100644
--- a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py
+++ b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py
@@ -1317,6 +1317,10 @@ def test_issue_14313():
assert Sum(S.Half**floor(n/2), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()
+def test_issue_16735():
+ assert Sum(5**n/gamma(n+1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is S.true
+
+
@XFAIL
def test_issue_14871():
assert Sum((Rational(1, 10))**x*RisingFactorial(0, x)/factorial(x), (x, 0, oo)).rewrite(factorial).doit() == 1
diff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limitseq.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limitseq.py
index 870c6c5d8da0..e55b7fcd2b58 100644
--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limitseq.py
+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limitseq.py
@@ -125,6 +125,10 @@ def test_issue_10382():
assert limit_seq(fibonacci(n+1)/fibonacci(n), n) == S.GoldenRatio
+def test_issue_16735():
+ assert limit_seq(5**n/factorial(n), n) == 0
+
+
@XFAIL
def test_limit_seq_fail():
# improve Summation algorithm or add ad-hoc criteria
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 1,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19546@b777e46
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,546
|
Modified order.py
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19545
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
The code `Order(1/n - 3/(3*n +2), (n, oo))` returns `1/n`, which
is not a sharp result.
As a consequence `Sum(1/n - 3/(3*n +2), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()`
gives the wrong result `False`.
In the lines 208-214 of `order.py`, if the number of variables are >= 2,
then the expression is expanded and is handled in `expr.is_Add` case.
However in the case of a single variable,
the alghorithm for the other case seems better.
Factorizing the expression forces to use the better alghoritm in the case
of a single variable.
modified: sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py
modified: sympy/series/order.py
modified: sympy/series/tests/test_order.py
#### Other comments
See also #18340
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
- series
- modified order.py to better work with Add objects.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-06-13T13:20:39Z
|
is_convergent() returns a wrong result
The code
```
expr1 = 1/n - 3/(3*n +2)
res1 = Sum(expr1, (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()
```
returns the wrong result `False`.
The code
```
expr2 = simplify(expr1)
res2 = Sum(expr2, (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()
```
returns the correct result `True`.
The different behaviour is in line 471 of `summations.py`. In the first case order is `1/n` (correct, but not sharp), while in the second one `n**(-2)`, which is sharp.
|
[
{
"body": "The code\r\n```\r\nexpr1 = 1/n - 3/(3*n +2)\r\nres1 = Sum(expr1, (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()\r\n```\r\nreturns the wrong result `False`.\r\n\r\nThe code\r\n```\r\nexpr2 = simplify(expr1)\r\nres2 = Sum(expr2, (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()\r\n```\r\nreturns the correct result `True`.\r\n\r\nThe different behaviour is in line 471 of `summations.py`. In the first case order is `1/n` (correct, but not sharp), while in the second one `n**(-2)`, which is sharp.",
"number": 19545,
"title": "is_convergent() returns a wrong result"
}
] |
bfd2fa05de2db76a73c16e5c94604cdfd9d74e60
|
{
"head_commit": "b777e4693084cf731595594d5389c5cd7901fbb8",
"head_commit_message": "Modified order.py\n\nReferences to other Issues or PRs\nFixes #19545\n\nBrief description of what is fixed or changed\n\nThe code `Order(1/n - 3/(3*n +2), (n, oo))` returns `1/n`, which\nis not a sharp result.\nAs a consequence `Sum(1/n - 3/(3*n +2), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()`\ngives the wrong result `False`.\nIn the lines 208-214 of `order.py`, if the number of variables are >= 2,\nthen the expression is expanded and is handled in `expr.is_Add` case.\nHowever in the case of a single variable,\nthe alghorithm for the other case seems better.\nFactorizing the expression forces to use the better alghoritm in the case\nof a single variable.\n\nSee also PR#18340\n\nOn branch issue-19545\nChanges to be committed:\n modified: sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py\n modified: sympy/series/order.py\n modified: sympy/series/tests/test_order.py",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py\nindex 258f98acdd63..18a9f850d573 100644\n--- a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py\n+++ b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py\n@@ -1050,6 +1050,8 @@ def test_is_convergent():\n assert Sum(1/(x**3), (x, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is S.true\n assert Sum(1/(x**S.Half), (x, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is S.false\n \n+ # issue 19545\n+ assert Sum(1/n - 3/(3*n +2), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is S.true\n \n def test_is_absolutely_convergent():\n assert Sum((-1)**n, (n, 1, oo)).is_absolutely_convergent() is S.false\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/order.py b/sympy/series/order.py\nindex 362edd4aded4..0320ce599525 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/order.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/order.py\n@@ -212,6 +212,8 @@ def __new__(cls, expr, *args, **kwargs):\n # x*y (wrong order term!). That's why we want to deal with\n # expand()'ed expr (handled in \"if expr.is_Add\" branch below).\n expr = expr.expand()\n+ else:\n+ expr = expr.factor()\n \n old_expr = None\n while old_expr != expr:\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_order.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_order.py\nindex f98247fd511b..76f433bcecbc 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_order.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_order.py\n@@ -376,6 +376,8 @@ def test_order_at_infinity():\n assert Order(exp(x), (x, oo)).expr == Order(2*exp(x), (x, oo)).expr == exp(x)\n assert Order(y**x, (x, oo)).expr == Order(2*y**x, (x, oo)).expr == exp(log(y)*x)\n \n+ # issue 19545\n+ assert Order(1/x - 3/(3*x + 2), (x, oo)).expr == x**(-2)\n \n def test_mixing_order_at_zero_and_infinity():\n assert (Order(x, (x, 0)) + Order(x, (x, oo))).is_Add\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -212,6 +212,8 @@ def __new__(cls, expr, *args, **kwargs):\n # x*y (wrong order term!). That's why we want to deal with\n # expand()'ed expr (handled in \"if expr.is_Add\" branch below).\n expr = expr.expand()\n+ else:\n+ expr = expr.factor()",
"line": null,
"original_line": 216,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/series/order.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIt seems that this aims to transform the sum `1/x - 3/(3*x + 2)` into a product, so it looks like it should only be applied to instances of `Add`. The code would probably be better placed here: https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/f7318dbfef2bf61e5ed8bc55f3e374880ec6ea67/sympy/series/order.py#L199-L201\r\n\r\nIt is possible that `expand_multinomial` could be removed and replaced by this. You could also test something like\r\n```\r\n num, den = expr.as_numer_denom()\r\n expr = num/den\r\n```\r\ninstead of `expr.factor()` which may be more expensive.\n\n@author:\n> It seems that this aims to transform the sum 1/x - 3/(3*x + 2) into a product, so it looks like it should only be applied to instances of Add. The code would probably be better placed here:\r\n> \r\n> sympy/sympy/series/order.py\r\n> \r\n> Lines 199 to 201 in f7318db\r\n> if expr.is_Add: \r\n> from sympy import expand_multinomial \r\n> expr = expand_multinomial(expr) \r\n\r\nRight. I changed the location of `factor`.\r\n\r\n> It is possible that expand_multinomial could be removed\r\n\r\nYes, I run the tests and they pass also without `expand_multinomial`.\r\n\r\n> You could also test something like\r\n> \r\n> num, den = expr.as_numer_denom()\r\n> expr = num/den\r\n> \r\n> instead of expr.factor() which may be more expensive.\r\n> \r\n\r\nPutting this instead of `expr.factor()` causes 2 failures in tests. The tests which failure are:\r\n\r\n- `test_wester.py` at lines 2088-2090.\r\n- `test_trigonometric.py` at llines 1224-1225.\r\n\r\n\n\n@user2:\n> Putting this instead of `expr.factor()` causes 2 failures in tests. The tests which failure are:\r\n> \r\n> * `test_wester.py` at lines 2088-2090.\r\n> * `test_trigonometric.py` at llines 1224-1225.\r\n\r\nCan you tell what is `expr` in these cases using `num/den` and when you use `expr.factor()` ?\r\n\r\n\n\n@author:\nFor `test_wester`.\r\n\r\n```\r\nexpr = -exp(-_p**2/(_p + 1) + _p)*exp(_p**2/(_p + 1) - _p)/2 - exp(-_p**2/(_p + 1) + _p)*exp(_p**2/(_p + 1) - _p)/(2*_p)\r\nexpr.factor() = -(_p + 1)/(2*_p)\r\nnum = -_p*exp(-_p**2/(_p + 1) + _p)*exp(_p**2/(_p + 1) - _p) - exp(-_p**2/(_p + 1) + _p)*exp(_p**2/(_p + 1) - _p)\r\nden = 2*_p\r\n```\r\nIn this case the test does not give an error, but it never finishes.\r\n\r\nFor `test_trigonometric`.\r\n```\r\nexpr = -4*_Dummy_69 + (_Dummy_69 + 1)**4 - 4*(_Dummy_69 + 1)**3 + 6*(_Dummy_69 + 1)**2 - 3\r\nexpr.factor() = _Dummy_69**4\r\nnum = -4*_Dummy_69 + (_Dummy_69 + 1)**4 - 4*(_Dummy_69 + 1)**3 + 6*(_Dummy_69 + 1)**2 - 3\r\nden = 1\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n\n\n@user1:\nIt looks like only `factor` factor will help here."
}
] |
7ab97483ca459ed90421e1c92d2d523c421d6a6c
|
diff --git a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py
index 258f98acdd63..18a9f850d573 100644
--- a/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py
+++ b/sympy/concrete/tests/test_sums_products.py
@@ -1050,6 +1050,8 @@ def test_is_convergent():
assert Sum(1/(x**3), (x, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is S.true
assert Sum(1/(x**S.Half), (x, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is S.false
+ # issue 19545
+ assert Sum(1/n - 3/(3*n +2), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent() is S.true
def test_is_absolutely_convergent():
assert Sum((-1)**n, (n, 1, oo)).is_absolutely_convergent() is S.false
diff --git a/sympy/series/order.py b/sympy/series/order.py
index 362edd4aded4..132cff6a2f3f 100644
--- a/sympy/series/order.py
+++ b/sympy/series/order.py
@@ -197,8 +197,7 @@ def __new__(cls, expr, *args, **kwargs):
expr = expr.subs(s)
if expr.is_Add:
- from sympy import expand_multinomial
- expr = expand_multinomial(expr)
+ expr = expr.factor()
if s:
args = tuple([r[0] for r in rs.items()])
diff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_order.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_order.py
index f98247fd511b..76f433bcecbc 100644
--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_order.py
+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_order.py
@@ -376,6 +376,8 @@ def test_order_at_infinity():
assert Order(exp(x), (x, oo)).expr == Order(2*exp(x), (x, oo)).expr == exp(x)
assert Order(y**x, (x, oo)).expr == Order(2*y**x, (x, oo)).expr == exp(log(y)*x)
+ # issue 19545
+ assert Order(1/x - 3/(3*x + 2), (x, oo)).expr == x**(-2)
def test_mixing_order_at_zero_and_infinity():
assert (Order(x, (x, 0)) + Order(x, (x, oo))).is_Add
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-19406@f6e5af5
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,406
|
Clean up flake8 warnings from doctests
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19374
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
running `flake8 --doctests sympy/` returns a bunch of errors. This PR is to fix them
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* other
* Improve code quality by cleaning the doctests up
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-05-22T23:46:05Z
|
Clean up flake8 warnings from doctests
Currently flake8 runs on the main code but not on doctests. It has a `--doctests` argument to check the doctests as well.
For example:
```console
$ flake8 --doctests sympy/matrices/determinant.py
sympy/matrices/determinant.py:545:9: F401 'sympy.MatrixSymbol' imported but unused
sympy/matrices/determinant.py:545:9: F401 'sympy.eye' imported but unused
sympy/matrices/determinant.py:545:9: F401 'sympy.det' imported but unused
```
That can be fixed with
```diff
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/determinant.py b/sympy/matrices/determinant.py
index 647541afef..f3bb9a4067 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/determinant.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/determinant.py
@@ -542,7 +542,7 @@ def _det(M, method="bareiss", iszerofunc=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Matrix, MatrixSymbol, eye, det
+ >>> from sympy import Matrix
>>> M = Matrix([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
>>> M.det()
-2
```
Running flake8 on the whole of sympy with
```
$ flake8 --doctests sympy
```
leads to 698 warnings almost all of which are F401 (unnecessary import) and so easily fixable.
These should all be fixed and then we should add the `--doctest` argument on Travis.
I'm marking this as easy to fix.
|
I'd like to take up on the task of cleaning the imports if I may
Yes, go ahead.
I was working on this cleanup and I found a curious situation:
sympy supports multiple dispatch per argument type, as defined in the docs of `sympy/multipledispatch/core.py`(lines 22-38):
```
Examples
--------
>>> from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
>>> @dispatch(int)
... def f(x):
... return x + 1
>>> @dispatch(float)
... def f(x):
... return x - 1
>>> f(3)
4
>>> f(3.0)
2.0
```
`flake8`, on the other hand, reports an error `F811 redefinition of unused 'f' from line 27`
which makes sense from its point of view but it seems that this is actually a wanted behaviour
This could be easily solved by invoking `flake8 --doctests --ignore=F811` in Travis, but I just wanted to make sure that's a correct way, and if it's not I'd like to know a better solution
Also, doctest from `sympy/core/singleton.py` (line 49) throws a warning about comparing Singleton and a literal with `is`, and although technically not an error, I'd like to know is there anything for me to do to remove this warning
This is the output I get:

I think we can write it like:
```
>>> x = 0
>>> x is S.Zero
```
to avoid the warning.
Multiple dispatch gives lots of flake8 warnings. These have been suppressed with a flake8 flag:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/0f598f042929f9de97bd8ba25ac06a0e4d36881b/sympy/sets/handlers/intersection.py#L14-L16
I guess we can do the same in the doctests if needed.
Ultimately it would be good to find a better way of using multiple dispatch so we don't repeat the same function name #17795.
I will add the noqa then, since I feel this second solution is out of my scope
I've said this before, but I'm not a fan of when linters force you to write code in a less clear way, and especially when this is done so in documentation.
Having noqa cluttering the documentation is also not great. Although it isn't so bad if Sphinx automatically removes it like it does for # DOCTEST: +SKIP.
Hey, what would you like me to do with `sympy/utilities/runtests.py`? `flake8 --doctests sympy/utilities/runtests.py` reports an `F403` (which is interesting I guess since it has no doctest code)
edit: same for `benchmarking.py`, `randtest.py`, `tmpfiles.py`, and `quality_unicode.py`.
I think we can avoid using noqa for multiple dispatch by making all the functions called `_` as is done for single dispatch.
|
[
{
"body": "Currently flake8 runs on the main code but not on doctests. It has a `--doctests` argument to check the doctests as well.\r\n\r\nFor example:\r\n```console\r\n$ flake8 --doctests sympy/matrices/determinant.py \r\nsympy/matrices/determinant.py:545:9: F401 'sympy.MatrixSymbol' imported but unused\r\nsympy/matrices/determinant.py:545:9: F401 'sympy.eye' imported but unused\r\nsympy/matrices/determinant.py:545:9: F401 'sympy.det' imported but unused\r\n```\r\nThat can be fixed with\r\n```diff\r\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/determinant.py b/sympy/matrices/determinant.py\r\nindex 647541afef..f3bb9a4067 100644\r\n--- a/sympy/matrices/determinant.py\r\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/determinant.py\r\n@@ -542,7 +542,7 @@ def _det(M, method=\"bareiss\", iszerofunc=None):\r\n Examples\r\n ========\r\n \r\n- >>> from sympy import Matrix, MatrixSymbol, eye, det\r\n+ >>> from sympy import Matrix\r\n >>> M = Matrix([[1, 2], [3, 4]])\r\n >>> M.det()\r\n -2\r\n```\r\n\r\nRunning flake8 on the whole of sympy with\r\n```\r\n$ flake8 --doctests sympy\r\n```\r\nleads to 698 warnings almost all of which are F401 (unnecessary import) and so easily fixable.\r\n\r\nThese should all be fixed and then we should add the `--doctest` argument on Travis.\r\n\r\nI'm marking this as easy to fix.",
"number": 19374,
"title": "Clean up flake8 warnings from doctests"
}
] |
6de346061821d2bc5b7e11be0382baaf2b22083d
|
{
"head_commit": "f6e5af56777605bd33872ab1a91db003fb697edd",
"head_commit_message": "quality(doc): Test doctests with flake8 on Travis\n\nMostly removes no longer needed imports.\n\nCo-authored-by: Marijan Smetko <[email protected]>",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/bin/test_travis.sh b/bin/test_travis.sh\nindex 51f553cbbf91..104a464bed00 100755\n--- a/bin/test_travis.sh\n+++ b/bin/test_travis.sh\n@@ -7,6 +7,7 @@ set -x\n \n if [[ \"${TEST_FLAKE8}\" == \"true\" ]]; then\n flake8 sympy;\n+ flake8 --doctests --per-file-ignores='sympy/interactive/session.py:F821' sympy;\n fi\n \n if [[ \"${TEST_SETUP}\" == \"true\" ]]; then\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/assume.py b/sympy/assumptions/assume.py\nindex 7efa484c0b9c..92e459320d22 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/assume.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/assume.py\n@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ class to create your own local assumptions contexts. It is basically a thin\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import AppliedPredicate, Q\n+ >>> from sympy import Q\n >>> from sympy.assumptions.assume import global_assumptions\n >>> global_assumptions\n AssumptionsContext()\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py\nindex 702972eb3091..4bab975a4fbc 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py\n@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ class AskFiniteHandler(CommonHandler):\n \n Examples of usage:\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q\n+ >>> from sympy import Q\n >>> from sympy.assumptions.handlers.calculus import AskFiniteHandler\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> a = AskFiniteHandler()\n@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ def Symbol(expr, assumptions):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q\n+ >>> from sympy import Q\n >>> from sympy.assumptions.handlers.calculus import AskFiniteHandler\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> a = AskFiniteHandler()\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/refine.py b/sympy/assumptions/refine.py\nindex cfe630a63d65..a50d506a8fe0 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/refine.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/refine.py\n@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ def refine_abs(expr, assumptions):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q, refine, Abs\n+ >>> from sympy import Q, Abs\n >>> from sympy.assumptions.refine import refine_abs\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> refine_abs(Abs(x), Q.real(x))\n@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ def refine_Pow(expr, assumptions):\n \"\"\"\n Handler for instances of Pow.\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q\n+ >>> from sympy import Q\n >>> from sympy.assumptions.refine import refine_Pow\n >>> from sympy.abc import x,y,z\n >>> refine_Pow((-1)**x, Q.real(x))\n@@ -190,7 +190,7 @@ def refine_atan2(expr, assumptions):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q, refine, atan2\n+ >>> from sympy import Q, atan2\n >>> from sympy.assumptions.refine import refine_atan2\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> refine_atan2(atan2(y,x), Q.real(y) & Q.positive(x))\ndiff --git a/sympy/calculus/finite_diff.py b/sympy/calculus/finite_diff.py\nindex f09fca706069..c91589c22a06 100644\n--- a/sympy/calculus/finite_diff.py\n+++ b/sympy/calculus/finite_diff.py\n@@ -441,7 +441,7 @@ def differentiate_finite(expr, *symbols,\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import cos, sin, Function, differentiate_finite\n+ >>> from sympy import sin, Function, differentiate_finite\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, h\n >>> f, g = Function('f'), Function('g')\n >>> differentiate_finite(f(x)*g(x), x, points=[x-h, x+h])\ndiff --git a/sympy/calculus/util.py b/sympy/calculus/util.py\nindex dc893b0531c9..50a9be1c8282 100644\n--- a/sympy/calculus/util.py\n+++ b/sympy/calculus/util.py\n@@ -720,7 +720,7 @@ def stationary_points(f, symbol, domain=S.Reals):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, S, sin, log, pi, pprint, stationary_points\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, S, sin, pi, pprint, stationary_points\n >>> from sympy.sets import Interval\n >>> x = Symbol('x')\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/categories/baseclasses.py b/sympy/categories/baseclasses.py\nindex 98fdbab91372..a29fa82e92eb 100644\n--- a/sympy/categories/baseclasses.py\n+++ b/sympy/categories/baseclasses.py\n@@ -563,7 +563,7 @@ class Diagram(Basic):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.categories import Object, NamedMorphism, Diagram\n- >>> from sympy import FiniteSet, pprint, default_sort_key\n+ >>> from sympy import pprint, default_sort_key\n >>> A = Object(\"A\")\n >>> B = Object(\"B\")\n >>> C = Object(\"C\")\ndiff --git a/sympy/codegen/array_utils.py b/sympy/codegen/array_utils.py\nindex 1fca53698284..bae4a9930295 100644\n--- a/sympy/codegen/array_utils.py\n+++ b/sympy/codegen/array_utils.py\n@@ -299,8 +299,8 @@ def _get_contraction_tuples(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol\n- >>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N\n+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import N\n >>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import CodegenArrayContraction, CodegenArrayTensorProduct\n >>> A = MatrixSymbol(\"A\", N, N)\n >>> B = MatrixSymbol(\"B\", N, N)\n@@ -362,8 +362,8 @@ def sort_args_by_name(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol\n- >>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N\n+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import N\n >>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import parse_matrix_expression\n >>> A = MatrixSymbol(\"A\", N, N)\n >>> B = MatrixSymbol(\"B\", N, N)\n@@ -402,8 +402,8 @@ def _get_contraction_links(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol\n- >>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N\n+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import N\n >>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import parse_matrix_expression\n >>> A = MatrixSymbol(\"A\", N, N)\n >>> B = MatrixSymbol(\"B\", N, N)\n@@ -566,7 +566,6 @@ def nest_permutation(self):\n \n >>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import (CodegenArrayPermuteDims, CodegenArrayTensorProduct, nest_permutation)\n >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n \n >>> M = MatrixSymbol(\"M\", 3, 3)\n >>> N = MatrixSymbol(\"N\", 3, 3)\n@@ -1061,7 +1060,6 @@ def parse_indexed_expression(expr, first_indices=None):\n \n >>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import parse_indexed_expression\n >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, Sum, symbols\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n \n >>> i, j, k, d = symbols(\"i j k d\")\n >>> M = MatrixSymbol(\"M\", d, d)\n@@ -1250,7 +1248,7 @@ def recognize_matrix_expression(expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, Sum\n >>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N\n >>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import CodegenArrayContraction, CodegenArrayTensorProduct\n >>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import recognize_matrix_expression, parse_indexed_expression, parse_matrix_expression\ndiff --git a/sympy/codegen/ast.py b/sympy/codegen/ast.py\nindex b25bf0850bc8..7f2ebc2f4eb0 100644\n--- a/sympy/codegen/ast.py\n+++ b/sympy/codegen/ast.py\n@@ -968,7 +968,6 @@ class Type(Token):\n ...\n ValueError: Casting gives a significantly different value.\n >>> boost_mp50 = Type('boost::multiprecision::cpp_dec_float_50')\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> from sympy.printing.cxxcode import cxxcode\n >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import Declaration, Variable\n >>> cxxcode(Declaration(Variable('x', type=boost_mp50)))\n@@ -1052,7 +1051,7 @@ def cast_check(self, value, rtol=None, atol=0, limits=None, precision_targets=No\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import Type, integer, float32, int8\n+ >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import integer, float32, int8\n >>> integer.cast_check(3.0) == 3\n True\n >>> float32.cast_check(1e-40) # doctest: +ELLIPSIS\n@@ -1168,7 +1167,7 @@ class FloatType(FloatBaseType):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, Float\n+ >>> from sympy import S\n >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FloatType\n >>> half_precision = FloatType('f16', nbits=16, nmant=10, nexp=5)\n >>> half_precision.max\n@@ -1564,8 +1563,7 @@ class Declaration(Token):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol\n- >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import Declaration, Type, Variable, NoneToken, integer, untyped\n+ >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import Declaration, NoneToken, untyped\n >>> z = Declaration('z')\n >>> z.variable.type == untyped\n True\ndiff --git a/sympy/codegen/fnodes.py b/sympy/codegen/fnodes.py\nindex 5f34e3aef46a..18a08ac7ef5a 100644\n--- a/sympy/codegen/fnodes.py\n+++ b/sympy/codegen/fnodes.py\n@@ -454,7 +454,7 @@ def size(array, dim=None, kind=None):\n \n >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> from sympy.printing import fcode\n- >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FunctionDefinition, real, Return, Variable\n+ >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FunctionDefinition, real, Return\n >>> from sympy.codegen.fnodes import array, sum_, size\n >>> a = Symbol('a', real=True)\n >>> body = [Return((sum_(a**2)/size(a))**.5)]\n@@ -505,8 +505,8 @@ def bind_C(name=None):\n \n >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> from sympy.printing import fcode\n- >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FunctionDefinition, real, Return, Variable\n- >>> from sympy.codegen.fnodes import array, sum_, size, bind_C\n+ >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FunctionDefinition, real, Return\n+ >>> from sympy.codegen.fnodes import array, sum_, bind_C\n >>> a = Symbol('a', real=True)\n >>> s = Symbol('s', integer=True)\n >>> arr = array(a, dim=[s], intent='in')\ndiff --git a/sympy/codegen/rewriting.py b/sympy/codegen/rewriting.py\nindex 790a3995c4a2..df2cb513bc31 100644\n--- a/sympy/codegen/rewriting.py\n+++ b/sympy/codegen/rewriting.py\n@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ class ReplaceOptim(Optimization):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Pow\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> from sympy.codegen.rewriting import ReplaceOptim\n >>> from sympy.codegen.cfunctions import exp2\n >>> x = Symbol('x')\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/coset_table.py b/sympy/combinatorics/coset_table.py\nindex 9e9b2b0f7ecf..e99d3b6af546 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/coset_table.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/coset_table.py\n@@ -1171,7 +1171,7 @@ def modified_coset_enumeration_r(fp_grp, Y, max_cosets=None, draft=None,\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.free_groups import free_group\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import FpGroup, coset_enumeration_r\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import FpGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.coset_table import modified_coset_enumeration_r\n >>> F, x, y = free_group(\"x, y\")\n >>> f = FpGroup(F, [x**3, y**3, x**-1*y**-1*x*y])\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/fp_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/fp_groups.py\nindex 1313c3d3ee6d..379a9b8c9bad 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/fp_groups.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/fp_groups.py\n@@ -127,7 +127,7 @@ def subgroup(self, gens, C=None, homomorphism=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import (FpGroup, FpSubgroup)\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import FpGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.free_groups import free_group\n >>> F, x, y = free_group(\"x, y\")\n >>> f = FpGroup(F, [x**3, y**5, (x*y)**2])\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/free_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/free_groups.py\nindex 26a3afbef724..6f670a114c74 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/free_groups.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/free_groups.py\n@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ def vfree_group(symbols):\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.free_groups import vfree_group\n >>> vfree_group(\"x, y, z\")\n <free group on the generators (x, y, z)>\n- >>> x**2*y**-2*z\n+ >>> x**2*y**-2*z # noqa: F821\n x**2*y**-2*z\n >>> type(_)\n <class 'sympy.combinatorics.free_groups.FreeGroupElement'>\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/generators.py b/sympy/combinatorics/generators.py\nindex 02d8b5e2c38c..3104c2fc3afc 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/generators.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/generators.py\n@@ -11,7 +11,6 @@ def symmetric(n):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.generators import symmetric\n >>> list(symmetric(3))\n [(2), (1 2), (2)(0 1), (0 1 2), (0 2 1), (0 2)]\n@@ -27,7 +26,6 @@ def cyclic(n):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.generators import cyclic\n >>> list(cyclic(5))\n [(4), (0 1 2 3 4), (0 2 4 1 3),\n@@ -51,7 +49,6 @@ def alternating(n):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.generators import alternating\n >>> list(alternating(3))\n [(2), (0 1 2), (0 2 1)]\n@@ -73,7 +70,6 @@ def dihedral(n):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.generators import dihedral\n >>> list(dihedral(3))\n [(2), (0 2), (0 1 2), (1 2), (0 2 1), (2)(0 1)]\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/homomorphisms.py b/sympy/combinatorics/homomorphisms.py\nindex 9612121b85da..9e6610eb6b08 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/homomorphisms.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/homomorphisms.py\n@@ -447,7 +447,7 @@ def group_isomorphism(G, H, isomorphism=True):\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.free_groups import free_group\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import FpGroup\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.homomorphisms import homomorphism, group_isomorphism\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.homomorphisms import group_isomorphism\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup, AlternatingGroup\n \n >>> D = DihedralGroup(8)\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/named_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/named_groups.py\nindex c0c37e40cc0c..dbdb0706d787 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/named_groups.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/named_groups.py\n@@ -16,7 +16,6 @@ def AbelianGroup(*cyclic_orders):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import AbelianGroup\n >>> AbelianGroup(3, 4)\n PermutationGroup([\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py\nindex 2220c4e8a953..de94ddabb4af 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py\n@@ -33,7 +33,6 @@ class PermutationGroup(Basic):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Cycle\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.polyhedron import Polyhedron\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n \n@@ -254,7 +253,6 @@ def __mul__(self, other):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import CyclicGroup\n >>> G = CyclicGroup(5)\n >>> H = G*G\n@@ -912,7 +910,6 @@ def center(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> D = DihedralGroup(4)\n >>> G = D.center()\n@@ -1464,7 +1461,6 @@ def generate(self, method=\"coset\", af=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.polyhedron import tetrahedron\n \n@@ -1957,7 +1953,6 @@ def is_alt_sym(self, eps=0.05, _random_prec=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> D = DihedralGroup(10)\n >>> D.is_alt_sym()\n@@ -2101,7 +2096,6 @@ def is_primitive(self, randomized=True):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> D = DihedralGroup(10)\n >>> D.is_primitive()\n@@ -2516,7 +2510,6 @@ def minimal_block(self, points):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> D = DihedralGroup(10)\n >>> D.minimal_block([0, 5])\n@@ -2801,8 +2794,6 @@ def orbit_rep(self, alpha, beta, schreier_vector=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import AlternatingGroup\n >>> G = AlternatingGroup(5)\n >>> G.orbit_rep(0, 4)\n@@ -2843,8 +2834,6 @@ def orbit_transversal(self, alpha, pairs=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> G = DihedralGroup(6)\n >>> G.orbit_transversal(0)\n@@ -3429,7 +3418,6 @@ def schreier_sims_incremental(self, base=None, gens=None, slp_dict=False):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import AlternatingGroup\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import _verify_bsgs\n >>> A = AlternatingGroup(7)\n >>> base = [2, 3]\n@@ -3614,7 +3602,6 @@ def schreier_sims_random(self, base=None, gens=None, consec_succ=10,\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import _verify_bsgs\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup\n >>> S = SymmetricGroup(5)\n@@ -3769,8 +3756,6 @@ def stabilizer(self, alpha):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> G = DihedralGroup(6)\n >>> G.stabilizer(5)\n@@ -3872,7 +3857,6 @@ def subgroup_search(self, prop, base=None, strong_gens=None, tests=None,\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import (SymmetricGroup,\n ... AlternatingGroup)\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import _verify_bsgs\n >>> S = SymmetricGroup(7)\n >>> prop_even = lambda x: x.is_even\n@@ -4598,7 +4582,6 @@ def strong_presentation(G):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> P = DihedralGroup(4)\n >>> G = P.strong_presentation()\n@@ -4949,7 +4932,7 @@ def _orbits(degree, generators):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup, _orbits\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import _orbits\n >>> a = Permutation([0, 2, 1])\n >>> b = Permutation([1, 0, 2])\n >>> _orbits(a.size, [a, b])\n@@ -4991,7 +4974,6 @@ def _orbit_transversal(degree, generators, alpha, pairs, af=False, slp=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import _orbit_transversal\n >>> G = DihedralGroup(6)\n@@ -5043,7 +5025,6 @@ def _stabilizer(degree, generators, alpha):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import _stabilizer\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> G = DihedralGroup(6)\n@@ -5119,7 +5100,7 @@ def order(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, SymmetricPermutationGroup\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics import SymmetricPermutationGroup\n >>> G = SymmetricPermutationGroup(4)\n >>> G.order()\n 24\n@@ -5138,7 +5119,7 @@ def degree(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, SymmetricPermutationGroup\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics import SymmetricPermutationGroup\n >>> G = SymmetricPermutationGroup(4)\n >>> G.degree\n 4\n@@ -5154,7 +5135,7 @@ def identity(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, SymmetricPermutationGroup\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics import SymmetricPermutationGroup\n >>> G = SymmetricPermutationGroup(4)\n >>> G.identity()\n (3)\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py b/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py\nindex de7bfd918993..da19cbf50601 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py\n@@ -322,7 +322,6 @@ def __call__(self, *other):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Cycle as C\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation as Perm\n >>> C(1, 2)(2, 3)\n (1 3 2)\n \n@@ -355,7 +354,6 @@ def list(self, size=None):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Cycle\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n >>> p = Cycle(2, 3)(4, 5)\n >>> p.list()\n [0, 1, 3, 2, 5, 4]\n@@ -1195,7 +1193,7 @@ def rmul(*args):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import _af_rmul, Permutation\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n \n >>> a, b = [1, 0, 2], [0, 2, 1]\n >>> a = Permutation(a); b = Permutation(b)\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/polyhedron.py b/sympy/combinatorics/polyhedron.py\nindex aadb3e8fde20..78176f11fed4 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/polyhedron.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/polyhedron.py\n@@ -425,7 +425,6 @@ def array_form(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, Cycle\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.polyhedron import tetrahedron\n >>> tetrahedron = tetrahedron.copy()\n >>> tetrahedron.array_form\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/tensor_can.py b/sympy/combinatorics/tensor_can.py\nindex 75797b3f20cd..937a25fdf47e 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/tensor_can.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/tensor_can.py\n@@ -387,7 +387,6 @@ def double_coset_can_rep(dummies, sym, b_S, sgens, S_transversals, g):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import double_coset_can_rep, get_transversals\n >>> gens = [Permutation(x) for x in [[2, 1, 0, 3, 4, 5, 7, 6], [4, 1, 2, 3, 0, 5, 7, 6]]]\n >>> base = [0, 2]\n@@ -913,7 +912,6 @@ def bsgs_direct_product(base1, gens1, base2, gens2, signed=True):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import (get_symmetric_group_sgs, bsgs_direct_product)\n >>> base1, gens1 = get_symmetric_group_sgs(1)\n >>> base2, gens2 = get_symmetric_group_sgs(2)\n@@ -947,7 +945,6 @@ def get_symmetric_group_sgs(n, antisym=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import get_symmetric_group_sgs\n >>> get_symmetric_group_sgs(3)\n ([0, 1], [(4)(0 1), (4)(1 2)])\n@@ -1051,7 +1048,6 @@ def tensor_gens(base, gens, list_free_indices, sym=0):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import tensor_gens, get_symmetric_group_sgs\n \n two symmetric tensors with 3 indices without free indices\n@@ -1167,7 +1163,6 @@ def gens_products(*v):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import get_symmetric_group_sgs, gens_products\n >>> base, gens = get_symmetric_group_sgs(2)\n >>> gens_products((base, gens, [[], []], 0))\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/testutil.py b/sympy/combinatorics/testutil.py\nindex d9d80db949c5..c34c1665824e 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/testutil.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/testutil.py\n@@ -215,7 +215,7 @@ def canonicalize_naive(g, dummies, sym, *v):\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import canonicalize_naive\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import get_symmetric_group_sgs\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, PermutationGroup\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> g = Permutation([1, 3, 2, 0, 4, 5])\n >>> base2, gens2 = get_symmetric_group_sgs(2)\n >>> canonicalize_naive(g, [2, 3], 0, (base2, gens2, 2, 0))\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/util.py b/sympy/combinatorics/util.py\nindex 9019f77b3f85..fe7e33c0081a 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/util.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/util.py\n@@ -139,7 +139,6 @@ def _distribute_gens_by_base(base, gens):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _distribute_gens_by_base\n >>> D = DihedralGroup(3)\n@@ -206,7 +205,6 @@ def _handle_precomputed_bsgs(base, strong_gens, transversals=None,\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _handle_precomputed_bsgs\n >>> D = DihedralGroup(3)\n@@ -265,16 +263,13 @@ def _orbits_transversals_from_bsgs(base, strong_gens_distr,\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _orbits_transversals_from_bsgs\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import (_orbits_transversals_from_bsgs,\n- ... _distribute_gens_by_base)\n+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _distribute_gens_by_base\n >>> S = SymmetricGroup(3)\n >>> S.schreier_sims()\n >>> strong_gens_distr = _distribute_gens_by_base(S.base, S.strong_gens)\n- >>> _orbits_transversals_from_bsgs(S.base, strong_gens_distr)\n- ([[0, 1, 2], [1, 2]], [{0: (2), 1: (0 1 2), 2: (0 2 1)}, {1: (2), 2: (1 2)}])\n+ >>> (S.base, strong_gens_distr)\n+ ([0, 1], [[(0 1 2), (2)(0 1), (1 2)], [(1 2)]])\n \n See Also\n ========\n@@ -326,7 +321,6 @@ def _remove_gens(base, strong_gens, basic_orbits=None, strong_gens_distr=None):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup\n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _remove_gens\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import _verify_bsgs\n >>> S = SymmetricGroup(15)\n@@ -408,7 +402,6 @@ def _strip(g, base, orbits, transversals):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _strip\n@@ -501,7 +494,6 @@ def _strong_gens_from_distr(strong_gens_distr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup\n >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import (_strong_gens_from_distr,\n ... _distribute_gens_by_base)\ndiff --git a/sympy/concrete/delta.py b/sympy/concrete/delta.py\nindex a53a9fdad606..7c9f28b5035d 100644\n--- a/sympy/concrete/delta.py\n+++ b/sympy/concrete/delta.py\n@@ -267,7 +267,7 @@ def deltasummation(f, limit, no_piecewise=False):\n >>> from sympy.abc import k\n >>> i, j = symbols('i, j', integer=True, finite=True)\n >>> from sympy.concrete.delta import deltasummation\n- >>> from sympy import KroneckerDelta, Piecewise\n+ >>> from sympy import KroneckerDelta\n >>> deltasummation(KroneckerDelta(i, k), (k, -oo, oo))\n 1\n >>> deltasummation(KroneckerDelta(i, k), (k, 0, oo))\ndiff --git a/sympy/concrete/gosper.py b/sympy/concrete/gosper.py\nindex 5b7c3148986e..794a51c5673e 100644\n--- a/sympy/concrete/gosper.py\n+++ b/sympy/concrete/gosper.py\n@@ -173,7 +173,7 @@ def gosper_sum(f, k):\n \n >>> from sympy.concrete.gosper import gosper_sum\n >>> from sympy.functions import factorial\n- >>> from sympy.abc import i, n, k\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import n, k\n \n >>> f = (4*k + 1)*factorial(k)/factorial(2*k + 1)\n >>> gosper_sum(f, (k, 0, n))\ndiff --git a/sympy/concrete/guess.py b/sympy/concrete/guess.py\nindex b6c2a847c37b..688fe04c4828 100644\n--- a/sympy/concrete/guess.py\n+++ b/sympy/concrete/guess.py\n@@ -248,7 +248,7 @@ def guess_generating_function(v, X=Symbol('x'), types=['all'], maxsqrtn=2):\n >>> ggf([fibonacci(k) for k in range(5, 15)], types=['ogf'])\n {'ogf': (3*x + 5)/(-x**2 - x + 1)}\n \n- >>> from sympy import simplify, factorial\n+ >>> from sympy import factorial\n >>> ggf([factorial(k) for k in range(12)], types=['ogf', 'egf', 'lgf'])\n {'egf': 1/(1 - x)}\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/concrete/products.py b/sympy/concrete/products.py\nindex b54e7dac0c90..a2c593270c7f 100644\n--- a/sympy/concrete/products.py\n+++ b/sympy/concrete/products.py\n@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ class Product(ExprWithIntLimits):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, i, k, m, n, x\n- >>> from sympy import Product, factorial, oo\n+ >>> from sympy import Product, oo\n >>> Product(k, (k, 1, m))\n Product(k, (k, 1, m))\n >>> Product(k, (k, 1, m)).doit()\n@@ -428,7 +428,7 @@ def is_convergent(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Interval, S, Product, Symbol, cos, pi, exp, oo\n+ >>> from sympy import Product, Symbol, cos, pi, exp, oo\n >>> n = Symbol('n', integer=True)\n >>> Product(n/(n + 1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()\n False\n@@ -474,7 +474,7 @@ def reverse_order(expr, *indices):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Product, simplify, RisingFactorial, gamma, Sum\n+ >>> from sympy import Product, simplify, Sum\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, a, b, c, d\n >>> P = Product(x, (x, a, b))\n >>> Pr = P.reverse_order(x)\ndiff --git a/sympy/concrete/summations.py b/sympy/concrete/summations.py\nindex 27633a7c25e2..b4f1d413501c 100644\n--- a/sympy/concrete/summations.py\n+++ b/sympy/concrete/summations.py\n@@ -628,7 +628,7 @@ def is_absolutely_convergent(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Sum, Symbol, sin, oo\n+ >>> from sympy import Sum, Symbol, oo\n >>> n = Symbol('n', integer=True)\n >>> Sum((-1)**n, (n, 1, oo)).is_absolutely_convergent()\n False\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/basic.py b/sympy/core/basic.py\nindex 53beba2396f7..8b024abea205 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/basic.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/basic.py\n@@ -554,7 +554,7 @@ def as_dummy(self):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Integral, Symbol\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> r = Symbol('r', real=True)\n >>> Integral(r, (r, x)).as_dummy()\n Integral(_0, (_0, x))\n@@ -569,7 +569,6 @@ def as_dummy(self):\n Any object that has structurally bound variables should have\n a property, `bound_symbols` that returns those symbols\n appearing in the object.\n-\n \"\"\"\n from sympy.core.symbol import Dummy, Symbol\n def can(x):\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/cache.py b/sympy/core/cache.py\nindex 0bad6fbeefcd..7c5045093749 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/cache.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/cache.py\n@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ def __cacheit(maxsize):\n ... return a+b\n \n >>> @cacheit\n- ... def f(a, b):\n+ ... def f(a, b): # noqa: F811\n ... return [a, b] # <-- WRONG, returns mutable object\n \n to force cacheit to check returned results mutability and consistency,\n@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ def __cacheit(maxsize):\n ... return a+b\n \n >>> @cacheit\n- ... def f(a, b):\n+ ... def f(a, b): # noqa: F811\n ... return [a, b] # <-- WRONG, returns mutable object\n \n to force cacheit to check returned results mutability and consistency,\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py\nindex beec0ba0b1f6..b5490207ae9c 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/expr.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py\n@@ -434,7 +434,7 @@ def is_number(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import log, Integral, cos, sin, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import Integral, cos, sin, pi\n >>> from sympy.core.function import Function\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\n@@ -2827,7 +2827,7 @@ def series(self, x=None, x0=0, n=6, dir=\"+\", logx=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import cos, exp, tan, oo, series\n+ >>> from sympy import cos, exp, tan\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> cos(x).series()\n 1 - x**2/2 + x**4/24 + O(x**6)\n@@ -3043,7 +3043,7 @@ def aseries(self, x=None, n=6, bound=0, hir=False):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import sin, exp\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \n >>> e = sin(1/x + exp(-x)) - sin(1/x)\n \n@@ -3688,7 +3688,7 @@ def round(self, n=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import pi, E, I, S, Add, Mul, Number\n+ >>> from sympy import pi, E, I, S, Number\n >>> pi.round()\n 3\n >>> pi.round(2)\n@@ -3921,7 +3921,7 @@ class UnevaluatedExpr(Expr):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import UnevaluatedExpr\n- >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> x*(1/x)\n 1\n >>> x*UnevaluatedExpr(1/x)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/exprtools.py b/sympy/core/exprtools.py\nindex 820006e447a9..7ff6ef54596d 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/exprtools.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/exprtools.py\n@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ def _monotonic_sign(self):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.core.exprtools import _monotonic_sign as F\n- >>> from sympy import Dummy, S\n+ >>> from sympy import Dummy\n >>> nn = Dummy(integer=True, nonnegative=True)\n >>> p = Dummy(integer=True, positive=True)\n >>> p2 = Dummy(integer=True, positive=True)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/function.py b/sympy/core/function.py\nindex d76995116387..c02df2331536 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/function.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/function.py\n@@ -216,7 +216,6 @@ def nargs(self):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.core.function import Function\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> f = Function('f')\n \n If the function can take any number of arguments, the set of whole\n@@ -1090,7 +1089,7 @@ class Derivative(Expr):\n automatically simplified in a fairly conservative fashion unless the\n keyword ``simplify`` is set to False.\n \n- >>> from sympy import cos, sin, sqrt, diff, Function, symbols\n+ >>> from sympy import sqrt, diff, Function, symbols\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n >>> f, g = symbols('f,g', cls=Function)\n \n@@ -1524,7 +1523,7 @@ def _sort_variable_count(cls, vc):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Derivative, Function, symbols, cos\n+ >>> from sympy import Derivative, Function, symbols\n >>> vsort = Derivative._sort_variable_count\n >>> x, y, z = symbols('x y z')\n >>> f, g, h = symbols('f g h', cls=Function)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/numbers.py b/sympy/core/numbers.py\nindex 9a01dd27e1d8..27b671e148c9 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/numbers.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/numbers.py\n@@ -2583,7 +2583,7 @@ class Zero(IntegerConstant, metaclass=Singleton):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, Integer, zoo\n+ >>> from sympy import S, Integer\n >>> Integer(0) is S.Zero\n True\n >>> 1/S.Zero\n@@ -3290,7 +3290,7 @@ class ComplexInfinity(AtomicExpr, metaclass=Singleton):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import zoo, oo\n+ >>> from sympy import zoo\n >>> zoo + 42\n zoo\n >>> 42/zoo\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/relational.py b/sympy/core/relational.py\nindex 33672037e46b..c65577b561b9 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/relational.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/relational.py\n@@ -680,7 +680,7 @@ def as_poly(self, *gens, **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Eq\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> Eq(x**2, 1).as_poly(x)\n Poly(x**2 - 1, x, domain='ZZ')\n '''\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/singleton.py b/sympy/core/singleton.py\nindex 4ae3ec3e7131..1f9447021df5 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/singleton.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/singleton.py\n@@ -46,7 +46,8 @@ class SingletonRegistry(Registry):\n When using ``is`` comparison, make sure the argument is sympified. For\n instance,\n \n- >>> 0 is S.Zero\n+ >>> x = 0\n+ >>> x is S.Zero\n False\n \n This problem is not an issue when using ``==``, which is recommended for\n@@ -137,7 +138,6 @@ class is instantiated. Additionally, this instance can be accessed through\n \n >>> from sympy import S, Basic\n >>> from sympy.core.singleton import Singleton\n- >>> from sympy.core.compatibility import with_metaclass\n >>> class MySingleton(Basic, metaclass=Singleton):\n ... pass\n >>> Basic() is Basic()\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/symbol.py b/sympy/core/symbol.py\nindex 1839feccc05e..214bf4ffe4a7 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/symbol.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/symbol.py\n@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ def _symbol(s, matching_symbol=None, **assumptions):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Dummy\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> from sympy.core.symbol import _symbol\n >>> _symbol('y')\n y\n@@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ def _uniquely_named_symbol(xname, exprs=(), compare=str, modify=None, **assumpti\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.core.symbol import _uniquely_named_symbol as usym, Dummy\n+ >>> from sympy.core.symbol import _uniquely_named_symbol as usym\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> usym('x', x)\n _x\n@@ -720,17 +720,17 @@ def var(names, **args):\n \n >>> var('x')\n x\n- >>> x\n+ >>> x # noqa: F821\n x\n \n >>> var('a,ab,abc')\n (a, ab, abc)\n- >>> abc\n+ >>> abc # noqa: F821\n abc\n \n >>> var('x,y', real=True)\n (x, y)\n- >>> x.is_real and y.is_real\n+ >>> x.is_real and y.is_real # noqa: F821\n True\n \n See :func:`symbols` documentation for more details on what kinds of\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/sympify.py b/sympy/core/sympify.py\nindex a75546544696..a3f1ce2851ba 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/sympify.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/sympify.py\n@@ -448,7 +448,7 @@ def kernS(s):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.core.sympify import kernS\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n \n The 2-arg Mul distributes a number (or minus sign) across the terms\n of an expression, but kernS will prevent that:\ndiff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\nindex a4d1ed30b8e3..44edd4596808 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\n@@ -482,8 +482,7 @@ class BaseScalarField(Expr):\n Define boilerplate Manifold, Patch and coordinate systems:\n \n >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, pi, Function\n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom import (\n- ... Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, Point, BaseScalarField)\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField\n >>> r0, theta0 = symbols('r0, theta0')\n >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)\n >>> p = Patch('P', m)\n@@ -574,7 +573,7 @@ class BaseVectorField(Expr):\n \n Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols, pi, Function\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Function\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_p, R2_r\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import BaseVectorField\n >>> from sympy import pprint\n@@ -681,7 +680,6 @@ class Commutator(Expr):\n \n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Commutator\n- >>> from sympy import pprint\n >>> from sympy.simplify import simplify\n \n Vector fields:\n@@ -1204,7 +1202,7 @@ def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeff\n Use the predefined R2 manifold:\n \n >>> from sympy.abc import t, x, y\n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_p, R2_r\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_p, R2_r\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import intcurve_series\n \n Specify a starting point and a vector field:\ndiff --git a/sympy/discrete/convolutions.py b/sympy/discrete/convolutions.py\nindex 9875c185a492..faf1c18b029a 100644\n--- a/sympy/discrete/convolutions.py\n+++ b/sympy/discrete/convolutions.py\n@@ -296,7 +296,7 @@ def convolution_subset(a, b):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols, S, I\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols, S\n >>> from sympy.discrete.convolutions import convolution_subset\n >>> u, v, x, y, z = symbols('u v x y z')\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py\nindex 0078ce06f55b..240d4ddf2874 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py\n@@ -396,7 +396,8 @@ class factorial2(CombinatorialFunction):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import factorial2, var\n- >>> var('n')\n+ >>> n = var('n')\n+ >>> n\n n\n >>> factorial2(n + 1)\n factorial2(n + 1)\n@@ -649,7 +650,7 @@ class FallingFactorial(CombinatorialFunction):\n Factorial Factorization and Symbolic Summation\", Journal of\n Symbolic Computation, vol. 20, pp. 235-268, 1995.\n \n- >>> from sympy import ff, factorial, rf, gamma, polygamma, binomial, symbols, Poly\n+ >>> from sympy import ff, factorial, rf, gamma, binomial, symbols, Poly\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, k\n >>> n, m = symbols('n m', integer=True)\n >>> ff(x, 0)\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/numbers.py b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/numbers.py\nindex bde58ed85a74..2591fa00bf5a 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/numbers.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/numbers.py\n@@ -1081,8 +1081,8 @@ class catalan(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import (Symbol, binomial, gamma, hyper, polygamma,\n- ... catalan, diff, combsimp, Rational, I)\n+ >>> from sympy import (Symbol, binomial, gamma, hyper, catalan,\n+ ... diff, combsimp, Rational, I)\n \n >>> [catalan(i) for i in range(1,10)]\n [1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862]\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py\nindex 9defa46aa857..7fda45982bc6 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py\n@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ class re(Function):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import re, im, I, E\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> re(2*E)\n 2*E\n >>> re(2*I + 17)\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py\nindex 908bd4d712ab..960121c8aa73 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py\n@@ -362,7 +362,7 @@ class frac(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, frac, Rational, floor, ceiling, I\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, frac, Rational, floor, I\n >>> frac(Rational(4, 3))\n 1/3\n >>> frac(-Rational(4, 3))\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py\nindex a80432889715..3e958c55f8b1 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py\n@@ -250,7 +250,7 @@ def root(arg, n, k=0, evaluate=None):\n The following examples show the roots of unity for n\n equal 2, 3 and 4:\n \n- >>> from sympy import rootof, I\n+ >>> from sympy import rootof\n \n >>> [rootof(x**2 - 1, i) for i in range(2)]\n [-1, 1]\n@@ -329,8 +329,7 @@ def real_root(arg, n=None, evaluate=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import root, real_root, Rational\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, n\n+ >>> from sympy import root, real_root\n \n >>> real_root(-8, 3)\n -2\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\nindex 9b5c1862a063..b7ccb6943ace 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\n@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ class Piecewise(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Piecewise, log, ITE, piecewise_fold\n+ >>> from sympy import Piecewise, log, piecewise_fold\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> f = x**2\n >>> g = log(x)\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/trigonometric.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/trigonometric.py\nindex ac8fddf94a2a..4a8adc4b1aed 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/trigonometric.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/trigonometric.py\n@@ -137,7 +137,7 @@ def _pi_coeff(arg, cycles=1):\n \n >>> from sympy.functions.elementary.trigonometric import _pi_coeff as coeff\n >>> from sympy import pi, Dummy\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> coeff(3*x*pi)\n 3*x\n >>> coeff(11*pi/7)\n@@ -1879,7 +1879,7 @@ class sinc(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import sinc, oo, jn, Product, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import sinc, oo, jn\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> sinc(x)\n sinc(x)\n@@ -2057,11 +2057,15 @@ class asin(InverseTrigonometricFunction):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import asin, oo, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import asin, oo\n >>> asin(1)\n pi/2\n >>> asin(-1)\n -pi/2\n+ >>> asin(-oo)\n+ oo*I\n+ >>> asin(oo)\n+ -oo*I\n \n See Also\n ========\n@@ -2227,7 +2231,7 @@ class acos(InverseTrigonometricFunction):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import acos, oo, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import acos, oo\n >>> acos(1)\n 0\n >>> acos(0)\n@@ -2395,7 +2399,7 @@ class atan(InverseTrigonometricFunction):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import atan, oo, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import atan, oo\n >>> atan(0)\n 0\n >>> atan(1)\n@@ -2758,11 +2762,15 @@ class asec(InverseTrigonometricFunction):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import asec, oo, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import asec, oo\n >>> asec(1)\n 0\n >>> asec(-1)\n pi\n+ >>> asec(0)\n+ zoo\n+ >>> asec(-oo)\n+ pi/2\n \n See Also\n ========\n@@ -2876,11 +2884,17 @@ class acsc(InverseTrigonometricFunction):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import acsc, oo, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import acsc, oo\n >>> acsc(1)\n pi/2\n >>> acsc(-1)\n -pi/2\n+ >>> acsc(oo)\n+ 0\n+ >>> acsc(-oo) == acsc(oo)\n+ True\n+ >>> acsc(0)\n+ zoo\n \n See Also\n ========\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py b/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py\nindex db8f55d221f4..30bddffbbddc 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py\n@@ -660,7 +660,6 @@ class jn(SphericalBesselBase):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Symbol, jn, sin, cos, expand_func, besselj, bessely\n- >>> from sympy import simplify\n >>> z = Symbol(\"z\")\n >>> nu = Symbol(\"nu\", integer=True)\n >>> print(expand_func(jn(0, z)))\n@@ -1742,7 +1741,7 @@ class marcumq(Function):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import marcumq\n- >>> from sympy.abc import m, a, b, x\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import m, a, b\n >>> marcumq(m, a, b)\n marcumq(m, a, b)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py\nindex 23229a55ca20..be38c348d443 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py\n@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ class DiracDelta(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, diff, pi, Piecewise\n+ >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, diff, pi\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n \n >>> DiracDelta(x)\n@@ -160,7 +160,7 @@ class is about to be instantiated and it returns either some simplified\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, S, Subs\n+ >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, S\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \n >>> DiracDelta(x)\n@@ -335,7 +335,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Piecewise(self, *args, **kwargs):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, Piecewise, Symbol, SingularityFunction\n+ >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, Piecewise, Symbol\n >>> x = Symbol('x')\n \n >>> DiracDelta(x).rewrite(Piecewise)\n@@ -549,7 +549,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Piecewise(self, arg, H0=None, **kwargs):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Piecewise, Symbol, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Piecewise, Symbol\n >>> x = Symbol('x')\n \n >>> Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise)\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/elliptic_integrals.py b/sympy/functions/special/elliptic_integrals.py\nindex e1a242a9180a..5e6854521925 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/elliptic_integrals.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/elliptic_integrals.py\n@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ class elliptic_k(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import elliptic_k, I, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import elliptic_k, I\n >>> from sympy.abc import m\n >>> elliptic_k(0)\n pi/2\n@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ class elliptic_f(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import elliptic_f, I, O\n+ >>> from sympy import elliptic_f, I\n >>> from sympy.abc import z, m\n >>> elliptic_f(z, m).series(z)\n z + z**5*(3*m**2/40 - m/30) + m*z**3/6 + O(z**6)\n@@ -217,7 +217,7 @@ class elliptic_e(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import elliptic_e, I, pi, O\n+ >>> from sympy import elliptic_e, I\n >>> from sympy.abc import z, m\n >>> elliptic_e(z, m).series(z)\n z + z**5*(-m**2/40 + m/30) - m*z**3/6 + O(z**6)\n@@ -338,7 +338,7 @@ class elliptic_pi(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import elliptic_pi, I, pi, O, S\n+ >>> from sympy import elliptic_pi, I\n >>> from sympy.abc import z, n, m\n >>> elliptic_pi(n, z, m).series(z, n=4)\n z + z**3*(m/6 + n/3) + O(z**4)\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/error_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/error_functions.py\nindex 5e8a51ad309f..699d39c53e3e 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/error_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/error_functions.py\n@@ -608,7 +608,7 @@ class erf2(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import I, oo, erf2\n+ >>> from sympy import oo, erf2\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n \n Several special values are known:\n@@ -748,7 +748,7 @@ class erfinv(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import I, oo, erfinv\n+ >>> from sympy import erfinv\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \n Several special values are known:\n@@ -842,7 +842,7 @@ class erfcinv (Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import I, oo, erfcinv\n+ >>> from sympy import erfcinv\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \n Several special values are known:\n@@ -918,7 +918,7 @@ class erf2inv(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import I, oo, erf2inv, erfinv, erfcinv\n+ >>> from sympy import erf2inv, oo\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n \n Several special values are known:\n@@ -1064,7 +1064,7 @@ class Ei(Function):\n The exponential integral is related to many other special functions.\n For example:\n \n- >>> from sympy import uppergamma, expint, Shi\n+ >>> from sympy import expint, Shi\n >>> Ei(x).rewrite(expint)\n -expint(1, x*exp_polar(I*pi)) - I*pi\n >>> Ei(x).rewrite(Shi)\n@@ -1536,7 +1536,7 @@ class Li(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import I, oo, Li\n+ >>> from sympy import Li\n >>> from sympy.abc import z\n \n The following special value is known:\n@@ -2213,7 +2213,7 @@ class fresnels(FresnelIntegral):\n \n Defining the Fresnel functions via an integral:\n \n- >>> from sympy import integrate, pi, sin, gamma, expand_func\n+ >>> from sympy import integrate, pi, sin, expand_func\n >>> integrate(sin(pi*z**2/2), z)\n 3*fresnels(z)*gamma(3/4)/(4*gamma(7/4))\n >>> expand_func(integrate(sin(pi*z**2/2), z))\n@@ -2354,7 +2354,7 @@ class fresnelc(FresnelIntegral):\n \n Defining the Fresnel functions via an integral:\n \n- >>> from sympy import integrate, pi, cos, gamma, expand_func\n+ >>> from sympy import integrate, pi, cos, expand_func\n >>> integrate(cos(pi*z**2/2), z)\n fresnelc(z)*gamma(1/4)/(4*gamma(5/4))\n >>> expand_func(integrate(cos(pi*z**2/2), z))\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py\nindex 4d92e373519e..d9793fd4a971 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py\n@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ class gamma(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, I, pi, oo, gamma\n+ >>> from sympy import S, I, pi, gamma\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \n Several special values are known:\n@@ -868,7 +868,7 @@ class loggamma(Function):\n \n For half-integral values:\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import S\n >>> loggamma(S(5)/2)\n log(3*sqrt(pi)/4)\n >>> loggamma(n/2)\n@@ -1241,7 +1241,7 @@ class multigamma(Function):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, I, pi, oo, gamma, multigamma\n+ >>> from sympy import S, multigamma\n >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> x = Symbol('x')\n >>> p = Symbol('p', positive=True, integer=True)\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/special/polynomials.py b/sympy/functions/special/polynomials.py\nindex 8d202083c8f4..161d84d5be32 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/special/polynomials.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/special/polynomials.py\n@@ -441,7 +441,7 @@ class chebyshevt(OrthogonalPolynomial):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import chebyshevt, chebyshevu, diff\n+ >>> from sympy import chebyshevt, diff\n >>> from sympy.abc import n,x\n >>> chebyshevt(0, x)\n 1\n@@ -553,7 +553,7 @@ class chebyshevu(OrthogonalPolynomial):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import chebyshevt, chebyshevu, diff\n+ >>> from sympy import chebyshevu, diff\n >>> from sympy.abc import n,x\n >>> chebyshevu(0, x)\n 1\n@@ -1169,7 +1169,7 @@ class assoc_laguerre(OrthogonalPolynomial):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import laguerre, assoc_laguerre, diff\n+ >>> from sympy import assoc_laguerre, diff\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, n, a\n >>> assoc_laguerre(0, a, x)\n 1\ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/curve.py b/sympy/geometry/curve.py\nindex c03a58575b2c..6aab8d79be35 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/curve.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/curve.py\n@@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ class Curve(GeometrySet):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import sin, cos, Symbol, interpolate\n+ >>> from sympy import sin, cos, interpolate\n >>> from sympy.abc import t, a\n >>> from sympy.geometry import Curve\n >>> C = Curve((sin(t), cos(t)), (t, 0, 2))\n@@ -257,7 +257,6 @@ def length(self):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.geometry.curve import Curve\n- >>> from sympy import cos, sin\n >>> from sympy.abc import t\n >>> Curve((t, t), (t, 0, 1)).length\n sqrt(2)\n@@ -290,7 +289,7 @@ def plot_interval(self, parameter='t'):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Curve, sin\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, t, s\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, s\n >>> Curve((x, sin(x)), (x, 1, 2)).plot_interval()\n [t, 1, 2]\n >>> Curve((x, sin(x)), (x, 1, 2)).plot_interval(s)\n@@ -337,7 +336,6 @@ def scale(self, x=1, y=1, pt=None):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.geometry.curve import Curve\n- >>> from sympy import pi\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> Curve((x, x), (x, 0, 1)).scale(2)\n Curve((2*x, x), (x, 0, 1))\n@@ -355,7 +353,6 @@ def translate(self, x=0, y=0):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.geometry.curve import Curve\n- >>> from sympy import pi\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> Curve((x, x), (x, 0, 1)).translate(1, 2)\n Curve((x + 1, x + 2), (x, 0, 1))\ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/ellipse.py b/sympy/geometry/ellipse.py\nindex 06ec340fb75a..b8bcdbaf793a 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/ellipse.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/ellipse.py\n@@ -635,7 +635,7 @@ def intersection(self, o):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Ellipse, Point, Line, sqrt\n+ >>> from sympy import Ellipse, Point, Line\n >>> e = Ellipse(Point(0, 0), 5, 7)\n >>> e.intersection(Point(0, 0))\n []\n@@ -879,7 +879,7 @@ def normal_lines(self, p, prec=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Line, Point, Ellipse\n+ >>> from sympy import Point, Ellipse\n >>> e = Ellipse((0, 0), 2, 3)\n >>> c = e.center\n >>> e.normal_lines(c + Point(1, 0))\n@@ -1016,7 +1016,7 @@ def auxiliary_circle(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Circle, Ellipse, Point, symbols\n+ >>> from sympy import Ellipse, Point, symbols\n >>> c = Point(1, 2)\n >>> Ellipse(c, 8, 7).auxiliary_circle()\n Circle(Point2D(1, 2), 8)\n@@ -1040,7 +1040,7 @@ def director_circle(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Circle, Ellipse, Point, symbols\n+ >>> from sympy import Ellipse, Point, symbols\n >>> c = Point(3,8)\n >>> Ellipse(c, 7, 9).director_circle()\n Circle(Point2D(3, 8), sqrt(130))\n@@ -1094,7 +1094,7 @@ def random_point(self, seed=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, Ellipse, Segment\n+ >>> from sympy import Point, Ellipse\n >>> e1 = Ellipse(Point(0, 0), 3, 2)\n >>> e1.random_point() # gives some random point\n Point2D(...)\ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/line.py b/sympy/geometry/line.py\nindex a2773b9a3e15..33805b37e757 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/line.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/line.py\n@@ -172,7 +172,7 @@ def angle_between(l1, l2):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, Line, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import Line\n >>> e = Line((0, 0), (1, 0))\n >>> ne = Line((0, 0), (1, 1))\n >>> sw = Line((1, 1), (0, 0))\n@@ -224,7 +224,7 @@ def smallest_angle_between(l1, l2):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, Line, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import Point, Line\n >>> p1, p2, p3 = Point(0, 0), Point(0, 4), Point(2, -2)\n >>> l1, l2 = Line(p1, p2), Line(p1, p3)\n >>> l1.smallest_angle_between(l2)\n@@ -319,7 +319,7 @@ def are_concurrent(*lines):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, Line, Line3D\n+ >>> from sympy import Point, Line\n >>> p1, p2 = Point(0, 0), Point(3, 5)\n >>> p3, p4 = Point(-2, -2), Point(0, 2)\n >>> l1, l2, l3 = Line(p1, p2), Line(p1, p3), Line(p1, p4)\n@@ -1969,7 +1969,6 @@ class Line2D(LinearEntity2D, Line):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Point\n- >>> from sympy.abc import L\n >>> from sympy.geometry import Line, Segment\n >>> L = Line(Point(2,3), Point(3,5))\n >>> L\n@@ -2496,7 +2495,7 @@ class Line3D(LinearEntity3D, Line):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Point3D\n- >>> from sympy.geometry import Line3D, Segment3D\n+ >>> from sympy.geometry import Line3D\n >>> L = Line3D(Point3D(2, 3, 4), Point3D(3, 5, 1))\n >>> L\n Line3D(Point3D(2, 3, 4), Point3D(3, 5, 1))\ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/plane.py b/sympy/geometry/plane.py\nindex 804698250cff..cd4ee63aa3eb 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/plane.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/plane.py\n@@ -40,7 +40,6 @@ class Plane(GeometryEntity):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 1), Point3D(2, 3, 4), Point3D(2, 2, 2))\n Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 1), (-1, 2, -1))\n >>> Plane((1, 1, 1), (2, 3, 4), (2, 2, 2))\n@@ -267,7 +266,7 @@ def distance(self, o):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, Point3D, Line, Line3D, Plane\n+ >>> from sympy import Point3D, Line3D, Plane\n >>> a = Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 1), normal_vector=(1, 1, 1))\n >>> b = Point3D(1, 2, 3)\n >>> a.distance(b)\n@@ -362,7 +361,7 @@ def intersection(self, o):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, Point3D, Line, Line3D, Plane\n+ >>> from sympy import Point3D, Line3D, Plane\n >>> a = Plane(Point3D(1, 2, 3), normal_vector=(1, 1, 1))\n >>> b = Point3D(1, 2, 3)\n >>> a.intersection(b)\n@@ -438,7 +437,7 @@ def is_coplanar(self, o):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D\n+ >>> from sympy import Plane\n >>> o = (0, 0, 0)\n >>> p = Plane(o, (1, 1, 1))\n >>> p2 = Plane(o, (2, 2, 2))\n@@ -621,7 +620,7 @@ def perpendicular_line(self, pt):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D, Line3D\n+ >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D\n >>> a = Plane(Point3D(1,4,6), normal_vector=(2, 4, 6))\n >>> a.perpendicular_line(Point3D(9, 8, 7))\n Line3D(Point3D(9, 8, 7), Point3D(11, 12, 13))\n@@ -656,7 +655,7 @@ def perpendicular_plane(self, *pts):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D, Line3D\n+ >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D\n >>> a, b = Point3D(0, 0, 0), Point3D(0, 1, 0)\n >>> Z = (0, 0, 1)\n >>> p = Plane(a, normal_vector=Z)\n@@ -722,7 +721,7 @@ def projection_line(self, line):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Plane, Line, Line3D, Point, Point3D\n+ >>> from sympy import Plane, Line, Line3D, Point3D\n >>> a = Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 1), normal_vector=(1, 1, 1))\n >>> b = Line(Point3D(1, 1), Point3D(2, 2))\n >>> a.projection_line(b)\n@@ -764,7 +763,7 @@ def projection(self, pt):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point, Point3D\n+ >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D\n >>> A = Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 2), normal_vector=(1, 1, 1))\n \n The projection is along the normal vector direction, not the z\n@@ -828,7 +827,8 @@ def parameter_value(self, other, u, v=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import pi\n+ >>> from sympy.geometry import Plane\n >>> from sympy.abc import t, u, v\n >>> p = Plane((2, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 0))\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/point.py b/sympy/geometry/point.py\nindex 51a5705123ff..a8e79b277792 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/point.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/point.py\n@@ -1153,7 +1153,7 @@ def are_collinear(*points):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point3D, Matrix\n+ >>> from sympy import Point3D\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> p1, p2 = Point3D(0, 0, 0), Point3D(1, 1, 1)\n >>> p3, p4, p5 = Point3D(2, 2, 2), Point3D(x, x, x), Point3D(1, 2, 6)\ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/polygon.py b/sympy/geometry/polygon.py\nindex f3b283a40728..502c0fdbdadb 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/polygon.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/polygon.py\n@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ class Polygon(GeometrySet):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, Polygon, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import Polygon, pi\n >>> p1, p2, p3, p4, p5 = [(0, 0), (1, 0), (5, 1), (0, 1), (3, 0)]\n >>> Polygon(p1, p2, p3, p4)\n Polygon(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(1, 0), Point2D(5, 1), Point2D(0, 1))\n@@ -397,7 +397,7 @@ def second_moment_of_area(self, point=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, Polygon, symbols\n+ >>> from sympy import Polygon, symbols\n >>> a, b = symbols('a, b')\n >>> p1, p2, p3, p4, p5 = [(0, 0), (a, 0), (a, b), (0, b), (a/3, b/3)]\n >>> rectangle = Polygon(p1, p2, p3, p4)\n@@ -718,7 +718,6 @@ def encloses_point(self, p):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Polygon, Point\n- >>> from sympy.abc import t\n >>> p = Polygon((0, 0), (4, 0), (4, 4))\n >>> p.encloses_point(Point(2, 1))\n True\n@@ -811,7 +810,7 @@ def arbitrary_point(self, parameter='t'):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Polygon, S, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import Polygon, Symbol\n >>> t = Symbol('t', real=True)\n >>> tri = Polygon((0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1))\n >>> p = tri.arbitrary_point('t')\n@@ -978,7 +977,7 @@ def cut_section(self, line):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, Symbol, Polygon, Line\n+ >>> from sympy import Polygon, Line\n >>> a, b = 20, 10\n >>> p1, p2, p3, p4 = [(0, b), (0, 0), (a, 0), (a, b)]\n >>> rectangle = Polygon(p1, p2, p3, p4)\n@@ -1919,7 +1918,7 @@ def rotate(self, angle, pt=None):\n \"\"\"Override GeometryEntity.rotate to first rotate the RegularPolygon\n about its center.\n \n- >>> from sympy import Point, RegularPolygon, Polygon, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import Point, RegularPolygon, pi\n >>> t = RegularPolygon(Point(1, 0), 1, 3)\n >>> t.vertices[0] # vertex on x-axis\n Point2D(2, 0)\n@@ -2625,7 +2624,7 @@ def exradii(self):\n The exradius touches the side of the triangle to which it is keyed, e.g.\n the exradius touching side 2 is:\n \n- >>> from sympy.geometry import Point, Triangle, Segment2D, Point2D\n+ >>> from sympy.geometry import Point, Triangle\n >>> p1, p2, p3 = Point(0, 0), Point(6, 0), Point(0, 2)\n >>> t = Triangle(p1, p2, p3)\n >>> t.exradii[t.sides[2]]\ndiff --git a/sympy/geometry/util.py b/sympy/geometry/util.py\nindex 809a78dcc68f..92342457912a 100644\n--- a/sympy/geometry/util.py\n+++ b/sympy/geometry/util.py\n@@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ def closest_points(*args):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.geometry import closest_points, Point2D, Triangle\n+ >>> from sympy.geometry import closest_points, Triangle\n >>> Triangle(sss=(3, 4, 5)).args\n (Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(3, 0), Point2D(3, 4))\n >>> closest_points(*_)\n@@ -374,7 +374,7 @@ def convex_hull(*args, polygon=True):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.geometry import Point, convex_hull\n+ >>> from sympy.geometry import convex_hull\n >>> points = [(1, 1), (1, 2), (3, 1), (-5, 2), (15, 4)]\n >>> convex_hull(*points)\n Polygon(Point2D(-5, 2), Point2D(1, 1), Point2D(3, 1), Point2D(15, 4))\n@@ -474,7 +474,7 @@ def farthest_points(*args):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.geometry import farthest_points, Point2D, Triangle\n+ >>> from sympy.geometry import farthest_points, Triangle\n >>> Triangle(sss=(3, 4, 5)).args\n (Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(3, 0), Point2D(3, 4))\n >>> farthest_points(*_)\ndiff --git a/sympy/holonomic/holonomic.py b/sympy/holonomic/holonomic.py\nindex ba804252db94..e00c7064f1ba 100644\n--- a/sympy/holonomic/holonomic.py\n+++ b/sympy/holonomic/holonomic.py\n@@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ class DifferentialOperator:\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import DifferentialOperator, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -397,7 +397,7 @@ class HolonomicFunction:\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ\n >>> from sympy import symbols, S\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -714,7 +714,7 @@ def integrate(self, limits, initcond=False):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -841,7 +841,7 @@ def diff(self, *args, **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -1177,7 +1177,7 @@ def composition(self, expr, *args, **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -1257,7 +1257,7 @@ def to_sequence(self, lb=True):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ\n >>> from sympy import symbols, S\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -1647,7 +1647,7 @@ def series(self, n=6, coefficient=False, order=True, _recur=None):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -1781,7 +1781,7 @@ def evalf(self, points, method='RK4', h=0.05, derivatives=False):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -1883,7 +1883,7 @@ def to_hyper(self, as_list=False, _recur=None):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -2056,7 +2056,7 @@ def to_expr(self):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ\n >>> from sympy import symbols, S\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')\n@@ -2077,7 +2077,7 @@ def change_ics(self, b, lenics=None):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic import expr_to_holonomic\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, exp\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, exp\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n \n >>> expr_to_holonomic(sin(x)).change_ics(1)\n@@ -2148,7 +2148,7 @@ def from_hyper(func, x0=0, evalf=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import from_hyper, DifferentialOperators\n+ >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import from_hyper\n >>> from sympy import symbols, hyper, S\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> from_hyper(hyper([], [S(3)/2], x**2/4))\n@@ -2222,7 +2222,7 @@ def from_meijerg(func, x0=0, evalf=False, initcond=True, domain=QQ):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import from_meijerg, DifferentialOperators\n+ >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import from_meijerg\n >>> from sympy import symbols, meijerg, S\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> from_meijerg(meijerg(([], []), ([S(1)/2], [0]), x**2/4))\ndiff --git a/sympy/holonomic/recurrence.py b/sympy/holonomic/recurrence.py\nindex 368b5ad1abfb..7202898d98c4 100644\n--- a/sympy/holonomic/recurrence.py\n+++ b/sympy/holonomic/recurrence.py\n@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ class RecurrenceOperator:\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.holonomic.recurrence import RecurrenceOperator, RecurrenceOperators\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> n = symbols('n', integer=True)\n >>> R, Sn = RecurrenceOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(n),'Sn')\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py b/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py\nindex 1d9b348846e5..66a1d548e307 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py\n@@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ def deltaintegrate(f, x):\n \n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n >>> from sympy.integrals.deltafunctions import deltaintegrate\n- >>> from sympy import sin, cos, DiracDelta, Heaviside\n+ >>> from sympy import sin, cos, DiracDelta\n >>> deltaintegrate(x*sin(x)*cos(x)*DiracDelta(x - 1), x)\n sin(1)*cos(1)*Heaviside(x - 1)\n >>> deltaintegrate(y**2*DiracDelta(x - z)*DiracDelta(y - z), y)\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/heurisch.py b/sympy/integrals/heurisch.py\nindex 676e4019780c..97b2eb9c6c6b 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/heurisch.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/heurisch.py\n@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ def components(f, x):\n minimal, positive exponents.\n \n >>> from sympy import cos, sin\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> from sympy.integrals.heurisch import components\n \n >>> components(sin(x)*cos(x)**2, x)\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/integrals.py b/sympy/integrals/integrals.py\nindex b079c5c3fbb3..57ee907a1cb1 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/integrals.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/integrals.py\n@@ -194,8 +194,8 @@ def transform(self, x, u):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, x, u, y\n- >>> from sympy import Integral, S, cos, sqrt\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import a, x, u\n+ >>> from sympy import Integral, cos, sqrt\n \n >>> i = Integral(x*cos(x**2 - 1), (x, 0, 1))\n \n@@ -376,7 +376,7 @@ def doit(self, **hints):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Integral, Piecewise, S\n+ >>> from sympy import Piecewise, S\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, t\n >>> p = x**2 + Piecewise((0, x/t < 0), (1, True))\n >>> p.integrate((t, S(4)/5, 1), (x, -1, 1))\n@@ -1333,10 +1333,9 @@ def principal_value(self, **kwargs):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Dummy, symbols, integrate, limit, oo\n+ >>> from sympy import oo\n >>> from sympy.integrals.integrals import Integral\n- >>> from sympy.calculus.singularities import singularities\n- >>> x = symbols('x')\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> Integral(x+1, (x, -oo, oo)).principal_value()\n oo\n >>> f = 1 / (x**3)\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/intpoly.py b/sympy/integrals/intpoly.py\nindex a1ee0957174a..99c05d1259a4 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/intpoly.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/intpoly.py\n@@ -164,7 +164,6 @@ def main_integrate3d(expr, facets, vertices, hp_params, max_degree=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import main_integrate3d, \\\n hyperplane_parameters\n >>> cube = [[(0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 5), (0, 5, 0), (0, 5, 5), (5, 0, 0),\\\n@@ -326,7 +325,6 @@ def polygon_integrate(facet, hp_param, index, facets, vertices, expr, degree):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import polygon_integrate\n >>> cube = [[(0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 5), (0, 5, 0), (0, 5, 5), (5, 0, 0),\\\n (5, 0, 5), (5, 5, 0), (5, 5, 5)],\\\n@@ -561,8 +559,8 @@ def integration_reduction_dynamic(facets, index, a, b, expr, degree, dims,\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n- >>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import integration_reduction_dynamic,\\\n- hyperplane_parameters, gradient_terms\n+ >>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import (integration_reduction_dynamic, \\\n+ hyperplane_parameters)\n >>> from sympy.geometry.point import Point\n >>> from sympy.geometry.polygon import Polygon\n >>> triangle = Polygon(Point(0, 3), Point(5, 3), Point(1, 1))\n@@ -629,7 +627,6 @@ def left_integral3D(facets, index, expr, vertices, hp_param, degree):\n hp_param : The hyperplane parameters of the face\n degree : Degree of the expr\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import left_integral3D\n >>> cube = [[(0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 5), (0, 5, 0), (0, 5, 5), (5, 0, 0),\\\n (5, 0, 5), (5, 5, 0), (5, 5, 5)],\\\n@@ -664,7 +661,6 @@ def gradient_terms(binomial_power=0, no_of_gens=2):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import gradient_terms\n >>> gradient_terms(2)\n [[1, 0, 0, 0], [y, 0, 1, 0], [y**2, 0, 2, 0], [x, 1, 0, 0],\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py b/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py\nindex 6aa5abd999f5..d1d61fb96250 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py\n@@ -1213,7 +1213,7 @@ def integral_steps(integrand, symbol, **options):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import exp, sin, cos\n+ >>> from sympy import exp, sin\n >>> from sympy.integrals.manualintegrate import integral_steps\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> print(repr(integral_steps(exp(x) / (1 + exp(2 * x)), x))) \\\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py b/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py\nindex 1f1c1a2a6e08..1871f0743f9c 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py\n@@ -381,7 +381,7 @@ def _find_splitting_points(expr, x):\n \n >>> from sympy.integrals.meijerint import _find_splitting_points as fsp\n >>> from sympy import sin\n- >>> from sympy.abc import a, x\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> fsp(x, x)\n {0}\n >>> fsp((x-1)**3, x)\n@@ -587,7 +587,7 @@ def _condsimp(cond):\n added as need arises rather than following any logical pattern.\n \n >>> from sympy.integrals.meijerint import _condsimp as simp\n- >>> from sympy import Or, Eq, unbranched_argument as arg, And\n+ >>> from sympy import Or, Eq, And\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n >>> simp(Or(x < y, z, Eq(x, y)))\n z | (x <= y)\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/quadrature.py b/sympy/integrals/quadrature.py\nindex 27a845bb0a8c..d8866d02ba26 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/quadrature.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/quadrature.py\n@@ -327,7 +327,6 @@ def gauss_chebyshev_t(n, n_digits):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S\n >>> from sympy.integrals.quadrature import gauss_chebyshev_t\n >>> x, w = gauss_chebyshev_t(3, 5)\n >>> x\n@@ -394,7 +393,6 @@ def gauss_chebyshev_u(n, n_digits):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S\n >>> from sympy.integrals.quadrature import gauss_chebyshev_u\n >>> x, w = gauss_chebyshev_u(3, 5)\n >>> x\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/rationaltools.py b/sympy/integrals/rationaltools.py\nindex 9d7d9b48483f..54bda63ccd3d 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/rationaltools.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/rationaltools.py\n@@ -320,7 +320,7 @@ def log_to_real(h, q, x, t):\n \n >>> from sympy.integrals.rationaltools import log_to_real\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n- >>> from sympy import Poly, sqrt, S\n+ >>> from sympy import Poly, S\n >>> log_to_real(Poly(x + 3*y/2 + S(1)/2, x, domain='QQ[y]'),\n ... Poly(3*y**2 + 1, y, domain='ZZ'), x, y)\n 2*sqrt(3)*atan(2*sqrt(3)*x/3 + sqrt(3)/3)/3\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/transforms.py b/sympy/integrals/transforms.py\nindex 0154c44f1d1b..754fd5808f11 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/transforms.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/transforms.py\n@@ -1609,7 +1609,7 @@ def inverse_sine_transform(F, k, x, **hints):\n :func:`sympy.integrals.transforms.IntegralTransform.doit`.\n Note that for this transform, by default ``noconds=True``.\n \n- >>> from sympy import inverse_sine_transform, exp, sqrt, gamma, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import inverse_sine_transform, exp, sqrt, gamma\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, k, a\n >>> inverse_sine_transform(2**((1-2*a)/2)*k**(a - 1)*\n ... gamma(-a/2 + 1)/gamma((a+1)/2), k, x)\n@@ -1716,7 +1716,7 @@ def inverse_cosine_transform(F, k, x, **hints):\n :func:`sympy.integrals.transforms.IntegralTransform.doit`.\n Note that for this transform, by default ``noconds=True``.\n \n- >>> from sympy import inverse_cosine_transform, exp, sqrt, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import inverse_cosine_transform, sqrt, pi\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, k, a\n >>> inverse_cosine_transform(sqrt(2)*a/(sqrt(pi)*(a**2 + k**2)), k, x)\n exp(-a*x)\n@@ -1816,7 +1816,7 @@ def hankel_transform(f, r, k, nu, **hints):\n Note that for this transform, by default ``noconds=True``.\n \n >>> from sympy import hankel_transform, inverse_hankel_transform\n- >>> from sympy import gamma, exp, sinh, cosh\n+ >>> from sympy import exp\n >>> from sympy.abc import r, k, m, nu, a\n \n >>> ht = hankel_transform(1/r**m, r, k, nu)\n@@ -1871,8 +1871,8 @@ def inverse_hankel_transform(F, k, r, nu, **hints):\n :func:`sympy.integrals.transforms.IntegralTransform.doit`.\n Note that for this transform, by default ``noconds=True``.\n \n- >>> from sympy import hankel_transform, inverse_hankel_transform, gamma\n- >>> from sympy import gamma, exp, sinh, cosh\n+ >>> from sympy import hankel_transform, inverse_hankel_transform\n+ >>> from sympy import exp\n >>> from sympy.abc import r, k, m, nu, a\n \n >>> ht = hankel_transform(1/r**m, r, k, nu)\ndiff --git a/sympy/integrals/trigonometry.py b/sympy/integrals/trigonometry.py\nindex adcad981c7ac..009a7c4280b4 100644\n--- a/sympy/integrals/trigonometry.py\n+++ b/sympy/integrals/trigonometry.py\n@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ def _pat_sincos(x):\n def trigintegrate(f, x, conds='piecewise'):\n \"\"\"Integrate f = Mul(trig) over x\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, sin, cos, tan, sec, csc, cot\n+ >>> from sympy import sin, cos, tan, sec\n >>> from sympy.integrals.trigonometry import trigintegrate\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/interactive/session.py b/sympy/interactive/session.py\nindex a756b42bebd6..af4edb3e3dbc 100644\n--- a/sympy/interactive/session.py\n+++ b/sympy/interactive/session.py\n@@ -95,8 +95,8 @@ def int_to_Integer(s):\n ========\n \n >>> from __future__ import division\n+ >>> from sympy import Integer # noqa: F401\n >>> from sympy.interactive.session import int_to_Integer\n- >>> from sympy import Integer\n >>> s = '1.2 + 1/2 - 0x12 + a1'\n >>> int_to_Integer(s)\n '1.2 +Integer (1 )/Integer (2 )-Integer (0x12 )+a1 '\ndiff --git a/sympy/logic/algorithms/dpll.py b/sympy/logic/algorithms/dpll.py\nindex e43441daac43..61f846186ce2 100644\n--- a/sympy/logic/algorithms/dpll.py\n+++ b/sympy/logic/algorithms/dpll.py\n@@ -181,7 +181,6 @@ def unit_propagate(clauses, symbol):\n \n Arguments are expected to be in CNF.\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> from sympy.abc import A, B, D\n >>> from sympy.logic.algorithms.dpll import unit_propagate\n >>> unit_propagate([A | B, D | ~B, B], B)\n@@ -223,7 +222,6 @@ def find_pure_symbol(symbols, unknown_clauses):\n Find a symbol and its value if it appears only as a positive literal\n (or only as a negative) in clauses.\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> from sympy.abc import A, B, D\n >>> from sympy.logic.algorithms.dpll import find_pure_symbol\n >>> find_pure_symbol([A, B, D], [A|~B,~B|~D,D|A])\n@@ -269,7 +267,6 @@ def find_unit_clause(clauses, model):\n \"\"\"\n A unit clause has only 1 variable that is not bound in the model.\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> from sympy.abc import A, B, D\n >>> from sympy.logic.algorithms.dpll import find_unit_clause\n >>> find_unit_clause([A | B | D, B | ~D, A | ~B], {A:True})\ndiff --git a/sympy/logic/boolalg.py b/sympy/logic/boolalg.py\nindex 979d61a68f69..60cee03c90eb 100644\n--- a/sympy/logic/boolalg.py\n+++ b/sympy/logic/boolalg.py\n@@ -27,6 +27,8 @@ def as_Boolean(e):\n >>> from sympy import true, false, nan\n >>> from sympy.logic.boolalg import as_Boolean\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n+ >>> as_Boolean(0) is false\n+ True\n >>> as_Boolean(1) is true\n True\n >>> as_Boolean(x)\n@@ -35,6 +37,10 @@ def as_Boolean(e):\n Traceback (most recent call last):\n ...\n TypeError: expecting bool or Boolean, not `2`.\n+ >>> as_Boolean(nan)\n+ Traceback (most recent call last):\n+ ...\n+ TypeError: expecting bool or Boolean, not `nan`.\n \n \"\"\"\n from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol\n@@ -651,7 +657,6 @@ class And(LatticeOp, BooleanFunction):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.core import symbols\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy.logic.boolalg import And\n >>> x & y\n@@ -798,7 +803,6 @@ class Or(LatticeOp, BooleanFunction):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.core import symbols\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy.logic.boolalg import Or\n >>> x | y\n@@ -1323,7 +1327,7 @@ class Equivalent(BooleanFunction):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.logic.boolalg import Equivalent, And\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> Equivalent(False, False, False)\n True\n >>> Equivalent(True, False, False)\ndiff --git a/sympy/logic/inference.py b/sympy/logic/inference.py\nindex d5aec52eb3ac..e0628f3ec3ab 100644\n--- a/sympy/logic/inference.py\n+++ b/sympy/logic/inference.py\n@@ -144,7 +144,7 @@ def pl_true(expr, model={}, deep=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import A, B, C\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import A, B\n >>> from sympy.logic.inference import pl_true\n >>> pl_true( A & B, {A: True, B: True})\n True\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/common.py b/sympy/matrices/common.py\nindex e0c7701621ed..a21d4f9d6d9e 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/common.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/common.py\n@@ -522,7 +522,7 @@ def diagonal(self, k=0):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Matrix, SparseMatrix\n+ >>> from sympy import Matrix\n >>> m = Matrix(3, 3, lambda i, j: j - i); m\n Matrix([\n [ 0, 1, 2],\n@@ -607,7 +607,7 @@ def todok(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Matrix, SparseMatrix\n+ >>> from sympy import Matrix\n >>> M = Matrix.eye(3)\n >>> M.todok()\n {(0, 0): 1, (1, 1): 1, (2, 2): 1}\n@@ -1246,6 +1246,12 @@ def atoms(self, *types):\n Matrix([[x]])\n >>> _.atoms()\n {x}\n+ >>> Matrix([[x, y], [y, x]])\n+ Matrix([\n+ [x, y],\n+ [y, x]])\n+ >>> _.atoms()\n+ {x, y}\n \"\"\"\n \n types = tuple(t if isinstance(t, type) else type(t) for t in types)\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/dense.py b/sympy/matrices/dense.py\nindex e16ccd9379d3..21d836b99430 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/dense.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/dense.py\n@@ -225,7 +225,6 @@ def equals(self, other, failing_expression=False):\n \n >>> from sympy.matrices import Matrix\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n- >>> from sympy import cos\n >>> A = Matrix([x*(x - 1), 0])\n >>> B = Matrix([x**2 - x, 0])\n >>> A == B\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/determinant.py b/sympy/matrices/determinant.py\nindex 647541afef9b..b2cccf0d2ae5 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/determinant.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/determinant.py\n@@ -542,10 +542,15 @@ def _det(M, method=\"bareiss\", iszerofunc=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Matrix, MatrixSymbol, eye, det\n+ >>> from sympy import Matrix, eye, det\n+ >>> I3 = eye(3)\n+ >>> det(I3)\n+ 1\n >>> M = Matrix([[1, 2], [3, 4]])\n- >>> M.det()\n+ >>> det(M)\n -2\n+ >>> det(M) == M.det()\n+ True\n \"\"\"\n \n # sanitize `method`\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py\nindex 22f0ba693250..4e1bb444e01f 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py\n@@ -219,7 +219,7 @@ def transpose(self):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, BlockMatrix, ZeroMatrix\n- >>> from sympy.abc import l, m, n\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import m, n\n >>> X = MatrixSymbol('X', n, n)\n >>> Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', m ,m)\n >>> Z = MatrixSymbol('Z', n, m)\n@@ -287,7 +287,7 @@ class BlockDiagMatrix(BlockMatrix):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, BlockDiagMatrix, symbols, Identity\n+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, BlockDiagMatrix, symbols\n >>> n, m, l = symbols('n m l')\n >>> X = MatrixSymbol('X', n, n)\n >>> Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', m ,m)\n@@ -408,7 +408,7 @@ def block_collapse(expr):\n \"\"\"Evaluates a block matrix expression\n \n >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, BlockMatrix, symbols, \\\n- Identity, Matrix, ZeroMatrix, block_collapse\n+ Identity, ZeroMatrix, block_collapse\n >>> n,m,l = symbols('n m l')\n >>> X = MatrixSymbol('X', n, n)\n >>> Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', m ,m)\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/funcmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/funcmatrix.py\nindex 09059d970dbb..5d08fd66cbc6 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/funcmatrix.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/funcmatrix.py\n@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ class FunctionMatrix(MatrixExpr):\n \n Creating a ``FunctionMatrix`` from ``Lambda``:\n \n- >>> from sympy import FunctionMatrix, symbols, Lambda, MatPow, Matrix\n+ >>> from sympy import FunctionMatrix, symbols, Lambda, MatPow\n >>> i, j, n, m = symbols('i,j,n,m')\n >>> FunctionMatrix(n, m, Lambda((i, j), i + j))\n FunctionMatrix(n, m, Lambda((i, j), i + j))\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\nindex 4b2bb1d4eb19..31f1226cce69 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\n@@ -414,7 +414,7 @@ def from_index_summation(expr, first_index=None, last_index=None, dimensions=Non\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum\n >>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N\n >>> A = MatrixSymbol(\"A\", N, N)\n >>> B = MatrixSymbol(\"B\", N, N)\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py\nindex fc19c1fdc643..af9e09695852 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py\n@@ -233,7 +233,7 @@ def any_zeros(mul):\n def merge_explicit(matmul):\n \"\"\" Merge explicit MatrixBase arguments\n \n- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, eye, Matrix, MatMul, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, Matrix, MatMul, pprint\n >>> from sympy.matrices.expressions.matmul import merge_explicit\n >>> A = MatrixSymbol('A', 2, 2)\n >>> B = Matrix([[1, 1], [1, 1]])\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py\nindex edcfd9ab7ea8..1bfeb44660fa 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py\n@@ -15,6 +15,13 @@ class Trace(Expr):\n >>> A = MatrixSymbol('A', 3, 3)\n >>> Trace(A)\n Trace(A)\n+ >>> Trace(eye(3))\n+ Trace(Matrix([\n+ [1, 0, 0],\n+ [0, 1, 0],\n+ [0, 0, 1]]))\n+ >>> Trace(eye(3)).simplify()\n+ 3\n \"\"\"\n is_Trace = True\n is_commutative = True\n@@ -117,7 +124,7 @@ def trace(expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import trace, Symbol, MatrixSymbol, pprint, eye\n+ >>> from sympy import trace, Symbol, MatrixSymbol, eye\n >>> n = Symbol('n')\n >>> X = MatrixSymbol('X', n, n) # A square matrix\n >>> trace(2*X)\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/matrices.py b/sympy/matrices/matrices.py\nindex ae6f9e10d9d7..1e97c753d2d1 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/matrices.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/matrices.py\n@@ -1517,7 +1517,7 @@ def analytic_func(self, f, x):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Matrix, exp, S, log\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, Matrix, S, log\n \n >>> x = Symbol('x')\n >>> m = Matrix([[S(5)/4, S(3)/4], [S(3)/4, S(5)/4]])\ndiff --git a/sympy/multipledispatch/core.py b/sympy/multipledispatch/core.py\nindex f53d4e1516ee..5bebd2a11c01 100644\n--- a/sympy/multipledispatch/core.py\n+++ b/sympy/multipledispatch/core.py\n@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ def dispatch(*types, **kwargs):\n ... return x + 1\n \n >>> @dispatch(float)\n- ... def f(x):\n+ ... def f(x): # noqa: F811\n ... return x - 1\n \n >>> f(3)\n@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ def dispatch(*types, **kwargs):\n ... def __init__(self, data):\n ... self.data = data\n ... @dispatch(int)\n- ... def __init__(self, datum):\n+ ... def __init__(self, datum): # noqa: F811\n ... self.data = [datum]\n \"\"\"\n namespace = kwargs.get('namespace', global_namespace)\ndiff --git a/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py b/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py\nindex 239a25937984..9c5f38651183 100644\n--- a/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py\n+++ b/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py\n@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ class Dispatcher:\n ... return x + 1\n \n >>> @dispatch(float)\n- ... def f(x):\n+ ... def f(x): # noqa: F811\n ... return x - 1\n \n >>> f(3)\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/continued_fraction.py b/sympy/ntheory/continued_fraction.py\nindex ba3ed62a1d7c..8ea00d5eaf0e 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/continued_fraction.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/continued_fraction.py\n@@ -314,7 +314,7 @@ def continued_fraction_convergents(cf):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.core import Rational, pi\n+ >>> from sympy.core import pi\n >>> from sympy import S\n >>> from sympy.ntheory.continued_fraction import \\\n continued_fraction_convergents, continued_fraction_iterator\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/digits.py b/sympy/ntheory/digits.py\nindex 57c652dee1a1..1453dcee53ea 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/digits.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/digits.py\n@@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ def count_digits(n, b=10):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.ntheory import count_digits, digits\n+ >>> from sympy.ntheory import count_digits\n \n >>> count_digits(1111339)\n {1: 4, 3: 2, 9: 1}\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/elliptic_curve.py b/sympy/ntheory/elliptic_curve.py\nindex f86055379482..3b51952ae0bb 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/elliptic_curve.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/elliptic_curve.py\n@@ -241,7 +241,6 @@ def order(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import FF\n >>> from sympy.ntheory.elliptic_curve import EllipticCurve\n >>> e2 = EllipticCurve(1, 0, modulus=19)\n >>> e2.order\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py b/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py\nindex 9b02fa7bee71..60d4c611f524 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py\n@@ -730,7 +730,7 @@ def pollard_pm1(n, B=10, a=2, retries=0, seed=1234):\n \n With the default smoothness bound, this number can't be cracked:\n \n- >>> from sympy.ntheory import pollard_pm1, primefactors\n+ >>> from sympy.ntheory import pollard_pm1\n >>> pollard_pm1(21477639576571)\n \n Increasing the smoothness bound helps:\n@@ -740,7 +740,6 @@ def pollard_pm1(n, B=10, a=2, retries=0, seed=1234):\n \n Looking at the smoothness of the factors of this number we find:\n \n- >>> from sympy.utilities import flatten\n >>> from sympy.ntheory.factor_ import smoothness_p, factorint\n >>> print(smoothness_p(21477639576571, visual=1))\n p**i=4410317**1 has p-1 B=1787, B-pow=1787\n@@ -1048,7 +1047,7 @@ def factorint(n, limit=None, use_trial=True, use_rho=True, use_pm1=True,\n You can easily switch between the two forms by sending them back to\n factorint:\n \n- >>> from sympy import Mul, Pow\n+ >>> from sympy import Mul\n >>> regular = factorint(1764); regular\n {2: 2, 3: 2, 7: 2}\n >>> pprint(factorint(regular))\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/generate.py b/sympy/ntheory/generate.py\nindex 5ecea6c7e0e1..28a943d857c8 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/generate.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/generate.py\n@@ -766,7 +766,7 @@ def primorial(n, nth=True):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.ntheory.generate import primorial, randprime, primerange\n+ >>> from sympy.ntheory.generate import primorial, primerange\n >>> from sympy import factorint, Mul, primefactors, sqrt\n >>> primorial(4) # the first 4 primes are 2, 3, 5, 7\n 210\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/modular.py b/sympy/ntheory/modular.py\nindex c6f28e12f94b..32d3bf13430b 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/modular.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/modular.py\n@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ def crt(m, v, symmetric=False, check=True):\n As an example consider a set of residues ``U = [49, 76, 65]``\n and a set of moduli ``M = [99, 97, 95]``. Then we have::\n \n- >>> from sympy.ntheory.modular import crt, solve_congruence\n+ >>> from sympy.ntheory.modular import crt\n \n >>> crt([99, 97, 95], [49, 76, 65])\n (639985, 912285)\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py b/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py\nindex 69ab7f7964e4..ca944ed4a5f3 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py\n@@ -975,7 +975,7 @@ def jacobi_symbol(m, n):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.ntheory import jacobi_symbol, legendre_symbol\n- >>> from sympy import Mul, S\n+ >>> from sympy import S\n >>> jacobi_symbol(45, 77)\n -1\n >>> jacobi_symbol(60, 121)\n@@ -1516,7 +1516,6 @@ def polynomial_congruence(expr, m):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.ntheory import polynomial_congruence\n- >>> from sympy import Poly\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> expr = x**6 - 2*x**5 -35\n >>> polynomial_congruence(expr, 6125)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/continuum_mechanics/beam.py b/sympy/physics/continuum_mechanics/beam.py\nindex d04496717cac..e2312690d7ab 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/continuum_mechanics/beam.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/continuum_mechanics/beam.py\n@@ -754,7 +754,7 @@ def solve_for_reaction_loads(self, *reactions):\n being positive.\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.continuum_mechanics.beam import Beam\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, linsolve, limit\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> E, I = symbols('E, I')\n >>> R1, R2 = symbols('R1, R2')\n >>> b = Beam(30, E, I)\n@@ -1513,7 +1513,6 @@ def plot_loading_results(self, subs=None):\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.continuum_mechanics.beam import Beam\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n- >>> from sympy.plotting import PlotGrid\n >>> R1, R2 = symbols('R1, R2')\n >>> b = Beam(8, 200*(10**9), 400*(10**-6))\n >>> b.apply_load(5000, 2, -1)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/hydrogen.py b/sympy/physics/hydrogen.py\nindex 8ec8e6c2da15..219200c882a9 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/hydrogen.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/hydrogen.py\n@@ -21,9 +21,7 @@ def R_nl(n, l, r, Z=1):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.hydrogen import R_nl\n- >>> from sympy import var\n- >>> var(\"r Z\")\n- (r, Z)\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import r, Z\n >>> R_nl(1, 0, r, Z)\n 2*sqrt(Z**3)*exp(-Z*r)\n >>> R_nl(2, 0, r, Z)\n@@ -151,10 +149,8 @@ def E_nl(n, Z=1):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import var\n >>> from sympy.physics.hydrogen import E_nl\n- >>> var(\"n Z\")\n- (n, Z)\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import n, Z\n >>> E_nl(n, Z)\n -Z**2/(2*n**2)\n >>> E_nl(1)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/mechanics/lagrange.py b/sympy/physics/mechanics/lagrange.py\nindex 7f44352ebf46..148884e7fa61 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/mechanics/lagrange.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/mechanics/lagrange.py\n@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ class LagrangesMethod(object):\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import LagrangesMethod, Lagrangian\n >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import ReferenceFrame, Particle, Point\n- >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import dynamicsymbols, kinetic_energy\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import dynamicsymbols\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')\n >>> qd = dynamicsymbols('q', 1)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/mechanics/rigidbody.py b/sympy/physics/mechanics/rigidbody.py\nindex 140b64fd9900..b56f9f3b23b2 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/mechanics/rigidbody.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/mechanics/rigidbody.py\n@@ -285,7 +285,7 @@ def potential_energy(self, scalar):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import Particle, Point, outer\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import Point, outer\n >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import RigidBody, ReferenceFrame\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> b = ReferenceFrame('b')\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/optics/polarization.py b/sympy/physics/optics/polarization.py\nindex 56ca4d15801d..a0ccd62797ae 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/optics/polarization.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/optics/polarization.py\n@@ -307,7 +307,7 @@ def jones_2_stokes(e):\n --------\n The axes on the Poincaré sphere.\n \n- >>> from sympy import pprint, Matrix, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import pprint, pi\n >>> from sympy.physics.optics.polarization import jones_vector\n >>> from sympy.physics.optics.polarization import jones_2_stokes\n >>> H = jones_vector(0, 0)\n@@ -557,7 +557,7 @@ def mueller_matrix(J):\n --------\n Generic optical components.\n \n- >>> from sympy import pprint, symbols, pi, simplify\n+ >>> from sympy import pprint, symbols\n >>> from sympy.physics.optics.polarization import (mueller_matrix,\n ... linear_polarizer, half_wave_retarder, quarter_wave_retarder)\n >>> theta = symbols(\"theta\", real=True)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/optics/utils.py b/sympy/physics/optics/utils.py\nindex 02cc3211b5c1..fe644a7f154b 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/optics/utils.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/optics/utils.py\n@@ -638,7 +638,6 @@ def hyperfocal_distance(f, N, c):\n Example\n =======\n >>> from sympy.physics.optics import hyperfocal_distance\n- >>> from sympy.abc import f, N, c\n >>> round(hyperfocal_distance(f = 0.5, N = 8, c = 0.0033), 2)\n 9.47\n \"\"\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/paulialgebra.py b/sympy/physics/paulialgebra.py\nindex 1b7e68139bd5..a9b19e5c396f 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/paulialgebra.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/paulialgebra.py\n@@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ def evaluate_pauli_product(arg):\n >>> evaluate_pauli_product(I*Pauli(1)*Pauli(2))\n -sigma3\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import x,y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> evaluate_pauli_product(x**2*Pauli(2)*Pauli(1))\n -I*x**2*sigma3\n '''\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/pring.py b/sympy/physics/pring.py\nindex fd5a8a546c7f..797f85568846 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/pring.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/pring.py\n@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ def wavefunction(n, x):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.pring import wavefunction, energy\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.pring import wavefunction\n >>> from sympy import Symbol, integrate, pi\n >>> x=Symbol(\"x\")\n >>> wavefunction(1, x)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/qho_1d.py b/sympy/physics/qho_1d.py\nindex b4ab64d6adbd..6bceb345ee30 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/qho_1d.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/qho_1d.py\n@@ -23,9 +23,7 @@ def psi_n(n, x, m, omega):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.qho_1d import psi_n\n- >>> from sympy import var\n- >>> var(\"x m omega\")\n- (x, m, omega)\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import m, x, omega\n >>> psi_n(0, x, m, omega)\n (m*omega)**(1/4)*exp(-m*omega*x**2/(2*hbar))/(hbar**(1/4)*pi**(1/4))\n \n@@ -58,9 +56,7 @@ def E_n(n, omega):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.qho_1d import E_n\n- >>> from sympy import var\n- >>> var(\"x omega\")\n- (x, omega)\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, omega\n >>> E_n(x, omega)\n hbar*omega*(x + 1/2)\n \"\"\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py\nindex 5f05a3ec327b..514c9dcf24c9 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py\n@@ -339,7 +339,7 @@ def convert_to_real_indices(seq, qubit_map):\n \n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.circuitutils import convert_to_real_indices\n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, Z, H\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, H\n >>> i0, i1 = symbols('i:2')\n >>> index_map = {i0 : 0, i1 : 1}\n >>> convert_to_real_indices(X(i0)*Y(i1)*H(i0)*X(i1), index_map)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/density.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/density.py\nindex 496d9c3a67b1..d0f2da8b1df8 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/density.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/density.py\n@@ -228,10 +228,8 @@ def entropy(density):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.density import Density, entropy\n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.represent import represent\n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.matrixutils import scipy_sparse_matrix\n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.spin import JzKet, Jz\n- >>> from sympy import S, log\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.spin import JzKet\n+ >>> from sympy import S\n >>> up = JzKet(S(1)/2,S(1)/2)\n >>> down = JzKet(S(1)/2,-S(1)/2)\n >>> d = Density((up,S(1)/2),(down,S(1)/2))\n@@ -275,7 +273,7 @@ def fidelity(state1, state2):\n >>> from sympy import S, sqrt\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.dagger import Dagger\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.spin import JzKet\n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.density import Density, fidelity\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.density import fidelity\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.represent import represent\n >>>\n >>> up = JzKet(S(1)/2,S(1)/2)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/hilbert.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/hilbert.py\nindex 7f57ce90180b..b4bc7e1369fe 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/hilbert.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/hilbert.py\n@@ -452,7 +452,6 @@ class DirectSumHilbertSpace(HilbertSpace):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.hilbert import ComplexSpace, FockSpace\n- >>> from sympy import symbols\n \n >>> c = ComplexSpace(2)\n >>> f = FockSpace()\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py\nindex 83f637b9c87c..268ab3430749 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py\n@@ -725,8 +725,7 @@ def is_reducible(circuit, nqubits, begin, end):\n \n Check if the circuit can be reduced:\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.identitysearch import (\n- ... GateIdentity, is_reducible)\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.identitysearch import is_reducible\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, Z\n >>> x = X(0); y = Y(0); z = Z(0)\n >>> is_reducible((x, y, z), 1, 0, 3)\n@@ -780,7 +779,7 @@ def bfs_identity_search(gate_list, nqubits, max_depth=None,\n Find a list of gate identities:\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.identitysearch import bfs_identity_search\n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, Z, H\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, Z\n >>> x = X(0); y = Y(0); z = Z(0)\n >>> bfs_identity_search([x], 1, max_depth=2)\n {GateIdentity(X(0), X(0))}\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/innerproduct.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/innerproduct.py\nindex 8154416bc4e0..f8a726192eb5 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/innerproduct.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/innerproduct.py\n@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ class InnerProduct(Expr):\n \n Create an InnerProduct and check its properties:\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Bra, Ket, InnerProduct\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Bra, Ket\n >>> b = Bra('b')\n >>> k = Ket('k')\n >>> ip = b*k\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py\nindex 1a8db4b3c30f..8b1e339644c3 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py\n@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ class Operator(QExpr):\n Create an operator and examine its attributes::\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Operator\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, I\n+ >>> from sympy import I\n >>> A = Operator('A')\n >>> A\n A\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/qubit.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/qubit.py\nindex 536843aeb71c..1c1d4e2ddb86 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/qubit.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/qubit.py\n@@ -446,7 +446,6 @@ def matrix_to_qubit(matrix):\n Represent a state and then go back to its qubit form:\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qubit import matrix_to_qubit, Qubit\n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import Z\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.represent import represent\n >>> q = Qubit('01')\n >>> matrix_to_qubit(represent(q))\n@@ -556,7 +555,7 @@ def measure_all(qubit, format='sympy', normalize=True):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qubit import Qubit, measure_all\n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import H, X, Y, Z\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import H\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qapply import qapply\n \n >>> c = H(0)*H(1)*Qubit('00')\n@@ -614,7 +613,7 @@ def measure_partial(qubit, bits, format='sympy', normalize=True):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qubit import Qubit, measure_partial\n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import H, X, Y, Z\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import H\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qapply import qapply\n \n >>> c = H(0)*H(1)*Qubit('00')\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/represent.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/represent.py\nindex 6ff8be3c867c..3371823c2a6b 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/represent.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/represent.py\n@@ -306,7 +306,7 @@ def rep_expectation(expr, **options):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.cartesian import XOp, XKet, PxOp, PxKet\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.cartesian import XOp, PxOp, PxKet\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.represent import rep_expectation\n >>> rep_expectation(XOp())\n x_1*DiracDelta(x_1 - x_2)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/state.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/state.py\nindex 51fc26fce198..0b87cfee5c97 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/state.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/state.py\n@@ -354,7 +354,7 @@ class for all physical, time-independent Kets in a system. This class\n \n Create a simple Ket and looking at its properties::\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Ket, Bra\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Ket\n >>> from sympy import symbols, I\n >>> k = Ket('psi')\n >>> k\n@@ -418,7 +418,7 @@ class and its subclasses will be the main classes that users will use for\n \n Create a simple Bra and look at its properties::\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Ket, Bra\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Bra\n >>> from sympy import symbols, I\n >>> b = Bra('psi')\n >>> b\n@@ -600,7 +600,6 @@ class TimeDepBra(TimeDepState, BraBase):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import TimeDepBra\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, I\n >>> b = TimeDepBra('psi', 't')\n >>> b\n <psi;t|\n@@ -629,7 +628,7 @@ class OrthogonalKet(OrthogonalState, KetBase):\n The inner product of two states with different labels will give zero,\n states with the same label will give one.\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import OrthogonalBra, OrthogonalKet, qapply\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import OrthogonalBra, OrthogonalKet\n >>> from sympy.abc import m, n\n >>> (OrthogonalBra(n)*OrthogonalKet(n)).doit()\n 1\n@@ -968,7 +967,7 @@ def normalize(self):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import symbols, pi\n- >>> from sympy.functions import sqrt, sin\n+ >>> from sympy.functions import sin\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.state import Wavefunction\n >>> x = symbols('x', real=True)\n >>> L = symbols('L', positive=True)\n@@ -994,7 +993,7 @@ def prob(self):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import symbols, pi\n- >>> from sympy.functions import sqrt, sin\n+ >>> from sympy.functions import sin\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.state import Wavefunction\n >>> x, L = symbols('x,L', real=True)\n >>> n = symbols('n', integer=True)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/tensorproduct.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/tensorproduct.py\nindex 5ebfe9a405cc..6ff0b6a72863 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/tensorproduct.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/tensorproduct.py\n@@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ class TensorProduct(Expr):\n \n Start with a simple tensor product of sympy matrices::\n \n- >>> from sympy import I, Matrix, symbols\n+ >>> from sympy import Matrix\n >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import TensorProduct\n \n >>> m1 = Matrix([[1,2],[3,4]])\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/secondquant.py b/sympy/physics/secondquant.py\nindex 3923c9c68b0a..0e22a282422c 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/secondquant.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/secondquant.py\n@@ -2771,8 +2771,8 @@ def wicks(e, **kw_args):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols, Function, Dummy\n- >>> from sympy.physics.secondquant import wicks, F, Fd, NO\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Dummy\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.secondquant import wicks, F, Fd\n >>> p, q, r = symbols('p,q,r')\n >>> wicks(Fd(p)*F(q))\n KroneckerDelta(_i, q)*KroneckerDelta(p, q) + NO(CreateFermion(p)*AnnihilateFermion(q))\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/sho.py b/sympy/physics/sho.py\nindex 2f4c2b2fc953..4a38c5cc4a95 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/sho.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/sho.py\n@@ -25,9 +25,7 @@ def R_nl(n, l, nu, r):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.sho import R_nl\n- >>> from sympy import var\n- >>> var(\"r nu l\")\n- (r, nu, l)\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import r, nu, l\n >>> R_nl(0, 0, 1, r)\n 2*2**(3/4)*exp(-r**2)/pi**(1/4)\n >>> R_nl(1, 0, 1, r)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/units/prefixes.py b/sympy/physics/units/prefixes.py\nindex a49e9d13199a..c6995d4d0073 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/units/prefixes.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/units/prefixes.py\n@@ -126,7 +126,6 @@ def prefix_unit(unit, prefixes):\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.units.prefixes import (PREFIXES,\n ... prefix_unit)\n- >>> from sympy.physics.units.systems import MKS\n >>> from sympy.physics.units import m\n >>> pref = {\"m\": PREFIXES[\"m\"], \"c\": PREFIXES[\"c\"], \"d\": PREFIXES[\"d\"]}\n >>> prefix_unit(m, pref) # doctest: +SKIP\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/units/util.py b/sympy/physics/units/util.py\nindex 3e2ce1a434f5..067893854ad2 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/units/util.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/units/util.py\n@@ -76,7 +76,6 @@ def convert_to(expr, target_units, unit_system=\"SI\"):\n \n Conversion to Planck units:\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.units import gravitational_constant, hbar\n >>> convert_to(atomic_mass_constant, [gravitational_constant, speed_of_light, hbar]).n()\n 7.62963085040767e-20*gravitational_constant**(-0.5)*hbar**0.5*speed_of_light**0.5\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py b/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py\nindex bb9d710b8476..57b78b0c873e 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py\n@@ -341,7 +341,7 @@ def ang_acc_in(self, otherframe):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> A = ReferenceFrame('A')\n >>> V = 10 * N.x\n@@ -374,7 +374,7 @@ def ang_vel_in(self, otherframe):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> A = ReferenceFrame('A')\n >>> V = 10 * N.x\n@@ -942,7 +942,7 @@ def set_ang_acc(self, otherframe, value):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> A = ReferenceFrame('A')\n >>> V = 10 * N.x\n@@ -978,7 +978,7 @@ def set_ang_vel(self, otherframe, value):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> A = ReferenceFrame('A')\n >>> V = 10 * N.x\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/point.py b/sympy/physics/vector/point.py\nindex 2441a6018370..21c86a410b03 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/vector/point.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/point.py\n@@ -110,7 +110,7 @@ def a1pt_theory(self, otherpoint, outframe, interframe):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame\n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Vector, dynamicsymbols\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import dynamicsymbols\n >>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')\n >>> q2 = dynamicsymbols('q2')\n >>> qd = dynamicsymbols('q', 1)\n@@ -387,7 +387,7 @@ def v1pt_theory(self, otherpoint, outframe, interframe):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame\n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Vector, dynamicsymbols\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import dynamicsymbols\n >>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')\n >>> q2 = dynamicsymbols('q2')\n >>> qd = dynamicsymbols('q', 1)\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/vector.py b/sympy/physics/vector/vector.py\nindex 888e91a54c6b..89ff52745a2b 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/vector/vector.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/vector.py\n@@ -402,7 +402,7 @@ def __xor__(self, other):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> q1 = symbols('q1')\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n@@ -595,7 +595,7 @@ def express(self, otherframe, variables=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector, dynamicsymbols\n+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, dynamicsymbols\n >>> q1 = dynamicsymbols('q1')\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> A = N.orientnew('A', 'Axis', [q1, N.y])\n@@ -625,7 +625,6 @@ def to_matrix(self, reference_frame):\n \n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame\n- >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics.functions import inertia\n >>> a, b, c = symbols('a, b, c')\n >>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')\n >>> vector = a * N.x + b * N.y + c * N.z\ndiff --git a/sympy/physics/wigner.py b/sympy/physics/wigner.py\nindex 80a790b91ee1..7e82caaab56c 100644\n--- a/sympy/physics/wigner.py\n+++ b/sympy/physics/wigner.py\n@@ -921,7 +921,6 @@ def wigner_d(J, alpha, beta, gamma):\n \n >>> from sympy.physics.wigner import wigner_d\n >>> from sympy import Integer, symbols, pprint\n- >>> from sympy.physics.wigner import wigner_d_small\n >>> half = 1/Integer(2)\n >>> alpha, beta, gamma = symbols(\"alpha, beta, gamma\", real=True)\n >>> pprint(wigner_d(half, alpha, beta, gamma), use_unicode=True)\ndiff --git a/sympy/plotting/experimental_lambdify.py b/sympy/plotting/experimental_lambdify.py\nindex 74c244c9324b..9b3d940ba99b 100644\n--- a/sympy/plotting/experimental_lambdify.py\n+++ b/sympy/plotting/experimental_lambdify.py\n@@ -545,7 +545,7 @@ def tree2str(cls, tree):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n- >>> from sympy import Integral, sin\n+ >>> from sympy import sin\n >>> from sympy.plotting.experimental_lambdify import Lambdifier\n >>> str2tree = Lambdifier([x], x).str2tree\n >>> tree2str = Lambdifier([x], x).tree2str\ndiff --git a/sympy/plotting/plot.py b/sympy/plotting/plot.py\nindex ae612e144226..f910b8a267d3 100644\n--- a/sympy/plotting/plot.py\n+++ b/sympy/plotting/plot.py\n@@ -2280,7 +2280,7 @@ def check_arguments(args, expr_len, nb_of_free_symbols):\n :format: doctest\n :include-source: True\n \n- >>> from sympy import plot, cos, sin, symbols\n+ >>> from sympy import cos, sin, symbols\n >>> from sympy.plotting.plot import check_arguments\n >>> x = symbols('x')\n >>> check_arguments([cos(x), sin(x)], 2, 1)\ndiff --git a/sympy/plotting/plot_implicit.py b/sympy/plotting/plot_implicit.py\nindex 2aa257cda8c7..fa75cd2c6f44 100644\n--- a/sympy/plotting/plot_implicit.py\n+++ b/sympy/plotting/plot_implicit.py\n@@ -262,7 +262,7 @@ def plot_implicit(expr, x_var=None, y_var=None, adaptive=True, depth=0,\n :format: doctest\n :include-source: True\n \n- >>> from sympy import plot_implicit, cos, sin, symbols, Eq, And\n+ >>> from sympy import plot_implicit, symbols, Eq, And\n >>> x, y = symbols('x y')\n \n Without any ranges for the symbols in the expression:\ndiff --git a/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/__init__.py b/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/__init__.py\nindex 7007a80d647e..cd86a505d8c4 100644\n--- a/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/__init__.py\n+++ b/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/__init__.py\n@@ -13,7 +13,6 @@ def PygletPlot(*args, **kwargs):\n See examples/advanced/pyglet_plotting.py for many more examples.\n \n >>> from sympy.plotting.pygletplot import PygletPlot as Plot\n- >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n \n >>> Plot(x*y**3-y*x**3)\ndiff --git a/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/plot.py b/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/plot.py\nindex c8ce706797ef..7fdb1defdf5f 100644\n--- a/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/plot.py\n+++ b/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/plot.py\n@@ -165,7 +165,6 @@ def __init__(self, *fargs, **win_args):\n other words...\n \n >>> from sympy.plotting.pygletplot import PygletPlot as Plot\n- >>> from sympy.core import Symbol\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> p = Plot(x**2, visible=False)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/distributedmodules.py b/sympy/polys/distributedmodules.py\nindex 5093a2aee41e..6a6cfd78fea1 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/distributedmodules.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/distributedmodules.py\n@@ -381,7 +381,7 @@ def sdm_to_vector(f, gens, K, n=None):\n \n >>> from sympy.polys.distributedmodules import sdm_to_vector\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n- >>> from sympy.polys import QQ, lex\n+ >>> from sympy.polys import QQ\n >>> f = [((1, 0, 0, 1), QQ(2)), ((0, 2, 0, 0), QQ(1)), ((0, 0, 2, 0), QQ(1))]\n >>> sdm_to_vector(f, [x, y, z], QQ)\n [x**2 + y**2, 2*z]\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/galoistools.py b/sympy/polys/galoistools.py\nindex 87c49d109b98..840823930ab5 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/galoistools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/galoistools.py\n@@ -29,7 +29,6 @@ def gf_crt(U, M, K=None):\n \n >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ\n >>> from sympy.polys.galoistools import gf_crt\n- >>> from sympy.ntheory.modular import solve_congruence\n \n >>> gf_crt([49, 76, 65], [99, 97, 95], ZZ)\n 639985\n@@ -315,7 +314,6 @@ def gf_from_int_poly(f, p):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ\n >>> from sympy.polys.galoistools import gf_from_int_poly\n \n >>> gf_from_int_poly([7, -2, 3], 5)\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/monomials.py b/sympy/polys/monomials.py\nindex 844840d121f5..5df7ed0cfc65 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/monomials.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/monomials.py\n@@ -82,8 +82,6 @@ def itermonomials(variables, max_degrees, min_degrees=None):\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> from sympy.polys.monomials import itermonomials\n >>> from sympy.polys.orderings import monomial_key\n- >>> from itertools import product\n- >>> from sympy.core import Mul\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n \n >>> sorted(itermonomials([x, y], [2, 4], [1, 2]), reverse=True, key=monomial_key('lex', [x, y]))\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/orderings.py b/sympy/polys/orderings.py\nindex 59269461d9f3..464eabf144f4 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/orderings.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/orderings.py\n@@ -266,7 +266,7 @@ def build_product_order(arg, gens):\n \n For example, build a product of two grlex orders:\n \n- >>> from sympy.polys.orderings import grlex, build_product_order\n+ >>> from sympy.polys.orderings import build_product_order\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z, t\n \n >>> O = build_product_order(((\"grlex\", x, y), (\"grlex\", z, t)), [x, y, z, t])\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/partfrac.py b/sympy/polys/partfrac.py\nindex 2d75731af8eb..ee5ffdc6403c 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/partfrac.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/partfrac.py\n@@ -428,7 +428,7 @@ def assemble_partfrac_list(partial_list):\n This example is taken from Bronstein's original paper:\n \n >>> from sympy.polys.partfrac import apart_list, assemble_partfrac_list\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \n >>> f = 36 / (x**5 - 2*x**4 - 2*x**3 + 4*x**2 + x - 2)\n >>> pfd = apart_list(f)\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/polyroots.py b/sympy/polys/polyroots.py\nindex d9a9f53249bb..979b27483bee 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/polyroots.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/polyroots.py\n@@ -265,7 +265,7 @@ def roots_quartic(f):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Poly, symbols, I\n+ >>> from sympy import Poly\n >>> from sympy.polys.polyroots import roots_quartic\n \n >>> r = roots_quartic(Poly('x**4-6*x**3+17*x**2-26*x+20'))\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/polytools.py b/sympy/polys/polytools.py\nindex f066202e69f3..a0110db39476 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/polytools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/polytools.py\n@@ -4484,7 +4484,7 @@ def total_degree(f, *gens):\n Examples\n ========\n >>> from sympy import total_degree, Poly\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n \n >>> total_degree(1)\n 0\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/rings.py b/sympy/polys/rings.py\nindex d836fd482e02..4e02e9de0f46 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/rings.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/rings.py\n@@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ def vring(symbols, domain, order=lex):\n \n >>> vring(\"x,y,z\", ZZ, lex)\n Polynomial ring in x, y, z over ZZ with lex order\n- >>> x + y + z\n+ >>> x + y + z # noqa:\n x + y + z\n >>> type(_)\n <class 'sympy.polys.rings.PolyElement'>\n@@ -141,8 +141,6 @@ def sring(exprs, *symbols, **options):\n \n >>> from sympy.core import symbols\n >>> from sympy.polys.rings import sring\n- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ\n- >>> from sympy.polys.orderings import lex\n \n >>> x, y, z = symbols(\"x,y,z\")\n >>> R, f = sring(x + 2*y + 3*z)\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/rootisolation.py b/sympy/polys/rootisolation.py\nindex fccdac6ced45..3108de55304f 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/rootisolation.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/rootisolation.py\n@@ -1796,7 +1796,7 @@ class ComplexInterval(object):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import CRootOf, Rational, S\n+ >>> from sympy import CRootOf, S\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> CRootOf.clear_cache() # for doctest reproducibility\n >>> root = CRootOf(x**10 - 2*x + 3, 9)\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py b/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py\nindex 3a3eaca75632..8d8a199ff826 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py\n@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ class _pure_key_dict(object):\n Only the following actions are guaranteed:\n \n >>> from sympy.polys.rootoftools import _pure_key_dict\n- >>> from sympy import S, PurePoly\n+ >>> from sympy import PurePoly\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n \n 1) creation\n@@ -907,7 +907,7 @@ def eval_rational(self, dx=None, dy=None, n=15):\n ensure the decimal representation of the approximation will be\n correct (including rounding) to 6 digits:\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, legendre_poly, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import legendre_poly, Symbol\n >>> x = Symbol(\"x\")\n >>> p = legendre_poly(4, x, polys=True)\n >>> r = p.real_roots()[-1]\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/dot.py b/sympy/printing/dot.py\nindex 5ae80e28ed4a..a08d21f817f6 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/dot.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/dot.py\n@@ -33,7 +33,8 @@ def purestr(x, with_args=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Integer, Float, Symbol, MatrixSymbol\n+ >>> from sympy import Float, Symbol, MatrixSymbol\n+ >>> from sympy import Integer # noqa: F401\n >>> from sympy.printing.dot import purestr\n \n Applying ``purestr`` for basic symbolic object:\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/julia.py b/sympy/printing/julia.py\nindex ee3dad2fc1d8..0e01c2986fc4 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/julia.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/julia.py\n@@ -547,7 +547,7 @@ def julia_code(expr, assign_to=None, **settings):\n >>> julia_code(sin(x).series(x).removeO())\n 'x.^5/120 - x.^3/6 + x'\n \n- >>> from sympy import Rational, ceiling, Abs\n+ >>> from sympy import Rational, ceiling\n >>> x, y, tau = symbols(\"x, y, tau\")\n >>> julia_code((2*tau)**Rational(7, 2))\n '8*sqrt(2)*tau.^(7/2)'\n@@ -628,7 +628,7 @@ def julia_code(expr, assign_to=None, **settings):\n ``contract=False`` will just print the assignment expression that should be\n looped over:\n \n- >>> from sympy import Eq, IndexedBase, Idx, ccode\n+ >>> from sympy import Eq, IndexedBase, Idx\n >>> len_y = 5\n >>> y = IndexedBase('y', shape=(len_y,))\n >>> t = IndexedBase('t', shape=(len_y,))\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/llvmjitcode.py b/sympy/printing/llvmjitcode.py\nindex 09facc44be0b..b2623744e457 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/llvmjitcode.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/llvmjitcode.py\n@@ -429,7 +429,7 @@ def llvm_callable(args, expr, callback_type=None):\n The 'cubature' callback handles multiple expressions (set `fdim`\n to match in the integration call.)\n >>> import sympy.printing.llvmjitcode as jit\n- >>> from sympy import cse, exp\n+ >>> from sympy import cse\n >>> from sympy.abc import x,y\n >>> e1 = x*x + y*y\n >>> e2 = 4*(x*x + y*y) + 8.0\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/octave.py b/sympy/printing/octave.py\nindex 5d3be42ad1ee..66479e4db5ce 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/octave.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/octave.py\n@@ -631,7 +631,7 @@ def octave_code(expr, assign_to=None, **settings):\n >>> octave_code(sin(x).series(x).removeO())\n 'x.^5/120 - x.^3/6 + x'\n \n- >>> from sympy import Rational, ceiling, Abs\n+ >>> from sympy import Rational, ceiling\n >>> x, y, tau = symbols(\"x, y, tau\")\n >>> octave_code((2*tau)**Rational(7, 2))\n '8*sqrt(2)*tau.^(7/2)'\n@@ -712,7 +712,7 @@ def octave_code(expr, assign_to=None, **settings):\n ``contract=False`` will just print the assignment expression that should be\n looped over:\n \n- >>> from sympy import Eq, IndexedBase, Idx, ccode\n+ >>> from sympy import Eq, IndexedBase, Idx\n >>> len_y = 5\n >>> y = IndexedBase('y', shape=(len_y,))\n >>> t = IndexedBase('t', shape=(len_y,))\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/formal.py b/sympy/series/formal.py\nindex acbdab6181be..5f31c26ff82c 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/formal.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/formal.py\n@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ def rational_algorithm(f, x, k, order=4, full=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import log, atan, I\n+ >>> from sympy import log, atan\n >>> from sympy.series.formal import rational_algorithm as ra\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, k\n \n@@ -1172,7 +1172,7 @@ def product(self, other, x=None, n=6):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp, convolution\n+ >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f1 = fps(sin(x))\n >>> f2 = fps(exp(x))\n@@ -1264,7 +1264,7 @@ def compose(self, other, x=None, n=6):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp, bell\n+ >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f1 = fps(exp(x))\n >>> f2 = fps(sin(x))\n@@ -1337,7 +1337,7 @@ def inverse(self, x=None, n=6):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import fps, exp, cos, bell\n+ >>> from sympy import fps, exp, cos\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f1 = fps(exp(x))\n >>> f2 = fps(cos(x))\n@@ -1531,7 +1531,7 @@ def _eval_terms(self, n):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp, convolution\n+ >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f1 = fps(sin(x))\n >>> f2 = fps(exp(x))\n@@ -1596,7 +1596,7 @@ def _eval_terms(self, n):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp, bell\n+ >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f1 = fps(exp(x))\n >>> f2 = fps(sin(x))\n@@ -1681,7 +1681,7 @@ def _eval_terms(self, n):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import fps, exp, cos, bell\n+ >>> from sympy import fps, exp, cos\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f1 = fps(exp(x))\n >>> f2 = fps(cos(x))\n@@ -1751,7 +1751,7 @@ def fps(f, x=None, x0=0, dir=1, hyper=True, order=4, rational=True, full=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import fps, O, ln, atan, sin\n+ >>> from sympy import fps, ln, atan, sin\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, n\n \n Rational Functions\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/fourier.py b/sympy/series/fourier.py\nindex ddd5eaf2e286..5030e3ff5c18 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/fourier.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/fourier.py\n@@ -48,7 +48,6 @@ def _process_limits(func, limits):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import pi\n >>> from sympy.series.fourier import _process_limits as pari\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> pari(x**2, (x, -2, 2))\n@@ -645,9 +644,8 @@ def fourier_series(f, limits=None, finite=True):\n \n Computing the Fourier series of $f(x) = x^2$:\n \n- >>> from sympy import fourier_series, pi, cos\n+ >>> from sympy import fourier_series, pi\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n-\n >>> f = x**2\n >>> s = fourier_series(f, (x, -pi, pi))\n >>> s1 = s.truncate(n=3)\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/kauers.py b/sympy/series/kauers.py\nindex bb0d48e32d87..4d8458e8c334 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/kauers.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/kauers.py\n@@ -11,9 +11,8 @@ def finite_diff(expression, variable, increment=1):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z, k, n\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n >>> from sympy.series.kauers import finite_diff\n- >>> from sympy import Sum\n >>> finite_diff(x**2, x)\n 2*x + 1\n >>> finite_diff(y**3 + 2*y**2 + 3*y + 4, y)\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/limits.py b/sympy/series/limits.py\nindex 01b23ea89866..009ae26fdf28 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/limits.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/limits.py\n@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ def limit(e, z, z0, dir=\"+\"):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import limit, sin, Symbol, oo\n+ >>> from sympy import limit, sin, oo\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> limit(sin(x)/x, x, 0)\n 1\n@@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ class Limit(Expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Limit, sin, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import Limit, sin\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> Limit(sin(x)/x, x, 0)\n Limit(sin(x)/x, x, 0)\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/sequences.py b/sympy/series/sequences.py\nindex eac7276eae5e..1062f0dbd4a7 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/sequences.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/sequences.py\n@@ -188,7 +188,7 @@ def coeff_mul(self, other):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula\n+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula\n >>> from sympy.abc import n\n >>> SeqFormula(n**2).coeff_mul(2)\n SeqFormula(2*n**2, (n, 0, oo))\n@@ -208,7 +208,7 @@ def __add__(self, other):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula\n+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula\n >>> from sympy.abc import n\n >>> SeqFormula(n**2) + SeqFormula(n**3)\n SeqFormula(n**3 + n**2, (n, 0, oo))\n@@ -229,7 +229,7 @@ def __sub__(self, other):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula\n+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula\n >>> from sympy.abc import n\n >>> SeqFormula(n**2) - (SeqFormula(n))\n SeqFormula(n**2 - n, (n, 0, oo))\n@@ -248,7 +248,7 @@ def __neg__(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula\n+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula\n >>> from sympy.abc import n\n >>> -SeqFormula(n**2)\n SeqFormula(-n**2, (n, 0, oo))\n@@ -264,7 +264,7 @@ def __mul__(self, other):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula\n+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula\n >>> from sympy.abc import n\n >>> SeqFormula(n**2) * (SeqFormula(n))\n SeqFormula(n**3, (n, 0, oo))\n@@ -379,7 +379,7 @@ class EmptySequence(SeqBase, metaclass=Singleton):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import EmptySequence, SeqPer, oo\n+ >>> from sympy import EmptySequence, SeqPer\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> EmptySequence\n EmptySequence\n@@ -917,7 +917,7 @@ def sequence(seq, limits=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import sequence, SeqPer, SeqFormula\n+ >>> from sympy import sequence\n >>> from sympy.abc import n\n >>> sequence(n**2, (n, 0, 5))\n SeqFormula(n**2, (n, 0, 5))\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/series.py b/sympy/series/series.py\nindex 95ac89b34c79..93bcb61323ff 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/series.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/series.py\n@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ def series(expr, x=None, x0=0, n=6, dir=\"+\"):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, series, tan, oo\n+ >>> from sympy import series, tan, oo\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = tan(x)\n >>> series(f, x, 2, 6, \"+\")\ndiff --git a/sympy/sets/fancysets.py b/sympy/sets/fancysets.py\nindex 0a94d81db36f..bf013522e14a 100644\n--- a/sympy/sets/fancysets.py\n+++ b/sympy/sets/fancysets.py\n@@ -241,7 +241,7 @@ class Reals(Interval, metaclass=Singleton):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, Interval, Rational, pi, I\n+ >>> from sympy import S, Rational, pi, I\n >>> 5 in S.Reals\n True\n >>> Rational(-1, 2) in S.Reals\ndiff --git a/sympy/sets/ordinals.py b/sympy/sets/ordinals.py\nindex 9326163c104f..3b1eadb28880 100644\n--- a/sympy/sets/ordinals.py\n+++ b/sympy/sets/ordinals.py\n@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ class Ordinal(Basic):\n Internally, this class is just a list of instances of OmegaPower\n Examples\n ========\n- >>> from sympy.sets import Ordinal, ord0, OmegaPower\n+ >>> from sympy.sets import Ordinal, OmegaPower\n >>> from sympy.sets.ordinals import omega\n >>> w = omega\n >>> w.is_limit_ordinal\ndiff --git a/sympy/sets/sets.py b/sympy/sets/sets.py\nindex 1e3c9d292fca..7788e7a9fb65 100644\n--- a/sympy/sets/sets.py\n+++ b/sympy/sets/sets.py\n@@ -479,11 +479,10 @@ def powerset(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import EmptySet, FiniteSet, Interval, PowerSet\n+ >>> from sympy import EmptySet, FiniteSet, Interval\n \n A power set of an empty set:\n \n- >>> from sympy import FiniteSet, EmptySet\n >>> A = EmptySet\n >>> A.powerset()\n FiniteSet(EmptySet)\n@@ -814,7 +813,7 @@ def is_iterable(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import FiniteSet, Interval, ProductSet\n+ >>> from sympy import FiniteSet, Interval\n >>> I = Interval(0, 1)\n >>> A = FiniteSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)\n >>> I.is_iterable\n@@ -2200,8 +2199,8 @@ def imageset(*args):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import S, Interval, Symbol, imageset, sin, Lambda\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy import S, Interval, imageset, sin, Lambda\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \n >>> imageset(x, 2*x, Interval(0, 2))\n Interval(0, 4)\ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/fu.py b/sympy/simplify/fu.py\nindex d0e85f759719..d564357c0403 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/fu.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/fu.py\n@@ -451,7 +451,6 @@ def TR4(rv):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR4\n >>> from sympy import pi\n >>> from sympy import cos, sin, tan, cot\n >>> for s in (0, pi/6, pi/4, pi/3, pi/2):\n@@ -599,7 +598,7 @@ def TR8(rv, first=True):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR8, TR7\n+ >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR8\n >>> from sympy import cos, sin\n >>> TR8(cos(2)*cos(3))\n cos(5)/2 + cos(1)/2\n@@ -816,8 +815,8 @@ def TR10i(rv):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR10i\n- >>> from sympy import cos, sin, pi, Add, Mul, sqrt, Symbol\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy import cos, sin, sqrt\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \n >>> TR10i(cos(1)*cos(3) + sin(1)*sin(3))\n cos(2)\n@@ -1088,7 +1087,6 @@ def TR12(rv, first=True):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR12\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy import tan\n >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR12\n@@ -1250,7 +1248,7 @@ def TR13(rv):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR13\n- >>> from sympy import tan, cot, cos\n+ >>> from sympy import tan, cot\n >>> TR13(tan(3)*tan(2))\n -tan(2)/tan(5) - tan(3)/tan(5) + 1\n >>> TR13(cot(3)*cot(2))\n@@ -1541,7 +1539,7 @@ def TR15(rv, max=4, pow=False):\n \n >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR15\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n- >>> from sympy import cos, sin\n+ >>> from sympy import sin\n >>> TR15(1 - 1/sin(x)**2)\n -cot(x)**2\n \n@@ -1570,7 +1568,7 @@ def TR16(rv, max=4, pow=False):\n \n >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR16\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n- >>> from sympy import cos, sin\n+ >>> from sympy import cos\n >>> TR16(1 - 1/cos(x)**2)\n -tan(x)**2\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/gammasimp.py b/sympy/simplify/gammasimp.py\nindex f4659c8aa6d4..b65d03e9d9bc 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/gammasimp.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/gammasimp.py\n@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ def gammasimp(expr):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.simplify import gammasimp\n- >>> from sympy import gamma, factorial, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import gamma, Symbol\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> n = Symbol('n', integer = True)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/hyperexpand.py b/sympy/simplify/hyperexpand.py\nindex bb1efc04ab83..b8b1fdd44181 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/hyperexpand.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/hyperexpand.py\n@@ -637,7 +637,7 @@ def compute_buckets(self):\n \n >>> from sympy.simplify.hyperexpand import G_Function\n >>> from sympy.abc import y\n- >>> from sympy import S, symbols\n+ >>> from sympy import S\n \n >>> a, b = [1, 3, 2, S(3)/2], [1 + y, y, 2, y + 3]\n >>> G_Function(a, b, [2], [y]).compute_buckets()\ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/powsimp.py b/sympy/simplify/powsimp.py\nindex baed0aac8359..280bd9e98fe6 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/powsimp.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/powsimp.py\n@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ def powsimp(expr, deep=False, combine='all', force=False, measure=count_ops):\n \n Radicals with Mul bases will be combined if combine='exp'\n \n- >>> from sympy import sqrt, Mul\n+ >>> from sympy import sqrt\n >>> x, y = symbols('x y')\n \n Two radicals are automatically joined through Mul:\ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/radsimp.py b/sympy/simplify/radsimp.py\nindex 945792100876..9d96b18e3d0b 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/radsimp.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/radsimp.py\n@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ def collect(expr, syms, func=None, evaluate=None, exact=False, distribute_order_\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import S, collect, expand, factor, Wild\n- >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, x, y, z\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, x, y\n \n This function can collect symbolic coefficients in polynomials or\n rational expressions. It will manage to find all integer or rational\n@@ -634,7 +634,7 @@ def collect_const(expr, *vars, **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import sqrt\n- >>> from sympy.abc import a, s, x, y, z\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import s, x, y, z\n >>> from sympy.simplify.radsimp import collect_const\n >>> collect_const(sqrt(3) + sqrt(3)*(1 + sqrt(2)))\n sqrt(3)*(sqrt(2) + 2)\n@@ -757,7 +757,7 @@ def radsimp(expr, symbolic=True, max_terms=4):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import radsimp, sqrt, Symbol, denom, pprint, I\n+ >>> from sympy import radsimp, sqrt, Symbol, pprint\n >>> from sympy import factor_terms, fraction, signsimp\n >>> from sympy.simplify.radsimp import collect_sqrt\n >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c\ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/simplify.py b/sympy/simplify/simplify.py\nindex 828db06ac083..b79aba30f508 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/simplify.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/simplify.py\n@@ -787,7 +787,7 @@ def factor_sum(self, limits=None, radical=False, clear=False, fraction=False, si\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Sum, Integral\n+ >>> from sympy import Sum\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy.simplify.simplify import factor_sum\n >>> s = Sum(x*y, (x, 1, 3))\n@@ -1169,8 +1169,8 @@ def kroneckersimp(expr):\n The only simplification currently attempted is to identify multiplicative cancellation:\n \n >>> from sympy import KroneckerDelta, kroneckersimp\n- >>> from sympy.abc import i, j\n- >>> kroneckersimp(1 + KroneckerDelta(0, j) * KroneckerDelta(1, j))\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import i\n+ >>> kroneckersimp(1 + KroneckerDelta(0, i) * KroneckerDelta(1, i))\n 1\n \"\"\"\n def args_cancel(args1, args2):\n@@ -1346,7 +1346,7 @@ def nthroot(expr, n, max_len=4, prec=15):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.simplify.simplify import nthroot\n- >>> from sympy import Rational, sqrt\n+ >>> from sympy import sqrt\n >>> nthroot(90 + 34*sqrt(7), 3)\n sqrt(7) + 3\n \n@@ -1414,7 +1414,7 @@ def nsimplify(expr, constants=(), tolerance=None, full=False, rational=None,\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import nsimplify, sqrt, GoldenRatio, exp, I, exp, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import nsimplify, sqrt, GoldenRatio, exp, I, pi\n >>> nsimplify(4/(1+sqrt(5)), [GoldenRatio])\n -2 + 2*GoldenRatio\n >>> nsimplify((1/(exp(3*pi*I/5)+1)))\n@@ -1527,7 +1527,6 @@ def _real_to_rational(expr, tolerance=None, rational_conversion='base10'):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Rational\n >>> from sympy.simplify.simplify import _real_to_rational\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/trigsimp.py b/sympy/simplify/trigsimp.py\nindex 60f795ca57a2..d1a11d60d03c 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/trigsimp.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/trigsimp.py\n@@ -444,7 +444,7 @@ def trigsimp(expr, **opts):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import trigsimp, sin, cos, log\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> e = 2*sin(x)**2 + 2*cos(x)**2\n >>> trigsimp(e)\n 2\n@@ -638,8 +638,8 @@ def trigsimp_old(expr, **opts):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import trigsimp, sin, cos, log, cosh, sinh, tan, cot\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy import trigsimp, sin, cos, log, cot\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> e = 2*sin(x)**2 + 2*cos(x)**2\n >>> trigsimp(e, old=True)\n 2\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/bivariate.py b/sympy/solvers/bivariate.py\nindex 19994fd43327..4442c9814e8a 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/bivariate.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/bivariate.py\n@@ -59,7 +59,6 @@ def _mostfunc(lhs, func, X=None):\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.bivariate import _mostfunc\n >>> from sympy.functions.elementary.exponential import exp\n- >>> from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> _mostfunc(exp(x) + exp(exp(x) + 2), exp)\n exp(exp(x) + 2)\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/deutils.py b/sympy/solvers/deutils.py\nindex 9bdbfad82019..6a45534b9c2a 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/deutils.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/deutils.py\n@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ def _preprocess(expr, func=None, hint='_Integral'):\n function to be solved for.\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.deutils import _preprocess\n- >>> from sympy import Derivative, Function, Integral, sin\n+ >>> from sympy import Derivative, Function\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n >>> f, g = map(Function, 'fg')\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py\nindex c67eabfe927f..4e2c7afdbc45 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py\n@@ -867,7 +867,7 @@ def diop_linear(eq, param=symbols(\"t\", integer=True)):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.diophantine.diophantine import diop_linear\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z, t\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n >>> diop_linear(2*x - 3*y - 5) # solves equation 2*x - 3*y - 5 == 0\n (3*t_0 - 5, 2*t_0 - 5)\n \n@@ -2026,7 +2026,6 @@ def transformation_to_DN(eq):\n \n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy.solvers.diophantine.diophantine import transformation_to_DN\n- >>> from sympy.solvers.diophantine import classify_diop\n >>> A, B = transformation_to_DN(x**2 - 3*x*y - y**2 - 2*y + 1)\n >>> A\n Matrix([\n@@ -3129,7 +3128,7 @@ def diop_general_sum_of_squares(eq, limit=1):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.diophantine.diophantine import diop_general_sum_of_squares\n- >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, e, f\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, e\n >>> diop_general_sum_of_squares(a**2 + b**2 + c**2 + d**2 + e**2 - 2345)\n {(15, 22, 22, 24, 24)}\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/inequalities.py b/sympy/solvers/inequalities.py\nindex 01341ea54b5a..5ce0e102e012 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/inequalities.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/inequalities.py\n@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ def reduce_rational_inequalities(exprs, gen, relational=True):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Poly, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> from sympy.solvers.inequalities import reduce_rational_inequalities\n \n >>> x = Symbol('x', real=True)\n@@ -374,7 +374,6 @@ def reduce_abs_inequalities(exprs, gen):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Abs, Symbol\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> from sympy.solvers.inequalities import reduce_abs_inequalities\n >>> x = Symbol('x', extended_real=True)\n \n@@ -941,7 +940,6 @@ def reduce_inequalities(inequalities, symbols=[]):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import sympify as S, Symbol\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy.solvers.inequalities import reduce_inequalities\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py\nindex c0d3eb1624ed..4a28f813f4a6 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py\n@@ -1818,9 +1818,8 @@ def classify_sysode(eq, funcs=None, **kwargs):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, Eq, symbols, diff, Rational\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, Eq, symbols, diff\n >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import classify_sysode\n- >>> from sympy.matrices.dense import Matrix\n >>> from sympy.abc import t\n >>> f, x, y = symbols('f, x, y', cls=Function)\n >>> k, l, m, n = symbols('k, l, m, n', Integer=True)\n@@ -2537,7 +2536,7 @@ def ode_sol_simplicity(sol, func, trysolving=True):\n such as ``min(listofsolutions, key=lambda i: ode_sol_simplicity(i,\n f(x)))``.\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols, Function, Eq, tan, cos, sqrt, Integral\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Function, Eq, tan, Integral\n >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import ode_sol_simplicity\n >>> x, C1, C2 = symbols('x, C1, C2')\n >>> f = Function('f')\n@@ -2838,7 +2837,7 @@ def constant_renumber(expr, variables=None, newconstants=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols, Eq, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols\n >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import constant_renumber\n >>> x, C1, C2, C3 = symbols('x,C1:4')\n >>> expr = C3 + C2*x + C1*x**2\n@@ -3466,7 +3465,7 @@ def ode_2nd_power_series_ordinary(eq, func, order, match):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import dsolve, Function, pprint\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function(\"f\")\n >>> eq = f(x).diff(x, 2) + f(x)\n >>> pprint(dsolve(eq, hint='2nd_power_series_ordinary'))\n@@ -3603,7 +3602,7 @@ def ode_2nd_linear_airy(eq, func, order, match):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import dsolve, Function, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import dsolve, Function\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function(\"f\")\n >>> eq = f(x).diff(x, 2) - x*f(x)\n@@ -3660,7 +3659,7 @@ def ode_2nd_power_series_regular(eq, func, order, match):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import dsolve, Function, pprint\n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function(\"f\")\n >>> eq = x*(f(x).diff(x, 2)) + 2*(f(x).diff(x)) + x*f(x)\n >>> pprint(dsolve(eq, hint='2nd_power_series_regular'))\n@@ -3761,11 +3760,11 @@ def ode_2nd_linear_bessel(eq, func, order, match):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, a\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> v = Symbol('v', positive=True)\n- >>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve, checkodesol\n- >>> from sympy import pprint, Function\n+ >>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve\n+ >>> from sympy import Function\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> y = f(x)\n >>> genform = x**2*y.diff(x, 2) + x*y.diff(x) + (x**2 - v**2)*y\n@@ -4104,7 +4103,7 @@ def ode_nth_linear_euler_eq_homogeneous(eq, func, order, match, returns='sol'):\n :py:obj:`~.ComplexRootOf` instance will be returned\n instead.\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> dsolve(4*x**2*f(x).diff(x, 2) + f(x), f(x),\n@@ -4470,8 +4469,8 @@ def ode_linear_coefficients(eq, func, order, match):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, Derivative, pprint\n- >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve, classify_ode\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> df = f(x).diff(x)\n@@ -4508,7 +4507,7 @@ def ode_separable_reduced(eq, func, order, match):\n \n The general solution is:\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, pprint\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, n\n >>> f, g = map(Function, ['f', 'g'])\n >>> genform = f(x).diff(x) + (f(x)/x)*g(x**n*f(x))\n@@ -4535,8 +4534,8 @@ def ode_separable_reduced(eq, func, order, match):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, Derivative, pprint\n- >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve, classify_ode\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> d = f(x).diff(x)\n@@ -4591,7 +4590,7 @@ def ode_1st_power_series(eq, func, order, match):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, Derivative, pprint, exp\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint, exp\n >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\n@@ -4672,7 +4671,7 @@ def ode_nth_linear_constant_coeff_homogeneous(eq, func, order, match,\n :py:class:`~sympy.polys.rootoftools.ComplexRootOf` instance will be return\n instead.\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> dsolve(f(x).diff(x, 5) + 10*f(x).diff(x) - 2*f(x), f(x),\n@@ -5508,7 +5507,7 @@ def ode_lie_group(eq, func, order, match):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq, exp, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, exp, pprint\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> pprint(dsolve(f(x).diff(x) + 2*x*f(x) - x*exp(-x**2), f(x),\n@@ -5621,7 +5620,7 @@ def infinitesimals(eq, func=None, order=None, hint='default', match=None):\n \n The infinitesimals can be found by solving the following PDE:\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, Eq, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, Eq, pprint\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> xi, eta, h = map(Function, ['xi', 'eta', 'h'])\n >>> h = h(x, y) # dy/dx = h\n@@ -5649,7 +5648,7 @@ def infinitesimals(eq, func=None, order=None, hint='default', match=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, diff\n+ >>> from sympy import Function\n >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import infinitesimals\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py\nindex 3a00e3320cf2..663132dc11ae 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py\n@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ class SingleODEProblem:\n This class is used internally by dsolve. To instantiate an instance\n directly first define an ODE problem:\n \n- >>> from sympy import Eq, Function, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, Symbol\n >>> x = Symbol('x')\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> eq = f(x).diff(x, 2)\n@@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ class SingleODESolver:\n You can use a subclass of SingleODEProblem to solve a particular type of\n ODE. We first define a particular ODE problem:\n \n- >>> from sympy import Eq, Function, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, Symbol\n >>> x = Symbol('x')\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> eq = f(x).diff(x, 2)\n@@ -466,8 +466,8 @@ class AlmostLinear(SinglePatternODESolver):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, Derivative, pprint, sin, cos\n- >>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve, classify_ode\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint, sin, cos\n+ >>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> d = f(x).diff(x)\n@@ -650,7 +650,7 @@ class Factorable(SingleODESolver):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq, pprint, Derivative\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, pprint\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> eq = (f(x)**2-4)*(f(x).diff(x)+f(x))\n@@ -727,7 +727,7 @@ class RiccatiSpecial(SinglePatternODESolver):\n and is valid when neither `a` nor `b` are zero and either `c` or `d` is\n zero.\n \n- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, a, b, c, d\n+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, a, b, c, d\n >>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve, checkodesol\n >>> from sympy import pprint, Function\n >>> f = Function('f')\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/pde.py b/sympy/solvers/pde.py\nindex b0946d881791..834d1109b885 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/pde.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/pde.py\n@@ -151,7 +151,7 @@ def pdsolve(eq, func=None, hint='default', dict=False, solvefun=None, **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.pde import pdsolve\n- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, Eq\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, Eq\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> u = f(x, y)\n@@ -256,7 +256,7 @@ def classify_pde(eq, func=None, dict=False, **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.pde import classify_pde\n- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, Eq\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, Eq\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> u = f(x, y)\n@@ -418,7 +418,7 @@ def checkpdesol(pde, sol, func=None, solve_for_func=True):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Function, symbols, diff\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, symbols\n >>> from sympy.solvers.pde import checkpdesol, pdsolve\n >>> x, y = symbols('x y')\n >>> f = Function('f')\n@@ -525,10 +525,8 @@ def pde_1st_linear_constant_coeff_homogeneous(eq, func, order, match, solvefun):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.solvers.pde import (\n- ... pde_1st_linear_constant_coeff_homogeneous)\n >>> from sympy import pdsolve\n- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint\n >>> from sympy.abc import x,y\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> pdsolve(f(x,y) + f(x,y).diff(x) + f(x,y).diff(y))\n@@ -639,7 +637,7 @@ def pde_1st_linear_constant_coeff(eq, func, order, match, solvefun):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.pde import pdsolve\n- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, pprint, exp\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint, exp\n >>> from sympy.abc import x,y\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> eq = -2*f(x,y).diff(x) + 4*f(x,y).diff(y) + 5*f(x,y) - exp(x + 3*y)\n@@ -701,7 +699,6 @@ def pde_1st_linear_variable_coeff(eq, func, order, match, solvefun):\n \n which can be solved using ``dsolve``.\n \n- >>> from sympy.solvers.pde import pdsolve\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> from sympy import Function, pprint\n >>> a, b, c, G, f= [Function(i) for i in ['a', 'b', 'c', 'G', 'f']]\n@@ -719,7 +716,7 @@ def pde_1st_linear_variable_coeff(eq, func, order, match, solvefun):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.pde import pdsolve\n- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, pprint, exp\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint\n >>> from sympy.abc import x,y\n >>> f = Function('f')\n >>> eq = x*(u.diff(x)) - y*(u.diff(y)) + y**2*u - y**2\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\nindex b131fb46ae66..914cd8b2c701 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n@@ -137,7 +137,6 @@ def denoms(eq, *symbols):\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.solvers import denoms\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n- >>> from sympy import sqrt\n \n >>> denoms(x/y)\n {y}\n@@ -2866,7 +2865,6 @@ def nsolve(*args, **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy import Symbol, nsolve\n- >>> import sympy\n >>> import mpmath\n >>> mpmath.mp.dps = 15\n >>> x1 = Symbol('x1')\n@@ -2910,7 +2908,6 @@ def nsolve(*args, **kwargs):\n independently verify the solution.\n \n >>> from sympy import cos, cosh\n- >>> from sympy.abc import i\n >>> f = cos(x)*cosh(x) - 1\n >>> nsolve(f, 3.14*100)\n Traceback (most recent call last):\n@@ -3283,7 +3280,7 @@ def unrad(eq, *syms, **flags):\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.solvers import unrad\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n- >>> from sympy import sqrt, Rational, root, real_roots, solve\n+ >>> from sympy import sqrt, Rational, root\n \n >>> unrad(sqrt(x)*x**Rational(1, 3) + 2)\n (x**5 - 64, [])\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\nindex c07a58e2bfef..1e35500be49c 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py\n@@ -134,7 +134,7 @@ def _invert(f_x, y, x, domain=S.Complexes):\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.solveset import invert_complex, invert_real\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n- >>> from sympy import exp, log\n+ >>> from sympy import exp\n \n When does exp(x) == y?\n \n@@ -1260,7 +1260,7 @@ def _solve_modular(f, symbol, domain):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.solvers.solveset import _solve_modular as solve_modulo\n- >>> from sympy import S, Symbol, sin, Intersection, Range, Interval\n+ >>> from sympy import S, Symbol, sin, Intersection, Interval\n >>> from sympy.core.mod import Mod\n >>> x = Symbol('x')\n >>> solve_modulo(Mod(5*x - 8, 7) - 3, x, S.Integers)\n@@ -2127,7 +2127,7 @@ def solvify(f, symbol, domain):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.solvers.solveset import solvify, solveset\n+ >>> from sympy.solvers.solveset import solvify\n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> from sympy import S, tan, sin, exp\n >>> solvify(x**2 - 9, x, S.Reals)\n@@ -2443,7 +2443,7 @@ def linsolve(system, *symbols):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import Matrix, S, linsolve, symbols\n+ >>> from sympy import Matrix, linsolve, symbols\n >>> x, y, z = symbols(\"x, y, z\")\n >>> A = Matrix([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 10]])\n >>> b = Matrix([3, 6, 9])\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/crv_types.py b/sympy/stats/crv_types.py\nindex a3e11443b616..ce46b146c8c2 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/crv_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/crv_types.py\n@@ -252,7 +252,7 @@ def Arcsin(name, a=0, b=1):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import Arcsin, density, cdf\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n \n >>> a = Symbol(\"a\", real=True)\n >>> b = Symbol(\"b\", real=True)\n@@ -334,7 +334,7 @@ def Benini(name, alpha, beta, sigma):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import Benini, density, cdf\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> alpha = Symbol(\"alpha\", positive=True)\n >>> beta = Symbol(\"beta\", positive=True)\n@@ -1403,8 +1403,8 @@ def ExponentialPower(name, mu, alpha, beta):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import ExponentialPower, density, E, variance, cdf\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import ExponentialPower, density, cdf\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n >>> z = Symbol(\"z\")\n >>> mu = Symbol(\"mu\")\n >>> alpha = Symbol(\"alpha\", positive=True)\n@@ -1486,7 +1486,7 @@ def FDistribution(name, d1, d2):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import FDistribution, density\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> d1 = Symbol(\"d1\", positive=True)\n >>> d2 = Symbol(\"d2\", positive=True)\n@@ -1561,7 +1561,7 @@ def FisherZ(name, d1, d2):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import FisherZ, density\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> d1 = Symbol(\"d1\", positive=True)\n >>> d2 = Symbol(\"d2\", positive=True)\n@@ -1644,8 +1644,8 @@ def Frechet(name, a, s=1, m=0):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import Frechet, density, E, std, cdf\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import Frechet, density, cdf\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n \n >>> a = Symbol(\"a\", positive=True)\n >>> s = Symbol(\"s\", positive=True)\n@@ -1828,7 +1828,7 @@ def GammaInverse(name, a, b):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import GammaInverse, density, cdf, E, variance\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import GammaInverse, density, cdf\n >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> a = Symbol(\"a\", positive=True)\n@@ -1933,8 +1933,8 @@ def Gumbel(name, beta, mu, minimum=False):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import Gumbel, density, E, variance, cdf\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import Gumbel, density, cdf\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> x = Symbol(\"x\")\n >>> mu = Symbol(\"mu\")\n >>> beta = Symbol(\"beta\", positive=True)\n@@ -2005,8 +2005,8 @@ def Gompertz(name, b, eta):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import Gompertz, density, E, variance\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import Gompertz, density\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n \n >>> b = Symbol(\"b\", positive=True)\n >>> eta = Symbol(\"eta\", positive=True)\n@@ -2075,8 +2075,8 @@ def Kumaraswamy(name, a, b):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import Kumaraswamy, density, E, variance, cdf\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import Kumaraswamy, density, cdf\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> a = Symbol(\"a\", positive=True)\n >>> b = Symbol(\"b\", positive=True)\n@@ -2251,7 +2251,7 @@ def Levy(name, mu, c):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import Levy, density, cdf\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n \n >>> mu = Symbol(\"mu\", real=True)\n >>> c = Symbol(\"c\", positive=True)\n@@ -2498,7 +2498,7 @@ def LogNormal(name, mean, std):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import LogNormal, density\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> mu = Symbol(\"mu\", real=True)\n >>> sigma = Symbol(\"sigma\", positive=True)\n@@ -2897,7 +2897,7 @@ def Normal(name, mean, std):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import Normal, density, E, std, cdf, skewness, quantile\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint, factor, together, factor_terms\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n \n >>> mu = Symbol(\"mu\")\n >>> sigma = Symbol(\"sigma\", positive=True)\n@@ -3027,7 +3027,7 @@ def GaussianInverse(name, mean, shape):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import GaussianInverse, density, cdf, E, std, skewness\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import GaussianInverse, density, E, std, skewness\n >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> mu = Symbol(\"mu\", positive=True)\n@@ -3202,7 +3202,7 @@ def PowerFunction(name, alpha, a, b):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import PowerFunction, density, cdf, E, variance\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n >>> alpha = Symbol(\"alpha\", positive=True)\n >>> a = Symbol(\"a\", real=True)\n >>> b = Symbol(\"b\", real=True)\n@@ -3295,8 +3295,8 @@ def QuadraticU(name, a, b):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import QuadraticU, density, E, variance\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, factor, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import QuadraticU, density\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> a = Symbol(\"a\", real=True)\n >>> b = Symbol(\"b\", real=True)\n@@ -3381,8 +3381,8 @@ def RaisedCosine(name, mu, s):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import RaisedCosine, density, E, variance\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import RaisedCosine, density\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> mu = Symbol(\"mu\", real=True)\n >>> s = Symbol(\"s\", positive=True)\n@@ -3464,7 +3464,7 @@ def Rayleigh(name, sigma):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import Rayleigh, density, E, variance\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n \n >>> sigma = Symbol(\"sigma\", positive=True)\n >>> z = Symbol(\"z\")\n@@ -3590,7 +3590,7 @@ def ShiftedGompertz(name, b, eta):\n \n Examples\n ========\n- >>> from sympy.stats import ShiftedGompertz, density, E, variance\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import ShiftedGompertz, density\n >>> from sympy import Symbol\n \n >>> b = Symbol(\"b\", positive=True)\n@@ -3659,8 +3659,8 @@ def StudentT(name, nu):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import StudentT, density, E, variance, cdf\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import StudentT, density, cdf\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> nu = Symbol(\"nu\", positive=True)\n >>> z = Symbol(\"z\")\n@@ -3755,7 +3755,7 @@ def Trapezoidal(name, a, b, c, d):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import Trapezoidal, density, E\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import Trapezoidal, density\n >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> a = Symbol(\"a\")\n@@ -3854,7 +3854,7 @@ def Triangular(name, a, b, c):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import Triangular, density, E\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import Triangular, density\n >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> a = Symbol(\"a\")\n@@ -3966,7 +3966,7 @@ def Uniform(name, left, right):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import Uniform, density, cdf, E, variance, skewness\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import Uniform, density, cdf, E, variance\n >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify\n \n >>> a = Symbol(\"a\", negative=True)\n@@ -4144,8 +4144,8 @@ def VonMises(name, mu, k):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import VonMises, density, E, variance\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import VonMises, density\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> mu = Symbol(\"mu\")\n >>> k = Symbol(\"k\", positive=True)\n@@ -4297,7 +4297,7 @@ def WignerSemicircle(name, R):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import WignerSemicircle, density, E\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol\n \n >>> R = Symbol(\"R\", positive=True)\n >>> z = Symbol(\"z\")\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/drv_types.py b/sympy/stats/drv_types.py\nindex 399336b015a3..6a30a2fe12b0 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/drv_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/drv_types.py\n@@ -592,7 +592,7 @@ def Skellam(name, mu1, mu2):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import Skellam, density, E, variance\n- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint\n+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint\n \n >>> z = Symbol(\"z\", integer=True)\n >>> mu1 = Symbol(\"mu1\", positive=True)\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py b/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py\nindex 756b97f1c490..2438237c7706 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py\n@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ def JointRV(symbol, pdf, _set=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols, exp, pi, Indexed, S\n+ >>> from sympy import exp, pi, Indexed, S\n >>> from sympy.stats import density\n >>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import JointRV\n \n@@ -518,7 +518,6 @@ def GeneralizedMultivariateLogGamma(syms, delta, v, lamda, mu):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import density\n- >>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv import marginal_distribution\n >>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import GeneralizedMultivariateLogGamma\n >>> from sympy import symbols, S\n >>> v = 1\n@@ -573,7 +572,6 @@ def GeneralizedMultivariateLogGammaOmega(syms, omega, v, lamda, mu):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import density\n- >>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv import marginal_distribution\n >>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import GeneralizedMultivariateLogGammaOmega\n >>> from sympy import Matrix, symbols, S\n >>> omega = Matrix([[1, S.Half, S.Half], [S.Half, 1, S.Half], [S.Half, S.Half, 1]])\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py b/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py\nindex 02717ee24a0b..a04e2f3bc104 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py\n@@ -234,7 +234,7 @@ class CircularUnitaryEnsemble(CircularEnsemble):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import CircularUnitaryEnsemble as CUE, density\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import CircularUnitaryEnsemble as CUE\n >>> from sympy.stats import joint_eigen_distribution\n >>> C = CUE('U', 1)\n >>> joint_eigen_distribution(C)\n@@ -257,7 +257,7 @@ class CircularOrthogonalEnsemble(CircularEnsemble):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import CircularOrthogonalEnsemble as COE, density\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import CircularOrthogonalEnsemble as COE\n >>> from sympy.stats import joint_eigen_distribution\n >>> C = COE('O', 1)\n >>> joint_eigen_distribution(C)\n@@ -280,7 +280,7 @@ class CircularSymplecticEnsemble(CircularEnsemble):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import CircularSymplecticEnsemble as CSE, density\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import CircularSymplecticEnsemble as CSE\n >>> from sympy.stats import joint_eigen_distribution\n >>> C = CSE('S', 1)\n >>> joint_eigen_distribution(C)\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/rv.py b/sympy/stats/rv.py\nindex 378e5fc0aba8..6537c7bd4df5 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/rv.py\n@@ -575,7 +575,6 @@ def pspace(expr):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import pspace, Normal\n- >>> from sympy.stats.rv import IndependentProductPSpace\n >>> X = Normal('X', 0, 1)\n >>> pspace(2*X + 1) == X.pspace\n True\n@@ -1004,7 +1003,7 @@ def where(condition, given_condition=None, **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import where, Die, Normal\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, And\n+ >>> from sympy import And\n \n >>> D1, D2 = Die('a', 6), Die('b', 6)\n >>> a, b = D1.symbol, D2.symbol\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py b/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py\nindex 236f774a9441..d725e6f07ddc 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py\n@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ def variance(X, condition=None, **kwargs):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.stats import Die, E, Bernoulli, variance\n+ >>> from sympy.stats import Die, Bernoulli, variance\n >>> from sympy import simplify, Symbol\n \n >>> X = Die('X', 6)\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\nindex 9380a06b92e0..9cc5ec33f272 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n@@ -744,7 +744,7 @@ class ContinuousMarkovChain(ContinuousTimeStochasticProcess, MarkovProcess):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import ContinuousMarkovChain\n- >>> from sympy import Matrix, S, MatrixSymbol\n+ >>> from sympy import Matrix, S\n >>> G = Matrix([[-S(1), S(1)], [S(1), -S(1)]])\n >>> C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1], gen_mat=G)\n >>> C.limiting_distribution()\n@@ -820,7 +820,7 @@ class BernoulliProcess(DiscreteTimeStochasticProcess):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.stats import BernoulliProcess, P, E\n- >>> from sympy import Eq, Gt, Lt\n+ >>> from sympy import Eq, Gt\n >>> B = BernoulliProcess(\"B\", p=0.7, success=1, failure=0)\n >>> B.state_space\n FiniteSet(0, 1)\ndiff --git a/sympy/tensor/index_methods.py b/sympy/tensor/index_methods.py\nindex 08581cfd9230..372263a689ac 100644\n--- a/sympy/tensor/index_methods.py\n+++ b/sympy/tensor/index_methods.py\n@@ -212,7 +212,7 @@ def get_indices(expr):\n \n >>> from sympy.tensor.index_methods import get_indices\n >>> from sympy import symbols\n- >>> from sympy.tensor import IndexedBase, Idx\n+ >>> from sympy.tensor import IndexedBase\n >>> x, y, A = map(IndexedBase, ['x', 'y', 'A'])\n >>> i, j, a, z = symbols('i j a z', integer=True)\n \n@@ -329,7 +329,7 @@ def get_contraction_structure(expr):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.tensor.index_methods import get_contraction_structure\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, default_sort_key\n+ >>> from sympy import default_sort_key\n >>> from sympy.tensor import IndexedBase, Idx\n >>> x, y, A = map(IndexedBase, ['x', 'y', 'A'])\n >>> i, j, k, l = map(Idx, ['i', 'j', 'k', 'l'])\ndiff --git a/sympy/tensor/indexed.py b/sympy/tensor/indexed.py\nindex a4fde4cb72ea..b8b4da9461e7 100644\n--- a/sympy/tensor/indexed.py\n+++ b/sympy/tensor/indexed.py\n@@ -496,7 +496,7 @@ def shape(self):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import IndexedBase, Idx, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy import IndexedBase, Idx\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y\n >>> IndexedBase('A', shape=(x, y)).shape\n (x, y)\n@@ -601,7 +601,7 @@ class Idx(Expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy import IndexedBase, Idx, symbols, oo\n+ >>> from sympy import Idx, symbols, oo\n >>> n, i, L, U = symbols('n i L U', integer=True)\n \n If a string is given for the label an integer ``Symbol`` is created and the\ndiff --git a/sympy/testing/pytest.py b/sympy/testing/pytest.py\nindex 9843d62ffcbb..174fc590a035 100644\n--- a/sympy/testing/pytest.py\n+++ b/sympy/testing/pytest.py\n@@ -222,8 +222,6 @@ def warns_deprecated_sympy():\n \n >>> from sympy.testing.pytest import warns_deprecated_sympy\n >>> from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning\n- >>> import warnings\n-\n >>> with warns_deprecated_sympy():\n ... SymPyDeprecationWarning(\"Don't use\", feature=\"old thing\",\n ... deprecated_since_version=\"1.0\", issue=123).warn()\ndiff --git a/sympy/unify/usympy.py b/sympy/unify/usympy.py\nindex 668bfabd8bec..71a19248a8ae 100644\n--- a/sympy/unify/usympy.py\n+++ b/sympy/unify/usympy.py\n@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ def unify(x, y, s=None, variables=(), **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.unify.usympy import unify\n- >>> from sympy import Basic, cos\n+ >>> from sympy import Basic\n >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z, p, q\n \n >>> next(unify(Basic(1, 2), Basic(1, x), variables=[x]))\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/_compilation/compilation.py b/sympy/utilities/_compilation/compilation.py\nindex 7a72b786c5bb..df640524cd4f 100644\n--- a/sympy/utilities/_compilation/compilation.py\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/_compilation/compilation.py\n@@ -505,13 +505,6 @@ def compile_link_import_py_ext(sources, extname=None, build_dir='.', compile_kwa\n =======\n \n The imported module from of the python extension.\n-\n- Examples\n- ========\n-\n- >>> mod = compile_link_import_py_ext(['fft.f90', 'conv.cpp', '_fft.pyx']) # doctest: +SKIP\n- >>> Aprim = mod.fft(A) # doctest: +SKIP\n-\n \"\"\"\n if extname is None:\n extname = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(sources[-1]))[0]\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/decorator.py b/sympy/utilities/decorator.py\nindex d6d290452e1b..97152bd08748 100644\n--- a/sympy/utilities/decorator.py\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/decorator.py\n@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ def public(obj):\n \n >>> from sympy.utilities.decorator import public\n \n- >>> __all__\n+ >>> __all__ # noqa: F821\n Traceback (most recent call last):\n ...\n NameError: name '__all__' is not defined\n@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ def public(obj):\n ... def some_function():\n ... pass\n \n- >>> __all__\n+ >>> __all__ # noqa: F821\n ['some_function']\n \n \"\"\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\nindex 2cc512612919..94c6b700b68f 100644\n--- a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\n@@ -2535,12 +2535,12 @@ def kbins(l, k, ordered=None):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.utilities.iterables import kbins\n+ >>> from __future__ import print_function\n \n The default is to give the items in the same order, but grouped\n into k partitions without any reordering:\n \n- >>> from __future__ import print_function\n+ >>> from sympy.utilities.iterables import kbins\n >>> for p in kbins(list(range(5)), 2):\n ... print(p)\n ...\n@@ -2565,9 +2565,9 @@ def kbins(l, k, ordered=None):\n 10 means A == D\n 11 means A == A\n \n- >>> for ordered in [None, 0, 1, 10, 11]:\n- ... print('ordered = %s' % ordered)\n- ... for p in kbins(list(range(3)), 2, ordered=ordered):\n+ >>> for ordered_flag in [None, 0, 1, 10, 11]:\n+ ... print('ordered = %s' % ordered_flag)\n+ ... for p in kbins(list(range(3)), 2, ordered=ordered_flag):\n ... print(' %s' % p)\n ...\n ordered = None\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py b/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py\nindex 583864f8d443..4d24aafb14a4 100644\n--- a/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py\n@@ -351,7 +351,6 @@ def lambdify(args, expr, modules=None, printer=None, use_imps=True,\n functions. This may be preferable to using ``evalf`` (which uses mpmath on\n the backend) in some cases.\n \n- >>> import mpmath\n >>> f = lambdify(x, sin(x), 'mpmath')\n >>> f(1)\n 0.8414709848078965\n@@ -1287,7 +1286,6 @@ def implemented_function(symfunc, implementation):\n \n >>> from sympy.abc import x\n >>> from sympy.utilities.lambdify import lambdify, implemented_function\n- >>> from sympy import Function\n >>> f = implemented_function('f', lambda x: x+1)\n >>> lam_f = lambdify(x, f(x))\n >>> lam_f(4)\ndiff --git a/sympy/vector/functions.py b/sympy/vector/functions.py\nindex e3a08c716b7b..8b75445f002d 100644\n--- a/sympy/vector/functions.py\n+++ b/sympy/vector/functions.py\n@@ -354,7 +354,7 @@ def scalar_potential_difference(field, coord_sys, point1, point2):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D, Point\n+ >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D\n >>> from sympy.vector import scalar_potential_difference\n >>> R = CoordSys3D('R')\n >>> P = R.origin.locate_new('P', R.x*R.i + R.y*R.j + R.z*R.k)\n@@ -483,7 +483,6 @@ def orthogonalize(*vlist, **kwargs):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.vector.coordsysrect import CoordSys3D\n- >>> from sympy.vector.vector import Vector, BaseVector\n >>> from sympy.vector.functions import orthogonalize\n >>> C = CoordSys3D('C')\n >>> i, j, k = C.base_vectors()\ndiff --git a/sympy/vector/point.py b/sympy/vector/point.py\nindex 2a29bdbdea20..bfcd13e88da8 100644\n--- a/sympy/vector/point.py\n+++ b/sympy/vector/point.py\n@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ def position_wrt(self, other):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.vector import Point, CoordSys3D\n+ >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D\n >>> N = CoordSys3D('N')\n >>> p1 = N.origin.locate_new('p1', 10 * N.i)\n >>> N.origin.position_wrt(p1)\n@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ def locate_new(self, name, position):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.vector import Point, CoordSys3D\n+ >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D\n >>> N = CoordSys3D('N')\n >>> p1 = N.origin.locate_new('p1', 10 * N.i)\n >>> p1.position_wrt(N.origin)\n@@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ def express_coordinates(self, coordinate_system):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.vector import Point, CoordSys3D\n+ >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D\n >>> N = CoordSys3D('N')\n >>> p1 = N.origin.locate_new('p1', 10 * N.i)\n >>> p2 = p1.locate_new('p2', 5 * N.j)\ndiff --git a/sympy/vector/vector.py b/sympy/vector/vector.py\nindex 999937b6c3cb..84237b478e2b 100644\n--- a/sympy/vector/vector.py\n+++ b/sympy/vector/vector.py\n@@ -223,7 +223,6 @@ def projection(self, other, scalar=False):\n ========\n \n >>> from sympy.vector.coordsysrect import CoordSys3D\n- >>> from sympy.vector.vector import Vector, BaseVector\n >>> C = CoordSys3D('C')\n >>> i, j, k = C.base_vectors()\n >>> v1 = i + j + k\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -7,6 +7,7 @@ set -x\n \n if [[ \"${TEST_FLAKE8}\" == \"true\" ]]; then\n flake8 sympy;\n+ flake8 --doctests --per-file-ignores='sympy/interactive/session.py:F821' sympy;",
"line": null,
"original_line": 10,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "bin/test_travis.sh",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nDoes this run the normal flake8 checking twice?\n\n@author:\nI'm not sure. It seems so, but I can't find anything in the `flake8` documentation that says whether or not the code is also checked with the `--doctests` flag.\r\n\r\nedit: I found a reference here: https://bugs.launchpad.net/pyflakes/+bug/1223150 so it seems that the normal checking truly is done twice."
}
] |
e30d6003d3a7d4d5f446ad579660554000aa38b9
|
diff --git a/setup.cfg b/setup.cfg
index 894363b62eb4..9fb55ed67489 100644
--- a/setup.cfg
+++ b/setup.cfg
@@ -3,12 +3,14 @@ long_description = file: README.md
long_description_content_type = text/markdown
[flake8]
+doctests = True
ignore = F403
select = F,E722
exclude = sympy/parsing/latex/_antlr/*,
sympy/parsing/autolev/_antlr/*,
sympy/parsing/autolev/test-examples/*,
sympy/integrals/rubi/*
+per-file-ignores = sympy/interactive/session.py:F821
# Global mypy settings:
[mypy]
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/assume.py b/sympy/assumptions/assume.py
index 7efa484c0b9c..92e459320d22 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/assume.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/assume.py
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ class to create your own local assumptions contexts. It is basically a thin
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import AppliedPredicate, Q
+ >>> from sympy import Q
>>> from sympy.assumptions.assume import global_assumptions
>>> global_assumptions
AssumptionsContext()
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py
index 702972eb3091..4bab975a4fbc 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/calculus.py
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ class AskFiniteHandler(CommonHandler):
Examples of usage:
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q
+ >>> from sympy import Q
>>> from sympy.assumptions.handlers.calculus import AskFiniteHandler
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> a = AskFiniteHandler()
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ def Symbol(expr, assumptions):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q
+ >>> from sympy import Q
>>> from sympy.assumptions.handlers.calculus import AskFiniteHandler
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> a = AskFiniteHandler()
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/refine.py b/sympy/assumptions/refine.py
index cfe630a63d65..a50d506a8fe0 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/refine.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/refine.py
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ def refine_abs(expr, assumptions):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q, refine, Abs
+ >>> from sympy import Q, Abs
>>> from sympy.assumptions.refine import refine_abs
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> refine_abs(Abs(x), Q.real(x))
@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ def refine_Pow(expr, assumptions):
"""
Handler for instances of Pow.
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q
+ >>> from sympy import Q
>>> from sympy.assumptions.refine import refine_Pow
>>> from sympy.abc import x,y,z
>>> refine_Pow((-1)**x, Q.real(x))
@@ -190,7 +190,7 @@ def refine_atan2(expr, assumptions):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Q, refine, atan2
+ >>> from sympy import Q, atan2
>>> from sympy.assumptions.refine import refine_atan2
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> refine_atan2(atan2(y,x), Q.real(y) & Q.positive(x))
diff --git a/sympy/calculus/finite_diff.py b/sympy/calculus/finite_diff.py
index f09fca706069..c91589c22a06 100644
--- a/sympy/calculus/finite_diff.py
+++ b/sympy/calculus/finite_diff.py
@@ -441,7 +441,7 @@ def differentiate_finite(expr, *symbols,
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import cos, sin, Function, differentiate_finite
+ >>> from sympy import sin, Function, differentiate_finite
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, h
>>> f, g = Function('f'), Function('g')
>>> differentiate_finite(f(x)*g(x), x, points=[x-h, x+h])
diff --git a/sympy/calculus/util.py b/sympy/calculus/util.py
index dc893b0531c9..50a9be1c8282 100644
--- a/sympy/calculus/util.py
+++ b/sympy/calculus/util.py
@@ -720,7 +720,7 @@ def stationary_points(f, symbol, domain=S.Reals):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, S, sin, log, pi, pprint, stationary_points
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, S, sin, pi, pprint, stationary_points
>>> from sympy.sets import Interval
>>> x = Symbol('x')
diff --git a/sympy/categories/baseclasses.py b/sympy/categories/baseclasses.py
index 98fdbab91372..a29fa82e92eb 100644
--- a/sympy/categories/baseclasses.py
+++ b/sympy/categories/baseclasses.py
@@ -563,7 +563,7 @@ class Diagram(Basic):
========
>>> from sympy.categories import Object, NamedMorphism, Diagram
- >>> from sympy import FiniteSet, pprint, default_sort_key
+ >>> from sympy import pprint, default_sort_key
>>> A = Object("A")
>>> B = Object("B")
>>> C = Object("C")
diff --git a/sympy/codegen/array_utils.py b/sympy/codegen/array_utils.py
index 1fca53698284..bae4a9930295 100644
--- a/sympy/codegen/array_utils.py
+++ b/sympy/codegen/array_utils.py
@@ -299,8 +299,8 @@ def _get_contraction_tuples(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol
- >>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N
+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol
+ >>> from sympy.abc import N
>>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import CodegenArrayContraction, CodegenArrayTensorProduct
>>> A = MatrixSymbol("A", N, N)
>>> B = MatrixSymbol("B", N, N)
@@ -362,8 +362,8 @@ def sort_args_by_name(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol
- >>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N
+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol
+ >>> from sympy.abc import N
>>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import parse_matrix_expression
>>> A = MatrixSymbol("A", N, N)
>>> B = MatrixSymbol("B", N, N)
@@ -402,8 +402,8 @@ def _get_contraction_links(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol
- >>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N
+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol
+ >>> from sympy.abc import N
>>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import parse_matrix_expression
>>> A = MatrixSymbol("A", N, N)
>>> B = MatrixSymbol("B", N, N)
@@ -566,7 +566,6 @@ def nest_permutation(self):
>>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import (CodegenArrayPermuteDims, CodegenArrayTensorProduct, nest_permutation)
>>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> M = MatrixSymbol("M", 3, 3)
>>> N = MatrixSymbol("N", 3, 3)
@@ -1061,7 +1060,6 @@ def parse_indexed_expression(expr, first_indices=None):
>>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import parse_indexed_expression
>>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, Sum, symbols
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> i, j, k, d = symbols("i j k d")
>>> M = MatrixSymbol("M", d, d)
@@ -1250,7 +1248,7 @@ def recognize_matrix_expression(expr):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, Sum
>>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N
>>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import CodegenArrayContraction, CodegenArrayTensorProduct
>>> from sympy.codegen.array_utils import recognize_matrix_expression, parse_indexed_expression, parse_matrix_expression
diff --git a/sympy/codegen/ast.py b/sympy/codegen/ast.py
index b25bf0850bc8..7f2ebc2f4eb0 100644
--- a/sympy/codegen/ast.py
+++ b/sympy/codegen/ast.py
@@ -968,7 +968,6 @@ class Type(Token):
...
ValueError: Casting gives a significantly different value.
>>> boost_mp50 = Type('boost::multiprecision::cpp_dec_float_50')
- >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> from sympy.printing.cxxcode import cxxcode
>>> from sympy.codegen.ast import Declaration, Variable
>>> cxxcode(Declaration(Variable('x', type=boost_mp50)))
@@ -1052,7 +1051,7 @@ def cast_check(self, value, rtol=None, atol=0, limits=None, precision_targets=No
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import Type, integer, float32, int8
+ >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import integer, float32, int8
>>> integer.cast_check(3.0) == 3
True
>>> float32.cast_check(1e-40) # doctest: +ELLIPSIS
@@ -1168,7 +1167,7 @@ class FloatType(FloatBaseType):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, Float
+ >>> from sympy import S
>>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FloatType
>>> half_precision = FloatType('f16', nbits=16, nmant=10, nexp=5)
>>> half_precision.max
@@ -1564,8 +1563,7 @@ class Declaration(Token):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol
- >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import Declaration, Type, Variable, NoneToken, integer, untyped
+ >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import Declaration, NoneToken, untyped
>>> z = Declaration('z')
>>> z.variable.type == untyped
True
diff --git a/sympy/codegen/fnodes.py b/sympy/codegen/fnodes.py
index 5f34e3aef46a..18a08ac7ef5a 100644
--- a/sympy/codegen/fnodes.py
+++ b/sympy/codegen/fnodes.py
@@ -454,7 +454,7 @@ def size(array, dim=None, kind=None):
>>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> from sympy.printing import fcode
- >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FunctionDefinition, real, Return, Variable
+ >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FunctionDefinition, real, Return
>>> from sympy.codegen.fnodes import array, sum_, size
>>> a = Symbol('a', real=True)
>>> body = [Return((sum_(a**2)/size(a))**.5)]
@@ -505,8 +505,8 @@ def bind_C(name=None):
>>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> from sympy.printing import fcode
- >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FunctionDefinition, real, Return, Variable
- >>> from sympy.codegen.fnodes import array, sum_, size, bind_C
+ >>> from sympy.codegen.ast import FunctionDefinition, real, Return
+ >>> from sympy.codegen.fnodes import array, sum_, bind_C
>>> a = Symbol('a', real=True)
>>> s = Symbol('s', integer=True)
>>> arr = array(a, dim=[s], intent='in')
diff --git a/sympy/codegen/rewriting.py b/sympy/codegen/rewriting.py
index 790a3995c4a2..df2cb513bc31 100644
--- a/sympy/codegen/rewriting.py
+++ b/sympy/codegen/rewriting.py
@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ class ReplaceOptim(Optimization):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Pow
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> from sympy.codegen.rewriting import ReplaceOptim
>>> from sympy.codegen.cfunctions import exp2
>>> x = Symbol('x')
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/coset_table.py b/sympy/combinatorics/coset_table.py
index 9e9b2b0f7ecf..e99d3b6af546 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/coset_table.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/coset_table.py
@@ -1171,7 +1171,7 @@ def modified_coset_enumeration_r(fp_grp, Y, max_cosets=None, draft=None,
========
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.free_groups import free_group
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import FpGroup, coset_enumeration_r
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import FpGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.coset_table import modified_coset_enumeration_r
>>> F, x, y = free_group("x, y")
>>> f = FpGroup(F, [x**3, y**3, x**-1*y**-1*x*y])
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/fp_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/fp_groups.py
index 1313c3d3ee6d..379a9b8c9bad 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/fp_groups.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/fp_groups.py
@@ -127,7 +127,7 @@ def subgroup(self, gens, C=None, homomorphism=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import (FpGroup, FpSubgroup)
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import FpGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.free_groups import free_group
>>> F, x, y = free_group("x, y")
>>> f = FpGroup(F, [x**3, y**5, (x*y)**2])
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/free_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/free_groups.py
index 26a3afbef724..6f670a114c74 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/free_groups.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/free_groups.py
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ def vfree_group(symbols):
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.free_groups import vfree_group
>>> vfree_group("x, y, z")
<free group on the generators (x, y, z)>
- >>> x**2*y**-2*z
+ >>> x**2*y**-2*z # noqa: F821
x**2*y**-2*z
>>> type(_)
<class 'sympy.combinatorics.free_groups.FreeGroupElement'>
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/generators.py b/sympy/combinatorics/generators.py
index 02d8b5e2c38c..3104c2fc3afc 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/generators.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/generators.py
@@ -11,7 +11,6 @@ def symmetric(n):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.generators import symmetric
>>> list(symmetric(3))
[(2), (1 2), (2)(0 1), (0 1 2), (0 2 1), (0 2)]
@@ -27,7 +26,6 @@ def cyclic(n):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.generators import cyclic
>>> list(cyclic(5))
[(4), (0 1 2 3 4), (0 2 4 1 3),
@@ -51,7 +49,6 @@ def alternating(n):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.generators import alternating
>>> list(alternating(3))
[(2), (0 1 2), (0 2 1)]
@@ -73,7 +70,6 @@ def dihedral(n):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.generators import dihedral
>>> list(dihedral(3))
[(2), (0 2), (0 1 2), (1 2), (0 2 1), (2)(0 1)]
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/homomorphisms.py b/sympy/combinatorics/homomorphisms.py
index 9612121b85da..9e6610eb6b08 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/homomorphisms.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/homomorphisms.py
@@ -447,7 +447,7 @@ def group_isomorphism(G, H, isomorphism=True):
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.free_groups import free_group
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.fp_groups import FpGroup
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.homomorphisms import homomorphism, group_isomorphism
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.homomorphisms import group_isomorphism
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup, AlternatingGroup
>>> D = DihedralGroup(8)
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/named_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/named_groups.py
index c0c37e40cc0c..dbdb0706d787 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/named_groups.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/named_groups.py
@@ -16,7 +16,6 @@ def AbelianGroup(*cyclic_orders):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import AbelianGroup
>>> AbelianGroup(3, 4)
PermutationGroup([
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py
index 2220c4e8a953..de94ddabb4af 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py
@@ -33,7 +33,6 @@ class PermutationGroup(Basic):
========
>>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Cycle
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.polyhedron import Polyhedron
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
@@ -254,7 +253,6 @@ def __mul__(self, other):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import CyclicGroup
>>> G = CyclicGroup(5)
>>> H = G*G
@@ -912,7 +910,6 @@ def center(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> D = DihedralGroup(4)
>>> G = D.center()
@@ -1464,7 +1461,6 @@ def generate(self, method="coset", af=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.polyhedron import tetrahedron
@@ -1957,7 +1953,6 @@ def is_alt_sym(self, eps=0.05, _random_prec=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> D = DihedralGroup(10)
>>> D.is_alt_sym()
@@ -2101,7 +2096,6 @@ def is_primitive(self, randomized=True):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> D = DihedralGroup(10)
>>> D.is_primitive()
@@ -2516,7 +2510,6 @@ def minimal_block(self, points):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> D = DihedralGroup(10)
>>> D.minimal_block([0, 5])
@@ -2801,8 +2794,6 @@ def orbit_rep(self, alpha, beta, schreier_vector=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import AlternatingGroup
>>> G = AlternatingGroup(5)
>>> G.orbit_rep(0, 4)
@@ -2843,8 +2834,6 @@ def orbit_transversal(self, alpha, pairs=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> G = DihedralGroup(6)
>>> G.orbit_transversal(0)
@@ -3429,7 +3418,6 @@ def schreier_sims_incremental(self, base=None, gens=None, slp_dict=False):
========
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import AlternatingGroup
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import _verify_bsgs
>>> A = AlternatingGroup(7)
>>> base = [2, 3]
@@ -3614,7 +3602,6 @@ def schreier_sims_random(self, base=None, gens=None, consec_succ=10,
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import _verify_bsgs
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup
>>> S = SymmetricGroup(5)
@@ -3769,8 +3756,6 @@ def stabilizer(self, alpha):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> G = DihedralGroup(6)
>>> G.stabilizer(5)
@@ -3872,7 +3857,6 @@ def subgroup_search(self, prop, base=None, strong_gens=None, tests=None,
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import (SymmetricGroup,
... AlternatingGroup)
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import _verify_bsgs
>>> S = SymmetricGroup(7)
>>> prop_even = lambda x: x.is_even
@@ -4598,7 +4582,6 @@ def strong_presentation(G):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> P = DihedralGroup(4)
>>> G = P.strong_presentation()
@@ -4949,7 +4932,7 @@ def _orbits(degree, generators):
========
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup, _orbits
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import _orbits
>>> a = Permutation([0, 2, 1])
>>> b = Permutation([1, 0, 2])
>>> _orbits(a.size, [a, b])
@@ -4991,7 +4974,6 @@ def _orbit_transversal(degree, generators, alpha, pairs, af=False, slp=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import _orbit_transversal
>>> G = DihedralGroup(6)
@@ -5043,7 +5025,6 @@ def _stabilizer(degree, generators, alpha):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import _stabilizer
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> G = DihedralGroup(6)
@@ -5119,7 +5100,7 @@ def order(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, SymmetricPermutationGroup
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics import SymmetricPermutationGroup
>>> G = SymmetricPermutationGroup(4)
>>> G.order()
24
@@ -5138,7 +5119,7 @@ def degree(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, SymmetricPermutationGroup
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics import SymmetricPermutationGroup
>>> G = SymmetricPermutationGroup(4)
>>> G.degree
4
@@ -5154,7 +5135,7 @@ def identity(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, SymmetricPermutationGroup
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics import SymmetricPermutationGroup
>>> G = SymmetricPermutationGroup(4)
>>> G.identity()
(3)
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py b/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py
index de7bfd918993..da19cbf50601 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py
@@ -322,7 +322,6 @@ def __call__(self, *other):
========
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Cycle as C
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation as Perm
>>> C(1, 2)(2, 3)
(1 3 2)
@@ -355,7 +354,6 @@ def list(self, size=None):
========
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Cycle
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
>>> p = Cycle(2, 3)(4, 5)
>>> p.list()
[0, 1, 3, 2, 5, 4]
@@ -1195,7 +1193,7 @@ def rmul(*args):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import _af_rmul, Permutation
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
>>> a, b = [1, 0, 2], [0, 2, 1]
>>> a = Permutation(a); b = Permutation(b)
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/polyhedron.py b/sympy/combinatorics/polyhedron.py
index aadb3e8fde20..78176f11fed4 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/polyhedron.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/polyhedron.py
@@ -425,7 +425,6 @@ def array_form(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, Cycle
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.polyhedron import tetrahedron
>>> tetrahedron = tetrahedron.copy()
>>> tetrahedron.array_form
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/tensor_can.py b/sympy/combinatorics/tensor_can.py
index 75797b3f20cd..937a25fdf47e 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/tensor_can.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/tensor_can.py
@@ -387,7 +387,6 @@ def double_coset_can_rep(dummies, sym, b_S, sgens, S_transversals, g):
========
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import double_coset_can_rep, get_transversals
>>> gens = [Permutation(x) for x in [[2, 1, 0, 3, 4, 5, 7, 6], [4, 1, 2, 3, 0, 5, 7, 6]]]
>>> base = [0, 2]
@@ -913,7 +912,6 @@ def bsgs_direct_product(base1, gens1, base2, gens2, signed=True):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import (get_symmetric_group_sgs, bsgs_direct_product)
>>> base1, gens1 = get_symmetric_group_sgs(1)
>>> base2, gens2 = get_symmetric_group_sgs(2)
@@ -947,7 +945,6 @@ def get_symmetric_group_sgs(n, antisym=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import get_symmetric_group_sgs
>>> get_symmetric_group_sgs(3)
([0, 1], [(4)(0 1), (4)(1 2)])
@@ -1051,7 +1048,6 @@ def tensor_gens(base, gens, list_free_indices, sym=0):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import tensor_gens, get_symmetric_group_sgs
two symmetric tensors with 3 indices without free indices
@@ -1167,7 +1163,6 @@ def gens_products(*v):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import get_symmetric_group_sgs, gens_products
>>> base, gens = get_symmetric_group_sgs(2)
>>> gens_products((base, gens, [[], []], 0))
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/testutil.py b/sympy/combinatorics/testutil.py
index d9d80db949c5..c34c1665824e 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/testutil.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/testutil.py
@@ -215,7 +215,7 @@ def canonicalize_naive(g, dummies, sym, *v):
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import canonicalize_naive
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.tensor_can import get_symmetric_group_sgs
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation, PermutationGroup
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> g = Permutation([1, 3, 2, 0, 4, 5])
>>> base2, gens2 = get_symmetric_group_sgs(2)
>>> canonicalize_naive(g, [2, 3], 0, (base2, gens2, 2, 0))
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/util.py b/sympy/combinatorics/util.py
index 9019f77b3f85..fe7e33c0081a 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/util.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/util.py
@@ -139,7 +139,6 @@ def _distribute_gens_by_base(base, gens):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _distribute_gens_by_base
>>> D = DihedralGroup(3)
@@ -206,7 +205,6 @@ def _handle_precomputed_bsgs(base, strong_gens, transversals=None,
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import DihedralGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _handle_precomputed_bsgs
>>> D = DihedralGroup(3)
@@ -265,16 +263,13 @@ def _orbits_transversals_from_bsgs(base, strong_gens_distr,
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _orbits_transversals_from_bsgs
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import (_orbits_transversals_from_bsgs,
- ... _distribute_gens_by_base)
+ >>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _distribute_gens_by_base
>>> S = SymmetricGroup(3)
>>> S.schreier_sims()
>>> strong_gens_distr = _distribute_gens_by_base(S.base, S.strong_gens)
- >>> _orbits_transversals_from_bsgs(S.base, strong_gens_distr)
- ([[0, 1, 2], [1, 2]], [{0: (2), 1: (0 1 2), 2: (0 2 1)}, {1: (2), 2: (1 2)}])
+ >>> (S.base, strong_gens_distr)
+ ([0, 1], [[(0 1 2), (2)(0 1), (1 2)], [(1 2)]])
See Also
========
@@ -326,7 +321,6 @@ def _remove_gens(base, strong_gens, basic_orbits=None, strong_gens_distr=None):
========
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics.perm_groups import PermutationGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _remove_gens
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.testutil import _verify_bsgs
>>> S = SymmetricGroup(15)
@@ -408,7 +402,6 @@ def _strip(g, base, orbits, transversals):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import _strip
@@ -501,7 +494,6 @@ def _strong_gens_from_distr(strong_gens_distr):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup
>>> from sympy.combinatorics.util import (_strong_gens_from_distr,
... _distribute_gens_by_base)
diff --git a/sympy/concrete/delta.py b/sympy/concrete/delta.py
index a53a9fdad606..7c9f28b5035d 100644
--- a/sympy/concrete/delta.py
+++ b/sympy/concrete/delta.py
@@ -267,7 +267,7 @@ def deltasummation(f, limit, no_piecewise=False):
>>> from sympy.abc import k
>>> i, j = symbols('i, j', integer=True, finite=True)
>>> from sympy.concrete.delta import deltasummation
- >>> from sympy import KroneckerDelta, Piecewise
+ >>> from sympy import KroneckerDelta
>>> deltasummation(KroneckerDelta(i, k), (k, -oo, oo))
1
>>> deltasummation(KroneckerDelta(i, k), (k, 0, oo))
diff --git a/sympy/concrete/gosper.py b/sympy/concrete/gosper.py
index 5b7c3148986e..794a51c5673e 100644
--- a/sympy/concrete/gosper.py
+++ b/sympy/concrete/gosper.py
@@ -173,7 +173,7 @@ def gosper_sum(f, k):
>>> from sympy.concrete.gosper import gosper_sum
>>> from sympy.functions import factorial
- >>> from sympy.abc import i, n, k
+ >>> from sympy.abc import n, k
>>> f = (4*k + 1)*factorial(k)/factorial(2*k + 1)
>>> gosper_sum(f, (k, 0, n))
diff --git a/sympy/concrete/guess.py b/sympy/concrete/guess.py
index b6c2a847c37b..688fe04c4828 100644
--- a/sympy/concrete/guess.py
+++ b/sympy/concrete/guess.py
@@ -248,7 +248,7 @@ def guess_generating_function(v, X=Symbol('x'), types=['all'], maxsqrtn=2):
>>> ggf([fibonacci(k) for k in range(5, 15)], types=['ogf'])
{'ogf': (3*x + 5)/(-x**2 - x + 1)}
- >>> from sympy import simplify, factorial
+ >>> from sympy import factorial
>>> ggf([factorial(k) for k in range(12)], types=['ogf', 'egf', 'lgf'])
{'egf': 1/(1 - x)}
diff --git a/sympy/concrete/products.py b/sympy/concrete/products.py
index b54e7dac0c90..a2c593270c7f 100644
--- a/sympy/concrete/products.py
+++ b/sympy/concrete/products.py
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ class Product(ExprWithIntLimits):
========
>>> from sympy.abc import a, b, i, k, m, n, x
- >>> from sympy import Product, factorial, oo
+ >>> from sympy import Product, oo
>>> Product(k, (k, 1, m))
Product(k, (k, 1, m))
>>> Product(k, (k, 1, m)).doit()
@@ -428,7 +428,7 @@ def is_convergent(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Interval, S, Product, Symbol, cos, pi, exp, oo
+ >>> from sympy import Product, Symbol, cos, pi, exp, oo
>>> n = Symbol('n', integer=True)
>>> Product(n/(n + 1), (n, 1, oo)).is_convergent()
False
@@ -474,7 +474,7 @@ def reverse_order(expr, *indices):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Product, simplify, RisingFactorial, gamma, Sum
+ >>> from sympy import Product, simplify, Sum
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, a, b, c, d
>>> P = Product(x, (x, a, b))
>>> Pr = P.reverse_order(x)
diff --git a/sympy/concrete/summations.py b/sympy/concrete/summations.py
index 27633a7c25e2..b4f1d413501c 100644
--- a/sympy/concrete/summations.py
+++ b/sympy/concrete/summations.py
@@ -628,7 +628,7 @@ def is_absolutely_convergent(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Sum, Symbol, sin, oo
+ >>> from sympy import Sum, Symbol, oo
>>> n = Symbol('n', integer=True)
>>> Sum((-1)**n, (n, 1, oo)).is_absolutely_convergent()
False
diff --git a/sympy/core/basic.py b/sympy/core/basic.py
index 53beba2396f7..8b024abea205 100644
--- a/sympy/core/basic.py
+++ b/sympy/core/basic.py
@@ -554,7 +554,7 @@ def as_dummy(self):
========
>>> from sympy import Integral, Symbol
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> r = Symbol('r', real=True)
>>> Integral(r, (r, x)).as_dummy()
Integral(_0, (_0, x))
@@ -569,7 +569,6 @@ def as_dummy(self):
Any object that has structurally bound variables should have
a property, `bound_symbols` that returns those symbols
appearing in the object.
-
"""
from sympy.core.symbol import Dummy, Symbol
def can(x):
diff --git a/sympy/core/cache.py b/sympy/core/cache.py
index 0bad6fbeefcd..7c5045093749 100644
--- a/sympy/core/cache.py
+++ b/sympy/core/cache.py
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ def __cacheit(maxsize):
... return a+b
>>> @cacheit
- ... def f(a, b):
+ ... def f(a, b): # noqa: F811
... return [a, b] # <-- WRONG, returns mutable object
to force cacheit to check returned results mutability and consistency,
@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ def __cacheit(maxsize):
... return a+b
>>> @cacheit
- ... def f(a, b):
+ ... def f(a, b): # noqa: F811
... return [a, b] # <-- WRONG, returns mutable object
to force cacheit to check returned results mutability and consistency,
diff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py
index beec0ba0b1f6..b5490207ae9c 100644
--- a/sympy/core/expr.py
+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py
@@ -434,7 +434,7 @@ def is_number(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import log, Integral, cos, sin, pi
+ >>> from sympy import Integral, cos, sin, pi
>>> from sympy.core.function import Function
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
@@ -2827,7 +2827,7 @@ def series(self, x=None, x0=0, n=6, dir="+", logx=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import cos, exp, tan, oo, series
+ >>> from sympy import cos, exp, tan
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> cos(x).series()
1 - x**2/2 + x**4/24 + O(x**6)
@@ -3043,7 +3043,7 @@ def aseries(self, x=None, n=6, bound=0, hir=False):
========
>>> from sympy import sin, exp
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> e = sin(1/x + exp(-x)) - sin(1/x)
@@ -3688,7 +3688,7 @@ def round(self, n=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import pi, E, I, S, Add, Mul, Number
+ >>> from sympy import pi, E, I, S, Number
>>> pi.round()
3
>>> pi.round(2)
@@ -3921,7 +3921,7 @@ class UnevaluatedExpr(Expr):
========
>>> from sympy import UnevaluatedExpr
- >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> x*(1/x)
1
>>> x*UnevaluatedExpr(1/x)
diff --git a/sympy/core/exprtools.py b/sympy/core/exprtools.py
index 820006e447a9..7ff6ef54596d 100644
--- a/sympy/core/exprtools.py
+++ b/sympy/core/exprtools.py
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ def _monotonic_sign(self):
========
>>> from sympy.core.exprtools import _monotonic_sign as F
- >>> from sympy import Dummy, S
+ >>> from sympy import Dummy
>>> nn = Dummy(integer=True, nonnegative=True)
>>> p = Dummy(integer=True, positive=True)
>>> p2 = Dummy(integer=True, positive=True)
diff --git a/sympy/core/function.py b/sympy/core/function.py
index d76995116387..c02df2331536 100644
--- a/sympy/core/function.py
+++ b/sympy/core/function.py
@@ -216,7 +216,6 @@ def nargs(self):
========
>>> from sympy.core.function import Function
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> f = Function('f')
If the function can take any number of arguments, the set of whole
@@ -1090,7 +1089,7 @@ class Derivative(Expr):
automatically simplified in a fairly conservative fashion unless the
keyword ``simplify`` is set to False.
- >>> from sympy import cos, sin, sqrt, diff, Function, symbols
+ >>> from sympy import sqrt, diff, Function, symbols
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
>>> f, g = symbols('f,g', cls=Function)
@@ -1524,7 +1523,7 @@ def _sort_variable_count(cls, vc):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Derivative, Function, symbols, cos
+ >>> from sympy import Derivative, Function, symbols
>>> vsort = Derivative._sort_variable_count
>>> x, y, z = symbols('x y z')
>>> f, g, h = symbols('f g h', cls=Function)
diff --git a/sympy/core/numbers.py b/sympy/core/numbers.py
index 9a01dd27e1d8..27b671e148c9 100644
--- a/sympy/core/numbers.py
+++ b/sympy/core/numbers.py
@@ -2583,7 +2583,7 @@ class Zero(IntegerConstant, metaclass=Singleton):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, Integer, zoo
+ >>> from sympy import S, Integer
>>> Integer(0) is S.Zero
True
>>> 1/S.Zero
@@ -3290,7 +3290,7 @@ class ComplexInfinity(AtomicExpr, metaclass=Singleton):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import zoo, oo
+ >>> from sympy import zoo
>>> zoo + 42
zoo
>>> 42/zoo
diff --git a/sympy/core/relational.py b/sympy/core/relational.py
index 33672037e46b..c65577b561b9 100644
--- a/sympy/core/relational.py
+++ b/sympy/core/relational.py
@@ -680,7 +680,7 @@ def as_poly(self, *gens, **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy import Eq
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> Eq(x**2, 1).as_poly(x)
Poly(x**2 - 1, x, domain='ZZ')
'''
diff --git a/sympy/core/singleton.py b/sympy/core/singleton.py
index 4ae3ec3e7131..1f9447021df5 100644
--- a/sympy/core/singleton.py
+++ b/sympy/core/singleton.py
@@ -46,7 +46,8 @@ class SingletonRegistry(Registry):
When using ``is`` comparison, make sure the argument is sympified. For
instance,
- >>> 0 is S.Zero
+ >>> x = 0
+ >>> x is S.Zero
False
This problem is not an issue when using ``==``, which is recommended for
@@ -137,7 +138,6 @@ class is instantiated. Additionally, this instance can be accessed through
>>> from sympy import S, Basic
>>> from sympy.core.singleton import Singleton
- >>> from sympy.core.compatibility import with_metaclass
>>> class MySingleton(Basic, metaclass=Singleton):
... pass
>>> Basic() is Basic()
diff --git a/sympy/core/symbol.py b/sympy/core/symbol.py
index 1839feccc05e..214bf4ffe4a7 100644
--- a/sympy/core/symbol.py
+++ b/sympy/core/symbol.py
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ def _symbol(s, matching_symbol=None, **assumptions):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Dummy
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> from sympy.core.symbol import _symbol
>>> _symbol('y')
y
@@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ def _uniquely_named_symbol(xname, exprs=(), compare=str, modify=None, **assumpti
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.core.symbol import _uniquely_named_symbol as usym, Dummy
+ >>> from sympy.core.symbol import _uniquely_named_symbol as usym
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> usym('x', x)
_x
@@ -720,17 +720,17 @@ def var(names, **args):
>>> var('x')
x
- >>> x
+ >>> x # noqa: F821
x
>>> var('a,ab,abc')
(a, ab, abc)
- >>> abc
+ >>> abc # noqa: F821
abc
>>> var('x,y', real=True)
(x, y)
- >>> x.is_real and y.is_real
+ >>> x.is_real and y.is_real # noqa: F821
True
See :func:`symbols` documentation for more details on what kinds of
diff --git a/sympy/core/sympify.py b/sympy/core/sympify.py
index a75546544696..a3f1ce2851ba 100644
--- a/sympy/core/sympify.py
+++ b/sympy/core/sympify.py
@@ -448,7 +448,7 @@ def kernS(s):
========
>>> from sympy.core.sympify import kernS
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
The 2-arg Mul distributes a number (or minus sign) across the terms
of an expression, but kernS will prevent that:
diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py
index a4d1ed30b8e3..44edd4596808 100644
--- a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py
+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py
@@ -482,8 +482,7 @@ class BaseScalarField(Expr):
Define boilerplate Manifold, Patch and coordinate systems:
>>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, pi, Function
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom import (
- ... Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, Point, BaseScalarField)
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField
>>> r0, theta0 = symbols('r0, theta0')
>>> m = Manifold('M', 2)
>>> p = Patch('P', m)
@@ -574,7 +573,7 @@ class BaseVectorField(Expr):
Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.
- >>> from sympy import symbols, pi, Function
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Function
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_p, R2_r
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import BaseVectorField
>>> from sympy import pprint
@@ -681,7 +680,6 @@ class Commutator(Expr):
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import Commutator
- >>> from sympy import pprint
>>> from sympy.simplify import simplify
Vector fields:
@@ -1204,7 +1202,7 @@ def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeff
Use the predefined R2 manifold:
>>> from sympy.abc import t, x, y
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_p, R2_r
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_p, R2_r
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import intcurve_series
Specify a starting point and a vector field:
diff --git a/sympy/discrete/convolutions.py b/sympy/discrete/convolutions.py
index 9875c185a492..faf1c18b029a 100644
--- a/sympy/discrete/convolutions.py
+++ b/sympy/discrete/convolutions.py
@@ -296,7 +296,7 @@ def convolution_subset(a, b):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import symbols, S, I
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, S
>>> from sympy.discrete.convolutions import convolution_subset
>>> u, v, x, y, z = symbols('u v x y z')
diff --git a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py
index 0078ce06f55b..240d4ddf2874 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py
@@ -396,7 +396,8 @@ class factorial2(CombinatorialFunction):
========
>>> from sympy import factorial2, var
- >>> var('n')
+ >>> n = var('n')
+ >>> n
n
>>> factorial2(n + 1)
factorial2(n + 1)
@@ -649,7 +650,7 @@ class FallingFactorial(CombinatorialFunction):
Factorial Factorization and Symbolic Summation", Journal of
Symbolic Computation, vol. 20, pp. 235-268, 1995.
- >>> from sympy import ff, factorial, rf, gamma, polygamma, binomial, symbols, Poly
+ >>> from sympy import ff, factorial, rf, gamma, binomial, symbols, Poly
>>> from sympy.abc import x, k
>>> n, m = symbols('n m', integer=True)
>>> ff(x, 0)
diff --git a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/numbers.py b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/numbers.py
index bde58ed85a74..2591fa00bf5a 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/numbers.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/numbers.py
@@ -1081,8 +1081,8 @@ class catalan(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import (Symbol, binomial, gamma, hyper, polygamma,
- ... catalan, diff, combsimp, Rational, I)
+ >>> from sympy import (Symbol, binomial, gamma, hyper, catalan,
+ ... diff, combsimp, Rational, I)
>>> [catalan(i) for i in range(1,10)]
[1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862]
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
index 9defa46aa857..7fda45982bc6 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ class re(Function):
========
>>> from sympy import re, im, I, E
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> re(2*E)
2*E
>>> re(2*I + 17)
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py
index 908bd4d712ab..960121c8aa73 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py
@@ -362,7 +362,7 @@ class frac(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, frac, Rational, floor, ceiling, I
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, frac, Rational, floor, I
>>> frac(Rational(4, 3))
1/3
>>> frac(-Rational(4, 3))
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py
index a80432889715..3e958c55f8b1 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/miscellaneous.py
@@ -250,7 +250,7 @@ def root(arg, n, k=0, evaluate=None):
The following examples show the roots of unity for n
equal 2, 3 and 4:
- >>> from sympy import rootof, I
+ >>> from sympy import rootof
>>> [rootof(x**2 - 1, i) for i in range(2)]
[-1, 1]
@@ -329,8 +329,7 @@ def real_root(arg, n=None, evaluate=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import root, real_root, Rational
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, n
+ >>> from sympy import root, real_root
>>> real_root(-8, 3)
-2
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py
index 9b5c1862a063..b7ccb6943ace 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ class Piecewise(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Piecewise, log, ITE, piecewise_fold
+ >>> from sympy import Piecewise, log, piecewise_fold
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> f = x**2
>>> g = log(x)
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/trigonometric.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/trigonometric.py
index ac8fddf94a2a..4a8adc4b1aed 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/trigonometric.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/trigonometric.py
@@ -137,7 +137,7 @@ def _pi_coeff(arg, cycles=1):
>>> from sympy.functions.elementary.trigonometric import _pi_coeff as coeff
>>> from sympy import pi, Dummy
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> coeff(3*x*pi)
3*x
>>> coeff(11*pi/7)
@@ -1879,7 +1879,7 @@ class sinc(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import sinc, oo, jn, Product, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import sinc, oo, jn
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> sinc(x)
sinc(x)
@@ -2057,11 +2057,15 @@ class asin(InverseTrigonometricFunction):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import asin, oo, pi
+ >>> from sympy import asin, oo
>>> asin(1)
pi/2
>>> asin(-1)
-pi/2
+ >>> asin(-oo)
+ oo*I
+ >>> asin(oo)
+ -oo*I
See Also
========
@@ -2227,7 +2231,7 @@ class acos(InverseTrigonometricFunction):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import acos, oo, pi
+ >>> from sympy import acos, oo
>>> acos(1)
0
>>> acos(0)
@@ -2395,7 +2399,7 @@ class atan(InverseTrigonometricFunction):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import atan, oo, pi
+ >>> from sympy import atan, oo
>>> atan(0)
0
>>> atan(1)
@@ -2758,11 +2762,15 @@ class asec(InverseTrigonometricFunction):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import asec, oo, pi
+ >>> from sympy import asec, oo
>>> asec(1)
0
>>> asec(-1)
pi
+ >>> asec(0)
+ zoo
+ >>> asec(-oo)
+ pi/2
See Also
========
@@ -2876,11 +2884,17 @@ class acsc(InverseTrigonometricFunction):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import acsc, oo, pi
+ >>> from sympy import acsc, oo
>>> acsc(1)
pi/2
>>> acsc(-1)
-pi/2
+ >>> acsc(oo)
+ 0
+ >>> acsc(-oo) == acsc(oo)
+ True
+ >>> acsc(0)
+ zoo
See Also
========
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py b/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py
index db8f55d221f4..30bddffbbddc 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/bessel.py
@@ -660,7 +660,6 @@ class jn(SphericalBesselBase):
========
>>> from sympy import Symbol, jn, sin, cos, expand_func, besselj, bessely
- >>> from sympy import simplify
>>> z = Symbol("z")
>>> nu = Symbol("nu", integer=True)
>>> print(expand_func(jn(0, z)))
@@ -1742,7 +1741,7 @@ class marcumq(Function):
========
>>> from sympy import marcumq
- >>> from sympy.abc import m, a, b, x
+ >>> from sympy.abc import m, a, b
>>> marcumq(m, a, b)
marcumq(m, a, b)
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py
index 23229a55ca20..be38c348d443 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/delta_functions.py
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ class DiracDelta(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, diff, pi, Piecewise
+ >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, diff, pi
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> DiracDelta(x)
@@ -160,7 +160,7 @@ class is about to be instantiated and it returns either some simplified
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, S, Subs
+ >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, S
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> DiracDelta(x)
@@ -335,7 +335,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Piecewise(self, *args, **kwargs):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, Piecewise, Symbol, SingularityFunction
+ >>> from sympy import DiracDelta, Piecewise, Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> DiracDelta(x).rewrite(Piecewise)
@@ -549,7 +549,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Piecewise(self, arg, H0=None, **kwargs):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Piecewise, Symbol, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Heaviside, Piecewise, Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> Heaviside(x).rewrite(Piecewise)
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/elliptic_integrals.py b/sympy/functions/special/elliptic_integrals.py
index e1a242a9180a..5e6854521925 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/elliptic_integrals.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/elliptic_integrals.py
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ class elliptic_k(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import elliptic_k, I, pi
+ >>> from sympy import elliptic_k, I
>>> from sympy.abc import m
>>> elliptic_k(0)
pi/2
@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ class elliptic_f(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import elliptic_f, I, O
+ >>> from sympy import elliptic_f, I
>>> from sympy.abc import z, m
>>> elliptic_f(z, m).series(z)
z + z**5*(3*m**2/40 - m/30) + m*z**3/6 + O(z**6)
@@ -217,7 +217,7 @@ class elliptic_e(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import elliptic_e, I, pi, O
+ >>> from sympy import elliptic_e, I
>>> from sympy.abc import z, m
>>> elliptic_e(z, m).series(z)
z + z**5*(-m**2/40 + m/30) - m*z**3/6 + O(z**6)
@@ -338,7 +338,7 @@ class elliptic_pi(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import elliptic_pi, I, pi, O, S
+ >>> from sympy import elliptic_pi, I
>>> from sympy.abc import z, n, m
>>> elliptic_pi(n, z, m).series(z, n=4)
z + z**3*(m/6 + n/3) + O(z**4)
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/error_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/error_functions.py
index 5e8a51ad309f..699d39c53e3e 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/error_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/error_functions.py
@@ -608,7 +608,7 @@ class erf2(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import I, oo, erf2
+ >>> from sympy import oo, erf2
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
Several special values are known:
@@ -748,7 +748,7 @@ class erfinv(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import I, oo, erfinv
+ >>> from sympy import erfinv
>>> from sympy.abc import x
Several special values are known:
@@ -842,7 +842,7 @@ class erfcinv (Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import I, oo, erfcinv
+ >>> from sympy import erfcinv
>>> from sympy.abc import x
Several special values are known:
@@ -918,7 +918,7 @@ class erf2inv(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import I, oo, erf2inv, erfinv, erfcinv
+ >>> from sympy import erf2inv, oo
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
Several special values are known:
@@ -1064,7 +1064,7 @@ class Ei(Function):
The exponential integral is related to many other special functions.
For example:
- >>> from sympy import uppergamma, expint, Shi
+ >>> from sympy import expint, Shi
>>> Ei(x).rewrite(expint)
-expint(1, x*exp_polar(I*pi)) - I*pi
>>> Ei(x).rewrite(Shi)
@@ -1536,7 +1536,7 @@ class Li(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import I, oo, Li
+ >>> from sympy import Li
>>> from sympy.abc import z
The following special value is known:
@@ -2213,7 +2213,7 @@ class fresnels(FresnelIntegral):
Defining the Fresnel functions via an integral:
- >>> from sympy import integrate, pi, sin, gamma, expand_func
+ >>> from sympy import integrate, pi, sin, expand_func
>>> integrate(sin(pi*z**2/2), z)
3*fresnels(z)*gamma(3/4)/(4*gamma(7/4))
>>> expand_func(integrate(sin(pi*z**2/2), z))
@@ -2354,7 +2354,7 @@ class fresnelc(FresnelIntegral):
Defining the Fresnel functions via an integral:
- >>> from sympy import integrate, pi, cos, gamma, expand_func
+ >>> from sympy import integrate, pi, cos, expand_func
>>> integrate(cos(pi*z**2/2), z)
fresnelc(z)*gamma(1/4)/(4*gamma(5/4))
>>> expand_func(integrate(cos(pi*z**2/2), z))
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py b/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py
index 4d92e373519e..d9793fd4a971 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/gamma_functions.py
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ class gamma(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, I, pi, oo, gamma
+ >>> from sympy import S, I, pi, gamma
>>> from sympy.abc import x
Several special values are known:
@@ -868,7 +868,7 @@ class loggamma(Function):
For half-integral values:
- >>> from sympy import S, pi
+ >>> from sympy import S
>>> loggamma(S(5)/2)
log(3*sqrt(pi)/4)
>>> loggamma(n/2)
@@ -1241,7 +1241,7 @@ class multigamma(Function):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, I, pi, oo, gamma, multigamma
+ >>> from sympy import S, multigamma
>>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> p = Symbol('p', positive=True, integer=True)
diff --git a/sympy/functions/special/polynomials.py b/sympy/functions/special/polynomials.py
index 8d202083c8f4..161d84d5be32 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/special/polynomials.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/special/polynomials.py
@@ -441,7 +441,7 @@ class chebyshevt(OrthogonalPolynomial):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import chebyshevt, chebyshevu, diff
+ >>> from sympy import chebyshevt, diff
>>> from sympy.abc import n,x
>>> chebyshevt(0, x)
1
@@ -553,7 +553,7 @@ class chebyshevu(OrthogonalPolynomial):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import chebyshevt, chebyshevu, diff
+ >>> from sympy import chebyshevu, diff
>>> from sympy.abc import n,x
>>> chebyshevu(0, x)
1
@@ -1169,7 +1169,7 @@ class assoc_laguerre(OrthogonalPolynomial):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import laguerre, assoc_laguerre, diff
+ >>> from sympy import assoc_laguerre, diff
>>> from sympy.abc import x, n, a
>>> assoc_laguerre(0, a, x)
1
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/curve.py b/sympy/geometry/curve.py
index c03a58575b2c..6aab8d79be35 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/curve.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/curve.py
@@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ class Curve(GeometrySet):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import sin, cos, Symbol, interpolate
+ >>> from sympy import sin, cos, interpolate
>>> from sympy.abc import t, a
>>> from sympy.geometry import Curve
>>> C = Curve((sin(t), cos(t)), (t, 0, 2))
@@ -257,7 +257,6 @@ def length(self):
========
>>> from sympy.geometry.curve import Curve
- >>> from sympy import cos, sin
>>> from sympy.abc import t
>>> Curve((t, t), (t, 0, 1)).length
sqrt(2)
@@ -290,7 +289,7 @@ def plot_interval(self, parameter='t'):
========
>>> from sympy import Curve, sin
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, t, s
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, s
>>> Curve((x, sin(x)), (x, 1, 2)).plot_interval()
[t, 1, 2]
>>> Curve((x, sin(x)), (x, 1, 2)).plot_interval(s)
@@ -337,7 +336,6 @@ def scale(self, x=1, y=1, pt=None):
========
>>> from sympy.geometry.curve import Curve
- >>> from sympy import pi
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> Curve((x, x), (x, 0, 1)).scale(2)
Curve((2*x, x), (x, 0, 1))
@@ -355,7 +353,6 @@ def translate(self, x=0, y=0):
========
>>> from sympy.geometry.curve import Curve
- >>> from sympy import pi
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> Curve((x, x), (x, 0, 1)).translate(1, 2)
Curve((x + 1, x + 2), (x, 0, 1))
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/ellipse.py b/sympy/geometry/ellipse.py
index 06ec340fb75a..b8bcdbaf793a 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/ellipse.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/ellipse.py
@@ -635,7 +635,7 @@ def intersection(self, o):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Ellipse, Point, Line, sqrt
+ >>> from sympy import Ellipse, Point, Line
>>> e = Ellipse(Point(0, 0), 5, 7)
>>> e.intersection(Point(0, 0))
[]
@@ -879,7 +879,7 @@ def normal_lines(self, p, prec=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Line, Point, Ellipse
+ >>> from sympy import Point, Ellipse
>>> e = Ellipse((0, 0), 2, 3)
>>> c = e.center
>>> e.normal_lines(c + Point(1, 0))
@@ -1016,7 +1016,7 @@ def auxiliary_circle(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Circle, Ellipse, Point, symbols
+ >>> from sympy import Ellipse, Point, symbols
>>> c = Point(1, 2)
>>> Ellipse(c, 8, 7).auxiliary_circle()
Circle(Point2D(1, 2), 8)
@@ -1040,7 +1040,7 @@ def director_circle(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Circle, Ellipse, Point, symbols
+ >>> from sympy import Ellipse, Point, symbols
>>> c = Point(3,8)
>>> Ellipse(c, 7, 9).director_circle()
Circle(Point2D(3, 8), sqrt(130))
@@ -1094,7 +1094,7 @@ def random_point(self, seed=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point, Ellipse, Segment
+ >>> from sympy import Point, Ellipse
>>> e1 = Ellipse(Point(0, 0), 3, 2)
>>> e1.random_point() # gives some random point
Point2D(...)
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/line.py b/sympy/geometry/line.py
index a2773b9a3e15..33805b37e757 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/line.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/line.py
@@ -172,7 +172,7 @@ def angle_between(l1, l2):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point, Line, pi
+ >>> from sympy import Line
>>> e = Line((0, 0), (1, 0))
>>> ne = Line((0, 0), (1, 1))
>>> sw = Line((1, 1), (0, 0))
@@ -224,7 +224,7 @@ def smallest_angle_between(l1, l2):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point, Line, pi
+ >>> from sympy import Point, Line
>>> p1, p2, p3 = Point(0, 0), Point(0, 4), Point(2, -2)
>>> l1, l2 = Line(p1, p2), Line(p1, p3)
>>> l1.smallest_angle_between(l2)
@@ -319,7 +319,7 @@ def are_concurrent(*lines):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point, Line, Line3D
+ >>> from sympy import Point, Line
>>> p1, p2 = Point(0, 0), Point(3, 5)
>>> p3, p4 = Point(-2, -2), Point(0, 2)
>>> l1, l2, l3 = Line(p1, p2), Line(p1, p3), Line(p1, p4)
@@ -1969,7 +1969,6 @@ class Line2D(LinearEntity2D, Line):
========
>>> from sympy import Point
- >>> from sympy.abc import L
>>> from sympy.geometry import Line, Segment
>>> L = Line(Point(2,3), Point(3,5))
>>> L
@@ -2496,7 +2495,7 @@ class Line3D(LinearEntity3D, Line):
========
>>> from sympy import Point3D
- >>> from sympy.geometry import Line3D, Segment3D
+ >>> from sympy.geometry import Line3D
>>> L = Line3D(Point3D(2, 3, 4), Point3D(3, 5, 1))
>>> L
Line3D(Point3D(2, 3, 4), Point3D(3, 5, 1))
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/plane.py b/sympy/geometry/plane.py
index 804698250cff..cd4ee63aa3eb 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/plane.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/plane.py
@@ -40,7 +40,6 @@ class Plane(GeometryEntity):
========
>>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D
- >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 1), Point3D(2, 3, 4), Point3D(2, 2, 2))
Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 1), (-1, 2, -1))
>>> Plane((1, 1, 1), (2, 3, 4), (2, 2, 2))
@@ -267,7 +266,7 @@ def distance(self, o):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point, Point3D, Line, Line3D, Plane
+ >>> from sympy import Point3D, Line3D, Plane
>>> a = Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 1), normal_vector=(1, 1, 1))
>>> b = Point3D(1, 2, 3)
>>> a.distance(b)
@@ -362,7 +361,7 @@ def intersection(self, o):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point, Point3D, Line, Line3D, Plane
+ >>> from sympy import Point3D, Line3D, Plane
>>> a = Plane(Point3D(1, 2, 3), normal_vector=(1, 1, 1))
>>> b = Point3D(1, 2, 3)
>>> a.intersection(b)
@@ -438,7 +437,7 @@ def is_coplanar(self, o):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D
+ >>> from sympy import Plane
>>> o = (0, 0, 0)
>>> p = Plane(o, (1, 1, 1))
>>> p2 = Plane(o, (2, 2, 2))
@@ -621,7 +620,7 @@ def perpendicular_line(self, pt):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D, Line3D
+ >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D
>>> a = Plane(Point3D(1,4,6), normal_vector=(2, 4, 6))
>>> a.perpendicular_line(Point3D(9, 8, 7))
Line3D(Point3D(9, 8, 7), Point3D(11, 12, 13))
@@ -656,7 +655,7 @@ def perpendicular_plane(self, *pts):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D, Line3D
+ >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D
>>> a, b = Point3D(0, 0, 0), Point3D(0, 1, 0)
>>> Z = (0, 0, 1)
>>> p = Plane(a, normal_vector=Z)
@@ -722,7 +721,7 @@ def projection_line(self, line):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Plane, Line, Line3D, Point, Point3D
+ >>> from sympy import Plane, Line, Line3D, Point3D
>>> a = Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 1), normal_vector=(1, 1, 1))
>>> b = Line(Point3D(1, 1), Point3D(2, 2))
>>> a.projection_line(b)
@@ -764,7 +763,7 @@ def projection(self, pt):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point, Point3D
+ >>> from sympy import Plane, Point3D
>>> A = Plane(Point3D(1, 1, 2), normal_vector=(1, 1, 1))
The projection is along the normal vector direction, not the z
@@ -828,7 +827,8 @@ def parameter_value(self, other, u, v=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Plane, Point, pi
+ >>> from sympy import pi
+ >>> from sympy.geometry import Plane
>>> from sympy.abc import t, u, v
>>> p = Plane((2, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 0))
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/point.py b/sympy/geometry/point.py
index 51a5705123ff..a8e79b277792 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/point.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/point.py
@@ -1153,7 +1153,7 @@ def are_collinear(*points):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point3D, Matrix
+ >>> from sympy import Point3D
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> p1, p2 = Point3D(0, 0, 0), Point3D(1, 1, 1)
>>> p3, p4, p5 = Point3D(2, 2, 2), Point3D(x, x, x), Point3D(1, 2, 6)
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/polygon.py b/sympy/geometry/polygon.py
index f3b283a40728..502c0fdbdadb 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/polygon.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/polygon.py
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ class Polygon(GeometrySet):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point, Polygon, pi
+ >>> from sympy import Polygon, pi
>>> p1, p2, p3, p4, p5 = [(0, 0), (1, 0), (5, 1), (0, 1), (3, 0)]
>>> Polygon(p1, p2, p3, p4)
Polygon(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(1, 0), Point2D(5, 1), Point2D(0, 1))
@@ -397,7 +397,7 @@ def second_moment_of_area(self, point=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point, Polygon, symbols
+ >>> from sympy import Polygon, symbols
>>> a, b = symbols('a, b')
>>> p1, p2, p3, p4, p5 = [(0, 0), (a, 0), (a, b), (0, b), (a/3, b/3)]
>>> rectangle = Polygon(p1, p2, p3, p4)
@@ -718,7 +718,6 @@ def encloses_point(self, p):
========
>>> from sympy import Polygon, Point
- >>> from sympy.abc import t
>>> p = Polygon((0, 0), (4, 0), (4, 4))
>>> p.encloses_point(Point(2, 1))
True
@@ -811,7 +810,7 @@ def arbitrary_point(self, parameter='t'):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Polygon, S, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import Polygon, Symbol
>>> t = Symbol('t', real=True)
>>> tri = Polygon((0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1))
>>> p = tri.arbitrary_point('t')
@@ -978,7 +977,7 @@ def cut_section(self, line):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Point, Symbol, Polygon, Line
+ >>> from sympy import Polygon, Line
>>> a, b = 20, 10
>>> p1, p2, p3, p4 = [(0, b), (0, 0), (a, 0), (a, b)]
>>> rectangle = Polygon(p1, p2, p3, p4)
@@ -1919,7 +1918,7 @@ def rotate(self, angle, pt=None):
"""Override GeometryEntity.rotate to first rotate the RegularPolygon
about its center.
- >>> from sympy import Point, RegularPolygon, Polygon, pi
+ >>> from sympy import Point, RegularPolygon, pi
>>> t = RegularPolygon(Point(1, 0), 1, 3)
>>> t.vertices[0] # vertex on x-axis
Point2D(2, 0)
@@ -2625,7 +2624,7 @@ def exradii(self):
The exradius touches the side of the triangle to which it is keyed, e.g.
the exradius touching side 2 is:
- >>> from sympy.geometry import Point, Triangle, Segment2D, Point2D
+ >>> from sympy.geometry import Point, Triangle
>>> p1, p2, p3 = Point(0, 0), Point(6, 0), Point(0, 2)
>>> t = Triangle(p1, p2, p3)
>>> t.exradii[t.sides[2]]
diff --git a/sympy/geometry/util.py b/sympy/geometry/util.py
index 809a78dcc68f..92342457912a 100644
--- a/sympy/geometry/util.py
+++ b/sympy/geometry/util.py
@@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ def closest_points(*args):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.geometry import closest_points, Point2D, Triangle
+ >>> from sympy.geometry import closest_points, Triangle
>>> Triangle(sss=(3, 4, 5)).args
(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(3, 0), Point2D(3, 4))
>>> closest_points(*_)
@@ -374,7 +374,7 @@ def convex_hull(*args, polygon=True):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.geometry import Point, convex_hull
+ >>> from sympy.geometry import convex_hull
>>> points = [(1, 1), (1, 2), (3, 1), (-5, 2), (15, 4)]
>>> convex_hull(*points)
Polygon(Point2D(-5, 2), Point2D(1, 1), Point2D(3, 1), Point2D(15, 4))
@@ -474,7 +474,7 @@ def farthest_points(*args):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.geometry import farthest_points, Point2D, Triangle
+ >>> from sympy.geometry import farthest_points, Triangle
>>> Triangle(sss=(3, 4, 5)).args
(Point2D(0, 0), Point2D(3, 0), Point2D(3, 4))
>>> farthest_points(*_)
diff --git a/sympy/holonomic/holonomic.py b/sympy/holonomic/holonomic.py
index ba804252db94..e00c7064f1ba 100644
--- a/sympy/holonomic/holonomic.py
+++ b/sympy/holonomic/holonomic.py
@@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ class DifferentialOperator:
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import DifferentialOperator, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -397,7 +397,7 @@ class HolonomicFunction:
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ
>>> from sympy import symbols, S
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -714,7 +714,7 @@ def integrate(self, limits, initcond=False):
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -841,7 +841,7 @@ def diff(self, *args, **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -1177,7 +1177,7 @@ def composition(self, expr, *args, **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -1257,7 +1257,7 @@ def to_sequence(self, lb=True):
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ
>>> from sympy import symbols, S
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -1647,7 +1647,7 @@ def series(self, n=6, coefficient=False, order=True, _recur=None):
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -1781,7 +1781,7 @@ def evalf(self, points, method='RK4', h=0.05, derivatives=False):
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import QQ
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(QQ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -1883,7 +1883,7 @@ def to_hyper(self, as_list=False, _recur=None):
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -2056,7 +2056,7 @@ def to_expr(self):
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import HolonomicFunction, DifferentialOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ
>>> from sympy import symbols, S
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> R, Dx = DifferentialOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(x),'Dx')
@@ -2077,7 +2077,7 @@ def change_ics(self, b, lenics=None):
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic import expr_to_holonomic
- >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, exp
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, exp
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> expr_to_holonomic(sin(x)).change_ics(1)
@@ -2148,7 +2148,7 @@ def from_hyper(func, x0=0, evalf=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import from_hyper, DifferentialOperators
+ >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import from_hyper
>>> from sympy import symbols, hyper, S
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> from_hyper(hyper([], [S(3)/2], x**2/4))
@@ -2222,7 +2222,7 @@ def from_meijerg(func, x0=0, evalf=False, initcond=True, domain=QQ):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import from_meijerg, DifferentialOperators
+ >>> from sympy.holonomic.holonomic import from_meijerg
>>> from sympy import symbols, meijerg, S
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> from_meijerg(meijerg(([], []), ([S(1)/2], [0]), x**2/4))
diff --git a/sympy/holonomic/recurrence.py b/sympy/holonomic/recurrence.py
index 368b5ad1abfb..7202898d98c4 100644
--- a/sympy/holonomic/recurrence.py
+++ b/sympy/holonomic/recurrence.py
@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ class RecurrenceOperator:
========
>>> from sympy.holonomic.recurrence import RecurrenceOperator, RecurrenceOperators
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+ >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> n = symbols('n', integer=True)
>>> R, Sn = RecurrenceOperators(ZZ.old_poly_ring(n),'Sn')
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py b/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py
index 1d9b348846e5..66a1d548e307 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/deltafunctions.py
@@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ def deltaintegrate(f, x):
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
>>> from sympy.integrals.deltafunctions import deltaintegrate
- >>> from sympy import sin, cos, DiracDelta, Heaviside
+ >>> from sympy import sin, cos, DiracDelta
>>> deltaintegrate(x*sin(x)*cos(x)*DiracDelta(x - 1), x)
sin(1)*cos(1)*Heaviside(x - 1)
>>> deltaintegrate(y**2*DiracDelta(x - z)*DiracDelta(y - z), y)
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/heurisch.py b/sympy/integrals/heurisch.py
index 676e4019780c..97b2eb9c6c6b 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/heurisch.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/heurisch.py
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ def components(f, x):
minimal, positive exponents.
>>> from sympy import cos, sin
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> from sympy.integrals.heurisch import components
>>> components(sin(x)*cos(x)**2, x)
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/integrals.py b/sympy/integrals/integrals.py
index b079c5c3fbb3..57ee907a1cb1 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/integrals.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/integrals.py
@@ -194,8 +194,8 @@ def transform(self, x, u):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, x, u, y
- >>> from sympy import Integral, S, cos, sqrt
+ >>> from sympy.abc import a, x, u
+ >>> from sympy import Integral, cos, sqrt
>>> i = Integral(x*cos(x**2 - 1), (x, 0, 1))
@@ -376,7 +376,7 @@ def doit(self, **hints):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Integral, Piecewise, S
+ >>> from sympy import Piecewise, S
>>> from sympy.abc import x, t
>>> p = x**2 + Piecewise((0, x/t < 0), (1, True))
>>> p.integrate((t, S(4)/5, 1), (x, -1, 1))
@@ -1333,10 +1333,9 @@ def principal_value(self, **kwargs):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Dummy, symbols, integrate, limit, oo
+ >>> from sympy import oo
>>> from sympy.integrals.integrals import Integral
- >>> from sympy.calculus.singularities import singularities
- >>> x = symbols('x')
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> Integral(x+1, (x, -oo, oo)).principal_value()
oo
>>> f = 1 / (x**3)
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/intpoly.py b/sympy/integrals/intpoly.py
index a1ee0957174a..99c05d1259a4 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/intpoly.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/intpoly.py
@@ -164,7 +164,6 @@ def main_integrate3d(expr, facets, vertices, hp_params, max_degree=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import main_integrate3d, \
hyperplane_parameters
>>> cube = [[(0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 5), (0, 5, 0), (0, 5, 5), (5, 0, 0),\
@@ -326,7 +325,6 @@ def polygon_integrate(facet, hp_param, index, facets, vertices, expr, degree):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import polygon_integrate
>>> cube = [[(0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 5), (0, 5, 0), (0, 5, 5), (5, 0, 0),\
(5, 0, 5), (5, 5, 0), (5, 5, 5)],\
@@ -561,8 +559,8 @@ def integration_reduction_dynamic(facets, index, a, b, expr, degree, dims,
========
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
- >>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import integration_reduction_dynamic,\
- hyperplane_parameters, gradient_terms
+ >>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import (integration_reduction_dynamic, \
+ hyperplane_parameters)
>>> from sympy.geometry.point import Point
>>> from sympy.geometry.polygon import Polygon
>>> triangle = Polygon(Point(0, 3), Point(5, 3), Point(1, 1))
@@ -629,7 +627,6 @@ def left_integral3D(facets, index, expr, vertices, hp_param, degree):
hp_param : The hyperplane parameters of the face
degree : Degree of the expr
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import left_integral3D
>>> cube = [[(0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 5), (0, 5, 0), (0, 5, 5), (5, 0, 0),\
(5, 0, 5), (5, 5, 0), (5, 5, 5)],\
@@ -664,7 +661,6 @@ def gradient_terms(binomial_power=0, no_of_gens=2):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy.integrals.intpoly import gradient_terms
>>> gradient_terms(2)
[[1, 0, 0, 0], [y, 0, 1, 0], [y**2, 0, 2, 0], [x, 1, 0, 0],
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py b/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py
index 6aa5abd999f5..d1d61fb96250 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/manualintegrate.py
@@ -1213,7 +1213,7 @@ def integral_steps(integrand, symbol, **options):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import exp, sin, cos
+ >>> from sympy import exp, sin
>>> from sympy.integrals.manualintegrate import integral_steps
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> print(repr(integral_steps(exp(x) / (1 + exp(2 * x)), x))) \
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py b/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py
index 1f1c1a2a6e08..1871f0743f9c 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/meijerint.py
@@ -381,7 +381,7 @@ def _find_splitting_points(expr, x):
>>> from sympy.integrals.meijerint import _find_splitting_points as fsp
>>> from sympy import sin
- >>> from sympy.abc import a, x
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> fsp(x, x)
{0}
>>> fsp((x-1)**3, x)
@@ -587,7 +587,7 @@ def _condsimp(cond):
added as need arises rather than following any logical pattern.
>>> from sympy.integrals.meijerint import _condsimp as simp
- >>> from sympy import Or, Eq, unbranched_argument as arg, And
+ >>> from sympy import Or, Eq, And
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
>>> simp(Or(x < y, z, Eq(x, y)))
z | (x <= y)
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/quadrature.py b/sympy/integrals/quadrature.py
index 27a845bb0a8c..d8866d02ba26 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/quadrature.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/quadrature.py
@@ -327,7 +327,6 @@ def gauss_chebyshev_t(n, n_digits):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S
>>> from sympy.integrals.quadrature import gauss_chebyshev_t
>>> x, w = gauss_chebyshev_t(3, 5)
>>> x
@@ -394,7 +393,6 @@ def gauss_chebyshev_u(n, n_digits):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S
>>> from sympy.integrals.quadrature import gauss_chebyshev_u
>>> x, w = gauss_chebyshev_u(3, 5)
>>> x
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/rationaltools.py b/sympy/integrals/rationaltools.py
index 9d7d9b48483f..54bda63ccd3d 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/rationaltools.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/rationaltools.py
@@ -320,7 +320,7 @@ def log_to_real(h, q, x, t):
>>> from sympy.integrals.rationaltools import log_to_real
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
- >>> from sympy import Poly, sqrt, S
+ >>> from sympy import Poly, S
>>> log_to_real(Poly(x + 3*y/2 + S(1)/2, x, domain='QQ[y]'),
... Poly(3*y**2 + 1, y, domain='ZZ'), x, y)
2*sqrt(3)*atan(2*sqrt(3)*x/3 + sqrt(3)/3)/3
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/transforms.py b/sympy/integrals/transforms.py
index 0154c44f1d1b..754fd5808f11 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/transforms.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/transforms.py
@@ -1609,7 +1609,7 @@ def inverse_sine_transform(F, k, x, **hints):
:func:`sympy.integrals.transforms.IntegralTransform.doit`.
Note that for this transform, by default ``noconds=True``.
- >>> from sympy import inverse_sine_transform, exp, sqrt, gamma, pi
+ >>> from sympy import inverse_sine_transform, exp, sqrt, gamma
>>> from sympy.abc import x, k, a
>>> inverse_sine_transform(2**((1-2*a)/2)*k**(a - 1)*
... gamma(-a/2 + 1)/gamma((a+1)/2), k, x)
@@ -1716,7 +1716,7 @@ def inverse_cosine_transform(F, k, x, **hints):
:func:`sympy.integrals.transforms.IntegralTransform.doit`.
Note that for this transform, by default ``noconds=True``.
- >>> from sympy import inverse_cosine_transform, exp, sqrt, pi
+ >>> from sympy import inverse_cosine_transform, sqrt, pi
>>> from sympy.abc import x, k, a
>>> inverse_cosine_transform(sqrt(2)*a/(sqrt(pi)*(a**2 + k**2)), k, x)
exp(-a*x)
@@ -1816,7 +1816,7 @@ def hankel_transform(f, r, k, nu, **hints):
Note that for this transform, by default ``noconds=True``.
>>> from sympy import hankel_transform, inverse_hankel_transform
- >>> from sympy import gamma, exp, sinh, cosh
+ >>> from sympy import exp
>>> from sympy.abc import r, k, m, nu, a
>>> ht = hankel_transform(1/r**m, r, k, nu)
@@ -1871,8 +1871,8 @@ def inverse_hankel_transform(F, k, r, nu, **hints):
:func:`sympy.integrals.transforms.IntegralTransform.doit`.
Note that for this transform, by default ``noconds=True``.
- >>> from sympy import hankel_transform, inverse_hankel_transform, gamma
- >>> from sympy import gamma, exp, sinh, cosh
+ >>> from sympy import hankel_transform, inverse_hankel_transform
+ >>> from sympy import exp
>>> from sympy.abc import r, k, m, nu, a
>>> ht = hankel_transform(1/r**m, r, k, nu)
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/trigonometry.py b/sympy/integrals/trigonometry.py
index adcad981c7ac..009a7c4280b4 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/trigonometry.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/trigonometry.py
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ def _pat_sincos(x):
def trigintegrate(f, x, conds='piecewise'):
"""Integrate f = Mul(trig) over x
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, sin, cos, tan, sec, csc, cot
+ >>> from sympy import sin, cos, tan, sec
>>> from sympy.integrals.trigonometry import trigintegrate
>>> from sympy.abc import x
diff --git a/sympy/interactive/session.py b/sympy/interactive/session.py
index a756b42bebd6..af4edb3e3dbc 100644
--- a/sympy/interactive/session.py
+++ b/sympy/interactive/session.py
@@ -95,8 +95,8 @@ def int_to_Integer(s):
========
>>> from __future__ import division
+ >>> from sympy import Integer # noqa: F401
>>> from sympy.interactive.session import int_to_Integer
- >>> from sympy import Integer
>>> s = '1.2 + 1/2 - 0x12 + a1'
>>> int_to_Integer(s)
'1.2 +Integer (1 )/Integer (2 )-Integer (0x12 )+a1 '
diff --git a/sympy/logic/algorithms/dpll.py b/sympy/logic/algorithms/dpll.py
index e43441daac43..61f846186ce2 100644
--- a/sympy/logic/algorithms/dpll.py
+++ b/sympy/logic/algorithms/dpll.py
@@ -181,7 +181,6 @@ def unit_propagate(clauses, symbol):
Arguments are expected to be in CNF.
- >>> from sympy import symbols
>>> from sympy.abc import A, B, D
>>> from sympy.logic.algorithms.dpll import unit_propagate
>>> unit_propagate([A | B, D | ~B, B], B)
@@ -223,7 +222,6 @@ def find_pure_symbol(symbols, unknown_clauses):
Find a symbol and its value if it appears only as a positive literal
(or only as a negative) in clauses.
- >>> from sympy import symbols
>>> from sympy.abc import A, B, D
>>> from sympy.logic.algorithms.dpll import find_pure_symbol
>>> find_pure_symbol([A, B, D], [A|~B,~B|~D,D|A])
@@ -269,7 +267,6 @@ def find_unit_clause(clauses, model):
"""
A unit clause has only 1 variable that is not bound in the model.
- >>> from sympy import symbols
>>> from sympy.abc import A, B, D
>>> from sympy.logic.algorithms.dpll import find_unit_clause
>>> find_unit_clause([A | B | D, B | ~D, A | ~B], {A:True})
diff --git a/sympy/logic/boolalg.py b/sympy/logic/boolalg.py
index 979d61a68f69..60cee03c90eb 100644
--- a/sympy/logic/boolalg.py
+++ b/sympy/logic/boolalg.py
@@ -27,6 +27,8 @@ def as_Boolean(e):
>>> from sympy import true, false, nan
>>> from sympy.logic.boolalg import as_Boolean
>>> from sympy.abc import x
+ >>> as_Boolean(0) is false
+ True
>>> as_Boolean(1) is true
True
>>> as_Boolean(x)
@@ -35,6 +37,10 @@ def as_Boolean(e):
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
TypeError: expecting bool or Boolean, not `2`.
+ >>> as_Boolean(nan)
+ Traceback (most recent call last):
+ ...
+ TypeError: expecting bool or Boolean, not `nan`.
"""
from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol
@@ -651,7 +657,6 @@ class And(LatticeOp, BooleanFunction):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.core import symbols
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy.logic.boolalg import And
>>> x & y
@@ -798,7 +803,6 @@ class Or(LatticeOp, BooleanFunction):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.core import symbols
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy.logic.boolalg import Or
>>> x | y
@@ -1323,7 +1327,7 @@ class Equivalent(BooleanFunction):
========
>>> from sympy.logic.boolalg import Equivalent, And
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> Equivalent(False, False, False)
True
>>> Equivalent(True, False, False)
diff --git a/sympy/logic/inference.py b/sympy/logic/inference.py
index d5aec52eb3ac..e0628f3ec3ab 100644
--- a/sympy/logic/inference.py
+++ b/sympy/logic/inference.py
@@ -144,7 +144,7 @@ def pl_true(expr, model={}, deep=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.abc import A, B, C
+ >>> from sympy.abc import A, B
>>> from sympy.logic.inference import pl_true
>>> pl_true( A & B, {A: True, B: True})
True
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/common.py b/sympy/matrices/common.py
index e0c7701621ed..a21d4f9d6d9e 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/common.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/common.py
@@ -522,7 +522,7 @@ def diagonal(self, k=0):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Matrix, SparseMatrix
+ >>> from sympy import Matrix
>>> m = Matrix(3, 3, lambda i, j: j - i); m
Matrix([
[ 0, 1, 2],
@@ -607,7 +607,7 @@ def todok(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Matrix, SparseMatrix
+ >>> from sympy import Matrix
>>> M = Matrix.eye(3)
>>> M.todok()
{(0, 0): 1, (1, 1): 1, (2, 2): 1}
@@ -1246,6 +1246,12 @@ def atoms(self, *types):
Matrix([[x]])
>>> _.atoms()
{x}
+ >>> Matrix([[x, y], [y, x]])
+ Matrix([
+ [x, y],
+ [y, x]])
+ >>> _.atoms()
+ {x, y}
"""
types = tuple(t if isinstance(t, type) else type(t) for t in types)
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/dense.py b/sympy/matrices/dense.py
index e16ccd9379d3..21d836b99430 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/dense.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/dense.py
@@ -225,7 +225,6 @@ def equals(self, other, failing_expression=False):
>>> from sympy.matrices import Matrix
>>> from sympy.abc import x
- >>> from sympy import cos
>>> A = Matrix([x*(x - 1), 0])
>>> B = Matrix([x**2 - x, 0])
>>> A == B
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/determinant.py b/sympy/matrices/determinant.py
index 647541afef9b..b2cccf0d2ae5 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/determinant.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/determinant.py
@@ -542,10 +542,15 @@ def _det(M, method="bareiss", iszerofunc=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Matrix, MatrixSymbol, eye, det
+ >>> from sympy import Matrix, eye, det
+ >>> I3 = eye(3)
+ >>> det(I3)
+ 1
>>> M = Matrix([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
- >>> M.det()
+ >>> det(M)
-2
+ >>> det(M) == M.det()
+ True
"""
# sanitize `method`
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py
index 22f0ba693250..4e1bb444e01f 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py
@@ -219,7 +219,7 @@ def transpose(self):
========
>>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, BlockMatrix, ZeroMatrix
- >>> from sympy.abc import l, m, n
+ >>> from sympy.abc import m, n
>>> X = MatrixSymbol('X', n, n)
>>> Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', m ,m)
>>> Z = MatrixSymbol('Z', n, m)
@@ -287,7 +287,7 @@ class BlockDiagMatrix(BlockMatrix):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, BlockDiagMatrix, symbols, Identity
+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, BlockDiagMatrix, symbols
>>> n, m, l = symbols('n m l')
>>> X = MatrixSymbol('X', n, n)
>>> Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', m ,m)
@@ -408,7 +408,7 @@ def block_collapse(expr):
"""Evaluates a block matrix expression
>>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, BlockMatrix, symbols, \
- Identity, Matrix, ZeroMatrix, block_collapse
+ Identity, ZeroMatrix, block_collapse
>>> n,m,l = symbols('n m l')
>>> X = MatrixSymbol('X', n, n)
>>> Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', m ,m)
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/funcmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/funcmatrix.py
index 09059d970dbb..5d08fd66cbc6 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/funcmatrix.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/funcmatrix.py
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ class FunctionMatrix(MatrixExpr):
Creating a ``FunctionMatrix`` from ``Lambda``:
- >>> from sympy import FunctionMatrix, symbols, Lambda, MatPow, Matrix
+ >>> from sympy import FunctionMatrix, symbols, Lambda, MatPow
>>> i, j, n, m = symbols('i,j,n,m')
>>> FunctionMatrix(n, m, Lambda((i, j), i + j))
FunctionMatrix(n, m, Lambda((i, j), i + j))
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
index 4b2bb1d4eb19..31f1226cce69 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
@@ -414,7 +414,7 @@ def from_index_summation(expr, first_index=None, last_index=None, dimensions=Non
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatrixExpr, Sum
>>> from sympy.abc import i, j, k, l, N
>>> A = MatrixSymbol("A", N, N)
>>> B = MatrixSymbol("B", N, N)
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
index fc19c1fdc643..af9e09695852 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
@@ -233,7 +233,7 @@ def any_zeros(mul):
def merge_explicit(matmul):
""" Merge explicit MatrixBase arguments
- >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, eye, Matrix, MatMul, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, Matrix, MatMul, pprint
>>> from sympy.matrices.expressions.matmul import merge_explicit
>>> A = MatrixSymbol('A', 2, 2)
>>> B = Matrix([[1, 1], [1, 1]])
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py
index edcfd9ab7ea8..1bfeb44660fa 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py
@@ -15,6 +15,13 @@ class Trace(Expr):
>>> A = MatrixSymbol('A', 3, 3)
>>> Trace(A)
Trace(A)
+ >>> Trace(eye(3))
+ Trace(Matrix([
+ [1, 0, 0],
+ [0, 1, 0],
+ [0, 0, 1]]))
+ >>> Trace(eye(3)).simplify()
+ 3
"""
is_Trace = True
is_commutative = True
@@ -117,7 +124,7 @@ def trace(expr):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import trace, Symbol, MatrixSymbol, pprint, eye
+ >>> from sympy import trace, Symbol, MatrixSymbol, eye
>>> n = Symbol('n')
>>> X = MatrixSymbol('X', n, n) # A square matrix
>>> trace(2*X)
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/matrices.py b/sympy/matrices/matrices.py
index ae6f9e10d9d7..1e97c753d2d1 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/matrices.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/matrices.py
@@ -1517,7 +1517,7 @@ def analytic_func(self, f, x):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, Matrix, exp, S, log
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, Matrix, S, log
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> m = Matrix([[S(5)/4, S(3)/4], [S(3)/4, S(5)/4]])
diff --git a/sympy/multipledispatch/core.py b/sympy/multipledispatch/core.py
index f53d4e1516ee..5bebd2a11c01 100644
--- a/sympy/multipledispatch/core.py
+++ b/sympy/multipledispatch/core.py
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ def dispatch(*types, **kwargs):
... return x + 1
>>> @dispatch(float)
- ... def f(x):
+ ... def f(x): # noqa: F811
... return x - 1
>>> f(3)
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ def dispatch(*types, **kwargs):
... def __init__(self, data):
... self.data = data
... @dispatch(int)
- ... def __init__(self, datum):
+ ... def __init__(self, datum): # noqa: F811
... self.data = [datum]
"""
namespace = kwargs.get('namespace', global_namespace)
diff --git a/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py b/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py
index 239a25937984..9c5f38651183 100644
--- a/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py
+++ b/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ class Dispatcher:
... return x + 1
>>> @dispatch(float)
- ... def f(x):
+ ... def f(x): # noqa: F811
... return x - 1
>>> f(3)
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/continued_fraction.py b/sympy/ntheory/continued_fraction.py
index ba3ed62a1d7c..8ea00d5eaf0e 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/continued_fraction.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/continued_fraction.py
@@ -314,7 +314,7 @@ def continued_fraction_convergents(cf):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.core import Rational, pi
+ >>> from sympy.core import pi
>>> from sympy import S
>>> from sympy.ntheory.continued_fraction import \
continued_fraction_convergents, continued_fraction_iterator
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/digits.py b/sympy/ntheory/digits.py
index 57c652dee1a1..1453dcee53ea 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/digits.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/digits.py
@@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ def count_digits(n, b=10):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.ntheory import count_digits, digits
+ >>> from sympy.ntheory import count_digits
>>> count_digits(1111339)
{1: 4, 3: 2, 9: 1}
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/elliptic_curve.py b/sympy/ntheory/elliptic_curve.py
index f86055379482..3b51952ae0bb 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/elliptic_curve.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/elliptic_curve.py
@@ -241,7 +241,6 @@ def order(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import FF
>>> from sympy.ntheory.elliptic_curve import EllipticCurve
>>> e2 = EllipticCurve(1, 0, modulus=19)
>>> e2.order
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py b/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py
index 9b02fa7bee71..60d4c611f524 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py
@@ -730,7 +730,7 @@ def pollard_pm1(n, B=10, a=2, retries=0, seed=1234):
With the default smoothness bound, this number can't be cracked:
- >>> from sympy.ntheory import pollard_pm1, primefactors
+ >>> from sympy.ntheory import pollard_pm1
>>> pollard_pm1(21477639576571)
Increasing the smoothness bound helps:
@@ -740,7 +740,6 @@ def pollard_pm1(n, B=10, a=2, retries=0, seed=1234):
Looking at the smoothness of the factors of this number we find:
- >>> from sympy.utilities import flatten
>>> from sympy.ntheory.factor_ import smoothness_p, factorint
>>> print(smoothness_p(21477639576571, visual=1))
p**i=4410317**1 has p-1 B=1787, B-pow=1787
@@ -1048,7 +1047,7 @@ def factorint(n, limit=None, use_trial=True, use_rho=True, use_pm1=True,
You can easily switch between the two forms by sending them back to
factorint:
- >>> from sympy import Mul, Pow
+ >>> from sympy import Mul
>>> regular = factorint(1764); regular
{2: 2, 3: 2, 7: 2}
>>> pprint(factorint(regular))
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/generate.py b/sympy/ntheory/generate.py
index 5ecea6c7e0e1..28a943d857c8 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/generate.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/generate.py
@@ -766,7 +766,7 @@ def primorial(n, nth=True):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.ntheory.generate import primorial, randprime, primerange
+ >>> from sympy.ntheory.generate import primorial, primerange
>>> from sympy import factorint, Mul, primefactors, sqrt
>>> primorial(4) # the first 4 primes are 2, 3, 5, 7
210
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/modular.py b/sympy/ntheory/modular.py
index c6f28e12f94b..32d3bf13430b 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/modular.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/modular.py
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ def crt(m, v, symmetric=False, check=True):
As an example consider a set of residues ``U = [49, 76, 65]``
and a set of moduli ``M = [99, 97, 95]``. Then we have::
- >>> from sympy.ntheory.modular import crt, solve_congruence
+ >>> from sympy.ntheory.modular import crt
>>> crt([99, 97, 95], [49, 76, 65])
(639985, 912285)
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py b/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py
index 69ab7f7964e4..ca944ed4a5f3 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/residue_ntheory.py
@@ -975,7 +975,7 @@ def jacobi_symbol(m, n):
========
>>> from sympy.ntheory import jacobi_symbol, legendre_symbol
- >>> from sympy import Mul, S
+ >>> from sympy import S
>>> jacobi_symbol(45, 77)
-1
>>> jacobi_symbol(60, 121)
@@ -1516,7 +1516,6 @@ def polynomial_congruence(expr, m):
========
>>> from sympy.ntheory import polynomial_congruence
- >>> from sympy import Poly
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> expr = x**6 - 2*x**5 -35
>>> polynomial_congruence(expr, 6125)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/continuum_mechanics/beam.py b/sympy/physics/continuum_mechanics/beam.py
index d04496717cac..e2312690d7ab 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/continuum_mechanics/beam.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/continuum_mechanics/beam.py
@@ -754,7 +754,7 @@ def solve_for_reaction_loads(self, *reactions):
being positive.
>>> from sympy.physics.continuum_mechanics.beam import Beam
- >>> from sympy import symbols, linsolve, limit
+ >>> from sympy import symbols
>>> E, I = symbols('E, I')
>>> R1, R2 = symbols('R1, R2')
>>> b = Beam(30, E, I)
@@ -1513,7 +1513,6 @@ def plot_loading_results(self, subs=None):
>>> from sympy.physics.continuum_mechanics.beam import Beam
>>> from sympy import symbols
- >>> from sympy.plotting import PlotGrid
>>> R1, R2 = symbols('R1, R2')
>>> b = Beam(8, 200*(10**9), 400*(10**-6))
>>> b.apply_load(5000, 2, -1)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/hydrogen.py b/sympy/physics/hydrogen.py
index 8ec8e6c2da15..219200c882a9 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/hydrogen.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/hydrogen.py
@@ -21,9 +21,7 @@ def R_nl(n, l, r, Z=1):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.hydrogen import R_nl
- >>> from sympy import var
- >>> var("r Z")
- (r, Z)
+ >>> from sympy.abc import r, Z
>>> R_nl(1, 0, r, Z)
2*sqrt(Z**3)*exp(-Z*r)
>>> R_nl(2, 0, r, Z)
@@ -151,10 +149,8 @@ def E_nl(n, Z=1):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import var
>>> from sympy.physics.hydrogen import E_nl
- >>> var("n Z")
- (n, Z)
+ >>> from sympy.abc import n, Z
>>> E_nl(n, Z)
-Z**2/(2*n**2)
>>> E_nl(1)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/mechanics/lagrange.py b/sympy/physics/mechanics/lagrange.py
index 7f44352ebf46..148884e7fa61 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/mechanics/lagrange.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/mechanics/lagrange.py
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ class LagrangesMethod(object):
>>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import LagrangesMethod, Lagrangian
>>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import ReferenceFrame, Particle, Point
- >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import dynamicsymbols, kinetic_energy
+ >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import dynamicsymbols
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')
>>> qd = dynamicsymbols('q', 1)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/mechanics/rigidbody.py b/sympy/physics/mechanics/rigidbody.py
index 140b64fd9900..b56f9f3b23b2 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/mechanics/rigidbody.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/mechanics/rigidbody.py
@@ -285,7 +285,7 @@ def potential_energy(self, scalar):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import Particle, Point, outer
+ >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import Point, outer
>>> from sympy.physics.mechanics import RigidBody, ReferenceFrame
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> b = ReferenceFrame('b')
diff --git a/sympy/physics/optics/polarization.py b/sympy/physics/optics/polarization.py
index 56ca4d15801d..a0ccd62797ae 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/optics/polarization.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/optics/polarization.py
@@ -307,7 +307,7 @@ def jones_2_stokes(e):
--------
The axes on the Poincaré sphere.
- >>> from sympy import pprint, Matrix, pi
+ >>> from sympy import pprint, pi
>>> from sympy.physics.optics.polarization import jones_vector
>>> from sympy.physics.optics.polarization import jones_2_stokes
>>> H = jones_vector(0, 0)
@@ -557,7 +557,7 @@ def mueller_matrix(J):
--------
Generic optical components.
- >>> from sympy import pprint, symbols, pi, simplify
+ >>> from sympy import pprint, symbols
>>> from sympy.physics.optics.polarization import (mueller_matrix,
... linear_polarizer, half_wave_retarder, quarter_wave_retarder)
>>> theta = symbols("theta", real=True)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/optics/utils.py b/sympy/physics/optics/utils.py
index 02cc3211b5c1..fe644a7f154b 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/optics/utils.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/optics/utils.py
@@ -638,7 +638,6 @@ def hyperfocal_distance(f, N, c):
Example
=======
>>> from sympy.physics.optics import hyperfocal_distance
- >>> from sympy.abc import f, N, c
>>> round(hyperfocal_distance(f = 0.5, N = 8, c = 0.0033), 2)
9.47
"""
diff --git a/sympy/physics/paulialgebra.py b/sympy/physics/paulialgebra.py
index 1b7e68139bd5..a9b19e5c396f 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/paulialgebra.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/paulialgebra.py
@@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ def evaluate_pauli_product(arg):
>>> evaluate_pauli_product(I*Pauli(1)*Pauli(2))
-sigma3
- >>> from sympy.abc import x,y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> evaluate_pauli_product(x**2*Pauli(2)*Pauli(1))
-I*x**2*sigma3
'''
diff --git a/sympy/physics/pring.py b/sympy/physics/pring.py
index fd5a8a546c7f..797f85568846 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/pring.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/pring.py
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ def wavefunction(n, x):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.pring import wavefunction, energy
+ >>> from sympy.physics.pring import wavefunction
>>> from sympy import Symbol, integrate, pi
>>> x=Symbol("x")
>>> wavefunction(1, x)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/qho_1d.py b/sympy/physics/qho_1d.py
index b4ab64d6adbd..6bceb345ee30 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/qho_1d.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/qho_1d.py
@@ -23,9 +23,7 @@ def psi_n(n, x, m, omega):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.qho_1d import psi_n
- >>> from sympy import var
- >>> var("x m omega")
- (x, m, omega)
+ >>> from sympy.abc import m, x, omega
>>> psi_n(0, x, m, omega)
(m*omega)**(1/4)*exp(-m*omega*x**2/(2*hbar))/(hbar**(1/4)*pi**(1/4))
@@ -58,9 +56,7 @@ def E_n(n, omega):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.qho_1d import E_n
- >>> from sympy import var
- >>> var("x omega")
- (x, omega)
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, omega
>>> E_n(x, omega)
hbar*omega*(x + 1/2)
"""
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py
index 5f05a3ec327b..514c9dcf24c9 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/circuitutils.py
@@ -339,7 +339,7 @@ def convert_to_real_indices(seq, qubit_map):
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.circuitutils import convert_to_real_indices
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, Z, H
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, H
>>> i0, i1 = symbols('i:2')
>>> index_map = {i0 : 0, i1 : 1}
>>> convert_to_real_indices(X(i0)*Y(i1)*H(i0)*X(i1), index_map)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/density.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/density.py
index 496d9c3a67b1..d0f2da8b1df8 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/density.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/density.py
@@ -228,10 +228,8 @@ def entropy(density):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.density import Density, entropy
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.represent import represent
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.matrixutils import scipy_sparse_matrix
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.spin import JzKet, Jz
- >>> from sympy import S, log
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.spin import JzKet
+ >>> from sympy import S
>>> up = JzKet(S(1)/2,S(1)/2)
>>> down = JzKet(S(1)/2,-S(1)/2)
>>> d = Density((up,S(1)/2),(down,S(1)/2))
@@ -275,7 +273,7 @@ def fidelity(state1, state2):
>>> from sympy import S, sqrt
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.dagger import Dagger
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.spin import JzKet
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.density import Density, fidelity
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.density import fidelity
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.represent import represent
>>>
>>> up = JzKet(S(1)/2,S(1)/2)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/hilbert.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/hilbert.py
index 7f57ce90180b..b4bc7e1369fe 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/hilbert.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/hilbert.py
@@ -452,7 +452,6 @@ class DirectSumHilbertSpace(HilbertSpace):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.hilbert import ComplexSpace, FockSpace
- >>> from sympy import symbols
>>> c = ComplexSpace(2)
>>> f = FockSpace()
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py
index 83f637b9c87c..268ab3430749 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/identitysearch.py
@@ -725,8 +725,7 @@ def is_reducible(circuit, nqubits, begin, end):
Check if the circuit can be reduced:
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.identitysearch import (
- ... GateIdentity, is_reducible)
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.identitysearch import is_reducible
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, Z
>>> x = X(0); y = Y(0); z = Z(0)
>>> is_reducible((x, y, z), 1, 0, 3)
@@ -780,7 +779,7 @@ def bfs_identity_search(gate_list, nqubits, max_depth=None,
Find a list of gate identities:
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.identitysearch import bfs_identity_search
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, Z, H
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import X, Y, Z
>>> x = X(0); y = Y(0); z = Z(0)
>>> bfs_identity_search([x], 1, max_depth=2)
{GateIdentity(X(0), X(0))}
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/innerproduct.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/innerproduct.py
index 8154416bc4e0..f8a726192eb5 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/innerproduct.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/innerproduct.py
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ class InnerProduct(Expr):
Create an InnerProduct and check its properties:
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Bra, Ket, InnerProduct
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Bra, Ket
>>> b = Bra('b')
>>> k = Ket('k')
>>> ip = b*k
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py
index 1a8db4b3c30f..8b1e339644c3 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/operator.py
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ class Operator(QExpr):
Create an operator and examine its attributes::
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Operator
- >>> from sympy import symbols, I
+ >>> from sympy import I
>>> A = Operator('A')
>>> A
A
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/qubit.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/qubit.py
index 536843aeb71c..1c1d4e2ddb86 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/qubit.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/qubit.py
@@ -446,7 +446,6 @@ def matrix_to_qubit(matrix):
Represent a state and then go back to its qubit form:
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qubit import matrix_to_qubit, Qubit
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import Z
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.represent import represent
>>> q = Qubit('01')
>>> matrix_to_qubit(represent(q))
@@ -556,7 +555,7 @@ def measure_all(qubit, format='sympy', normalize=True):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qubit import Qubit, measure_all
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import H, X, Y, Z
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import H
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qapply import qapply
>>> c = H(0)*H(1)*Qubit('00')
@@ -614,7 +613,7 @@ def measure_partial(qubit, bits, format='sympy', normalize=True):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qubit import Qubit, measure_partial
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import H, X, Y, Z
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.gate import H
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.qapply import qapply
>>> c = H(0)*H(1)*Qubit('00')
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/represent.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/represent.py
index 6ff8be3c867c..3371823c2a6b 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/represent.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/represent.py
@@ -306,7 +306,7 @@ def rep_expectation(expr, **options):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.cartesian import XOp, XKet, PxOp, PxKet
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum.cartesian import XOp, PxOp, PxKet
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.represent import rep_expectation
>>> rep_expectation(XOp())
x_1*DiracDelta(x_1 - x_2)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/state.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/state.py
index 51fc26fce198..0b87cfee5c97 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/state.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/state.py
@@ -354,7 +354,7 @@ class for all physical, time-independent Kets in a system. This class
Create a simple Ket and looking at its properties::
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Ket, Bra
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Ket
>>> from sympy import symbols, I
>>> k = Ket('psi')
>>> k
@@ -418,7 +418,7 @@ class and its subclasses will be the main classes that users will use for
Create a simple Bra and look at its properties::
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Ket, Bra
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import Bra
>>> from sympy import symbols, I
>>> b = Bra('psi')
>>> b
@@ -600,7 +600,6 @@ class TimeDepBra(TimeDepState, BraBase):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum import TimeDepBra
- >>> from sympy import symbols, I
>>> b = TimeDepBra('psi', 't')
>>> b
<psi;t|
@@ -629,7 +628,7 @@ class OrthogonalKet(OrthogonalState, KetBase):
The inner product of two states with different labels will give zero,
states with the same label will give one.
- >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import OrthogonalBra, OrthogonalKet, qapply
+ >>> from sympy.physics.quantum import OrthogonalBra, OrthogonalKet
>>> from sympy.abc import m, n
>>> (OrthogonalBra(n)*OrthogonalKet(n)).doit()
1
@@ -968,7 +967,7 @@ def normalize(self):
========
>>> from sympy import symbols, pi
- >>> from sympy.functions import sqrt, sin
+ >>> from sympy.functions import sin
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.state import Wavefunction
>>> x = symbols('x', real=True)
>>> L = symbols('L', positive=True)
@@ -994,7 +993,7 @@ def prob(self):
========
>>> from sympy import symbols, pi
- >>> from sympy.functions import sqrt, sin
+ >>> from sympy.functions import sin
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum.state import Wavefunction
>>> x, L = symbols('x,L', real=True)
>>> n = symbols('n', integer=True)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/quantum/tensorproduct.py b/sympy/physics/quantum/tensorproduct.py
index 5ebfe9a405cc..6ff0b6a72863 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/quantum/tensorproduct.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/quantum/tensorproduct.py
@@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ class TensorProduct(Expr):
Start with a simple tensor product of sympy matrices::
- >>> from sympy import I, Matrix, symbols
+ >>> from sympy import Matrix
>>> from sympy.physics.quantum import TensorProduct
>>> m1 = Matrix([[1,2],[3,4]])
diff --git a/sympy/physics/secondquant.py b/sympy/physics/secondquant.py
index 3923c9c68b0a..0e22a282422c 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/secondquant.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/secondquant.py
@@ -2771,8 +2771,8 @@ def wicks(e, **kw_args):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import symbols, Function, Dummy
- >>> from sympy.physics.secondquant import wicks, F, Fd, NO
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Dummy
+ >>> from sympy.physics.secondquant import wicks, F, Fd
>>> p, q, r = symbols('p,q,r')
>>> wicks(Fd(p)*F(q))
KroneckerDelta(_i, q)*KroneckerDelta(p, q) + NO(CreateFermion(p)*AnnihilateFermion(q))
diff --git a/sympy/physics/sho.py b/sympy/physics/sho.py
index 2f4c2b2fc953..4a38c5cc4a95 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/sho.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/sho.py
@@ -25,9 +25,7 @@ def R_nl(n, l, nu, r):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.sho import R_nl
- >>> from sympy import var
- >>> var("r nu l")
- (r, nu, l)
+ >>> from sympy.abc import r, nu, l
>>> R_nl(0, 0, 1, r)
2*2**(3/4)*exp(-r**2)/pi**(1/4)
>>> R_nl(1, 0, 1, r)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/units/prefixes.py b/sympy/physics/units/prefixes.py
index a49e9d13199a..c6995d4d0073 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/units/prefixes.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/units/prefixes.py
@@ -126,7 +126,6 @@ def prefix_unit(unit, prefixes):
>>> from sympy.physics.units.prefixes import (PREFIXES,
... prefix_unit)
- >>> from sympy.physics.units.systems import MKS
>>> from sympy.physics.units import m
>>> pref = {"m": PREFIXES["m"], "c": PREFIXES["c"], "d": PREFIXES["d"]}
>>> prefix_unit(m, pref) # doctest: +SKIP
diff --git a/sympy/physics/units/util.py b/sympy/physics/units/util.py
index 3e2ce1a434f5..067893854ad2 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/units/util.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/units/util.py
@@ -76,7 +76,6 @@ def convert_to(expr, target_units, unit_system="SI"):
Conversion to Planck units:
- >>> from sympy.physics.units import gravitational_constant, hbar
>>> convert_to(atomic_mass_constant, [gravitational_constant, speed_of_light, hbar]).n()
7.62963085040767e-20*gravitational_constant**(-0.5)*hbar**0.5*speed_of_light**0.5
diff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py b/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py
index bb9d710b8476..57b78b0c873e 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/frame.py
@@ -341,7 +341,7 @@ def ang_acc_in(self, otherframe):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector
+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame
>>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')
>>> A = ReferenceFrame('A')
>>> V = 10 * N.x
@@ -374,7 +374,7 @@ def ang_vel_in(self, otherframe):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector
+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame
>>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')
>>> A = ReferenceFrame('A')
>>> V = 10 * N.x
@@ -942,7 +942,7 @@ def set_ang_acc(self, otherframe, value):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector
+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame
>>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')
>>> A = ReferenceFrame('A')
>>> V = 10 * N.x
@@ -978,7 +978,7 @@ def set_ang_vel(self, otherframe, value):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector
+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame
>>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')
>>> A = ReferenceFrame('A')
>>> V = 10 * N.x
diff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/point.py b/sympy/physics/vector/point.py
index 2441a6018370..21c86a410b03 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/vector/point.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/point.py
@@ -110,7 +110,7 @@ def a1pt_theory(self, otherpoint, outframe, interframe):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame
- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Vector, dynamicsymbols
+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import dynamicsymbols
>>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')
>>> q2 = dynamicsymbols('q2')
>>> qd = dynamicsymbols('q', 1)
@@ -387,7 +387,7 @@ def v1pt_theory(self, otherpoint, outframe, interframe):
========
>>> from sympy.physics.vector import Point, ReferenceFrame
- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import Vector, dynamicsymbols
+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import dynamicsymbols
>>> q = dynamicsymbols('q')
>>> q2 = dynamicsymbols('q2')
>>> qd = dynamicsymbols('q', 1)
diff --git a/sympy/physics/vector/vector.py b/sympy/physics/vector/vector.py
index 888e91a54c6b..89ff52745a2b 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/vector/vector.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/vector/vector.py
@@ -402,7 +402,7 @@ def __xor__(self, other):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector
+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> q1 = symbols('q1')
>>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')
@@ -595,7 +595,7 @@ def express(self, otherframe, variables=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, Vector, dynamicsymbols
+ >>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame, dynamicsymbols
>>> q1 = dynamicsymbols('q1')
>>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')
>>> A = N.orientnew('A', 'Axis', [q1, N.y])
@@ -625,7 +625,6 @@ def to_matrix(self, reference_frame):
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> from sympy.physics.vector import ReferenceFrame
- >>> from sympy.physics.mechanics.functions import inertia
>>> a, b, c = symbols('a, b, c')
>>> N = ReferenceFrame('N')
>>> vector = a * N.x + b * N.y + c * N.z
diff --git a/sympy/physics/wigner.py b/sympy/physics/wigner.py
index 80a790b91ee1..7e82caaab56c 100644
--- a/sympy/physics/wigner.py
+++ b/sympy/physics/wigner.py
@@ -921,7 +921,6 @@ def wigner_d(J, alpha, beta, gamma):
>>> from sympy.physics.wigner import wigner_d
>>> from sympy import Integer, symbols, pprint
- >>> from sympy.physics.wigner import wigner_d_small
>>> half = 1/Integer(2)
>>> alpha, beta, gamma = symbols("alpha, beta, gamma", real=True)
>>> pprint(wigner_d(half, alpha, beta, gamma), use_unicode=True)
diff --git a/sympy/plotting/experimental_lambdify.py b/sympy/plotting/experimental_lambdify.py
index 74c244c9324b..9b3d940ba99b 100644
--- a/sympy/plotting/experimental_lambdify.py
+++ b/sympy/plotting/experimental_lambdify.py
@@ -545,7 +545,7 @@ def tree2str(cls, tree):
========
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
- >>> from sympy import Integral, sin
+ >>> from sympy import sin
>>> from sympy.plotting.experimental_lambdify import Lambdifier
>>> str2tree = Lambdifier([x], x).str2tree
>>> tree2str = Lambdifier([x], x).tree2str
diff --git a/sympy/plotting/plot.py b/sympy/plotting/plot.py
index ae612e144226..f910b8a267d3 100644
--- a/sympy/plotting/plot.py
+++ b/sympy/plotting/plot.py
@@ -2280,7 +2280,7 @@ def check_arguments(args, expr_len, nb_of_free_symbols):
:format: doctest
:include-source: True
- >>> from sympy import plot, cos, sin, symbols
+ >>> from sympy import cos, sin, symbols
>>> from sympy.plotting.plot import check_arguments
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> check_arguments([cos(x), sin(x)], 2, 1)
diff --git a/sympy/plotting/plot_implicit.py b/sympy/plotting/plot_implicit.py
index 2aa257cda8c7..fa75cd2c6f44 100644
--- a/sympy/plotting/plot_implicit.py
+++ b/sympy/plotting/plot_implicit.py
@@ -262,7 +262,7 @@ def plot_implicit(expr, x_var=None, y_var=None, adaptive=True, depth=0,
:format: doctest
:include-source: True
- >>> from sympy import plot_implicit, cos, sin, symbols, Eq, And
+ >>> from sympy import plot_implicit, symbols, Eq, And
>>> x, y = symbols('x y')
Without any ranges for the symbols in the expression:
diff --git a/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/__init__.py b/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/__init__.py
index 7007a80d647e..cd86a505d8c4 100644
--- a/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/__init__.py
+++ b/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/__init__.py
@@ -13,7 +13,6 @@ def PygletPlot(*args, **kwargs):
See examples/advanced/pyglet_plotting.py for many more examples.
>>> from sympy.plotting.pygletplot import PygletPlot as Plot
- >>> from sympy import symbols
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
>>> Plot(x*y**3-y*x**3)
diff --git a/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/plot.py b/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/plot.py
index c8ce706797ef..7fdb1defdf5f 100644
--- a/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/plot.py
+++ b/sympy/plotting/pygletplot/plot.py
@@ -165,7 +165,6 @@ def __init__(self, *fargs, **win_args):
other words...
>>> from sympy.plotting.pygletplot import PygletPlot as Plot
- >>> from sympy.core import Symbol
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> p = Plot(x**2, visible=False)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/distributedmodules.py b/sympy/polys/distributedmodules.py
index 5093a2aee41e..6a6cfd78fea1 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/distributedmodules.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/distributedmodules.py
@@ -381,7 +381,7 @@ def sdm_to_vector(f, gens, K, n=None):
>>> from sympy.polys.distributedmodules import sdm_to_vector
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
- >>> from sympy.polys import QQ, lex
+ >>> from sympy.polys import QQ
>>> f = [((1, 0, 0, 1), QQ(2)), ((0, 2, 0, 0), QQ(1)), ((0, 0, 2, 0), QQ(1))]
>>> sdm_to_vector(f, [x, y, z], QQ)
[x**2 + y**2, 2*z]
diff --git a/sympy/polys/galoistools.py b/sympy/polys/galoistools.py
index 87c49d109b98..840823930ab5 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/galoistools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/galoistools.py
@@ -29,7 +29,6 @@ def gf_crt(U, M, K=None):
>>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ
>>> from sympy.polys.galoistools import gf_crt
- >>> from sympy.ntheory.modular import solve_congruence
>>> gf_crt([49, 76, 65], [99, 97, 95], ZZ)
639985
@@ -315,7 +314,6 @@ def gf_from_int_poly(f, p):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ
>>> from sympy.polys.galoistools import gf_from_int_poly
>>> gf_from_int_poly([7, -2, 3], 5)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/monomials.py b/sympy/polys/monomials.py
index 844840d121f5..5df7ed0cfc65 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/monomials.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/monomials.py
@@ -82,8 +82,6 @@ def itermonomials(variables, max_degrees, min_degrees=None):
>>> from sympy import symbols
>>> from sympy.polys.monomials import itermonomials
>>> from sympy.polys.orderings import monomial_key
- >>> from itertools import product
- >>> from sympy.core import Mul
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> sorted(itermonomials([x, y], [2, 4], [1, 2]), reverse=True, key=monomial_key('lex', [x, y]))
diff --git a/sympy/polys/orderings.py b/sympy/polys/orderings.py
index 59269461d9f3..464eabf144f4 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/orderings.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/orderings.py
@@ -266,7 +266,7 @@ def build_product_order(arg, gens):
For example, build a product of two grlex orders:
- >>> from sympy.polys.orderings import grlex, build_product_order
+ >>> from sympy.polys.orderings import build_product_order
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z, t
>>> O = build_product_order((("grlex", x, y), ("grlex", z, t)), [x, y, z, t])
diff --git a/sympy/polys/partfrac.py b/sympy/polys/partfrac.py
index 2d75731af8eb..ee5ffdc6403c 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/partfrac.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/partfrac.py
@@ -428,7 +428,7 @@ def assemble_partfrac_list(partial_list):
This example is taken from Bronstein's original paper:
>>> from sympy.polys.partfrac import apart_list, assemble_partfrac_list
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = 36 / (x**5 - 2*x**4 - 2*x**3 + 4*x**2 + x - 2)
>>> pfd = apart_list(f)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/polyroots.py b/sympy/polys/polyroots.py
index d9a9f53249bb..979b27483bee 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/polyroots.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/polyroots.py
@@ -265,7 +265,7 @@ def roots_quartic(f):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Poly, symbols, I
+ >>> from sympy import Poly
>>> from sympy.polys.polyroots import roots_quartic
>>> r = roots_quartic(Poly('x**4-6*x**3+17*x**2-26*x+20'))
diff --git a/sympy/polys/polytools.py b/sympy/polys/polytools.py
index f066202e69f3..a0110db39476 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/polytools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/polytools.py
@@ -4484,7 +4484,7 @@ def total_degree(f, *gens):
Examples
========
>>> from sympy import total_degree, Poly
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> total_degree(1)
0
diff --git a/sympy/polys/rings.py b/sympy/polys/rings.py
index d836fd482e02..4e02e9de0f46 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/rings.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/rings.py
@@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ def vring(symbols, domain, order=lex):
>>> vring("x,y,z", ZZ, lex)
Polynomial ring in x, y, z over ZZ with lex order
- >>> x + y + z
+ >>> x + y + z # noqa:
x + y + z
>>> type(_)
<class 'sympy.polys.rings.PolyElement'>
@@ -141,8 +141,6 @@ def sring(exprs, *symbols, **options):
>>> from sympy.core import symbols
>>> from sympy.polys.rings import sring
- >>> from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ
- >>> from sympy.polys.orderings import lex
>>> x, y, z = symbols("x,y,z")
>>> R, f = sring(x + 2*y + 3*z)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/rootisolation.py b/sympy/polys/rootisolation.py
index fccdac6ced45..3108de55304f 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/rootisolation.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/rootisolation.py
@@ -1796,7 +1796,7 @@ class ComplexInterval(object):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import CRootOf, Rational, S
+ >>> from sympy import CRootOf, S
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> CRootOf.clear_cache() # for doctest reproducibility
>>> root = CRootOf(x**10 - 2*x + 3, 9)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py b/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py
index 3a3eaca75632..8d8a199ff826 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ class _pure_key_dict(object):
Only the following actions are guaranteed:
>>> from sympy.polys.rootoftools import _pure_key_dict
- >>> from sympy import S, PurePoly
+ >>> from sympy import PurePoly
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
1) creation
@@ -907,7 +907,7 @@ def eval_rational(self, dx=None, dy=None, n=15):
ensure the decimal representation of the approximation will be
correct (including rounding) to 6 digits:
- >>> from sympy import S, legendre_poly, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import legendre_poly, Symbol
>>> x = Symbol("x")
>>> p = legendre_poly(4, x, polys=True)
>>> r = p.real_roots()[-1]
diff --git a/sympy/printing/dot.py b/sympy/printing/dot.py
index 5ae80e28ed4a..a08d21f817f6 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/dot.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/dot.py
@@ -33,7 +33,8 @@ def purestr(x, with_args=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Integer, Float, Symbol, MatrixSymbol
+ >>> from sympy import Float, Symbol, MatrixSymbol
+ >>> from sympy import Integer # noqa: F401
>>> from sympy.printing.dot import purestr
Applying ``purestr`` for basic symbolic object:
diff --git a/sympy/printing/julia.py b/sympy/printing/julia.py
index ee3dad2fc1d8..0e01c2986fc4 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/julia.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/julia.py
@@ -547,7 +547,7 @@ def julia_code(expr, assign_to=None, **settings):
>>> julia_code(sin(x).series(x).removeO())
'x.^5/120 - x.^3/6 + x'
- >>> from sympy import Rational, ceiling, Abs
+ >>> from sympy import Rational, ceiling
>>> x, y, tau = symbols("x, y, tau")
>>> julia_code((2*tau)**Rational(7, 2))
'8*sqrt(2)*tau.^(7/2)'
@@ -628,7 +628,7 @@ def julia_code(expr, assign_to=None, **settings):
``contract=False`` will just print the assignment expression that should be
looped over:
- >>> from sympy import Eq, IndexedBase, Idx, ccode
+ >>> from sympy import Eq, IndexedBase, Idx
>>> len_y = 5
>>> y = IndexedBase('y', shape=(len_y,))
>>> t = IndexedBase('t', shape=(len_y,))
diff --git a/sympy/printing/llvmjitcode.py b/sympy/printing/llvmjitcode.py
index 09facc44be0b..b2623744e457 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/llvmjitcode.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/llvmjitcode.py
@@ -429,7 +429,7 @@ def llvm_callable(args, expr, callback_type=None):
The 'cubature' callback handles multiple expressions (set `fdim`
to match in the integration call.)
>>> import sympy.printing.llvmjitcode as jit
- >>> from sympy import cse, exp
+ >>> from sympy import cse
>>> from sympy.abc import x,y
>>> e1 = x*x + y*y
>>> e2 = 4*(x*x + y*y) + 8.0
diff --git a/sympy/printing/octave.py b/sympy/printing/octave.py
index 5d3be42ad1ee..66479e4db5ce 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/octave.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/octave.py
@@ -631,7 +631,7 @@ def octave_code(expr, assign_to=None, **settings):
>>> octave_code(sin(x).series(x).removeO())
'x.^5/120 - x.^3/6 + x'
- >>> from sympy import Rational, ceiling, Abs
+ >>> from sympy import Rational, ceiling
>>> x, y, tau = symbols("x, y, tau")
>>> octave_code((2*tau)**Rational(7, 2))
'8*sqrt(2)*tau.^(7/2)'
@@ -712,7 +712,7 @@ def octave_code(expr, assign_to=None, **settings):
``contract=False`` will just print the assignment expression that should be
looped over:
- >>> from sympy import Eq, IndexedBase, Idx, ccode
+ >>> from sympy import Eq, IndexedBase, Idx
>>> len_y = 5
>>> y = IndexedBase('y', shape=(len_y,))
>>> t = IndexedBase('t', shape=(len_y,))
diff --git a/sympy/series/formal.py b/sympy/series/formal.py
index acbdab6181be..5f31c26ff82c 100644
--- a/sympy/series/formal.py
+++ b/sympy/series/formal.py
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ def rational_algorithm(f, x, k, order=4, full=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import log, atan, I
+ >>> from sympy import log, atan
>>> from sympy.series.formal import rational_algorithm as ra
>>> from sympy.abc import x, k
@@ -1172,7 +1172,7 @@ def product(self, other, x=None, n=6):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp, convolution
+ >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f1 = fps(sin(x))
>>> f2 = fps(exp(x))
@@ -1264,7 +1264,7 @@ def compose(self, other, x=None, n=6):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp, bell
+ >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f1 = fps(exp(x))
>>> f2 = fps(sin(x))
@@ -1337,7 +1337,7 @@ def inverse(self, x=None, n=6):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import fps, exp, cos, bell
+ >>> from sympy import fps, exp, cos
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f1 = fps(exp(x))
>>> f2 = fps(cos(x))
@@ -1531,7 +1531,7 @@ def _eval_terms(self, n):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp, convolution
+ >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f1 = fps(sin(x))
>>> f2 = fps(exp(x))
@@ -1596,7 +1596,7 @@ def _eval_terms(self, n):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp, bell
+ >>> from sympy import fps, sin, exp
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f1 = fps(exp(x))
>>> f2 = fps(sin(x))
@@ -1681,7 +1681,7 @@ def _eval_terms(self, n):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import fps, exp, cos, bell
+ >>> from sympy import fps, exp, cos
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f1 = fps(exp(x))
>>> f2 = fps(cos(x))
@@ -1751,7 +1751,7 @@ def fps(f, x=None, x0=0, dir=1, hyper=True, order=4, rational=True, full=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import fps, O, ln, atan, sin
+ >>> from sympy import fps, ln, atan, sin
>>> from sympy.abc import x, n
Rational Functions
diff --git a/sympy/series/fourier.py b/sympy/series/fourier.py
index ddd5eaf2e286..5030e3ff5c18 100644
--- a/sympy/series/fourier.py
+++ b/sympy/series/fourier.py
@@ -48,7 +48,6 @@ def _process_limits(func, limits):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import pi
>>> from sympy.series.fourier import _process_limits as pari
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> pari(x**2, (x, -2, 2))
@@ -645,9 +644,8 @@ def fourier_series(f, limits=None, finite=True):
Computing the Fourier series of $f(x) = x^2$:
- >>> from sympy import fourier_series, pi, cos
+ >>> from sympy import fourier_series, pi
>>> from sympy.abc import x
-
>>> f = x**2
>>> s = fourier_series(f, (x, -pi, pi))
>>> s1 = s.truncate(n=3)
diff --git a/sympy/series/kauers.py b/sympy/series/kauers.py
index bb0d48e32d87..4d8458e8c334 100644
--- a/sympy/series/kauers.py
+++ b/sympy/series/kauers.py
@@ -11,9 +11,8 @@ def finite_diff(expression, variable, increment=1):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z, k, n
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
>>> from sympy.series.kauers import finite_diff
- >>> from sympy import Sum
>>> finite_diff(x**2, x)
2*x + 1
>>> finite_diff(y**3 + 2*y**2 + 3*y + 4, y)
diff --git a/sympy/series/limits.py b/sympy/series/limits.py
index 01b23ea89866..009ae26fdf28 100644
--- a/sympy/series/limits.py
+++ b/sympy/series/limits.py
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ def limit(e, z, z0, dir="+"):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import limit, sin, Symbol, oo
+ >>> from sympy import limit, sin, oo
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> limit(sin(x)/x, x, 0)
1
@@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ class Limit(Expr):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Limit, sin, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import Limit, sin
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> Limit(sin(x)/x, x, 0)
Limit(sin(x)/x, x, 0)
diff --git a/sympy/series/sequences.py b/sympy/series/sequences.py
index eac7276eae5e..1062f0dbd4a7 100644
--- a/sympy/series/sequences.py
+++ b/sympy/series/sequences.py
@@ -188,7 +188,7 @@ def coeff_mul(self, other):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula
+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula
>>> from sympy.abc import n
>>> SeqFormula(n**2).coeff_mul(2)
SeqFormula(2*n**2, (n, 0, oo))
@@ -208,7 +208,7 @@ def __add__(self, other):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula
+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula
>>> from sympy.abc import n
>>> SeqFormula(n**2) + SeqFormula(n**3)
SeqFormula(n**3 + n**2, (n, 0, oo))
@@ -229,7 +229,7 @@ def __sub__(self, other):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula
+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula
>>> from sympy.abc import n
>>> SeqFormula(n**2) - (SeqFormula(n))
SeqFormula(n**2 - n, (n, 0, oo))
@@ -248,7 +248,7 @@ def __neg__(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula
+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula
>>> from sympy.abc import n
>>> -SeqFormula(n**2)
SeqFormula(-n**2, (n, 0, oo))
@@ -264,7 +264,7 @@ def __mul__(self, other):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, oo, SeqFormula
+ >>> from sympy import SeqFormula
>>> from sympy.abc import n
>>> SeqFormula(n**2) * (SeqFormula(n))
SeqFormula(n**3, (n, 0, oo))
@@ -379,7 +379,7 @@ class EmptySequence(SeqBase, metaclass=Singleton):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import EmptySequence, SeqPer, oo
+ >>> from sympy import EmptySequence, SeqPer
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> EmptySequence
EmptySequence
@@ -917,7 +917,7 @@ def sequence(seq, limits=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import sequence, SeqPer, SeqFormula
+ >>> from sympy import sequence
>>> from sympy.abc import n
>>> sequence(n**2, (n, 0, 5))
SeqFormula(n**2, (n, 0, 5))
diff --git a/sympy/series/series.py b/sympy/series/series.py
index 95ac89b34c79..93bcb61323ff 100644
--- a/sympy/series/series.py
+++ b/sympy/series/series.py
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ def series(expr, x=None, x0=0, n=6, dir="+"):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, series, tan, oo
+ >>> from sympy import series, tan, oo
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = tan(x)
>>> series(f, x, 2, 6, "+")
diff --git a/sympy/sets/fancysets.py b/sympy/sets/fancysets.py
index 0a94d81db36f..bf013522e14a 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/fancysets.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/fancysets.py
@@ -241,7 +241,7 @@ class Reals(Interval, metaclass=Singleton):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, Interval, Rational, pi, I
+ >>> from sympy import S, Rational, pi, I
>>> 5 in S.Reals
True
>>> Rational(-1, 2) in S.Reals
diff --git a/sympy/sets/ordinals.py b/sympy/sets/ordinals.py
index 9326163c104f..3b1eadb28880 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/ordinals.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/ordinals.py
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ class Ordinal(Basic):
Internally, this class is just a list of instances of OmegaPower
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.sets import Ordinal, ord0, OmegaPower
+ >>> from sympy.sets import Ordinal, OmegaPower
>>> from sympy.sets.ordinals import omega
>>> w = omega
>>> w.is_limit_ordinal
diff --git a/sympy/sets/sets.py b/sympy/sets/sets.py
index 1e3c9d292fca..7788e7a9fb65 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/sets.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/sets.py
@@ -479,11 +479,10 @@ def powerset(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import EmptySet, FiniteSet, Interval, PowerSet
+ >>> from sympy import EmptySet, FiniteSet, Interval
A power set of an empty set:
- >>> from sympy import FiniteSet, EmptySet
>>> A = EmptySet
>>> A.powerset()
FiniteSet(EmptySet)
@@ -814,7 +813,7 @@ def is_iterable(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import FiniteSet, Interval, ProductSet
+ >>> from sympy import FiniteSet, Interval
>>> I = Interval(0, 1)
>>> A = FiniteSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
>>> I.is_iterable
@@ -2200,8 +2199,8 @@ def imageset(*args):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import S, Interval, Symbol, imageset, sin, Lambda
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy import S, Interval, imageset, sin, Lambda
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> imageset(x, 2*x, Interval(0, 2))
Interval(0, 4)
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/fu.py b/sympy/simplify/fu.py
index d0e85f759719..d564357c0403 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/fu.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/fu.py
@@ -451,7 +451,6 @@ def TR4(rv):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR4
>>> from sympy import pi
>>> from sympy import cos, sin, tan, cot
>>> for s in (0, pi/6, pi/4, pi/3, pi/2):
@@ -599,7 +598,7 @@ def TR8(rv, first=True):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR8, TR7
+ >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR8
>>> from sympy import cos, sin
>>> TR8(cos(2)*cos(3))
cos(5)/2 + cos(1)/2
@@ -816,8 +815,8 @@ def TR10i(rv):
========
>>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR10i
- >>> from sympy import cos, sin, pi, Add, Mul, sqrt, Symbol
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy import cos, sin, sqrt
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> TR10i(cos(1)*cos(3) + sin(1)*sin(3))
cos(2)
@@ -1088,7 +1087,6 @@ def TR12(rv, first=True):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR12
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy import tan
>>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR12
@@ -1250,7 +1248,7 @@ def TR13(rv):
========
>>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR13
- >>> from sympy import tan, cot, cos
+ >>> from sympy import tan, cot
>>> TR13(tan(3)*tan(2))
-tan(2)/tan(5) - tan(3)/tan(5) + 1
>>> TR13(cot(3)*cot(2))
@@ -1541,7 +1539,7 @@ def TR15(rv, max=4, pow=False):
>>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR15
>>> from sympy.abc import x
- >>> from sympy import cos, sin
+ >>> from sympy import sin
>>> TR15(1 - 1/sin(x)**2)
-cot(x)**2
@@ -1570,7 +1568,7 @@ def TR16(rv, max=4, pow=False):
>>> from sympy.simplify.fu import TR16
>>> from sympy.abc import x
- >>> from sympy import cos, sin
+ >>> from sympy import cos
>>> TR16(1 - 1/cos(x)**2)
-tan(x)**2
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/gammasimp.py b/sympy/simplify/gammasimp.py
index f4659c8aa6d4..b65d03e9d9bc 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/gammasimp.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/gammasimp.py
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ def gammasimp(expr):
========
>>> from sympy.simplify import gammasimp
- >>> from sympy import gamma, factorial, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import gamma, Symbol
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> n = Symbol('n', integer = True)
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/hyperexpand.py b/sympy/simplify/hyperexpand.py
index bb1efc04ab83..b8b1fdd44181 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/hyperexpand.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/hyperexpand.py
@@ -637,7 +637,7 @@ def compute_buckets(self):
>>> from sympy.simplify.hyperexpand import G_Function
>>> from sympy.abc import y
- >>> from sympy import S, symbols
+ >>> from sympy import S
>>> a, b = [1, 3, 2, S(3)/2], [1 + y, y, 2, y + 3]
>>> G_Function(a, b, [2], [y]).compute_buckets()
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/powsimp.py b/sympy/simplify/powsimp.py
index baed0aac8359..280bd9e98fe6 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/powsimp.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/powsimp.py
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ def powsimp(expr, deep=False, combine='all', force=False, measure=count_ops):
Radicals with Mul bases will be combined if combine='exp'
- >>> from sympy import sqrt, Mul
+ >>> from sympy import sqrt
>>> x, y = symbols('x y')
Two radicals are automatically joined through Mul:
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/radsimp.py b/sympy/simplify/radsimp.py
index 945792100876..9d96b18e3d0b 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/radsimp.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/radsimp.py
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ def collect(expr, syms, func=None, evaluate=None, exact=False, distribute_order_
========
>>> from sympy import S, collect, expand, factor, Wild
- >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, x, y, z
+ >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, x, y
This function can collect symbolic coefficients in polynomials or
rational expressions. It will manage to find all integer or rational
@@ -634,7 +634,7 @@ def collect_const(expr, *vars, **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy import sqrt
- >>> from sympy.abc import a, s, x, y, z
+ >>> from sympy.abc import s, x, y, z
>>> from sympy.simplify.radsimp import collect_const
>>> collect_const(sqrt(3) + sqrt(3)*(1 + sqrt(2)))
sqrt(3)*(sqrt(2) + 2)
@@ -757,7 +757,7 @@ def radsimp(expr, symbolic=True, max_terms=4):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import radsimp, sqrt, Symbol, denom, pprint, I
+ >>> from sympy import radsimp, sqrt, Symbol, pprint
>>> from sympy import factor_terms, fraction, signsimp
>>> from sympy.simplify.radsimp import collect_sqrt
>>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/simplify.py b/sympy/simplify/simplify.py
index 828db06ac083..b79aba30f508 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/simplify.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/simplify.py
@@ -787,7 +787,7 @@ def factor_sum(self, limits=None, radical=False, clear=False, fraction=False, si
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Sum, Integral
+ >>> from sympy import Sum
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy.simplify.simplify import factor_sum
>>> s = Sum(x*y, (x, 1, 3))
@@ -1169,8 +1169,8 @@ def kroneckersimp(expr):
The only simplification currently attempted is to identify multiplicative cancellation:
>>> from sympy import KroneckerDelta, kroneckersimp
- >>> from sympy.abc import i, j
- >>> kroneckersimp(1 + KroneckerDelta(0, j) * KroneckerDelta(1, j))
+ >>> from sympy.abc import i
+ >>> kroneckersimp(1 + KroneckerDelta(0, i) * KroneckerDelta(1, i))
1
"""
def args_cancel(args1, args2):
@@ -1346,7 +1346,7 @@ def nthroot(expr, n, max_len=4, prec=15):
========
>>> from sympy.simplify.simplify import nthroot
- >>> from sympy import Rational, sqrt
+ >>> from sympy import sqrt
>>> nthroot(90 + 34*sqrt(7), 3)
sqrt(7) + 3
@@ -1414,7 +1414,7 @@ def nsimplify(expr, constants=(), tolerance=None, full=False, rational=None,
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import nsimplify, sqrt, GoldenRatio, exp, I, exp, pi
+ >>> from sympy import nsimplify, sqrt, GoldenRatio, exp, I, pi
>>> nsimplify(4/(1+sqrt(5)), [GoldenRatio])
-2 + 2*GoldenRatio
>>> nsimplify((1/(exp(3*pi*I/5)+1)))
@@ -1527,7 +1527,6 @@ def _real_to_rational(expr, tolerance=None, rational_conversion='base10'):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Rational
>>> from sympy.simplify.simplify import _real_to_rational
>>> from sympy.abc import x
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/trigsimp.py b/sympy/simplify/trigsimp.py
index 60f795ca57a2..d1a11d60d03c 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/trigsimp.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/trigsimp.py
@@ -444,7 +444,7 @@ def trigsimp(expr, **opts):
========
>>> from sympy import trigsimp, sin, cos, log
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> e = 2*sin(x)**2 + 2*cos(x)**2
>>> trigsimp(e)
2
@@ -638,8 +638,8 @@ def trigsimp_old(expr, **opts):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import trigsimp, sin, cos, log, cosh, sinh, tan, cot
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy import trigsimp, sin, cos, log, cot
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> e = 2*sin(x)**2 + 2*cos(x)**2
>>> trigsimp(e, old=True)
2
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/bivariate.py b/sympy/solvers/bivariate.py
index 19994fd43327..4442c9814e8a 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/bivariate.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/bivariate.py
@@ -59,7 +59,6 @@ def _mostfunc(lhs, func, X=None):
>>> from sympy.solvers.bivariate import _mostfunc
>>> from sympy.functions.elementary.exponential import exp
- >>> from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> _mostfunc(exp(x) + exp(exp(x) + 2), exp)
exp(exp(x) + 2)
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/deutils.py b/sympy/solvers/deutils.py
index 9bdbfad82019..6a45534b9c2a 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/deutils.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/deutils.py
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ def _preprocess(expr, func=None, hint='_Integral'):
function to be solved for.
>>> from sympy.solvers.deutils import _preprocess
- >>> from sympy import Derivative, Function, Integral, sin
+ >>> from sympy import Derivative, Function
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
>>> f, g = map(Function, 'fg')
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py
index c67eabfe927f..4e2c7afdbc45 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py
@@ -867,7 +867,7 @@ def diop_linear(eq, param=symbols("t", integer=True)):
========
>>> from sympy.solvers.diophantine.diophantine import diop_linear
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z, t
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
>>> diop_linear(2*x - 3*y - 5) # solves equation 2*x - 3*y - 5 == 0
(3*t_0 - 5, 2*t_0 - 5)
@@ -2026,7 +2026,6 @@ def transformation_to_DN(eq):
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy.solvers.diophantine.diophantine import transformation_to_DN
- >>> from sympy.solvers.diophantine import classify_diop
>>> A, B = transformation_to_DN(x**2 - 3*x*y - y**2 - 2*y + 1)
>>> A
Matrix([
@@ -3129,7 +3128,7 @@ def diop_general_sum_of_squares(eq, limit=1):
========
>>> from sympy.solvers.diophantine.diophantine import diop_general_sum_of_squares
- >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, e, f
+ >>> from sympy.abc import a, b, c, d, e
>>> diop_general_sum_of_squares(a**2 + b**2 + c**2 + d**2 + e**2 - 2345)
{(15, 22, 22, 24, 24)}
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/inequalities.py b/sympy/solvers/inequalities.py
index 01341ea54b5a..5ce0e102e012 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/inequalities.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/inequalities.py
@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ def reduce_rational_inequalities(exprs, gen, relational=True):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Poly, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> from sympy.solvers.inequalities import reduce_rational_inequalities
>>> x = Symbol('x', real=True)
@@ -374,7 +374,6 @@ def reduce_abs_inequalities(exprs, gen):
========
>>> from sympy import Abs, Symbol
- >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> from sympy.solvers.inequalities import reduce_abs_inequalities
>>> x = Symbol('x', extended_real=True)
@@ -941,7 +940,6 @@ def reduce_inequalities(inequalities, symbols=[]):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import sympify as S, Symbol
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy.solvers.inequalities import reduce_inequalities
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py
index c0d3eb1624ed..4a28f813f4a6 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/ode.py
@@ -1818,9 +1818,8 @@ def classify_sysode(eq, funcs=None, **kwargs):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Function, Eq, symbols, diff, Rational
+ >>> from sympy import Function, Eq, symbols, diff
>>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import classify_sysode
- >>> from sympy.matrices.dense import Matrix
>>> from sympy.abc import t
>>> f, x, y = symbols('f, x, y', cls=Function)
>>> k, l, m, n = symbols('k, l, m, n', Integer=True)
@@ -2537,7 +2536,7 @@ def ode_sol_simplicity(sol, func, trysolving=True):
such as ``min(listofsolutions, key=lambda i: ode_sol_simplicity(i,
f(x)))``.
- >>> from sympy import symbols, Function, Eq, tan, cos, sqrt, Integral
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Function, Eq, tan, Integral
>>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import ode_sol_simplicity
>>> x, C1, C2 = symbols('x, C1, C2')
>>> f = Function('f')
@@ -2838,7 +2837,7 @@ def constant_renumber(expr, variables=None, newconstants=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import symbols, Eq, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import symbols
>>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import constant_renumber
>>> x, C1, C2, C3 = symbols('x,C1:4')
>>> expr = C3 + C2*x + C1*x**2
@@ -3466,7 +3465,7 @@ def ode_2nd_power_series_ordinary(eq, func, order, match):
========
>>> from sympy import dsolve, Function, pprint
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function("f")
>>> eq = f(x).diff(x, 2) + f(x)
>>> pprint(dsolve(eq, hint='2nd_power_series_ordinary'))
@@ -3603,7 +3602,7 @@ def ode_2nd_linear_airy(eq, func, order, match):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import dsolve, Function, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import dsolve, Function
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function("f")
>>> eq = f(x).diff(x, 2) - x*f(x)
@@ -3660,7 +3659,7 @@ def ode_2nd_power_series_regular(eq, func, order, match):
========
>>> from sympy import dsolve, Function, pprint
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function("f")
>>> eq = x*(f(x).diff(x, 2)) + 2*(f(x).diff(x)) + x*f(x)
>>> pprint(dsolve(eq, hint='2nd_power_series_regular'))
@@ -3761,11 +3760,11 @@ def ode_2nd_linear_bessel(eq, func, order, match):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, a
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> v = Symbol('v', positive=True)
- >>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve, checkodesol
- >>> from sympy import pprint, Function
+ >>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve
+ >>> from sympy import Function
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> y = f(x)
>>> genform = x**2*y.diff(x, 2) + x*y.diff(x) + (x**2 - v**2)*y
@@ -4104,7 +4103,7 @@ def ode_nth_linear_euler_eq_homogeneous(eq, func, order, match, returns='sol'):
:py:obj:`~.ComplexRootOf` instance will be returned
instead.
- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq
+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> dsolve(4*x**2*f(x).diff(x, 2) + f(x), f(x),
@@ -4470,8 +4469,8 @@ def ode_linear_coefficients(eq, func, order, match):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Function, Derivative, pprint
- >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve, classify_ode
+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> df = f(x).diff(x)
@@ -4508,7 +4507,7 @@ def ode_separable_reduced(eq, func, order, match):
The general solution is:
- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, pprint
>>> from sympy.abc import x, n
>>> f, g = map(Function, ['f', 'g'])
>>> genform = f(x).diff(x) + (f(x)/x)*g(x**n*f(x))
@@ -4535,8 +4534,8 @@ def ode_separable_reduced(eq, func, order, match):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Function, Derivative, pprint
- >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve, classify_ode
+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> d = f(x).diff(x)
@@ -4591,7 +4590,7 @@ def ode_1st_power_series(eq, func, order, match):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Function, Derivative, pprint, exp
+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint, exp
>>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import dsolve
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
@@ -4672,7 +4671,7 @@ def ode_nth_linear_constant_coeff_homogeneous(eq, func, order, match,
:py:class:`~sympy.polys.rootoftools.ComplexRootOf` instance will be return
instead.
- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq
+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> dsolve(f(x).diff(x, 5) + 10*f(x).diff(x) - 2*f(x), f(x),
@@ -5508,7 +5507,7 @@ def ode_lie_group(eq, func, order, match):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq, exp, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, exp, pprint
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> pprint(dsolve(f(x).diff(x) + 2*x*f(x) - x*exp(-x**2), f(x),
@@ -5621,7 +5620,7 @@ def infinitesimals(eq, func=None, order=None, hint='default', match=None):
The infinitesimals can be found by solving the following PDE:
- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, Eq, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Function, Eq, pprint
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> xi, eta, h = map(Function, ['xi', 'eta', 'h'])
>>> h = h(x, y) # dy/dx = h
@@ -5649,7 +5648,7 @@ def infinitesimals(eq, func=None, order=None, hint='default', match=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Function, diff
+ >>> from sympy import Function
>>> from sympy.solvers.ode.ode import infinitesimals
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
index 3a00e3320cf2..663132dc11ae 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/single.py
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ class SingleODEProblem:
This class is used internally by dsolve. To instantiate an instance
directly first define an ODE problem:
- >>> from sympy import Eq, Function, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import Function, Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> eq = f(x).diff(x, 2)
@@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ class SingleODESolver:
You can use a subclass of SingleODEProblem to solve a particular type of
ODE. We first define a particular ODE problem:
- >>> from sympy import Eq, Function, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import Function, Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> eq = f(x).diff(x, 2)
@@ -466,8 +466,8 @@ class AlmostLinear(SinglePatternODESolver):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Function, Derivative, pprint, sin, cos
- >>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve, classify_ode
+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint, sin, cos
+ >>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> d = f(x).diff(x)
@@ -650,7 +650,7 @@ class Factorable(SingleODESolver):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, Eq, pprint, Derivative
+ >>> from sympy import Function, dsolve, pprint
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> eq = (f(x)**2-4)*(f(x).diff(x)+f(x))
@@ -727,7 +727,7 @@ class RiccatiSpecial(SinglePatternODESolver):
and is valid when neither `a` nor `b` are zero and either `c` or `d` is
zero.
- >>> from sympy.abc import x, y, a, b, c, d
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x, a, b, c, d
>>> from sympy.solvers.ode import dsolve, checkodesol
>>> from sympy import pprint, Function
>>> f = Function('f')
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/pde.py b/sympy/solvers/pde.py
index b0946d881791..834d1109b885 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/pde.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/pde.py
@@ -151,7 +151,7 @@ def pdsolve(eq, func=None, hint='default', dict=False, solvefun=None, **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy.solvers.pde import pdsolve
- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, Eq
+ >>> from sympy import Function, Eq
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> u = f(x, y)
@@ -256,7 +256,7 @@ def classify_pde(eq, func=None, dict=False, **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy.solvers.pde import classify_pde
- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, Eq
+ >>> from sympy import Function, Eq
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> u = f(x, y)
@@ -418,7 +418,7 @@ def checkpdesol(pde, sol, func=None, solve_for_func=True):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Function, symbols, diff
+ >>> from sympy import Function, symbols
>>> from sympy.solvers.pde import checkpdesol, pdsolve
>>> x, y = symbols('x y')
>>> f = Function('f')
@@ -525,10 +525,8 @@ def pde_1st_linear_constant_coeff_homogeneous(eq, func, order, match, solvefun):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.solvers.pde import (
- ... pde_1st_linear_constant_coeff_homogeneous)
>>> from sympy import pdsolve
- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint
>>> from sympy.abc import x,y
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> pdsolve(f(x,y) + f(x,y).diff(x) + f(x,y).diff(y))
@@ -639,7 +637,7 @@ def pde_1st_linear_constant_coeff(eq, func, order, match, solvefun):
========
>>> from sympy.solvers.pde import pdsolve
- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, pprint, exp
+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint, exp
>>> from sympy.abc import x,y
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> eq = -2*f(x,y).diff(x) + 4*f(x,y).diff(y) + 5*f(x,y) - exp(x + 3*y)
@@ -701,7 +699,6 @@ def pde_1st_linear_variable_coeff(eq, func, order, match, solvefun):
which can be solved using ``dsolve``.
- >>> from sympy.solvers.pde import pdsolve
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> from sympy import Function, pprint
>>> a, b, c, G, f= [Function(i) for i in ['a', 'b', 'c', 'G', 'f']]
@@ -719,7 +716,7 @@ def pde_1st_linear_variable_coeff(eq, func, order, match, solvefun):
========
>>> from sympy.solvers.pde import pdsolve
- >>> from sympy import Function, diff, pprint, exp
+ >>> from sympy import Function, pprint
>>> from sympy.abc import x,y
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> eq = x*(u.diff(x)) - y*(u.diff(y)) + y**2*u - y**2
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index b131fb46ae66..914cd8b2c701 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -137,7 +137,6 @@ def denoms(eq, *symbols):
>>> from sympy.solvers.solvers import denoms
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
- >>> from sympy import sqrt
>>> denoms(x/y)
{y}
@@ -2866,7 +2865,6 @@ def nsolve(*args, **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy import Symbol, nsolve
- >>> import sympy
>>> import mpmath
>>> mpmath.mp.dps = 15
>>> x1 = Symbol('x1')
@@ -2910,7 +2908,6 @@ def nsolve(*args, **kwargs):
independently verify the solution.
>>> from sympy import cos, cosh
- >>> from sympy.abc import i
>>> f = cos(x)*cosh(x) - 1
>>> nsolve(f, 3.14*100)
Traceback (most recent call last):
@@ -3283,7 +3280,7 @@ def unrad(eq, *syms, **flags):
>>> from sympy.solvers.solvers import unrad
>>> from sympy.abc import x
- >>> from sympy import sqrt, Rational, root, real_roots, solve
+ >>> from sympy import sqrt, Rational, root
>>> unrad(sqrt(x)*x**Rational(1, 3) + 2)
(x**5 - 64, [])
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
index c07a58e2bfef..1e35500be49c 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solveset.py
@@ -134,7 +134,7 @@ def _invert(f_x, y, x, domain=S.Complexes):
>>> from sympy.solvers.solveset import invert_complex, invert_real
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
- >>> from sympy import exp, log
+ >>> from sympy import exp
When does exp(x) == y?
@@ -1260,7 +1260,7 @@ def _solve_modular(f, symbol, domain):
========
>>> from sympy.solvers.solveset import _solve_modular as solve_modulo
- >>> from sympy import S, Symbol, sin, Intersection, Range, Interval
+ >>> from sympy import S, Symbol, sin, Intersection, Interval
>>> from sympy.core.mod import Mod
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> solve_modulo(Mod(5*x - 8, 7) - 3, x, S.Integers)
@@ -2127,7 +2127,7 @@ def solvify(f, symbol, domain):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.solvers.solveset import solvify, solveset
+ >>> from sympy.solvers.solveset import solvify
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> from sympy import S, tan, sin, exp
>>> solvify(x**2 - 9, x, S.Reals)
@@ -2443,7 +2443,7 @@ def linsolve(system, *symbols):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import Matrix, S, linsolve, symbols
+ >>> from sympy import Matrix, linsolve, symbols
>>> x, y, z = symbols("x, y, z")
>>> A = Matrix([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 10]])
>>> b = Matrix([3, 6, 9])
diff --git a/sympy/stats/crv_types.py b/sympy/stats/crv_types.py
index a3e11443b616..ce46b146c8c2 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/crv_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/crv_types.py
@@ -252,7 +252,7 @@ def Arcsin(name, a=0, b=1):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import Arcsin, density, cdf
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> a = Symbol("a", real=True)
>>> b = Symbol("b", real=True)
@@ -334,7 +334,7 @@ def Benini(name, alpha, beta, sigma):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import Benini, density, cdf
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> alpha = Symbol("alpha", positive=True)
>>> beta = Symbol("beta", positive=True)
@@ -1403,8 +1403,8 @@ def ExponentialPower(name, mu, alpha, beta):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import ExponentialPower, density, E, variance, cdf
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.stats import ExponentialPower, density, cdf
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> z = Symbol("z")
>>> mu = Symbol("mu")
>>> alpha = Symbol("alpha", positive=True)
@@ -1486,7 +1486,7 @@ def FDistribution(name, d1, d2):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import FDistribution, density
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> d1 = Symbol("d1", positive=True)
>>> d2 = Symbol("d2", positive=True)
@@ -1561,7 +1561,7 @@ def FisherZ(name, d1, d2):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import FisherZ, density
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> d1 = Symbol("d1", positive=True)
>>> d2 = Symbol("d2", positive=True)
@@ -1644,8 +1644,8 @@ def Frechet(name, a, s=1, m=0):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import Frechet, density, E, std, cdf
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify
+ >>> from sympy.stats import Frechet, density, cdf
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> a = Symbol("a", positive=True)
>>> s = Symbol("s", positive=True)
@@ -1828,7 +1828,7 @@ def GammaInverse(name, a, b):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import GammaInverse, density, cdf, E, variance
+ >>> from sympy.stats import GammaInverse, density, cdf
>>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> a = Symbol("a", positive=True)
@@ -1933,8 +1933,8 @@ def Gumbel(name, beta, mu, minimum=False):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import Gumbel, density, E, variance, cdf
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.stats import Gumbel, density, cdf
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol("x")
>>> mu = Symbol("mu")
>>> beta = Symbol("beta", positive=True)
@@ -2005,8 +2005,8 @@ def Gompertz(name, b, eta):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import Gompertz, density, E, variance
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.stats import Gompertz, density
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> b = Symbol("b", positive=True)
>>> eta = Symbol("eta", positive=True)
@@ -2075,8 +2075,8 @@ def Kumaraswamy(name, a, b):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import Kumaraswamy, density, E, variance, cdf
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.stats import Kumaraswamy, density, cdf
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> a = Symbol("a", positive=True)
>>> b = Symbol("b", positive=True)
@@ -2251,7 +2251,7 @@ def Levy(name, mu, c):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import Levy, density, cdf
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> mu = Symbol("mu", real=True)
>>> c = Symbol("c", positive=True)
@@ -2498,7 +2498,7 @@ def LogNormal(name, mean, std):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import LogNormal, density
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> mu = Symbol("mu", real=True)
>>> sigma = Symbol("sigma", positive=True)
@@ -2897,7 +2897,7 @@ def Normal(name, mean, std):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import Normal, density, E, std, cdf, skewness, quantile
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint, factor, together, factor_terms
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
>>> mu = Symbol("mu")
>>> sigma = Symbol("sigma", positive=True)
@@ -3027,7 +3027,7 @@ def GaussianInverse(name, mean, shape):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import GaussianInverse, density, cdf, E, std, skewness
+ >>> from sympy.stats import GaussianInverse, density, E, std, skewness
>>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> mu = Symbol("mu", positive=True)
@@ -3202,7 +3202,7 @@ def PowerFunction(name, alpha, a, b):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import PowerFunction, density, cdf, E, variance
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> alpha = Symbol("alpha", positive=True)
>>> a = Symbol("a", real=True)
>>> b = Symbol("b", real=True)
@@ -3295,8 +3295,8 @@ def QuadraticU(name, a, b):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import QuadraticU, density, E, variance
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, factor, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.stats import QuadraticU, density
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> a = Symbol("a", real=True)
>>> b = Symbol("b", real=True)
@@ -3381,8 +3381,8 @@ def RaisedCosine(name, mu, s):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import RaisedCosine, density, E, variance
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.stats import RaisedCosine, density
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> mu = Symbol("mu", real=True)
>>> s = Symbol("s", positive=True)
@@ -3464,7 +3464,7 @@ def Rayleigh(name, sigma):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import Rayleigh, density, E, variance
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> sigma = Symbol("sigma", positive=True)
>>> z = Symbol("z")
@@ -3590,7 +3590,7 @@ def ShiftedGompertz(name, b, eta):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import ShiftedGompertz, density, E, variance
+ >>> from sympy.stats import ShiftedGompertz, density
>>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> b = Symbol("b", positive=True)
@@ -3659,8 +3659,8 @@ def StudentT(name, nu):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import StudentT, density, E, variance, cdf
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.stats import StudentT, density, cdf
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> nu = Symbol("nu", positive=True)
>>> z = Symbol("z")
@@ -3755,7 +3755,7 @@ def Trapezoidal(name, a, b, c, d):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import Trapezoidal, density, E
+ >>> from sympy.stats import Trapezoidal, density
>>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> a = Symbol("a")
@@ -3854,7 +3854,7 @@ def Triangular(name, a, b, c):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import Triangular, density, E
+ >>> from sympy.stats import Triangular, density
>>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> a = Symbol("a")
@@ -3966,7 +3966,7 @@ def Uniform(name, left, right):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import Uniform, density, cdf, E, variance, skewness
+ >>> from sympy.stats import Uniform, density, cdf, E, variance
>>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify
>>> a = Symbol("a", negative=True)
@@ -4144,8 +4144,8 @@ def VonMises(name, mu, k):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import VonMises, density, E, variance
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy.stats import VonMises, density
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> mu = Symbol("mu")
>>> k = Symbol("k", positive=True)
@@ -4297,7 +4297,7 @@ def WignerSemicircle(name, R):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import WignerSemicircle, density, E
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> R = Symbol("R", positive=True)
>>> z = Symbol("z")
diff --git a/sympy/stats/drv_types.py b/sympy/stats/drv_types.py
index 399336b015a3..6a30a2fe12b0 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/drv_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/drv_types.py
@@ -592,7 +592,7 @@ def Skellam(name, mu1, mu2):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import Skellam, density, E, variance
- >>> from sympy import Symbol, simplify, pprint
+ >>> from sympy import Symbol, pprint
>>> z = Symbol("z", integer=True)
>>> mu1 = Symbol("mu1", positive=True)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py b/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py
index 756b97f1c490..2438237c7706 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/joint_rv_types.py
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ def JointRV(symbol, pdf, _set=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import symbols, exp, pi, Indexed, S
+ >>> from sympy import exp, pi, Indexed, S
>>> from sympy.stats import density
>>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import JointRV
@@ -518,7 +518,6 @@ def GeneralizedMultivariateLogGamma(syms, delta, v, lamda, mu):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import density
- >>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv import marginal_distribution
>>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import GeneralizedMultivariateLogGamma
>>> from sympy import symbols, S
>>> v = 1
@@ -573,7 +572,6 @@ def GeneralizedMultivariateLogGammaOmega(syms, omega, v, lamda, mu):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import density
- >>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv import marginal_distribution
>>> from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import GeneralizedMultivariateLogGammaOmega
>>> from sympy import Matrix, symbols, S
>>> omega = Matrix([[1, S.Half, S.Half], [S.Half, 1, S.Half], [S.Half, S.Half, 1]])
diff --git a/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py b/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py
index 02717ee24a0b..a04e2f3bc104 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py
@@ -234,7 +234,7 @@ class CircularUnitaryEnsemble(CircularEnsemble):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import CircularUnitaryEnsemble as CUE, density
+ >>> from sympy.stats import CircularUnitaryEnsemble as CUE
>>> from sympy.stats import joint_eigen_distribution
>>> C = CUE('U', 1)
>>> joint_eigen_distribution(C)
@@ -257,7 +257,7 @@ class CircularOrthogonalEnsemble(CircularEnsemble):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import CircularOrthogonalEnsemble as COE, density
+ >>> from sympy.stats import CircularOrthogonalEnsemble as COE
>>> from sympy.stats import joint_eigen_distribution
>>> C = COE('O', 1)
>>> joint_eigen_distribution(C)
@@ -280,7 +280,7 @@ class CircularSymplecticEnsemble(CircularEnsemble):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import CircularSymplecticEnsemble as CSE, density
+ >>> from sympy.stats import CircularSymplecticEnsemble as CSE
>>> from sympy.stats import joint_eigen_distribution
>>> C = CSE('S', 1)
>>> joint_eigen_distribution(C)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/rv.py b/sympy/stats/rv.py
index 378e5fc0aba8..6537c7bd4df5 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/rv.py
@@ -575,7 +575,6 @@ def pspace(expr):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import pspace, Normal
- >>> from sympy.stats.rv import IndependentProductPSpace
>>> X = Normal('X', 0, 1)
>>> pspace(2*X + 1) == X.pspace
True
@@ -1004,7 +1003,7 @@ def where(condition, given_condition=None, **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import where, Die, Normal
- >>> from sympy import symbols, And
+ >>> from sympy import And
>>> D1, D2 = Die('a', 6), Die('b', 6)
>>> a, b = D1.symbol, D2.symbol
diff --git a/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py b/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py
index 236f774a9441..d725e6f07ddc 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ def variance(X, condition=None, **kwargs):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.stats import Die, E, Bernoulli, variance
+ >>> from sympy.stats import Die, Bernoulli, variance
>>> from sympy import simplify, Symbol
>>> X = Die('X', 6)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
index 9380a06b92e0..9cc5ec33f272 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
@@ -744,7 +744,7 @@ class ContinuousMarkovChain(ContinuousTimeStochasticProcess, MarkovProcess):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import ContinuousMarkovChain
- >>> from sympy import Matrix, S, MatrixSymbol
+ >>> from sympy import Matrix, S
>>> G = Matrix([[-S(1), S(1)], [S(1), -S(1)]])
>>> C = ContinuousMarkovChain('C', state_space=[0, 1], gen_mat=G)
>>> C.limiting_distribution()
@@ -820,7 +820,7 @@ class BernoulliProcess(DiscreteTimeStochasticProcess):
========
>>> from sympy.stats import BernoulliProcess, P, E
- >>> from sympy import Eq, Gt, Lt
+ >>> from sympy import Eq, Gt
>>> B = BernoulliProcess("B", p=0.7, success=1, failure=0)
>>> B.state_space
FiniteSet(0, 1)
diff --git a/sympy/tensor/index_methods.py b/sympy/tensor/index_methods.py
index 08581cfd9230..372263a689ac 100644
--- a/sympy/tensor/index_methods.py
+++ b/sympy/tensor/index_methods.py
@@ -212,7 +212,7 @@ def get_indices(expr):
>>> from sympy.tensor.index_methods import get_indices
>>> from sympy import symbols
- >>> from sympy.tensor import IndexedBase, Idx
+ >>> from sympy.tensor import IndexedBase
>>> x, y, A = map(IndexedBase, ['x', 'y', 'A'])
>>> i, j, a, z = symbols('i j a z', integer=True)
@@ -329,7 +329,7 @@ def get_contraction_structure(expr):
========
>>> from sympy.tensor.index_methods import get_contraction_structure
- >>> from sympy import symbols, default_sort_key
+ >>> from sympy import default_sort_key
>>> from sympy.tensor import IndexedBase, Idx
>>> x, y, A = map(IndexedBase, ['x', 'y', 'A'])
>>> i, j, k, l = map(Idx, ['i', 'j', 'k', 'l'])
diff --git a/sympy/tensor/indexed.py b/sympy/tensor/indexed.py
index a4fde4cb72ea..b8b4da9461e7 100644
--- a/sympy/tensor/indexed.py
+++ b/sympy/tensor/indexed.py
@@ -496,7 +496,7 @@ def shape(self):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import IndexedBase, Idx, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy import IndexedBase, Idx
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y
>>> IndexedBase('A', shape=(x, y)).shape
(x, y)
@@ -601,7 +601,7 @@ class Idx(Expr):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy import IndexedBase, Idx, symbols, oo
+ >>> from sympy import Idx, symbols, oo
>>> n, i, L, U = symbols('n i L U', integer=True)
If a string is given for the label an integer ``Symbol`` is created and the
diff --git a/sympy/testing/pytest.py b/sympy/testing/pytest.py
index 9843d62ffcbb..174fc590a035 100644
--- a/sympy/testing/pytest.py
+++ b/sympy/testing/pytest.py
@@ -222,8 +222,6 @@ def warns_deprecated_sympy():
>>> from sympy.testing.pytest import warns_deprecated_sympy
>>> from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning
- >>> import warnings
-
>>> with warns_deprecated_sympy():
... SymPyDeprecationWarning("Don't use", feature="old thing",
... deprecated_since_version="1.0", issue=123).warn()
diff --git a/sympy/unify/usympy.py b/sympy/unify/usympy.py
index 668bfabd8bec..71a19248a8ae 100644
--- a/sympy/unify/usympy.py
+++ b/sympy/unify/usympy.py
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ def unify(x, y, s=None, variables=(), **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy.unify.usympy import unify
- >>> from sympy import Basic, cos
+ >>> from sympy import Basic
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z, p, q
>>> next(unify(Basic(1, 2), Basic(1, x), variables=[x]))
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/_compilation/compilation.py b/sympy/utilities/_compilation/compilation.py
index 7a72b786c5bb..df640524cd4f 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/_compilation/compilation.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/_compilation/compilation.py
@@ -505,13 +505,6 @@ def compile_link_import_py_ext(sources, extname=None, build_dir='.', compile_kwa
=======
The imported module from of the python extension.
-
- Examples
- ========
-
- >>> mod = compile_link_import_py_ext(['fft.f90', 'conv.cpp', '_fft.pyx']) # doctest: +SKIP
- >>> Aprim = mod.fft(A) # doctest: +SKIP
-
"""
if extname is None:
extname = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(sources[-1]))[0]
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/decorator.py b/sympy/utilities/decorator.py
index d6d290452e1b..97152bd08748 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/decorator.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/decorator.py
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ def public(obj):
>>> from sympy.utilities.decorator import public
- >>> __all__
+ >>> __all__ # noqa: F821
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
NameError: name '__all__' is not defined
@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ def public(obj):
... def some_function():
... pass
- >>> __all__
+ >>> __all__ # noqa: F821
['some_function']
"""
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
index 2cc512612919..94c6b700b68f 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py
@@ -2535,12 +2535,12 @@ def kbins(l, k, ordered=None):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.utilities.iterables import kbins
+ >>> from __future__ import print_function
The default is to give the items in the same order, but grouped
into k partitions without any reordering:
- >>> from __future__ import print_function
+ >>> from sympy.utilities.iterables import kbins
>>> for p in kbins(list(range(5)), 2):
... print(p)
...
@@ -2565,9 +2565,9 @@ def kbins(l, k, ordered=None):
10 means A == D
11 means A == A
- >>> for ordered in [None, 0, 1, 10, 11]:
- ... print('ordered = %s' % ordered)
- ... for p in kbins(list(range(3)), 2, ordered=ordered):
+ >>> for ordered_flag in [None, 0, 1, 10, 11]:
+ ... print('ordered = %s' % ordered_flag)
+ ... for p in kbins(list(range(3)), 2, ordered=ordered_flag):
... print(' %s' % p)
...
ordered = None
diff --git a/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py b/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py
index 583864f8d443..4d24aafb14a4 100644
--- a/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py
+++ b/sympy/utilities/lambdify.py
@@ -351,7 +351,6 @@ def lambdify(args, expr, modules=None, printer=None, use_imps=True,
functions. This may be preferable to using ``evalf`` (which uses mpmath on
the backend) in some cases.
- >>> import mpmath
>>> f = lambdify(x, sin(x), 'mpmath')
>>> f(1)
0.8414709848078965
@@ -1287,7 +1286,6 @@ def implemented_function(symfunc, implementation):
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> from sympy.utilities.lambdify import lambdify, implemented_function
- >>> from sympy import Function
>>> f = implemented_function('f', lambda x: x+1)
>>> lam_f = lambdify(x, f(x))
>>> lam_f(4)
diff --git a/sympy/vector/functions.py b/sympy/vector/functions.py
index e3a08c716b7b..8b75445f002d 100644
--- a/sympy/vector/functions.py
+++ b/sympy/vector/functions.py
@@ -354,7 +354,7 @@ def scalar_potential_difference(field, coord_sys, point1, point2):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D, Point
+ >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D
>>> from sympy.vector import scalar_potential_difference
>>> R = CoordSys3D('R')
>>> P = R.origin.locate_new('P', R.x*R.i + R.y*R.j + R.z*R.k)
@@ -483,7 +483,6 @@ def orthogonalize(*vlist, **kwargs):
========
>>> from sympy.vector.coordsysrect import CoordSys3D
- >>> from sympy.vector.vector import Vector, BaseVector
>>> from sympy.vector.functions import orthogonalize
>>> C = CoordSys3D('C')
>>> i, j, k = C.base_vectors()
diff --git a/sympy/vector/point.py b/sympy/vector/point.py
index 2a29bdbdea20..bfcd13e88da8 100644
--- a/sympy/vector/point.py
+++ b/sympy/vector/point.py
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ def position_wrt(self, other):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.vector import Point, CoordSys3D
+ >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D
>>> N = CoordSys3D('N')
>>> p1 = N.origin.locate_new('p1', 10 * N.i)
>>> N.origin.position_wrt(p1)
@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ def locate_new(self, name, position):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.vector import Point, CoordSys3D
+ >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D
>>> N = CoordSys3D('N')
>>> p1 = N.origin.locate_new('p1', 10 * N.i)
>>> p1.position_wrt(N.origin)
@@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ def express_coordinates(self, coordinate_system):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.vector import Point, CoordSys3D
+ >>> from sympy.vector import CoordSys3D
>>> N = CoordSys3D('N')
>>> p1 = N.origin.locate_new('p1', 10 * N.i)
>>> p2 = p1.locate_new('p2', 5 * N.j)
diff --git a/sympy/vector/vector.py b/sympy/vector/vector.py
index 999937b6c3cb..84237b478e2b 100644
--- a/sympy/vector/vector.py
+++ b/sympy/vector/vector.py
@@ -223,7 +223,6 @@ def projection(self, other, scalar=False):
========
>>> from sympy.vector.coordsysrect import CoordSys3D
- >>> from sympy.vector.vector import Vector, BaseVector
>>> C = CoordSys3D('C')
>>> i, j, k = C.base_vectors()
>>> v1 = i + j + k
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 1,
"problem_domain": "Code Style, Linting, Formatting Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19463@53d2c02
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,463
|
Introduce general add, mul, and pow function
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Closes #18769
Fixes #18768
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
- core
- Extensible `add`, `mul` and `power` functions are introduced to allow sympy objects to define what classes should be used for them in place of `Add`, `Mul` and `Pow` (e.g. matrices use `MatAdd`). This is an experimental approach aimed at enabling the behaviour of core routines (expand, collect, etc) to be customised by user-defined types (e.g. `MatAdd` rather than `Add`). This mechanism is still experimental, is not fully implemented across the core and might be changed or removed in a future release of sympy.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-05-30T05:28:37Z
|
Connecting Add, Mul to MatAdd, MatMul
Current matrix module uses `Basic._exec_constructor_postprocessor` method to convert `Add` and `Mul` containing `MatrixExpr` to `MatAdd` and `MatMul`, respectly.
However, this behavior seems to be somewhat unefficient...
1. It does not pass any option to `MatAdd` and `MatMul`.
```python
>>> from sympy import Add, MatAdd, MatrixSymbol
>>> A,B = MatrixSymbol('A', 2,2), MatrixSymbol('B', 3,3)
>>> MatAdd(A,B, check=True) # Raises error
Traceback (most recent call last)
...
ShapeError: Matrices A and B are not aligned
>>> Add(A,B, check=True) # Does not raise error
A + B
```
2. It takes every steps (`flatten` and `_from_args` methods of `Add` and `Mul`) to create `Add` or `Mul` object, then takes every steps of `MatAdd` or `MatMul` again.
Current approach behaves in the way that, if new classes with their own postprocessors are added in the future, every postprocessors will be executed one by one.
Suggestion: make the arguments 'preprocessed' rather than 'postprocessed'. This can be done by comparing `_op_priority` of the arguments.
|
[
{
"body": "Current matrix module uses `Basic._exec_constructor_postprocessor` method to convert `Add` and `Mul` containing `MatrixExpr` to `MatAdd` and `MatMul`, respectly. \r\nHowever, this behavior seems to be somewhat unefficient...\r\n\r\n1. It does not pass any option to `MatAdd` and `MatMul`.\r\n ```python\r\n >>> from sympy import Add, MatAdd, MatrixSymbol\r\n >>> A,B = MatrixSymbol('A', 2,2), MatrixSymbol('B', 3,3)\r\n >>> MatAdd(A,B, check=True) # Raises error\r\n Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n ...\r\n ShapeError: Matrices A and B are not aligned\r\n >>> Add(A,B, check=True) # Does not raise error\r\n A + B\r\n ```\r\n\r\n2. It takes every steps (`flatten` and `_from_args` methods of `Add` and `Mul`) to create `Add` or `Mul` object, then takes every steps of `MatAdd` or `MatMul` again.\r\nCurrent approach behaves in the way that, if new classes with their own postprocessors are added in the future, every postprocessors will be executed one by one.\r\n\r\nSuggestion: make the arguments 'preprocessed' rather than 'postprocessed'. This can be done by comparing `_op_priority` of the arguments.",
"number": 18768,
"title": "Connecting Add, Mul to MatAdd, MatMul"
}
] |
4063fa8437fc4319bdbdf1735075a2f9853f4498
|
{
"head_commit": "53d2c02bcbf22e76efdcc56add548e3dec9472cf",
"head_commit_message": "Apply suggestions from code review\n\nCo-authored-by: Eric Wieser <[email protected]>",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/add.py b/sympy/core/add.py\nindex a37140b836cc..651f6b627caa 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/add.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/add.py\n@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@\n from .parameters import global_parameters\n from .logic import _fuzzy_group, fuzzy_or, fuzzy_not\n from .singleton import S\n-from .operations import AssocOp\n+from .operations import AssocOp, AssocOpDispatcher\n from .cache import cacheit\n from .numbers import ilcm, igcd\n from .expr import Expr\n@@ -66,7 +66,6 @@ def _unevaluated_Add(*args):\n newargs.insert(0, co)\n return Add._from_args(newargs)\n \n-\n class Add(Expr, AssocOp):\n \n __slots__ = ()\n@@ -1127,6 +1126,7 @@ def __neg__(self):\n return super().__neg__()\n return Add(*[-i for i in self.args])\n \n+add = AssocOpDispatcher('add')\n \n from .mul import Mul, _keep_coeff, prod\n from sympy.core.numbers import Rational\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py\nindex 1e5d6ca9e357..1337d116fd8b 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/expr.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py\n@@ -163,6 +163,18 @@ def __eq__(self, other):\n # something better and more powerful. See issue 5510.\n _op_priority = 10.0\n \n+ # Handler methods for dispatching\n+ # See operations.AssocOpDispatcher\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ from .add import Add\n+ return Add(*args, **kwargs)\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _mul_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ from .mul import Mul\n+ return Mul(*args, **kwargs)\n+\n def __pos__(self):\n return self\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/core/mul.py b/sympy/core/mul.py\nindex d4af08fa7390..95969074dae1 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/mul.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/mul.py\n@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@\n from .sympify import sympify\n from .basic import Basic\n from .singleton import S\n-from .operations import AssocOp\n+from .operations import AssocOp, AssocOpDispatcher\n from .cache import cacheit\n from .logic import fuzzy_not, _fuzzy_group, fuzzy_and\n from .compatibility import reduce\n@@ -1901,6 +1901,7 @@ def as_ordered_factors(self, order=None):\n def _sorted_args(self):\n return tuple(self.as_ordered_factors())\n \n+mul = AssocOpDispatcher('mul')\n \n def prod(a, start=1):\n \"\"\"Return product of elements of a. Start with int 1 so if only\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/operations.py b/sympy/core/operations.py\nindex d36a32e538ae..ca33d6d1eb7c 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/operations.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/operations.py\n@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@\n+import itertools\n+from operator import attrgetter\n from typing import Tuple\n \n from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning\n@@ -8,7 +10,9 @@\n from sympy.core.compatibility import ordered\n from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and\n from sympy.core.parameters import global_parameters\n-from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift\n+from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift, tied_max\n+from sympy.multipledispatch.dispatcher import (Dispatcher, ambiguity_register_error,\n+ str_signature)\n \n \n class AssocOp(Basic):\n@@ -21,6 +25,20 @@ class AssocOp(Basic):\n \n This is an abstract base class, concrete derived classes must define\n the attribute `identity`.\n+\n+ Parameters\n+ ==========\n+\n+ *args :\n+ Arguments which are operated\n+\n+ sympify : bool, optional\n+ Default is ``True``. ``False`` may be passed only when all arguments are\n+ already sympified, for faster processing.\n+\n+ evaluate : bool, optional\n+ Default is ``True``. If ``False``, do not evaluate the operation.\n+\n \"\"\"\n \n # for performance reason, we don't let is_commutative go to assumptions,\n@@ -30,9 +48,13 @@ class AssocOp(Basic):\n _args_type = None\n \n @cacheit\n- def __new__(cls, *args, **options):\n+ def __new__(cls, *args, sympify=True, **options):\n from sympy import Order\n- args = list(map(_sympify, args))\n+\n+ # Allow faster processing by passing ``sympify=False``, if all arguments\n+ # are already sympified.\n+ if sympify:\n+ args = list(map(_sympify, args))\n \n # Disallow non-Expr args in Add/Mul\n typ = cls._args_type\n@@ -504,3 +526,188 @@ def args(self):\n @staticmethod\n def _compare_pretty(a, b):\n return (str(a) > str(b)) - (str(a) < str(b))\n+\n+class AssocOpDispatcher:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Handler dispatcher for associative operators\n+\n+ .. notes::\n+ This approach is experimental, and can be replaced or deleted in the future.\n+ See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/19463.\n+\n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n+ If arguments of different kind are passed, their ``_op_priority`` are compared to\n+ choose the type with the highest priority. If this is ambiguous, priority relations\n+ which are registered by ``register_priority`` method are referred to.\n+ Once a type is selected, handler method of the type, which is a static method, is used\n+ to perform the operation.\n+\n+ Priority registration is unordered. You cannot make ``A*B`` and ``B*A`` use different\n+ handler method. All logic dealing with the order of arguments must be implemented in\n+ the handler method.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import Add, Expr, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy.core.add import add\n+\n+ >>> class NewExpr(Expr):\n+ ... @staticmethod\n+ ... def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ ... return NewAdd(*args, **kwargs)\n+ >>> class NewAdd(NewExpr, Add):\n+ ... pass\n+\n+ >>> @add.register_priority(Expr, NewExpr)\n+ ... @add.register_priority(NewExpr, NewExpr)\n+ ... def _(_1, _2):\n+ ... return NewExpr\n+\n+ >>> a, b = Symbol('a'), NewExpr()\n+ >>> add(a, b) == NewAdd(a, b)\n+ True\n+\n+ Registered priority selector can return any type.\n+\n+ >>> class Foo(Expr):\n+ ... @staticmethod\n+ ... def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ ... raise NotImplementedError\n+ >>> class Bar(Expr):\n+ ... @staticmethod\n+ ... def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ ... raise NotImplementedError\n+ >>> class FooBar(Expr):\n+ ... @staticmethod\n+ ... def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ ... return NewAdd(*args, **kwargs)\n+\n+ >>> @add.register_priority(Foo, Bar)\n+ ... def _(_1, _2):\n+ ... return FooBar\n+\n+ >>> add(Foo(), Bar()) == NewAdd(Foo(), Bar())\n+ True\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ def __init__(self, name, doc=None):\n+ self.name = name\n+ self.doc = doc\n+ self.handlermethod = \"_%s_handler\" % name\n+ self._handlergetter = attrgetter(self.handlermethod)\n+ self._dispatcher = Dispatcher(name)\n+\n+ def __repr__(self):\n+ return \"<dispatched %s>\" % self.name\n+\n+ def register_priority(self, cls1, cls2, on_ambiguity=ambiguity_register_error):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Register the priority between two types, in both straight and reversed order.\n+ Registered function must return the class which has the handler that is to be used.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ def _(func):\n+ self._dispatcher.add((cls1, cls2), func, on_ambiguity=on_ambiguity)\n+ self._dispatcher.add((cls2, cls1), func, on_ambiguity=on_ambiguity)\n+ return func\n+ return _\n+\n+ @cacheit\n+ def __call__(self, *args, sympify=True, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Parameters\n+ ==========\n+\n+ *args :\n+ Arguments which are operated\n+\n+ sympify : bool, optional\n+ Default is ``True``. ``False`` may be passed only when all arguments are\n+ already sympified, for faster processing.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if sympify:\n+ args = tuple(map(_sympify, args))\n+ types = frozenset(map(type, args))\n+\n+ # If sympify=True was passed, no need to sympify again so pass sympify=False.\n+ # If sympify=False was passed, all args are already sympified so pass sympify=False.\n+ return self.dispatch(types)(*args, sympify=False, **kwargs)\n+\n+ @cacheit\n+ def dispatch(self, types):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Select the type with highest priority, and return its handler.\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ # Quick exit for the case where all arguments are of same type\n+ # or all handlermethods are same\n+ handlers = set(map(self._handlergetter, types))\n+ if len(handlers) == 1:\n+ h, = handlers\n+ return h\n+\n+ # Sieve the types with low op_priority or no handler\n+ # This makes it faster than using dispatcher on every types.\n+ sieved_data = tied_max(\n+ types, key=lambda typ: getattr(typ, '_op_priority', 0)\n+ )\n+\n+ # Only one type remains\n+ if len(sieved_data) == 1:\n+ typ, = sieved_data\n+ return self._handlergetter(typ)\n+\n+ # Recursively select with registered binary priority\n+ for i, typ in enumerate(sieved_data):\n+ if i == 0:\n+ result_type = typ\n+ else:\n+ dispatched_selector = self._dispatcher.dispatch(result_type, typ)\n+ selected_type = dispatched_selector(result_type, typ)\n+\n+ if not isinstance(selected_type, type):\n+ raise RuntimeError(\n+ \"Dispatcher for {!r} and {!r} must return a type, but got {!r}\".format(\n+ result_type, typ, selected_type\n+ ))\n+\n+ handler = self._handlergetter(selected_type)\n+ if handler is None:\n+ raise RuntimeError(\n+ \"Dispatcher for {!r} and {!r} returned {!r} which does not have {!r} method.\".format(\n+ result_type, typ, selected_type, self.handlermethod\n+ ))\n+\n+ result_type = selected_type\n+\n+ # return handler method of selected argument\n+ return handler\n+\n+ @property\n+ def __doc__(self):\n+ docs = [\n+ \"Multiply dispatched associative operator: %s\" % self.name,\n+ \"Note that support for this is experimental, see the docs for :class:`AssocOpDispatcher` for details\"\n+ ]\n+\n+ if self.doc:\n+ docs.append(self.doc)\n+\n+ docs.append(\"Registered priority relations are as follows:\")\n+\n+ other = []\n+ for func, sigs in itertools.groupby(self._dispatcher.ordering[::-1], lambda sig: self._dispatcher.funcs[sig]):\n+ if func.__doc__:\n+ s = 'Inputs: %s\\n' % ', '.join('<%s>' % str_signature(sig) for sig in sigs)\n+ s += '-' * len(s) + '\\n'\n+ s += func.__doc__.strip()\n+ docs.append(s)\n+ else:\n+ other += list(sigs)\n+\n+ if other:\n+ docs.append('Other signatures:\\n ' + '\\n '.join(other))\n+\n+ return '\\n\\n'.join(docs)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/power.py b/sympy/core/power.py\nindex 0a3b8b564c42..6a610be5ad60 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/power.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/power.py\n@@ -12,6 +12,7 @@\n from .parameters import global_parameters\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift\n from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import Dispatcher\n \n from mpmath.libmp import sqrtrem as mpmath_sqrtrem\n \n@@ -1732,6 +1733,8 @@ def _eval_difference_delta(self, n, step):\n new_e = e.subs(n, n + step)\n return (b**(new_e - e) - 1) * self\n \n+power = Dispatcher('power')\n+power.add((object, object), Pow)\n \n from .add import Add\n from .numbers import Integer\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_operations.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_operations.py\nindex 7555398f4395..a2424b3afd61 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_operations.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_operations.py\n@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@\n-from sympy import Integer, S, symbols, Mul\n+from sympy import Integer, S, Symbol, symbols, Expr\n from sympy.core.operations import AssocOp, LatticeOp\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n from sympy.core.sympify import SympifyError\n-from sympy.core.add import Add\n+from sympy.core.add import Add, add\n+from sympy.core.mul import Mul, mul\n \n # create the simplest possible Lattice class\n \n@@ -64,3 +65,69 @@ class MyAssoc(AssocOp):\n assert v.args == (u, d)\n # like Add, any unevaluated outer call will flatten inner args\n assert MyAssoc(a, v).args == (a, b, c, d)\n+\n+def test_add_dispatcher():\n+\n+ class NewBase1(Expr):\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ return NewAdd1(*args, **kwargs)\n+ class NewAdd1(NewBase1, Add):\n+ pass\n+ class NewBase2(Expr):\n+ _op_priority = 11\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ return NewAdd2(*args, **kwargs)\n+ class NewAdd2(NewBase2, Add):\n+ pass\n+ a, b, c = Symbol('a'), NewBase1(), NewBase2()\n+\n+ @add.register_priority(Expr, NewBase1)\n+ @add.register_priority(NewBase1, NewBase1)\n+ def _(_1, _2):\n+ return NewBase1\n+\n+ # Add called as fallback\n+ assert add(1, 2) == Add(1, 2)\n+ assert add(a, a) == Add(a, a)\n+\n+ # selection by registered priority\n+ assert add(a,b,a) == NewAdd1(2*a, b)\n+\n+ # selection by _op_priority\n+ assert add(a,c,a) == NewAdd2(2*a, c)\n+ assert add(a,b,c) == NewAdd2(a,b,c)\n+\n+def test_mul_dispatcher():\n+\n+ class NewBase1(Expr):\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _mul_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ return NewMul1(*args, **kwargs)\n+ class NewMul1(NewBase1, Mul):\n+ pass\n+ class NewBase2(Expr):\n+ _op_priority = 11\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _mul_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ return NewMul2(*args, **kwargs)\n+ class NewMul2(NewBase2, Mul):\n+ pass\n+ a, b, c = Symbol('a'), NewBase1(), NewBase2()\n+\n+ @mul.register_priority(Expr, NewBase1)\n+ @mul.register_priority(NewBase1, NewBase1)\n+ def _(_1, _2):\n+ return NewBase1\n+\n+ # Mul called as fallback\n+ assert mul(1, 2) == Mul(1, 2)\n+ assert mul(a, a) == Mul(a, a)\n+\n+ # selection by registered priority\n+ assert mul(a,b,a) == NewMul1(a**2, b)\n+\n+ # selection by _op_priority\n+ assert mul(a,c,a) == NewMul2(a**2, c)\n+ assert mul(a,b,c) == NewMul2(a,b,c)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py\nindex 6aa6ef2e57cc..413fbd453217 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py\n@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@\n from sympy.series.order import O\n from sympy.sets import FiniteSet\n from sympy.core.expr import unchanged\n-\n+from sympy.core.power import power\n from sympy.testing.pytest import warns_deprecated_sympy\n \n \n@@ -555,3 +555,27 @@ def test_issue_18762():\n e, p = symbols('e p')\n g0 = sqrt(1 + e**2 - 2*e*cos(p))\n assert len(g0.series(e, 1, 3).args) == 4\n+\n+def test_power_dispatcher():\n+\n+ class NewBase(Expr):\n+ pass\n+ class NewPow(NewBase, Pow):\n+ pass\n+ a, b = Symbol('a'), NewBase()\n+\n+ @power.register(Expr, NewBase)\n+ @power.register(NewBase, Expr)\n+ @power.register(NewBase, NewBase)\n+ def _(a, b):\n+ return NewPow(a, b)\n+\n+ # Pow called as fallback\n+ assert power(2, 3) == 8*S.One\n+ assert power(a, 2) == Pow(a, 2)\n+ assert power(a, a) == Pow(a, a)\n+\n+ # NewPow called by dispatch\n+ assert power(a, b) == NewPow(a, b)\n+ assert power(b, a) == NewPow(b, a)\n+ assert power(b, b) == NewPow(b, b)\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\nindex 83596decde7d..066b174a0a37 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\n@@ -5,6 +5,8 @@\n import collections\n \n from sympy.core import S, Symbol, Tuple, Integer, Basic, Expr, Mul, Add\n+from sympy.core.add import add\n+from sympy.core.mul import mul\n from sympy.core.decorators import call_highest_priority\n from sympy.core.compatibility import SYMPY_INTS, default_sort_key\n from sympy.core.sympify import SympifyError, _sympify\n@@ -593,6 +595,14 @@ def applyfunc(self, func):\n from .applyfunc import ElementwiseApplyFunction\n return ElementwiseApplyFunction(func, self)\n \n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ return MatAdd(*args, **kwargs)\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _mul_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ return MatMul(*args, **kwargs)\n+\n @dispatch(MatrixExpr, Expr)\n def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n return False\n@@ -648,6 +658,13 @@ def _postprocessor(expr):\n \"Add\": [get_postprocessor(Add)],\n }\n \[email protected]_priority(Expr, MatrixExpr)\[email protected]_priority(MatrixExpr, MatrixExpr)\[email protected]_priority(Expr, MatrixExpr)\[email protected]_priority(MatrixExpr, MatrixExpr)\n+def _(_1, _2):\n+ \"Use MatrixExpr's handler method.\"\n+ return MatrixExpr\n \n def _matrix_derivative(expr, x):\n from sympy import Derivative\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py\nindex b4d0ec046106..d13890557cca 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py\n@@ -2,24 +2,27 @@\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.special import GenericZeroMatrix, ZeroMatrix\n from sympy.matrices import eye, ImmutableMatrix\n from sympy.core import Add, Basic, S\n+from sympy.core.add import add\n from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, raises\n \n X = MatrixSymbol('X', 2, 2)\n Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', 2, 2)\n \n def test_evaluate():\n- assert MatAdd(X, X, evaluate=True) == MatAdd(X, X).doit()\n+ assert MatAdd(X, X, evaluate=True) == add(X, X, evaluate=True) == MatAdd(X, X).doit()\n \n def test_sort_key():\n- assert MatAdd(Y, X).doit().args == (X, Y)\n+ assert MatAdd(Y, X).doit().args == add(Y, X).doit().args == (X, Y)\n \n \n def test_matadd_sympify():\n assert isinstance(MatAdd(eye(1), eye(1)).args[0], Basic)\n+ assert isinstance(add(eye(1), eye(1)).args[0], Basic)\n \n \n def test_matadd_of_matrices():\n assert MatAdd(eye(2), 4*eye(2), eye(2)).doit() == ImmutableMatrix(6*eye(2))\n+ assert add(eye(2), 4*eye(2), eye(2)).doit() == ImmutableMatrix(6*eye(2))\n \n \n def test_doit_args():\n@@ -28,7 +31,8 @@ def test_doit_args():\n assert MatAdd(A, MatPow(B, 2)).doit() == A + B**2\n assert MatAdd(A, MatMul(A, B)).doit() == A + A*B\n assert (MatAdd(A, X, MatMul(A, B), Y, MatAdd(2*A, B)).doit() ==\n- MatAdd(3*A + A*B + B, X, Y))\n+ add(A, X, MatMul(A, B), Y, add(2*A, B)).doit() ==\n+ MatAdd(3*A + A*B + B, X, Y))\n \n \n def test_generic_identity():\n@@ -40,5 +44,5 @@ def test_zero_matrix_add():\n assert Add(ZeroMatrix(2, 2), ZeroMatrix(2, 2)) == ZeroMatrix(2, 2)\n \n @XFAIL\n-def test_matrix_add_with_scalar():\n+def test_matrix_Add_with_scalar():\n raises(TypeError, lambda: Add(0, ZeroMatrix(2, 2)))\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py\nindex 340dd3456db0..529be8559f13 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py\n@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@\n from sympy.core import I, symbols, Basic, Mul, S\n+from sympy.core.mul import mul\n from sympy.functions import adjoint, transpose\n from sympy.matrices import (Identity, Inverse, Matrix, MatrixSymbol, ZeroMatrix,\n eye, ImmutableMatrix)\n@@ -153,6 +154,11 @@ def test_construction_with_Mul():\n assert Mul(C, D) == MatMul(C, D)\n assert Mul(D, C) == MatMul(D, C)\n \n+def test_construction_with_mul():\n+ assert mul(C, D) == MatMul(C, D)\n+ assert mul(D, C) == MatMul(D, C)\n+ assert mul(C, D) != MatMul(D, C)\n+\n def test_generic_identity():\n assert MatMul.identity == GenericIdentity()\n assert MatMul.identity != S.One\ndiff --git a/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py b/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py\nindex 9c5f38651183..6cb30c1d4209 100644\n--- a/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py\n+++ b/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py\n@@ -28,6 +28,34 @@ def ambiguity_warn(dispatcher, ambiguities):\n warn(warning_text(dispatcher.name, ambiguities), AmbiguityWarning)\n \n \n+def ambiguity_register_error(dispatcher, ambiguities):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Automatically register function which raises error when ambiguous types\n+ are registered.\n+\n+ Parameters\n+ ----------\n+ dispatcher : Dispatcher\n+ The dispatcher on which the ambiguity was detected\n+ ambiguities : set\n+ Set of type signature pairs that are ambiguous within this dispatcher\n+\n+ See Also:\n+ Dispatcher.add\n+ ambiguity_warn\n+ \"\"\"\n+ for amb in ambiguities:\n+ @dispatcher.register(*super_signature(amb))\n+ def _(*args, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\" Unimplemented handler \"\"\"\n+ types = tuple(type(a) for a in args)\n+ raise NotImplementedError(\n+ \"Ambiguous signature for %s: <%s>\" % (\n+ dispatcher.name, str_signature(types)\n+ )\n+ )\n+\n+\n _unresolved_dispatchers = set() # type: Set[Dispatcher]\n _resolve = [True]\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/multipledispatch/tests/test_dispatcher.py b/sympy/multipledispatch/tests/test_dispatcher.py\nindex b980a8b19afc..8edaae2eb6eb 100644\n--- a/sympy/multipledispatch/tests/test_dispatcher.py\n+++ b/sympy/multipledispatch/tests/test_dispatcher.py\n@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@\n from sympy.multipledispatch.dispatcher import (Dispatcher, MDNotImplementedError,\n MethodDispatcher, halt_ordering,\n- restart_ordering)\n+ restart_ordering,\n+ ambiguity_register_error)\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, warns\n \n \n@@ -262,3 +263,13 @@ def _(a):\n raise MDNotImplementedError()\n \n assert raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: f(1.0))\n+\n+def test_ambiguity_register_error():\n+ f = Dispatcher('add')\n+\n+ # suppress warning for registering ambiguous signal\n+ f.add((int, object), lambda x,y: x+y, ambiguity_register_error)\n+ f.add((object, int), lambda x,y: x+y, ambiguity_register_error)\n+\n+ # raises error if ambiguous signal is passed\n+ assert raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: f(1,2))\ndiff --git a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\nindex dd36dea304b5..da4258439c7d 100644\n--- a/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\n+++ b/sympy/utilities/iterables.py\n@@ -819,6 +819,37 @@ def sift(seq, keyfunc, binary=False):\n return T, F\n \n \n+def tied_max(iterable, *, key):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Return the list of items from *iterable* which returns\n+ highest value when *key* is applied.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy.utilities.iterables import tied_max\n+ >>> iterable = ['abc', 'de', 'fgh', 'i']\n+ >>> tied_max(iterable, key=len)\n+ ['abc', 'fgh']\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ it = iter(iterable)\n+ try:\n+ first = next(it)\n+ except StopIteration:\n+ return []\n+ max_key = key(first)\n+ max_vals = [first]\n+ for val in it:\n+ k = key(val)\n+ if k == max_key:\n+ max_vals.append(val)\n+ elif k > max_key:\n+ max_key = k\n+ max_vals = [val]\n+ return max_vals\n+\n+\n def take(iter, n):\n \"\"\"Return ``n`` items from ``iter`` iterator. \"\"\"\n return [ value for _, value in zip(range(n), iter) ]\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -21,6 +25,20 @@ class AssocOp(Basic):\n \n This is an abstract base class, concrete derived classes must define\n the attribute `identity`.\n+\n+ Parameters\n+ ==========\n+\n+ *args :\n+ Arguments which are operated\n+\n+ sympify : bool, optional",
"line": null,
"original_line": 35,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/operations.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nPerhaps this should be made private (`_sympify` and not documented). This is good for core library code, but I don't think it would be a good idea for most users to use this."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -504,3 +526,188 @@ def args(self):\n @staticmethod\n def _compare_pretty(a, b):\n return (str(a) > str(b)) - (str(a) < str(b))\n+\n+class AssocOpDispatcher:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Handler dispatcher for associative operators\n+\n+ .. notes::\n+ This approach is experimental, and can be replaced or deleted in the future.\n+ See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/19463.\n+\n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n+ If arguments of different kind are passed, their ``_op_priority`` are compared to\n+ choose the type with the highest priority. If this is ambiguous, priority relations\n+ which are registered by ``register_priority`` method are referred to.\n+ Once a type is selected, handler method of the type, which is a static method, is used\n+ to perform the operation.\n+\n+ Priority registration is unordered. You cannot make ``A*B`` and ``B*A`` use different\n+ handler method. All logic dealing with the order of arguments must be implemented in\n+ the handler method.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import Add, Expr, Symbol\n+ >>> from sympy.core.add import add\n+\n+ >>> class NewExpr(Expr):\n+ ... @staticmethod\n+ ... def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ ... return NewAdd(*args, **kwargs)\n+ >>> class NewAdd(NewExpr, Add):\n+ ... pass\n+\n+ >>> @add.register_priority(Expr, NewExpr)\n+ ... @add.register_priority(NewExpr, NewExpr)\n+ ... def _(_1, _2):\n+ ... return NewExpr\n+\n+ >>> a, b = Symbol('a'), NewExpr()\n+ >>> add(a, b) == NewAdd(a, b)\n+ True\n+\n+ Registered priority selector can return any type.\n+\n+ >>> class Foo(Expr):\n+ ... @staticmethod\n+ ... def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ ... raise NotImplementedError\n+ >>> class Bar(Expr):\n+ ... @staticmethod\n+ ... def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ ... raise NotImplementedError\n+ >>> class FooBar(Expr):\n+ ... @staticmethod\n+ ... def _add_handler(*args, **kwargs):\n+ ... return NewAdd(*args, **kwargs)\n+\n+ >>> @add.register_priority(Foo, Bar)\n+ ... def _(_1, _2):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 589,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/operations.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis relates to my other question, but I'm not a fan of using `_` for decorated function names. \n\n@author:\nMaybe I can modify this to `register_priority(type1, type2, result_type)` while keeping `(type1, type2)` be dispatched.\n\n@author:\nDone.\n\n@user2:\nUsing `_` as a decorated function name seems to be a blessed idiom for the cases where the function name is irrelevant because it's being used in e.g. single dispatch. I think flake8 special cases the name for this purpose."
}
] |
1f289377e24ade8f8f2c040602914a75bf03d02d
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/add.py b/sympy/core/add.py
index a37140b836cc..651f6b627caa 100644
--- a/sympy/core/add.py
+++ b/sympy/core/add.py
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
from .parameters import global_parameters
from .logic import _fuzzy_group, fuzzy_or, fuzzy_not
from .singleton import S
-from .operations import AssocOp
+from .operations import AssocOp, AssocOpDispatcher
from .cache import cacheit
from .numbers import ilcm, igcd
from .expr import Expr
@@ -66,7 +66,6 @@ def _unevaluated_Add(*args):
newargs.insert(0, co)
return Add._from_args(newargs)
-
class Add(Expr, AssocOp):
__slots__ = ()
@@ -1127,6 +1126,7 @@ def __neg__(self):
return super().__neg__()
return Add(*[-i for i in self.args])
+add = AssocOpDispatcher('add')
from .mul import Mul, _keep_coeff, prod
from sympy.core.numbers import Rational
diff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py
index 1e5d6ca9e357..2ef4ce2f2a0c 100644
--- a/sympy/core/expr.py
+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py
@@ -163,6 +163,14 @@ def __eq__(self, other):
# something better and more powerful. See issue 5510.
_op_priority = 10.0
+ @property
+ def _add_handler(self):
+ return Add
+
+ @property
+ def _mul_handler(self):
+ return Mul
+
def __pos__(self):
return self
diff --git a/sympy/core/mul.py b/sympy/core/mul.py
index d4af08fa7390..95969074dae1 100644
--- a/sympy/core/mul.py
+++ b/sympy/core/mul.py
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
from .sympify import sympify
from .basic import Basic
from .singleton import S
-from .operations import AssocOp
+from .operations import AssocOp, AssocOpDispatcher
from .cache import cacheit
from .logic import fuzzy_not, _fuzzy_group, fuzzy_and
from .compatibility import reduce
@@ -1901,6 +1901,7 @@ def as_ordered_factors(self, order=None):
def _sorted_args(self):
return tuple(self.as_ordered_factors())
+mul = AssocOpDispatcher('mul')
def prod(a, start=1):
"""Return product of elements of a. Start with int 1 so if only
diff --git a/sympy/core/operations.py b/sympy/core/operations.py
index d36a32e538ae..5778df268427 100644
--- a/sympy/core/operations.py
+++ b/sympy/core/operations.py
@@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
+from operator import attrgetter
from typing import Tuple
+from collections import defaultdict
from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning
@@ -9,6 +11,9 @@
from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and
from sympy.core.parameters import global_parameters
from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift
+from sympy.multipledispatch.dispatcher import (Dispatcher,
+ ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup,
+ str_signature, RaiseNotImplementedError)
class AssocOp(Basic):
@@ -21,6 +26,15 @@ class AssocOp(Basic):
This is an abstract base class, concrete derived classes must define
the attribute `identity`.
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ *args :
+ Arguments which are operated
+
+ evaluate : bool, optional
+ Default is ``True``. If ``False``, do not evaluate the operation.
"""
# for performance reason, we don't let is_commutative go to assumptions,
@@ -32,7 +46,11 @@ class AssocOp(Basic):
@cacheit
def __new__(cls, *args, **options):
from sympy import Order
- args = list(map(_sympify, args))
+
+ # Allow faster processing by passing ``_sympify=False``, if all arguments
+ # are already sympified.
+ if options.get('_sympify', True):
+ args = list(map(_sympify, args))
# Disallow non-Expr args in Add/Mul
typ = cls._args_type
@@ -504,3 +522,174 @@ def args(self):
@staticmethod
def _compare_pretty(a, b):
return (str(a) > str(b)) - (str(a) < str(b))
+
+
+class AssocOpDispatcher:
+ """
+ Handler dispatcher for associative operators
+
+ .. notes::
+ This approach is experimental, and can be replaced or deleted in the future.
+ See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/19463.
+
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
+ If arguments of different types are passed, the classes which handle the operation for each type
+ are collected. Then, a class which performs the operation is selected by recursive binary dispatching.
+ Dispatching relation can be registered by ``register_handlerclass`` method.
+
+ Priority registration is unordered. You cannot make ``A*B`` and ``B*A`` refer to
+ different handler classes. All logic dealing with the order of arguments must be implemented
+ in the handler class.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import Add, Expr, Symbol
+ >>> from sympy.core.add import add
+
+ >>> class NewExpr(Expr):
+ ... @property
+ ... def _add_handler(self):
+ ... return NewAdd
+ >>> class NewAdd(NewExpr, Add):
+ ... pass
+ >>> add.register_handlerclass((Add, NewAdd), NewAdd)
+
+ >>> a, b = Symbol('a'), NewExpr()
+ >>> add(a, b) == NewAdd(a, b)
+ True
+
+ """
+ def __init__(self, name, doc=None):
+ self.name = name
+ self.doc = doc
+ self.handlerattr = "_%s_handler" % name
+ self._handlergetter = attrgetter(self.handlerattr)
+ self._dispatcher = Dispatcher(name)
+
+ def __repr__(self):
+ return "<dispatched %s>" % self.name
+
+ def register_handlerclass(self, classes, typ, on_ambiguity=ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup):
+ """
+ Register the handler class for two classes, in both straight and reversed order.
+
+ Paramteters
+ ===========
+
+ classes : tuple of two types
+ Classes who are compared with each other.
+
+ typ:
+ Class which is registered to represent *cls1* and *cls2*.
+ Handler method of *self* must be implemented in this class.
+ """
+ if not len(classes) == 2:
+ raise RuntimeError(
+ "Only binary dispatch is supported, but got %s types: <%s>." % (
+ len(classes), str_signature(classes)
+ ))
+ if len(set(classes)) == 1:
+ raise RuntimeError(
+ "Duplicate types <%s> cannot be dispatched." % str_signature(classes)
+ )
+ self._dispatcher.add(tuple(classes), typ, on_ambiguity=on_ambiguity)
+ self._dispatcher.add(tuple(reversed(classes)), typ, on_ambiguity=on_ambiguity)
+
+ @cacheit
+ def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
+ """
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ *args :
+ Arguments which are operated
+ """
+ if kwargs.get('_sympify', True):
+ args = tuple(map(_sympify, args))
+ handlers = frozenset(map(self._handlergetter, args))
+
+ # If _sympify=True was passed, no need to sympify again so pass _sympify=False.
+ # If _sympify=False was passed, all args are already sympified so pass _sympify=False.
+ kwargs.update(_sympify=False)
+ return self.dispatch(handlers)(*args, **kwargs)
+
+ @cacheit
+ def dispatch(self, handlers):
+ """
+ Select the handler class, and return its handler method.
+ """
+
+ # Quick exit for the case where all handlers are same
+ if len(handlers) == 1:
+ h, = handlers
+ if not isinstance(h, type):
+ raise RuntimeError("Handler {!r} is not a type.".format(h))
+ return h
+
+ # Recursively select with registered binary priority
+ for i, typ in enumerate(handlers):
+
+ if not isinstance(typ, type):
+ raise RuntimeError("Handler {!r} is not a type.".format(typ))
+
+ if i == 0:
+ handler = typ
+ else:
+ prev_handler = handler
+ handler = self._dispatcher.dispatch(prev_handler, typ)
+
+ if not isinstance(handler, type):
+ raise RuntimeError(
+ "Dispatcher for {!r} and {!r} must return a type, but got {!r}".format(
+ prev_handler, typ, handler
+ ))
+
+ # return handler class
+ return handler
+
+ @property
+ def __doc__(self):
+ docs = [
+ "Multiply dispatched associative operator: %s" % self.name,
+ "Note that support for this is experimental, see the docs for :class:`AssocOpDispatcher` for details"
+ ]
+
+ if self.doc:
+ docs.append(self.doc)
+
+ s = "Registered handler classes\n"
+ s += '=' * len(s)
+ docs.append(s)
+
+ amb_sigs = []
+
+ typ_sigs = defaultdict(list)
+ for sigs in self._dispatcher.ordering[::-1]:
+ key = self._dispatcher.funcs[sigs]
+ typ_sigs[key].append(sigs)
+
+ for typ, sigs in typ_sigs.items():
+
+ sigs_str = ', '.join('<%s>' % str_signature(sig) for sig in sigs)
+
+ if isinstance(typ, RaiseNotImplementedError):
+ amb_sigs.append(sigs_str)
+ continue
+
+ s = 'Inputs: %s\n' % sigs_str
+ s += '-' * len(s) + '\n'
+ s += typ.__name__
+ docs.append(s)
+
+ if amb_sigs:
+ s = "Ambiguous handler classes\n"
+ s += '=' * len(s)
+ docs.append(s)
+
+ s = '\n'.join(amb_sigs)
+ docs.append(s)
+
+ return '\n\n'.join(docs)
diff --git a/sympy/core/power.py b/sympy/core/power.py
index 0a3b8b564c42..6a610be5ad60 100644
--- a/sympy/core/power.py
+++ b/sympy/core/power.py
@@ -12,6 +12,7 @@
from .parameters import global_parameters
from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift
from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning
+from sympy.multipledispatch import Dispatcher
from mpmath.libmp import sqrtrem as mpmath_sqrtrem
@@ -1732,6 +1733,8 @@ def _eval_difference_delta(self, n, step):
new_e = e.subs(n, n + step)
return (b**(new_e - e) - 1) * self
+power = Dispatcher('power')
+power.add((object, object), Pow)
from .add import Add
from .numbers import Integer
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_operations.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_operations.py
index 7555398f4395..6f07446bd17a 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_operations.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_operations.py
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
-from sympy import Integer, S, symbols, Mul
+from sympy import Integer, S, Symbol, symbols, Expr
from sympy.core.operations import AssocOp, LatticeOp
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
from sympy.core.sympify import SympifyError
-from sympy.core.add import Add
+from sympy.core.add import Add, add
+from sympy.core.mul import Mul, mul
# create the simplest possible Lattice class
@@ -64,3 +65,43 @@ class MyAssoc(AssocOp):
assert v.args == (u, d)
# like Add, any unevaluated outer call will flatten inner args
assert MyAssoc(a, v).args == (a, b, c, d)
+
+
+def test_add_dispatcher():
+
+ class NewBase(Expr):
+ @property
+ def _add_handler(self):
+ return NewAdd
+ class NewAdd(NewBase, Add):
+ pass
+ add.register_handlerclass((Add, NewAdd), NewAdd)
+
+ a, b = Symbol('a'), NewBase()
+
+ # Add called as fallback
+ assert add(1, 2) == Add(1, 2)
+ assert add(a, a) == Add(a, a)
+
+ # selection by registered priority
+ assert add(a,b,a) == NewAdd(2*a, b)
+
+
+def test_mul_dispatcher():
+
+ class NewBase(Expr):
+ @property
+ def _mul_handler(self):
+ return NewMul
+ class NewMul(NewBase, Mul):
+ pass
+ mul.register_handlerclass((Mul, NewMul), NewMul)
+
+ a, b = Symbol('a'), NewBase()
+
+ # Mul called as fallback
+ assert mul(1, 2) == Mul(1, 2)
+ assert mul(a, a) == Mul(a, a)
+
+ # selection by registered priority
+ assert mul(a,b,a) == NewMul(a**2, b)
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py
index 6aa6ef2e57cc..413fbd453217 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_power.py
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
from sympy.series.order import O
from sympy.sets import FiniteSet
from sympy.core.expr import unchanged
-
+from sympy.core.power import power
from sympy.testing.pytest import warns_deprecated_sympy
@@ -555,3 +555,27 @@ def test_issue_18762():
e, p = symbols('e p')
g0 = sqrt(1 + e**2 - 2*e*cos(p))
assert len(g0.series(e, 1, 3).args) == 4
+
+def test_power_dispatcher():
+
+ class NewBase(Expr):
+ pass
+ class NewPow(NewBase, Pow):
+ pass
+ a, b = Symbol('a'), NewBase()
+
+ @power.register(Expr, NewBase)
+ @power.register(NewBase, Expr)
+ @power.register(NewBase, NewBase)
+ def _(a, b):
+ return NewPow(a, b)
+
+ # Pow called as fallback
+ assert power(2, 3) == 8*S.One
+ assert power(a, 2) == Pow(a, 2)
+ assert power(a, a) == Pow(a, a)
+
+ # NewPow called by dispatch
+ assert power(a, b) == NewPow(a, b)
+ assert power(b, a) == NewPow(b, a)
+ assert power(b, b) == NewPow(b, b)
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py
index d8e6704b2996..3db532c341a9 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
from sympy.core.compatibility import reduce
-from operator import add
+import operator
from sympy.core import Add, Basic, sympify
+from sympy.core.add import add
from sympy.functions import adjoint
from sympy.matrices.common import ShapeError
from sympy.matrices.matrices import MatrixBase
@@ -85,6 +86,7 @@ def _eval_derivative_matrix_lines(self, x):
add_lines = [arg._eval_derivative_matrix_lines(x) for arg in self.args]
return [j for i in add_lines for j in i]
+add.register_handlerclass((Add, MatAdd), MatAdd)
def validate(*args):
if not all(arg.is_Matrix for arg in args):
@@ -127,7 +129,7 @@ def merge_explicit(matadd):
"""
groups = sift(matadd.args, lambda arg: isinstance(arg, MatrixBase))
if len(groups[True]) > 1:
- return MatAdd(*(groups[False] + [reduce(add, groups[True])]))
+ return MatAdd(*(groups[False] + [reduce(operator.add, groups[True])]))
else:
return matadd
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
index 83596decde7d..32c9a39d7b11 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
@@ -78,6 +78,15 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
return Basic.__new__(cls, *args, **kwargs)
# The following is adapted from the core Expr object
+
+ @property
+ def _add_handler(self):
+ return MatAdd
+
+ @property
+ def _mul_handler(self):
+ return MatMul
+
def __neg__(self):
return MatMul(S.NegativeOne, self).doit()
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
index 473ed74081a2..83e8b46e71d7 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
from sympy import Number
from sympy.core import Mul, Basic, sympify, S
+from sympy.core.mul import mul
from sympy.functions import adjoint
from sympy.strategies import (rm_id, unpack, typed, flatten, exhaust,
do_one, new)
@@ -207,6 +208,7 @@ def _eval_derivative_matrix_lines(self, x):
return lines
+mul.register_handlerclass((Mul, MatMul), MatMul)
def validate(*matrices):
""" Checks for valid shapes for args of MatMul """
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py
index b4d0ec046106..d13890557cca 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py
@@ -2,24 +2,27 @@
from sympy.matrices.expressions.special import GenericZeroMatrix, ZeroMatrix
from sympy.matrices import eye, ImmutableMatrix
from sympy.core import Add, Basic, S
+from sympy.core.add import add
from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, raises
X = MatrixSymbol('X', 2, 2)
Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', 2, 2)
def test_evaluate():
- assert MatAdd(X, X, evaluate=True) == MatAdd(X, X).doit()
+ assert MatAdd(X, X, evaluate=True) == add(X, X, evaluate=True) == MatAdd(X, X).doit()
def test_sort_key():
- assert MatAdd(Y, X).doit().args == (X, Y)
+ assert MatAdd(Y, X).doit().args == add(Y, X).doit().args == (X, Y)
def test_matadd_sympify():
assert isinstance(MatAdd(eye(1), eye(1)).args[0], Basic)
+ assert isinstance(add(eye(1), eye(1)).args[0], Basic)
def test_matadd_of_matrices():
assert MatAdd(eye(2), 4*eye(2), eye(2)).doit() == ImmutableMatrix(6*eye(2))
+ assert add(eye(2), 4*eye(2), eye(2)).doit() == ImmutableMatrix(6*eye(2))
def test_doit_args():
@@ -28,7 +31,8 @@ def test_doit_args():
assert MatAdd(A, MatPow(B, 2)).doit() == A + B**2
assert MatAdd(A, MatMul(A, B)).doit() == A + A*B
assert (MatAdd(A, X, MatMul(A, B), Y, MatAdd(2*A, B)).doit() ==
- MatAdd(3*A + A*B + B, X, Y))
+ add(A, X, MatMul(A, B), Y, add(2*A, B)).doit() ==
+ MatAdd(3*A + A*B + B, X, Y))
def test_generic_identity():
@@ -40,5 +44,5 @@ def test_zero_matrix_add():
assert Add(ZeroMatrix(2, 2), ZeroMatrix(2, 2)) == ZeroMatrix(2, 2)
@XFAIL
-def test_matrix_add_with_scalar():
+def test_matrix_Add_with_scalar():
raises(TypeError, lambda: Add(0, ZeroMatrix(2, 2)))
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py
index 340dd3456db0..529be8559f13 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
from sympy.core import I, symbols, Basic, Mul, S
+from sympy.core.mul import mul
from sympy.functions import adjoint, transpose
from sympy.matrices import (Identity, Inverse, Matrix, MatrixSymbol, ZeroMatrix,
eye, ImmutableMatrix)
@@ -153,6 +154,11 @@ def test_construction_with_Mul():
assert Mul(C, D) == MatMul(C, D)
assert Mul(D, C) == MatMul(D, C)
+def test_construction_with_mul():
+ assert mul(C, D) == MatMul(C, D)
+ assert mul(D, C) == MatMul(D, C)
+ assert mul(C, D) != MatMul(D, C)
+
def test_generic_identity():
assert MatMul.identity == GenericIdentity()
assert MatMul.identity != S.One
diff --git a/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py b/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py
index 9c5f38651183..dd3a88f1fac0 100644
--- a/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py
+++ b/sympy/multipledispatch/dispatcher.py
@@ -11,6 +11,8 @@ class MDNotImplementedError(NotImplementedError):
""" A NotImplementedError for multiple dispatch """
+### Functions for on_ambiguity
+
def ambiguity_warn(dispatcher, ambiguities):
""" Raise warning when ambiguity is detected
@@ -28,6 +30,47 @@ def ambiguity_warn(dispatcher, ambiguities):
warn(warning_text(dispatcher.name, ambiguities), AmbiguityWarning)
+class RaiseNotImplementedError:
+ """Raise ``NotImplementedError`` when called."""
+
+ def __init__(self, dispatcher):
+ self.dispatcher = dispatcher
+
+ def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
+ types = tuple(type(a) for a in args)
+ raise NotImplementedError(
+ "Ambiguous signature for %s: <%s>" % (
+ self.dispatcher.name, str_signature(types)
+ ))
+
+def ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup(dispatcher, ambiguities):
+ """
+ If super signature for ambiguous types is duplicate types, ignore it.
+ Else, register instance of ``RaiseNotImplementedError`` for ambiguous types.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ dispatcher : Dispatcher
+ The dispatcher on which the ambiguity was detected
+ ambiguities : set
+ Set of type signature pairs that are ambiguous within this dispatcher
+
+ See Also:
+ Dispatcher.add
+ ambiguity_warn
+ """
+ for amb in ambiguities:
+ signature = tuple(super_signature(amb))
+ if len(set(signature)) == 1:
+ continue
+ dispatcher.add(
+ signature, RaiseNotImplementedError(dispatcher),
+ on_ambiguity=ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup
+ )
+
+###
+
+
_unresolved_dispatchers = set() # type: Set[Dispatcher]
_resolve = [True]
diff --git a/sympy/multipledispatch/tests/test_dispatcher.py b/sympy/multipledispatch/tests/test_dispatcher.py
index b980a8b19afc..437ae02597c6 100644
--- a/sympy/multipledispatch/tests/test_dispatcher.py
+++ b/sympy/multipledispatch/tests/test_dispatcher.py
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
from sympy.multipledispatch.dispatcher import (Dispatcher, MDNotImplementedError,
MethodDispatcher, halt_ordering,
- restart_ordering)
+ restart_ordering,
+ ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup)
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, warns
@@ -262,3 +263,22 @@ def _(a):
raise MDNotImplementedError()
assert raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: f(1.0))
+
+def test_ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup():
+ f = Dispatcher('f')
+
+ class A:
+ pass
+ class B(A):
+ pass
+ class C(A):
+ pass
+
+ # suppress warning for registering ambiguous signal
+ f.add((A, B), lambda x,y: None, ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup)
+ f.add((B, A), lambda x,y: None, ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup)
+ f.add((A, C), lambda x,y: None, ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup)
+ f.add((C, A), lambda x,y: None, ambiguity_register_error_ignore_dup)
+
+ # raises error if ambiguous signal is passed
+ assert raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: f(B(), C()))
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Code Refactoring / Architectural Improvement"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-19485@9615d1f
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,485
|
feat(polys): Add Gaussian domains to Poly
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19579
Follows on from #15396
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Add the Gaussian domains to Poly so that they are used when appropriate e.g.:
```julia
In [1]: Poly(I*x, x)
Out[1]: Poly(I*x, x, domain='ZZ_I')
```
#### Other comments
There are still some problems here most notably this line
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/46469d714a095fde59f9c4d83aaa528c68b0be0f/sympy/polys/euclidtools.py#L996
because `is_negative` does not work in the Gaussian domains.
Also there needs to be an `lcm` function for Gaussian domains.
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-06-03T22:50:42Z
|
Gaussian integer division raises TypeError
Gaussian integer division raises error when `auto=True` is enabled, which is default behavior.
```python3
>>> from sympy import *
>>> from sympy.polys.domains.gaussiandomains import ZZ_I, QQ_I
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> p = Poly(2+3*I, x, domain=ZZ_I)
>>> q = Poly(1-I, x, domain=ZZ_I)
>>> p.div(q, auto=False)
(Poly(0, x, domain='ZZ_I'), Poly(2 + 3*I, x, domain='ZZ_I'))
>>> p.div(q, auto=True)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "C:\Users\sylee\Documents\Github\sympy\sympy\polys\polytools.py", line 1663, in div
F, G = F.to_field(), G.to_field()
File "C:\Users\sylee\Documents\Github\sympy\sympy\polys\polyclasses.py", line 289, in to_field
return f.convert(f.dom.get_field())
File "C:\Users\sylee\Documents\Github\sympy\sympy\polys\polyclasses.py", line 300, in convert
return DMP(dmp_convert(f.rep, f.lev, f.dom, dom), dom, f.lev)
File "C:\Users\sylee\Documents\Github\sympy\sympy\polys\densebasic.py", line 562, in dmp_convert
return dup_convert(f, K0, K1)
File "C:\Users\sylee\Documents\Github\sympy\sympy\polys\densebasic.py", line 539, in dup_convert
return dup_strip([ K1.convert(c, K0) for c in f ])
File "C:\Users\sylee\Documents\Github\sympy\sympy\polys\densebasic.py", line 539, in <listcomp>
return dup_strip([ K1.convert(c, K0) for c in f ])
TypeError: convert() takes 2 positional arguments but 3 were given
```
It works fine with Gaussian rationals.
```python3
>>> p = Poly(2+3*I, x, domain=QQ_I)
>>> q = Poly(1-I, x, domain=QQ_I)
>>> p.div(q, auto=True)
(Poly(-1/2 + 5*I/2, x, domain='QQ_I'), Poly(0, x, domain='QQ_I'))
>>> p.div(q, auto=False)
(Poly(-1/2 + 5*I/2, x, domain='QQ_I'), Poly(0, x, domain='QQ_I'))
```
|
[
{
"body": "Gaussian integer division raises error when `auto=True` is enabled, which is default behavior. \r\n```python3\r\n>>> from sympy import *\r\n>>> from sympy.polys.domains.gaussiandomains import ZZ_I, QQ_I\r\n>>> x = Symbol('x')\r\n>>> p = Poly(2+3*I, x, domain=ZZ_I)\r\n>>> q = Poly(1-I, x, domain=ZZ_I)\r\n>>> p.div(q, auto=False)\r\n(Poly(0, x, domain='ZZ_I'), Poly(2 + 3*I, x, domain='ZZ_I'))\r\n>>> p.div(q, auto=True)\r\nTraceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"<stdin>\", line 1, in <module>\r\n File \"C:\\Users\\sylee\\Documents\\Github\\sympy\\sympy\\polys\\polytools.py\", line 1663, in div\r\n F, G = F.to_field(), G.to_field()\r\n File \"C:\\Users\\sylee\\Documents\\Github\\sympy\\sympy\\polys\\polyclasses.py\", line 289, in to_field\r\n return f.convert(f.dom.get_field())\r\n File \"C:\\Users\\sylee\\Documents\\Github\\sympy\\sympy\\polys\\polyclasses.py\", line 300, in convert\r\n return DMP(dmp_convert(f.rep, f.lev, f.dom, dom), dom, f.lev)\r\n File \"C:\\Users\\sylee\\Documents\\Github\\sympy\\sympy\\polys\\densebasic.py\", line 562, in dmp_convert\r\n return dup_convert(f, K0, K1)\r\n File \"C:\\Users\\sylee\\Documents\\Github\\sympy\\sympy\\polys\\densebasic.py\", line 539, in dup_convert\r\n return dup_strip([ K1.convert(c, K0) for c in f ])\r\n File \"C:\\Users\\sylee\\Documents\\Github\\sympy\\sympy\\polys\\densebasic.py\", line 539, in <listcomp>\r\n return dup_strip([ K1.convert(c, K0) for c in f ])\r\nTypeError: convert() takes 2 positional arguments but 3 were given\r\n```\r\n\r\nIt works fine with Gaussian rationals. \r\n```python3\r\n>>> p = Poly(2+3*I, x, domain=QQ_I)\r\n>>> q = Poly(1-I, x, domain=QQ_I)\r\n>>> p.div(q, auto=True)\r\n(Poly(-1/2 + 5*I/2, x, domain='QQ_I'), Poly(0, x, domain='QQ_I'))\r\n>>> p.div(q, auto=False)\r\n(Poly(-1/2 + 5*I/2, x, domain='QQ_I'), Poly(0, x, domain='QQ_I'))\r\n```",
"number": 19579,
"title": "Gaussian integer division raises TypeError"
}
] |
25e8a795088c33abfa68021e2a5f22a4fc312447
|
{
"head_commit": "9615d1fd7005e50e5e6739b5f93f43d5a83e08f0",
"head_commit_message": "feat(polys): Add Gaussian domains to Poly\n\nUse AlgebraicField instead of the Gaussian domains for factoring in\napart. The factorisation algorithms are not provided for Gaussian\ndomains yet.",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/__init__.py b/sympy/__init__.py\nindex 4603b62f94eb..d7d1863af367 100644\n--- a/sympy/__init__.py\n+++ b/sympy/__init__.py\n@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ def __sympy_debug():\n GMPYFiniteField, PythonIntegerRing, GMPYIntegerRing, PythonRational,\n GMPYRationalField, AlgebraicField, PolynomialRing, FractionField,\n ExpressionDomain, FF_python, FF_gmpy, ZZ_python, ZZ_gmpy, QQ_python,\n- QQ_gmpy, GF, FF, ZZ, QQ, RR, CC, EX, construct_domain,\n+ QQ_gmpy, GF, FF, ZZ, QQ, ZZ_I, QQ_I, RR, CC, EX, construct_domain,\n swinnerton_dyer_poly, cyclotomic_poly, symmetric_poly, random_poly,\n interpolating_poly, jacobi_poly, chebyshevt_poly, chebyshevu_poly,\n hermite_poly, legendre_poly, laguerre_poly, apart, apart_list,\n@@ -314,7 +314,7 @@ def __sympy_debug():\n 'GMPYIntegerRing', 'PythonRational', 'GMPYRationalField',\n 'AlgebraicField', 'PolynomialRing', 'FractionField', 'ExpressionDomain',\n 'FF_python', 'FF_gmpy', 'ZZ_python', 'ZZ_gmpy', 'QQ_python', 'QQ_gmpy',\n- 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'RR', 'CC', 'EX', 'construct_domain',\n+ 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'ZZ_I', 'QQ_I', 'RR', 'CC', 'EX', 'construct_domain',\n 'swinnerton_dyer_poly', 'cyclotomic_poly', 'symmetric_poly',\n 'random_poly', 'interpolating_poly', 'jacobi_poly', 'chebyshevt_poly',\n 'chebyshevu_poly', 'hermite_poly', 'legendre_poly', 'laguerre_poly',\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/__init__.py b/sympy/polys/__init__.py\nindex 40ec0acb5879..0ad0d9014290 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/__init__.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/__init__.py\n@@ -41,7 +41,8 @@\n 'PythonIntegerRing', 'GMPYIntegerRing', 'PythonRational',\n 'GMPYRationalField', 'AlgebraicField', 'PolynomialRing', 'FractionField',\n 'ExpressionDomain', 'FF_python', 'FF_gmpy', 'ZZ_python', 'ZZ_gmpy',\n- 'QQ_python', 'QQ_gmpy', 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'RR', 'CC', 'EX',\n+ 'QQ_python', 'QQ_gmpy', 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'ZZ_I', 'QQ_I', 'RR',\n+ 'CC', 'EX',\n \n 'construct_domain',\n \n@@ -101,7 +102,7 @@\n PythonIntegerRing, GMPYIntegerRing, PythonRational, GMPYRationalField,\n AlgebraicField, PolynomialRing, FractionField, ExpressionDomain,\n FF_python, FF_gmpy, ZZ_python, ZZ_gmpy, QQ_python, QQ_gmpy, GF, FF,\n- ZZ, QQ, RR, CC, EX)\n+ ZZ, QQ, ZZ_I, QQ_I, RR, CC, EX)\n \n from .constructor import construct_domain\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/constructor.py b/sympy/polys/constructor.py\nindex 12d9de96e9ae..a04306741408 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/constructor.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/constructor.py\n@@ -3,7 +3,9 @@\n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n from sympy.core import sympify\n+from sympy.core.evalf import pure_complex\n from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ, EX\n+from sympy.polys.domains.gaussiandomains import ZZ_I, QQ_I\n from sympy.polys.domains.realfield import RealField\n from sympy.polys.polyoptions import build_options\n from sympy.polys.polyutils import parallel_dict_from_basic\n@@ -12,33 +14,44 @@\n \n def _construct_simple(coeffs, opt):\n \"\"\"Handle simple domains, e.g.: ZZ, QQ, RR and algebraic domains. \"\"\"\n- result, rationals, reals, algebraics = {}, False, False, False\n+ rationals = reals = gaussians = algebraics = False\n \n if opt.extension is True:\n is_algebraic = lambda coeff: coeff.is_number and coeff.is_algebraic\n else:\n is_algebraic = lambda coeff: False\n \n- # XXX: add support for a + b*I coefficients\n for coeff in coeffs:\n if coeff.is_Rational:\n if not coeff.is_Integer:\n rationals = True\n elif coeff.is_Float:\n- if not algebraics:\n- reals = True\n- else:\n+ if algebraics or gaussians:\n # there are both reals and algebraics -> EX\n return False\n- elif is_algebraic(coeff):\n- if not reals:\n- algebraics = True\n else:\n- # there are both algebraics and reals -> EX\n- return False\n+ reals = True\n else:\n- # this is a composite domain, e.g. ZZ[X], EX\n- return None\n+ is_complex = pure_complex(coeff)\n+ if is_complex:\n+ # there are both reals and algebraics -> EX\n+ if reals:\n+ return False\n+ x, y = is_complex\n+ if x.is_Rational and y.is_Rational:\n+ gaussians = True\n+ if not (x.is_Integer and y.is_Integer):\n+ rationals = True\n+ continue\n+ if is_algebraic(coeff):\n+ if not reals:\n+ algebraics = True\n+ else:\n+ # there are both algebraics and reals -> EX\n+ return False\n+ else:\n+ # this is a composite domain, e.g. ZZ[X], EX\n+ return None\n \n if algebraics:\n domain, result = _construct_algebraic(coeffs, opt)\n@@ -50,9 +63,9 @@ def _construct_simple(coeffs, opt):\n domain = RealField(prec=max_prec)\n else:\n if opt.field or rationals:\n- domain = QQ\n+ domain = QQ_I if gaussians else QQ\n else:\n- domain = ZZ\n+ domain = ZZ_I if gaussians else ZZ\n \n result = []\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/__init__.py b/sympy/polys/domains/__init__.py\nindex 928938af6c9e..3263e68545ff 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/__init__.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/__init__.py\n@@ -1,11 +1,15 @@\n \"\"\"Implementation of mathematical domains. \"\"\"\n \n-__all__ = ['Domain', 'FiniteField', 'IntegerRing', 'RationalField',\n- 'RealField', 'ComplexField', 'PythonFiniteField',\n- 'GMPYFiniteField', 'PythonIntegerRing',\n- 'GMPYIntegerRing', 'PythonRational',\n- 'GMPYRationalField', 'AlgebraicField', 'PolynomialRing',\n- 'FractionField', 'ExpressionDomain', 'PythonRational']\n+__all__ = [\n+ 'Domain', 'FiniteField', 'IntegerRing', 'RationalField', 'RealField',\n+ 'ComplexField', 'PythonFiniteField', 'GMPYFiniteField',\n+ 'PythonIntegerRing', 'GMPYIntegerRing', 'PythonRational',\n+ 'GMPYRationalField', 'AlgebraicField', 'PolynomialRing', 'FractionField',\n+ 'ExpressionDomain', 'PythonRational',\n+\n+ 'FF_python', 'FF_gmpy', 'ZZ_python', 'ZZ_gmpy', 'QQ_python', 'QQ_gmpy',\n+ 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'ZZ_I', 'QQ_I', 'RR', 'CC', 'EX',\n+]\n \n from .domain import Domain\n from .finitefield import FiniteField\n@@ -49,13 +53,9 @@\n except KeyError:\n raise ValueError(\"invalid ground types: %s\" % GROUND_TYPES)\n \n+# Needs to be after ZZ and QQ are defined:\n+from .gaussiandomains import ZZ_I, QQ_I\n+\n GF = FF\n \n EX = ExpressionDomain()\n-\n-__all__.extend([\n- \"FF_python\", \"FF_gmpy\",\n- \"ZZ_python\", \"ZZ_gmpy\",\n- \"QQ_python\", \"QQ_gmpy\",\n- \"GF\", \"FF\", \"ZZ\", \"QQ\", \"RR\", \"CC\", \"EX\",\n-])\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/algebraicfield.py b/sympy/polys/domains/algebraicfield.py\nindex 028a29e7a811..ec1135dc1425 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/algebraicfield.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/algebraicfield.py\n@@ -130,3 +130,7 @@ def denom(self, a):\n def from_AlgebraicField(K1, a, K0):\n \"\"\"Convert AlgebraicField element 'a' to another AlgebraicField \"\"\"\n return K1.from_sympy(K0.to_sympy(a))\n+\n+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):\n+ \"\"\"Convert GaussianInteger element 'a' to an AlgebraicField \"\"\"\n+ return K1.from_sympy(K0.to_sympy(a))\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/domain.py b/sympy/polys/domains/domain.py\nindex 9af62b6a8f17..31b4f64c8145 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/domain.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/domain.py\n@@ -30,6 +30,8 @@ class Domain(object):\n is_FiniteField = is_FF = False\n is_IntegerRing = is_ZZ = False\n is_RationalField = is_QQ = False\n+ is_GaussianRing = is_ZZ_I = False\n+ is_GaussianField = is_QQ_I = False\n is_RealField = is_RR = False\n is_ComplexField = is_CC = False\n is_AlgebraicField = is_Algebraic = False\n@@ -324,6 +326,20 @@ def mkinexact(cls, K0, K1):\n elif K1.is_AlgebraicField:\n return K1\n \n+ if K0.is_GaussianField:\n+ return K0\n+ if K1.is_GaussianField:\n+ return K1\n+\n+ if K0.is_GaussianRing:\n+ if K1.is_RationalField:\n+ K0 = K0.get_field()\n+ return K0\n+ if K1.is_GaussianRing:\n+ if K0.is_RationalField:\n+ K1 = K1.get_field()\n+ return K1\n+\n if K0.is_RationalField:\n return K0\n if K1.is_RationalField:\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/expressiondomain.py b/sympy/polys/domains/expressiondomain.py\nindex 9d3c88bddb11..a610775fac25 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/expressiondomain.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/expressiondomain.py\n@@ -173,6 +173,14 @@ def from_QQ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):\n \"\"\"Convert a GMPY ``mpq`` object to ``dtype``. \"\"\"\n return K1(K0.to_sympy(a))\n \n+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):\n+ \"\"\"Convert a ``GaussianRational`` object to ``dtype``. \"\"\"\n+ return K1(K0.to_sympy(a))\n+\n+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):\n+ \"\"\"Convert a ``GaussianRational`` object to ``dtype``. \"\"\"\n+ return K1(K0.to_sympy(a))\n+\n def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):\n \"\"\"Convert a mpmath ``mpf`` object to ``dtype``. \"\"\"\n return K1(K0.to_sympy(a))\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/fractionfield.py b/sympy/polys/domains/fractionfield.py\nindex 1221f5359078..53b9e9b083f1 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/fractionfield.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/fractionfield.py\n@@ -93,6 +93,14 @@ def from_QQ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):\n \"\"\"Convert a GMPY `mpq` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))\n \n+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):\n+ \"\"\"Convert a `GaussianRational` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n+ return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))\n+\n+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):\n+ \"\"\"Convert a `GaussianInteger` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n+ return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))\n+\n def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):\n \"\"\"Convert a mpmath `mpf` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/gaussiandomains.py b/sympy/polys/domains/gaussiandomains.py\nindex ee1bc87f094a..80eb0728f599 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/gaussiandomains.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/gaussiandomains.py\n@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@\n \"\"\"Domains of Gaussian type.\"\"\"\n \n from sympy.core.basic import Basic\n-from sympy.core.numbers import I\n+from sympy.core.numbers import Rational, I\n from sympy.polys.polyerrors import CoercionFailed\n from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ\n+from sympy.polys.domains.algebraicfield import AlgebraicField\n from sympy.polys.domains.domainelement import DomainElement\n from sympy.polys.domains.field import Field\n from sympy.polys.domains.ring import Ring\n@@ -16,11 +17,14 @@ class GaussianElement(DomainElement):\n \n __slots__ = ('x', 'y')\n \n- def __init__(self, x, y):\n+ def __init__(self, x, y=0):\n conv = self.base.convert\n self.x = conv(x)\n self.y = conv(y)\n \n+ def as_expr(self):\n+ return Rational(self.x) + I * Rational(self.y)\n+\n def parent(self):\n return self._parent\n \n@@ -79,9 +83,21 @@ def __mul__(self, other):\n if x is not None:\n return self.__class__(self.x*x - self.y*y,\n self.x*y + self.y*x)\n+ else:\n+ return NotImplemented\n \n __rmul__ = __mul__\n \n+ def __pow__(self, exp):\n+ if exp == 0:\n+ return self.__class__(1, 0)\n+ if exp < 0:\n+ self, exp = 1/self, -exp\n+ prod = self\n+ for n in range(exp-1):\n+ prod *= self\n+ return prod\n+\n def __bool__(self):\n return bool(self.x) or bool(self.y)\n \n@@ -239,7 +255,7 @@ def from_sympy(self, a):\n else:\n raise CoercionFailed(\"{} is not Gaussian\".format(a))\n \n- def convert(self, element):\n+ def convert(self, element, base=None):\n \"\"\"Convert ``element`` to ``self.dtype``.\n \n Raises CoercionFailed on failure.\n@@ -253,6 +269,32 @@ def convert(self, element):\n else: # convertible to base type or failure\n return self.new(element, 0)\n \n+ def inject(self, *gens):\n+ \"\"\"Inject generators into this domain. \"\"\"\n+ return self.poly_ring(*gens)\n+\n+ def as_AlgebraicField(self):\n+ \"\"\"Get equivalent domain as an ``AlgebraicField``. \"\"\"\n+ return AlgebraicField(self.base, I)\n+\n+ # Override the negative etc handlers because this isn't an ordered domain.\n+\n+ def is_negative(self, element):\n+ \"\"\"Returns ``False`` for any ``GaussianElement``. \"\"\"\n+ return False\n+\n+ def is_positive(self, element):\n+ \"\"\"Returns ``False`` for any ``GaussianElement``. \"\"\"\n+ return False\n+\n+ def is_nonnegative(self, element):\n+ \"\"\"Returns ``False`` for any ``GaussianElement``. \"\"\"\n+ return False\n+\n+ def is_nonpositive(self, element):\n+ \"\"\"Returns ``False`` for any ``GaussianElement``. \"\"\"\n+ return False\n+\n \n class GaussianIntegerRing(GaussianDomain, Ring):\n \"\"\"Ring of Gaussian integers.\"\"\"\n@@ -265,6 +307,9 @@ class GaussianIntegerRing(GaussianDomain, Ring):\n \n rep = 'ZZ_I'\n \n+ is_GaussianRing = True\n+ is_ZZ_I = True\n+\n def __init__(self): # override Domain.__init__\n \"\"\"For constructing ZZ_I.\"\"\"\n \n@@ -291,6 +336,9 @@ def gcd(self, a, b):\n a, b = b, a % b\n return self.normalize(a)\n \n+ def lcm(self, a, b):\n+ return (a * b) // self.gcd(a, b)\n+\n ZZ_I = GaussianInteger._parent = GaussianIntegerRing()\n \n \n@@ -303,6 +351,9 @@ class GaussianRationalField(GaussianDomain, Field):\n \n rep = 'QQ_I'\n \n+ is_GaussianField = True\n+ is_QQ_I = True\n+\n def __init__(self): # override Domain.__init__\n \"\"\"For constructing QQ_I.\"\"\"\n \n@@ -314,4 +365,12 @@ def get_field(self):\n \"\"\"Returns a field associated with ``self``. \"\"\"\n return self\n \n+ def denom(self, a):\n+ \"\"\"Get the denominator of ``a``.\"\"\"\n+ ZZ = self.base.get_ring()\n+ QQ = self.base\n+ ZZ_I = self.get_ring()\n+ denom_ZZ = ZZ.lcm(QQ.denom(a.x), QQ.denom(a.y))\n+ return ZZ_I(denom_ZZ, ZZ.zero)\n+\n QQ_I = GaussianRational._parent = GaussianRationalField()\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyintegerring.py b/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyintegerring.py\nindex 523d9a6d8fdc..20d24735557f 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyintegerring.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyintegerring.py\n@@ -70,6 +70,10 @@ def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):\n if q == 1:\n return GMPYInteger(p)\n \n+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):\n+ if a.y == 0:\n+ return a.x\n+\n def gcdex(self, a, b):\n \"\"\"Compute extended GCD of ``a`` and ``b``. \"\"\"\n h, s, t = gmpy_gcdex(a, b)\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyrationalfield.py b/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyrationalfield.py\nindex 086e659ff354..069e42aae53e 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyrationalfield.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyrationalfield.py\n@@ -59,6 +59,11 @@ def from_QQ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):\n \"\"\"Convert a GMPY `mpq` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n return a\n \n+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):\n+ \"\"\"Convert a `GaussianElement` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n+ if a.y == 0:\n+ return GMPYRational(a.x)\n+\n def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):\n \"\"\"Convert a mpmath `mpf` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n return GMPYRational(*map(int, K0.to_rational(a)))\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/polynomialring.py b/sympy/polys/domains/polynomialring.py\nindex d23bafea0ee2..cb499dce626b 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/polynomialring.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/polynomialring.py\n@@ -92,6 +92,14 @@ def from_QQ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):\n \"\"\"Convert a GMPY `mpq` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))\n \n+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):\n+ \"\"\"Convert a `GaussianInteger` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n+ return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))\n+\n+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):\n+ \"\"\"Convert a `GaussianRational` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n+ return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))\n+\n def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):\n \"\"\"Convert a mpmath `mpf` object to `dtype`. \"\"\"\n return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/partfrac.py b/sympy/polys/partfrac.py\nindex ee5ffdc6403c..183759298f2e 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/partfrac.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/partfrac.py\n@@ -116,6 +116,16 @@ def apart(f, x=None, full=False, **options):\n pass\n return f.xreplace(dict(reps))\n \n+ # Factorization over ZZ_I or QQ_I is not supported so we use the\n+ # factorization routines for AlgebraicField instead.\n+ dom = P.domain\n+ if dom.is_ZZ_I or dom.is_QQ_I:\n+ if dom.is_ZZ_I:\n+ dom = dom.get_field()\n+ dom_alg = dom.as_AlgebraicField()\n+ P = P.per(P.rep.convert(dom_alg))\n+ Q = Q.per(Q.rep.convert(dom_alg))\n+\n if P.is_multivariate:\n fc = f.cancel()\n if fc != f:\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/polyoptions.py b/sympy/polys/polyoptions.py\nindex 399588be0bce..d138ea06b84b 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/polyoptions.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/polyoptions.py\n@@ -423,6 +423,12 @@ def preprocess(cls, domain):\n if domain in ['Q', 'QQ']:\n return sympy.polys.domains.QQ\n \n+ if domain == 'ZZ_I':\n+ return sympy.polys.domains.ZZ_I\n+\n+ if domain == 'QQ_I':\n+ return sympy.polys.domains.QQ_I\n+\n if domain == 'EX':\n return sympy.polys.domains.EX\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/polyroots.py b/sympy/polys/polyroots.py\nindex 979b27483bee..9f985b176fa5 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/polyroots.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/polyroots.py\n@@ -18,6 +18,7 @@\n from sympy.functions import exp, sqrt, im, cos, acos, Piecewise\n from sympy.functions.elementary.miscellaneous import root\n from sympy.ntheory import divisors, isprime, nextprime\n+from sympy.polys.domains import EX\n from sympy.polys.polyerrors import (PolynomialError, GeneratorsNeeded,\n DomainError)\n from sympy.polys.polyquinticconst import PolyQuintic\n@@ -970,6 +971,10 @@ def _try_heuristics(f):\n \n return result\n \n+ # Convert the generators to symbols\n+ dumgens = symbols('x:%d' % len(f.gens), cls=Dummy)\n+ f = f.per(f.rep, dumgens)\n+\n (k,), f = f.terms_gcd()\n \n if not k:\n@@ -982,6 +987,10 @@ def _try_heuristics(f):\n if auto and f.get_domain().is_Ring:\n f = f.to_field()\n \n+ # Use EX instead of ZZ_I or QQ_I\n+ if f.get_domain().is_QQ_I:\n+ f = f.per(f.rep.convert(EX))\n+\n rescale_x = None\n translate_x = None\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py\nindex 911a0b10ad6c..42884149182c 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py\n@@ -372,8 +372,8 @@ def test_Poly():\n assert str(\n Poly(x**2 - 1 + y, x)) == \"Poly(x**2 + y - 1, x, domain='ZZ[y]')\"\n \n- assert str(Poly(x**2 + I*x, x)) == \"Poly(x**2 + I*x, x, domain='EX')\"\n- assert str(Poly(x**2 - I*x, x)) == \"Poly(x**2 - I*x, x, domain='EX')\"\n+ assert str(Poly(x**2 + I*x, x)) == \"Poly(x**2 + I*x, x, domain='ZZ_I')\"\n+ assert str(Poly(x**2 - I*x, x)) == \"Poly(x**2 - I*x, x, domain='ZZ_I')\"\n \n assert str(Poly(-x*y*z + x*y - 1, x, y, z)\n ) == \"Poly(-x*y*z + x*y - 1, x, y, z, domain='ZZ')\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -116,6 +116,16 @@ def apart(f, x=None, full=False, **options):\n pass\n return f.xreplace(dict(reps))\n \n+ # Factorization over ZZ_I or QQ_I is not supported so we use the\n+ # factorization routines for AlgebraicField instead.\n+ dom = P.domain\n+ if dom.is_ZZ_I or dom.is_QQ_I:\n+ if dom.is_ZZ_I:\n+ dom = dom.get_field()\n+ dom_alg = dom.as_AlgebraicField()\n+ P = P.per(P.rep.convert(dom_alg))\n+ Q = Q.per(Q.rep.convert(dom_alg))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 127,
"original_start_line": 119,
"path": "sympy/polys/partfrac.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@author:\nFactorisation over `ZZ_I` and `QQ_I` does not work so I've prevented them from being used in `apart` here. Instead `QQ<I>` will be used.\r\n```julia\r\nIn [16]: p1 = Poly(x**2 + 1, x) \r\n\r\nIn [17]: p2 = Poly(x**2 + 1, x, domain=QQ_I.as_AlgebraicField()) \r\n\r\nIn [18]: p1.factor_list() \r\nOut[18]: (1, [(Poly(x**2 + 1, x, domain='ZZ'), 1)])\r\n\r\nIn [19]: p2.factor_list() \r\nOut[19]: (1, [(Poly(x - I, x, domain='QQ<I>'), 1), (Poly(x + I, x, domain='QQ<I>'), 1)])\r\n```\r\nWould it be better to make factorisation over `QQ_I` and `ZZ_I` work?\r\n\r\nI wonder if it's possible to make `dup/dmp` treat `QQ_I` as an algebraic field when factorising. I guess that factorising over `ZZ_I` is harder...\r\n\n\n@user1:\n> Would it be better to make factorisation over `QQ_I` and `ZZ_I` work?\r\n\r\nI think that `QQ_I` should be replaced by `QQ<I>` somewhere, maybe in `dup/dmp_ext_factor`.\n\n@author:\nWould it be possible to add attributes or methods to `QQ_I` so that `dup/dmp` can treat it transparently as an algebraic field without needing any conversion?\r\n\r\nWould it make sense to have `QQ_I.is_AlgebraicField` or some other attribute that is common between `QQ_I` and the `AlgebraicField` domains?\r\n\r\nIt looks like the main attributes needed for an algebraic field are `ext` and `mod`...\n\n@user1:\nIt looks like at least new versions of `dup/dmp_sqf_norm` would be needed. `QQ_I` should have `conjugate` and the norm of `f` will be `f*cf` where `cf` is `f` with all coefficients conjugated.\n\n@author:\nWould it make sense for `ZZ_I` to factorise like `QQ_I` or perhaps like `ZZ[I]`?\r\n\r\nOn master factor can factorise in some cases by treating `I` as a generator:\r\n```julia\r\nIn [14]: e = expand((x - I)*(x + 1)) \r\n\r\nIn [15]: e \r\nOut[15]: \r\n 2 \r\nx + x - ⅈ⋅x - ⅈ\r\n\r\nIn [16]: factor(e) \r\nOut[16]: (x + 1)⋅(x - ⅈ)\r\n```\r\nThe PR currently gives:\r\n```julia\r\nIn [14]: factor(e) \r\nOut[14]: \r\n 2 \r\nx + x⋅(1 - ⅈ) - ⅈ\r\n```\n\n@user1:\nFactorizing polynomials over `ZZ_I` should be done in two steps, factorizing the primitive part over `QQ_I` and the content in `ZZ_I`.\n\n@author:\nWhat would `factor_list` return in that case?\r\n\r\nAt the moment `factor_list` returns a tuple of the content and then a list of factors of the primitive:\r\n```julia\r\nIn [21]: Poly(x**2/2 - 2, x).factor_list() \r\nOut[21]: (1/2, [(Poly(x - 2, x, domain='QQ'), 1), (Poly(x + 2, x, domain='QQ'), 1)])\r\n```\r\nIf the content itself factorises where would that go in this data structure?\r\n\r\nIs there an implementation for factorisation of gaussian integers anywhere?\r\n\r\nPerhaps if not then for now `factor_list` can return the content unfactorised...\n\n@user1:\n> Is there an implementation for factorisation of gaussian integers anywhere?\r\n\r\nNo, but that would not be hard to implement if desired. First factorize the norm in `ZZ` and then factor those prime factors that split in `ZZ_I`."
}
] |
23a1d9ccf81c5208e0f0e6aea2d86d2527cdb8f3
|
diff --git a/sympy/__init__.py b/sympy/__init__.py
index 4603b62f94eb..d7d1863af367 100644
--- a/sympy/__init__.py
+++ b/sympy/__init__.py
@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ def __sympy_debug():
GMPYFiniteField, PythonIntegerRing, GMPYIntegerRing, PythonRational,
GMPYRationalField, AlgebraicField, PolynomialRing, FractionField,
ExpressionDomain, FF_python, FF_gmpy, ZZ_python, ZZ_gmpy, QQ_python,
- QQ_gmpy, GF, FF, ZZ, QQ, RR, CC, EX, construct_domain,
+ QQ_gmpy, GF, FF, ZZ, QQ, ZZ_I, QQ_I, RR, CC, EX, construct_domain,
swinnerton_dyer_poly, cyclotomic_poly, symmetric_poly, random_poly,
interpolating_poly, jacobi_poly, chebyshevt_poly, chebyshevu_poly,
hermite_poly, legendre_poly, laguerre_poly, apart, apart_list,
@@ -314,7 +314,7 @@ def __sympy_debug():
'GMPYIntegerRing', 'PythonRational', 'GMPYRationalField',
'AlgebraicField', 'PolynomialRing', 'FractionField', 'ExpressionDomain',
'FF_python', 'FF_gmpy', 'ZZ_python', 'ZZ_gmpy', 'QQ_python', 'QQ_gmpy',
- 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'RR', 'CC', 'EX', 'construct_domain',
+ 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'ZZ_I', 'QQ_I', 'RR', 'CC', 'EX', 'construct_domain',
'swinnerton_dyer_poly', 'cyclotomic_poly', 'symmetric_poly',
'random_poly', 'interpolating_poly', 'jacobi_poly', 'chebyshevt_poly',
'chebyshevu_poly', 'hermite_poly', 'legendre_poly', 'laguerre_poly',
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
index 7fda45982bc6..caa2b781fa12 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
@@ -395,7 +395,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Heaviside(self, arg, **kwargs):
return Heaviside(arg, H0=S(1)/2) * 2 - 1
def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):
- return self.func(self.args[0].factor()) # XXX include doit?
+ return self.func(factor_terms(self.args[0])) # XXX include doit?
class Abs(Function):
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_exponential.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_exponential.py
index 058ddaa4652e..46e1d66b7b08 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_exponential.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/tests/test_exponential.py
@@ -162,7 +162,8 @@ def test_exp_rewrite():
assert Sum((exp(pi*I/2)/2)**n, (n, 0, oo)).rewrite(sqrt).doit() == Rational(4, 5) + I*Rational(2, 5)
assert Sum((exp(pi*I/4)/2)**n, (n, 0, oo)).rewrite(sqrt).doit() == 1/(1 - sqrt(2)*(1 + I)/4)
- assert Sum((exp(pi*I/3)/2)**n, (n, 0, oo)).rewrite(sqrt).doit() == 1/(Rational(3, 4) - sqrt(3)*I/4)
+ assert (Sum((exp(pi*I/3)/2)**n, (n, 0, oo)).rewrite(sqrt).doit().cancel()
+ == 4/(3 - sqrt(3)*I))
def test_exp_leading_term():
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_rde.py b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_rde.py
index feb81023e748..9f8fc4e214af 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_rde.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_rde.py
@@ -81,7 +81,9 @@ def test_special_denom():
DE.decrement_level()
assert special_denom(Poly(1, t0), Poly(I*k, t0), Poly(1, t0), Poly(t0, t0),
Poly(1, t0), DE) == \
- (Poly(1, t0), Poly(I*k, t0), Poly(t0, t0), Poly(1, t0))
+ (Poly(1, t0, domain='ZZ'), Poly(I*k, t0, domain='ZZ_I[k,x]'),
+ Poly(t0, t0, domain='ZZ'), Poly(1, t0, domain='ZZ'))
+
assert special_denom(Poly(1, t), Poly(t**2, t), Poly(1, t), Poly(t**2 - 1, t),
Poly(t, t), DE, case='tan') == \
diff --git a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_transforms.py b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_transforms.py
index 919aa1f156bd..4c3e79984ffb 100644
--- a/sympy/integrals/tests/test_transforms.py
+++ b/sympy/integrals/tests/test_transforms.py
@@ -833,6 +833,8 @@ def test_issue_8514():
- cos(t*sin(atan2(0, -4*a*c + b**2)/2)*sqrt(Abs(4*a*c -
b**2))/(2*a)))*exp(-t*(b + cos(atan2(0, -4*a*c + b**2)/2)
*sqrt(Abs(4*a*c - b**2)))/(2*a))/sqrt(-4*a*c + b**2)
+
+
def test_issue_12591():
x, y = symbols("x y", real=True)
assert fourier_transform(exp(x), x, y) == FourierTransform(exp(x), x, y)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/__init__.py b/sympy/polys/__init__.py
index 40ec0acb5879..0ad0d9014290 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/__init__.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/__init__.py
@@ -41,7 +41,8 @@
'PythonIntegerRing', 'GMPYIntegerRing', 'PythonRational',
'GMPYRationalField', 'AlgebraicField', 'PolynomialRing', 'FractionField',
'ExpressionDomain', 'FF_python', 'FF_gmpy', 'ZZ_python', 'ZZ_gmpy',
- 'QQ_python', 'QQ_gmpy', 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'RR', 'CC', 'EX',
+ 'QQ_python', 'QQ_gmpy', 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'ZZ_I', 'QQ_I', 'RR',
+ 'CC', 'EX',
'construct_domain',
@@ -101,7 +102,7 @@
PythonIntegerRing, GMPYIntegerRing, PythonRational, GMPYRationalField,
AlgebraicField, PolynomialRing, FractionField, ExpressionDomain,
FF_python, FF_gmpy, ZZ_python, ZZ_gmpy, QQ_python, QQ_gmpy, GF, FF,
- ZZ, QQ, RR, CC, EX)
+ ZZ, QQ, ZZ_I, QQ_I, RR, CC, EX)
from .constructor import construct_domain
diff --git a/sympy/polys/compatibility.py b/sympy/polys/compatibility.py
index 217a481b461a..df4b20f63849 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/compatibility.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/compatibility.py
@@ -174,6 +174,10 @@
from sympy.polys.factortools import dmp_zz_wang_hensel_lifting
from sympy.polys.factortools import dmp_zz_wang
from sympy.polys.factortools import dmp_zz_factor
+from sympy.polys.factortools import dup_qq_i_factor
+from sympy.polys.factortools import dup_zz_i_factor
+from sympy.polys.factortools import dmp_qq_i_factor
+from sympy.polys.factortools import dmp_zz_i_factor
from sympy.polys.factortools import dup_ext_factor
from sympy.polys.factortools import dmp_ext_factor
from sympy.polys.factortools import dup_gf_factor
@@ -811,6 +815,20 @@ def dmp_zz_factor(self, f):
coeff, factors = dmp_zz_factor(self.to_dense(f), self.ngens-1, self.domain)
return (coeff, [ (self.from_dense(g), k) for g, k in factors ])
+ def dup_qq_i_factor(self, f):
+ coeff, factors = dup_qq_i_factor(self.to_dense(f), self.domain)
+ return (coeff, [ (self.from_dense(g), k) for g, k in factors ])
+ def dmp_qq_i_factor(self, f):
+ coeff, factors = dmp_qq_i_factor(self.to_dense(f), self.ngens-1, self.domain)
+ return (coeff, [ (self.from_dense(g), k) for g, k in factors ])
+
+ def dup_zz_i_factor(self, f):
+ coeff, factors = dup_zz_i_factor(self.to_dense(f), self.domain)
+ return (coeff, [ (self.from_dense(g), k) for g, k in factors ])
+ def dmp_zz_i_factor(self, f):
+ coeff, factors = dmp_zz_i_factor(self.to_dense(f), self.ngens-1, self.domain)
+ return (coeff, [ (self.from_dense(g), k) for g, k in factors ])
+
def dup_ext_factor(self, f):
coeff, factors = dup_ext_factor(self.to_dense(f), self.domain)
return (coeff, [ (self.from_dense(g), k) for g, k in factors ])
diff --git a/sympy/polys/constructor.py b/sympy/polys/constructor.py
index 12d9de96e9ae..bb4125bdc1dc 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/constructor.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/constructor.py
@@ -3,7 +3,8 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
from sympy.core import sympify
-from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ, EX
+from sympy.core.evalf import pure_complex
+from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ, ZZ_I, QQ_I, EX
from sympy.polys.domains.realfield import RealField
from sympy.polys.polyoptions import build_options
from sympy.polys.polyutils import parallel_dict_from_basic
@@ -12,33 +13,44 @@
def _construct_simple(coeffs, opt):
"""Handle simple domains, e.g.: ZZ, QQ, RR and algebraic domains. """
- result, rationals, reals, algebraics = {}, False, False, False
+ rationals = reals = gaussians = algebraics = False
if opt.extension is True:
is_algebraic = lambda coeff: coeff.is_number and coeff.is_algebraic
else:
is_algebraic = lambda coeff: False
- # XXX: add support for a + b*I coefficients
for coeff in coeffs:
if coeff.is_Rational:
if not coeff.is_Integer:
rationals = True
elif coeff.is_Float:
- if not algebraics:
- reals = True
- else:
+ if algebraics or gaussians:
# there are both reals and algebraics -> EX
return False
- elif is_algebraic(coeff):
- if not reals:
- algebraics = True
else:
- # there are both algebraics and reals -> EX
- return False
+ reals = True
else:
- # this is a composite domain, e.g. ZZ[X], EX
- return None
+ is_complex = pure_complex(coeff)
+ if is_complex:
+ # there are both reals and algebraics -> EX
+ if reals:
+ return False
+ x, y = is_complex
+ if x.is_Rational and y.is_Rational:
+ gaussians = True
+ if not (x.is_Integer and y.is_Integer):
+ rationals = True
+ continue
+ if is_algebraic(coeff):
+ if not reals:
+ algebraics = True
+ else:
+ # there are both algebraics and reals -> EX
+ return False
+ else:
+ # this is a composite domain, e.g. ZZ[X], EX
+ return None
if algebraics:
domain, result = _construct_algebraic(coeffs, opt)
@@ -50,9 +62,9 @@ def _construct_simple(coeffs, opt):
domain = RealField(prec=max_prec)
else:
if opt.field or rationals:
- domain = QQ
+ domain = QQ_I if gaussians else QQ
else:
- domain = ZZ
+ domain = ZZ_I if gaussians else ZZ
result = []
@@ -164,7 +176,7 @@ def _construct_composite(coeffs, opt):
coeffs.update(list(numer.values()))
coeffs.update(list(denom.values()))
- rationals, reals = False, False
+ rationals = reals = gaussians = False
for coeff in coeffs:
if coeff.is_Rational:
@@ -173,10 +185,25 @@ def _construct_composite(coeffs, opt):
elif coeff.is_Float:
reals = True
break
+ else:
+ is_complex = pure_complex(coeff)
+ if is_complex is not None:
+ x, y = is_complex
+ if x.is_Rational and y.is_Rational:
+ if not (x.is_Integer and y.is_Integer):
+ rationals = True
+ gaussians = True
+ else:
+ pass # XXX: CC?
if reals:
max_prec = max([c._prec for c in coeffs])
ground = RealField(prec=max_prec)
+ elif gaussians:
+ if rationals:
+ ground = QQ_I
+ else:
+ ground = ZZ_I
elif rationals:
ground = QQ
else:
diff --git a/sympy/polys/densetools.py b/sympy/polys/densetools.py
index fb52236de75b..b318ba57bae3 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/densetools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/densetools.py
@@ -1112,6 +1112,11 @@ def dmp_lift(f, u, K):
x**8 + 2*x**6 + 9*x**4 - 8*x**2 + 16
"""
+ if K.is_GaussianField:
+ K1 = K.as_AlgebraicField()
+ f = dmp_convert(f, u, K, K1)
+ K = K1
+
if not K.is_Algebraic:
raise DomainError(
'computation can be done only in an algebraic domain')
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/__init__.py b/sympy/polys/domains/__init__.py
index 928938af6c9e..3263e68545ff 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/__init__.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/__init__.py
@@ -1,11 +1,15 @@
"""Implementation of mathematical domains. """
-__all__ = ['Domain', 'FiniteField', 'IntegerRing', 'RationalField',
- 'RealField', 'ComplexField', 'PythonFiniteField',
- 'GMPYFiniteField', 'PythonIntegerRing',
- 'GMPYIntegerRing', 'PythonRational',
- 'GMPYRationalField', 'AlgebraicField', 'PolynomialRing',
- 'FractionField', 'ExpressionDomain', 'PythonRational']
+__all__ = [
+ 'Domain', 'FiniteField', 'IntegerRing', 'RationalField', 'RealField',
+ 'ComplexField', 'PythonFiniteField', 'GMPYFiniteField',
+ 'PythonIntegerRing', 'GMPYIntegerRing', 'PythonRational',
+ 'GMPYRationalField', 'AlgebraicField', 'PolynomialRing', 'FractionField',
+ 'ExpressionDomain', 'PythonRational',
+
+ 'FF_python', 'FF_gmpy', 'ZZ_python', 'ZZ_gmpy', 'QQ_python', 'QQ_gmpy',
+ 'GF', 'FF', 'ZZ', 'QQ', 'ZZ_I', 'QQ_I', 'RR', 'CC', 'EX',
+]
from .domain import Domain
from .finitefield import FiniteField
@@ -49,13 +53,9 @@
except KeyError:
raise ValueError("invalid ground types: %s" % GROUND_TYPES)
+# Needs to be after ZZ and QQ are defined:
+from .gaussiandomains import ZZ_I, QQ_I
+
GF = FF
EX = ExpressionDomain()
-
-__all__.extend([
- "FF_python", "FF_gmpy",
- "ZZ_python", "ZZ_gmpy",
- "QQ_python", "QQ_gmpy",
- "GF", "FF", "ZZ", "QQ", "RR", "CC", "EX",
-])
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/algebraicfield.py b/sympy/polys/domains/algebraicfield.py
index 028a29e7a811..3a9305e4ad3c 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/algebraicfield.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/algebraicfield.py
@@ -130,3 +130,11 @@ def denom(self, a):
def from_AlgebraicField(K1, a, K0):
"""Convert AlgebraicField element 'a' to another AlgebraicField """
return K1.from_sympy(K0.to_sympy(a))
+
+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a GaussianInteger element 'a' to ``dtype``. """
+ return K1.from_sympy(K0.to_sympy(a))
+
+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a GaussianRational element 'a' to ``dtype``. """
+ return K1.from_sympy(K0.to_sympy(a))
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/domain.py b/sympy/polys/domains/domain.py
index 9af62b6a8f17..1ea0c9ea4eb2 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/domain.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/domain.py
@@ -30,6 +30,8 @@ class Domain(object):
is_FiniteField = is_FF = False
is_IntegerRing = is_ZZ = False
is_RationalField = is_QQ = False
+ is_GaussianRing = is_ZZ_I = False
+ is_GaussianField = is_QQ_I = False
is_RealField = is_RR = False
is_ComplexField = is_CC = False
is_AlgebraicField = is_Algebraic = False
@@ -304,24 +306,49 @@ def mkinexact(cls, K0, K1):
tol = max(K0.tolerance, K1.tolerance)
return cls(prec=prec, tol=tol)
- if K0.is_ComplexField and K1.is_ComplexField:
- return mkinexact(K0.__class__, K0, K1)
- if K0.is_ComplexField and K1.is_RealField:
- return mkinexact(K0.__class__, K0, K1)
- if K0.is_RealField and K1.is_ComplexField:
- return mkinexact(K1.__class__, K1, K0)
- if K0.is_RealField and K1.is_RealField:
- return mkinexact(K0.__class__, K0, K1)
- if K0.is_ComplexField or K0.is_RealField:
+ if K1.is_ComplexField:
+ K0, K1 = K1, K0
+ if K0.is_ComplexField:
+ if K1.is_ComplexField or K1.is_RealField:
+ return mkinexact(K0.__class__, K0, K1)
+ else:
+ return K0
+
+ if K1.is_RealField:
+ K0, K1 = K1, K0
+ if K0.is_RealField:
+ if K1.is_RealField:
+ return mkinexact(K0.__class__, K0, K1)
+ elif K1.is_GaussianRing or K1.is_GaussianField:
+ from sympy.polys.domains.complexfield import ComplexField
+ return ComplexField(prec=K0.precision, tol=K0.tolerance)
+ else:
+ return K0
+
+ if K1.is_AlgebraicField:
+ K0, K1 = K1, K0
+ if K0.is_AlgebraicField:
+ if K1.is_GaussianRing:
+ K1 = K1.get_field()
+ if K1.is_GaussianField:
+ K1 = K1.as_AlgebraicField()
+ if K1.is_AlgebraicField:
+ return K0.__class__(K0.dom.unify(K1.dom), *_unify_gens(K0.orig_ext, K1.orig_ext))
+ else:
+ return K0
+
+ if K0.is_GaussianField:
return K0
- if K1.is_ComplexField or K1.is_RealField:
+ if K1.is_GaussianField:
return K1
- if K0.is_AlgebraicField and K1.is_AlgebraicField:
- return K0.__class__(K0.dom.unify(K1.dom), *_unify_gens(K0.orig_ext, K1.orig_ext))
- elif K0.is_AlgebraicField:
+ if K0.is_GaussianRing:
+ if K1.is_RationalField:
+ K0 = K0.get_field()
return K0
- elif K1.is_AlgebraicField:
+ if K1.is_GaussianRing:
+ if K0.is_RationalField:
+ K1 = K1.get_field()
return K1
if K0.is_RationalField:
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/expressiondomain.py b/sympy/polys/domains/expressiondomain.py
index 9d3c88bddb11..a610775fac25 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/expressiondomain.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/expressiondomain.py
@@ -173,6 +173,14 @@ def from_QQ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):
"""Convert a GMPY ``mpq`` object to ``dtype``. """
return K1(K0.to_sympy(a))
+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a ``GaussianRational`` object to ``dtype``. """
+ return K1(K0.to_sympy(a))
+
+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a ``GaussianRational`` object to ``dtype``. """
+ return K1(K0.to_sympy(a))
+
def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):
"""Convert a mpmath ``mpf`` object to ``dtype``. """
return K1(K0.to_sympy(a))
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/fractionfield.py b/sympy/polys/domains/fractionfield.py
index 1221f5359078..53b9e9b083f1 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/fractionfield.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/fractionfield.py
@@ -93,6 +93,14 @@ def from_QQ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):
"""Convert a GMPY `mpq` object to `dtype`. """
return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))
+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a `GaussianRational` object to `dtype`. """
+ return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))
+
+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a `GaussianInteger` object to `dtype`. """
+ return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))
+
def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):
"""Convert a mpmath `mpf` object to `dtype`. """
return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/gaussiandomains.py b/sympy/polys/domains/gaussiandomains.py
index ee1bc87f094a..c75e29915e04 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/gaussiandomains.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/gaussiandomains.py
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
"""Domains of Gaussian type."""
-from sympy.core.basic import Basic
from sympy.core.numbers import I
from sympy.polys.polyerrors import CoercionFailed
from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ
+from sympy.polys.domains.algebraicfield import AlgebraicField
from sympy.polys.domains.domainelement import DomainElement
from sympy.polys.domains.field import Field
from sympy.polys.domains.ring import Ring
@@ -16,12 +16,18 @@ class GaussianElement(DomainElement):
__slots__ = ('x', 'y')
- def __init__(self, x, y):
+ def __init__(self, x, y=0):
conv = self.base.convert
self.x = conv(x)
self.y = conv(y)
+ @classmethod
+ def new(cls, x, y):
+ """Create a new GaussianElement of the same domain."""
+ return cls(x, y)
+
def parent(self):
+ """The domain that this is an element of (ZZ_I or QQ_I)"""
return self._parent
def __hash__(self):
@@ -33,11 +39,16 @@ def __eq__(self, other):
else:
return NotImplemented
+ def __lt__(self, other):
+ if not isinstance(other, GaussianElement):
+ return NotImplemented
+ return [self.y, self.x] < [other.y, other.x]
+
def __neg__(self):
- return self.__class__(-self.x, -self.y)
+ return self.new(-self.x, -self.y)
def __repr__(self):
- return "%s(%s, %s)" % (type(self).__name__, self.x, self.y)
+ return "%s(%s, %s)" % (self._parent.rep, self.x, self.y)
def __str__(self):
return str(self._parent.to_sympy(self))
@@ -54,7 +65,7 @@ def _get_xy(cls, other):
def __add__(self, other):
x, y = self._get_xy(other)
if x is not None:
- return self.__class__(self.x + x, self.y + y)
+ return self.new(self.x + x, self.y + y)
else:
return NotImplemented
@@ -63,30 +74,46 @@ def __add__(self, other):
def __sub__(self, other):
x, y = self._get_xy(other)
if x is not None:
- return self.__class__(self.x - x, self.y - y)
+ return self.new(self.x - x, self.y - y)
else:
return NotImplemented
def __rsub__(self, other):
x, y = self._get_xy(other)
if x is not None:
- return self.__class__(x - self.x, y - self.y)
+ return self.new(x - self.x, y - self.y)
else:
return NotImplemented
def __mul__(self, other):
x, y = self._get_xy(other)
if x is not None:
- return self.__class__(self.x*x - self.y*y,
- self.x*y + self.y*x)
+ return self.new(self.x*x - self.y*y, self.x*y + self.y*x)
+ else:
+ return NotImplemented
__rmul__ = __mul__
+ def __pow__(self, exp):
+ if exp == 0:
+ return self.new(1, 0)
+ if exp < 0:
+ self, exp = 1/self, -exp
+ if exp == 1:
+ return self
+ pow2 = self
+ prod = self if exp % 2 else self._parent.one
+ exp //= 2
+ while exp:
+ pow2 *= pow2
+ if exp % 2:
+ prod *= pow2
+ exp //= 2
+ return prod
+
def __bool__(self):
return bool(self.x) or bool(self.y)
- __nonzero__ = __bool__ # for Python 2
-
def quadrant(self):
"""Return quadrant index 0-3.
@@ -99,6 +126,38 @@ def quadrant(self):
else:
return 0 if self.x >= 0 else 2
+ def __rdivmod__(self, other):
+ try:
+ other = self._parent.convert(other)
+ except CoercionFailed:
+ return NotImplemented
+ else:
+ return other.__divmod__(self)
+
+ def __rtruediv__(self, other):
+ try:
+ other = QQ_I.convert(other)
+ except CoercionFailed:
+ return NotImplemented
+ else:
+ return other.__truediv__(self)
+
+ def __floordiv__(self, other):
+ qr = self.__divmod__(other)
+ return qr if qr is NotImplemented else qr[0]
+
+ def __rfloordiv__(self, other):
+ qr = self.__rdivmod__(other)
+ return qr if qr is NotImplemented else qr[0]
+
+ def __mod__(self, other):
+ qr = self.__divmod__(other)
+ return qr if qr is NotImplemented else qr[1]
+
+ def __rmod__(self, other):
+ qr = self.__rdivmod__(other)
+ return qr if qr is NotImplemented else qr[1]
+
class GaussianInteger(GaussianElement):
base = ZZ
@@ -107,13 +166,6 @@ def __truediv__(self, other):
"""Return a Gaussian rational."""
return QQ_I.convert(self)/other
- __div__ = __truediv__
-
- def __rtruediv__(self, other):
- return other/QQ_I.convert(self)
-
- __rdiv__ = __rtruediv__
-
def __divmod__(self, other):
if not other:
raise ZeroDivisionError('divmod({}, 0)'.format(self))
@@ -138,35 +190,11 @@ def __divmod__(self, other):
return q, self - q*other # |r| < |other|
- def __rdivmod__(self, other):
- try:
- other = self._parent.convert(other)
- except CoercionFailed:
- return NotImplemented
- else:
- return other.__divmod__(self)
-
- def __floordiv__(self, other):
- qr = self.__divmod__(other)
- return qr if qr is NotImplemented else qr[0]
-
- def __rfloordiv__(self, other):
- qr = self.__rdivmod__(other)
- return qr if qr is NotImplemented else qr[0]
-
- def __mod__(self, other):
- qr = self.__divmod__(other)
- return qr if qr is NotImplemented else qr[1]
-
- def __rmod__(self, other):
- qr = self.__rdivmod__(other)
- return qr if qr is NotImplemented else qr[1]
-
-
class GaussianRational(GaussianElement):
base = QQ
def __truediv__(self, other):
+ """Return a Gaussian rational."""
if not other:
raise ZeroDivisionError('{} / 0'.format(self))
x, y = self._get_xy(other)
@@ -177,19 +205,7 @@ def __truediv__(self, other):
return GaussianRational((self.x*x + self.y*y)/c,
(-self.x*y + self.y*x)/c)
- __floordiv__ = __div__ = __truediv__
-
- def __rtruediv__(self, other):
- try:
- other = self._parent.convert(other)
- except CoercionFailed:
- return NotImplemented
- else:
- return other.__truediv__(self)
-
- __rfloordiv__ = __rdiv__ = __rtruediv__
-
- def __mod__(self, other):
+ def __divmod__(self, other):
try:
other = self._parent.convert(other)
except CoercionFailed:
@@ -197,66 +213,84 @@ def __mod__(self, other):
if not other:
raise ZeroDivisionError('{} % 0'.format(self))
else:
- return self._parent.zero # XXX always 0?
-
- def __rmod__(self, other):
- try:
- other = self._parent.convert(other)
- except CoercionFailed:
- return NotImplemented
- else:
- return other.__mod__(self)
-
- def __divmod__(self, other):
- return self.__truediv__(other), self.__mod__(other)
-
- def __rdivmod__(self, other):
- return self.__rtruediv__(other), self.__rmod__(other)
+ return self/other, QQ_I.zero
class GaussianDomain():
"""Base class for Gaussian domains."""
- base = None # base domain, ZZ or QQ
+ dom = None # base domain, ZZ or QQ
+
+ is_Numerical = True
+ is_Exact = True
has_assoc_Ring = True
has_assoc_Field = True
def to_sympy(self, a):
"""Convert ``a`` to a SymPy object. """
- conv = self.base.to_sympy
+ conv = self.dom.to_sympy
return conv(a.x) + I*conv(a.y)
def from_sympy(self, a):
"""Convert a SymPy object to ``self.dtype``."""
r, b = a.as_coeff_Add()
- x = self.base.from_sympy(r) # may raise CoercionFailed
+ x = self.dom.from_sympy(r) # may raise CoercionFailed
if not b:
return self.new(x, 0)
r, b = b.as_coeff_Mul()
- y = self.base.from_sympy(r)
+ y = self.dom.from_sympy(r)
if b is I:
return self.new(x, y)
else:
raise CoercionFailed("{} is not Gaussian".format(a))
- def convert(self, element):
- """Convert ``element`` to ``self.dtype``.
+ def inject(self, *gens):
+ """Inject generators into this domain. """
+ return self.poly_ring(*gens)
- Raises CoercionFailed on failure.
- """
- if isinstance(element, self.dtype):
- return element
- elif isinstance(element, GaussianElement):
- return self.new(element.x, element.y)
- elif isinstance(element, Basic):
- return self.from_sympy(element)
- else: # convertible to base type or failure
- return self.new(element, 0)
+ # Override the negative etc handlers because this isn't an ordered domain.
+
+ def is_negative(self, element):
+ """Returns ``False`` for any ``GaussianElement``. """
+ return False
+
+ def is_positive(self, element):
+ """Returns ``False`` for any ``GaussianElement``. """
+ return False
+
+ def is_nonnegative(self, element):
+ """Returns ``False`` for any ``GaussianElement``. """
+ return False
+
+ def is_nonpositive(self, element):
+ """Returns ``False`` for any ``GaussianElement``. """
+ return False
+
+ def from_ZZ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a GMPY mpz to ``self.dtype``."""
+ return K1(a)
+
+ def from_ZZ_python(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a ZZ_python element to ``self.dtype``."""
+ return K1(a)
+
+ def from_QQ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a GMPY mpq to ``self.dtype``."""
+ return K1(a)
+
+ def from_QQ_python(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a QQ_python element to ``self.dtype``."""
+ return K1(a)
+
+ def from_AlgebraicField(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert an element from ZZ<I> or QQ<I> to ``self.dtype``."""
+ if K0.ext.args[0] == I:
+ return K1.from_sympy(K0.to_sympy(a))
class GaussianIntegerRing(GaussianDomain, Ring):
"""Ring of Gaussian integers."""
- base = ZZ
+ dom = ZZ
dtype = GaussianInteger
zero = dtype(0, 0)
one = dtype(1, 0)
@@ -265,6 +299,9 @@ class GaussianIntegerRing(GaussianDomain, Ring):
rep = 'ZZ_I'
+ is_GaussianRing = True
+ is_ZZ_I = True
+
def __init__(self): # override Domain.__init__
"""For constructing ZZ_I."""
@@ -287,22 +324,38 @@ def normalize(self, d, *args):
return (d,) + args if args else d
def gcd(self, a, b):
+ """Greatest common divisor of a and b over ZZ_I."""
while b:
a, b = b, a % b
return self.normalize(a)
+ def lcm(self, a, b):
+ """Least common multiple of a and b over ZZ_I."""
+ return (a * b) // self.gcd(a, b)
+
+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a ZZ_I element to ZZ_I."""
+ return a
+
+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a QQ_I element to ZZ_I."""
+ return K1.new(ZZ.convert(a.x), ZZ.convert(a.y))
+
ZZ_I = GaussianInteger._parent = GaussianIntegerRing()
class GaussianRationalField(GaussianDomain, Field):
"""Field of Gaussian rational numbers."""
- base = QQ
+ dom = QQ
dtype = GaussianRational
zero = dtype(0, 0)
one = dtype(1, 0)
rep = 'QQ_I'
+ is_GaussianField = True
+ is_QQ_I = True
+
def __init__(self): # override Domain.__init__
"""For constructing QQ_I."""
@@ -314,4 +367,29 @@ def get_field(self):
"""Returns a field associated with ``self``. """
return self
+ def as_AlgebraicField(self):
+ """Get equivalent domain as an ``AlgebraicField``. """
+ return AlgebraicField(self.dom, I)
+
+ def numer(self, a):
+ """Get the numerator of ``a``."""
+ ZZ_I = self.get_ring()
+ return ZZ_I.convert(a * self.denom(a))
+
+ def denom(self, a):
+ """Get the denominator of ``a``."""
+ ZZ = self.dom.get_ring()
+ QQ = self.dom
+ ZZ_I = self.get_ring()
+ denom_ZZ = ZZ.lcm(QQ.denom(a.x), QQ.denom(a.y))
+ return ZZ_I(denom_ZZ, ZZ.zero)
+
+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a ZZ_I element to QQ_I."""
+ return K1.new(a.x, a.y)
+
+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a QQ_I element to QQ_I."""
+ return a
+
QQ_I = GaussianRational._parent = GaussianRationalField()
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyintegerring.py b/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyintegerring.py
index 523d9a6d8fdc..20d24735557f 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyintegerring.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyintegerring.py
@@ -70,6 +70,10 @@ def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):
if q == 1:
return GMPYInteger(p)
+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):
+ if a.y == 0:
+ return a.x
+
def gcdex(self, a, b):
"""Compute extended GCD of ``a`` and ``b``. """
h, s, t = gmpy_gcdex(a, b)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyrationalfield.py b/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyrationalfield.py
index 086e659ff354..069e42aae53e 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyrationalfield.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/gmpyrationalfield.py
@@ -59,6 +59,11 @@ def from_QQ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):
"""Convert a GMPY `mpq` object to `dtype`. """
return a
+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a `GaussianElement` object to `dtype`. """
+ if a.y == 0:
+ return GMPYRational(a.x)
+
def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):
"""Convert a mpmath `mpf` object to `dtype`. """
return GMPYRational(*map(int, K0.to_rational(a)))
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/polynomialring.py b/sympy/polys/domains/polynomialring.py
index d23bafea0ee2..cb499dce626b 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/polynomialring.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/polynomialring.py
@@ -92,6 +92,14 @@ def from_QQ_gmpy(K1, a, K0):
"""Convert a GMPY `mpq` object to `dtype`. """
return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))
+ def from_GaussianIntegerRing(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a `GaussianInteger` object to `dtype`. """
+ return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))
+
+ def from_GaussianRationalField(K1, a, K0):
+ """Convert a `GaussianRational` object to `dtype`. """
+ return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))
+
def from_RealField(K1, a, K0):
"""Convert a mpmath `mpf` object to `dtype`. """
return K1(K1.domain.convert(a, K0))
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/pythonrational.py b/sympy/polys/domains/pythonrational.py
index 461002b33f36..41ed6c1c21cb 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/pythonrational.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/pythonrational.py
@@ -243,7 +243,7 @@ def __eq__(self, other):
elif isinstance(other, int):
return self.q == 1 and self.p == other
else:
- return False
+ return NotImplemented
def __ne__(self, other):
return not self == other
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/tests/test_domains.py b/sympy/polys/domains/tests/test_domains.py
index 068ef65d8920..255e51be37ce 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/tests/test_domains.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/tests/test_domains.py
@@ -1,11 +1,16 @@
"""Tests for classes defining properties of ground domains, e.g. ZZ, QQ, ZZ[x] ... """
-from sympy import S, sqrt, sin, oo, Poly, Float, Rational, pi
+from sympy import I, S, sqrt, sin, oo, Poly, Float, Rational, pi
from sympy.abc import x, y, z
-from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ, RR, CC, FF, GF, EX
-from sympy.polys.domains.realfield import RealField
+from sympy.core.compatibility import HAS_GMPY
+
+from sympy.polys.domains import (ZZ, QQ, RR, CC, FF, GF, EX, ZZ_gmpy,
+ ZZ_python, QQ_gmpy, QQ_python)
+from sympy.polys.domains.algebraicfield import AlgebraicField
from sympy.polys.domains.gaussiandomains import ZZ_I, QQ_I
+from sympy.polys.domains.polynomialring import PolynomialRing
+from sympy.polys.domains.realfield import RealField
from sympy.polys.rings import ring
from sympy.polys.fields import field
@@ -58,6 +63,36 @@ def test_Domain_unify():
assert unify(QQ, ZZ.frac_field(x)) == QQ.frac_field(x)
assert unify(QQ, EX) == EX
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, F3) == ZZ_I
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, ZZ) == ZZ_I
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, ZZ_I) == ZZ_I
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, QQ) == QQ_I
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, ALG) == QQ.algebraic_field(I, sqrt(2), sqrt(3))
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, RR) == CC
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, CC) == CC
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, ZZ[x]) == ZZ_I[x]
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, ZZ_I[x]) == ZZ_I[x]
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, ZZ.frac_field(x)) == ZZ_I.frac_field(x)
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, ZZ_I.frac_field(x)) == ZZ_I.frac_field(x)
+ assert unify(ZZ_I, EX) == EX
+
+ assert unify(QQ_I, F3) == QQ_I
+ assert unify(QQ_I, ZZ) == QQ_I
+ assert unify(QQ_I, ZZ_I) == QQ_I
+ assert unify(QQ_I, QQ) == QQ_I
+ assert unify(QQ_I, ALG) == QQ.algebraic_field(I, sqrt(2), sqrt(3))
+ assert unify(QQ_I, RR) == CC
+ assert unify(QQ_I, CC) == CC
+ assert unify(QQ_I, ZZ[x]) == QQ_I[x]
+ assert unify(QQ_I, ZZ_I[x]) == QQ_I[x]
+ assert unify(QQ_I, QQ[x]) == QQ_I[x]
+ assert unify(QQ_I, QQ_I[x]) == QQ_I[x]
+ assert unify(QQ_I, ZZ.frac_field(x)) == QQ_I.frac_field(x)
+ assert unify(QQ_I, ZZ_I.frac_field(x)) == QQ_I.frac_field(x)
+ assert unify(QQ_I, QQ.frac_field(x)) == QQ_I.frac_field(x)
+ assert unify(QQ_I, QQ_I.frac_field(x)) == QQ_I.frac_field(x)
+ assert unify(QQ_I, EX) == EX
+
assert unify(RR, F3) == RR
assert unify(RR, ZZ) == RR
assert unify(RR, QQ) == RR
@@ -787,40 +822,101 @@ def test_CC_double():
def test_gaussian_domains():
I = S.ImaginaryUnit
- a, b, c = [ZZ_I.convert(x) for x in (5, 2 + I, 3 - I)]
+ a, b, c, d = [ZZ_I.convert(x) for x in (5, 2 + I, 3 - I, 5 - 5)]
ZZ_I.gcd(a, b) == b
ZZ_I.gcd(a, c) == b
+ ZZ_I.lcm(a, b) == a
+ ZZ_I.lcm(a, c) == d
assert ZZ_I(3, 4) != QQ_I(3, 4) # XXX is this right or should QQ->ZZ if possible?
assert ZZ_I(3, 0) != 3 # and should this go to Integer?
assert QQ_I(S(3)/4, 0) != S(3)/4 # and this to Rational?
assert ZZ_I(0, 0).quadrant() == 0
assert ZZ_I(-1, 0).quadrant() == 2
for G in (QQ_I, ZZ_I):
+
q = G(3, 4)
+ assert str(q) == '3 + 4*I'
+ assert q.parent() == G
assert q._get_xy(pi) == (None, None)
assert q._get_xy(2) == (2, 0)
assert q._get_xy(2*I) == (0, 2)
+
assert hash(q) == hash((3, 4))
+ assert G(1, 2) == G(1, 2)
+ assert G(1, 2) != G(1, 3)
+ assert G(3, 0) == G(3)
+
assert q + q == G(6, 8)
assert q - q == G(0, 0)
assert 3 - q == -q + 3 == G(0, -4)
assert 3 + q == q + 3 == G(6, 4)
- assert repr(q) in ('GaussianInteger(3, 4)', 'GaussianRational(3, 4)')
- assert str(q) == '3 + 4*I'
- assert q.parent() == G
+ assert q * q == G(-7, 24)
+ assert 3 * q == q * 3 == G(9, 12)
+ assert q ** 0 == G(1, 0)
+ assert q ** 1 == q
+ assert q ** 2 == q * q == G(-7, 24)
+ assert q ** 3 == q * q * q == G(-117, 44)
+ assert 1 / q == q ** -1 == QQ_I(S(3)/25, - S(4)/25)
+ assert q / 1 == QQ_I(3, 4)
+ assert q / 2 == QQ_I(S(3)/2, 2)
assert q/3 == QQ_I(1, S(4)/3)
assert 3/q == QQ_I(S(9)/25, -S(12)/25)
i, r = divmod(q, 2)
assert 2*i + r == q
i, r = divmod(2, q)
- assert G.from_sympy(S(2)) == G(2, 0)
+ assert q*i + r == G(2, 0)
+
raises(ZeroDivisionError, lambda: q % 0)
raises(ZeroDivisionError, lambda: q / 0)
raises(ZeroDivisionError, lambda: q // 0)
raises(ZeroDivisionError, lambda: divmod(q, 0))
raises(ZeroDivisionError, lambda: divmod(q, 0))
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: q + x)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: q - x)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: x + q)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: x - q)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: q * x)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: x * q)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: q / x)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: x / q)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: q // x)
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: x // q)
+
+ assert G.from_sympy(S(2)) == G(2, 0)
+ assert G.to_sympy(G(2, 0)) == S(2)
raises(CoercionFailed, lambda: G.from_sympy(pi))
+
+ PR = G.inject(x)
+ assert isinstance(PR, PolynomialRing)
+ assert PR.domain == G
+ assert len(PR.gens) == 1 and PR.gens[0].as_expr() == x
+
+ if G is QQ_I:
+ AF = G.as_AlgebraicField()
+ assert isinstance(AF, AlgebraicField)
+ assert AF.domain == QQ
+ assert AF.ext.args[0] == I
+
+ for qi in [G(-1, 0), G(1, 0), G(0, -1), G(0, 1)]:
+ assert G.is_negative(qi) is False
+ assert G.is_positive(qi) is False
+ assert G.is_nonnegative(qi) is False
+ assert G.is_nonpositive(qi) is False
+
+ domains = [ZZ_python(), QQ_python(), AlgebraicField(QQ, I)]
+ if HAS_GMPY:
+ domains += [ZZ_gmpy(), QQ_gmpy()]
+
+ for K in domains:
+ assert G.convert(K(2)) == G(2, 0)
+ assert G.convert(K(2), K) == G(2, 0)
+
+ for K in ZZ_I, QQ_I:
+ assert G.convert(K(1, 1)) == G(1, 1)
+ assert G.convert(K(1, 1), K) == G(1, 1)
+
if G == ZZ_I:
+ assert repr(q) == 'ZZ_I(3, 4)'
assert q//3 == G(1, 1)
assert 12//q == G(1, -2)
assert 12 % q == G(1, 2)
@@ -830,6 +926,7 @@ def test_gaussian_domains():
assert G.get_ring() == G
assert G.get_field() == QQ_I
else:
+ assert repr(q) == 'QQ_I(3, 4)'
assert G.get_ring() == ZZ_I
assert G.get_field() == G
assert q//3 == G(1, S(4)/3)
@@ -838,6 +935,9 @@ def test_gaussian_domains():
assert q % 2 == G(0, 0)
assert i == G(S(6)/25, -S(8)/25), (G,i)
assert r == G(0, 0)
+ q2 = G(S(3)/2, S(5)/3)
+ assert G.numer(q2) == ZZ_I(9, 10)
+ assert G.denom(q2) == ZZ_I(6)
def test_issue_18278():
diff --git a/sympy/polys/factortools.py b/sympy/polys/factortools.py
index d846ef75ef31..01c76058433f 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/factortools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/factortools.py
@@ -1155,6 +1155,72 @@ def dmp_zz_factor(f, u, K):
return cont, _sort_factors(factors)
+def dup_qq_i_factor(f, K0):
+ """Factor univariate polynomials into irreducibles in `QQ_I[x]`. """
+ # Factor in QQ<I>
+ K1 = K0.as_AlgebraicField()
+ f = dup_convert(f, K0, K1)
+ coeff, factors = dup_factor_list(f, K1)
+ factors = [(dup_convert(fac, K1, K0), i) for fac, i in factors]
+ coeff = K0.convert(coeff, K1)
+ return coeff, factors
+
+
+def dup_zz_i_factor(f, K0):
+ """Factor univariate polynomials into irreducibles in `ZZ_I[x]`. """
+ # First factor in QQ_I
+ K1 = K0.get_field()
+ f = dup_convert(f, K0, K1)
+ coeff, factors = dup_qq_i_factor(f, K1)
+
+ new_factors = []
+ for fac, i in factors:
+ # Extract content
+ fac_denom, fac_num = dup_clear_denoms(fac, K1)
+ fac_num_ZZ_I = dup_convert(fac_num, K1, K0)
+ content, fac_prim = dmp_ground_primitive(fac_num_ZZ_I, 0, K1)
+
+ coeff = (coeff * content ** i) // fac_denom ** i
+ new_factors.append((fac_prim, i))
+
+ factors = new_factors
+ coeff = K0.convert(coeff, K1)
+ return coeff, factors
+
+
+def dmp_qq_i_factor(f, u, K0):
+ """Factor multivariate polynomials into irreducibles in `QQ_I[X]`. """
+ # Factor in QQ<I>
+ K1 = K0.as_AlgebraicField()
+ f = dmp_convert(f, u, K0, K1)
+ coeff, factors = dmp_factor_list(f, u, K1)
+ factors = [(dmp_convert(fac, u, K1, K0), i) for fac, i in factors]
+ coeff = K0.convert(coeff, K1)
+ return coeff, factors
+
+
+def dmp_zz_i_factor(f, u, K0):
+ """Factor multivariate polynomials into irreducibles in `ZZ_I[X]`. """
+ # First factor in QQ_I
+ K1 = K0.get_field()
+ f = dmp_convert(f, u, K0, K1)
+ coeff, factors = dmp_qq_i_factor(f, u, K1)
+
+ new_factors = []
+ for fac, i in factors:
+ # Extract content
+ fac_denom, fac_num = dmp_clear_denoms(fac, u, K1)
+ fac_num_ZZ_I = dmp_convert(fac_num, u, K1, K0)
+ content, fac_prim = dmp_ground_primitive(fac_num_ZZ_I, u, K1)
+
+ coeff = (coeff * content ** i) // fac_denom ** i
+ new_factors.append((fac_prim, i))
+
+ factors = new_factors
+ coeff = K0.convert(coeff, K1)
+ return coeff, factors
+
+
def dup_ext_factor(f, K):
"""Factor univariate polynomials over algebraic number fields. """
n, lc = dup_degree(f), dup_LC(f, K)
@@ -1242,6 +1308,10 @@ def dup_factor_list(f, K0):
coeff, factors = dup_gf_factor(f, K0)
elif K0.is_Algebraic:
coeff, factors = dup_ext_factor(f, K0)
+ elif K0.is_GaussianRing:
+ coeff, factors = dup_zz_i_factor(f, K0)
+ elif K0.is_GaussianField:
+ coeff, factors = dup_qq_i_factor(f, K0)
else:
if not K0.is_Exact:
K0_inexact, K0 = K0, K0.get_exact()
@@ -1318,6 +1388,10 @@ def dmp_factor_list(f, u, K0):
coeff, factors = dmp_gf_factor(f, u, K0)
elif K0.is_Algebraic:
coeff, factors = dmp_ext_factor(f, u, K0)
+ elif K0.is_GaussianRing:
+ coeff, factors = dmp_zz_i_factor(f, u, K0)
+ elif K0.is_GaussianField:
+ coeff, factors = dmp_qq_i_factor(f, u, K0)
else:
if not K0.is_Exact:
K0_inexact, K0 = K0, K0.get_exact()
diff --git a/sympy/polys/polyoptions.py b/sympy/polys/polyoptions.py
index 399588be0bce..7d572f615f93 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/polyoptions.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/polyoptions.py
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Type
-from sympy.core import S, Basic, sympify
+from sympy.core import Basic, sympify
from sympy.polys.polyerrors import GeneratorsError, OptionError, FlagError
from sympy.utilities import numbered_symbols, topological_sort, public
from sympy.utilities.iterables import has_dups
@@ -406,7 +406,7 @@ class Domain(Option, metaclass=OptionType):
_re_realfield = re.compile(r"^(R|RR)(_(\d+))?$")
_re_complexfield = re.compile(r"^(C|CC)(_(\d+))?$")
_re_finitefield = re.compile(r"^(FF|GF)\((\d+)\)$")
- _re_polynomial = re.compile(r"^(Z|ZZ|Q|QQ|R|RR|C|CC)\[(.+)\]$")
+ _re_polynomial = re.compile(r"^(Z|ZZ|Q|QQ|ZZ_I|QQ_I|R|RR|C|CC)\[(.+)\]$")
_re_fraction = re.compile(r"^(Z|ZZ|Q|QQ)\((.+)\)$")
_re_algebraic = re.compile(r"^(Q|QQ)\<(.+)\>$")
@@ -423,6 +423,12 @@ def preprocess(cls, domain):
if domain in ['Q', 'QQ']:
return sympy.polys.domains.QQ
+ if domain == 'ZZ_I':
+ return sympy.polys.domains.ZZ_I
+
+ if domain == 'QQ_I':
+ return sympy.polys.domains.QQ_I
+
if domain == 'EX':
return sympy.polys.domains.EX
@@ -464,6 +470,10 @@ def preprocess(cls, domain):
return sympy.polys.domains.QQ.poly_ring(*gens)
elif ground in ['R', 'RR']:
return sympy.polys.domains.RR.poly_ring(*gens)
+ elif ground == 'ZZ_I':
+ return sympy.polys.domains.ZZ_I.poly_ring(*gens)
+ elif ground == 'QQ_I':
+ return sympy.polys.domains.QQ_I.poly_ring(*gens)
else:
return sympy.polys.domains.CC.poly_ring(*gens)
@@ -525,7 +535,7 @@ class Gaussian(BooleanOption, metaclass=OptionType):
@classmethod
def postprocess(cls, options):
if 'gaussian' in options and options['gaussian'] is True:
- options['extension'] = set([S.ImaginaryUnit])
+ options['domain'] = sympy.polys.domains.QQ_I
Extension.postprocess(options)
diff --git a/sympy/polys/polyroots.py b/sympy/polys/polyroots.py
index 979b27483bee..9f985b176fa5 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/polyroots.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/polyroots.py
@@ -18,6 +18,7 @@
from sympy.functions import exp, sqrt, im, cos, acos, Piecewise
from sympy.functions.elementary.miscellaneous import root
from sympy.ntheory import divisors, isprime, nextprime
+from sympy.polys.domains import EX
from sympy.polys.polyerrors import (PolynomialError, GeneratorsNeeded,
DomainError)
from sympy.polys.polyquinticconst import PolyQuintic
@@ -970,6 +971,10 @@ def _try_heuristics(f):
return result
+ # Convert the generators to symbols
+ dumgens = symbols('x:%d' % len(f.gens), cls=Dummy)
+ f = f.per(f.rep, dumgens)
+
(k,), f = f.terms_gcd()
if not k:
@@ -982,6 +987,10 @@ def _try_heuristics(f):
if auto and f.get_domain().is_Ring:
f = f.to_field()
+ # Use EX instead of ZZ_I or QQ_I
+ if f.get_domain().is_QQ_I:
+ f = f.per(f.rep.convert(EX))
+
rescale_x = None
translate_x = None
diff --git a/sympy/polys/polytools.py b/sympy/polys/polytools.py
index 24347f3ae061..ca93fb883334 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/polytools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/polytools.py
@@ -11,6 +11,7 @@
from sympy.core.basic import preorder_traversal
from sympy.core.compatibility import iterable, ordered
from sympy.core.decorators import _sympifyit
+from sympy.core.evalf import pure_complex
from sympy.core.function import Derivative
from sympy.core.mul import _keep_coeff
from sympy.core.relational import Relational
@@ -5916,7 +5917,7 @@ def _symbolic_factor_list(expr, opt, method):
args = [i._eval_factor() if hasattr(i, '_eval_factor') else i
for i in Mul.make_args(expr)]
for arg in args:
- if arg.is_Number:
+ if arg.is_Number or (isinstance(arg, Expr) and pure_complex(arg)):
coeff *= arg
continue
elif arg.is_Pow:
diff --git a/sympy/polys/polyutils.py b/sympy/polys/polyutils.py
index acb0b96fc7d4..dc4d32fa5f14 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/polyutils.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/polyutils.py
@@ -238,7 +238,7 @@ def _is_coeff(factor):
return factor.is_algebraic
elif opt.greedy is not False:
def _is_coeff(factor):
- return False
+ return factor is S.ImaginaryUnit
else:
def _is_coeff(factor):
return factor.is_number
diff --git a/sympy/polys/rings.py b/sympy/polys/rings.py
index 4e02e9de0f46..2d2058a3d181 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/rings.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/rings.py
@@ -790,17 +790,17 @@ def str(self, printer, precedence, exp_pattern, mul_symbol):
zm = ring.zero_monom
sexpvs = []
for expv, coeff in self.terms():
- positive = ring.domain.is_positive(coeff)
- sign = " + " if positive else " - "
+ negative = ring.domain.is_negative(coeff)
+ sign = " - " if negative else " + "
sexpvs.append(sign)
if expv == zm:
scoeff = printer._print(coeff)
- if scoeff.startswith("-"):
+ if negative and scoeff.startswith("-"):
scoeff = scoeff[1:]
else:
- if not positive:
+ if negative:
coeff = -coeff
- if coeff != 1:
+ if coeff != self.ring.one:
scoeff = printer.parenthesize(coeff, prec_mul, strict=True)
else:
scoeff = ''
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py
index 035e3437ac80..d7ecebdeb02a 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_constructor.py
@@ -1,14 +1,15 @@
"""Tests for tools for constructing domains for expressions. """
from sympy.polys.constructor import construct_domain
-from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ, RR, EX
+from sympy.polys.domains import ZZ, QQ, ZZ_I, QQ_I, RR, EX
from sympy.polys.domains.realfield import RealField
-from sympy import S, sqrt, sin, Float, E, GoldenRatio, pi, Catalan, Rational
+from sympy import S, sqrt, sin, Float, E, I, GoldenRatio, pi, Catalan, Rational
from sympy.abc import x, y
def test_construct_domain():
+
assert construct_domain([1, 2, 3]) == (ZZ, [ZZ(1), ZZ(2), ZZ(3)])
assert construct_domain([1, 2, 3], field=True) == (QQ, [QQ(1), QQ(2), QQ(3)])
@@ -20,6 +21,9 @@ def test_construct_domain():
assert isinstance(result[0], RealField)
assert result[1] == [RR(3.14), RR(1.0), RR(0.5)]
+ assert construct_domain([1, I]) == (ZZ_I, [ZZ_I(1, 0), ZZ_I(0, 1)])
+ assert construct_domain([1, I/2]) == (QQ_I, [QQ_I(1, 0), QQ_I(0, S.Half)])
+
assert construct_domain([3.14, sqrt(2)], extension=None) == (EX, [EX(3.14), EX(sqrt(2))])
assert construct_domain([3.14, sqrt(2)], extension=True) == (EX, [EX(3.14), EX(sqrt(2))])
@@ -58,6 +62,26 @@ def test_construct_domain():
assert construct_domain([x/2, 3*y]) == \
(dom, [dom.convert(x/2), dom.convert(3*y)])
+ dom = ZZ_I[x]
+
+ assert construct_domain([2*x, I]) == \
+ (dom, [dom.convert(2*x), dom.convert(I)])
+
+ dom = ZZ_I[x, y]
+
+ assert construct_domain([2*x, I*y]) == \
+ (dom, [dom.convert(2*x), dom.convert(I*y)])
+
+ dom = QQ_I[x]
+
+ assert construct_domain([x/2, I]) == \
+ (dom, [dom.convert(x/2), dom.convert(I)])
+
+ dom = QQ_I[x, y]
+
+ assert construct_domain([x/2, I*y]) == \
+ (dom, [dom.convert(x/2), dom.convert(I*y)])
+
dom = RR[x]
assert construct_domain([x/2, 3.5]) == \
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py
index 34fbe8826711..f8537b195c0e 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
"""Tools for polynomial factorization routines in characteristic zero. """
from sympy.polys.rings import ring, xring
-from sympy.polys.domains import FF, ZZ, QQ, RR, EX
+from sympy.polys.domains import FF, ZZ, QQ, ZZ_I, QQ_I, RR, EX
from sympy.polys import polyconfig as config
from sympy.polys.polyerrors import DomainError
@@ -403,6 +403,90 @@ def test_dmp_zz_factor():
(x**4 + 6*x**2*y + y**2, 1)])
+def test_dup_qq_i_factor():
+ R, x = ring("x", QQ_I)
+ i = QQ_I(0, 1)
+
+ assert R.dup_qq_i_factor(x**2 - 2) == (QQ_I(1, 0), [(x**2 - 2, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dup_qq_i_factor(x**2 - 1) == (QQ_I(1, 0), [(x - 1, 1), (x + 1, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dup_qq_i_factor(x**2 + 1) == (QQ_I(1, 0), [(x - i, 1), (x + i, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dup_qq_i_factor(x**2/4 + 1) == \
+ (QQ_I(QQ(1, 4), 0), [(x - 2*i, 1), (x + 2*i, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dup_qq_i_factor(x**2 + 4) == \
+ (QQ_I(1, 0), [(x - 2*i, 1), (x + 2*i, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dup_qq_i_factor(x**2 + 2*x + 1) == \
+ (QQ_I(1, 0), [(x + 1, 2)])
+
+ assert R.dup_qq_i_factor(x**2 + 2*i*x - 1) == \
+ (QQ_I(1, 0), [(x + i, 2)])
+
+ f = 8192*x**2 + x*(22656 + 175232*i) - 921416 + 242313*i
+
+ assert R.dup_qq_i_factor(f) == \
+ (QQ_I(8192, 0), [(x + QQ_I(QQ(177, 128), QQ(1369, 128)), 2)])
+
+
+def test_dmp_qq_i_factor():
+ R, x, y = ring("x, y", QQ_I)
+ i = QQ_I(0, 1)
+
+ assert R.dmp_qq_i_factor(x**2 + 2*y**2) == \
+ (QQ_I(1, 0), [(x**2 + 2*y**2, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dmp_qq_i_factor(x**2 + y**2) == \
+ (QQ_I(1, 0), [(x - i*y, 1), (x + i*y, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dmp_qq_i_factor(x**2 + y**2/4) == \
+ (QQ_I(1, 0), [(x - i*y/2, 1), (x + i*y/2, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dmp_qq_i_factor(4*x**2 + y**2) == \
+ (QQ_I(4, 0), [(x - i*y/2, 1), (x + i*y/2, 1)])
+
+
+def test_dup_zz_i_factor():
+ R, x = ring("x", ZZ_I)
+ i = ZZ_I(0, 1)
+
+ assert R.dup_zz_i_factor(x**2 - 2) == (ZZ_I(1, 0), [(x**2 - 2, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dup_zz_i_factor(x**2 - 1) == (ZZ_I(1, 0), [(x - 1, 1), (x + 1, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dup_zz_i_factor(x**2 + 1) == (ZZ_I(1, 0), [(x - i, 1), (x + i, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dup_zz_i_factor(x**2 + 4) == \
+ (ZZ_I(1, 0), [(x - 2*i, 1), (x + 2*i, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dup_zz_i_factor(x**2 + 2*x + 1) == \
+ (ZZ_I(1, 0), [(x + 1, 2)])
+
+ assert R.dup_zz_i_factor(x**2 + 2*i*x - 1) == \
+ (ZZ_I(1, 0), [(x + i, 2)])
+
+ f = 8192*x**2 + x*(22656 + 175232*i) - 921416 + 242313*i
+
+ assert R.dup_zz_i_factor(f) == \
+ (ZZ_I(0, 1), [((64 - 64*i)*x + (773 + 596*i), 2)])
+
+
+def test_dmp_zz_i_factor():
+ R, x, y = ring("x, y", ZZ_I)
+ i = ZZ_I(0, 1)
+
+ assert R.dmp_zz_i_factor(x**2 + 2*y**2) == \
+ (ZZ_I(1, 0), [(x**2 + 2*y**2, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dmp_zz_i_factor(x**2 + y**2) == \
+ (ZZ_I(1, 0), [(x - i*y, 1), (x + i*y, 1)])
+
+ assert R.dmp_zz_i_factor(4*x**2 + y**2) == \
+ (ZZ_I(1, 0), [(2*x - i*y, 1), (2*x + i*y, 1)])
+
+
def test_dup_ext_factor():
R, x = ring("x", QQ.algebraic_field(I))
def anp(element):
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyoptions.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyoptions.py
index 84ee8d6d35d4..d820c72210ab 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyoptions.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polyoptions.py
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
Frac, Formal, Polys, Include, All, Gen, Symbols, Method)
from sympy.polys.orderings import lex
-from sympy.polys.domains import FF, GF, ZZ, QQ, RR, CC, EX
+from sympy.polys.domains import FF, GF, ZZ, QQ, QQ_I, RR, CC, EX
from sympy.polys.polyerrors import OptionError, GeneratorsError
@@ -257,8 +257,7 @@ def test_Gaussian_postprocess():
assert opt == {
'gaussian': True,
- 'extension': {I},
- 'domain': QQ.algebraic_field(I),
+ 'domain': QQ_I,
}
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
index d6b94aa8762e..893d1502fc03 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@
from sympy.polys.polyclasses import DMP
from sympy.polys.fields import field
-from sympy.polys.domains import FF, ZZ, QQ, RR, EX
+from sympy.polys.domains import FF, ZZ, QQ, ZZ_I, QQ_I, RR, EX
from sympy.polys.domains.realfield import RealField
from sympy.polys.orderings import lex, grlex, grevlex
@@ -456,6 +456,9 @@ def test_Poly__unify():
assert Poly(x + 1, y, x, domain='QQ')._unify(Poly(x + 2, x, y))[2:] == (DMP([[1, 1]], QQ), DMP([[1, 2]], QQ))
assert Poly(x + 1, y, x)._unify(Poly(x + 2, x, y, domain='QQ'))[2:] == (DMP([[1, 1]], QQ), DMP([[1, 2]], QQ))
+ assert Poly(x**2 + I, x, domain=ZZ_I).unify(Poly(x**2 + sqrt(2), x, extension=True)) == \
+ (Poly(x**2 + I, x, domain='QQ<sqrt(2) + I>'), Poly(x**2 + sqrt(2), x, domain='QQ<sqrt(2) + I>'))
+
F, A, B = field("a,b", ZZ)
assert Poly(a*x, x, domain='ZZ[a]')._unify(Poly(a*b*x, x, domain='ZZ(a,b)'))[2:] == \
@@ -1744,6 +1747,14 @@ def test_div():
q, r = f.div(g)
assert q.get_domain().is_Frac and r.get_domain().is_Frac
+ # https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/19579
+ p = Poly(2+3*I, x, domain=ZZ_I)
+ q = Poly(1-I, x, domain=ZZ_I)
+ assert p.div(q, auto=False) == \
+ (Poly(0, x, domain='ZZ_I'), Poly(2 + 3*I, x, domain='ZZ_I'))
+ assert p.div(q, auto=True) == \
+ (Poly(-S(1)/2 + 5*I/2, x, domain='QQ_I'), Poly(0, x, domain='QQ_I'))
+
def test_issue_7864():
q, r = div(a, .408248290463863*a)
@@ -2000,7 +2011,7 @@ def test_gcd():
assert gcd(a, b) == gcd(b, a) == a
a, b = sqrt(-2), -sqrt(-2)
- assert gcd(a, b) == a
+ assert gcd(a, b) in (a, b)
raises(TypeError, lambda: gcd(x))
raises(TypeError, lambda: lcm(x))
@@ -2424,6 +2435,20 @@ def test_factor():
assert factor(
f, extension=sqrt(2)) == (x**2 + sqrt(2)*x + 1)*(x**2 - sqrt(2)*x + 1)
+ assert factor(x**2 + 4*I*x - 4) == (x + 2*I)**2
+
+ f = x**2 + 2*I*x - 4
+
+ assert factor(f) == f
+
+ f = 8192*x**2 + x*(22656 + 175232*I) - 921416 + 242313*I
+ f_zzi = I*(x*(64 - 64*I) + 773 + 596*I)**2
+ f_qqi = 8192*(x + S(177)/128 + 1369*I/128)**2
+
+ assert factor(f) == f_zzi
+ assert factor(f, domain=ZZ_I) == f_zzi
+ assert factor(f, domain=QQ_I) == f_qqi
+
f = x**2 + 2*sqrt(2)*x + 2
assert factor(f, extension=sqrt(2)) == (x + sqrt(2))**2
@@ -3004,6 +3029,9 @@ def test_cancel():
expr = sin(M[1, 4] + M[2, 1] * 5 * M[4, 0]) - 5 * M[1, 2] / z
assert cancel(expr) == (z*sin(M[1, 4] + M[2, 1] * 5 * M[4, 0]) - 5 * M[1, 2]) / z
+ assert cancel((x**2 + 1)/(x - I)) == x + I
+
+
def test_reduced():
f = 2*x**4 + y**2 - x**2 + y**3
G = [x**3 - x, y**3 - y]
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_rings.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_rings.py
index 3b155330c9f4..3da673f77c2c 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_rings.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_rings.py
@@ -207,6 +207,9 @@ def test_PolyElement___eq__():
assert ((x*y - x*y) != 1) == True
assert (1 != (x*y - x*y)) == True
+ assert R.one == QQ(1, 1) == R.one
+ assert R.one == 1 == R.one
+
Rt, t = ring("t", ZZ)
R, x, y = ring("x,y", Rt)
diff --git a/sympy/printing/str.py b/sympy/printing/str.py
index 7a296c40cb4e..2639a9a5d570 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/str.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/str.py
@@ -465,6 +465,9 @@ def _print_FracField(self, field):
def _print_FreeGroupElement(self, elm):
return elm.__str__()
+ def _print_GaussianElement(self, poly):
+ return "(%s + %s*I)" % (poly.x, poly.y)
+
def _print_PolyElement(self, poly):
return poly.str(self, PRECEDENCE, "%s**%s", "*")
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py
index 911a0b10ad6c..d05052fe0c8c 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py
@@ -7,7 +7,8 @@
AccumBounds, UnevaluatedExpr, Eq, Ne, Quaternion, Subs, MatrixSymbol, MatrixSlice)
from sympy.core import Expr, Mul
from sympy.physics.units import second, joule
-from sympy.polys import Poly, rootof, RootSum, groebner, ring, field, ZZ, QQ, lex, grlex
+from sympy.polys import (Poly, rootof, RootSum, groebner, ring, field, ZZ, QQ,
+ ZZ_I, QQ_I, lex, grlex)
from sympy.geometry import Point, Circle, Polygon, Ellipse, Triangle
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
@@ -372,8 +373,8 @@ def test_Poly():
assert str(
Poly(x**2 - 1 + y, x)) == "Poly(x**2 + y - 1, x, domain='ZZ[y]')"
- assert str(Poly(x**2 + I*x, x)) == "Poly(x**2 + I*x, x, domain='EX')"
- assert str(Poly(x**2 - I*x, x)) == "Poly(x**2 - I*x, x, domain='EX')"
+ assert str(Poly(x**2 + I*x, x)) == "Poly(x**2 + I*x, x, domain='ZZ_I')"
+ assert str(Poly(x**2 - I*x, x)) == "Poly(x**2 - I*x, x, domain='ZZ_I')"
assert str(Poly(-x*y*z + x*y - 1, x, y, z)
) == "Poly(-x*y*z + x*y - 1, x, y, z, domain='ZZ')"
@@ -399,6 +400,7 @@ def test_FracField():
def test_PolyElement():
Ruv, u,v = ring("u,v", ZZ)
Rxyz, x,y,z = ring("x,y,z", Ruv)
+ Rx_zzi, xz = ring("x", ZZ_I)
assert str(x - x) == "0"
assert str(x - 1) == "x - 1"
@@ -415,10 +417,14 @@ def test_PolyElement():
assert str(-(v**2 + v + 1)*x + 3*u*v + 1) == "-(v**2 + v + 1)*x + 3*u*v + 1"
assert str(-(v**2 + v + 1)*x - 3*u*v + 1) == "-(v**2 + v + 1)*x - 3*u*v + 1"
+ assert str((1+I)*xz + 2) == "(1 + 1*I)*x + (2 + 0*I)"
+
def test_FracElement():
Fuv, u,v = field("u,v", ZZ)
Fxyzt, x,y,z,t = field("x,y,z,t", Fuv)
+ Rx_zzi, xz = field("x", QQ_I)
+ i = QQ_I(0, 1)
assert str(x - x) == "0"
assert str(x - 1) == "x - 1"
@@ -440,6 +446,28 @@ def test_FracElement():
assert str(((u + 1)*x*y + 1)/((v - 1)*z - 1)) == "((u + 1)*x*y + 1)/((v - 1)*z - 1)"
assert str(((u + 1)*x*y + 1)/((v - 1)*z - t*u*v - 1)) == "((u + 1)*x*y + 1)/((v - 1)*z - u*v*t - 1)"
+ assert str((1+i)/xz) == "(1 + 1*I)/x"
+ assert str(((1+i)*xz - i)/xz) == "((1 + 1*I)*x + (0 + -1*I))/x"
+
+
+def test_GaussianInteger():
+ assert str(ZZ_I(1, 0)) == "1"
+ assert str(ZZ_I(-1, 0)) == "-1"
+ assert str(ZZ_I(0, 1)) == "I"
+ assert str(ZZ_I(0, -1)) == "-I"
+ assert str(ZZ_I(0, 2)) == "2*I"
+ assert str(ZZ_I(0, -2)) == "-2*I"
+ assert str(ZZ_I(1, 1)) == "1 + I"
+ assert str(ZZ_I(-1, -1)) == "-1 - I"
+ assert str(ZZ_I(-1, -2)) == "-1 - 2*I"
+
+
+def test_GaussianRational():
+ assert str(QQ_I(1, 0)) == "1"
+ assert str(QQ_I(QQ(2, 3), 0)) == "2/3"
+ assert str(QQ_I(0, QQ(2, 3))) == "2*I/3"
+ assert str(QQ_I(QQ(1, 2), QQ(-2, 3))) == "1/2 - 2*I/3"
+
def test_Pow():
assert str(x**-1) == "1/x"
diff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_gruntz.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_gruntz.py
index a74b618fd5df..63b6001d4b63 100644
--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_gruntz.py
+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_gruntz.py
@@ -392,12 +392,11 @@ def test_MrvTestCase_page47_ex3_21():
def test_I():
- from sympy.functions import sign as sgn
y = Symbol("y")
assert gruntz(I*x, x, oo) == I*oo
assert gruntz(y*I*x, x, oo) == y*I*oo
assert gruntz(y*3*I*x, x, oo) == y*I*oo
- assert gruntz(y*3*sin(I)*x, x, oo).simplify() == sgn(y)*I*oo
+ assert gruntz(y*3*sin(I)*x, x, oo).simplify() == y*I*oo
def test_issue_4814():
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py
index 8aa488e9a2a5..56f6dbaf6d90 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_single.py
@@ -949,8 +949,8 @@ def _get_examples_ode_sol_nth_order_reducible():
'reducible_11': {
'eq': f(x).diff(x, 2) - f(x).diff(x)**3,
- 'sol': [Eq(f(x), C1 - sqrt(2)*I*(C2 + x)*sqrt(1/(C2 + x))),
- Eq(f(x), C1 + sqrt(2)*I*(C2 + x)*sqrt(1/(C2 + x)))],
+ 'sol': [Eq(f(x), C1 - sqrt(2)*(I*C2 + I*x)*sqrt(1/(C2 + x))),
+ Eq(f(x), C1 + sqrt(2)*(I*C2 + I*x)*sqrt(1/(C2 + x)))],
'slow': True,
},
}
@@ -994,7 +994,7 @@ def _get_examples_ode_sol_nth_linear_undetermined_coefficients():
'undet_05': {
'eq': f2 + 3*f(x).diff(x) + 2*f(x) - exp(I*x),
- 'sol': [Eq(f(x), C1*exp(-2*x) + C2*exp(-x) + exp(I*x)/10 - 3*I*exp(I*x)/10)],
+ 'sol': [Eq(f(x), (S(3)/10 + I/10)*(C1*exp(-2*x) + C2*exp(-x) - I*exp(I*x)))],
'slow': True,
},
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_systems.py b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_systems.py
index 445cc472b460..f710dfad2f04 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_systems.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/ode/tests/test_systems.py
@@ -992,46 +992,38 @@ def _de_lorentz_solution():
-e3 * q + m * Derivative(v3(t), t) - q * (-b1 * v2(t) + b2 * v1(t))
]
- x1 = sqrt(b1 ** 2 + b2 ** 2 + b3 ** 2)
- x2 = exp(q * t * sqrt(-b1 ** 2 - b2 ** 2 - b3 ** 2) / m)
- x3 = 1 / (b1 ** 2 * x1 * x2 + b2 ** 2 * x1 * x2)
- x4 = 1 / (2 * b1 ** 2 * m * x2 + 2 * b2 ** 2 * m * x2 + 2 * b3 ** 2 * m * x2)
- x5 = Integral(
- b1 * b3 * e1 * q / (b1 ** 2 * m + b2 ** 2 * m + b3 ** 2 * m)
- + b2 * b3 * e2 * q / (b1 ** 2 * m + b2 ** 2 * m + b3 ** 2 * m)
- + b3 ** 2 * e3 * q / (b1 ** 2 * m + b2 ** 2 * m + b3 ** 2 * m), t)
- x6 = 1 / (2 * b1 ** 3 * b3 * m + 2 * I * b1 ** 2 * b2 * m * x1 + 2 * b1 * b2 ** 2 * b3 * m
- + 2 * b1 * b3 ** 3 * m + 2 * I * b2 ** 3 * m * x1 + 2 * I * b2 * b3 ** 2 * m * x1)
- x7 = Integral(
- b1 ** 2 * e3 * q * x4 - b1 * b3 * e1 * q * x4 + I * b1 * e2 * q * x1 * x4
- + b2 ** 2 * e3 * q * x4 - b2 * b3 * e2 * q * x4 - I * b2 * e1 * q * x1 * x4, t)
- x8 = Integral(
- b1 ** 3 * b2 * e2 * q * x2 * x6 - b1 ** 2 * b2 ** 2 * e1 * q * x2 * x6 - b1 ** 2 * b3 ** 2 * e1 * q * x2 * x6
- - I * b1 ** 2 * b3 * e2 * q * x1 * x2 * x6 + b1 ** 2 * e3 * q * x2 / (
- 2 * b1 ** 2 * m + 2 * b2 ** 2 * m + 2 * b3 ** 2 * m)
- + b1 * b2 ** 3 * e2 * q * x2 * x6 - b2 ** 4 * e1 * q * x2 * x6 - b2 ** 2 * b3 ** 2 * e1 * q * x2 * x6
- - I * b2 ** 2 * b3 * e2 * q * x1 * x2 * x6 + b2 ** 2 * e3 * q * x2 / (
- 2 * b1 ** 2 * m + 2 * b2 ** 2 * m + 2 * b3 ** 2 * m), t)
+ # The code for the solution here is made using
+ # printsol from https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/19574
+ z1 = sqrt(-b1**2 - b2**2 - b3**2)
+ z2 = sqrt(b1**2 + b2**2 + b3**2)
+ z3 = exp(q*t*z1/m)
+ z4 = 1/(-2*I*b1**2*m*z2*z3 - 2*I*b2**2*m*z2*z3 - 2*I*b3**2*m*z2*z3)
+ z5 = 1/(b1**2*m + b2**2*m + b3**2*m)
+ z6 = Integral(b1*b3*e1*q*z5 + b2*b3*e2*q*z5 + b3**2*e3*q*z5, t)
+ z7 = 1/(2*b1**3*b3*m + 2*I*b1**2*b2*m*z2 + 2*b1*b2**2*b3*m + 2*b1*b3**3*m + 2*I*b2**3*m*z2 + 2*I*b2*b3**2*m*z2)
+ z8 = 1/(-2*b1**3*b3*m - 2*I*b1**2*b2*m*z2 - 2*b1*b2**2*b3*m - 2*b1*b3**3*m - 2*I*b2**3*m*z2 - 2*I*b2*b3**2*m*z2)
+ z9 = 1/(2*b1**2*m*z3 + 2*b2**2*m*z3 + 2*b3**2*m*z3)
+ z10 = Integral(-b1**2*b2*e1*q*z4 + b1**2*e3*q*z9 + I*b1*b3*e1*q*z2*z4 + I*b1*e2*q*z2*z9
+ - b2**3*e1*q*z4 + b2**2*e3*q*z9 - b2*b3**2*e1*q*z4 - b2*b3*e2*q*z9, t)
+ z11 = 1/(b1**2*z2 + b2**2*z2)
+ z12 = 1/(b1**2*z2*z3 + b2**2*z2*z3)
+ z13 = Integral(b1**3*b2*e2*q*z3*z7 + b1**2*b2**2*e1*q*z3*z8 + b1**2*b3**2*e1*q*z3*z8
+ - I*b1**2*b3*e2*q*z2*z3*z7 - b1**2*e3*q*z3/(-2*b1**2*m - 2*b2**2*m - 2*b3**2*m)
+ + b1*b2**3*e2*q*z3*z7 + b2**4*e1*q*z3*z8 + b2**2*b3**2*e1*q*z3*z8
+ - I*b2**2*b3*e2*q*z2*z3*z7 - b2**2*e3*q*z3/(-2*b1**2*m - 2*b2**2*m - 2*b3**2*m), t)
sol = [
Eq(v1(t),
- C1 * b1 / b3
- - I * C2 * b1 ** 2 * b2 * x3 - C2 * b1 * b3 * x1 * x3 - I * C2 * b2 ** 3 * x3 - I * C2 * b2 * b3 ** 2 * x3
- + I * C3 * b1 ** 2 * b2 * x2 / (b1 ** 2 * x1 + b2 ** 2 * x1) - C3 * b1 * b3 * x1 * x2 / (
- b1 ** 2 * x1 + b2 ** 2 * x1)
- + I * C3 * b2 ** 3 * x2 / (b1 ** 2 * x1 + b2 ** 2 * x1) + I * C3 * b2 * b3 ** 2 * x2 / (
- b1 ** 2 * x1 + b2 ** 2 * x1)
- + I * b1 ** 2 * b2 * x2 * x7 / (b1 ** 2 * x1 + b2 ** 2 * x1) - I * b1 ** 2 * b2 * x3 * x8
- - b1 * b3 * x1 * x2 * x7 / (b1 ** 2 * x1 + b2 ** 2 * x1) - b1 * b3 * x1 * x3 * x8 + b1 * x5 / b3
- + I * b2 ** 3 * x2 * x7 / (b1 ** 2 * x1 + b2 ** 2 * x1) - I * b2 ** 3 * x3 * x8
- + I * b2 * b3 ** 2 * x2 * x7 / (b1 ** 2 * x1 + b2 ** 2 * x1) - I * b2 * b3 ** 2 * x3 * x8),
+ C1*b1/b3
+ - I*C2*b1**2*b2*z12 + I*C2*b1*b3*z1*z12 - I*C2*b2**3*z12 - I*C2*b2*b3**2*z12
+ + I*C3*b1**2*b2*z11*z3 + I*C3*b1*b3*z1*z11*z3 + I*C3*b2**3*z11*z3 + I*C3*b2*b3**2*z11*z3
+ + I*b1**2*b2*z10*z11*z3 - I*b1**2*b2*z12*z13 + I*b1*b3*z1*z10*z11*z3 + I*b1*b3*z1*z12*z13
+ + b1*z6/b3 + I*b2**3*z10*z11*z3 - I*b2**3*z12*z13 + I*b2*b3**2*z10*z11*z3 - I*b2*b3**2*z12*z13),
Eq(v2(t),
- C1 * b2 / b3
- + C2 * b1 * sqrt(-b1 ** 2 - b2 ** 2 - b3 ** 2) / (b1 ** 2 * x2 + b2 ** 2 * x2)
- - C2 * b2 * b3 / (b1 ** 2 * x2 + b2 ** 2 * x2) - I * C3 * b1 * x1 * x2 / (b1 ** 2 + b2 ** 2)
- - C3 * b2 * b3 * x2 / (b1 ** 2 + b2 ** 2) - I * b1 * x1 * x2 * x7 / (b1 ** 2 + b2 ** 2)
- + b1 * x8 * sqrt(-b1 ** 2 - b2 ** 2 - b3 ** 2) / (b1 ** 2 * x2 + b2 ** 2 * x2)
- - b2 * b3 * x2 * x7 / (b1 ** 2 + b2 ** 2) - b2 * b3 * x8 / (b1 ** 2 * x2 + b2 ** 2 * x2) + b2 * x5 / b3),
- Eq(v3(t), C1 + C3 * x2 + x2 * x7 + x5 + (C2 + x8) * exp(-q * t * sqrt(-b1 ** 2 - b2 ** 2 - b3 ** 2) / m)),
+ C1*b2/b3
+ + C2*b1*z1/(b1**2*z3 + b2**2*z3) - C2*b2*b3/(b1**2*z3 + b2**2*z3)
+ - I*C3*b1*z2*z3/(b1**2 + b2**2) - C3*b2*b3*z3/(b1**2 + b2**2) + b1*z1*z13/(b1**2*z3 + b2**2*z3)
+ - I*b1*z10*z2*z3/(b1**2 + b2**2) - b2*b3*z10*z3/(b1**2 + b2**2) - b2*b3*z13/(b1**2*z3 + b2**2*z3) + b2*z6/b3),
+ Eq(v3(t), C1 + C3*z3 + z10*z3 + z6 + (C2 + z13)*exp(-q*t*z1/m)),
]
return eqs, sol
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-19368@83edeba
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,368
|
Make classes in diffgeom module immutable
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19321
Fixes #19318
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
`Manifold.patches` attribute is deprecated.
`Patch.coord_systems` attribute is deprecated.
Class signature *names* of `CoordSystem` is deprecated. `CoordinateSymbol` class and `CoordSystem.symbols` attribute are introduced instead.
`CoordSystem.transforms` attribute, `CoordSystem.connect_to` method, and `CoordSystem.coord_tuple_transform_to` method are deprecated. Class signature *relations*, `CoordSystem.transformation` and `CoordSystem.transform` methods are introduced instead.
`CoordSystem.jacobian_determinant` method is introduced.
methods are introduced instead.
#### Other comments
`Manifold.patches`, `Patch.coord_systems`, and `CoordSystem.transforms` attributes are deprecated because these make classes mutable.
`CoordSystem._dummies` is replaced with `CoordinateSymbol` class to use `Dummy` less. Also, this makes the coordinate symbols know which coordinate system they belong to.
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
- diffgeom
- `Manifold.patches` attribute is deprecated.
- `Patch.coord_systems` attribute is deprecated.
- Class signature *names* of `CoordSystem` is deprecated. `CoordinateSymbol` class and `CoordSystem.symbols` attribute are introduced instead.
- `CoordSystem.transforms`, `CoordSystem.connect_to`, and `CoordSystem.coord_tuple_transform_to` are deprecated. Class signature *relations*, `CoordSystem.transformation` and `CoordSystem.transform` are introduced instead.
- `CoordSystem.jacobian_determinant` method is introduced.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-05-19T13:24:16Z
|
Idea to implement CoordSystem's _fill_gaps_in_transformations
Currently, `CoordSystem` in `diffgeom` module has unimplemented method called `_fill_gaps_in_transformations`. This method is supposed to establish the transformation relation between two non-directly connected coordinate systems.
I am planning to implement this method. Using path finding algorithm, the shortest path to connect two systems (the coordinate systems between these) will be found. Then, the base scalars will be transformed successively. Once the relation is found, both coordinate systems will be added to each other's `transforms`.
Should there be anything more needed, or something that I should keep in mind, please leave a comment here.
Classes in diffgeom module could be made more strictly immutable
In `diffgeom` module, `Manifold`, `Patch` and `CoordSystem` have mutable features:
1. `Manifold.patches` and `Patch.coord_systems`. They store the patches and coordinate systems defined on themselves, respectively. However, they are not used really, and I doubt that these are necessary.
2. `CoordSystem.transforms`. This actually matters; it stores the coordinate trasform relations. If new coordinate system is defined and connected to existing one, old one's `transforms` will be mutated.
I think that instead of establishing the connection after construction, this `transforms` can be included to `CoordSystem`'s class signal. If new coordinate system B is constructed and connected to the existing one A, both relations "from A to B" and "from B to A" will be stored in `B.transforms`, not A's.
|
I think that some classes in the `diffgeom` are using mutable objects like `transforms` or `coord_systems`, but they shouldn't be using them extensively than cacheing.
And I think that this makes the future unclear about whether `transforms` dict should be replaced by other stuff and be deprecated.
@sylee957
I totally agree. Especially, I have tried many times to make `transforms` immutable, but none of them were successful. Perhaps I'll make another issue page, and resolve that matter first.
As @sylee957 mentioned in #19318, doing this will deprecate the old behavior. I think we need to, but I'd like to hear other opinions first.
|
[
{
"body": "Currently, `CoordSystem` in `diffgeom` module has unimplemented method called `_fill_gaps_in_transformations`. This method is supposed to establish the transformation relation between two non-directly connected coordinate systems.\r\n\r\nI am planning to implement this method. Using path finding algorithm, the shortest path to connect two systems (the coordinate systems between these) will be found. Then, the base scalars will be transformed successively. Once the relation is found, both coordinate systems will be added to each other's `transforms`.\r\n\r\nShould there be anything more needed, or something that I should keep in mind, please leave a comment here.",
"number": 19318,
"title": "Idea to implement CoordSystem's _fill_gaps_in_transformations"
},
{
"body": "In `diffgeom` module, `Manifold`, `Patch` and `CoordSystem` have mutable features:\r\n\r\n1. `Manifold.patches` and `Patch.coord_systems`. They store the patches and coordinate systems defined on themselves, respectively. However, they are not used really, and I doubt that these are necessary.\r\n\r\n2. `CoordSystem.transforms`. This actually matters; it stores the coordinate trasform relations. If new coordinate system is defined and connected to existing one, old one's `transforms` will be mutated.\r\n\r\nI think that instead of establishing the connection after construction, this `transforms` can be included to `CoordSystem`'s class signal. If new coordinate system B is constructed and connected to the existing one A, both relations \"from A to B\" and \"from B to A\" will be stored in `B.transforms`, not A's.",
"number": 19321,
"title": "Classes in diffgeom module could be made more strictly immutable"
}
] |
c0bfc81f3ffee97c6d6732ac5e5ccf399e5ab3e2
|
{
"head_commit": "83edebae76094cbb5606a29aa9d1bc2ef5d0cf08",
"head_commit_message": "Fix References underline length",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/doc/src/modules/diffgeom.rst b/doc/src/modules/diffgeom.rst\nindex 02fc0416af80..764d9f31412d 100644\n--- a/doc/src/modules/diffgeom.rst\n+++ b/doc/src/modules/diffgeom.rst\n@@ -18,6 +18,9 @@ Base Class Reference\n .. autoclass:: CoordSystem\n :members:\n \n+.. autoclass:: CoordinateSymbol\n+ :members:\n+\n .. autoclass:: Point\n :members:\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py\nindex 6bdc452c62c2..0b8109e5854e 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py\n@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@\n \n from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, SKIP\n \n-x, y, z = symbols('x,y,z')\n+a, b, c, x, y, z = symbols('a,b,c,x,y,z')\n \n \n def test_all_classes_are_tested():\n@@ -4420,38 +4420,42 @@ def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Patch():\n \n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__CoordSystem():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem\n- assert _test_args(CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3))))\n+ assert _test_args(CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c]))\n+\n+\n+def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__CoordinateSymbol():\n+ from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, CoordinateSymbol\n+ assert _test_args(CoordinateSymbol(CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c]), 0))\n \n \n-@XFAIL\n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Point():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, Point\n assert _test_args(Point(\n- CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3))), [x, y]))\n+ CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c]), [x, y]))\n \n \n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__BaseScalarField():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField\n- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n assert _test_args(BaseScalarField(cs, 0))\n \n \n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__BaseVectorField():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseVectorField\n- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n assert _test_args(BaseVectorField(cs, 0))\n \n \n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Differential():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential\n- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n assert _test_args(Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 0)))\n \n \n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Commutator():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseVectorField, Commutator\n- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n- cs1 = CoordSystem('name1', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n+ cs1 = CoordSystem('name1', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n v = BaseVectorField(cs, 0)\n v1 = BaseVectorField(cs1, 0)\n assert _test_args(Commutator(v, v1))\n@@ -4459,14 +4463,14 @@ def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Commutator():\n \n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__TensorProduct():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential, TensorProduct\n- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n d = Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 0))\n assert _test_args(TensorProduct(d, d))\n \n \n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__WedgeProduct():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential, WedgeProduct\n- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n d = Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 0))\n d1 = Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 1))\n assert _test_args(WedgeProduct(d, d1))\n@@ -4474,7 +4478,7 @@ def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__WedgeProduct():\n \n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__LieDerivative():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential, BaseVectorField, LieDerivative\n- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n d = Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 0))\n v = BaseVectorField(cs, 0)\n assert _test_args(LieDerivative(v, d))\n@@ -4483,13 +4487,13 @@ def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__LieDerivative():\n @XFAIL\n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__BaseCovarDerivativeOp():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseCovarDerivativeOp\n- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n assert _test_args(BaseCovarDerivativeOp(cs, 0, [[[0, ]*3, ]*3, ]*3))\n \n \n def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__CovarDerivativeOp():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseVectorField, CovarDerivativeOp\n- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))\n+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])\n v = BaseVectorField(cs, 0)\n _test_args(CovarDerivativeOp(v, [[[0, ]*3, ]*3, ]*3))\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/__init__.py b/sympy/diffgeom/__init__.py\nindex 140f00539472..8846a9951060 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/__init__.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/__init__.py\n@@ -1,18 +1,18 @@\n from .diffgeom import (\n BaseCovarDerivativeOp, BaseScalarField, BaseVectorField, Commutator,\n- contravariant_order, CoordSystem, CovarDerivativeOp, covariant_order,\n- Differential, intcurve_diffequ, intcurve_series, LieDerivative,\n- Manifold, metric_to_Christoffel_1st, metric_to_Christoffel_2nd,\n- metric_to_Ricci_components, metric_to_Riemann_components, Patch,\n- Point, TensorProduct, twoform_to_matrix, vectors_in_basis,\n- WedgeProduct,\n+ contravariant_order, CoordSystem, CoordinateSymbol,\n+ CovarDerivativeOp, covariant_order, Differential, intcurve_diffequ,\n+ intcurve_series, LieDerivative, Manifold, metric_to_Christoffel_1st,\n+ metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, metric_to_Ricci_components,\n+ metric_to_Riemann_components, Patch, Point, TensorProduct, twoform_to_matrix,\n+ vectors_in_basis, WedgeProduct,\n )\n \n __all__ = [\n- 'BaseCovarDerivativeOp', 'BaseScalarField', 'BaseVectorField',\n- 'Commutator', 'contravariant_order', 'CoordSystem', 'CovarDerivativeOp',\n- 'covariant_order', 'Differential', 'intcurve_diffequ', 'intcurve_series',\n- 'LieDerivative', 'Manifold', 'metric_to_Christoffel_1st',\n+ 'BaseCovarDerivativeOp', 'BaseScalarField', 'BaseVectorField', 'Commutator',\n+ 'contravariant_order', 'CoordSystem', 'CoordinateSymbol',\n+ 'CovarDerivativeOp', 'covariant_order', 'Differential', 'intcurve_diffequ',\n+ 'intcurve_series', 'LieDerivative', 'Manifold', 'metric_to_Christoffel_1st',\n 'metric_to_Christoffel_2nd', 'metric_to_Ricci_components',\n 'metric_to_Riemann_components', 'Patch', 'Point', 'TensorProduct',\n 'twoform_to_matrix', 'vectors_in_basis', 'WedgeProduct',\ndiff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\nindex 643b032399c4..d4e87f8fb3df 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py\n@@ -4,18 +4,20 @@\n \n from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\n from sympy.core import (\n- Basic, Expr, Dummy, Function, diff,\n- Pow, Mul, Add, Atom\n+ Basic, Expr, Function, diff,\n+ Pow, Mul, Add, Atom, Lambda, S, Tuple, Dict\n )\n+from sympy.core.cache import cacheit\n from sympy.core.compatibility import reduce\n-from sympy.core.numbers import Zero\n+from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol, Dummy\n from sympy.core.symbol import Str\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n from sympy.functions import factorial\n-from sympy.matrices import Matrix\n+from sympy.matrices import ImmutableDenseMatrix as Matrix\n from sympy.simplify import simplify\n from sympy.solvers import solve\n \n+from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning\n \n # TODO you are a bit excessive in the use of Dummies\n # TODO dummy point, literal field\n@@ -23,34 +25,58 @@\n # tests and find out why\n from sympy.tensor.array import ImmutableDenseNDimArray\n \n-\n class Manifold(Atom):\n \"\"\"A mathematical manifold.\n \n Explanation\n ===========\n \n- The only role that this object plays is to keep a list of all patches\n- defined on the manifold. It does not provide any means to study the\n- topological characteristics of the manifold that it represents.\n+ A manifold is a topological space that locally resembles\n+ Euclidean space near each point [1].\n+\n+ This class does not provide any means to study the topological\n+ characteristics of the manifold that it represents, though.\n \n Parameters\n ==========\n+\n name : str\n The name of the manifold.\n \n dim : int\n The dimension of the manifold.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold\n+ >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)\n+\n+ >>> m.name\n+ 'M'\n+ >>> m.dim\n+ 2\n+\n+ References\n+ ==========\n+\n+ .. [1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manifold\n+\n \"\"\"\n \n- def __new__(cls, name, dim):\n+ def __new__(cls, name, dim, **kwargs):\n if not isinstance(name, Str):\n name = Str(name)\n dim = _sympify(dim)\n obj = super().__new__(cls, name, dim)\n- obj.patches = []\n- # The patches list is necessary if a Patch instance needs to enumerate\n- # other Patch instance on the same manifold.\n+\n+ obj.patches = _deprecated_list(\n+ \"Manifold.patches\",\n+ \"external container for registry\",\n+ 19321,\n+ \"1.7\",\n+ []\n+ )\n return obj\n \n @property\n@@ -67,17 +93,19 @@ class Patch(Atom):\n Explanation\n ===========\n \n- On a manifold one can have many patches that do not always include the\n- whole manifold. On these patches coordinate charts can be defined that\n- permit the parameterization of any point on the patch in terms of a tuple\n- of real numbers (the coordinates).\n+ Coordinate patch, or patch in short, is a simply-connected open set around a point\n+ in the manifold [1]. On a manifold one can have many patches that do not always\n+ include the whole manifold. On these patches coordinate charts can be defined that\n+ permit the parameterization of any point on the patch in terms of a tuple of\n+ real numbers (the coordinates).\n \n- This object serves as a container/parent for all coordinate system charts\n- that can be defined on the patch it represents.\n+ This class does not provide any means to study the topological\n+ characteristics of the patch that it represents.\n \n Parameters\n ==========\n- name : string\n+\n+ name : str\n The name of the patch.\n \n manifold : Manifold\n@@ -86,25 +114,34 @@ class Patch(Atom):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- Define a Manifold and a Patch on that Manifold:\n-\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch\n- >>> m = Manifold('M', 3)\n+ >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)\n >>> p = Patch('P', m)\n- >>> p in m.patches\n- True\n+\n+ >>> p.name\n+ 'P'\n+ >>> p.dim\n+ 2\n+\n+ References\n+ ==========\n+\n+ .. [1] G. Sussman, J. Wisdom, W. Farr, Functional Differential Geometry (2013)\n \n \"\"\"\n- # Contains a reference to the parent manifold in order to be able to access\n- # other patches.\n- def __new__(cls, name, manifold):\n+ def __new__(cls, name, manifold, **kwargs):\n if not isinstance(name, Str):\n name = Str(name)\n obj = super().__new__(cls, name, manifold)\n- obj.manifold.patches.append(obj)\n- obj.coord_systems = []\n- # The list of coordinate systems is necessary for an instance of\n- # CoordSystem to enumerate other coord systems on the patch.\n+\n+ obj.manifold.patches.append(obj) # deprecated\n+ obj.coord_systems = _deprecated_list(\n+ \"Patch.coord_systems\",\n+ \"external container for registry\",\n+ 19321,\n+ \"1.7\",\n+ []\n+ )\n return obj\n \n @property\n@@ -120,134 +157,155 @@ def dim(self):\n return self.manifold.dim\n \n class CoordSystem(Atom):\n- \"\"\"A coordinate system defined on the patch\n+ \"\"\"A coordinate system defined on the patch.\n \n Explanation\n ===========\n \n- This class contains all coordinate transformation logic.\n+ Coordinate system is a system that uses one or more coordinates to uniquely determine\n+ the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold [1].\n+\n+ By passing Symbols to *symbols* parameter, user can define the name and assumptions\n+ of coordinate symbols of the coordinate system.\n+ By passing *relations* parameter, user can define the tranform relations of coordinate\n+ systems. Inverse transformation and indirect transformation can be found automatically.\n+ If this parameter is not passed, coordinate transformation cannot be done.\n \n Parameters\n ==========\n \n- name : string\n+ name : str\n The name of the coordinate system.\n \n patch : Patch\n The patch where the coordinate system is defined.\n \n- names : list of strings, optional\n- Determines how base scalar fields will be printed.\n+ symbols : list of Symbols\n+ Defines the names and assumptions of coordinate symbols.\n+\n+ relations : dict, optional\n+ - key : tuple of two strings, who are the names of systems where\n+ the coordinates transform from and transform to.\n+ - value : Lambda returning the transformed coordinates.\n \n Examples\n ========\n \n- Define a Manifold and a Patch, and then define two coord systems on that\n- patch:\n-\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols, pi, Lambda, Matrix, sqrt, atan2, cos, sin\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem\n- >>> from sympy.simplify import simplify\n- >>> r, theta = symbols('r, theta')\n >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)\n- >>> patch = Patch('P', m)\n- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', patch)\n- >>> polar = CoordSystem('polar', patch)\n- >>> rect in patch.coord_systems\n- True\n+ >>> p = Patch('P', m)\n \n- Connect the coordinate systems. An inverse transformation is automatically\n- found by ``solve`` when possible:\n+ >>> x, y = symbols('x y', real=True)\n+ >>> r, theta = symbols('r theta', nonnegative=True)\n+ >>> relation_dict = {\n+ ... ('Car2D', 'Pol'): Lambda((x, y), Matrix([sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)])),\n+ ... ('Pol', 'Car2D'): Lambda((r, theta), Matrix([r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)]))\n+ ... }\n+ >>> Car2D = CoordSystem('Car2D', p, [x, y], relation_dict)\n+ >>> Pol = CoordSystem('Pol', p, [r, theta], relation_dict)\n+\n+ >>> Car2D.name\n+ 'Car2D'\n+ >>> Car2D.dim\n+ 2\n+ >>> Car2D.symbols\n+ [x, y]\n+ >>> Car2D.transformation(Pol)\n+ Lambda((x, y), Matrix([\n+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2)],\n+ [ atan2(y, x)]]))\n \n- >>> polar.connect_to(rect, [r, theta], [r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)])\n- >>> polar.coord_tuple_transform_to(rect, [0, 2])\n+ >>> Car2D.transform(Pol)\n Matrix([\n- [0],\n- [0]])\n- >>> polar.coord_tuple_transform_to(rect, [2, pi/2])\n- Matrix([\n- [0],\n- [2]])\n- >>> rect.coord_tuple_transform_to(polar, [1, 1]).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2)],\n+ [ atan2(y, x)]])\n+ >>> Car2D.transform(Pol, [1, 2])\n Matrix([\n- [sqrt(2)],\n- [ pi/4]])\n+ [sqrt(5)],\n+ [atan(2)]])\n \n- Calculate the jacobian of the polar to cartesian transformation:\n-\n- >>> polar.jacobian(rect, [r, theta])\n+ >>> Pol.jacobian_matrix(Car2D)\n Matrix([\n [cos(theta), -r*sin(theta)],\n [sin(theta), r*cos(theta)]])\n-\n- Define a point using coordinates in one of the coordinate systems:\n-\n- >>> p = polar.point([1, 3*pi/4])\n- >>> rect.point_to_coords(p)\n+ >>> Pol.jacobian_matrix(Car2D, [1, pi/2])\n Matrix([\n- [-sqrt(2)/2],\n- [ sqrt(2)/2]])\n-\n- Define a basis scalar field (i.e. a coordinate function), that takes a\n- point and returns its coordinates. It is an instance of ``BaseScalarField``.\n-\n- >>> rect.coord_function(0)(p)\n- -sqrt(2)/2\n- >>> rect.coord_function(1)(p)\n- sqrt(2)/2\n+ [0, -1],\n+ [1, 0]])\n \n- Define a basis vector field (i.e. a unit vector field along the coordinate\n- line). Vectors are also differential operators on scalar fields. It is an\n- instance of ``BaseVectorField``.\n-\n- >>> v_x = rect.base_vector(0)\n- >>> x = rect.coord_function(0)\n- >>> v_x(x)\n- 1\n- >>> v_x(v_x(x))\n- 0\n-\n- Define a basis oneform field:\n-\n- >>> dx = rect.base_oneform(0)\n- >>> dx(v_x)\n- 1\n-\n- If you provide a list of names the fields will print nicely:\n- - without provided names:\n-\n- >>> x, v_x, dx\n- (rect_0, e_rect_0, drect_0)\n-\n- - with provided names\n+ References\n+ ==========\n \n- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', patch, ['x', 'y'])\n- >>> rect.coord_function(0), rect.base_vector(0), rect.base_oneform(0)\n- (x, e_x, dx)\n+ .. [1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coordinate_system\n \n \"\"\"\n- # Contains a reference to the parent patch in order to be able to access\n- # other coordinate system charts.\n- def __new__(cls, name, patch, names=None):\n+ def __new__(cls, name, patch, symbols=None, relations={}, **kwargs):\n if not isinstance(name, Str):\n name = Str(name)\n- # names is not in args because it is related only to printing, not to\n- # identifying the CoordSystem instance.\n- obj = super().__new__(cls, name, patch)\n- if not names:\n- names = ['%s_%d' % (name, i) for i in range(patch.dim)]\n- obj._names = tuple(str(i) for i in names)\n- obj.patch.coord_systems.append(obj)\n- obj.transforms = {}\n- # All the coordinate transformation logic is in this dictionary in the\n- # form of:\n- # key = other coordinate system\n- # value = tuple of # TODO make these Lambda instances\n- # - list of `Dummy` coordinates in this coordinate system\n- # - list of expressions as a function of the Dummies giving\n- # the coordinates in another coordinate system\n- obj._dummies = [Dummy(str(n)) for n in names]\n+\n+ # canonicallize the symbols\n+ if symbols is None or any(not isinstance(s, Symbol) for s in symbols) :\n+ # support deprecated signature\n+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(\n+ feature=\"Class signature 'names' of CoordSystem\",\n+ useinstead=\"class signature 'symbols'\",\n+ issue=19321,\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.7\"\n+ ).warn()\n+\n+ if symbols is None:\n+ names = kwargs.get('names', None)\n+ else:\n+ names = symbols\n+\n+ if names is None:\n+ symbols = Tuple(*[Symbol('%s_%d' % (name, i), real=True) for i in range(patch.dim)])\n+ else:\n+ symbols = Tuple(*[Symbol(n, real=True) for n in names])\n+ else:\n+ symbols = Tuple(*[Symbol(s.name, **s._assumptions.generator) for s in symbols])\n+\n+ # canonicallize the relations\n+ rel_temp = {}\n+ for k,v in relations.items():\n+ s1, s2 = k\n+ if not isinstance(s1, Str):\n+ s1 = Str(s1)\n+ if not isinstance(s2, Str):\n+ s2 = Str(s2)\n+ key = Tuple(s1, s2)\n+ rel_temp[key] = v\n+ relations = Dict(rel_temp)\n+\n+ # construct the object\n+ obj = super().__new__(cls, name, patch, symbols, relations)\n+\n+ # Add deprecated attributes\n+ obj.transforms = _deprecated_dict(\n+ \"Mutable CoordSystem.transforms\",\n+ \"'relations' parameter in class signature\",\n+ 19321,\n+ \"1.7\",\n+ {}\n+ )\n+ obj._names =_deprecated_list(\n+ \"CoordSystem._names\",\n+ \"CoordSystem.symbols\",\n+ 19321,\n+ \"1.7\",\n+ [str(n) for n in symbols]\n+ )\n+ obj.patch.coord_systems.append(obj) # deprecated\n+ obj._dummies = _deprecated_list(\n+ \"CoordSystem._dummies\",\n+ \"CoordSystem.symbols\",\n+ 19321,\n+ \"1.7\",\n+ [Dummy(str(n)) for n in symbols]\n+ )\n obj._dummy = Dummy()\n+\n return obj\n \n @property\n@@ -258,34 +316,132 @@ def name(self):\n def patch(self):\n return self.args[1]\n \n+ @property\n+ def manifold(self):\n+ return self.patch.manifold\n+\n+ @property\n+ def symbols(self):\n+ return [\n+ CoordinateSymbol(\n+ self, i, **s._assumptions.generator\n+ ) for i,s in enumerate(self.args[2])\n+ ]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def relations(self):\n+ return self.args[3]\n+\n @property\n def dim(self):\n return self.patch.dim\n \n ##########################################################################\n- # Coordinate transformations.\n+ # Finding transformation relation\n ##########################################################################\n \n+ def transformation(self, sys):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Return coordinate transform relation from *self* to *sys* as Lambda.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if self.relations != sys.relations:\n+ raise TypeError(\n+ \"Two coordinate systems have different relations\")\n+\n+ key = Tuple(self.name, sys.name)\n+ if key in self.relations:\n+ return self.relations[key]\n+ elif key[::-1] in self.relations:\n+ return self._inverse_transformation(sys, self)\n+ else:\n+ return self._indirect_transformation(self, sys)\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _inverse_transformation(sys1, sys2):\n+ # Find the transformation relation from sys2 to sys1\n+ forward_transform = sys1.transform(sys2)\n+ forward_syms, forward_results = forward_transform.args\n+\n+ inv_syms = [i.as_dummy() for i in forward_syms]\n+ inv_results = solve(\n+ [t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(inv_syms, forward_results)],\n+ list(forward_syms), dict=True)[0]\n+ inv_results = [inv_results[s] for s in forward_syms]\n+\n+ signature = tuple(inv_syms)\n+ expr = Matrix(inv_results)\n+ return Lambda(signature, expr)\n+\n+ @classmethod\n+ @cacheit\n+ def _indirect_transformation(cls, sys1, sys2):\n+ # Find the transformation relation between two indirectly connected coordinate systems\n+ path = cls._dijkstra(sys1, sys2)\n+ Lambdas = []\n+ for i in range(len(path) - 1):\n+ s1, s2 = path[i], path[i + 1]\n+ Lambdas.append(s1.transformation(s2))\n+ syms = Lambdas[-1].signature\n+ expr = syms\n+ for l in reversed(Lambdas):\n+ expr = l(*expr)\n+ return Lambda(syms, expr)\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _dijkstra(sys1, sys2):\n+ # Use Dijkstra algorithm to find the shortest path between two indirectly-connected\n+ # coordinate systems\n+ relations = sys1.relations\n+ graph = {}\n+ for s1, s2 in relations.keys():\n+ if s1 not in graph:\n+ graph[s1] = {s2}\n+ else:\n+ graph[s1].add(s2)\n+ if s2 not in graph:\n+ graph[s2] = {s1}\n+ else:\n+ graph[s2].add(s1)\n+\n+ path_dict = {sys:[0, [], 0] for sys in graph} # minimum distance, path, times of visited\n+\n+ def visit(sys):\n+ path_dict[sys][2] = 1\n+ for newsys in graph[sys]:\n+ distance = path_dict[sys][0] + 1\n+ if path_dict[newsys][0] >= distance or not path_dict[newsys][1]:\n+ path_dict[newsys][0] = distance\n+ path_dict[newsys][1] = [i for i in path_dict[sys][1]]\n+ path_dict[newsys][1].append(sys)\n+\n+ visit(sys1)\n+\n+ while True:\n+ min_distance = max(path_dict.values(), key=lambda x:x[0])[0]\n+ newsys = None\n+ for sys, lst in path_dict.items():\n+ if 0 < lst[0] <= min_distance and not lst[2]:\n+ min_distance = lst[0]\n+ newsys = sys\n+ if newsys is None:\n+ break\n+ visit(newsys)\n+\n+ result = path_dict[sys2][1]\n+ result.append(sys2)\n+\n+ if result == [sys2]:\n+ raise KeyError(\"Two coordinate systems are not connected.\")\n+ return result\n+\n def connect_to(self, to_sys, from_coords, to_exprs, inverse=True, fill_in_gaps=False):\n- \"\"\"Register the transformation used to switch to another coordinate system.\n-\n- Parameters\n- ==========\n-\n- to_sys\n- another instance of ``CoordSystem``\n- from_coords\n- list of symbols in terms of which ``to_exprs`` is given\n- to_exprs\n- list of the expressions of the new coordinate tuple\n- inverse\n- try to deduce and register the inverse transformation\n- fill_in_gaps\n- try to deduce other transformation that are made\n- possible by composing the present transformation with other already\n- registered transformation\n+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(\n+ feature=\"CoordSystem.connect_to\",\n+ useinstead=\"new instance generated with new 'transforms' parameter\",\n+ issue=19321,\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.7\"\n+ ).warn()\n \n- \"\"\"\n from_coords, to_exprs = dummyfy(from_coords, to_exprs)\n self.transforms[to_sys] = Matrix(from_coords), Matrix(to_exprs)\n \n@@ -297,6 +453,7 @@ def connect_to(self, to_sys, from_coords, to_exprs, inverse=True, fill_in_gaps=F\n \n @staticmethod\n def _inv_transf(from_coords, to_exprs):\n+ # Will be removed when connect_to is removed\n inv_from = [i.as_dummy() for i in from_coords]\n inv_to = solve(\n [t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(inv_from, to_exprs)],\n@@ -306,13 +463,49 @@ def _inv_transf(from_coords, to_exprs):\n \n @staticmethod\n def _fill_gaps_in_transformations():\n+ # Will be removed when connect_to is removed\n raise NotImplementedError\n- # TODO\n+\n+ ##########################################################################\n+ # Coordinate transformations\n+ ##########################################################################\n+\n+ def transform(self, sys, coordinates=None):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Return the result of coordinate transformation from *self* to *sys*.\n+ If coordinates are not given, coordinate symbols of *self* are used.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if coordinates is None:\n+ coordinates = Matrix(self.symbols)\n+ else:\n+ coordinates = Matrix(coordinates)\n+ if self != sys:\n+ transf = self.transformation(sys)\n+ coordinates = transf(*coordinates)\n+ return coordinates\n+\n+ def jacobian_matrix(self, sys, coordinates=None):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Return the jacobian matrix of a transformation.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ result = self.transform(sys).jacobian(self.symbols)\n+ if coordinates is not None:\n+ result = result.subs(list(zip(self.symbols, coordinates)))\n+ return result\n+\n+ def jacobian_determinant(self, sys, coordinates=None):\n+ \"\"\"Return the jacobian determinant of a transformation.\"\"\"\n+ return self.jacobian_matrix(sys, coordinates).det()\n \n def coord_tuple_transform_to(self, to_sys, coords):\n- \"\"\"Transform ``coords`` to coord system ``to_sys``.\n+ \"\"\"Transform ``coords`` to coord system ``to_sys``.\"\"\"\n+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(\n+ feature=\"CoordSystem.coord_tuple_transform_to\",\n+ useinstead=\"CoordSystem.transform\",\n+ issue=19321,\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.7\"\n+ ).warn()\n \n- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples.\"\"\"\n coords = Matrix(coords)\n if self != to_sys:\n transf = self.transforms[to_sys]\n@@ -321,77 +514,122 @@ def coord_tuple_transform_to(self, to_sys, coords):\n \n def jacobian(self, to_sys, coords):\n \"\"\"Return the jacobian matrix of a transformation.\"\"\"\n+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(\n+ feature=\"CoordSystem.jacobian\",\n+ useinstead=\"CoordSystem.jacobian_matrix\",\n+ issue=19321,\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.7\"\n+ ).warn()\n+\n with_dummies = self.coord_tuple_transform_to(\n to_sys, self._dummies).jacobian(self._dummies)\n return with_dummies.subs(list(zip(self._dummies, coords)))\n \n ##########################################################################\n- # Base fields.\n+ # Points\n ##########################################################################\n \n- def coord_function(self, coord_index):\n- \"\"\"Return a ``BaseScalarField`` that takes a point and returns one of the coords.\n+ def point(self, coords):\n+ \"\"\"Create a ``Point`` with coordinates given in this coord system.\"\"\"\n+ return Point(self, coords)\n+\n+ def point_to_coords(self, point):\n+ \"\"\"Calculate the coordinates of a point in this coord system.\"\"\"\n+ return point.coords(self)\n \n- Takes a point and returns its coordinate in this coordinate system.\n+ ##########################################################################\n+ # Base fields.\n+ ##########################################################################\n \n- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples.\"\"\"\n+ def base_scalar(self, coord_index):\n+ \"\"\"Return ``BaseScalarField`` that takes a point and returns one of the coordinates.\"\"\"\n return BaseScalarField(self, coord_index)\n+ coord_function = base_scalar\n \n- def coord_functions(self):\n+ def base_scalars(self):\n \"\"\"Returns a list of all coordinate functions.\n-\n- For more details see the ``coord_function`` method of this class.\"\"\"\n- return [self.coord_function(i) for i in range(self.dim)]\n+ For more details see the ``base_scalar`` method of this class.\"\"\"\n+ return [self.base_scalar(i) for i in range(self.dim)]\n+ coord_functions = base_scalars\n \n def base_vector(self, coord_index):\n \"\"\"Return a basis vector field.\n-\n The basis vector field for this coordinate system. It is also an\n- operator on scalar fields.\n-\n- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples.\"\"\"\n+ operator on scalar fields.\"\"\"\n return BaseVectorField(self, coord_index)\n \n def base_vectors(self):\n \"\"\"Returns a list of all base vectors.\n-\n For more details see the ``base_vector`` method of this class.\"\"\"\n return [self.base_vector(i) for i in range(self.dim)]\n \n def base_oneform(self, coord_index):\n \"\"\"Return a basis 1-form field.\n-\n The basis one-form field for this coordinate system. It is also an\n- operator on vector fields.\n-\n- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples.\"\"\"\n+ operator on vector fields.\"\"\"\n return Differential(self.coord_function(coord_index))\n \n def base_oneforms(self):\n \"\"\"Returns a list of all base oneforms.\n-\n For more details see the ``base_oneform`` method of this class.\"\"\"\n return [self.base_oneform(i) for i in range(self.dim)]\n \n- ##########################################################################\n- # Points.\n- ##########################################################################\n+class CoordinateSymbol(Symbol):\n+ \"\"\"A symbol which denotes an abstract value of i-th coordinate of\n+ the coordinate system with given context.\n \n- def point(self, coords):\n- \"\"\"Create a ``Point`` with coordinates given in this coord system.\n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n \n- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples.\"\"\"\n- return Point(self, coords)\n+ Each coordinates in coordinate system are represented by unique symbol,\n+ such as x, y, z in Cartesian coordinate system.\n \n- def point_to_coords(self, point):\n- \"\"\"Calculate the coordinates of a point in this coord system.\n+ You may not construct this class directly. Instead, use `symbols` method\n+ of CoordSystem.\n \n- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples.\"\"\"\n- return point.coords(self)\n+ Parameters\n+ ==========\n \n- ##########################################################################\n- # Printing.\n- ##########################################################################\n+ coord_sys : CoordSystem\n+\n+ index : integer\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem\n+ >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)\n+ >>> p = Patch('P', m)\n+ >>> _x, _y = symbols('x y', nonnegative=True)\n+\n+ >>> C = CoordSystem('C', p, [_x, _y])\n+ >>> x, y = C.symbols\n+\n+ >>> x.name\n+ 'x'\n+ >>> x.coord_sys == C\n+ True\n+ >>> x.index\n+ 0\n+ >>> x.is_nonnegative\n+ True\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index, **assumptions):\n+ name = coord_sys.args[2][index].name\n+ obj = super().__new__(cls, name, **assumptions)\n+ obj.coord_sys = coord_sys\n+ obj.index = index\n+ return obj\n+\n+ def __getnewargs__(self):\n+ return (self.coord_sys, self.index)\n+\n+ def _hashable_content(self):\n+ return (\n+ self.coord_sys, self.index\n+ ) + tuple(sorted(self.assumptions0.items()))\n \n class Point(Basic):\n \"\"\"Point defined in a coordinate system.\n@@ -399,7 +637,10 @@ class Point(Basic):\n Explanation\n ===========\n \n- To define a point you must supply coordinates and a coordinate system.\n+ Mathematically, point is defined in the manifold and does not have any coordinates\n+ by itself. Coordinate system is what imbues the coordinates to the point by coordinate\n+ chart. However, due to the difficulty of realizing such logic, you must supply\n+ a coordinate system and coordinates to define a Point here.\n \n The usage of this object after its definition is independent of the\n coordinate system that was used in order to define it, however due to\n@@ -411,67 +652,74 @@ class Point(Basic):\n \n coord_sys : CoordSystem\n \n- coords: list of sympy expressions\n+ coords : list\n The coordinates of the point.\n \n Examples\n ========\n \n- Define the boilerplate Manifold, Patch and coordinate systems:\n+ >>> from sympy import pi\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Point\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_r, R2_p\n+ >>> rho, theta = R2_p.symbols\n \n- >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, pi\n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom import (\n- ... Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, Point)\n- >>> r, theta = symbols('r, theta')\n- >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)\n- >>> p = Patch('P', m)\n- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)\n- >>> polar = CoordSystem('polar', p)\n- >>> polar.connect_to(rect, [r, theta], [r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)])\n+ >>> p = Point(R2_p, [rho, 3*pi/4])\n \n- Define a point using coordinates from one of the coordinate systems:\n+ >>> p.manifold == R2\n+ True\n \n- >>> p = Point(polar, [r, 3*pi/4])\n >>> p.coords()\n Matrix([\n- [ r],\n+ [ rho],\n [3*pi/4]])\n- >>> p.coords(rect)\n+ >>> p.coords(R2_r)\n Matrix([\n- [-sqrt(2)*r/2],\n- [ sqrt(2)*r/2]])\n+ [-sqrt(2)*rho/2],\n+ [ sqrt(2)*rho/2]])\n \n \"\"\"\n- def __new__(cls, coord_sys, coords):\n+\n+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, coords, **kwargs):\n coords = Matrix(coords)\n obj = super().__new__(cls, coord_sys, coords)\n obj._coord_sys = coord_sys\n obj._coords = coords\n return obj\n \n- def coords(self, to_sys=None):\n- \"\"\"Coordinates of the point in a given coordinate system.\n+ @property\n+ def patch(self):\n+ return self._coord_sys.patch\n \n- If ``to_sys`` is ``None`` it returns the coordinates in the system in\n- which the point was defined.\"\"\"\n- if to_sys:\n- return self._coord_sys.coord_tuple_transform_to(to_sys, self._coords)\n- else:\n+ @property\n+ def manifold(self):\n+ return self._coord_sys.manifold\n+\n+ @property\n+ def dim(self):\n+ return self.manifold.dim\n+\n+ def coords(self, sys=None):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Coordinates of the point in given coordinate system. If coordinate system\n+ is not passed, it returns the coordinates in the coordinate system in which\n+ the poin was defined.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if sys is None:\n return self._coords\n+ else:\n+ return self._coord_sys.transform(sys, self._coords)\n \n @property\n def free_symbols(self):\n return self._coords.free_symbols\n \n-\n class BaseScalarField(Expr):\n- \"\"\"Base Scalar Field over a Manifold for a given Coordinate System.\n+ \"\"\"Base scalar field over a manifold for a given coordinate system.\n \n Explanation\n ===========\n \n A scalar field takes a point as an argument and returns a scalar.\n-\n A base scalar field of a coordinate system takes a point and returns one of\n the coordinates of that point in the coordinate system in question.\n \n@@ -482,7 +730,6 @@ class BaseScalarField(Expr):\n coordinate system in which it was defined, however due to limitations in\n the simplification routines you may arrive at more complicated\n expression if you use unappropriate coordinate systems.\n-\n You can build complicated scalar fields by just building up SymPy\n expressions containing ``BaseScalarField`` instances.\n \n@@ -496,30 +743,23 @@ class BaseScalarField(Expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- Define boilerplate Manifold, Patch and coordinate systems:\n-\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, pi, Function\n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField\n- >>> r0, theta0 = symbols('r0, theta0')\n- >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)\n- >>> p = Patch('P', m)\n- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)\n- >>> polar = CoordSystem('polar', p)\n- >>> polar.connect_to(rect, [r0, theta0], [r0*cos(theta0), r0*sin(theta0)])\n-\n- Point to be used as an argument for the filed:\n-\n- >>> point = polar.point([r0, 0])\n-\n- Examples of fields:\n+ >>> from sympy import Function, pi\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import BaseScalarField\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r, R2_p\n+ >>> rho, _ = R2_p.symbols\n+ >>> point = R2_p.point([rho, 0])\n+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()\n+ >>> ftheta = BaseScalarField(R2_r, 1)\n+\n+ >>> fx(point)\n+ rho\n+ >>> fy(point)\n+ 0\n \n- >>> fx = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n- >>> fy = BaseScalarField(rect, 1)\n >>> (fx**2+fy**2).rcall(point)\n- r0**2\n+ rho**2\n \n >>> g = Function('g')\n- >>> ftheta = BaseScalarField(polar, 1)\n >>> fg = g(ftheta-pi)\n >>> fg.rcall(point)\n g(-pi)\n@@ -528,16 +768,35 @@ class BaseScalarField(Expr):\n \n is_commutative = True\n \n- def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index):\n+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index, **kwargs):\n index = _sympify(index)\n obj = super().__new__(cls, coord_sys, index)\n obj._coord_sys = coord_sys\n obj._index = index\n return obj\n \n+ @property\n+ def coord_sys(self):\n+ return self.args[0]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def index(self):\n+ return self.args[1]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def patch(self):\n+ return self.coord_sys.patch\n+\n+ @property\n+ def manifold(self):\n+ return self.coord_sys.manifold\n+\n+ @property\n+ def dim(self):\n+ return self.manifold.dim\n+\n def __call__(self, *args):\n \"\"\"Evaluating the field at a point or doing nothing.\n-\n If the argument is a ``Point`` instance, the field is evaluated at that\n point. The field is returned itself if the argument is any other\n object. It is so in order to have working recursive calling mechanics\n@@ -559,14 +818,13 @@ def doit(self):\n \n \n class BaseVectorField(Expr):\n- r\"\"\"Vector Field over a Manifold.\n+ r\"\"\"Base vector field over a manifold for a given coordinate system.\n \n Explanation\n ===========\n \n A vector field is an operator taking a scalar field and returning a\n directional derivative (which is also a scalar field).\n-\n A base vector field is the same type of operator, however the derivation is\n specifically done with respect to a chosen coordinate.\n \n@@ -580,7 +838,6 @@ class BaseVectorField(Expr):\n \n Parameters\n ==========\n-\n coord_sys : CoordSystem\n \n index : integer\n@@ -588,29 +845,19 @@ class BaseVectorField(Expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.\n-\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, Function\n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_p, R2_r\n+ >>> from sympy import Function\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_p, R2_r\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import BaseVectorField\n >>> from sympy import pprint\n- >>> x0, y0, r0, theta0 = symbols('x0, y0, r0, theta0')\n \n- Points to be used as arguments for the field:\n-\n- >>> point_p = R2_p.point([r0, theta0])\n- >>> point_r = R2_r.point([x0, y0])\n-\n- Scalar field to operate on:\n+ >>> x, y = R2_r.symbols\n+ >>> rho, theta = R2_p.symbols\n+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()\n+ >>> point_p = R2_p.point([rho, theta])\n+ >>> point_r = R2_r.point([x, y])\n \n >>> g = Function('g')\n- >>> s_field = g(R2.x, R2.y)\n- >>> s_field.rcall(point_r)\n- g(x0, y0)\n- >>> s_field.rcall(point_p)\n- g(r0*cos(theta0), r0*sin(theta0))\n-\n- Vector field:\n+ >>> s_field = g(fx, fy)\n \n >>> v = BaseVectorField(R2_r, 1)\n >>> pprint(v(s_field))\n@@ -618,31 +865,49 @@ class BaseVectorField(Expr):\n |---(g(x, xi))||\n \\dxi /|xi=y\n >>> pprint(v(s_field).rcall(point_r).doit())\n- d\n- ---(g(x0, y0))\n- dy0\n+ d\n+ --(g(x, y))\n+ dy\n >>> pprint(v(s_field).rcall(point_p))\n / d \\|\n- |---(g(r0*cos(theta0), xi))||\n- \\dxi /|xi=r0*sin(theta0)\n+ |---(g(rho*cos(theta), xi))||\n+ \\dxi /|xi=rho*sin(theta)\n \n \"\"\"\n \n is_commutative = False\n \n- def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index):\n+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index, **kwargs):\n index = _sympify(index)\n obj = super().__new__(cls, coord_sys, index)\n obj._coord_sys = coord_sys\n obj._index = index\n return obj\n \n+ @property\n+ def coord_sys(self):\n+ return self.args[0]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def index(self):\n+ return self.args[1]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def patch(self):\n+ return self.coord_sys.patch\n+\n+ @property\n+ def manifold(self):\n+ return self.coord_sys.manifold\n+\n+ @property\n+ def dim(self):\n+ return self.manifold.dim\n+\n def __call__(self, scalar_field):\n \"\"\"Apply on a scalar field.\n-\n The action of a vector field on a scalar field is a directional\n differentiation.\n-\n If the argument is not a scalar field an error is raised.\n \"\"\"\n if covariant_order(scalar_field) or contravariant_order(scalar_field):\n@@ -662,11 +927,11 @@ def __call__(self, scalar_field):\n d_result = d_result.diff(d_var)\n \n # Second step: e_x(x) -> 1 and e_x(r) -> cos(atan2(x, y))\n- coords = self._coord_sys._dummies\n+ coords = self._coord_sys.symbols\n d_funcs_deriv = [f.diff(d_var) for f in d_funcs]\n d_funcs_deriv_sub = []\n for b in base_scalars:\n- jac = self._coord_sys.jacobian(b._coord_sys, coords)\n+ jac = self._coord_sys.jacobian_matrix(b._coord_sys, coords)\n d_funcs_deriv_sub.append(jac[b._index, self._index])\n d_result = d_result.subs(list(zip(d_funcs_deriv, d_funcs_deriv_sub)))\n \n@@ -686,6 +951,9 @@ def _find_coords(expr):\n class Commutator(Expr):\n r\"\"\"Commutator of two vector fields.\n \n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n The commutator of two vector fields `v_1` and `v_2` is defined as the\n vector field `[v_1, v_2]` that evaluated on each scalar field `f` is equal\n to `v_1(v_2(f)) - v_2(v_1(f))`.\n@@ -693,15 +961,15 @@ class Commutator(Expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.\n \n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_p, R2_r\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Commutator\n >>> from sympy.simplify import simplify\n \n- Vector fields:\n+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()\n+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()\n+ >>> e_r = R2_p.base_vector(0)\n \n- >>> e_x, e_y, e_r = R2.e_x, R2.e_y, R2.e_r\n >>> c_xy = Commutator(e_x, e_y)\n >>> c_xr = Commutator(e_x, e_r)\n >>> c_xy\n@@ -710,9 +978,8 @@ class Commutator(Expr):\n Unfortunately, the current code is not able to compute everything:\n \n >>> c_xr\n- Commutator(e_x, e_r)\n-\n- >>> simplify(c_xr(R2.y**2))\n+ Commutator(e_x, e_rho)\n+ >>> simplify(c_xr(fy**2))\n -2*cos(theta)*y**2/(x**2 + y**2)\n \n \"\"\"\n@@ -722,13 +989,13 @@ def __new__(cls, v1, v2):\n raise ValueError(\n 'Only commutators of vector fields are supported.')\n if v1 == v2:\n- return Zero()\n+ return S.Zero\n coord_sys = set().union(*[_find_coords(v) for v in (v1, v2)])\n if len(coord_sys) == 1:\n # Only one coordinate systems is used, hence it is easy enough to\n # actually evaluate the commutator.\n if all(isinstance(v, BaseVectorField) for v in (v1, v2)):\n- return Zero()\n+ return S.Zero\n bases_1, bases_2 = [list(v.atoms(BaseVectorField))\n for v in (v1, v2)]\n coeffs_1 = [v1.expand().coeff(b) for b in bases_1]\n@@ -739,53 +1006,51 @@ def __new__(cls, v1, v2):\n res += c1*b1(c2)*b2 - c2*b2(c1)*b1\n return res\n else:\n- return super().__new__(cls, v1, v2)\n+ obj = super().__new__(cls, v1, v2)\n+ obj._v1 = v1 # deprecated assignment\n+ obj._v2 = v2 # deprecated assignment\n+ return obj\n \n- def __init__(self, v1, v2):\n- super().__init__()\n- self._args = (v1, v2)\n- self._v1 = v1\n- self._v2 = v2\n+ @property\n+ def v1(self):\n+ return self.args[0]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def v2(self):\n+ return self.args[1]\n \n def __call__(self, scalar_field):\n \"\"\"Apply on a scalar field.\n-\n If the argument is not a scalar field an error is raised.\n \"\"\"\n- return self._v1(self._v2(scalar_field)) - self._v2(self._v1(scalar_field))\n+ return self.v1(self.v2(scalar_field)) - self.v2(self.v1(scalar_field))\n \n \n class Differential(Expr):\n r\"\"\"Return the differential (exterior derivative) of a form field.\n \n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n The differential of a form (i.e. the exterior derivative) has a complicated\n definition in the general case.\n-\n The differential `df` of the 0-form `f` is defined for any vector field `v`\n as `df(v) = v(f)`.\n \n Examples\n ========\n \n- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.\n-\n >>> from sympy import Function\n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Differential\n >>> from sympy import pprint\n \n- Scalar field (0-forms):\n-\n+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()\n+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()\n >>> g = Function('g')\n- >>> s_field = g(R2.x, R2.y)\n-\n- Vector fields:\n-\n- >>> e_x, e_y, = R2.e_x, R2.e_y\n-\n- Differentials:\n-\n+ >>> s_field = g(fx, fy)\n >>> dg = Differential(s_field)\n+\n >>> dg\n d(g(x, y))\n >>> pprint(dg(e_x))\n@@ -801,7 +1066,6 @@ class Differential(Expr):\n \n >>> Differential(dg)\n 0\n-\n \"\"\"\n \n is_commutative = False\n@@ -811,18 +1075,22 @@ def __new__(cls, form_field):\n raise ValueError(\n 'A vector field was supplied as an argument to Differential.')\n if isinstance(form_field, Differential):\n- return Zero()\n+ return S.Zero\n else:\n- return super().__new__(cls, form_field)\n+ obj = super().__new__(cls, form_field)\n+ obj._form_field = form_field # deprecated assignment\n+ return obj\n \n- def __init__(self, form_field):\n- super().__init__()\n- self._form_field = form_field\n- self._args = (self._form_field, )\n+ @property\n+ def form_field(self):\n+ return self.args[0]\n \n def __call__(self, *vector_fields):\n \"\"\"Apply on a list of vector_fields.\n \n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n If the number of vector fields supplied is not equal to 1 + the order of\n the form field inside the differential the result is undefined.\n \n@@ -867,10 +1135,12 @@ def __call__(self, *vector_fields):\n ret += (-1)**(i + j)*t\n return ret\n \n-\n class TensorProduct(Expr):\n \"\"\"Tensor product of forms.\n \n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n The tensor product permits the creation of multilinear functionals (i.e.\n higher order tensors) out of lower order fields (e.g. 1-forms and vector\n fields). However, the higher tensors thus created lack the interesting\n@@ -880,27 +1150,28 @@ class TensorProduct(Expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.\n-\n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import TensorProduct\n \n- >>> TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)(R2.e_x, R2.e_y)\n+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()\n+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()\n+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()\n+\n+ >>> TensorProduct(dx, dy)(e_x, e_y)\n 1\n- >>> TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)(R2.e_y, R2.e_x)\n+ >>> TensorProduct(dx, dy)(e_y, e_x)\n 0\n- >>> TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.x*R2.dy)(R2.x*R2.e_x, R2.e_y)\n+ >>> TensorProduct(dx, fx*dy)(fx*e_x, e_y)\n x**2\n- >>> TensorProduct(R2.e_x, R2.e_y)(R2.x**2, R2.y**2)\n+ >>> TensorProduct(e_x, e_y)(fx**2, fy**2)\n 4*x*y\n- >>> TensorProduct(R2.e_y, R2.dx)(R2.y)\n+ >>> TensorProduct(e_y, dx)(fy)\n dx\n \n-\n You can nest tensor products.\n \n- >>> tp1 = TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)\n- >>> TensorProduct(tp1, R2.dx)(R2.e_x, R2.e_y, R2.e_x)\n+ >>> tp1 = TensorProduct(dx, dy)\n+ >>> TensorProduct(tp1, dx)(e_x, e_y, e_x)\n 1\n \n You can make partial contraction for instance when 'raising an index'.\n@@ -908,13 +1179,13 @@ class TensorProduct(Expr):\n respective position in the tensor product is left as it is.\n \n >>> TP = TensorProduct\n- >>> metric = TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + 3*TP(R2.dy, R2.dy)\n- >>> metric.rcall(R2.e_y, None)\n+ >>> metric = TP(dx, dx) + 3*TP(dy, dy)\n+ >>> metric.rcall(e_y, None)\n 3*dy\n \n Or automatically pad the args with ``None`` without specifying them.\n \n- >>> metric.rcall(R2.e_y)\n+ >>> metric.rcall(e_y)\n 3*dy\n \n \"\"\"\n@@ -928,10 +1199,6 @@ def __new__(cls, *args):\n else:\n return scalar\n \n- def __init__(self, *args):\n- super().__init__()\n- self._args = args\n-\n def __call__(self, *fields):\n \"\"\"Apply on a list of fields.\n \n@@ -942,6 +1209,7 @@ def __call__(self, *fields):\n the forms inside the tensor product. The sublists are provided as\n arguments to these forms and the resulting expressions are given to the\n constructor of ``TensorProduct``.\n+\n \"\"\"\n tot_order = covariant_order(self) + contravariant_order(self)\n tot_args = len(fields)\n@@ -957,30 +1225,35 @@ def __call__(self, *fields):\n class WedgeProduct(TensorProduct):\n \"\"\"Wedge product of forms.\n \n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n In the context of integration only completely antisymmetric forms make\n sense. The wedge product permits the creation of such forms.\n \n Examples\n ========\n \n- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.\n-\n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import WedgeProduct\n \n- >>> WedgeProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)(R2.e_x, R2.e_y)\n+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()\n+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()\n+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()\n+\n+ >>> WedgeProduct(dx, dy)(e_x, e_y)\n 1\n- >>> WedgeProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)(R2.e_y, R2.e_x)\n+ >>> WedgeProduct(dx, dy)(e_y, e_x)\n -1\n- >>> WedgeProduct(R2.dx, R2.x*R2.dy)(R2.x*R2.e_x, R2.e_y)\n+ >>> WedgeProduct(dx, fx*dy)(fx*e_x, e_y)\n x**2\n- >>> WedgeProduct(R2.e_x,R2.e_y)(R2.y,None)\n+ >>> WedgeProduct(e_x, e_y)(fy, None)\n -e_x\n \n You can nest wedge products.\n \n- >>> wp1 = WedgeProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)\n- >>> WedgeProduct(wp1, R2.dx)(R2.e_x, R2.e_y, R2.e_x)\n+ >>> wp1 = WedgeProduct(dx, dy)\n+ >>> WedgeProduct(wp1, dx)(e_x, e_y, e_x)\n 0\n \n \"\"\"\n@@ -988,7 +1261,6 @@ class WedgeProduct(TensorProduct):\n # TODO you do not need all these permutations (neither the prefactor)\n def __call__(self, *fields):\n \"\"\"Apply on a list of vector_fields.\n-\n The expression is rewritten internally in terms of tensor products and evaluated.\"\"\"\n orders = (covariant_order(e) + contravariant_order(e) for e in self.args)\n mul = 1/Mul(*(factorial(o) for o in orders))\n@@ -1002,6 +1274,9 @@ def __call__(self, *fields):\n class LieDerivative(Expr):\n \"\"\"Lie derivative with respect to a vector field.\n \n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n The transport operator that defines the Lie derivative is the pushforward of\n the field to be derived along the integral curve of the field with respect\n to which one derives.\n@@ -1009,27 +1284,35 @@ class LieDerivative(Expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r, R2_p\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import (LieDerivative, TensorProduct)\n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, R2.y)\n+\n+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()\n+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()\n+ >>> e_rho, e_theta = R2_p.base_vectors()\n+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()\n+\n+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, fy)\n 0\n- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, R2.x)\n+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, fx)\n 1\n- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, R2.e_x)\n+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, e_x)\n 0\n \n The Lie derivative of a tensor field by another tensor field is equal to\n their commutator:\n \n- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, R2.e_r)\n- Commutator(e_x, e_r)\n- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x + R2.e_y, R2.x)\n+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, e_rho)\n+ Commutator(e_x, e_rho)\n+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x + e_y, fx)\n 1\n- >>> tp = TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)\n- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, tp)\n+\n+ >>> tp = TensorProduct(dx, dy)\n+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, tp)\n LieDerivative(e_x, TensorProduct(dx, dy))\n- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, tp)\n+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, tp)\n LieDerivative(e_x, TensorProduct(dx, dy))\n+\n \"\"\"\n def __new__(cls, v_field, expr):\n expr_form_ord = covariant_order(expr)\n@@ -1038,21 +1321,27 @@ def __new__(cls, v_field, expr):\n ' vector fields. The supplied argument was not a '\n 'vector field.')\n if expr_form_ord > 0:\n- return super().__new__(cls, v_field, expr)\n+ obj = super().__new__(cls, v_field, expr)\n+ # deprecated assignments\n+ obj._v_field = v_field\n+ obj._expr = expr\n+ return obj\n if expr.atoms(BaseVectorField):\n return Commutator(v_field, expr)\n else:\n return v_field.rcall(expr)\n \n- def __init__(self, v_field, expr):\n- super().__init__()\n- self._v_field = v_field\n- self._expr = expr\n- self._args = (self._v_field, self._expr)\n+ @property\n+ def v_field(self):\n+ return self.args[0]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def expr(self):\n+ return self.args[1]\n \n def __call__(self, *args):\n- v = self._v_field\n- expr = self._expr\n+ v = self.v_field\n+ expr = self.expr\n lead_term = v(expr(*args))\n rest = Add(*[Mul(*args[:i] + (Commutator(v, args[i]),) + args[i + 1:])\n for i in range(len(args))])\n@@ -1065,32 +1354,52 @@ class BaseCovarDerivativeOp(Expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_r\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import BaseCovarDerivativeOp\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, TensorProduct\n+\n >>> TP = TensorProduct\n- >>> ch = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))\n+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()\n+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()\n+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()\n+\n+ >>> ch = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(dx, dx) + TP(dy, dy))\n >>> ch\n [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]\n >>> cvd = BaseCovarDerivativeOp(R2_r, 0, ch)\n- >>> cvd(R2.x)\n+ >>> cvd(fx)\n 1\n- >>> cvd(R2.x*R2.e_x)\n+ >>> cvd(fx*e_x)\n e_x\n \"\"\"\n- def __init__(self, coord_sys, index, christoffel):\n- super().__init__()\n- self._coord_sys = coord_sys\n- self._index = index\n- self._christoffel = christoffel\n- self._args = self._coord_sys, self._index, self._christoffel\n+\n+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index, christoffel):\n+ index = _sympify(index)\n+ christoffel = ImmutableDenseNDimArray(christoffel)\n+ obj = super().__new__(cls, coord_sys, index, christoffel)\n+ # deprecated assignments\n+ obj._coord_sys = coord_sys\n+ obj._index = index\n+ obj._christoffel = christoffel\n+ return obj\n+\n+ @property\n+ def coord_sys(self):\n+ return self.args[0]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def index(self):\n+ return self.args[1]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def christoffel(self):\n+ return self.args[2]\n \n def __call__(self, field):\n \"\"\"Apply on a scalar field.\n \n The action of a vector field on a scalar field is a directional\n differentiation.\n-\n If the argument is not a scalar field the behaviour is undefined.\n \"\"\"\n if covariant_order(field) != 0:\n@@ -1136,31 +1445,44 @@ class CovarDerivativeOp(Expr):\n Examples\n ========\n \n- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import CovarDerivativeOp\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, TensorProduct\n >>> TP = TensorProduct\n- >>> ch = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))\n+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()\n+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()\n+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()\n+ >>> ch = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(dx, dx) + TP(dy, dy))\n+\n >>> ch\n [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]\n- >>> cvd = CovarDerivativeOp(R2.x*R2.e_x, ch)\n- >>> cvd(R2.x)\n+ >>> cvd = CovarDerivativeOp(fx*e_x, ch)\n+ >>> cvd(fx)\n x\n- >>> cvd(R2.x*R2.e_x)\n+ >>> cvd(fx*e_x)\n x*e_x\n \n \"\"\"\n- def __init__(self, wrt, christoffel):\n- super().__init__()\n+\n+ def __new__(cls, wrt, christoffel):\n if len({v._coord_sys for v in wrt.atoms(BaseVectorField)}) > 1:\n raise NotImplementedError()\n if contravariant_order(wrt) != 1 or covariant_order(wrt):\n raise ValueError('Covariant derivatives are defined only with '\n 'respect to vector fields. The supplied argument '\n 'was not a vector field.')\n- self._wrt = wrt\n- self._christoffel = christoffel\n- self._args = self._wrt, self._christoffel\n+ obj = super().__new__(cls, wrt, christoffel)\n+ # deprecated assigments\n+ obj._wrt = wrt\n+ obj._christoffel = christoffel\n+ return obj\n+\n+ @property\n+ def wrt(self):\n+ return self.args[0]\n+\n+ def christoffel(self):\n+ return self.args[1]\n \n def __call__(self, field):\n vectors = list(self._wrt.atoms(BaseVectorField))\n@@ -1175,6 +1497,9 @@ def __call__(self, field):\n def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeffs=False):\n r\"\"\"Return the series expansion for an integral curve of the field.\n \n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n Integral curve is a function `\\gamma` taking a parameter in `R` to a point\n in the manifold. It verifies the equation:\n \n@@ -1184,7 +1509,6 @@ def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeff\n value `t` for the parameter and any scalar field `f`.\n \n This equation can also be decomposed of a basis of coordinate functions\n-\n `V(f_i)\\big(\\gamma(t)\\big) = \\frac{d}{dt}f_i\\big(\\gamma(t)\\big) \\quad \\forall i`\n \n This function returns a series expansion of `\\gamma(t)` in terms of the\n@@ -1193,22 +1517,20 @@ def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeff\n represent movement between points on the manifold (i.e. there is no such\n thing as a difference of points for a general manifold).\n \n- See Also\n- ========\n-\n- intcurve_diffequ\n-\n Parameters\n ==========\n-\n vector_field\n the vector field for which an integral curve will be given\n+\n param\n the argument of the function `\\gamma` from R to the curve\n+\n start_point\n the point which corresponds to `\\gamma(0)`\n+\n n\n the order to which to expand\n+\n coord_sys\n the coordinate system in which to expand\n coeffs (default False) - if True return a list of elements of the expansion\n@@ -1267,6 +1589,11 @@ def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeff\n [t**2*(-x**2/(x**2 + y**2)**(3/2) + 1/sqrt(x**2 + y**2))/2],\n [ t**2*x*y/(x**2 + y**2)**2]])\n \n+ See Also\n+ ========\n+\n+ intcurve_diffequ\n+\n \"\"\"\n if contravariant_order(vector_field) != 1 or covariant_order(vector_field):\n raise ValueError('The supplied field was not a vector field.')\n@@ -1291,6 +1618,9 @@ def taylor_terms_per_coord(coord_function):\n def intcurve_diffequ(vector_field, param, start_point, coord_sys=None):\n r\"\"\"Return the differential equation for an integral curve of the field.\n \n+ Explanation\n+ ===========\n+\n Integral curve is a function `\\gamma` taking a parameter in `R` to a point\n in the manifold. It verifies the equation:\n \n@@ -1305,25 +1635,24 @@ def intcurve_diffequ(vector_field, param, start_point, coord_sys=None):\n represent movement between points on the manifold (i.e. there is no such\n thing as a difference of points for a general manifold).\n \n- See Also\n- ========\n-\n- intcurve_series\n-\n Parameters\n ==========\n \n vector_field\n the vector field for which an integral curve will be given\n+\n param\n the argument of the function `\\gamma` from R to the curve\n+\n start_point\n the point which corresponds to `\\gamma(0)`\n+\n coord_sys\n the coordinate system in which to give the equations\n \n Returns\n =======\n+\n a tuple of (equations, initial conditions)\n \n Examples\n@@ -1356,6 +1685,11 @@ def intcurve_diffequ(vector_field, param, start_point, coord_sys=None):\n >>> init_cond\n [f_0(0) - 1, f_1(0) - pi/2]\n \n+ See Also\n+ ========\n+\n+ intcurve_series\n+\n \"\"\"\n if contravariant_order(vector_field) != 1 or covariant_order(vector_field):\n raise ValueError('The supplied field was not a vector field.')\n@@ -1394,6 +1728,7 @@ def contravariant_order(expr, _strict=False):\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import contravariant_order\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n >>> from sympy.abc import a\n+\n >>> contravariant_order(a)\n 0\n >>> contravariant_order(a*R2.x + 2)\n@@ -1439,6 +1774,7 @@ def covariant_order(expr, _strict=False):\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import covariant_order\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n >>> from sympy.abc import a\n+\n >>> covariant_order(a)\n 0\n >>> covariant_order(a*R2.x + 2)\n@@ -1480,7 +1816,6 @@ def covariant_order(expr, _strict=False):\n ###############################################################################\n def vectors_in_basis(expr, to_sys):\n \"\"\"Transform all base vectors in base vectors of a specified coord basis.\n-\n While the new base vectors are in the new coordinate system basis, any\n coefficients are kept in the old system.\n \n@@ -1489,16 +1824,18 @@ def vectors_in_basis(expr, to_sys):\n \n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import vectors_in_basis\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r, R2_p\n+\n >>> vectors_in_basis(R2_r.e_x, R2_p)\n- -y*e_theta/(x**2 + y**2) + x*e_r/sqrt(x**2 + y**2)\n+ -y*e_theta/(x**2 + y**2) + x*e_rho/sqrt(x**2 + y**2)\n >>> vectors_in_basis(R2_p.e_r, R2_r)\n sin(theta)*e_y + cos(theta)*e_x\n+\n \"\"\"\n vectors = list(expr.atoms(BaseVectorField))\n new_vectors = []\n for v in vectors:\n cs = v._coord_sys\n- jac = cs.jacobian(to_sys, cs.coord_functions())\n+ jac = cs.jacobian_matrix(to_sys, cs.coord_functions())\n new = (jac.T*Matrix(to_sys.base_vectors()))[v._index]\n new_vectors.append(new)\n return expr.subs(list(zip(vectors, new_vectors)))\n@@ -1520,6 +1857,7 @@ def twoform_to_matrix(expr):\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import twoform_to_matrix, TensorProduct\n >>> TP = TensorProduct\n+\n >>> twoform_to_matrix(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))\n Matrix([\n [1, 0],\n@@ -1551,7 +1889,6 @@ def twoform_to_matrix(expr):\n \n def metric_to_Christoffel_1st(expr):\n \"\"\"Return the nested list of Christoffel symbols for the given metric.\n-\n This returns the Christoffel symbol of first kind that represents the\n Levi-Civita connection for the given metric.\n \n@@ -1561,6 +1898,7 @@ def metric_to_Christoffel_1st(expr):\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Christoffel_1st, TensorProduct\n >>> TP = TensorProduct\n+\n >>> metric_to_Christoffel_1st(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))\n [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]\n >>> metric_to_Christoffel_1st(R2.x*TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))\n@@ -1584,7 +1922,6 @@ def metric_to_Christoffel_1st(expr):\n \n def metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(expr):\n \"\"\"Return the nested list of Christoffel symbols for the given metric.\n-\n This returns the Christoffel symbol of second kind that represents the\n Levi-Civita connection for the given metric.\n \n@@ -1594,6 +1931,7 @@ def metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(expr):\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, TensorProduct\n >>> TP = TensorProduct\n+\n >>> metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))\n [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]\n >>> metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(R2.x*TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))\n@@ -1611,7 +1949,7 @@ def metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(expr):\n for e in matrix:\n s_fields.update(e.atoms(BaseScalarField))\n s_fields = list(s_fields)\n- dums = coord_sys._dummies\n+ dums = coord_sys.symbols\n matrix = matrix.subs(list(zip(s_fields, dums))).inv().subs(list(zip(dums, s_fields)))\n # XXX end of workaround\n christoffel = [[[Add(*[matrix[i, l]*ch_1st[l, j, k] for l in indices])\n@@ -1635,18 +1973,18 @@ def metric_to_Riemann_components(expr):\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Riemann_components, TensorProduct\n >>> TP = TensorProduct\n+\n >>> metric_to_Riemann_components(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))\n [[[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]], [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]]\n-\n >>> non_trivial_metric = exp(2*R2.r)*TP(R2.dr, R2.dr) + \\\n R2.r**2*TP(R2.dtheta, R2.dtheta)\n >>> non_trivial_metric\n- exp(2*r)*TensorProduct(dr, dr) + r**2*TensorProduct(dtheta, dtheta)\n+ exp(2*rho)*TensorProduct(drho, drho) + rho**2*TensorProduct(dtheta, dtheta)\n >>> riemann = metric_to_Riemann_components(non_trivial_metric)\n >>> riemann[0, :, :, :]\n- [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, exp(-2*r)*r], [-exp(-2*r)*r, 0]]]\n+ [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, exp(-2*rho)*rho], [-exp(-2*rho)*rho, 0]]]\n >>> riemann[1, :, :, :]\n- [[[0, -1/r], [1/r, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]\n+ [[[0, -1/rho], [1/rho, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]\n \n \"\"\"\n ch_2nd = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(expr)\n@@ -1676,6 +2014,7 @@ def metric_to_Riemann_components(expr):\n \n \n def metric_to_Ricci_components(expr):\n+\n \"\"\"Return the components of the Ricci tensor expressed in a given basis.\n \n Given a metric it calculates the components of the Ricci tensor in the\n@@ -1689,15 +2028,15 @@ def metric_to_Ricci_components(expr):\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Ricci_components, TensorProduct\n >>> TP = TensorProduct\n+\n >>> metric_to_Ricci_components(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))\n [[0, 0], [0, 0]]\n-\n >>> non_trivial_metric = exp(2*R2.r)*TP(R2.dr, R2.dr) + \\\n R2.r**2*TP(R2.dtheta, R2.dtheta)\n >>> non_trivial_metric\n- exp(2*r)*TensorProduct(dr, dr) + r**2*TensorProduct(dtheta, dtheta)\n+ exp(2*rho)*TensorProduct(drho, drho) + rho**2*TensorProduct(dtheta, dtheta)\n >>> metric_to_Ricci_components(non_trivial_metric)\n- [[1/r, 0], [0, exp(-2*r)*r]]\n+ [[1/rho, 0], [0, exp(-2*rho)*rho]]\n \n \"\"\"\n riemann = metric_to_Riemann_components(expr)\n@@ -1707,3 +2046,43 @@ def metric_to_Ricci_components(expr):\n for j in indices]\n for i in indices]\n return ImmutableDenseNDimArray(ricci)\n+\n+###############################################################################\n+# Classes for deprecation\n+###############################################################################\n+\n+class _deprecated_container(object):\n+ # This class gives deprecation warning.\n+ # When deprecated features are completely deleted, this should be removed as well.\n+ # See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/19368\n+ def __init__(self, feature, useinstead, issue, version, data):\n+ super().__init__(data)\n+ self.feature = feature\n+ self.useinstead = useinstead\n+ self.issue = issue\n+ self.version = version\n+\n+ def warn(self):\n+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(\n+ feature=self.feature,\n+ useinstead=self.useinstead,\n+ issue=self.issue,\n+ deprecated_since_version=self.version).warn()\n+\n+ def __iter__(self):\n+ self.warn()\n+ return super().__iter__()\n+\n+ def __getitem__(self, key):\n+ self.warn()\n+ return super().__getitem__(key)\n+\n+ def __contains__(self, key):\n+ self.warn()\n+ return super().__contains__(key)\n+\n+class _deprecated_list(_deprecated_container, list):\n+ pass\n+\n+class _deprecated_dict(_deprecated_container, dict):\n+ pass\ndiff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py b/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py\nindex 1226a63f0377..55c964ccbd2b 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py\n@@ -9,28 +9,44 @@\n \"\"\"\n \n from typing import Any\n+import warnings\n \n+from sympy import sqrt, atan2, acos, sin, cos, Lambda, Matrix, symbols, Dummy\n from .diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem\n-from sympy import sqrt, atan2, acos, sin, cos, Dummy\n+\n+__all__ = [\n+ 'R2', 'R2_origin', 'relations_2d', 'R2_r', 'R2_p',\n+ 'R3', 'R3_origin', 'relations_3d', 'R3_r', 'R3_c', 'R3_s'\n+]\n \n ###############################################################################\n # R2\n ###############################################################################\n R2 = Manifold('R^2', 2) # type: Any\n-# Patch and coordinate systems.\n+\n R2_origin = Patch('origin', R2) # type: Any\n-R2_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R2_origin, ['x', 'y']) # type: Any\n-R2_p = CoordSystem('polar', R2_origin, ['r', 'theta']) # type: Any\n-\n-# Connecting the coordinate charts.\n-x, y, r, theta = [Dummy(s) for s in ['x', 'y', 'r', 'theta']]\n-R2_r.connect_to(R2_p, [x, y],\n- [sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)],\n- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n-R2_p.connect_to(R2_r, [r, theta],\n- [r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)],\n- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n-del x, y, r, theta\n+\n+x, y = symbols('x y', real=True)\n+r, theta = symbols('rho theta', nonnegative=True)\n+\n+relations_2d = {\n+ ('rectangular', 'polar'): Lambda((x, y), Matrix([sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)])),\n+ ('polar', 'rectangular'): Lambda((r, theta), Matrix([r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)])),\n+}\n+\n+R2_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R2_origin, [x, y], relations_2d) # type: Any\n+R2_p = CoordSystem('polar', R2_origin, [r, theta], relations_2d) # type: Any\n+\n+# support deprecated feature\n+with warnings.catch_warnings():\n+ warnings.simplefilter(\"ignore\")\n+ x, y, r, theta = symbols('x y r theta', cls=Dummy)\n+ R2_r.connect_to(R2_p, [x, y],\n+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)],\n+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n+ R2_p.connect_to(R2_r, [r, theta],\n+ [r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)],\n+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n \n # Defining the basis coordinate functions and adding shortcuts for them to the\n # manifold and the patch.\n@@ -51,39 +67,69 @@\n # R3\n ###############################################################################\n R3 = Manifold('R^3', 3) # type: Any\n-# Patch and coordinate systems.\n+\n R3_origin = Patch('origin', R3) # type: Any\n-R3_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R3_origin, ['x', 'y', 'z']) # type: Any\n-R3_c = CoordSystem('cylindrical', R3_origin, ['rho', 'psi', 'z']) # type: Any\n-R3_s = CoordSystem('spherical', R3_origin, ['r', 'theta', 'phi']) # type: Any\n-\n-# Connecting the coordinate charts.\n-x, y, z, rho, psi, r, theta, phi = [Dummy(s) for s in ['x', 'y', 'z',\n- 'rho', 'psi', 'r', 'theta', 'phi']]\n-## rectangular <-> cylindrical\n-R3_r.connect_to(R3_c, [x, y, z],\n- [sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z],\n- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n-R3_c.connect_to(R3_r, [rho, psi, z],\n- [rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z],\n- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n-## rectangular <-> spherical\n-R3_r.connect_to(R3_s, [x, y, z],\n- [sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2), acos(z/\n- sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)), atan2(y, x)],\n- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n-R3_s.connect_to(R3_r, [r, theta, phi],\n- [r*sin(theta)*cos(phi), r*sin(\n- theta)*sin(phi), r*cos(theta)],\n- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n-## cylindrical <-> spherical\n-R3_c.connect_to(R3_s, [rho, psi, z],\n- [sqrt(rho**2 + z**2), acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)), psi],\n- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n-R3_s.connect_to(R3_c, [r, theta, phi],\n- [r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta)],\n- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n-del x, y, z, rho, psi, r, theta, phi\n+\n+x, y, z = symbols('x y z', real=True)\n+rho, psi, r, theta, phi = symbols('rho psi r theta phi', nonnegative=True)\n+\n+relations_3d = {\n+ ('rectangular', 'cylindrical'):\n+ Lambda((x, y, z), Matrix([sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z])),\n+ ('cylindrical', 'rectangular'):\n+ Lambda((rho, psi, z), Matrix([rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z])),\n+ ('rectangular', 'spherical'):\n+ Lambda(\n+ (x, y, z),\n+ Matrix([\n+ sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2),\n+ acos(z/sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)),\n+ atan2(y, x)])\n+ ),\n+ ('spherical', 'rectangular'):\n+ Lambda(\n+ (r, theta, phi),\n+ Matrix([r*sin(theta)*cos(phi), r*sin(theta)*sin(phi), r*cos(theta)])\n+ ),\n+ ('cylindrical', 'spherical'):\n+ Lambda(\n+ (rho, psi, z),\n+ Matrix([sqrt(rho**2 + z**2), acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)), psi])\n+ ),\n+ ('spherical', 'cylindrical'):\n+ Lambda((r, theta, phi), Matrix([r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta)])),\n+}\n+\n+R3_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R3_origin, [x, y, z], relations_3d) # type: Any\n+R3_c = CoordSystem('cylindrical', R3_origin, [rho, psi, z], relations_3d) # type: Any\n+R3_s = CoordSystem('spherical', R3_origin, [r, theta, phi], relations_3d) # type: Any\n+\n+# support deprecated feature\n+with warnings.catch_warnings():\n+ warnings.simplefilter(\"ignore\")\n+ x, y, z, rho, psi, r, theta, phi = symbols('x y z rho psi r theta phi', cls=Dummy)\n+ R3_r.connect_to(R3_c, [x, y, z],\n+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z],\n+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n+ R3_c.connect_to(R3_r, [rho, psi, z],\n+ [rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z],\n+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n+ ## rectangular <-> spherical\n+ R3_r.connect_to(R3_s, [x, y, z],\n+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2), acos(z/\n+ sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)), atan2(y, x)],\n+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n+ R3_s.connect_to(R3_r, [r, theta, phi],\n+ [r*sin(theta)*cos(phi), r*sin(\n+ theta)*sin(phi), r*cos(theta)],\n+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n+ ## cylindrical <-> spherical\n+ R3_c.connect_to(R3_s, [rho, psi, z],\n+ [sqrt(rho**2 + z**2), acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)), psi],\n+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n+ R3_s.connect_to(R3_c, [r, theta, phi],\n+ [r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta)],\n+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)\n \n # Defining the basis coordinate functions.\n R3_r.x, R3_r.y, R3_r.z = R3_r.coord_functions()\ndiff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_class_structure.py b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_class_structure.py\nindex 519eed5bfa42..68ab461ed61e 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_class_structure.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_class_structure.py\n@@ -1,33 +1,23 @@\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, Point\n from sympy import symbols, Function\n+from sympy.testing.pytest import warns_deprecated_sympy\n \n m = Manifold('m', 2)\n p = Patch('p', m)\n-cs = CoordSystem('cs', p, ['a', 'b'])\n-cs_noname = CoordSystem('cs', p)\n+a, b = symbols('a b')\n+cs = CoordSystem('cs', p, [a, b])\n x, y = symbols('x y')\n f = Function('f')\n s1, s2 = cs.coord_functions()\n v1, v2 = cs.base_vectors()\n f1, f2 = cs.base_oneforms()\n \n-\n def test_point():\n point = Point(cs, [x, y])\n- assert point == point.func(*point.args)\n assert point != Point(cs, [2, y])\n #TODO assert point.subs(x, 2) == Point(cs, [2, y])\n #TODO assert point.free_symbols == set([x, y])\n \n-def test_rebuild():\n- assert m == m.func(*m.args)\n- assert p == p.func(*p.args)\n- assert cs == cs.func(*cs.args)\n- assert cs_noname == cs_noname.func(*cs_noname.args)\n- assert s1 == s1.func(*s1.args)\n- assert v1 == v1.func(*v1.args)\n- assert f1 == f1.func(*f1.args)\n-\n def test_subs():\n assert s1.subs(s1, s2) == s2\n assert v1.subs(v1, v2) == v2\n@@ -35,3 +25,10 @@ def test_subs():\n assert (x*f(s1) + y).subs(s1, s2) == x*f(s2) + y\n assert (f(s1)*v1).subs(v1, v2) == f(s1)*v2\n assert (y*f(s1)*f1).subs(f1, f2) == y*f(s1)*f2\n+\n+def test_deprecated():\n+ with warns_deprecated_sympy():\n+ cs_wname = CoordSystem('cs', p, ['a', 'b'])\n+ cs_noname = CoordSystem('cs', p)\n+ assert cs_wname == cs_wname.func(*cs_wname.args)\n+ assert cs_noname == cs_wname.func(*cs_noname.args)\ndiff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py\nindex 7c63cc67e5d1..0c9cc397cb12 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py\n@@ -9,6 +9,7 @@\n from sympy.functions import sqrt, atan2, sin\n from sympy.matrices import Matrix\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, nocache_fail\n+from sympy.testing.pytest import warns_deprecated_sympy\n \n TP = TensorProduct\n \n@@ -26,23 +27,38 @@ def test_R2():\n # polar->rect->polar == Id\n a, b = symbols('a b', positive=True)\n m = Matrix([[a], [b]])\n- #TODO assert m == R2_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_p, R2_p.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_r, [a, b])).applyfunc(simplify)\n- assert m == R2_p.coord_tuple_transform_to(\n- R2_r, R2_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_p, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n \n+ #TODO assert m == R2_r.transform(R2_p, R2_p.transform(R2_r, [a, b])).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ assert m == R2_p.transform(R2_r, R2_r.transform(R2_p, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+\n+ # deprecated method\n+ with warns_deprecated_sympy():\n+ assert m == R2_p.coord_tuple_transform_to(\n+ R2_r, R2_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_p, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n \n def test_R3():\n a, b, c = symbols('a b c', positive=True)\n m = Matrix([[a], [b], [c]])\n- assert m == R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(\n- R3_r, R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n- #TODO assert m == R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n- assert m == R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(\n- R3_r, R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n- #TODO assert m == R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n- assert m == R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(\n- R3_c, R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n- #TODO assert m == R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+\n+ assert m == R3_c.transform(R3_r, R3_r.transform(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ #TODO assert m == R3_r.transform(R3_c, R3_c.transform(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ assert m == R3_s.transform(\n+ R3_r, R3_r.transform(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ #TODO assert m == R3_r.transform(R3_s, R3_s.transform(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ assert m == R3_s.transform(\n+ R3_c, R3_c.transform(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ #TODO assert m == R3_c.transform(R3_s, R3_s.transform(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+\n+ with warns_deprecated_sympy():\n+ assert m == R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(\n+ R3_r, R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ #TODO assert m == R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ assert m == R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(\n+ R3_r, R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ #TODO assert m == R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ assert m == R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(\n+ R3_c, R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ #TODO assert m == R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)\n \n \n def test_point():\ndiff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_function_diffgeom_book.py b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_function_diffgeom_book.py\nindex a7317a7d1191..20297cd6e1eb 100644\n--- a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_function_diffgeom_book.py\n+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_function_diffgeom_book.py\n@@ -4,6 +4,7 @@\n from sympy.simplify import trigsimp, simplify\n from sympy.functions import sqrt, atan2, sin, cos\n from sympy.matrices import Matrix\n+from sympy.testing.pytest import warns_deprecated_sympy\n \n # Most of the functionality is covered in the\n # test_functional_diffgeom_ch* tests which are based on the\n@@ -25,8 +26,12 @@ def test_functional_diffgeom_ch2():\n assert (R2_r.point_to_coords(R2_p.point([r0, theta0])) ==\n Matrix([r0*cos(theta0), r0*sin(theta0)]))\n \n- assert R2_p.jacobian(R2_r, [r0, theta0]) == Matrix(\n- [[cos(theta0), -r0*sin(theta0)], [sin(theta0), r0*cos(theta0)]])\n+ assert R2_p.jacobian_matrix(R2_r, [r0, theta0]) == Matrix(\n+ [[cos(theta0), -r0*sin(theta0)], [sin(theta0), r0*cos(theta0)]])\n+\n+ with warns_deprecated_sympy():\n+ assert R2_p.jacobian(R2_r, [r0, theta0]) == Matrix(\n+ [[cos(theta0), -r0*sin(theta0)], [sin(theta0), r0*cos(theta0)]])\n \n field = f(R2.x, R2.y)\n p1_in_rect = R2_r.point([x0, y0])\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/latex.py b/sympy/printing/latex.py\nindex c695b344fc5a..6d28f6005909 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/latex.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/latex.py\n@@ -2506,31 +2506,52 @@ def _print_MatrixHomomorphism(self, h):\n self._print(h.domain), self._print(h.codomain))\n \n def _print_Manifold(self, manifold):\n- return r'\\text{%s}' % manifold.name\n+ string = manifold.name.name\n+ if '{' in string:\n+ name, supers, subs = string, [], []\n+ else:\n+ name, supers, subs = split_super_sub(string)\n+\n+ name = translate(name)\n+ supers = [translate(sup) for sup in supers]\n+ subs = [translate(sub) for sub in subs]\n+\n+ name = r'\\text{%s}' % name\n+ if supers:\n+ name += \"^{%s}\" % \" \".join(supers)\n+ if subs:\n+ name += \"_{%s}\" % \" \".join(subs)\n+\n+ return name\n \n def _print_Patch(self, patch):\n- return r'\\text{%s}_{\\text{%s}}' % (patch.name, patch.manifold.name)\n+ return r'\\text{%s}_{%s}' % (self._print(patch.name), self._print(patch.manifold))\n+\n+ def _print_CoordSystem(self, coordsys):\n+ return r'\\text{%s}^{\\text{%s}}_{%s}' % (\n+ self._print(coordsys.name), self._print(coordsys.patch.name), self._print(coordsys.manifold)\n+ )\n \n- def _print_CoordSystem(self, coords):\n- return r'\\text{%s}^{\\text{%s}}_{\\text{%s}}' % (\n- coords.name, coords.patch.name, coords.patch.manifold.name\n+ def _print_Point(self, point):\n+ return '{%s}_{%s}' % (\n+ self._print(point.coordinates()), self._print(point._coord_sys)\n )\n \n def _print_CovarDerivativeOp(self, cvd):\n return r'\\mathbb{\\nabla}_{%s}' % self._print(cvd._wrt)\n \n def _print_BaseScalarField(self, field):\n- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]\n+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name\n return r'\\mathbf{{{}}}'.format(self._print(Symbol(string)))\n \n def _print_BaseVectorField(self, field):\n- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]\n+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name\n return r'\\partial_{{{}}}'.format(self._print(Symbol(string)))\n \n def _print_Differential(self, diff):\n field = diff._form_field\n if hasattr(field, '_coord_sys'):\n- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]\n+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name\n return r'\\operatorname{{d}}{}'.format(self._print(Symbol(string)))\n else:\n string = self._print(field)\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py\nindex 5fe19d241f16..c4c3630fd38c 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py\n@@ -2608,17 +2608,17 @@ def _print_CoordSystem(self, coords):\n return self._print(coords.name)\n \n def _print_BaseScalarField(self, field):\n- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]\n+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name\n return self._print(pretty_symbol(string))\n \n def _print_BaseVectorField(self, field):\n- s = U('PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL') + '_' + field._coord_sys._names[field._index]\n+ s = U('PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL') + '_' + field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name\n return self._print(pretty_symbol(s))\n \n def _print_Differential(self, diff):\n field = diff._form_field\n if hasattr(field, '_coord_sys'):\n- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]\n+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name\n return self._print(u'\\N{DOUBLE-STRUCK ITALIC SMALL D} ' + pretty_symbol(string))\n else:\n pform = self._print(field)\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py\nindex a7cdbd79e3d2..742fb34b81b1 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py\n@@ -7051,11 +7051,12 @@ def test_issue_18272():\n \n def test_diffgeom():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField\n+ x,y = symbols('x y', real=True)\n m = Manifold('M', 2)\n assert pretty(m) == 'M'\n p = Patch('P', m)\n assert pretty(p) == \"P\"\n- rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)\n+ rect = CoordSystem('rect', p, [x, y])\n assert pretty(rect) == \"rect\"\n b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n- assert pretty(b) == \"rect_0\"\n+ assert pretty(b) == \"x\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/repr.py b/sympy/printing/repr.py\nindex d156c6f3121d..1d33861800e9 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/repr.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/repr.py\n@@ -248,6 +248,24 @@ def _print_Symbol(self, expr):\n return \"%s(%s, %s)\" % (expr.__class__.__name__,\n self._print(expr.name), ', '.join(attr))\n \n+ def _print_CoordinateSymbol(self, expr):\n+ d = expr._assumptions.generator\n+\n+ if d == {}:\n+ return \"%s(%s, %s)\" % (\n+ expr.__class__.__name__,\n+ self._print(expr.coordinate_system),\n+ self._print(expr.index)\n+ )\n+ else:\n+ attr = ['%s=%s' % (k, v) for k, v in d.items()]\n+ return \"%s(%s, %s, %s)\" % (\n+ expr.__class__.__name__,\n+ self._print(expr.coordinate_system),\n+ self._print(expr.index),\n+ ', '.join(attr)\n+ )\n+\n def _print_Predicate(self, expr):\n return \"%s(%s)\" % (expr.__class__.__name__, self._print(expr.name))\n \n@@ -328,19 +346,6 @@ def _print_ExtensionElement(self, f):\n ext = self._print(f.ext)\n return \"ExtElem(%s, %s)\" % (rep, ext)\n \n- def _print_CoordSystem(self, coords):\n- class_name = coords.func.__name__\n- name = self._print(coords.name)\n- patch = self._print(coords.patch)\n- names = self._print(coords._names)\n- return \"%s(%s, %s, %s)\" % (class_name, name, patch, names)\n-\n- def _print_BaseScalarField(self, bsf):\n- class_name = bsf.func.__name__\n- coords = self._print(bsf._coord_sys)\n- idx = self._print(bsf._index)\n- return \"%s(%s, %s)\" % (class_name, coords, idx)\n-\n def srepr(expr, **settings):\n \"\"\"return expr in repr form\"\"\"\n return ReprPrinter(settings).doprint(expr)\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/str.py b/sympy/printing/str.py\nindex 2639a9a5d570..16e5d8cf905c 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/str.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/str.py\n@@ -876,24 +876,24 @@ def _print_Category(self, category):\n return 'Category(\"%s\")' % category.name\n \n def _print_Manifold(self, manifold):\n- return manifold.name\n+ return self._print(manifold.name)\n \n def _print_Patch(self, patch):\n- return patch.name\n+ return self._print(patch.name)\n \n def _print_CoordSystem(self, coords):\n- return coords.name\n+ return self._print(coords.name)\n \n def _print_BaseScalarField(self, field):\n- return field._coord_sys._names[field._index]\n+ return field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name\n \n def _print_BaseVectorField(self, field):\n- return 'e_%s' % field._coord_sys._names[field._index]\n+ return 'e_%s' % field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name\n \n def _print_Differential(self, diff):\n field = diff._form_field\n if hasattr(field, '_coord_sys'):\n- return 'd%s' % field._coord_sys._names[field._index]\n+ return 'd%s' % field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name\n else:\n return 'd(%s)' % self._print(field)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py\nindex 9c2d37e97546..675ac0ab76d5 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py\n@@ -2535,14 +2535,15 @@ def test_text_re_im():\n def test_latex_diffgeom():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential\n from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2\n+ x,y = symbols('x y', real=True)\n m = Manifold('M', 2)\n assert latex(m) == r'\\text{M}'\n p = Patch('P', m)\n assert latex(p) == r'\\text{P}_{\\text{M}}'\n- rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)\n+ rect = CoordSystem('rect', p, [x, y])\n assert latex(rect) == r'\\text{rect}^{\\text{P}}_{\\text{M}}'\n b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n- assert latex(b) == r'\\mathbf{rect_{0}}'\n+ assert latex(b) == r'\\mathbf{x}'\n \n g = Function('g')\n s_field = g(R2.x, R2.y)\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py\nindex ed892c1801ca..481547cd2646 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py\n@@ -312,16 +312,6 @@ def test_Permutation():\n import_stmt = \"from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation\"\n sT(Permutation(1, 2), \"Permutation(1, 2)\", import_stmt)\n \n-\n-def test_diffgeom():\n- from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField\n- m = Manifold('M', 2)\n- p = Patch('P', m)\n- rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)\n- assert srepr(rect) == \"CoordSystem(Str('rect'), Patch(Str('P'), Manifold(Str('M'), Integer(2))), ('rect_0', 'rect_1'))\"\n- b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n- assert srepr(b) == \"BaseScalarField(CoordSystem(Str('rect'), Patch(Str('P'), Manifold(Str('M'), Integer(2))), ('rect_0', 'rect_1')), Integer(0))\"\n-\n def test_dict():\n from sympy import srepr\n from sympy.abc import x, y, z\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py\nindex d05052fe0c8c..bc185de760d1 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py\n@@ -936,11 +936,12 @@ def test_issue_14567():\n \n def test_diffgeom():\n from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField\n+ x,y = symbols('x y', real=True)\n m = Manifold('M', 2)\n assert str(m) == \"M\"\n p = Patch('P', m)\n assert str(p) == \"P\"\n- rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)\n+ rect = CoordSystem('rect', p, [x, y])\n assert str(rect) == \"rect\"\n b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n- assert str(b) == \"rect_0\"\n+ assert str(b) == \"x\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -321,85 +514,133 @@ def coord_tuple_transform_to(self, to_sys, coords):\n \n def jacobian(self, to_sys, coords):\n \"\"\"Return the jacobian matrix of a transformation.\"\"\"\n+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(",
"line": null,
"original_line": 517,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nAlthough I acknowledge that the term `jacobian` was not used consistently across sympy as well as the general scientific community, I'm not sure this had been necessary to deprecate and introduce new methods\n\n@author:\nI'm convinced. Instead, I made `jacobian_matrix` as an alias of `jacobian`."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -120,134 +157,155 @@ def dim(self):\n return self.manifold.dim\n \n class CoordSystem(Atom):\n- \"\"\"A coordinate system defined on the patch\n+ \"\"\"A coordinate system defined on the patch.\n \n Explanation\n ===========\n \n- This class contains all coordinate transformation logic.\n+ Coordinate system is a system that uses one or more coordinates to uniquely determine\n+ the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold [1].\n+\n+ By passing Symbols to *symbols* parameter, user can define the name and assumptions\n+ of coordinate symbols of the coordinate system.\n+ By passing *relations* parameter, user can define the tranform relations of coordinate\n+ systems. Inverse transformation and indirect transformation can be found automatically.\n+ If this parameter is not passed, coordinate transformation cannot be done.\n \n Parameters\n ==========\n \n- name : string\n+ name : str\n The name of the coordinate system.\n \n patch : Patch\n The patch where the coordinate system is defined.\n \n- names : list of strings, optional\n- Determines how base scalar fields will be printed.\n+ symbols : list of Symbols\n+ Defines the names and assumptions of coordinate symbols.\n+\n+ relations : dict, optional\n+ - key : tuple of two strings, who are the names of systems where\n+ the coordinates transform from and transform to.\n+ - value : Lambda returning the transformed coordinates.\n \n Examples\n ========\n \n- Define a Manifold and a Patch, and then define two coord systems on that\n- patch:\n-\n- >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, pi\n+ >>> from sympy import symbols, pi, Lambda, Matrix, sqrt, atan2, cos, sin\n >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem\n- >>> from sympy.simplify import simplify\n- >>> r, theta = symbols('r, theta')\n >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)\n- >>> patch = Patch('P', m)\n- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', patch)\n- >>> polar = CoordSystem('polar', patch)\n- >>> rect in patch.coord_systems\n- True\n+ >>> p = Patch('P', m)\n \n- Connect the coordinate systems. An inverse transformation is automatically\n- found by ``solve`` when possible:\n+ >>> x, y = symbols('x y', real=True)\n+ >>> r, theta = symbols('r theta', nonnegative=True)\n+ >>> relation_dict = {\n+ ... ('Car2D', 'Pol'): Lambda((x, y), Matrix([sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)])),\n+ ... ('Pol', 'Car2D'): Lambda((r, theta), Matrix([r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)]))\n+ ... }\n+ >>> Car2D = CoordSystem('Car2D', p, [x, y], relation_dict)\n+ >>> Pol = CoordSystem('Pol', p, [r, theta], relation_dict)\n+\n+ >>> Car2D.name\n+ 'Car2D'\n+ >>> Car2D.dim\n+ 2\n+ >>> Car2D.symbols\n+ [x, y]\n+ >>> Car2D.transformation(Pol)\n+ Lambda((x, y), Matrix([\n+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2)],\n+ [ atan2(y, x)]]))\n \n- >>> polar.connect_to(rect, [r, theta], [r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)])\n- >>> polar.coord_tuple_transform_to(rect, [0, 2])\n+ >>> Car2D.transform(Pol)\n Matrix([\n- [0],\n- [0]])\n- >>> polar.coord_tuple_transform_to(rect, [2, pi/2])\n- Matrix([\n- [0],\n- [2]])\n- >>> rect.coord_tuple_transform_to(polar, [1, 1]).applyfunc(simplify)\n+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2)],\n+ [ atan2(y, x)]])\n+ >>> Car2D.transform(Pol, [1, 2])\n Matrix([\n- [sqrt(2)],\n- [ pi/4]])\n+ [sqrt(5)],\n+ [atan(2)]])\n \n- Calculate the jacobian of the polar to cartesian transformation:\n-\n- >>> polar.jacobian(rect, [r, theta])\n+ >>> Pol.jacobian_matrix(Car2D)\n Matrix([\n [cos(theta), -r*sin(theta)],\n [sin(theta), r*cos(theta)]])\n-\n- Define a point using coordinates in one of the coordinate systems:\n-\n- >>> p = polar.point([1, 3*pi/4])\n- >>> rect.point_to_coords(p)\n+ >>> Pol.jacobian_matrix(Car2D, [1, pi/2])\n Matrix([\n- [-sqrt(2)/2],\n- [ sqrt(2)/2]])\n-\n- Define a basis scalar field (i.e. a coordinate function), that takes a\n- point and returns its coordinates. It is an instance of ``BaseScalarField``.\n-\n- >>> rect.coord_function(0)(p)\n- -sqrt(2)/2\n- >>> rect.coord_function(1)(p)\n- sqrt(2)/2\n+ [0, -1],\n+ [1, 0]])\n \n- Define a basis vector field (i.e. a unit vector field along the coordinate\n- line). Vectors are also differential operators on scalar fields. It is an\n- instance of ``BaseVectorField``.\n-\n- >>> v_x = rect.base_vector(0)\n- >>> x = rect.coord_function(0)\n- >>> v_x(x)\n- 1\n- >>> v_x(v_x(x))\n- 0\n-\n- Define a basis oneform field:\n-\n- >>> dx = rect.base_oneform(0)\n- >>> dx(v_x)\n- 1\n-\n- If you provide a list of names the fields will print nicely:\n- - without provided names:\n-\n- >>> x, v_x, dx\n- (rect_0, e_rect_0, drect_0)\n-\n- - with provided names\n+ References\n+ ==========\n \n- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', patch, ['x', 'y'])\n- >>> rect.coord_function(0), rect.base_vector(0), rect.base_oneform(0)\n- (x, e_x, dx)\n+ .. [1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coordinate_system\n \n \"\"\"\n- # Contains a reference to the parent patch in order to be able to access\n- # other coordinate system charts.\n- def __new__(cls, name, patch, names=None):\n+ def __new__(cls, name, patch, symbols=None, relations={}, **kwargs):\n if not isinstance(name, Str):\n name = Str(name)\n- # names is not in args because it is related only to printing, not to\n- # identifying the CoordSystem instance.\n- obj = super().__new__(cls, name, patch)\n- if not names:\n- names = ['%s_%d' % (name, i) for i in range(patch.dim)]\n- obj._names = tuple(str(i) for i in names)\n- obj.patch.coord_systems.append(obj)\n- obj.transforms = {}\n- # All the coordinate transformation logic is in this dictionary in the\n- # form of:\n- # key = other coordinate system\n- # value = tuple of # TODO make these Lambda instances\n- # - list of `Dummy` coordinates in this coordinate system\n- # - list of expressions as a function of the Dummies giving\n- # the coordinates in another coordinate system\n- obj._dummies = [Dummy(str(n)) for n in names]\n+\n+ # canonicallize the symbols\n+ if symbols is None or any(not isinstance(s, Symbol) for s in symbols) :\n+ # support deprecated signature\n+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(\n+ feature=\"Class signature 'names' of CoordSystem\",\n+ useinstead=\"class signature 'symbols'\",\n+ issue=19321,\n+ deprecated_since_version=\"1.7\"\n+ ).warn()\n+\n+ if symbols is None:\n+ names = kwargs.get('names', None)\n+ else:\n+ names = symbols\n+\n+ if names is None:\n+ symbols = Tuple(*[Symbol('%s_%d' % (name, i), real=True) for i in range(patch.dim)])\n+ else:\n+ symbols = Tuple(*[Symbol(n, real=True) for n in names])\n+ else:\n+ symbols = Tuple(*[Symbol(s.name, **s._assumptions.generator) for s in symbols])\n+\n+ # canonicallize the relations\n+ rel_temp = {}\n+ for k,v in relations.items():\n+ s1, s2 = k\n+ if not isinstance(s1, Str):\n+ s1 = Str(s1)\n+ if not isinstance(s2, Str):\n+ s2 = Str(s2)\n+ key = Tuple(s1, s2)\n+ rel_temp[key] = v\n+ relations = Dict(rel_temp)\n+\n+ # construct the object\n+ obj = super().__new__(cls, name, patch, symbols, relations)\n+\n+ # Add deprecated attributes\n+ obj.transforms = _deprecated_dict(\n+ \"Mutable CoordSystem.transforms\",\n+ \"'relations' parameter in class signature\",\n+ 19321,\n+ \"1.7\",\n+ {}\n+ )\n+ obj._names =_deprecated_list(\n+ \"CoordSystem._names\",\n+ \"CoordSystem.symbols\",\n+ 19321,\n+ \"1.7\",\n+ [str(n) for n in symbols]\n+ )\n+ obj.patch.coord_systems.append(obj) # deprecated\n+ obj._dummies = _deprecated_list(",
"line": null,
"original_line": 300,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThese are private methods, so it can be overwhelming to raise deprecation warnings for `_names` and `_dummies`\n\n@author:\nI guess you're right. I un-deprecated them."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2506,31 +2506,52 @@ def _print_MatrixHomomorphism(self, h):\n self._print(h.domain), self._print(h.codomain))\n \n def _print_Manifold(self, manifold):\n- return r'\\text{%s}' % manifold.name\n+ string = manifold.name.name\n+ if '{' in string:\n+ name, supers, subs = string, [], []\n+ else:\n+ name, supers, subs = split_super_sub(string)\n+\n+ name = translate(name)\n+ supers = [translate(sup) for sup in supers]\n+ subs = [translate(sub) for sub in subs]\n+\n+ name = r'\\text{%s}' % name\n+ if supers:\n+ name += \"^{%s}\" % \" \".join(supers)\n+ if subs:\n+ name += \"_{%s}\" % \" \".join(subs)\n+\n+ return name\n \n def _print_Patch(self, patch):\n- return r'\\text{%s}_{\\text{%s}}' % (patch.name, patch.manifold.name)\n+ return r'\\text{%s}_{%s}' % (self._print(patch.name), self._print(patch.manifold))\n+\n+ def _print_CoordSystem(self, coordsys):\n+ return r'\\text{%s}^{\\text{%s}}_{%s}' % (\n+ self._print(coordsys.name), self._print(coordsys.patch.name), self._print(coordsys.manifold)\n+ )\n \n- def _print_CoordSystem(self, coords):\n- return r'\\text{%s}^{\\text{%s}}_{\\text{%s}}' % (\n- coords.name, coords.patch.name, coords.patch.manifold.name\n+ def _print_Point(self, point):\n+ return '{%s}_{%s}' % (\n+ self._print(point.coordinates()), self._print(point._coord_sys)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 2537,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/latex.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think that `_print_Point` should not be defined because it conflicts with printing of `Point` of `sympy.geometry` or `sympy.vector`. Maybe it was a bad idea to have duplicate names for classes at the first place, but it works better if you just leave it undefined and have some reasonable tuple notation of args.\n\n@user1:\nI have thought as a same idea to rename the Point in diffgeom. But it may be noted in the release notes.\n\n@author:\nDeleted this. I think we can give different name to class and introduce aliasing, but that would better be handled in another PR."
}
] |
3430cbf6bf8546544b9309e4b542f99c1c34b8af
|
diff --git a/doc/src/modules/diffgeom.rst b/doc/src/modules/diffgeom.rst
index 02fc0416af80..764d9f31412d 100644
--- a/doc/src/modules/diffgeom.rst
+++ b/doc/src/modules/diffgeom.rst
@@ -18,6 +18,9 @@ Base Class Reference
.. autoclass:: CoordSystem
:members:
+.. autoclass:: CoordinateSymbol
+ :members:
+
.. autoclass:: Point
:members:
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py
index 6bdc452c62c2..998af7ea474d 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, SKIP
-x, y, z = symbols('x,y,z')
+a, b, c, x, y, z = symbols('a,b,c,x,y,z')
def test_all_classes_are_tested():
@@ -4421,37 +4421,42 @@ def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Patch():
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__CoordSystem():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem
assert _test_args(CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3))))
+ assert _test_args(CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c]))
+
+
+def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__CoordinateSymbol():
+ from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, CoordinateSymbol
+ assert _test_args(CoordinateSymbol(CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c]), 0))
-@XFAIL
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Point():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, Point
assert _test_args(Point(
- CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3))), [x, y]))
+ CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c]), [x, y]))
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__BaseScalarField():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField
- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
assert _test_args(BaseScalarField(cs, 0))
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__BaseVectorField():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseVectorField
- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
assert _test_args(BaseVectorField(cs, 0))
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Differential():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential
- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
assert _test_args(Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 0)))
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Commutator():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseVectorField, Commutator
- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
- cs1 = CoordSystem('name1', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
+ cs1 = CoordSystem('name1', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
v = BaseVectorField(cs, 0)
v1 = BaseVectorField(cs1, 0)
assert _test_args(Commutator(v, v1))
@@ -4459,14 +4464,14 @@ def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__Commutator():
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__TensorProduct():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential, TensorProduct
- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
d = Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 0))
assert _test_args(TensorProduct(d, d))
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__WedgeProduct():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential, WedgeProduct
- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
d = Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 0))
d1 = Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 1))
assert _test_args(WedgeProduct(d, d1))
@@ -4474,7 +4479,7 @@ def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__WedgeProduct():
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__LieDerivative():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential, BaseVectorField, LieDerivative
- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
d = Differential(BaseScalarField(cs, 0))
v = BaseVectorField(cs, 0)
assert _test_args(LieDerivative(v, d))
@@ -4483,13 +4488,13 @@ def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__LieDerivative():
@XFAIL
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__BaseCovarDerivativeOp():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseCovarDerivativeOp
- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
assert _test_args(BaseCovarDerivativeOp(cs, 0, [[[0, ]*3, ]*3, ]*3))
def test_sympy__diffgeom__diffgeom__CovarDerivativeOp():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseVectorField, CovarDerivativeOp
- cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)))
+ cs = CoordSystem('name', Patch('name', Manifold('name', 3)), [a, b, c])
v = BaseVectorField(cs, 0)
_test_args(CovarDerivativeOp(v, [[[0, ]*3, ]*3, ]*3))
diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/__init__.py b/sympy/diffgeom/__init__.py
index 140f00539472..8846a9951060 100644
--- a/sympy/diffgeom/__init__.py
+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/__init__.py
@@ -1,18 +1,18 @@
from .diffgeom import (
BaseCovarDerivativeOp, BaseScalarField, BaseVectorField, Commutator,
- contravariant_order, CoordSystem, CovarDerivativeOp, covariant_order,
- Differential, intcurve_diffequ, intcurve_series, LieDerivative,
- Manifold, metric_to_Christoffel_1st, metric_to_Christoffel_2nd,
- metric_to_Ricci_components, metric_to_Riemann_components, Patch,
- Point, TensorProduct, twoform_to_matrix, vectors_in_basis,
- WedgeProduct,
+ contravariant_order, CoordSystem, CoordinateSymbol,
+ CovarDerivativeOp, covariant_order, Differential, intcurve_diffequ,
+ intcurve_series, LieDerivative, Manifold, metric_to_Christoffel_1st,
+ metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, metric_to_Ricci_components,
+ metric_to_Riemann_components, Patch, Point, TensorProduct, twoform_to_matrix,
+ vectors_in_basis, WedgeProduct,
)
__all__ = [
- 'BaseCovarDerivativeOp', 'BaseScalarField', 'BaseVectorField',
- 'Commutator', 'contravariant_order', 'CoordSystem', 'CovarDerivativeOp',
- 'covariant_order', 'Differential', 'intcurve_diffequ', 'intcurve_series',
- 'LieDerivative', 'Manifold', 'metric_to_Christoffel_1st',
+ 'BaseCovarDerivativeOp', 'BaseScalarField', 'BaseVectorField', 'Commutator',
+ 'contravariant_order', 'CoordSystem', 'CoordinateSymbol',
+ 'CovarDerivativeOp', 'covariant_order', 'Differential', 'intcurve_diffequ',
+ 'intcurve_series', 'LieDerivative', 'Manifold', 'metric_to_Christoffel_1st',
'metric_to_Christoffel_2nd', 'metric_to_Ricci_components',
'metric_to_Riemann_components', 'Patch', 'Point', 'TensorProduct',
'twoform_to_matrix', 'vectors_in_basis', 'WedgeProduct',
diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py
index 643b032399c4..1d2ab0b27aa0 100644
--- a/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py
+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/diffgeom.py
@@ -4,18 +4,20 @@
from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation
from sympy.core import (
- Basic, Expr, Dummy, Function, diff,
- Pow, Mul, Add, Atom
+ Basic, Expr, Function, diff,
+ Pow, Mul, Add, Atom, Lambda, S, Tuple, Dict
)
+from sympy.core.cache import cacheit
from sympy.core.compatibility import reduce
-from sympy.core.numbers import Zero
+from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol, Dummy
from sympy.core.symbol import Str
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
from sympy.functions import factorial
-from sympy.matrices import Matrix
+from sympy.matrices import ImmutableDenseMatrix as Matrix
from sympy.simplify import simplify
from sympy.solvers import solve
+from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning
# TODO you are a bit excessive in the use of Dummies
# TODO dummy point, literal field
@@ -23,34 +25,58 @@
# tests and find out why
from sympy.tensor.array import ImmutableDenseNDimArray
-
class Manifold(Atom):
"""A mathematical manifold.
Explanation
===========
- The only role that this object plays is to keep a list of all patches
- defined on the manifold. It does not provide any means to study the
- topological characteristics of the manifold that it represents.
+ A manifold is a topological space that locally resembles
+ Euclidean space near each point [1].
+
+ This class does not provide any means to study the topological
+ characteristics of the manifold that it represents, though.
Parameters
==========
+
name : str
The name of the manifold.
dim : int
The dimension of the manifold.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold
+ >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)
+
+ >>> m.name
+ 'M'
+ >>> m.dim
+ 2
+
+ References
+ ==========
+
+ .. [1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manifold
+
"""
- def __new__(cls, name, dim):
+ def __new__(cls, name, dim, **kwargs):
if not isinstance(name, Str):
name = Str(name)
dim = _sympify(dim)
obj = super().__new__(cls, name, dim)
- obj.patches = []
- # The patches list is necessary if a Patch instance needs to enumerate
- # other Patch instance on the same manifold.
+
+ obj.patches = _deprecated_list(
+ "Manifold.patches",
+ "external container for registry",
+ 19321,
+ "1.7",
+ []
+ )
return obj
@property
@@ -67,17 +93,19 @@ class Patch(Atom):
Explanation
===========
- On a manifold one can have many patches that do not always include the
- whole manifold. On these patches coordinate charts can be defined that
- permit the parameterization of any point on the patch in terms of a tuple
- of real numbers (the coordinates).
+ Coordinate patch, or patch in short, is a simply-connected open set around a point
+ in the manifold [1]. On a manifold one can have many patches that do not always
+ include the whole manifold. On these patches coordinate charts can be defined that
+ permit the parameterization of any point on the patch in terms of a tuple of
+ real numbers (the coordinates).
- This object serves as a container/parent for all coordinate system charts
- that can be defined on the patch it represents.
+ This class does not provide any means to study the topological
+ characteristics of the patch that it represents.
Parameters
==========
- name : string
+
+ name : str
The name of the patch.
manifold : Manifold
@@ -86,25 +114,34 @@ class Patch(Atom):
Examples
========
- Define a Manifold and a Patch on that Manifold:
-
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch
- >>> m = Manifold('M', 3)
+ >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)
>>> p = Patch('P', m)
- >>> p in m.patches
- True
+
+ >>> p.name
+ 'P'
+ >>> p.dim
+ 2
+
+ References
+ ==========
+
+ .. [1] G. Sussman, J. Wisdom, W. Farr, Functional Differential Geometry (2013)
"""
- # Contains a reference to the parent manifold in order to be able to access
- # other patches.
- def __new__(cls, name, manifold):
+ def __new__(cls, name, manifold, **kwargs):
if not isinstance(name, Str):
name = Str(name)
obj = super().__new__(cls, name, manifold)
- obj.manifold.patches.append(obj)
- obj.coord_systems = []
- # The list of coordinate systems is necessary for an instance of
- # CoordSystem to enumerate other coord systems on the patch.
+
+ obj.manifold.patches.append(obj) # deprecated
+ obj.coord_systems = _deprecated_list(
+ "Patch.coord_systems",
+ "external container for registry",
+ 19321,
+ "1.7",
+ []
+ )
return obj
@property
@@ -120,134 +157,154 @@ def dim(self):
return self.manifold.dim
class CoordSystem(Atom):
- """A coordinate system defined on the patch
+ """A coordinate system defined on the patch.
Explanation
===========
- This class contains all coordinate transformation logic.
+ Coordinate system is a system that uses one or more coordinates to uniquely determine
+ the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold [1].
+
+ By passing Symbols to *symbols* parameter, user can define the name and assumptions
+ of coordinate symbols of the coordinate system. If not passed, these symbols are
+ generated automatically and are assumed to be real valued.
+ By passing *relations* parameter, user can define the tranform relations of coordinate
+ systems. Inverse transformation and indirect transformation can be found automatically.
+ If this parameter is not passed, coordinate transformation cannot be done.
Parameters
==========
- name : string
+ name : str
The name of the coordinate system.
patch : Patch
The patch where the coordinate system is defined.
- names : list of strings, optional
- Determines how base scalar fields will be printed.
+ symbols : list of Symbols, optional
+ Defines the names and assumptions of coordinate symbols.
+
+ relations : dict, optional
+ - key : tuple of two strings, who are the names of systems where
+ the coordinates transform from and transform to.
+ - value : Lambda returning the transformed coordinates.
Examples
========
- Define a Manifold and a Patch, and then define two coord systems on that
- patch:
-
- >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, pi
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, pi, Lambda, Matrix, sqrt, atan2, cos, sin
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem
- >>> from sympy.simplify import simplify
- >>> r, theta = symbols('r, theta')
>>> m = Manifold('M', 2)
- >>> patch = Patch('P', m)
- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', patch)
- >>> polar = CoordSystem('polar', patch)
- >>> rect in patch.coord_systems
- True
+ >>> p = Patch('P', m)
- Connect the coordinate systems. An inverse transformation is automatically
- found by ``solve`` when possible:
+ >>> x, y = symbols('x y', real=True)
+ >>> r, theta = symbols('r theta', nonnegative=True)
+ >>> relation_dict = {
+ ... ('Car2D', 'Pol'): Lambda((x, y), Matrix([sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)])),
+ ... ('Pol', 'Car2D'): Lambda((r, theta), Matrix([r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)]))
+ ... }
+ >>> Car2D = CoordSystem('Car2D', p, [x, y], relation_dict)
+ >>> Pol = CoordSystem('Pol', p, [r, theta], relation_dict)
+
+ >>> Car2D.name
+ 'Car2D'
+ >>> Car2D.dim
+ 2
+ >>> Car2D.symbols
+ [x, y]
+ >>> Car2D.transformation(Pol)
+ Lambda((x, y), Matrix([
+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2)],
+ [ atan2(y, x)]]))
- >>> polar.connect_to(rect, [r, theta], [r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)])
- >>> polar.coord_tuple_transform_to(rect, [0, 2])
+ >>> Car2D.transform(Pol)
Matrix([
- [0],
- [0]])
- >>> polar.coord_tuple_transform_to(rect, [2, pi/2])
- Matrix([
- [0],
- [2]])
- >>> rect.coord_tuple_transform_to(polar, [1, 1]).applyfunc(simplify)
+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2)],
+ [ atan2(y, x)]])
+ >>> Car2D.transform(Pol, [1, 2])
Matrix([
- [sqrt(2)],
- [ pi/4]])
+ [sqrt(5)],
+ [atan(2)]])
- Calculate the jacobian of the polar to cartesian transformation:
-
- >>> polar.jacobian(rect, [r, theta])
+ >>> Pol.jacobian(Car2D)
Matrix([
[cos(theta), -r*sin(theta)],
[sin(theta), r*cos(theta)]])
-
- Define a point using coordinates in one of the coordinate systems:
-
- >>> p = polar.point([1, 3*pi/4])
- >>> rect.point_to_coords(p)
+ >>> Pol.jacobian(Car2D, [1, pi/2])
Matrix([
- [-sqrt(2)/2],
- [ sqrt(2)/2]])
-
- Define a basis scalar field (i.e. a coordinate function), that takes a
- point and returns its coordinates. It is an instance of ``BaseScalarField``.
-
- >>> rect.coord_function(0)(p)
- -sqrt(2)/2
- >>> rect.coord_function(1)(p)
- sqrt(2)/2
+ [0, -1],
+ [1, 0]])
- Define a basis vector field (i.e. a unit vector field along the coordinate
- line). Vectors are also differential operators on scalar fields. It is an
- instance of ``BaseVectorField``.
-
- >>> v_x = rect.base_vector(0)
- >>> x = rect.coord_function(0)
- >>> v_x(x)
- 1
- >>> v_x(v_x(x))
- 0
-
- Define a basis oneform field:
-
- >>> dx = rect.base_oneform(0)
- >>> dx(v_x)
- 1
-
- If you provide a list of names the fields will print nicely:
- - without provided names:
-
- >>> x, v_x, dx
- (rect_0, e_rect_0, drect_0)
-
- - with provided names
+ References
+ ==========
- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', patch, ['x', 'y'])
- >>> rect.coord_function(0), rect.base_vector(0), rect.base_oneform(0)
- (x, e_x, dx)
+ .. [1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coordinate_system
"""
- # Contains a reference to the parent patch in order to be able to access
- # other coordinate system charts.
- def __new__(cls, name, patch, names=None):
+ def __new__(cls, name, patch, symbols=None, relations={}, **kwargs):
if not isinstance(name, Str):
name = Str(name)
- # names is not in args because it is related only to printing, not to
- # identifying the CoordSystem instance.
- obj = super().__new__(cls, name, patch)
- if not names:
- names = ['%s_%d' % (name, i) for i in range(patch.dim)]
- obj._names = tuple(str(i) for i in names)
- obj.patch.coord_systems.append(obj)
- obj.transforms = {}
- # All the coordinate transformation logic is in this dictionary in the
- # form of:
- # key = other coordinate system
- # value = tuple of # TODO make these Lambda instances
- # - list of `Dummy` coordinates in this coordinate system
- # - list of expressions as a function of the Dummies giving
- # the coordinates in another coordinate system
- obj._dummies = [Dummy(str(n)) for n in names]
+
+ # canonicallize the symbols
+ if symbols is None:
+ names = kwargs.get('names', None)
+ if names is None:
+ symbols = Tuple(
+ *[Symbol('%s_%s' % (name.name, i), real=True) for i in range(patch.dim)]
+ )
+ else:
+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(
+ feature="Class signature 'names' of CoordSystem",
+ useinstead="class signature 'symbols'",
+ issue=19321,
+ deprecated_since_version="1.7"
+ ).warn()
+ symbols = Tuple(
+ *[Symbol(n, real=True) for n in names]
+ )
+ else:
+ syms = []
+ for s in symbols:
+ if isinstance(s, Symbol):
+ syms.append(Symbol(s.name, **s._assumptions.generator))
+ elif isinstance(s, str):
+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(
+ feature="Passing str as coordinate symbol's name",
+ useinstead="Symbol which contains the name and assumption for coordinate symbol",
+ issue=19321,
+ deprecated_since_version="1.7"
+ ).warn()
+ syms.append(Symbol(s, real=True))
+ symbols = Tuple(*syms)
+
+ # canonicallize the relations
+ rel_temp = {}
+ for k,v in relations.items():
+ s1, s2 = k
+ if not isinstance(s1, Str):
+ s1 = Str(s1)
+ if not isinstance(s2, Str):
+ s2 = Str(s2)
+ key = Tuple(s1, s2)
+ rel_temp[key] = v
+ relations = Dict(rel_temp)
+
+ # construct the object
+ obj = super().__new__(cls, name, patch, symbols, relations)
+
+ # Add deprecated attributes
+ obj.transforms = _deprecated_dict(
+ "Mutable CoordSystem.transforms",
+ "'relations' parameter in class signature",
+ 19321,
+ "1.7",
+ {}
+ )
+ obj._names = [str(n) for n in symbols]
+ obj.patch.coord_systems.append(obj) # deprecated
+ obj._dummies = [Dummy(str(n)) for n in symbols] # deprecated
obj._dummy = Dummy()
+
return obj
@property
@@ -258,34 +315,132 @@ def name(self):
def patch(self):
return self.args[1]
+ @property
+ def manifold(self):
+ return self.patch.manifold
+
+ @property
+ def symbols(self):
+ return [
+ CoordinateSymbol(
+ self, i, **s._assumptions.generator
+ ) for i,s in enumerate(self.args[2])
+ ]
+
+ @property
+ def relations(self):
+ return self.args[3]
+
@property
def dim(self):
return self.patch.dim
##########################################################################
- # Coordinate transformations.
+ # Finding transformation relation
##########################################################################
+ def transformation(self, sys):
+ """
+ Return coordinate transform relation from *self* to *sys* as Lambda.
+ """
+ if self.relations != sys.relations:
+ raise TypeError(
+ "Two coordinate systems have different relations")
+
+ key = Tuple(self.name, sys.name)
+ if key in self.relations:
+ return self.relations[key]
+ elif key[::-1] in self.relations:
+ return self._inverse_transformation(sys, self)
+ else:
+ return self._indirect_transformation(self, sys)
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def _inverse_transformation(sys1, sys2):
+ # Find the transformation relation from sys2 to sys1
+ forward_transform = sys1.transform(sys2)
+ forward_syms, forward_results = forward_transform.args
+
+ inv_syms = [i.as_dummy() for i in forward_syms]
+ inv_results = solve(
+ [t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(inv_syms, forward_results)],
+ list(forward_syms), dict=True)[0]
+ inv_results = [inv_results[s] for s in forward_syms]
+
+ signature = tuple(inv_syms)
+ expr = Matrix(inv_results)
+ return Lambda(signature, expr)
+
+ @classmethod
+ @cacheit
+ def _indirect_transformation(cls, sys1, sys2):
+ # Find the transformation relation between two indirectly connected coordinate systems
+ path = cls._dijkstra(sys1, sys2)
+ Lambdas = []
+ for i in range(len(path) - 1):
+ s1, s2 = path[i], path[i + 1]
+ Lambdas.append(s1.transformation(s2))
+ syms = Lambdas[-1].signature
+ expr = syms
+ for l in reversed(Lambdas):
+ expr = l(*expr)
+ return Lambda(syms, expr)
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def _dijkstra(sys1, sys2):
+ # Use Dijkstra algorithm to find the shortest path between two indirectly-connected
+ # coordinate systems
+ relations = sys1.relations
+ graph = {}
+ for s1, s2 in relations.keys():
+ if s1 not in graph:
+ graph[s1] = {s2}
+ else:
+ graph[s1].add(s2)
+ if s2 not in graph:
+ graph[s2] = {s1}
+ else:
+ graph[s2].add(s1)
+
+ path_dict = {sys:[0, [], 0] for sys in graph} # minimum distance, path, times of visited
+
+ def visit(sys):
+ path_dict[sys][2] = 1
+ for newsys in graph[sys]:
+ distance = path_dict[sys][0] + 1
+ if path_dict[newsys][0] >= distance or not path_dict[newsys][1]:
+ path_dict[newsys][0] = distance
+ path_dict[newsys][1] = [i for i in path_dict[sys][1]]
+ path_dict[newsys][1].append(sys)
+
+ visit(sys1)
+
+ while True:
+ min_distance = max(path_dict.values(), key=lambda x:x[0])[0]
+ newsys = None
+ for sys, lst in path_dict.items():
+ if 0 < lst[0] <= min_distance and not lst[2]:
+ min_distance = lst[0]
+ newsys = sys
+ if newsys is None:
+ break
+ visit(newsys)
+
+ result = path_dict[sys2][1]
+ result.append(sys2)
+
+ if result == [sys2]:
+ raise KeyError("Two coordinate systems are not connected.")
+ return result
+
def connect_to(self, to_sys, from_coords, to_exprs, inverse=True, fill_in_gaps=False):
- """Register the transformation used to switch to another coordinate system.
-
- Parameters
- ==========
-
- to_sys
- another instance of ``CoordSystem``
- from_coords
- list of symbols in terms of which ``to_exprs`` is given
- to_exprs
- list of the expressions of the new coordinate tuple
- inverse
- try to deduce and register the inverse transformation
- fill_in_gaps
- try to deduce other transformation that are made
- possible by composing the present transformation with other already
- registered transformation
+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(
+ feature="CoordSystem.connect_to",
+ useinstead="new instance generated with new 'transforms' parameter",
+ issue=19321,
+ deprecated_since_version="1.7"
+ ).warn()
- """
from_coords, to_exprs = dummyfy(from_coords, to_exprs)
self.transforms[to_sys] = Matrix(from_coords), Matrix(to_exprs)
@@ -297,6 +452,7 @@ def connect_to(self, to_sys, from_coords, to_exprs, inverse=True, fill_in_gaps=F
@staticmethod
def _inv_transf(from_coords, to_exprs):
+ # Will be removed when connect_to is removed
inv_from = [i.as_dummy() for i in from_coords]
inv_to = solve(
[t[0] - t[1] for t in zip(inv_from, to_exprs)],
@@ -306,92 +462,162 @@ def _inv_transf(from_coords, to_exprs):
@staticmethod
def _fill_gaps_in_transformations():
+ # Will be removed when connect_to is removed
raise NotImplementedError
- # TODO
+
+ ##########################################################################
+ # Coordinate transformations
+ ##########################################################################
+
+ def transform(self, sys, coordinates=None):
+ """
+ Return the result of coordinate transformation from *self* to *sys*.
+ If coordinates are not given, coordinate symbols of *self* are used.
+ """
+ if coordinates is None:
+ coordinates = Matrix(self.symbols)
+ else:
+ coordinates = Matrix(coordinates)
+ if self != sys:
+ transf = self.transformation(sys)
+ coordinates = transf(*coordinates)
+ return coordinates
def coord_tuple_transform_to(self, to_sys, coords):
- """Transform ``coords`` to coord system ``to_sys``.
+ """Transform ``coords`` to coord system ``to_sys``."""
+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(
+ feature="CoordSystem.coord_tuple_transform_to",
+ useinstead="CoordSystem.transform",
+ issue=19321,
+ deprecated_since_version="1.7"
+ ).warn()
- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples."""
coords = Matrix(coords)
if self != to_sys:
transf = self.transforms[to_sys]
coords = transf[1].subs(list(zip(transf[0], coords)))
return coords
- def jacobian(self, to_sys, coords):
- """Return the jacobian matrix of a transformation."""
- with_dummies = self.coord_tuple_transform_to(
- to_sys, self._dummies).jacobian(self._dummies)
- return with_dummies.subs(list(zip(self._dummies, coords)))
+ def jacobian(self, sys, coordinates=None):
+ """
+ Return the jacobian matrix of a transformation.
+ """
+ result = self.transform(sys).jacobian(self.symbols)
+ if coordinates is not None:
+ result = result.subs(list(zip(self.symbols, coordinates)))
+ return result
+ jacobian_matrix = jacobian
+
+ def jacobian_determinant(self, sys, coordinates=None):
+ """Return the jacobian determinant of a transformation."""
+ return self.jacobian(sys, coordinates).det()
+
##########################################################################
- # Base fields.
+ # Points
##########################################################################
- def coord_function(self, coord_index):
- """Return a ``BaseScalarField`` that takes a point and returns one of the coords.
+ def point(self, coords):
+ """Create a ``Point`` with coordinates given in this coord system."""
+ return Point(self, coords)
+
+ def point_to_coords(self, point):
+ """Calculate the coordinates of a point in this coord system."""
+ return point.coords(self)
- Takes a point and returns its coordinate in this coordinate system.
+ ##########################################################################
+ # Base fields.
+ ##########################################################################
- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples."""
+ def base_scalar(self, coord_index):
+ """Return ``BaseScalarField`` that takes a point and returns one of the coordinates."""
return BaseScalarField(self, coord_index)
+ coord_function = base_scalar
- def coord_functions(self):
+ def base_scalars(self):
"""Returns a list of all coordinate functions.
-
- For more details see the ``coord_function`` method of this class."""
- return [self.coord_function(i) for i in range(self.dim)]
+ For more details see the ``base_scalar`` method of this class."""
+ return [self.base_scalar(i) for i in range(self.dim)]
+ coord_functions = base_scalars
def base_vector(self, coord_index):
"""Return a basis vector field.
-
The basis vector field for this coordinate system. It is also an
- operator on scalar fields.
-
- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples."""
+ operator on scalar fields."""
return BaseVectorField(self, coord_index)
def base_vectors(self):
"""Returns a list of all base vectors.
-
For more details see the ``base_vector`` method of this class."""
return [self.base_vector(i) for i in range(self.dim)]
def base_oneform(self, coord_index):
"""Return a basis 1-form field.
-
The basis one-form field for this coordinate system. It is also an
- operator on vector fields.
-
- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples."""
+ operator on vector fields."""
return Differential(self.coord_function(coord_index))
def base_oneforms(self):
"""Returns a list of all base oneforms.
-
For more details see the ``base_oneform`` method of this class."""
return [self.base_oneform(i) for i in range(self.dim)]
- ##########################################################################
- # Points.
- ##########################################################################
+class CoordinateSymbol(Symbol):
+ """A symbol which denotes an abstract value of i-th coordinate of
+ the coordinate system with given context.
- def point(self, coords):
- """Create a ``Point`` with coordinates given in this coord system.
+ Explanation
+ ===========
- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples."""
- return Point(self, coords)
+ Each coordinates in coordinate system are represented by unique symbol,
+ such as x, y, z in Cartesian coordinate system.
- def point_to_coords(self, point):
- """Calculate the coordinates of a point in this coord system.
+ You may not construct this class directly. Instead, use `symbols` method
+ of CoordSystem.
- See the docstring of ``CoordSystem`` for examples."""
- return point.coords(self)
+ Parameters
+ ==========
- ##########################################################################
- # Printing.
- ##########################################################################
+ coord_sys : CoordSystem
+
+ index : integer
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import symbols
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem
+ >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)
+ >>> p = Patch('P', m)
+ >>> _x, _y = symbols('x y', nonnegative=True)
+
+ >>> C = CoordSystem('C', p, [_x, _y])
+ >>> x, y = C.symbols
+
+ >>> x.name
+ 'x'
+ >>> x.coord_sys == C
+ True
+ >>> x.index
+ 0
+ >>> x.is_nonnegative
+ True
+
+ """
+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index, **assumptions):
+ name = coord_sys.args[2][index].name
+ obj = super().__new__(cls, name, **assumptions)
+ obj.coord_sys = coord_sys
+ obj.index = index
+ return obj
+
+ def __getnewargs__(self):
+ return (self.coord_sys, self.index)
+
+ def _hashable_content(self):
+ return (
+ self.coord_sys, self.index
+ ) + tuple(sorted(self.assumptions0.items()))
class Point(Basic):
"""Point defined in a coordinate system.
@@ -399,7 +625,10 @@ class Point(Basic):
Explanation
===========
- To define a point you must supply coordinates and a coordinate system.
+ Mathematically, point is defined in the manifold and does not have any coordinates
+ by itself. Coordinate system is what imbues the coordinates to the point by coordinate
+ chart. However, due to the difficulty of realizing such logic, you must supply
+ a coordinate system and coordinates to define a Point here.
The usage of this object after its definition is independent of the
coordinate system that was used in order to define it, however due to
@@ -411,67 +640,74 @@ class Point(Basic):
coord_sys : CoordSystem
- coords: list of sympy expressions
+ coords : list
The coordinates of the point.
Examples
========
- Define the boilerplate Manifold, Patch and coordinate systems:
+ >>> from sympy import pi
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Point
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_r, R2_p
+ >>> rho, theta = R2_p.symbols
- >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, pi
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom import (
- ... Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, Point)
- >>> r, theta = symbols('r, theta')
- >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)
- >>> p = Patch('P', m)
- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)
- >>> polar = CoordSystem('polar', p)
- >>> polar.connect_to(rect, [r, theta], [r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)])
+ >>> p = Point(R2_p, [rho, 3*pi/4])
- Define a point using coordinates from one of the coordinate systems:
+ >>> p.manifold == R2
+ True
- >>> p = Point(polar, [r, 3*pi/4])
>>> p.coords()
Matrix([
- [ r],
+ [ rho],
[3*pi/4]])
- >>> p.coords(rect)
+ >>> p.coords(R2_r)
Matrix([
- [-sqrt(2)*r/2],
- [ sqrt(2)*r/2]])
+ [-sqrt(2)*rho/2],
+ [ sqrt(2)*rho/2]])
"""
- def __new__(cls, coord_sys, coords):
+
+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, coords, **kwargs):
coords = Matrix(coords)
obj = super().__new__(cls, coord_sys, coords)
obj._coord_sys = coord_sys
obj._coords = coords
return obj
- def coords(self, to_sys=None):
- """Coordinates of the point in a given coordinate system.
+ @property
+ def patch(self):
+ return self._coord_sys.patch
- If ``to_sys`` is ``None`` it returns the coordinates in the system in
- which the point was defined."""
- if to_sys:
- return self._coord_sys.coord_tuple_transform_to(to_sys, self._coords)
- else:
+ @property
+ def manifold(self):
+ return self._coord_sys.manifold
+
+ @property
+ def dim(self):
+ return self.manifold.dim
+
+ def coords(self, sys=None):
+ """
+ Coordinates of the point in given coordinate system. If coordinate system
+ is not passed, it returns the coordinates in the coordinate system in which
+ the poin was defined.
+ """
+ if sys is None:
return self._coords
+ else:
+ return self._coord_sys.transform(sys, self._coords)
@property
def free_symbols(self):
return self._coords.free_symbols
-
class BaseScalarField(Expr):
- """Base Scalar Field over a Manifold for a given Coordinate System.
+ """Base scalar field over a manifold for a given coordinate system.
Explanation
===========
A scalar field takes a point as an argument and returns a scalar.
-
A base scalar field of a coordinate system takes a point and returns one of
the coordinates of that point in the coordinate system in question.
@@ -482,7 +718,6 @@ class BaseScalarField(Expr):
coordinate system in which it was defined, however due to limitations in
the simplification routines you may arrive at more complicated
expression if you use unappropriate coordinate systems.
-
You can build complicated scalar fields by just building up SymPy
expressions containing ``BaseScalarField`` instances.
@@ -496,30 +731,23 @@ class BaseScalarField(Expr):
Examples
========
- Define boilerplate Manifold, Patch and coordinate systems:
-
- >>> from sympy import symbols, sin, cos, pi, Function
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField
- >>> r0, theta0 = symbols('r0, theta0')
- >>> m = Manifold('M', 2)
- >>> p = Patch('P', m)
- >>> rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)
- >>> polar = CoordSystem('polar', p)
- >>> polar.connect_to(rect, [r0, theta0], [r0*cos(theta0), r0*sin(theta0)])
-
- Point to be used as an argument for the filed:
-
- >>> point = polar.point([r0, 0])
-
- Examples of fields:
+ >>> from sympy import Function, pi
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom import BaseScalarField
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r, R2_p
+ >>> rho, _ = R2_p.symbols
+ >>> point = R2_p.point([rho, 0])
+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()
+ >>> ftheta = BaseScalarField(R2_r, 1)
+
+ >>> fx(point)
+ rho
+ >>> fy(point)
+ 0
- >>> fx = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)
- >>> fy = BaseScalarField(rect, 1)
>>> (fx**2+fy**2).rcall(point)
- r0**2
+ rho**2
>>> g = Function('g')
- >>> ftheta = BaseScalarField(polar, 1)
>>> fg = g(ftheta-pi)
>>> fg.rcall(point)
g(-pi)
@@ -528,16 +756,35 @@ class BaseScalarField(Expr):
is_commutative = True
- def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index):
+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index, **kwargs):
index = _sympify(index)
obj = super().__new__(cls, coord_sys, index)
obj._coord_sys = coord_sys
obj._index = index
return obj
+ @property
+ def coord_sys(self):
+ return self.args[0]
+
+ @property
+ def index(self):
+ return self.args[1]
+
+ @property
+ def patch(self):
+ return self.coord_sys.patch
+
+ @property
+ def manifold(self):
+ return self.coord_sys.manifold
+
+ @property
+ def dim(self):
+ return self.manifold.dim
+
def __call__(self, *args):
"""Evaluating the field at a point or doing nothing.
-
If the argument is a ``Point`` instance, the field is evaluated at that
point. The field is returned itself if the argument is any other
object. It is so in order to have working recursive calling mechanics
@@ -559,14 +806,13 @@ def doit(self):
class BaseVectorField(Expr):
- r"""Vector Field over a Manifold.
+ r"""Base vector field over a manifold for a given coordinate system.
Explanation
===========
A vector field is an operator taking a scalar field and returning a
directional derivative (which is also a scalar field).
-
A base vector field is the same type of operator, however the derivation is
specifically done with respect to a chosen coordinate.
@@ -580,7 +826,6 @@ class BaseVectorField(Expr):
Parameters
==========
-
coord_sys : CoordSystem
index : integer
@@ -588,29 +833,19 @@ class BaseVectorField(Expr):
Examples
========
- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.
-
- >>> from sympy import symbols, Function
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_p, R2_r
+ >>> from sympy import Function
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_p, R2_r
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import BaseVectorField
>>> from sympy import pprint
- >>> x0, y0, r0, theta0 = symbols('x0, y0, r0, theta0')
-
- Points to be used as arguments for the field:
- >>> point_p = R2_p.point([r0, theta0])
- >>> point_r = R2_r.point([x0, y0])
-
- Scalar field to operate on:
+ >>> x, y = R2_r.symbols
+ >>> rho, theta = R2_p.symbols
+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()
+ >>> point_p = R2_p.point([rho, theta])
+ >>> point_r = R2_r.point([x, y])
>>> g = Function('g')
- >>> s_field = g(R2.x, R2.y)
- >>> s_field.rcall(point_r)
- g(x0, y0)
- >>> s_field.rcall(point_p)
- g(r0*cos(theta0), r0*sin(theta0))
-
- Vector field:
+ >>> s_field = g(fx, fy)
>>> v = BaseVectorField(R2_r, 1)
>>> pprint(v(s_field))
@@ -618,31 +853,49 @@ class BaseVectorField(Expr):
|---(g(x, xi))||
\dxi /|xi=y
>>> pprint(v(s_field).rcall(point_r).doit())
- d
- ---(g(x0, y0))
- dy0
+ d
+ --(g(x, y))
+ dy
>>> pprint(v(s_field).rcall(point_p))
/ d \|
- |---(g(r0*cos(theta0), xi))||
- \dxi /|xi=r0*sin(theta0)
+ |---(g(rho*cos(theta), xi))||
+ \dxi /|xi=rho*sin(theta)
"""
is_commutative = False
- def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index):
+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index, **kwargs):
index = _sympify(index)
obj = super().__new__(cls, coord_sys, index)
obj._coord_sys = coord_sys
obj._index = index
return obj
+ @property
+ def coord_sys(self):
+ return self.args[0]
+
+ @property
+ def index(self):
+ return self.args[1]
+
+ @property
+ def patch(self):
+ return self.coord_sys.patch
+
+ @property
+ def manifold(self):
+ return self.coord_sys.manifold
+
+ @property
+ def dim(self):
+ return self.manifold.dim
+
def __call__(self, scalar_field):
"""Apply on a scalar field.
-
The action of a vector field on a scalar field is a directional
differentiation.
-
If the argument is not a scalar field an error is raised.
"""
if covariant_order(scalar_field) or contravariant_order(scalar_field):
@@ -662,7 +915,7 @@ def __call__(self, scalar_field):
d_result = d_result.diff(d_var)
# Second step: e_x(x) -> 1 and e_x(r) -> cos(atan2(x, y))
- coords = self._coord_sys._dummies
+ coords = self._coord_sys.symbols
d_funcs_deriv = [f.diff(d_var) for f in d_funcs]
d_funcs_deriv_sub = []
for b in base_scalars:
@@ -686,6 +939,9 @@ def _find_coords(expr):
class Commutator(Expr):
r"""Commutator of two vector fields.
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
The commutator of two vector fields `v_1` and `v_2` is defined as the
vector field `[v_1, v_2]` that evaluated on each scalar field `f` is equal
to `v_1(v_2(f)) - v_2(v_1(f))`.
@@ -693,15 +949,15 @@ class Commutator(Expr):
Examples
========
- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_p, R2_r
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import Commutator
>>> from sympy.simplify import simplify
- Vector fields:
+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()
+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()
+ >>> e_r = R2_p.base_vector(0)
- >>> e_x, e_y, e_r = R2.e_x, R2.e_y, R2.e_r
>>> c_xy = Commutator(e_x, e_y)
>>> c_xr = Commutator(e_x, e_r)
>>> c_xy
@@ -710,9 +966,8 @@ class Commutator(Expr):
Unfortunately, the current code is not able to compute everything:
>>> c_xr
- Commutator(e_x, e_r)
-
- >>> simplify(c_xr(R2.y**2))
+ Commutator(e_x, e_rho)
+ >>> simplify(c_xr(fy**2))
-2*cos(theta)*y**2/(x**2 + y**2)
"""
@@ -722,13 +977,13 @@ def __new__(cls, v1, v2):
raise ValueError(
'Only commutators of vector fields are supported.')
if v1 == v2:
- return Zero()
+ return S.Zero
coord_sys = set().union(*[_find_coords(v) for v in (v1, v2)])
if len(coord_sys) == 1:
# Only one coordinate systems is used, hence it is easy enough to
# actually evaluate the commutator.
if all(isinstance(v, BaseVectorField) for v in (v1, v2)):
- return Zero()
+ return S.Zero
bases_1, bases_2 = [list(v.atoms(BaseVectorField))
for v in (v1, v2)]
coeffs_1 = [v1.expand().coeff(b) for b in bases_1]
@@ -739,53 +994,51 @@ def __new__(cls, v1, v2):
res += c1*b1(c2)*b2 - c2*b2(c1)*b1
return res
else:
- return super().__new__(cls, v1, v2)
+ obj = super().__new__(cls, v1, v2)
+ obj._v1 = v1 # deprecated assignment
+ obj._v2 = v2 # deprecated assignment
+ return obj
+
+ @property
+ def v1(self):
+ return self.args[0]
- def __init__(self, v1, v2):
- super().__init__()
- self._args = (v1, v2)
- self._v1 = v1
- self._v2 = v2
+ @property
+ def v2(self):
+ return self.args[1]
def __call__(self, scalar_field):
"""Apply on a scalar field.
-
If the argument is not a scalar field an error is raised.
"""
- return self._v1(self._v2(scalar_field)) - self._v2(self._v1(scalar_field))
+ return self.v1(self.v2(scalar_field)) - self.v2(self.v1(scalar_field))
class Differential(Expr):
r"""Return the differential (exterior derivative) of a form field.
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
The differential of a form (i.e. the exterior derivative) has a complicated
definition in the general case.
-
The differential `df` of the 0-form `f` is defined for any vector field `v`
as `df(v) = v(f)`.
Examples
========
- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.
-
>>> from sympy import Function
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import Differential
>>> from sympy import pprint
- Scalar field (0-forms):
-
+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()
+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()
>>> g = Function('g')
- >>> s_field = g(R2.x, R2.y)
-
- Vector fields:
-
- >>> e_x, e_y, = R2.e_x, R2.e_y
-
- Differentials:
-
+ >>> s_field = g(fx, fy)
>>> dg = Differential(s_field)
+
>>> dg
d(g(x, y))
>>> pprint(dg(e_x))
@@ -801,7 +1054,6 @@ class Differential(Expr):
>>> Differential(dg)
0
-
"""
is_commutative = False
@@ -811,18 +1063,22 @@ def __new__(cls, form_field):
raise ValueError(
'A vector field was supplied as an argument to Differential.')
if isinstance(form_field, Differential):
- return Zero()
+ return S.Zero
else:
- return super().__new__(cls, form_field)
+ obj = super().__new__(cls, form_field)
+ obj._form_field = form_field # deprecated assignment
+ return obj
- def __init__(self, form_field):
- super().__init__()
- self._form_field = form_field
- self._args = (self._form_field, )
+ @property
+ def form_field(self):
+ return self.args[0]
def __call__(self, *vector_fields):
"""Apply on a list of vector_fields.
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
If the number of vector fields supplied is not equal to 1 + the order of
the form field inside the differential the result is undefined.
@@ -867,10 +1123,12 @@ def __call__(self, *vector_fields):
ret += (-1)**(i + j)*t
return ret
-
class TensorProduct(Expr):
"""Tensor product of forms.
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
The tensor product permits the creation of multilinear functionals (i.e.
higher order tensors) out of lower order fields (e.g. 1-forms and vector
fields). However, the higher tensors thus created lack the interesting
@@ -880,27 +1138,28 @@ class TensorProduct(Expr):
Examples
========
- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.
-
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import TensorProduct
- >>> TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)(R2.e_x, R2.e_y)
+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()
+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()
+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()
+
+ >>> TensorProduct(dx, dy)(e_x, e_y)
1
- >>> TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)(R2.e_y, R2.e_x)
+ >>> TensorProduct(dx, dy)(e_y, e_x)
0
- >>> TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.x*R2.dy)(R2.x*R2.e_x, R2.e_y)
+ >>> TensorProduct(dx, fx*dy)(fx*e_x, e_y)
x**2
- >>> TensorProduct(R2.e_x, R2.e_y)(R2.x**2, R2.y**2)
+ >>> TensorProduct(e_x, e_y)(fx**2, fy**2)
4*x*y
- >>> TensorProduct(R2.e_y, R2.dx)(R2.y)
+ >>> TensorProduct(e_y, dx)(fy)
dx
-
You can nest tensor products.
- >>> tp1 = TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)
- >>> TensorProduct(tp1, R2.dx)(R2.e_x, R2.e_y, R2.e_x)
+ >>> tp1 = TensorProduct(dx, dy)
+ >>> TensorProduct(tp1, dx)(e_x, e_y, e_x)
1
You can make partial contraction for instance when 'raising an index'.
@@ -908,13 +1167,13 @@ class TensorProduct(Expr):
respective position in the tensor product is left as it is.
>>> TP = TensorProduct
- >>> metric = TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + 3*TP(R2.dy, R2.dy)
- >>> metric.rcall(R2.e_y, None)
+ >>> metric = TP(dx, dx) + 3*TP(dy, dy)
+ >>> metric.rcall(e_y, None)
3*dy
Or automatically pad the args with ``None`` without specifying them.
- >>> metric.rcall(R2.e_y)
+ >>> metric.rcall(e_y)
3*dy
"""
@@ -928,10 +1187,6 @@ def __new__(cls, *args):
else:
return scalar
- def __init__(self, *args):
- super().__init__()
- self._args = args
-
def __call__(self, *fields):
"""Apply on a list of fields.
@@ -942,6 +1197,7 @@ def __call__(self, *fields):
the forms inside the tensor product. The sublists are provided as
arguments to these forms and the resulting expressions are given to the
constructor of ``TensorProduct``.
+
"""
tot_order = covariant_order(self) + contravariant_order(self)
tot_args = len(fields)
@@ -957,30 +1213,35 @@ def __call__(self, *fields):
class WedgeProduct(TensorProduct):
"""Wedge product of forms.
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
In the context of integration only completely antisymmetric forms make
sense. The wedge product permits the creation of such forms.
Examples
========
- Use the predefined R2 manifold, setup some boilerplate.
-
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import WedgeProduct
- >>> WedgeProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)(R2.e_x, R2.e_y)
+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()
+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()
+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()
+
+ >>> WedgeProduct(dx, dy)(e_x, e_y)
1
- >>> WedgeProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)(R2.e_y, R2.e_x)
+ >>> WedgeProduct(dx, dy)(e_y, e_x)
-1
- >>> WedgeProduct(R2.dx, R2.x*R2.dy)(R2.x*R2.e_x, R2.e_y)
+ >>> WedgeProduct(dx, fx*dy)(fx*e_x, e_y)
x**2
- >>> WedgeProduct(R2.e_x,R2.e_y)(R2.y,None)
+ >>> WedgeProduct(e_x, e_y)(fy, None)
-e_x
You can nest wedge products.
- >>> wp1 = WedgeProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)
- >>> WedgeProduct(wp1, R2.dx)(R2.e_x, R2.e_y, R2.e_x)
+ >>> wp1 = WedgeProduct(dx, dy)
+ >>> WedgeProduct(wp1, dx)(e_x, e_y, e_x)
0
"""
@@ -988,7 +1249,6 @@ class WedgeProduct(TensorProduct):
# TODO you do not need all these permutations (neither the prefactor)
def __call__(self, *fields):
"""Apply on a list of vector_fields.
-
The expression is rewritten internally in terms of tensor products and evaluated."""
orders = (covariant_order(e) + contravariant_order(e) for e in self.args)
mul = 1/Mul(*(factorial(o) for o in orders))
@@ -1002,6 +1262,9 @@ def __call__(self, *fields):
class LieDerivative(Expr):
"""Lie derivative with respect to a vector field.
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
The transport operator that defines the Lie derivative is the pushforward of
the field to be derived along the integral curve of the field with respect
to which one derives.
@@ -1009,27 +1272,35 @@ class LieDerivative(Expr):
Examples
========
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r, R2_p
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import (LieDerivative, TensorProduct)
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, R2.y)
+
+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()
+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()
+ >>> e_rho, e_theta = R2_p.base_vectors()
+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()
+
+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, fy)
0
- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, R2.x)
+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, fx)
1
- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, R2.e_x)
+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, e_x)
0
The Lie derivative of a tensor field by another tensor field is equal to
their commutator:
- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, R2.e_r)
- Commutator(e_x, e_r)
- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x + R2.e_y, R2.x)
+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, e_rho)
+ Commutator(e_x, e_rho)
+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x + e_y, fx)
1
- >>> tp = TensorProduct(R2.dx, R2.dy)
- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, tp)
+
+ >>> tp = TensorProduct(dx, dy)
+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, tp)
LieDerivative(e_x, TensorProduct(dx, dy))
- >>> LieDerivative(R2.e_x, tp)
+ >>> LieDerivative(e_x, tp)
LieDerivative(e_x, TensorProduct(dx, dy))
+
"""
def __new__(cls, v_field, expr):
expr_form_ord = covariant_order(expr)
@@ -1038,21 +1309,27 @@ def __new__(cls, v_field, expr):
' vector fields. The supplied argument was not a '
'vector field.')
if expr_form_ord > 0:
- return super().__new__(cls, v_field, expr)
+ obj = super().__new__(cls, v_field, expr)
+ # deprecated assignments
+ obj._v_field = v_field
+ obj._expr = expr
+ return obj
if expr.atoms(BaseVectorField):
return Commutator(v_field, expr)
else:
return v_field.rcall(expr)
- def __init__(self, v_field, expr):
- super().__init__()
- self._v_field = v_field
- self._expr = expr
- self._args = (self._v_field, self._expr)
+ @property
+ def v_field(self):
+ return self.args[0]
+
+ @property
+ def expr(self):
+ return self.args[1]
def __call__(self, *args):
- v = self._v_field
- expr = self._expr
+ v = self.v_field
+ expr = self.expr
lead_term = v(expr(*args))
rest = Add(*[Mul(*args[:i] + (Commutator(v, args[i]),) + args[i + 1:])
for i in range(len(args))])
@@ -1065,32 +1342,52 @@ class BaseCovarDerivativeOp(Expr):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2, R2_r
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import BaseCovarDerivativeOp
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, TensorProduct
+
>>> TP = TensorProduct
- >>> ch = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))
+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()
+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()
+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()
+
+ >>> ch = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(dx, dx) + TP(dy, dy))
>>> ch
[[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]
>>> cvd = BaseCovarDerivativeOp(R2_r, 0, ch)
- >>> cvd(R2.x)
+ >>> cvd(fx)
1
- >>> cvd(R2.x*R2.e_x)
+ >>> cvd(fx*e_x)
e_x
"""
- def __init__(self, coord_sys, index, christoffel):
- super().__init__()
- self._coord_sys = coord_sys
- self._index = index
- self._christoffel = christoffel
- self._args = self._coord_sys, self._index, self._christoffel
+
+ def __new__(cls, coord_sys, index, christoffel):
+ index = _sympify(index)
+ christoffel = ImmutableDenseNDimArray(christoffel)
+ obj = super().__new__(cls, coord_sys, index, christoffel)
+ # deprecated assignments
+ obj._coord_sys = coord_sys
+ obj._index = index
+ obj._christoffel = christoffel
+ return obj
+
+ @property
+ def coord_sys(self):
+ return self.args[0]
+
+ @property
+ def index(self):
+ return self.args[1]
+
+ @property
+ def christoffel(self):
+ return self.args[2]
def __call__(self, field):
"""Apply on a scalar field.
The action of a vector field on a scalar field is a directional
differentiation.
-
If the argument is not a scalar field the behaviour is undefined.
"""
if covariant_order(field) != 0:
@@ -1136,31 +1433,45 @@ class CovarDerivativeOp(Expr):
Examples
========
- >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
+ >>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import CovarDerivativeOp
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, TensorProduct
>>> TP = TensorProduct
- >>> ch = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))
+ >>> fx, fy = R2_r.base_scalars()
+ >>> e_x, e_y = R2_r.base_vectors()
+ >>> dx, dy = R2_r.base_oneforms()
+ >>> ch = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(dx, dx) + TP(dy, dy))
+
>>> ch
[[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]
- >>> cvd = CovarDerivativeOp(R2.x*R2.e_x, ch)
- >>> cvd(R2.x)
+ >>> cvd = CovarDerivativeOp(fx*e_x, ch)
+ >>> cvd(fx)
x
- >>> cvd(R2.x*R2.e_x)
+ >>> cvd(fx*e_x)
x*e_x
"""
- def __init__(self, wrt, christoffel):
- super().__init__()
+
+ def __new__(cls, wrt, christoffel):
if len({v._coord_sys for v in wrt.atoms(BaseVectorField)}) > 1:
raise NotImplementedError()
if contravariant_order(wrt) != 1 or covariant_order(wrt):
raise ValueError('Covariant derivatives are defined only with '
'respect to vector fields. The supplied argument '
'was not a vector field.')
- self._wrt = wrt
- self._christoffel = christoffel
- self._args = self._wrt, self._christoffel
+ obj = super().__new__(cls, wrt, christoffel)
+ # deprecated assigments
+ obj._wrt = wrt
+ obj._christoffel = christoffel
+ return obj
+
+ @property
+ def wrt(self):
+ return self.args[0]
+
+ @property
+ def christoffel(self):
+ return self.args[1]
def __call__(self, field):
vectors = list(self._wrt.atoms(BaseVectorField))
@@ -1175,6 +1486,9 @@ def __call__(self, field):
def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeffs=False):
r"""Return the series expansion for an integral curve of the field.
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
Integral curve is a function `\gamma` taking a parameter in `R` to a point
in the manifold. It verifies the equation:
@@ -1184,7 +1498,6 @@ def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeff
value `t` for the parameter and any scalar field `f`.
This equation can also be decomposed of a basis of coordinate functions
-
`V(f_i)\big(\gamma(t)\big) = \frac{d}{dt}f_i\big(\gamma(t)\big) \quad \forall i`
This function returns a series expansion of `\gamma(t)` in terms of the
@@ -1193,22 +1506,20 @@ def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeff
represent movement between points on the manifold (i.e. there is no such
thing as a difference of points for a general manifold).
- See Also
- ========
-
- intcurve_diffequ
-
Parameters
==========
-
vector_field
the vector field for which an integral curve will be given
+
param
the argument of the function `\gamma` from R to the curve
+
start_point
the point which corresponds to `\gamma(0)`
+
n
the order to which to expand
+
coord_sys
the coordinate system in which to expand
coeffs (default False) - if True return a list of elements of the expansion
@@ -1267,6 +1578,11 @@ def intcurve_series(vector_field, param, start_point, n=6, coord_sys=None, coeff
[t**2*(-x**2/(x**2 + y**2)**(3/2) + 1/sqrt(x**2 + y**2))/2],
[ t**2*x*y/(x**2 + y**2)**2]])
+ See Also
+ ========
+
+ intcurve_diffequ
+
"""
if contravariant_order(vector_field) != 1 or covariant_order(vector_field):
raise ValueError('The supplied field was not a vector field.')
@@ -1291,6 +1607,9 @@ def taylor_terms_per_coord(coord_function):
def intcurve_diffequ(vector_field, param, start_point, coord_sys=None):
r"""Return the differential equation for an integral curve of the field.
+ Explanation
+ ===========
+
Integral curve is a function `\gamma` taking a parameter in `R` to a point
in the manifold. It verifies the equation:
@@ -1305,25 +1624,24 @@ def intcurve_diffequ(vector_field, param, start_point, coord_sys=None):
represent movement between points on the manifold (i.e. there is no such
thing as a difference of points for a general manifold).
- See Also
- ========
-
- intcurve_series
-
Parameters
==========
vector_field
the vector field for which an integral curve will be given
+
param
the argument of the function `\gamma` from R to the curve
+
start_point
the point which corresponds to `\gamma(0)`
+
coord_sys
the coordinate system in which to give the equations
Returns
=======
+
a tuple of (equations, initial conditions)
Examples
@@ -1356,6 +1674,11 @@ def intcurve_diffequ(vector_field, param, start_point, coord_sys=None):
>>> init_cond
[f_0(0) - 1, f_1(0) - pi/2]
+ See Also
+ ========
+
+ intcurve_series
+
"""
if contravariant_order(vector_field) != 1 or covariant_order(vector_field):
raise ValueError('The supplied field was not a vector field.')
@@ -1394,6 +1717,7 @@ def contravariant_order(expr, _strict=False):
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import contravariant_order
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
>>> from sympy.abc import a
+
>>> contravariant_order(a)
0
>>> contravariant_order(a*R2.x + 2)
@@ -1439,6 +1763,7 @@ def covariant_order(expr, _strict=False):
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import covariant_order
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
>>> from sympy.abc import a
+
>>> covariant_order(a)
0
>>> covariant_order(a*R2.x + 2)
@@ -1480,7 +1805,6 @@ def covariant_order(expr, _strict=False):
###############################################################################
def vectors_in_basis(expr, to_sys):
"""Transform all base vectors in base vectors of a specified coord basis.
-
While the new base vectors are in the new coordinate system basis, any
coefficients are kept in the old system.
@@ -1489,10 +1813,12 @@ def vectors_in_basis(expr, to_sys):
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import vectors_in_basis
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2_r, R2_p
+
>>> vectors_in_basis(R2_r.e_x, R2_p)
- -y*e_theta/(x**2 + y**2) + x*e_r/sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
+ -y*e_theta/(x**2 + y**2) + x*e_rho/sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
>>> vectors_in_basis(R2_p.e_r, R2_r)
sin(theta)*e_y + cos(theta)*e_x
+
"""
vectors = list(expr.atoms(BaseVectorField))
new_vectors = []
@@ -1520,6 +1846,7 @@ def twoform_to_matrix(expr):
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import twoform_to_matrix, TensorProduct
>>> TP = TensorProduct
+
>>> twoform_to_matrix(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))
Matrix([
[1, 0],
@@ -1551,7 +1878,6 @@ def twoform_to_matrix(expr):
def metric_to_Christoffel_1st(expr):
"""Return the nested list of Christoffel symbols for the given metric.
-
This returns the Christoffel symbol of first kind that represents the
Levi-Civita connection for the given metric.
@@ -1561,6 +1887,7 @@ def metric_to_Christoffel_1st(expr):
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Christoffel_1st, TensorProduct
>>> TP = TensorProduct
+
>>> metric_to_Christoffel_1st(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))
[[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]
>>> metric_to_Christoffel_1st(R2.x*TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))
@@ -1584,7 +1911,6 @@ def metric_to_Christoffel_1st(expr):
def metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(expr):
"""Return the nested list of Christoffel symbols for the given metric.
-
This returns the Christoffel symbol of second kind that represents the
Levi-Civita connection for the given metric.
@@ -1594,6 +1920,7 @@ def metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(expr):
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Christoffel_2nd, TensorProduct
>>> TP = TensorProduct
+
>>> metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))
[[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]
>>> metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(R2.x*TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))
@@ -1611,7 +1938,7 @@ def metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(expr):
for e in matrix:
s_fields.update(e.atoms(BaseScalarField))
s_fields = list(s_fields)
- dums = coord_sys._dummies
+ dums = coord_sys.symbols
matrix = matrix.subs(list(zip(s_fields, dums))).inv().subs(list(zip(dums, s_fields)))
# XXX end of workaround
christoffel = [[[Add(*[matrix[i, l]*ch_1st[l, j, k] for l in indices])
@@ -1635,18 +1962,18 @@ def metric_to_Riemann_components(expr):
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Riemann_components, TensorProduct
>>> TP = TensorProduct
+
>>> metric_to_Riemann_components(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))
[[[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]], [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]]
-
>>> non_trivial_metric = exp(2*R2.r)*TP(R2.dr, R2.dr) + \
R2.r**2*TP(R2.dtheta, R2.dtheta)
>>> non_trivial_metric
- exp(2*r)*TensorProduct(dr, dr) + r**2*TensorProduct(dtheta, dtheta)
+ exp(2*rho)*TensorProduct(drho, drho) + rho**2*TensorProduct(dtheta, dtheta)
>>> riemann = metric_to_Riemann_components(non_trivial_metric)
>>> riemann[0, :, :, :]
- [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, exp(-2*r)*r], [-exp(-2*r)*r, 0]]]
+ [[[0, 0], [0, 0]], [[0, exp(-2*rho)*rho], [-exp(-2*rho)*rho, 0]]]
>>> riemann[1, :, :, :]
- [[[0, -1/r], [1/r, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]
+ [[[0, -1/rho], [1/rho, 0]], [[0, 0], [0, 0]]]
"""
ch_2nd = metric_to_Christoffel_2nd(expr)
@@ -1676,6 +2003,7 @@ def metric_to_Riemann_components(expr):
def metric_to_Ricci_components(expr):
+
"""Return the components of the Ricci tensor expressed in a given basis.
Given a metric it calculates the components of the Ricci tensor in the
@@ -1689,15 +2017,15 @@ def metric_to_Ricci_components(expr):
>>> from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
>>> from sympy.diffgeom import metric_to_Ricci_components, TensorProduct
>>> TP = TensorProduct
+
>>> metric_to_Ricci_components(TP(R2.dx, R2.dx) + TP(R2.dy, R2.dy))
[[0, 0], [0, 0]]
-
>>> non_trivial_metric = exp(2*R2.r)*TP(R2.dr, R2.dr) + \
R2.r**2*TP(R2.dtheta, R2.dtheta)
>>> non_trivial_metric
- exp(2*r)*TensorProduct(dr, dr) + r**2*TensorProduct(dtheta, dtheta)
+ exp(2*rho)*TensorProduct(drho, drho) + rho**2*TensorProduct(dtheta, dtheta)
>>> metric_to_Ricci_components(non_trivial_metric)
- [[1/r, 0], [0, exp(-2*r)*r]]
+ [[1/rho, 0], [0, exp(-2*rho)*rho]]
"""
riemann = metric_to_Riemann_components(expr)
@@ -1707,3 +2035,43 @@ def metric_to_Ricci_components(expr):
for j in indices]
for i in indices]
return ImmutableDenseNDimArray(ricci)
+
+###############################################################################
+# Classes for deprecation
+###############################################################################
+
+class _deprecated_container(object):
+ # This class gives deprecation warning.
+ # When deprecated features are completely deleted, this should be removed as well.
+ # See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/19368
+ def __init__(self, feature, useinstead, issue, version, data):
+ super().__init__(data)
+ self.feature = feature
+ self.useinstead = useinstead
+ self.issue = issue
+ self.version = version
+
+ def warn(self):
+ SymPyDeprecationWarning(
+ feature=self.feature,
+ useinstead=self.useinstead,
+ issue=self.issue,
+ deprecated_since_version=self.version).warn()
+
+ def __iter__(self):
+ self.warn()
+ return super().__iter__()
+
+ def __getitem__(self, key):
+ self.warn()
+ return super().__getitem__(key)
+
+ def __contains__(self, key):
+ self.warn()
+ return super().__contains__(key)
+
+class _deprecated_list(_deprecated_container, list):
+ pass
+
+class _deprecated_dict(_deprecated_container, dict):
+ pass
diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py b/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py
index 1226a63f0377..55c964ccbd2b 100644
--- a/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py
+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/rn.py
@@ -9,28 +9,44 @@
"""
from typing import Any
+import warnings
+from sympy import sqrt, atan2, acos, sin, cos, Lambda, Matrix, symbols, Dummy
from .diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem
-from sympy import sqrt, atan2, acos, sin, cos, Dummy
+
+__all__ = [
+ 'R2', 'R2_origin', 'relations_2d', 'R2_r', 'R2_p',
+ 'R3', 'R3_origin', 'relations_3d', 'R3_r', 'R3_c', 'R3_s'
+]
###############################################################################
# R2
###############################################################################
R2 = Manifold('R^2', 2) # type: Any
-# Patch and coordinate systems.
+
R2_origin = Patch('origin', R2) # type: Any
-R2_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R2_origin, ['x', 'y']) # type: Any
-R2_p = CoordSystem('polar', R2_origin, ['r', 'theta']) # type: Any
-
-# Connecting the coordinate charts.
-x, y, r, theta = [Dummy(s) for s in ['x', 'y', 'r', 'theta']]
-R2_r.connect_to(R2_p, [x, y],
- [sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)],
- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
-R2_p.connect_to(R2_r, [r, theta],
- [r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)],
- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
-del x, y, r, theta
+
+x, y = symbols('x y', real=True)
+r, theta = symbols('rho theta', nonnegative=True)
+
+relations_2d = {
+ ('rectangular', 'polar'): Lambda((x, y), Matrix([sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)])),
+ ('polar', 'rectangular'): Lambda((r, theta), Matrix([r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)])),
+}
+
+R2_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R2_origin, [x, y], relations_2d) # type: Any
+R2_p = CoordSystem('polar', R2_origin, [r, theta], relations_2d) # type: Any
+
+# support deprecated feature
+with warnings.catch_warnings():
+ warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
+ x, y, r, theta = symbols('x y r theta', cls=Dummy)
+ R2_r.connect_to(R2_p, [x, y],
+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x)],
+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
+ R2_p.connect_to(R2_r, [r, theta],
+ [r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)],
+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
# Defining the basis coordinate functions and adding shortcuts for them to the
# manifold and the patch.
@@ -51,39 +67,69 @@
# R3
###############################################################################
R3 = Manifold('R^3', 3) # type: Any
-# Patch and coordinate systems.
+
R3_origin = Patch('origin', R3) # type: Any
-R3_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R3_origin, ['x', 'y', 'z']) # type: Any
-R3_c = CoordSystem('cylindrical', R3_origin, ['rho', 'psi', 'z']) # type: Any
-R3_s = CoordSystem('spherical', R3_origin, ['r', 'theta', 'phi']) # type: Any
-
-# Connecting the coordinate charts.
-x, y, z, rho, psi, r, theta, phi = [Dummy(s) for s in ['x', 'y', 'z',
- 'rho', 'psi', 'r', 'theta', 'phi']]
-## rectangular <-> cylindrical
-R3_r.connect_to(R3_c, [x, y, z],
- [sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z],
- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
-R3_c.connect_to(R3_r, [rho, psi, z],
- [rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z],
- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
-## rectangular <-> spherical
-R3_r.connect_to(R3_s, [x, y, z],
- [sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2), acos(z/
- sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)), atan2(y, x)],
- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
-R3_s.connect_to(R3_r, [r, theta, phi],
- [r*sin(theta)*cos(phi), r*sin(
- theta)*sin(phi), r*cos(theta)],
- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
-## cylindrical <-> spherical
-R3_c.connect_to(R3_s, [rho, psi, z],
- [sqrt(rho**2 + z**2), acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)), psi],
- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
-R3_s.connect_to(R3_c, [r, theta, phi],
- [r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta)],
- inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
-del x, y, z, rho, psi, r, theta, phi
+
+x, y, z = symbols('x y z', real=True)
+rho, psi, r, theta, phi = symbols('rho psi r theta phi', nonnegative=True)
+
+relations_3d = {
+ ('rectangular', 'cylindrical'):
+ Lambda((x, y, z), Matrix([sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z])),
+ ('cylindrical', 'rectangular'):
+ Lambda((rho, psi, z), Matrix([rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z])),
+ ('rectangular', 'spherical'):
+ Lambda(
+ (x, y, z),
+ Matrix([
+ sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2),
+ acos(z/sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)),
+ atan2(y, x)])
+ ),
+ ('spherical', 'rectangular'):
+ Lambda(
+ (r, theta, phi),
+ Matrix([r*sin(theta)*cos(phi), r*sin(theta)*sin(phi), r*cos(theta)])
+ ),
+ ('cylindrical', 'spherical'):
+ Lambda(
+ (rho, psi, z),
+ Matrix([sqrt(rho**2 + z**2), acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)), psi])
+ ),
+ ('spherical', 'cylindrical'):
+ Lambda((r, theta, phi), Matrix([r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta)])),
+}
+
+R3_r = CoordSystem('rectangular', R3_origin, [x, y, z], relations_3d) # type: Any
+R3_c = CoordSystem('cylindrical', R3_origin, [rho, psi, z], relations_3d) # type: Any
+R3_s = CoordSystem('spherical', R3_origin, [r, theta, phi], relations_3d) # type: Any
+
+# support deprecated feature
+with warnings.catch_warnings():
+ warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
+ x, y, z, rho, psi, r, theta, phi = symbols('x y z rho psi r theta phi', cls=Dummy)
+ R3_r.connect_to(R3_c, [x, y, z],
+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2), atan2(y, x), z],
+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
+ R3_c.connect_to(R3_r, [rho, psi, z],
+ [rho*cos(psi), rho*sin(psi), z],
+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
+ ## rectangular <-> spherical
+ R3_r.connect_to(R3_s, [x, y, z],
+ [sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2), acos(z/
+ sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2)), atan2(y, x)],
+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
+ R3_s.connect_to(R3_r, [r, theta, phi],
+ [r*sin(theta)*cos(phi), r*sin(
+ theta)*sin(phi), r*cos(theta)],
+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
+ ## cylindrical <-> spherical
+ R3_c.connect_to(R3_s, [rho, psi, z],
+ [sqrt(rho**2 + z**2), acos(z/sqrt(rho**2 + z**2)), psi],
+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
+ R3_s.connect_to(R3_c, [r, theta, phi],
+ [r*sin(theta), phi, r*cos(theta)],
+ inverse=False, fill_in_gaps=False)
# Defining the basis coordinate functions.
R3_r.x, R3_r.y, R3_r.z = R3_r.coord_functions()
diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_class_structure.py b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_class_structure.py
index 519eed5bfa42..920180be669a 100644
--- a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_class_structure.py
+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_class_structure.py
@@ -1,33 +1,23 @@
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, Point
from sympy import symbols, Function
+from sympy.testing.pytest import warns_deprecated_sympy
m = Manifold('m', 2)
p = Patch('p', m)
-cs = CoordSystem('cs', p, ['a', 'b'])
-cs_noname = CoordSystem('cs', p)
+a, b = symbols('a b')
+cs = CoordSystem('cs', p, [a, b])
x, y = symbols('x y')
f = Function('f')
s1, s2 = cs.coord_functions()
v1, v2 = cs.base_vectors()
f1, f2 = cs.base_oneforms()
-
def test_point():
point = Point(cs, [x, y])
- assert point == point.func(*point.args)
assert point != Point(cs, [2, y])
#TODO assert point.subs(x, 2) == Point(cs, [2, y])
#TODO assert point.free_symbols == set([x, y])
-def test_rebuild():
- assert m == m.func(*m.args)
- assert p == p.func(*p.args)
- assert cs == cs.func(*cs.args)
- assert cs_noname == cs_noname.func(*cs_noname.args)
- assert s1 == s1.func(*s1.args)
- assert v1 == v1.func(*v1.args)
- assert f1 == f1.func(*f1.args)
-
def test_subs():
assert s1.subs(s1, s2) == s2
assert v1.subs(v1, v2) == v2
@@ -35,3 +25,8 @@ def test_subs():
assert (x*f(s1) + y).subs(s1, s2) == x*f(s2) + y
assert (f(s1)*v1).subs(v1, v2) == f(s1)*v2
assert (y*f(s1)*f1).subs(f1, f2) == y*f(s1)*f2
+
+def test_deprecated():
+ with warns_deprecated_sympy():
+ cs_wname = CoordSystem('cs', p, ['a', 'b'])
+ assert cs_wname == cs_wname.func(*cs_wname.args)
diff --git a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py
index 7c63cc67e5d1..0c9cc397cb12 100644
--- a/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py
+++ b/sympy/diffgeom/tests/test_diffgeom.py
@@ -9,6 +9,7 @@
from sympy.functions import sqrt, atan2, sin
from sympy.matrices import Matrix
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, nocache_fail
+from sympy.testing.pytest import warns_deprecated_sympy
TP = TensorProduct
@@ -26,23 +27,38 @@ def test_R2():
# polar->rect->polar == Id
a, b = symbols('a b', positive=True)
m = Matrix([[a], [b]])
- #TODO assert m == R2_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_p, R2_p.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_r, [a, b])).applyfunc(simplify)
- assert m == R2_p.coord_tuple_transform_to(
- R2_r, R2_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_p, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ #TODO assert m == R2_r.transform(R2_p, R2_p.transform(R2_r, [a, b])).applyfunc(simplify)
+ assert m == R2_p.transform(R2_r, R2_r.transform(R2_p, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+
+ # deprecated method
+ with warns_deprecated_sympy():
+ assert m == R2_p.coord_tuple_transform_to(
+ R2_r, R2_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R2_p, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
def test_R3():
a, b, c = symbols('a b c', positive=True)
m = Matrix([[a], [b], [c]])
- assert m == R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(
- R3_r, R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
- #TODO assert m == R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
- assert m == R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(
- R3_r, R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
- #TODO assert m == R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
- assert m == R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(
- R3_c, R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
- #TODO assert m == R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+
+ assert m == R3_c.transform(R3_r, R3_r.transform(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ #TODO assert m == R3_r.transform(R3_c, R3_c.transform(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ assert m == R3_s.transform(
+ R3_r, R3_r.transform(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ #TODO assert m == R3_r.transform(R3_s, R3_s.transform(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ assert m == R3_s.transform(
+ R3_c, R3_c.transform(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ #TODO assert m == R3_c.transform(R3_s, R3_s.transform(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+
+ with warns_deprecated_sympy():
+ assert m == R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(
+ R3_r, R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ #TODO assert m == R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ assert m == R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(
+ R3_r, R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ #TODO assert m == R3_r.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_r, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ assert m == R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(
+ R3_c, R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
+ #TODO assert m == R3_c.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_s, R3_s.coord_tuple_transform_to(R3_c, m)).applyfunc(simplify)
def test_point():
diff --git a/sympy/printing/latex.py b/sympy/printing/latex.py
index c695b344fc5a..f17c042d1b1e 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/latex.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/latex.py
@@ -2506,31 +2506,47 @@ def _print_MatrixHomomorphism(self, h):
self._print(h.domain), self._print(h.codomain))
def _print_Manifold(self, manifold):
- return r'\text{%s}' % manifold.name
+ string = manifold.name.name
+ if '{' in string:
+ name, supers, subs = string, [], []
+ else:
+ name, supers, subs = split_super_sub(string)
+
+ name = translate(name)
+ supers = [translate(sup) for sup in supers]
+ subs = [translate(sub) for sub in subs]
+
+ name = r'\text{%s}' % name
+ if supers:
+ name += "^{%s}" % " ".join(supers)
+ if subs:
+ name += "_{%s}" % " ".join(subs)
+
+ return name
def _print_Patch(self, patch):
- return r'\text{%s}_{\text{%s}}' % (patch.name, patch.manifold.name)
+ return r'\text{%s}_{%s}' % (self._print(patch.name), self._print(patch.manifold))
- def _print_CoordSystem(self, coords):
- return r'\text{%s}^{\text{%s}}_{\text{%s}}' % (
- coords.name, coords.patch.name, coords.patch.manifold.name
+ def _print_CoordSystem(self, coordsys):
+ return r'\text{%s}^{\text{%s}}_{%s}' % (
+ self._print(coordsys.name), self._print(coordsys.patch.name), self._print(coordsys.manifold)
)
def _print_CovarDerivativeOp(self, cvd):
return r'\mathbb{\nabla}_{%s}' % self._print(cvd._wrt)
def _print_BaseScalarField(self, field):
- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]
+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name
return r'\mathbf{{{}}}'.format(self._print(Symbol(string)))
def _print_BaseVectorField(self, field):
- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]
+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name
return r'\partial_{{{}}}'.format(self._print(Symbol(string)))
def _print_Differential(self, diff):
field = diff._form_field
if hasattr(field, '_coord_sys'):
- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]
+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name
return r'\operatorname{{d}}{}'.format(self._print(Symbol(string)))
else:
string = self._print(field)
diff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py
index 5fe19d241f16..c4c3630fd38c 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/pretty.py
@@ -2608,17 +2608,17 @@ def _print_CoordSystem(self, coords):
return self._print(coords.name)
def _print_BaseScalarField(self, field):
- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]
+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name
return self._print(pretty_symbol(string))
def _print_BaseVectorField(self, field):
- s = U('PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL') + '_' + field._coord_sys._names[field._index]
+ s = U('PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL') + '_' + field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name
return self._print(pretty_symbol(s))
def _print_Differential(self, diff):
field = diff._form_field
if hasattr(field, '_coord_sys'):
- string = field._coord_sys._names[field._index]
+ string = field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name
return self._print(u'\N{DOUBLE-STRUCK ITALIC SMALL D} ' + pretty_symbol(string))
else:
pform = self._print(field)
diff --git a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py
index a7cdbd79e3d2..742fb34b81b1 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/pretty/tests/test_pretty.py
@@ -7051,11 +7051,12 @@ def test_issue_18272():
def test_diffgeom():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField
+ x,y = symbols('x y', real=True)
m = Manifold('M', 2)
assert pretty(m) == 'M'
p = Patch('P', m)
assert pretty(p) == "P"
- rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)
+ rect = CoordSystem('rect', p, [x, y])
assert pretty(rect) == "rect"
b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)
- assert pretty(b) == "rect_0"
+ assert pretty(b) == "x"
diff --git a/sympy/printing/repr.py b/sympy/printing/repr.py
index d156c6f3121d..1d33861800e9 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/repr.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/repr.py
@@ -248,6 +248,24 @@ def _print_Symbol(self, expr):
return "%s(%s, %s)" % (expr.__class__.__name__,
self._print(expr.name), ', '.join(attr))
+ def _print_CoordinateSymbol(self, expr):
+ d = expr._assumptions.generator
+
+ if d == {}:
+ return "%s(%s, %s)" % (
+ expr.__class__.__name__,
+ self._print(expr.coordinate_system),
+ self._print(expr.index)
+ )
+ else:
+ attr = ['%s=%s' % (k, v) for k, v in d.items()]
+ return "%s(%s, %s, %s)" % (
+ expr.__class__.__name__,
+ self._print(expr.coordinate_system),
+ self._print(expr.index),
+ ', '.join(attr)
+ )
+
def _print_Predicate(self, expr):
return "%s(%s)" % (expr.__class__.__name__, self._print(expr.name))
@@ -328,19 +346,6 @@ def _print_ExtensionElement(self, f):
ext = self._print(f.ext)
return "ExtElem(%s, %s)" % (rep, ext)
- def _print_CoordSystem(self, coords):
- class_name = coords.func.__name__
- name = self._print(coords.name)
- patch = self._print(coords.patch)
- names = self._print(coords._names)
- return "%s(%s, %s, %s)" % (class_name, name, patch, names)
-
- def _print_BaseScalarField(self, bsf):
- class_name = bsf.func.__name__
- coords = self._print(bsf._coord_sys)
- idx = self._print(bsf._index)
- return "%s(%s, %s)" % (class_name, coords, idx)
-
def srepr(expr, **settings):
"""return expr in repr form"""
return ReprPrinter(settings).doprint(expr)
diff --git a/sympy/printing/str.py b/sympy/printing/str.py
index 2639a9a5d570..16e5d8cf905c 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/str.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/str.py
@@ -876,24 +876,24 @@ def _print_Category(self, category):
return 'Category("%s")' % category.name
def _print_Manifold(self, manifold):
- return manifold.name
+ return self._print(manifold.name)
def _print_Patch(self, patch):
- return patch.name
+ return self._print(patch.name)
def _print_CoordSystem(self, coords):
- return coords.name
+ return self._print(coords.name)
def _print_BaseScalarField(self, field):
- return field._coord_sys._names[field._index]
+ return field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name
def _print_BaseVectorField(self, field):
- return 'e_%s' % field._coord_sys._names[field._index]
+ return 'e_%s' % field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name
def _print_Differential(self, diff):
field = diff._form_field
if hasattr(field, '_coord_sys'):
- return 'd%s' % field._coord_sys._names[field._index]
+ return 'd%s' % field._coord_sys.symbols[field._index].name
else:
return 'd(%s)' % self._print(field)
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py
index 9c2d37e97546..675ac0ab76d5 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_latex.py
@@ -2535,14 +2535,15 @@ def test_text_re_im():
def test_latex_diffgeom():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField, Differential
from sympy.diffgeom.rn import R2
+ x,y = symbols('x y', real=True)
m = Manifold('M', 2)
assert latex(m) == r'\text{M}'
p = Patch('P', m)
assert latex(p) == r'\text{P}_{\text{M}}'
- rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)
+ rect = CoordSystem('rect', p, [x, y])
assert latex(rect) == r'\text{rect}^{\text{P}}_{\text{M}}'
b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)
- assert latex(b) == r'\mathbf{rect_{0}}'
+ assert latex(b) == r'\mathbf{x}'
g = Function('g')
s_field = g(R2.x, R2.y)
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py
index ed892c1801ca..481547cd2646 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py
@@ -312,16 +312,6 @@ def test_Permutation():
import_stmt = "from sympy.combinatorics import Permutation"
sT(Permutation(1, 2), "Permutation(1, 2)", import_stmt)
-
-def test_diffgeom():
- from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField
- m = Manifold('M', 2)
- p = Patch('P', m)
- rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)
- assert srepr(rect) == "CoordSystem(Str('rect'), Patch(Str('P'), Manifold(Str('M'), Integer(2))), ('rect_0', 'rect_1'))"
- b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)
- assert srepr(b) == "BaseScalarField(CoordSystem(Str('rect'), Patch(Str('P'), Manifold(Str('M'), Integer(2))), ('rect_0', 'rect_1')), Integer(0))"
-
def test_dict():
from sympy import srepr
from sympy.abc import x, y, z
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py
index d05052fe0c8c..bc185de760d1 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_str.py
@@ -936,11 +936,12 @@ def test_issue_14567():
def test_diffgeom():
from sympy.diffgeom import Manifold, Patch, CoordSystem, BaseScalarField
+ x,y = symbols('x y', real=True)
m = Manifold('M', 2)
assert str(m) == "M"
p = Patch('P', m)
assert str(p) == "P"
- rect = CoordSystem('rect', p)
+ rect = CoordSystem('rect', p, [x, y])
assert str(rect) == "rect"
b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)
- assert str(b) == "rect_0"
+ assert str(b) == "x"
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19596@7097b50
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,596
|
Improved simplification for expressions containing sign()
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19484
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Simplification for `sign()` now woks due to addition of `sign._eval_rewrite_as_Abs()`.
Working examples:
```
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> e = x + sign(x + x**3)
>>> simplify(Abs(x + x**3) * e)
x**3 + x*Abs(x**3 + x) + x
>>> e = x**2 + sign(x**3 + 1)
>>> simplify(Abs(x**3 + 1) * e)
x**3 + x**2*Abs(x**3 + 1) + 1
>>> simplify(sign(x) * Abs(x))
x
```
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* simplify
* Improved simplification for sign()
* functions
* Improved condition checking in `piecewise_simplify()`
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-06-19T11:03:13Z
|
sympy cannot simplify sign(x) * abs(x)
```
>>> from sympy import Symbol, sign
>>> x = Symbol('x', real=True)
>>> x_new = abs(x)*sign(x)
>>> x_new
Abs(x)*sign(x)
>>> x_new.simplify()
Abs(x)*sign(x)
```
I would expect the result to be just `x`. gh-19277 may be related.
|
The rewrite suggested in #19277 would be able to make this work:
```julia
In [19]: e = sign(x)*Abs(x)
In [20]: e
Out[20]: │x│⋅sign(x)
In [21]: simplify(e)
Out[21]: │x│⋅sign(x)
In [22]: e2 = e.subs(sign(x), Piecewise((0, Eq(x, 0)), (x/Abs(x), True)))
In [23]: e2
Out[23]:
⎛⎧ 0 for x = 0⎞
⎜⎪ ⎟
⎜⎨ x ⎟⋅│x│
⎜⎪─── otherwise⎟
⎝⎩│x│ ⎠
In [24]: simplify(e2)
Out[24]: x
```
Although the equivalent with the Piecewise conditions inverted does not simplify:
```julia
In [25]: e2 = e.subs(sign(x), Piecewise((x/Abs(x), Ne(x, 0)), (0, True)))
In [26]: e2
Out[26]:
⎛⎧ x ⎞
⎜⎪─── for x ≠ 0⎟
⎜⎨│x│ ⎟⋅│x│
⎜⎪ ⎟
⎝⎩ 0 otherwise⎠
In [27]: simplify(e2)
Out[27]:
⎧x for x ≠ 0
⎨
⎩0 otherwise
```
What's the mechanism for making simplify do this automatically?
First we need `sign.eval_rewrite_as_Abs` so that you can do `sign(x).rewrite(Abs)` (#19277).
Then we need simplify to do something like `if expr.has(sign): expr.rewrite(Abs)` to see if it helps with simplifying.
Ideally I would prefer the second form of the Piecewise. That doesn't work because `piecewise_fold` is unable to detect this case so `piecewise_fold` or `Piecewise._eval_simplify` should be improved to handle that case. Specifically when we have:
```julia
In [1]: Piecewise((f(x), Ne(x, 0)), (f(0), True))
Out[1]:
⎧f(x) for x ≠ 0
⎨
⎩f(0) otherwise
```
It should be possible to spot that for cases after the `Ne` condition we can substitute the opposite of that condition in to the first expression and if that gives the same result as the next case we can combine the cases giving the expression from the first case with the `Or` of the conditions e.g.:
```julia
In [4]: p = Piecewise((f(x), Ne(x, 0)), (f(0), True))
In [5]: p
Out[5]:
⎧f(x) for x ≠ 0
⎨
⎩f(0) otherwise
In [6]: p.args[0]
Out[6]: (f(x), x ≠ 0)
In [7]: p.args[0][0]
Out[7]: f(x)
In [8]: p.args[0][0].subs(p.args[0][1].lhs, p.args[0][1].rhs) == p.args[1][0]
Out[8]: True
In [11]: p2 = Piecewise((p.args[0][0], Or(p.args[0][1], p.args[1][1])))
In [12]: p2
Out[12]: f(x)
```
After adding `sign._eval_rewrite_as_Abs` and `if expr.has(sign): expr.rewrite(Abs)` in
` simplify()` the outputs are ;
```
>>> simplify(sign(x) * Abs(x))
x
>>> e = x**2 + sign(x**3 + 1)
>>> simplify(Abs(x**3 + 1) * e)
/ 2 | 3 | 3
| x *|x + 1| for x = -1
<
| 3 2 | 3 |
\x + x *|x + 1| + 1 otherwise
>>> f = Function('f')
>>> e = x + sign(x + f(x)**3)
>>> simplify(Abs(x + x**3) * e)
/ | 3 | 3
| x*|x + x| for x + f (x) = 0
|
| | / 2 \|
</ | 3 | 3 \ |x*\x + 1/|
|\x*|x + f (x)| + x + f (x)/*|----------| otherwise
| | 3 |
| |x + f (x) |
\
```
@oscarbenjamin should I add this to the existing PR #19487
I'm not sure if those are actually simpler or not. In some parts of simplify things like this are tried and the transformation is only kept if it seems to make the result simpler so maybe the rewrite should be tested there.
Those outputs are not fully simplified, but the first one is definitely better.
All of those long outputs are of the form
```
/ x for y = 0
<
\ x + y otherwise
```
This looks like a bug in simplifying `Piecewise`
I think the problem here is that expressions like `x**3 + 1` don't satisfy the `_blessed()` condition https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/25fbcce5b1a4c7e3956e6062930f4a44ce95a632/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py#L1243
as value of `_diff_wrt` is False for such expressions.
See #7027.
@oscarbenjamin @eric-wieser Removing the `if _blessed()` condition works fine in this case and does not break any tests. Would it be fine to make such a change?
It's hard to discuss these changes without seeing them. You can push them to the PR or to a new PR and then ask about them.
|
[
{
"body": "```\r\n>>> from sympy import Symbol, sign\r\n>>> x = Symbol('x', real=True)\r\n>>> x_new = abs(x)*sign(x)\r\n>>> x_new\r\nAbs(x)*sign(x)\r\n>>> x_new.simplify()\r\nAbs(x)*sign(x)\r\n```\r\n\r\nI would expect the result to be just `x`. gh-19277 may be related.\r\n",
"number": 19484,
"title": "sympy cannot simplify sign(x) * abs(x)"
}
] |
4fa55af041c632f522e622de4b175f03927a7f95
|
{
"head_commit": "7097b50fb410dc4c4fd30b504e861ef10f258447",
"head_commit_message": "Impoved simplification for sign()\n\nSimplify() for sign(x)*Abs(x) now works due to\nsign._eval_rewrite_as_Abs().",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\nindex b7ccb6943ace..c423e8bb5219 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\n@@ -1238,11 +1238,8 @@ def piecewise_simplify(expr, **kwargs):\n if eqs and not other:\n eqs = list(ordered(eqs))\n for e in eqs:\n- # these blessed lhs objects behave like Symbols\n- # and the rhs are simple replacements for the \"symbols\"\n- if _blessed(e):\n- _prevexpr = _prevexpr.subs(*e.args)\n- _expr = _expr.subs(*e.args)\n+ _prevexpr = _prevexpr.subs(*e.args)\n+ _expr = _expr.subs(*e.args)\n # Did it evaluate to the same?\n if _prevexpr == _expr:\n # Set the expression for the Not equal section to the same\ndiff --git a/sympy/simplify/simplify.py b/sympy/simplify/simplify.py\nindex b79aba30f508..0819a332d7b0 100644\n--- a/sympy/simplify/simplify.py\n+++ b/sympy/simplify/simplify.py\n@@ -615,6 +615,10 @@ def done(e):\n from sympy.simplify.hyperexpand import hyperexpand\n from sympy.functions.special.bessel import BesselBase\n from sympy import Sum, Product, Integral\n+ from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import sign, Abs\n+\n+ if expr.has(sign):\n+ expr = expr.rewrite(Abs)\n \n # Deal with Piecewise separately to avoid recursive growth of expressions\n if expr.has(Piecewise):\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -615,6 +615,10 @@ def done(e):\n from sympy.simplify.hyperexpand import hyperexpand\n from sympy.functions.special.bessel import BesselBase\n from sympy import Sum, Product, Integral\n+ from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import sign, Abs\n+\n+ if expr.has(sign):",
"line": 621,
"original_line": 620,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/simplify/simplify.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n # must come before `Piecewise` since this introduces more `Piecewise` terms\r\n if expr.has(sign):\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -615,6 +615,10 @@ def done(e):\n from sympy.simplify.hyperexpand import hyperexpand\n from sympy.functions.special.bessel import BesselBase\n from sympy import Sum, Product, Integral\n+ from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import sign, Abs\n+\n+ if expr.has(sign):\n+ expr = expr.rewrite(Abs)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 621,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/simplify/simplify.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n expr = expr.rewrite(Abs)\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1238,11 +1238,8 @@ def piecewise_simplify(expr, **kwargs):\n if eqs and not other:\n eqs = list(ordered(eqs))\n for e in eqs:\n- # these blessed lhs objects behave like Symbols\n- # and the rhs are simple replacements for the \"symbols\"\n- if _blessed(e):",
"line": 1243,
"original_line": 1243,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThere must have been a reason for adding this check. Some substitutions aren't valid. I thought maybe that substituting for an ExprCondPair in a Piecewise would fail. Has that been changed?\n\n@author:\n> I thought maybe that substituting for an ExprCondPair in a Piecewise would fail. Has that been changed?\r\n```\r\neq = Piecewise((x, Eq(y, 0)), (y, True))\r\nprint(eq.subs([(x, 2), (y, 1)]))\r\n```\r\nThis does work.\r\n> There must have been a reason for adding this check.\r\n\r\nI understand this but the `_blessed()` condition checks on the basis of `_diff_wrt` which is False by default for all expressions. \n\n@author:\nCan you give some examples which should not be valid ?\n\n@user1:\nThere are lots of possible invalid substitutions e.g.:\r\n```julia\r\nIn [1]: Piecewise((x, y<1), (z, True)) \r\nOut[1]: \r\n⎧x for y < 1\r\n⎨ \r\n⎩z otherwise\r\n\r\nIn [2]: Piecewise((x, y<1), (z, True)).subs(y < 1, exp(2)) \r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nTypeError\r\n```\r\nHere we are substituting an `Expr` in place of a `Boolean` and `Piecewise` rightly complains.\r\n\r\nI would investigate this by using git blame to find the commit/PR where this piece of code was introduced and who the author was or who merged it. The discussion in the PR might explain the reason. Also you could CC the author giving them a chance to explain.\n\n@author:\nThe example that you showed does raise a TypeError for me as well. Also I found the commit and I get https://github.com/sympy/sympy/commit/9d3fa8b4d4963c059c139f3860b8cc1d611adbae\r\nIt appears there is something wrong with the commit/blame history as mentioned in the PR https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/18488 and issue https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/19181.\n\n@user1:\nIt looks like that commit has ruined the history in this file\n\n@user1:\nYou can find the blame from before that commit here:\r\nhttps://github.com/sympy/sympy/blame/d5df2bd6a274db8b8d3a5cf2622d16dfb3f3d8a4/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py\n\n@user2:\nFor sake of simplicity it is attempting only straightforward subs that are in the form (s1, s2) or (s, ns) or (s, r) where s is a symbol-like entity and ns and r are number symbol and rational, respectively. It was added in #17259\n\n@author:\nAs this does not work on instances of `Expr`, would removing the condition be fine?\n\n@author:\n@user2 It seems that in the PR you mentioned `piecewise_simplify()` was introduced and did the same work as `_eval_simplify()`. I think the condition specifically was modified/added in https://github.com/sympy/sympy/commit/5e34c1b1370d5996c10cb2e72841cbc752cb419f\n\n@user2:\nsubstitution of non-symbol-like entities is not as simple as for the others. What test fails if you leave this optimization in place? Is there an impact on speed?\n\n@author:\nNone of the tests fail. I used timeit for measuring the execution time and ran it multiple times. The results I got are: \r\nWith `_blessed()`: 0.3315324999999998 , 0.3113937\r\nwithout : 0.35980409999999985 , 0.32984559999999874\r\nAlthough the condition helps with speed I am not sure if it is significant enough.\n\n@author:\n@user2 @user1 Is it merge able now? \n\n@user2:\nI would like to see the use of `_blessed` retained. It is used above and it is used here, likely, for the same reason. So without good reason to do otherwise I would like to keep it.\n\n@author:\nThe condition prevents from any non-symbol like objects (like the ones mentioned in the issue) to be simplified. If removing it isn't recommended, I think I could be modified to include `Expr` objects as well. Do you think such a change would be fine?\n\n@user2:\n> like the ones mentioned in the issue\r\n\r\nOne of these expressions should be added as a test because nothing currently fails if this code is reverted back to using `_blessed`.\n\n@author:\nOn the local branch same as #19487 where `_eval_rewrite_as_Abs()` is implemented and `_blessed` is used, the following are the results:\r\n`Abs(x) * sign(x)` gives `|𝑥|sign(𝑥)` and\r\n\r\n`simplify(Piecewise((x*Abs(x + f(x)**3), Eq(x + f(x)**3, 0)),(x*Abs(x + f(x)**3) + x + f(x)**3, True)))` gives\r\n`Piecewise((x*Abs(x + f(x)**3), Eq(x + f(x)**3, 0)), (x*Abs(x + f(x)**3) + x + f(x)**3, True))`\r\n\r\nOn this branch these cases are simplified.\n\n@user2:\nI added the test that would fail if the `_blessed` was not removed. I wonder if a compromise would be to only do this `if len(args) == 2 or _blessed(e):`\n\n@author:\nI don't think `len(args) ==2` would work for a general case. I tried \r\n```\r\n_blessed = lambda e: (getattr(e.lhs, '_diff_wrt', False) or isinstance(e.lhs, Expr)) and (\r\n getattr(e.rhs, '_diff_wrt', None) or\r\n isinstance(e.rhs, (Rational, NumberSymbol, Expr)))\r\n```\r\nAlthough it works but I think it is very similar to removing the condition.\n\n@user2:\nI wasn't thinking to modify `_blessed`, just to make the change roosed below.\n\n@user2:\nI applied the suggestion...let's see if that passes.\n\n@author:\nI think it would pass but `len(args) == 2` would work only for Piecewise containing 2 arguments. What about a general case for any number of arguments?"
}
] |
f9bd1d432b59f6487044519d1db9d44b56453a8a
|
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py
index c4a3d60fb6f5..7b8eea208e20 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/piecewise.py
@@ -1238,9 +1238,10 @@ def piecewise_simplify(expr, **kwargs):
if eqs and not other:
eqs = list(ordered(eqs))
for e in eqs:
- # these blessed lhs objects behave like Symbols
- # and the rhs are simple replacements for the "symbols"
- if _blessed(e):
+ # allow 2 args to collapse into 1 for any e
+ # otherwise limit simplification to only simple-arg
+ # Eq instances
+ if len(args) == 2 or _blessed(e):
_prevexpr = _prevexpr.subs(*e.args)
_expr = _expr.subs(*e.args)
# Did it evaluate to the same?
diff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_gruntz.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_gruntz.py
index a7fa3199d799..c1b2b55db310 100644
--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_gruntz.py
+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_gruntz.py
@@ -397,7 +397,7 @@ def test_I():
assert gruntz(I*x, x, oo) == I*oo
assert gruntz(y*I*x, x, oo) == y*I*oo
assert gruntz(y*3*I*x, x, oo) == y*I*oo
- assert gruntz(y*3*sin(I)*x, x, oo).simplify() == sign(y)*I*oo
+ assert gruntz(y*3*sin(I)*x, x, oo).simplify().rewrite(sign) == sign(y)*I*oo
def test_issue_4814():
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/simplify.py b/sympy/simplify/simplify.py
index b79aba30f508..33c8e58ae63e 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/simplify.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/simplify.py
@@ -615,6 +615,11 @@ def done(e):
from sympy.simplify.hyperexpand import hyperexpand
from sympy.functions.special.bessel import BesselBase
from sympy import Sum, Product, Integral
+ from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import sign, Abs
+
+ # must come before `Piecewise` since this introduces more `Piecewise` terms
+ if expr.has(sign):
+ expr = expr.rewrite(Abs)
# Deal with Piecewise separately to avoid recursive growth of expressions
if expr.has(Piecewise):
diff --git a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_simplify.py b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_simplify.py
index 3a137151b94a..52934ff97fdb 100644
--- a/sympy/simplify/tests/test_simplify.py
+++ b/sympy/simplify/tests/test_simplify.py
@@ -897,3 +897,16 @@ def test_issue_17292():
assert simplify(abs(x)/abs(x**2)) == 1/abs(x)
# this is bigger than the issue: check that deep processing works
assert simplify(5*abs((x**2 - 1)/(x - 1))) == 5*Abs(x + 1)
+
+def test_issue_19484():
+ assert simplify(sign(x) * Abs(x)) == x
+
+ e = x + sign(x + x**3)
+ assert simplify(Abs(x + x**3)*e) == x**3 + x*Abs(x**3 + x) + x
+
+ e = x**2 + sign(x**3 + 1)
+ assert simplify(Abs(x**3 + 1) * e) == x**3 + x**2*Abs(x**3 + 1) + 1
+
+ f = Function('f')
+ e = x + sign(x + f(x)**3)
+ assert simplify(Abs(x + f(x)**3) * e) == x*Abs(x + f(x)**3) + x + f(x)**3
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19387@1d00f17
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,387
|
[GSoC] Added Poisson, Wiener and Gamma Process
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
Added Poisson, Wiener and Gamma Process
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19274
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* stats
* Added Poisson, Wiener and Gamma Processes
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-05-21T03:57:13Z
|
[GSoC Discussion] Adding Poisson Process
Currently, we have DTMC, CTMC, and Bernoulli Process as the stochastic processes in `stats/stochatic_process_types.py`. Therefore, I plan to add more such processes.
We can divide(for API discussion) the stochastic processes into two categories:
**Case 1** The processes which follow certain distribution at any time t:
(i) Poisson Process -> Poisson Distribution
(ii) Gamma Process -> Gamma Distribution
(iiI) Wiener Process -> Normal Distribution
(iv) Bernoulli Process -> Bernoulli Distribution(0/1) (Implemented)
(v) Random Walks -> Bernoulli Distribution(-1/1)
**Case 2** The processes which have no distribution:
(i) Birth Death process (should be inherited from CTMC)
So, for **Case 1** we can create a generalized framework to calculate( Expectation and Probability), in order to avoid the repetition of code in each of the classes. As, in Bernoulli Process, we will convert the Random Indexed RV to simple RV with the same name and distribution (As we already have ready-made functions for simple RV for calculating E and P) and return the E and P.
For **Case 2**, we already have P and E in CTMC and requires testing of its generalization.
ping @czgdp1807 @Upabjojr @jmig5776
|
I'd suggest to start with designing APIs with the help of some use cases(like picking up examples from textbooks, wikipedia, research papers). In addition, some processes can be built on top of Markov chains.
For, the examples of using the processes in the **Case 1**, I have found some real-life example problems related to them [here](https://www.probabilitycourse.com/chapter11/11_1_2_basic_concepts_of_the_poisson_process.php)
Suppose if we take example 1 from the given link, then we could possibly solve it as:
```python
>>> from sympy import Eq, S
>>> from sympy.stats import PoissonProcess , P
>>> X = PoissonProcess ('X', lamda=10)
>>> P(Eq(X(S(1)/3), 2))
xxxxx
```
In the same way, we could solve the examples of other processes too.
Therefore, the API will be the same as the API of simple RV/ simple distribution classes as in `*_types.py`, i.e, at the initialization, we need to provide the parameters that are necessary to define the distribution of the Process. The only internal difference here would be on the developer side to take care of the distribution as they vary with the time. But at the user end, we will have the same API as we have for simple RV.
For the implementation details:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/585377cc1f8876fec65968dacffd284a4572b3c9/sympy/stats/stochastic_process.py#L49-L63
As we point to the individual classes to handle the expectation and probability of the indexed RV, we need to define these methods in the respective process classes. So, to calculate E and P of expression of indexed RV using the available functions in stats, we need to convert them to simple RV with the same name and distribution and indexed RV.
So, we will globally define two functions say, `_expectation_stoch` and `_probablility_stoc`,
(i) which will take the expression of the indexed RV,
(ii) covert it to simple RV expression based on given process.
(iii) calculate E/P and return to the calling method of respective process classes.
Therefore all the processes in **Case 1** will commonly share two functions, which will avoid us from code repetition.
So, it will be like:
```python
class ProcessName(...):
def __init__(...):
pass
@property
def symbol(self):
pass
@property
def state_space(self):
pass
def distribution(self):
pass
def expectation(...):
return _expectation_stoch(...)
def probability(...):
return _probability_stoch(...)
```
How will we solve the following part of Example 11.2 in the same link,
```
Given that the third arrival occurred at time t=2, find the probability that the fourth arrival occurs after t=4.
```
> `Given that the third arrival occurred at time t=2, find the probability that the fourth arrival occurs after t=4.`
Consider, PP as Poisson process with `lamda=2`
X1 = PP(1)
X2 = PP(2)
X05 = PP(0.5)
We can use as :
```python
>>> X05 = Poisson('X05', 2*0.5)
>>> X2 = Poisson('X2', 2*2)
>>> P(Eq(X05, 1))
exp(-1) # Answer of 'a' there will be 1st arrival at time 0.5 secs
>>> P(Eq(X2, 0))
exp(-4) # Answer of 'c' as there will be no arrival between t=2 and t=4, so using memory less property
```
They can be done in the above way, if we want to handle them directly as `P(Eq(X4, 4), Eq(X2, 3))`
then we need to add some additional code which will handle the memoryless property( can't be directly converted to simple RV as it will treat both of them independent and will generate wrong answer.)
Or, we can directly provide a computation of Arrival times by adding the distribution which the Arrival times follow for a particular class, and it will work fine as they are mutually independent(so they can be directly used as converting to simple RV).
What about?
```python
>>> N = PoissonProcess('N', 2)
>>> P(Eq(N(4), 4), Eq(N(2), 3))
```
Converting them to simple RV, will consider them as independent and produce an incorrect result. So, we need to add some code to apply the memory less property by which it gets converted to
```python
>>> P(Eq(N(2), 0)
```
> Converting them to simple RV
Where are they converted to simple RVs? I think we are just discussing how the interface should like. `N(t)` should be handled by `probability` to forward the call to the method of `PoissonProcess` which will solve the given query.
I think that `probability` methods of each sub-class of stochastic processes should be able to handle the queries. If there is anything common down the hierarchy in these methods then that should be factored out and placed into the parent class.
P.S. Class design isn't a concern as of now. We should just make the interface as good as possible and then discuss about the details of implementation, that too in a PR which you will make to implement that interface. I couldn't get what's going on in https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/19274#issuecomment-626131730 or how the problem is solved. All the RVs and stuff should be kept hidden from the user, they should be able to make any query using `P`, and an object of `PoissonProcess` and may be if needed, some utility objects(like Matrices, assumptions).
> Where are they converted to simple RVs? I think we are just discussing how the interface should like.
I understand I am trying to explain how we will use the available E and P if possible to use in our code. When the call will go to the method of the given process, I think this should happen,
(i) Using the given condition, we will apply memoryless property, and convert `P(expr, condition)` to `P(expr_new)` which satisfies the given conditions. We will then solve P(expr_new).
For, solving `P(expr_new)` we need to decide whether to implement new method or use the existing ones, as we had used while adding Bernoulli Process
> We should just make the interface as good as possible and then discuss about the details of implementation
The interface will allow handling the queries in the same way, as in the current implementation,
```python
>>> N = PoissonProcess('N', 2)
>>> P(Eq(N(4), 4), Eq(N(2), 3))
# This will produce required answer of 'c'
>>> P(Eq(N(0.5), 1)
# This will produce required answer of 'a'
```
|
[
{
"body": "Currently, we have DTMC, CTMC, and Bernoulli Process as the stochastic processes in `stats/stochatic_process_types.py`. Therefore, I plan to add more such processes.\r\nWe can divide(for API discussion) the stochastic processes into two categories:\r\n\r\n**Case 1** The processes which follow certain distribution at any time t:\r\n(i) Poisson Process -> Poisson Distribution\r\n(ii) Gamma Process -> Gamma Distribution\r\n(iiI) Wiener Process -> Normal Distribution\r\n(iv) Bernoulli Process -> Bernoulli Distribution(0/1) (Implemented)\r\n(v) Random Walks -> Bernoulli Distribution(-1/1)\r\n\r\n**Case 2** The processes which have no distribution:\r\n(i) Birth Death process (should be inherited from CTMC)\r\n\r\nSo, for **Case 1** we can create a generalized framework to calculate( Expectation and Probability), in order to avoid the repetition of code in each of the classes. As, in Bernoulli Process, we will convert the Random Indexed RV to simple RV with the same name and distribution (As we already have ready-made functions for simple RV for calculating E and P) and return the E and P.\r\n\r\nFor **Case 2**, we already have P and E in CTMC and requires testing of its generalization.\r\n\r\nping @czgdp1807 @Upabjojr @jmig5776 ",
"number": 19274,
"title": "[GSoC Discussion] Adding Poisson Process"
}
] |
726b440029153fa25d8582c577c709c2350be720
|
{
"head_commit": "1d00f17959839d8494ce34bf923bfd3bd487de44",
"head_commit_message": "add poisson process",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/stats/rv.py b/sympy/stats/rv.py\nindex cd0014de6914..7e042340b312 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/rv.py\n@@ -742,6 +742,10 @@ def expectation(expr, condition=None, numsamples=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n evalf = kwargs.get('evalf', True)\n return sampling_E(expr, condition, numsamples=numsamples, evalf=evalf)\n \n+ from sympy.stats.stochastic_process_types import StochasticProcess\n+ if expr.has(StochasticProcess):\n+ process = list(expr.atoms(StochasticProcess))[0]\n+ return process.expectation(expr, condition, evaluate, **kwargs)\n if expr.has(RandomIndexedSymbol):\n return pspace(expr).compute_expectation(expr, condition, evaluate, **kwargs)\n \n@@ -801,7 +805,10 @@ def probability(condition, given_condition=None, numsamples=None,\n \n condition = sympify(condition)\n given_condition = sympify(given_condition)\n-\n+ from sympy.stats.stochastic_process_types import StochasticProcess\n+ if condition.has(StochasticProcess):\n+ process = list(condition.atoms(StochasticProcess))[0]\n+ return process.probability(condition, given_condition, evaluate, **kwargs)\n if condition.has(RandomIndexedSymbol):\n return pspace(condition).probability(condition, given_condition, evaluate, **kwargs)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\nindex 9380a06b92e0..fe5510252857 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n@@ -2,8 +2,8 @@\n \n from sympy import (Matrix, MatrixSymbol, S, Indexed, Basic,\n Set, And, Eq, FiniteSet, ImmutableMatrix,\n- Lambda, Mul, Dummy, IndexedBase, Add,\n- linsolve, eye, Or, Not, Intersection,\n+ Lambda, Mul, Dummy, IndexedBase, Add, Interval, oo,\n+ linsolve, eye, Or, Not, Intersection, factorial,\n Union, Expr, Function, exp, cacheit,\n Ge, Piecewise, Symbol, NonSquareMatrixError)\n from sympy.core.relational import Relational\n@@ -15,6 +15,7 @@\n from sympy.stats.stochastic_process import StochasticPSpace\n from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability, Expectation\n from sympy.stats.frv_types import Bernoulli, BernoulliDistribution\n+from sympy.stats.drv_types import Poisson, PoissonDistribution\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n \n __all__ = [\n@@ -179,7 +180,7 @@ def joint_distribution(self, *args):\n raise ValueError(\"Expected a RandomIndexedSymbol or \"\n \"key not %s\"%(type(arg)))\n \n- if args[0].pspace.distribution == None: # checks if there is any distribution available\n+ if not hasattr(args[0].pspace.process, 'distribution'): # checks if there is any distribution available\n return JointDistribution(*args)\n \n pdf = Lambda(tuple(args),\n@@ -225,7 +226,8 @@ def __call__(self, time):\n if time not in self.index_set:\n raise IndexError(\"%s is not in the index set of %s\"%(time, self.symbol))\n func_obj = Function(self.symbol)(time)\n- pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self)\n+ distribution = getattr(self, 'distribution', None)\n+ pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self, distribution)\n return RandomIndexedSymbol(func_obj, pspace_obj)\n \n class TransitionMatrixOf(Boolean):\n@@ -892,11 +894,78 @@ def state_space(self):\n def distribution(self):\n return BernoulliDistribution(self.p)\n \n- def _rvindexed_subs(self, expr, condition=None):\n+ def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Computes expectation.\n+\n+ Parameters\n+ ==========\n+\n+ expr: RandomIndexedSymbol, Relational, Logic\n+ Condition for which expectation has to be computed. Must\n+ contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.\n+ condition: Relational, Logic\n+ The given conditions under which computations should be done.\n+\n+ Returns\n+ =======\n+\n+ Expectation of the RandomIndexedSymbol.\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ return _expectation_stoch('Bernoulli', expr, condition, evaluate, **kwargs)\n+\n+ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Computes probability.\n+\n+ Parameters\n+ ==========\n+\n+ condition: Relational\n+ Condition for which probability has to be computed. Must\n+ contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.\n+ given_condition: Relational/And\n+ The given conditions under which computations should be done.\n+\n+ Returns\n+ =======\n+\n+ Probability of the condition.\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ return _probability_stoch('Bernoulli', condition, given_condition, evaluate, **kwargs)\n+\n+ def density(self, x):\n+ return Piecewise((self.p, Eq(x, self.success)),\n+ (1 - self.p, Eq(x, self.failure)),\n+ (S.Zero, True))\n+\n+\n+dict_rv_subs = {'Poisson': lambda rv: Poisson(rv.name, lamda=rv.pspace.process.lamda*rv.key),\n+ 'Bernoulli': lambda rv: Bernoulli(rv.name, p=rv.pspace.process.p,\n+ succ=rv.pspace.process.success, fail=rv.pspace.process.failure)\n+ }\n+\n+\n+def _rvindexed_subs(process, expr, condition=None):\n \"\"\"\n Substitutes the RandomIndexedSymbol with the RandomSymbol with\n same name, distribution and probability as RandomIndexedSymbol.\n \n+ Parameters\n+ ==========\n+\n+ process : str\n+ Key value of dict_rv_subs RandomVariable used to substitute\n+ expr: RandomIndexedSymbol, Relational, Logic\n+ Condition for which expectation has to be computed. Must\n+ contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.\n+ condition: Relational, Logic\n+ The given conditions under which computations should be done.\n+\n \"\"\"\n \n rvs_expr = random_symbols(expr)\n@@ -904,29 +973,30 @@ def _rvindexed_subs(self, expr, condition=None):\n swapdict_expr = {}\n for rv in rvs_expr:\n if isinstance(rv, RandomIndexedSymbol):\n- newrv = Bernoulli(rv.name, p=rv.pspace.process.p,\n- succ=self.success, fail=self.failure)\n+ newrv = dict_rv_subs[process](rv)\n swapdict_expr[rv] = newrv\n expr = expr.subs(swapdict_expr)\n rvs_cond = random_symbols(condition)\n if len(rvs_cond)!=0:\n swapdict_cond = {}\n- if condition is not None:\n- for rv in rvs_cond:\n- if isinstance(rv, RandomIndexedSymbol):\n- newrv = Bernoulli(rv.name, p=rv.pspace.process.p,\n- succ=self.success, fail=self.failure)\n- swapdict_cond[rv] = newrv\n- condition = condition.subs(swapdict_cond)\n+ for rv in rvs_cond:\n+ if isinstance(rv, RandomIndexedSymbol):\n+ newrv = dict_rv_subs[process](rv)\n+ swapdict_cond[rv] = newrv\n+ condition = condition.subs(swapdict_cond)\n return expr, condition\n \n- def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n+\n+def _expectation_stoch(process, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n \"\"\"\n Computes expectation.\n \n Parameters\n ==========\n \n+\n+ process : str\n+ Key value of dict_rv_subs RandomVariable used to substitute\n expr: RandomIndexedSymbol, Relational, Logic\n Condition for which expectation has to be computed. Must\n contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.\n@@ -939,7 +1009,7 @@ def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n Expectation of the RandomIndexedSymbol.\n \n \"\"\"\n- new_expr, new_condition = self._rvindexed_subs(expr, condition)\n+ new_expr, new_condition = _rvindexed_subs(process, expr, condition)\n \n new_pspace = pspace(new_expr)\n if new_condition is not None:\n@@ -951,14 +1021,15 @@ def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n return new_pspace.compute_expectation(\n new_expr, evaluate=evaluate, **kwargs)\n \n-\n- def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n+def _probability_stoch(process, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n \"\"\"\n Computes probability.\n \n Parameters\n ==========\n \n+ process : str\n+ Key value of dict_rv_subs RandomVariable used to substitute\n condition: Relational\n Condition for which probability has to be computed. Must\n contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.\n@@ -971,17 +1042,17 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n Probability of the condition.\n \n \"\"\"\n- new_condition, new_givencondition = self._rvindexed_subs(condition, given_condition)\n+ new_condition, new_givencondition = _rvindexed_subs(process, condition, given_condition)\n \n if isinstance(new_givencondition, RandomSymbol):\n condrv = random_symbols(new_condition)\n if len(condrv) == 1 and condrv[0] == new_givencondition:\n- return BernoulliDistribution(self.probability(new_condition), 0, 1)\n+ return BernoulliDistribution(_probability_stoch(process, new_condition), 0, 1)\n \n if any([dependent(rv, new_givencondition) for rv in condrv]):\n return Probability(new_condition, new_givencondition)\n else:\n- return self.probability(new_condition)\n+ return _probability_stoch(process, new_condition)\n \n if new_givencondition is not None and \\\n not isinstance(new_givencondition, (Relational, Boolean)):\n@@ -998,10 +1069,58 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n % (new_condition))\n if new_givencondition is not None: # If there is a condition\n # Recompute on new conditional expr\n- return self.probability(given(new_condition, new_givencondition, **kwargs), **kwargs)\n- return pspace(new_condition).probability(new_condition, **kwargs)\n+ return _probability_stoch(process, given(new_condition, new_givencondition, **kwargs), **kwargs)\n+ result = pspace(new_condition).probability(new_condition, **kwargs)\n+ if evaluate and hasattr(result, 'doit'):\n+ return result.doit()\n+ else:\n+ return result\n+\n+\n+class PoissonProcess(ContinuousTimeStochasticProcess):\n+ index_set = _set_converter(Interval(0, oo))\n+\n+ def __new__(cls, sym, lamda):\n+ sym = _symbol_converter(sym)\n+ lamda = _sympify(lamda)\n+ return Basic.__new__(cls, sym, lamda)\n+\n+ @property\n+ def state_space(self):\n+ return _set_converter(Interval(0, oo))\n+\n+ @property\n+ def symbol(self):\n+ return self.args[0]\n+\n+ @property\n+ def lamda(self):\n+ return self.args[1]\n+\n+\n+ def distribution(self, rv):\n+ return PoissonDistribution(self.lamda*rv.key)\n \n def density(self, x):\n- return Piecewise((self.p, Eq(x, self.success)),\n- (1 - self.p, Eq(x, self.failure)),\n- (S.Zero, True))\n+ return (self.lamda*x.key)**x / factorial(x) * exp(-(self.lamda*x.key))\n+\n+\n+ def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n+ if given_condition is not None: # use of memory less property\n+ if not isinstance(given_condition, Interval):\n+ raise TypeError(\"Expecting an Interval as a given condition\")\n+ if not condition.has(PoissonProcess):\n+ raise TypeError(\"expr should contain an instance of PoissonProcess\")\n+ lhs = condition.args[0](given_condition._sup - given_condition._inf)\n+ condition = condition.__class__(lhs, condition.args[1])\n+ return _expectation_stoch('Poisson', expr, condition=condition, evaluate=True, **kwargs)\n+\n+ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n+ if given_condition is not None: # use of memory less property\n+ if not isinstance(given_condition, Interval):\n+ raise TypeError(\"Expecting an Interval as a given condition\")\n+ if not condition.has(PoissonProcess):\n+ raise TypeError(\"Condition should contain an instance of PoissonProcess\")\n+ lhs = condition.args[0](given_condition._sup - given_condition._inf)\n+ condition = condition.__class__(lhs, condition.args[1])\n+ return _probability_stoch('Poisson', condition, evaluate=True, **kwargs)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -998,10 +1069,58 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n % (new_condition))\n if new_givencondition is not None: # If there is a condition\n # Recompute on new conditional expr\n- return self.probability(given(new_condition, new_givencondition, **kwargs), **kwargs)\n- return pspace(new_condition).probability(new_condition, **kwargs)\n+ return _probability_stoch(process, given(new_condition, new_givencondition, **kwargs), **kwargs)\n+ result = pspace(new_condition).probability(new_condition, **kwargs)\n+ if evaluate and hasattr(result, 'doit'):\n+ return result.doit()\n+ else:\n+ return result\n+\n+\n+class PoissonProcess(ContinuousTimeStochasticProcess):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1080,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nInclude it in the `sympy.stats` namespace."
}
] |
1e5404a892b031e1ef50f8190becbf8bb2182248
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py
index 3bc13f6db3a8..1c8941760975 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_args.py
@@ -1676,6 +1676,22 @@ def test_sympy__stats__stochastic_process_types__BernoulliProcess():
from sympy.stats.stochastic_process_types import BernoulliProcess
assert _test_args(BernoulliProcess("B", 0.5, 1, 0))
+def test_sympy__stats__stochastic_process_types__CountingProcess():
+ from sympy.stats.stochastic_process_types import CountingProcess
+ assert _test_args(CountingProcess("C"))
+
+def test_sympy__stats__stochastic_process_types__PoissonProcess():
+ from sympy.stats.stochastic_process_types import PoissonProcess
+ assert _test_args(PoissonProcess("X", 2))
+
+def test_sympy__stats__stochastic_process_types__WienerProcess():
+ from sympy.stats.stochastic_process_types import WienerProcess
+ assert _test_args(WienerProcess("X"))
+
+def test_sympy__stats__stochastic_process_types__GammaProcess():
+ from sympy.stats.stochastic_process_types import GammaProcess
+ assert _test_args(GammaProcess("X", 1, 2))
+
def test_sympy__stats__random_matrix__RandomMatrixPSpace():
from sympy.stats.random_matrix import RandomMatrixPSpace
from sympy.stats.random_matrix_models import RandomMatrixEnsemble
diff --git a/sympy/stats/__init__.py b/sympy/stats/__init__.py
index 0f8d2bfcc94a..94ea5d9edbcb 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/__init__.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/__init__.py
@@ -133,6 +133,7 @@
'StochasticProcess', 'DiscreteTimeStochasticProcess',
'DiscreteMarkovChain', 'TransitionMatrixOf', 'StochasticStateSpaceOf',
'GeneratorMatrixOf', 'ContinuousMarkovChain', 'BernoulliProcess',
+ 'PoissonProcess', 'WienerProcess', 'GammaProcess',
'CircularEnsemble', 'CircularUnitaryEnsemble',
'CircularOrthogonalEnsemble', 'CircularSymplecticEnsemble',
@@ -177,7 +178,8 @@
from .stochastic_process_types import (StochasticProcess,
DiscreteTimeStochasticProcess, DiscreteMarkovChain,
TransitionMatrixOf, StochasticStateSpaceOf, GeneratorMatrixOf,
- ContinuousMarkovChain, BernoulliProcess)
+ ContinuousMarkovChain, BernoulliProcess, PoissonProcess, WienerProcess,
+ GammaProcess)
from .random_matrix_models import (CircularEnsemble, CircularUnitaryEnsemble,
CircularOrthogonalEnsemble, CircularSymplecticEnsemble,
diff --git a/sympy/stats/rv.py b/sympy/stats/rv.py
index 9c05b8035c66..4e9fc1e5c03e 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/rv.py
@@ -18,8 +18,8 @@
from functools import singledispatch
from typing import Tuple as tTuple
-from sympy import (Basic, S, Expr, Symbol, Tuple, And, Add, Eq, lambdify,
- Equality, Lambda, sympify, Dummy, Ne, KroneckerDelta,
+from sympy import (Basic, S, Expr, Symbol, Tuple, And, Add, Eq, lambdify, Or,
+ Equality, Lambda, sympify, Dummy, Ne, KroneckerDelta, Not,
DiracDelta, Mul, Indexed, MatrixSymbol, Function, Integral)
from sympy.core.relational import Relational
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
@@ -426,6 +426,10 @@ def probability(self, condition, **kwargs):
if isinstance(condition, Ne):
condition = Eq(condition.args[0], condition.args[1])
cond_inv = True
+ elif isinstance(condition, And): # they are independent
+ return Mul(*[self.probability(arg) for arg in condition.args])
+ elif isinstance(condition, Or): # they are independent
+ return Add(*[self.probability(arg) for arg in condition.args])
expr = condition.lhs - condition.rhs
rvs = random_symbols(expr)
dens = self.compute_density(expr)
@@ -787,6 +791,9 @@ def probability(condition, given_condition=None, numsamples=None,
condition = sympify(condition)
given_condition = sympify(given_condition)
+ if isinstance(condition, Not):
+ return S.One - probability(condition.args[0], given_condition, evaluate, **kwargs)
+
if condition.has(RandomIndexedSymbol):
return pspace(condition).probability(condition, given_condition, evaluate, **kwargs)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
index ea7e7b880480..9070b171a26d 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
@@ -1,12 +1,14 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
import random
+import itertools
+
from sympy import (Matrix, MatrixSymbol, S, Indexed, Basic,
Set, And, Eq, FiniteSet, ImmutableMatrix,
- Lambda, Mul, Dummy, IndexedBase, Add,
- linsolve, eye, Or, Not, Intersection,
- Union, Expr, Function, exp, cacheit,
- Ge, Piecewise, Symbol, NonSquareMatrixError)
+ Lambda, Mul, Dummy, IndexedBase, Add, Interval, oo,
+ linsolve, eye, Or, Not, Intersection, factorial, Contains,
+ Union, Expr, Function, exp, cacheit, sqrt, pi, gamma,
+ Ge, Piecewise, Symbol, NonSquareMatrixError, EmptySet)
from sympy.core.relational import Relational
from sympy.logic.boolalg import Boolean
from sympy.stats.joint_rv import JointDistributionHandmade, JointDistribution
@@ -16,6 +18,8 @@
from sympy.stats.stochastic_process import StochasticPSpace
from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability, Expectation
from sympy.stats.frv_types import Bernoulli, BernoulliDistribution, FiniteRV
+from sympy.stats.drv_types import Poisson, PoissonDistribution
+from sympy.stats.crv_types import Normal, NormalDistribution, Gamma, GammaDistribution
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
__all__ = [
@@ -26,7 +30,10 @@
'StochasticStateSpaceOf',
'GeneratorMatrixOf',
'ContinuousMarkovChain',
- 'BernoulliProcess'
+ 'BernoulliProcess',
+ 'PoissonProcess',
+ 'WienerProcess',
+ 'GammaProcess'
]
@@ -129,6 +136,10 @@ def symbol(self):
def state_space(self):
return self.args[1]
+ @property
+ def distribution(self):
+ return None
+
def __call__(self, time):
"""
Overridden in ContinuousTimeStochasticProcess.
@@ -209,8 +220,7 @@ def __getitem__(self, time):
if time not in self.index_set:
raise IndexError("%s is not in the index set of %s"%(time, self.symbol))
idx_obj = Indexed(self.symbol, time)
- distribution = getattr(self, 'distribution', None)
- pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self, distribution)
+ pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self, self.distribution)
return RandomIndexedSymbol(idx_obj, pspace_obj)
class ContinuousTimeStochasticProcess(StochasticProcess):
@@ -229,7 +239,7 @@ def __call__(self, time):
if time not in self.index_set:
raise IndexError("%s is not in the index set of %s"%(time, self.symbol))
func_obj = Function(self.symbol)(time)
- pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self)
+ pspace_obj = StochasticPSpace(self.symbol, self, self.distribution)
return RandomIndexedSymbol(func_obj, pspace_obj)
class TransitionMatrixOf(Boolean):
@@ -921,11 +931,80 @@ def state_space(self):
def distribution(self):
return BernoulliDistribution(self.p)
- def _rvindexed_subs(self, expr, condition=None):
+ def simple_rv(self, rv):
+ return Bernoulli(rv.name, p=self.p,
+ succ=self.success, fail=self.failure)
+
+ def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
+ """
+ Computes expectation.
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ expr: RandomIndexedSymbol, Relational, Logic
+ Condition for which expectation has to be computed. Must
+ contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.
+ condition: Relational, Logic
+ The given conditions under which computations should be done.
+
+ Returns
+ =======
+
+ Expectation of the RandomIndexedSymbol.
+
+ """
+
+ return _SubstituteRV._expectation(expr, condition, evaluate, **kwargs)
+
+ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
+ """
+ Computes probability.
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ condition: Relational
+ Condition for which probability has to be computed. Must
+ contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.
+ given_condition: Relational/And
+ The given conditions under which computations should be done.
+
+ Returns
+ =======
+
+ Probability of the condition.
+
+ """
+
+ return _SubstituteRV._probability(condition, given_condition, evaluate, **kwargs)
+
+ def density(self, x):
+ return Piecewise((self.p, Eq(x, self.success)),
+ (1 - self.p, Eq(x, self.failure)),
+ (S.Zero, True))
+
+class _SubstituteRV:
+ """
+ Internal class to handle the queries of expectation and probability
+ by substitution.
+ """
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def _rvindexed_subs(expr, condition=None):
"""
Substitutes the RandomIndexedSymbol with the RandomSymbol with
same name, distribution and probability as RandomIndexedSymbol.
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ expr: RandomIndexedSymbol, Relational, Logic
+ Condition for which expectation has to be computed. Must
+ contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.
+ condition: Relational, Logic
+ The given conditions under which computations should be done.
+
"""
rvs_expr = random_symbols(expr)
@@ -933,25 +1012,23 @@ def _rvindexed_subs(self, expr, condition=None):
swapdict_expr = {}
for rv in rvs_expr:
if isinstance(rv, RandomIndexedSymbol):
- newrv = Bernoulli(rv.name, p=rv.pspace.process.p,
- succ=self.success, fail=self.failure)
+ newrv = rv.pspace.process.simple_rv(rv) # substitute with equivalent simple rv
swapdict_expr[rv] = newrv
expr = expr.subs(swapdict_expr)
rvs_cond = random_symbols(condition)
if len(rvs_cond)!=0:
swapdict_cond = {}
- if condition is not None:
- for rv in rvs_cond:
- if isinstance(rv, RandomIndexedSymbol):
- newrv = Bernoulli(rv.name, p=rv.pspace.process.p,
- succ=self.success, fail=self.failure)
- swapdict_cond[rv] = newrv
- condition = condition.subs(swapdict_cond)
+ for rv in rvs_cond:
+ if isinstance(rv, RandomIndexedSymbol):
+ newrv = rv.pspace.process.simple_rv(rv)
+ swapdict_cond[rv] = newrv
+ condition = condition.subs(swapdict_cond)
return expr, condition
- def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
+ @classmethod
+ def _expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
"""
- Computes expectation.
+ Internal method for computing expectation of indexed RV.
Parameters
==========
@@ -970,6 +1047,8 @@ def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
"""
new_expr, new_condition = self._rvindexed_subs(expr, condition)
+ if not is_random(new_expr):
+ return new_expr
new_pspace = pspace(new_expr)
if new_condition is not None:
new_expr = given(new_expr, new_condition)
@@ -980,10 +1059,10 @@ def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
return new_pspace.compute_expectation(
new_expr, evaluate=evaluate, **kwargs)
-
- def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
+ @classmethod
+ def _probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
"""
- Computes probability.
+ Internal method for computing probability of indexed RV
Parameters
==========
@@ -1005,32 +1084,503 @@ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
if isinstance(new_givencondition, RandomSymbol):
condrv = random_symbols(new_condition)
if len(condrv) == 1 and condrv[0] == new_givencondition:
- return BernoulliDistribution(self.probability(new_condition), 0, 1)
+ return BernoulliDistribution(self._probability(new_condition), 0, 1)
if any([dependent(rv, new_givencondition) for rv in condrv]):
return Probability(new_condition, new_givencondition)
else:
- return self.probability(new_condition)
+ return self._probability(new_condition)
if new_givencondition is not None and \
not isinstance(new_givencondition, (Relational, Boolean)):
raise ValueError("%s is not a relational or combination of relationals"
% (new_givencondition))
- if new_givencondition == False:
+ if new_givencondition == False or new_condition == False:
return S.Zero
if new_condition == True:
return S.One
- if new_condition == False:
- return S.Zero
if not isinstance(new_condition, (Relational, Boolean)):
raise ValueError("%s is not a relational or combination of relationals"
% (new_condition))
+
if new_givencondition is not None: # If there is a condition
# Recompute on new conditional expr
- return self.probability(given(new_condition, new_givencondition, **kwargs), **kwargs)
- return pspace(new_condition).probability(new_condition, **kwargs)
+ return self._probability(given(new_condition, new_givencondition, **kwargs), **kwargs)
+ result = pspace(new_condition).probability(new_condition, **kwargs)
+ if evaluate and hasattr(result, 'doit'):
+ return result.doit()
+ else:
+ return result
+
+def get_timerv_swaps(expr, condition):
+ """
+ Finds the appropriate interval for each time stamp in expr by parsing
+ the given condition and returns intervals for each timestamp and
+ dictionary that maps variable time-stamped Random Indexed Symbol to its
+ corresponding Random Indexed variable with fixed time stamp.
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ expr: Sympy Expression
+ Expression containing Random Indexed Symbols with variable time stamps
+ condition: Relational/Boolean Expression
+ Expression containing time bounds of variable time stamps in expr
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.stats.stochastic_process_types import get_timerv_swaps, PoissonProcess
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Contains, Interval
+ >>> x, t, d = symbols('x t d', positive=True)
+ >>> X = PoissonProcess("X", 3)
+ >>> get_timerv_swaps(x*X(t), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1)))
+ ([Interval.Lopen(0, 1)], {X(t): X(1)})
+ >>> get_timerv_swaps((X(t)**2 + X(d)**2), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ ... & Contains(d, Interval.Ropen(1, 4))) # doctest: +SKIP
+ ([Interval.Ropen(1, 4), Interval.Lopen(0, 1)], {X(d): X(3), X(t): X(1)})
+
+ Returns
+ =======
+
+ intervals: list
+ List of Intervals/FiniteSet on which each time stamp is defined
+ rv_swap: dict
+ Dictionary mapping variable time Random Indexed Symbol to constant time
+ Random Indexed Variable
+
+ """
+
+ if not isinstance(condition, (Relational, Boolean)):
+ raise ValueError("%s is not a relational or combination of relationals"
+ % (condition))
+ expr_syms = list(expr.atoms(RandomIndexedSymbol))
+ if isinstance(condition, (And, Or)):
+ given_cond_args = condition.args
+ else: # single condition
+ given_cond_args = (condition, )
+ rv_swap = {}
+ intervals = []
+ for expr_sym in expr_syms:
+ for arg in given_cond_args:
+ if arg.has(expr_sym.key) and isinstance(expr_sym.key, Symbol):
+ intv = _set_converter(arg.args[1])
+ diff_key = intv._sup - intv._inf
+ if diff_key == oo:
+ raise ValueError("%s should have finite bounds" % str(expr_sym.name))
+ elif diff_key == S.Zero: # has singleton set
+ diff_key = intv._sup
+ rv_swap[expr_sym] = expr_sym.subs({expr_sym.key: diff_key})
+ intervals.append(intv)
+ return intervals, rv_swap
+
+
+class CountingProcess(ContinuousTimeStochasticProcess):
+ """
+ This class handles the common methods of the Counting Processes
+ such as Poisson, Wiener and Gamma Processes
+ """
+ index_set = _set_converter(Interval(0, oo))
+
+ @property
+ def state_space(self):
+ return _set_converter(Interval(0, oo))
+
+ @property
+ def symbol(self):
+ return self.args[0]
+
+ def expectation(self, expr, condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
+ """
+ Computes expectation
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ expr: RandomIndexedSymbol, Relational, Logic
+ Condition for which expectation has to be computed. Must
+ contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.
+ condition: Relational, Boolean
+ The given conditions under which computations should be done, i.e,
+ the intervals on which each variable time stamp in expr is defined
+
+ Returns
+ =======
+
+ Expectation of the given expr
+
+ """
+ if condition is not None:
+ intervals, rv_swap = get_timerv_swaps(expr, condition)
+ # they are independent when they have non-overlapping intervals
+ if len(intervals) == 1 or all(Intersection(*intv_comb) == EmptySet
+ for intv_comb in itertools.combinations(intervals, 2)):
+ if expr.is_Add:
+ return Add.fromiter(self.expectation(arg, condition)
+ for arg in expr.args)
+ expr = expr.subs(rv_swap)
+ else:
+ return Expectation(expr, condition)
+
+ return _SubstituteRV._expectation(expr, evaluate=evaluate, **kwargs)
+
+ def _solve_argwith_tworvs(self, arg):
+ if arg.args[0].key >= arg.args[1].key or isinstance(arg, Eq):
+ diff_key = abs(arg.args[0].key - arg.args[1].key)
+ rv = arg.args[0]
+ arg = arg.__class__(rv.pspace.process(diff_key), 0)
+ else:
+ diff_key = arg.args[1].key - arg.args[0].key
+ rv = arg.args[1]
+ arg = arg.__class__(rv.pspace.process(diff_key), 0)
+ return arg
+
+ def _solve_numerical(self, condition, given_condition=None):
+ if isinstance(condition, And):
+ args_list = list(condition.args)
+ else:
+ args_list = [condition]
+ if given_condition is not None:
+ if isinstance(given_condition, And):
+ args_list.extend(list(given_condition.args))
+ else:
+ args_list.extend([given_condition])
+ # sort the args based on timestamp to get the independent increments in
+ # each segment using all the condition args as well as given_condition args
+ args_list = sorted(args_list, key=lambda x: x.args[0].key)
+ result = []
+ cond_args = list(condition.args) if isinstance(condition, And) else [condition]
+ if args_list[0] in cond_args and not (is_random(args_list[0].args[0])
+ and is_random(args_list[0].args[1])):
+ result.append(_SubstituteRV._probability(args_list[0]))
+
+ if is_random(args_list[0].args[0]) and is_random(args_list[0].args[1]):
+ arg = self._solve_argwith_tworvs(args_list[0])
+ result.append(_SubstituteRV._probability(arg))
+
+ for i in range(len(args_list) - 1):
+ curr, nex = args_list[i], args_list[i + 1]
+ diff_key = nex.args[0].key - curr.args[0].key
+ working_set = curr.args[0].pspace.process.state_space
+ if curr.args[1] > nex.args[1]: #impossible condition so return 0
+ result.append(0)
+ break
+ if isinstance(curr, Eq):
+ working_set = Intersection(working_set, Interval.Lopen(curr.args[1], oo))
+ else:
+ working_set = Intersection(working_set, curr.as_set())
+ if isinstance(nex, Eq):
+ working_set = Intersection(working_set, Interval(-oo, nex.args[1]))
+ else:
+ working_set = Intersection(working_set, nex.as_set())
+ if working_set == EmptySet:
+ rv = Eq(curr.args[0].pspace.process(diff_key), 0)
+ result.append(_SubstituteRV._probability(rv))
+ else:
+ if working_set.is_finite_set:
+ if isinstance(curr, Eq) and isinstance(nex, Eq):
+ rv = Eq(curr.args[0].pspace.process(diff_key), len(working_set))
+ result.append(_SubstituteRV._probability(rv))
+ elif isinstance(curr, Eq) ^ isinstance(nex, Eq):
+ result.append(Add.fromiter(_SubstituteRV._probability(Eq(
+ curr.args[0].pspace.process(diff_key), x))
+ for x in range(len(working_set))))
+ else:
+ n = len(working_set)
+ result.append(Add.fromiter((n - x)*_SubstituteRV._probability(Eq(
+ curr.args[0].pspace.process(diff_key), x)) for x in range(n)))
+ else:
+ result.append(_SubstituteRV._probability(
+ curr.args[0].pspace.process(diff_key) <= working_set._sup - working_set._inf))
+ return Mul.fromiter(result)
+
+
+ def probability(self, condition, given_condition=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
+ """
+ Computes probability
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ condition: Relational
+ Condition for which probability has to be computed. Must
+ contain a RandomIndexedSymbol of the process.
+ given_condition: Relational, Boolean
+ The given conditions under which computations should be done, i.e,
+ the intervals on which each variable time stamp in expr is defined
+
+ Returns
+ =======
+
+ Probability of the condition
+
+ """
+ check_numeric = True
+ if isinstance(condition, (And, Or)):
+ cond_args = condition.args
+ else:
+ cond_args = (condition, )
+ # check that condition args are numeric or not
+ if not all(arg.args[0].key.is_number for arg in cond_args):
+ check_numeric = False
+ if given_condition is not None:
+ check_given_numeric = True
+ if isinstance(given_condition, (And, Or)):
+ given_cond_args = given_condition.args
+ else:
+ given_cond_args = (given_condition, )
+ # check that given condition args are numeric or not
+ if given_condition.has(Contains):
+ check_given_numeric = False
+ # Handle numerical queries
+ if check_numeric and check_given_numeric:
+ res = []
+ if isinstance(condition, Or):
+ res.append(Add.fromiter(self._solve_numerical(arg, given_condition)
+ for arg in condition.args))
+ if isinstance(given_condition, Or):
+ res.append(Add.fromiter(self._solve_numerical(condition, arg)
+ for arg in given_condition.args))
+ if res:
+ return Add.fromiter(res)
+ return self._solve_numerical(condition, given_condition)
+
+ # No numeric queries, go by Contains?... then check that all the
+ # given condition are in form of `Contains`
+ if not all(arg.has(Contains) for arg in given_cond_args):
+ raise ValueError("If given condition is passed with `Contains`, then "
+ "please pass the evaluated condition with its corresponding information "
+ "in terms of intervals of each time stamp to be passed in given condition.")
+
+ intervals, rv_swap = get_timerv_swaps(condition, given_condition)
+ # they are independent when they have non-overlapping intervals
+ if len(intervals) == 1 or all(Intersection(*intv_comb) == EmptySet
+ for intv_comb in itertools.combinations(intervals, 2)):
+ if isinstance(condition, And):
+ return Mul.fromiter(self.probability(arg, given_condition)
+ for arg in condition.args)
+ elif isinstance(condition, Or):
+ return Add.fromiter(self.probability(arg, given_condition)
+ for arg in condition.args)
+ condition = condition.subs(rv_swap)
+ else:
+ return Probability(condition, given_condition)
+ if check_numeric:
+ return self._solve_numerical(condition)
+ return _SubstituteRV._probability(condition, evaluate=evaluate, **kwargs)
+
+class PoissonProcess(CountingProcess):
+ """
+ The Poisson process is a counting process. It is usually used in scenarios
+ where we are counting the occurrences of certain events that appear
+ to happen at a certain rate, but completely at random.
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ sym: Symbol/str
+ lamda: Positive number
+ Rate of the process, ``lamda > 0``
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.stats import PoissonProcess, P, E
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Eq, Ne, Contains, Interval
+ >>> X = PoissonProcess("X", lamda=3)
+ >>> X.state_space
+ Naturals0
+ >>> X.lamda
+ 3
+ >>> t1, t2 = symbols('t1 t2', positive=True)
+ >>> P(X(t1) < 4)
+ (9*t1**3/2 + 9*t1**2/2 + 3*t1 + 1)*exp(-3*t1)
+ >>> P(Eq(X(t1), 2) | Ne(X(t1), 4), Contains(t1, Interval.Ropen(2, 4)))
+ 1 - 36*exp(-6)
+ >>> P(Eq(X(t1), 2) & Eq(X(t2), 3), Contains(t1, Interval.Lopen(0, 2))
+ ... & Contains(t2, Interval.Lopen(2, 4)))
+ 648*exp(-12)
+ >>> E(X(t1))
+ 3*t1
+ >>> E(X(t1)**2 + 2*X(t2), Contains(t1, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ ... & Contains(t2, Interval.Lopen(1, 2)))
+ 18
+ >>> P(X(3) < 1, Eq(X(1), 0))
+ exp(-6)
+ >>> P(Eq(X(4), 3), Eq(X(2), 3))
+ exp(-6)
+ >>> P(X(2) <= 3, X(1) > 1)
+ 5*exp(-3)
+
+ Merging two Poisson Processes
+
+ >>> Y = PoissonProcess("Y", lamda=4)
+ >>> Z = X + Y
+ >>> Z.lamda
+ 7
+
+ Splitting a Poisson Process into two independent Poisson Processes
+
+ >>> N, M = Z.split(l1=2, l2=5)
+ >>> N.lamda, M.lamda
+ (2, 5)
+
+ References
+ ==========
+
+ .. [1] https://www.probabilitycourse.com
+ .. [2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poisson_point_process
+
+ """
+
+ def __new__(cls, sym, lamda):
+ _value_check(lamda > 0, 'lamda should be a positive number.')
+ sym = _symbol_converter(sym)
+ lamda = _sympify(lamda)
+ return Basic.__new__(cls, sym, lamda)
+
+ @property
+ def lamda(self):
+ return self.args[1]
+
+ @property
+ def state_space(self):
+ return S.Naturals0
+
+ def distribution(self, rv):
+ return PoissonDistribution(self.lamda*rv.key)
def density(self, x):
- return Piecewise((self.p, Eq(x, self.success)),
- (1 - self.p, Eq(x, self.failure)),
- (S.Zero, True))
+ return (self.lamda*x.key)**x / factorial(x) * exp(-(self.lamda*x.key))
+
+ def simple_rv(self, rv):
+ return Poisson(rv.name, lamda=self.lamda*rv.key)
+
+ def __add__(self, other):
+ if not isinstance(other, PoissonProcess):
+ raise ValueError("Only instances of Poisson Process can be merged")
+ return PoissonProcess(Dummy(self.symbol.name + other.symbol.name),
+ self.lamda + other.lamda)
+
+ def split(self, l1, l2):
+ if _sympify(l1 + l2) != self.lamda:
+ raise ValueError("Sum of l1 and l2 should be %s" % str(self.lamda))
+ return PoissonProcess(Dummy("l1"), l1), PoissonProcess(Dummy("l2"), l2)
+
+class WienerProcess(CountingProcess):
+ """
+ The Wiener process is a real valued continuous-time stochastic process.
+ In physics it is used to study Brownian motion and therefore also known as
+ Brownian Motion.
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ sym: Symbol/str
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.stats import WienerProcess, P, E
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Contains, Interval
+ >>> X = WienerProcess("X")
+ >>> X.state_space
+ Interval(0, oo)
+ >>> t1, t2 = symbols('t1 t2', positive=True)
+ >>> P(X(t1) < 7).simplify()
+ erf(7*sqrt(2)/(2*sqrt(t1)))/2 + 1/2
+ >>> P((X(t1) > 2) | (X(t1) < 4), Contains(t1, Interval.Ropen(2, 4))).simplify()
+ -erf(1)/2 + erf(2)/2 + 1
+ >>> E(X(t1))
+ 0
+ >>> E(X(t1) + 2*X(t2), Contains(t1, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ ... & Contains(t2, Interval.Lopen(1, 2)))
+ 0
+
+ References
+ ==========
+
+ .. [1] https://www.probabilitycourse.com
+ .. [2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wiener_process
+
+ """
+ def __new__(cls, sym):
+ sym = _symbol_converter(sym)
+ return Basic.__new__(cls, sym)
+
+ def distribution(self, rv):
+ return NormalDistribution(0, sqrt(rv.key))
+
+ def density(self, x):
+ return exp(-x**2/(2*x.key)) / (sqrt(2*pi)*sqrt(x.key))
+
+ def simple_rv(self, rv):
+ return Normal(rv.name, 0, sqrt(rv.key))
+
+
+class GammaProcess(CountingProcess):
+ """
+ A Gamma process is a random process with independent gamma distributed
+ increments. It is a pure-jump increasing Levy process.
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ sym: Symbol/str
+ lamda: Positive number
+ Jump size of the process, ``lamda > 0``
+ gamma: Positive number
+ Rate of jump arrivals, ``gamma > 0``
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.stats import GammaProcess, E, P, variance
+ >>> from sympy import symbols, Contains, Interval, Not
+ >>> t, d, x, l, g = symbols('t d x l g', positive=True)
+ >>> X = GammaProcess("X", l, g)
+ >>> E(X(t))
+ g*t/l
+ >>> variance(X(t)).simplify()
+ g*t/l**2
+ >>> X = GammaProcess('X', 1, 2)
+ >>> P(X(t) < 1).simplify()
+ lowergamma(2*t, 1)/gamma(2*t)
+ >>> P(Not((X(t) < 5) & (X(d) > 3)), Contains(t, Interval.Ropen(2, 4)) &
+ ... Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(7, 8))).simplify()
+ -4*exp(-3) + 472*exp(-8)/3 + 1
+ >>> E(X(2) + x*E(X(5)))
+ 10*x + 4
+
+ References
+ ==========
+
+ .. [1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_process
+
+ """
+ def __new__(cls, sym, lamda, gamma):
+ _value_check(lamda > 0, 'lamda should be a positive number')
+ _value_check(gamma > 0, 'gamma should be a positive number')
+ sym = _symbol_converter(sym)
+ gamma = _sympify(gamma)
+ lamda = _sympify(lamda)
+ return Basic.__new__(cls, sym, lamda, gamma)
+
+ @property
+ def lamda(self):
+ return self.args[1]
+
+ @property
+ def gamma(self):
+ return self.args[2]
+
+ def distribution(self, rv):
+ return GammaDistribution(self.gamma*rv.key, 1/self.lamda)
+
+ def density(self, x):
+ k = self.gamma*x.key
+ theta = 1/self.lamda
+ return x**(k - 1) * exp(-x/theta) / (gamma(k)*theta**k)
+
+ def simple_rv(self, rv):
+ return Gamma(rv.name, self.gamma*rv.key, 1/self.lamda)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
index 9ee71deabab0..56ce08c0ea19 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_stochastic_process.py
@@ -1,15 +1,19 @@
from sympy import (S, symbols, FiniteSet, Eq, Matrix, MatrixSymbol, Float, And,
- ImmutableMatrix, Ne, Lt, Gt, exp, Not, Rational, Lambda, Sum,
- Piecewise)
+ ImmutableMatrix, Ne, Lt, Gt, exp, Not, Rational, Lambda, erf,
+ Piecewise, factorial, Interval, oo, Contains, sqrt, pi,
+ gamma, lowergamma, Sum)
from sympy.stats import (DiscreteMarkovChain, P, TransitionMatrixOf, E,
StochasticStateSpaceOf, variance, ContinuousMarkovChain,
- BernoulliProcess, sample_stochastic_process)
+ BernoulliProcess, PoissonProcess, WienerProcess,
+ GammaProcess, sample_stochastic_process)
from sympy.stats.joint_rv import JointDistribution, JointDistributionHandmade
from sympy.stats.rv import RandomIndexedSymbol
from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability, Expectation
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, skip
from sympy.external import import_module
from sympy.stats.frv_types import BernoulliDistribution
+from sympy.stats.drv_types import PoissonDistribution
+from sympy.stats.crv_types import NormalDistribution, GammaDistribution
def test_DiscreteMarkovChain():
@@ -231,3 +235,206 @@ def test_BernoulliProcess():
assert B[2*t].free_symbols == {B[2*t], t}
assert B[4].free_symbols == {B[4]}
assert B[x*t].free_symbols == {B[x*t], x, t}
+
+
+def test_PoissonProcess():
+ X = PoissonProcess("X", 3)
+ assert X.state_space == S.Naturals0
+ assert X.index_set == Interval(0, oo)
+ assert X.lamda == 3
+
+ t, d, x, y = symbols('t d x y', positive=True)
+ assert isinstance(X(t), RandomIndexedSymbol)
+ assert X.distribution(X(t)) == PoissonDistribution(3*t)
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: PoissonProcess("X", -1))
+ raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: X[t])
+ raises(IndexError, lambda: X(-5))
+
+ assert X.joint_distribution(X(2), X(3)) == JointDistributionHandmade(Lambda((X(2), X(3)),
+ 6**X(2)*9**X(3)*exp(-15)/(factorial(X(2))*factorial(X(3)))))
+
+ assert X.joint_distribution(4, 6) == JointDistributionHandmade(Lambda((X(4), X(6)),
+ 12**X(4)*18**X(6)*exp(-30)/(factorial(X(4))*factorial(X(6)))))
+
+ assert P(X(t) < 1) == exp(-3*t)
+ assert P(Eq(X(t), 0), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(3, 5))) == exp(-6) # exp(-2*lamda)
+ res = P(Eq(X(t), 1), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(3, 4)))
+ assert res == 3*exp(-3)
+
+ # Equivalent to P(Eq(X(t), 1))**4 because of non-overlapping intervals
+ assert P(Eq(X(t), 1) & Eq(X(d), 1) & Eq(X(x), 1) & Eq(X(y), 1), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(1, 2)) & Contains(x, Interval.Lopen(2, 3))
+ & Contains(y, Interval.Lopen(3, 4))) == res**4
+
+ # Return Probability because of overlapping intervals
+ assert P(Eq(X(t), 2) & Eq(X(d), 3), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 2))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Ropen(2, 4))) == \
+ Probability(Eq(X(d), 3) & Eq(X(t), 2), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 2))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Ropen(2, 4)))
+
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: P(Eq(X(t), 2) & Eq(X(d), 3),
+ Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 4)) & Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(3, oo)))) # no bound on d
+ assert P(Eq(X(3), 2)) == 81*exp(-9)/2
+ assert P(Eq(X(t), 2), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 5))) == 225*exp(-15)/2
+
+ # Check that probability works correctly by adding it to 1
+ res1 = P(X(t) <= 3, Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 5)))
+ res2 = P(X(t) > 3, Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 5)))
+ assert res1 == 691*exp(-15)
+ assert (res1 + res2).simplify() == 1
+
+ # Check Not and Or
+ assert P(Not(Eq(X(t), 2) & (X(d) > 3)), Contains(t, Interval.Ropen(2, 4)) & \
+ Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(7, 8))).simplify() == -18*exp(-6) + 234*exp(-9) + 1
+ assert P(Eq(X(t), 2) | Ne(X(t), 4), Contains(t, Interval.Ropen(2, 4))) == 1 - 36*exp(-6)
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: P(X(t) > 2, X(t) + X(d)))
+ assert E(X(t)) == 3*t # property of the distribution at a given timestamp
+ assert E(X(t)**2 + X(d)*2 + X(y)**3, Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(1, 2)) & Contains(y, Interval.Ropen(3, 4))) == 75
+ assert E(X(t)**2, Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))) == 12
+ assert E(x*(X(t) + X(d))*(X(t)**2+X(d)**2), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Ropen(1, 2))) == \
+ Expectation(x*(X(d) + X(t))*(X(d)**2 + X(t)**2), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Ropen(1, 2)))
+
+ # Value Error because of infinite time bound
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: E(X(t)**3, Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(1, oo))))
+
+ # Equivalent to E(X(t)**2) - E(X(d)**2) == E(X(1)**2) - E(X(1)**2) == 0
+ assert E((X(t) + X(d))*(X(t) - X(d)), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(1, 2))) == 0
+ assert E(X(2) + x*E(X(5))) == 15*x + 6
+ assert E(x*X(1) + y) == 3*x + y
+ assert P(Eq(X(1), 2) & Eq(X(t), 3), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(1, 2))) == 81*exp(-6)/4
+ Y = PoissonProcess("Y", 6)
+ Z = X + Y
+ assert Z.lamda == X.lamda + Y.lamda == 9
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: X + 5) # should be added be only PoissonProcess instance
+ N, M = Z.split(4, 5)
+ assert N.lamda == 4
+ assert M.lamda == 5
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: Z.split(3, 2)) # 2+3 != 9
+
+ raises(ValueError, lambda :P(Eq(X(t), 0), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(1, 3)) & Eq(X(1), 0)))
+ # check if it handles queries with two random variables in one args
+ res1 = P(Eq(N(3), N(5)))
+ assert res1 == P(Eq(N(t), 0), Contains(t, Interval(3, 5)))
+ res2 = P(N(3) > N(1))
+ assert res2 == P((N(t) > 0), Contains(t, Interval(1, 3)))
+ assert P(N(3) < N(1)) == 0 # condition is not possible
+ res3 = P(N(3) <= N(1)) # holds only for Eq(N(3), N(1))
+ assert res3 == P(Eq(N(t), 0), Contains(t, Interval(1, 3)))
+
+ # tests from https://www.probabilitycourse.com/chapter11/11_1_2_basic_concepts_of_the_poisson_process.php
+ X = PoissonProcess('X', 10) # 11.1
+ assert P(Eq(X(S(1)/3), 3) & Eq(X(1), 10)) == exp(-10)*Rational(8000000000, 11160261)
+ assert P(Eq(X(1), 1), Eq(X(S(1)/3), 3)) == 0
+ assert P(Eq(X(1), 10), Eq(X(S(1)/3), 3)) == P(Eq(X(S(2)/3), 7))
+
+ X = PoissonProcess('X', 2) # 11.2
+ assert P(X(S(1)/2) < 1) == exp(-1)
+ assert P(X(3) < 1, Eq(X(1), 0)) == exp(-4)
+ assert P(Eq(X(4), 3), Eq(X(2), 3)) == exp(-4)
+
+ X = PoissonProcess('X', 3)
+ assert P(Eq(X(2), 5) & Eq(X(1), 2)) == Rational(81, 4)*exp(-6)
+
+ # check few properties
+ assert P(X(2) <= 3, X(1)>=1) == 3*P(Eq(X(1), 0)) + 2*P(Eq(X(1), 1)) + P(Eq(X(1), 2))
+ assert P(X(2) <= 3, X(1) > 1) == 2*P(Eq(X(1), 0)) + 1*P(Eq(X(1), 1))
+ assert P(Eq(X(2), 5) & Eq(X(1), 2)) == P(Eq(X(1), 3))*P(Eq(X(1), 2))
+ assert P(Eq(X(3), 4), Eq(X(1), 3)) == P(Eq(X(2), 1))
+
+def test_WienerProcess():
+ X = WienerProcess("X")
+ assert X.state_space == Interval(0, oo)
+ assert X.index_set == Interval(0, oo)
+
+ t, d, x, y = symbols('t d x y', positive=True)
+ assert isinstance(X(t), RandomIndexedSymbol)
+ assert X.distribution(X(t)) == NormalDistribution(0, sqrt(t))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: PoissonProcess("X", -1))
+ raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: X[t])
+ raises(IndexError, lambda: X(-2))
+
+ assert X.joint_distribution(X(2), X(3)) == JointDistributionHandmade(
+ Lambda((X(2), X(3)), sqrt(6)*exp(-X(2)**2/4)*exp(-X(3)**2/6)/(12*pi)))
+ assert X.joint_distribution(4, 6) == JointDistributionHandmade(
+ Lambda((X(4), X(6)), sqrt(6)*exp(-X(4)**2/8)*exp(-X(6)**2/12)/(24*pi)))
+
+ assert P(X(t) < 3).simplify() == erf(3*sqrt(2)/(2*sqrt(t)))/2 + S(1)/2
+ assert P(X(t) > 2, Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(3, 7))).simplify() == S(1)/2 -\
+ erf(sqrt(2)/2)/2
+
+ # Equivalent to P(X(1)>1)**4
+ assert P((X(t) > 4) & (X(d) > 3) & (X(x) > 2) & (X(y) > 1),
+ Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1)) & Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(1, 2))
+ & Contains(x, Interval.Lopen(2, 3)) & Contains(y, Interval.Lopen(3, 4))).simplify() ==\
+ (1 - erf(sqrt(2)/2))*(1 - erf(sqrt(2)))*(1 - erf(3*sqrt(2)/2))*(1 - erf(2*sqrt(2)))/16
+
+ # Contains an overlapping interval so, return Probability
+ assert P((X(t)< 2) & (X(d)> 3), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 2))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Ropen(2, 4))) == Probability((X(d) > 3) & (X(t) < 2),
+ Contains(d, Interval.Ropen(2, 4)) & Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 2)))
+
+ assert str(P(Not((X(t) < 5) & (X(d) > 3)), Contains(t, Interval.Ropen(2, 4)) &
+ Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(7, 8))).simplify()) == \
+ '-(1 - erf(3*sqrt(2)/2))*(2 - erfc(5/2))/4 + 1'
+ # Distribution has mean 0 at each timestamp
+ assert E(X(t)) == 0
+ assert E(x*(X(t) + X(d))*(X(t)**2+X(d)**2), Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Ropen(1, 2))) == Expectation(x*(X(d) + X(t))*(X(d)**2 + X(t)**2),
+ Contains(d, Interval.Ropen(1, 2)) & Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1)))
+ assert E(X(t) + x*E(X(3))) == 0
+
+
+def test_GammaProcess_symbolic():
+ t, d, x, y, g, l = symbols('t d x y g l', positive=True)
+ X = GammaProcess("X", l, g)
+
+ raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: X[t])
+ raises(IndexError, lambda: X(-1))
+ assert isinstance(X(t), RandomIndexedSymbol)
+
+ assert X.distribution(X(t)) == GammaDistribution(g*t, 1/l)
+ assert X.joint_distribution(5, X(3)) == JointDistributionHandmade(Lambda(
+ (X(5), X(3)), l**(8*g)*exp(-l*X(3))*exp(-l*X(5))*X(3)**(3*g - 1)*X(5)**(5*g
+ - 1)/(gamma(3*g)*gamma(5*g))))
+ # property of the gamma process at any given timestamp
+ assert E(X(t)) == g*t/l
+ assert variance(X(t)).simplify() == g*t/l**2
+
+ # Equivalent to E(2*X(1)) + E(X(1)**2) + E(X(1)**3), where E(X(1)) == g/l
+ assert E(X(t)**2 + X(d)*2 + X(y)**3, Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(0, 1))
+ & Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(1, 2)) & Contains(y, Interval.Ropen(3, 4))) == \
+ 2*g/l + (g**2 + g)/l**2 + (g**3 + 3*g**2 + 2*g)/l**3
+
+ assert P(X(t) > 3, Contains(t, Interval.Lopen(3, 4))).simplify() == \
+ 1 - lowergamma(g, 3*l)/gamma(g) # equivalent to P(X(1)>3)
+
+def test_GammaProcess_numeric():
+ t, d, x, y = symbols('t d x y', positive=True)
+ X = GammaProcess("X", 1, 2)
+ assert X.state_space == Interval(0, oo)
+ assert X.index_set == Interval(0, oo)
+ assert X.lamda == 1
+ assert X.gamma == 2
+
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: GammaProcess("X", -1, 2))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: GammaProcess("X", 0, -2))
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: GammaProcess("X", -1, -2))
+
+ # all are independent because of non-overlapping intervals
+ assert P((X(t) > 4) & (X(d) > 3) & (X(x) > 2) & (X(y) > 1), Contains(t,
+ Interval.Lopen(0, 1)) & Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(1, 2)) & Contains(x,
+ Interval.Lopen(2, 3)) & Contains(y, Interval.Lopen(3, 4))).simplify() == \
+ 120*exp(-10)
+
+ # Check working with Not and Or
+ assert P(Not((X(t) < 5) & (X(d) > 3)), Contains(t, Interval.Ropen(2, 4)) &
+ Contains(d, Interval.Lopen(7, 8))).simplify() == -4*exp(-3) + 472*exp(-8)/3 + 1
+ assert P((X(t) > 2) | (X(t) < 4), Contains(t, Interval.Ropen(1, 4))).simplify() == \
+ -643*exp(-4)/15 + 109*exp(-2)/15 + 1
+
+ assert E(X(t)) == 2*t # E(X(t)) == gamma*t/l
+ assert E(X(2) + x*E(X(5))) == 10*x + 4
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19346@b8b80cf
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,346
|
Fixed: srepr not printing dict and set properly
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #19329
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Added two methods `_print_dict` and `_print_set` to `ReprPrinter`.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* printing
* fixed a bug where `srepr` function would not print dictionary and set properly
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-05-17T12:23:33Z
|
srepr not printing dict and set properly
`srepr` prints the element in `list` and `tuple` correctly.
```python
>>> from sympy import srepr
>>> from sympy.abc import x,y
>>> srepr([x,y])
[Symbol('x'), Symbol('y')]
>>> srepr((x,y))
(Symbol('x'), Symbol('y'))
```
However, `srepr` prints the elements in `dict` and `set` wrong.
```python
>>> srepr({x, y})
{x, y}
>>> srepr({x: y})
{x: y}
```
Is this behavior intended? If it isn't, fixing it will be an easy job.
|
[
{
"body": "`srepr` prints the element in `list` and `tuple` correctly.\r\n```python\r\n>>> from sympy import srepr\r\n>>> from sympy.abc import x,y\r\n>>> srepr([x,y])\r\n[Symbol('x'), Symbol('y')]\r\n>>> srepr((x,y))\r\n(Symbol('x'), Symbol('y'))\r\n```\r\n\r\nHowever, `srepr` prints the elements in `dict` and `set` wrong.\r\n```python\r\n>>> srepr({x, y})\r\n{x, y}\r\n>>> srepr({x: y})\r\n{x: y}\r\n```\r\n\r\nIs this behavior intended? If it isn't, fixing it will be an easy job.",
"number": 19329,
"title": "srepr not printing dict and set properly"
}
] |
94fb720696f5f5d12bad8bc813699fd696afd2fb
|
{
"head_commit": "b8b80cf44b9fdcb7198911784aba8b707309d99f",
"head_commit_message": "fixed: srepr not printing dict and set properly",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/printing/repr.py b/sympy/printing/repr.py\nindex c936a692c0cd..3c6aa1264f6b 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/repr.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/repr.py\n@@ -144,6 +144,14 @@ def _print_EmptySequence(self, expr):\n def _print_list(self, expr):\n return \"[%s]\" % self.reprify(expr, \", \")\n \n+ def _print_dict(self, expr):\n+ sep = \", \"\n+ dict_kvs = [\"%s: %s\" % (self.doprint(key), self.doprint(value)) for key, value in expr.items()]\n+ return \"{%s}\" % sep.join(dict_kvs)\n+\n+ def _print_set(self, expr):\n+ return \"{%s}\" % self.reprify(expr, \", \")\n+\n def _print_MatrixBase(self, expr):\n # special case for some empty matrices\n if (expr.rows == 0) ^ (expr.cols == 0):\ndiff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py\nindex f749683ff743..54dbb100e2aa 100644\n--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py\n+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py\n@@ -318,3 +318,23 @@ def test_diffgeom():\n assert srepr(rect) == \"CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1'))\"\n b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n assert srepr(b) == \"BaseScalarField(CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1')), Integer(0))\"\n+\n+def test_dict():\n+ from sympy import srepr\n+ from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n+ d = {}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{}\"\n+ d = {x: y}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y')}\"\n+ d = {x: y, y: z}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y'), Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}\"\n+ d = {x: {y: z}}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): {Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}}\"\n+\n+def test_set():\n+ from sympy import srepr\n+ from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ s = {x}\n+ assert srepr(s) == \"{Symbol('x')}\"\n+ s = {x, y}\n+ assert srepr(s) == \"{Symbol('x'), Symbol('y')}\"\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -318,3 +318,23 @@ def test_diffgeom():\n assert srepr(rect) == \"CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1'))\"\n b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n assert srepr(b) == \"BaseScalarField(CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1')), Integer(0))\"\n+\n+def test_dict():\n+ from sympy import srepr\n+ from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n+ d = {}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{}\"\n+ d = {x: y}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y')}\"\n+ d = {x: y, y: z}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y'), Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 330,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis test won't work in Python 3.5, because dicts are not ordered. You need:\r\n```suggestion\r\n # dict order is arbitrary until CPython 3.6 or Python 3.7\r\n assert srepr(d) in (\r\n \"{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y'), Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}\",\r\n \"{Symbol('y'): Symbol('z'), Symbol('x'): Symbol('y')}\",\r\n )\r\n```\n\n@user1:\n@user2-kunal, CI will randomly fail unless you also make this change."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -144,6 +144,14 @@ def _print_EmptySequence(self, expr):\n def _print_list(self, expr):\n return \"[%s]\" % self.reprify(expr, \", \")\n \n+ def _print_dict(self, expr):\n+ sep = \", \"\n+ dict_kvs = [\"%s: %s\" % (self.doprint(key), self.doprint(value)) for key, value in expr.items()]\n+ return \"{%s}\" % sep.join(dict_kvs)\n+\n+ def _print_set(self, expr):\n+ return \"{%s}\" % self.reprify(expr, \", \")",
"line": 155,
"original_line": 153,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/repr.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThis is wrong, and prints empty sets as empty dictionaries\r\n```suggestion\r\n if not expr:\r\n return \"set()\"\r\n else:\r\n return \"{%s}\" % self.reprify(expr, \", \")\r\n```\r\n\r\nEdit: Done, thanks!"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -318,3 +318,23 @@ def test_diffgeom():\n assert srepr(rect) == \"CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1'))\"\n b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n assert srepr(b) == \"BaseScalarField(CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1')), Integer(0))\"\n+\n+def test_dict():\n+ from sympy import srepr\n+ from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n+ d = {}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{}\"\n+ d = {x: y}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y')}\"\n+ d = {x: y, y: z}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y'), Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}\"\n+ d = {x: {y: z}}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): {Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}}\"\n+\n+def test_set():\n+ from sympy import srepr\n+ from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ s = {x}\n+ assert srepr(s) == \"{Symbol('x')}\"\n+ s = {x, y}\n+ assert srepr(s) == \"{Symbol('x'), Symbol('y')}\"",
"line": null,
"original_line": 340,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nCI is failing from this test, because `set`s are not ordered.\r\n\r\n```suggestion\r\n # set order is arbitrary\r\n assert srepr(s) in (\r\n \"{Symbol('x'), Symbol('y')}\",\r\n \"{Symbol('y'), Symbol('x')}\",\r\n )\r\n```\n\n@author:\nI didn't account for that, thanks!"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -318,3 +318,23 @@ def test_diffgeom():\n assert srepr(rect) == \"CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1'))\"\n b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)\n assert srepr(b) == \"BaseScalarField(CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1')), Integer(0))\"\n+\n+def test_dict():\n+ from sympy import srepr\n+ from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n+ d = {}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{}\"\n+ d = {x: y}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y')}\"\n+ d = {x: y, y: z}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y'), Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}\"\n+ d = {x: {y: z}}\n+ assert srepr(d) == \"{Symbol('x'): {Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}}\"\n+\n+def test_set():\n+ from sympy import srepr\n+ from sympy.abc import x, y\n+ s = {x}",
"line": null,
"original_line": 337,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n s = {}\r\n assert srepr(s) == \"set()\"\r\n s = {x}\r\n```"
}
] |
2a7b8a475b4a9883d6821bb3412518381d4fa797
|
diff --git a/sympy/printing/repr.py b/sympy/printing/repr.py
index c936a692c0cd..04cfee5c3e61 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/repr.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/repr.py
@@ -144,6 +144,16 @@ def _print_EmptySequence(self, expr):
def _print_list(self, expr):
return "[%s]" % self.reprify(expr, ", ")
+ def _print_dict(self, expr):
+ sep = ", "
+ dict_kvs = ["%s: %s" % (self.doprint(key), self.doprint(value)) for key, value in expr.items()]
+ return "{%s}" % sep.join(dict_kvs)
+
+ def _print_set(self, expr):
+ if not expr:
+ return "set()"
+ return "{%s}" % self.reprify(expr, ", ")
+
def _print_MatrixBase(self, expr):
# special case for some empty matrices
if (expr.rows == 0) ^ (expr.cols == 0):
diff --git a/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py b/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py
index f749683ff743..d3298da71dfd 100644
--- a/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py
+++ b/sympy/printing/tests/test_repr.py
@@ -318,3 +318,26 @@ def test_diffgeom():
assert srepr(rect) == "CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1'))"
b = BaseScalarField(rect, 0)
assert srepr(b) == "BaseScalarField(CoordSystem('rect', Patch('P', Manifold('M', 2)), ('rect_0', 'rect_1')), Integer(0))"
+
+def test_dict():
+ from sympy import srepr
+ from sympy.abc import x, y, z
+ d = {}
+ assert srepr(d) == "{}"
+ d = {x: y}
+ assert srepr(d) == "{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y')}"
+ d = {x: y, y: z}
+ assert srepr(d) in (
+ "{Symbol('x'): Symbol('y'), Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}",
+ "{Symbol('y'): Symbol('z'), Symbol('x'): Symbol('y')}",
+ )
+ d = {x: {y: z}}
+ assert srepr(d) == "{Symbol('x'): {Symbol('y'): Symbol('z')}}"
+
+def test_set():
+ from sympy import srepr
+ from sympy.abc import x, y
+ s = set()
+ assert srepr(s) == "set()"
+ s = {x, y}
+ assert srepr(s) in ("{Symbol('x'), Symbol('y')}", "{Symbol('y'), Symbol('x')}")
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 2,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
yt-dlp__yt-dlp-1200@b2685d5
|
yt-dlp/yt-dlp
|
Python
| 1,200
|
[on24] Add new extractor
|
## Please follow the guide below
- You will be asked some questions, please read them **carefully** and answer honestly
- Put an `x` into all the boxes [ ] relevant to your *pull request* (like that [x])
- Use *Preview* tab to see how your *pull request* will actually look like
---
### Before submitting a *pull request* make sure you have:
- [x] At least skimmed through [adding new extractor tutorial](https://github.com/ytdl-org/youtube-dl#adding-support-for-a-new-site) and [youtube-dl coding conventions](https://github.com/ytdl-org/youtube-dl#youtube-dl-coding-conventions) sections
- [x] [Searched](https://github.com/yt-dlp/yt-dlp/search?q=is%3Apr&type=Issues) the bugtracker for similar pull requests
- [x] Checked the code with [flake8](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/flake8)
### In order to be accepted and merged into yt-dlp each piece of code must be in public domain or released under [Unlicense](http://unlicense.org/). Check one of the following options:
- [x] I am the original author of this code and I am willing to release it under [Unlicense](http://unlicense.org/)
- [ ] I am not the original author of this code but it is in public domain or released under [Unlicense](http://unlicense.org/) (provide reliable evidence)
### What is the purpose of your *pull request*?
- [ ] Bug fix
- [ ] Improvement
- [x] New extractor
- [ ] New feature
---
### Description of your *pull request* and other information
This PR adds a new extractor for ON24 events.
(Fixes ytdl-org/youtube-dl#24775)
|
2021-10-07T22:40:24Z
|
Add on24 downloader
## Checklist
- [x] I'm reporting a feature request
- [x] I've verified that I'm running youtube-dl version **2020.03.24**
- [x] I've searched the bugtracker for similar feature requests including closed ones
## Description
ON24 is used for online trainings like from the O'Reilly learning platform. Replays are available after the training but it seems they cannot be downloaded. I'd like to ask for a download functionality.
|
@chbndrhnns you need to find **stream.mpd** file using chrome developer tool.
then use the command
`youtube-dl -f bestvideo+bestaudio https://dashod.akamaized.net/media/cv/events/XYZ/stream.mpd`
you need ffmpeg for merging formats.
see this stackoverflow [link](https://stackoverflow.com/a/55071769)
I've used this method and it works on on24 platform.
@VioletLightning thanks for sharing! If it's possible like that, I would not even need a native implementation.
I think that the main issue there is that they are separating video with audio with actually slides.
Of course, they are providing pdfs, but it would be cool to have a video, audio with actual slides at a particular moment at the time
@chbndrhnns You don't absolutely need it, but then again we don't /need/ most of the extractors either. They just make downloads of common media easier. Please change the label of this request to "site-support-request"
I would also like to plus +1 this request. As an example for why this would be useful: on24 is the streaming media platform behind many Microsoft learning materials.
@remitamine Examples can be found with this google search: `site:event.on24.com`. Many require a registration. Here is one that is available without registration:
https://event.on24.com/wcc/r/1886661/005F80F25EA62BDC10904B02AE9FD43D
Thank you, @remitamine. Here is another example of a recent Microsoft online learning event URL:
> https://ve.on24.com/vshow/MSFTWindowsVirtual/exhibits/WVDMC?regPageId=18844
If I remember correctly, registration for this event is/was required, but is/was open and basic.
I'm interested. How can I help with this effort?
> @chbndrhnns you need to find **stream.mpd** file using chrome developer tool.
> then use the command
> `youtube-dl -f bestvideo+bestaudio https://dashod.akamaized.net/media/cv/events/XYZ/stream.mpd`
> you need ffmpeg for merging formats.
> see this stackoverflow [link](https://stackoverflow.com/a/55071769)
> I've used this method and it works on on24 platform.
The StackOverflow comment just after the one that @chbndrhnns mentioned also works perfectly for O'Reilly Live Events hosted on ON24. https://stackoverflow.com/a/55071769/5559588
|
[
{
"body": "## Checklist\r\n\r\n- [x] I'm reporting a feature request\r\n- [x] I've verified that I'm running youtube-dl version **2020.03.24**\r\n- [x] I've searched the bugtracker for similar feature requests including closed ones\r\n\r\n\r\n## Description\r\n\r\nON24 is used for online trainings like from the O'Reilly learning platform. Replays are available after the training but it seems they cannot be downloaded. I'd like to ask for a download functionality.",
"number": 24775,
"title": "Add on24 downloader"
}
] |
6ff34542d2ddfe3369f7e1b321891f155690ae80
|
{
"head_commit": "b2685d5223b50ae22eca47ff5e088a07d00271e5",
"head_commit_message": "Remove whitespace\n\nFixes Flake8 warning",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/yt_dlp/extractor/extractors.py b/yt_dlp/extractor/extractors.py\nindex 8c5b8b16077a..7ed8fb450cb3 100644\n--- a/yt_dlp/extractor/extractors.py\n+++ b/yt_dlp/extractor/extractors.py\n@@ -983,6 +983,7 @@\n from .odnoklassniki import OdnoklassnikiIE\n from .oktoberfesttv import OktoberfestTVIE\n from .olympics import OlympicsReplayIE\n+from .on24 import On24IE\n from .ondemandkorea import OnDemandKoreaIE\n from .onet import (\n OnetIE,\ndiff --git a/yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py b/yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py\nnew file mode 100644\nindex 000000000000..3c0a4fd2241c\n--- /dev/null\n+++ b/yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py\n@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@\n+# coding: utf-8\n+from __future__ import unicode_literals\n+\n+import re\n+\n+from .common import InfoExtractor\n+from ..compat import (\n+ compat_str,\n+ compat_urlparse,\n+)\n+from ..utils import strip_or_none\n+\n+\n+class On24IE(InfoExtractor):\n+ IE_NAME = 'on24'\n+ IE_DESC = 'ON24'\n+\n+ _VALID_URL = r'''(?x)\n+ (?:\n+ https?://event\\.on24\\.com/\n+ (?:\n+ wcc/r/(?P<id_1>\\d{7})/(?P<key_1>[0-9A-F]{32})|\n+ eventRegistration/\n+ (?:\n+ console/EventConsoleApollo\\.jsp\\?|\n+ EventLobbyServlet\\?target=lobby30\\.jsp&\n+ )\n+ (?:uimode=nextgeneration&)?(?:&)?eventid=(?P<id_2>\\d{7})(?:&sessionid=1)?.*&key=(?P<key_2>[0-9A-F]{32})\n+ )\n+ )\n+ '''\n+\n+ _TESTS = [{\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?uimode=nextgeneration&eventid=2197467&sessionid=1&key=5DF57BE53237F36A43B478DD36277A84&contenttype=A&eventuserid=305999&playerwidth=1000&playerheight=650&caller=previewLobby&text_language_id=en&format=fhaudio&newConsole=false',\n+ 'info_dict': {\n+ 'id': '2197467',\n+ 'ext': 'wav',\n+ 'title': 'Pearson Test of English General/Pearson English International Certificate Teacher Training Guide',\n+ 'upload_date': '20200219',\n+ 'timestamp': 1582149600.0,\n+ }\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/wcc/r/2639291/82829018E813065A122363877975752E?mode=login&[email protected]',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?&eventid=2639291&sessionid=1&username=&partnerref=&format=fhvideo1&mobile=&flashsupportedmobiledevice=&helpcenter=&key=82829018E813065A122363877975752E&newConsole=true&nxChe=true&newTabCon=true&text_language_id=en&playerwidth=748&playerheight=526&eventuserid=338788762&contenttype=A&mediametricsessionid=384764716&mediametricid=3558192&usercd=369267058&mode=launch',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }]\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _is_absolute(url):\n+ return bool(compat_urlparse.urlparse(url).netloc)\n+\n+ def _real_extract(self, url):\n+ mobj = re.match(self._VALID_URL, url)\n+ event_id = mobj.group('id_1') or mobj.group('id_2')\n+ event_key = mobj.group('key_1') or mobj.group('key_2')\n+\n+ event_data = self._download_json(\n+ 'https://event.on24.com/apic/utilApp/EventConsoleCachedServlet',\n+ event_id, query={\n+ 'eventId': event_id,\n+ 'displayProfile': 'player',\n+ 'key': event_key,\n+ 'contentType': 'A'\n+ })\n+\n+ event_id = compat_str(event_data.get('presentationLogInfo', {}).get('eventid')) or event_id\n+\n+ info_media = event_data.get('mediaUrlInfo', {})\n+ info_media.sort(key=lambda m: m['id'])\n+\n+ formats = []\n+ for m in info_media:\n+ media_url = compat_str(m['url'])\n+ if not self._is_absolute(media_url):\n+ media_url = 'https://event.on24.com/media/news/corporatevideo/events/%s' % media_url\n+ if m['code'] == 'fhvideo1':\n+ formats.append({\n+ 'format_id': 'video',\n+ 'url': media_url,\n+ 'ext': 'mp4',\n+ 'vcodec': 'avc1.640020',\n+ 'acodec': 'mp4a.40.2',\n+ })\n+ elif m['code'] == 'audio':\n+ formats.append({\n+ 'format_id': 'audio',\n+ 'url': media_url,\n+ 'ext': 'wav',\n+ 'vcodec': 'none',\n+ 'acodec': 'wav'\n+ })\n+ self._sort_formats(formats)\n+\n+ return {\n+ 'id': event_id,\n+ 'title': strip_or_none(event_data.get('description')),\n+ 'language': event_data.get('localelanguagecode'),\n+ 'timestamp': (event_data.get('session', {}).get('startdate') / 1000\n+ if event_data.get('session', {}).get('startdate') is not None else None),\n+ 'webpage_url': 'https://event.on24.com/wcc/r/%s/%s' % (event_id, event_key),\n+ 'view_count': event_data.get('registrantcount'),\n+ 'formats': formats,\n+ }\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@\n+# coding: utf-8\n+from __future__ import unicode_literals\n+\n+import re\n+\n+from .common import InfoExtractor\n+from ..compat import (\n+ compat_str,\n+ compat_urlparse,\n+)\n+from ..utils import strip_or_none\n+\n+\n+class On24IE(InfoExtractor):\n+ IE_NAME = 'on24'\n+ IE_DESC = 'ON24'\n+\n+ _VALID_URL = r'''(?x)\n+ (?:\n+ https?://event\\.on24\\.com/\n+ (?:\n+ wcc/r/(?P<id_1>\\d{7})/(?P<key_1>[0-9A-F]{32})|\n+ eventRegistration/\n+ (?:\n+ console/EventConsoleApollo\\.jsp\\?|\n+ EventLobbyServlet\\?target=lobby30\\.jsp&\n+ )\n+ (?:uimode=nextgeneration&)?(?:&)?eventid=(?P<id_2>\\d{7})(?:&sessionid=1)?.*&key=(?P<key_2>[0-9A-F]{32})\n+ )\n+ )\n+ '''\n+\n+ _TESTS = [{\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?uimode=nextgeneration&eventid=2197467&sessionid=1&key=5DF57BE53237F36A43B478DD36277A84&contenttype=A&eventuserid=305999&playerwidth=1000&playerheight=650&caller=previewLobby&text_language_id=en&format=fhaudio&newConsole=false',\n+ 'info_dict': {\n+ 'id': '2197467',\n+ 'ext': 'wav',\n+ 'title': 'Pearson Test of English General/Pearson English International Certificate Teacher Training Guide',\n+ 'upload_date': '20200219',\n+ 'timestamp': 1582149600.0,\n+ }\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/wcc/r/2639291/82829018E813065A122363877975752E?mode=login&[email protected]',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?&eventid=2639291&sessionid=1&username=&partnerref=&format=fhvideo1&mobile=&flashsupportedmobiledevice=&helpcenter=&key=82829018E813065A122363877975752E&newConsole=true&nxChe=true&newTabCon=true&text_language_id=en&playerwidth=748&playerheight=526&eventuserid=338788762&contenttype=A&mediametricsessionid=384764716&mediametricid=3558192&usercd=369267058&mode=launch',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }]\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _is_absolute(url):\n+ return bool(compat_urlparse.urlparse(url).netloc)\n+\n+ def _real_extract(self, url):\n+ mobj = re.match(self._VALID_URL, url)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 55,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nuse self._match_valid_url"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@\n+# coding: utf-8\n+from __future__ import unicode_literals\n+\n+import re\n+\n+from .common import InfoExtractor\n+from ..compat import (\n+ compat_str,\n+ compat_urlparse,\n+)\n+from ..utils import strip_or_none\n+\n+\n+class On24IE(InfoExtractor):\n+ IE_NAME = 'on24'\n+ IE_DESC = 'ON24'\n+\n+ _VALID_URL = r'''(?x)\n+ (?:\n+ https?://event\\.on24\\.com/\n+ (?:\n+ wcc/r/(?P<id_1>\\d{7})/(?P<key_1>[0-9A-F]{32})|\n+ eventRegistration/\n+ (?:\n+ console/EventConsoleApollo\\.jsp\\?|\n+ EventLobbyServlet\\?target=lobby30\\.jsp&\n+ )\n+ (?:uimode=nextgeneration&)?(?:&)?eventid=(?P<id_2>\\d{7})(?:&sessionid=1)?.*&key=(?P<key_2>[0-9A-F]{32})\n+ )\n+ )\n+ '''\n+\n+ _TESTS = [{\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?uimode=nextgeneration&eventid=2197467&sessionid=1&key=5DF57BE53237F36A43B478DD36277A84&contenttype=A&eventuserid=305999&playerwidth=1000&playerheight=650&caller=previewLobby&text_language_id=en&format=fhaudio&newConsole=false',\n+ 'info_dict': {\n+ 'id': '2197467',\n+ 'ext': 'wav',\n+ 'title': 'Pearson Test of English General/Pearson English International Certificate Teacher Training Guide',\n+ 'upload_date': '20200219',\n+ 'timestamp': 1582149600.0,\n+ }\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/wcc/r/2639291/82829018E813065A122363877975752E?mode=login&[email protected]',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?&eventid=2639291&sessionid=1&username=&partnerref=&format=fhvideo1&mobile=&flashsupportedmobiledevice=&helpcenter=&key=82829018E813065A122363877975752E&newConsole=true&nxChe=true&newTabCon=true&text_language_id=en&playerwidth=748&playerheight=526&eventuserid=338788762&contenttype=A&mediametricsessionid=384764716&mediametricid=3558192&usercd=369267058&mode=launch',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }]\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _is_absolute(url):\n+ return bool(compat_urlparse.urlparse(url).netloc)\n+\n+ def _real_extract(self, url):\n+ mobj = re.match(self._VALID_URL, url)\n+ event_id = mobj.group('id_1') or mobj.group('id_2')\n+ event_key = mobj.group('key_1') or mobj.group('key_2')\n+\n+ event_data = self._download_json(\n+ 'https://event.on24.com/apic/utilApp/EventConsoleCachedServlet',\n+ event_id, query={\n+ 'eventId': event_id,\n+ 'displayProfile': 'player',\n+ 'key': event_key,\n+ 'contentType': 'A'\n+ })\n+\n+ event_id = compat_str(event_data.get('presentationLogInfo', {}).get('eventid')) or event_id",
"line": null,
"original_line": 68,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI personally wouldn't use `compat_str` just so that the code can't be blindly ported back to py2 😈 \r\nBut it's okay to use it if u want\n\n@user1:\nAlso don't use .get chains.\r\nUse try_get with expected type set"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@\n+# coding: utf-8\n+from __future__ import unicode_literals\n+\n+import re\n+\n+from .common import InfoExtractor\n+from ..compat import (\n+ compat_str,\n+ compat_urlparse,\n+)\n+from ..utils import strip_or_none\n+\n+\n+class On24IE(InfoExtractor):\n+ IE_NAME = 'on24'\n+ IE_DESC = 'ON24'\n+\n+ _VALID_URL = r'''(?x)\n+ (?:\n+ https?://event\\.on24\\.com/\n+ (?:\n+ wcc/r/(?P<id_1>\\d{7})/(?P<key_1>[0-9A-F]{32})|\n+ eventRegistration/\n+ (?:\n+ console/EventConsoleApollo\\.jsp\\?|\n+ EventLobbyServlet\\?target=lobby30\\.jsp&\n+ )\n+ (?:uimode=nextgeneration&)?(?:&)?eventid=(?P<id_2>\\d{7})(?:&sessionid=1)?.*&key=(?P<key_2>[0-9A-F]{32})\n+ )\n+ )\n+ '''\n+\n+ _TESTS = [{\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?uimode=nextgeneration&eventid=2197467&sessionid=1&key=5DF57BE53237F36A43B478DD36277A84&contenttype=A&eventuserid=305999&playerwidth=1000&playerheight=650&caller=previewLobby&text_language_id=en&format=fhaudio&newConsole=false',\n+ 'info_dict': {\n+ 'id': '2197467',\n+ 'ext': 'wav',\n+ 'title': 'Pearson Test of English General/Pearson English International Certificate Teacher Training Guide',\n+ 'upload_date': '20200219',\n+ 'timestamp': 1582149600.0,\n+ }\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/wcc/r/2639291/82829018E813065A122363877975752E?mode=login&[email protected]',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?&eventid=2639291&sessionid=1&username=&partnerref=&format=fhvideo1&mobile=&flashsupportedmobiledevice=&helpcenter=&key=82829018E813065A122363877975752E&newConsole=true&nxChe=true&newTabCon=true&text_language_id=en&playerwidth=748&playerheight=526&eventuserid=338788762&contenttype=A&mediametricsessionid=384764716&mediametricid=3558192&usercd=369267058&mode=launch',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }]\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _is_absolute(url):\n+ return bool(compat_urlparse.urlparse(url).netloc)\n+\n+ def _real_extract(self, url):\n+ mobj = re.match(self._VALID_URL, url)\n+ event_id = mobj.group('id_1') or mobj.group('id_2')\n+ event_key = mobj.group('key_1') or mobj.group('key_2')\n+\n+ event_data = self._download_json(\n+ 'https://event.on24.com/apic/utilApp/EventConsoleCachedServlet',\n+ event_id, query={\n+ 'eventId': event_id,\n+ 'displayProfile': 'player',\n+ 'key': event_key,\n+ 'contentType': 'A'\n+ })\n+\n+ event_id = compat_str(event_data.get('presentationLogInfo', {}).get('eventid')) or event_id\n+\n+ info_media = event_data.get('mediaUrlInfo', {})\n+ info_media.sort(key=lambda m: m['id'])\n+\n+ formats = []\n+ for m in info_media:\n+ media_url = compat_str(m['url'])\n+ if not self._is_absolute(media_url):\n+ media_url = 'https://event.on24.com/media/news/corporatevideo/events/%s' % media_url\n+ if m['code'] == 'fhvideo1':\n+ formats.append({\n+ 'format_id': 'video',\n+ 'url': media_url,\n+ 'ext': 'mp4',\n+ 'vcodec': 'avc1.640020',\n+ 'acodec': 'mp4a.40.2',\n+ })\n+ elif m['code'] == 'audio':\n+ formats.append({\n+ 'format_id': 'audio',\n+ 'url': media_url,\n+ 'ext': 'wav',\n+ 'vcodec': 'none',\n+ 'acodec': 'wav'\n+ })\n+ self._sort_formats(formats)\n+\n+ return {\n+ 'id': event_id,\n+ 'title': strip_or_none(event_data.get('description')),\n+ 'language': event_data.get('localelanguagecode'),\n+ 'timestamp': (event_data.get('session', {}).get('startdate') / 1000\n+ if event_data.get('session', {}).get('startdate') is not None else None),",
"line": null,
"original_line": 101,
"original_start_line": 100,
"path": "yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nif you going to inline return, better keep it 1 line imo\r\n\r\ntherefore move timestamp above\r\n\r\nAlso don't use .get chains"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@\n+# coding: utf-8\n+from __future__ import unicode_literals\n+\n+import re\n+\n+from .common import InfoExtractor\n+from ..compat import (\n+ compat_str,\n+ compat_urlparse,\n+)\n+from ..utils import strip_or_none\n+\n+\n+class On24IE(InfoExtractor):\n+ IE_NAME = 'on24'\n+ IE_DESC = 'ON24'\n+\n+ _VALID_URL = r'''(?x)\n+ (?:\n+ https?://event\\.on24\\.com/\n+ (?:\n+ wcc/r/(?P<id_1>\\d{7})/(?P<key_1>[0-9A-F]{32})|\n+ eventRegistration/\n+ (?:\n+ console/EventConsoleApollo\\.jsp\\?|\n+ EventLobbyServlet\\?target=lobby30\\.jsp&\n+ )\n+ (?:uimode=nextgeneration&)?(?:&)?eventid=(?P<id_2>\\d{7})(?:&sessionid=1)?.*&key=(?P<key_2>[0-9A-F]{32})\n+ )\n+ )\n+ '''\n+\n+ _TESTS = [{\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?uimode=nextgeneration&eventid=2197467&sessionid=1&key=5DF57BE53237F36A43B478DD36277A84&contenttype=A&eventuserid=305999&playerwidth=1000&playerheight=650&caller=previewLobby&text_language_id=en&format=fhaudio&newConsole=false',\n+ 'info_dict': {\n+ 'id': '2197467',\n+ 'ext': 'wav',\n+ 'title': 'Pearson Test of English General/Pearson English International Certificate Teacher Training Guide',\n+ 'upload_date': '20200219',\n+ 'timestamp': 1582149600.0,\n+ }\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/wcc/r/2639291/82829018E813065A122363877975752E?mode=login&[email protected]',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }, {\n+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?&eventid=2639291&sessionid=1&username=&partnerref=&format=fhvideo1&mobile=&flashsupportedmobiledevice=&helpcenter=&key=82829018E813065A122363877975752E&newConsole=true&nxChe=true&newTabCon=true&text_language_id=en&playerwidth=748&playerheight=526&eventuserid=338788762&contenttype=A&mediametricsessionid=384764716&mediametricid=3558192&usercd=369267058&mode=launch',\n+ 'only_matching': True,\n+ }]\n+\n+ @staticmethod\n+ def _is_absolute(url):\n+ return bool(compat_urlparse.urlparse(url).netloc)\n+\n+ def _real_extract(self, url):\n+ mobj = re.match(self._VALID_URL, url)\n+ event_id = mobj.group('id_1') or mobj.group('id_2')\n+ event_key = mobj.group('key_1') or mobj.group('key_2')\n+\n+ event_data = self._download_json(\n+ 'https://event.on24.com/apic/utilApp/EventConsoleCachedServlet',\n+ event_id, query={\n+ 'eventId': event_id,\n+ 'displayProfile': 'player',\n+ 'key': event_key,\n+ 'contentType': 'A'\n+ })\n+\n+ event_id = compat_str(event_data.get('presentationLogInfo', {}).get('eventid')) or event_id\n+\n+ info_media = event_data.get('mediaUrlInfo', {})\n+ info_media.sort(key=lambda m: m['id'])",
"line": null,
"original_line": 71,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhy sort?\n\n@author:\nThe sorting could be removed."
}
] |
5b4071da360c7d2681418724107096d79758b90b
|
diff --git a/yt_dlp/extractor/extractors.py b/yt_dlp/extractor/extractors.py
index 8c5b8b16077a..7ed8fb450cb3 100644
--- a/yt_dlp/extractor/extractors.py
+++ b/yt_dlp/extractor/extractors.py
@@ -983,6 +983,7 @@
from .odnoklassniki import OdnoklassnikiIE
from .oktoberfesttv import OktoberfestTVIE
from .olympics import OlympicsReplayIE
+from .on24 import On24IE
from .ondemandkorea import OnDemandKoreaIE
from .onet import (
OnetIE,
diff --git a/yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py b/yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..d4d824430f9f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/yt_dlp/extractor/on24.py
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+# coding: utf-8
+from __future__ import unicode_literals
+
+from .common import InfoExtractor
+from ..utils import (
+ int_or_none,
+ strip_or_none,
+ try_get,
+ urljoin,
+)
+
+
+class On24IE(InfoExtractor):
+ IE_NAME = 'on24'
+ IE_DESC = 'ON24'
+
+ _VALID_URL = r'''(?x)
+ https?://event\.on24\.com/(?:
+ wcc/r/(?P<id_1>\d{7})/(?P<key_1>[0-9A-F]{32})|
+ eventRegistration/(?:console/EventConsoleApollo|EventLobbyServlet\?target=lobby30)
+ \.jsp\?(?:[^/#?]*&)?eventid=(?P<id_2>\d{7})[^/#?]*&key=(?P<key_2>[0-9A-F]{32})
+ )'''
+
+ _TESTS = [{
+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?uimode=nextgeneration&eventid=2197467&sessionid=1&key=5DF57BE53237F36A43B478DD36277A84&contenttype=A&eventuserid=305999&playerwidth=1000&playerheight=650&caller=previewLobby&text_language_id=en&format=fhaudio&newConsole=false',
+ 'info_dict': {
+ 'id': '2197467',
+ 'ext': 'wav',
+ 'title': 'Pearson Test of English General/Pearson English International Certificate Teacher Training Guide',
+ 'upload_date': '20200219',
+ 'timestamp': 1582149600.0,
+ 'view_count': int,
+ }
+ }, {
+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/wcc/r/2639291/82829018E813065A122363877975752E?mode=login&[email protected]',
+ 'only_matching': True,
+ }, {
+ 'url': 'https://event.on24.com/eventRegistration/console/EventConsoleApollo.jsp?&eventid=2639291&sessionid=1&username=&partnerref=&format=fhvideo1&mobile=&flashsupportedmobiledevice=&helpcenter=&key=82829018E813065A122363877975752E&newConsole=true&nxChe=true&newTabCon=true&text_language_id=en&playerwidth=748&playerheight=526&eventuserid=338788762&contenttype=A&mediametricsessionid=384764716&mediametricid=3558192&usercd=369267058&mode=launch',
+ 'only_matching': True,
+ }]
+
+ def _real_extract(self, url):
+ mobj = self._match_valid_url(url)
+ event_id = mobj.group('id_1') or mobj.group('id_2')
+ event_key = mobj.group('key_1') or mobj.group('key_2')
+
+ event_data = self._download_json(
+ 'https://event.on24.com/apic/utilApp/EventConsoleCachedServlet',
+ event_id, query={
+ 'eventId': event_id,
+ 'displayProfile': 'player',
+ 'key': event_key,
+ 'contentType': 'A'
+ })
+ event_id = str(try_get(event_data, lambda x: x['presentationLogInfo']['eventid'])) or event_id
+ language = event_data.get('localelanguagecode')
+
+ formats = []
+ for media in event_data.get('mediaUrlInfo', []):
+ media_url = urljoin('https://event.on24.com/media/news/corporatevideo/events/', str(media.get('url')))
+ if not media_url:
+ continue
+ media_type = media.get('code')
+ if media_type == 'fhvideo1':
+ formats.append({
+ 'format_id': 'video',
+ 'url': media_url,
+ 'language': language,
+ 'ext': 'mp4',
+ 'vcodec': 'avc1.640020',
+ 'acodec': 'mp4a.40.2',
+ })
+ elif media_type == 'audio':
+ formats.append({
+ 'format_id': 'audio',
+ 'url': media_url,
+ 'language': language,
+ 'ext': 'wav',
+ 'vcodec': 'none',
+ 'acodec': 'wav'
+ })
+ self._sort_formats(formats)
+
+ return {
+ 'id': event_id,
+ 'title': strip_or_none(event_data.get('description')),
+ 'timestamp': int_or_none(try_get(event_data, lambda x: x['session']['startdate']), 1000),
+ 'webpage_url': f'https://event.on24.com/wcc/r/{event_id}/{event_key}',
+ 'view_count': event_data.get('registrantcount'),
+ 'formats': formats,
+ }
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19297@49641ad
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,297
|
[GSoC] Series: Fixing incorrect limit evaluations caused due to bug in rewriting
|
Fixes: #18378
Fixes: #18482
Closes #18947
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
**Incorrect limit evaluation** takes place because of **bug in rewriting.**
The function `xreplace()` in the `rewrite()` function of `gruntz.py` is not substituting properly.
As a result, it has been replaced by the `subs()` function which resolves the issue.
#### Other Comments
Regression Tests have been added.
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* series
* Replaces `xreplace()` with `subs()` in `rewrite() function of gruntz.py` resolving incorrect limit evaluations
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-05-12T08:29:38Z
|
Invalid result in Limit
`Limit(ln(exp(3*x)+x)/ln(exp(x)+x**100), x, oo).doit()` gives the output of `9` although `3` was expected.
Sympy 1.5 on CPython 3.7.4 on Windows 10 64 bit.
Incorrect evaluation of limit
`limit(sqrt (x**2 + 6*x) + (x**3 + x**2)/(x**2 + 1),x,-oo)` is `2`
`limit((x**3 + x**2 + sqrt(x*(x + 6))*(x**2 + 1))/(x**2 + 1),x,-oo)` is `1`, but should be `-2`, since expressions are equivalent.
|
On 1.6.dev, I get this:
```
In [10]: Limit(ln(exp(3*x)+x)/ln(exp(x)+x**100), x, oo).doit()
Out[10]: 3
```
1.5.1 also gives 9
Also, `limit((2*exp(3*x)/(exp(2*x) + 1))**(1/x),x,oo)` should be `E`.
Same as above.
`limit(x + (1 - x**2)*exp(1/x)/(x + 2),x,oo)` is `1`. `imit((x*(x + 2) + (1 - x**2)*exp(1/x))/(x + 2),x,oo)` should be `1`, but it is `2`.
No longer an issue. All limits are getting evaluated correctly. The issue can be closed @oscarbenjamin @czgdp1807.
Most examples do seem to be fixed. When were they fixed?
This example is still incorrect:
```
In [6]: limit((2*exp(3*x)/(exp(2*x) + 1))**(1/x),x,oo)
Out[6]:
7/3
ℯ
```
>Most examples do seem to be fixed. When were they fixed?
I myself don't know, perhaps: https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/18340
Merged 18 days ago, and the issue was opened 26 days ago.
> This example is still incorrect:
>
> ```
> In [6]: limit((2*exp(3*x)/(exp(2*x) + 1))**(1/x),x,oo)
> Out[6]:
> 7/3
> ℯ
> ```
Will have to debug mrv_leadterm for this in gruntz.py
@oscarbenjamin can you give some directions on how to start with it? I have gone through all the steps which is involved in calculating the above limit but unable to get the bug
> Same as above.
> `limit(x + (1 - x**2)*exp(1/x)/(x + 2),x,oo)` is `1`. `imit((x*(x + 2) + (1 - x**2)*exp(1/x))/(x + 2),x,oo)` should be `1`, but it is `2`.
The above query is showing the expected result which is 1
|
[
{
"body": "`Limit(ln(exp(3*x)+x)/ln(exp(x)+x**100), x, oo).doit()` gives the output of `9` although `3` was expected.\r\nSympy 1.5 on CPython 3.7.4 on Windows 10 64 bit.",
"number": 18378,
"title": "Invalid result in Limit"
},
{
"body": "`limit(sqrt (x**2 + 6*x) + (x**3 + x**2)/(x**2 + 1),x,-oo)` is `2`\r\n`limit((x**3 + x**2 + sqrt(x*(x + 6))*(x**2 + 1))/(x**2 + 1),x,-oo)` is `1`, but should be `-2`, since expressions are equivalent.",
"number": 18482,
"title": "Incorrect evaluation of limit"
}
] |
7a3e06478304045a54000341ff81ab20ab074a05
|
{
"head_commit": "49641ad4938b2ce2d0324732a6d51dc15a6b6f74",
"head_commit_message": "Fixing incorrect limit evaluations caused due to bug in rewriting",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/series/gruntz.py b/sympy/series/gruntz.py\nindex e857f14c9d2f..12aa2dd467cb 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/gruntz.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/gruntz.py\n@@ -628,7 +628,7 @@ def rewrite(e, Omega, x, wsym):\n # Some parts of sympy have difficulty computing series expansions with\n # non-integral exponents. The following heuristic improves the situation:\n exponent = reduce(ilcm, denominators, 1)\n- f = f.xreplace({wsym: wsym**exponent})\n+ f = f.subs({wsym: wsym**exponent})\n logw /= exponent\n \n return f, logw\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\nindex 8da9c0cbfeb4..467f2b7fd62a 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\n@@ -652,10 +652,18 @@ def test_issue_18306():\n assert limit(sin(sqrt(x))/sqrt(sin(x)), x, 0, '+') == 1\n \n \n+def test_issue_18378():\n+ assert limit(log(exp(3*x) + x)/log(exp(x) + x**100), x, oo).doit() == 3\n+\n+\n def test_issue_18442():\n assert limit(tan(x)**(2**(sqrt(pi))), x, oo, dir='-') == AccumBounds(-oo, oo)\n \n \n+def test_issue_18482():\n+ assert limit((2*exp(3*x)/(exp(2*x) + 1))**(1/x), x, oo) == exp(1)\n+\n+\n def test_issue_18501():\n assert limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1), x, 1, '+') == oo\n \n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -652,10 +652,18 @@ def test_issue_18306():\n assert limit(sin(sqrt(x))/sqrt(sin(x)), x, 0, '+') == 1\n \n \n+def test_issue_18378():\n+ assert limit(log(exp(3*x) + x)/log(exp(x) + x**100), x, oo).doit() == 3",
"line": null,
"original_line": 656,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhy `doit()`?\n\n@author:\nYeah actually not needed. Will change it asap. Anything else?"
}
] |
53adee580afb2ce4a31ccd2909d6e272b0c65245
|
diff --git a/sympy/series/gruntz.py b/sympy/series/gruntz.py
index e857f14c9d2f..12aa2dd467cb 100644
--- a/sympy/series/gruntz.py
+++ b/sympy/series/gruntz.py
@@ -628,7 +628,7 @@ def rewrite(e, Omega, x, wsym):
# Some parts of sympy have difficulty computing series expansions with
# non-integral exponents. The following heuristic improves the situation:
exponent = reduce(ilcm, denominators, 1)
- f = f.xreplace({wsym: wsym**exponent})
+ f = f.subs({wsym: wsym**exponent})
logw /= exponent
return f, logw
diff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
index 8da9c0cbfeb4..ea4edd52e1d4 100644
--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
@@ -652,10 +652,18 @@ def test_issue_18306():
assert limit(sin(sqrt(x))/sqrt(sin(x)), x, 0, '+') == 1
+def test_issue_18378():
+ assert limit(log(exp(3*x) + x)/log(exp(x) + x**100), x, oo) == 3
+
+
def test_issue_18442():
assert limit(tan(x)**(2**(sqrt(pi))), x, oo, dir='-') == AccumBounds(-oo, oo)
+def test_issue_18482():
+ assert limit((2*exp(3*x)/(exp(2*x) + 1))**(1/x), x, oo) == exp(1)
+
+
def test_issue_18501():
assert limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1), x, 1, '+') == oo
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19254@8adfdbe
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,254
|
Improvement_of_dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K)
|
So, this is our change in the `dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K)` method. Also, we have replace the old value in the test_factortools.py file. If it is asked, we can cite our test_file with the comparison of the bounds. As it was mentioned, we have not create a new method but just change the code in the `dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K)`.
Fixes #19253
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
`dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K)` implemented with Knuth-Cohen
#### Other comments
As it was mentioned in the issue, `dmp_zz_mignotte_bound(f, u, K)` should also be cared of.
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* polys
* improvement of `dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K)` by Knuth-Cohen bound
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-05-04T13:38:13Z
|
sympy.polys.factortools.dmp_zz_mignotte_bound improvement
The method `dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K)` can be significantly improved by using the **Knuth-Cohen bound** instead. After our research with Prof. Ag.Akritas we have implemented the Knuth-Cohen bound among others, and compare them among dozens of polynomials with different degree, density and coefficients range. Considering the results and the feedback from Mr.Kalevi Suominen, our proposal is that the mignotte_bound should be replaced by the knuth-cohen bound.
Also, `dmp_zz_mignotte_bound(f, u, K)` for mutli-variants polynomials should be replaced appropriately.
|
[
{
"body": "The method `dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K)` can be significantly improved by using the **Knuth-Cohen bound** instead. After our research with Prof. Ag.Akritas we have implemented the Knuth-Cohen bound among others, and compare them among dozens of polynomials with different degree, density and coefficients range. Considering the results and the feedback from Mr.Kalevi Suominen, our proposal is that the mignotte_bound should be replaced by the knuth-cohen bound.\r\nAlso, `dmp_zz_mignotte_bound(f, u, K)` for mutli-variants polynomials should be replaced appropriately.",
"number": 19253,
"title": "sympy.polys.factortools.dmp_zz_mignotte_bound improvement"
}
] |
e0ef1da13e2ab2a77866c05246f73c871ca9388c
|
{
"head_commit": "8adfdbed18e6a0e06d862213752d2cb96a84218a",
"head_commit_message": "19253_Replacement_of_dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K)\n\nSo, this is our change in the `dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K)` method. Also, we have replace the old value in the test_factortools.py file. If it is asked, we can cite our test_file with the comparison of the bounds.",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/polys/factortools.py b/sympy/polys/factortools.py\nindex 93298f47e671..99b754382a9e 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/factortools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/factortools.py\n@@ -124,13 +124,29 @@ def dmp_trial_division(f, factors, u, K):\n \n \n def dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K):\n- \"\"\"Mignotte bound for univariate polynomials in `K[x]`. \"\"\"\n- a = dup_max_norm(f, K)\n- b = abs(dup_LC(f, K))\n- n = dup_degree(f)\n-\n- return K.sqrt(K(n + 1))*2**n*a*b\n+ \"\"\"\n+ The Knuth-Cohen variant of Mignotte bound for\n+ univariate polynomials in `K[x]`.\n \n+ Reference: John Abbott, Journal of Symbolic Computation 50 (2013) 532–563.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ d = dup_degree(f)\n+ delta = _ceil( d / 2 )\n+ \n+ # euclidean-norm\n+ eucl_norm = K.sqrt( sum( [cf**2 for cf in f] ) )\n+\n+ # biggest values of binomial coefficients (p. 538 of reference)\n+ t1 = binomial( delta - 1, _ceil( delta / 2 ) )\n+ t2 = binomial( delta - 1, _ceil( delta / 2 ) - 1 )\n+\n+ lc = abs( dup_LC(f, K) ) # leading coefficient\n+ \n+ bound = t1 * eucl_norm + t2 * lc # (p. 538 of reference)\n+ \n+ bound = _ceil( bound / 2 ) * 2 # round up to even integer\n+ \n+ return bound + dup_max_norm(f, K) # add max_coeff for irreducible polys\n \n def dmp_zz_mignotte_bound(f, u, K):\n \"\"\"Mignotte bound for multivariate polynomials in `K[X]`. \"\"\"\n@@ -1147,7 +1163,7 @@ def dmp_ext_factor(f, u, K):\n return lc, []\n \n f, F = dmp_sqf_part(f, u, K), f\n- s, g, r = dmp_sqf_norm(F, u, K)\n+ s, g, r = dmp_sqf_norm(f, u, K)\n \n factors = dmp_factor_list_include(r, u, K.dom)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py\nindex 7bcd9357569a..77524e43deff 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py\n@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ def test_dmp_trial_division():\n \n def test_dup_zz_mignotte_bound():\n R, x = ring(\"x\", ZZ)\n- assert R.dup_zz_mignotte_bound(2*x**2 + 3*x + 4) == 32\n+ assert R.dup_zz_mignotte_bound(2*x**2 + 3*x + 4) == 6\n \n \n def test_dmp_zz_mignotte_bound():\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -124,13 +124,29 @@ def dmp_trial_division(f, factors, u, K):\n \n \n def dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K):\n- \"\"\"Mignotte bound for univariate polynomials in `K[x]`. \"\"\"\n- a = dup_max_norm(f, K)\n- b = abs(dup_LC(f, K))\n- n = dup_degree(f)\n-\n- return K.sqrt(K(n + 1))*2**n*a*b\n+ \"\"\"\n+ The Knuth-Cohen variant of Mignotte bound for\n+ univariate polynomials in `K[x]`.\n \n+ Reference: John Abbott, Journal of Symbolic Computation 50 (2013) 532–563.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ d = dup_degree(f)\n+ delta = _ceil( d / 2 )\n+ \n+ # euclidean-norm\n+ eucl_norm = K.sqrt( sum( [cf**2 for cf in f] ) )\n+\n+ # biggest values of binomial coefficients (p. 538 of reference)\n+ t1 = binomial( delta - 1, _ceil( delta / 2 ) )",
"line": null,
"original_line": 140,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/polys/factortools.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n`binomial` is not defined.\n\n@author:\nYou are right, checking the log now i see: \"ImportError: cannot import name 'binomial' from partially initialized module 'sympy' (most likely due to a circular import)\"\r\nWhat is the correct way of importing the binomial function?\n\n@user2:\nIf you want to resolve the circular import issue, you should import inside the function block itself."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -124,13 +124,29 @@ def dmp_trial_division(f, factors, u, K):\n \n \n def dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K):\n- \"\"\"Mignotte bound for univariate polynomials in `K[x]`. \"\"\"\n- a = dup_max_norm(f, K)\n- b = abs(dup_LC(f, K))\n- n = dup_degree(f)\n-\n- return K.sqrt(K(n + 1))*2**n*a*b\n+ \"\"\"\n+ The Knuth-Cohen variant of Mignotte bound for\n+ univariate polynomials in `K[x]`.\n \n+ Reference: John Abbott, Journal of Symbolic Computation 50 (2013) 532–563.",
"line": null,
"original_line": 131,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/polys/factortools.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nPlease see other methods on how to include references.\n\n@author:\nCan you please give me a link with this?\n\n@user1:\nHave a look at [references](https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/8adfdbed18e6a0e06d862213752d2cb96a84218a/sympy/polys/factortools.py#L182)\n\n@author:\nThink i got it right!"
}
] |
ad5638b5189f92bcda642b93d195a5e4746c8166
|
diff --git a/sympy/polys/factortools.py b/sympy/polys/factortools.py
index 93298f47e671..cfa59ae9b8b5 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/factortools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/factortools.py
@@ -124,13 +124,64 @@ def dmp_trial_division(f, factors, u, K):
def dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f, K):
- """Mignotte bound for univariate polynomials in `K[x]`. """
- a = dup_max_norm(f, K)
- b = abs(dup_LC(f, K))
- n = dup_degree(f)
+ """
+ The Knuth-Cohen variant of Mignotte bound for
+ univariate polynomials in `K[x]`.
- return K.sqrt(K(n + 1))*2**n*a*b
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy.polys import ring, ZZ
+ >>> R, x = ring("x", ZZ)
+
+ >>> f = x**3 + 14*x**2 + 56*x + 64
+ >>> R.dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f)
+ 152
+
+ By checking `factor(f)` we can see that max coeff is 8
+
+ Also consider a case that `f` is irreducible for example `f = 2*x**2 + 3*x + 4`
+ To avoid a bug for these cases, we return the bound plus the max coefficient of `f`
+
+ >>> f = 2*x**2 + 3*x + 4
+ >>> R.dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f)
+ 6
+
+ Lastly,To see the difference between the new and the old Mignotte bound
+ consider the irreducible polynomial::
+
+ >>> f = 87*x**7 + 4*x**6 + 80*x**5 + 17*x**4 + 9*x**3 + 12*x**2 + 49*x + 26
+ >>> R.dup_zz_mignotte_bound(f)
+ 744
+
+ The new Mignotte bound is 744 whereas the old one (SymPy 1.5.1) is 1937664.
+
+
+ References
+ ==========
+
+ ..[1] [Abbott2013]_
+
+ """
+ from sympy import binomial
+
+ d = dup_degree(f)
+ delta = _ceil(d / 2)
+ delta2 = _ceil(delta / 2)
+
+ # euclidean-norm
+ eucl_norm = K.sqrt( sum( [cf**2 for cf in f] ) )
+
+ # biggest values of binomial coefficients (p. 538 of reference)
+ t1 = binomial(delta - 1, delta2)
+ t2 = binomial(delta - 1, delta2 - 1)
+
+ lc = K.abs(dup_LC(f, K)) # leading coefficient
+ bound = t1 * eucl_norm + t2 * lc # (p. 538 of reference)
+ bound += dup_max_norm(f, K) # add max coeff for irreducible polys
+ bound = _ceil(bound / 2) * 2 # round up to even integer
+ return bound
def dmp_zz_mignotte_bound(f, u, K):
"""Mignotte bound for multivariate polynomials in `K[X]`. """
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py
index 7bcd9357569a..34fbe8826711 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_factortools.py
@@ -27,7 +27,8 @@ def test_dmp_trial_division():
def test_dup_zz_mignotte_bound():
R, x = ring("x", ZZ)
- assert R.dup_zz_mignotte_bound(2*x**2 + 3*x + 4) == 32
+ assert R.dup_zz_mignotte_bound(2*x**2 + 3*x + 4) == 6
+ assert R.dup_zz_mignotte_bound(x**3 + 14*x**2 + 56*x + 64) == 152
def test_dmp_zz_mignotte_bound():
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Performance Optimizations"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-19093@bcb7880
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,093
|
Various block matrix improvements
|
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #2460
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Various improvements regarding BlockMatrix:
- Improve inversion of 2x2 block matrices
- Add assumption handlers for OneMatrix
- Raise more correct and more specific exceptions for matrices
- Allow creating BlockDiagMatrix from mutable matrices
- Improve evaluation of BlockMatrix trace/determinant
- Fix BlockDiagMatrix with non-square blocks
#### Other comments
Please let me know if smaller pull requests are better.
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-04-08T21:22:25Z
|
Regression: can't make expressions with mutable BlockDiagMatrix's
This used to work in 0.7.3 :
``` Python
>>> from sympy import Matrix, BlockDiagMatrix
>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z
>>> bdm1 = BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([x]), Matrix([y]))
>>> bdm2 = BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([y]), Matrix([z]))
>>> bdm1 + bdm2
TypeError: unhashable type: 'MutableDenseMatrix'
```
|
The solution clearly is that BlockDiagMatrix should convert MutableMatrix to ImmutableMatrix.
I bisected to b085bab7427ce6b5c2ad7657f216445659b5c4a1
|
[
{
"body": "This used to work in 0.7.3 :\n\n``` Python\n>>> from sympy import Matrix, BlockDiagMatrix\n>>> from sympy.abc import x, y, z\n>>> bdm1 = BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([x]), Matrix([y]))\n>>> bdm2 = BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([y]), Matrix([z]))\n>>> bdm1 + bdm2\nTypeError: unhashable type: 'MutableDenseMatrix'\n```\n",
"number": 2460,
"title": "Regression: can't make expressions with mutable BlockDiagMatrix's"
}
] |
64d28fe0534f6993695d11244ea740f783958dc8
|
{
"head_commit": "bcb78804ce7ff60864697ccf023fd31c66a98721",
"head_commit_message": "Improve inversion of 2x2 block matrices\n\nIt previously tried to apply the formula even when A wasn't square. It now\nalso considers invertibility of matrices to choose which formula to apply.",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/matrices.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/matrices.py\nindex 98762511fab7..e1f60893e7a8 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/matrices.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/matrices.py\n@@ -78,6 +78,8 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):\n def ZeroMatrix(expr, assumptions):\n return ask(Q.square(expr), assumptions)\n \n+ OneMatrix = ZeroMatrix\n+\n @staticmethod\n def Transpose(expr, assumptions):\n return ask(Q.symmetric(expr.arg), assumptions)\n@@ -138,6 +140,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):\n \n ZeroMatrix = staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysFalse)\n \n+ @staticmethod\n+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):\n+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1\n+\n @staticmethod\n def Transpose(expr, assumptions):\n return ask(Q.invertible(expr.arg), assumptions)\n@@ -286,6 +292,10 @@ def MatPow(expr, assumptions):\n \n ZeroMatrix = staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysFalse)\n \n+ @staticmethod\n+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):\n+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1\n+\n @staticmethod\n def Transpose(expr, assumptions):\n return ask(Q.fullrank(expr.arg), assumptions)\n@@ -337,6 +347,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):\n \n ZeroMatrix = staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysFalse)\n \n+ @staticmethod\n+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):\n+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1\n+\n @staticmethod\n def Transpose(expr, assumptions):\n return ask(Q.positive_definite(expr.arg), assumptions)\n@@ -386,6 +400,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):\n \n Identity, ZeroMatrix = [staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysTrue)]*2\n \n+ @staticmethod\n+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):\n+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1\n+\n @staticmethod\n def Transpose(expr, assumptions):\n return ask(Q.lower_triangular(expr.arg), assumptions)\n@@ -439,6 +457,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):\n \n Identity, ZeroMatrix = [staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysTrue)]*2\n \n+ @staticmethod\n+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):\n+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1\n+\n @staticmethod\n def Transpose(expr, assumptions):\n return ask(Q.upper_triangular(expr.arg), assumptions)\n@@ -502,6 +524,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):\n def ZeroMatrix(expr, assumptions):\n return True\n \n+ @staticmethod\n+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):\n+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1\n+\n @staticmethod\n def Transpose(expr, assumptions):\n return ask(Q.diagonal(expr.arg), assumptions)\n@@ -567,7 +593,7 @@ def MatPow(expr, assumptions):\n \n HadamardProduct, Determinant, Trace, Transpose = [MatAdd]*4\n \n- ZeroMatrix, Identity = [staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysTrue)]*2\n+ ZeroMatrix, OneMatrix, Identity = [staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysTrue)]*3\n \n MatMul = staticmethod(partial(MatMul_elements, Q.integer_elements,\n Q.integer))\ndiff --git a/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_matrices.py b/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_matrices.py\nindex d5176e29c67e..0888c1e9a42e 100644\n--- a/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_matrices.py\n+++ b/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_matrices.py\n@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@\n from sympy import Q, ask, Symbol, DiagMatrix, DiagonalMatrix\n from sympy.matrices.expressions import (MatrixSymbol, Identity, ZeroMatrix,\n- Trace, MatrixSlice, Determinant)\n+ OneMatrix, Trace, MatrixSlice, Determinant)\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.factorizations import LofLU\n from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL\n \n@@ -29,6 +29,8 @@ def test_invertible():\n assert ask(Q.invertible(X.I)) is True\n assert ask(Q.invertible(Identity(3))) is True\n assert ask(Q.invertible(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.invertible(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.invertible(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False\n assert ask(Q.invertible(X), Q.fullrank(X) & Q.square(X))\n \n def test_singular():\n@@ -58,6 +60,9 @@ def test_symmetric():\n assert ask(Q.symmetric(V1.T*(V1 + V2))) is True\n assert ask(Q.symmetric(V1.T*(V1 + V2) + A1x1)) is True\n assert ask(Q.symmetric(MatrixSlice(Y, (0, 1), (1, 2)))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.symmetric(Identity(3))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.symmetric(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.symmetric(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is True\n \n def _test_orthogonal_unitary(predicate):\n assert ask(predicate(X), predicate(X))\n@@ -89,6 +94,8 @@ def test_fullrank():\n assert ask(Q.fullrank(X*Z), Q.fullrank(X) & Q.fullrank(Z)) is True\n assert ask(Q.fullrank(Identity(3))) is True\n assert ask(Q.fullrank(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.fullrank(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.fullrank(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False\n assert ask(Q.invertible(X), ~Q.fullrank(X)) == False\n \n \n@@ -107,6 +114,8 @@ def test_positive_definite():\n assert not ask(Q.positive_definite(Y.T*X*Y), Q.positive_definite(X))\n assert ask(Q.positive_definite(Identity(3))) is True\n assert ask(Q.positive_definite(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.positive_definite(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.positive_definite(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False\n assert ask(Q.positive_definite(X + Z), Q.positive_definite(X) &\n Q.positive_definite(Z)) is True\n assert not ask(Q.positive_definite(-X), Q.positive_definite(X))\n@@ -119,6 +128,11 @@ def test_triangular():\n Q.lower_triangular(Z)) is True\n assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(Identity(3))) is True\n assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.upper_triangular(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.upper_triangular(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False\n+ assert ask(Q.upper_triangular(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False\n assert ask(Q.triangular(X), Q.unit_triangular(X))\n assert ask(Q.upper_triangular(X**3), Q.upper_triangular(X))\n assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(X**3), Q.lower_triangular(X))\n@@ -128,6 +142,8 @@ def test_diagonal():\n assert ask(Q.diagonal(X + Z.T + Identity(2)), Q.diagonal(X) &\n Q.diagonal(Z)) is True\n assert ask(Q.diagonal(ZeroMatrix(3, 3)))\n+ assert ask(Q.diagonal(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True\n+ assert ask(Q.diagonal(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False\n assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(X) & Q.upper_triangular(X), Q.diagonal(X))\n assert ask(Q.diagonal(X), Q.lower_triangular(X) & Q.upper_triangular(X))\n assert ask(Q.symmetric(X), Q.diagonal(X))\n@@ -214,6 +230,7 @@ def test_matrix_element_sets():\n assert ask(Q.complex(X[1, 2]), Q.complex_elements(X))\n assert ask(Q.integer_elements(Identity(3)))\n assert ask(Q.integer_elements(ZeroMatrix(3, 3)))\n+ assert ask(Q.integer_elements(OneMatrix(3, 3)))\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.fourier import DFT\n assert ask(Q.complex_elements(DFT(3)))\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py\nindex 0f55936effdd..a8fda1eaef7a 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py\n@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@\n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n from sympy import ask, Q\n-from sympy.core import Basic, Add\n+from sympy.core import Basic, Add, Mul, S\n+from sympy.matrices.common import NonInvertibleMatrixError\n from sympy.strategies import typed, exhaust, condition, do_one, unpack\n from sympy.strategies.traverse import bottom_up\n from sympy.utilities import sift\n@@ -12,11 +13,11 @@\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.matadd import MatAdd\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.matpow import MatPow\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.transpose import Transpose, transpose\n-from sympy.matrices.expressions.trace import Trace\n+from sympy.matrices.expressions.trace import trace\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.determinant import det, Determinant\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.slice import MatrixSlice\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.inverse import Inverse\n-from sympy.matrices import Matrix, ShapeError\n+from sympy.matrices import Matrix, ShapeError, MutableMatrix\n from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import re, im\n \n class BlockMatrix(MatrixExpr):\n@@ -186,12 +187,14 @@ def _eval_transpose(self):\n \n def _eval_trace(self):\n if self.rowblocksizes == self.colblocksizes:\n- return Add(*[Trace(self.blocks[i, i])\n+ return Add(*[trace(self.blocks[i, i])\n for i in range(self.blockshape[0])])\n raise NotImplementedError(\n \"Can't perform trace of irregular blockshape\")\n \n def _eval_determinant(self):\n+ if self.blockshape == (1, 1):\n+ return det(self.blocks[0, 0])\n if self.blockshape == (2, 2):\n [[A, B],\n [C, D]] = self.blocks.tolist()\n@@ -306,6 +309,7 @@ class BlockDiagMatrix(BlockMatrix):\n sympy.matrices.dense.diag\n \"\"\"\n def __new__(cls, *mats):\n+ mats = [m.as_immutable() if isinstance(m, MutableMatrix) else m for m in mats]\n return Basic.__new__(BlockDiagMatrix, *mats)\n \n @property\n@@ -339,8 +343,22 @@ def rowblocksizes(self):\n def colblocksizes(self):\n return [block.cols for block in self.args]\n \n+ def _all_square_blocks(self):\n+ \"\"\"Returns true if all blocks are square\"\"\"\n+ return all(mat.is_square for mat in self.args)\n+\n+ def _eval_determinant(self):\n+ if self._all_square_blocks():\n+ return Mul(*[det(mat) for mat in self.args])\n+ # At least one block is non-square. Since the entire matrix must be square we know there must\n+ # be at least two blocks in this matrix, in which case the entire matrix is necessarily rank-deficient\n+ return S.Zero\n+\n def _eval_inverse(self, expand='ignored'):\n- return BlockDiagMatrix(*[mat.inverse() for mat in self.args])\n+ if self._all_square_blocks():\n+ return BlockDiagMatrix(*[mat.inverse() for mat in self.args])\n+ # See comment in _eval_determinant()\n+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError('Matrix det == 0; not invertible.')\n \n def _eval_transpose(self):\n return BlockDiagMatrix(*[mat.transpose() for mat in self.args])\n@@ -526,7 +544,7 @@ def bc_transpose(expr):\n \n def bc_inverse(expr):\n if isinstance(expr.arg, BlockDiagMatrix):\n- return expr._eval_inverse()\n+ return expr.inverse()\n \n expr2 = blockinverse_1x1(expr)\n if expr != expr2:\n@@ -540,15 +558,36 @@ def blockinverse_1x1(expr):\n return expr\n \n def blockinverse_2x2(expr):\n- if isinstance(expr.arg, BlockMatrix) and expr.arg.blockshape == (2, 2):\n+ if isinstance(expr.arg, BlockMatrix) and expr.arg.blockshape == (2, 2) and expr.arg.blocks[0, 0].is_square:\n # Cite: The Matrix Cookbook Section 9.1.3\n [[A, B],\n [C, D]] = expr.arg.blocks.tolist()\n \n- return BlockMatrix([[ (A - B*D.I*C).I, (-A).I*B*(D - C*A.I*B).I],\n- [-(D - C*A.I*B).I*C*A.I, (D - C*A.I*B).I]])\n- else:\n- return expr\n+ # Use one or the other formula, depending on whether A or D is known to be invertible or at least not known\n+ # to not be invertible. Note that invertAbility of the other expressions M is not checked.\n+ A_invertible = ask(Q.invertible(A))\n+ D_invertible = ask(Q.invertible(D))\n+ if A_invertible == True:\n+ invert_A = True\n+ elif D_invertible == True:\n+ invert_A = False\n+ elif A_invertible != False:\n+ invert_A = True\n+ elif D_invertible != False:\n+ invert_A = False\n+ else:\n+ invert_A = True\n+\n+ if invert_A:\n+ AI = A.I\n+ MI = (D - C * AI * B).I\n+ return BlockMatrix([[AI + AI * B * MI * C * AI, -AI * B * MI], [-MI * C * AI, MI]])\n+ else:\n+ DI = D.I\n+ MI = (A - B * DI * C).I\n+ return BlockMatrix([[MI, -MI * B * DI], [-DI * C * MI, DI + DI * C * MI * B * DI]])\n+\n+ return expr\n \n def deblock(B):\n \"\"\" Flatten a BlockMatrix of BlockMatrices \"\"\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/determinant.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/determinant.py\nindex f0b568510030..9df21dbcf86b 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/determinant.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/determinant.py\n@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@\n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n from sympy import Basic, Expr, S, sympify\n-from .matexpr import ShapeError\n+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError\n \n \n class Determinant(Expr):\n@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ def __new__(cls, mat):\n raise TypeError(\"Input to Determinant, %s, not a matrix\" % str(mat))\n \n if not mat.is_square:\n- raise ShapeError(\"Det of a non-square matrix\")\n+ raise NonSquareMatrixError(\"Det of a non-square matrix\")\n \n return Basic.__new__(cls, mat)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/inverse.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/inverse.py\nindex 7bfe41299220..97d7c9f7a4a6 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/inverse.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/inverse.py\n@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n from sympy.core import S, Basic\n \n-from sympy.matrices.expressions.matexpr import ShapeError\n+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.matpow import MatPow\n \n \n@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ def __new__(cls, mat, exp=S.NegativeOne):\n if not mat.is_Matrix:\n raise TypeError(\"mat should be a matrix\")\n if not mat.is_square:\n- raise ShapeError(\"Inverse of non-square matrix %s\" % mat)\n+ raise NonSquareMatrixError(\"Inverse of non-square matrix %s\" % mat)\n return Basic.__new__(cls, mat, exp)\n \n @property\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\nindex c4dcd4aedcf8..155f72d8b225 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\n@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@\n from sympy.core.sympify import SympifyError, _sympify\n from sympy.functions import conjugate, adjoint\n from sympy.functions.special.tensor_functions import KroneckerDelta\n-from sympy.matrices import ShapeError\n+from sympy.matrices.common import ShapeError, NonSquareMatrixError, NonInvertibleMatrixError\n from sympy.simplify import simplify\n from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent\n \n@@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ def __rmatmul__(self, other):\n @call_highest_priority('__rpow__')\n def __pow__(self, other):\n if not self.is_square:\n- raise ShapeError(\"Power of non-square matrix %s\" % self)\n+ raise NonSquareMatrixError(\"Power of non-square matrix %s\" % self)\n elif self.is_Identity:\n return self\n elif other == S.Zero:\n@@ -265,6 +265,8 @@ def T(self):\n return self.transpose()\n \n def inverse(self):\n+ if not self.is_square:\n+ raise NonSquareMatrixError('Inverse of non-square matrix')\n return self._eval_inverse()\n \n def inv(self):\n@@ -969,11 +971,11 @@ def shape(self):\n @call_highest_priority('__rpow__')\n def __pow__(self, other):\n if other != 1 and not self.is_square:\n- raise ShapeError(\"Power of non-square matrix %s\" % self)\n+ raise NonSquareMatrixError(\"Power of non-square matrix %s\" % self)\n if other == 0:\n return Identity(self.rows)\n if other < 1:\n- raise ValueError(\"Matrix det == 0; not invertible.\")\n+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError(\"Matrix det == 0; not invertible\")\n return self\n \n def _eval_transpose(self):\n@@ -985,6 +987,9 @@ def _eval_trace(self):\n def _eval_determinant(self):\n return S.Zero\n \n+ def _eval_inverse(self):\n+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError(\"Matrix det == 0; not invertible.\")\n+\n def conjugate(self):\n return self\n \n@@ -1069,8 +1074,13 @@ def _eval_transpose(self):\n def _eval_trace(self):\n return S.One*self.rows\n \n+ def _is_1x1(self):\n+ \"\"\"Returns true if the matrix is known to be 1x1\"\"\"\n+ shape = self.shape\n+ return Eq(shape[0], 1) & Eq(shape[1], 1)\n+\n def _eval_determinant(self):\n- condition = Eq(self.shape[0], 1) & Eq(self.shape[1], 1)\n+ condition = self._is_1x1()\n if condition == True:\n return S.One\n elif condition == False:\n@@ -1079,6 +1089,15 @@ def _eval_determinant(self):\n from sympy import Determinant\n return Determinant(self)\n \n+ def _eval_inverse(self):\n+ condition = self._is_1x1()\n+ if condition == True:\n+ return Identity(1)\n+ elif condition == False:\n+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError(\"Matrix det == 0; not invertible.\")\n+ else:\n+ return Inverse(self)\n+\n def conjugate(self):\n return self\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py\nindex ca372a38ba78..d64746d0fd71 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py\n@@ -1,9 +1,11 @@\n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n-from .matexpr import MatrixExpr, ShapeError, Identity, ZeroMatrix\n+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError\n+from .matexpr import MatrixExpr, Identity, ZeroMatrix\n from sympy.core import S\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n from sympy.matrices import MatrixBase\n+from sympy.matrices.common import NonInvertibleMatrixError\n \n from .permutation import PermutationMatrix\n \n@@ -40,7 +42,7 @@ def _entry(self, i, j, **kwargs):\n if isinstance(A, MatPow):\n # We still have a MatPow, make an explicit MatMul out of it.\n if not A.base.is_square:\n- raise ShapeError(\"Power of non-square matrix %s\" % A.base)\n+ raise NonSquareMatrixError(\"Power of non-square matrix %s\" % A.base)\n elif A.exp.is_Integer and A.exp.is_positive:\n A = MatMul(*[A.base for k in range(A.exp)])\n #elif A.exp.is_Integer and self.exp.is_negative:\n@@ -74,7 +76,7 @@ def doit(self, **kwargs):\n return base.func(Identity(base.shape[0]))\n return Identity(base.shape[0])\n elif isinstance(base, ZeroMatrix) and exp.is_negative:\n- raise ValueError(\"Matrix determinant is 0, not invertible.\")\n+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError(\"Matrix determinant is 0, not invertible\")\n elif isinstance(base, (Identity, ZeroMatrix)):\n return base\n elif isinstance(base, PermutationMatrix):\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_blockmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_blockmatrix.py\nindex 07d8d3ce0e5b..d92fbe5a36a6 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_blockmatrix.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_blockmatrix.py\n@@ -1,10 +1,12 @@\n+from sympy import Trace\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.blockmatrix import (\n block_collapse, bc_matmul, bc_block_plus_ident, BlockDiagMatrix,\n BlockMatrix, bc_dist, bc_matadd, bc_transpose, bc_inverse,\n blockcut, reblock_2x2, deblock)\n from sympy.matrices.expressions import (MatrixSymbol, Identity,\n- Inverse, trace, Transpose, det, ZeroMatrix)\n+ Inverse, trace, Transpose, det, ZeroMatrix, OneMatrix)\n+from sympy.matrices.common import NonInvertibleMatrixError\n from sympy.matrices import (\n Matrix, ImmutableMatrix, ImmutableSparseMatrix)\n from sympy.core import Tuple, symbols, Expr\n@@ -119,6 +121,7 @@ def test_BlockMatrix_trace():\n A, B, C, D = [MatrixSymbol(s, 3, 3) for s in 'ABCD']\n X = BlockMatrix([[A, B], [C, D]])\n assert trace(X) == trace(A) + trace(D)\n+ assert trace(BlockMatrix([ZeroMatrix(n, n)])) == 0\n \n def test_BlockMatrix_Determinant():\n A, B, C, D = [MatrixSymbol(s, 3, 3) for s in 'ABCD']\n@@ -128,6 +131,8 @@ def test_BlockMatrix_Determinant():\n assert det(X) == det(A) * det(D - C*A.I*B)\n \n assert isinstance(det(X), Expr)\n+ assert det(BlockMatrix([A])) == det(A)\n+ assert det(BlockMatrix([ZeroMatrix(n, n)])) == 0\n \n def test_squareBlockMatrix():\n A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)\n@@ -147,9 +152,6 @@ def test_squareBlockMatrix():\n assert (X * MatrixSymbol('Q', n + m, n + m)).is_MatMul\n \n assert block_collapse(Y.I) == A.I\n- assert block_collapse(X.inverse()) == BlockMatrix([\n- [(-B*D.I*C + A).I, -A.I*B*(D + -C*A.I*B).I],\n- [-(D - C*A.I*B).I*C*A.I, (D - C*A.I*B).I]])\n \n assert isinstance(X.inverse(), Inverse)\n \n@@ -158,6 +160,34 @@ def test_squareBlockMatrix():\n Z = BlockMatrix([[Identity(n), B], [C, D]])\n assert not Z.is_Identity\n \n+def test_BlockMatrix_inverse():\n+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, m)\n+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', n, n)\n+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', m, m)\n+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', m, n)\n+ X = BlockMatrix([[A, B], [C, D]])\n+ assert X.is_square\n+ assert isinstance(block_collapse(X.inverse()), Inverse) # Can't inverse when A, D aren't square\n+\n+ # test code path for non-invertible D matrix\n+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)\n+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', n, m)\n+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', m, n)\n+ D = OneMatrix(m, m)\n+ X = BlockMatrix([[A, B], [C, D]])\n+ assert block_collapse(X.inverse()) == BlockMatrix([\n+ [A.I + A.I * B * (D - C * A.I * B).I * C * A.I, -A.I * B * (D - C * A.I * B).I],\n+ [-(D - C * A.I * B).I * C * A.I, (D - C * A.I * B).I],\n+ ])\n+\n+ # test code path for non-invertible A matrix\n+ A = OneMatrix(n, n)\n+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', m, m)\n+ X = BlockMatrix([[A, B], [C, D]])\n+ assert block_collapse(X.inverse()) == BlockMatrix([\n+ [(A - B * D.I * C).I, -(A - B * D.I * C).I * B * D.I],\n+ [-D.I * C * (A - B * D.I * C).I, D.I + D.I * C * (A - B * D.I * C).I * B * D.I],\n+ ])\n \n def test_BlockDiagMatrix():\n A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)\n@@ -191,6 +221,58 @@ def test_BlockDiagMatrix():\n assert (X._blockmul(M)).is_MatMul\n assert (X._blockadd(M)).is_MatAdd\n \n+def test_BlockDiagMatrix_nonsquare():\n+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, m)\n+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', k, l)\n+ X = BlockDiagMatrix(A, B)\n+ assert X.shape == (n + k, m + l)\n+ assert X.shape == (n + k, m + l)\n+ assert X.rowblocksizes == [n, k]\n+ assert X.colblocksizes == [m, l]\n+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', n, m)\n+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', k, l)\n+ Y = BlockDiagMatrix(C, D)\n+ assert block_collapse(X + Y) == BlockDiagMatrix(A + C, B + D)\n+ assert block_collapse(X * Y.T) == BlockDiagMatrix(A * C.T, B * D.T)\n+ raises(NonInvertibleMatrixError, lambda: BlockDiagMatrix(A, C.T).inverse())\n+\n+def test_BlockDiagMatrix_determinant():\n+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)\n+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', m, m)\n+ assert det(BlockDiagMatrix()) == 1\n+ assert det(BlockDiagMatrix(A)) == det(A)\n+ assert det(BlockDiagMatrix(A, B)) == det(A) * det(B)\n+\n+ # non-square blocks\n+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', m, n)\n+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', n, m)\n+ assert det(BlockDiagMatrix(C, D)) == 0\n+\n+def test_BlockDiagMatrix_trace():\n+ assert trace(BlockDiagMatrix()) == 0\n+ assert trace(BlockDiagMatrix(ZeroMatrix(n, n))) == 0\n+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)\n+ assert trace(BlockDiagMatrix(A)) == trace(A)\n+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', m, m)\n+ assert trace(BlockDiagMatrix(A, B)) == trace(A) + trace(B)\n+\n+ # non-square blocks\n+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', m, n)\n+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', n, m)\n+ assert isinstance(trace(BlockDiagMatrix(C, D)), Trace)\n+\n+def test_BlockDiagMatrix_transpose():\n+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, m)\n+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', k, l)\n+ assert transpose(BlockDiagMatrix()) == BlockDiagMatrix()\n+ assert transpose(BlockDiagMatrix(A)) == BlockDiagMatrix(A.T)\n+ assert transpose(BlockDiagMatrix(A, B)) == BlockDiagMatrix(A.T, B.T)\n+\n+def test_issue_2460():\n+ bdm1 = BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([i]), Matrix([j]))\n+ bdm2 = BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([k]), Matrix([l]))\n+ assert block_collapse(bdm1 + bdm2) == BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([i + k]), Matrix([j + l]))\n+\n def test_blockcut():\n A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, m)\n B = blockcut(A, (n/2, n/2), (m/2, m/2))\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_inverse.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_inverse.py\nindex 2fad7f110614..4fe753870f7f 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_inverse.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_inverse.py\n@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@\n from sympy.core import symbols, S\n-from sympy.matrices.expressions import MatrixSymbol, Inverse, MatPow\n-from sympy.matrices import eye, Identity, ShapeError\n+from sympy.matrices.expressions import MatrixSymbol, Inverse, MatPow, ZeroMatrix, OneMatrix\n+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError, NonInvertibleMatrixError\n+from sympy.matrices import eye, Identity\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises\n from sympy import refine, Q\n \n@@ -13,9 +14,6 @@\n \n \n def test_inverse():\n- raises(ShapeError, lambda: Inverse(A))\n- raises(ShapeError, lambda: Inverse(A*B))\n-\n assert Inverse(C).args == (C, S.NegativeOne)\n assert Inverse(C).shape == (n, n)\n assert Inverse(A*E).shape == (n, n)\n@@ -41,6 +39,16 @@ def test_inverse():\n assert Inverse(eye(3)).doit() == eye(3)\n assert Inverse(eye(3)).doit(deep=False) == eye(3)\n \n+ assert OneMatrix(1, 1).I == Identity(1)\n+ assert isinstance(OneMatrix(n, n).I, Inverse)\n+\n+def test_inverse_non_invertible():\n+ raises(NonSquareMatrixError, lambda: Inverse(A))\n+ raises(NonSquareMatrixError, lambda: Inverse(A*B))\n+ raises(NonSquareMatrixError, lambda: ZeroMatrix(n, m).I)\n+ raises(NonInvertibleMatrixError, lambda: ZeroMatrix(n, n).I)\n+ raises(NonSquareMatrixError, lambda: OneMatrix(n, m).I)\n+ raises(NonInvertibleMatrixError, lambda: OneMatrix(2, 2).I)\n \n def test_refine():\n assert refine(C.I, Q.orthogonal(C)) == C.T\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py\nindex 3beccefd35a7..5fa6985badf7 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py\n@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@\n \n from sympy import Basic, Expr, sympify, S\n from sympy.matrices.matrices import MatrixBase\n-from .matexpr import ShapeError\n+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError\n \n \n class Trace(Expr):\n@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ def __new__(cls, mat):\n raise TypeError(\"input to Trace, %s, is not a matrix\" % str(mat))\n \n if not mat.is_square:\n- raise ShapeError(\"Trace of a non-square matrix\")\n+ raise NonSquareMatrixError(\"Trace of a non-square matrix\")\n \n return Basic.__new__(cls, mat)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/matrices.py b/sympy/matrices/matrices.py\nindex 69be53842860..cfc55bf9fde1 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/matrices.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/matrices.py\n@@ -2141,7 +2141,7 @@ def vech(self, diagonal=True, check_symmetry=True):\n \n c = self.cols\n if c != self.rows:\n- raise ShapeError(\"Matrix must be square\")\n+ raise NonSquareMatrixError(\"Matrix must be square\")\n if check_symmetry:\n self.simplify()\n if self != self.transpose():\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\nindex ecc408c22fd9..00ab5320e9ed 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n@@ -41,6 +41,7 @@\n separatevars)\n from sympy.simplify.sqrtdenest import sqrt_depth\n from sympy.simplify.fu import TR1\n+from sympy.matrices.common import NonInvertibleMatrixError\n from sympy.matrices import Matrix, zeros\n from sympy.polys import roots, cancel, factor, Poly, degree\n from sympy.polys.polyerrors import GeneratorsNeeded, PolynomialError\n@@ -2645,7 +2646,7 @@ def inv_quick(M):\n n = M.rows\n d = det(M)\n if d == S.Zero:\n- raise ValueError(\"Matrix det == 0; not invertible.\")\n+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError(\"Matrix det == 0; not invertible\")\n ret = zeros(n)\n s1 = -1\n for i in range(n):\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\nindex 5d6b5e70a335..e29fc349be2e 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py\n@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@\n Lambda, Mul, Dummy, IndexedBase, Add,\n linsolve, eye, Or, Not, Intersection,\n Union, Expr, Function, exp, cacheit,\n- Ge, Piecewise, Symbol)\n+ Ge, Piecewise, Symbol, NonSquareMatrixError)\n from sympy.core.relational import Relational\n from sympy.logic.boolalg import Boolean\n from sympy.stats.joint_rv import JointDistributionHandmade, JointDistribution\n@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ def _matrix_checks(matrix):\n raise TypeError(\"Transition probabilities either should \"\n \"be a Matrix or a MatrixSymbol.\")\n if matrix.shape[0] != matrix.shape[1]:\n- raise ValueError(\"%s is not a square matrix\"%(matrix))\n+ raise NonSquareMatrixError(\"%s is not a square matrix\"%(matrix))\n if isinstance(matrix, Matrix):\n matrix = ImmutableMatrix(matrix.tolist())\n return matrix\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -306,6 +309,7 @@ class BlockDiagMatrix(BlockMatrix):\n sympy.matrices.dense.diag\n \"\"\"\n def __new__(cls, *mats):\n+ mats = [m.as_immutable() if isinstance(m, MutableMatrix) else m for m in mats]",
"line": null,
"original_line": 312,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIt's better to use _sympify here."
}
] |
4987d2ea0a218b9c698bcbec98b91ec95e5b5e88
|
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/matrices.py b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/matrices.py
index 98762511fab7..e1f60893e7a8 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/handlers/matrices.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/handlers/matrices.py
@@ -78,6 +78,8 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):
def ZeroMatrix(expr, assumptions):
return ask(Q.square(expr), assumptions)
+ OneMatrix = ZeroMatrix
+
@staticmethod
def Transpose(expr, assumptions):
return ask(Q.symmetric(expr.arg), assumptions)
@@ -138,6 +140,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):
ZeroMatrix = staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysFalse)
+ @staticmethod
+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):
+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1
+
@staticmethod
def Transpose(expr, assumptions):
return ask(Q.invertible(expr.arg), assumptions)
@@ -286,6 +292,10 @@ def MatPow(expr, assumptions):
ZeroMatrix = staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysFalse)
+ @staticmethod
+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):
+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1
+
@staticmethod
def Transpose(expr, assumptions):
return ask(Q.fullrank(expr.arg), assumptions)
@@ -337,6 +347,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):
ZeroMatrix = staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysFalse)
+ @staticmethod
+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):
+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1
+
@staticmethod
def Transpose(expr, assumptions):
return ask(Q.positive_definite(expr.arg), assumptions)
@@ -386,6 +400,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):
Identity, ZeroMatrix = [staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysTrue)]*2
+ @staticmethod
+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):
+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1
+
@staticmethod
def Transpose(expr, assumptions):
return ask(Q.lower_triangular(expr.arg), assumptions)
@@ -439,6 +457,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):
Identity, ZeroMatrix = [staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysTrue)]*2
+ @staticmethod
+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):
+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1
+
@staticmethod
def Transpose(expr, assumptions):
return ask(Q.upper_triangular(expr.arg), assumptions)
@@ -502,6 +524,10 @@ def MatrixSymbol(expr, assumptions):
def ZeroMatrix(expr, assumptions):
return True
+ @staticmethod
+ def OneMatrix(expr, assumptions):
+ return expr.shape[0] == 1 and expr.shape[1] == 1
+
@staticmethod
def Transpose(expr, assumptions):
return ask(Q.diagonal(expr.arg), assumptions)
@@ -567,7 +593,7 @@ def MatPow(expr, assumptions):
HadamardProduct, Determinant, Trace, Transpose = [MatAdd]*4
- ZeroMatrix, Identity = [staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysTrue)]*2
+ ZeroMatrix, OneMatrix, Identity = [staticmethod(CommonHandler.AlwaysTrue)]*3
MatMul = staticmethod(partial(MatMul_elements, Q.integer_elements,
Q.integer))
diff --git a/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_matrices.py b/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_matrices.py
index d5176e29c67e..0888c1e9a42e 100644
--- a/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_matrices.py
+++ b/sympy/assumptions/tests/test_matrices.py
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
from sympy import Q, ask, Symbol, DiagMatrix, DiagonalMatrix
from sympy.matrices.expressions import (MatrixSymbol, Identity, ZeroMatrix,
- Trace, MatrixSlice, Determinant)
+ OneMatrix, Trace, MatrixSlice, Determinant)
from sympy.matrices.expressions.factorizations import LofLU
from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL
@@ -29,6 +29,8 @@ def test_invertible():
assert ask(Q.invertible(X.I)) is True
assert ask(Q.invertible(Identity(3))) is True
assert ask(Q.invertible(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is False
+ assert ask(Q.invertible(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.invertible(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False
assert ask(Q.invertible(X), Q.fullrank(X) & Q.square(X))
def test_singular():
@@ -58,6 +60,9 @@ def test_symmetric():
assert ask(Q.symmetric(V1.T*(V1 + V2))) is True
assert ask(Q.symmetric(V1.T*(V1 + V2) + A1x1)) is True
assert ask(Q.symmetric(MatrixSlice(Y, (0, 1), (1, 2)))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.symmetric(Identity(3))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.symmetric(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.symmetric(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is True
def _test_orthogonal_unitary(predicate):
assert ask(predicate(X), predicate(X))
@@ -89,6 +94,8 @@ def test_fullrank():
assert ask(Q.fullrank(X*Z), Q.fullrank(X) & Q.fullrank(Z)) is True
assert ask(Q.fullrank(Identity(3))) is True
assert ask(Q.fullrank(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is False
+ assert ask(Q.fullrank(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.fullrank(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False
assert ask(Q.invertible(X), ~Q.fullrank(X)) == False
@@ -107,6 +114,8 @@ def test_positive_definite():
assert not ask(Q.positive_definite(Y.T*X*Y), Q.positive_definite(X))
assert ask(Q.positive_definite(Identity(3))) is True
assert ask(Q.positive_definite(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is False
+ assert ask(Q.positive_definite(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.positive_definite(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False
assert ask(Q.positive_definite(X + Z), Q.positive_definite(X) &
Q.positive_definite(Z)) is True
assert not ask(Q.positive_definite(-X), Q.positive_definite(X))
@@ -119,6 +128,11 @@ def test_triangular():
Q.lower_triangular(Z)) is True
assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(Identity(3))) is True
assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.upper_triangular(ZeroMatrix(3, 3))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.upper_triangular(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False
+ assert ask(Q.upper_triangular(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False
assert ask(Q.triangular(X), Q.unit_triangular(X))
assert ask(Q.upper_triangular(X**3), Q.upper_triangular(X))
assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(X**3), Q.lower_triangular(X))
@@ -128,6 +142,8 @@ def test_diagonal():
assert ask(Q.diagonal(X + Z.T + Identity(2)), Q.diagonal(X) &
Q.diagonal(Z)) is True
assert ask(Q.diagonal(ZeroMatrix(3, 3)))
+ assert ask(Q.diagonal(OneMatrix(1, 1))) is True
+ assert ask(Q.diagonal(OneMatrix(3, 3))) is False
assert ask(Q.lower_triangular(X) & Q.upper_triangular(X), Q.diagonal(X))
assert ask(Q.diagonal(X), Q.lower_triangular(X) & Q.upper_triangular(X))
assert ask(Q.symmetric(X), Q.diagonal(X))
@@ -214,6 +230,7 @@ def test_matrix_element_sets():
assert ask(Q.complex(X[1, 2]), Q.complex_elements(X))
assert ask(Q.integer_elements(Identity(3)))
assert ask(Q.integer_elements(ZeroMatrix(3, 3)))
+ assert ask(Q.integer_elements(OneMatrix(3, 3)))
from sympy.matrices.expressions.fourier import DFT
assert ask(Q.complex_elements(DFT(3)))
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py
index 0f55936effdd..4572c3442345 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/blockmatrix.py
@@ -1,7 +1,9 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
from sympy import ask, Q
-from sympy.core import Basic, Add
+from sympy.core import Basic, Add, Mul, S
+from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonInvertibleMatrixError
from sympy.strategies import typed, exhaust, condition, do_one, unpack
from sympy.strategies.traverse import bottom_up
from sympy.utilities import sift
@@ -12,7 +14,7 @@
from sympy.matrices.expressions.matadd import MatAdd
from sympy.matrices.expressions.matpow import MatPow
from sympy.matrices.expressions.transpose import Transpose, transpose
-from sympy.matrices.expressions.trace import Trace
+from sympy.matrices.expressions.trace import trace
from sympy.matrices.expressions.determinant import det, Determinant
from sympy.matrices.expressions.slice import MatrixSlice
from sympy.matrices.expressions.inverse import Inverse
@@ -186,12 +188,14 @@ def _eval_transpose(self):
def _eval_trace(self):
if self.rowblocksizes == self.colblocksizes:
- return Add(*[Trace(self.blocks[i, i])
+ return Add(*[trace(self.blocks[i, i])
for i in range(self.blockshape[0])])
raise NotImplementedError(
"Can't perform trace of irregular blockshape")
def _eval_determinant(self):
+ if self.blockshape == (1, 1):
+ return det(self.blocks[0, 0])
if self.blockshape == (2, 2):
[[A, B],
[C, D]] = self.blocks.tolist()
@@ -306,7 +310,7 @@ class BlockDiagMatrix(BlockMatrix):
sympy.matrices.dense.diag
"""
def __new__(cls, *mats):
- return Basic.__new__(BlockDiagMatrix, *mats)
+ return Basic.__new__(BlockDiagMatrix, *[_sympify(m) for m in mats])
@property
def diag(self):
@@ -339,8 +343,22 @@ def rowblocksizes(self):
def colblocksizes(self):
return [block.cols for block in self.args]
+ def _all_square_blocks(self):
+ """Returns true if all blocks are square"""
+ return all(mat.is_square for mat in self.args)
+
+ def _eval_determinant(self):
+ if self._all_square_blocks():
+ return Mul(*[det(mat) for mat in self.args])
+ # At least one block is non-square. Since the entire matrix must be square we know there must
+ # be at least two blocks in this matrix, in which case the entire matrix is necessarily rank-deficient
+ return S.Zero
+
def _eval_inverse(self, expand='ignored'):
- return BlockDiagMatrix(*[mat.inverse() for mat in self.args])
+ if self._all_square_blocks():
+ return BlockDiagMatrix(*[mat.inverse() for mat in self.args])
+ # See comment in _eval_determinant()
+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError('Matrix det == 0; not invertible.')
def _eval_transpose(self):
return BlockDiagMatrix(*[mat.transpose() for mat in self.args])
@@ -526,7 +544,7 @@ def bc_transpose(expr):
def bc_inverse(expr):
if isinstance(expr.arg, BlockDiagMatrix):
- return expr._eval_inverse()
+ return expr.inverse()
expr2 = blockinverse_1x1(expr)
if expr != expr2:
@@ -540,15 +558,36 @@ def blockinverse_1x1(expr):
return expr
def blockinverse_2x2(expr):
- if isinstance(expr.arg, BlockMatrix) and expr.arg.blockshape == (2, 2):
+ if isinstance(expr.arg, BlockMatrix) and expr.arg.blockshape == (2, 2) and expr.arg.blocks[0, 0].is_square:
# Cite: The Matrix Cookbook Section 9.1.3
[[A, B],
[C, D]] = expr.arg.blocks.tolist()
- return BlockMatrix([[ (A - B*D.I*C).I, (-A).I*B*(D - C*A.I*B).I],
- [-(D - C*A.I*B).I*C*A.I, (D - C*A.I*B).I]])
- else:
- return expr
+ # Use one or the other formula, depending on whether A or D is known to be invertible or at least not known
+ # to not be invertible. Note that invertAbility of the other expressions M is not checked.
+ A_invertible = ask(Q.invertible(A))
+ D_invertible = ask(Q.invertible(D))
+ if A_invertible == True:
+ invert_A = True
+ elif D_invertible == True:
+ invert_A = False
+ elif A_invertible != False:
+ invert_A = True
+ elif D_invertible != False:
+ invert_A = False
+ else:
+ invert_A = True
+
+ if invert_A:
+ AI = A.I
+ MI = (D - C * AI * B).I
+ return BlockMatrix([[AI + AI * B * MI * C * AI, -AI * B * MI], [-MI * C * AI, MI]])
+ else:
+ DI = D.I
+ MI = (A - B * DI * C).I
+ return BlockMatrix([[MI, -MI * B * DI], [-DI * C * MI, DI + DI * C * MI * B * DI]])
+
+ return expr
def deblock(B):
""" Flatten a BlockMatrix of BlockMatrices """
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/determinant.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/determinant.py
index f0b568510030..9df21dbcf86b 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/determinant.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/determinant.py
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
from sympy import Basic, Expr, S, sympify
-from .matexpr import ShapeError
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError
class Determinant(Expr):
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ def __new__(cls, mat):
raise TypeError("Input to Determinant, %s, not a matrix" % str(mat))
if not mat.is_square:
- raise ShapeError("Det of a non-square matrix")
+ raise NonSquareMatrixError("Det of a non-square matrix")
return Basic.__new__(cls, mat)
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py
index c152ece87736..5f1be929cf7e 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
from sympy.core import Mul, sympify
+from sympy.matrices.common import ShapeError
from sympy.matrices.expressions.matexpr import (
- MatrixExpr, ShapeError, OneMatrix, ZeroMatrix
+ MatrixExpr, OneMatrix, ZeroMatrix
)
from sympy.strategies import (
unpack, flatten, condition, exhaust, rm_id, sort
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/inverse.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/inverse.py
index 7bfe41299220..97d7c9f7a4a6 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/inverse.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/inverse.py
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
from sympy.core import S, Basic
-from sympy.matrices.expressions.matexpr import ShapeError
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError
from sympy.matrices.expressions.matpow import MatPow
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ def __new__(cls, mat, exp=S.NegativeOne):
if not mat.is_Matrix:
raise TypeError("mat should be a matrix")
if not mat.is_square:
- raise ShapeError("Inverse of non-square matrix %s" % mat)
+ raise NonSquareMatrixError("Inverse of non-square matrix %s" % mat)
return Basic.__new__(cls, mat, exp)
@property
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/kronecker.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/kronecker.py
index ab278e82869b..7ede71fd1325 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/kronecker.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/kronecker.py
@@ -4,7 +4,8 @@
from sympy.core import Mul, prod, sympify
from sympy.functions import adjoint
-from sympy.matrices.expressions.matexpr import MatrixExpr, ShapeError, Identity
+from sympy.matrices.common import ShapeError
+from sympy.matrices.expressions.matexpr import MatrixExpr, Identity
from sympy.matrices.expressions.transpose import transpose
from sympy.matrices.matrices import MatrixBase
from sympy.strategies import (
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py
index f5290ff539c4..ad867f8ce892 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py
@@ -5,12 +5,13 @@
from sympy.core import Add, Basic, sympify
from sympy.functions import adjoint
+from sympy.matrices.common import ShapeError
from sympy.matrices.matrices import MatrixBase
from sympy.matrices.expressions.transpose import transpose
from sympy.strategies import (rm_id, unpack, flatten, sort, condition,
exhaust, do_one, glom)
-from sympy.matrices.expressions.matexpr import (MatrixExpr, ShapeError,
- ZeroMatrix, GenericZeroMatrix)
+from sympy.matrices.expressions.matexpr import (MatrixExpr, ZeroMatrix,
+ GenericZeroMatrix)
from sympy.utilities import default_sort_key, sift
# XXX: MatAdd should perhaps not subclass directly from Add
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
index c4dcd4aedcf8..dea1f8a8667b 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
from sympy.core.sympify import SympifyError, _sympify
from sympy.functions import conjugate, adjoint
from sympy.functions.special.tensor_functions import KroneckerDelta
-from sympy.matrices import ShapeError
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError, NonInvertibleMatrixError
from sympy.simplify import simplify
from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent
@@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ def __rmatmul__(self, other):
@call_highest_priority('__rpow__')
def __pow__(self, other):
if not self.is_square:
- raise ShapeError("Power of non-square matrix %s" % self)
+ raise NonSquareMatrixError("Power of non-square matrix %s" % self)
elif self.is_Identity:
return self
elif other == S.Zero:
@@ -265,6 +265,8 @@ def T(self):
return self.transpose()
def inverse(self):
+ if not self.is_square:
+ raise NonSquareMatrixError('Inverse of non-square matrix')
return self._eval_inverse()
def inv(self):
@@ -969,11 +971,11 @@ def shape(self):
@call_highest_priority('__rpow__')
def __pow__(self, other):
if other != 1 and not self.is_square:
- raise ShapeError("Power of non-square matrix %s" % self)
+ raise NonSquareMatrixError("Power of non-square matrix %s" % self)
if other == 0:
return Identity(self.rows)
if other < 1:
- raise ValueError("Matrix det == 0; not invertible.")
+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError("Matrix det == 0; not invertible")
return self
def _eval_transpose(self):
@@ -985,6 +987,9 @@ def _eval_trace(self):
def _eval_determinant(self):
return S.Zero
+ def _eval_inverse(self):
+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError("Matrix det == 0; not invertible.")
+
def conjugate(self):
return self
@@ -1069,8 +1074,13 @@ def _eval_transpose(self):
def _eval_trace(self):
return S.One*self.rows
+ def _is_1x1(self):
+ """Returns true if the matrix is known to be 1x1"""
+ shape = self.shape
+ return Eq(shape[0], 1) & Eq(shape[1], 1)
+
def _eval_determinant(self):
- condition = Eq(self.shape[0], 1) & Eq(self.shape[1], 1)
+ condition = self._is_1x1()
if condition == True:
return S.One
elif condition == False:
@@ -1079,6 +1089,15 @@ def _eval_determinant(self):
from sympy import Determinant
return Determinant(self)
+ def _eval_inverse(self):
+ condition = self._is_1x1()
+ if condition == True:
+ return Identity(1)
+ elif condition == False:
+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError("Matrix det == 0; not invertible.")
+ else:
+ return Inverse(self)
+
def conjugate(self):
return self
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
index d84f0b8365bb..adeed1d7dc40 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
@@ -5,11 +5,12 @@
from sympy.functions import adjoint
from sympy.strategies import (rm_id, unpack, typed, flatten, exhaust,
do_one, new)
+from sympy.matrices.common import ShapeError
from sympy.matrices.matrices import MatrixBase
from .inverse import Inverse
from .matexpr import \
- MatrixExpr, ShapeError, Identity, ZeroMatrix, OneMatrix, GenericIdentity
+ MatrixExpr, Identity, ZeroMatrix, OneMatrix, GenericIdentity
from .matpow import MatPow
from .transpose import transpose
from .permutation import PermutationMatrix
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py
index ca372a38ba78..d64746d0fd71 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py
@@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
-from .matexpr import MatrixExpr, ShapeError, Identity, ZeroMatrix
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError
+from .matexpr import MatrixExpr, Identity, ZeroMatrix
from sympy.core import S
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
from sympy.matrices import MatrixBase
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonInvertibleMatrixError
from .permutation import PermutationMatrix
@@ -40,7 +42,7 @@ def _entry(self, i, j, **kwargs):
if isinstance(A, MatPow):
# We still have a MatPow, make an explicit MatMul out of it.
if not A.base.is_square:
- raise ShapeError("Power of non-square matrix %s" % A.base)
+ raise NonSquareMatrixError("Power of non-square matrix %s" % A.base)
elif A.exp.is_Integer and A.exp.is_positive:
A = MatMul(*[A.base for k in range(A.exp)])
#elif A.exp.is_Integer and self.exp.is_negative:
@@ -74,7 +76,7 @@ def doit(self, **kwargs):
return base.func(Identity(base.shape[0]))
return Identity(base.shape[0])
elif isinstance(base, ZeroMatrix) and exp.is_negative:
- raise ValueError("Matrix determinant is 0, not invertible.")
+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError("Matrix determinant is 0, not invertible")
elif isinstance(base, (Identity, ZeroMatrix)):
return base
elif isinstance(base, PermutationMatrix):
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_blockmatrix.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_blockmatrix.py
index 07d8d3ce0e5b..d92fbe5a36a6 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_blockmatrix.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_blockmatrix.py
@@ -1,10 +1,12 @@
+from sympy import Trace
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
from sympy.matrices.expressions.blockmatrix import (
block_collapse, bc_matmul, bc_block_plus_ident, BlockDiagMatrix,
BlockMatrix, bc_dist, bc_matadd, bc_transpose, bc_inverse,
blockcut, reblock_2x2, deblock)
from sympy.matrices.expressions import (MatrixSymbol, Identity,
- Inverse, trace, Transpose, det, ZeroMatrix)
+ Inverse, trace, Transpose, det, ZeroMatrix, OneMatrix)
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonInvertibleMatrixError
from sympy.matrices import (
Matrix, ImmutableMatrix, ImmutableSparseMatrix)
from sympy.core import Tuple, symbols, Expr
@@ -119,6 +121,7 @@ def test_BlockMatrix_trace():
A, B, C, D = [MatrixSymbol(s, 3, 3) for s in 'ABCD']
X = BlockMatrix([[A, B], [C, D]])
assert trace(X) == trace(A) + trace(D)
+ assert trace(BlockMatrix([ZeroMatrix(n, n)])) == 0
def test_BlockMatrix_Determinant():
A, B, C, D = [MatrixSymbol(s, 3, 3) for s in 'ABCD']
@@ -128,6 +131,8 @@ def test_BlockMatrix_Determinant():
assert det(X) == det(A) * det(D - C*A.I*B)
assert isinstance(det(X), Expr)
+ assert det(BlockMatrix([A])) == det(A)
+ assert det(BlockMatrix([ZeroMatrix(n, n)])) == 0
def test_squareBlockMatrix():
A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)
@@ -147,9 +152,6 @@ def test_squareBlockMatrix():
assert (X * MatrixSymbol('Q', n + m, n + m)).is_MatMul
assert block_collapse(Y.I) == A.I
- assert block_collapse(X.inverse()) == BlockMatrix([
- [(-B*D.I*C + A).I, -A.I*B*(D + -C*A.I*B).I],
- [-(D - C*A.I*B).I*C*A.I, (D - C*A.I*B).I]])
assert isinstance(X.inverse(), Inverse)
@@ -158,6 +160,34 @@ def test_squareBlockMatrix():
Z = BlockMatrix([[Identity(n), B], [C, D]])
assert not Z.is_Identity
+def test_BlockMatrix_inverse():
+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, m)
+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', n, n)
+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', m, m)
+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', m, n)
+ X = BlockMatrix([[A, B], [C, D]])
+ assert X.is_square
+ assert isinstance(block_collapse(X.inverse()), Inverse) # Can't inverse when A, D aren't square
+
+ # test code path for non-invertible D matrix
+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)
+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', n, m)
+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', m, n)
+ D = OneMatrix(m, m)
+ X = BlockMatrix([[A, B], [C, D]])
+ assert block_collapse(X.inverse()) == BlockMatrix([
+ [A.I + A.I * B * (D - C * A.I * B).I * C * A.I, -A.I * B * (D - C * A.I * B).I],
+ [-(D - C * A.I * B).I * C * A.I, (D - C * A.I * B).I],
+ ])
+
+ # test code path for non-invertible A matrix
+ A = OneMatrix(n, n)
+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', m, m)
+ X = BlockMatrix([[A, B], [C, D]])
+ assert block_collapse(X.inverse()) == BlockMatrix([
+ [(A - B * D.I * C).I, -(A - B * D.I * C).I * B * D.I],
+ [-D.I * C * (A - B * D.I * C).I, D.I + D.I * C * (A - B * D.I * C).I * B * D.I],
+ ])
def test_BlockDiagMatrix():
A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)
@@ -191,6 +221,58 @@ def test_BlockDiagMatrix():
assert (X._blockmul(M)).is_MatMul
assert (X._blockadd(M)).is_MatAdd
+def test_BlockDiagMatrix_nonsquare():
+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, m)
+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', k, l)
+ X = BlockDiagMatrix(A, B)
+ assert X.shape == (n + k, m + l)
+ assert X.shape == (n + k, m + l)
+ assert X.rowblocksizes == [n, k]
+ assert X.colblocksizes == [m, l]
+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', n, m)
+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', k, l)
+ Y = BlockDiagMatrix(C, D)
+ assert block_collapse(X + Y) == BlockDiagMatrix(A + C, B + D)
+ assert block_collapse(X * Y.T) == BlockDiagMatrix(A * C.T, B * D.T)
+ raises(NonInvertibleMatrixError, lambda: BlockDiagMatrix(A, C.T).inverse())
+
+def test_BlockDiagMatrix_determinant():
+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)
+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', m, m)
+ assert det(BlockDiagMatrix()) == 1
+ assert det(BlockDiagMatrix(A)) == det(A)
+ assert det(BlockDiagMatrix(A, B)) == det(A) * det(B)
+
+ # non-square blocks
+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', m, n)
+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', n, m)
+ assert det(BlockDiagMatrix(C, D)) == 0
+
+def test_BlockDiagMatrix_trace():
+ assert trace(BlockDiagMatrix()) == 0
+ assert trace(BlockDiagMatrix(ZeroMatrix(n, n))) == 0
+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, n)
+ assert trace(BlockDiagMatrix(A)) == trace(A)
+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', m, m)
+ assert trace(BlockDiagMatrix(A, B)) == trace(A) + trace(B)
+
+ # non-square blocks
+ C = MatrixSymbol('C', m, n)
+ D = MatrixSymbol('D', n, m)
+ assert isinstance(trace(BlockDiagMatrix(C, D)), Trace)
+
+def test_BlockDiagMatrix_transpose():
+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, m)
+ B = MatrixSymbol('B', k, l)
+ assert transpose(BlockDiagMatrix()) == BlockDiagMatrix()
+ assert transpose(BlockDiagMatrix(A)) == BlockDiagMatrix(A.T)
+ assert transpose(BlockDiagMatrix(A, B)) == BlockDiagMatrix(A.T, B.T)
+
+def test_issue_2460():
+ bdm1 = BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([i]), Matrix([j]))
+ bdm2 = BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([k]), Matrix([l]))
+ assert block_collapse(bdm1 + bdm2) == BlockDiagMatrix(Matrix([i + k]), Matrix([j + l]))
+
def test_blockcut():
A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, m)
B = blockcut(A, (n/2, n/2), (m/2, m/2))
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_inverse.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_inverse.py
index 2fad7f110614..4fe753870f7f 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_inverse.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_inverse.py
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
from sympy.core import symbols, S
-from sympy.matrices.expressions import MatrixSymbol, Inverse, MatPow
-from sympy.matrices import eye, Identity, ShapeError
+from sympy.matrices.expressions import MatrixSymbol, Inverse, MatPow, ZeroMatrix, OneMatrix
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError, NonInvertibleMatrixError
+from sympy.matrices import eye, Identity
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
from sympy import refine, Q
@@ -13,9 +14,6 @@
def test_inverse():
- raises(ShapeError, lambda: Inverse(A))
- raises(ShapeError, lambda: Inverse(A*B))
-
assert Inverse(C).args == (C, S.NegativeOne)
assert Inverse(C).shape == (n, n)
assert Inverse(A*E).shape == (n, n)
@@ -41,6 +39,16 @@ def test_inverse():
assert Inverse(eye(3)).doit() == eye(3)
assert Inverse(eye(3)).doit(deep=False) == eye(3)
+ assert OneMatrix(1, 1).I == Identity(1)
+ assert isinstance(OneMatrix(n, n).I, Inverse)
+
+def test_inverse_non_invertible():
+ raises(NonSquareMatrixError, lambda: Inverse(A))
+ raises(NonSquareMatrixError, lambda: Inverse(A*B))
+ raises(NonSquareMatrixError, lambda: ZeroMatrix(n, m).I)
+ raises(NonInvertibleMatrixError, lambda: ZeroMatrix(n, n).I)
+ raises(NonSquareMatrixError, lambda: OneMatrix(n, m).I)
+ raises(NonInvertibleMatrixError, lambda: OneMatrix(2, 2).I)
def test_refine():
assert refine(C.I, Q.orthogonal(C)) == C.T
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matpow.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matpow.py
index 55fe655c700f..b52d80751385 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matpow.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matpow.py
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
from sympy.core import symbols, pi, S
from sympy.matrices import Identity, MatrixSymbol, ImmutableMatrix, ZeroMatrix
from sympy.matrices.expressions import MatPow, MatAdd, MatMul
-from sympy.matrices.expressions.matexpr import ShapeError
+from sympy.matrices.common import ShapeError
n, m, l, k = symbols('n m l k', integer=True)
A = MatrixSymbol('A', n, m)
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py
index 3beccefd35a7..5fa6985badf7 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/trace.py
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
from sympy import Basic, Expr, sympify, S
from sympy.matrices.matrices import MatrixBase
-from .matexpr import ShapeError
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonSquareMatrixError
class Trace(Expr):
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ def __new__(cls, mat):
raise TypeError("input to Trace, %s, is not a matrix" % str(mat))
if not mat.is_square:
- raise ShapeError("Trace of a non-square matrix")
+ raise NonSquareMatrixError("Trace of a non-square matrix")
return Basic.__new__(cls, mat)
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/matrices.py b/sympy/matrices/matrices.py
index 69be53842860..cfc55bf9fde1 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/matrices.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/matrices.py
@@ -2141,7 +2141,7 @@ def vech(self, diagonal=True, check_symmetry=True):
c = self.cols
if c != self.rows:
- raise ShapeError("Matrix must be square")
+ raise NonSquareMatrixError("Matrix must be square")
if check_symmetry:
self.simplify()
if self != self.transpose():
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index ecc408c22fd9..00ab5320e9ed 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -41,6 +41,7 @@
separatevars)
from sympy.simplify.sqrtdenest import sqrt_depth
from sympy.simplify.fu import TR1
+from sympy.matrices.common import NonInvertibleMatrixError
from sympy.matrices import Matrix, zeros
from sympy.polys import roots, cancel, factor, Poly, degree
from sympy.polys.polyerrors import GeneratorsNeeded, PolynomialError
@@ -2645,7 +2646,7 @@ def inv_quick(M):
n = M.rows
d = det(M)
if d == S.Zero:
- raise ValueError("Matrix det == 0; not invertible.")
+ raise NonInvertibleMatrixError("Matrix det == 0; not invertible")
ret = zeros(n)
s1 = -1
for i in range(n):
diff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
index 5d6b5e70a335..e29fc349be2e 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
Lambda, Mul, Dummy, IndexedBase, Add,
linsolve, eye, Or, Not, Intersection,
Union, Expr, Function, exp, cacheit,
- Ge, Piecewise, Symbol)
+ Ge, Piecewise, Symbol, NonSquareMatrixError)
from sympy.core.relational import Relational
from sympy.logic.boolalg import Boolean
from sympy.stats.joint_rv import JointDistributionHandmade, JointDistribution
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ def _matrix_checks(matrix):
raise TypeError("Transition probabilities either should "
"be a Matrix or a MatrixSymbol.")
if matrix.shape[0] != matrix.shape[1]:
- raise ValueError("%s is not a square matrix"%(matrix))
+ raise NonSquareMatrixError("%s is not a square matrix"%(matrix))
if isinstance(matrix, Matrix):
matrix = ImmutableMatrix(matrix.tolist())
return matrix
|
{
"difficulty": "high",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19037@a927b13
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,037
|
Functions: Resolves Extraneous Variable in Limit results
|
Fixes: #18501
Fixes: #18997
Fixes: #19026
The root cause of the issue is the `_eval_nseries() function of Abs() class`.
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
**Previously:**
```
In[1]: limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1), x, 1, '+')
Out[1]: -oo*sign(log(_w)**3)
```
A bit of substitution was missing in `_eval_nseries() function of Abs() class in complexes.py` which was causing extraneous variable in Limit results.
**Now the limit evaluates correctly:**
```
In[1]: limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1), x, 1, '+')
Out[1]: oo
```
#### Other Comments
Regression Tests have been added.
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* functions
* Adds substitution to `_eval_nseries() function of Abs() class` resolving incorrect limit evaluations
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-03-31T14:07:57Z
|
Extraneous variable in limit result
`limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1),x,1,'+')` returns expression involving `w`:
```python
>>> limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1),x,1,'+')
-oo*sign(log(_w)**3)
```
Incorrect limit result involving Abs, returns expression involving a symbol
`limit(Abs(log(x)),x,0)` returns incorrect result. Similar result with `limit(Abs(log(Abs(x))),x,0)`
Both return expression `-oo*sign(log(_w))` involving a symbol `_w`
while `limit(log(Abs(x)),x,0)` works just fine.
```
>>> limit(Abs(log(x)),x,0)
-oo*sign(log(_w))
```
```
>>> limit(Abs(log(Abs(x))),x,0)
-oo*sign(log(_w))
```
```
>>> limit(log(Abs(x)),x,0)
-oo
```
Bug in Limit
There is a bug in limit
> x=symbols('x',positive=True)
limit(Abs(log(x)+1)/log(x),x,oo)
results in
> -sign(log(_w))
which is not the expected result. The expected result should be 1
|
[
{
"body": "`limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1),x,1,'+')` returns expression involving `w`:\r\n```python\r\n>>> limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1),x,1,'+')\r\n-oo*sign(log(_w)**3)\r\n```",
"number": 18501,
"title": "Extraneous variable in limit result"
},
{
"body": "`limit(Abs(log(x)),x,0)` returns incorrect result. Similar result with `limit(Abs(log(Abs(x))),x,0)`\r\n\r\nBoth return expression `-oo*sign(log(_w))` involving a symbol `_w`\r\n\r\nwhile `limit(log(Abs(x)),x,0)` works just fine.\r\n\r\n```\r\n>>> limit(Abs(log(x)),x,0)\r\n-oo*sign(log(_w))\r\n```\r\n```\r\n>>> limit(Abs(log(Abs(x))),x,0)\r\n-oo*sign(log(_w))\r\n```\r\n```\r\n>>> limit(log(Abs(x)),x,0)\r\n-oo\r\n```\r\n\r\n",
"number": 18997,
"title": "Incorrect limit result involving Abs, returns expression involving a symbol"
},
{
"body": "There is a bug in limit\r\n\r\n> x=symbols('x',positive=True)\r\n limit(Abs(log(x)+1)/log(x),x,oo)\r\n\r\nresults in \r\n\r\n> -sign(log(_w))\r\n\r\nwhich is not the expected result. The expected result should be 1",
"number": 19026,
"title": "Bug in Limit"
}
] |
2586bae98d76d12d98d2b21b33f9931df9dccac4
|
{
"head_commit": "a927b13f1e6f423f22b2f7d5bf0f5a4e8ac1b258",
"head_commit_message": "Made changes to fix a minor bug",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py\nindex fad4b28dae82..ac5e7a658568 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py\n@@ -591,6 +591,8 @@ def _eval_power(self, exponent):\n \n def _eval_nseries(self, x, n, logx):\n direction = self.args[0].leadterm(x)[0]\n+ if direction.has(log(x)):\n+ direction = direction.subs(log(x), logx)\n s = self.args[0]._eval_nseries(x, n=n, logx=logx)\n when = Eq(direction, 0)\n return Piecewise(\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/limitseq.py b/sympy/series/limitseq.py\nindex dec3cd328eb8..07e3f31ceb1e 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/limitseq.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/limitseq.py\n@@ -242,5 +242,5 @@ def limit_seq(expr, n=None, trials=5):\n # Maybe the absolute value is easier to deal with (though not if\n # it has a Sum). If it tends to 0, the limit is 0.\n elif not expr.has(Sum):\n- if _limit_seq(Abs(expr.xreplace({n: n_})), n_, trials).is_zero:\n+ if _limit_seq(Abs(expr.xreplace({n: n_})), n_, trials) is not None and _limit_seq(Abs(expr.xreplace({n: n_})), n_, trials).is_zero:\n return S.Zero\ndiff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\nindex 8a6fbcd50890..f523f0fdeff1 100644\n--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\n+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py\n@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@\n \n from sympy import (\n limit, exp, oo, log, sqrt, Limit, sin, floor, cos, ceiling,\n- atan, gamma, Symbol, S, pi, Integral, Rational, I,\n+ atan, Abs, gamma, Symbol, S, pi, Integral, Rational, I,\n tan, cot, integrate, Sum, sign, Function, subfactorial, symbols,\n binomial, simplify, frac, Float, sec, zoo, fresnelc, fresnels,\n acos, erfi, LambertW, factorial, Ei, EulerGamma)\n@@ -641,11 +641,26 @@ def test_issue_18442():\n assert limit(tan(x)**(2**(sqrt(pi))), x, oo, dir='-') == AccumBounds(-oo, oo)\n \n \n+def test_issue_18501():\n+ assert limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1), x, 1, '+') == oo\n+\n+\n def test_issue_18508():\n assert limit(sin(x)/sqrt(1-cos(x)), x, 0) == sqrt(2)\n assert limit(sin(x)/sqrt(1-cos(x)), x, 0, dir='+') == sqrt(2)\n assert limit(sin(x)/sqrt(1-cos(x)), x, 0, dir='-') == -sqrt(2)\n \n+\n+def test_issue_18997():\n+ assert limit(Abs(log(x)), x, 0) == oo\n+ assert limit(Abs(log(Abs(x))), x, 0) == oo\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_19026():\n+ x = Symbol('x', positive=True)\n+ assert limit(Abs(log(x) + 1)/log(x), x, oo) == 1\n+\n+\n def test_issue_13715():\n n = Symbol('n')\n p = Symbol('p', zero=True)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -242,5 +242,5 @@ def limit_seq(expr, n=None, trials=5):\n # Maybe the absolute value is easier to deal with (though not if\n # it has a Sum). If it tends to 0, the limit is 0.\n elif not expr.has(Sum):\n- if _limit_seq(Abs(expr.xreplace({n: n_})), n_, trials).is_zero:\n+ if _limit_seq(Abs(expr.xreplace({n: n_})), n_, trials) is not None and _limit_seq(Abs(expr.xreplace({n: n_})), n_, trials).is_zero:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 245,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/series/limitseq.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n`_limit_seq` should not be computed twice. Do something like this instead:\r\n\r\n lim = _limit_seq(Abs(expr.xreplace({n: n_})), n_, trials)\r\n if lim is not None and lim.is_zero:\n\n@author:\nOkay will make the changes."
}
] |
0007815efa13cdbf265a29038eadf26fa38dbb22
|
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
index fad4b28dae82..ac5e7a658568 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/complexes.py
@@ -591,6 +591,8 @@ def _eval_power(self, exponent):
def _eval_nseries(self, x, n, logx):
direction = self.args[0].leadterm(x)[0]
+ if direction.has(log(x)):
+ direction = direction.subs(log(x), logx)
s = self.args[0]._eval_nseries(x, n=n, logx=logx)
when = Eq(direction, 0)
return Piecewise(
diff --git a/sympy/series/limitseq.py b/sympy/series/limitseq.py
index dec3cd328eb8..c51cb9b92aa3 100644
--- a/sympy/series/limitseq.py
+++ b/sympy/series/limitseq.py
@@ -242,5 +242,6 @@ def limit_seq(expr, n=None, trials=5):
# Maybe the absolute value is easier to deal with (though not if
# it has a Sum). If it tends to 0, the limit is 0.
elif not expr.has(Sum):
- if _limit_seq(Abs(expr.xreplace({n: n_})), n_, trials).is_zero:
+ lim = _limit_seq(Abs(expr.xreplace({n: n_})), n_, trials)
+ if lim is not None and lim.is_zero:
return S.Zero
diff --git a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
index 8a6fbcd50890..f523f0fdeff1 100644
--- a/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
+++ b/sympy/series/tests/test_limits.py
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
from sympy import (
limit, exp, oo, log, sqrt, Limit, sin, floor, cos, ceiling,
- atan, gamma, Symbol, S, pi, Integral, Rational, I,
+ atan, Abs, gamma, Symbol, S, pi, Integral, Rational, I,
tan, cot, integrate, Sum, sign, Function, subfactorial, symbols,
binomial, simplify, frac, Float, sec, zoo, fresnelc, fresnels,
acos, erfi, LambertW, factorial, Ei, EulerGamma)
@@ -641,11 +641,26 @@ def test_issue_18442():
assert limit(tan(x)**(2**(sqrt(pi))), x, oo, dir='-') == AccumBounds(-oo, oo)
+def test_issue_18501():
+ assert limit(Abs(log(x - 1)**3 - 1), x, 1, '+') == oo
+
+
def test_issue_18508():
assert limit(sin(x)/sqrt(1-cos(x)), x, 0) == sqrt(2)
assert limit(sin(x)/sqrt(1-cos(x)), x, 0, dir='+') == sqrt(2)
assert limit(sin(x)/sqrt(1-cos(x)), x, 0, dir='-') == -sqrt(2)
+
+def test_issue_18997():
+ assert limit(Abs(log(x)), x, 0) == oo
+ assert limit(Abs(log(Abs(x))), x, 0) == oo
+
+
+def test_issue_19026():
+ x = Symbol('x', positive=True)
+ assert limit(Abs(log(x) + 1)/log(x), x, oo) == 1
+
+
def test_issue_13715():
n = Symbol('n')
p = Symbol('p', zero=True)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-18993@44a510f
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,993
|
Solves key error in creating polycyclic group, Improves _sift, induced_pcgs
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #18804
Fixes #18989
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
- Improved `collected_word`, `_sift`, `induced_pcgs`.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-03-28T16:43:16Z
|
KeyError in creating a polycylic group from Dihedral Group
I am getting this error when `n>2`and `n` is `even` is there any reason we are getting this?if yes should we raise a `exception` instead?
```
>>> G = DihedralGroup(10)
>>> A = G.polycyclic_group()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py", line 4862, in polycyclic_group
return PolycyclicGroup(pc_sequence, pc_series, relative_order, collector=None)
File "/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py", line 33, in __init__
self.collector = Collector(self.pcgs, pc_series, relative_order) if not collector else collector
File "/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py", line 80, in __init__
self.pc_presentation = self.pc_relators()
File "/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py", line 477, in pc_relators
word = self.collected_word(word)
File "/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py", line 318, in collected_word
w = self.minimal_uncollected_subword(word)
File "/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py", line 123, in minimal_uncollected_subword
if re[index[s1]] and (e1 < 0 or e1 > re[index[s1]]-1):
KeyError: x2**4
>>> G.is_solvable
True
```
creating an induced polycyclic sequence from Alt(4) group takes infinite time.
```
>>> a = AlternatingGroup(4)
>>> g = a.polycyclic_group()
>>> collector = g.collector
>>> gens = [a[0],a[1]]
>>> ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)
```
It does not evaluate.
|
Ping @jksuom @divyanshu132
I think this should work, may be there is some problem with the collection of word.
The problem seems in the `pc_relators` function because on line `335` of `pc_groups.py` this (`self.pc_presentation[key]`) is returning a `x2**4` which is a exponential value.
Mapped value can be exponential.
Replace that line with below lines.
```
presentation = self.pc_presentation[key].array_form
sym, exp = presentation[0]
word_ = ((w[0][0], r), (sym, q*exp))
```
Probably, this will fix the above issue.
@sylee957 Can I get your help in the above pr?
|
[
{
"body": "I am getting this error when `n>2`and `n` is `even` is there any reason we are getting this?if yes should we raise a `exception` instead?\r\n```\r\n>>> G = DihedralGroup(10)\r\n>>> A = G.polycyclic_group()\r\nTraceback (most recent call last):\r\n File \"<stdin>\", line 1, in <module>\r\n File \"/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/perm_groups.py\", line 4862, in polycyclic_group\r\n return PolycyclicGroup(pc_sequence, pc_series, relative_order, collector=None)\r\n File \"/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py\", line 33, in __init__\r\n self.collector = Collector(self.pcgs, pc_series, relative_order) if not collector else collector\r\n File \"/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py\", line 80, in __init__\r\n self.pc_presentation = self.pc_relators()\r\n File \"/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py\", line 477, in pc_relators\r\n word = self.collected_word(word)\r\n File \"/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py\", line 318, in collected_word\r\n w = self.minimal_uncollected_subword(word)\r\n File \"/home/mohit/Documents/sympy-master/sympy/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py\", line 123, in minimal_uncollected_subword\r\n if re[index[s1]] and (e1 < 0 or e1 > re[index[s1]]-1):\r\nKeyError: x2**4\r\n>>> G.is_solvable\r\nTrue\r\n```",
"number": 18804,
"title": "KeyError in creating a polycylic group from Dihedral Group"
},
{
"body": "```\r\n>>> a = AlternatingGroup(4)\r\n>>> g = a.polycyclic_group()\r\n>>> collector = g.collector\r\n>>> gens = [a[0],a[1]]\r\n>>> ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)\r\n```\r\nIt does not evaluate.",
"number": 18989,
"title": "creating an induced polycyclic sequence from Alt(4) group takes infinite time."
}
] |
3f305ce157071f9667a9c9dc395eeee537d1f939
|
{
"head_commit": "44a510fbe31bb89a7dc0ecbefb553295568718d9",
"head_commit_message": "changes example",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py\nindex 3080f5970ef1..a68be2b382c3 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py\n@@ -332,7 +332,9 @@ def collected_word(self, word):\n key = ((w[0][0], re), )\n key = free_group.dtype(key)\n if self.pc_presentation[key]:\n- word_ = ((w[0][0], r), (self.pc_presentation[key], q))\n+ presentation = self.pc_presentation[key].array_form\n+ sym, exp = presentation[0]\n+ word_ = ((w[0][0], r), (sym, q*exp))\n word_ = free_group.dtype(word_)\n else:\n if r != 0:\n@@ -603,7 +605,7 @@ def _sift(self, z, g):\n d = self.depth(h)\n while d < len(self.pcgs) and z[d-1] != 1:\n k = z[d-1]\n- e = self.leading_exponent(h)*self.leading_exponent(k**-1)\n+ e = self.leading_exponent(h)*(self.leading_exponent(k))**-1\n e = e % self.relative_order[d-1]\n h = k**-e*h\n d = self.depth(h)\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_pc_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_pc_groups.py\nindex ef4cdf3ee439..daaf07a50c76 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_pc_groups.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_pc_groups.py\n@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@\n from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation\n-from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup\n-\n+from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup, AlternatingGroup, DihedralGroup\n+from sympy.matrices import Matrix\n \n def test_pc_presentation():\n Groups = [SymmetricGroup(3), SymmetricGroup(4), SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(3),\n- SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(2), SymmetricGroup(8).sylow_subgroup(2)]\n+ SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(2), SymmetricGroup(8).sylow_subgroup(2), DihedralGroup(10)]\n \n S = SymmetricGroup(125).sylow_subgroup(5)\n G = S.derived_series()[2]\n@@ -73,18 +73,18 @@ def test_exponent_vector():\n \n \n def test_induced_pcgs():\n- G = SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(3)\n- PcGroup = G.polycyclic_group()\n- collector = PcGroup.collector\n- gens = [G[0], G[1]]\n- ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)\n- order = [gen.order() for gen in ipcgs]\n- assert order == [3, 3]\n-\n- G = SymmetricGroup(20).sylow_subgroup(2)\n- PcGroup = G.polycyclic_group()\n- collector = PcGroup.collector\n- gens = [G[0], G[1], G[2], G[3]]\n- ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)\n- order = [gen.order() for gen in ipcgs]\n- assert order ==[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]\n+ G = [SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(3), SymmetricGroup(20).sylow_subgroup(2), AlternatingGroup(4),\n+ DihedralGroup(4), SymmetricGroup(3), SymmetricGroup(4)]\n+\n+ for g in G:\n+ PcGroup = g.polycyclic_group()\n+ collector = PcGroup.collector\n+ gens = []\n+ genr = g.generators\n+ for i in range(len(genr)):\n+ gens.append(genr[i])\n+ ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)\n+ m = []\n+ for i in ipcgs:\n+ m.append(collector.exponent_vector(i))\n+ assert Matrix(m).is_upper\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -73,18 +73,18 @@ def test_exponent_vector():\n \n \n def test_induced_pcgs():\n- G = SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(3)\n- PcGroup = G.polycyclic_group()\n- collector = PcGroup.collector\n- gens = [G[0], G[1]]\n- ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)\n- order = [gen.order() for gen in ipcgs]\n- assert order == [3, 3]\n-\n- G = SymmetricGroup(20).sylow_subgroup(2)\n- PcGroup = G.polycyclic_group()\n- collector = PcGroup.collector\n- gens = [G[0], G[1], G[2], G[3]]\n- ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)\n- order = [gen.order() for gen in ipcgs]\n- assert order ==[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]\n+ G = [SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(3), SymmetricGroup(20).sylow_subgroup(2), AlternatingGroup(4),\n+ DihedralGroup(4), SymmetricGroup(3), SymmetricGroup(4)]\n+\n+ for g in G:\n+ PcGroup = g.polycyclic_group()\n+ collector = PcGroup.collector\n+ gens = []\n+ genr = g.generators\n+ for i in range(len(genr)):\n+ gens.append(genr[i])",
"line": null,
"original_line": 85,
"original_start_line": 82,
"path": "sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_pc_groups.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n`gens = [gen for gen in g.generators]`"
}
] |
3cb3027afa22219dfd6eca9e56f71b605143e171
|
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py
index 3080f5970ef1..a68be2b382c3 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/pc_groups.py
@@ -332,7 +332,9 @@ def collected_word(self, word):
key = ((w[0][0], re), )
key = free_group.dtype(key)
if self.pc_presentation[key]:
- word_ = ((w[0][0], r), (self.pc_presentation[key], q))
+ presentation = self.pc_presentation[key].array_form
+ sym, exp = presentation[0]
+ word_ = ((w[0][0], r), (sym, q*exp))
word_ = free_group.dtype(word_)
else:
if r != 0:
@@ -603,7 +605,7 @@ def _sift(self, z, g):
d = self.depth(h)
while d < len(self.pcgs) and z[d-1] != 1:
k = z[d-1]
- e = self.leading_exponent(h)*self.leading_exponent(k**-1)
+ e = self.leading_exponent(h)*(self.leading_exponent(k))**-1
e = e % self.relative_order[d-1]
h = k**-e*h
d = self.depth(h)
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_pc_groups.py b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_pc_groups.py
index ef4cdf3ee439..dbf11a992265 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_pc_groups.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/tests/test_pc_groups.py
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
from sympy.combinatorics.permutations import Permutation
-from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup
-
+from sympy.combinatorics.named_groups import SymmetricGroup, AlternatingGroup, DihedralGroup
+from sympy.matrices import Matrix
def test_pc_presentation():
Groups = [SymmetricGroup(3), SymmetricGroup(4), SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(3),
- SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(2), SymmetricGroup(8).sylow_subgroup(2)]
+ SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(2), SymmetricGroup(8).sylow_subgroup(2), DihedralGroup(10)]
S = SymmetricGroup(125).sylow_subgroup(5)
G = S.derived_series()[2]
@@ -73,18 +73,15 @@ def test_exponent_vector():
def test_induced_pcgs():
- G = SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(3)
- PcGroup = G.polycyclic_group()
- collector = PcGroup.collector
- gens = [G[0], G[1]]
- ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)
- order = [gen.order() for gen in ipcgs]
- assert order == [3, 3]
-
- G = SymmetricGroup(20).sylow_subgroup(2)
- PcGroup = G.polycyclic_group()
- collector = PcGroup.collector
- gens = [G[0], G[1], G[2], G[3]]
- ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)
- order = [gen.order() for gen in ipcgs]
- assert order ==[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]
+ G = [SymmetricGroup(9).sylow_subgroup(3), SymmetricGroup(20).sylow_subgroup(2), AlternatingGroup(4),
+ DihedralGroup(4), DihedralGroup(10), DihedralGroup(9), SymmetricGroup(3), SymmetricGroup(4)]
+
+ for g in G:
+ PcGroup = g.polycyclic_group()
+ collector = PcGroup.collector
+ gens = [gen for gen in g.generators]
+ ipcgs = collector.induced_pcgs(gens)
+ m = []
+ for i in ipcgs:
+ m.append(collector.exponent_vector(i))
+ assert Matrix(m).is_upper
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19304@ce9d4e1
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,304
|
[GSoC] Added `is_random` to check random expressions of stats
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
Added `is_random` function to check if expression contains random variables.
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #12283
References from #19299
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
* Added a function `is_random` to check if the expression contains random variables in it.
For example:
```python
>>> from sympy.stats.rv import is_random
>>> from sympy.stats import Normal, BernoulliProcess
>>> from sympy.abc import x
>>> X = Normal('X',1,2)
>>> is_random(X)
True
>>> is_random(X>3)
True
>>> is_random(x>3)
False
>>> is_random(x)
False
>>> Y = BernoulliProcess('Y',0.3)
>>> is_random(Y[2])
True
```
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* stats
* Added `is_random` in `sympy.stats.rv` to check if expression contains random variables
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
ping @czgdp1807 @Upabjojr @jmig5776
|
2020-05-13T06:19:30Z
|
SymPy stats expansion
Add
- `is_random` to every SymPy object (returns true if expression contains random symbols).
- test `is_random` on undefined functions and indexed bases.
- stats functions such as `P`, `E`, `var`, and `cov` should return their respective objects in case the `RandomSymbol` has no specified probability distribution.
|
May be, `is_random` property can be added to `Basic` class(or whatever is the top most parent class) which can compute it's value by using the `OR` over all the `is_random` values of the objects args. Default value of `Symbol.is_random` should be `False` and `RandomSymbol.is_random` should be `True` and since every expression contains symbols, so for an expression `is_random` can be computed in O(number of args) complexity.
@czgdp1807 since Python 3.5 methods can be added externally to the class through singledispatch.
We have dropped support for Python 2.7 and 3.4 this year, so we should start using this way in order not to overload too much `sympy/core`.
I see, that's also possible. However, any thoughts on the approach?
ping @Smit-create
One way is to add a method in class Expr
```python
@property
def is_random(self):
from sympy.stats.rv import random_symbols
if random_symbols(self):
return True
return False
```
I am trying to get an exact approach and will come up with that soon
Both Basic and Expr have far too many methods, attributes and properties. Why can't this just be a normal function?
> Why can't this just be a normal function?
We presently have a function `random_symbols` to get the random symbols from an expression.
So why is a method needed?
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/19299/files#diff-91b28bab28724762f84e77df3facdb54R15
I will update it in my PR #19290
I would recommend to add `is_random` in a separate PR, it's easier to review.
|
[
{
"body": "Add\r\n\r\n- `is_random` to every SymPy object (returns true if expression contains random symbols).\r\n- test `is_random` on undefined functions and indexed bases.\r\n- stats functions such as `P`, `E`, `var`, and `cov` should return their respective objects in case the `RandomSymbol` has no specified probability distribution.",
"number": 12283,
"title": "SymPy stats expansion"
}
] |
94fb720696f5f5d12bad8bc813699fd696afd2fb
|
{
"head_commit": "ce9d4e16be9d15032046e991f13aae609f4d946a",
"head_commit_message": "return objects when no pspace",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/stats/crv.py b/sympy/stats/crv.py\nindex 61a8fb7a1935..c38f6966ef3f 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/crv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/crv.py\n@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@\n from sympy.solvers.inequalities import reduce_rational_inequalities\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n from sympy.external import import_module\n-from sympy.stats.rv import (RandomDomain, SingleDomain, ConditionalDomain,\n+from sympy.stats.rv import (RandomDomain, SingleDomain, ConditionalDomain, is_random,\n ProductDomain, PSpace, SinglePSpace, random_symbols, NamedArgsMixin)\n \n scipy = import_module('scipy')\n@@ -555,7 +555,7 @@ def probability(self, condition, **kwargs):\n except NotImplementedError:\n from sympy.stats.rv import density\n expr = condition.lhs - condition.rhs\n- if not random_symbols(expr):\n+ if not is_random(expr):\n dens = self.density\n comp = condition.rhs\n else:\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/crv_types.py b/sympy/stats/crv_types.py\nindex 576ad128b952..7120fc5bcf95 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/crv_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/crv_types.py\n@@ -65,7 +65,7 @@\n from sympy.stats.crv import SingleContinuousPSpace, SingleContinuousDistribution\n from sympy.stats.joint_rv import JointPSpace, CompoundDistribution\n from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import multivariate_rv\n-from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, RandomSymbol\n+from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, is_random\n \n oo = S.Infinity\n \n@@ -127,7 +127,7 @@ def rv(symbol, cls, args):\n dist = cls(*args)\n dist.check(*args)\n pspace = SingleContinuousPSpace(symbol, dist)\n- if any(isinstance(arg, RandomSymbol) for arg in args):\n+ if any(is_random(arg) for arg in args):\n pspace = JointPSpace(symbol, CompoundDistribution(dist))\n return pspace.value\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/drv_types.py b/sympy/stats/drv_types.py\nindex 14914df119b1..399336b015a3 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/drv_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/drv_types.py\n@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@\n from sympy.stats import density\n from sympy.stats.drv import SingleDiscreteDistribution, SingleDiscretePSpace\n from sympy.stats.joint_rv import JointPSpace, CompoundDistribution\n-from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, RandomSymbol\n+from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, is_random\n from sympy.external import import_module\n \n numpy = import_module('numpy')\n@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ def rv(symbol, cls, *args):\n dist = cls(*args)\n dist.check(*args)\n pspace = SingleDiscretePSpace(symbol, dist)\n- if any(isinstance(arg, RandomSymbol) for arg in args):\n+ if any(is_random(arg) for arg in args):\n pspace = JointPSpace(symbol, CompoundDistribution(dist))\n return pspace.value\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/error_prop.py b/sympy/stats/error_prop.py\nindex 44c6862e52e9..ecc24dec1adf 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/error_prop.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/error_prop.py\n@@ -5,6 +5,7 @@\n \n from sympy import S, Symbol, Add, Mul, simplify, Pow, exp\n from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import RandomSymbol, Variance, Covariance\n+from sympy.stats.rv import is_random\n \n _arg0_or_var = lambda var: var.args[0] if len(var.args) > 0 else var\n \n@@ -59,7 +60,7 @@ def variance_prop(expr, consts=(), include_covar=False):\n if len(args) == 0:\n if expr in consts:\n return S.Zero\n- elif isinstance(expr, RandomSymbol):\n+ elif is_random(expr):\n return Variance(expr).doit()\n elif isinstance(expr, Symbol):\n return Variance(RandomSymbol(expr)).doit()\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/frv_types.py b/sympy/stats/frv_types.py\nindex 5f4a3185f920..10c8db3c1d25 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/frv_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/frv_types.py\n@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@\n from sympy.tensor.array import ArrayComprehensionMap\n from sympy.stats.frv import (SingleFiniteDistribution,\n SingleFinitePSpace)\n-from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, Density, RandomSymbol\n+from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, Density, is_random\n \n numpy = import_module('numpy')\n scipy = import_module('scipy')\n@@ -214,7 +214,7 @@ def set(self):\n \n def pmf(self, x):\n x = sympify(x)\n- if not (x.is_number or x.is_Symbol or isinstance(x, RandomSymbol)):\n+ if not (x.is_number or x.is_Symbol or is_random(x)):\n raise ValueError(\"'x' expected as an argument of type 'number' or 'Symbol' or , \"\n \"'RandomSymbol' not %s\" % (type(x)))\n cond = Ge(x, 1) & Le(x, self.sides) & Contains(x, S.Integers)\n@@ -396,7 +396,7 @@ def set(self):\n def pmf(self, x):\n n, p = self.n, self.p\n x = sympify(x)\n- if not (x.is_number or x.is_Symbol or isinstance(x, RandomSymbol)):\n+ if not (x.is_number or x.is_Symbol or is_random(x)):\n raise ValueError(\"'x' expected as an argument of type 'number' or 'Symbol' or , \"\n \"'RandomSymbol' not %s\" % (type(x)))\n cond = Ge(x, 0) & Le(x, n) & Contains(x, S.Integers)\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py b/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py\nindex 0735a7bcbc2d..871a92bdf978 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py\n@@ -3,12 +3,12 @@\n from sympy import (Basic, exp, pi, Lambda, Trace, S, MatrixSymbol, Integral,\n gamma, Product, Dummy, Sum, Abs, IndexedBase, I)\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n-from sympy.stats.rv import (_symbol_converter, Density, RandomMatrixSymbol,\n- RandomSymbol)\n+from sympy.stats.rv import _symbol_converter, Density, RandomMatrixSymbol, is_random\n from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import JointDistributionHandmade\n from sympy.stats.random_matrix import RandomMatrixPSpace\n from sympy.tensor.array import ArrayComprehension\n \n+\n __all__ = [\n 'CircularEnsemble',\n 'CircularUnitaryEnsemble',\n@@ -351,7 +351,7 @@ def JointEigenDistribution(mat):\n \n \"\"\"\n eigenvals = mat.eigenvals(multiple=True)\n- if any(not eigenval.has(RandomSymbol) for eigenval in set(eigenvals)):\n+ if any(not is_random(eigenval) for eigenval in set(eigenvals)):\n raise ValueError(\"Eigen values don't have any random expression, \"\n \"joint distribution cannot be generated.\")\n return JointDistributionHandmade(*eigenvals)\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/rv.py b/sympy/stats/rv.py\nindex 2a427915cd47..aa7a3478c07a 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/rv.py\n@@ -15,11 +15,12 @@\n \n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n+from functools import singledispatch\n from typing import Tuple as tTuple\n \n from sympy import (Basic, S, Expr, Symbol, Tuple, And, Add, Eq, lambdify,\n Equality, Lambda, sympify, Dummy, Ne, KroneckerDelta,\n- DiracDelta, Mul, Indexed, MatrixSymbol, Function)\n+ DiracDelta, Mul, Indexed, MatrixSymbol, Function, MatrixBase)\n from sympy.core.relational import Relational\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n from sympy.logic.boolalg import Boolean\n@@ -243,8 +244,10 @@ def __new__(cls, symbol, pspace=None):\n if pspace is None:\n # Allow single arg, representing pspace == PSpace()\n pspace = PSpace()\n+ if isinstance(symbol, str):\n+ symbol = Symbol(symbol)\n if not isinstance(symbol, Symbol):\n- raise TypeError(\"symbol should be of type Symbol\")\n+ raise TypeError(\"symbol should be of type Symbol or string\")\n if not isinstance(pspace, PSpace):\n raise TypeError(\"pspace variable should be of type PSpace\")\n if cls == JointRandomSymbol and isinstance(pspace, SinglePSpace):\n@@ -640,7 +643,7 @@ def given(expr, condition=None, **kwargs):\n 2*\\/ pi\n \"\"\"\n \n- if not random_symbols(condition) or pspace_independent(expr, condition):\n+ if not is_random(condition) or pspace_independent(expr, condition):\n return expr\n \n if isinstance(condition, RandomSymbol):\n@@ -718,7 +721,7 @@ def expectation(expr, condition=None, numsamples=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n 5\n \"\"\"\n \n- if not random_symbols(expr): # expr isn't random?\n+ if not is_random(expr): # expr isn't random?\n return expr\n if numsamples: # Computing by monte carlo sampling?\n evalf = kwargs.get('evalf', True)\n@@ -738,6 +741,10 @@ def expectation(expr, condition=None, numsamples=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):\n for arg in expr.args])\n \n # Otherwise case is simple, pass work off to the ProbabilitySpace\n+ if pspace(expr) == PSpace():\n+ from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Expectation\n+ return Expectation(expr)\n+\n result = pspace(expr).compute_expectation(expr, evaluate=evaluate, **kwargs)\n if evaluate and hasattr(result, 'doit'):\n return result.doit(**kwargs)\n@@ -816,6 +823,10 @@ def probability(condition, given_condition=None, numsamples=None,\n return probability(given(condition, given_condition, **kwargs), **kwargs)\n \n # Otherwise pass work off to the ProbabilitySpace\n+ if pspace(condition) == PSpace():\n+ from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability\n+ return Probability(condition, given_condition)\n+\n result = pspace(condition).probability(condition, **kwargs)\n if evaluate and hasattr(result, 'doit'):\n return result.doit()\n@@ -1514,3 +1525,40 @@ def _symbol_converter(sym):\n if not isinstance(sym, Symbol):\n raise TypeError(\"%s is neither a Symbol nor a string\"%(sym))\n return sym\n+\n+\n+@singledispatch\n+def is_random(x):\n+ return False\n+\n+@is_random.register(RandomSymbol)\n+def _(x):\n+ return True\n+\n+@is_random.register(Expr)\n+def _(x):\n+ atoms = x.free_symbols\n+ if len(atoms) == 1 and next(iter(atoms)) == x:\n+ return False\n+ return any([is_random(i) for i in atoms])\n+\n+@is_random.register(Boolean)\n+def _(x):\n+ atoms = x.free_symbols\n+ return any([is_random(i) for i in atoms])\n+\n+@is_random.register(Indexed)\n+def _(x):\n+ return is_random(x.base)\n+\n+@is_random.register(MatrixBase)\n+def _(x):\n+ return any([is_random(i) for i in x])\n+\n+@is_random.register(RandomMatrixSymbol)\n+def _(x):\n+ return True\n+\n+@is_random.register(RandomIndexedSymbol)\n+def _(x):\n+ return True\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py b/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py\nindex fa63a6ca429a..f305c61da9d1 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py\n@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@\n from __future__ import print_function, division\n from sympy.sets import FiniteSet\n from sympy import sqrt, log, exp, FallingFactorial, Rational, Eq, Dummy, piecewise_fold, solveset\n-from .rv import (probability, expectation, density, where, given, pspace, cdf,\n+from .rv import (probability, expectation, density, where, given, pspace, cdf, PSpace,\n characteristic_function, sample, sample_iter, random_symbols, independent, dependent,\n sampling_density, moment_generating_function, quantile)\n \n@@ -57,6 +57,10 @@ def variance(X, condition=None, **kwargs):\n >>> simplify(variance(B))\n p*(1 - p)\n \"\"\"\n+ if pspace(X) == PSpace():\n+ from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Variance\n+ return Variance(X, condition)\n+\n return cmoment(X, 2, condition, **kwargs)\n \n \n@@ -148,6 +152,10 @@ def covariance(X, Y, condition=None, **kwargs):\n >>> covariance(X, Y + rate*X)\n 1/lambda\n \"\"\"\n+ if pspace(X) == PSpace() or pspace(Y) == PSpace():\n+ from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Covariance\n+ return Covariance(X, Y, condition)\n+\n return expectation(\n (X - expectation(X, condition, **kwargs)) *\n (Y - expectation(Y, condition, **kwargs)),\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/symbolic_probability.py b/sympy/stats/symbolic_probability.py\nindex 0f114bc1c39c..4bd53d122724 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/symbolic_probability.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/symbolic_probability.py\n@@ -5,7 +5,8 @@\n from sympy.core.parameters import global_parameters\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n from sympy.stats import variance, covariance\n-from sympy.stats.rv import RandomSymbol, probability, expectation\n+from sympy.stats.rv import RandomSymbol, probability, expectation, is_random\n+\n \n __all__ = ['Probability', 'Expectation', 'Variance', 'Covariance']\n \n@@ -102,7 +103,7 @@ class Expectation(Expr):\n def __new__(cls, expr, condition=None, **kwargs):\n expr = _sympify(expr)\n if condition is None:\n- if not expr.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ if not is_random(expr):\n return expr\n obj = Expr.__new__(cls, expr)\n else:\n@@ -115,7 +116,7 @@ def doit(self, **hints):\n expr = self.args[0]\n condition = self._condition\n \n- if not expr.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ if not is_random(expr):\n return expr\n \n if isinstance(expr, Add):\n@@ -124,7 +125,7 @@ def doit(self, **hints):\n rv = []\n nonrv = []\n for a in expr.args:\n- if isinstance(a, RandomSymbol) or a.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ if is_random(a):\n rv.append(a)\n else:\n nonrv.append(a)\n@@ -229,7 +230,7 @@ def doit(self, **hints):\n arg = self.args[0]\n condition = self._condition\n \n- if not arg.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ if not is_random(arg):\n return S.Zero\n \n if isinstance(arg, RandomSymbol):\n@@ -237,7 +238,7 @@ def doit(self, **hints):\n elif isinstance(arg, Add):\n rv = []\n for a in arg.args:\n- if a.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ if is_random(a):\n rv.append(a)\n variances = Add(*map(lambda xv: Variance(xv, condition).doit(), rv))\n map_to_covar = lambda x: 2*Covariance(*x, condition=condition).doit()\n@@ -247,7 +248,7 @@ def doit(self, **hints):\n nonrv = []\n rv = []\n for a in arg.args:\n- if a.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ if is_random(a):\n rv.append(a)\n else:\n nonrv.append(a**2)\n@@ -343,9 +344,9 @@ def doit(self, **hints):\n if arg1 == arg2:\n return Variance(arg1, condition).doit()\n \n- if not arg1.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ if not is_random(arg1):\n return S.Zero\n- if not arg2.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ if not is_random(arg2):\n return S.Zero\n \n arg1, arg2 = sorted([arg1, arg2], key=default_sort_key)\n@@ -370,13 +371,13 @@ def _expand_single_argument(cls, expr):\n for a in expr.args:\n if isinstance(a, Mul):\n outval.append(cls._get_mul_nonrv_rv_tuple(a))\n- elif isinstance(a, RandomSymbol):\n+ elif is_random(a):\n outval.append((S.One, a))\n \n return outval\n elif isinstance(expr, Mul):\n return [cls._get_mul_nonrv_rv_tuple(expr)]\n- elif expr.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ elif is_random(expr):\n return [(S.One, expr)]\n \n @classmethod\n@@ -384,7 +385,7 @@ def _get_mul_nonrv_rv_tuple(cls, m):\n rv = []\n nonrv = []\n for a in m.args:\n- if a.has(RandomSymbol):\n+ if is_random(a):\n rv.append(a)\n else:\n nonrv.append(a)\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py\nindex 6d91e3097d4a..035bc01e31be 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py\n@@ -1,13 +1,14 @@\n from __future__ import unicode_literals\n from sympy import (S, Symbol, Interval, exp,\n symbols, Eq, cos, And, Tuple, integrate, oo, sin, Sum, Basic,\n- DiracDelta, Lambda, log, pi, FallingFactorial, Rational)\n+ DiracDelta, Lambda, log, pi, FallingFactorial, Rational, Matrix)\n from sympy.stats import (Die, Normal, Exponential, FiniteRV, P, E, H, variance,\n- density, given, independent, dependent, where, pspace,\n+ density, given, independent, dependent, where, pspace, GaussianUnitaryEnsemble,\n random_symbols, sample, Geometric, factorial_moment, Binomial, Hypergeometric,\n- DiscreteUniform, Poisson, characteristic_function, moment_generating_function)\n+ DiscreteUniform, Poisson, characteristic_function, moment_generating_function,\n+ BernoulliProcess, Variance, Expectation, Probability, Covariance, covariance)\n from sympy.stats.rv import (IndependentProductPSpace, rs_swap, Density, NamedArgsMixin,\n- RandomSymbol, sample_iter, PSpace)\n+ RandomSymbol, sample_iter, PSpace, is_random)\n from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, skip, XFAIL, ignore_warnings\n from sympy.external import import_module\n from sympy.core.numbers import comp\n@@ -338,3 +339,33 @@ def test_issue_12237():\n assert W == P(X + Y > 0, X)\n assert U == BernoulliDistribution(S.Half, S.Zero, S.One)\n assert V == S.Half\n+\n+def test_is_random():\n+ X = Normal('X', 0, 1)\n+ Y = Normal('Y', 0, 1)\n+ a, b = symbols('a, b')\n+ G = GaussianUnitaryEnsemble('U', 2)\n+ B = BernoulliProcess('B', 0.9)\n+ assert not is_random(a)\n+ assert not is_random(a + b)\n+ assert not is_random(a * b)\n+ assert not is_random(Matrix([a**2, b**2]))\n+ assert is_random(X)\n+ assert is_random(X**2 + Y)\n+ assert is_random(Y + b**2)\n+ assert is_random(Y > 5)\n+ assert is_random(B[3] < 1)\n+ assert is_random(G)\n+ assert is_random(X * Y * B[1])\n+ assert is_random(Matrix([[X, B[2]], [G, Y]]))\n+ assert is_random(Eq(X, 4))\n+\n+def test_issue_12283():\n+ x = symbols('x')\n+ X = RandomSymbol(x)\n+ Y = RandomSymbol('Y')\n+ assert pspace(X) == PSpace()\n+ assert E(X) == Expectation(X)\n+ assert P(X > 3) == Probability(X > 3)\n+ assert variance(X) == Variance(X)\n+ assert covariance(X, Y) == Covariance(X, Y)\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_symbolic_probability.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_symbolic_probability.py\nindex 4dca7d1e3d77..01ae5b899d6c 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_symbolic_probability.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_symbolic_probability.py\n@@ -66,7 +66,6 @@ def test_literal_probability():\n assert Covariance(X, X**2).doit() == Covariance(X, X**2)\n assert Covariance(X, sin(X)).doit() == Covariance(sin(X), X)\n assert Covariance(X**2, sin(X)*Y).doit() == Covariance(sin(X)*Y, X**2)\n- assert Covariance(w, X).evaluate_integral() == 0\n \n \n def test_probability_rewrite():\n@@ -102,9 +101,5 @@ def test_probability_rewrite():\n assert Variance(X).rewrite(Sum) == Variance(X).rewrite(Integral)\n assert Expectation(X).rewrite(Sum) == Expectation(X).rewrite(Integral)\n \n- assert Covariance(w, X).rewrite(Sum) == 0\n-\n- assert Covariance(w, X).rewrite(Integral) == 0\n-\n assert Variance(X, condition=Y).rewrite(Probability) == Integral(x**2*Probability(Eq(X, x), Y), (x, -oo, oo)) - \\\n Integral(x*Probability(Eq(X, x), Y), (x, -oo, oo))**2\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -66,7 +66,6 @@ def test_literal_probability():\n assert Covariance(X, X**2).doit() == Covariance(X, X**2)\n assert Covariance(X, sin(X)).doit() == Covariance(sin(X), X)\n assert Covariance(X**2, sin(X)*Y).doit() == Covariance(sin(X)*Y, X**2)\n- assert Covariance(w, X).evaluate_integral() == 0",
"line": null,
"original_line": 69,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/stats/tests/test_symbolic_probability.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWere the deleted results wrong?\n\n@author:\nOops, will add them. Actually while debugging an error, I deleted it mistakenly"
}
] |
aae8109eec5d00097e87b36edb6429829dd891aa
|
diff --git a/sympy/stats/crv.py b/sympy/stats/crv.py
index 61a8fb7a1935..c38f6966ef3f 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/crv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/crv.py
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@
from sympy.solvers.inequalities import reduce_rational_inequalities
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
from sympy.external import import_module
-from sympy.stats.rv import (RandomDomain, SingleDomain, ConditionalDomain,
+from sympy.stats.rv import (RandomDomain, SingleDomain, ConditionalDomain, is_random,
ProductDomain, PSpace, SinglePSpace, random_symbols, NamedArgsMixin)
scipy = import_module('scipy')
@@ -555,7 +555,7 @@ def probability(self, condition, **kwargs):
except NotImplementedError:
from sympy.stats.rv import density
expr = condition.lhs - condition.rhs
- if not random_symbols(expr):
+ if not is_random(expr):
dens = self.density
comp = condition.rhs
else:
diff --git a/sympy/stats/crv_types.py b/sympy/stats/crv_types.py
index 9b089055c086..a3e11443b616 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/crv_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/crv_types.py
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@
from sympy.stats.crv import SingleContinuousPSpace, SingleContinuousDistribution
from sympy.stats.joint_rv import JointPSpace, CompoundDistribution
from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import multivariate_rv
-from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, RandomSymbol
+from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, is_random
oo = S.Infinity
@@ -125,13 +125,16 @@
]
+@is_random.register(MatrixBase)
+def _(x):
+ return any([is_random(i) for i in x])
def rv(symbol, cls, args):
args = list(map(sympify, args))
dist = cls(*args)
dist.check(*args)
pspace = SingleContinuousPSpace(symbol, dist)
- if any(isinstance(arg, RandomSymbol) for arg in args):
+ if any(is_random(arg) for arg in args):
pspace = JointPSpace(symbol, CompoundDistribution(dist))
return pspace.value
diff --git a/sympy/stats/drv_types.py b/sympy/stats/drv_types.py
index 14914df119b1..399336b015a3 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/drv_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/drv_types.py
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@
from sympy.stats import density
from sympy.stats.drv import SingleDiscreteDistribution, SingleDiscretePSpace
from sympy.stats.joint_rv import JointPSpace, CompoundDistribution
-from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, RandomSymbol
+from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, is_random
from sympy.external import import_module
numpy = import_module('numpy')
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ def rv(symbol, cls, *args):
dist = cls(*args)
dist.check(*args)
pspace = SingleDiscretePSpace(symbol, dist)
- if any(isinstance(arg, RandomSymbol) for arg in args):
+ if any(is_random(arg) for arg in args):
pspace = JointPSpace(symbol, CompoundDistribution(dist))
return pspace.value
diff --git a/sympy/stats/error_prop.py b/sympy/stats/error_prop.py
index 36ce9f1cff62..34f29db9f56b 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/error_prop.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/error_prop.py
@@ -5,6 +5,7 @@
from sympy import S, Symbol, Add, Mul, simplify, Pow, exp
from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import RandomSymbol, Variance, Covariance
+from sympy.stats.rv import is_random
_arg0_or_var = lambda var: var.args[0] if len(var.args) > 0 else var
@@ -59,7 +60,7 @@ def variance_prop(expr, consts=(), include_covar=False):
if len(args) == 0:
if expr in consts:
return S.Zero
- elif isinstance(expr, RandomSymbol):
+ elif is_random(expr):
return Variance(expr).doit()
elif isinstance(expr, Symbol):
return Variance(RandomSymbol(expr)).doit()
diff --git a/sympy/stats/frv_types.py b/sympy/stats/frv_types.py
index 5f4a3185f920..10c8db3c1d25 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/frv_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/frv_types.py
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@
from sympy.tensor.array import ArrayComprehensionMap
from sympy.stats.frv import (SingleFiniteDistribution,
SingleFinitePSpace)
-from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, Density, RandomSymbol
+from sympy.stats.rv import _value_check, Density, is_random
numpy = import_module('numpy')
scipy = import_module('scipy')
@@ -214,7 +214,7 @@ def set(self):
def pmf(self, x):
x = sympify(x)
- if not (x.is_number or x.is_Symbol or isinstance(x, RandomSymbol)):
+ if not (x.is_number or x.is_Symbol or is_random(x)):
raise ValueError("'x' expected as an argument of type 'number' or 'Symbol' or , "
"'RandomSymbol' not %s" % (type(x)))
cond = Ge(x, 1) & Le(x, self.sides) & Contains(x, S.Integers)
@@ -396,7 +396,7 @@ def set(self):
def pmf(self, x):
n, p = self.n, self.p
x = sympify(x)
- if not (x.is_number or x.is_Symbol or isinstance(x, RandomSymbol)):
+ if not (x.is_number or x.is_Symbol or is_random(x)):
raise ValueError("'x' expected as an argument of type 'number' or 'Symbol' or , "
"'RandomSymbol' not %s" % (type(x)))
cond = Ge(x, 0) & Le(x, n) & Contains(x, S.Integers)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py b/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py
index 0735a7bcbc2d..02717ee24a0b 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/random_matrix_models.py
@@ -3,8 +3,7 @@
from sympy import (Basic, exp, pi, Lambda, Trace, S, MatrixSymbol, Integral,
gamma, Product, Dummy, Sum, Abs, IndexedBase, I)
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
-from sympy.stats.rv import (_symbol_converter, Density, RandomMatrixSymbol,
- RandomSymbol)
+from sympy.stats.rv import _symbol_converter, Density, RandomMatrixSymbol, is_random
from sympy.stats.joint_rv_types import JointDistributionHandmade
from sympy.stats.random_matrix import RandomMatrixPSpace
from sympy.tensor.array import ArrayComprehension
@@ -23,6 +22,11 @@
'level_spacing_distribution'
]
+@is_random.register(RandomMatrixSymbol)
+def _(x):
+ return True
+
+
class RandomMatrixEnsemble(Basic):
"""
Base class for random matrix ensembles.
@@ -351,7 +355,7 @@ def JointEigenDistribution(mat):
"""
eigenvals = mat.eigenvals(multiple=True)
- if any(not eigenval.has(RandomSymbol) for eigenval in set(eigenvals)):
+ if any(not is_random(eigenval) for eigenval in set(eigenvals)):
raise ValueError("Eigen values don't have any random expression, "
"joint distribution cannot be generated.")
return JointDistributionHandmade(*eigenvals)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/rv.py b/sympy/stats/rv.py
index 2a427915cd47..cd0014de6914 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/rv.py
@@ -15,6 +15,7 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
+from functools import singledispatch
from typing import Tuple as tTuple
from sympy import (Basic, S, Expr, Symbol, Tuple, And, Add, Eq, lambdify,
@@ -32,6 +33,15 @@
x = Symbol('x')
+@singledispatch
+def is_random(x):
+ return False
+
+@is_random.register(Basic)
+def _(x):
+ atoms = x.free_symbols
+ return any([is_random(i) for i in atoms])
+
class RandomDomain(Basic):
"""
Represents a set of variables and the values which they can take
@@ -243,8 +253,10 @@ def __new__(cls, symbol, pspace=None):
if pspace is None:
# Allow single arg, representing pspace == PSpace()
pspace = PSpace()
+ if isinstance(symbol, str):
+ symbol = Symbol(symbol)
if not isinstance(symbol, Symbol):
- raise TypeError("symbol should be of type Symbol")
+ raise TypeError("symbol should be of type Symbol or string")
if not isinstance(pspace, PSpace):
raise TypeError("pspace variable should be of type PSpace")
if cls == JointRandomSymbol and isinstance(pspace, SinglePSpace):
@@ -281,6 +293,9 @@ def free_symbols(self):
class RandomIndexedSymbol(RandomSymbol):
def __new__(cls, idx_obj, pspace=None):
+ if pspace is None:
+ # Allow single arg, representing pspace == PSpace()
+ pspace = PSpace()
if not isinstance(idx_obj, (Indexed, Function)):
raise TypeError("An Function or Indexed object is expected not %s"%(idx_obj))
return Basic.__new__(cls, idx_obj, pspace)
@@ -299,6 +314,9 @@ class RandomMatrixSymbol(MatrixSymbol):
def __new__(cls, symbol, n, m, pspace=None):
n, m = _sympify(n), _sympify(m)
symbol = _symbol_converter(symbol)
+ if pspace is None:
+ # Allow single arg, representing pspace == PSpace()
+ pspace = PSpace()
return Basic.__new__(cls, symbol, n, m, pspace)
symbol = property(lambda self: self.args[0])
@@ -640,7 +658,7 @@ def given(expr, condition=None, **kwargs):
2*\/ pi
"""
- if not random_symbols(condition) or pspace_independent(expr, condition):
+ if not is_random(condition) or pspace_independent(expr, condition):
return expr
if isinstance(condition, RandomSymbol):
@@ -718,7 +736,7 @@ def expectation(expr, condition=None, numsamples=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
5
"""
- if not random_symbols(expr): # expr isn't random?
+ if not is_random(expr): # expr isn't random?
return expr
if numsamples: # Computing by monte carlo sampling?
evalf = kwargs.get('evalf', True)
@@ -738,6 +756,10 @@ def expectation(expr, condition=None, numsamples=None, evaluate=True, **kwargs):
for arg in expr.args])
# Otherwise case is simple, pass work off to the ProbabilitySpace
+ if pspace(expr) == PSpace():
+ from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Expectation
+ return Expectation(expr)
+
result = pspace(expr).compute_expectation(expr, evaluate=evaluate, **kwargs)
if evaluate and hasattr(result, 'doit'):
return result.doit(**kwargs)
@@ -816,6 +838,10 @@ def probability(condition, given_condition=None, numsamples=None,
return probability(given(condition, given_condition, **kwargs), **kwargs)
# Otherwise pass work off to the ProbabilitySpace
+ if pspace(condition) == PSpace():
+ from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability
+ return Probability(condition, given_condition)
+
result = pspace(condition).probability(condition, **kwargs)
if evaluate and hasattr(result, 'doit'):
return result.doit()
diff --git a/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py b/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py
index fa63a6ca429a..236f774a9441 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/rv_interface.py
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
from sympy.sets import FiniteSet
from sympy import sqrt, log, exp, FallingFactorial, Rational, Eq, Dummy, piecewise_fold, solveset
-from .rv import (probability, expectation, density, where, given, pspace, cdf,
+from .rv import (probability, expectation, density, where, given, pspace, cdf, PSpace,
characteristic_function, sample, sample_iter, random_symbols, independent, dependent,
- sampling_density, moment_generating_function, quantile)
+ sampling_density, moment_generating_function, quantile, is_random)
__all__ = ['P', 'E', 'H', 'density', 'where', 'given', 'sample', 'cdf',
@@ -57,6 +57,10 @@ def variance(X, condition=None, **kwargs):
>>> simplify(variance(B))
p*(1 - p)
"""
+ if is_random(X) and pspace(X) == PSpace():
+ from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Variance
+ return Variance(X, condition)
+
return cmoment(X, 2, condition, **kwargs)
@@ -148,6 +152,10 @@ def covariance(X, Y, condition=None, **kwargs):
>>> covariance(X, Y + rate*X)
1/lambda
"""
+ if (is_random(X) and pspace(X) == PSpace()) or (is_random(Y) and pspace(Y) == PSpace()):
+ from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Covariance
+ return Covariance(X, Y, condition)
+
return expectation(
(X - expectation(X, condition, **kwargs)) *
(Y - expectation(Y, condition, **kwargs)),
diff --git a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
index e29fc349be2e..9380a06b92e0 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/stochastic_process_types.py
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
from sympy.stats.joint_rv import JointDistributionHandmade, JointDistribution
from sympy.stats.rv import (RandomIndexedSymbol, random_symbols, RandomSymbol,
_symbol_converter, _value_check, pspace, given,
- dependent)
+ dependent, is_random)
from sympy.stats.stochastic_process import StochasticPSpace
from sympy.stats.symbolic_probability import Probability, Expectation
from sympy.stats.frv_types import Bernoulli, BernoulliDistribution
@@ -28,6 +28,15 @@
'BernoulliProcess'
]
+
+@is_random.register(Indexed)
+def _(x):
+ return is_random(x.base)
+
+@is_random.register(RandomIndexedSymbol)
+def _(x):
+ return True
+
def _set_converter(itr):
"""
Helper function for converting list/tuple/set to Set.
diff --git a/sympy/stats/symbolic_probability.py b/sympy/stats/symbolic_probability.py
index 385d4870ee3d..eafa5a9ff12d 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/symbolic_probability.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/symbolic_probability.py
@@ -5,11 +5,23 @@
from sympy.core.parameters import global_parameters
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
from sympy.stats import variance, covariance
-from sympy.stats.rv import RandomSymbol, probability, expectation
+from sympy.stats.rv import RandomSymbol, probability, expectation, is_random
__all__ = ['Probability', 'Expectation', 'Variance', 'Covariance']
+@is_random.register(Expr)
+def _(x):
+ atoms = x.free_symbols
+ if len(atoms) == 1 and next(iter(atoms)) == x:
+ return False
+ return any([is_random(i) for i in atoms])
+
+@is_random.register(RandomSymbol)
+def _(x):
+ return True
+
+
class Probability(Expr):
"""
Symbolic expression for the probability.
@@ -102,7 +114,7 @@ class Expectation(Expr):
def __new__(cls, expr, condition=None, **kwargs):
expr = _sympify(expr)
if condition is None:
- if not expr.has(RandomSymbol):
+ if not is_random(expr):
return expr
obj = Expr.__new__(cls, expr)
else:
@@ -115,7 +127,7 @@ def expand(self, **hints):
expr = self.args[0]
condition = self._condition
- if not expr.has(RandomSymbol):
+ if not is_random(expr):
return expr
if isinstance(expr, Add):
@@ -124,7 +136,7 @@ def expand(self, **hints):
rv = []
nonrv = []
for a in expr.args:
- if isinstance(a, RandomSymbol) or a.has(RandomSymbol):
+ if is_random(a):
rv.append(a)
else:
nonrv.append(a)
@@ -229,7 +241,7 @@ def expand(self, **hints):
arg = self.args[0]
condition = self._condition
- if not arg.has(RandomSymbol):
+ if not is_random(arg):
return S.Zero
if isinstance(arg, RandomSymbol):
@@ -237,7 +249,7 @@ def expand(self, **hints):
elif isinstance(arg, Add):
rv = []
for a in arg.args:
- if a.has(RandomSymbol):
+ if is_random(a):
rv.append(a)
variances = Add(*map(lambda xv: Variance(xv, condition).expand(), rv))
map_to_covar = lambda x: 2*Covariance(*x, condition=condition).expand()
@@ -247,7 +259,7 @@ def expand(self, **hints):
nonrv = []
rv = []
for a in arg.args:
- if a.has(RandomSymbol):
+ if is_random(a):
rv.append(a)
else:
nonrv.append(a**2)
@@ -343,9 +355,9 @@ def expand(self, **hints):
if arg1 == arg2:
return Variance(arg1, condition).expand()
- if not arg1.has(RandomSymbol):
+ if not is_random(arg1):
return S.Zero
- if not arg2.has(RandomSymbol):
+ if not is_random(arg2):
return S.Zero
arg1, arg2 = sorted([arg1, arg2], key=default_sort_key)
@@ -370,13 +382,13 @@ def _expand_single_argument(cls, expr):
for a in expr.args:
if isinstance(a, Mul):
outval.append(cls._get_mul_nonrv_rv_tuple(a))
- elif isinstance(a, RandomSymbol):
+ elif is_random(a):
outval.append((S.One, a))
return outval
elif isinstance(expr, Mul):
return [cls._get_mul_nonrv_rv_tuple(expr)]
- elif expr.has(RandomSymbol):
+ elif is_random(expr):
return [(S.One, expr)]
@classmethod
@@ -384,7 +396,7 @@ def _get_mul_nonrv_rv_tuple(cls, m):
rv = []
nonrv = []
for a in m.args:
- if a.has(RandomSymbol):
+ if is_random(a):
rv.append(a)
else:
nonrv.append(a)
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py
index 6d91e3097d4a..5c58913835dd 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_rv.py
@@ -1,13 +1,14 @@
from __future__ import unicode_literals
from sympy import (S, Symbol, Interval, exp,
- symbols, Eq, cos, And, Tuple, integrate, oo, sin, Sum, Basic,
- DiracDelta, Lambda, log, pi, FallingFactorial, Rational)
+ symbols, Eq, cos, And, Tuple, integrate, oo, sin, Sum, Basic, Indexed,
+ DiracDelta, Lambda, log, pi, FallingFactorial, Rational, Matrix)
from sympy.stats import (Die, Normal, Exponential, FiniteRV, P, E, H, variance,
- density, given, independent, dependent, where, pspace,
+ density, given, independent, dependent, where, pspace, GaussianUnitaryEnsemble,
random_symbols, sample, Geometric, factorial_moment, Binomial, Hypergeometric,
- DiscreteUniform, Poisson, characteristic_function, moment_generating_function)
+ DiscreteUniform, Poisson, characteristic_function, moment_generating_function,
+ BernoulliProcess, Variance, Expectation, Probability, Covariance, covariance)
from sympy.stats.rv import (IndependentProductPSpace, rs_swap, Density, NamedArgsMixin,
- RandomSymbol, sample_iter, PSpace)
+ RandomSymbol, sample_iter, PSpace, is_random, RandomIndexedSymbol, RandomMatrixSymbol)
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises, skip, XFAIL, ignore_warnings
from sympy.external import import_module
from sympy.core.numbers import comp
@@ -338,3 +339,39 @@ def test_issue_12237():
assert W == P(X + Y > 0, X)
assert U == BernoulliDistribution(S.Half, S.Zero, S.One)
assert V == S.Half
+
+def test_is_random():
+ X = Normal('X', 0, 1)
+ Y = Normal('Y', 0, 1)
+ a, b = symbols('a, b')
+ G = GaussianUnitaryEnsemble('U', 2)
+ B = BernoulliProcess('B', 0.9)
+ assert not is_random(a)
+ assert not is_random(a + b)
+ assert not is_random(a * b)
+ assert not is_random(Matrix([a**2, b**2]))
+ assert is_random(X)
+ assert is_random(X**2 + Y)
+ assert is_random(Y + b**2)
+ assert is_random(Y > 5)
+ assert is_random(B[3] < 1)
+ assert is_random(G)
+ assert is_random(X * Y * B[1])
+ assert is_random(Matrix([[X, B[2]], [G, Y]]))
+ assert is_random(Eq(X, 4))
+
+def test_issue_12283():
+ x = symbols('x')
+ X = RandomSymbol(x)
+ Y = RandomSymbol('Y')
+ Z = RandomMatrixSymbol('Z', 2, 3)
+ RI = RandomIndexedSymbol(Indexed('RI', 3))
+ assert pspace(Z) == PSpace()
+ assert pspace(RI) == PSpace()
+ assert pspace(X) == PSpace()
+ assert E(X) == Expectation(X)
+ assert P(Y > 3) == Probability(Y > 3)
+ assert variance(X) == Variance(X)
+ assert variance(RI) == Variance(RI)
+ assert covariance(X, Y) == Covariance(X, Y)
+ assert covariance(X, Z) == Covariance(X, Z)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-18927@c18ff69
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,927
|
expand log terms using factor.
|
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #18674, #18865
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
expand log term into its prime factors if factor flag is True
example:
`x = log(12)/log(2)`
`expand(x, factor=True) = log(3)/log(2) + 2
`
### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* functions
- expand log term into its prime factors if the factor flag is True.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-03-22T09:41:20Z
|
rewrite log(12)/log(2) as 2 + log(3)/log(2)
I am not sure how to rewrite the quotient of logs to remove powers of the denominator's factors. I thought it could be recognized in `logcombine` but that function already does this
```python
>>> logcombine(log(12)/log(2))
log(12**(1/log(2)))
```
So maybe this is something that should be done by `expand_log` with a keyword `factor` is used to factor arguments before running.
```
>>> (log(12)/log(2)).replace(
... lambda x: x.func is log and x.args[0].is_Integer,
... lambda x: log(factorint(x.args[0], visual=True)))
log(2**2*3**1)/log(2**1)
>>> expand_log(_)
(log(3) + 2*log(2))/log(2)
>>> expand(_)
log(3)/log(2) + 2
```
Not sure...seems like there should be an easy way to expand logs of integers.
|
I think logcombine is too aggressive with the power rule. I've noticed in other places that it can mess up other potential simplifications. Perhaps a good start here would be to have flags in logcombine() to selectively disable the two types of combination rules it does. But more generally, it should try to do power combination last, so that other types of combinations can be done first.
We can maybe write a new function, if that sees two log functions are being divided. Then it treats the denominator value as the base of numerator log function
Suppose in this case, if we can make
`log(12)/log(2) = log(12, 2)`
somehow, then we can easily reach
` log(3)/log(2) + 2`
Hello, Is this issue still open? I would like to contribute to this issue. I have been well versed with the codebase of sympy and have sufficient proficiency over python language. I also have a basic idea on how to move forward with this issue. Can I work on this issue?
SymPy cannot represent two-argument logs yet. log(x, y) is automatically rewritten as log(x)/log(y). I'm having a hard time finding the issue for this.
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/6888
We can check the number in the numerator and reduce it to the product of its prime factors.
For instance log(12) could be written as log( 2 x 2 x 3) and then pass this numerator to logcombine() to check if it is further simplified.
So here the numerator becomes log(2) + log(2) + log(3) = 2*log(2) + log(3).
> reduce it to the product of its prime factors
yes...see OP example using `replace`
|
[
{
"body": "I am not sure how to rewrite the quotient of logs to remove powers of the denominator's factors. I thought it could be recognized in `logcombine` but that function already does this\r\n```python\r\n>>> logcombine(log(12)/log(2))\r\nlog(12**(1/log(2)))\r\n```\r\nSo maybe this is something that should be done by `expand_log` with a keyword `factor` is used to factor arguments before running.\r\n```\r\n>>> (log(12)/log(2)).replace(\r\n... lambda x: x.func is log and x.args[0].is_Integer, \r\n... lambda x: log(factorint(x.args[0], visual=True)))\r\nlog(2**2*3**1)/log(2**1)\r\n>>> expand_log(_)\r\n(log(3) + 2*log(2))/log(2)\r\n>>> expand(_)\r\nlog(3)/log(2) + 2\r\n```\r\nNot sure...seems like there should be an easy way to expand logs of integers.",
"number": 18674,
"title": "rewrite log(12)/log(2) as 2 + log(3)/log(2)"
}
] |
c770bc7ede4c22962bacce96bb2388e5df1c47b7
|
{
"head_commit": "c18ff69aeb32cd3744a6152434ee45b48f0e8485",
"head_commit_message": "update expand_log to expand when factor is false.",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/function.py b/sympy/core/function.py\nindex 95301137d113..11e7ad07dc85 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/function.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/function.py\n@@ -2820,7 +2820,7 @@ def expand_multinomial(expr, deep=True):\n power_base=False, basic=False, multinomial=True, log=False)\n \n \n-def expand_log(expr, deep=True, force=False):\n+def expand_log(expr, deep=True, factor=False, force=False):\n \"\"\"\n Wrapper around expand that only uses the log hint. See the expand\n docstring for more information.\n@@ -2834,9 +2834,16 @@ def expand_log(expr, deep=True, force=False):\n (x + y)*(log(x) + 2*log(y))*exp(x + y)\n \n \"\"\"\n+ from sympy import Mul, log\n+ if factor is False:\n+ expr = expr.replace(\n+ lambda x: x.is_Mul and all(any(isinstance(i, log) and i.args[0].is_Rational\n+ for i in Mul.make_args(j)) for j in x.as_numer_denom()),\n+ lambda x: expand(x, factor=True))\n+\n return sympify(expr).expand(deep=deep, log=True, mul=False,\n power_exp=False, power_base=False, multinomial=False,\n- basic=False, force=force)\n+ basic=False, force=force, factor=factor)\n \n \n def expand_func(expr, deep=True):\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py\nindex bfd2e98f55f1..f552ff8f05cf 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py\n@@ -754,17 +754,28 @@ def taylor_term(n, x, *previous_terms): # of log(1+x)\n return (1 - 2*(n % 2)) * x**(n + 1)/(n + 1)\n \n def _eval_expand_log(self, deep=True, **hints):\n- from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log\n+ from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log, factorint\n from sympy.concrete import Sum, Product\n force = hints.get('force', False)\n+ factor = hints.get('factor', False)\n if (len(self.args) == 2):\n return expand_log(self.func(*self.args), deep=deep, force=force)\n arg = self.args[0]\n if arg.is_Integer:\n # remove perfect powers\n p = perfect_power(int(arg))\n+ logarg = None\n+ coeff = 1\n if p is not False:\n- return p[1]*self.func(p[0])\n+ arg, coeff = p\n+ logarg = self.func(arg)\n+ # expand as product of its prime factors if factor=True\n+ if factor:\n+ p = factorint(int(arg))\n+ if int(arg) not in p.keys():\n+ logarg = sum(n*log(val) for val, n in p.items())\n+ if logarg is not None:\n+ return coeff*logarg\n elif arg.is_Rational:\n return log(arg.p) - log(arg.q)\n elif arg.is_Mul:\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -754,17 +754,28 @@ def taylor_term(n, x, *previous_terms): # of log(1+x)\n return (1 - 2*(n % 2)) * x**(n + 1)/(n + 1)\n \n def _eval_expand_log(self, deep=True, **hints):\n- from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log\n+ from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log, factorint\n from sympy.concrete import Sum, Product\n force = hints.get('force', False)\n+ factor = hints.get('factor', False)\n if (len(self.args) == 2):\n return expand_log(self.func(*self.args), deep=deep, force=force)\n arg = self.args[0]\n if arg.is_Integer:\n # remove perfect powers\n p = perfect_power(int(arg))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 766,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n p = perfect_power(arg)\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -754,17 +754,28 @@ def taylor_term(n, x, *previous_terms): # of log(1+x)\n return (1 - 2*(n % 2)) * x**(n + 1)/(n + 1)\n \n def _eval_expand_log(self, deep=True, **hints):\n- from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log\n+ from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log, factorint\n from sympy.concrete import Sum, Product\n force = hints.get('force', False)\n+ factor = hints.get('factor', False)\n if (len(self.args) == 2):\n return expand_log(self.func(*self.args), deep=deep, force=force)\n arg = self.args[0]\n if arg.is_Integer:\n # remove perfect powers\n p = perfect_power(int(arg))\n+ logarg = None\n+ coeff = 1\n if p is not False:\n- return p[1]*self.func(p[0])\n+ arg, coeff = p\n+ logarg = self.func(arg)\n+ # expand as product of its prime factors if factor=True\n+ if factor:\n+ p = factorint(int(arg))\n+ if int(arg) not in p.keys():",
"line": null,
"original_line": 775,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n if arg not in p:\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -754,17 +754,28 @@ def taylor_term(n, x, *previous_terms): # of log(1+x)\n return (1 - 2*(n % 2)) * x**(n + 1)/(n + 1)\n \n def _eval_expand_log(self, deep=True, **hints):\n- from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log\n+ from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log, factorint\n from sympy.concrete import Sum, Product\n force = hints.get('force', False)\n+ factor = hints.get('factor', False)\n if (len(self.args) == 2):\n return expand_log(self.func(*self.args), deep=deep, force=force)\n arg = self.args[0]\n if arg.is_Integer:\n # remove perfect powers\n p = perfect_power(int(arg))\n+ logarg = None\n+ coeff = 1\n if p is not False:\n- return p[1]*self.func(p[0])\n+ arg, coeff = p\n+ logarg = self.func(arg)\n+ # expand as product of its prime factors if factor=True\n+ if factor:\n+ p = factorint(int(arg))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 774,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n p = factorint(arg)\r\n```"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2834,9 +2834,16 @@ def expand_log(expr, deep=True, force=False):\n (x + y)*(log(x) + 2*log(y))*exp(x + y)\n \n \"\"\"\n+ from sympy import Mul, log\n+ if factor is False:\n+ expr = expr.replace(\n+ lambda x: x.is_Mul and all(any(isinstance(i, log) and i.args[0].is_Rational\n+ for i in Mul.make_args(j)) for j in x.as_numer_denom()),\n+ lambda x: expand(x, factor=True))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 2842,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/function.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nSince this is just the `expand_log` hint, we probably shouldn't apply the general `expand`, just `expand_log`"
}
] |
97f540708a1d4a997bea946965e18f4c88e3747e
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/function.py b/sympy/core/function.py
index 95301137d113..482cfe10dedf 100644
--- a/sympy/core/function.py
+++ b/sympy/core/function.py
@@ -2820,7 +2820,7 @@ def expand_multinomial(expr, deep=True):
power_base=False, basic=False, multinomial=True, log=False)
-def expand_log(expr, deep=True, force=False):
+def expand_log(expr, deep=True, force=False, factor=False):
"""
Wrapper around expand that only uses the log hint. See the expand
docstring for more information.
@@ -2834,9 +2834,16 @@ def expand_log(expr, deep=True, force=False):
(x + y)*(log(x) + 2*log(y))*exp(x + y)
"""
+ from sympy import Mul, log
+ if factor is False:
+ expr = expr.replace(
+ lambda x: x.is_Mul and all(any(isinstance(i, log) and i.args[0].is_Rational
+ for i in Mul.make_args(j)) for j in x.as_numer_denom()),
+ lambda x: expand_log(x, deep=deep, force=force, factor=True))
+
return sympify(expr).expand(deep=deep, log=True, mul=False,
power_exp=False, power_base=False, multinomial=False,
- basic=False, force=force)
+ basic=False, force=force, factor=factor)
def expand_func(expr, deep=True):
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py
index bfd2e98f55f1..d7d47dbca69c 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/exponential.py
@@ -754,17 +754,28 @@ def taylor_term(n, x, *previous_terms): # of log(1+x)
return (1 - 2*(n % 2)) * x**(n + 1)/(n + 1)
def _eval_expand_log(self, deep=True, **hints):
- from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log
+ from sympy import unpolarify, expand_log, factorint
from sympy.concrete import Sum, Product
force = hints.get('force', False)
+ factor = hints.get('factor', False)
if (len(self.args) == 2):
return expand_log(self.func(*self.args), deep=deep, force=force)
arg = self.args[0]
if arg.is_Integer:
# remove perfect powers
- p = perfect_power(int(arg))
+ p = perfect_power(arg)
+ logarg = None
+ coeff = 1
if p is not False:
- return p[1]*self.func(p[0])
+ arg, coeff = p
+ logarg = self.func(arg)
+ # expand as product of its prime factors if factor=True
+ if factor:
+ p = factorint(arg)
+ if arg not in p.keys():
+ logarg = sum(n*log(val) for val, n in p.items())
+ if logarg is not None:
+ return coeff*logarg
elif arg.is_Rational:
return log(arg.p) - log(arg.q)
elif arg.is_Mul:
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Code Refactoring / Architectural Improvement"
}
|
sympy__sympy-18896@b650dae
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,896
|
Remove reference to Python2 in round
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
I believe this fixes #16686
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-03-18T04:43:18Z
|
remove Py2 code from `round` when dropping Python 2 support
The Notes section and two places in Expr.round (with inlines about Py2) need to be changed when Python 2 support is dropped. In the first case, all the rounding semantics can be handled by builtin `round` instead of the Expr.round code that follows in the if-block; in the second, the handling can be done in terms of `int` through `round` instead of through `Expr.round`.
|
[
{
"body": "The Notes section and two places in Expr.round (with inlines about Py2) need to be changed when Python 2 support is dropped. In the first case, all the rounding semantics can be handled by builtin `round` instead of the Expr.round code that follows in the if-block; in the second, the handling can be done in terms of `int` through `round` instead of through `Expr.round`.",
"number": 16686,
"title": "remove Py2 code from `round` when dropping Python 2 support"
}
] |
126485017c60e249c21dd68c46f70ea7b0584e1e
|
{
"head_commit": "b650dae3d337a0a1c859c25cc1c6b94f050467ed",
"head_commit_message": "Remove reference to Python2 in round",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py\nindex bd3cf4e36cbb..e3a71c74ac96 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/expr.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py\n@@ -3641,17 +3641,8 @@ def round(self, n=None):\n Notes\n =====\n \n- The Python builtin function, round, always returns a\n- float in Python 2 while the SymPy round method (and\n- round with a Number argument in Python 3) returns a\n- Number.\n-\n- >>> from sympy.core.compatibility import PY3\n- >>> isinstance(round(S(123), -2), Number if PY3 else float)\n- True\n-\n- For a consistent behavior, and Python 3 rounding\n- rules, import `round` from sympy.core.compatibility.\n+ When applied to a Number, `round` will return a Number, not a Python\n+ float or int:\n \n >>> isinstance(round(S(123), -2), Number)\n True\n@@ -3670,11 +3661,10 @@ def round(self, n=None):\n return x\n if not x.is_extended_real:\n i, r = x.as_real_imag()\n- return i.round(n) + S.ImaginaryUnit*r.round(n)\n+ return round(i, n) + S.ImaginaryUnit*round(r, n)\n if not x:\n return S.Zero if n is None else x\n \n-\n p = as_int(n or 0)\n \n if x.is_Integer:\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -3641,17 +3641,8 @@ def round(self, n=None):\n Notes\n =====\n \n- The Python builtin function, round, always returns a\n- float in Python 2 while the SymPy round method (and\n- round with a Number argument in Python 3) returns a\n- Number.\n-\n- >>> from sympy.core.compatibility import PY3\n- >>> isinstance(round(S(123), -2), Number if PY3 else float)\n- True\n-\n- For a consistent behavior, and Python 3 rounding\n- rules, import `round` from sympy.core.compatibility.\n+ When applied to a Number, `round` will return a Number, not a Python",
"line": null,
"original_line": 3644,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/expr.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think this whole note should be removed. I would automatically expect every SymPy function to return a SymPy type, which is all that this says now. \n\n@user2:\n`round` is a Python builtin -- that's why this note is added. It let's the user know that SymPy has defined a method call be `round` so a SymPy Number (not Python number) is returned:\r\n```python\r\n>>> type(round)\r\n<type 'builtin_function_or_method'>\r\n```"
}
] |
2f3cac8d7b9a9688cf8e5ae8b40d6900f7ddbb52
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py
index bd3cf4e36cbb..a41a68c4dcea 100644
--- a/sympy/core/expr.py
+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py
@@ -3641,17 +3641,8 @@ def round(self, n=None):
Notes
=====
- The Python builtin function, round, always returns a
- float in Python 2 while the SymPy round method (and
- round with a Number argument in Python 3) returns a
- Number.
-
- >>> from sympy.core.compatibility import PY3
- >>> isinstance(round(S(123), -2), Number if PY3 else float)
- True
-
- For a consistent behavior, and Python 3 rounding
- rules, import `round` from sympy.core.compatibility.
+ The Python ``round`` function uses the SymPy ``round`` method so it
+ will always return a SymPy number (not a Python float or int):
>>> isinstance(round(S(123), -2), Number)
True
@@ -3669,12 +3660,11 @@ def round(self, n=None):
elif x in (S.NaN, S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity, S.ComplexInfinity):
return x
if not x.is_extended_real:
- i, r = x.as_real_imag()
- return i.round(n) + S.ImaginaryUnit*r.round(n)
+ r, i = x.as_real_imag()
+ return r.round(n) + S.ImaginaryUnit*i.round(n)
if not x:
return S.Zero if n is None else x
-
p = as_int(n or 0)
if x.is_Integer:
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 1,
"problem_domain": "Code Refactoring / Architectural Improvement"
}
|
|
sympy__sympy-18802@cf7e36a
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,802
|
Update solvers to handle binomial.
|
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #10993
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Added conditions to expand binomial in solvers
Update expand function for binomial
#### Other comments
Please suggest changes.
### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* solvers
- Fix solvers to handle binomials
* functions
- Update expand function for binomials.
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-03-08T12:24:51Z
|
Solving equations with binomial coefficients should expand them first
When trying to solve an equation with a binomial coefficient with a symbol, the solver fails:
``` python
>>> solve(Eq(binomial(x, 3), 1000))
```
``` pytb
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-7-e56e9952e4b8>", line 1, in <module>
solve(Eq(binomial(x, 3), 1000))
File "sympy/solvers/solvers.py", line 1053, in solve
solution = _solve(f[0], *symbols, **flags)
File "sympy/solvers/solvers.py", line 1619, in _solve
raise NotImplementedError('\n'.join([msg, not_impl_msg % f]))
NotImplementedError:
No algorithms are implemented to solve equation binomial(x, 3) - 1000
```
But when expanding the binomial coefficient first, the solver succeeds:
``` python
>>> solve(Eq(binomial(x, 3).expand(func=True), 1000))[2].n()
19.1895499623678
```
Shouldn't the solver try to expand the binomial before failing?
|
I think it is expected because input for `solve` is :
- a single Expr or Poly that must be zero,
- an Equality
- a Relational expression or boolean
- iterable of one or more of the above
and `binomial` is a function.
But `binomial` is nothing more than a polynomial, in fact. Shouldn't `solve` recognize it, and expand it instead of raising? That sounds easy enough...
I think this makes sense. Could be worth noting that the current solution to the expanded equation is

Maybe one should add a list of functions that can be rewritten as polynomials and do that for instances of functions that are not solvable otherwise? (It turns out that there is no `_eval_rewrite_as_polynomial` for `binomial`, so that must be added, probably just `return self._eval_expand_func()`.)
Edit: something similar could be done for `solveset` as well.
i want to work on this issue can anyone give me some input since i am new to this community
@sylee957 @asmeurer I would like to take up this issue if no fix has been made for it.
|
[
{
"body": "When trying to solve an equation with a binomial coefficient with a symbol, the solver fails:\n\n``` python\n>>> solve(Eq(binomial(x, 3), 1000))\n```\n\n``` pytb\nTraceback (most recent call last):\n File \"<ipython-input-7-e56e9952e4b8>\", line 1, in <module>\n solve(Eq(binomial(x, 3), 1000))\n File \"sympy/solvers/solvers.py\", line 1053, in solve\n solution = _solve(f[0], *symbols, **flags)\n File \"sympy/solvers/solvers.py\", line 1619, in _solve\n raise NotImplementedError('\\n'.join([msg, not_impl_msg % f]))\nNotImplementedError: \nNo algorithms are implemented to solve equation binomial(x, 3) - 1000\n```\n\nBut when expanding the binomial coefficient first, the solver succeeds:\n\n``` python\n>>> solve(Eq(binomial(x, 3).expand(func=True), 1000))[2].n()\n19.1895499623678\n```\n\nShouldn't the solver try to expand the binomial before failing?\n",
"number": 10993,
"title": "Solving equations with binomial coefficients should expand them first"
}
] |
f469375c923d8dc50c6632b21f39b7da3d252548
|
{
"head_commit": "cf7e36a14ace26cb03d6fcffec752e18fb338c57",
"head_commit_message": "Add test.",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\nindex 54023e468260..bf4e42c3ac87 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py\n@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@\n \n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n-from sympy import divisors\n+from sympy import divisors, binomial, expand_func\n from sympy.core.compatibility import (iterable, is_sequence, ordered,\n default_sort_key)\n from sympy.core.sympify import sympify\n@@ -1027,6 +1027,11 @@ def _sympified_list(w):\n bare_f = False\n f[i: i + 1] = [fr, fi]\n \n+ #expand binomial terms\n+ for i, fi in enumerate(f):\n+ if fi.has(binomial):\n+ f[i] = fi.replace(lambda exp: binomial, lambda exp: expand_func(exp))\n+\n # real/imag handling -----------------------------\n if any(isinstance(fi, (bool, BooleanAtom)) for fi in f):\n if flags.get('set', False):\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\nindex 37301d8109ee..531abeed03e0 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py\n@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@\n from sympy import (\n Abs, And, Derivative, Dummy, Eq, Float, Function, Gt, I, Integral,\n LambertW, Lt, Matrix, Or, Poly, Q, Rational, S, Symbol, Ne,\n- Wild, acos, asin, atan, atanh, cos, cosh, diff, erf, erfinv, erfc,\n+ Wild, acos, asin, atan, atanh, binomial, cos, cosh, diff, erf, erfinv, erfc,\n erfcinv, exp, im, log, pi, re, sec, sin,\n sinh, solve, solve_linear, sqrt, sstr, symbols, sympify, tan, tanh,\n root, atan2, arg, Mul, SparseMatrix, ask, Tuple, nsolve, oo,\n@@ -2137,6 +2137,11 @@ def test_issue_17949():\n assert solve(exp(+x-x**2), x) == []\n assert solve(exp(-x-x**2), x) == []\n \n+def test_issue_10993():\n+ assert solve(Eq(binomial(x, 2), 3)) == [-2, 3]\n+ assert solve(Eq(pow(x,2) + binomial(x, 3), x)) == [-4, 0, 1]\n+ assert solve(Eq(binomial(x,2),0)) == [0, 1]\n+\n \n def test_issue_11553():\n eq1 = x + y + 1\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1027,6 +1027,11 @@ def _sympified_list(w):\n bare_f = False\n f[i: i + 1] = [fr, fi]\n \n+ #expand binomial terms\n+ for i, fi in enumerate(f):\n+ if fi.has(binomial):\n+ f[i] = fi.replace(lambda exp: binomial, lambda exp: expand_func(exp))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1033,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/solvers/solvers.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThe filter function here will still match non-binomial expressions.\n\n@author:\nI will correct it right away.\r\n\n\n@user1:\nHow about:\r\n```python\r\nexpand_binomial = lambda f: f.replace(binomial, lambda n, k: expand_func(binomial(n, k)))\r\nf = [expand_binomial(fi) for fi in f]\r\n```\n\n@author:\nThis one looks more efficient, I will make the changes.\n\n@author:\nI earlier thought that binomial expansion should be done in the previous loop as hyperbolic functions are checked and rewritten inside it.\n\n@author:\nplease review the changes."
}
] |
bdb47f3d5ce4dd3aa472dcc8912f2a8402aa48de
|
diff --git a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py
index 7f58a2863cc0..60381774b6e4 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/factorials.py
@@ -1012,7 +1012,7 @@ def _eval_expand_func(self, **hints):
return binomial(*self.args)
k = self.args[1]
- if k.is_Add and n in k.args:
+ if (n-k).is_Integer:
k = n - k
if k.is_Integer:
diff --git a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_factorials.py b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_factorials.py
index 54f3e89a2bbb..b73b0030ed2a 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_factorials.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/combinatorial/tests/test_comb_factorials.py
@@ -432,6 +432,12 @@ def test_binomial():
assert isinstance(binomial(x, x), binomial)
assert isinstance(binomial(x, x - 1), binomial)
+ #issue #18802
+ assert expand_func(binomial(x + 1, x)) == x + 1
+ assert expand_func(binomial(x, x - 1)) == x
+ assert expand_func(binomial(x + 1, x - 1)) == x*(x + 1)/2
+ assert expand_func(binomial(x**2 + 1, x**2)) == x**2 + 1
+
# issue #13980 and #13981
assert binomial(-7, -5) == 0
assert binomial(-23, -12) == 0
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
index 54023e468260..ecc408c22fd9 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/solvers.py
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
-from sympy import divisors
+from sympy import divisors, binomial, expand_func
from sympy.core.compatibility import (iterable, is_sequence, ordered,
default_sort_key)
from sympy.core.sympify import sympify
@@ -1460,6 +1460,10 @@ def _solve(f, *symbols, **flags):
raise NotImplementedError(not_impl_msg % f)
symbol = symbols[0]
+ #expand binomials only if it has the unknown symbol
+ f = f.replace(lambda e: isinstance(e, binomial) and e.has(symbol),
+ lambda e: expand_func(e))
+
# /!\ capture this flag then set it to False so that no checking in
# recursive calls will be done; only the final answer is checked
flags['check'] = checkdens = check = flags.pop('check', True)
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
index 37301d8109ee..c6669062f297 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/tests/test_solvers.py
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
from sympy import (
Abs, And, Derivative, Dummy, Eq, Float, Function, Gt, I, Integral,
LambertW, Lt, Matrix, Or, Poly, Q, Rational, S, Symbol, Ne,
- Wild, acos, asin, atan, atanh, cos, cosh, diff, erf, erfinv, erfc,
+ Wild, acos, asin, atan, atanh, binomial, cos, cosh, diff, erf, erfinv, erfc,
erfcinv, exp, im, log, pi, re, sec, sin,
sinh, solve, solve_linear, sqrt, sstr, symbols, sympify, tan, tanh,
root, atan2, arg, Mul, SparseMatrix, ask, Tuple, nsolve, oo,
@@ -2137,6 +2137,13 @@ def test_issue_17949():
assert solve(exp(+x-x**2), x) == []
assert solve(exp(-x-x**2), x) == []
+def test_issue_10993():
+ assert solve(Eq(binomial(x, 2), 3)) == [-2, 3]
+ assert solve(Eq(pow(x, 2) + binomial(x, 3), x)) == [-4, 0, 1]
+ assert solve(Eq(binomial(x, 2), 0)) == [0, 1]
+ assert solve(a+binomial(x, 3), a) == [-binomial(x, 3)]
+ assert solve(x-binomial(a, 3) + binomial(y, 2) + sin(a), x) == [-sin(a) + binomial(a, 3) - binomial(y, 2)]
+ assert solve((x+1)-binomial(x+1, 3), x) == [-2, -1, 3]
def test_issue_11553():
eq1 = x + y + 1
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-18765@528d346
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,765
|
Add 'evaluate' option to MatAdd and MatMul
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #18764
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
'evaluate' option is added to MatAdd and MatMul, which canonicalizes the object.
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
- matrices
- Added `evaluate` option to ``MatAdd`` and ``MatMul``
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-03-03T08:49:21Z
|
Introduce 'evaluate' keyword argument in MatAdd and MatMul
``MatAdd`` and ``MatMul`` are behaving differently from ``Add`` and ``Mul``.
Here is an example:
```python
>>> from sympy import Add, MatAdd, Symbol, MatrixSymbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> Add(x, x, evaluate=True)
2*x
>>> Add(x, x, evaluate=False)
x + x
>> A = MatrixSymbol('A', 2,2)
>>> MatAdd(A, A)
A + A
>>> MatAdd(A, A, evaluate=True)
A + A
```
I believe it would be better to add ``evaluate`` option which canonicallizes the object, so that
```python
>>> MatAdd(A, A, evaluate=True)
2*A
```
|
I had seen https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/16484#issuecomment-477878619 that things were not originally designed to use any automatic evaluation.
But I think that things can look different at this moment, and I also didn't like the inconsistency there before. But this may need some agreements because this is more of a design issue.
After `evaluate` is introduced in matadd, matmul, it should also be added in matpow or hadamard stuff.
@sylee957
I added it to matpow and hadamard.
If sympy's matrices are designed that way, then setting `evaluate`'s default value as `False` honours this.
This is similar to `Derivative`: since `Derivative` should not be automatically evaluated, its default `evaluate` is `False`.
`evaluate` is used everywhere in sympy core. Since this change does not break backward compatibility, I strongly suggest that it is necessary.
Handling evaluate consistently is important. I think it should be done in general across all of sympy as in #17372.
I don't see why we should change the default to `evaluate=True` for MatAdd etc though. You can use `a+b` or `MatAdd(a, b).doit()` if you want it to evaluate.
|
[
{
"body": "``MatAdd`` and ``MatMul`` are behaving differently from ``Add`` and ``Mul``.\r\n\r\nHere is an example:\r\n```python\r\n>>> from sympy import Add, MatAdd, Symbol, MatrixSymbol\r\n>>> x = Symbol('x')\r\n>>> Add(x, x, evaluate=True)\r\n2*x\r\n>>> Add(x, x, evaluate=False)\r\nx + x\r\n\r\n>> A = MatrixSymbol('A', 2,2)\r\n>>> MatAdd(A, A)\r\nA + A\r\n>>> MatAdd(A, A, evaluate=True)\r\nA + A\r\n```\r\n\r\nI believe it would be better to add ``evaluate`` option which canonicallizes the object, so that\r\n\r\n```python\r\n>>> MatAdd(A, A, evaluate=True)\r\n2*A\r\n```",
"number": 18764,
"title": "Introduce 'evaluate' keyword argument in MatAdd and MatMul"
}
] |
8501526ca26a80ac1b7866a4c1678fcf0045e971
|
{
"head_commit": "528d3461b8bf15d77be9b8de1c48796e6b0aba40",
"head_commit_message": "Improve code quality",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/parameters.py b/sympy/core/parameters.py\nindex 3c5ad8d6be5f..4db5fe371417 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/parameters.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/parameters.py\n@@ -65,7 +65,11 @@ def __setattr__(self, name, value):\n clear_cache()\n return super(_global_parameters, self).__setattr__(name, value)\n \n-global_parameters = _global_parameters(evaluate=True, distribute=True)\n+global_parameters = _global_parameters(\\\n+ evaluate=True,\\\n+ distribute=True,\\\n+ evaluate_matrix=False\\\n+)\n \n @contextmanager\n def evaluate(x):\n@@ -126,3 +130,30 @@ def distribute(x):\n yield\n finally:\n global_parameters.distribute = old\n+\n+\n+@contextmanager\n+def evaluate_matrix(x):\n+ \"\"\" Control automatic evaluation of MatExpr\n+\n+ Classes in matrices module are designed to prefer unevaluated result.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import MatrixSymbol, MatAdd\n+ >>> from sympy.core.parameters import evaluate_matrix\n+ >>> A = MatrixSymbol('A', 2,2)\n+ >>> print(MatAdd(A,-A))\n+ -A + A\n+ >>> with evaluate_matrix(True):\n+ ... print(MatAdd(A,-A))\n+ 0\n+ \"\"\"\n+ old = global_parameters.evaluate_matrix\n+\n+ try:\n+ global_parameters.evaluate_matrix = x\n+ yield\n+ finally:\n+ global_parameters.evaluate_matrix = old\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_parameters.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_parameters.py\nindex 84885533e3ff..f152aadfea3f 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_parameters.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_parameters.py\n@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@\n from sympy.abc import x, y\n-from sympy.core.parameters import evaluate\n+from sympy.core.parameters import evaluate, evaluate_matrix\n from sympy.core import Mul, Add, Pow, S\n-from sympy import sqrt, oo\n+from sympy import sqrt, oo, MatrixSymbol, MatAdd\n \n def test_add():\n with evaluate(False):\n@@ -82,3 +82,10 @@ def test_nested():\n expr = (x + x) + (y + y)\n assert expr.args == ((x + x), (y + y))\n assert expr.args[0].args == (x, x)\n+\n+def test_MatAdd():\n+ A = MatrixSymbol('A', 2,2)\n+ assert MatAdd(A,A).args == (A, A)\n+ with evaluate_matrix(True):\n+ expr = MatAdd(A,A)\n+ assert expr.args == (2, A)\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py\nindex 06ab396a498d..8e68f4fad0af 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py\n@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@\n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n from sympy.core import Mul, sympify\n+from sympy.core.parameters import global_parameters\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.matexpr import (\n MatrixExpr, ShapeError, OneMatrix, ZeroMatrix\n )\n@@ -60,13 +61,20 @@ class HadamardProduct(MatrixExpr):\n \"\"\"\n is_HadamardProduct = True\n \n- def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):\n+ def __new__(cls, *args, evaluate=None, **kwargs):\n args = list(map(sympify, args))\n check = kwargs.get('check', True)\n if check:\n validate(*args)\n \n- return super(HadamardProduct, cls).__new__(cls, *args)\n+ obj = super(HadamardProduct, cls).__new__(cls, *args)\n+\n+ if evaluate is None:\n+ evaluate = global_parameters.evaluate_matrix\n+\n+ if evaluate:\n+ obj = obj.doit(deep=False)\n+ return obj\n \n @property\n def shape(self):\n@@ -80,7 +88,7 @@ def _eval_transpose(self):\n return HadamardProduct(*list(map(transpose, self.args)))\n \n def doit(self, **ignored):\n- expr = self.func(*[i.doit(**ignored) for i in self.args])\n+ expr = self.func(*[i.doit(**ignored) for i in self.args], evaluate=False)\n # Check for explicit matrices:\n from sympy import MatrixBase\n from sympy.matrices.immutable import ImmutableMatrix\n@@ -279,7 +287,7 @@ def absorb(x):\n else:\n new_arg.append(HadamardPower(base, exp))\n \n- x = HadamardProduct(*new_arg)\n+ x = HadamardProduct(*new_arg, evaluate=False)\n \n # Commutativity\n fun = condition(\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py\nindex 84f826683b9c..fef9311063f6 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py\n@@ -4,6 +4,7 @@\n from operator import add\n \n from sympy.core import Add, Basic, sympify\n+from sympy.core.parameters import global_parameters\n from sympy.functions import adjoint\n from sympy.matrices.matrices import MatrixBase\n from sympy.matrices.expressions.transpose import transpose\n@@ -33,7 +34,7 @@ class MatAdd(MatrixExpr, Add):\n \n identity = GenericZeroMatrix()\n \n- def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):\n+ def __new__(cls, *args, evaluate=None, **kwargs):\n if not args:\n return cls.identity\n \n@@ -44,10 +45,20 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):\n check = kwargs.get('check', False)\n \n obj = Basic.__new__(cls, *args)\n+\n if check:\n if all(not isinstance(i, MatrixExpr) for i in args):\n return Add.fromiter(args)\n validate(*args)\n+\n+ if evaluate is None:\n+ evaluate = global_parameters.evaluate_matrix\n+\n+ if evaluate:\n+ if all(not isinstance(i, MatrixExpr) for i in args):\n+ return Add(*args, evaluate=True)\n+ obj = canonicalize(obj)\n+\n return obj\n \n @property\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py\nindex 9da77056932d..5bdefadf0411 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py\n@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@\n \n from sympy import Number\n from sympy.core import Mul, Basic, sympify, S\n+from sympy.core.parameters import global_parameters\n from sympy.functions import adjoint\n from sympy.strategies import (rm_id, unpack, typed, flatten, exhaust,\n do_one, new)\n@@ -34,7 +35,7 @@ class MatMul(MatrixExpr, Mul):\n \n identity = GenericIdentity()\n \n- def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):\n+ def __new__(cls, *args, evaluate=None, **kwargs):\n check = kwargs.get('check', True)\n \n if not args:\n@@ -46,13 +47,22 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):\n args = list(map(sympify, args))\n obj = Basic.__new__(cls, *args)\n factor, matrices = obj.as_coeff_matrices()\n+\n if check:\n validate(*matrices)\n+\n if not matrices:\n # Should it be\n #\n # return Basic.__neq__(cls, factor, GenericIdentity()) ?\n return factor\n+\n+ if evaluate is None:\n+ evaluate = global_parameters.evaluate_matrix\n+\n+ if evaluate:\n+ return canonicalize(obj)\n+\n return obj\n \n @property\n@@ -111,7 +121,7 @@ def as_coeff_matrices(self):\n \n def as_coeff_mmul(self):\n coeff, matrices = self.as_coeff_matrices()\n- return coeff, MatMul(*matrices)\n+ return coeff, MatMul(*matrices, evaluate=False)\n \n def _eval_transpose(self):\n \"\"\"Transposition of matrix multiplication.\n@@ -355,7 +365,7 @@ def combine_permutations(mul):\n else:\n result.append(B)\n \n- return MatMul(*result)\n+ return MatMul(*result, evaluate=False)\n \n rules = (\n any_zeros, remove_ids, combine_powers, unpack, rm_id(lambda x: x == 1),\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py\nindex 9d3cc529f161..e1498373cc4c 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py\n@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@\n \n from .matexpr import MatrixExpr, ShapeError, Identity, ZeroMatrix\n from sympy.core import S\n+from sympy.core.parameters import global_parameters\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n from sympy.matrices import MatrixBase\n \n@@ -10,12 +11,21 @@\n \n class MatPow(MatrixExpr):\n \n- def __new__(cls, base, exp):\n+ def __new__(cls, base, exp, evaluate=None, **options):\n base = _sympify(base)\n if not base.is_Matrix:\n raise TypeError(\"Function parameter should be a matrix\")\n exp = _sympify(exp)\n- return super(MatPow, cls).__new__(cls, base, exp)\n+\n+ obj = super(MatPow, cls).__new__(cls, base, exp)\n+\n+ if evaluate is None:\n+ evaluate = global_parameters.evaluate_matrix\n+\n+ if evaluate:\n+ obj = obj.doit(deep=False)\n+\n+ return obj\n \n @property\n def base(self):\n@@ -84,7 +94,7 @@ def doit(self, **kwargs):\n return Inverse(base).doit(**kwargs)\n elif exp is S.One:\n return base\n- return MatPow(base, exp)\n+ return MatPow(base, exp, evaluate=False)\n \n def _eval_transpose(self):\n base, exp = self.args\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py\nindex c7ce61761e30..5a2c9bdf8e9e 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py\n@@ -7,6 +7,9 @@\n X = MatrixSymbol('X', 2, 2)\n Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', 2, 2)\n \n+def test_evaluate():\n+ assert MatAdd(X, X, evaluate=True) == MatAdd(X, X).doit()\n+\n def test_sort_key():\n assert MatAdd(Y, X).doit().args == (X, Y)\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py\nindex 7d93e2f4e88d..e0d7b5333460 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py\n@@ -19,6 +19,8 @@\n D = MatrixSymbol('D', n, n)\n E = MatrixSymbol('E', m, n)\n \n+def test_evaluate():\n+ assert MatMul(C, C, evaluate=True) == MatMul(C, C).doit()\n \n def test_adjoint():\n assert adjoint(A*B) == Adjoint(B)*Adjoint(A)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -65,7 +65,11 @@ def __setattr__(self, name, value):\n clear_cache()\n return super(_global_parameters, self).__setattr__(name, value)\n \n-global_parameters = _global_parameters(evaluate=True, distribute=True)\n+global_parameters = _global_parameters(\\\n+ evaluate=True,\\\n+ distribute=True,\\\n+ evaluate_matrix=False\\",
"line": null,
"original_line": 71,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/parameters.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThese global flags are problematic and already don't work properly. We should not add new global flags.\r\n\r\nIn any case the argument for having evaluate does not apply to evaluate_matrix because evaluate is used for *disabling* automatic evaluation. If you want to make the matrix expressions evaluate you just have to call `.doit()`.\n\n@user2:\nI agree with Oscar, but as another note, the backslashes here are not needed and should be omitted. \n\n@author:\nYou're right. I will remove `global_parameters.evaluate_matrix`."
}
] |
f9b08dffd2098e7eda96a86283e65f35f86d1a46
|
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py
index 06ab396a498d..c152ece87736 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/hadamard.py
@@ -60,13 +60,16 @@ class HadamardProduct(MatrixExpr):
"""
is_HadamardProduct = True
- def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
+ def __new__(cls, *args, evaluate=False, **kwargs):
args = list(map(sympify, args))
check = kwargs.get('check', True)
if check:
validate(*args)
- return super(HadamardProduct, cls).__new__(cls, *args)
+ obj = super(HadamardProduct, cls).__new__(cls, *args)
+ if evaluate:
+ obj = obj.doit(deep=False)
+ return obj
@property
def shape(self):
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py
index 84f826683b9c..f5290ff539c4 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matadd.py
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ class MatAdd(MatrixExpr, Add):
identity = GenericZeroMatrix()
- def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
+ def __new__(cls, *args, evaluate=False, **kwargs):
if not args:
return cls.identity
@@ -44,10 +44,17 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
check = kwargs.get('check', False)
obj = Basic.__new__(cls, *args)
+
if check:
if all(not isinstance(i, MatrixExpr) for i in args):
return Add.fromiter(args)
validate(*args)
+
+ if evaluate:
+ if all(not isinstance(i, MatrixExpr) for i in args):
+ return Add(*args, evaluate=True)
+ obj = canonicalize(obj)
+
return obj
@property
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
index 9da77056932d..8c9e6016b223 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matmul.py
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ class MatMul(MatrixExpr, Mul):
identity = GenericIdentity()
- def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
+ def __new__(cls, *args, evaluate=False, **kwargs):
check = kwargs.get('check', True)
if not args:
@@ -46,13 +46,19 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
args = list(map(sympify, args))
obj = Basic.__new__(cls, *args)
factor, matrices = obj.as_coeff_matrices()
+
if check:
validate(*matrices)
+
if not matrices:
# Should it be
#
# return Basic.__neq__(cls, factor, GenericIdentity()) ?
return factor
+
+ if evaluate:
+ return canonicalize(obj)
+
return obj
@property
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py
index 9d3cc529f161..ca372a38ba78 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matpow.py
@@ -10,12 +10,17 @@
class MatPow(MatrixExpr):
- def __new__(cls, base, exp):
+ def __new__(cls, base, exp, evaluate=False, **options):
base = _sympify(base)
if not base.is_Matrix:
raise TypeError("Function parameter should be a matrix")
exp = _sympify(exp)
- return super(MatPow, cls).__new__(cls, base, exp)
+
+ obj = super(MatPow, cls).__new__(cls, base, exp)
+ if evaluate:
+ obj = obj.doit(deep=False)
+
+ return obj
@property
def base(self):
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py
index c7ce61761e30..5a2c9bdf8e9e 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matadd.py
@@ -7,6 +7,9 @@
X = MatrixSymbol('X', 2, 2)
Y = MatrixSymbol('Y', 2, 2)
+def test_evaluate():
+ assert MatAdd(X, X, evaluate=True) == MatAdd(X, X).doit()
+
def test_sort_key():
assert MatAdd(Y, X).doit().args == (X, Y)
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py
index 7d93e2f4e88d..e0d7b5333460 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/tests/test_matmul.py
@@ -19,6 +19,8 @@
D = MatrixSymbol('D', n, n)
E = MatrixSymbol('E', m, n)
+def test_evaluate():
+ assert MatMul(C, C, evaluate=True) == MatMul(C, C).doit()
def test_adjoint():
assert adjoint(A*B) == Adjoint(B)*Adjoint(A)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-19107@7150674
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 19,107
|
18778 fuzzy comparisons
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Fixes #18778
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Add to relational a function called cmp(lhs, rhs, op). Where op can be one of
In calculus utils, and under AccumulationBounds, move the logic into _eval_is_lt, _eval_is_gt.
Did the same thing for Indexed in the tensor module.
With this new pull request, any class that inherits from Expr should implement _eval_is_X, if you want to override the default comparison. Returning None if nothing can be evaluated.
Moved the logic from Expr cmp into cmp(lhs, rhs, op).
Moved the logic from Equlaity into cmp - which calls _is_eq
The logic under _InEquality also uses the cmp logic.
Examples:
>>> from sympy.core.relational import cmp
>>> from sympy import sympify
>>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> two = sympify(2)
>>> cmp(x,two, "<") is None
>>> from sympy.core.relational import cmp
>>> from sympy import sympify
>>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> two = sympify(2)
>>> cmp(x,two, "=") is None
>>> from sympy.core.relational import cmp
>>> from sympy import sympify
>>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> three = sympify(3)
>>> two = sympify(2)
>>> cmp(three,two, "<") is False
>>> from sympy.core.relational import cmp
>>> from sympy import sympify
>>> from sympy import Symbol
>>> three = sympify(3)
>>> two = sympify(2)
>>> cmp(three,two, ">") is True
#### Other comments
_eval_Eq doesn't match with _eval_is_gt however,there are already a great number of classes
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-04-11T20:55:17Z
|
Add fuzzy logic comparison functions
There are many bugs in sympy that come from using inequalities in a bool context e.g.:
```julia
In [5]: def f(x):
...: if x < 0:
...: return 'negative'
...: else:
...: return 'nonnegative'
...:
In [6]: f(1)
Out[6]: 'nonnegative'
In [7]: f(-1)
Out[7]: 'negative'
In [8]: f(Symbol('y'))
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError: cannot determine truth value of Relational
```
The solution to this is to use `x.is_negative` which gives a fuzzy bool (True, False, None) and does not raise. That works for comparisons with zero but not for other comparisons like `x<1`:
```
if x < 1: # raises for symbol x
if (x - 1).is_negative: # works but creates a new expression needlessly
if (x < 1) is S.true: # works but not obvious
if (x < 1) == True: # works but not obvious
```
I suggest adding new functions that can replace the use of `Eq`, `Ne`, `Lt` etc and return fuzzy bools. The new functions can have names analogous to those of the old assumptions that also use fuzzy logic e.g.:
```python
is_equal(x, y)
is_unequal(x, y)
is_less_than(x, y)
is_less_than_or_equal(x, y)
...
```
These can be used in place of e.g. `Eq(x, y) is S.true` and return True, False, None. The implementation of `Eq` should then become
```python
class Eq(Relational):
def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs):
value = is_equal(lhs, rhs)
if value is True:
return S.true
elif value is False:
return S.false
else:
# Return unevaluated
return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs)
```
This would cleanly separate the evaluation layer from the querying layer so that evaluation is built on top of querying and querying does not in itself involve creating new instances and evaluating them. Internal code should be changed to use these functions rather than creating Relational instances.
Some of the names can be long e.g. `is_less_than_or_equal` so perhaps an alternative is to use LaTeX-style short names:
```
is_eq(x, y)
is_ne(x, y)
is_lt(x, y)
is_le(x, y)
```
Another possibility is something like
```
cmp(x, '<=', y)
```
which might be more readable for someone new to the codebase.
Making this happen is as simple as taking the code out of the various `Relational.__new__` methods and putting them into separate functions.
|
> works but creates a new expression needlessly
Wouldn't that happen internally anyway?
I only have concerns that this can make things like `is_eq` big because it can accept any expressions.
So managing such things would be an another concern.
I was also undecided about how things like `x > 2` should be handled in binary evaluations or should be coerced into `(x-2).is_positive`.
As far as I can see, sympy doesn't have logics for simple inequalities like triangle inequality, so the things should be directed to make such implementations easier.
The `is_eq` function would just be the body of `Equality.__new__` so it won't be any bigger than that would be anyway. Currently `Equality.__new__` defers to `_eval_Eq` where appropriate.
Currently `Expr.__lt__` and `Lt.__new__` will usually end up doing `(lhs-rhs).is_negative` but that's partly just because there is no `is_lt` function to call. Asking whether `Add(a, -b)` is negative is not inherently any easier than asking whether `a < b`. We just only have an API for one of these and not the other. If we had `is_lt` we could move some of the logic from `Add._eval_is_negative` there and use `is_lt` as part of `Add._eval_is_negative`.
For inequalities the current situation is this:
- `LessThan(a, b)` calls `a.__lt__(b)` (not `a<b` because of #7951)
- `Expr.__lt__(a, b)` usually calls `(a - b).is_extended_negative`
- If `is_extended_negative` is None then `Expr.__lt__` returns `LessThan(a, b, evaluate=False)`
I would propose to change that to:
- `Expr.__lt__` returns `LessThan(a, b)`.
- `LessThan(a, b)` calls `is_lt(a, b)` and evaluates or not from there.
- The `is_lt` function has some logic of its own (taken from current `Expr.__lt__`) and calls `_eval_is_lt` if present.
- At least for now `is_lt` will mostly defer to `(a - b).is_extended_negative`.
- Various `__lt__` methods around sympy should become `_eval_is_lt` instead.
That way all logic always go through the same function `is_lt`.
Ideally `ask(x < y)` would work.
> Ideally `ask(x < y)` would work.
Yes, but that doesn't help us here unless we plan to stop evaluating `x < y` automatically.
I think it isn't a problem if it gives True or False, since ask(True) and ask(False) do what you'd expect. However, this is a problem
```py
>>> I > 3
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "./sympy/core/expr.py", line 403, in __gt__
return self._cmp(other, ">", StrictGreaterThan)
File "./sympy/core/expr.py", line 348, in _cmp
raise TypeError("Invalid comparison of non-real %s" % me)
TypeError: Invalid comparison of non-real I
```
I think we should strongly consider making that return False instead, for reasons I've outlined in other issues.
how can I work with this issue?
> [regarding `I > 3`]...I think we should strongly consider making that return False instead, for reasons I've outlined in other issues.
I thought it would be better to leave it unevaluated, but I am now in favor with returning False since a pure imaginary evaluates as False in terms of sign:
```python
>>> ok = Dummy(negative=False, positive=False, zero=False) # not inconsistent
>>> I.is_negative
False
>>> I.is_positive
False
>>> I.is_zero
False
```
Do we want the same thing for `nan`?
> Some of the names can be long e.g. `is_less_than_or_equal` so perhaps an alternative is to use LaTeX-style short names:
>
> ```
> is_eq(x, y)
> is_ne(x, y)
> is_lt(x, y)
> is_le(x, y)
> ```
>
> Another possibility is something like
>
> ```
> cmp(x, '<=', y)
> ```
>
> which might be more readable for someone new to the codebase.
What about `x.lt(y)` or just `lt(x,y)` which is very similar to the current Lt(x, y)? The difference being that the lowercase version always returns something while the uppercase can remain unevaluated in keeping with things like `sum vs Sum`.
The `is_*` naming scheme can be extended to the `fuzzy_*` names, too: `is_and(*x) -> fuzzy_and(x)` (note different signature).
|
[
{
"body": "There are many bugs in sympy that come from using inequalities in a bool context e.g.:\r\n```julia\r\nIn [5]: def f(x): \r\n ...: if x < 0: \r\n ...: return 'negative' \r\n ...: else: \r\n ...: return 'nonnegative' \r\n ...: \r\n\r\nIn [6]: f(1) \r\nOut[6]: 'nonnegative'\r\n\r\nIn [7]: f(-1) \r\nOut[7]: 'negative'\r\n\r\nIn [8]: f(Symbol('y')) \r\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nTypeError: cannot determine truth value of Relational\r\n```\r\nThe solution to this is to use `x.is_negative` which gives a fuzzy bool (True, False, None) and does not raise. That works for comparisons with zero but not for other comparisons like `x<1`:\r\n```\r\nif x < 1: # raises for symbol x\r\n\r\nif (x - 1).is_negative: # works but creates a new expression needlessly\r\n\r\nif (x < 1) is S.true: # works but not obvious\r\n\r\nif (x < 1) == True: # works but not obvious\r\n```\r\nI suggest adding new functions that can replace the use of `Eq`, `Ne`, `Lt` etc and return fuzzy bools. The new functions can have names analogous to those of the old assumptions that also use fuzzy logic e.g.:\r\n```python\r\nis_equal(x, y)\r\nis_unequal(x, y)\r\nis_less_than(x, y)\r\nis_less_than_or_equal(x, y)\r\n...\r\n```\r\nThese can be used in place of e.g. `Eq(x, y) is S.true` and return True, False, None. The implementation of `Eq` should then become\r\n```python\r\nclass Eq(Relational):\r\n def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs):\r\n value = is_equal(lhs, rhs)\r\n if value is True:\r\n return S.true\r\n elif value is False:\r\n return S.false\r\n else:\r\n # Return unevaluated\r\n return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs)\r\n```\r\nThis would cleanly separate the evaluation layer from the querying layer so that evaluation is built on top of querying and querying does not in itself involve creating new instances and evaluating them. Internal code should be changed to use these functions rather than creating Relational instances.\r\n\r\nSome of the names can be long e.g. `is_less_than_or_equal` so perhaps an alternative is to use LaTeX-style short names:\r\n```\r\nis_eq(x, y)\r\nis_ne(x, y)\r\nis_lt(x, y)\r\nis_le(x, y)\r\n```\r\nAnother possibility is something like\r\n```\r\ncmp(x, '<=', y)\r\n```\r\nwhich might be more readable for someone new to the codebase.\r\n\r\nMaking this happen is as simple as taking the code out of the various `Relational.__new__` methods and putting them into separate functions.",
"number": 18778,
"title": "Add fuzzy logic comparison functions"
}
] |
f46f4488c7cb7aff9666e26ce1bfb980f98e97a7
|
{
"head_commit": "715067463fffbbe855ae35fd305c8f02f2671ef0",
"head_commit_message": "feat(core): Add fuzzy comparison functions\n\nRemove unneeded imports and blank lines",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/calculus/util.py b/sympy/calculus/util.py\nindex 50a9be1c8282..71ecb0050754 100644\n--- a/sympy/calculus/util.py\n+++ b/sympy/calculus/util.py\n@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@\n from sympy.sets.fancysets import ImageSet\n from sympy.solvers.inequalities import solve_univariate_inequality\n from sympy.utilities import filldedent\n-\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n \n def continuous_domain(f, symbol, domain):\n \"\"\"\n@@ -1372,153 +1372,7 @@ def __abs__(self):\n else:\n return self\n \n- def __lt__(self, other):\n- \"\"\"\n- Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds\n- object is less than the range of values attained by `other`, where\n- other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or extended\n- real number value, False if `other` satisfies the same property, else\n- an unevaluated Relational\n \n- Examples\n- ========\n-\n- >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) < AccumBounds(4, oo)\n- True\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) < AccumBounds(3, 4)\n- AccumBounds(1, 4) < AccumBounds(3, 4)\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) < -1\n- False\n-\n- \"\"\"\n- other = _sympify(other)\n- if isinstance(other, AccumBounds):\n- if self.max < other.min:\n- return True\n- if self.min >= other.max:\n- return False\n- elif not other.is_extended_real:\n- raise TypeError(\n- \"Invalid comparison of %s %s\" %\n- (type(other), other))\n- elif other.is_comparable:\n- if self.max < other:\n- return True\n- if self.min >= other:\n- return False\n- return super().__lt__(other)\n-\n- def __le__(self, other):\n- \"\"\"\n- Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds\n- object is less than or equal to the range of values attained by\n- `other`, where other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds\n- object or extended real number value, False if `other`\n- satisfies the same property, else an unevaluated Relational.\n-\n- Examples\n- ========\n-\n- >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) <= AccumBounds(4, oo)\n- True\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) <= AccumBounds(3, 4)\n- AccumBounds(1, 4) <= AccumBounds(3, 4)\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) <= 0\n- False\n-\n- \"\"\"\n- other = _sympify(other)\n- if isinstance(other, AccumBounds):\n- if self.max <= other.min:\n- return True\n- if self.min > other.max:\n- return False\n- elif not other.is_extended_real:\n- raise TypeError(\n- \"Invalid comparison of %s %s\" %\n- (type(other), other))\n- elif other.is_comparable:\n- if self.max <= other:\n- return True\n- if self.min > other:\n- return False\n- return super().__le__(other)\n-\n- def __gt__(self, other):\n- \"\"\"\n- Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds\n- object is greater than the range of values attained by `other`,\n- where other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or\n- extended real number value, False if `other` satisfies\n- the same property, else an unevaluated Relational.\n-\n- Examples\n- ========\n-\n- >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) > AccumBounds(4, oo)\n- False\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)\n- AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) > -1\n- True\n-\n- \"\"\"\n- other = _sympify(other)\n- if isinstance(other, AccumBounds):\n- if self.min > other.max:\n- return True\n- if self.max <= other.min:\n- return False\n- elif not other.is_extended_real:\n- raise TypeError(\n- \"Invalid comparison of %s %s\" %\n- (type(other), other))\n- elif other.is_comparable:\n- if self.min > other:\n- return True\n- if self.max <= other:\n- return False\n- return super().__gt__(other)\n-\n- def __ge__(self, other):\n- \"\"\"\n- Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds\n- object is less that the range of values attained by `other`, where\n- other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or extended\n- real number value, False if `other` satisfies the same\n- property, else an unevaluated Relational.\n-\n- Examples\n- ========\n-\n- >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) >= AccumBounds(4, oo)\n- False\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) >= AccumBounds(3, 4)\n- AccumBounds(1, 4) >= AccumBounds(3, 4)\n- >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) >= 1\n- True\n-\n- \"\"\"\n- other = _sympify(other)\n- if isinstance(other, AccumBounds):\n- if self.min >= other.max:\n- return True\n- if self.max < other.min:\n- return False\n- elif not other.is_extended_real:\n- raise TypeError(\n- \"Invalid comparison of %s %s\" %\n- (type(other), other))\n- elif other.is_comparable:\n- if self.min >= other:\n- return True\n- if self.max < other:\n- return False\n- return super().__ge__(other)\n \n def __contains__(self, other):\n \"\"\"\n@@ -1627,5 +1481,103 @@ def union(self, other):\n return AccumBounds(other.min, Max(self.max, other.max))\n \n \n+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, AccumulationBounds) # type: ignore # noqa:F811\n+def _eval_is_le(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ if lhs.max <= rhs.min:\n+ return True\n+ if lhs.min > rhs.max:\n+ return False\n+\n+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, Basic) # type: ignore # noqa:F811\n+def _eval_is_le(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds\n+ object is greater than the range of values attained by `other`,\n+ where other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or\n+ extended real number value, False if `other` satisfies\n+ the same property, else an unevaluated Relational.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo\n+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) > AccumBounds(4, oo)\n+ False\n+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)\n+ AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)\n+ >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) > -1\n+ True\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if not rhs.is_extended_real:\n+ raise TypeError(\n+ \"Invalid comparison of %s %s\" %\n+ (type(rhs), rhs))\n+ elif rhs.is_comparable:\n+ if lhs.max <= rhs:\n+ return True\n+ if lhs.min > rhs:\n+ return False\n+\n+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, AccumulationBounds)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ if lhs.min >= rhs.max:\n+ return True\n+ if lhs.max < rhs.min:\n+ return False\n+\n+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, Basic)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Returns True if range of values attained by `lhs` AccumulationBounds\n+ object is less that the range of values attained by `rhs`, where\n+ other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or extended\n+ real number value, False if `rhs` satisfies the same\n+ property, else an unevaluated Relational.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo\n+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) >= AccumBounds(4, oo)\n+ False\n+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) >= AccumBounds(3, 4)\n+ AccumBounds(1, 4) >= AccumBounds(3, 4)\n+ >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) >= 1\n+ True\n+ \"\"\"\n+\n+ if not rhs.is_extended_real:\n+ raise TypeError(\n+ \"Invalid comparison of %s %s\" %\n+ (type(rhs), rhs))\n+ elif rhs.is_comparable:\n+ if lhs.min >= rhs:\n+ return True\n+ if lhs.max < rhs:\n+ return False\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, AccumulationBounds)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ if not lhs.is_extended_real:\n+ raise TypeError(\n+ \"Invalid comparison of %s %s\" %\n+ (type(lhs), lhs))\n+ elif lhs.is_comparable:\n+ if rhs.max <= lhs:\n+ return True\n+ if rhs.min > lhs:\n+ return False\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, AccumulationBounds)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ if lhs.min >= rhs.max:\n+ return True\n+ if lhs.max < rhs.min:\n+ return False\n+\n # setting an alias for AccumulationBounds\n AccumBounds = AccumulationBounds\ndiff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py b/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py\nindex da19cbf50601..874c093219a7 100644\n--- a/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py\n+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py\n@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import (flatten, has_variety, minlex,\n has_dups, runs)\n from mpmath.libmp.libintmath import ifac\n-\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n \n def _af_rmul(a, b):\n \"\"\"\n@@ -950,15 +950,7 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):\n \n return cls._af_new(aform)\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- other = _sympify(other)\n- if not isinstance(other, Permutation):\n- return None\n-\n- if self._size != other._size:\n- return None\n \n- return as_Boolean(self._array_form == other._array_form)\n \n @classmethod\n def _af_new(cls, perm):\n@@ -3020,3 +3012,10 @@ def __new__(cls, perm, x, evaluate=None):\n \n obj = super().__new__(cls, perm, x)\n return obj\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Permutation, Permutation)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ if lhs._size != rhs._size:\n+ return None\n+ return as_Boolean(lhs._array_form == rhs._array_form)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/containers.py b/sympy/core/containers.py\nindex 5db2885d0a88..8acf6b4a19f9 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/containers.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/containers.py\n@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@\n from sympy.core.compatibility import as_int, MutableSet\n from sympy.core.sympify import sympify, converter\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import iterable\n-\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n \n \n class Tuple(Basic):\n@@ -141,25 +141,27 @@ def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None):\n else:\n return self.args.index(value, start, stop)\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef\n- from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool\n- from sympy.core.relational import Eq\n \n- if other.is_Symbol or isinstance(other, AppliedUndef):\n- return None\n+converter[tuple] = lambda tup: Tuple(*tup)\n+\n \n- if not isinstance(other, Tuple) or len(self) != len(other):\n- return S.false\n+@dispatch(Tuple, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef\n+ from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool\n+ from sympy.core.relational import Eq\n \n- r = fuzzy_and(fuzzy_bool(Eq(s, o)) for s, o in zip(self, other))\n- if r is True:\n- return S.true\n- elif r is False:\n- return S.false\n+ if rhs.is_Symbol or isinstance(rhs, AppliedUndef):\n+ return None\n \n+ if not isinstance(rhs, Tuple) or len(lhs) != len(rhs):\n+ return S.false\n \n-converter[tuple] = lambda tup: Tuple(*tup)\n+ r = fuzzy_and(fuzzy_bool(Eq(s, o)) for s, o in zip(lhs, rhs))\n+ if r is True:\n+ return S.true\n+ elif r is False:\n+ return S.false\n \n \n def tuple_wrapper(method):\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py\nindex 2b16305db3d4..d13715c31445 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/expr.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py\n@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@\n+from __future__ import print_function, division\n from typing import Tuple as tTuple\n \n from .sympify import sympify, _sympify, SympifyError\n@@ -23,6 +24,10 @@ class Expr(Basic, EvalfMixin):\n used only for argument storage and expression manipulation, i.e.\n pattern matching, substitutions, etc).\n \n+ If you want to override the comparisons of expressions:\n+ Should use _eval_is_X (where X is gt, ge, lt, or Eq).\n+ _eval_is_X should return None if you want to return the object unevaluated\n+\n See Also\n ========\n \n@@ -339,78 +344,30 @@ def __complex__(self):\n re, im = result.as_real_imag()\n return complex(float(re), float(im))\n \n- def _cmp(self, other, op, cls):\n- assert op in (\"<\", \">\", \"<=\", \">=\")\n- try:\n- other = _sympify(other)\n- except SympifyError:\n- return NotImplemented\n-\n- if not isinstance(other, Expr):\n- return NotImplemented\n-\n- for me in (self, other):\n- if me.is_extended_real is False:\n- raise TypeError(\"Invalid comparison of non-real %s\" % me)\n- if me is S.NaN:\n- raise TypeError(\"Invalid NaN comparison\")\n-\n- n2 = _n2(self, other)\n- if n2 is not None:\n- # use float comparison for infinity.\n- # otherwise get stuck in infinite recursion\n- if n2 in (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity):\n- n2 = float(n2)\n- if op == \"<\":\n- return _sympify(n2 < 0)\n- elif op == \">\":\n- return _sympify(n2 > 0)\n- elif op == \"<=\":\n- return _sympify(n2 <= 0)\n- else: # >=\n- return _sympify(n2 >= 0)\n-\n- if self.is_extended_real and other.is_extended_real:\n- if op in (\"<=\", \">\") \\\n- and ((self.is_infinite and self.is_extended_negative) \\\n- or (other.is_infinite and other.is_extended_positive)):\n- return S.true if op == \"<=\" else S.false\n- if op in (\"<\", \">=\") \\\n- and ((self.is_infinite and self.is_extended_positive) \\\n- or (other.is_infinite and other.is_extended_negative)):\n- return S.true if op == \">=\" else S.false\n- diff = self - other\n- if diff is not S.NaN:\n- if op == \"<\":\n- test = diff.is_extended_negative\n- elif op == \">\":\n- test = diff.is_extended_positive\n- elif op == \"<=\":\n- test = diff.is_extended_nonpositive\n- else: # >=\n- test = diff.is_extended_nonnegative\n-\n- if test is not None:\n- return S.true if test == True else S.false\n-\n- # return unevaluated comparison object\n- return cls(self, other, evaluate=False)\n-\n def __ge__(self, other):\n- from sympy import GreaterThan\n- return self._cmp(other, \">=\", GreaterThan)\n+ from .relational import GreaterThan\n+ return self._cmp(other, GreaterThan)\n \n def __le__(self, other):\n- from sympy import LessThan\n- return self._cmp(other, \"<=\", LessThan)\n+ from .relational import LessThan\n+ return self._cmp(other, LessThan)\n \n def __gt__(self, other):\n- from sympy import StrictGreaterThan\n- return self._cmp(other, \">\", StrictGreaterThan)\n+ from .relational import StrictGreaterThan\n+ return self._cmp(other, StrictGreaterThan)\n \n def __lt__(self, other):\n- from sympy import StrictLessThan\n- return self._cmp(other, \"<\", StrictLessThan)\n+ from .relational import StrictLessThan\n+ return self._cmp(other, StrictLessThan)\n+\n+ def _cmp(self, other, cls):\n+ try:\n+ other = _sympify(other)\n+ except SympifyError:\n+ return NotImplemented\n+ if not isinstance(other, Expr):\n+ return NotImplemented\n+ return cls(self, other)\n \n def __trunc__(self):\n if not self.is_number:\n@@ -3955,17 +3912,6 @@ def doit(self, **kwargs):\n return self.args[0]\n \n \n-def _n2(a, b):\n- \"\"\"Return (a - b).evalf(2) if a and b are comparable, else None.\n- This should only be used when a and b are already sympified.\n- \"\"\"\n- # /!\\ it is very important (see issue 8245) not to\n- # use a re-evaluated number in the calculation of dif\n- if a.is_comparable and b.is_comparable:\n- dif = (a - b).evalf(2)\n- if dif.is_comparable:\n- return dif\n-\n \n def unchanged(func, *args):\n \"\"\"Return True if `func` applied to the `args` is unchanged.\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/numbers.py b/sympy/core/numbers.py\nindex 27b671e148c9..bf1a7c1a8109 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/numbers.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/numbers.py\n@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@\n from sympy.core.compatibility import (as_int, HAS_GMPY, SYMPY_INTS,\n int_info, gmpy)\n from sympy.core.cache import lru_cache\n-\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n import mpmath\n import mpmath.libmp as mlib\n from mpmath.libmp import bitcount\n@@ -276,6 +276,8 @@ def _igcd2_python(a, b):\n \n \n # Use Lehmer's algorithm only for very large numbers.\n+# The limit could be different on Python 2.7 and 3.x.\n+# If so, then this could be defined in compatibility.py.\n BIGBITS = 5000\n def igcd_lehmer(a, b):\n \"\"\"Computes greatest common divisor of two integers.\n@@ -3264,10 +3266,6 @@ def __eq__(self, other):\n def __ne__(self, other):\n return other is not S.NaN\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- # NaN is not mathematically equal to anything, even NaN\n- return S.false\n-\n # Expr will _sympify and raise TypeError\n __gt__ = Expr.__gt__\n __ge__ = Expr.__ge__\n@@ -3276,6 +3274,9 @@ def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n \n nan = S.NaN\n \n+@dispatch(NaN, Expr)\n+def _eval_Eq(a, b): # noqa:F811\n+ return S.false\n \n class ComplexInfinity(AtomicExpr, metaclass=Singleton):\n r\"\"\"Complex infinity.\n@@ -3413,7 +3414,6 @@ def __long__(self):\n def __hash__(self):\n return super().__hash__()\n \n-\n class Exp1(NumberSymbol, metaclass=Singleton):\n r\"\"\"The `e` constant.\n \n@@ -3889,6 +3889,9 @@ def _mpc_(self):\n \n I = S.ImaginaryUnit\n \n+@dispatch(Tuple, Number)\n+def _eval_Eq(self, other): # noqa: F811\n+ return S.false\n \n def sympify_fractions(f):\n return Rational(f.numerator, f.denominator, 1)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/relational.py b/sympy/core/relational.py\nindex c65577b561b9..38819b77d9fe 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/relational.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/relational.py\n@@ -1,15 +1,13 @@\n from typing import Dict, Type, Union\n \n from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning\n-from .add import _unevaluated_Add, Add\n from .basic import S, Atom\n from .compatibility import ordered\n from .basic import Basic\n-from .expr import Expr\n from .evalf import EvalfMixin\n-from .sympify import _sympify\n+from .sympify import _sympify, SympifyError\n from .parameters import global_parameters\n-\n+from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_bool, fuzzy_xor, fuzzy_and, fuzzy_not\n from sympy.logic.boolalg import Boolean, BooleanAtom\n \n __all__ = (\n@@ -18,14 +16,21 @@\n 'StrictGreaterThan', 'GreaterThan',\n )\n \n+from .expr import Expr\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n+\n+\n \n def _nontrivBool(side):\n return isinstance(side, Boolean) and \\\n- not isinstance(side, (BooleanAtom, Atom))\n+ not isinstance(side, Atom)\n+\n \n \n # Note, see issue 4986. Ideally, we wouldn't want to subclass both Boolean\n # and Expr.\n+# from .. import Expr\n+\n \n def _canonical(cond):\n # return a condition in which all relationals are canonical\n@@ -291,6 +296,7 @@ def equals(self, other, failing_expression=False):\n return left\n \n def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):\n+ from .add import Add\n r = self\n r = r.func(*[i.simplify(**kwargs) for i in r.args])\n if r.is_Relational:\n@@ -318,9 +324,9 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):\n if m.is_negative:\n # Dividing with a negative number, so change order of arguments\n # canonical will put the symbol back on the lhs later\n- r = r.func(-b/m, x)\n+ r = r.func(-b / m, x)\n else:\n- r = r.func(x, -b/m)\n+ r = r.func(x, -b / m)\n else:\n r = r.func(b, S.zero)\n except ValueError:\n@@ -332,8 +338,8 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):\n constant = c[-1]\n c[-1] = 0\n scale = gcd(c)\n- c = [ctmp/scale for ctmp in c]\n- r = r.func(Poly.from_list(c, x).as_expr(), -constant/scale)\n+ c = [ctmp / scale for ctmp in c]\n+ r = r.func(Poly.from_list(c, x).as_expr(), -constant / scale)\n except PolynomialError:\n pass\n elif len(free) >= 2:\n@@ -346,18 +352,18 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):\n constant = m[-1]\n del m[-1]\n scale = gcd(m)\n- m = [mtmp/scale for mtmp in m]\n+ m = [mtmp / scale for mtmp in m]\n nzm = list(filter(lambda f: f[0] != 0, list(zip(m, free))))\n if scale.is_zero is False:\n if constant != 0:\n # lhs: expression, rhs: constant\n- newexpr = Add(*[i*j for i, j in nzm])\n- r = r.func(newexpr, -constant/scale)\n+ newexpr = Add(*[i * j for i, j in nzm])\n+ r = r.func(newexpr, -constant / scale)\n else:\n # keep first term on lhs\n- lhsterm = nzm[0][0]*nzm[0][1]\n+ lhsterm = nzm[0][0] * nzm[0][1]\n del nzm[0]\n- newexpr = Add(*[i*j for i, j in nzm])\n+ newexpr = Add(*[i * j for i, j in nzm])\n r = r.func(lhsterm, -newexpr)\n \n else:\n@@ -367,7 +373,7 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):\n # Did we get a simplified result?\n r = r.canonical\n measure = kwargs['measure']\n- if measure(r) < kwargs['ratio']*measure(self):\n+ if measure(r) < kwargs['ratio'] * measure(self):\n return r\n else:\n return self\n@@ -475,12 +481,6 @@ class Equality(Relational):\n is_Equality = True\n \n def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs=None, **options):\n- from sympy.core.add import Add\n- from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_bool, fuzzy_xor, fuzzy_and, fuzzy_not\n- from sympy.core.expr import _n2\n- from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import arg\n- from sympy.simplify.simplify import clear_coefficients\n- from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift\n \n if rhs is None:\n SymPyDeprecationWarning(\n@@ -490,122 +490,25 @@ def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs=None, **options):\n deprecated_since_version=\"1.5\"\n ).warn()\n rhs = 0\n-\n+ evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)\n lhs = _sympify(lhs)\n rhs = _sympify(rhs)\n-\n- evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)\n-\n if evaluate:\n- if isinstance(lhs, Boolean) != isinstance(lhs, Boolean):\n- # e.g. 0/1 not recognized as Boolean in SymPy\n- return S.false\n-\n- # If one expression has an _eval_Eq, return its results.\n- if hasattr(lhs, '_eval_Eq'):\n- r = lhs._eval_Eq(rhs)\n- if r is not None:\n- return r\n- if hasattr(rhs, '_eval_Eq'):\n- r = rhs._eval_Eq(lhs)\n- if r is not None:\n- return r\n- # If expressions have the same structure, they must be equal.\n- if lhs == rhs:\n- return S.true # e.g. True == True\n- elif all(isinstance(i, BooleanAtom) for i in (rhs, lhs)):\n- return S.false # True != False\n- elif not (lhs.is_Symbol or rhs.is_Symbol) and (\n- isinstance(lhs, Boolean) !=\n- isinstance(rhs, Boolean)):\n- return S.false # only Booleans can equal Booleans\n-\n- if lhs.is_infinite or rhs.is_infinite:\n- if fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_infinite, rhs.is_infinite]):\n- return S.false\n- if fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_extended_real, rhs.is_extended_real]):\n- return S.false\n- if fuzzy_and([lhs.is_extended_real, rhs.is_extended_real]):\n- r = fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_extended_positive, fuzzy_not(rhs.is_extended_positive)])\n- return S(r)\n-\n- # Try to split real/imaginary parts and equate them\n- I = S.ImaginaryUnit\n-\n- def split_real_imag(expr):\n- real_imag = lambda t: (\n- 'real' if t.is_extended_real else\n- 'imag' if (I*t).is_extended_real else None)\n- return sift(Add.make_args(expr), real_imag)\n-\n- lhs_ri = split_real_imag(lhs)\n- if not lhs_ri[None]:\n- rhs_ri = split_real_imag(rhs)\n- if not rhs_ri[None]:\n- eq_real = Eq(Add(*lhs_ri['real']), Add(*rhs_ri['real']))\n- eq_imag = Eq(I*Add(*lhs_ri['imag']), I*Add(*rhs_ri['imag']))\n- res = fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, [eq_real, eq_imag]))\n- if res is not None:\n- return S(res)\n-\n- # Compare e.g. zoo with 1+I*oo by comparing args\n- arglhs = arg(lhs)\n- argrhs = arg(rhs)\n- # Guard against Eq(nan, nan) -> False\n- if not (arglhs == S.NaN and argrhs == S.NaN):\n- res = fuzzy_bool(Eq(arglhs, argrhs))\n- if res is not None:\n- return S(res)\n-\n- return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)\n-\n- if all(isinstance(i, Expr) for i in (lhs, rhs)):\n- # see if the difference evaluates\n- dif = lhs - rhs\n- z = dif.is_zero\n- if z is not None:\n- if z is False and dif.is_commutative: # issue 10728\n- return S.false\n- if z:\n- return S.true\n- # evaluate numerically if possible\n- n2 = _n2(lhs, rhs)\n- if n2 is not None:\n- return _sympify(n2 == 0)\n- # see if the ratio evaluates\n- n, d = dif.as_numer_denom()\n- rv = None\n- if n.is_zero:\n- rv = d.is_nonzero\n- elif n.is_finite:\n- if d.is_infinite:\n- rv = S.true\n- elif n.is_zero is False:\n- rv = d.is_infinite\n- if rv is None:\n- # if the condition that makes the denominator\n- # infinite does not make the original expression\n- # True then False can be returned\n- l, r = clear_coefficients(d, S.Infinity)\n- args = [_.subs(l, r) for _ in (lhs, rhs)]\n- if args != [lhs, rhs]:\n- rv = fuzzy_bool(Eq(*args))\n- if rv is True:\n- rv = None\n- elif any(a.is_infinite for a in Add.make_args(n)):\n- # (inf or nan)/x != 0\n- rv = S.false\n- if rv is not None:\n- return _sympify(rv)\n+ val = is_eq(lhs, rhs)\n+ if val is None:\n+ return cls(lhs, rhs, evaluate=False)\n+ else:\n+ return _sympify(val)\n \n- return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)\n+ return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs)\n \n @classmethod\n def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n return _sympify(lhs == rhs)\n \n def _eval_rewrite_as_Add(self, *args, **kwargs):\n- \"\"\"return Eq(L, R) as L - R. To control the evaluation of\n+ \"\"\"\n+ return Eq(L, R) as L - R. To control the evaluation of\n the result set pass `evaluate=True` to give L - R;\n if `evaluate=None` then terms in L and R will not cancel\n but they will be listed in canonical order; otherwise\n@@ -624,6 +527,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Add(self, *args, **kwargs):\n >>> eq.rewrite(Add, evaluate=False).args\n (b, x, b, -x)\n \"\"\"\n+ from .add import _unevaluated_Add, Add\n L, R = args\n evaluate = kwargs.get('evaluate', True)\n if evaluate:\n@@ -646,6 +550,7 @@ def binary_symbols(self):\n return set()\n \n def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):\n+ from .add import Add\n from sympy.solvers.solveset import linear_coeffs\n # standard simplify\n e = super()._eval_simplify(**kwargs)\n@@ -658,11 +563,11 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):\n m, b = linear_coeffs(\n e.rewrite(Add, evaluate=False), x)\n if m.is_zero is False:\n- enew = e.func(x, -b/m)\n+ enew = e.func(x, -b / m)\n else:\n- enew = e.func(m*x, -b)\n+ enew = e.func(m * x, -b)\n measure = kwargs['measure']\n- if measure(enew) <= kwargs['ratio']*measure(e):\n+ if measure(enew) <= kwargs['ratio'] * measure(e):\n e = enew\n except ValueError:\n pass\n@@ -727,17 +632,13 @@ class Unequality(Relational):\n def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options):\n lhs = _sympify(lhs)\n rhs = _sympify(rhs)\n-\n evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)\n-\n if evaluate:\n- if isinstance(lhs, Boolean) != isinstance(lhs, Boolean):\n- # e.g. 0/1 not recognized as Boolean in SymPy\n- return S.true\n-\n- is_equal = Equality(lhs, rhs)\n- if isinstance(is_equal, BooleanAtom):\n- return is_equal.negated\n+ val = is_neq(lhs, rhs)\n+ if val is None:\n+ return cls(lhs, rhs, evaluate=False)\n+ else:\n+ return _sympify(val)\n \n return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)\n \n@@ -776,12 +677,20 @@ class _Inequality(Relational):\n __slots__ = ()\n \n def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options):\n- lhs = _sympify(lhs)\n- rhs = _sympify(rhs)\n \n- evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)\n+ try:\n+ lhs = _sympify(lhs)\n+ rhs = _sympify(rhs)\n+ except SympifyError:\n+ return NotImplemented\n \n+ evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)\n if evaluate:\n+ for me in (lhs, rhs):\n+ if me.is_extended_real is False:\n+ raise TypeError(\"Invalid comparison of non-real %s\" % me)\n+ if me is S.NaN:\n+ raise TypeError(\"Invalid NaN comparison\")\n # First we invoke the appropriate inequality method of `lhs`\n # (e.g., `lhs.__lt__`). That method will try to reduce to\n # boolean or raise an exception. It may keep calling\n@@ -790,16 +699,17 @@ def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options):\n # nor a subclass was able to reduce to boolean or raise an\n # exception). In that case, it must call us with\n # `evaluate=False` to prevent infinite recursion.\n- r = cls._eval_relation(lhs, rhs)\n- if r is not None:\n- return r\n- # Note: not sure r could be None, perhaps we never take this\n- # path? In principle, could use this to shortcut out if a\n- # class realizes the inequality cannot be evaluated further.\n+ return cls._eval_relation(lhs, rhs, **options)\n \n # make a \"non-evaluated\" Expr for the inequality\n return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)\n \n+ @classmethod\n+ def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs, **options):\n+ return cls._eval_fuzzy_relation(lhs, rhs)\n+\n+\n+\n class _Greater(_Inequality):\n \"\"\"Not intended for general use\n \n@@ -1066,9 +976,12 @@ class GreaterThan(_Greater):\n rel_op = '>='\n \n @classmethod\n- def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n- # We don't use the op symbol here: workaround issue #7951\n- return _sympify(lhs.__ge__(rhs))\n+ def _eval_fuzzy_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n+ val = is_ge(lhs, rhs)\n+ if val is None:\n+ return cls(lhs, rhs, evaluate=False)\n+ else:\n+ return _sympify(val)\n \n \n Ge = GreaterThan\n@@ -1081,9 +994,12 @@ class LessThan(_Less):\n rel_op = '<='\n \n @classmethod\n- def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n- # We don't use the op symbol here: workaround issue #7951\n- return _sympify(lhs.__le__(rhs))\n+ def _eval_fuzzy_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n+ val = is_le(lhs, rhs)\n+ if val is None:\n+ return cls(lhs, rhs, evaluate=False)\n+ else:\n+ return _sympify(val)\n \n \n Le = LessThan\n@@ -1096,9 +1012,12 @@ class StrictGreaterThan(_Greater):\n rel_op = '>'\n \n @classmethod\n- def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n- # We don't use the op symbol here: workaround issue #7951\n- return _sympify(lhs.__gt__(rhs))\n+ def _eval_fuzzy_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n+ val = is_gt(lhs, rhs)\n+ if val is None:\n+ return cls(lhs, rhs, evaluate=False)\n+ else:\n+ return _sympify(val)\n \n \n Gt = StrictGreaterThan\n@@ -1111,13 +1030,16 @@ class StrictLessThan(_Less):\n rel_op = '<'\n \n @classmethod\n- def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n- # We don't use the op symbol here: workaround issue #7951\n- return _sympify(lhs.__lt__(rhs))\n+ def _eval_fuzzy_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n+ val = is_lt(lhs, rhs)\n+ if val is None:\n+ return cls(lhs, rhs, evaluate=False)\n+ else:\n+ return _sympify(val)\n \n \n-Lt = StrictLessThan\n \n+Lt = StrictLessThan\n \n # A class-specific (not object-specific) data item used for a minor speedup.\n # It is defined here, rather than directly in the class, because the classes\n@@ -1138,3 +1060,169 @@ def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n '<': StrictLessThan,\n 'lt': StrictLessThan,\n }\n+\n+\n+def _n2(a, b):\n+ \"\"\"Return (a - b).evalf(2) if a and b are comparable, else None.\n+ This should only be used when a and b are already sympified.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # /!\\ it is very important (see issue 8245) not to\n+ # use a re-evaluated number in the calculation of dif\n+ if a.is_comparable and b.is_comparable:\n+ dif = (a - b).evalf(2)\n+ if dif.is_comparable:\n+ return dif\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)\n+def _eval_is_le(lhs, rhs):\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs):\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+\n+def is_lt(lhs, rhs):\n+ return fuzzy_not(is_ge(lhs, rhs))\n+\n+\n+def is_gt(lhs, rhs):\n+ return fuzzy_not(is_le(lhs, rhs))\n+\n+\n+def is_le(lhs, rhs):\n+ return is_ge(rhs, lhs)\n+\n+\n+def is_ge(lhs, rhs):\n+ retval = _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs)\n+ if retval is not None:\n+ return retval\n+ else:\n+ n2 = _n2(lhs, rhs)\n+ if n2 is not None:\n+ # use float comparison for infinity.\n+ # otherwise get stuck in infinite recursion\n+ if n2 in (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity):\n+ n2 = float(n2)\n+ return _sympify(n2 >= 0)\n+ if lhs.is_extended_real and rhs.is_extended_real:\n+ if (lhs.is_infinite and lhs.is_extended_positive) \\\n+ or (rhs.is_infinite and rhs.is_extended_negative):\n+ return S.true\n+ diff = lhs - rhs\n+ if diff is not S.NaN:\n+ rv = diff.is_extended_nonnegative\n+ if rv is not None:\n+ return rv\n+\n+\n+def is_neq(lhs, rhs):\n+ from .logic import fuzzy_not\n+ return fuzzy_not(is_eq(lhs, rhs))\n+\n+\n+def is_eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ from sympy.core.add import Add\n+ from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import arg\n+ from sympy.simplify.simplify import clear_coefficients\n+ from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift\n+\n+ retval = _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs)\n+ if retval is not None:\n+ return retval\n+\n+ retval = _eval_Eq(rhs, lhs)\n+ if retval is not None:\n+ return retval\n+ else:\n+ # retval is still None, so go through the equality logic\n+ # If expressions have the same structure, they must be equal.\n+ if lhs == rhs:\n+ return S.true # e.g. True == True\n+ elif all(isinstance(i, BooleanAtom) for i in (rhs, lhs)):\n+ return S.false # True != False\n+ elif not (lhs.is_Symbol or rhs.is_Symbol) and (\n+ isinstance(lhs, Boolean) !=\n+ isinstance(rhs, Boolean)):\n+ return S.false # only Booleans can equal Booleans\n+\n+ if lhs.is_infinite or rhs.is_infinite:\n+ if fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_infinite, rhs.is_infinite]):\n+ return S.false\n+ if fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_extended_real, rhs.is_extended_real]):\n+ return S.false\n+ if fuzzy_and([lhs.is_extended_real, rhs.is_extended_real]):\n+ return fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_extended_positive, fuzzy_not(rhs.is_extended_positive)])\n+\n+ # Try to split real/imaginary parts and equate them\n+ I = S.ImaginaryUnit\n+\n+ def split_real_imag(expr):\n+ real_imag = lambda t: (\n+ 'real' if t.is_extended_real else\n+ 'imag' if (I * t).is_extended_real else None)\n+ return sift(Add.make_args(expr), real_imag)\n+\n+ lhs_ri = split_real_imag(lhs)\n+ if not lhs_ri[None]:\n+ rhs_ri = split_real_imag(rhs)\n+ if not rhs_ri[None]:\n+ eq_real = Eq(Add(*lhs_ri['real']), Add(*rhs_ri['real']))\n+ eq_imag = Eq(I * Add(*lhs_ri['imag']), I * Add(*rhs_ri['imag']))\n+ return fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, [eq_real, eq_imag]))\n+\n+ # Compare e.g. zoo with 1+I*oo by comparing args\n+ arglhs = arg(lhs)\n+ argrhs = arg(rhs)\n+ # Guard against Eq(nan, nan) -> False\n+ if not (arglhs == S.NaN and argrhs == S.NaN):\n+ return fuzzy_bool(Eq(arglhs, argrhs))\n+\n+ if all(isinstance(i, Expr) for i in (lhs, rhs)):\n+ # see if the difference evaluates\n+ dif = lhs - rhs\n+ z = dif.is_zero\n+ if z is not None:\n+ if z is False and dif.is_commutative: # issue 10728\n+ return S.false\n+ if z:\n+ return S.true\n+\n+ n2 = _n2(lhs, rhs)\n+ if n2 is not None:\n+ return _sympify(n2 == 0)\n+\n+ # see if the ratio evaluates\n+ n, d = dif.as_numer_denom()\n+ rv = None\n+ if n.is_zero:\n+ rv = d.is_nonzero\n+ elif n.is_finite:\n+ if d.is_infinite:\n+ rv = True\n+ elif n.is_zero is False:\n+ rv = d.is_infinite\n+ if rv is None:\n+ # if the condition that makes the denominator\n+ # infinite does not make the original expression\n+ # True then False can be returned\n+ l, r = clear_coefficients(d, S.Infinity)\n+ args = [_.subs(l, r) for _ in (lhs, rhs)]\n+ if args != [lhs, rhs]:\n+ rv = fuzzy_bool(Eq(*args))\n+ if rv is True:\n+ rv = None\n+ elif any(a.is_infinite for a in Add.make_args(n)):\n+ # (inf or nan)/x != 0\n+ rv = S.false\n+ if rv is not None:\n+ return rv\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py\nindex 915af7fe4b8f..4ee5ab4810af 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py\n@@ -690,7 +690,7 @@ def test_issue_8245():\n r = Rational(str(a.n(29)))\n assert rel_check(a, r)\n \n- assert Eq(log(cos(2)**2 + sin(2)**2), 0) == True\n+ assert Eq(log(cos(2)**2 + sin(2)**2), 0) is S.true\n \n \n def test_issue_8449():\ndiff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py\nindex 960121c8aa73..ac91311c1715 100644\n--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py\n+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py\n@@ -1,3 +1,8 @@\n+\n+from __future__ import print_function, division\n+\n+from sympy import Basic\n+\n from sympy.core import Add, S\n from sympy.core.evalf import get_integer_part, PrecisionExhausted\n from sympy.core.function import Function\n@@ -6,7 +11,7 @@\n from sympy.core.relational import Gt, Lt, Ge, Le, Relational\n from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n-\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n \n ###############################################################################\n ######################### FLOOR and CEILING FUNCTIONS #########################\n@@ -154,11 +159,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_ceiling(self, arg, **kwargs):\n def _eval_rewrite_as_frac(self, arg, **kwargs):\n return arg - frac(arg)\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- if isinstance(self, floor):\n- if (self.rewrite(ceiling) == other) or \\\n- (self.rewrite(frac) == other):\n- return S.true\n+\n \n def __le__(self, other):\n other = S(other)\n@@ -216,6 +217,12 @@ def __lt__(self, other):\n \n return Lt(self, other, evaluate=False)\n \n+@dispatch(floor, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ if (lhs.rewrite(ceiling) == rhs) or \\\n+ (lhs.rewrite(frac) == rhs):\n+ return S.true\n+\n class ceiling(RoundFunction):\n \"\"\"\n Ceiling is a univariate function which returns the smallest integer\n@@ -289,11 +296,7 @@ def _eval_is_positive(self):\n def _eval_is_nonpositive(self):\n return self.args[0].is_nonpositive\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- if isinstance(self, ceiling):\n- if (self.rewrite(floor) == other) or \\\n- (self.rewrite(frac) == other):\n- return S.true\n+\n \n def __lt__(self, other):\n other = S(other)\n@@ -351,6 +354,12 @@ def __le__(self, other):\n \n return Le(self, other, evaluate=False)\n \n+@dispatch(ceiling, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ if (lhs.rewrite(floor) == rhs) or \\\n+ (lhs.rewrite(frac) == rhs):\n+ return S.true\n+\n class frac(Function):\n r\"\"\"Represents the fractional part of x\n \n@@ -442,18 +451,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_floor(self, arg, **kwargs):\n def _eval_rewrite_as_ceiling(self, arg, **kwargs):\n return arg + ceiling(-arg)\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- if isinstance(self, frac):\n- if (self.rewrite(floor) == other) or \\\n- (self.rewrite(ceiling) == other):\n- return S.true\n- # Check if other < 0\n- if other.is_extended_negative:\n- return S.false\n- # Check if other >= 1\n- res = self._value_one_or_more(other)\n- if res is not None:\n- return S.false\n+\n \n def _eval_is_finite(self):\n return True\n@@ -529,3 +527,16 @@ def _value_one_or_more(self, other):\n return S.true\n if other.is_integer and other.is_positive:\n return S.true\n+\n+@dispatch(frac, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ if (lhs.rewrite(floor) == rhs) or \\\n+ (lhs.rewrite(ceiling) == rhs):\n+ return S.true\n+ # Check if other < 0\n+ if rhs.is_extended_negative:\n+ return S.false\n+ # Check if other >= 1\n+ res = lhs._value_one_or_more(rhs)\n+ if res is not None:\n+ return S.false\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\nindex 31f1226cce69..f1c1f021f499 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py\n@@ -14,6 +14,7 @@\n from sympy.simplify import simplify\n from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent\n from sympy.assumptions.ask import ask, Q\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n \n \n def _sympifyit(arg, retval=None):\n@@ -593,15 +594,16 @@ def applyfunc(self, func):\n from .applyfunc import ElementwiseApplyFunction\n return ElementwiseApplyFunction(func, self)\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- if not isinstance(other, MatrixExpr):\n- return False\n- if self.shape != other.shape:\n- return False\n- if (self - other).is_ZeroMatrix:\n- return True\n- return Eq(self, other, evaluate=False)\n+@dispatch(MatrixExpr, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ return False\n \n+@dispatch(MatrixExpr, MatrixExpr)\n+def _eval_Eq(self, other): # noqa:F811\n+ if self.shape != other.shape:\n+ return False\n+ if (self - other).is_ZeroMatrix:\n+ return True\n \n def get_postprocessor(cls):\n def _postprocessor(expr):\ndiff --git a/sympy/matrices/immutable.py b/sympy/matrices/immutable.py\nindex b559180b3ac2..175a34a0d660 100644\n--- a/sympy/matrices/immutable.py\n+++ b/sympy/matrices/immutable.py\n@@ -7,20 +7,26 @@\n from sympy.matrices.expressions import MatrixExpr\n from sympy.matrices.matrices import MatrixBase\n from sympy.matrices.sparse import MutableSparseMatrix, SparseMatrix\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n \n \n def sympify_matrix(arg):\n return arg.as_immutable()\n+\n+\n sympify_converter[MatrixBase] = sympify_matrix\n \n \n def sympify_mpmath_matrix(arg):\n mat = [_sympify(x) for x in arg]\n return ImmutableDenseMatrix(arg.rows, arg.cols, mat)\n+\n+\n sympify_converter[_matrix] = sympify_mpmath_matrix\n \n \n-class ImmutableDenseMatrix(DenseMatrix, MatrixExpr):\n+\n+class ImmutableDenseMatrix(DenseMatrix, MatrixExpr): # type: ignore\n \"\"\"Create an immutable version of a matrix.\n \n Examples\n@@ -77,27 +83,6 @@ def _entry(self, i, j, **kwargs):\n def __setitem__(self, *args):\n raise TypeError(\"Cannot set values of {}\".format(self.__class__))\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- \"\"\"Helper method for Equality with matrices.\n-\n- Relational automatically converts matrices to ImmutableDenseMatrix\n- instances, so this method only applies here. Returns True if the\n- matrices are definitively the same, False if they are definitively\n- different, and None if undetermined (e.g. if they contain Symbols).\n- Returning None triggers default handling of Equalities.\n-\n- \"\"\"\n- if not hasattr(other, 'shape') or self.shape != other.shape:\n- return S.false\n- if isinstance(other, MatrixExpr) and not isinstance(\n- other, ImmutableDenseMatrix):\n- return None\n- diff = (self - other).is_zero_matrix\n- if diff is True:\n- return S.true\n- elif diff is False:\n- return S.false\n-\n def _eval_extract(self, rowsList, colsList):\n # self._mat is a Tuple. It is slightly faster to index a\n # tuple over a Tuple, so grab the internal tuple directly\n@@ -125,6 +110,7 @@ def as_immutable(self):\n def is_diagonalizable(self, reals_only=False, **kwargs):\n return super().is_diagonalizable(\n reals_only=reals_only, **kwargs)\n+\n is_diagonalizable.__doc__ = DenseMatrix.is_diagonalizable.__doc__\n is_diagonalizable = cacheit(is_diagonalizable)\n \n@@ -179,7 +165,7 @@ def __setitem__(self, *args):\n def _entry(self, i, j, **kwargs):\n return SparseMatrix.__getitem__(self, (i, j))\n \n- _eval_Eq = ImmutableDenseMatrix._eval_Eq\n+ # _eval_Eq = ImmutableDenseMatrix._eval_Eq\n \n @property\n def cols(self):\n@@ -199,5 +185,27 @@ def as_immutable(self):\n def is_diagonalizable(self, reals_only=False, **kwargs):\n return super().is_diagonalizable(\n reals_only=reals_only, **kwargs)\n+\n is_diagonalizable.__doc__ = SparseMatrix.is_diagonalizable.__doc__\n is_diagonalizable = cacheit(is_diagonalizable)\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(ImmutableDenseMatrix, MatrixExpr)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(ImmutableDenseMatrix, ImmutableDenseMatrix)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ \"\"\"Helper method for Equality with matrices.sympy.\n+\n+ Relational automatically converts matrices to ImmutableDenseMatrix\n+ instances, so this method only applies here. Returns True if the\n+ matrices are definitively the same, False if they are definitively\n+ different, and None if undetermined (e.g. if they contain Symbols).\n+ Returning None triggers default handling of Equalities.\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if lhs.shape != rhs.shape:\n+ return S.false\n+ return (lhs - rhs).is_zero_matrix\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/finitefield.py b/sympy/polys/domains/finitefield.py\nindex 0b1cceee49a1..d60bbd990b24 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/domains/finitefield.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/finitefield.py\n@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@\n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n from sympy.polys.domains.field import Field\n-from sympy.polys.domains.groundtypes import SymPyInteger\n+\n from sympy.polys.domains.modularinteger import ModularIntegerFactory\n from sympy.polys.domains.simpledomain import SimpleDomain\n from sympy.polys.polyerrors import CoercionFailed\n@@ -57,6 +57,7 @@ def get_field(self):\n return self\n \n def to_sympy(self, a):\n+ from sympy.polys.domains.groundtypes import SymPyInteger\n \"\"\"Convert ``a`` to a SymPy object. \"\"\"\n return SymPyInteger(int(a))\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py b/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py\nindex 8d8a199ff826..e0ad45663ac4 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py\n@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@\n \n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n+from sympy import Basic\n from sympy.core import (S, Expr, Integer, Float, I, oo, Add, Lambda,\n symbols, sympify, Rational, Dummy)\n from sympy.core.cache import cacheit\n@@ -25,7 +26,7 @@\n \n from mpmath import mpf, mpc, findroot, workprec\n from mpmath.libmp.libmpf import dps_to_prec, prec_to_dps\n-\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n from itertools import chain\n \n \n@@ -970,42 +971,49 @@ def eval_rational(self, dx=None, dy=None, n=15):\n self._set_interval(interval)\n return real + I*imag\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- # CRootOf represents a Root, so if other is that root, it should set\n- # the expression to zero *and* it should be in the interval of the\n- # CRootOf instance. It must also be a number that agrees with the\n- # is_real value of the CRootOf instance.\n- if type(self) == type(other):\n- return sympify(self == other)\n- if not other.is_number:\n- return None\n- if not other.is_finite:\n- return S.false\n- z = self.expr.subs(self.expr.free_symbols.pop(), other).is_zero\n- if z is False: # all roots will make z True but we don't know\n- # whether this is the right root if z is True\n- return S.false\n- o = other.is_real, other.is_imaginary\n- s = self.is_real, self.is_imaginary\n- assert None not in s # this is part of initial refinement\n- if o != s and None not in o:\n- return S.false\n- re, im = other.as_real_imag()\n- if self.is_real:\n- if im:\n- return S.false\n- i = self._get_interval()\n- a, b = [Rational(str(_)) for _ in (i.a, i.b)]\n- return sympify(a <= other and other <= b)\n- i = self._get_interval()\n- r1, r2, i1, i2 = [Rational(str(j)) for j in (\n- i.ax, i.bx, i.ay, i.by)]\n- return sympify((\n- r1 <= re and re <= r2) and (\n- i1 <= im and im <= i2))\n \n CRootOf = ComplexRootOf\n \n+\n+@dispatch(ComplexRootOf, ComplexRootOf)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ return sympify(lhs == rhs)\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(ComplexRootOf, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ # CRootOf represents a Root, so if rhs is that root, it should set\n+ # the expression to zero *and* it should be in the interval of the\n+ # CRootOf instance. It must also be a number that agrees with the\n+ # is_real value of the CRootOf instance.\n+ if not rhs.is_number:\n+ return None\n+ if not rhs.is_finite:\n+ return S.false\n+ z = lhs.expr.subs(lhs.expr.free_symbols.pop(), rhs).is_zero\n+ if z is False: # all roots will make z True but we don't know\n+ # whether this is the right root if z is True\n+ return S.false\n+ o = rhs.is_real, rhs.is_imaginary\n+ s = lhs.is_real, lhs.is_imaginary\n+ assert None not in s # this is part of initial refinement\n+ if o != s and None not in o:\n+ return S.false\n+ re, im = rhs.as_real_imag()\n+ if lhs.is_real:\n+ if im:\n+ return S.false\n+ i = lhs._get_interval()\n+ a, b = [Rational(str(_)) for _ in (i.a, i.b)]\n+ return sympify(a <= rhs and rhs <= b)\n+ i = lhs._get_interval()\n+ r1, r2, i1, i2 = [Rational(str(j)) for j in (\n+ i.ax, i.bx, i.ay, i.by)]\n+ return sympify((\n+ r1 <= re and re <= r2) and (\n+ i1 <= im and im <= i2))\n+\n+\n @public\n class RootSum(Expr):\n \"\"\"Represents a sum of all roots of a univariate polynomial. \"\"\"\ndiff --git a/sympy/sets/sets.py b/sympy/sets/sets.py\nindex 64d52737d9f5..49abd73462f2 100644\n--- a/sympy/sets/sets.py\n+++ b/sympy/sets/sets.py\n@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@\n from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning\n from sympy.utilities.iterables import iproduct, sift, roundrobin\n from sympy.utilities.misc import func_name, filldedent\n-\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n from mpmath import mpi, mpf\n \n \n@@ -757,15 +757,7 @@ def _flatten(sets):\n yield s\n return ProductSet(*_flatten(self.sets))\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- if not other.is_ProductSet:\n- return\n \n- if len(self.sets) != len(other.sets):\n- return false\n-\n- eqs = (Eq(x, y) for x, y in zip(self.sets, other.sets))\n- return tfn[fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, eqs))]\n \n def _contains(self, element):\n \"\"\"\n@@ -920,7 +912,7 @@ def __new__(cls, start, end, left_open=False, right_open=False):\n raise ValueError(\"Non-real intervals are not supported\")\n \n # evaluate if possible\n- if (end < start) == True:\n+ if (end >= start) == False:\n return S.EmptySet\n elif (end - start).is_negative:\n return S.EmptySet\n@@ -1124,11 +1116,6 @@ def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n return None\n return false\n \n- return And(Eq(self.left, other.left),\n- Eq(self.right, other.right),\n- self.left_open == other.left_open,\n- self.right_open == other.right_open)\n-\n \n class Union(Set, LatticeOp, EvalfMixin):\n \"\"\"\n@@ -1787,24 +1774,6 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):\n obj._args_set = _args_set\n return obj\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- if not isinstance(other, FiniteSet):\n- # XXX: If Interval(x, x, evaluate=False) worked then the line\n- # below would mean that\n- # FiniteSet(x) & Interval(x, x, evaluate=False) -> false\n- if isinstance(other, Interval):\n- return false\n- elif isinstance(other, Set):\n- return None\n- return false\n-\n- def all_in_both():\n- s_set = set(self.args)\n- o_set = set(other.args)\n- yield fuzzy_and(self._contains(e) for e in o_set - s_set)\n- yield fuzzy_and(other._contains(e) for e in s_set - o_set)\n-\n- return tfn[fuzzy_and(all_in_both())]\n \n def __iter__(self):\n return iter(self.args)\n@@ -2516,3 +2485,46 @@ def set_pow(x, y):\n def set_function(f, x):\n from sympy.sets.handlers.functions import _set_function\n return _set_function(f, x)\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Interval, FiniteSet)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ return false\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(FiniteSet, Interval)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ return false\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Interval, Interval)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ return And(Eq(lhs.left, rhs.left),\n+ Eq(lhs.right, rhs.right),\n+ lhs.left_open == rhs.left_open,\n+ lhs.right_open == rhs.right_open)\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(FiniteSet, Interval)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ return False\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(FiniteSet, FiniteSet)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ def all_in_both():\n+ s_set = set(lhs.args)\n+ o_set = set(rhs.args)\n+ yield fuzzy_and(lhs._contains(e) for e in o_set - s_set)\n+ yield fuzzy_and(rhs._contains(e) for e in s_set - o_set)\n+\n+ return tfn[fuzzy_and(all_in_both())]\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(ProductSet, ProductSet)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ if len(lhs.sets) != len(rhs.sets):\n+ return false\n+\n+ eqs = (Eq(x, y) for x, y in zip(lhs.sets, rhs.sets))\n+ return tfn[fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, eqs))]\ndiff --git a/sympy/tensor/indexed.py b/sympy/tensor/indexed.py\nindex b8b4da9461e7..30deb7a6d94d 100644\n--- a/sympy/tensor/indexed.py\n+++ b/sympy/tensor/indexed.py\n@@ -106,6 +106,7 @@\n \n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n+from sympy import Number\n from sympy.core.assumptions import StdFactKB\n from sympy.core import Expr, Tuple, sympify, S\n from sympy.core.symbol import _filter_assumptions, Symbol\n@@ -114,6 +115,7 @@\n from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_bool, fuzzy_not\n from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify\n from sympy.functions.special.tensor_functions import KroneckerDelta\n+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch\n \n \n class IndexException(Exception):\n@@ -751,58 +753,41 @@ def name(self):\n def free_symbols(self):\n return {self}\n \n- def __le__(self, other):\n- if isinstance(other, Idx):\n- other_upper = other if other.upper is None else other.upper\n- other_lower = other if other.lower is None else other.lower\n- else:\n- other_upper = other\n- other_lower = other\n-\n- if self.upper is not None and (self.upper <= other_lower) == True:\n- return True\n- if self.lower is not None and (self.lower > other_upper) == True:\n- return False\n- return super(Idx, self).__le__(other)\n-\n- def __ge__(self, other):\n- if isinstance(other, Idx):\n- other_upper = other if other.upper is None else other.upper\n- other_lower = other if other.lower is None else other.lower\n- else:\n- other_upper = other\n- other_lower = other\n-\n- if self.lower is not None and (self.lower >= other_upper) == True:\n- return True\n- if self.upper is not None and (self.upper < other_lower) == True:\n- return False\n- return super(Idx, self).__ge__(other)\n-\n- def __lt__(self, other):\n- if isinstance(other, Idx):\n- other_upper = other if other.upper is None else other.upper\n- other_lower = other if other.lower is None else other.lower\n- else:\n- other_upper = other\n- other_lower = other\n-\n- if self.upper is not None and (self.upper < other_lower) == True:\n- return True\n- if self.lower is not None and (self.lower >= other_upper) == True:\n- return False\n- return super(Idx, self).__lt__(other)\n-\n- def __gt__(self, other):\n- if isinstance(other, Idx):\n- other_upper = other if other.upper is None else other.upper\n- other_lower = other if other.lower is None else other.lower\n- else:\n- other_upper = other\n- other_lower = other\n-\n- if self.lower is not None and (self.lower > other_upper) == True:\n- return True\n- if self.upper is not None and (self.upper <= other_lower) == True:\n- return False\n- return super(Idx, self).__gt__(other)\n+\n+@dispatch(Idx, Idx)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+\n+ other_upper = rhs if rhs.upper is None else rhs.upper\n+ other_lower = rhs if rhs.lower is None else rhs.lower\n+\n+ if lhs.lower is not None and (lhs.lower >= other_upper) == True:\n+ return True\n+ if lhs.upper is not None and (lhs.upper < other_lower) == True:\n+ return False\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Idx, Number)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+\n+ other_upper = rhs\n+ other_lower = rhs\n+\n+ if lhs.lower is not None and (lhs.lower >= other_upper) == True:\n+ return True\n+ if lhs.upper is not None and (lhs.upper < other_lower) == True:\n+ return False\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Number, Idx)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+\n+ other_upper = lhs\n+ other_lower = lhs\n+\n+ if rhs.upper is not None and (rhs.upper <= other_lower) == True:\n+ return True\n+ if rhs.lower is not None and (rhs.lower > other_upper) == True:\n+ return False\n+ return None\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -141,25 +141,27 @@ def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None):\n else:\n return self.args.index(value, start, stop)\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef\n- from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool\n- from sympy.core.relational import Eq\n \n- if other.is_Symbol or isinstance(other, AppliedUndef):\n- return None\n+converter[tuple] = lambda tup: Tuple(*tup)\n+\n \n- if not isinstance(other, Tuple) or len(self) != len(other):\n- return S.false\n+@dispatch(Tuple, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef\n+ from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool\n+ from sympy.core.relational import Eq\n \n- r = fuzzy_and(fuzzy_bool(Eq(s, o)) for s, o in zip(self, other))\n- if r is True:\n- return S.true\n- elif r is False:\n- return S.false\n+ if rhs.is_Symbol or isinstance(rhs, AppliedUndef):\n+ return None",
"line": null,
"original_line": 155,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/containers.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nMaybe it would make sense to do the type checking in dispatch by having one handler for `Symbol` and one for `AppliedUndef` and then another for `Tuple`.\n\n@author:\nIs every object with is_Symbol guaranteed to be of type Symbol? I think there is one case, I can find out more details for you, but if I do find that there is class that does not subclass Symbol but has is_Symbol set to true should I edit to subclass Symbol\n\n@user1:\nI'm not sure. What is the example?\n\n@author:\nnevermind, it did actually work."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -141,25 +141,27 @@ def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None):\n else:\n return self.args.index(value, start, stop)\n \n- def _eval_Eq(self, other):\n- from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef\n- from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool\n- from sympy.core.relational import Eq\n \n- if other.is_Symbol or isinstance(other, AppliedUndef):\n- return None\n+converter[tuple] = lambda tup: Tuple(*tup)\n+\n \n- if not isinstance(other, Tuple) or len(self) != len(other):\n- return S.false\n+@dispatch(Tuple, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef\n+ from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool\n+ from sympy.core.relational import Eq\n \n- r = fuzzy_and(fuzzy_bool(Eq(s, o)) for s, o in zip(self, other))\n- if r is True:\n- return S.true\n- elif r is False:\n- return S.false\n+ if rhs.is_Symbol or isinstance(rhs, AppliedUndef):\n+ return None\n \n+ if not isinstance(rhs, Tuple) or len(lhs) != len(rhs):\n+ return S.false\n \n-converter[tuple] = lambda tup: Tuple(*tup)\n+ r = fuzzy_and(fuzzy_bool(Eq(s, o)) for s, o in zip(lhs, rhs))",
"line": null,
"original_line": 160,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/containers.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nShould this use `is_eq` rather than `Eq`?\n\n@author:\nYes."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@\n+from __future__ import print_function, division",
"line": null,
"original_line": 1,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/expr.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWe don't need future imports for py3 things as python 2 isn't supported any more."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -3020,3 +3012,10 @@ def __new__(cls, perm, x, evaluate=None):\n \n obj = super().__new__(cls, perm, x)\n return obj\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Permutation, Permutation)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ if lhs._size != rhs._size:\n+ return None\n+ return as_Boolean(lhs._array_form == rhs._array_form)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 3021,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI wonder if `_eval_Eq` should return a fuzzy bool rather than a `Boolean`...\n\n@author:\nthat makes sense to me"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -276,6 +276,8 @@ def _igcd2_python(a, b):\n \n \n # Use Lehmer's algorithm only for very large numbers.\n+# The limit could be different on Python 2.7 and 3.x.\n+# If so, then this could be defined in compatibility.py.",
"line": null,
"original_line": 280,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/numbers.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think this is a hangover from a merge. These comments were probably removed because Python 2 is no longer supported."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -339,78 +344,30 @@ def __complex__(self):\n re, im = result.as_real_imag()\n return complex(float(re), float(im))\n \n- def _cmp(self, other, op, cls):\n- assert op in (\"<\", \">\", \"<=\", \">=\")\n- try:\n- other = _sympify(other)\n- except SympifyError:\n- return NotImplemented\n-\n- if not isinstance(other, Expr):\n- return NotImplemented\n-\n- for me in (self, other):\n- if me.is_extended_real is False:\n- raise TypeError(\"Invalid comparison of non-real %s\" % me)\n- if me is S.NaN:\n- raise TypeError(\"Invalid NaN comparison\")\n-\n- n2 = _n2(self, other)\n- if n2 is not None:\n- # use float comparison for infinity.\n- # otherwise get stuck in infinite recursion\n- if n2 in (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity):\n- n2 = float(n2)\n- if op == \"<\":\n- return _sympify(n2 < 0)\n- elif op == \">\":\n- return _sympify(n2 > 0)\n- elif op == \"<=\":\n- return _sympify(n2 <= 0)\n- else: # >=\n- return _sympify(n2 >= 0)\n-\n- if self.is_extended_real and other.is_extended_real:\n- if op in (\"<=\", \">\") \\\n- and ((self.is_infinite and self.is_extended_negative) \\\n- or (other.is_infinite and other.is_extended_positive)):\n- return S.true if op == \"<=\" else S.false\n- if op in (\"<\", \">=\") \\\n- and ((self.is_infinite and self.is_extended_positive) \\\n- or (other.is_infinite and other.is_extended_negative)):\n- return S.true if op == \">=\" else S.false\n- diff = self - other\n- if diff is not S.NaN:\n- if op == \"<\":\n- test = diff.is_extended_negative\n- elif op == \">\":\n- test = diff.is_extended_positive\n- elif op == \"<=\":\n- test = diff.is_extended_nonpositive\n- else: # >=\n- test = diff.is_extended_nonnegative\n-\n- if test is not None:\n- return S.true if test == True else S.false\n-\n- # return unevaluated comparison object\n- return cls(self, other, evaluate=False)\n-\n def __ge__(self, other):\n- from sympy import GreaterThan\n- return self._cmp(other, \">=\", GreaterThan)\n+ from .relational import GreaterThan\n+ return self._cmp(other, GreaterThan)",
"line": null,
"original_line": 349,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/expr.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIf the purpose of the `_cmp` method is just to sympy the argument can we use `sympify_return` instead?\r\n\r\nThat's what's used for e.g. `Expr.__add__`."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1138,3 +1060,169 @@ def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n '<': StrictLessThan,\n 'lt': StrictLessThan,\n }\n+\n+\n+def _n2(a, b):\n+ \"\"\"Return (a - b).evalf(2) if a and b are comparable, else None.\n+ This should only be used when a and b are already sympified.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # /!\\ it is very important (see issue 8245) not to\n+ # use a re-evaluated number in the calculation of dif\n+ if a.is_comparable and b.is_comparable:\n+ dif = (a - b).evalf(2)\n+ if dif.is_comparable:\n+ return dif\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)\n+def _eval_is_le(lhs, rhs):\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs):\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+\n+def is_lt(lhs, rhs):\n+ return fuzzy_not(is_ge(lhs, rhs))\n+\n+\n+def is_gt(lhs, rhs):\n+ return fuzzy_not(is_le(lhs, rhs))\n+\n+\n+def is_le(lhs, rhs):\n+ return is_ge(rhs, lhs)\n+\n+\n+def is_ge(lhs, rhs):\n+ retval = _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs)\n+ if retval is not None:\n+ return retval\n+ else:\n+ n2 = _n2(lhs, rhs)\n+ if n2 is not None:\n+ # use float comparison for infinity.\n+ # otherwise get stuck in infinite recursion\n+ if n2 in (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity):\n+ n2 = float(n2)\n+ return _sympify(n2 >= 0)\n+ if lhs.is_extended_real and rhs.is_extended_real:\n+ if (lhs.is_infinite and lhs.is_extended_positive) \\\n+ or (rhs.is_infinite and rhs.is_extended_negative):\n+ return S.true\n+ diff = lhs - rhs\n+ if diff is not S.NaN:\n+ rv = diff.is_extended_nonnegative\n+ if rv is not None:\n+ return rv\n+\n+\n+def is_neq(lhs, rhs):\n+ from .logic import fuzzy_not\n+ return fuzzy_not(is_eq(lhs, rhs))",
"line": 1223,
"original_line": 1130,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/relational.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think `fuzzy_not` is already imported."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1066,9 +976,12 @@ class GreaterThan(_Greater):\n rel_op = '>='\n \n @classmethod\n- def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n- # We don't use the op symbol here: workaround issue #7951\n- return _sympify(lhs.__ge__(rhs))\n+ def _eval_fuzzy_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n+ val = is_ge(lhs, rhs)\n+ if val is None:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 981,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/relational.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nThere are a few of these `_eval_fuzzy_relation` methods and they differ only in which function they call (here `is_ge` for evaluating). Perhaps it would make more sense to move the other logic to the superclass `_eval_relation` method keeping only the call to `is_ge` here since that's the only bit that it unique to this class...\r\n\r\n\n\n@author:\nYes, I agree that would be quite a bite better"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1138,3 +1060,169 @@ def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):\n '<': StrictLessThan,\n 'lt': StrictLessThan,\n }\n+\n+\n+def _n2(a, b):\n+ \"\"\"Return (a - b).evalf(2) if a and b are comparable, else None.\n+ This should only be used when a and b are already sympified.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # /!\\ it is very important (see issue 8245) not to\n+ # use a re-evaluated number in the calculation of dif\n+ if a.is_comparable and b.is_comparable:\n+ dif = (a - b).evalf(2)\n+ if dif.is_comparable:\n+ return dif\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)\n+def _eval_is_le(lhs, rhs):\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)\n+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs):\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ return None\n+\n+\n+\n+def is_lt(lhs, rhs):\n+ return fuzzy_not(is_ge(lhs, rhs))\n+\n+\n+def is_gt(lhs, rhs):\n+ return fuzzy_not(is_le(lhs, rhs))\n+\n+\n+def is_le(lhs, rhs):\n+ return is_ge(rhs, lhs)\n+\n+\n+def is_ge(lhs, rhs):\n+ retval = _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs)\n+ if retval is not None:\n+ return retval\n+ else:\n+ n2 = _n2(lhs, rhs)\n+ if n2 is not None:\n+ # use float comparison for infinity.\n+ # otherwise get stuck in infinite recursion\n+ if n2 in (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity):\n+ n2 = float(n2)\n+ return _sympify(n2 >= 0)\n+ if lhs.is_extended_real and rhs.is_extended_real:\n+ if (lhs.is_infinite and lhs.is_extended_positive) \\\n+ or (rhs.is_infinite and rhs.is_extended_negative):\n+ return S.true\n+ diff = lhs - rhs\n+ if diff is not S.NaN:\n+ rv = diff.is_extended_nonnegative\n+ if rv is not None:\n+ return rv\n+\n+\n+def is_neq(lhs, rhs):\n+ from .logic import fuzzy_not\n+ return fuzzy_not(is_eq(lhs, rhs))\n+\n+\n+def is_eq(lhs, rhs):\n+ from sympy.core.add import Add\n+ from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import arg\n+ from sympy.simplify.simplify import clear_coefficients\n+ from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift\n+\n+ retval = _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs)\n+ if retval is not None:\n+ return retval",
"line": 1314,
"original_line": 1141,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/relational.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI think this method will still need to check e.g. `lhs._eval_Eq` for backward compatibility. Users and downstream libraries have probably defined `_eval_Eq` methods and we need to try to ensure that their code would still work with these changes."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -216,6 +217,12 @@ def __lt__(self, other):\n \n return Lt(self, other, evaluate=False)\n \n+@dispatch(floor, Basic)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811",
"line": null,
"original_line": 221,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI don't think a `floor` could ever compare equal to a non-`Expr` so this should probably by `(floor, Expr)`."
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -1627,5 +1481,103 @@ def union(self, other):\n return AccumBounds(other.min, Max(self.max, other.max))\n \n \n+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, AccumulationBounds) # type: ignore # noqa:F811\n+def _eval_is_le(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ if lhs.max <= rhs.min:\n+ return True\n+ if lhs.min > rhs.max:\n+ return False\n+\n+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, Basic) # type: ignore # noqa:F811\n+def _eval_is_le(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds\n+ object is greater than the range of values attained by `other`,\n+ where other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or\n+ extended real number value, False if `other` satisfies\n+ the same property, else an unevaluated Relational.\n+\n+ Examples\n+ ========\n+\n+ >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo\n+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) > AccumBounds(4, oo)\n+ False\n+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)\n+ AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)\n+ >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) > -1\n+ True\n+\n+ \"\"\"\n+ if not rhs.is_extended_real:\n+ raise TypeError(\n+ \"Invalid comparison of %s %s\" %\n+ (type(rhs), rhs))\n+ elif rhs.is_comparable:\n+ if lhs.max <= rhs:\n+ return True\n+ if lhs.min > rhs:\n+ return False",
"line": 1522,
"original_line": 1521,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/calculus/util.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nWhat exactly does the use of inequalities here do? Would it make more sense to use `is_le`?\n\n@author:\nActually yeah it would make more sense, to use is_le on these functions"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2516,3 +2485,46 @@ def set_pow(x, y):\n def set_function(f, x):\n from sympy.sets.handlers.functions import _set_function\n return _set_function(f, x)\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(Interval, FiniteSet)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811\n+ return false",
"line": null,
"original_line": 2492,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/sets/sets.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nRather than have these things here I think they should go in a module in `sympy/sets/handlers/`"
},
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -199,5 +185,27 @@ def as_immutable(self):\n def is_diagonalizable(self, reals_only=False, **kwargs):\n return super().is_diagonalizable(\n reals_only=reals_only, **kwargs)\n+\n is_diagonalizable.__doc__ = SparseMatrix.is_diagonalizable.__doc__\n is_diagonalizable = cacheit(is_diagonalizable)\n+\n+\n+@dispatch(ImmutableDenseMatrix, MatrixExpr)\n+def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811\n+ return None",
"line": null,
"original_line": 195,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/matrices/immutable.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIs this handler needed? Can it not fall back to a general `Basic, Basic` handler that returns None?"
}
] |
b42109d76a8a2864be37602614f72119d35dff4e
|
diff --git a/sympy/calculus/util.py b/sympy/calculus/util.py
index 09ee391ae71e..006dfafdd873 100644
--- a/sympy/calculus/util.py
+++ b/sympy/calculus/util.py
@@ -5,6 +5,7 @@
from sympy.core.expr import AtomicExpr, Expr
from sympy.core.function import expand_mul
from sympy.core.numbers import _sympifyit, oo
+from sympy.core.relational import is_le, is_lt, is_ge, is_gt
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
from sympy.functions.elementary.miscellaneous import Min, Max
from sympy.logic.boolalg import And
@@ -13,7 +14,7 @@
from sympy.sets.fancysets import ImageSet
from sympy.solvers.inequalities import solve_univariate_inequality
from sympy.utilities import filldedent
-
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
def continuous_domain(f, symbol, domain):
"""
@@ -1372,155 +1373,6 @@ def __abs__(self):
else:
return self
- _eval_Abs = __abs__
-
- def __lt__(self, other):
- """
- Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds
- object is less than the range of values attained by `other`, where
- other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or extended
- real number value, False if `other` satisfies the same property, else
- an unevaluated Relational
-
- Examples
- ========
-
- >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo
- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) < AccumBounds(4, oo)
- True
- >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) < AccumBounds(3, 4)
- AccumBounds(1, 4) < AccumBounds(3, 4)
- >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) < -1
- False
-
- """
- other = _sympify(other)
- if isinstance(other, AccumBounds):
- if self.max < other.min:
- return True
- if self.min >= other.max:
- return False
- elif not other.is_extended_real:
- raise TypeError(
- "Invalid comparison of %s %s" %
- (type(other), other))
- elif other.is_comparable:
- if self.max < other:
- return True
- if self.min >= other:
- return False
- return super().__lt__(other)
-
- def __le__(self, other):
- """
- Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds
- object is less than or equal to the range of values attained by
- `other`, where other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds
- object or extended real number value, False if `other`
- satisfies the same property, else an unevaluated Relational.
-
- Examples
- ========
-
- >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo
- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) <= AccumBounds(4, oo)
- True
- >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) <= AccumBounds(3, 4)
- AccumBounds(1, 4) <= AccumBounds(3, 4)
- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) <= 0
- False
-
- """
- other = _sympify(other)
- if isinstance(other, AccumBounds):
- if self.max <= other.min:
- return True
- if self.min > other.max:
- return False
- elif not other.is_extended_real:
- raise TypeError(
- "Invalid comparison of %s %s" %
- (type(other), other))
- elif other.is_comparable:
- if self.max <= other:
- return True
- if self.min > other:
- return False
- return super().__le__(other)
-
- def __gt__(self, other):
- """
- Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds
- object is greater than the range of values attained by `other`,
- where other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or
- extended real number value, False if `other` satisfies
- the same property, else an unevaluated Relational.
-
- Examples
- ========
-
- >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo
- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) > AccumBounds(4, oo)
- False
- >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)
- AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)
- >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) > -1
- True
-
- """
- other = _sympify(other)
- if isinstance(other, AccumBounds):
- if self.min > other.max:
- return True
- if self.max <= other.min:
- return False
- elif not other.is_extended_real:
- raise TypeError(
- "Invalid comparison of %s %s" %
- (type(other), other))
- elif other.is_comparable:
- if self.min > other:
- return True
- if self.max <= other:
- return False
- return super().__gt__(other)
-
- def __ge__(self, other):
- """
- Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds
- object is less that the range of values attained by `other`, where
- other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or extended
- real number value, False if `other` satisfies the same
- property, else an unevaluated Relational.
-
- Examples
- ========
-
- >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo
- >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) >= AccumBounds(4, oo)
- False
- >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) >= AccumBounds(3, 4)
- AccumBounds(1, 4) >= AccumBounds(3, 4)
- >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) >= 1
- True
-
- """
- other = _sympify(other)
- if isinstance(other, AccumBounds):
- if self.min >= other.max:
- return True
- if self.max < other.min:
- return False
- elif not other.is_extended_real:
- raise TypeError(
- "Invalid comparison of %s %s" %
- (type(other), other))
- elif other.is_comparable:
- if self.min >= other:
- return True
- if self.max < other:
- return False
- return super().__ge__(other)
def __contains__(self, other):
"""
@@ -1629,5 +1481,104 @@ def union(self, other):
return AccumBounds(other.min, Max(self.max, other.max))
+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, AccumulationBounds) # type: ignore # noqa:F811
+def _eval_is_le(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ if is_le(lhs.max, rhs.min):
+ return True
+ if is_gt(lhs.min, rhs.max):
+ return False
+
+
+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, Basic) # type: ignore # noqa:F811
+def _eval_is_le(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+
+ """
+ Returns True if range of values attained by `self` AccumulationBounds
+ object is greater than the range of values attained by `other`,
+ where other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or
+ extended real number value, False if `other` satisfies
+ the same property, else an unevaluated Relational.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo
+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) > AccumBounds(4, oo)
+ False
+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)
+ AccumBounds(1, 4) > AccumBounds(3, 4)
+ >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) > -1
+ True
+
+ """
+ if not rhs.is_extended_real:
+ raise TypeError(
+ "Invalid comparison of %s %s" %
+ (type(rhs), rhs))
+ elif rhs.is_comparable:
+ if is_le(lhs.max, rhs):
+ return True
+ if is_gt(lhs.min, rhs):
+ return False
+
+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, AccumulationBounds)
+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ if is_ge(lhs.min, rhs.max):
+ return True
+ if is_lt(lhs.max, rhs.min):
+ return False
+
+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, Expr)
+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+ """
+ Returns True if range of values attained by `lhs` AccumulationBounds
+ object is less that the range of values attained by `rhs`, where
+ other may be any value of type AccumulationBounds object or extended
+ real number value, False if `rhs` satisfies the same
+ property, else an unevaluated Relational.
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+ >>> from sympy import AccumBounds, oo
+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 3) >= AccumBounds(4, oo)
+ False
+ >>> AccumBounds(1, 4) >= AccumBounds(3, 4)
+ AccumBounds(1, 4) >= AccumBounds(3, 4)
+ >>> AccumBounds(1, oo) >= 1
+ True
+ """
+
+ if not rhs.is_extended_real:
+ raise TypeError(
+ "Invalid comparison of %s %s" %
+ (type(rhs), rhs))
+ elif rhs.is_comparable:
+ if is_ge(lhs.min, rhs):
+ return True
+ if is_lt(lhs.max, rhs):
+ return False
+
+
+@dispatch(Expr, AccumulationBounds)
+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ if not lhs.is_extended_real:
+ raise TypeError(
+ "Invalid comparison of %s %s" %
+ (type(lhs), lhs))
+ elif lhs.is_comparable:
+ if is_le(rhs.max, lhs):
+ return True
+ if is_gt(rhs.min, lhs):
+ return False
+
+
+@dispatch(AccumulationBounds, AccumulationBounds)
+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ if is_ge(lhs.min, rhs.max):
+ return True
+ if is_lt(lhs.max, rhs.min):
+ return False
+
# setting an alias for AccumulationBounds
AccumBounds = AccumulationBounds
diff --git a/sympy/codegen/ast.py b/sympy/codegen/ast.py
index 7f2ebc2f4eb0..de68bd1b76ab 100644
--- a/sympy/codegen/ast.py
+++ b/sympy/codegen/ast.py
@@ -125,16 +125,16 @@
from typing import Any, Dict, List
from collections import defaultdict
+
+from sympy import Lt, Le, Ge, Gt
from sympy.core import Symbol, Tuple, Dummy
from sympy.core.basic import Basic
from sympy.core.expr import Expr
from sympy.core.numbers import Float, Integer, oo
-from sympy.core.relational import Lt, Le, Ge, Gt
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify, sympify, SympifyError
from sympy.utilities.iterables import iterable
-
def _mk_Tuple(args):
"""
Create a Sympy Tuple object from an iterable, converting Python strings to
@@ -1498,9 +1498,6 @@ def _relation(self, rhs, op):
__ge__ = lambda self, other: self._relation(other, Ge)
__gt__ = lambda self, other: self._relation(other, Gt)
-
-
-
class Pointer(Variable):
""" Represents a pointer. See ``Variable``.
diff --git a/sympy/codegen/tests/test_ast.py b/sympy/codegen/tests/test_ast.py
index 85fcfa28ef68..824f07604ce7 100644
--- a/sympy/codegen/tests/test_ast.py
+++ b/sympy/codegen/tests/test_ast.py
@@ -3,7 +3,6 @@
Float, Idx, IndexedBase, Integer, Matrix, MatrixSymbol, Range, sin,
symbols, Symbol, Tuple, Lt, nan, oo
)
-from sympy.core.relational import StrictLessThan
from sympy.testing.pytest import raises
@@ -411,8 +410,9 @@ def test_Declaration():
vn = Variable(n, type=Type.from_expr(n))
assert Declaration(vn).variable.type == integer
- lt = StrictLessThan(vu, vn)
- assert isinstance(lt, StrictLessThan)
+ # PR 19107, does not allow comparison between expressions and Basic
+ # lt = StrictLessThan(vu, vn)
+ # assert isinstance(lt, StrictLessThan)
vuc = Variable(u, Type.from_expr(u), value=3.0, attrs={value_const})
assert value_const in vuc.attrs
diff --git a/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py b/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py
index da19cbf50601..53c81d031a5b 100644
--- a/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py
+++ b/sympy/combinatorics/permutations.py
@@ -8,13 +8,12 @@
is_sequence, reduce, as_int, Iterable
from sympy.core.numbers import Integer
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
-from sympy.logic.boolalg import as_Boolean
from sympy.matrices import zeros
from sympy.polys.polytools import lcm
from sympy.utilities.iterables import (flatten, has_variety, minlex,
has_dups, runs)
from mpmath.libmp.libintmath import ifac
-
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
def _af_rmul(a, b):
"""
@@ -950,16 +949,6 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
return cls._af_new(aform)
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- other = _sympify(other)
- if not isinstance(other, Permutation):
- return None
-
- if self._size != other._size:
- return None
-
- return as_Boolean(self._array_form == other._array_form)
-
@classmethod
def _af_new(cls, perm):
"""A method to produce a Permutation object from a list;
@@ -3020,3 +3009,10 @@ def __new__(cls, perm, x, evaluate=None):
obj = super().__new__(cls, perm, x)
return obj
+
+
+@dispatch(Permutation, Permutation)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs):
+ if lhs._size != rhs._size:
+ return None
+ return lhs._array_form == rhs._array_form
diff --git a/sympy/core/basic.py b/sympy/core/basic.py
index b39022dde263..22f5c45e5525 100644
--- a/sympy/core/basic.py
+++ b/sympy/core/basic.py
@@ -1820,7 +1820,6 @@ def _exec_constructor_postprocessors(cls, obj):
return obj
-
class Atom(Basic):
"""
A parent class for atomic things. An atom is an expression with no subexpressions.
diff --git a/sympy/core/containers.py b/sympy/core/containers.py
index 5db2885d0a88..8a430b126a2d 100644
--- a/sympy/core/containers.py
+++ b/sympy/core/containers.py
@@ -8,14 +8,11 @@
from collections import OrderedDict
-from sympy.core import S
from sympy.core.basic import Basic
from sympy.core.compatibility import as_int, MutableSet
from sympy.core.sympify import sympify, converter
from sympy.utilities.iterables import iterable
-
-
class Tuple(Basic):
"""
Wrapper around the builtin tuple object
@@ -141,25 +138,11 @@ def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None):
else:
return self.args.index(value, start, stop)
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef
- from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool
- from sympy.core.relational import Eq
-
- if other.is_Symbol or isinstance(other, AppliedUndef):
- return None
- if not isinstance(other, Tuple) or len(self) != len(other):
- return S.false
+converter[tuple] = lambda tup: Tuple(*tup)
- r = fuzzy_and(fuzzy_bool(Eq(s, o)) for s, o in zip(self, other))
- if r is True:
- return S.true
- elif r is False:
- return S.false
-converter[tuple] = lambda tup: Tuple(*tup)
def tuple_wrapper(method):
diff --git a/sympy/core/expr.py b/sympy/core/expr.py
index e22ba57aede0..1e5d6ca9e357 100644
--- a/sympy/core/expr.py
+++ b/sympy/core/expr.py
@@ -23,6 +23,11 @@ class Expr(Basic, EvalfMixin):
used only for argument storage and expression manipulation, i.e.
pattern matching, substitutions, etc).
+ If you want to override the comparisons of expressions:
+ Should use _eval_is_ge for inequality, or _eval_is_eq, with multiple dispatch.
+ _eval_is_ge return true if x >= y, false if x < y, and None if the two types
+ are not comparable or the comparison is indeterminate
+
See Also
========
@@ -339,78 +344,25 @@ def __complex__(self):
re, im = result.as_real_imag()
return complex(float(re), float(im))
- def _cmp(self, other, op, cls):
- assert op in ("<", ">", "<=", ">=")
- try:
- other = _sympify(other)
- except SympifyError:
- return NotImplemented
-
- if not isinstance(other, Expr):
- return NotImplemented
-
- for me in (self, other):
- if me.is_extended_real is False:
- raise TypeError("Invalid comparison of non-real %s" % me)
- if me is S.NaN:
- raise TypeError("Invalid NaN comparison")
-
- n2 = _n2(self, other)
- if n2 is not None:
- # use float comparison for infinity.
- # otherwise get stuck in infinite recursion
- if n2 in (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity):
- n2 = float(n2)
- if op == "<":
- return _sympify(n2 < 0)
- elif op == ">":
- return _sympify(n2 > 0)
- elif op == "<=":
- return _sympify(n2 <= 0)
- else: # >=
- return _sympify(n2 >= 0)
-
- if self.is_extended_real and other.is_extended_real:
- if op in ("<=", ">") \
- and ((self.is_infinite and self.is_extended_negative) \
- or (other.is_infinite and other.is_extended_positive)):
- return S.true if op == "<=" else S.false
- if op in ("<", ">=") \
- and ((self.is_infinite and self.is_extended_positive) \
- or (other.is_infinite and other.is_extended_negative)):
- return S.true if op == ">=" else S.false
- diff = self - other
- if diff is not S.NaN:
- if op == "<":
- test = diff.is_extended_negative
- elif op == ">":
- test = diff.is_extended_positive
- elif op == "<=":
- test = diff.is_extended_nonpositive
- else: # >=
- test = diff.is_extended_nonnegative
-
- if test is not None:
- return S.true if test == True else S.false
-
- # return unevaluated comparison object
- return cls(self, other, evaluate=False)
-
+ @sympify_return([('other', 'Expr')], NotImplemented)
def __ge__(self, other):
- from sympy import GreaterThan
- return self._cmp(other, ">=", GreaterThan)
+ from .relational import GreaterThan
+ return GreaterThan(self, other)
+ @sympify_return([('other', 'Expr')], NotImplemented)
def __le__(self, other):
- from sympy import LessThan
- return self._cmp(other, "<=", LessThan)
+ from .relational import LessThan
+ return LessThan(self, other)
+ @sympify_return([('other', 'Expr')], NotImplemented)
def __gt__(self, other):
- from sympy import StrictGreaterThan
- return self._cmp(other, ">", StrictGreaterThan)
+ from .relational import StrictGreaterThan
+ return StrictGreaterThan(self, other)
+ @sympify_return([('other', 'Expr')], NotImplemented)
def __lt__(self, other):
- from sympy import StrictLessThan
- return self._cmp(other, "<", StrictLessThan)
+ from .relational import StrictLessThan
+ return StrictLessThan(self, other)
def __trunc__(self):
if not self.is_number:
@@ -3980,17 +3932,6 @@ def doit(self, **kwargs):
return self.args[0]
-def _n2(a, b):
- """Return (a - b).evalf(2) if a and b are comparable, else None.
- This should only be used when a and b are already sympified.
- """
- # /!\ it is very important (see issue 8245) not to
- # use a re-evaluated number in the calculation of dif
- if a.is_comparable and b.is_comparable:
- dif = (a - b).evalf(2)
- if dif.is_comparable:
- return dif
-
def unchanged(func, *args):
"""Return True if `func` applied to the `args` is unchanged.
diff --git a/sympy/core/numbers.py b/sympy/core/numbers.py
index 27b671e148c9..8d77510393f3 100644
--- a/sympy/core/numbers.py
+++ b/sympy/core/numbers.py
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
from sympy.core.compatibility import (as_int, HAS_GMPY, SYMPY_INTS,
int_info, gmpy)
from sympy.core.cache import lru_cache
-
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
import mpmath
import mpmath.libmp as mlib
from mpmath.libmp import bitcount
@@ -3264,10 +3264,6 @@ def __eq__(self, other):
def __ne__(self, other):
return other is not S.NaN
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- # NaN is not mathematically equal to anything, even NaN
- return S.false
-
# Expr will _sympify and raise TypeError
__gt__ = Expr.__gt__
__ge__ = Expr.__ge__
@@ -3276,6 +3272,9 @@ def _eval_Eq(self, other):
nan = S.NaN
+@dispatch(NaN, Expr)
+def _eval_is_eq(a, b): # noqa:F811
+ return False
class ComplexInfinity(AtomicExpr, metaclass=Singleton):
r"""Complex infinity.
@@ -3413,7 +3412,6 @@ def __long__(self):
def __hash__(self):
return super().__hash__()
-
class Exp1(NumberSymbol, metaclass=Singleton):
r"""The `e` constant.
@@ -3889,6 +3887,9 @@ def _mpc_(self):
I = S.ImaginaryUnit
+@dispatch(Tuple, Number)
+def _eval_is_eq(self, other): # noqa: F811
+ return False
def sympify_fractions(f):
return Rational(f.numerator, f.denominator, 1)
diff --git a/sympy/core/relational.py b/sympy/core/relational.py
index 86931db0a93a..031dd36c185e 100644
--- a/sympy/core/relational.py
+++ b/sympy/core/relational.py
@@ -1,15 +1,14 @@
# from typing import Dict, Union, Type
from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning
-from .add import _unevaluated_Add, Add
from .basic import S, Atom
from .compatibility import ordered
from .basic import Basic
-from .expr import Expr
from .evalf import EvalfMixin
-from .sympify import _sympify
+from .function import AppliedUndef
+from .sympify import _sympify, SympifyError
from .parameters import global_parameters
-
+from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_bool, fuzzy_xor, fuzzy_and, fuzzy_not
from sympy.logic.boolalg import Boolean, BooleanAtom
__all__ = (
@@ -18,14 +17,21 @@
'StrictGreaterThan', 'GreaterThan',
)
+from .expr import Expr
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
+from .containers import Tuple
+from .symbol import Symbol
+
def _nontrivBool(side):
return isinstance(side, Boolean) and \
- not isinstance(side, (BooleanAtom, Atom))
+ not isinstance(side, Atom)
# Note, see issue 4986. Ideally, we wouldn't want to subclass both Boolean
# and Expr.
+# from .. import Expr
+
def _canonical(cond):
# return a condition in which all relationals are canonical
@@ -291,6 +297,7 @@ def equals(self, other, failing_expression=False):
return left
def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):
+ from .add import Add
r = self
r = r.func(*[i.simplify(**kwargs) for i in r.args])
if r.is_Relational:
@@ -318,9 +325,9 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):
if m.is_negative:
# Dividing with a negative number, so change order of arguments
# canonical will put the symbol back on the lhs later
- r = r.func(-b/m, x)
+ r = r.func(-b / m, x)
else:
- r = r.func(x, -b/m)
+ r = r.func(x, -b / m)
else:
r = r.func(b, S.zero)
except ValueError:
@@ -332,8 +339,8 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):
constant = c[-1]
c[-1] = 0
scale = gcd(c)
- c = [ctmp/scale for ctmp in c]
- r = r.func(Poly.from_list(c, x).as_expr(), -constant/scale)
+ c = [ctmp / scale for ctmp in c]
+ r = r.func(Poly.from_list(c, x).as_expr(), -constant / scale)
except PolynomialError:
pass
elif len(free) >= 2:
@@ -346,18 +353,18 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):
constant = m[-1]
del m[-1]
scale = gcd(m)
- m = [mtmp/scale for mtmp in m]
+ m = [mtmp / scale for mtmp in m]
nzm = list(filter(lambda f: f[0] != 0, list(zip(m, free))))
if scale.is_zero is False:
if constant != 0:
# lhs: expression, rhs: constant
- newexpr = Add(*[i*j for i, j in nzm])
- r = r.func(newexpr, -constant/scale)
+ newexpr = Add(*[i * j for i, j in nzm])
+ r = r.func(newexpr, -constant / scale)
else:
# keep first term on lhs
- lhsterm = nzm[0][0]*nzm[0][1]
+ lhsterm = nzm[0][0] * nzm[0][1]
del nzm[0]
- newexpr = Add(*[i*j for i, j in nzm])
+ newexpr = Add(*[i * j for i, j in nzm])
r = r.func(lhsterm, -newexpr)
else:
@@ -367,7 +374,7 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):
# Did we get a simplified result?
r = r.canonical
measure = kwargs['measure']
- if measure(r) < kwargs['ratio']*measure(self):
+ if measure(r) < kwargs['ratio'] * measure(self):
return r
else:
return self
@@ -475,12 +482,6 @@ class Equality(Relational):
is_Equality = True
def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs=None, **options):
- from sympy.core.add import Add
- from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_bool, fuzzy_xor, fuzzy_and, fuzzy_not
- from sympy.core.expr import _n2
- from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import arg
- from sympy.simplify.simplify import clear_coefficients
- from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift
if rhs is None:
SymPyDeprecationWarning(
@@ -490,122 +491,25 @@ def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs=None, **options):
deprecated_since_version="1.5"
).warn()
rhs = 0
-
+ evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)
lhs = _sympify(lhs)
rhs = _sympify(rhs)
-
- evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)
-
if evaluate:
- if isinstance(lhs, Boolean) != isinstance(lhs, Boolean):
- # e.g. 0/1 not recognized as Boolean in SymPy
- return S.false
-
- # If one expression has an _eval_Eq, return its results.
- if hasattr(lhs, '_eval_Eq'):
- r = lhs._eval_Eq(rhs)
- if r is not None:
- return r
- if hasattr(rhs, '_eval_Eq'):
- r = rhs._eval_Eq(lhs)
- if r is not None:
- return r
- # If expressions have the same structure, they must be equal.
- if lhs == rhs:
- return S.true # e.g. True == True
- elif all(isinstance(i, BooleanAtom) for i in (rhs, lhs)):
- return S.false # True != False
- elif not (lhs.is_Symbol or rhs.is_Symbol) and (
- isinstance(lhs, Boolean) !=
- isinstance(rhs, Boolean)):
- return S.false # only Booleans can equal Booleans
-
- if lhs.is_infinite or rhs.is_infinite:
- if fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_infinite, rhs.is_infinite]):
- return S.false
- if fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_extended_real, rhs.is_extended_real]):
- return S.false
- if fuzzy_and([lhs.is_extended_real, rhs.is_extended_real]):
- r = fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_extended_positive, fuzzy_not(rhs.is_extended_positive)])
- return S(r)
-
- # Try to split real/imaginary parts and equate them
- I = S.ImaginaryUnit
-
- def split_real_imag(expr):
- real_imag = lambda t: (
- 'real' if t.is_extended_real else
- 'imag' if (I*t).is_extended_real else None)
- return sift(Add.make_args(expr), real_imag)
-
- lhs_ri = split_real_imag(lhs)
- if not lhs_ri[None]:
- rhs_ri = split_real_imag(rhs)
- if not rhs_ri[None]:
- eq_real = Eq(Add(*lhs_ri['real']), Add(*rhs_ri['real']))
- eq_imag = Eq(I*Add(*lhs_ri['imag']), I*Add(*rhs_ri['imag']))
- res = fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, [eq_real, eq_imag]))
- if res is not None:
- return S(res)
-
- # Compare e.g. zoo with 1+I*oo by comparing args
- arglhs = arg(lhs)
- argrhs = arg(rhs)
- # Guard against Eq(nan, nan) -> False
- if not (arglhs == S.NaN and argrhs == S.NaN):
- res = fuzzy_bool(Eq(arglhs, argrhs))
- if res is not None:
- return S(res)
-
- return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)
-
- if all(isinstance(i, Expr) for i in (lhs, rhs)):
- # see if the difference evaluates
- dif = lhs - rhs
- z = dif.is_zero
- if z is not None:
- if z is False and dif.is_commutative: # issue 10728
- return S.false
- if z:
- return S.true
- # evaluate numerically if possible
- n2 = _n2(lhs, rhs)
- if n2 is not None:
- return _sympify(n2 == 0)
- # see if the ratio evaluates
- n, d = dif.as_numer_denom()
- rv = None
- if n.is_zero:
- rv = d.is_nonzero
- elif n.is_finite:
- if d.is_infinite:
- rv = S.true
- elif n.is_zero is False:
- rv = d.is_infinite
- if rv is None:
- # if the condition that makes the denominator
- # infinite does not make the original expression
- # True then False can be returned
- l, r = clear_coefficients(d, S.Infinity)
- args = [_.subs(l, r) for _ in (lhs, rhs)]
- if args != [lhs, rhs]:
- rv = fuzzy_bool(Eq(*args))
- if rv is True:
- rv = None
- elif any(a.is_infinite for a in Add.make_args(n)):
- # (inf or nan)/x != 0
- rv = S.false
- if rv is not None:
- return _sympify(rv)
+ val = is_eq(lhs, rhs)
+ if val is None:
+ return cls(lhs, rhs, evaluate=False)
+ else:
+ return _sympify(val)
- return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)
+ return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs)
@classmethod
def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
return _sympify(lhs == rhs)
def _eval_rewrite_as_Add(self, *args, **kwargs):
- """return Eq(L, R) as L - R. To control the evaluation of
+ """
+ return Eq(L, R) as L - R. To control the evaluation of
the result set pass `evaluate=True` to give L - R;
if `evaluate=None` then terms in L and R will not cancel
but they will be listed in canonical order; otherwise
@@ -624,6 +528,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_Add(self, *args, **kwargs):
>>> eq.rewrite(Add, evaluate=False).args
(b, x, b, -x)
"""
+ from .add import _unevaluated_Add, Add
L, R = args
evaluate = kwargs.get('evaluate', True)
if evaluate:
@@ -646,6 +551,7 @@ def binary_symbols(self):
return set()
def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):
+ from .add import Add
from sympy.solvers.solveset import linear_coeffs
# standard simplify
e = super()._eval_simplify(**kwargs)
@@ -658,11 +564,11 @@ def _eval_simplify(self, **kwargs):
m, b = linear_coeffs(
e.rewrite(Add, evaluate=False), x)
if m.is_zero is False:
- enew = e.func(x, -b/m)
+ enew = e.func(x, -b / m)
else:
- enew = e.func(m*x, -b)
+ enew = e.func(m * x, -b)
measure = kwargs['measure']
- if measure(enew) <= kwargs['ratio']*measure(e):
+ if measure(enew) <= kwargs['ratio'] * measure(e):
e = enew
except ValueError:
pass
@@ -727,17 +633,13 @@ class Unequality(Relational):
def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options):
lhs = _sympify(lhs)
rhs = _sympify(rhs)
-
evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)
-
if evaluate:
- if isinstance(lhs, Boolean) != isinstance(lhs, Boolean):
- # e.g. 0/1 not recognized as Boolean in SymPy
- return S.true
-
- is_equal = Equality(lhs, rhs)
- if isinstance(is_equal, BooleanAtom):
- return is_equal.negated
+ val = is_neq(lhs, rhs)
+ if val is None:
+ return cls(lhs, rhs, evaluate=False)
+ else:
+ return _sympify(val)
return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)
@@ -776,12 +678,20 @@ class _Inequality(Relational):
__slots__ = ()
def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options):
- lhs = _sympify(lhs)
- rhs = _sympify(rhs)
- evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)
+ try:
+ lhs = _sympify(lhs)
+ rhs = _sympify(rhs)
+ except SympifyError:
+ return NotImplemented
+ evaluate = options.pop('evaluate', global_parameters.evaluate)
if evaluate:
+ for me in (lhs, rhs):
+ if me.is_extended_real is False:
+ raise TypeError("Invalid comparison of non-real %s" % me)
+ if me is S.NaN:
+ raise TypeError("Invalid NaN comparison")
# First we invoke the appropriate inequality method of `lhs`
# (e.g., `lhs.__lt__`). That method will try to reduce to
# boolean or raise an exception. It may keep calling
@@ -790,16 +700,20 @@ def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options):
# nor a subclass was able to reduce to boolean or raise an
# exception). In that case, it must call us with
# `evaluate=False` to prevent infinite recursion.
- r = cls._eval_relation(lhs, rhs)
- if r is not None:
- return r
- # Note: not sure r could be None, perhaps we never take this
- # path? In principle, could use this to shortcut out if a
- # class realizes the inequality cannot be evaluated further.
+ return cls._eval_relation(lhs, rhs, **options)
# make a "non-evaluated" Expr for the inequality
return Relational.__new__(cls, lhs, rhs, **options)
+ @classmethod
+ def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs, **options):
+ val = cls._eval_fuzzy_relation(lhs, rhs)
+ if val is None:
+ return cls(lhs, rhs, evaluate=False)
+ else:
+ return _sympify(val)
+
+
class _Greater(_Inequality):
"""Not intended for general use
@@ -1066,9 +980,8 @@ class GreaterThan(_Greater):
rel_op = '>='
@classmethod
- def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
- # We don't use the op symbol here: workaround issue #7951
- return _sympify(lhs.__ge__(rhs))
+ def _eval_fuzzy_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
+ return is_ge(lhs, rhs)
Ge = GreaterThan
@@ -1081,9 +994,8 @@ class LessThan(_Less):
rel_op = '<='
@classmethod
- def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
- # We don't use the op symbol here: workaround issue #7951
- return _sympify(lhs.__le__(rhs))
+ def _eval_fuzzy_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
+ return is_le(lhs, rhs)
Le = LessThan
@@ -1096,9 +1008,8 @@ class StrictGreaterThan(_Greater):
rel_op = '>'
@classmethod
- def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
- # We don't use the op symbol here: workaround issue #7951
- return _sympify(lhs.__gt__(rhs))
+ def _eval_fuzzy_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
+ return is_gt(lhs, rhs)
Gt = StrictGreaterThan
@@ -1111,14 +1022,12 @@ class StrictLessThan(_Less):
rel_op = '<'
@classmethod
- def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
- # We don't use the op symbol here: workaround issue #7951
- return _sympify(lhs.__lt__(rhs))
+ def _eval_fuzzy_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
+ return is_lt(lhs, rhs)
Lt = StrictLessThan
-
# A class-specific (not object-specific) data item used for a minor speedup.
# It is defined here, rather than directly in the class, because the classes
# that it references have not been defined until now (e.g. StrictLessThan).
@@ -1138,3 +1047,356 @@ def _eval_relation(cls, lhs, rhs):
'<': StrictLessThan,
'lt': StrictLessThan,
}
+
+
+def _n2(a, b):
+ """Return (a - b).evalf(2) if a and b are comparable, else None.
+ This should only be used when a and b are already sympified.
+ """
+ # /!\ it is very important (see issue 8245) not to
+ # use a re-evaluated number in the calculation of dif
+ if a.is_comparable and b.is_comparable:
+ dif = (a - b).evalf(2)
+ if dif.is_comparable:
+ return dif
+
+
+@dispatch(Expr, Expr)
+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs):
+ return None
+
+
+@dispatch(Basic, Basic)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs):
+ return None
+
+
+@dispatch(Tuple, Expr)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ return False
+
+
+@dispatch(Tuple, AppliedUndef)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ return None
+
+
+@dispatch(Tuple, Symbol)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ return None
+
+
+@dispatch(Tuple, Tuple)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ if len(lhs) != len(rhs):
+ return False
+
+ return fuzzy_and(fuzzy_bool(is_eq(s, o)) for s, o in zip(lhs, rhs))
+
+
+def is_lt(lhs, rhs):
+ """Fuzzy bool for lhs is strictly less than rhs.
+
+ See the docstring for is_ge for more
+ """
+ return fuzzy_not(is_ge(lhs, rhs))
+
+
+def is_gt(lhs, rhs):
+ """Fuzzy bool for lhs is strictly greater than rhs.
+
+ See the docstring for is_ge for more
+ """
+ return fuzzy_not(is_le(lhs, rhs))
+
+
+def is_le(lhs, rhs):
+ """Fuzzy bool for lhs is less than or equal to rhs.
+ is_gt calls is_lt
+ See the docstring for is_ge for more
+ """
+ return is_ge(rhs, lhs)
+
+
+def is_ge(lhs, rhs):
+ """
+ Fuzzy bool for lhs is greater than or equal to rhs.
+
+ :param lhs: the left-hand side of the expression, must be sympified, and an instance of expression
+ Throws an exception if lhs is not an instance of expression
+ :param rhs: the right-hand side of the expression, must be sympified and an instance of expression
+ Throws an exception if lhs is not an instance of expression
+ :return: True if lhs is greater than or equal to rhs, false is lhs is less than rhs, and
+ None if the comparison between lhs and rhs is indeterminate
+
+ The four comparison functions ``is_le``, ``is_lt``, ``is_ge``, and ``is_gt`` are
+ each implemented in terms of ``is_ge`` in the following way:
+
+ is_ge(x, y) := is_ge(x, y)
+ is_le(x, y) := is_ge(y, x)
+ is_lt(x, y) := fuzzy_not(is_ge(x, y))
+ is_gt(x, y) = fuzzy_not(is_ge(y, x))
+
+ To maintain these equivalences in fuzzy logic it is important that in cases where
+ either x or y is non-real all comparisons will give None.
+
+ InEquality classes, such as Lt, Gt, etc. Use one of is_ge, is_le, etc.
+ To implement comparisons with ``Gt(a, b)`` or ``a > b`` etc for an ``Expr`` subclass
+ it is only necessary to define a dispatcher method for ``_eval_is_ge`` like
+
+ >>> from sympy.core.relational import is_ge, is_lt, is_gt
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
+ >>> from sympy import S, Expr, sympify
+ >>> from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
+ >>> class MyExpr(Expr):
+ ... def __new__(cls, arg):
+ ... return Expr.__new__(cls, sympify(arg))
+ ... @property
+ ... def value(self):
+ ... return self.args[0]
+ ...
+ >>> @dispatch(MyExpr, MyExpr)
+ ... def _eval_is_ge(a, b):
+ ... return is_ge(a.value, b.value)
+ ...
+ >>> a = MyExpr(1)
+ >>> b = MyExpr(2)
+ >>> a < b
+ True
+ >>> a <= b
+ True
+ >>> a > b
+ False
+ >>> is_lt(a, b)
+ True
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+
+ >>> is_ge(S(2), S(0))
+ True
+ >>> is_ge(S(0), S(2))
+ False
+ >>> is_ge(S(0), x)
+
+ >>> is_gt(S(2), S(0))
+ True
+ >>> is_gt(S(0), S(2))
+ False
+ >>> is_lt(S(0), S(2))
+ True
+ >>> is_lt(S(2), S(0))
+ False
+
+ """
+ if not (isinstance(lhs, Expr) and isinstance(rhs, Expr)):
+ raise TypeError("Can only compare inequalities with Expr")
+
+ retval = _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs)
+
+ if retval is not None:
+ return retval
+ else:
+ n2 = _n2(lhs, rhs)
+ if n2 is not None:
+ # use float comparison for infinity.
+ # otherwise get stuck in infinite recursion
+ if n2 in (S.Infinity, S.NegativeInfinity):
+ n2 = float(n2)
+ return _sympify(n2 >= 0)
+ if lhs.is_extended_real and rhs.is_extended_real:
+ if (lhs.is_infinite and lhs.is_extended_positive) or (rhs.is_infinite and rhs.is_extended_negative):
+ return True
+ diff = lhs - rhs
+ if diff is not S.NaN:
+ rv = diff.is_extended_nonnegative
+ if rv is not None:
+ return rv
+
+
+def is_neq(lhs, rhs):
+ """Fuzzy bool for lhs does not equal rhs.
+
+ See the docstring for is_eq for more
+ """
+ return fuzzy_not(is_eq(lhs, rhs))
+
+
+def is_eq(lhs, rhs):
+ """
+ Fuzzy bool representing mathematical equality between lhs and rhs.
+
+ :param lhs: the left-hand side of the expression, must be sympified
+ :param rhs: the right-hand side of the expression, must be sympified
+ :return: True if lhs is equal to rhs, false is lhs is not equal to rhs, and
+ None if the comparison between lhs and rhs is indeterminate
+
+ Notes:
+
+ This function is intended to give a relatively fast determination and deliberately does not attempt slow
+ calculations that might help in obtaining a determination of True or False in more difficult cases.
+
+ InEquality classes, such as Lt, Gt, etc. Use one of is_ge, is_le, etc.
+ To implement comparisons with ``Gt(a, b)`` or ``a > b`` etc for an ``Expr`` subclass
+ it is only necessary to define a dispatcher method for ``_eval_is_ge`` like
+
+ >>> from sympy.core.relational import is_eq
+ >>> from sympy.core.relational import is_neq
+ >>> from sympy import S, Basic, Eq, sympify
+ >>> from sympy.abc import x
+ >>> from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
+ >>> class MyBasic(Basic):
+ ... def __new__(cls, arg):
+ ... return Basic.__new__(cls, sympify(arg))
+ ... @property
+ ... def value(self):
+ ... return self.args[0]
+ ...
+ >>> @dispatch(MyBasic, MyBasic)
+ ... def _eval_is_eq(a, b):
+ ... return is_eq(a.value, b.value)
+ ...
+ >>> a = MyBasic(1)
+ >>> b = MyBasic(1)
+ >>> a == b
+ True
+ >>> Eq(a, b)
+ True
+ >>> a != b
+ False
+ >>> is_eq(a, b)
+ True
+
+
+ Examples
+ ========
+
+
+
+ >>> is_eq(S(0), S(0))
+ True
+ >>> Eq(0, 0)
+ True
+ >>> is_neq(S(0), S(0))
+ False
+ >>> is_eq(S(0), S(2))
+ False
+ >>> Eq(0, 2)
+ False
+ >>> is_neq(S(0), S(2))
+ True
+ >>> is_eq(S(0), x)
+
+ >>> Eq(S(0), x)
+ Eq(0, x)
+
+
+
+ """
+ from sympy.core.add import Add
+ from sympy.functions.elementary.complexes import arg
+ from sympy.simplify.simplify import clear_coefficients
+ from sympy.utilities.iterables import sift
+
+ # here, _eval_Eq is only called for backwards compatibility
+ # new code should use is_eq with multiple dispatch as
+ # outlined in the docstring
+ for side1, side2 in (lhs, rhs), (rhs, lhs):
+ eval_func = getattr(side1, '_eval_Eq', None)
+ if eval_func is not None:
+ retval = eval_func(side2)
+ if retval is not None:
+ return retval
+
+ retval = _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs)
+ if retval is not None:
+ return retval
+
+ if dispatch(type(lhs), type(rhs)) != dispatch(type(rhs), type(lhs)):
+ retval = _eval_is_eq(rhs, lhs)
+ if retval is not None:
+ return retval
+
+ # retval is still None, so go through the equality logic
+ # If expressions have the same structure, they must be equal.
+ if lhs == rhs:
+ return True # e.g. True == True
+ elif all(isinstance(i, BooleanAtom) for i in (rhs, lhs)):
+ return False # True != False
+ elif not (lhs.is_Symbol or rhs.is_Symbol) and (
+ isinstance(lhs, Boolean) !=
+ isinstance(rhs, Boolean)):
+ return False # only Booleans can equal Booleans
+
+ if lhs.is_infinite or rhs.is_infinite:
+ if fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_infinite, rhs.is_infinite]):
+ return False
+ if fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_extended_real, rhs.is_extended_real]):
+ return False
+ if fuzzy_and([lhs.is_extended_real, rhs.is_extended_real]):
+ return fuzzy_xor([lhs.is_extended_positive, fuzzy_not(rhs.is_extended_positive)])
+
+ # Try to split real/imaginary parts and equate them
+ I = S.ImaginaryUnit
+
+ def split_real_imag(expr):
+ real_imag = lambda t: (
+ 'real' if t.is_extended_real else
+ 'imag' if (I * t).is_extended_real else None)
+ return sift(Add.make_args(expr), real_imag)
+
+ lhs_ri = split_real_imag(lhs)
+ if not lhs_ri[None]:
+ rhs_ri = split_real_imag(rhs)
+ if not rhs_ri[None]:
+ eq_real = Eq(Add(*lhs_ri['real']), Add(*rhs_ri['real']))
+ eq_imag = Eq(I * Add(*lhs_ri['imag']), I * Add(*rhs_ri['imag']))
+ return fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, [eq_real, eq_imag]))
+
+ # Compare e.g. zoo with 1+I*oo by comparing args
+ arglhs = arg(lhs)
+ argrhs = arg(rhs)
+ # Guard against Eq(nan, nan) -> Falsesymp
+ if not (arglhs == S.NaN and argrhs == S.NaN):
+ return fuzzy_bool(Eq(arglhs, argrhs))
+
+ if all(isinstance(i, Expr) for i in (lhs, rhs)):
+ # see if the difference evaluates
+ dif = lhs - rhs
+ z = dif.is_zero
+ if z is not None:
+ if z is False and dif.is_commutative: # issue 10728
+ return False
+ if z:
+ return True
+
+ n2 = _n2(lhs, rhs)
+ if n2 is not None:
+ return _sympify(n2 == 0)
+
+ # see if the ratio evaluates
+ n, d = dif.as_numer_denom()
+ rv = None
+ if n.is_zero:
+ rv = d.is_nonzero
+ elif n.is_finite:
+ if d.is_infinite:
+ rv = True
+ elif n.is_zero is False:
+ rv = d.is_infinite
+ if rv is None:
+ # if the condition that makes the denominator
+ # infinite does not make the original expression
+ # True then False can be returned
+ l, r = clear_coefficients(d, S.Infinity)
+ args = [_.subs(l, r) for _ in (lhs, rhs)]
+ if args != [lhs, rhs]:
+ rv = fuzzy_bool(Eq(*args))
+ if rv is True:
+ rv = None
+ elif any(a.is_infinite for a in Add.make_args(n)):
+ # (inf or nan)/x != 0
+ rv = False
+ if rv is not None:
+ return rv
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py
index 015c7953441c..e94437a575f2 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_relational.py
@@ -1,11 +1,14 @@
+from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and
+from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
from sympy.testing.pytest import XFAIL, raises, warns_deprecated_sympy
from sympy import (S, Symbol, symbols, nan, oo, I, pi, Float, And, Or,
- Not, Implies, Xor, zoo, sqrt, Rational, simplify, Function,
- log, cos, sin, Add, Mul, Pow, floor, ceiling, trigsimp, Reals)
+ Not, Implies, Xor, zoo, sqrt, Rational, simplify, Function,
+ log, cos, sin, Add, Mul, Pow, floor, ceiling, trigsimp, Reals, Basic, Expr)
from sympy.core.relational import (Relational, Equality, Unequality,
GreaterThan, LessThan, StrictGreaterThan,
StrictLessThan, Rel, Eq, Lt, Le,
- Gt, Ge, Ne)
+ Gt, Ge, Ne, is_le, is_gt, is_ge, is_lt, is_eq, is_neq)
from sympy.sets.sets import Interval, FiniteSet
from itertools import combinations
@@ -690,7 +693,7 @@ def test_issue_8245():
r = Rational(str(a.n(29)))
assert rel_check(a, r)
- assert Eq(log(cos(2)**2 + sin(2)**2), 0) == True
+ assert Eq(log(cos(2)**2 + sin(2)**2), 0) is S.true
def test_issue_8449():
@@ -1129,3 +1132,58 @@ def test_multivariate_linear_function_simplification():
def test_nonpolymonial_relations():
assert Eq(cos(x), 0).simplify() == Eq(cos(x), 0)
+
+def test_18778():
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: is_le(Basic(), Basic()))
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: is_gt(Basic(), Basic()))
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: is_ge(Basic(), Basic()))
+ raises(TypeError, lambda: is_lt(Basic(), Basic()))
+
+def test_EvalEq():
+ """
+
+ This test exists to ensure backwards compatibility.
+ The method to use is _eval_is_eq
+ """
+ from sympy import Expr
+
+ class PowTest(Expr):
+ def __new__(cls, base, exp):
+ return Basic.__new__(PowTest, _sympify(base), _sympify(exp))
+
+ def _eval_Eq(lhs, rhs):
+ if type(lhs) == PowTest and type(rhs) == PowTest:
+ return lhs.args[0] == rhs.args[0] and lhs.args[1] == rhs.args[1]
+
+ assert is_eq(PowTest(3, 4), PowTest(3,4))
+ assert is_eq(PowTest(3, 4), _sympify(4)) is None
+ assert is_neq(PowTest(3, 4), PowTest(3,7))
+
+def test_is_eq():
+ class PowTest(Expr):
+ def __new__(cls, base, exp):
+ return Basic.__new__(cls, _sympify(base), _sympify(exp))
+
+ @dispatch(PowTest, PowTest)
+ def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs):
+ if type(lhs) == PowTest and type(rhs) == PowTest:
+ return fuzzy_and([is_eq(lhs.args[0], rhs.args[0]), is_eq(lhs.args[1], rhs.args[1])])
+
+ assert is_eq(PowTest(3, 4), PowTest(3,4))
+ assert is_eq(PowTest(3, 4), _sympify(4)) is None
+ assert is_neq(PowTest(3, 4), PowTest(3,7))
+
+def test_is_ge_le():
+ class PowTest(Expr):
+ def __new__(cls, base, exp):
+ return Basic.__new__(cls, _sympify(base), _sympify(exp))
+
+ @dispatch(PowTest, PowTest)
+ def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs):
+ if type(lhs) == PowTest and type(rhs) == PowTest:
+ return fuzzy_and([is_ge(lhs.args[0], rhs.args[0]), is_ge(lhs.args[1], rhs.args[1])])
+
+ assert is_ge(PowTest(3, 9), PowTest(3,2))
+ assert is_gt(PowTest(3, 9), PowTest(3,2))
+ assert is_le(PowTest(3, 2), PowTest(3,9))
+ assert is_lt(PowTest(3, 2), PowTest(3,9))
diff --git a/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py b/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py
index cbf6a9ab3280..cd109a401af2 100644
--- a/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py
+++ b/sympy/functions/elementary/integers.py
@@ -1,12 +1,17 @@
+
+from __future__ import print_function, division
+
+from sympy import Basic, Expr
+
from sympy.core import Add, S
from sympy.core.evalf import get_integer_part, PrecisionExhausted
from sympy.core.function import Function
from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_or
from sympy.core.numbers import Integer
-from sympy.core.relational import Gt, Lt, Ge, Le, Relational
+from sympy.core.relational import Gt, Lt, Ge, Le, Relational, is_eq
from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
-
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
###############################################################################
######################### FLOOR and CEILING FUNCTIONS #########################
@@ -154,11 +159,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_ceiling(self, arg, **kwargs):
def _eval_rewrite_as_frac(self, arg, **kwargs):
return arg - frac(arg)
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- if isinstance(self, floor):
- if (self.rewrite(ceiling) == other) or \
- (self.rewrite(frac) == other):
- return S.true
+
def __le__(self, other):
other = S(other)
@@ -216,6 +217,11 @@ def __lt__(self, other):
return Lt(self, other, evaluate=False)
+@dispatch(floor, Expr)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ return is_eq(lhs.rewrite(ceiling), rhs) or \
+ is_eq(lhs.rewrite(frac),rhs)
+
class ceiling(RoundFunction):
"""
Ceiling is a univariate function which returns the smallest integer
@@ -289,11 +295,7 @@ def _eval_is_positive(self):
def _eval_is_nonpositive(self):
return self.args[0].is_nonpositive
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- if isinstance(self, ceiling):
- if (self.rewrite(floor) == other) or \
- (self.rewrite(frac) == other):
- return S.true
+
def __lt__(self, other):
other = S(other)
@@ -351,6 +353,10 @@ def __le__(self, other):
return Le(self, other, evaluate=False)
+@dispatch(ceiling, Basic)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ return is_eq(lhs.rewrite(floor), rhs) or is_eq(lhs.rewrite(frac),rhs)
+
class frac(Function):
r"""Represents the fractional part of x
@@ -442,18 +448,7 @@ def _eval_rewrite_as_floor(self, arg, **kwargs):
def _eval_rewrite_as_ceiling(self, arg, **kwargs):
return arg + ceiling(-arg)
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- if isinstance(self, frac):
- if (self.rewrite(floor) == other) or \
- (self.rewrite(ceiling) == other):
- return S.true
- # Check if other < 0
- if other.is_extended_negative:
- return S.false
- # Check if other >= 1
- res = self._value_one_or_more(other)
- if res is not None:
- return S.false
+
def _eval_is_finite(self):
return True
@@ -529,3 +524,16 @@ def _value_one_or_more(self, other):
return S.true
if other.is_integer and other.is_positive:
return S.true
+
+@dispatch(frac, Basic)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ if (lhs.rewrite(floor) == rhs) or \
+ (lhs.rewrite(ceiling) == rhs):
+ return True
+ # Check if other < 0
+ if rhs.is_extended_negative:
+ return False
+ # Check if other >= 1
+ res = lhs._value_one_or_more(rhs)
+ if res is not None:
+ return False
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
index 31f1226cce69..38c5f4d4d2bf 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/expressions/matexpr.py
@@ -14,6 +14,7 @@
from sympy.simplify import simplify
from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent
from sympy.assumptions.ask import ask, Q
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
def _sympifyit(arg, retval=None):
@@ -593,15 +594,16 @@ def applyfunc(self, func):
from .applyfunc import ElementwiseApplyFunction
return ElementwiseApplyFunction(func, self)
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- if not isinstance(other, MatrixExpr):
- return False
- if self.shape != other.shape:
- return False
- if (self - other).is_ZeroMatrix:
- return True
- return Eq(self, other, evaluate=False)
+@dispatch(MatrixExpr, Expr)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ return False
+@dispatch(MatrixExpr, MatrixExpr)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ if lhs.shape != rhs.shape:
+ return False
+ if (lhs - rhs).is_ZeroMatrix:
+ return True
def get_postprocessor(cls):
def _postprocessor(expr):
diff --git a/sympy/matrices/immutable.py b/sympy/matrices/immutable.py
index 668caaf45088..d50bb39091ae 100644
--- a/sympy/matrices/immutable.py
+++ b/sympy/matrices/immutable.py
@@ -1,26 +1,33 @@
from mpmath.matrices.matrices import _matrix
-from sympy.core import Basic, Dict, Integer, S, Tuple
+from sympy.core import Basic, Dict, Integer, Tuple
from sympy.core.cache import cacheit
from sympy.core.sympify import converter as sympify_converter, _sympify
from sympy.matrices.dense import DenseMatrix
from sympy.matrices.expressions import MatrixExpr
from sympy.matrices.matrices import MatrixBase
from sympy.matrices.sparse import SparseMatrix
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
+
def sympify_matrix(arg):
return arg.as_immutable()
+
+
sympify_converter[MatrixBase] = sympify_matrix
def sympify_mpmath_matrix(arg):
mat = [_sympify(x) for x in arg]
return ImmutableDenseMatrix(arg.rows, arg.cols, mat)
+
+
sympify_converter[_matrix] = sympify_mpmath_matrix
-class ImmutableDenseMatrix(DenseMatrix, MatrixExpr):
+
+class ImmutableDenseMatrix(DenseMatrix, MatrixExpr): # type: ignore
"""Create an immutable version of a matrix.
Examples
@@ -77,27 +84,6 @@ def _entry(self, i, j, **kwargs):
def __setitem__(self, *args):
raise TypeError("Cannot set values of {}".format(self.__class__))
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- """Helper method for Equality with matrices.
-
- Relational automatically converts matrices to ImmutableDenseMatrix
- instances, so this method only applies here. Returns True if the
- matrices are definitively the same, False if they are definitively
- different, and None if undetermined (e.g. if they contain Symbols).
- Returning None triggers default handling of Equalities.
-
- """
- if not hasattr(other, 'shape') or self.shape != other.shape:
- return S.false
- if isinstance(other, MatrixExpr) and not isinstance(
- other, ImmutableDenseMatrix):
- return None
- diff = (self - other).is_zero_matrix
- if diff is True:
- return S.true
- elif diff is False:
- return S.false
-
def _eval_extract(self, rowsList, colsList):
# self._mat is a Tuple. It is slightly faster to index a
# tuple over a Tuple, so grab the internal tuple directly
@@ -125,6 +111,7 @@ def as_immutable(self):
def is_diagonalizable(self, reals_only=False, **kwargs):
return super().is_diagonalizable(
reals_only=reals_only, **kwargs)
+
is_diagonalizable.__doc__ = DenseMatrix.is_diagonalizable.__doc__
is_diagonalizable = cacheit(is_diagonalizable)
@@ -178,8 +165,6 @@ def __setitem__(self, *args):
def _entry(self, i, j, **kwargs):
return SparseMatrix.__getitem__(self, (i, j))
- _eval_Eq = ImmutableDenseMatrix._eval_Eq
-
@property
def cols(self):
return self._cols
@@ -198,5 +183,22 @@ def as_immutable(self):
def is_diagonalizable(self, reals_only=False, **kwargs):
return super().is_diagonalizable(
reals_only=reals_only, **kwargs)
+
is_diagonalizable.__doc__ = SparseMatrix.is_diagonalizable.__doc__
is_diagonalizable = cacheit(is_diagonalizable)
+
+
+@dispatch(ImmutableDenseMatrix, ImmutableDenseMatrix)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ """Helper method for Equality with matrices.sympy.
+
+ Relational automatically converts matrices to ImmutableDenseMatrix
+ instances, so this method only applies here. Returns True if the
+ matrices are definitively the same, False if they are definitively
+ different, and None if undetermined (e.g. if they contain Symbols).
+ Returning None triggers default handling of Equalities.
+
+ """
+ if lhs.shape != rhs.shape:
+ return False
+ return (lhs - rhs).is_zero_matrix
diff --git a/sympy/polys/domains/finitefield.py b/sympy/polys/domains/finitefield.py
index 0b1cceee49a1..8dd5dba39b6e 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/domains/finitefield.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/domains/finitefield.py
@@ -3,11 +3,12 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
from sympy.polys.domains.field import Field
-from sympy.polys.domains.groundtypes import SymPyInteger
+
from sympy.polys.domains.modularinteger import ModularIntegerFactory
from sympy.polys.domains.simpledomain import SimpleDomain
from sympy.polys.polyerrors import CoercionFailed
from sympy.utilities import public
+from sympy.polys.domains.groundtypes import SymPyInteger
@public
class FiniteField(Field, SimpleDomain):
diff --git a/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py b/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py
index 8d8a199ff826..cae6cf4ee245 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/rootoftools.py
@@ -2,10 +2,12 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
+from sympy import Basic
from sympy.core import (S, Expr, Integer, Float, I, oo, Add, Lambda,
symbols, sympify, Rational, Dummy)
from sympy.core.cache import cacheit
from sympy.core.compatibility import ordered
+from sympy.core.relational import is_le
from sympy.polys.domains import QQ
from sympy.polys.polyerrors import (
MultivariatePolynomialError,
@@ -25,7 +27,7 @@
from mpmath import mpf, mpc, findroot, workprec
from mpmath.libmp.libmpf import dps_to_prec, prec_to_dps
-
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
from itertools import chain
@@ -970,42 +972,48 @@ def eval_rational(self, dx=None, dy=None, n=15):
self._set_interval(interval)
return real + I*imag
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- # CRootOf represents a Root, so if other is that root, it should set
- # the expression to zero *and* it should be in the interval of the
- # CRootOf instance. It must also be a number that agrees with the
- # is_real value of the CRootOf instance.
- if type(self) == type(other):
- return sympify(self == other)
- if not other.is_number:
- return None
- if not other.is_finite:
- return S.false
- z = self.expr.subs(self.expr.free_symbols.pop(), other).is_zero
- if z is False: # all roots will make z True but we don't know
- # whether this is the right root if z is True
- return S.false
- o = other.is_real, other.is_imaginary
- s = self.is_real, self.is_imaginary
- assert None not in s # this is part of initial refinement
- if o != s and None not in o:
- return S.false
- re, im = other.as_real_imag()
- if self.is_real:
- if im:
- return S.false
- i = self._get_interval()
- a, b = [Rational(str(_)) for _ in (i.a, i.b)]
- return sympify(a <= other and other <= b)
- i = self._get_interval()
- r1, r2, i1, i2 = [Rational(str(j)) for j in (
- i.ax, i.bx, i.ay, i.by)]
- return sympify((
- r1 <= re and re <= r2) and (
- i1 <= im and im <= i2))
CRootOf = ComplexRootOf
+
+@dispatch(ComplexRootOf, ComplexRootOf)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ # if we use is_eq to check here, we get infinite recurion
+ return lhs == rhs
+
+
+@dispatch(ComplexRootOf, Basic)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+ # CRootOf represents a Root, so if rhs is that root, it should set
+ # the expression to zero *and* it should be in the interval of the
+ # CRootOf instance. It must also be a number that agrees with the
+ # is_real value of the CRootOf instance.
+ if not rhs.is_number:
+ return None
+ if not rhs.is_finite:
+ return False
+ z = lhs.expr.subs(lhs.expr.free_symbols.pop(), rhs).is_zero
+ if z is False: # all roots will make z True but we don't know
+ # whether this is the right root if z is True
+ return False
+ o = rhs.is_real, rhs.is_imaginary
+ s = lhs.is_real, lhs.is_imaginary
+ assert None not in s # this is part of initial refinement
+ if o != s and None not in o:
+ return False
+ re, im = rhs.as_real_imag()
+ if lhs.is_real:
+ if im:
+ return False
+ i = lhs._get_interval()
+ a, b = [Rational(str(_)) for _ in (i.a, i.b)]
+ return sympify(a <= rhs and rhs <= b)
+ i = lhs._get_interval()
+ r1, r2, i1, i2 = [Rational(str(j)) for j in (
+ i.ax, i.bx, i.ay, i.by)]
+ return is_le(r1, re) and is_le(re,r2) and is_le(i1,im) and is_le(im,i2)
+
+
@public
class RootSum(Expr):
"""Represents a sum of all roots of a univariate polynomial. """
diff --git a/sympy/sets/__init__.py b/sympy/sets/__init__.py
index 5fa609b95370..c4773a76f482 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/__init__.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/__init__.py
@@ -1,13 +1,14 @@
from .sets import (Set, Interval, Union, FiniteSet, ProductSet,
Intersection, imageset, Complement, SymmetricDifference,
DisjointUnion)
+
from .fancysets import ImageSet, Range, ComplexRegion
from .contains import Contains
from .conditionset import ConditionSet
from .ordinals import Ordinal, OmegaPower, ord0
from .powerset import PowerSet
from ..core.singleton import S
-
+from .handlers.comparison import _eval_is_eq # noqa:F401
Reals = S.Reals
Naturals = S.Naturals
Naturals0 = S.Naturals0
diff --git a/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py b/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..5eea221c653c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sympy/sets/handlers/comparison.py
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+from sympy.core.relational import Eq, is_eq
+from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_and, fuzzy_bool
+from sympy.logic.boolalg import And
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
+from sympy.sets.sets import tfn, ProductSet, Interval, FiniteSet
+
+
+@dispatch(Interval, FiniteSet)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+ return False
+
+
+@dispatch(FiniteSet, Interval)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+ return False
+
+
+@dispatch(Interval, Interval)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+ return And(Eq(lhs.left, rhs.left),
+ Eq(lhs.right, rhs.right),
+ lhs.left_open == rhs.left_open,
+ lhs.right_open == rhs.right_open)
+
+
+@dispatch(FiniteSet, Interval)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+ return False
+
+
+@dispatch(FiniteSet, FiniteSet)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+ def all_in_both():
+ s_set = set(lhs.args)
+ o_set = set(rhs.args)
+ yield fuzzy_and(lhs._contains(e) for e in o_set - s_set)
+ yield fuzzy_and(rhs._contains(e) for e in s_set - o_set)
+
+ return tfn[fuzzy_and(all_in_both())]
+
+
+@dispatch(ProductSet, ProductSet)
+def _eval_is_eq(lhs, rhs): # noqa: F811
+ if len(lhs.sets) != len(rhs.sets):
+ return False
+
+ eqs = (is_eq(x, y) for x, y in zip(lhs.sets, rhs.sets))
+ return tfn[fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, eqs))]
diff --git a/sympy/sets/sets.py b/sympy/sets/sets.py
index ebe5a546a794..65e42a9480ab 100644
--- a/sympy/sets/sets.py
+++ b/sympy/sets/sets.py
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@
fuzzy_not)
from sympy.core.numbers import Float
from sympy.core.operations import LatticeOp
-from sympy.core.relational import Eq, Ne
+from sympy.core.relational import Eq, Ne, is_lt
from sympy.core.singleton import Singleton, S
from sympy.core.symbol import Symbol, Dummy, uniquely_named_symbol
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify, sympify, converter
@@ -27,7 +27,6 @@
from sympy.utilities.exceptions import SymPyDeprecationWarning
from sympy.utilities.iterables import iproduct, sift, roundrobin
from sympy.utilities.misc import func_name, filldedent
-
from mpmath import mpi, mpf
@@ -761,15 +760,7 @@ def _flatten(sets):
yield s
return ProductSet(*_flatten(self.sets))
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- if not other.is_ProductSet:
- return
- if len(self.sets) != len(other.sets):
- return false
-
- eqs = (Eq(x, y) for x, y in zip(self.sets, other.sets))
- return tfn[fuzzy_and(map(fuzzy_bool, eqs))]
def _contains(self, element):
"""
@@ -924,7 +915,7 @@ def __new__(cls, start, end, left_open=False, right_open=False):
raise ValueError("Non-real intervals are not supported")
# evaluate if possible
- if (end < start) == True:
+ if is_lt(end, start):
return S.EmptySet
elif (end - start).is_negative:
return S.EmptySet
@@ -1128,11 +1119,6 @@ def _eval_Eq(self, other):
return None
return false
- return And(Eq(self.left, other.left),
- Eq(self.right, other.right),
- self.left_open == other.left_open,
- self.right_open == other.right_open)
-
class Union(Set, LatticeOp, EvalfMixin):
"""
@@ -1791,24 +1777,6 @@ def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
obj._args_set = _args_set
return obj
- def _eval_Eq(self, other):
- if not isinstance(other, FiniteSet):
- # XXX: If Interval(x, x, evaluate=False) worked then the line
- # below would mean that
- # FiniteSet(x) & Interval(x, x, evaluate=False) -> false
- if isinstance(other, Interval):
- return false
- elif isinstance(other, Set):
- return None
- return false
-
- def all_in_both():
- s_set = set(self.args)
- o_set = set(other.args)
- yield fuzzy_and(self._contains(e) for e in o_set - s_set)
- yield fuzzy_and(other._contains(e) for e in s_set - o_set)
-
- return tfn[fuzzy_and(all_in_both())]
def __iter__(self):
return iter(self.args)
diff --git a/sympy/tensor/indexed.py b/sympy/tensor/indexed.py
index b8b4da9461e7..30deb7a6d94d 100644
--- a/sympy/tensor/indexed.py
+++ b/sympy/tensor/indexed.py
@@ -106,6 +106,7 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
+from sympy import Number
from sympy.core.assumptions import StdFactKB
from sympy.core import Expr, Tuple, sympify, S
from sympy.core.symbol import _filter_assumptions, Symbol
@@ -114,6 +115,7 @@
from sympy.core.logic import fuzzy_bool, fuzzy_not
from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
from sympy.functions.special.tensor_functions import KroneckerDelta
+from sympy.multipledispatch import dispatch
class IndexException(Exception):
@@ -751,58 +753,41 @@ def name(self):
def free_symbols(self):
return {self}
- def __le__(self, other):
- if isinstance(other, Idx):
- other_upper = other if other.upper is None else other.upper
- other_lower = other if other.lower is None else other.lower
- else:
- other_upper = other
- other_lower = other
-
- if self.upper is not None and (self.upper <= other_lower) == True:
- return True
- if self.lower is not None and (self.lower > other_upper) == True:
- return False
- return super(Idx, self).__le__(other)
-
- def __ge__(self, other):
- if isinstance(other, Idx):
- other_upper = other if other.upper is None else other.upper
- other_lower = other if other.lower is None else other.lower
- else:
- other_upper = other
- other_lower = other
-
- if self.lower is not None and (self.lower >= other_upper) == True:
- return True
- if self.upper is not None and (self.upper < other_lower) == True:
- return False
- return super(Idx, self).__ge__(other)
-
- def __lt__(self, other):
- if isinstance(other, Idx):
- other_upper = other if other.upper is None else other.upper
- other_lower = other if other.lower is None else other.lower
- else:
- other_upper = other
- other_lower = other
-
- if self.upper is not None and (self.upper < other_lower) == True:
- return True
- if self.lower is not None and (self.lower >= other_upper) == True:
- return False
- return super(Idx, self).__lt__(other)
-
- def __gt__(self, other):
- if isinstance(other, Idx):
- other_upper = other if other.upper is None else other.upper
- other_lower = other if other.lower is None else other.lower
- else:
- other_upper = other
- other_lower = other
-
- if self.lower is not None and (self.lower > other_upper) == True:
- return True
- if self.upper is not None and (self.upper <= other_lower) == True:
- return False
- return super(Idx, self).__gt__(other)
+
+@dispatch(Idx, Idx)
+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+
+ other_upper = rhs if rhs.upper is None else rhs.upper
+ other_lower = rhs if rhs.lower is None else rhs.lower
+
+ if lhs.lower is not None and (lhs.lower >= other_upper) == True:
+ return True
+ if lhs.upper is not None and (lhs.upper < other_lower) == True:
+ return False
+ return None
+
+
+@dispatch(Idx, Number)
+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+
+ other_upper = rhs
+ other_lower = rhs
+
+ if lhs.lower is not None and (lhs.lower >= other_upper) == True:
+ return True
+ if lhs.upper is not None and (lhs.upper < other_lower) == True:
+ return False
+ return None
+
+
+@dispatch(Number, Idx)
+def _eval_is_ge(lhs, rhs): # noqa:F811
+
+ other_upper = lhs
+ other_lower = lhs
+
+ if rhs.upper is not None and (rhs.upper <= other_lower) == True:
+ return True
+ if rhs.lower is not None and (rhs.lower > other_upper) == True:
+ return False
+ return None
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "New Feature Additions"
}
|
sympy__sympy-18717@ef8c567
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,717
|
Add class DiophantineEquationType and move classification logic
|
#### References to other Issues or PRs
#18493
Closes #18370.
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Introduce new class `DiophantineEquationType`. The class has various attributes for properties of the equation such as `homogeneous` and `total_degree`.
Move classification logic out of `classify_diop` and into individual equation type classes.
Generate `diop_known` from the list of equation type classes.
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
NO ENTRY
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-02-24T18:27:41Z
|
Confusing test cases in test_classify_diop
We have these two test cases:
```
assert classify_diop(x*y + z) == (
[x, y, z], {x*y: 1, z: 1}, 'inhomogeneous_ternary_quadratic')
assert classify_diop(x*y + z + w + x**2) == (
[w, x, y, z], {x*y: 1, w: 1, x**2: 1, z: 1}, 'inhomogeneous_general_quadratic')
```
In what way are these equations "inhomogeneous"?
|
~~Unfortunately it would not be the first time that dubious test results made their way into the test suite...~~
~~I'd say the tests you cited are bugs in `classify_diop`. (Or at least badly chosen default names for some classes of equations that diophantine is not currently capable of solving.) IMO it should be fixed.~~
hey how x*y+z & x*y + z + w + x**2 are homogeneous? I am considering this defination "A polynomial is homogeneous if all its terms have the same degree".
Oops, I retract my previous comment. I was probably thinking of linear equations where homogeneity reduces to the presence or absence of a constant term.
is this issue still valid?
`homogeneous` clearly is referring to the presence of a constant term here:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/9f98339b3344de9109f4d2780faf9822fb110848/sympy/solvers/diophantine.py#L497
Here the code checks that `homogeneous` is true and then immediately returns an inhomogeneous equation type:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/9f98339b3344de9109f4d2780faf9822fb110848/sympy/solvers/diophantine.py#L507-L509
In general,we look for the coefficient only in the case of linear equation which look like this `a1x1+a2x2+...+anxn=b` but ` xy+z & xy + z + w + x**2 are polynomial` in which the only thing that matters is the degree should be same for all the term.
This is why we look for constant to be zero in linear equation
`A homogeneous linear equation, say, 2x+3y+5z=0, is really special because it has an important property: if (x,y,z) is a solution then (λx,λy,λz) is also a solution for arbitrary constant factor λ. If you replace 0 in the right hand side of the equation by a non-zero constant, and get, say, 2x+3y+5z=1, this property is lost.`
@ethankward :
> `homogeneous` clearly is referring to the presence of a constant term here:
>
> https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/9f98339b3344de9109f4d2780faf9822fb110848/sympy/solvers/diophantine.py#L497
Logically that boolean variable expresses `possibly_homogeneous` and not (definitely) `homogeneous`.
> Here the code checks that `homogeneous` is true and then immediately returns an inhomogeneous equation type:
>
> https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/9f98339b3344de9109f4d2780faf9822fb110848/sympy/solvers/diophantine.py#L507-L509
As I understand it, the intersection of `set(coeff)` and `set(var)` is non-empty (hence the `if`-condition true) exactly when a "naked" element of `var` appears in the expression, i.e. a term of degree 1. But the total degree in this case is 2, so in order to have a properly homogeneous polynomial all terms would have to be of degree 2, which is not the case. Hence the equation is indeed inhomogeneous.
The naming of the `homogeneous` variable is indeed unfortunate... But the logic of that excerpt seems valid.
The ode module also makes use of both meanings of "homogeneous" and calls the uniform degree version "homogenous order" https://docs.sympy.org/1.5.1/modules/solvers/ode.html#homogeneous-order
We can also add new things such as whether polynomial is symmetric or not?
I am not sure that whether sympy contain a module or method for `Elementary Symmetric Polynomials`
If not then I think we can add that functionality too. @asmeurer
`Elementary Symmetric Polynomials` = https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elementary_symmetric_polynomial
|
[
{
"body": "We have these two test cases:\r\n\r\n```\r\nassert classify_diop(x*y + z) == (\r\n [x, y, z], {x*y: 1, z: 1}, 'inhomogeneous_ternary_quadratic')\r\nassert classify_diop(x*y + z + w + x**2) == (\r\n [w, x, y, z], {x*y: 1, w: 1, x**2: 1, z: 1}, 'inhomogeneous_general_quadratic')\r\n```\r\n\r\nIn what way are these equations \"inhomogeneous\"?",
"number": 18370,
"title": "Confusing test cases in test_classify_diop"
}
] |
31e815f084dc22977c6a2222aa8d4f45bda17188
|
{
"head_commit": "ef8c5672e1cded9d96cb1ae946398ca23063be1f",
"head_commit_message": "introduce DiophantineEquationType; simplify classify_diop; update diop_known",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py\nindex be94c6fcd30d..efa1dfa32740 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py\n@@ -36,22 +36,6 @@\n __all__ = ['diophantine', 'classify_diop']\n \n \n-# these types are known (but not necessarily handled)\n-diop_known = {\n- \"binary_quadratic\",\n- \"cubic_thue\",\n- \"general_pythagorean\",\n- \"general_sum_of_even_powers\",\n- \"general_sum_of_squares\",\n- \"homogeneous_general_quadratic\",\n- \"homogeneous_ternary_quadratic\",\n- \"homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal\",\n- \"inhomogeneous_general_quadratic\",\n- \"inhomogeneous_ternary_quadratic\",\n- \"linear\",\n- \"univariate\"}\n-\n-\n class DiophantineSolutionSet(set):\n \"\"\"\n Container for a set of solutions to a particular diophantine equation.\n@@ -152,6 +136,223 @@ def __call__(self, *args):\n return self.subs(zip(self.parameters, args))\n \n \n+class DiophantineEquationType:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Internal representation of a particular diophantine equation type.\n+\n+ Parameters\n+ ==========\n+\n+ equation\n+ The diophantine equation that is being solved.\n+ free_symbols: list (optional)\n+ The symbols being solved for.\n+\n+ Attributes\n+ ==========\n+\n+ total_degree\n+ The maximum of the degrees of all terms in the equation\n+ homogeneous\n+ Does the equation contain a term of degree 0\n+ homogeneous_order\n+ Does the equation contain any coefficient that is in the symbols being solved for\n+ dimension\n+ The number of symbols being solved for\n+ \"\"\"\n+ name = None\n+\n+ def __init__(self, equation, free_symbols=None):\n+ try:\n+ if free_symbols is None:\n+ free_symbols = list(equation.free_symbols)\n+ assert free_symbols\n+ except (AttributeError, AssertionError):\n+ raise ValueError('equation should have 1 or more free symbols')\n+\n+ free_symbols.sort(key=default_sort_key)\n+ self.free_symbols = free_symbols\n+ self.equation = equation.expand(force=True)\n+ self.coeff = self.equation.as_coefficients_dict()\n+ if not all(_is_int(c) for c in self.coeff.values()):\n+ raise TypeError(\"Coefficients should be Integers\")\n+\n+ self.total_degree = Poly(self.equation).total_degree()\n+ self.homogeneous = 1 not in self.coeff\n+ self.homogeneous_order = not (set(self.coeff) & set(self.free_symbols))\n+ self.dimension = len(self.free_symbols)\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Determine whether the given equation can be matched to the particular equation type.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ return False\n+\n+\n+class Univariate(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'univariate'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ return self.dimension == 1\n+\n+\n+class Linear(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'linear'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ return self.total_degree == 1\n+\n+\n+class BinaryQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'binary_quadratic'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ return self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension == 2\n+\n+\n+class InhomogeneousTernaryQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'inhomogeneous_ternary_quadratic'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension == 3):\n+ return False\n+ if not self.homogeneous:\n+ return False\n+ return not self.homogeneous_order\n+\n+\n+class HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension == 3):\n+ return False\n+ if not self.homogeneous:\n+ return False\n+ if not self.homogeneous_order:\n+ return False\n+\n+ nonzero = [k for k in self.coeff if self.coeff[k]]\n+ return len(nonzero) == 3 and all(i**2 in nonzero for i in self.free_symbols)\n+\n+\n+class HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension == 3):\n+ return False\n+ if not self.homogeneous:\n+ return False\n+ if not self.homogeneous_order:\n+ return False\n+\n+ nonzero = [k for k in self.coeff if self.coeff[k]]\n+ return not (len(nonzero) == 3 and all(i**2 in nonzero for i in self.free_symbols))\n+\n+\n+class InhomogeneousGeneralQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'inhomogeneous_general_quadratic'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension >= 3):\n+ return False\n+ if not self.homogeneous_order:\n+ return True\n+ else:\n+ # there may be Pow keys like x**2 or Mul keys like x*y\n+ if any(k.is_Mul for k in self.coeff): # cross terms\n+ return not self.homogeneous\n+ return False\n+\n+\n+class HomogeneousGeneralQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'homogeneous_general_quadratic'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension >= 3):\n+ return False\n+ if not self.homogeneous_order:\n+ return False\n+ else:\n+ # there may be Pow keys like x**2 or Mul keys like x*y\n+ if any(k.is_Mul for k in self.coeff): # cross terms\n+ return self.homogeneous\n+ return False\n+\n+\n+class GeneralSumOfSquares(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'general_sum_of_squares'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension >= 3):\n+ return False\n+ if not self.homogeneous_order:\n+ return False\n+ if any(k.is_Mul for k in self.coeff):\n+ return False\n+ return all(self.coeff[k] == 1 for k in self.coeff if k != 1)\n+\n+\n+class GeneralPythagorean(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'general_pythagorean'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension >= 3):\n+ return False\n+ if not self.homogeneous_order:\n+ return False\n+ if any(k.is_Mul for k in self.coeff):\n+ return False\n+ if all(self.coeff[k] == 1 for k in self.coeff if k != 1):\n+ return False\n+ if not all(is_square(abs(self.coeff[k])) for k in self.coeff):\n+ return False\n+ # all but one has the same sign\n+ # e.g. 4*x**2 + y**2 - 4*z**2\n+ return abs(sum(sign(self.coeff[k]) for k in self.coeff)) == self.dimension - 2\n+\n+\n+class CubicThue(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'cubic_thue'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ return self.total_degree == 3 and self.dimension == 2\n+\n+\n+class GeneralSumOfEvenPowers(DiophantineEquationType):\n+ name = 'general_sum_of_even_powers'\n+\n+ def matches(self):\n+ if not self.total_degree > 3:\n+ return False\n+ if self.total_degree % 2 != 0:\n+ return False\n+ if not all(k.is_Pow and k.exp == self.total_degree for k in self.coeff if k != 1):\n+ return False\n+ return all(self.coeff[k] == 1 for k in self.coeff if k != 1)\n+\n+\n+# these types are known (but not necessarily handled)\n+# note that order is important here (in the current solver state)\n+all_diop_classes = [\n+ Linear,\n+ Univariate,\n+ BinaryQuadratic,\n+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic,\n+ HomogeneousGeneralQuadratic,\n+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal,\n+ InhomogeneousTernaryQuadratic,\n+ InhomogeneousGeneralQuadratic,\n+ GeneralPythagorean,\n+ GeneralSumOfEvenPowers,\n+ GeneralSumOfSquares,\n+ CubicThue\n+]\n+\n+diop_known = set([diop_class.name for diop_class in all_diop_classes])\n+\n+\n def _is_int(i):\n try:\n as_int(i)\n@@ -322,12 +523,12 @@ def diophantine(eq, param=symbols(\"t\", integer=True), syms=None,\n if permute:\n len_var = len(v)\n permute_signs_for = [\n- 'general_sum_of_squares',\n- 'general_sum_of_even_powers']\n+ GeneralSumOfSquares.name,\n+ GeneralSumOfEvenPowers.name]\n permute_signs_check = [\n- 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic',\n- 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal',\n- 'binary_quadratic']\n+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic.name,\n+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal.name,\n+ BinaryQuadratic.name]\n if t in permute_signs_for:\n do_permute_signs_var = True\n elif t in permute_signs_check:\n@@ -413,17 +614,17 @@ def diophantine(eq, param=symbols(\"t\", integer=True), syms=None,\n solution = diop_solve(base, param)\n \n if eq_type in [\n- \"linear\",\n- \"homogeneous_ternary_quadratic\",\n- \"homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal\",\n- \"general_pythagorean\"]:\n+ Linear.name,\n+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic.name,\n+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal.name,\n+ GeneralPythagorean.name]:\n sols.add(merge_solution(var, var_t, solution))\n \n elif eq_type in [\n- \"binary_quadratic\",\n- \"general_sum_of_squares\",\n- \"general_sum_of_even_powers\",\n- \"univariate\"]:\n+ BinaryQuadratic.name,\n+ GeneralSumOfSquares.name,\n+ GeneralSumOfEvenPowers.name,\n+ Univariate.name]:\n for sol in solution:\n sols.add(merge_solution(var, var_t, sol))\n \n@@ -536,28 +737,28 @@ def diop_solve(eq, param=symbols(\"t\", integer=True)):\n \"\"\"\n var, coeff, eq_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n \n- if eq_type == \"linear\":\n+ if eq_type == Linear.name:\n return diop_linear(eq, param)\n \n- elif eq_type == \"binary_quadratic\":\n+ elif eq_type == BinaryQuadratic.name:\n return diop_quadratic(eq, param)\n \n- elif eq_type == \"homogeneous_ternary_quadratic\":\n+ elif eq_type == HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic.name:\n return diop_ternary_quadratic(eq, parameterize=True)\n \n- elif eq_type == \"homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal\":\n+ elif eq_type == HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal.name:\n return diop_ternary_quadratic_normal(eq, parameterize=True)\n \n- elif eq_type == \"general_pythagorean\":\n+ elif eq_type == GeneralPythagorean.name:\n return diop_general_pythagorean(eq, param)\n \n- elif eq_type == \"univariate\":\n+ elif eq_type == Univariate.name:\n return diop_univariate(eq)\n \n- elif eq_type == \"general_sum_of_squares\":\n+ elif eq_type == GeneralSumOfSquares.name:\n return diop_general_sum_of_squares(eq, limit=S.Infinity)\n \n- elif eq_type == \"general_sum_of_even_powers\":\n+ elif eq_type == GeneralSumOfEvenPowers.name:\n return diop_general_sum_of_even_powers(eq, limit=S.Infinity)\n \n if eq_type is not None and eq_type not in diop_known:\n@@ -574,69 +775,17 @@ def diop_solve(eq, param=symbols(\"t\", integer=True)):\n \n def classify_diop(eq, _dict=True):\n # docstring supplied externally\n- try:\n- var = list(eq.free_symbols)\n- assert var\n- except (AttributeError, AssertionError):\n- raise ValueError('equation should have 1 or more free symbols')\n- var.sort(key=default_sort_key)\n- eq = eq.expand(force=True)\n- coeff = eq.as_coefficients_dict()\n- if not all(_is_int(c) for c in coeff.values()):\n- raise TypeError(\"Coefficients should be Integers\")\n \n+ matched = False\n diop_type = None\n- total_degree = Poly(eq).total_degree()\n- homogeneous = 1 not in coeff\n- if total_degree == 1:\n- diop_type = \"linear\"\n-\n- elif len(var) == 1:\n- diop_type = \"univariate\"\n-\n- elif total_degree == 2 and len(var) == 2:\n- diop_type = \"binary_quadratic\"\n-\n- elif total_degree == 2 and len(var) == 3 and homogeneous:\n- if set(coeff) & set(var):\n- diop_type = \"inhomogeneous_ternary_quadratic\"\n- else:\n- nonzero = [k for k in coeff if coeff[k]]\n- if len(nonzero) == 3 and all(i**2 in nonzero for i in var):\n- diop_type = \"homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal\"\n- else:\n- diop_type = \"homogeneous_ternary_quadratic\"\n+ for diop_class in all_diop_classes:\n+ diop_type = diop_class(eq)\n+ if diop_type.matches():\n+ matched = True\n+ break\n \n- elif total_degree == 2 and len(var) >= 3:\n- if set(coeff) & set(var):\n- diop_type = \"inhomogeneous_general_quadratic\"\n- else:\n- # there may be Pow keys like x**2 or Mul keys like x*y\n- if any(k.is_Mul for k in coeff): # cross terms\n- if not homogeneous:\n- diop_type = \"inhomogeneous_general_quadratic\"\n- else:\n- diop_type = \"homogeneous_general_quadratic\"\n- else: # all squares: x**2 + y**2 + ... + constant\n- if all(coeff[k] == 1 for k in coeff if k != 1):\n- diop_type = \"general_sum_of_squares\"\n- elif all(is_square(abs(coeff[k])) for k in coeff):\n- if abs(sum(sign(coeff[k]) for k in coeff)) == \\\n- len(var) - 2:\n- # all but one has the same sign\n- # e.g. 4*x**2 + y**2 - 4*z**2\n- diop_type = \"general_pythagorean\"\n-\n- elif total_degree == 3 and len(var) == 2:\n- diop_type = \"cubic_thue\"\n-\n- elif (total_degree > 3 and total_degree % 2 == 0 and\n- all(k.is_Pow and k.exp == total_degree for k in coeff if k != 1)):\n- if all(coeff[k] == 1 for k in coeff if k != 1):\n- diop_type = 'general_sum_of_even_powers'\n-\n- if diop_type is not None:\n- return var, dict(coeff) if _dict else coeff, diop_type\n+ if matched:\n+ return diop_type.free_symbols, dict(diop_type.coeff) if _dict else diop_type.coeff, diop_type.name\n \n # new diop type instructions\n # --------------------------\n@@ -733,7 +882,7 @@ def diop_linear(eq, param=symbols(\"t\", integer=True)):\n \"\"\"\n var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n \n- if diop_type == \"linear\":\n+ if diop_type == Linear.name:\n result = _diop_linear(var, coeff, param)\n \n if param is None:\n@@ -1011,7 +1160,7 @@ def diop_univariate(eq):\n \"\"\"\n var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n \n- if diop_type == \"univariate\":\n+ if diop_type == Univariate.name:\n return set([(int(i),) for i in solveset_real(\n eq, var[0]).intersect(S.Integers)])\n \n@@ -1068,7 +1217,7 @@ def diop_quadratic(eq, param=symbols(\"t\", integer=True)):\n \"\"\"\n var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n \n- if diop_type == \"binary_quadratic\":\n+ if diop_type == BinaryQuadratic.name:\n return set(_diop_quadratic(var, coeff, param))\n \n \n@@ -1928,7 +2077,7 @@ def transformation_to_DN(eq):\n \"\"\"\n \n var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n- if diop_type == \"binary_quadratic\":\n+ if diop_type == BinaryQuadratic.name:\n return _transformation_to_DN(var, coeff)\n \n \n@@ -2023,7 +2172,7 @@ def find_DN(eq):\n http://www.jpr2718.org/ax2p.pdf\n \"\"\"\n var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n- if diop_type == \"binary_quadratic\":\n+ if diop_type == BinaryQuadratic.name:\n return _find_DN(var, coeff)\n \n \n@@ -2468,7 +2617,7 @@ def diop_ternary_quadratic_normal(eq, parameterize=False):\n (4, 9, 1)\n \"\"\"\n var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n- if diop_type == \"homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal\":\n+ if diop_type == HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal.name:\n sol = _diop_ternary_quadratic_normal(var, coeff)\n if len(sol) > 0:\n x_0, y_0, z_0 = list(sol)[0]\n@@ -2916,7 +3065,7 @@ def diop_general_pythagorean(eq, param=symbols(\"m\", integer=True)):\n \"\"\"\n var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n \n- if diop_type == \"general_pythagorean\":\n+ if diop_type == GeneralPythagorean.name:\n return list(_diop_general_pythagorean(var, coeff, param))[0]\n \n \n@@ -2991,7 +3140,7 @@ def diop_general_sum_of_squares(eq, limit=1):\n \"\"\"\n var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n \n- if diop_type == \"general_sum_of_squares\":\n+ if diop_type == GeneralSumOfSquares.name:\n return set(_diop_general_sum_of_squares(var, -int(coeff[1]), limit))\n \n \n@@ -3050,7 +3199,7 @@ def diop_general_sum_of_even_powers(eq, limit=1):\n \"\"\"\n var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)\n \n- if diop_type == \"general_sum_of_even_powers\":\n+ if diop_type == GeneralSumOfEvenPowers.name:\n for k in coeff.keys():\n if k.is_Pow and coeff[k]:\n p = k.exp\ndiff --git a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py\nindex d4c31b8e5b1b..8e5e8cc8a717 100644\n--- a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py\n+++ b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py\n@@ -70,6 +70,8 @@ def test_classify_diop():\n [x, y], {x*y**2: 1, 1: 1}, 'cubic_thue')\n assert classify_diop(x**4 + y**4 + z**4 - (1 + 16 + 81)) == (\n [x, y, z], {1: -98, x**4: 1, z**4: 1, y**4: 1}, 'general_sum_of_even_powers')\n+ assert classify_diop(x**2 + y**2 + z**2) == (\n+ [x, y, z], {x**2: 1, y**2: 1, z**2: 1}, 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal')\n \n \n def test_linear():\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -152,6 +136,223 @@ def __call__(self, *args):\n return self.subs(zip(self.parameters, args))\n \n \n+class DiophantineEquationType:\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Internal representation of a particular diophantine equation type.\n+\n+ Parameters\n+ ==========\n+\n+ equation\n+ The diophantine equation that is being solved.\n+ free_symbols: list (optional)\n+ The symbols being solved for.\n+\n+ Attributes\n+ ==========\n+\n+ total_degree\n+ The maximum of the degrees of all terms in the equation\n+ homogeneous\n+ Does the equation contain a term of degree 0\n+ homogeneous_order\n+ Does the equation contain any coefficient that is in the symbols being solved for\n+ dimension\n+ The number of symbols being solved for\n+ \"\"\"\n+ name = None\n+\n+ def __init__(self, equation, free_symbols=None):\n+ try:\n+ if free_symbols is None:\n+ free_symbols = list(equation.free_symbols)\n+ assert free_symbols\n+ except (AttributeError, AssertionError):\n+ raise ValueError('equation should have 1 or more free symbols')",
"line": 174,
"original_line": 171,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nI realise that you're just moving the code around here but I really don't like catching either `AttributeError` or `AssertionError` as these can hide bugs. Is it possible to remove them? Why is `AttributeError` being caught anyway?\n\n@author:\nIt's raised with the test `raises(ValueError, lambda: classify_diop(1))`. Probably it would be better to just sympify the argument."
}
] |
3bb4dab755ba5c1b0340315b0a232b95cf81da60
|
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py
index be94c6fcd30d..293f52629055 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/diophantine.py
@@ -36,22 +36,6 @@
__all__ = ['diophantine', 'classify_diop']
-# these types are known (but not necessarily handled)
-diop_known = {
- "binary_quadratic",
- "cubic_thue",
- "general_pythagorean",
- "general_sum_of_even_powers",
- "general_sum_of_squares",
- "homogeneous_general_quadratic",
- "homogeneous_ternary_quadratic",
- "homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal",
- "inhomogeneous_general_quadratic",
- "inhomogeneous_ternary_quadratic",
- "linear",
- "univariate"}
-
-
class DiophantineSolutionSet(set):
"""
Container for a set of solutions to a particular diophantine equation.
@@ -152,6 +136,225 @@ def __call__(self, *args):
return self.subs(zip(self.parameters, args))
+class DiophantineEquationType:
+ """
+ Internal representation of a particular diophantine equation type.
+
+ Parameters
+ ==========
+
+ equation
+ The diophantine equation that is being solved.
+ free_symbols: list (optional)
+ The symbols being solved for.
+
+ Attributes
+ ==========
+
+ total_degree
+ The maximum of the degrees of all terms in the equation
+ homogeneous
+ Does the equation contain a term of degree 0
+ homogeneous_order
+ Does the equation contain any coefficient that is in the symbols being solved for
+ dimension
+ The number of symbols being solved for
+ """
+ name = None
+
+ def __init__(self, equation, free_symbols=None):
+ self.equation = _sympify(equation).expand(force=True)
+
+ if free_symbols is not None:
+ self.free_symbols = free_symbols
+ else:
+ self.free_symbols = list(self.equation.free_symbols)
+
+ if not self.free_symbols:
+ raise ValueError('equation should have 1 or more free symbols')
+
+ self.free_symbols.sort(key=default_sort_key)
+
+ self.coeff = self.equation.as_coefficients_dict()
+ if not all(_is_int(c) for c in self.coeff.values()):
+ raise TypeError("Coefficients should be Integers")
+
+ self.total_degree = Poly(self.equation).total_degree()
+ self.homogeneous = 1 not in self.coeff
+ self.homogeneous_order = not (set(self.coeff) & set(self.free_symbols))
+ self.dimension = len(self.free_symbols)
+
+ def matches(self):
+ """
+ Determine whether the given equation can be matched to the particular equation type.
+ """
+ return False
+
+
+class Univariate(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'univariate'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ return self.dimension == 1
+
+
+class Linear(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'linear'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ return self.total_degree == 1
+
+
+class BinaryQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'binary_quadratic'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ return self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension == 2
+
+
+class InhomogeneousTernaryQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'inhomogeneous_ternary_quadratic'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension == 3):
+ return False
+ if not self.homogeneous:
+ return False
+ return not self.homogeneous_order
+
+
+class HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension == 3):
+ return False
+ if not self.homogeneous:
+ return False
+ if not self.homogeneous_order:
+ return False
+
+ nonzero = [k for k in self.coeff if self.coeff[k]]
+ return len(nonzero) == 3 and all(i**2 in nonzero for i in self.free_symbols)
+
+
+class HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension == 3):
+ return False
+ if not self.homogeneous:
+ return False
+ if not self.homogeneous_order:
+ return False
+
+ nonzero = [k for k in self.coeff if self.coeff[k]]
+ return not (len(nonzero) == 3 and all(i**2 in nonzero for i in self.free_symbols))
+
+
+class InhomogeneousGeneralQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'inhomogeneous_general_quadratic'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension >= 3):
+ return False
+ if not self.homogeneous_order:
+ return True
+ else:
+ # there may be Pow keys like x**2 or Mul keys like x*y
+ if any(k.is_Mul for k in self.coeff): # cross terms
+ return not self.homogeneous
+ return False
+
+
+class HomogeneousGeneralQuadratic(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'homogeneous_general_quadratic'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension >= 3):
+ return False
+ if not self.homogeneous_order:
+ return False
+ else:
+ # there may be Pow keys like x**2 or Mul keys like x*y
+ if any(k.is_Mul for k in self.coeff): # cross terms
+ return self.homogeneous
+ return False
+
+
+class GeneralSumOfSquares(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'general_sum_of_squares'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension >= 3):
+ return False
+ if not self.homogeneous_order:
+ return False
+ if any(k.is_Mul for k in self.coeff):
+ return False
+ return all(self.coeff[k] == 1 for k in self.coeff if k != 1)
+
+
+class GeneralPythagorean(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'general_pythagorean'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ if not (self.total_degree == 2 and self.dimension >= 3):
+ return False
+ if not self.homogeneous_order:
+ return False
+ if any(k.is_Mul for k in self.coeff):
+ return False
+ if all(self.coeff[k] == 1 for k in self.coeff if k != 1):
+ return False
+ if not all(is_square(abs(self.coeff[k])) for k in self.coeff):
+ return False
+ # all but one has the same sign
+ # e.g. 4*x**2 + y**2 - 4*z**2
+ return abs(sum(sign(self.coeff[k]) for k in self.coeff)) == self.dimension - 2
+
+
+class CubicThue(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'cubic_thue'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ return self.total_degree == 3 and self.dimension == 2
+
+
+class GeneralSumOfEvenPowers(DiophantineEquationType):
+ name = 'general_sum_of_even_powers'
+
+ def matches(self):
+ if not self.total_degree > 3:
+ return False
+ if self.total_degree % 2 != 0:
+ return False
+ if not all(k.is_Pow and k.exp == self.total_degree for k in self.coeff if k != 1):
+ return False
+ return all(self.coeff[k] == 1 for k in self.coeff if k != 1)
+
+
+# these types are known (but not necessarily handled)
+# note that order is important here (in the current solver state)
+all_diop_classes = [
+ Linear,
+ Univariate,
+ BinaryQuadratic,
+ InhomogeneousTernaryQuadratic,
+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal,
+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic,
+ InhomogeneousGeneralQuadratic,
+ HomogeneousGeneralQuadratic,
+ GeneralSumOfSquares,
+ GeneralPythagorean,
+ CubicThue,
+ GeneralSumOfEvenPowers,
+]
+
+diop_known = set([diop_class.name for diop_class in all_diop_classes])
+
+
def _is_int(i):
try:
as_int(i)
@@ -322,12 +525,12 @@ def diophantine(eq, param=symbols("t", integer=True), syms=None,
if permute:
len_var = len(v)
permute_signs_for = [
- 'general_sum_of_squares',
- 'general_sum_of_even_powers']
+ GeneralSumOfSquares.name,
+ GeneralSumOfEvenPowers.name]
permute_signs_check = [
- 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic',
- 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal',
- 'binary_quadratic']
+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic.name,
+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal.name,
+ BinaryQuadratic.name]
if t in permute_signs_for:
do_permute_signs_var = True
elif t in permute_signs_check:
@@ -413,17 +616,17 @@ def diophantine(eq, param=symbols("t", integer=True), syms=None,
solution = diop_solve(base, param)
if eq_type in [
- "linear",
- "homogeneous_ternary_quadratic",
- "homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal",
- "general_pythagorean"]:
+ Linear.name,
+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic.name,
+ HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal.name,
+ GeneralPythagorean.name]:
sols.add(merge_solution(var, var_t, solution))
elif eq_type in [
- "binary_quadratic",
- "general_sum_of_squares",
- "general_sum_of_even_powers",
- "univariate"]:
+ BinaryQuadratic.name,
+ GeneralSumOfSquares.name,
+ GeneralSumOfEvenPowers.name,
+ Univariate.name]:
for sol in solution:
sols.add(merge_solution(var, var_t, sol))
@@ -536,28 +739,28 @@ def diop_solve(eq, param=symbols("t", integer=True)):
"""
var, coeff, eq_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if eq_type == "linear":
+ if eq_type == Linear.name:
return diop_linear(eq, param)
- elif eq_type == "binary_quadratic":
+ elif eq_type == BinaryQuadratic.name:
return diop_quadratic(eq, param)
- elif eq_type == "homogeneous_ternary_quadratic":
+ elif eq_type == HomogeneousTernaryQuadratic.name:
return diop_ternary_quadratic(eq, parameterize=True)
- elif eq_type == "homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal":
+ elif eq_type == HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal.name:
return diop_ternary_quadratic_normal(eq, parameterize=True)
- elif eq_type == "general_pythagorean":
+ elif eq_type == GeneralPythagorean.name:
return diop_general_pythagorean(eq, param)
- elif eq_type == "univariate":
+ elif eq_type == Univariate.name:
return diop_univariate(eq)
- elif eq_type == "general_sum_of_squares":
+ elif eq_type == GeneralSumOfSquares.name:
return diop_general_sum_of_squares(eq, limit=S.Infinity)
- elif eq_type == "general_sum_of_even_powers":
+ elif eq_type == GeneralSumOfEvenPowers.name:
return diop_general_sum_of_even_powers(eq, limit=S.Infinity)
if eq_type is not None and eq_type not in diop_known:
@@ -574,69 +777,17 @@ def diop_solve(eq, param=symbols("t", integer=True)):
def classify_diop(eq, _dict=True):
# docstring supplied externally
- try:
- var = list(eq.free_symbols)
- assert var
- except (AttributeError, AssertionError):
- raise ValueError('equation should have 1 or more free symbols')
- var.sort(key=default_sort_key)
- eq = eq.expand(force=True)
- coeff = eq.as_coefficients_dict()
- if not all(_is_int(c) for c in coeff.values()):
- raise TypeError("Coefficients should be Integers")
+ matched = False
diop_type = None
- total_degree = Poly(eq).total_degree()
- homogeneous = 1 not in coeff
- if total_degree == 1:
- diop_type = "linear"
-
- elif len(var) == 1:
- diop_type = "univariate"
-
- elif total_degree == 2 and len(var) == 2:
- diop_type = "binary_quadratic"
-
- elif total_degree == 2 and len(var) == 3 and homogeneous:
- if set(coeff) & set(var):
- diop_type = "inhomogeneous_ternary_quadratic"
- else:
- nonzero = [k for k in coeff if coeff[k]]
- if len(nonzero) == 3 and all(i**2 in nonzero for i in var):
- diop_type = "homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal"
- else:
- diop_type = "homogeneous_ternary_quadratic"
+ for diop_class in all_diop_classes:
+ diop_type = diop_class(eq)
+ if diop_type.matches():
+ matched = True
+ break
- elif total_degree == 2 and len(var) >= 3:
- if set(coeff) & set(var):
- diop_type = "inhomogeneous_general_quadratic"
- else:
- # there may be Pow keys like x**2 or Mul keys like x*y
- if any(k.is_Mul for k in coeff): # cross terms
- if not homogeneous:
- diop_type = "inhomogeneous_general_quadratic"
- else:
- diop_type = "homogeneous_general_quadratic"
- else: # all squares: x**2 + y**2 + ... + constant
- if all(coeff[k] == 1 for k in coeff if k != 1):
- diop_type = "general_sum_of_squares"
- elif all(is_square(abs(coeff[k])) for k in coeff):
- if abs(sum(sign(coeff[k]) for k in coeff)) == \
- len(var) - 2:
- # all but one has the same sign
- # e.g. 4*x**2 + y**2 - 4*z**2
- diop_type = "general_pythagorean"
-
- elif total_degree == 3 and len(var) == 2:
- diop_type = "cubic_thue"
-
- elif (total_degree > 3 and total_degree % 2 == 0 and
- all(k.is_Pow and k.exp == total_degree for k in coeff if k != 1)):
- if all(coeff[k] == 1 for k in coeff if k != 1):
- diop_type = 'general_sum_of_even_powers'
-
- if diop_type is not None:
- return var, dict(coeff) if _dict else coeff, diop_type
+ if matched:
+ return diop_type.free_symbols, dict(diop_type.coeff) if _dict else diop_type.coeff, diop_type.name
# new diop type instructions
# --------------------------
@@ -733,7 +884,7 @@ def diop_linear(eq, param=symbols("t", integer=True)):
"""
var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if diop_type == "linear":
+ if diop_type == Linear.name:
result = _diop_linear(var, coeff, param)
if param is None:
@@ -1011,7 +1162,7 @@ def diop_univariate(eq):
"""
var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if diop_type == "univariate":
+ if diop_type == Univariate.name:
return set([(int(i),) for i in solveset_real(
eq, var[0]).intersect(S.Integers)])
@@ -1068,7 +1219,7 @@ def diop_quadratic(eq, param=symbols("t", integer=True)):
"""
var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if diop_type == "binary_quadratic":
+ if diop_type == BinaryQuadratic.name:
return set(_diop_quadratic(var, coeff, param))
@@ -1928,7 +2079,7 @@ def transformation_to_DN(eq):
"""
var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if diop_type == "binary_quadratic":
+ if diop_type == BinaryQuadratic.name:
return _transformation_to_DN(var, coeff)
@@ -2023,7 +2174,7 @@ def find_DN(eq):
http://www.jpr2718.org/ax2p.pdf
"""
var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if diop_type == "binary_quadratic":
+ if diop_type == BinaryQuadratic.name:
return _find_DN(var, coeff)
@@ -2468,7 +2619,7 @@ def diop_ternary_quadratic_normal(eq, parameterize=False):
(4, 9, 1)
"""
var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if diop_type == "homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal":
+ if diop_type == HomogeneousTernaryQuadraticNormal.name:
sol = _diop_ternary_quadratic_normal(var, coeff)
if len(sol) > 0:
x_0, y_0, z_0 = list(sol)[0]
@@ -2916,7 +3067,7 @@ def diop_general_pythagorean(eq, param=symbols("m", integer=True)):
"""
var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if diop_type == "general_pythagorean":
+ if diop_type == GeneralPythagorean.name:
return list(_diop_general_pythagorean(var, coeff, param))[0]
@@ -2991,7 +3142,7 @@ def diop_general_sum_of_squares(eq, limit=1):
"""
var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if diop_type == "general_sum_of_squares":
+ if diop_type == GeneralSumOfSquares.name:
return set(_diop_general_sum_of_squares(var, -int(coeff[1]), limit))
@@ -3050,7 +3201,7 @@ def diop_general_sum_of_even_powers(eq, limit=1):
"""
var, coeff, diop_type = classify_diop(eq, _dict=False)
- if diop_type == "general_sum_of_even_powers":
+ if diop_type == GeneralSumOfEvenPowers.name:
for k in coeff.keys():
if k.is_Pow and coeff[k]:
p = k.exp
diff --git a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py
index d4c31b8e5b1b..8e5e8cc8a717 100644
--- a/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py
+++ b/sympy/solvers/diophantine/tests/test_diophantine.py
@@ -70,6 +70,8 @@ def test_classify_diop():
[x, y], {x*y**2: 1, 1: 1}, 'cubic_thue')
assert classify_diop(x**4 + y**4 + z**4 - (1 + 16 + 81)) == (
[x, y, z], {1: -98, x**4: 1, z**4: 1, y**4: 1}, 'general_sum_of_even_powers')
+ assert classify_diop(x**2 + y**2 + z**2) == (
+ [x, y, z], {x**2: 1, y**2: 1, z**2: 1}, 'homogeneous_ternary_quadratic_normal')
def test_linear():
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 4,
"problem_domain": "Documentation Updates"
}
|
sympy__sympy-18698@70b501b
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,698
|
Fixes sqf_list to combine same multiplicity factors
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
Fixes sqf_list to combine same multiplicity factors
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #8695
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
Before fixing:
```
>>> sqf_list((x**2 + 1) * (x - 1)**2 * (x - 2)**3 * (x - 3)**3)
(1, [(x**2 + 1, 1), (x - 1, 2), (x - 3, 3), (x - 2, 3)])
```
After:
```
>>> sqf_list((x**2 + 1) * (x - 1)**2 * (x - 2)**3 * (x - 3)**3)
(1, [(x**2 + 1, 1), (x - 1, 2), (x**2 - 5*x + 6, 3)])
```
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* polys
* Combine factors of same multiplicity
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-02-21T05:46:56Z
|
sqf and sqf_list output is not consistant
The example below is wrong in the sense that we should have (x*_2 - 5_x + 6, 3) and not 2 factors of multiplicity 3.
```
> sqf_list( (x**2 + 1) * (x - 1)**2 * (x - 2)**3 * (x - 3)**3 )
> (1, [(x**2 + 1, 1), (x - 1, 2), (x - 3, 3), (x - 2, 3)])
```
whereas below is correct --- one factor of multiplicity 2
```
> sqf_list( x**5 - 2*x**4 - 2*x**3 + 4*x**2 + x - 2 )
> (1, [(x - 2, 1), (x**2 - 1, 2)])
```
|
I guess correct can be either the first or the second. But we should stick to it.
This [SO post](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57536689/sympys-sqf-and-sqf-list-give-different-results-once-i-use-poly-or-as-pol) highlights another problem, too:
```python
>>> v = (x1 + 2) ** 2 * (x2 + 4) ** 5
>>> sqf(v)
(x1 + 2)**2*(x2 + 4)**5
>>> sqf(v.expand())
(x1 + 2)**2 <-- where is the x2 factor?
```
The documentation is incomplete. The docstrings for low level methods in `sqfreetools` show that they are for univariate polynomials only but that is missing from `polytools`. The docstrings should be amended.
The issue in OP is valid. The `Poly` method works as expected:
```
>>> Poly((x**2 + 1)*(x - 1)**2*(x - 2)**3*(x - 3)**3, x).sqf_list()
(1, [(Poly(x**2 + 1, x, domain='ZZ'), 1), (Poly(x - 1, x, domain='ZZ'), 2), (Poly(x**2 - 5*x + 6, x, domain='ZZ'), 3)])
```
The two factors of multiplicity 3 are combined as they should be.
The `sqf_list` function fails to do that.
```
>>> sqf_list((x**2 + 1)*(x - 1)**2*(x - 2)**3*(x - 3)**3, x)
(1, [(x**2 + 1, 1), (x - 1, 2), (x - 3, 3), (x - 2, 3)])
```
It should scan the generic factor list and combine factors of same multiplicity before returning the list.
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/e4259125f63727b76d0a0c4743ba1cd8d433d3ea/sympy/polys/polytools.py#L6218
Hi, I am new to the sympy community and was looking to contribute to the project. I wanted to ask @akritas what's wrong in having 2 factors of multiplicity 3? Also, if the second issue (on SO) is still open, then I would like to work on it, @jksuom can you guide me from where I should start?
Sent from my iPad
> On 15 Dec 2019, at 5:24 PM, Akhil Rajput <[email protected]> wrote:
>
>
> Hi, I am new to the sympy community and was looking to contribute to the project. I wanted to ask @akritas what's wrong in having 2 factors of multiplicity 3?
>
Hi,
The square free algorithm should pull out all factors of _same_ degree and present them as one product of given multiplicity (in this case one factor with roots of multiplicity 3).
> Also, if the second issue (on SO) is still open, then I would like to work on it, @jksuom can you guide me from where I should start?
>
> —
> You are receiving this because you were mentioned.
> Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub, or unsubscribe.
I would start with the docstrings. The squarefree methods are intended for univariate polynomials. The generator should be given as an input parameter. It may be omitted if there is no danger of confusion (only one symbol in the expression). Otherwise the result may be indeterminate as shown by the [example above](https://github.com/sympy/sympy/issues/8695#issuecomment-522278244).
@jksuom, I'm still unclear. There is already an option to pass generators as an argument to sqf_list(). Should the function automatically find the generators present in the expression? Please guide me what should I do.
If there is only one symbol in the expression, then the function can find the generator automatically. Otherwise I think that exactly one symbol should be given as the generator.
Moreover, I would like to change the implementations of `sqf_list()` and related functions so that they would be based on the corresponding `Poly` methods. Then they would start by converting the input expression into `p = Poly(f, *gens, **args)` and check that `p` has exactly one generator. Then `p.sqf_list()` etc, would be called.
Then what will happen in case of multiple generators? Just confirming, generators here refer to symbols/variables.
> generators here refer to symbols/variables.
Yes.
> Then what will happen in case of multiple generators?
I think that ValueError could be raised. It seems that some kind of result is currently returned but there is no documentation, and I don't know of any reasonable use where the ordinary factorization would not suffice.
|
[
{
"body": "The example below is wrong in the sense that we should have (x*_2 - 5_x + 6, 3) and not 2 factors of multiplicity 3.\n\n```\n> sqf_list( (x**2 + 1) * (x - 1)**2 * (x - 2)**3 * (x - 3)**3 )\n\n> (1, [(x**2 + 1, 1), (x - 1, 2), (x - 3, 3), (x - 2, 3)])\n```\n\nwhereas below is correct --- one factor of multiplicity 2\n\n```\n> sqf_list( x**5 - 2*x**4 - 2*x**3 + 4*x**2 + x - 2 )\n\n> (1, [(x - 2, 1), (x**2 - 1, 2)])\n```\n",
"number": 8695,
"title": "sqf and sqf_list output is not consistant"
}
] |
3dff1b98a78f28c953ae2140b69356b8391e399c
|
{
"head_commit": "70b501ba7dcfd5b2ae39b4957cb6023d67446fb3",
"head_commit_message": "corrected docs",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/doc/src/modules/polys/basics.rst b/doc/src/modules/polys/basics.rst\nindex 5b5a4e1635e8..6df5105390d8 100644\n--- a/doc/src/modules/polys/basics.rst\n+++ b/doc/src/modules/polys/basics.rst\n@@ -536,11 +536,13 @@ factors (not necessarily irreducible) of degree 1, 2 etc.::\n >>> f = 2*x**2 + 5*x**3 + 4*x**4 + x**5\n \n >>> sqf_list(f)\n- (1, [(x + 2, 1), (x, 2), (x + 1, 2)])\n+ 2\n+ (1, [(x + 2, 1), (x + x, 2)])\n \n >>> sqf(f)\n- 2 2\n- x *(x + 1) *(x + 2)\n+ 2\n+ / 2 \\\n+ (x + 2)*\\x + x/\n \n Factorization\n -------------\ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/polytools.py b/sympy/polys/polytools.py\nindex c9e77a901f67..acb51d82c5a9 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/polytools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/polytools.py\n@@ -2,7 +2,8 @@\n \n from __future__ import print_function, division\n \n-from functools import wraps\n+from functools import wraps, reduce\n+from operator import mul\n \n from sympy.core import (\n S, Basic, Expr, I, Integer, Add, Mul, Dummy, Tuple\n@@ -5905,10 +5906,7 @@ def _symbolic_factor_list(expr, opt, method):\n if arg.is_Number:\n coeff *= arg\n continue\n- if arg.is_Mul:\n- args.extend(arg.args)\n- continue\n- if arg.is_Pow:\n+ elif arg.is_Pow:\n base, exp = arg.args\n if base.is_Number and exp.is_Number:\n coeff *= arg\n@@ -5949,6 +5947,9 @@ def _symbolic_factor_list(expr, opt, method):\n other.append((f, k))\n \n factors.append((_factors_product(other), exp))\n+ if method == 'sqf':\n+ factors = [(reduce(mul, (f for f, _ in factors if _ == k)), k)\n+ for k in set(dict(factors).values())]\n \n return coeff, factors\n \ndiff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py\nindex 82e5f4d6ddb7..b0b4cd61322a 100644\n--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py\n+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py\n@@ -3273,7 +3273,7 @@ def test_to_rational_coeffs():\n def test_factor_terms():\n # issue 7067\n assert factor_list(x*(x + y)) == (1, [(x, 1), (x + y, 1)])\n- assert sqf_list(x*(x + y)) == (1, [(x, 1), (x + y, 1)])\n+ assert sqf_list(x*(x + y)) == (1, [(x**2 + x*y, 1)])\n \n \n def test_as_list():\n@@ -3333,3 +3333,8 @@ def test_issue_17988():\n def test_issue_18205():\n assert cancel((2 + I)*(3 - I)) == 7 + I\n assert cancel((2 + I)*(2 - I)) == 5\n+\n+def test_issue_8695():\n+ p = (x**2 + 1) * (x - 1)**2 * (x - 2)**3 * (x - 3)**3\n+ result = (1, [(x**2 + 1, 1), (x - 1, 2), (x**2 - 5*x + 6, 3)])\n+ assert sqf_list(p) == result\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -5949,6 +5947,9 @@ def _symbolic_factor_list(expr, opt, method):\n other.append((f, k))\n \n factors.append((_factors_product(other), exp))\n+ if method == 'sqf':\n+ factors = [(reduce(mul, (f for f, _ in factors if _ == k)), k)\n+ for k in set(dict(factors).values())]",
"line": null,
"original_line": 5952,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/polys/polytools.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIt could be possible to avoid construction of a dictionary. Maybe something like this:\r\n\r\n set(i for _, i in factors)"
}
] |
7dc6fd979304b76428243082672266ed096688d2
|
diff --git a/doc/src/modules/polys/basics.rst b/doc/src/modules/polys/basics.rst
index 5b5a4e1635e8..6df5105390d8 100644
--- a/doc/src/modules/polys/basics.rst
+++ b/doc/src/modules/polys/basics.rst
@@ -536,11 +536,13 @@ factors (not necessarily irreducible) of degree 1, 2 etc.::
>>> f = 2*x**2 + 5*x**3 + 4*x**4 + x**5
>>> sqf_list(f)
- (1, [(x + 2, 1), (x, 2), (x + 1, 2)])
+ 2
+ (1, [(x + 2, 1), (x + x, 2)])
>>> sqf(f)
- 2 2
- x *(x + 1) *(x + 2)
+ 2
+ / 2 \
+ (x + 2)*\x + x/
Factorization
-------------
diff --git a/sympy/polys/polytools.py b/sympy/polys/polytools.py
index c9e77a901f67..68b69d1a241f 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/polytools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/polytools.py
@@ -2,7 +2,8 @@
from __future__ import print_function, division
-from functools import wraps
+from functools import wraps, reduce
+from operator import mul
from sympy.core import (
S, Basic, Expr, I, Integer, Add, Mul, Dummy, Tuple
@@ -5905,10 +5906,7 @@ def _symbolic_factor_list(expr, opt, method):
if arg.is_Number:
coeff *= arg
continue
- if arg.is_Mul:
- args.extend(arg.args)
- continue
- if arg.is_Pow:
+ elif arg.is_Pow:
base, exp = arg.args
if base.is_Number and exp.is_Number:
coeff *= arg
@@ -5949,6 +5947,9 @@ def _symbolic_factor_list(expr, opt, method):
other.append((f, k))
factors.append((_factors_product(other), exp))
+ if method == 'sqf':
+ factors = [(reduce(mul, (f for f, _ in factors if _ == k)), k)
+ for k in set(i for _, i in factors)]
return coeff, factors
diff --git a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
index 82e5f4d6ddb7..b0b4cd61322a 100644
--- a/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
+++ b/sympy/polys/tests/test_polytools.py
@@ -3273,7 +3273,7 @@ def test_to_rational_coeffs():
def test_factor_terms():
# issue 7067
assert factor_list(x*(x + y)) == (1, [(x, 1), (x + y, 1)])
- assert sqf_list(x*(x + y)) == (1, [(x, 1), (x + y, 1)])
+ assert sqf_list(x*(x + y)) == (1, [(x**2 + x*y, 1)])
def test_as_list():
@@ -3333,3 +3333,8 @@ def test_issue_17988():
def test_issue_18205():
assert cancel((2 + I)*(3 - I)) == 7 + I
assert cancel((2 + I)*(2 - I)) == 5
+
+def test_issue_8695():
+ p = (x**2 + 1) * (x - 1)**2 * (x - 2)**3 * (x - 3)**3
+ result = (1, [(x**2 + 1, 1), (x - 1, 2), (x**2 - 5*x + 6, 3)])
+ assert sqf_list(p) == result
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-18688@2ee4194
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,688
|
ntheory: divisor_sigma symbolic case recognition
|
Fixes: #16123
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
**Previously**, the only case which was recognized symbolically by divisor_sigma() function was: `divisor_sigma(a) -> a + 1.`
**Now**, it also recognizes:
`divisor_sigma(a**j*b**k)` where` a and b are prime` and` j and k are positive integers`
`divisor_sigma(a**j*b**k)-> (a**(j + 1) - 1)*(b**(k + 1) - 1)/((a - 1)*(b - 1))`
#### Other Comments
Regression Tests have been added
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* ntheory
* Made divisor_sigma() symbolically recognize the case: `divisor_sigma(a**j*b**k)`
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-02-19T22:11:19Z
|
symbolic divisor_sigma
`divisor_sigma(a**k*b**j, 1)` where `a` and `b` are prime and `k` and `j` are positive integers is `(a**(k+1)-1)/(a-1)*(b**(j + 1) -1)/(b - 1)`. Right now, the only case that is recognized symbolically is `divisor_sigma(a) -> a + 1`.
```python
def eval(cls, n):
...
if n.is_integer:
if n.is_Mul or n.is_Pow: # prime is already handled
p = []
for b, e in (_.as_base_exp() for _ in Mul.make_args(n)):
if b.is_prime and e.is_positive:
p.append((b**(e + 1) - 1)/(b - 1))
else:
return
return Mul(*p)
>>> divisor_sigma(2**3*3**5)
5460
>>> a,b = var('a b',prime=True)
>>> j,k=var('j k', integer=True, positive=True)
>>> eq = a**j*b**k
>>> eq.subs({a:2,j:3,b:3,k:5})
5460
```
|
I'm taking this.
@smichr can you please crosscheck the result of above substitution will be `1944` and for the current master I'm able to evaluate it.
sorry, I misunderstood the purpose of divisor_sigma(). I will do the required changes.
```
>>> divisors(1944)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 27, 36, 54, 72, 81, 108, 162, 216, 243, 324, 486, 648, 972, 1944]
>>> sum(divisors(1944))
5460
```
|
[
{
"body": "`divisor_sigma(a**k*b**j, 1)` where `a` and `b` are prime and `k` and `j` are positive integers is `(a**(k+1)-1)/(a-1)*(b**(j + 1) -1)/(b - 1)`. Right now, the only case that is recognized symbolically is `divisor_sigma(a) -> a + 1`.\r\n```python\r\ndef eval(cls, n):\r\n ...\r\n if n.is_integer:\r\n if n.is_Mul or n.is_Pow: # prime is already handled\r\n p = []\r\n for b, e in (_.as_base_exp() for _ in Mul.make_args(n)):\r\n if b.is_prime and e.is_positive:\r\n p.append((b**(e + 1) - 1)/(b - 1))\r\n else:\r\n return\r\n return Mul(*p)\r\n\r\n>>> divisor_sigma(2**3*3**5)\r\n5460\r\n>>> a,b = var('a b',prime=True)\r\n>>> j,k=var('j k', integer=True, positive=True)\r\n>>> eq = a**j*b**k\r\n>>> eq.subs({a:2,j:3,b:3,k:5})\r\n5460\r\n```",
"number": 16123,
"title": "symbolic divisor_sigma"
}
] |
a7606272bb8a9c8d05448b7d30505822db6af20e
|
{
"head_commit": "2ee4194713db00e044ebe084b3e0fbca6383bb68",
"head_commit_message": "Made the function recognise any value of k",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py b/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py\nindex 504c1e1ae674..b1811013d6e1 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py\n@@ -2039,8 +2039,20 @@ class divisor_sigma(Function):\n def eval(cls, n, k=1):\n n = sympify(n)\n k = sympify(k)\n+\n if n.is_prime:\n return 1 + n**k\n+\n+ if n.is_integer and not n.is_Integer:\n+ p = []\n+ for b, e in (_.as_base_exp() for _ in Mul.make_args(n)):\n+ if b.is_prime and e.is_positive:\n+ p.append((b**(k*(e + 1)) - 1)/(b**k - 1) if k != 0\n+ else e + 1)\n+ else:\n+ return\n+ return Mul(*p)\n+\n if n.is_Integer:\n if n <= 0:\n raise ValueError(\"n must be a positive integer\")\ndiff --git a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_factor_.py b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_factor_.py\nindex afea0d38eb04..ca9bd0e32544 100644\n--- a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_factor_.py\n+++ b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_factor_.py\n@@ -402,6 +402,12 @@ def test_divisor_sigma():\n assert divisor_sigma(23450, 2) == 730747500\n assert divisor_sigma(23450, 3) == 14666785333344\n \n+ a = Symbol(\"a\", prime=True)\n+ b = Symbol(\"b\", prime=True)\n+ j = Symbol(\"j\", integer=True, positive=True)\n+ k = Symbol(\"k\", integer=True, positive=True)\n+ assert divisor_sigma(a**j*b**k) == (a**(j + 1) - 1)*(b**(k + 1) - 1)/((a - 1)*(b - 1))\n+\n m = Symbol(\"m\", integer=True)\n k = Symbol(\"k\", integer=True)\n assert divisor_sigma(m)\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -2039,8 +2039,20 @@ class divisor_sigma(Function):\n def eval(cls, n, k=1):\n n = sympify(n)\n k = sympify(k)\n+\n if n.is_prime:\n return 1 + n**k\n+\n+ if n.is_integer and not n.is_Integer:\n+ p = []\n+ for b, e in (_.as_base_exp() for _ in Mul.make_args(n)):\n+ if b.is_prime and e.is_positive:",
"line": null,
"original_line": 2049,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/ntheory/factor_.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\nIf this fails then `None` will be returned? Is this expected? Any examples which can cause this to fail?\n\n@author:\nNo that same expression will be returned and this case is possible:\r\n\r\n```\r\nIn[1]: k, m, n = symbols('k m n', integer=True)\r\nIn[2]: divisor_sigma(k*m)\r\nOut[2]: divisor_sigma(k*m)\r\n```"
}
] |
24ae6a224adefcd73bce9c051c5bbacfbd4196b5
|
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py b/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py
index 504c1e1ae674..be2d654f592d 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/factor_.py
@@ -2039,8 +2039,10 @@ class divisor_sigma(Function):
def eval(cls, n, k=1):
n = sympify(n)
k = sympify(k)
+
if n.is_prime:
return 1 + n**k
+
if n.is_Integer:
if n <= 0:
raise ValueError("n must be a positive integer")
@@ -2053,6 +2055,17 @@ def eval(cls, n, k=1):
return Mul(*[(p**(k*(e + 1)) - 1)/(p**k - 1) if k != 0
else e + 1 for p, e in factorint(n).items()])
+ if n.is_integer: # symbolic case
+ args = []
+ for p, e in (_.as_base_exp() for _ in Mul.make_args(n)):
+ if p.is_prime and e.is_positive:
+ args.append((p**(k*(e + 1)) - 1)/(p**k - 1) if
+ k != 0 else e + 1)
+ else:
+ return
+ return Mul(*args)
+
+
def core(n, t=2):
r"""
Calculate core(n, t) = `core_t(n)` of a positive integer n
diff --git a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_factor_.py b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_factor_.py
index afea0d38eb04..7715dd8afb7a 100644
--- a/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_factor_.py
+++ b/sympy/ntheory/tests/test_factor_.py
@@ -402,6 +402,14 @@ def test_divisor_sigma():
assert divisor_sigma(23450, 2) == 730747500
assert divisor_sigma(23450, 3) == 14666785333344
+ a = Symbol("a", prime=True)
+ b = Symbol("b", prime=True)
+ j = Symbol("j", integer=True, positive=True)
+ k = Symbol("k", integer=True, positive=True)
+ assert divisor_sigma(a**j*b**k) == (a**(j + 1) - 1)*(b**(k + 1) - 1)/((a - 1)*(b - 1))
+ assert divisor_sigma(a**j*b**k, 2) == (a**(2*j + 2) - 1)*(b**(2*k + 2) - 1)/((a**2 - 1)*(b**2 - 1))
+ assert divisor_sigma(a**j*b**k, 0) == (j + 1)*(k + 1)
+
m = Symbol("m", integer=True)
k = Symbol("k", integer=True)
assert divisor_sigma(m)
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Code Refactoring / Architectural Improvement"
}
|
sympy__sympy-18651@b31b94b
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,651
|
Fix for numpy arrays when the size 1 arrays were treated as scalars
|
#### References to other Issues or PRs
Revives and closes #14720
Fixes #14706
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
--> Added a bug fix in sympify whereby the numpy arrays of size 1 won't be treated as scalars
#### Other comments
Example:
```
>>> from sympy import *
>>> from sympy.abc import *
>>> import numpy
>>> z = np.zeros((1,1))
```
Before the fix:
```
>>> f = x + z
x
```
After the fix:
```
>>> f = x + z
array([[x]], dtype=object)
```
#### Release Notes
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* core
* sympify no longer converts numpy arrays with size to scalars
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-02-13T18:56:45Z
|
Symbol violates the commutativity of addition when it sometimes converts one-element arrays to scalar
```
from sympy import symbols
import numpy as np
for i in [2, 1]:
z = np.zeros(i)
xz = symbols('x') + z
print(z.shape)
print(xz.shape)
print()
```
prints:
```
(2,)
(2,)
(1,)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-165-14d0a2118753> in <module>()
6 xz = symbols('x') + z
7 print(z.shape)
----> 8 print(xz.shape)
AttributeError: 'Symbol' object has no attribute 'shape'
```
A scalar is *definitely* not a numpy array with shape `(1,)`, `(1, 1)`, etc.
It's debatable whether a scalar is a numpy array with shape `()`, but I would simply return a numpy array in this case too. Every library that has ever made the mistake of doing this dimension contraction had to eventually undo it (e.g., Theano).
The problem is that it's very easy to get the lone element from an array of size 1:
```
In [1]: o = np.ones([1 for _ in range(10)])
In [2]: o
Out[2]: array([[[[[[[[[[1.]]]]]]]]]])
In [3]: o.item()
Out[3]: 1.0
```
But it's very hard to go from an element and try to figure out what the shape it should have had and then give it the right shape.
Since this breaks my code, I can submit a patch within about a day if it will be accepted and if someone can point me to the right place in the code (I'm guessing tensor.py).
|
Basic SymPy objects don't carry a shape attribute, `ImmutableDenseNDimArray` does however, have you had a look at: http://docs.sympy.org/latest/modules/tensor/array.html#module-sympy.tensor.array ?
Thanks for taking a look! Unfortunately, I don't think `Array` helps me.
I have a function, say `f`, that transforms numpy arrays (say `A, B, C`) into one vector `v1`. I want to pass in symbolic versions of those arrays to `f` to produce `v1`. Let `v2` be a list of unique elements of `v1`. From `v1` and `v2`, I want to find a matrix `M` that maps `v1` to `v2`.
Each time `A, B, C` are passed (this time they are regular numpy arrays of numbers rather than symbolic variables) I don't need to store `f(A, B, C)`, but rather `M @ f(A, B, C)`, which is shorter. In my case, it is much shorter.
Any inconsistencies between numpy and sympy complicate `f` greatly.
How is `Array` better than `ndarray` having `dtype=np.object` and containing `Symbol`? It seems to me that the `ndarray` will do the usual `numpy` broadcasting that `f` does with regular `ndarray`s? That seems to me to be better. This issue is about an inconsistency in sympy, which was apparently added as a feature (sympy.tensor.tensor.py, line 2258):
```
"""
When all indices are contracted and components data are added to the tensor,
accessing the data will return a scalar, no array object. In fact, arrays
are dropped to scalars if they contain only one element.
>>> A(i0, -i0)
A(L_0, -L_0)
>>> A(i0, -i0).data
-18
"""
```
At least in my case, this is not a feature.
SymPy expressions aren't designed to interact directly with NumPy arrays. Generally if you want to work with NumPy arrays from SymPy expressions you should `lambdify` the expression first to create a compatible NumPy function.
I don't need SymPy expressions to be "designed to interact with numpy arrays". SymPy doesn't need to know anything about numpy arrays. In fact, the whole reason this isn't working is because SymPy seems to know something about numpy arrays.
The numpy array is just like a rectangular list of objects. For example, if I have:
```
xs = np.array(symbols('x:5'))
ys = np.array(symbols('y:3'))
```
Then I can add all pairs like this:
```
np.add.outer(xs, ys)
```
to give
```
array([[x0 + y0, x0 + y1, x0 + y2],
[x1 + y0, x1 + y1, x1 + y2],
[x2 + y0, x2 + y1, x2 + y2],
[x3 + y0, x3 + y1, x3 + y2],
[x4 + y0, x4 + y1, x4 + y2]], dtype=object)
```
This works with any object that supports addition (e.g., `Fraction`, `Decimal`, and `str`):
```
from fractions import Fraction
xs = np.array([Fraction(i) for i in range(1, 5)])
ys = np.array([Fraction(i) for i in range(6, 9)])
np.divide.outer(xs, ys)
```
gives:
```
array([[Fraction(1, 6), Fraction(1, 7), Fraction(1, 8)],
[Fraction(1, 3), Fraction(2, 7), Fraction(1, 4)],
[Fraction(1, 2), Fraction(3, 7), Fraction(3, 8)],
[Fraction(2, 3), Fraction(4, 7), Fraction(1, 2)]], dtype=object)
```
The problem is that in some special cases when the shape of the numpy array contains one element (above), sympy is discarding shape information.
Playing with it a bit more, I see that SymPy is violating the commutativity of addition:
```
z = np.zeros((1, 1))
z + symbols('x')
```
gives the right answer: `array([[x]], dtype=object)`. But
```
symbols('x') + z
```
gives `x`!!
This suggests that `__add__` is handling addition with numpy arrays but `__radd__` is not. Ideally, neither method would do anything with numpy arrays. Just let numpy handle the addition in both cases.
Both SymPy and NumPy override the operators to try to "absorb" other objects into SymPy or NumPy (resp.) types. We could make `Symbol.__add__` return `NotImplemented` when it sees a NumPy array, but that could potentially break code that expects SymPy to convert NumPy arrays into SymPy NDimArray objects (the SymPy operators all just call `sympify`).
My best recommendation here is if you want to put SymPy objects (or any foreign objects, really) in NumPy arrays to always do it explicitly. Don't rely on NumPy's operators to create arrays automatically, because that will fail when the foreign objects have their own greedy operators.
With that being said, perhaps making SymPy's NDimArray objects not automatically flatten would be a good change. Maybe @Upabjojr can comment more on why that behavior is there.
> My best recommendation here is if you want to put SymPy objects (or any foreign objects, really) in NumPy arrays to always do it explicitly.
How can I do the addition (`z + symbols(x)`) explicitly? Using `np.broadcast_arrays` first? It seems ugly.
> With that being said, perhaps making SymPy's NDimArray objects not automatically flatten would be a good change. Maybe @Upabjojr can comment more on why that behavior is there.
Thank you. This is what I'm hoping for.
> How can I do the addition (z + symbols(x)) explicitly? Using np.broadcast_arrays first? It seems ugly.
Won't `z + numpy.array(x)` do what you want? I don't use NumPy that often, so I may be forgetting some of the details of broadcasting.
> Won't z + numpy.array(x) do what you want?
Yup.
Nevertheless, I'd like to feel safe adding signals and arrays without worrying about order. Therefore, I'm hoping that SymPy will keep addition commutative.
Also, since we can see that `ndarray + signal` does the right thing, I don't see why there should be a backwards compatibility question about changing `signal + ndarray` to match.
Addition is commutative in SymPy. If you mix NumPy and SymPy objects, you could have unexpected behaviours (such as your example).
|
[
{
"body": "```\r\nfrom sympy import symbols\r\nimport numpy as np\r\n\r\nfor i in [2, 1]:\r\n z = np.zeros(i)\r\n xz = symbols('x') + z\r\n print(z.shape)\r\n print(xz.shape)\r\n print()\r\n```\r\nprints:\r\n```\r\n(2,)\r\n(2,)\r\n\r\n(1,)\r\n---------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\nAttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)\r\n<ipython-input-165-14d0a2118753> in <module>()\r\n 6 xz = symbols('x') + z\r\n 7 print(z.shape)\r\n----> 8 print(xz.shape)\r\n\r\nAttributeError: 'Symbol' object has no attribute 'shape'\r\n```\r\n\r\nA scalar is *definitely* not a numpy array with shape `(1,)`, `(1, 1)`, etc.\r\nIt's debatable whether a scalar is a numpy array with shape `()`, but I would simply return a numpy array in this case too. Every library that has ever made the mistake of doing this dimension contraction had to eventually undo it (e.g., Theano).\r\n\r\nThe problem is that it's very easy to get the lone element from an array of size 1:\r\n```\r\nIn [1]: o = np.ones([1 for _ in range(10)])\r\n\r\nIn [2]: o\r\nOut[2]: array([[[[[[[[[[1.]]]]]]]]]])\r\n\r\nIn [3]: o.item()\r\nOut[3]: 1.0\r\n```\r\nBut it's very hard to go from an element and try to figure out what the shape it should have had and then give it the right shape.\r\n\r\nSince this breaks my code, I can submit a patch within about a day if it will be accepted and if someone can point me to the right place in the code (I'm guessing tensor.py).",
"number": 14706,
"title": "Symbol violates the commutativity of addition when it sometimes converts one-element arrays to scalar"
}
] |
fcefd30cfbc6c929fb50b99403a5764ca019a603
|
{
"head_commit": "b31b94bcb81ec36fbd6897bd90dd9f1c51816c15",
"head_commit_message": "core: More test cases for sympify\n\nParticularly related to the new changes, new tests were added to\nincrease the coverage.",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/core/numbers.py b/sympy/core/numbers.py\nindex 8ff2149dcf03..6933aae2b7d7 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/numbers.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/numbers.py\n@@ -7,7 +7,8 @@\n import re as regex\n \n from .containers import Tuple\n-from .sympify import converter, sympify, _sympify, SympifyError, _convert_numpy_types\n+from .sympify import (SympifyError, converter, sympify, _convert_numpy_types, _sympify,\n+ _is_numpy_instance)\n from .singleton import S, Singleton\n from .expr import Expr, AtomicExpr\n from .evalf import pure_complex\n@@ -1086,7 +1087,7 @@ def __new__(cls, num, dps=None, prec=None, precision=None):\n return num\n elif num is S.NaN:\n return num\n- elif type(num).__module__ == 'numpy': # support for numpy datatypes\n+ elif _is_numpy_instance(num): # support for numpy datatypes\n num = _convert_numpy_types(num)\n elif isinstance(num, mpmath.mpf):\n if precision is None:\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/sympify.py b/sympy/core/sympify.py\nindex 29ec61491d45..e04b8112d1c3 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/sympify.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/sympify.py\n@@ -55,6 +55,16 @@ class CantSympify(object):\n pass\n \n \n+def _is_numpy_instance(a):\n+ \"\"\"\n+ Checks if an object is an instance of a type from the numpy module.\n+ \"\"\"\n+ # This check avoids unnecessarily importing NumPy. We check the whole\n+ # __mro__ in case any base type is a numpy type.\n+ return any(type_.__module__ == 'numpy'\n+ for type_ in type(a).__mro__)\n+\n+\n def _convert_numpy_types(a, **sympify_args):\n \"\"\"\n Converts a numpy datatype input to an appropriate SymPy type.\n@@ -295,8 +305,7 @@ def sympify(a, locals=None, convert_xor=True, strict=False, rational=False,\n evaluate = global_parameters.evaluate\n \n # Support for basic numpy datatypes\n- # Note that this check exists to avoid importing NumPy when not necessary\n- if type(a).__module__ == 'numpy':\n+ if _is_numpy_instance(a):\n import numpy as np\n if np.isscalar(a):\n return _convert_numpy_types(a, locals=locals,\n@@ -324,15 +333,30 @@ def sympify(a, locals=None, convert_xor=True, strict=False, rational=False,\n return Array(a.flat, a.shape) # works with e.g. NumPy arrays\n \n if not isinstance(a, str):\n- for coerce in (float, int):\n- try:\n- coerced = coerce(a)\n- except (TypeError, ValueError):\n- continue\n- try:\n- return sympify(coerced)\n- except SympifyError:\n- continue\n+ if _is_numpy_instance(a):\n+ import numpy as np\n+ assert not isinstance(a, np.number)\n+ if isinstance(a, np.ndarray):\n+ # Scalar arrays (those with zero dimensions) have sympify\n+ # called on the scalar element.\n+ if a.ndim == 0:\n+ try:\n+ return sympify(a.item(),\n+ locals=locals,\n+ convert_xor=convert_xor,\n+ strict=strict,\n+ rational=rational,\n+ evaluate=evaluate)\n+ except SympifyError:\n+ pass\n+ else:\n+ # float and int can coerce size-one numpy arrays to their lone\n+ # element. See issue https://github.com/numpy/numpy/issues/10404.\n+ for coerce in (float, int):\n+ try:\n+ return sympify(coerce(a))\n+ except (TypeError, ValueError, AttributeError, SympifyError):\n+ continue\n \n if strict:\n raise SympifyError(a)\ndiff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_sympify.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_sympify.py\nindex e2d25e47b8a4..1e4e96958eed 100644\n--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_sympify.py\n+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_sympify.py\n@@ -632,6 +632,7 @@ def test_issue_13924():\n assert isinstance(a, ImmutableDenseNDimArray)\n assert a[0] == 1\n \n+\n def test_numpy_sympify_args():\n # Issue 15098. Make sure sympify args work with numpy types (like numpy.str_)\n if not numpy:\n@@ -695,3 +696,39 @@ def test_issue_16759():\n def test_issue_17811():\n a = Function('a')\n assert sympify('a(x)*5', evaluate=False) == Mul(a(x), 5, evaluate=False)\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_14706():\n+ if not numpy:\n+ skip(\"numpy not installed.\")\n+\n+ from sympy import symbols\n+\n+ x = symbols('x')\n+\n+ z1 = numpy.zeros((1,1), dtype=numpy.float)\n+ z2 = numpy.zeros((2,2), dtype=numpy.float)\n+ z3 = numpy.zeros((), dtype=numpy.float)\n+\n+ assert numpy.all(x + z1 == numpy.full((1, 1), x))\n+ assert numpy.all(x + z2 == numpy.full((2, 2), x))\n+ for z in [z3,\n+ numpy.int(0),\n+ numpy.float(0),\n+ numpy.complex(0)]:\n+ assert x + z == x\n+ assert isinstance(x + z, Symbol)\n+\n+ assert x + numpy.array(x) == 2 * x\n+ assert x + numpy.array([x]) == numpy.array([2*x], dtype=object)\n+\n+ assert sympify(numpy.array([1])) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([1], 1)\n+ assert sympify(numpy.array([[[1]]])) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([1], (1, 1, 1))\n+ assert sympify(z1) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([0], (1, 1))\n+ assert sympify(z2) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([0, 0, 0, 0], (2, 2))\n+ assert sympify(z3) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([0], ())\n+ assert sympify(z3, strict=True) == 0.0\n+\n+ raises(SympifyError, lambda: sympify(numpy.array([1]), strict=True))\n+ raises(SympifyError, lambda: sympify(z1, strict=True))\n+ raises(SympifyError, lambda: sympify(z2, strict=True))\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -695,3 +696,39 @@ def test_issue_16759():\n def test_issue_17811():\n a = Function('a')\n assert sympify('a(x)*5', evaluate=False) == Mul(a(x), 5, evaluate=False)\n+\n+\n+def test_issue_14706():\n+ if not numpy:\n+ skip(\"numpy not installed.\")\n+\n+ from sympy import symbols\n+\n+ x = symbols('x')",
"line": null,
"original_line": 707,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/core/tests/test_sympify.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n```suggestion\r\n```\r\n\r\nx is already imported at the top of the file"
}
] |
6a03bc304d7ab3990a3d6f43b9ca173a39c14eb9
|
diff --git a/sympy/core/numbers.py b/sympy/core/numbers.py
index 8ff2149dcf03..6933aae2b7d7 100644
--- a/sympy/core/numbers.py
+++ b/sympy/core/numbers.py
@@ -7,7 +7,8 @@
import re as regex
from .containers import Tuple
-from .sympify import converter, sympify, _sympify, SympifyError, _convert_numpy_types
+from .sympify import (SympifyError, converter, sympify, _convert_numpy_types, _sympify,
+ _is_numpy_instance)
from .singleton import S, Singleton
from .expr import Expr, AtomicExpr
from .evalf import pure_complex
@@ -1086,7 +1087,7 @@ def __new__(cls, num, dps=None, prec=None, precision=None):
return num
elif num is S.NaN:
return num
- elif type(num).__module__ == 'numpy': # support for numpy datatypes
+ elif _is_numpy_instance(num): # support for numpy datatypes
num = _convert_numpy_types(num)
elif isinstance(num, mpmath.mpf):
if precision is None:
diff --git a/sympy/core/sympify.py b/sympy/core/sympify.py
index 29ec61491d45..e04b8112d1c3 100644
--- a/sympy/core/sympify.py
+++ b/sympy/core/sympify.py
@@ -55,6 +55,16 @@ class CantSympify(object):
pass
+def _is_numpy_instance(a):
+ """
+ Checks if an object is an instance of a type from the numpy module.
+ """
+ # This check avoids unnecessarily importing NumPy. We check the whole
+ # __mro__ in case any base type is a numpy type.
+ return any(type_.__module__ == 'numpy'
+ for type_ in type(a).__mro__)
+
+
def _convert_numpy_types(a, **sympify_args):
"""
Converts a numpy datatype input to an appropriate SymPy type.
@@ -295,8 +305,7 @@ def sympify(a, locals=None, convert_xor=True, strict=False, rational=False,
evaluate = global_parameters.evaluate
# Support for basic numpy datatypes
- # Note that this check exists to avoid importing NumPy when not necessary
- if type(a).__module__ == 'numpy':
+ if _is_numpy_instance(a):
import numpy as np
if np.isscalar(a):
return _convert_numpy_types(a, locals=locals,
@@ -324,15 +333,30 @@ def sympify(a, locals=None, convert_xor=True, strict=False, rational=False,
return Array(a.flat, a.shape) # works with e.g. NumPy arrays
if not isinstance(a, str):
- for coerce in (float, int):
- try:
- coerced = coerce(a)
- except (TypeError, ValueError):
- continue
- try:
- return sympify(coerced)
- except SympifyError:
- continue
+ if _is_numpy_instance(a):
+ import numpy as np
+ assert not isinstance(a, np.number)
+ if isinstance(a, np.ndarray):
+ # Scalar arrays (those with zero dimensions) have sympify
+ # called on the scalar element.
+ if a.ndim == 0:
+ try:
+ return sympify(a.item(),
+ locals=locals,
+ convert_xor=convert_xor,
+ strict=strict,
+ rational=rational,
+ evaluate=evaluate)
+ except SympifyError:
+ pass
+ else:
+ # float and int can coerce size-one numpy arrays to their lone
+ # element. See issue https://github.com/numpy/numpy/issues/10404.
+ for coerce in (float, int):
+ try:
+ return sympify(coerce(a))
+ except (TypeError, ValueError, AttributeError, SympifyError):
+ continue
if strict:
raise SympifyError(a)
diff --git a/sympy/core/tests/test_sympify.py b/sympy/core/tests/test_sympify.py
index e2d25e47b8a4..57a8c4d0f1d9 100644
--- a/sympy/core/tests/test_sympify.py
+++ b/sympy/core/tests/test_sympify.py
@@ -632,6 +632,7 @@ def test_issue_13924():
assert isinstance(a, ImmutableDenseNDimArray)
assert a[0] == 1
+
def test_numpy_sympify_args():
# Issue 15098. Make sure sympify args work with numpy types (like numpy.str_)
if not numpy:
@@ -695,3 +696,62 @@ def test_issue_16759():
def test_issue_17811():
a = Function('a')
assert sympify('a(x)*5', evaluate=False) == Mul(a(x), 5, evaluate=False)
+
+
+def test_issue_14706():
+ if not numpy:
+ skip("numpy not installed.")
+
+ z1 = numpy.zeros((1, 1), dtype=numpy.float)
+ z2 = numpy.zeros((2, 2), dtype=numpy.float)
+ z3 = numpy.zeros((), dtype=numpy.float)
+
+ y1 = numpy.ones((1, 1), dtype=numpy.float)
+ y2 = numpy.ones((2, 2), dtype=numpy.float)
+ y3 = numpy.ones((), dtype=numpy.float)
+
+ assert numpy.all(x + z1 == numpy.full((1, 1), x))
+ assert numpy.all(x + z2 == numpy.full((2, 2), x))
+ assert numpy.all(z1 + x == numpy.full((1, 1), x))
+ assert numpy.all(z2 + x == numpy.full((2, 2), x))
+ for z in [z3,
+ numpy.int(0),
+ numpy.float(0),
+ numpy.complex(0)]:
+ assert x + z == x
+ assert z + x == x
+ assert isinstance(x + z, Symbol)
+ assert isinstance(z + x, Symbol)
+
+ # If these tests fail, then it means that numpy has finally
+ # fixed the issue of scalar conversion for rank>0 arrays
+ # which is mentioned in numpy/numpy#10404. In that case,
+ # some changes have to be made in sympify.py.
+ # Note: For future reference, for anyone who takes up this
+ # issue when numpy has finally fixed their side of the problem,
+ # the changes for this temporary fix were introduced in PR 18651
+ assert numpy.all(x + y1 == numpy.full((1, 1), x + 1.0))
+ assert numpy.all(x + y2 == numpy.full((2, 2), x + 1.0))
+ assert numpy.all(y1 + x == numpy.full((1, 1), x + 1.0))
+ assert numpy.all(y2 + x == numpy.full((2, 2), x + 1.0))
+ for y_ in [y3,
+ numpy.int(1),
+ numpy.float(1),
+ numpy.complex(1)]:
+ assert x + y_ == y_ + x
+ assert isinstance(x + y_, Add)
+ assert isinstance(y_ + x, Add)
+
+ assert x + numpy.array(x) == 2 * x
+ assert x + numpy.array([x]) == numpy.array([2*x], dtype=object)
+
+ assert sympify(numpy.array([1])) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([1], 1)
+ assert sympify(numpy.array([[[1]]])) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([1], (1, 1, 1))
+ assert sympify(z1) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([0], (1, 1))
+ assert sympify(z2) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([0, 0, 0, 0], (2, 2))
+ assert sympify(z3) == ImmutableDenseNDimArray([0], ())
+ assert sympify(z3, strict=True) == 0.0
+
+ raises(SympifyError, lambda: sympify(numpy.array([1]), strict=True))
+ raises(SympifyError, lambda: sympify(z1, strict=True))
+ raises(SympifyError, lambda: sympify(z2, strict=True))
|
{
"difficulty": "medium",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
sympy__sympy-18614@76fc537
|
sympy/sympy
|
Python
| 18,614
|
Fixed DiscreteUniform to produce correct density and cdf
|
<!-- Your title above should be a short description of what
was changed. Do not include the issue number in the title. -->
Fixed DiscreteUniform to produce correct density and cdf
#### References to other Issues or PRs
<!-- If this pull request fixes an issue, write "Fixes #NNNN" in that exact
format, e.g. "Fixes #1234" (see
https://tinyurl.com/auto-closing for more information). Also, please
write a comment on that issue linking back to this pull request once it is
open. -->
Fixes #18611
#### Brief description of what is fixed or changed
#### Other comments
#### Release Notes
<!-- Write the release notes for this release below. See
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Writing-Release-Notes for more information
on how to write release notes. The bot will check your release notes
automatically to see if they are formatted correctly. -->
<!-- BEGIN RELEASE NOTES -->
* stats
* `DiscreteUniform` raises ValueError for duplicate args
<!-- END RELEASE NOTES -->
|
2020-02-09T16:20:45Z
|
Incorrect density, cdf calculation in DiscreteUniform
```
>>> from sympy.stats import density, DiscreteUniform, cdf
>>> X = DiscreteUniform('X', [1, 1, 1, 2, 2])
>>> dict(density(X).items())
{1: 1/5, 2: 1/5}
>>> cdf(X)
{1: 1/5, 2: 2/5}
```
Issue is:
Considering that the arguments in the `DiscreteUniformDistribution`, it should be kept as finite set, and therefore should produce `density` as `{1: 1/2, 2: 1/2}`,
Also as `density` is wrongly evaluated, `cdf` produces wrong result, as it should attain value of `1` at some point in the domain of the distribution, which is not satisfied in the above result.
|
[
{
"body": "```\r\n>>> from sympy.stats import density, DiscreteUniform, cdf\r\n>>> X = DiscreteUniform('X', [1, 1, 1, 2, 2])\r\n>>> dict(density(X).items())\r\n{1: 1/5, 2: 1/5}\r\n>>> cdf(X)\r\n{1: 1/5, 2: 2/5}\r\n```\r\nIssue is:\r\nConsidering that the arguments in the `DiscreteUniformDistribution`, it should be kept as finite set, and therefore should produce `density` as `{1: 1/2, 2: 1/2}`,\r\nAlso as `density` is wrongly evaluated, `cdf` produces wrong result, as it should attain value of `1` at some point in the domain of the distribution, which is not satisfied in the above result.\r\n",
"number": 18611,
"title": "Incorrect density, cdf calculation in DiscreteUniform"
}
] |
928864c6cd1bcc339af60c2170a3821e77ca6fef
|
{
"head_commit": "76fc53728884908731ed40a30891d58c33a1155b",
"head_commit_message": "corrected to set of args",
"patch_to_review": "diff --git a/sympy/stats/frv_types.py b/sympy/stats/frv_types.py\nindex d5b35606dc67..4dcdeee4773e 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/frv_types.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/frv_types.py\n@@ -92,7 +92,7 @@ def FiniteRV(name, density):\n class DiscreteUniformDistribution(SingleFiniteDistribution):\n @property\n def p(self):\n- return Rational(1, len(self.args))\n+ return Rational(1, len(set(self.args)))\n \n @property # type: ignore\n @cacheit\n@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ def set(self):\n return set(self.args)\n \n def pmf(self, x):\n- if x in self.args:\n+ if x in set(self.args):\n return self.p\n else:\n return S.Zero\ndiff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py\nindex 040262f060c9..13d886a96288 100644\n--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py\n+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py\n@@ -45,6 +45,13 @@ def test_discreteuniform():\n \n assert characteristic_function(X)(t) == exp(I*a*t)/3 + exp(I*b*t)/3 + exp(I*c*t)/3\n assert moment_generating_function(X)(t) == exp(a*t)/3 + exp(b*t)/3 + exp(c*t)/3\n+ # issue 18611\n+ Z = DiscreteUniform('Z', [a, a, a, b, b, c])\n+ assert dict(density(Z).items()) == {a: S('1/3'), b: S('1/3'), c: S('1/3')}\n+ assert E(Z) == (a + b + c)/3\n+ Z = DiscreteUniform('Z', [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4])\n+ assert dict(density(Z).items()) == {1: S('1/4'), 2: S('1/4'), 3: S('1/4'), 4: S('1/4')}\n+ assert cdf(Z) == {1: S('1/4'), 2: S('1/2'), 3: S('3/4'), 4: 1}\n \n def test_dice():\n # TODO: Make iid method!\n"
}
|
[
{
"diff_hunk": "@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ def set(self):\n return set(self.args)\n \n def pmf(self, x):\n- if x in self.args:\n+ if x in set(self.args):",
"line": null,
"original_line": 107,
"original_start_line": null,
"path": "sympy/stats/frv_types.py",
"start_line": null,
"text": "@user1:\n`set` would not be necessary here.\n\n@author:\nOkay, will remove it. \n\n@author:\n@user1 Is it good to go now?"
}
] |
62bd4c1a9df0c2ae5135df62dcdb1826d92d6c4f
|
diff --git a/sympy/stats/frv_types.py b/sympy/stats/frv_types.py
index d5b35606dc67..b4c23833339b 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/frv_types.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/frv_types.py
@@ -90,6 +90,24 @@ def FiniteRV(name, density):
return rv(name, FiniteDistributionHandmade, density)
class DiscreteUniformDistribution(SingleFiniteDistribution):
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def check(*args):
+ # not using _value_check since there is a
+ # suggestion for the user
+ if len(set(args)) != len(args):
+ from sympy.utilities.iterables import multiset
+ from sympy.utilities.misc import filldedent
+ weights = multiset(args)
+ n = Integer(len(args))
+ for k in weights:
+ weights[k] /= n
+ raise ValueError(filldedent("""
+ Repeated args detected but set expected. For a
+ distribution having different weights for each
+ item use the following:""") + (
+ '\nS("FiniteRV(%s, %s)")' % ("'X'", weights)))
+
@property
def p(self):
return Rational(1, len(self.args))
diff --git a/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py b/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py
index 040262f060c9..4b72db14959d 100644
--- a/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py
+++ b/sympy/stats/tests/test_finite_rv.py
@@ -45,6 +45,8 @@ def test_discreteuniform():
assert characteristic_function(X)(t) == exp(I*a*t)/3 + exp(I*b*t)/3 + exp(I*c*t)/3
assert moment_generating_function(X)(t) == exp(a*t)/3 + exp(b*t)/3 + exp(c*t)/3
+ # issue 18611
+ raises(ValueError, lambda: DiscreteUniform('Z', [a, a, a, b, b, c]))
def test_dice():
# TODO: Make iid method!
|
{
"difficulty": "low",
"estimated_review_effort": 3,
"problem_domain": "Bug Fixes"
}
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.