Please be sure to provide your full legal name, date of birth, and full organization name with all corporate identifiers. Avoid the use of acronyms and special characters. Failure to follow these instructions may prevent you from accessing this model and others. You will not have the ability to edit this form after submission, so please ensure all information is accurate.
The information you provide will be collected, stored, processed and shared in accordance with the TNSA Privacy Policy.
- LICENSE DEFINITIONS & SCOPE
1.1 Core Definitions
1.1.1 "OpenWeight Models" means AI models where TNSA has made model weights, parameters, and architecture publicly available under open licensing terms.
1.1.2 "Model Weights" means the learned parameters, coefficients, and numerical values that define the behavior and capabilities of an AI model.
1.1.3 "Model Architecture" means the structural design, layer configuration, and computational framework of an AI model.
1.1.4 "Training Code" means software, scripts, and procedures used to train, fine-tune, or modify AI models.
1.1.5 "Inference Code" means software required to load, execute, and generate outputs from AI models.
1.1.6 "Model Card" means documentation describing model capabilities, limitations, training data, and intended use cases.
1.1.7 "Derivative Model" means any AI model created by modifying, fine-tuning, or building upon TNSA OpenWeight Models.
1.1.8 "Commercial Use" means any use of OpenWeight Models for commercial purposes, including but not limited to revenue generation, business operations, or competitive advantage.
1.1.9 "Research Use" means use for academic research, scientific investigation, or educational purposes without commercial intent.
1.1.10 "Distribution" means making OpenWeight Models or derivatives available to third parties through any means.
1.2 License Scope
1.2.1 This license applies to all TNSA OpenWeight Models and associated materials made available under open licensing terms.
1.2.2 The license covers model weights, architectures, training code, inference code, and documentation.
1.2.3 Different license terms may apply to different model versions or releases.
1.2.4 Supplemental terms may apply to specific models or use cases as indicated in model documentation.
1.2.5 This license does not grant rights to TNSA trademarks, service marks, or proprietary branding.
1.2.6 Training data used to create OpenWeight Models may be subject to separate licensing terms.
1.2.7 Third-party components integrated into OpenWeight Models retain their original licensing terms.
1.2.8 Geographic restrictions may apply based on export control laws and regulations.
1.2.9 Temporal limitations may apply to certain license grants or model versions.
1.2.10 Updates and modifications to licensing terms will be communicated through official TNSA channels.
1.3 License Types
1.3.1 "TNSA Open License" - Permissive license allowing broad commercial and research use with attribution.
1.3.2 "TNSA Research License" - License restricted to non-commercial research and educational use.
1.3.3 "TNSA Community License" - License for community-driven development with share-alike provisions.
1.3.4 "TNSA Evaluation License" - Time-limited license for evaluation and testing purposes.
1.3.5 "TNSA Custom License" - Negotiated license terms for specific use cases or organizations. - COVERED MODEL CATEGORIES
2.1 NGen Series Models
2.1.1 NGen3 OpenWeight Models - Latest generation large language models with full commercial licensing.
2.1.2 NGen2 OpenWeight Models - Previous generation models with continued support and licensing.
2.1.3 NGen Base Models - Foundation models suitable for fine-tuning and specialization.
2.1.4 NGen Instruct Models - Instruction-tuned variants optimized for conversational use.
2.1.5 NGen Code Models - Specialized variants trained for code generation and programming tasks.
2.1.6 NGen Reasoning Models - Enhanced variants with improved logical reasoning capabilities.
2.1.7 NGen Multimodal Models - Models capable of processing text, images, and other modalities.
2.1.8 NGen Domain Models - Specialized models for specific industries or use cases.
2.1.9 NGen Efficient Models - Optimized variants for resource-constrained environments.
2.1.10 NGen Experimental Models - Research variants with novel architectures or capabilities.
2.2 IGen Series Models
2.2.1 IGen 1 Nano Models - Compact image generation models for edge deployment.
2.2.2 IGen Base Models - Foundation models for image synthesis and manipulation.
2.2.3 IGen Style Models - Specialized models for artistic and stylistic image generation.
2.2.4 IGen Photo Models - Photorealistic image generation models with high fidelity output.
2.2.5 IGen Edit Models - Models specialized for image editing and modification tasks.
2.2.6 IGen Upscale Models - Super-resolution models for image enhancement and upscaling.
2.2.7 IGen Inpaint Models - Models for image inpainting and completion tasks.
2.2.8 IGen Control Models - Models with enhanced controllability and conditioning options.
2.2.9 IGen Fast Models - Optimized models for rapid image generation with reduced latency.
2.2.10 IGen Research Models - Experimental image generation models for research purposes.
2.3 Specialized Model Categories
2.3.1 Stellar v2 Models - Advanced reasoning and analysis models for complex problem-solving.
2.3.2 Audio Generation Models - Models for speech synthesis, music generation, and audio processing.
2.3.3 Video Generation Models - Models for video synthesis, editing, and temporal content creation.
2.3.4 Embedding Models - Models for generating vector representations of text, images, and other data.
2.3.5 Classification Models - Models for content classification, sentiment analysis, and categorization.
2.3.6 Translation Models - Models for language translation and cross-lingual understanding.
2.3.7 Summarization Models - Models specialized for text summarization and content condensation.
2.3.8 Question Answering Models - Models optimized for factual question answering and information retrieval.
2.3.9 Safety Models - Models for content moderation, safety classification, and harm detection.
2.3.10 Evaluation Models - Models for assessing quality, accuracy, and performance of other AI systems. - GRANTED PERMISSIONS
3.1 Usage Rights
3.1.1 Use OpenWeight Models for inference, prediction, and output generation.
3.1.2 Deploy models in production environments for commercial and non-commercial purposes.
3.1.3 Integrate models into applications, services, and platforms.
3.1.4 Process proprietary and confidential data through licensed models.
3.1.5 Scale usage according to computational resources and business needs.
3.1.6 Use models across multiple geographic regions and jurisdictions.
3.1.7 Combine multiple TNSA models in integrated solutions.
3.1.8 Use models for both batch processing and real-time inference.
3.1.9 Implement custom inference optimizations and performance enhancements.
3.1.10 Use models in research, development, and experimental applications.
3.2 Modification Rights
3.2.1 Fine-tune models on custom datasets for specialized applications.
3.2.2 Modify model architectures for performance or efficiency improvements.
3.2.3 Quantize, compress, or optimize models for specific hardware platforms.
3.2.4 Merge or ensemble multiple models for enhanced capabilities.
3.2.5 Extract and use individual model components or layers.
3.2.6 Adapt models for different programming languages or frameworks.
3.2.7 Create domain-specific variants through transfer learning.
3.2.8 Implement custom training procedures and optimization techniques.
3.2.9 Modify input/output interfaces and data preprocessing pipelines.
3.2.10 Develop novel applications and use cases based on model capabilities.
3.3 Distribution Rights
3.3.1 Distribute unmodified OpenWeight Models with proper attribution.
3.3.2 Share derivative models created through permitted modifications.
3.3.3 Include models in open-source projects and repositories.
3.3.4 Distribute models through academic and research channels.
3.3.5 Package models with applications and commercial products.
3.3.6 Provide models to customers, partners, and collaborators.
3.3.7 Host models on cloud platforms and model repositories.
3.3.8 Create and distribute model variants for different use cases.
3.3.9 Share models within organizations and affiliated entities.
3.3.10 Contribute models to community projects and initiatives. - USAGE RESTRICTIONS
4.1 Prohibited Uses
4.1.1 Using models to generate illegal content or facilitate criminal activities.
4.1.2 Creating deepfakes or synthetic media intended to deceive or harm individuals.
4.1.3 Developing surveillance systems that violate privacy rights or human dignity.
4.1.4 Training models on data obtained without proper consent or legal authorization.
4.1.5 Using models to discriminate against protected groups or individuals.
4.1.6 Generating content that promotes violence, hatred, or extremist ideologies.
4.1.7 Creating systems designed to manipulate democratic processes or elections.
4.1.8 Using models for military weapons development or autonomous weapons systems.
4.1.9 Developing applications that could cause mass harm or societal disruption.
4.1.10 Reverse engineering models to extract proprietary training data or methodologies.
4.2 Technical Restrictions
4.2.1 Removing or obscuring attribution notices, copyright statements, or license information.
4.2.2 Circumventing built-in safety measures, content filters, or usage monitoring.
4.2.3 Attempting to extract or reconstruct training data from model weights.
4.2.4 Using models in ways that exceed specified computational or usage limits.
4.2.5 Modifying models to remove safety guardrails or ethical constraints.
4.2.6 Distributing models without required documentation or safety information.
4.2.7 Using models in safety-critical applications without proper validation.
4.2.8 Combining models with malicious code or harmful software components.
4.2.9 Implementing models in ways that violate applicable privacy regulations.
4.2.10 Using models to create competing AI services that directly replicate TNSA offerings.
4.3 Commercial Restrictions
4.3.1 Certain models may require separate commercial licensing for revenue-generating use.
4.3.2 High-volume commercial usage may be subject to additional terms and fees.
4.3.3 Reselling unmodified models as standalone products is prohibited.
4.3.4 Using TNSA trademarks or branding without explicit permission is forbidden.
4.3.5 Creating derivative works that compete directly with TNSA services may be restricted.
Log in or Sign Up to review the conditions and access this model content.
NGen 3 - 3B-Instruct
NGen3 is a production-level foundational language model inspired by state-of-the-art architectures such as GPT-4, Claude-3, and Llama 2. It is designed for both research and production and supports model variants ranging from 7M to 1B parameters. The model is built with a modular transformer decoder architecture and provides a comprehensive command-line interface (CLI) for tokenization, training, sampling, exporting, knowledge distillation, and fine-tuning on conversational data.
Table of Contents
Overview
NGen3 is a flexible, self-contained implementation of a foundational language model built on a transformer decoder architecture. It enables users to:
- Tokenize text from local files, URLs, or directly from Hugging Face datasets.
- Train the model on tokenized datasets.
- Generate text samples from trained models.
- Export models (with minimal tokenizer configurations) to formats compatible with Hugging Face.
- Distill knowledge from larger teacher models into smaller student models.
- Fine-Tune on conversational datasets (using local files or datasets from Hugging Face).
Model Architecture
NGen3 uses a decoder-only transformer design with the following components:
- Token & Positional Embeddings: Learnable embeddings for tokens and their positions.
- Transformer Blocks: A stack of blocks, each containing:
- Causal Self-Attention: Multi-head attention with a lower-triangular mask to prevent attention to future tokens.
- Feed-Forward Network (MLP): With GELU activation.
- Residual Connections & Layer Normalization: To stabilize training.
- Final Projection Layer: Projects the hidden states to logits over the vocabulary.
The model comes in several variants:
- 7M Variant: 4 layers, 4 heads, 128-dimensional embeddings.
- 120M Variant: 12 layers, 8 heads, 512-dimensional embeddings.
- 300M, 500M, 700M, and 1B Variants: Increasing in depth and width.
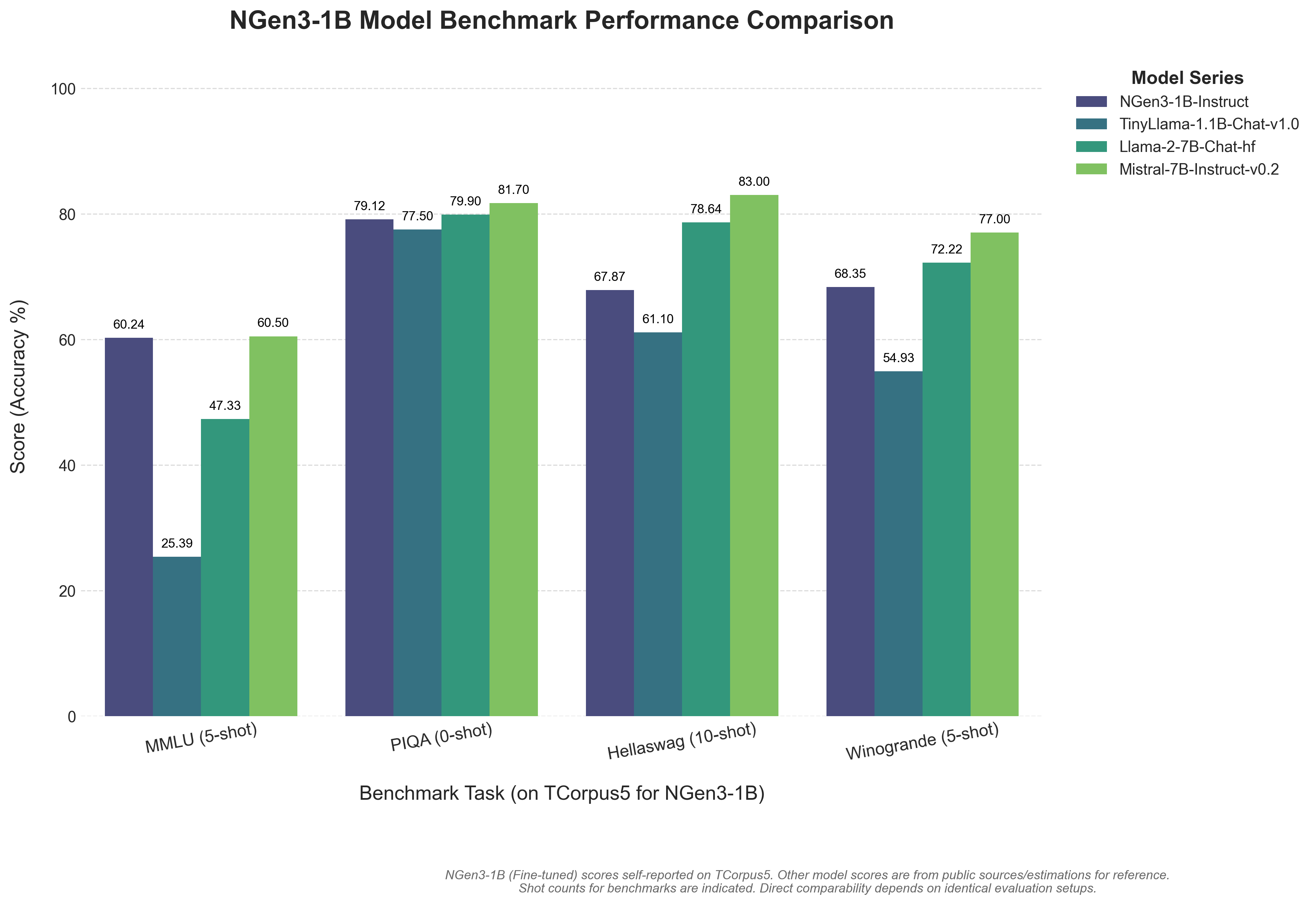
Evaluation Results
Installation
Ensure you have Python 3.8+ installed and install the necessary dependencies:
pip install torch transformers datasets tqdm safetensors
Usage
NGen3 is fully managed via a CLI. Below are examples for each command. Tokenization Local Text File or URL:
python _model_.py tokenize --dataset tinyshakespeare --txt "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/karpathy/char-rnn/master/data/tinyshakespeare/input.txt"
Hugging Face Dataset:
python _model_.py hf_tokenize --hf_dataset roskoN/dailydialog --hf_split train --hf_text_column utterances --dataset dailydialog_train
Training
Train a model variant (e.g., 7M):
python _model_.py train --variant 7M --data _data_tinyshakespeare_/data.bin
Sampling
Generate text samples from a trained model:
python _model_.py sample --variant 7M --model_checkpoint 7M_model.pt --prompt "To be, or not to be" --length 100 --temperature 1.0
Exporting
Export a trained model (and its tokenizer configuration) for Hugging Face:
python _model_.py export --variant 7M --model_path 7M_model.pt --output_dir exported_7M
Knowledge Distillation
Distill a larger teacher model (e.g., GPT-2 120M from HF) into a smaller student model (e.g., 7M):
python _model_.py distill --teacher_model_path hf --teacher_variant 120M --student_variant 7M --data _data_tinyshakespeare_/data.bin --temperature 2.0 --alpha 0.5
Fine-Tuning
Local Fine-Tuning on Conversational Data Fine-tune a distilled model using local conversation data:
python _model_.py finetune --variant 120M --model_checkpoint distilled_120M_model.pt --data _data_conversations_/data.bin --finetune_iters 1000 --prompt "Hello, how are you?" --sample_length 100 --sample_temperature 1.0
Hugging Face Fine-Tuning on a Conversational Dataset Fine-tune on a conversational dataset from Hugging Face (e.g., roskoN/dailydialog):
python _model_.py hf_finetune --variant 120M --model_checkpoint distilled_120M_model.pt --hf_dataset roskoN/dailydialog --hf_split train --hf_text_column utterances --finetune_iters 1000 --prompt "Hello, how are you?" --sample_length 100 --sample_temperature 1.0
Sampling and Exporting Fine-Tuned Models
After fine-tuning, you can sample from or export the fine-tuned model just as with any checkpoint. For example, if your fine-tuned model is saved as finetuned_120M_model.pt:
Sampling:
python _model_.py sample --variant 120M --model_checkpoint finetuned_120M_model.pt --prompt "What do you think about AI?" --length 100 --temperature 1.0
Exporting:
python _model_.py export --variant 120M --model_path finetuned_120M_model.pt --output_dir exported_finetuned_120M
Hyperparameters
Each model variant comes with predefined hyperparameters. For example:
7M Variant:
Layers: 4, Heads: 4, Embedding Dimension: 128 Block Size: 128, Batch Size: 16, Learning Rate: 3e-4 120M Variant:
Layers: 12, Heads: 8, Embedding Dimension: 512 Block Size: 256, Batch Size: 32, Learning Rate: 3e-4 300M, 500M, 700M, 1B Variants: Increasing layers, heads, and embedding dimensions for better performance.
Adjust max_iters, log_interval, and eval_interval to suit your dataset size and computational resources.
Acknowledgements
NGen3 is inspired by leading models including GPT-4, Claude-3, and Llama 2. Special thanks to the open-source community for:
- PyTorch
- Hugging Face Transformers
- Hugging Face Datasets
- safetensors
- Downloads last month
- 1
Model tree for TNSA/NGen3-3B
Base model
TNSA/NGen3-1BDatasets used to train TNSA/NGen3-3B
Collection including TNSA/NGen3-3B
Evaluation results
- MMLU on TCorpus5self-reported60.240
- PIQA on TCorpus5self-reported79.120
- Hellaswag on TCorpus5self-reported52.870
- Winogrande on TCorpus5self-reported68.350
.png)